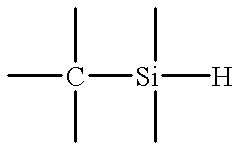Patents
Literature
552results about "Centrifugal wheel fertilisers" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
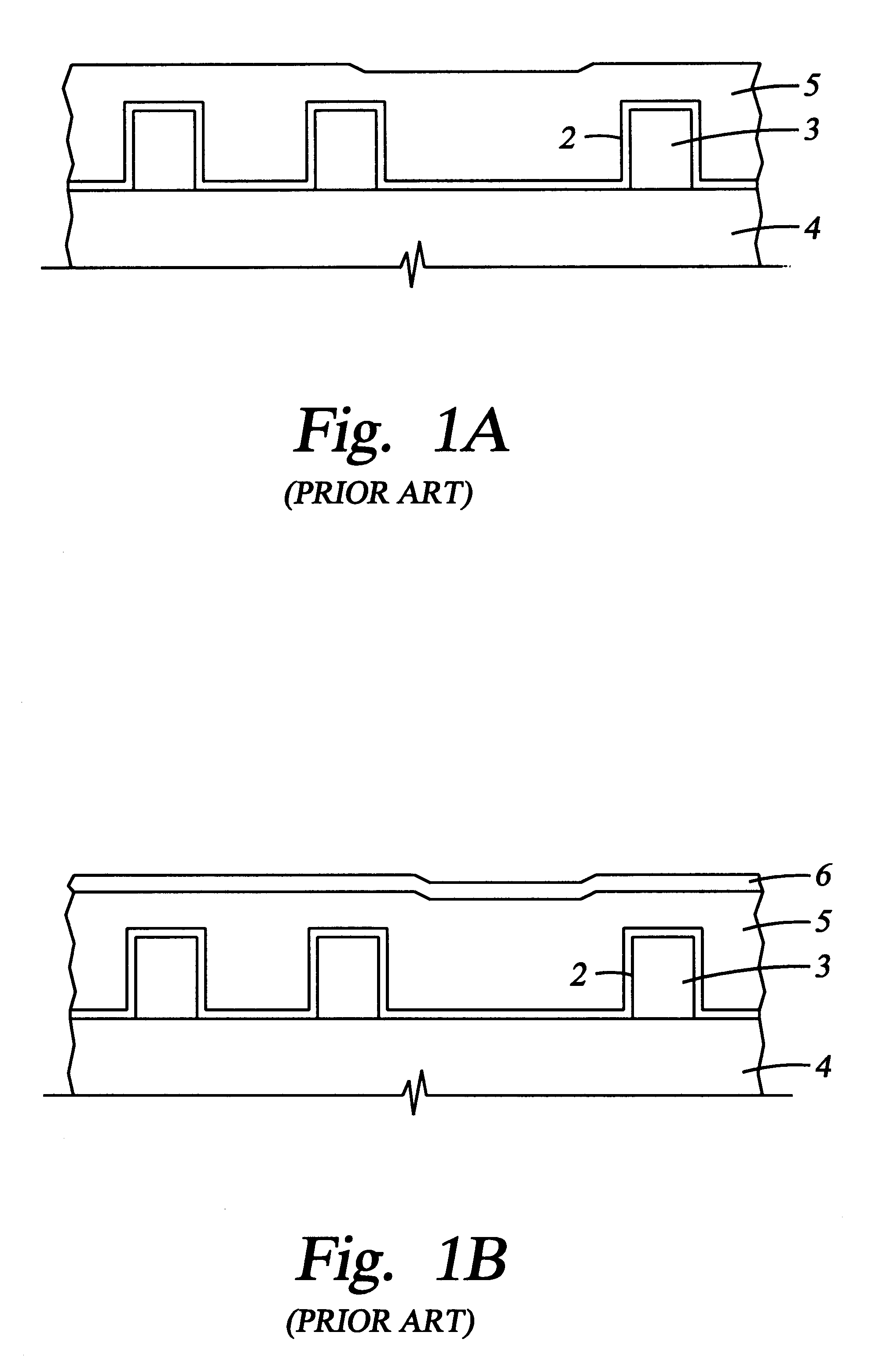
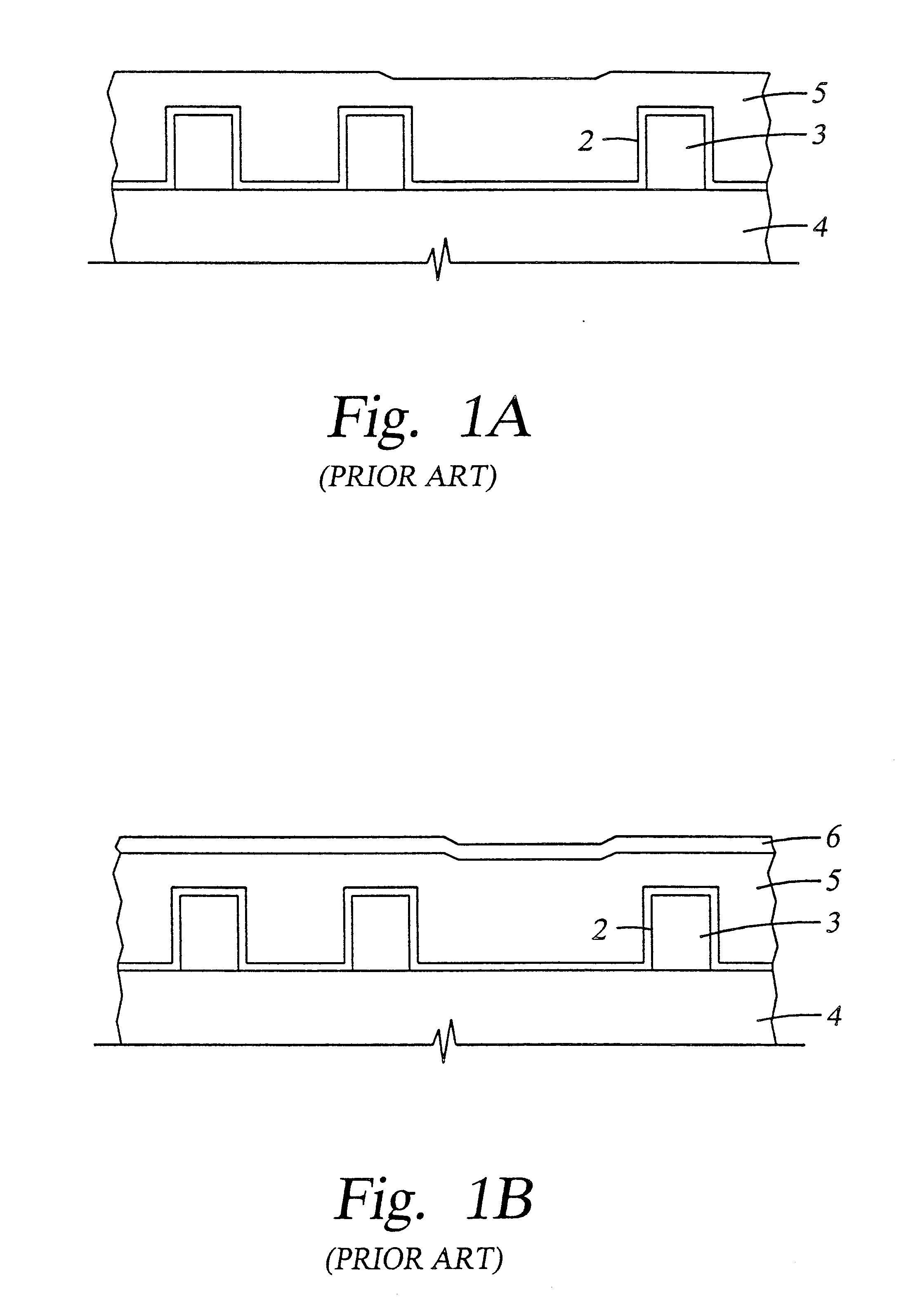
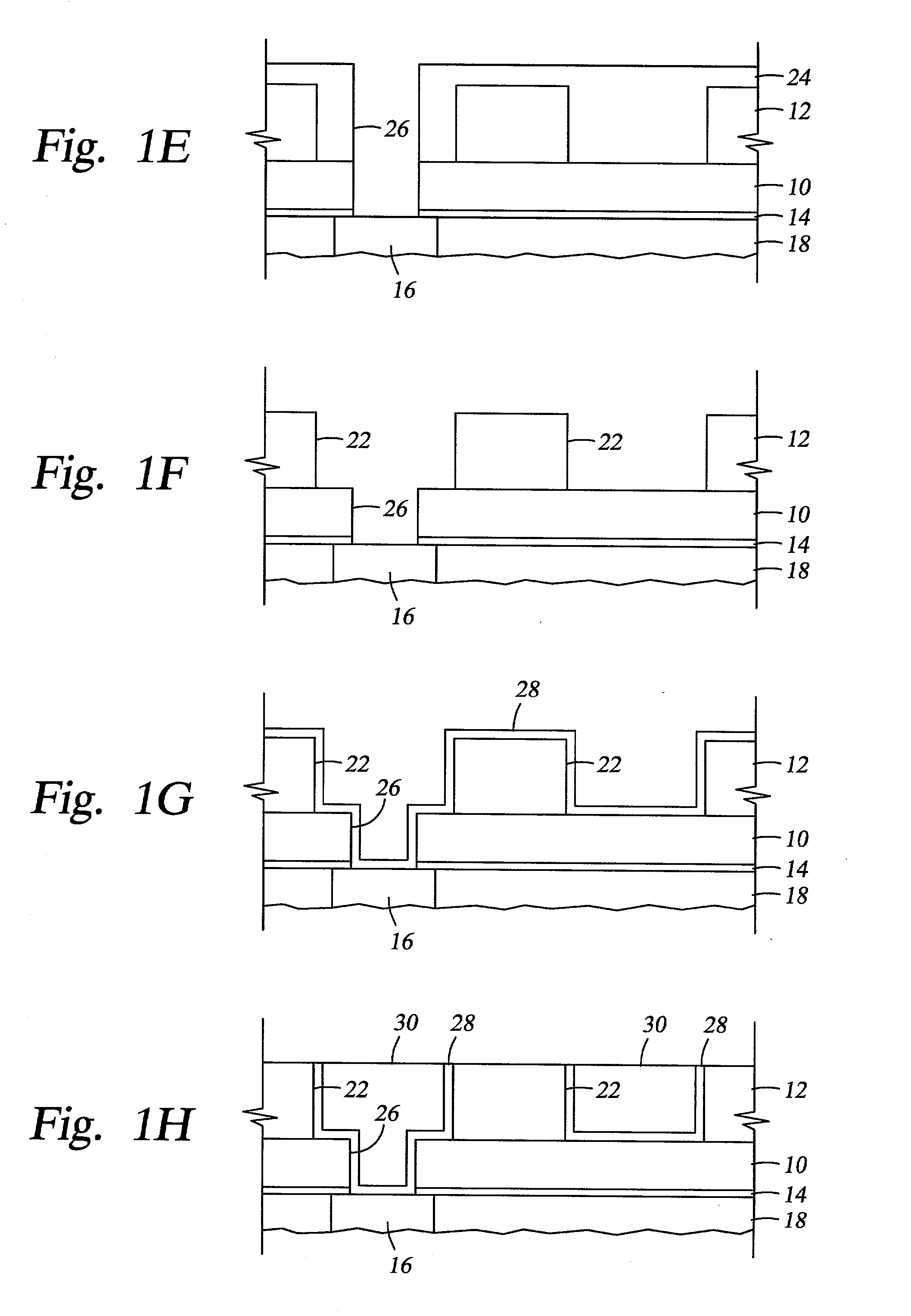
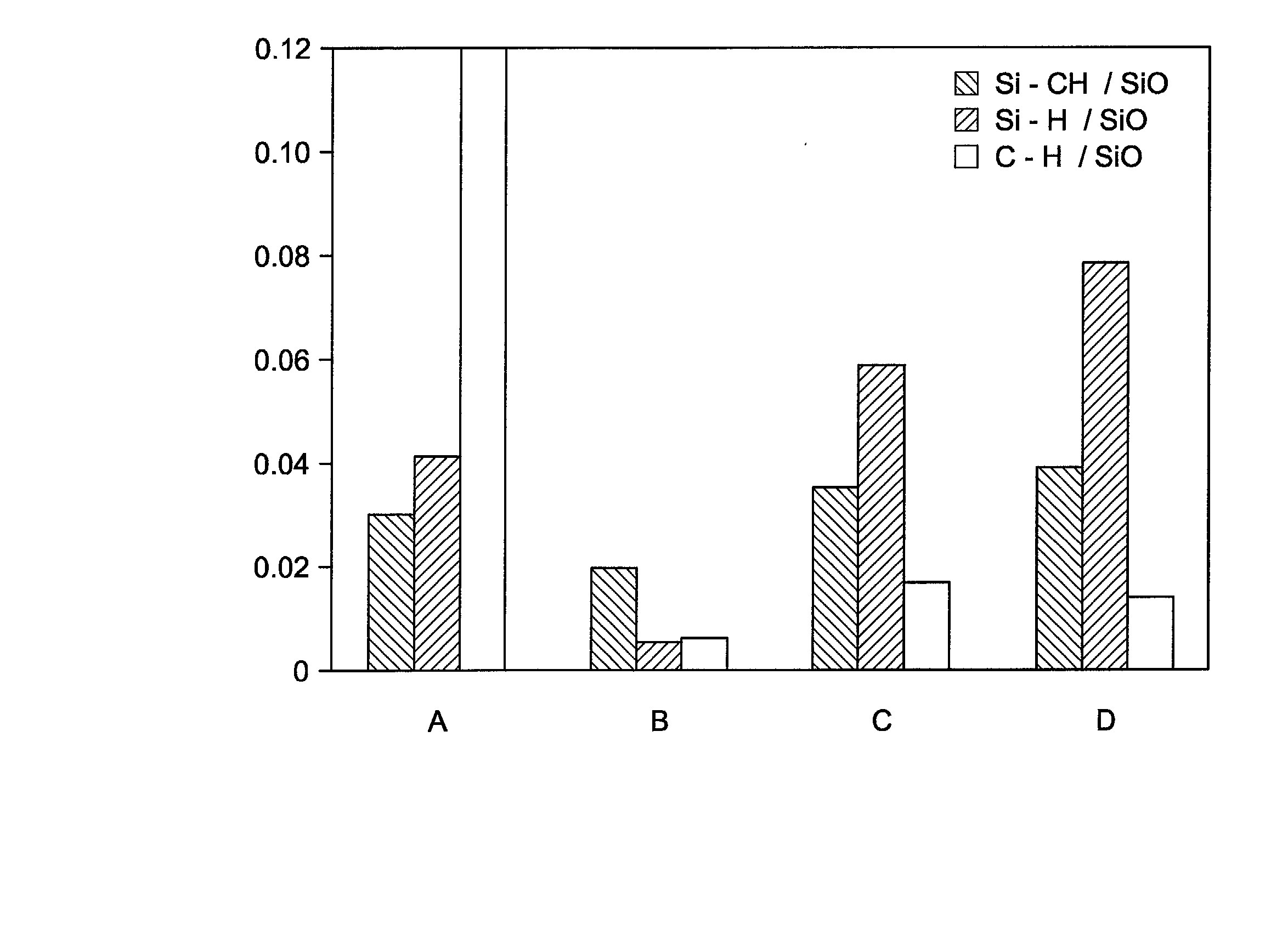
Integrated low K dielectrics and etch stops
InactiveUS6340435B1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogenFluorocarbon
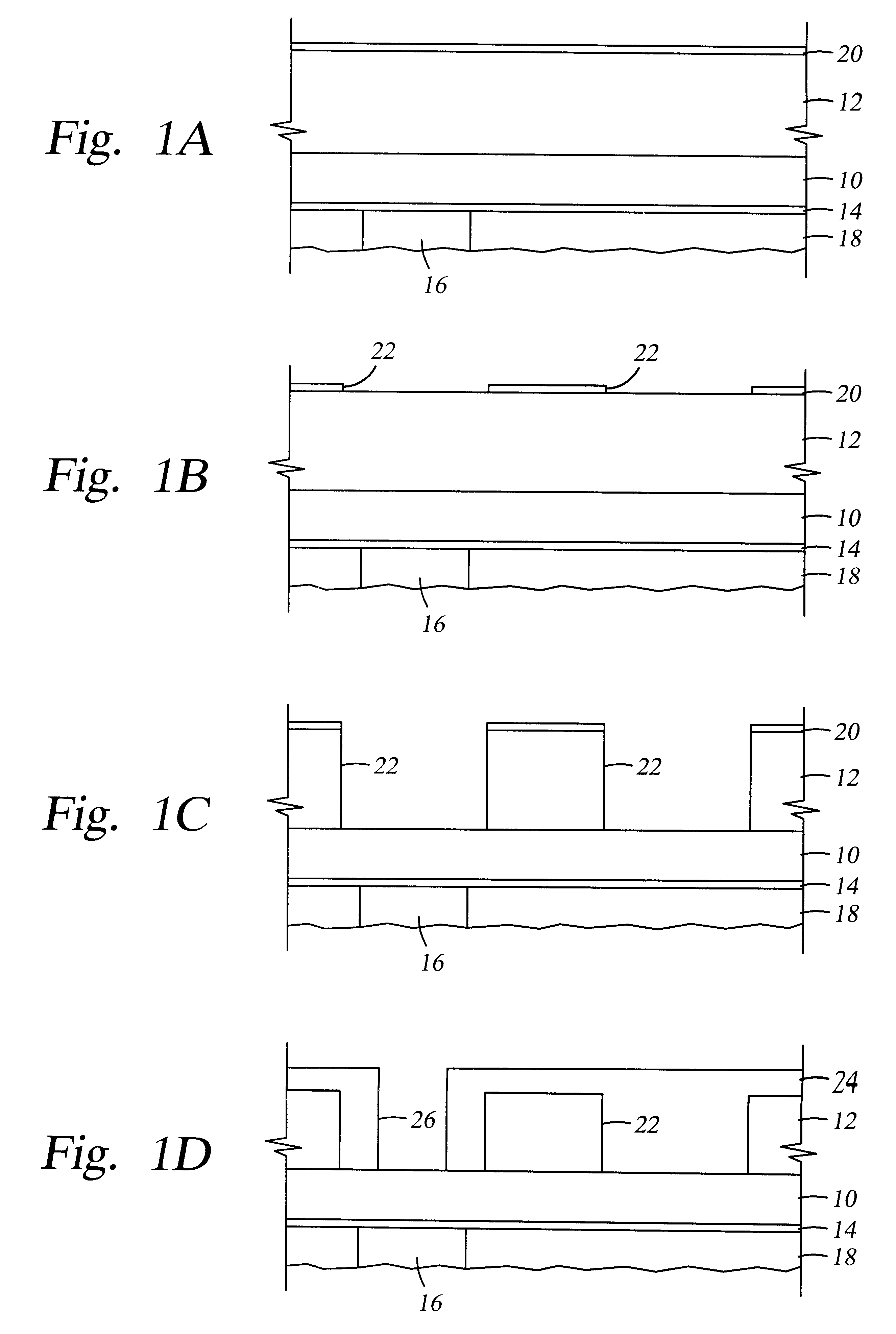
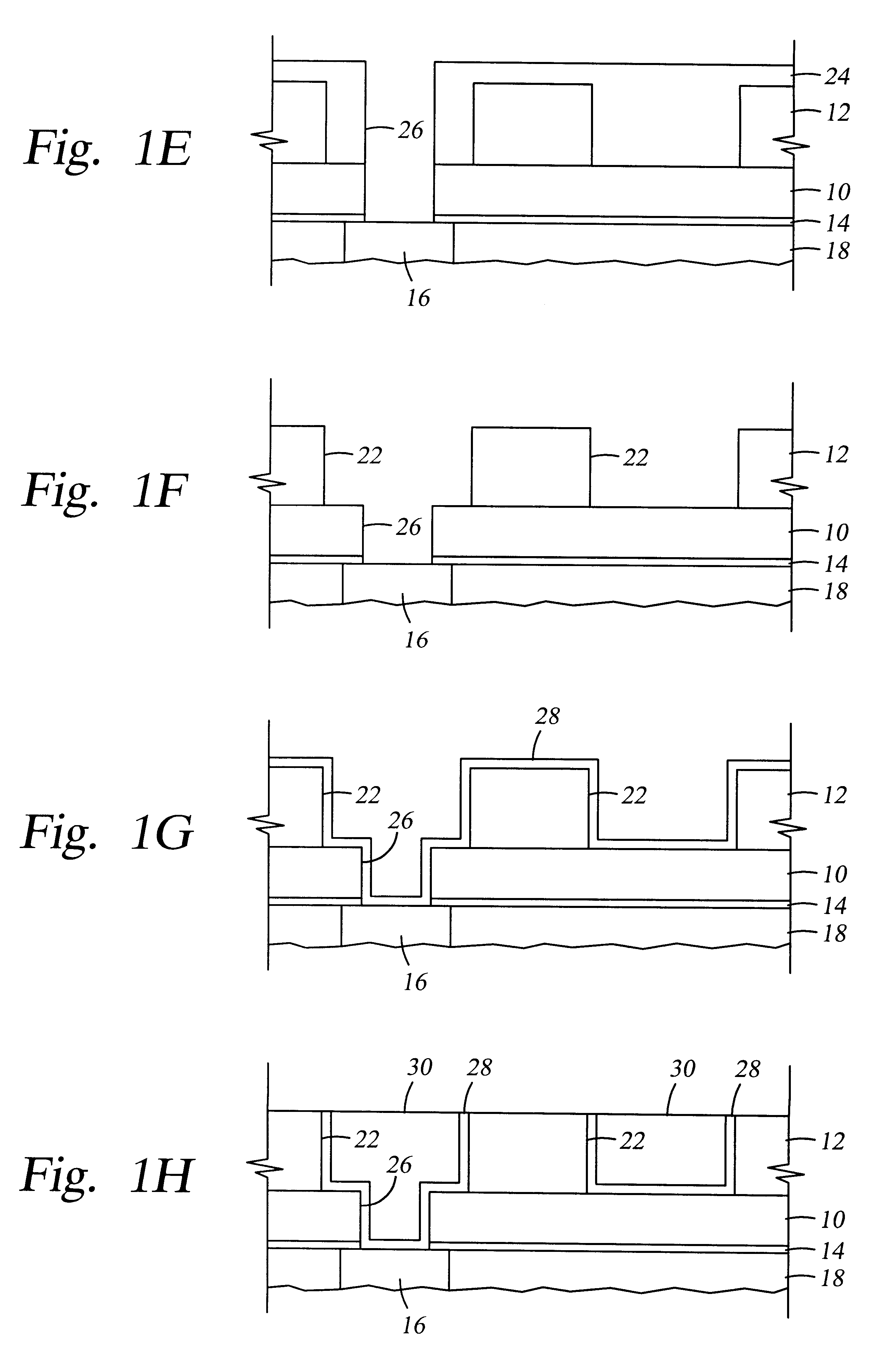
A method of depositing and etching dielectric layers having low dielectric constants and etch rates that vary by at least 3:1 for formation of horizontal interconnects. The amount of carbon or hydrogen in the dielectric layer is varied by changes in deposition conditions to provide low k dielectric layers that can replace etch stop layers or conventional dielectric layers in damascene applications. A dual damascene structure having two or more dielectric layers with dielectric constants lower than about 4 can be deposited in a single reactor and then etched to form vertical and horizontal interconnects by varying the concentration of a carbon:oxygen gas such as carbon monoxide. The etch gases for forming vertical interconnects preferably comprises CO and a fluorocarbon, and CO is preferably excluded from etch gases for forming horizontal interconnects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
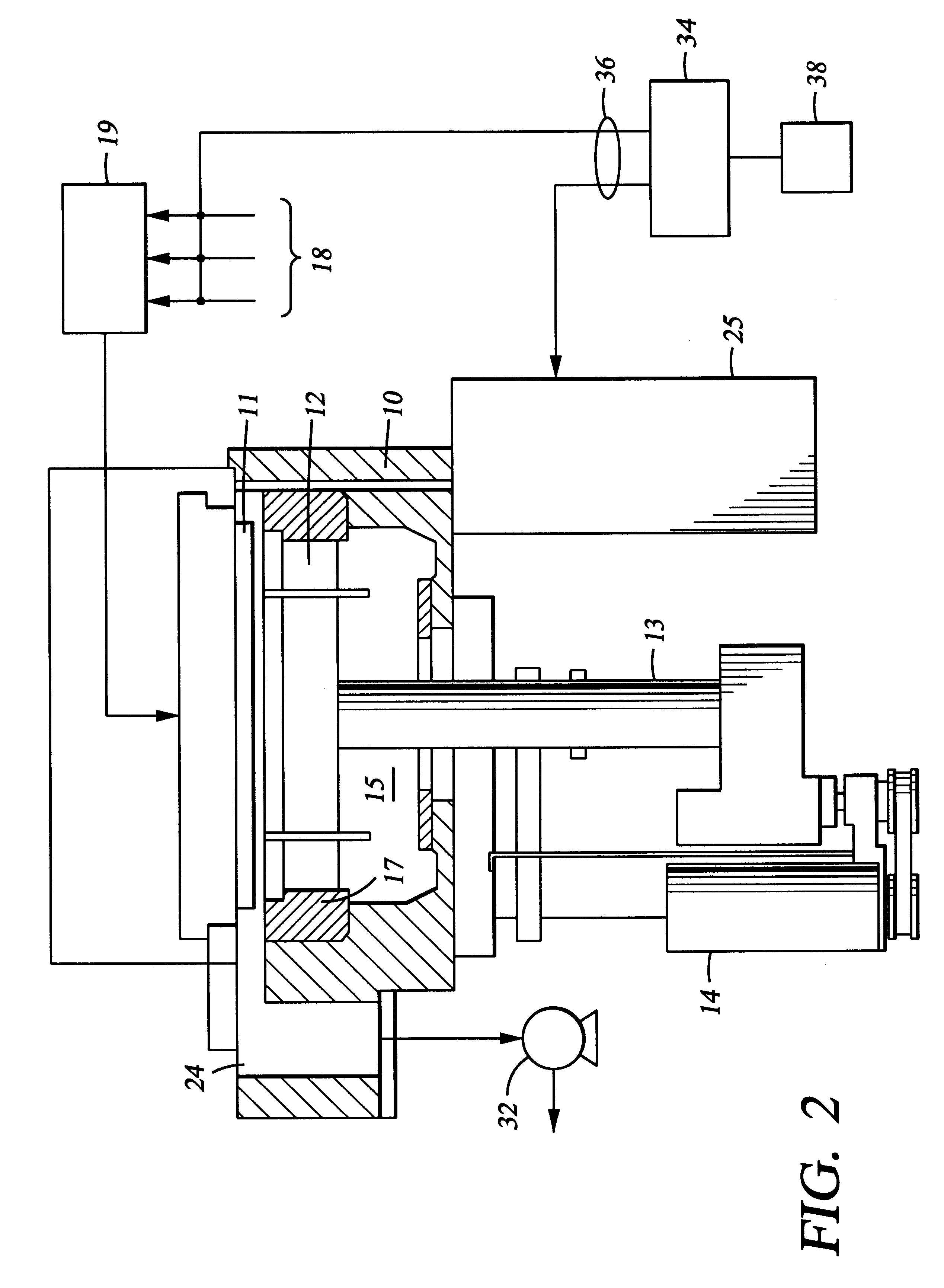
CVD plasma assisted low dielectric constant films
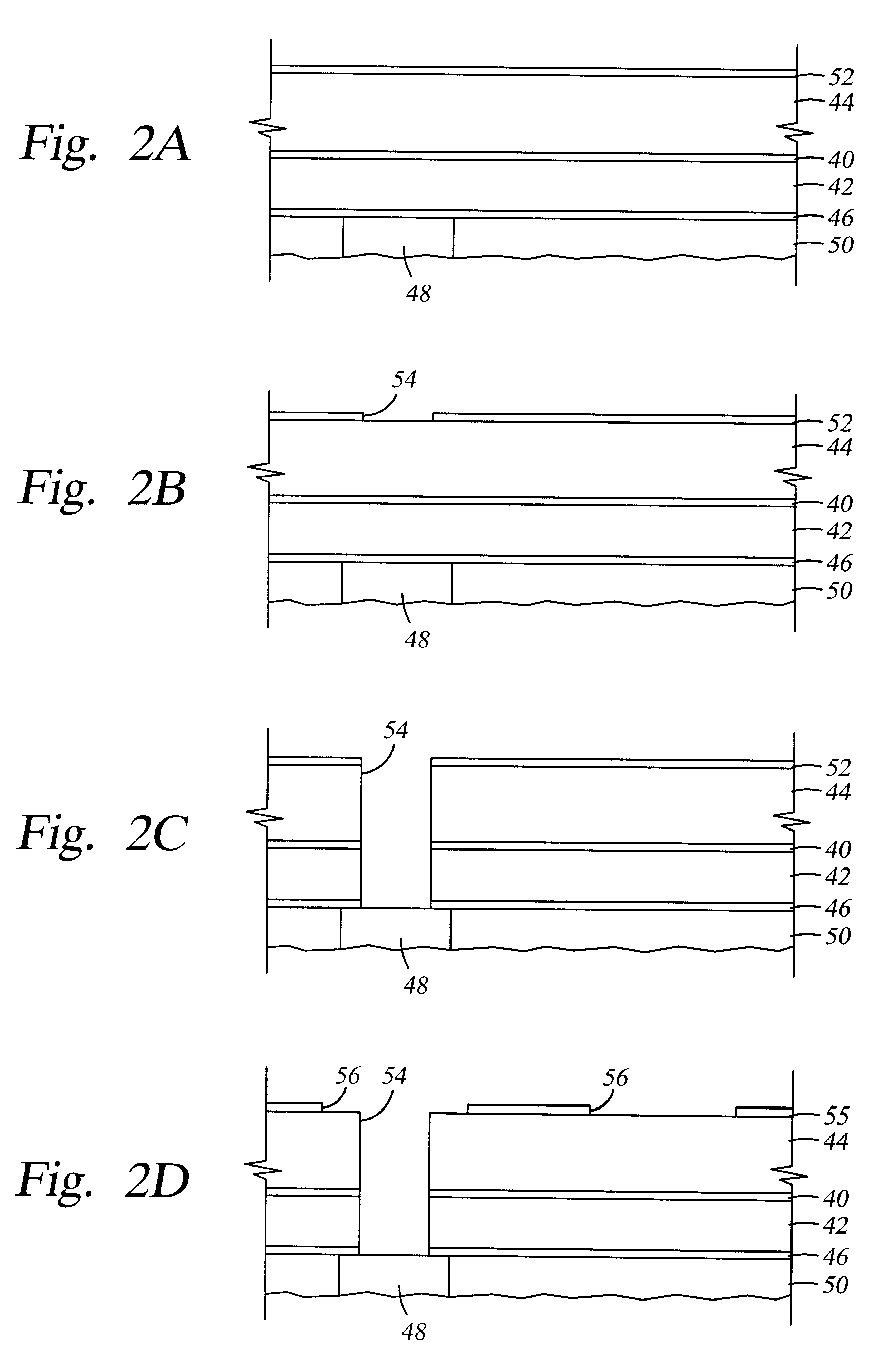
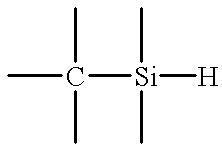
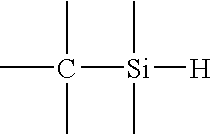
A method and apparatus for depositing a low dielectric constant film by reaction of an organosilane or organosiloxane compound and an oxidizing gas at a low RF power level from 10-250 W. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane film has good barrier properties for use as a liner or cap layer adjacent other dielectric layers. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane film may also be used as an etch stop or an intermetal dielectric layer for fabricating dual damascene structures. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane films also provide excellent adhesion between different dielectric layers. A preferred oxidized organosilane film is produced by reaction of methylsilane, CH3SiH3, or dimethylsilane, (CH3)2SiH2, and nitrous oxide, N2O, at an RF power level from about 10 to 200 W or a pulsed RF power level from about 20 to 250 W during 10-30% of the duty cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Plasma processes for depositing low dielectric constant films
A method and apparatus for depositing a low dielectric constant film by reaction of an organosilicon compound and an oxidizing gas at a constant RF power level from about 10W to about 200W or a pulsed RF power level from about 20W to about 500W. Dissociation of the oxidizing gas can be increased prior to mixing with the organosilicon compound, preferably within a separate microwave chamber, to assist in controlling the carbon content of the deposited film. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane film has good barrier properties for use as a liner or cap layer adjacent other dielectric layers. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane film may also be used as an etch stop and an intermetal dielectric layer for fabricating dual damascene structures. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane films also provide excellent adhesion between different dielectric layers. A preferred oxidized organosilane film is produced by reaction of methylsilane, CH3SiH3, dimethylsilane, (CH3)2SiH2, or 1,1,3,3-tetramethyl-disiloxane, (CH3)2-SiH-O-SiH-(CH3)2, and nitrous oxide, N2O, at a constant RF power level from about 10W to about 150W, or a pulsed RF power level from about 20W to about 250W during 10% to 30% of the duty cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
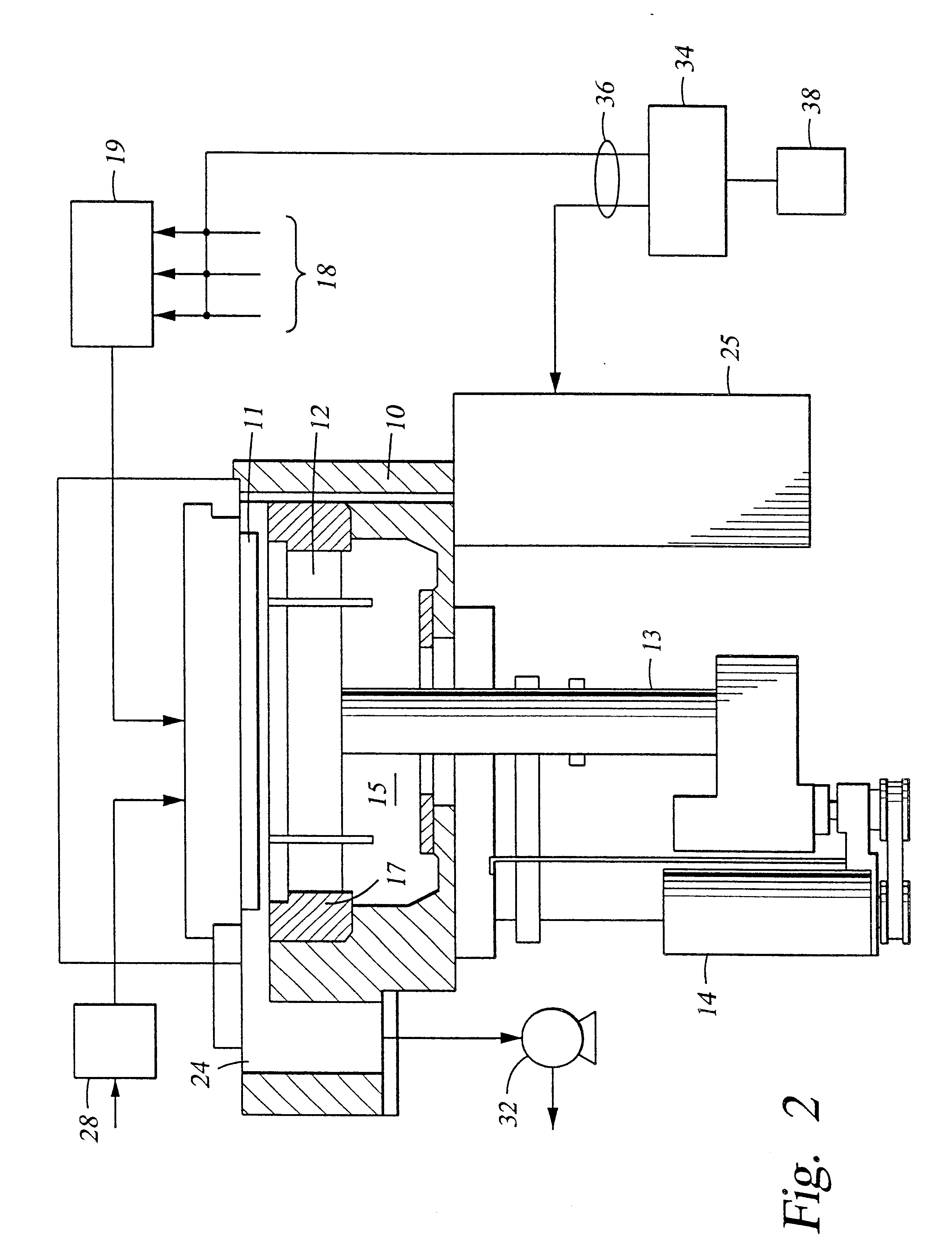
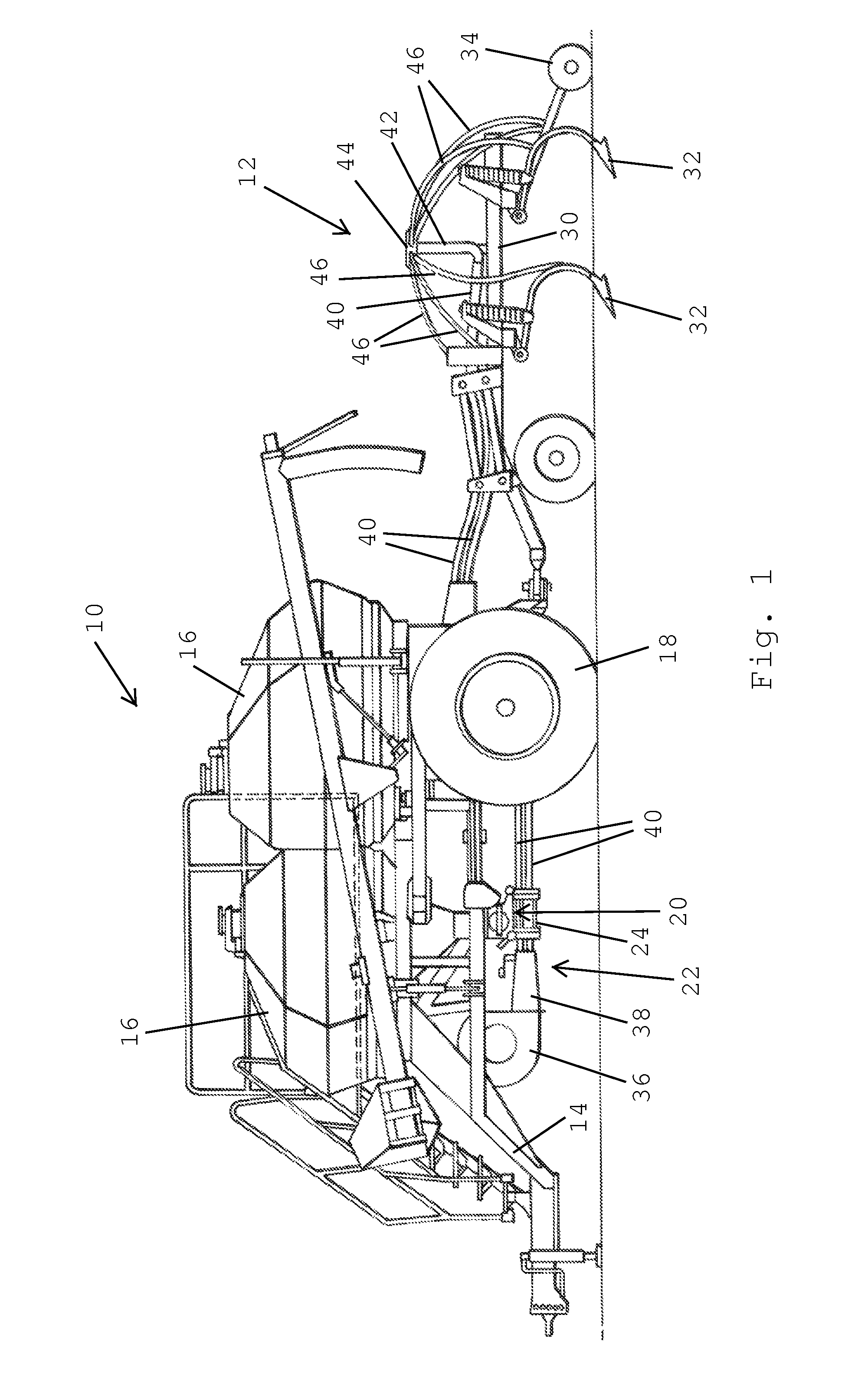
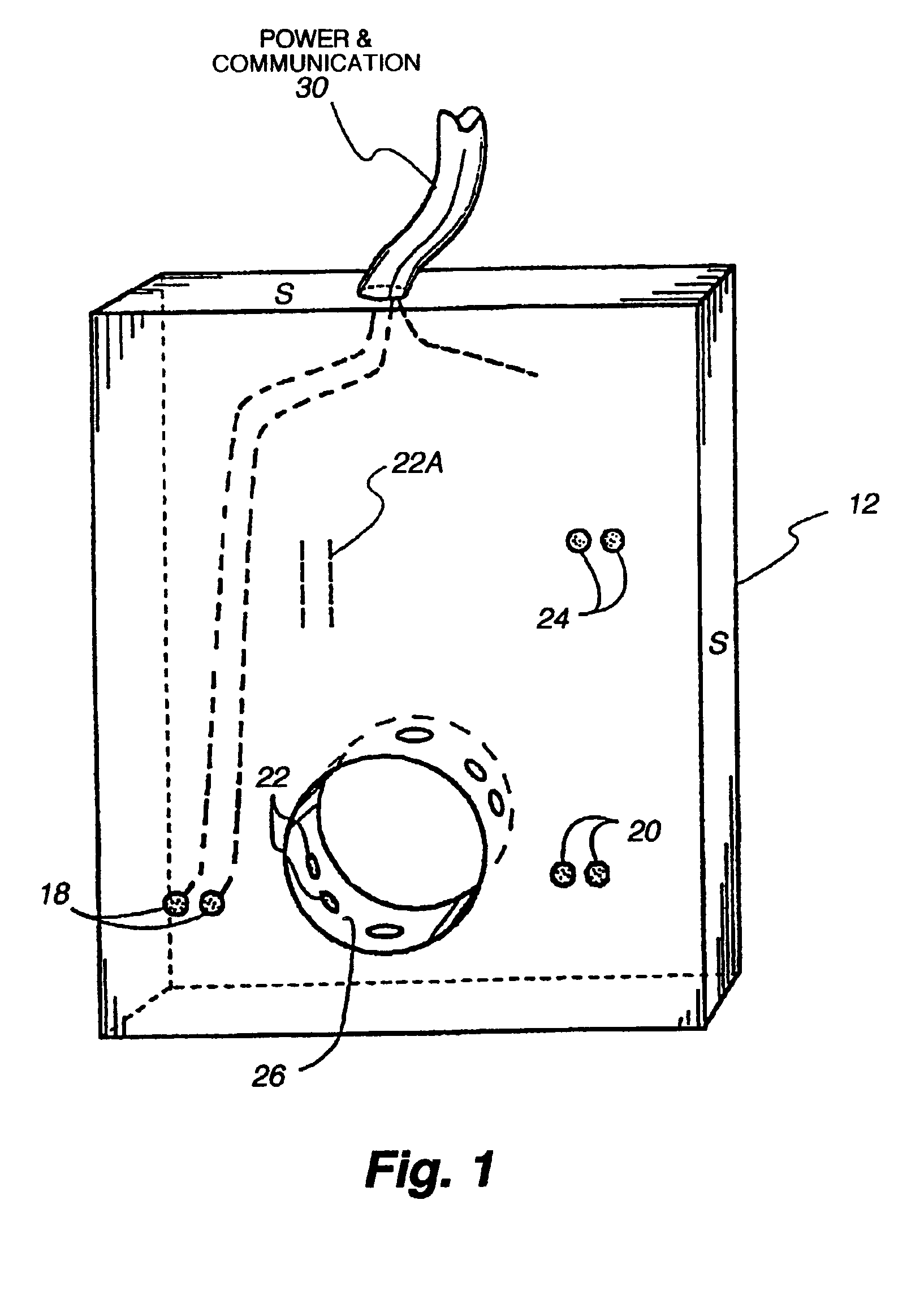
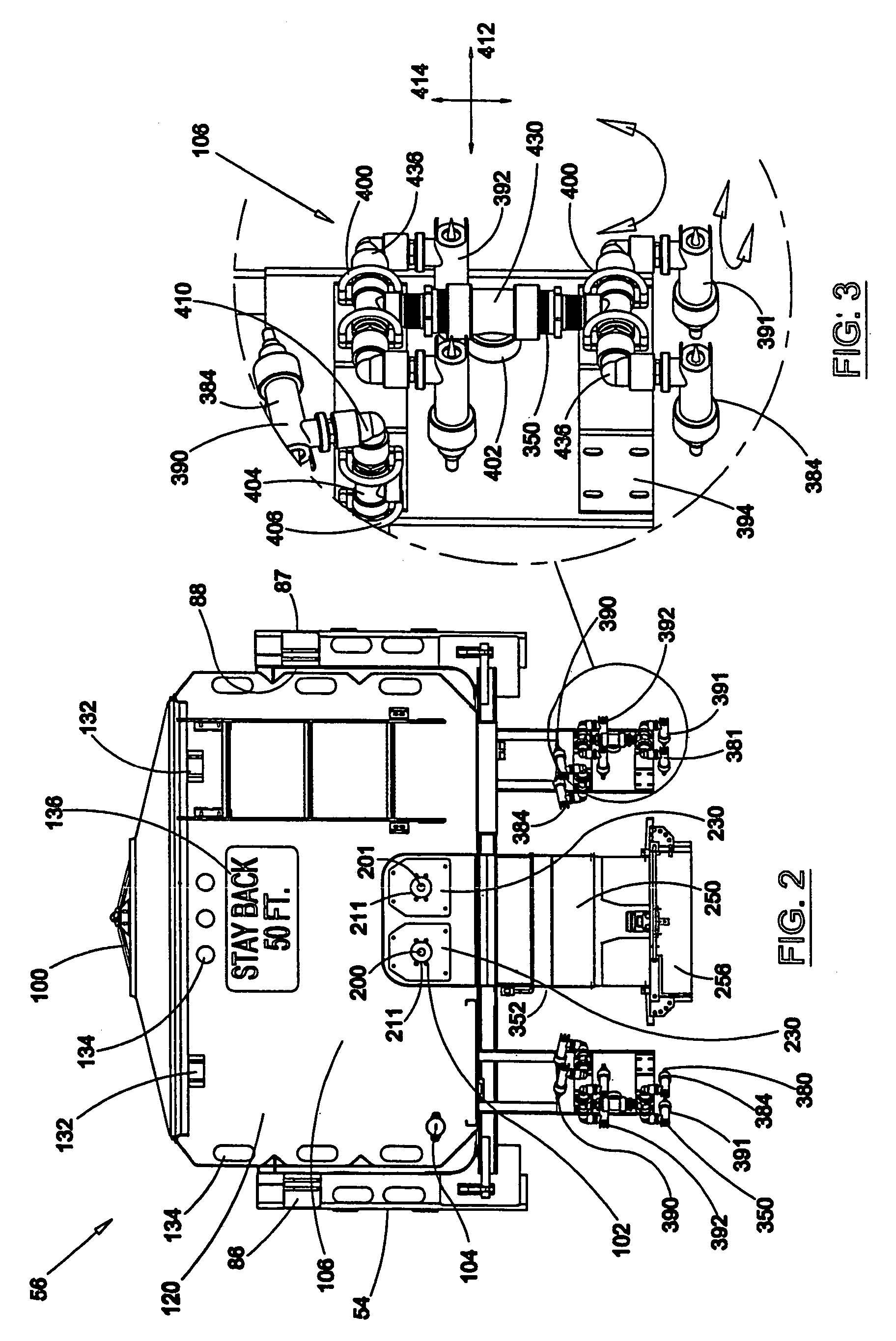
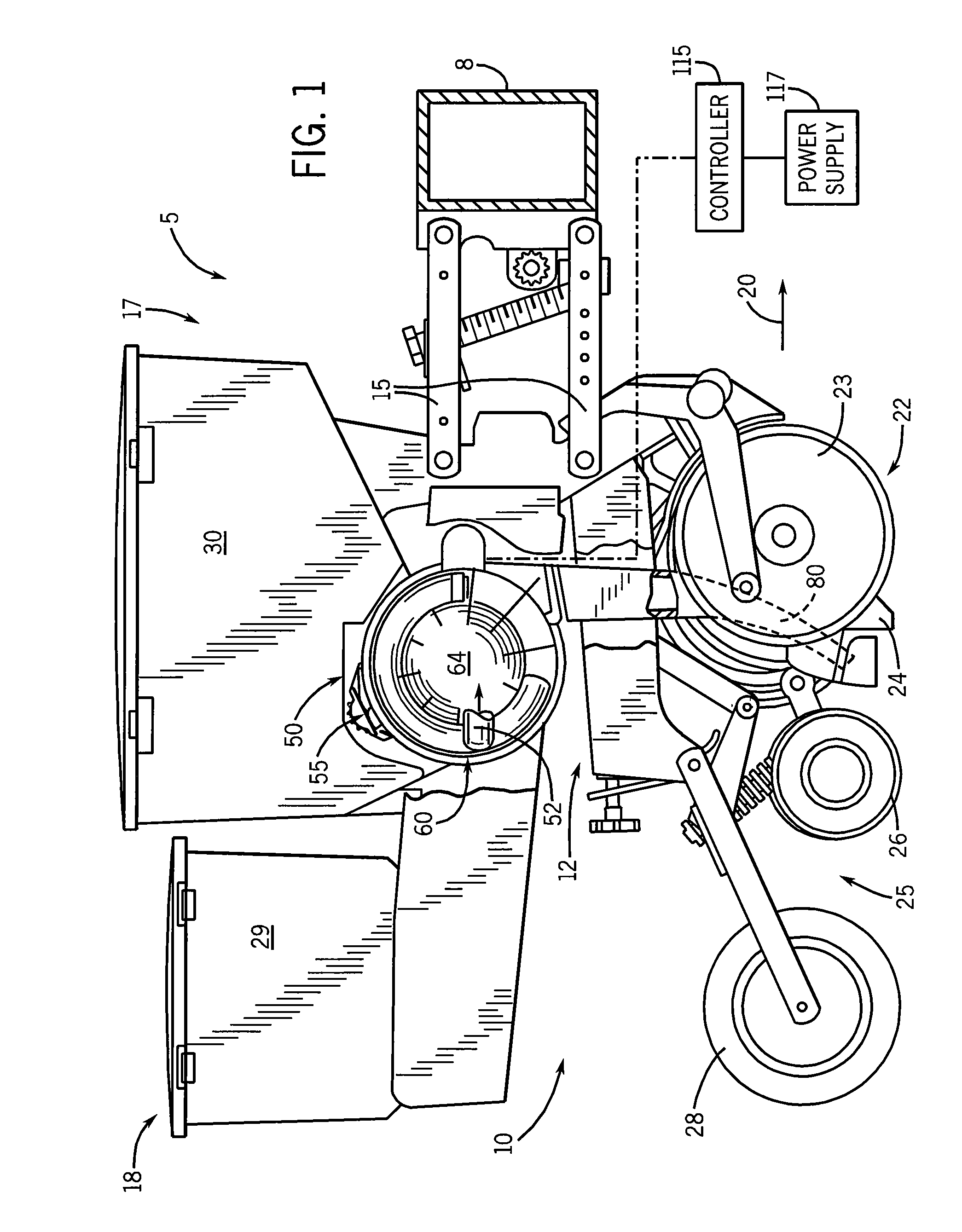
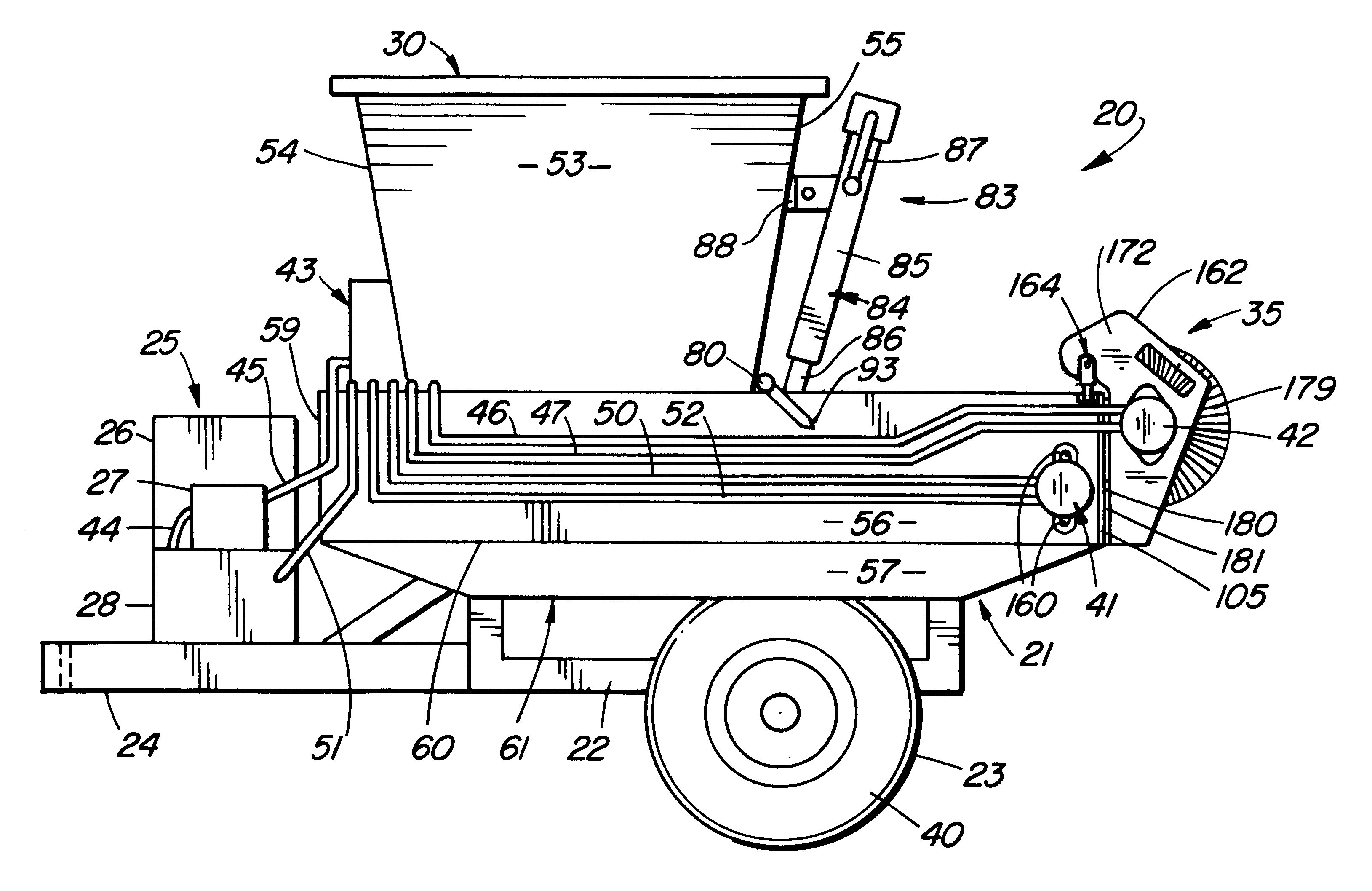
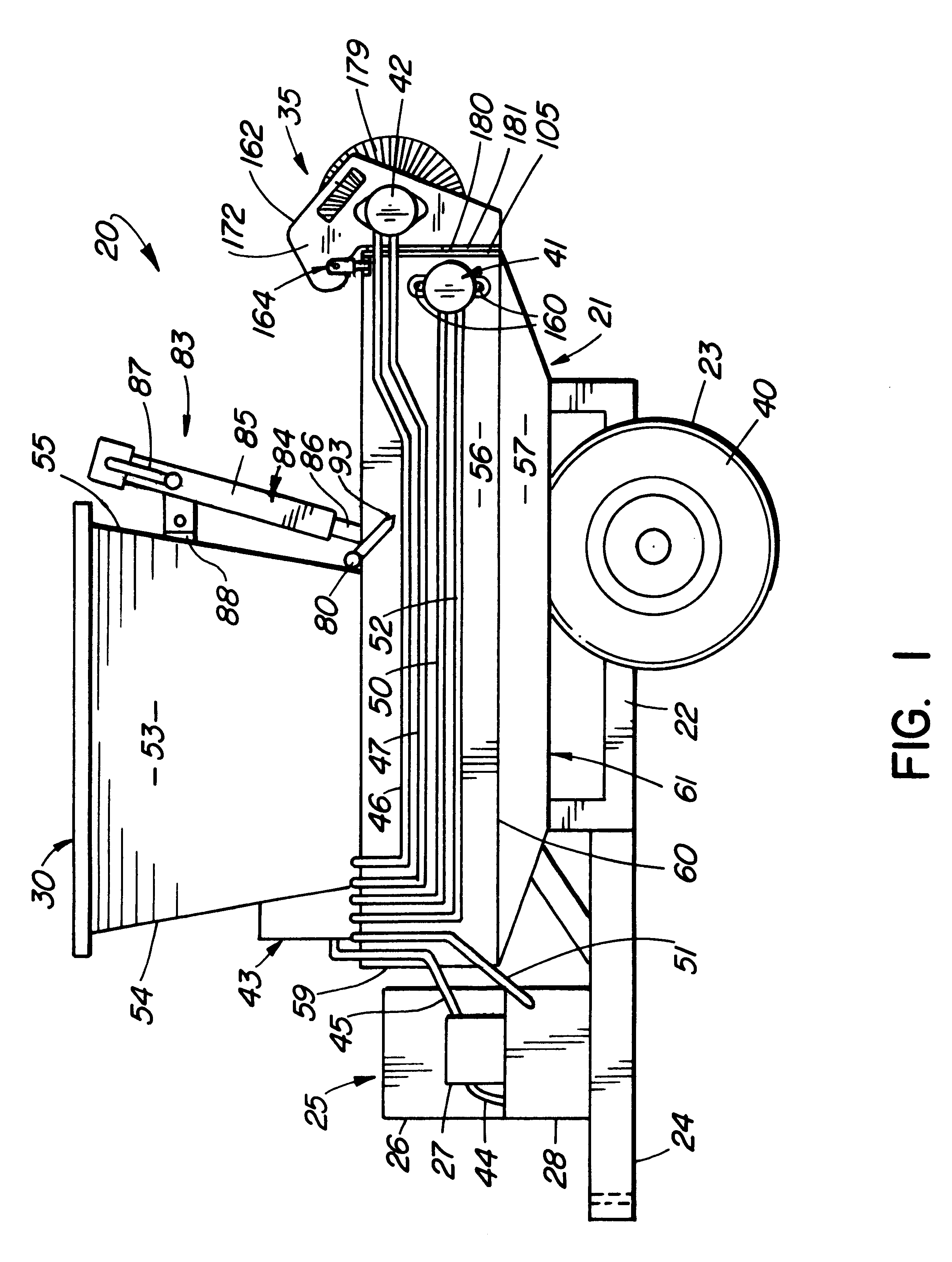
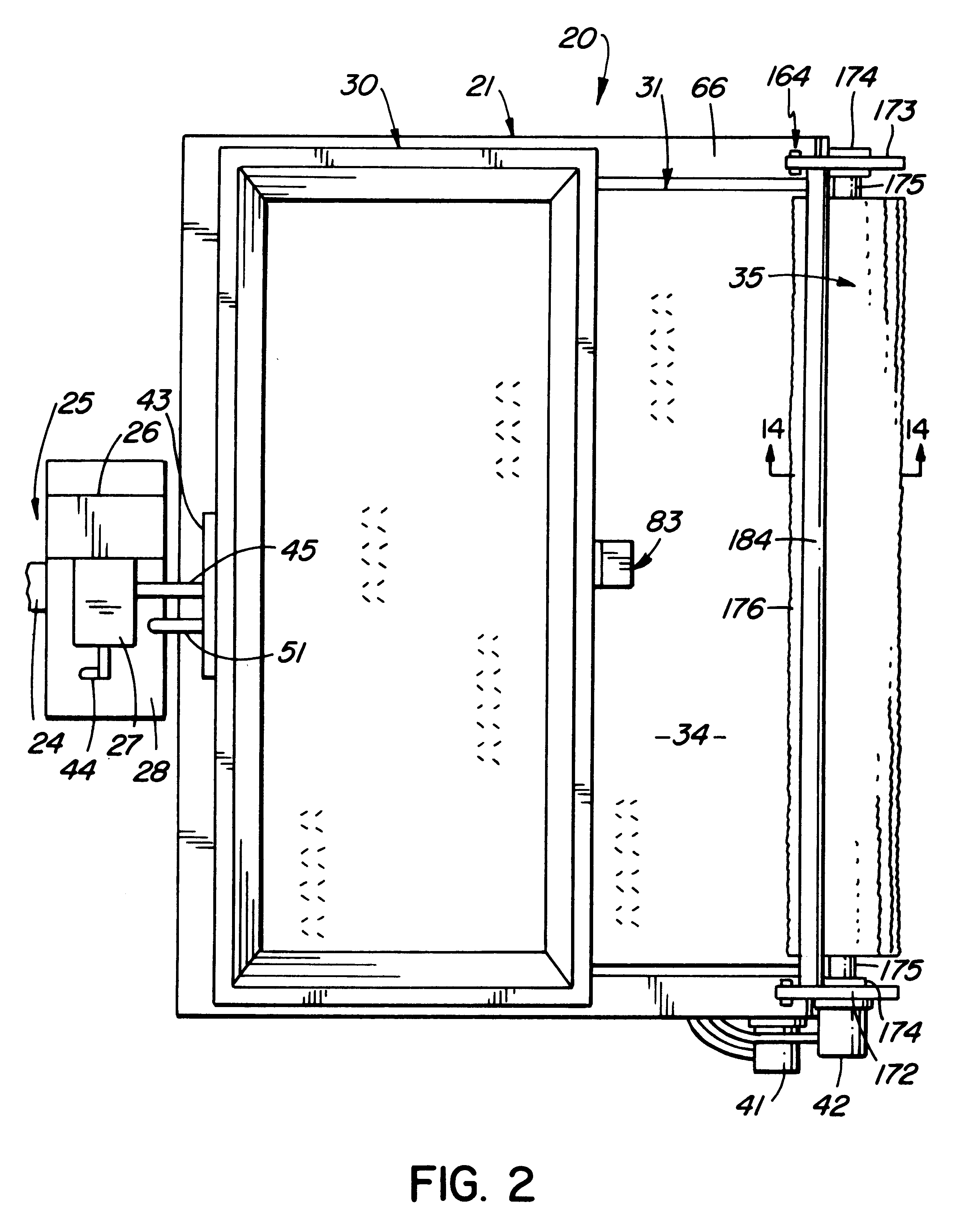
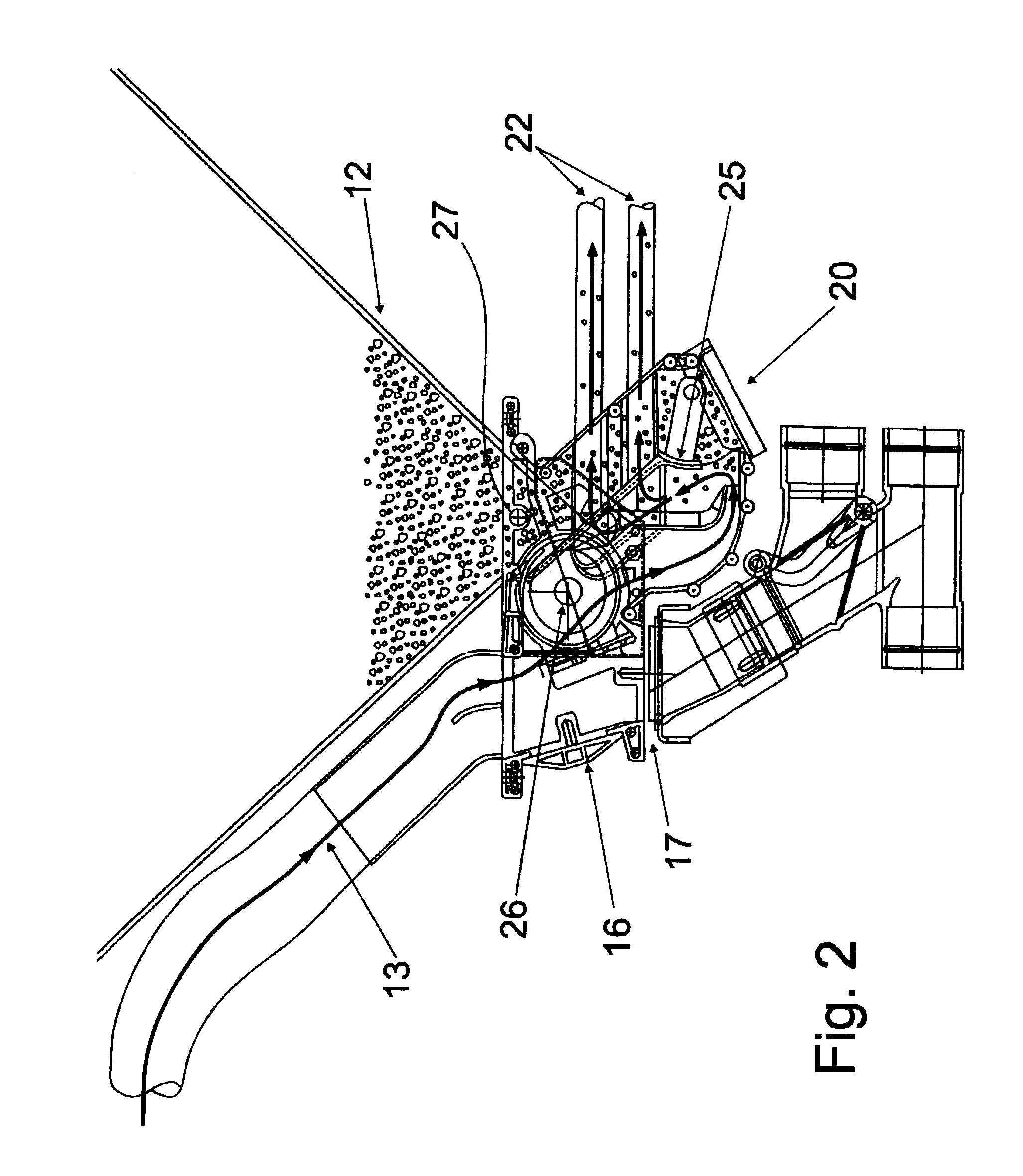
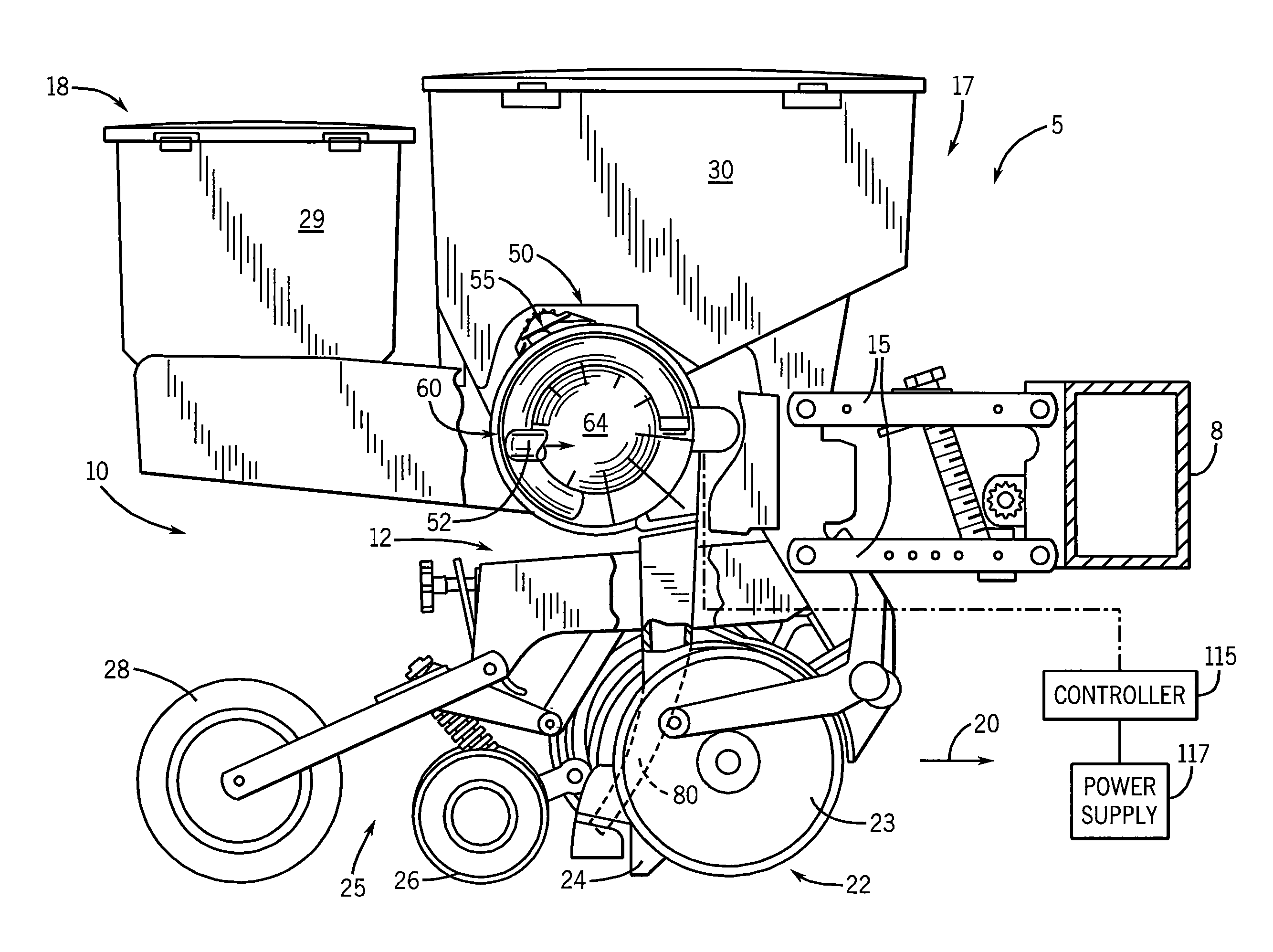
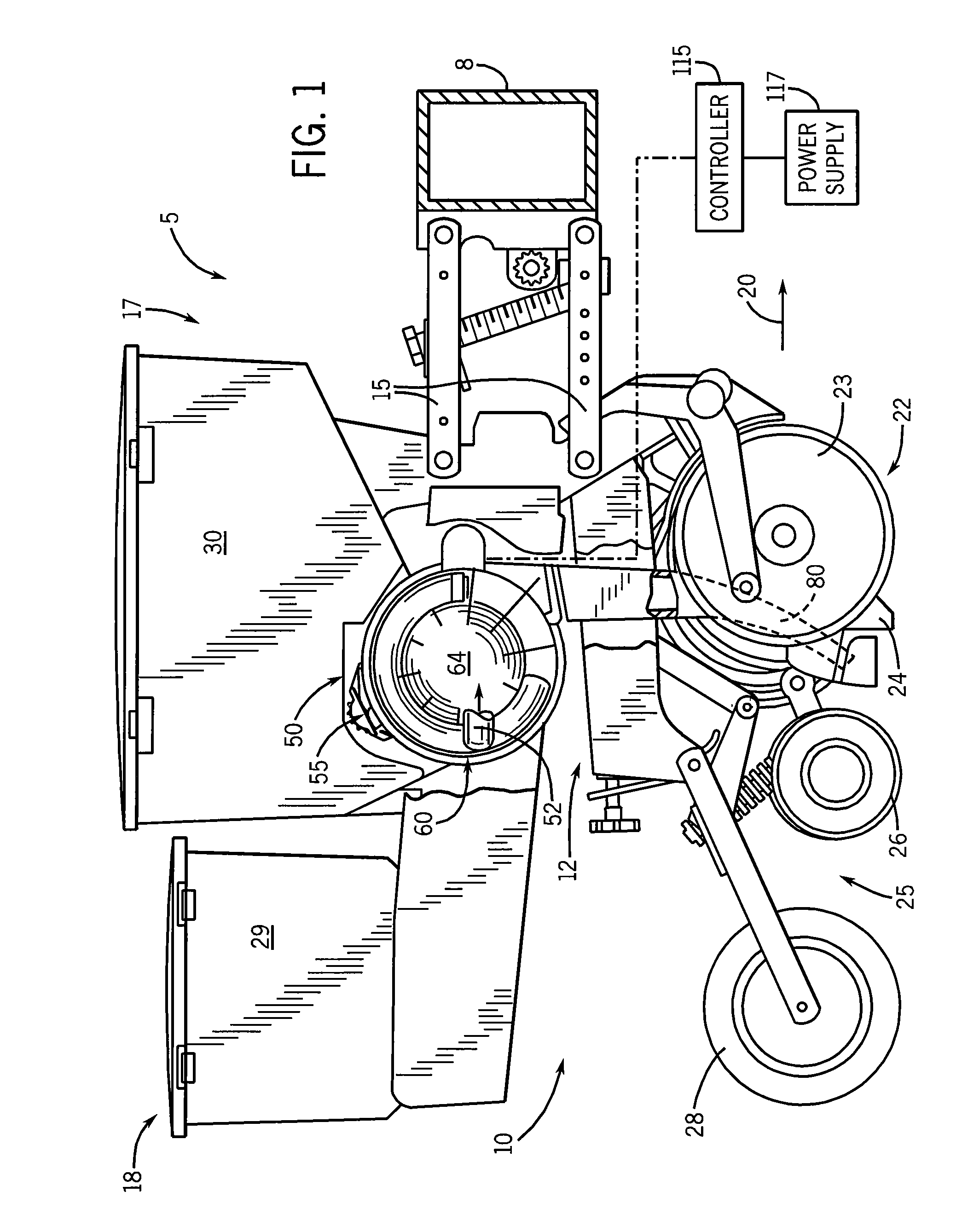
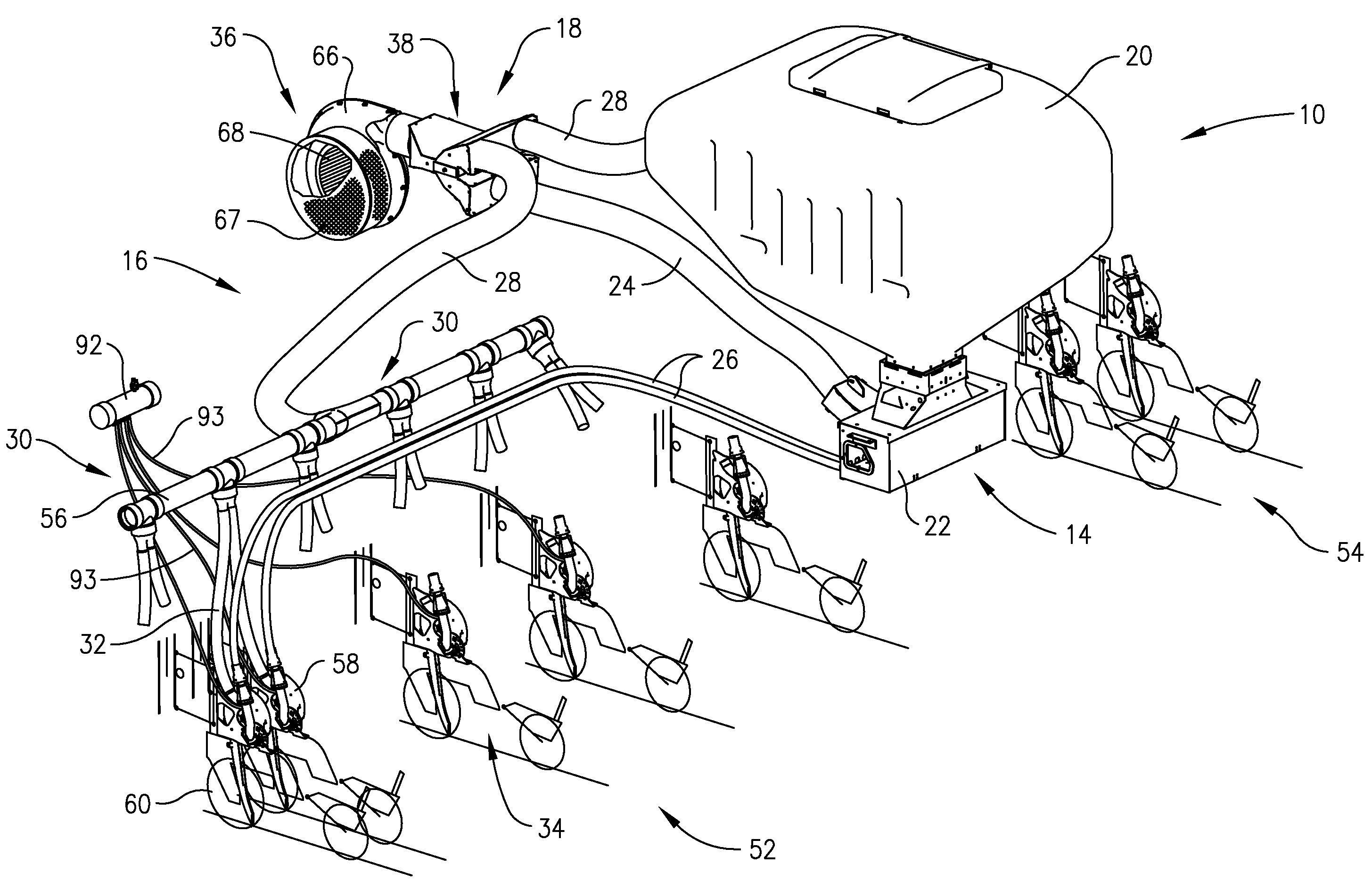
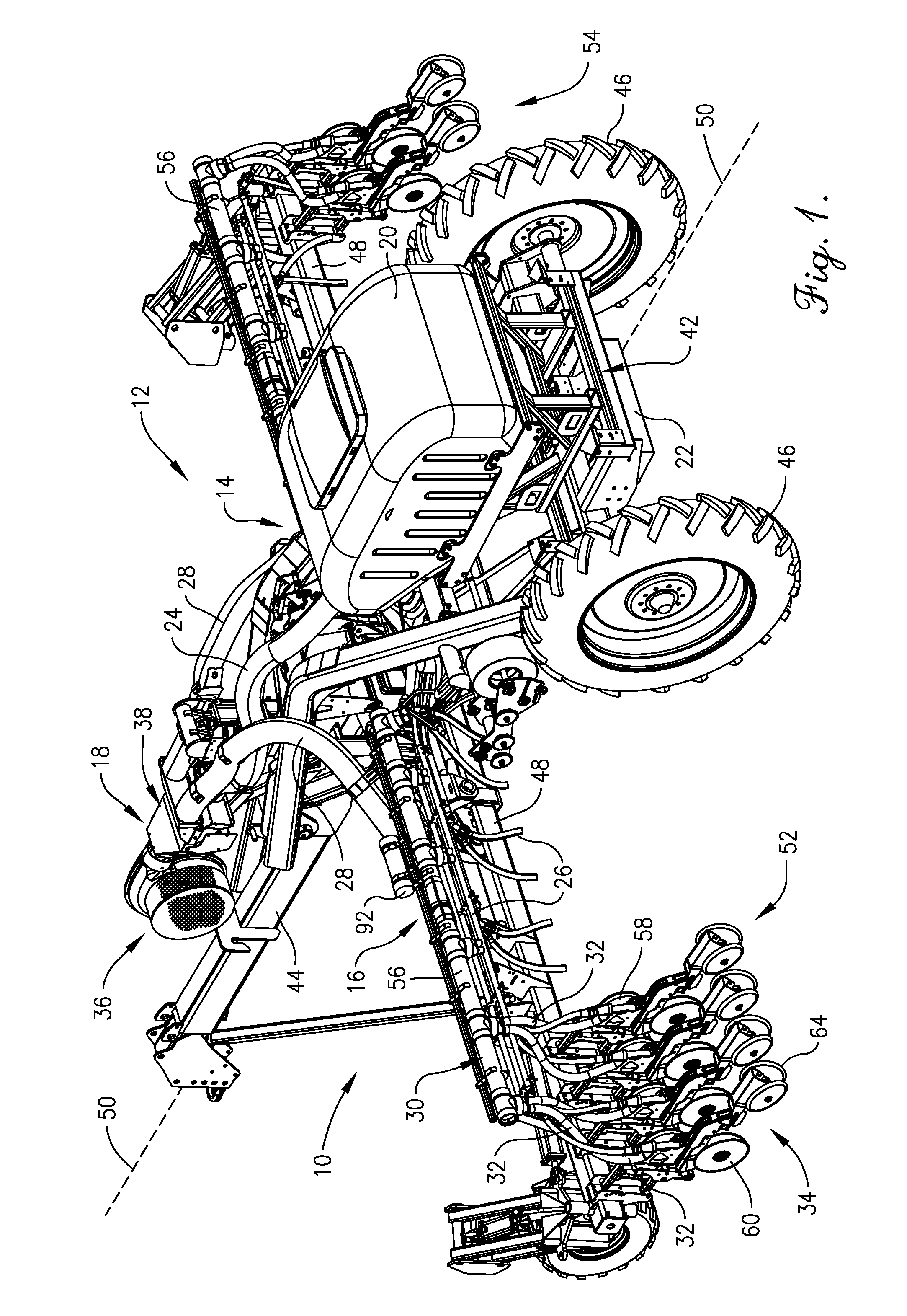
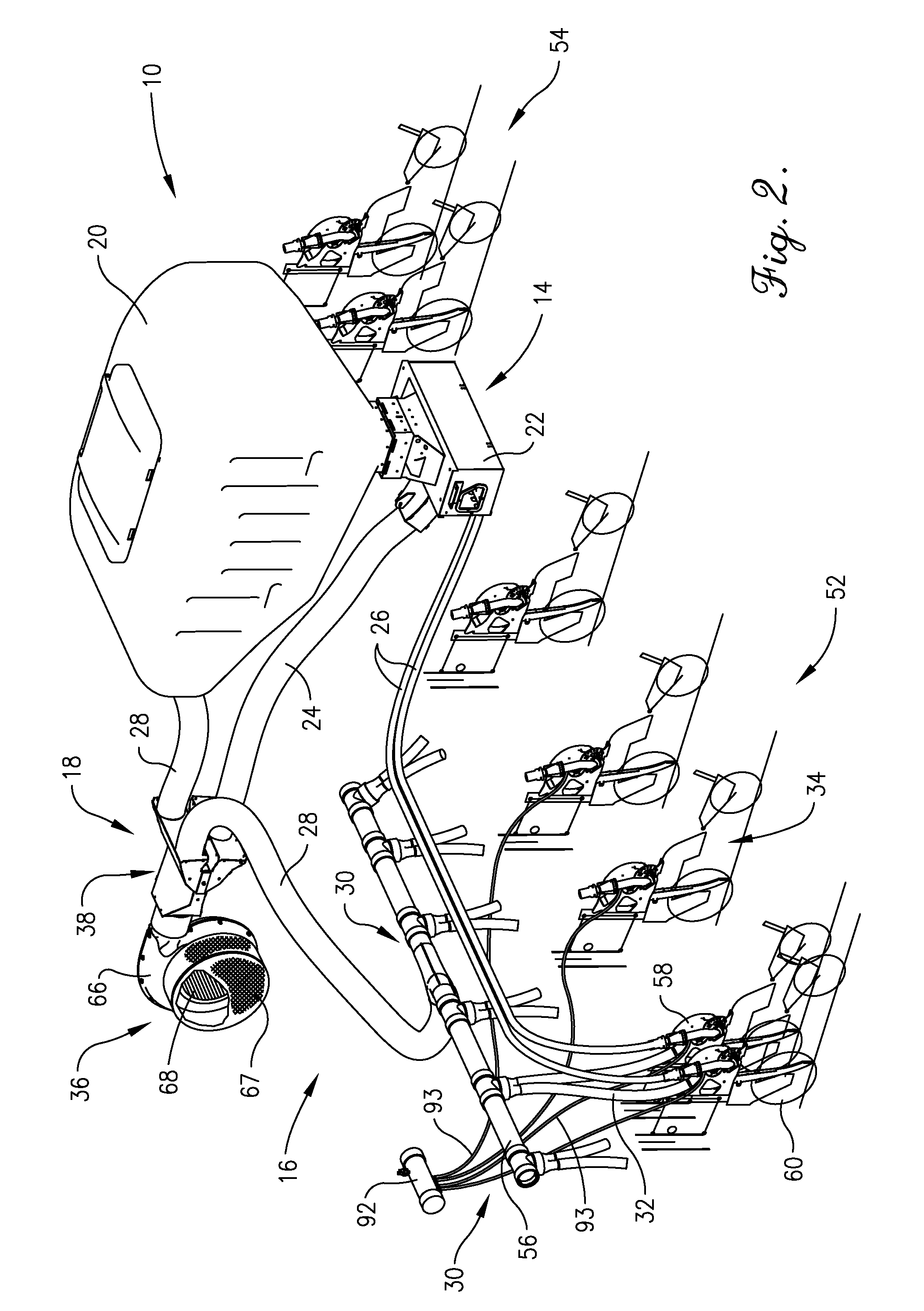
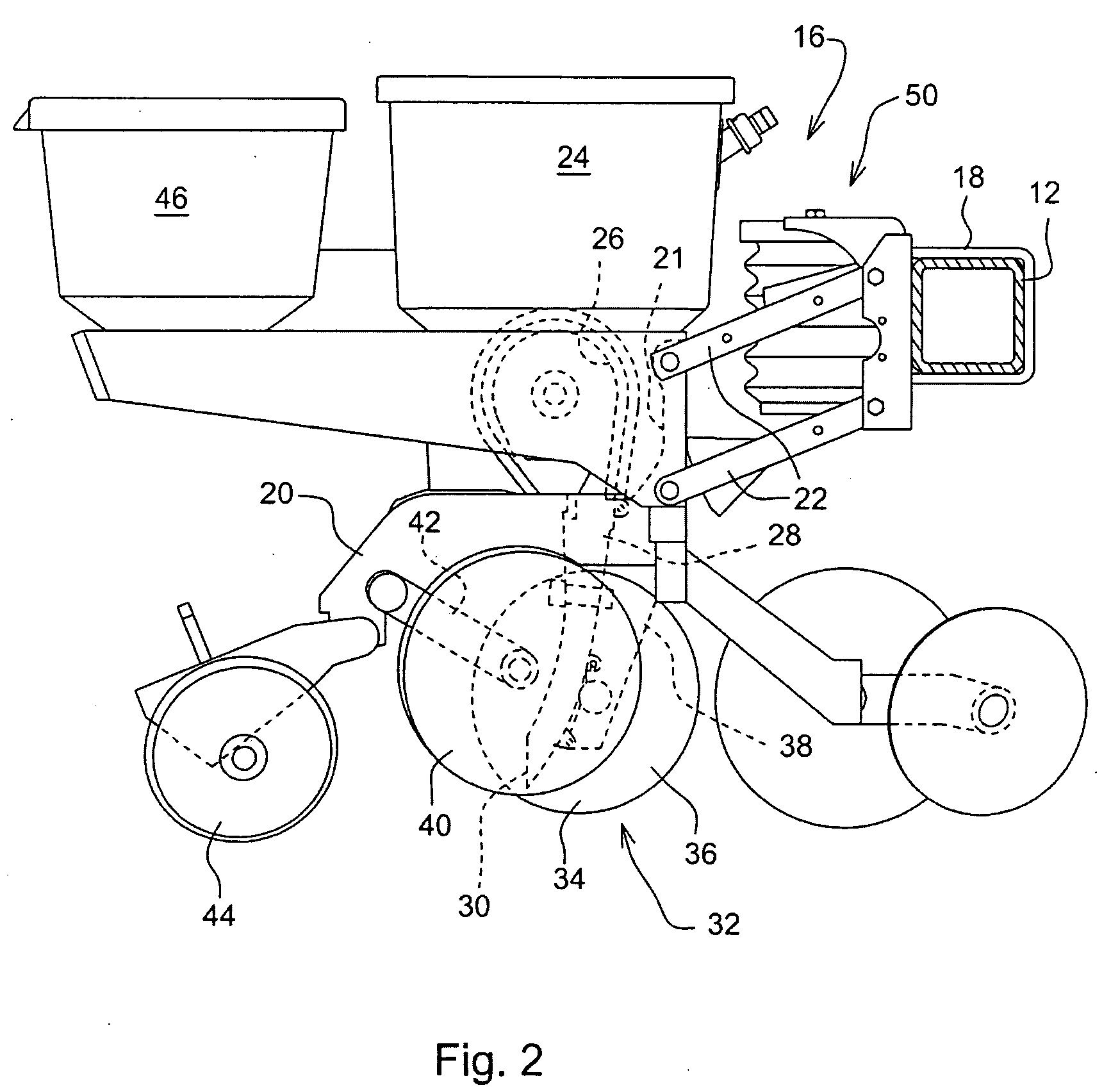
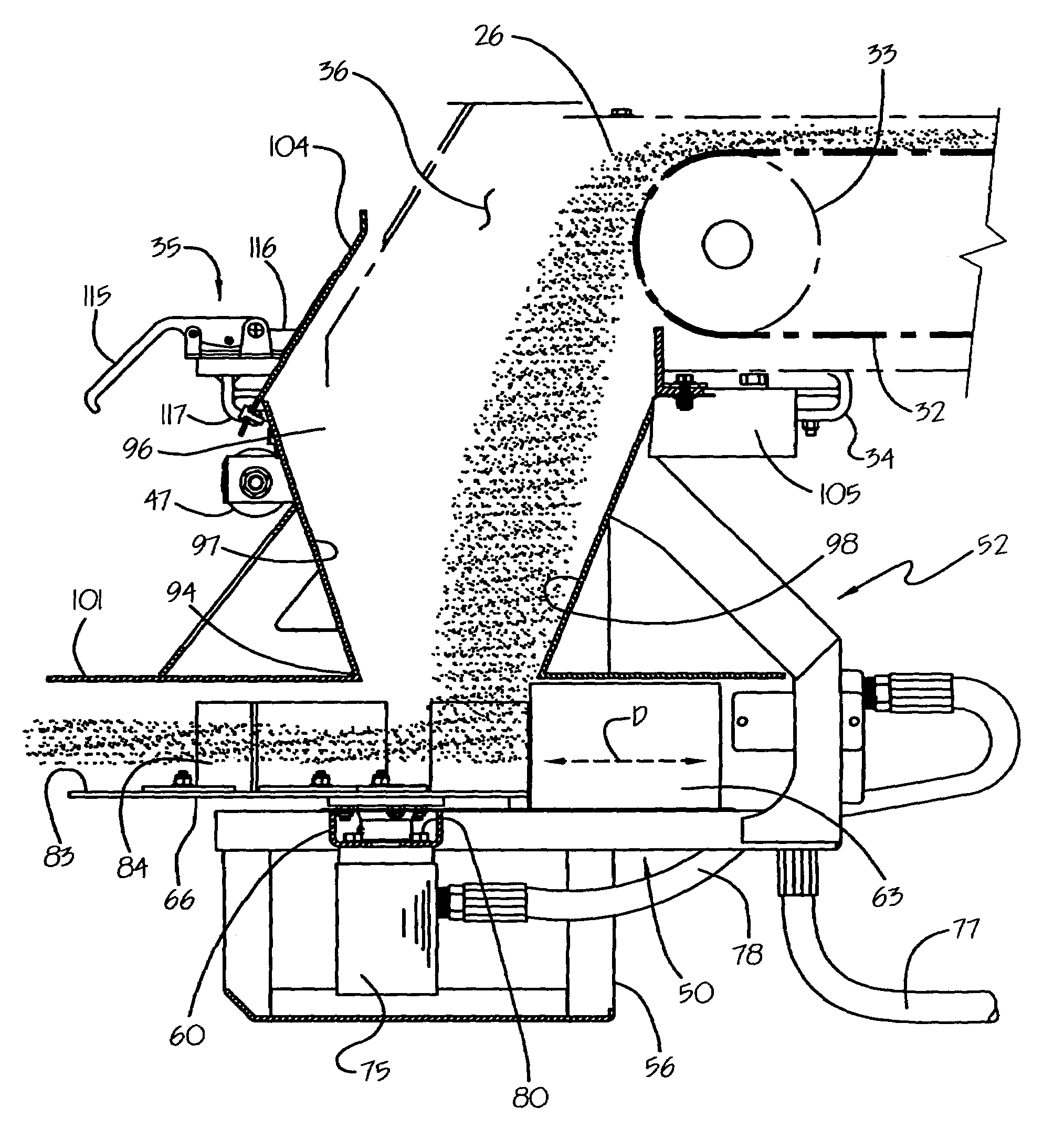
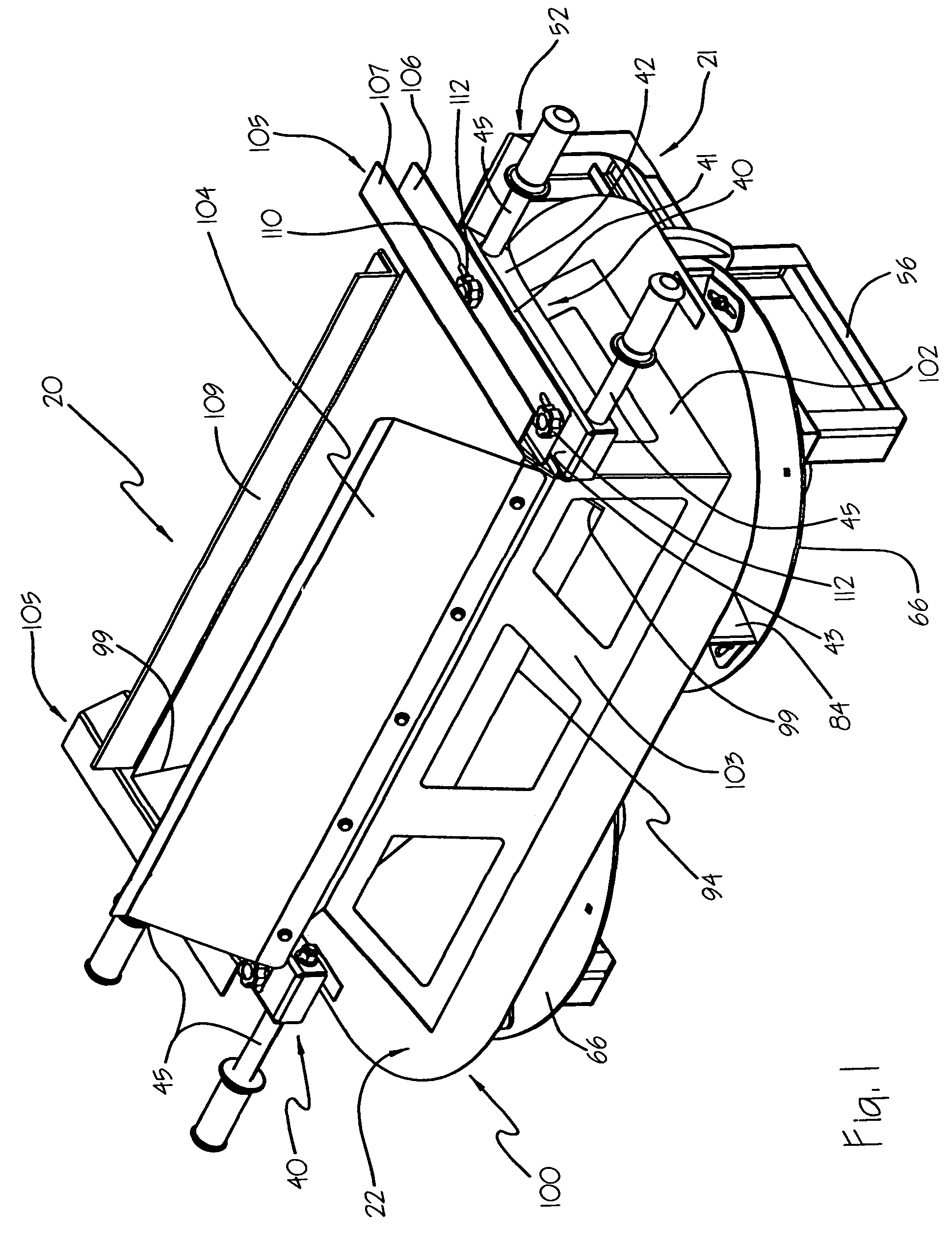
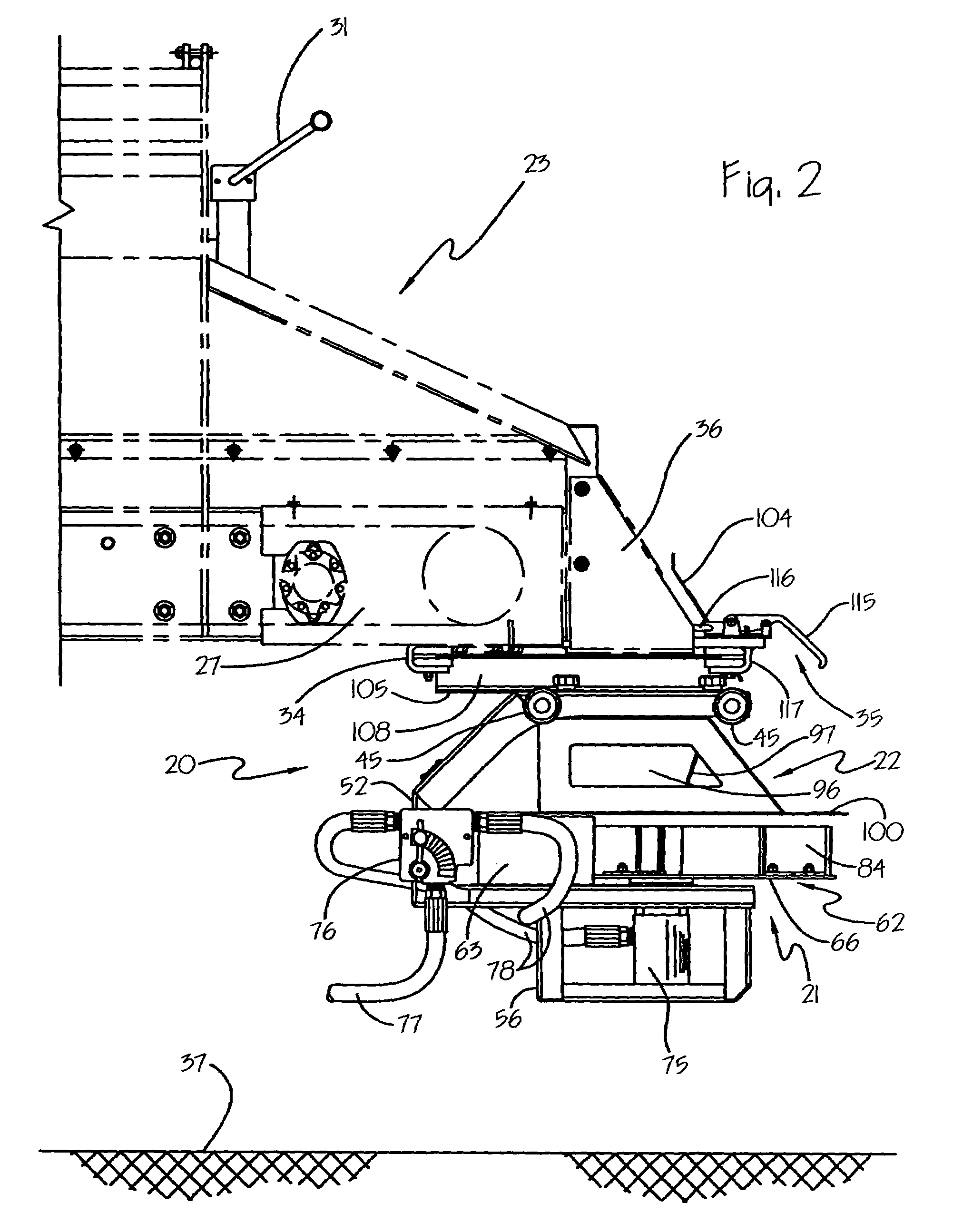
Pressure sensing system for a planter
A pressure sensing system for a seeding machine such as a planter to measure the down force on a planter row unit uses a wireless pressure sensor embedded in a load carrying wheel of the row unit. In a preferred embodiment, the pressure sensor is a passive piezoelectric pressure sensor that is a transmitter only, transmitting both pressure and RFID the information that identifies the particular sensor. Multiple sensors may be employed in each wheel and sensors may be employed in more than one wheel of the row unit, such as the gauge wheels on opposite sides of the trench opening disks. The sensors may be made of a PVDF, a known piezoelectric material. A wireless receiver is located on the planter frame or could be located elsewhere to receive the signals from the pressure sensor. A controller determines from the signal, any change in down force and commands the change to a down force generator on the row unit.
Owner:DEERE & CO
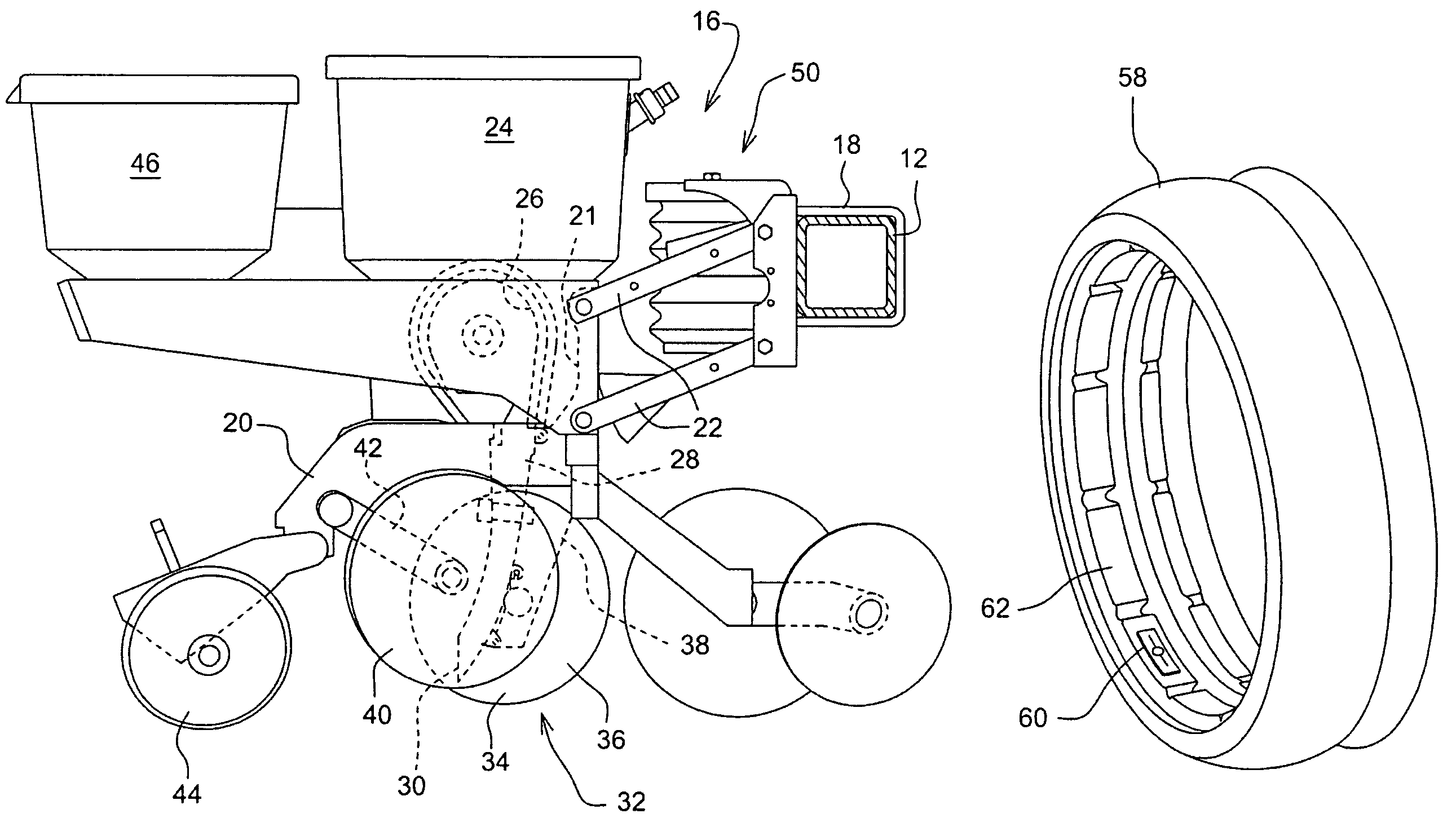
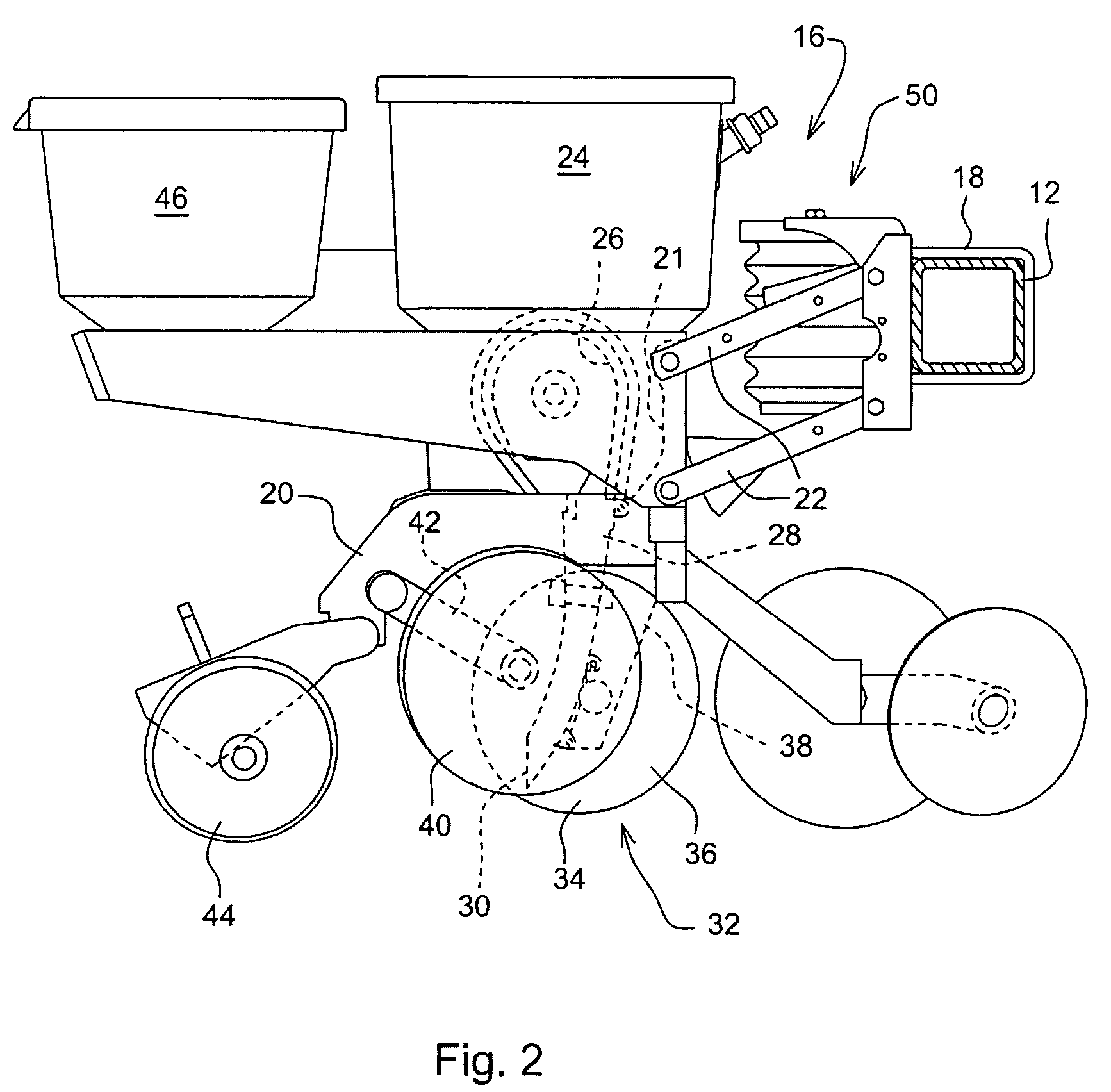
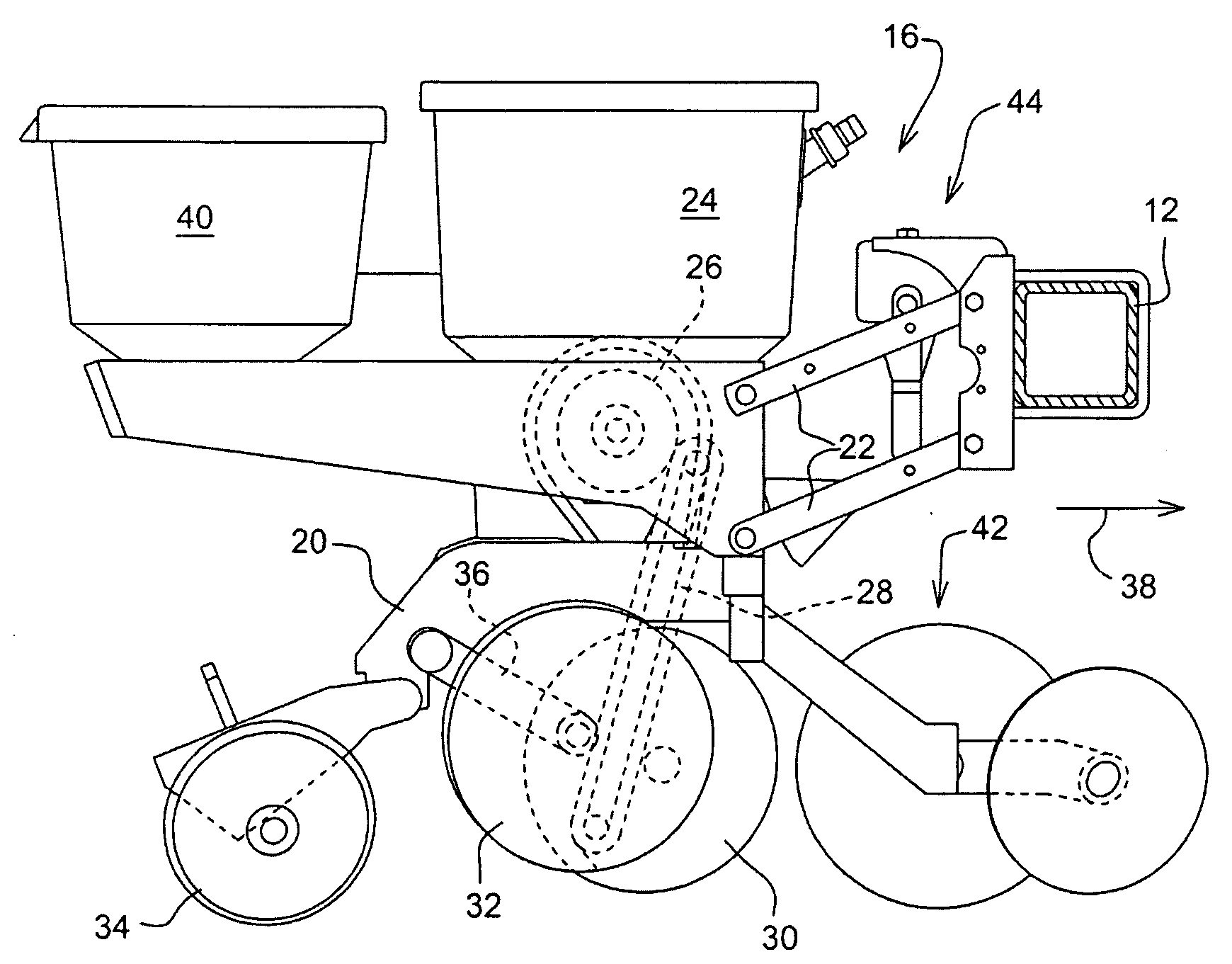
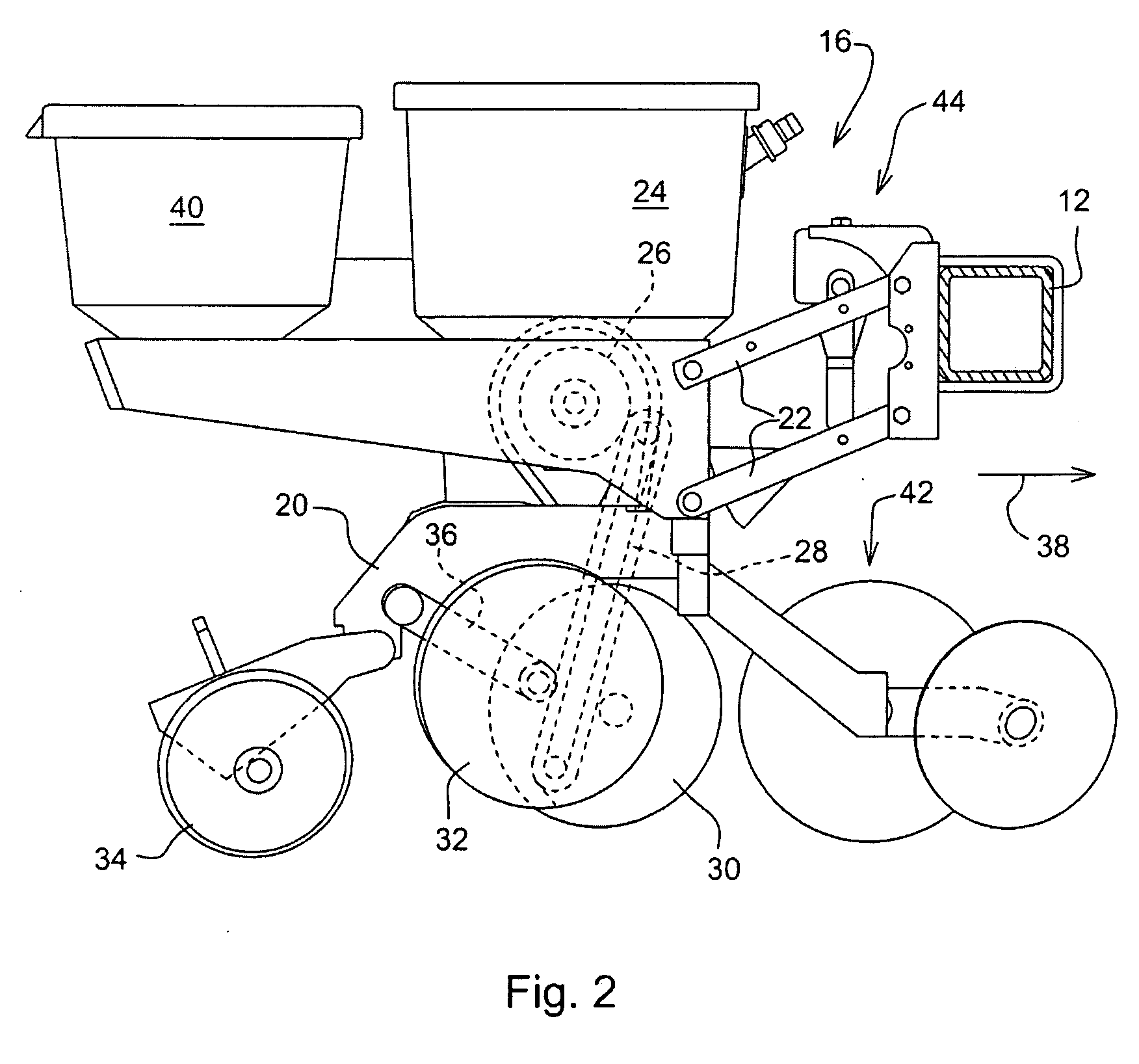
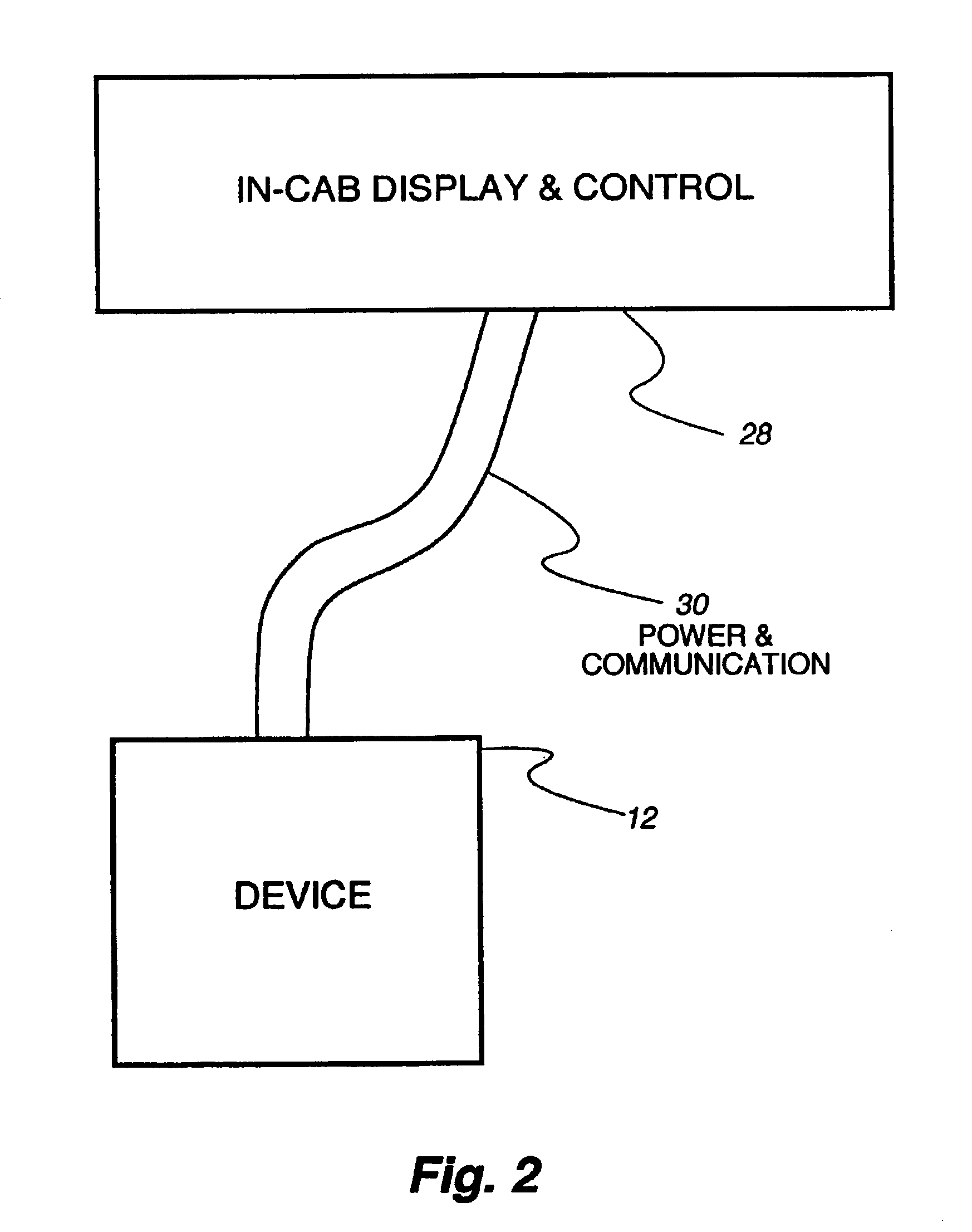
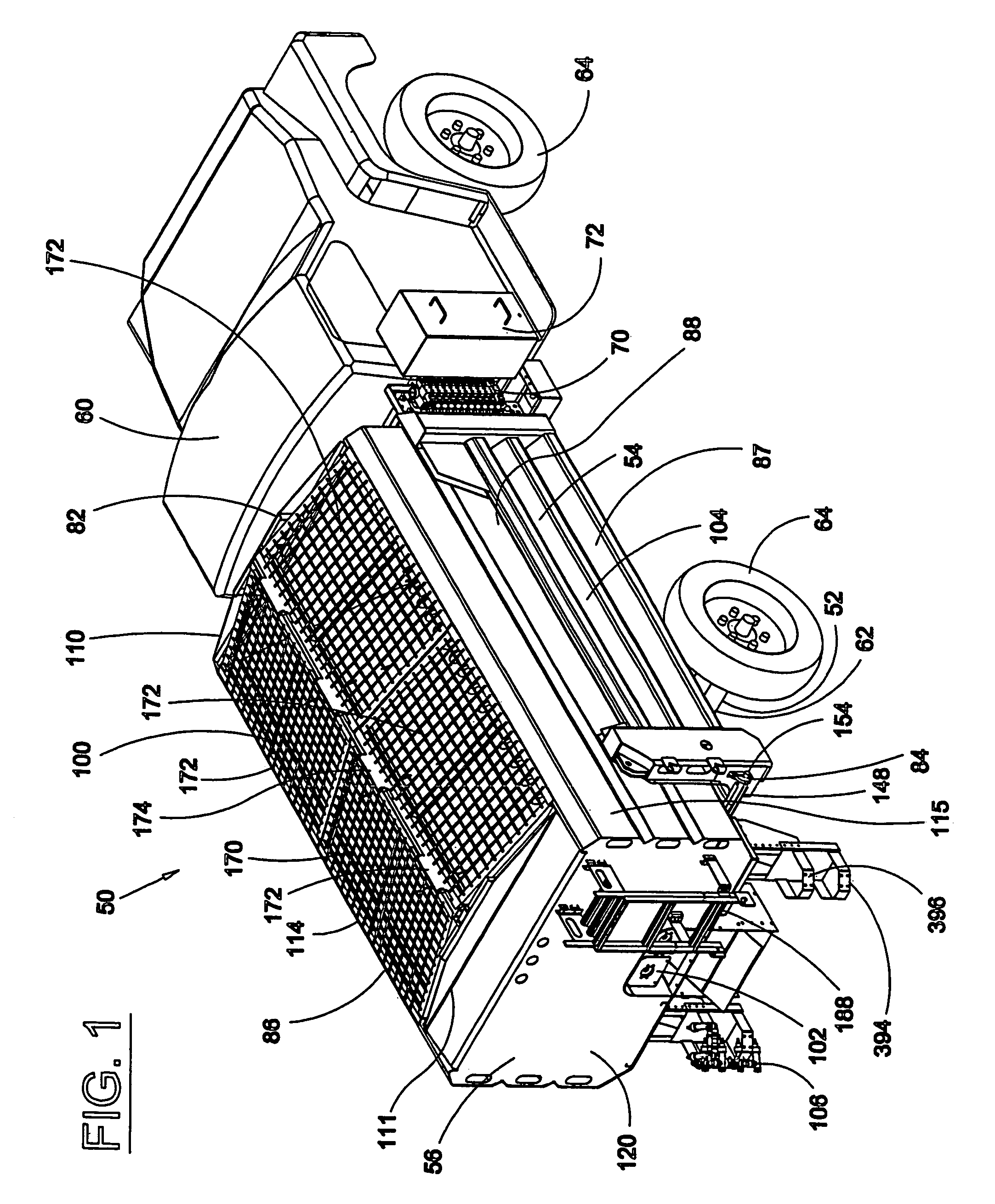
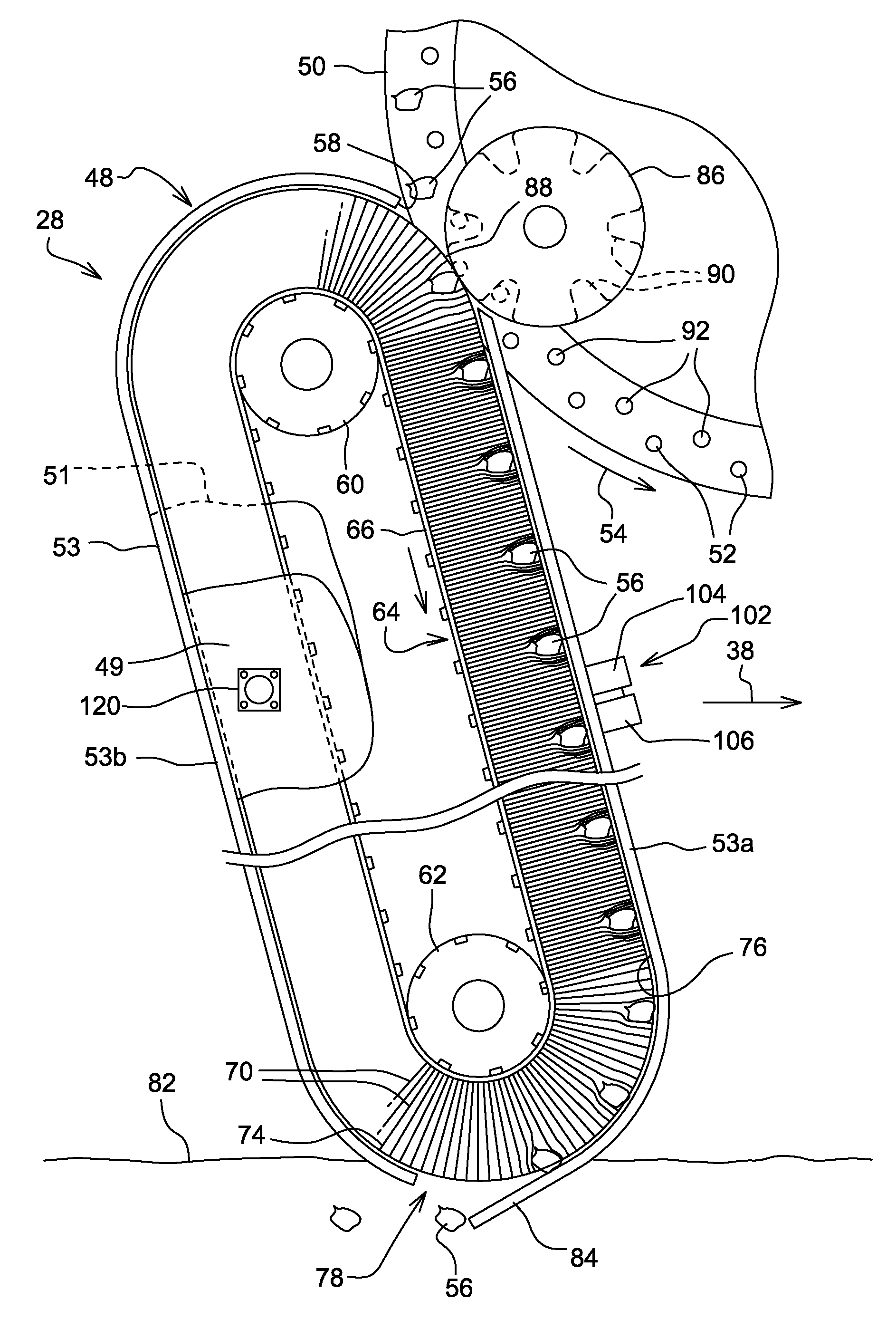
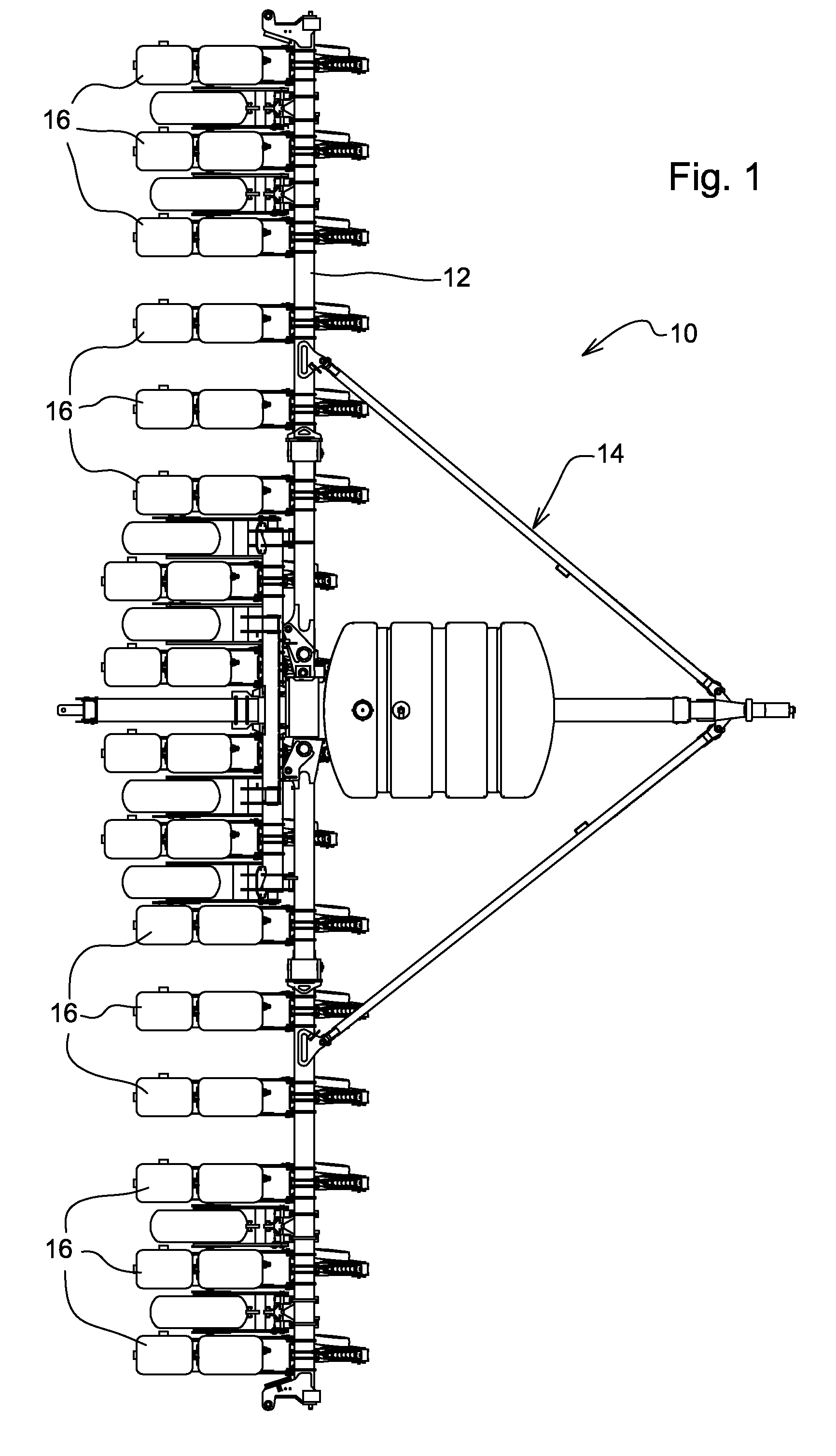
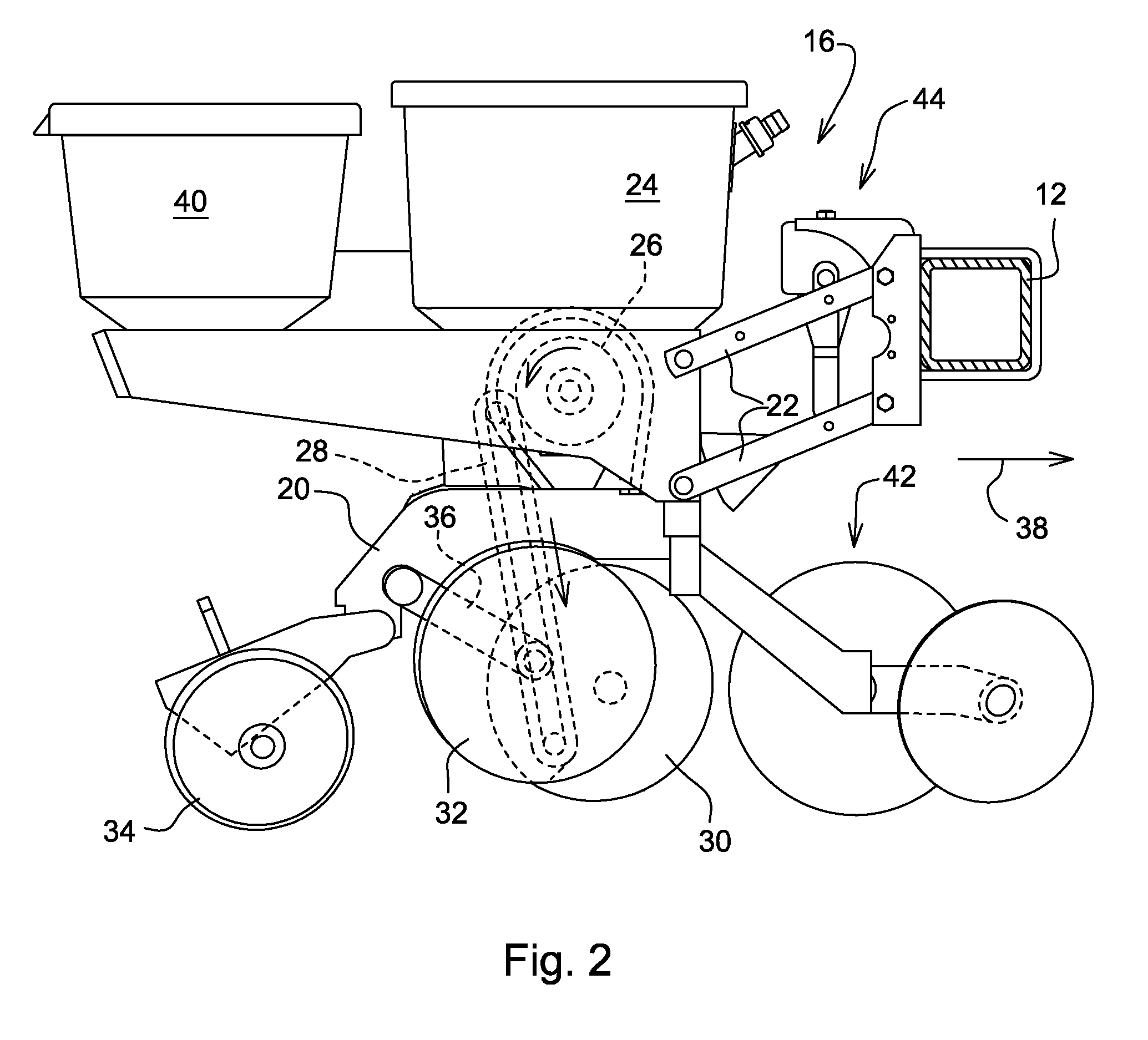
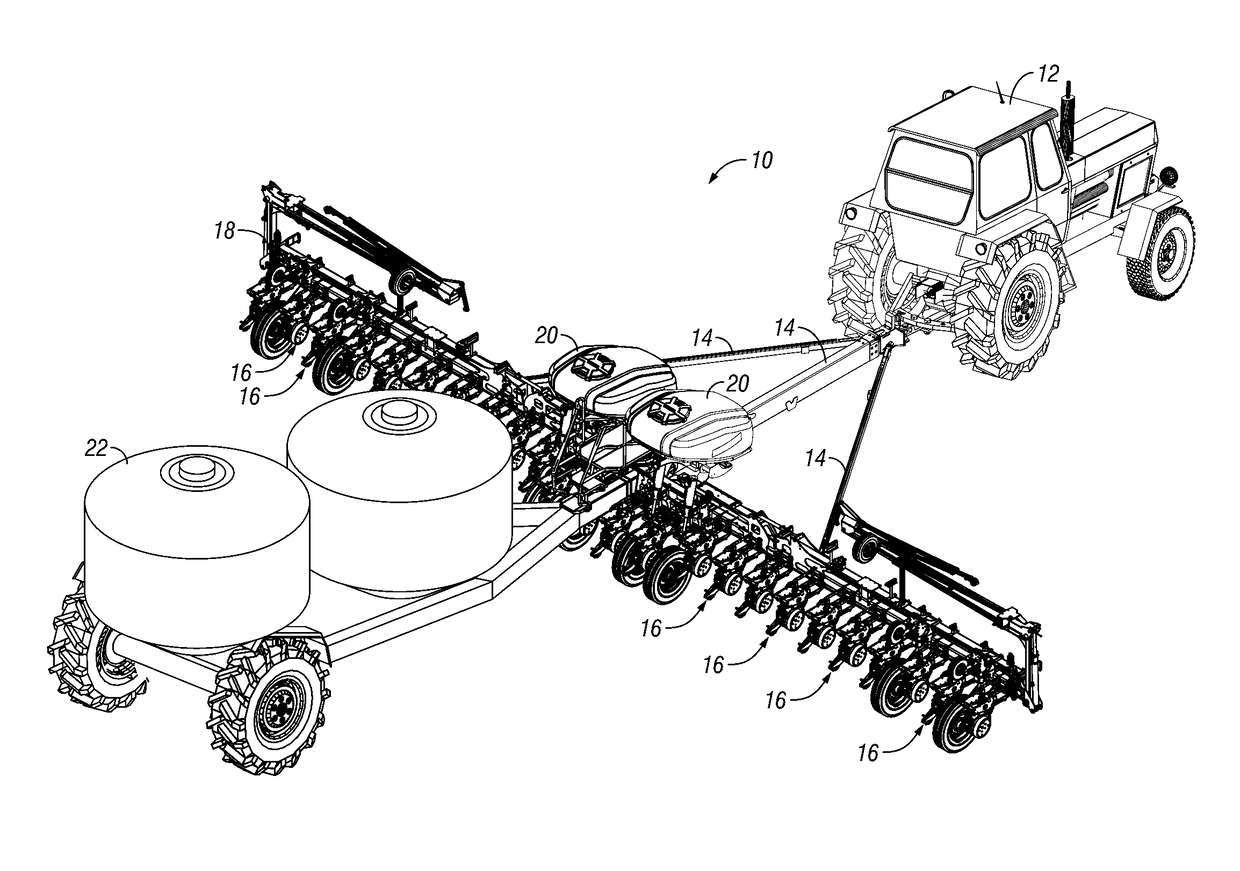
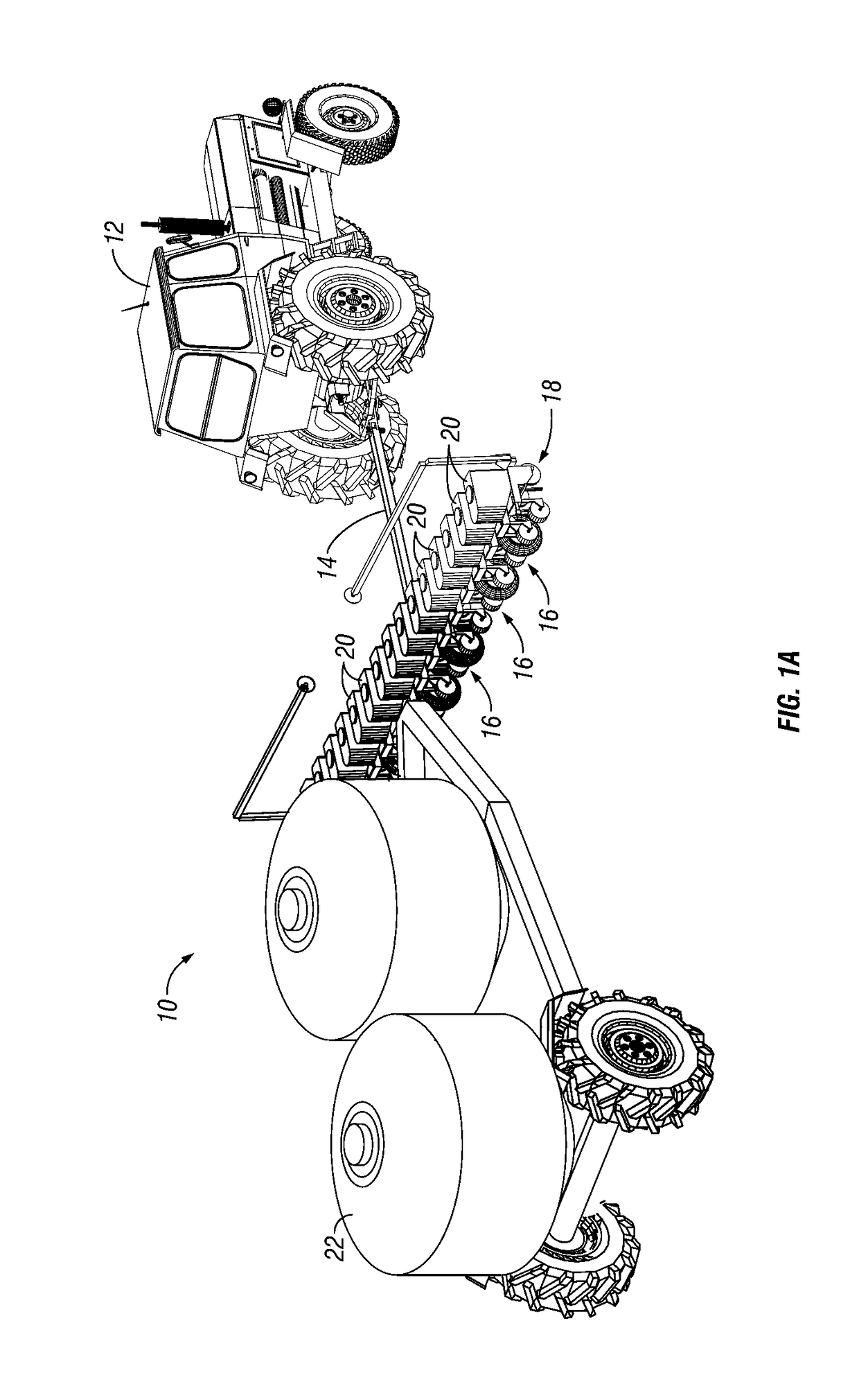
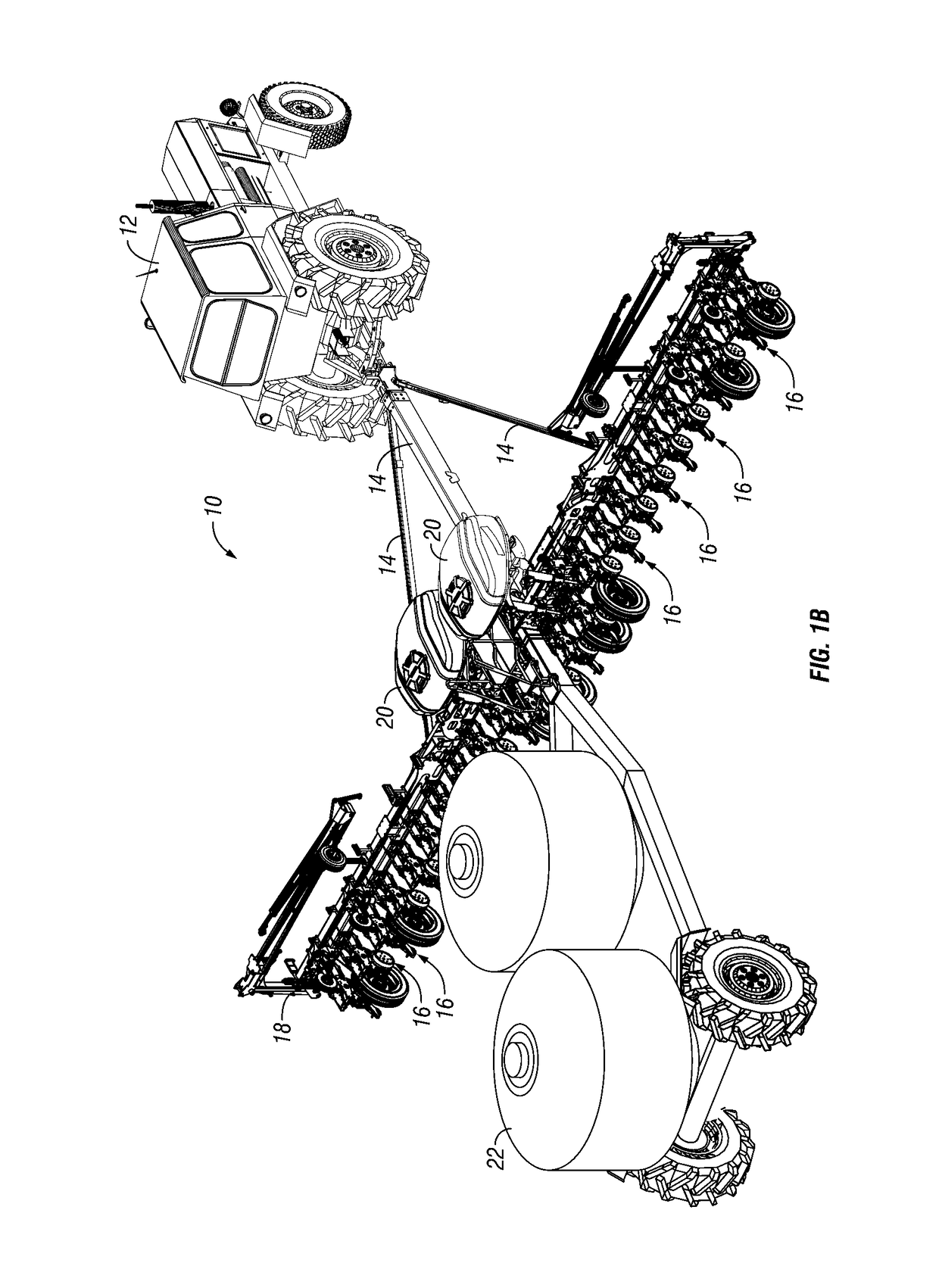
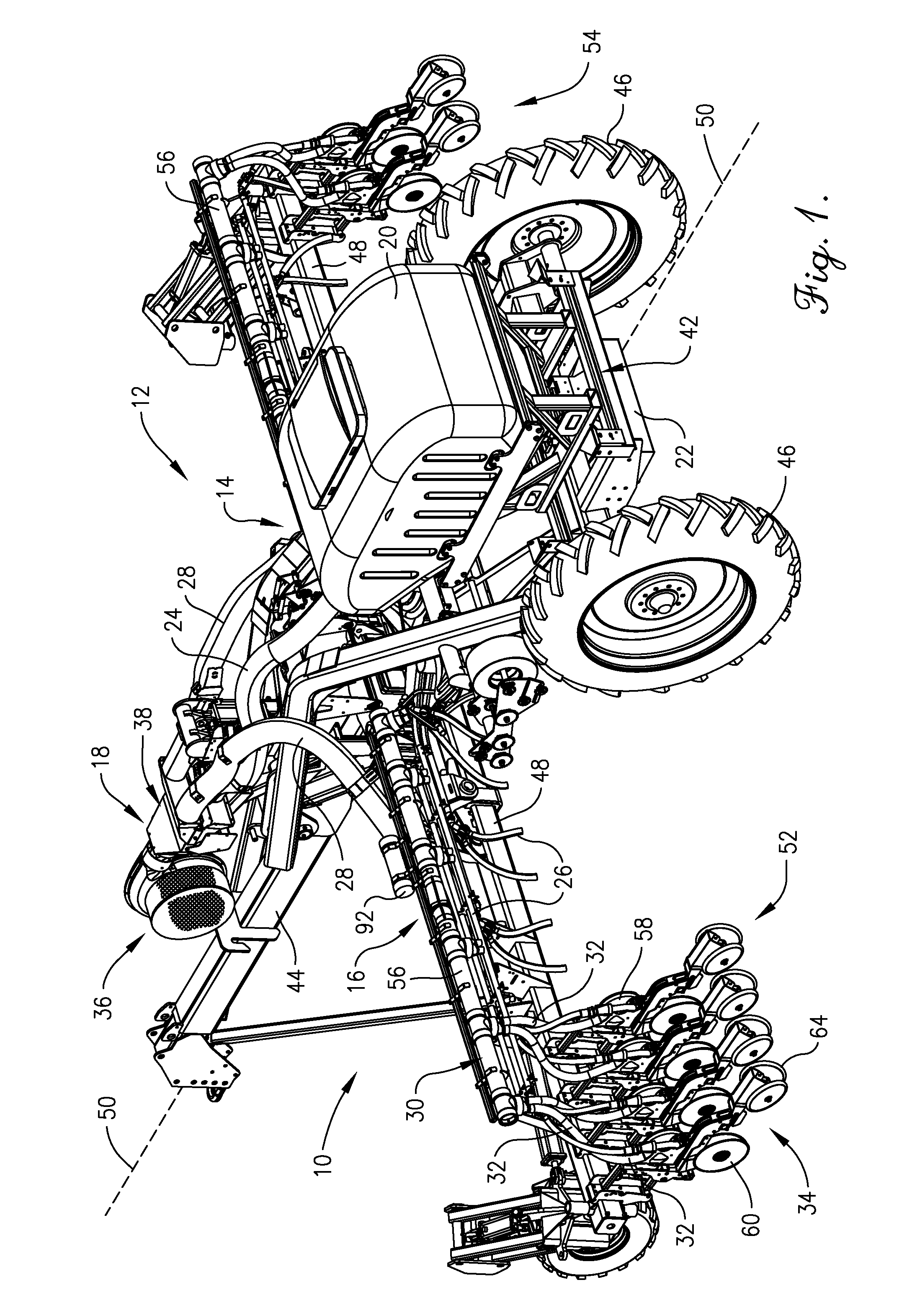
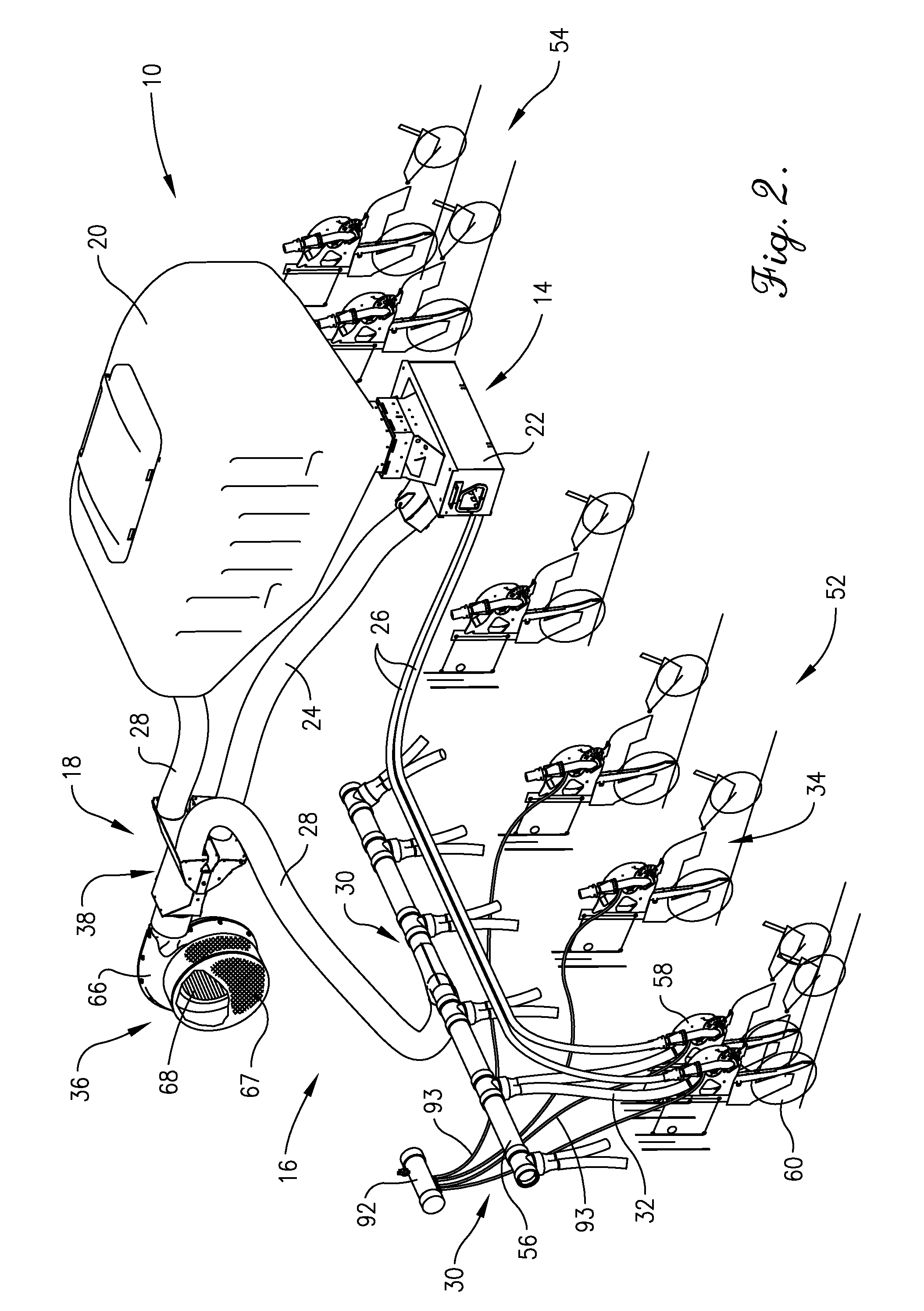
Seeding Machine With Seed Delivery System
ActiveUS20100192819A1Reduces seed spacing variabilityReduce scrollingFertiliser distributersCentrifugal wheel fertilisersEngineeringDelivery system
A seed delivery system for use in a seeding or planting machine that removes the seed from a seed meter by capturing the seed therefrom. The delivery system then moves the seed down to a lower discharge point and accelerates the seed horizontally rearward to a speed approximately equal to the forward travel speed of the seeding machine such that the seed, when discharged has a low or zero horizontal velocity relative to the ground. Rolling of the seed in the trench is thus reduced. Furthermore, as the seed only has a short drop from the outlet to the bottom of the seed trench, the seed has little vertical speed to induce bounce. The delivery system uses a brush belt to capture, move and accelerate the seed. By capturing the seed and moving it from the meter to the discharge, the seed is held in place relative to other seeds and the planter row unit. As a result, the seeds are isolated from row unit dynamics thereby maintaining seed spacing.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Seed metering gate assembly
Owner:RENOVATORS LLC
Plural bin metering system
ActiveUS7380733B2Low costLess-expensive to maintainFertiliser distributersCentrifugal wheel fertilisersOne passEngineering
A plural bin metering system for broadcasting material ingredients contained therein over a ground surface. The system includes at least two material ingredient hoppers, each of the hoppers having a material ingredient discharge port. At least one of the material ingredient hoppers includes a variably controllable metering unit associated therewith for variably controlling the discharge of material ingredients therefrom independently from the rate of discharge of material ingredients from the other material ingredient hopper. A conveyor is disposed below the hoppers for receiving material ingredients discharged from the hoppers, and a material ingredient broadcasting device disposed off of one end of the conveyor for receiving material ingredients conveyed thereon, received from the hoppers, for broadcasting the material ingredients over a ground surface. The metering unit is capable of metering material ingredients from its associated hopper at ultra low rates. In a preferred embodiment the system has three hoppers for broadcasting, for example fertilizer across a field in one pass.
Owner:SALFORD BBI
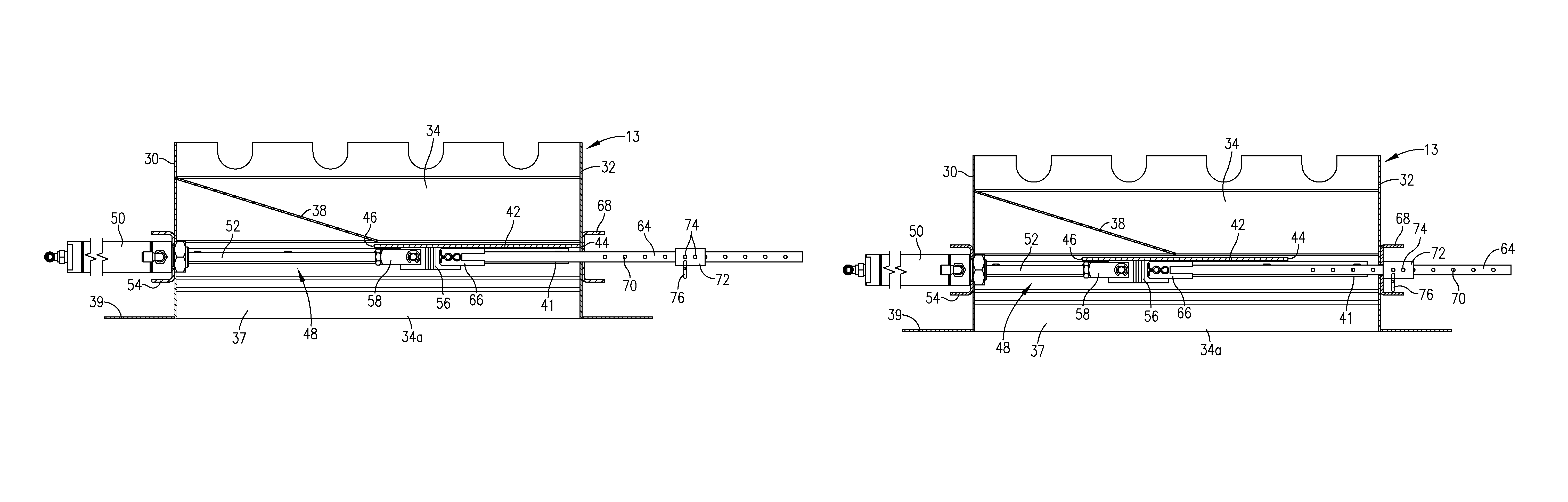
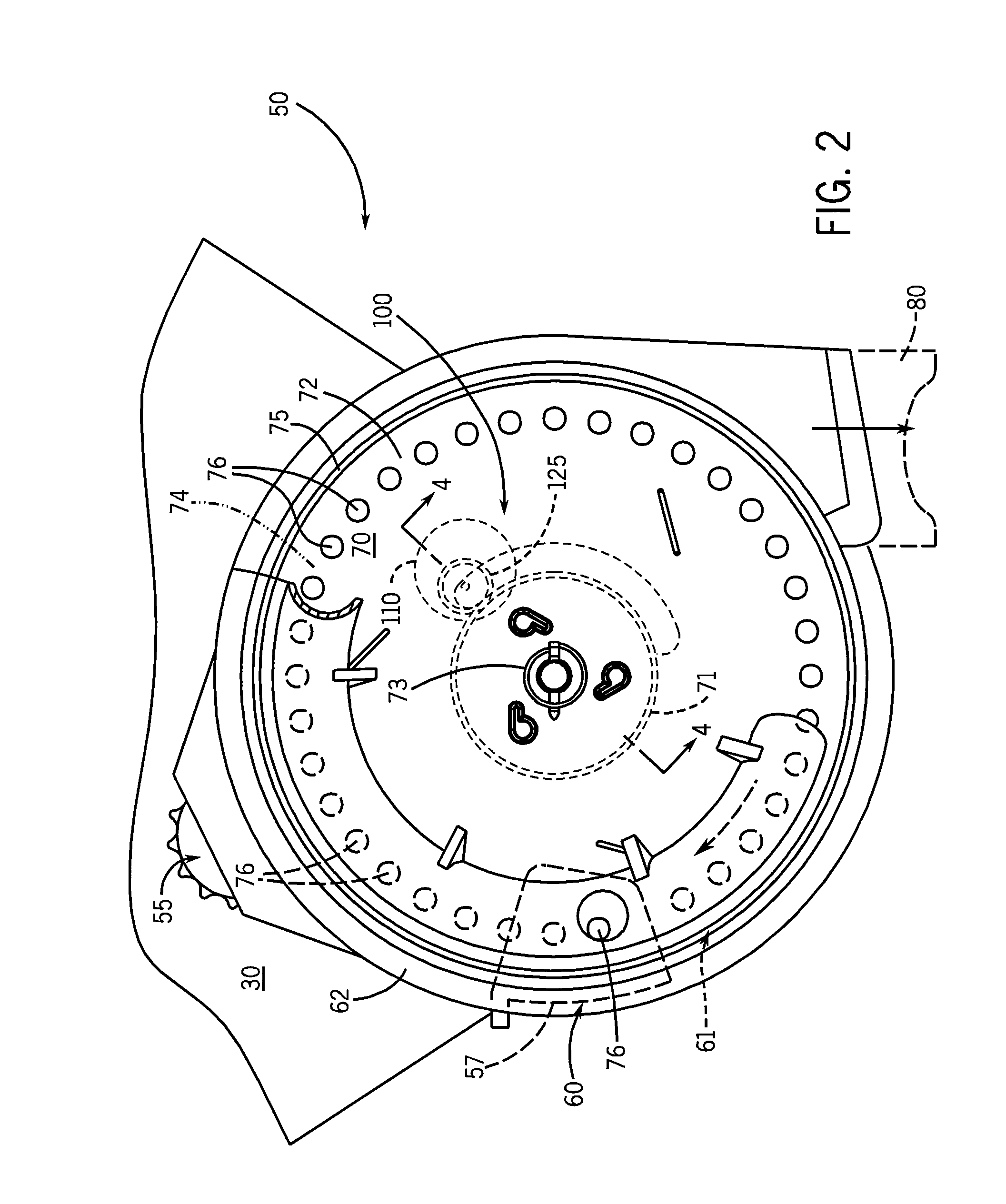
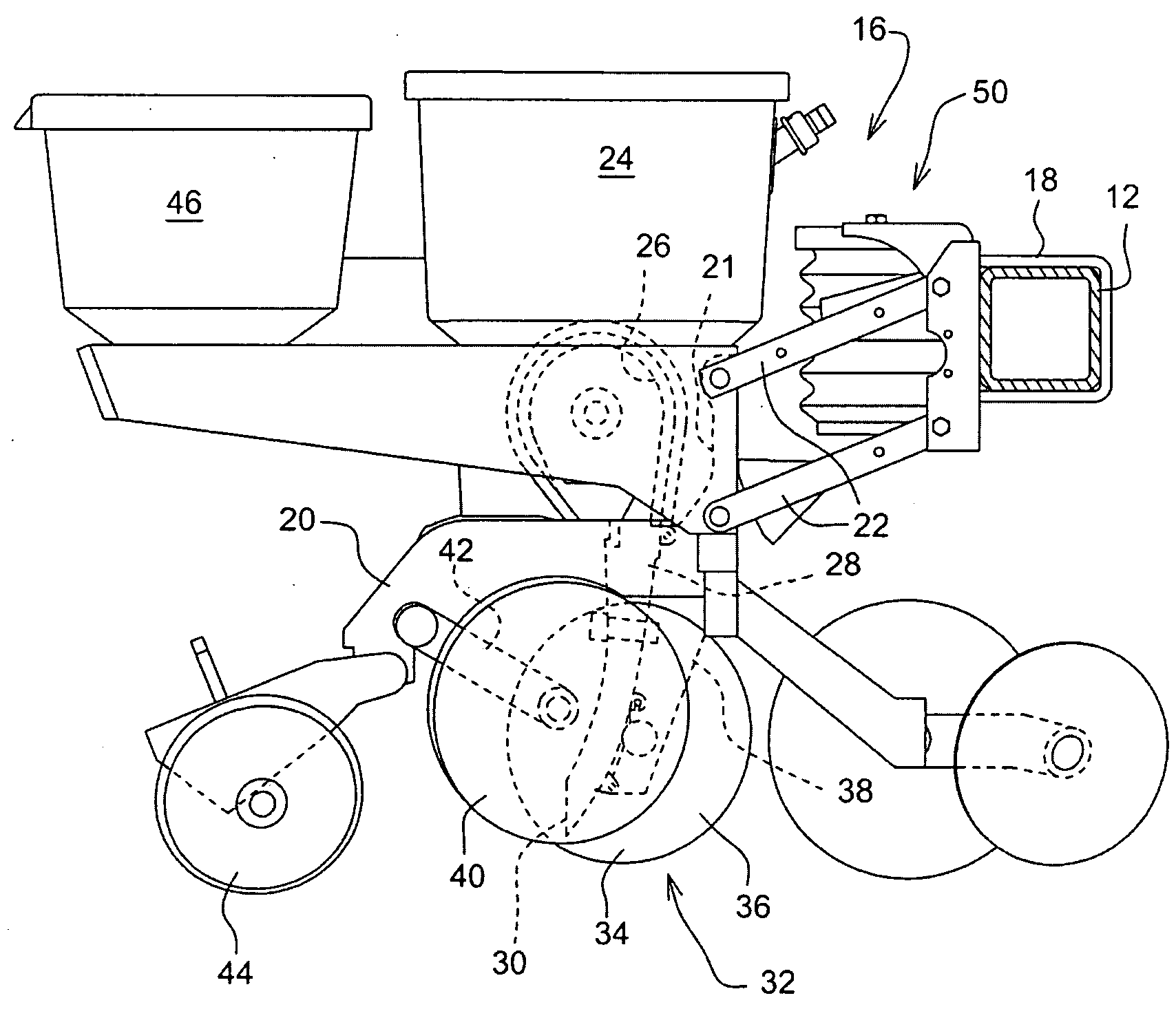
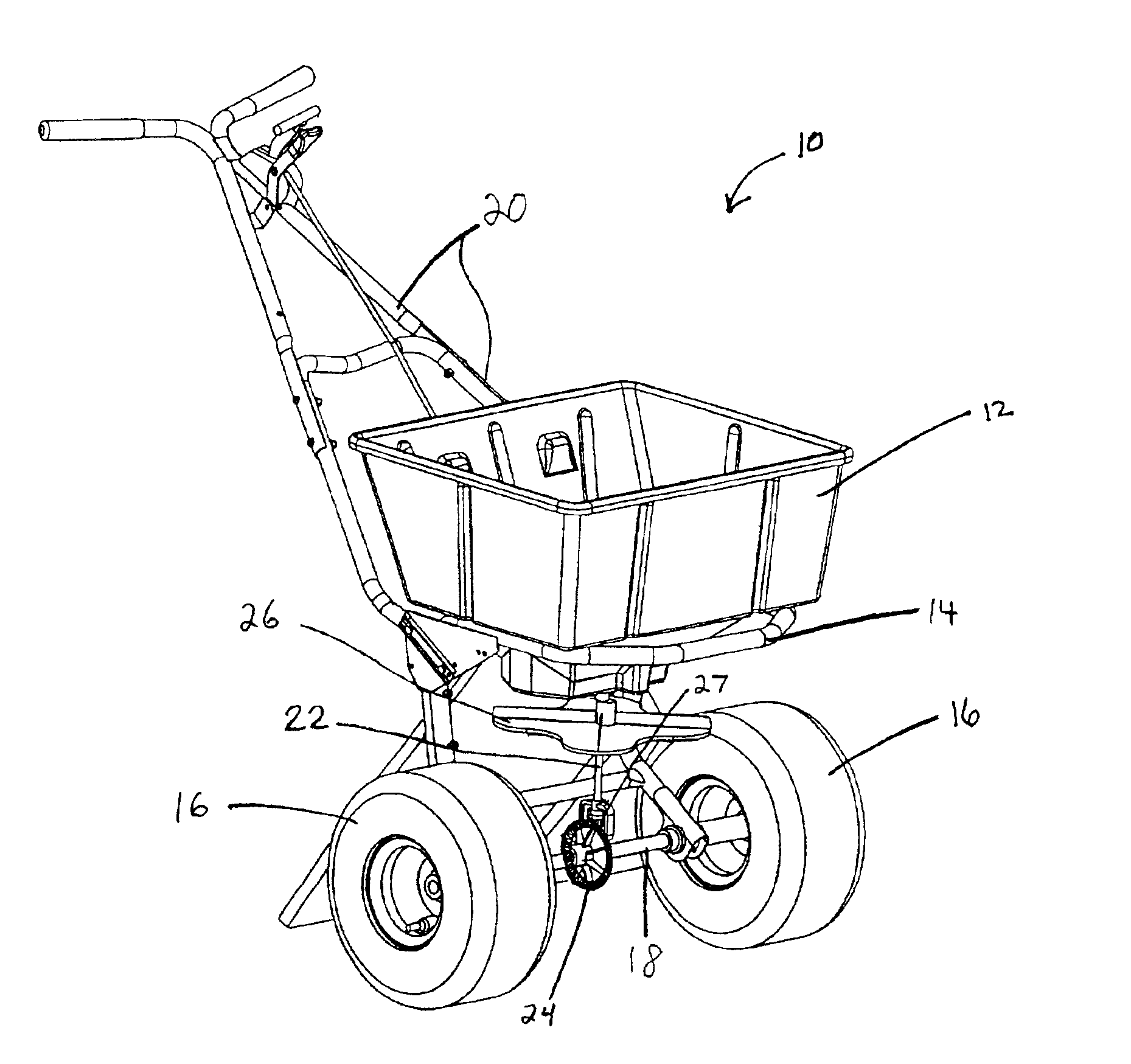
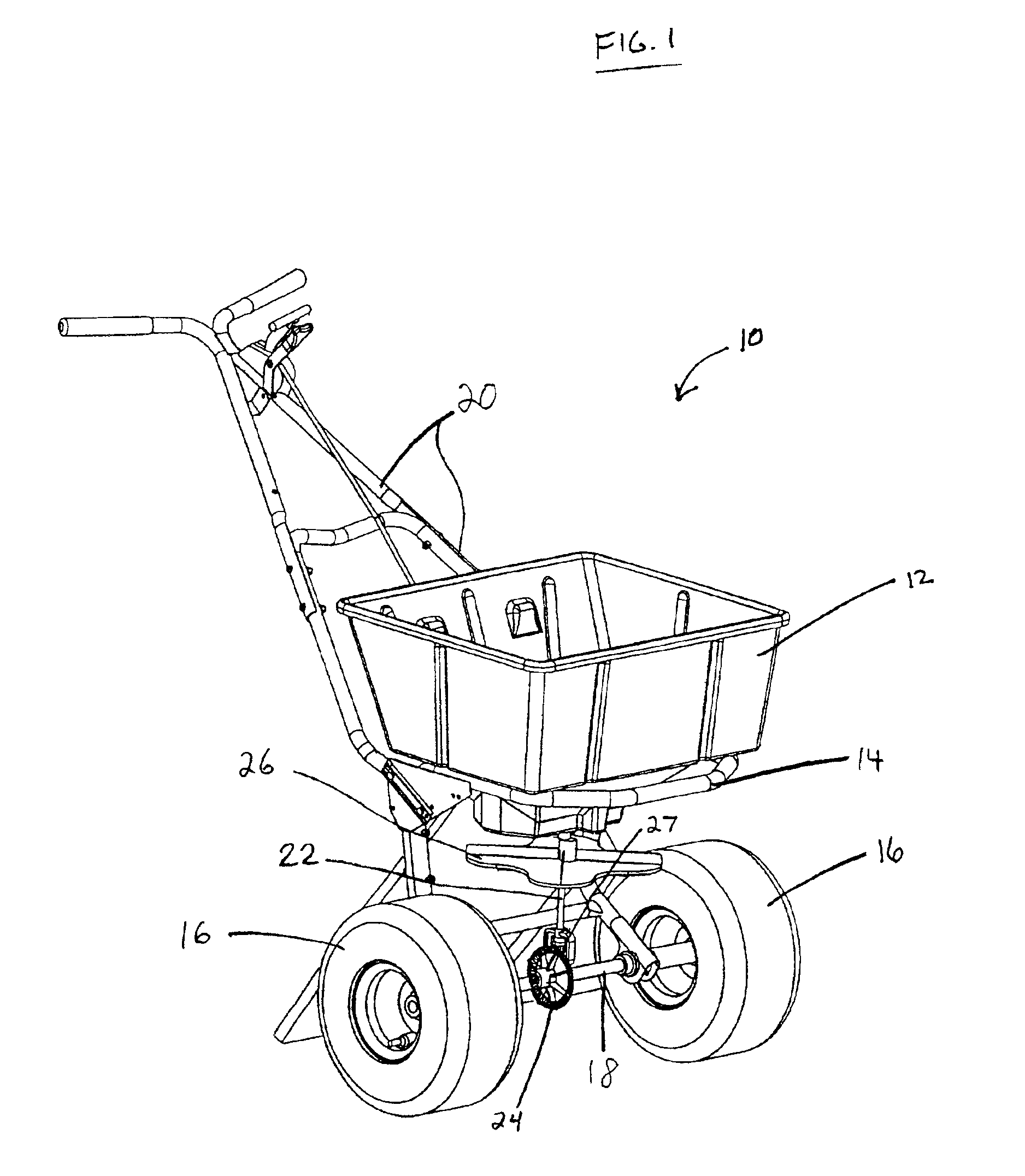
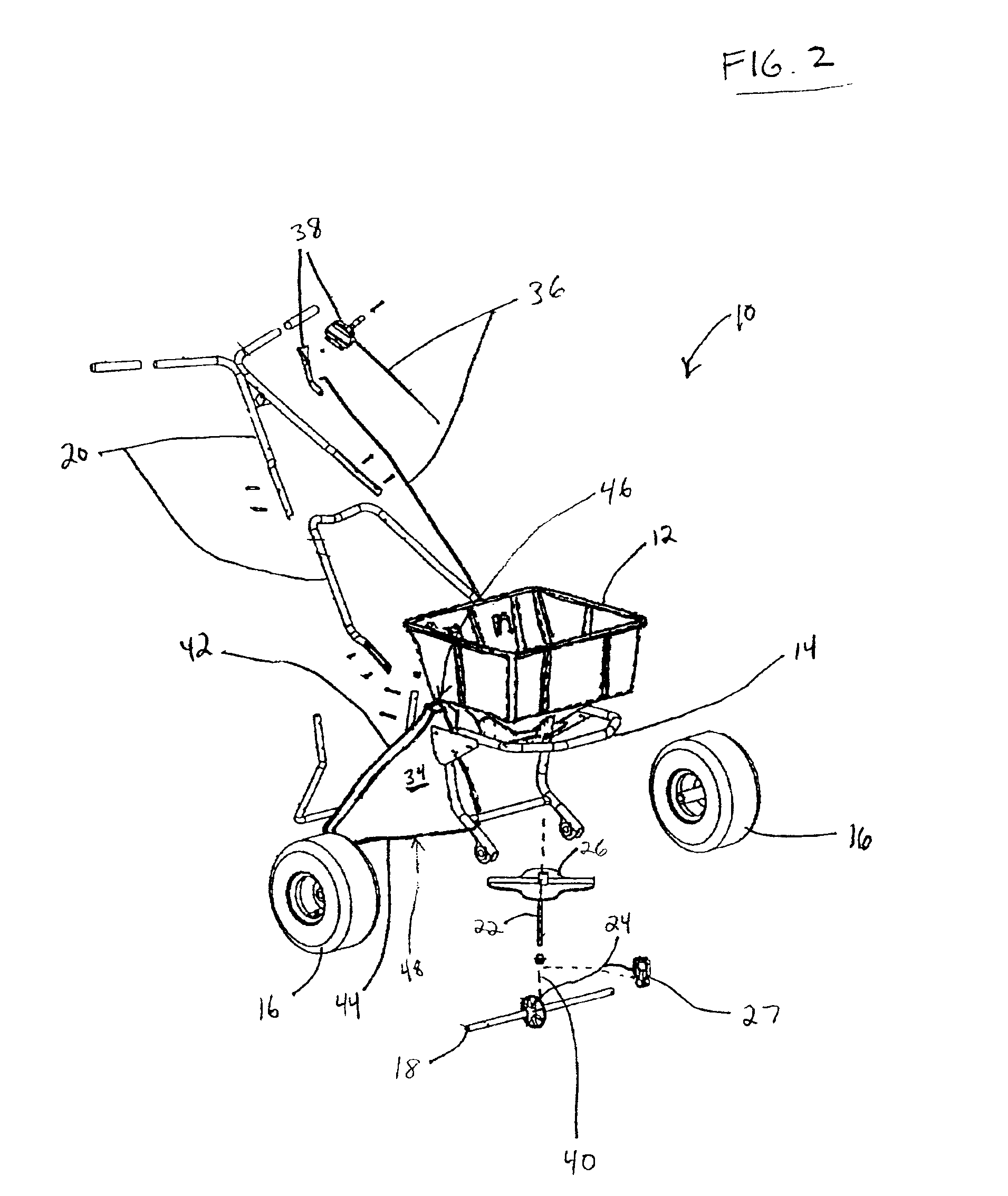
Seed metering gate assembly
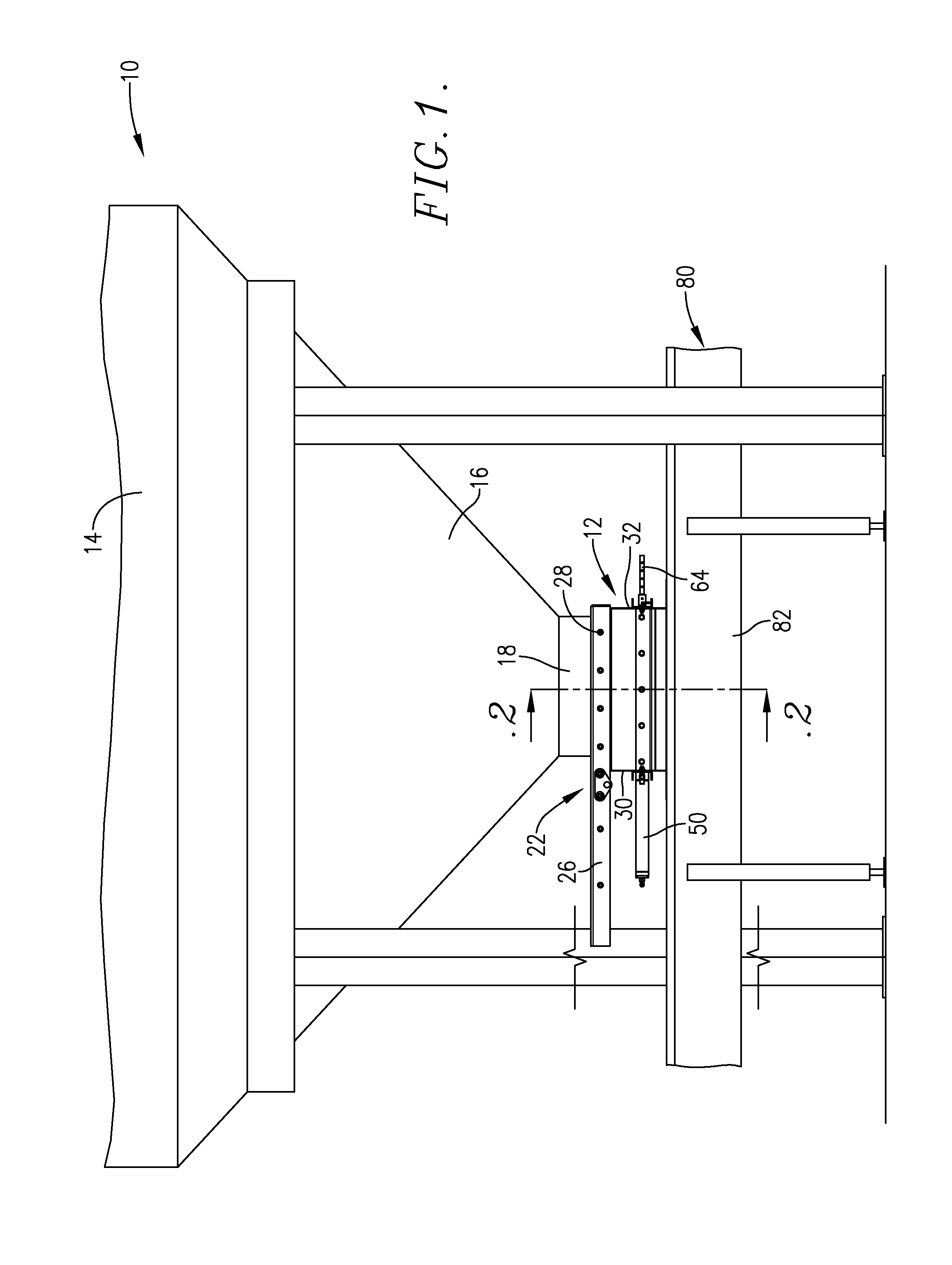
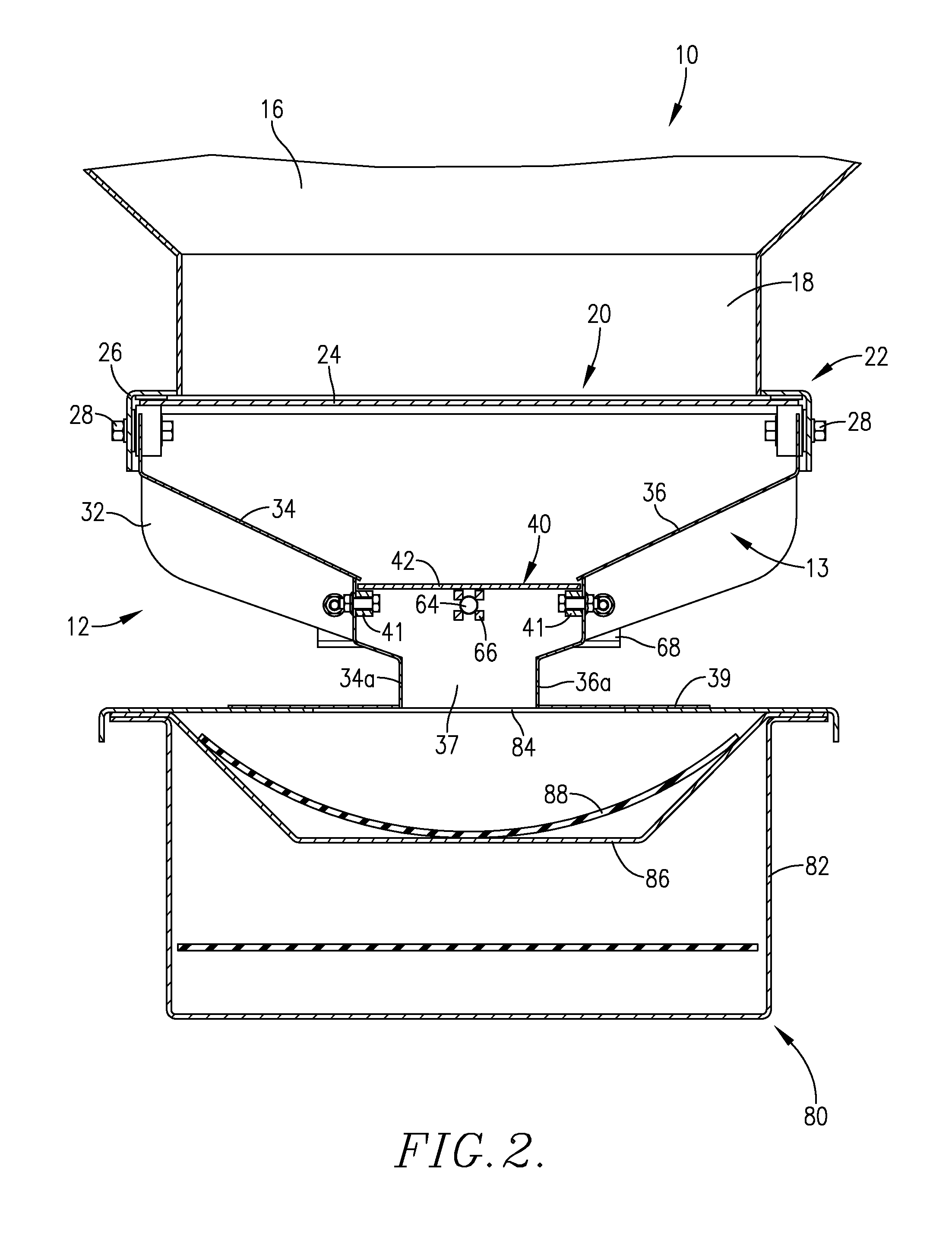
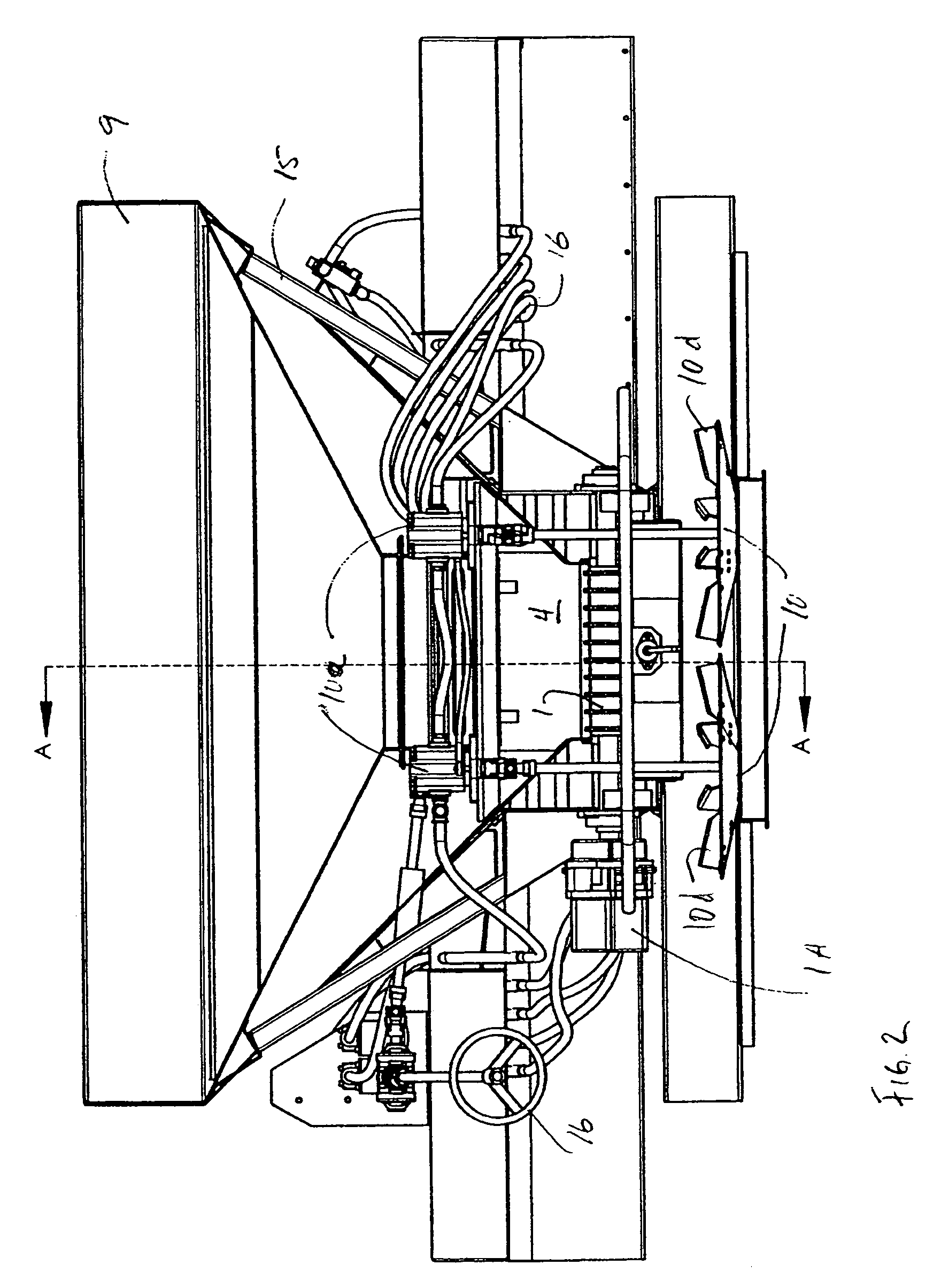
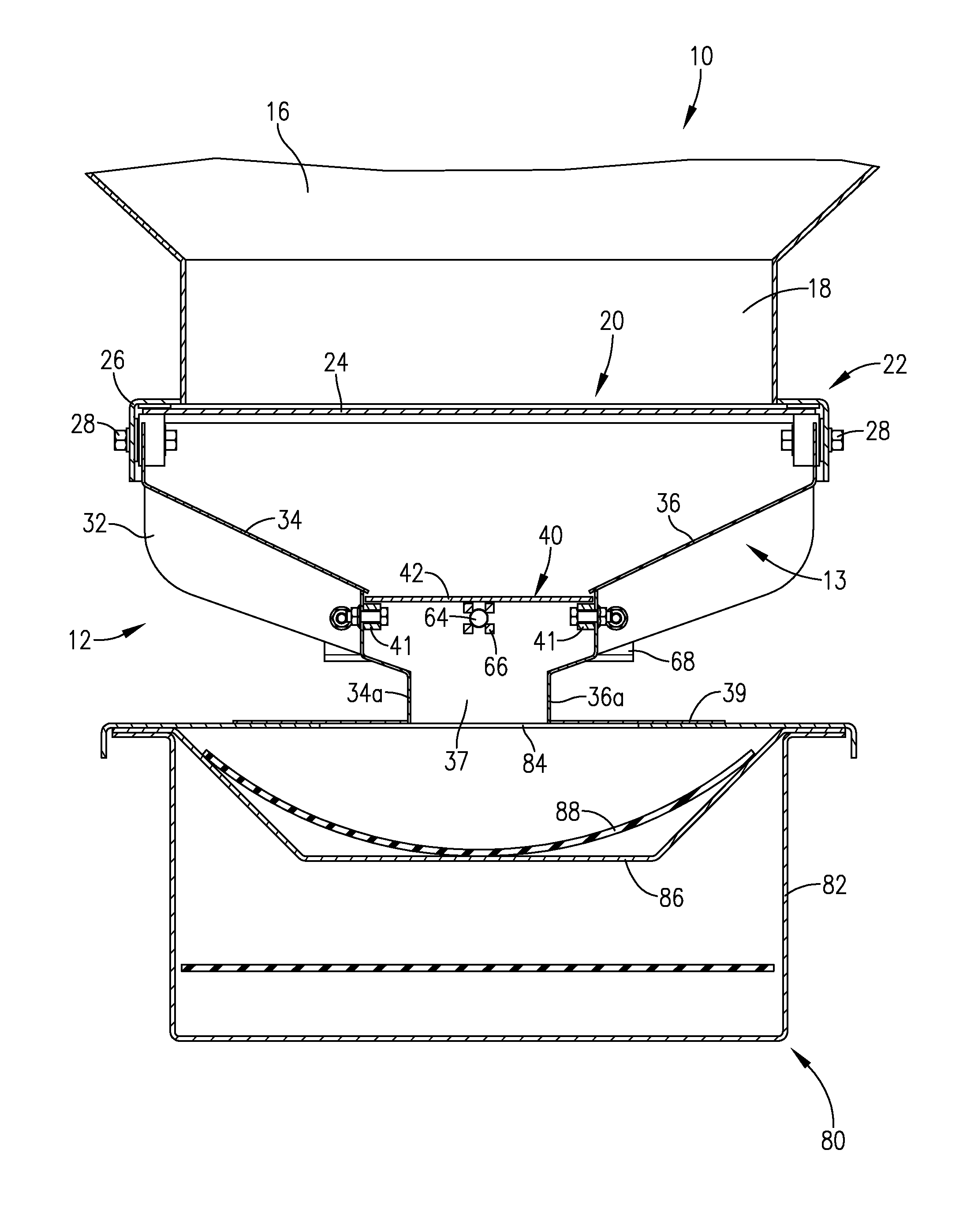
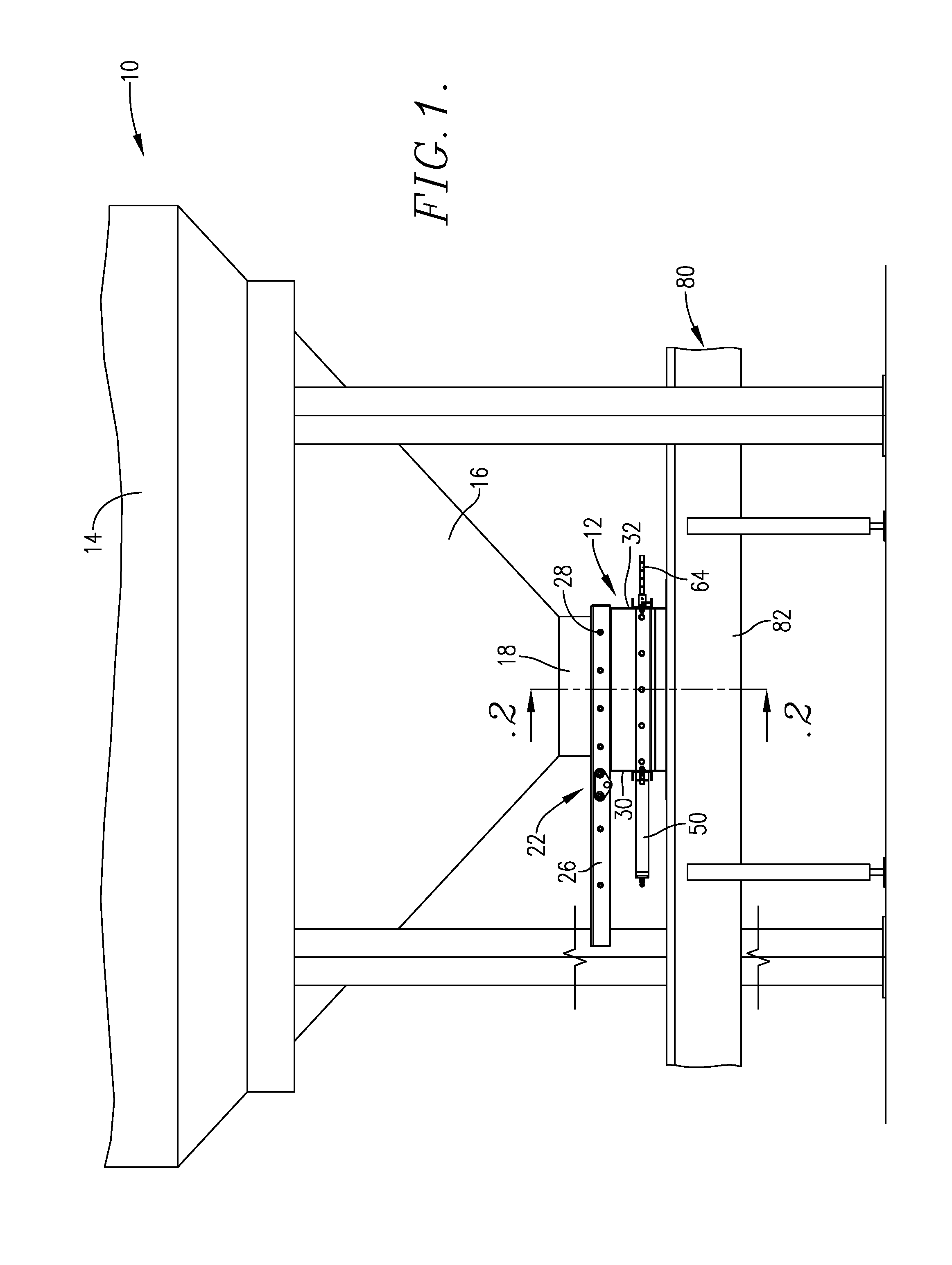
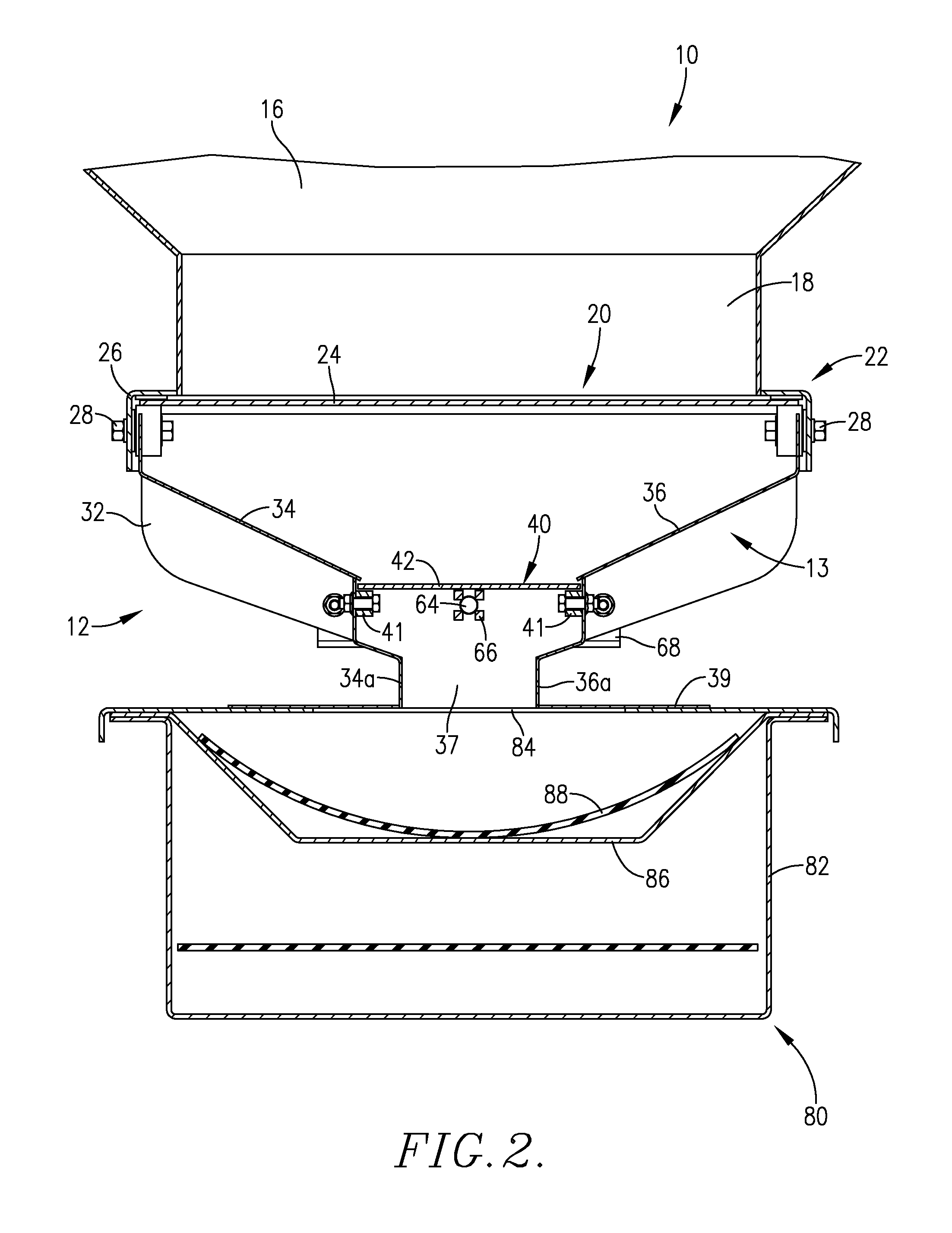
A seed metering gate assembly (12) is provided for use with an upright seed bin (10) having a shiftable primary gate (24), wherein the gate assembly (12) provides an additional seed flow control function allowing more accurate dispensing of seed from the bin (10). The gate assembly (12) includes a seed hopper (13) equipped with a fore and aft-shiftable metering gate (42) movable between a closed position and an open position presenting a seed output passageway (40). Apparatus (62) is operably coupled with the gate member (42) in order to determine the travel of metering gate member between the fully closed position and a plurality of open positions presenting respective, differently sized passageways (40). The apparatus (62) preferably includes a rod (64) having a series of through openings (70) and coupled with the gate member (42), with a shiftable, motion-limiting collar (72) mounted on the rod (64) and securable at any of the openings (70) by means of clip (76). The opening movement of the rod (64) is limited by engagement between the collar (72) and a bracket (68) affixed to hopper (13).
Owner:USC
Computer readable medium for holding a program for performing plasma-assisted CVD of low dielectric constant films formed from organosilane compounds
A method and apparatus for depositing a low dielectric constant film by reaction of an organosilane or organosiloxane compound and an oxidizing gas at a low RF power level from 10-250 W. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane film has good barrier properties for use as a liner or cap layer adjacent other dielectric layers. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane film may also be used as an etch stop or an intermetal dielectric layer for fabricating dual damascene structures. The oxidized organosilane or organosiloxane films also provide excellent adhesion between different dielectric layers. A preferred oxidized organosilane film is produced by reaction of methylsilane, CH3SiH3, or dimethylsilane, (CH3)2SiH2, and nitrous oxide, N2O, at an RF power level from about 10 to 200 W or a pulsed RF power level from about 20 to 250 W during 10-30% of the duty cycle.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
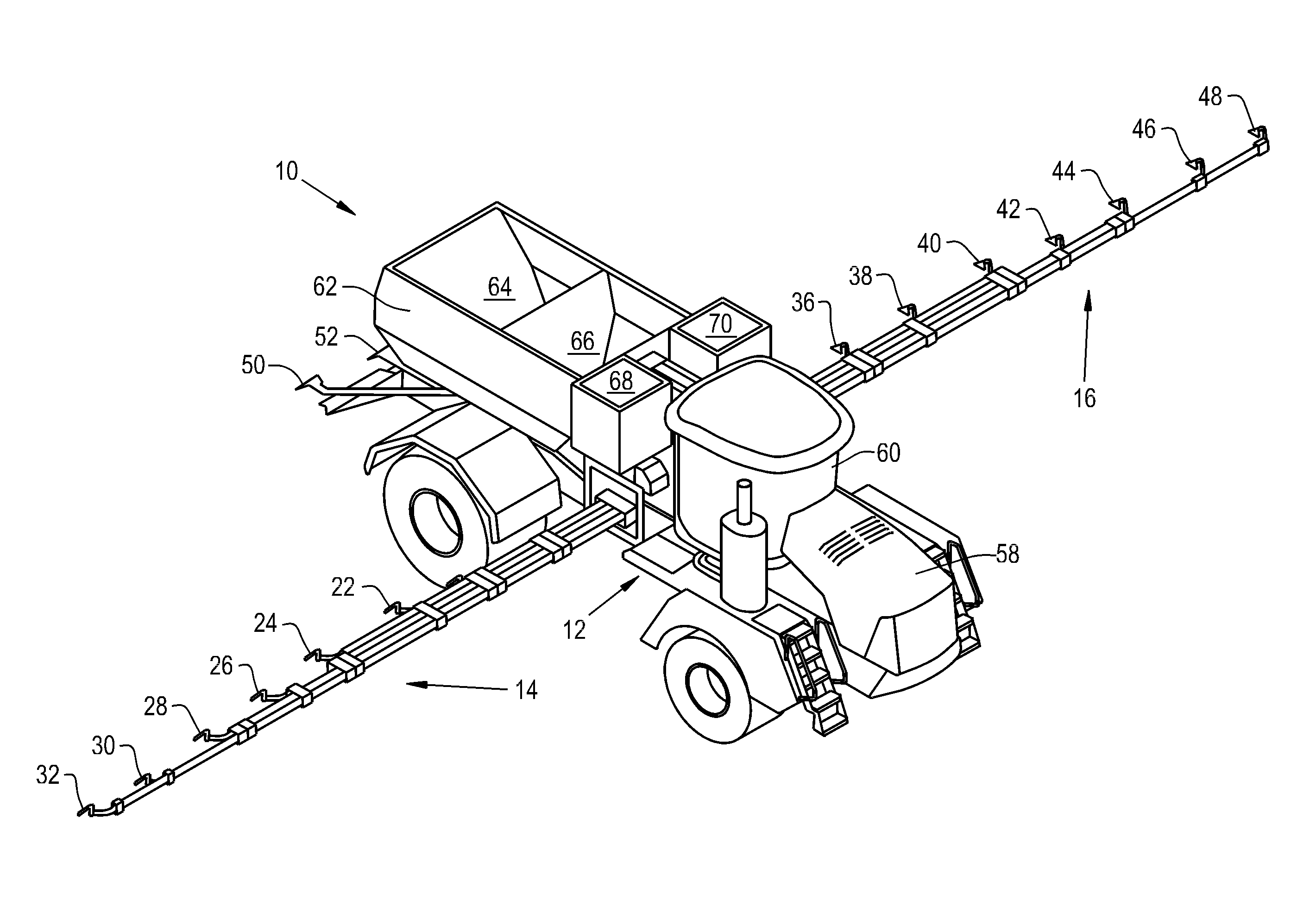
Volumetric metering system with clutch based sectional shut-off
A volumetric meter for seed or fertilizer having a plurality of roller segments driven by a common drive shaft is provided with clutch mechanisms radially between each roller segment and the drive shaft to enable the roller segments to be individually shut-off to provide section or swath control to the machine.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Vehicle mounted travel surface and weather condition monitoring system
InactiveUS6977597B2Show reliableReduce developmentArrangements for variable traffic instructionsWithdrawing sample devicesMonitoring systemVehicle detection
A system and apparatus for detecting and evaluating surface conditions on a road surface and atmospheric conditions simultaneously from a vehicle is disclosed. The system comprises a sensor for detecting the presence of deposited material on a road surface, a detector for determining one or more characteristics of the deposited material such as freezing temperature, process means for converting a detected signal and display means for displaying the condition of the road surface, and a sensor for detecting falling precipitation. An embodiment of the present invention includes a remote sensing apparatus which utilizes electromagnetic radiation to sense actual surface material conditions, temperatures, and composition and local atmospheric conditions at the vehicle as it is moving over a travel surface. This information is then processed through a computer in order to determine those additional steps necessary to apply additional materials to the road surface in order to minimize hazardous driving conditions.
Owner:WEATHER INSIGHTS
Broadcast width and location control for a combine spreader
Owner:DEERE & CO
Apparatus for treatment of snow and ice
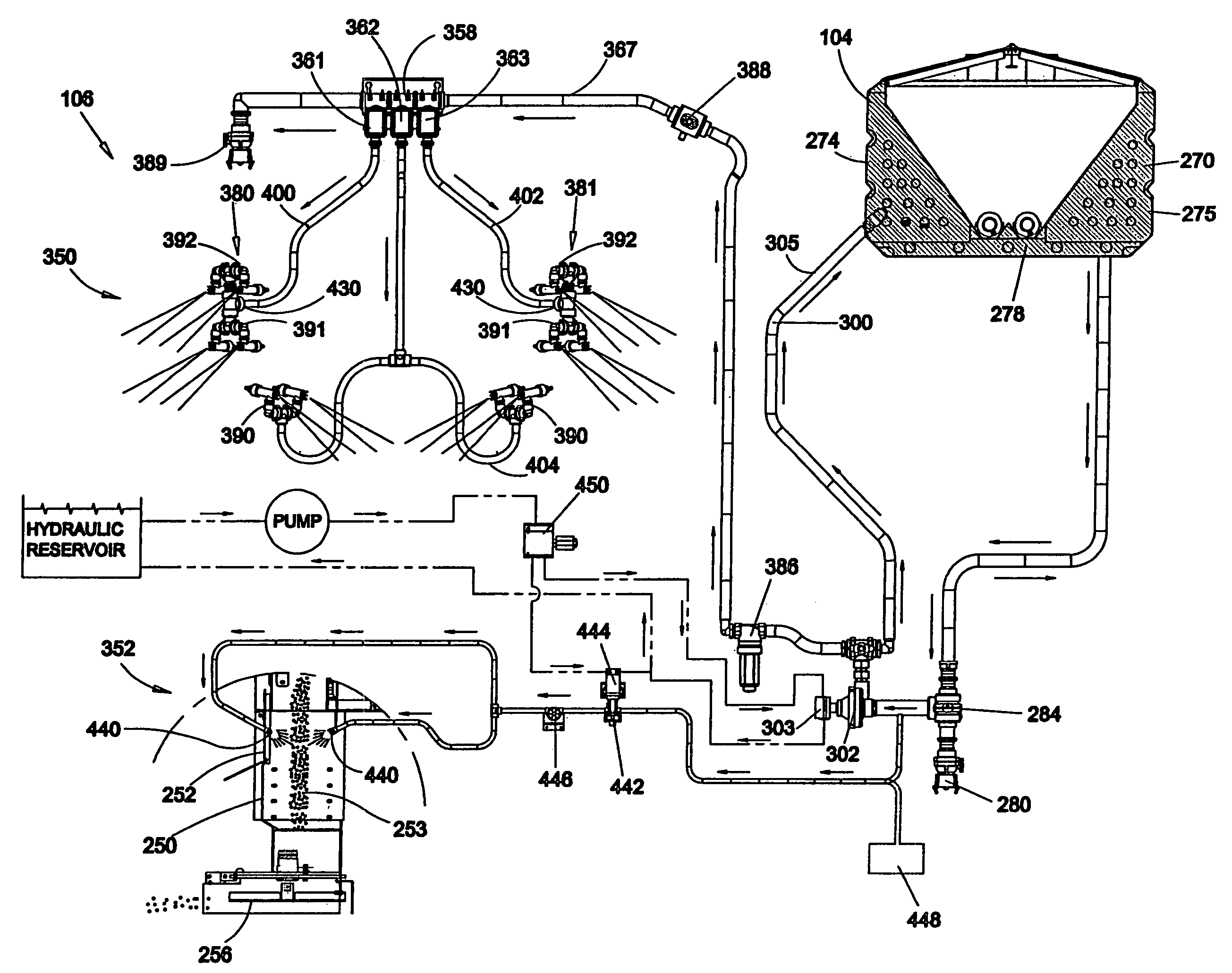
ActiveUS7370818B2Maximize payloadImprove space utilizationTank vehiclesSelf-acting watering devicesEngineeringWetting
A vehicle is disclosed which includes a chassis and a storage and dispensing apparatus. The storage and dispensing apparatus can be mounted directly to the chassis or disposed within or on a body, which in turn is mounted to the chassis. The storage and dispensing apparatus has an opening therein to permit material to be transported therethrough. A conveyor assembly for selectively conveying materials from the opening of the storage and dispensing apparatus is also included. The conveyor assembly can include a dual auger arrangement. The vehicle includes a spreader chute that is operably arranged with the conveyor assembly to direct the materials to a spreader. A liquid storage system for storing liquid is provided. A liquid dispensing system is provided for selectively dispensing liquid from the liquid storage system. The liquid dispensing system includes an anti-icing system for selectively dispensing liquid from the vehicle and a pre-wetting system for selectively dispensing liquid onto material being transported by the endless conveyor out of the vehicle.
Owner:HENDERSON PRODS
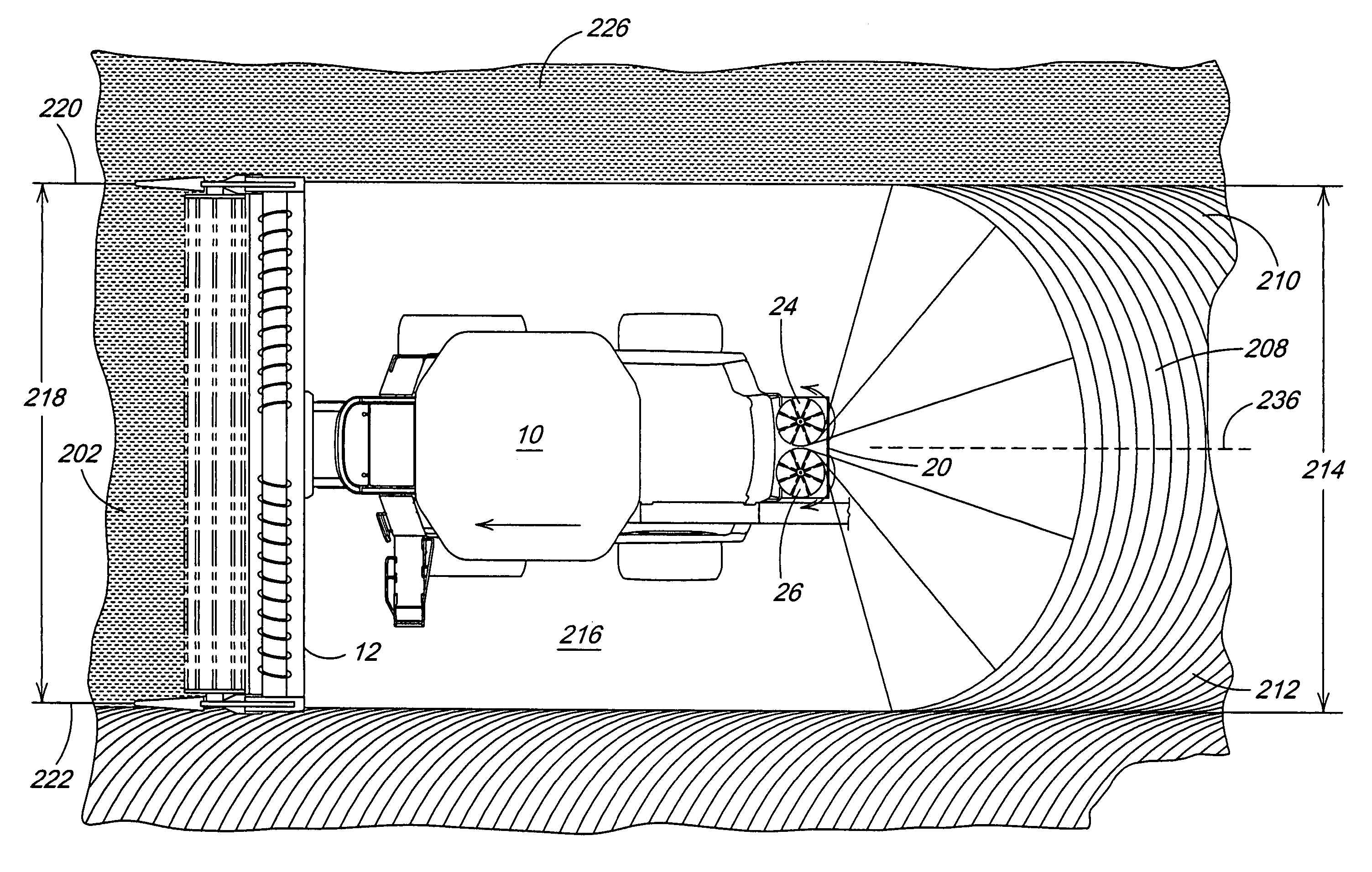
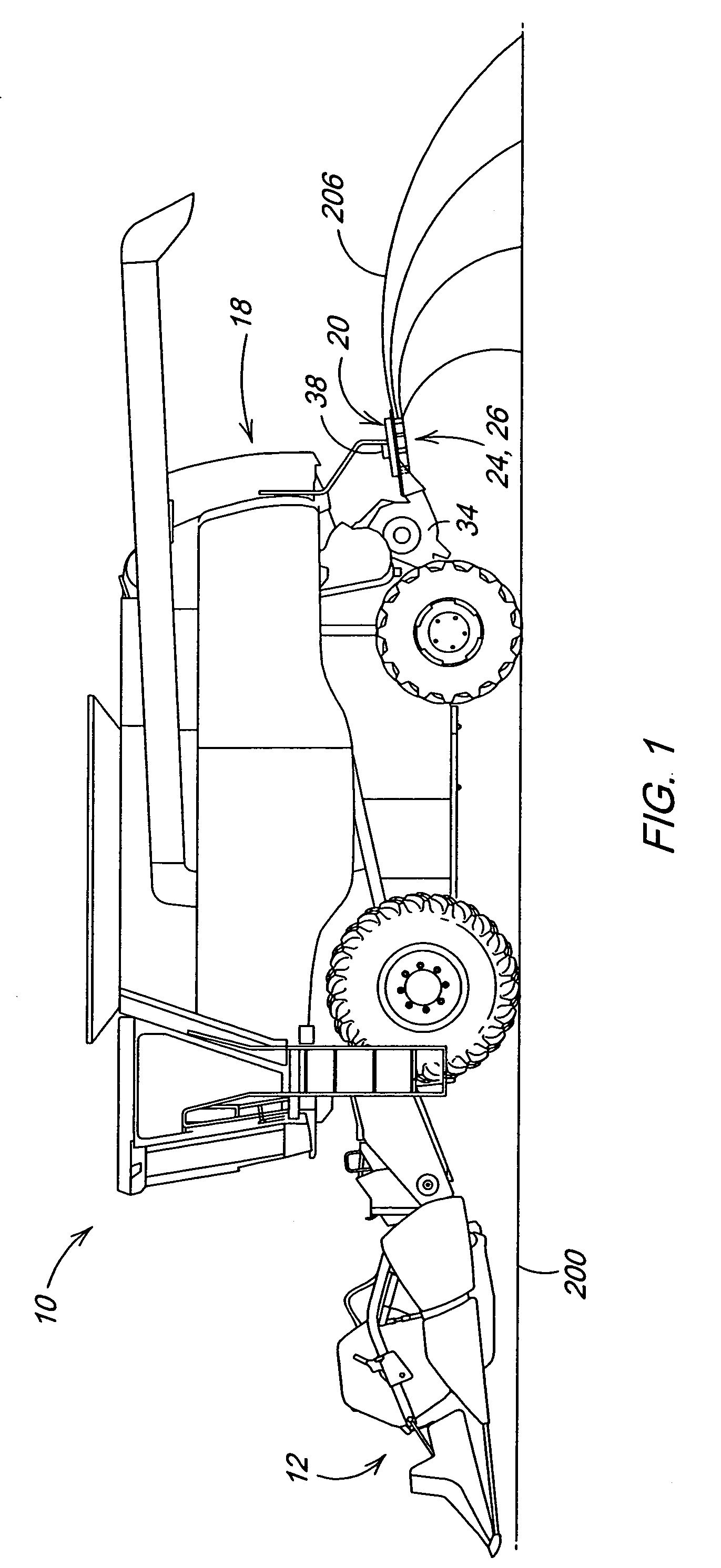
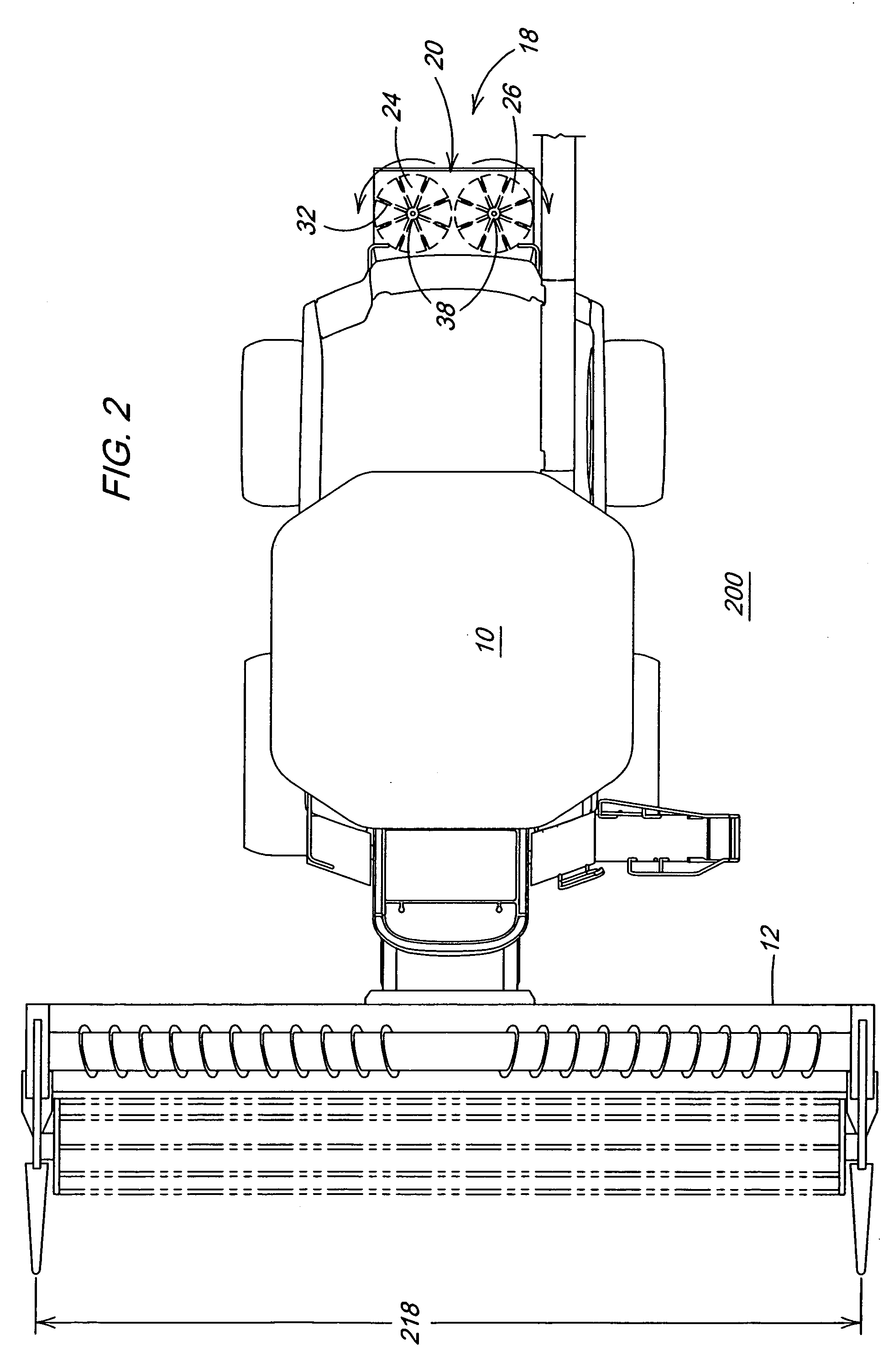
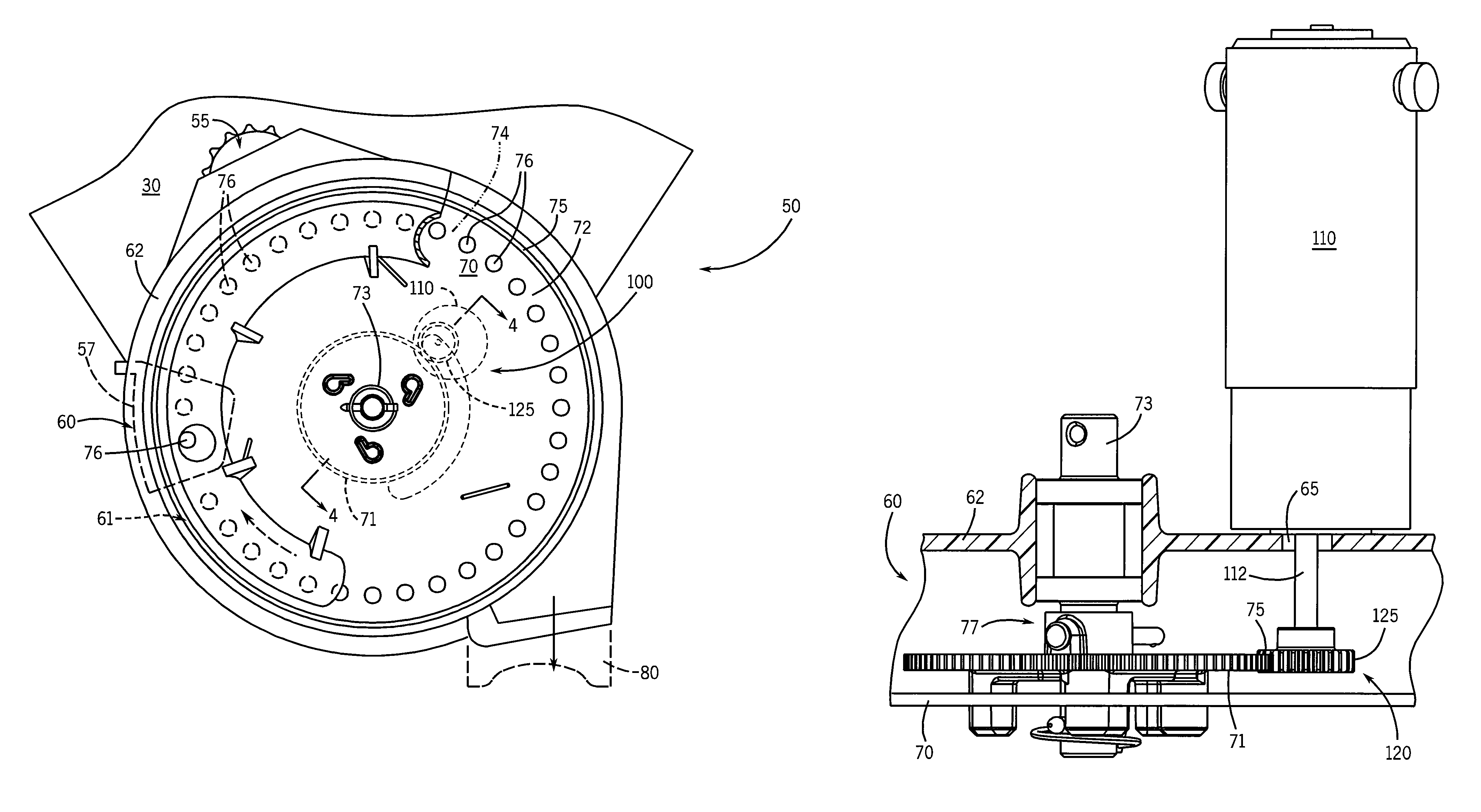
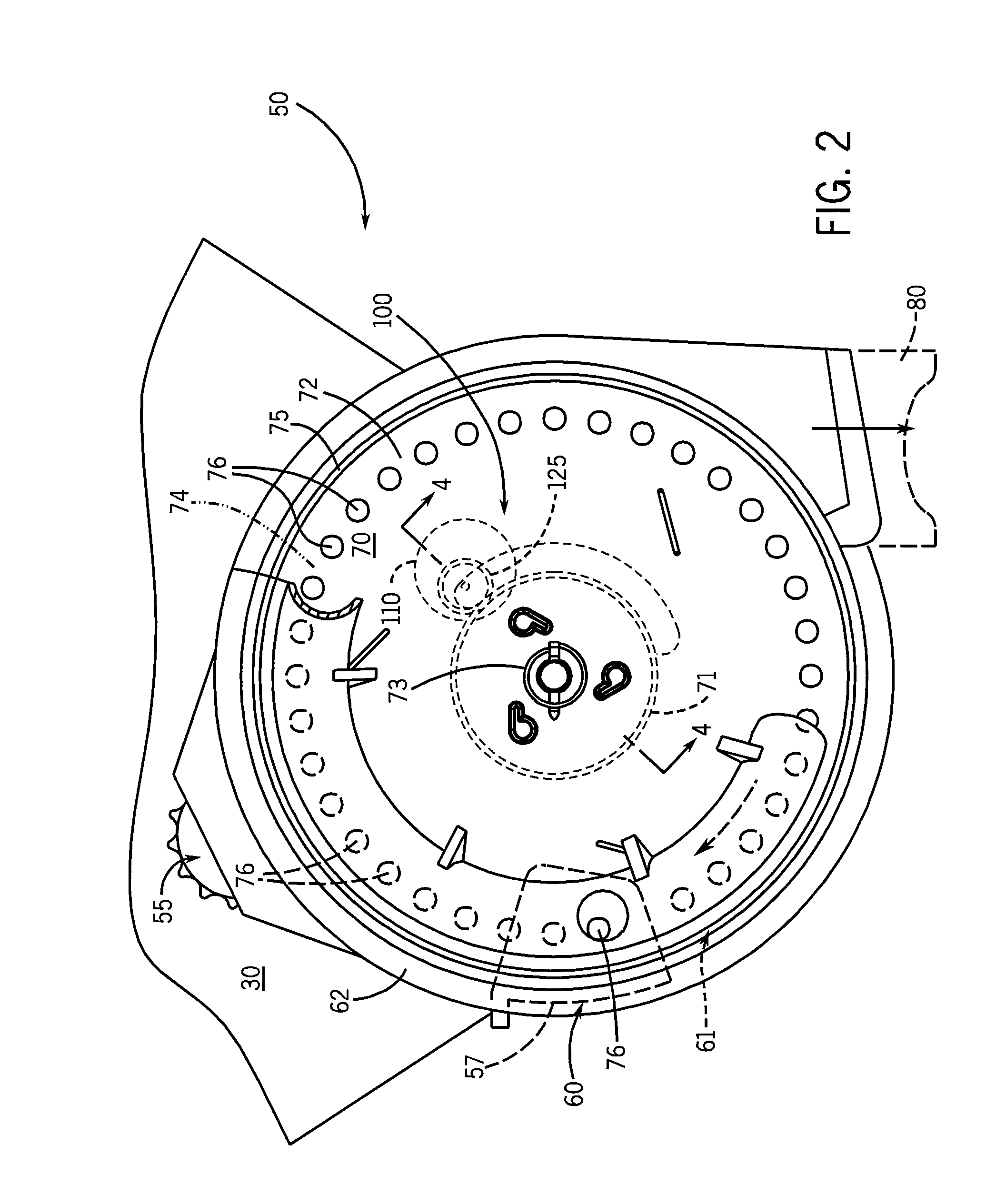
Seed delivery apparatus with sensor and moving member to capture and move seed to a lower outlet opening
ActiveUS20100192821A1Fertiliser distributersCentrifugal wheel fertilisersEngineeringLight emitting device
A seed delivery apparatus has a moving member that captures and entraps the seed from the seed meter and physically moves the seed from the meter to the lower outlet opening. In so doing, the seed engages and travels along an interior surface of the seed delivery apparatus. A seed sensor is mounted on the housing wall such that the seed passes directly in front of the sensor. The sensor has both the light emitting devices and the photo-sensitive elements on the same wall of the delivery apparatus, or on two opposed walls. The moving member prevents ambient light, dust and dirt from entering the housing and impacting the sensor output signal.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Intergrated low k dielectrics and etch stops
InactiveUS20020084257A1Decorative surface effectsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsHydrogenFluorocarbon
A method of depositing and etching dielectric layers having low dielectric constants and etch rates that vary by at least 3:1 for formation of horizontal interconnects. The amount of carbon or hydrogen in the dielectric layer is varied by changes in deposition conditions to provide low k dielectric layers that can replace etch stop layers or conventional dielectric layers in damascene applications. A dual damascene structure having two or more dielectric layers with dielectric constants lower than about 4 can be deposited in a single reactor and then etched to form vertical and horizontal interconnects by varying the concentration of a carbon:oxygen gas such as carbon monoxide. The etch gases for forming vertical interconnects preferably comprises CO and a fluorocarbon, and CO is preferably excluded from etch gases for forming horizontal interconnects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
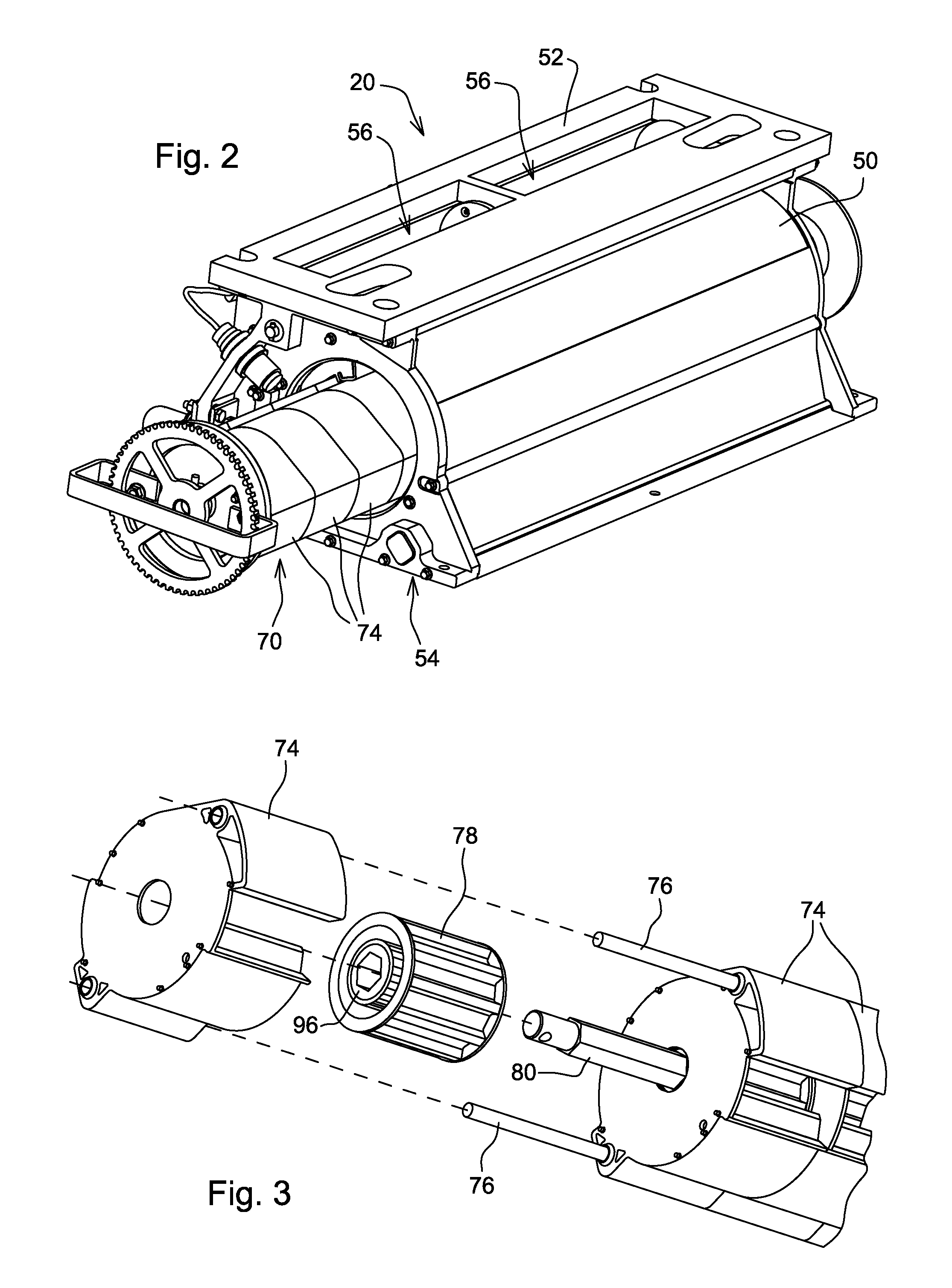
Directly driven seed meter hub drive
A direct drive electric seed metering system is provided for use with a row crop planter or seed planter that intakes a volume of multiple seeds from a seed hopper, draws individual seeds from the volume of multiple seeds and discharges them into a seed furrow formed in an agricultural field. The direct drive electric seed metering system includes a meter assembly having a meter housing and a seek disk rotatably mounted concentrically in the housing for singulating the seeds. A direct drive mechanism is mounted to the meter assembly for interfacing and driving the seek disk at an angular velocity which corresponds to the travel velocity of the seed planter. A single seed planter can have multiple direct drive electric seed metering systems, and each of the multiple direct drive electric seed metering systems preferably has its own prime mover to effectuate driving the seek disk.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
Material spreading apparatus
InactiveUS6202944B1Simple and economical designEasy to modifySowingFertiliser distributersBristleEngineering
A versatile and easily serviceable material spreading apparatus of the type for movement over a ground surface while broadcasting a material along a path on the ground surface. The apparatus includes a belt cartridge which can be slid into or pulled out of a chassis compartment having ledges for supporting the cartridge. The belt cartridge provides an upper flight on which material is carried from a hopper supported on the chassis to a broadcasting unit carried at one end of the chassis. A plurality of broadcasting units each of which has an attachment component, which in combination with a mating attachment component carried by the chassis, permits quick fastening and removal of each unit relative to the chassis. One of the broadcasting units mounts an elongated rotatable member below a drop-offend of the upper flight of the belt cartridge, and the rotatable member is driven in a direction so that the upper rotating periphery of the rotating member propels the material upward and away from the chassis. The rotating member has strips of bristles which spiral around a core of the member towards opposite ends thereof so that the material also has imparted to it from bristles of the rotating member a direction of flight having a side-ways component to thereby increase the width of the path of distribution.
Owner:TORO CO THE
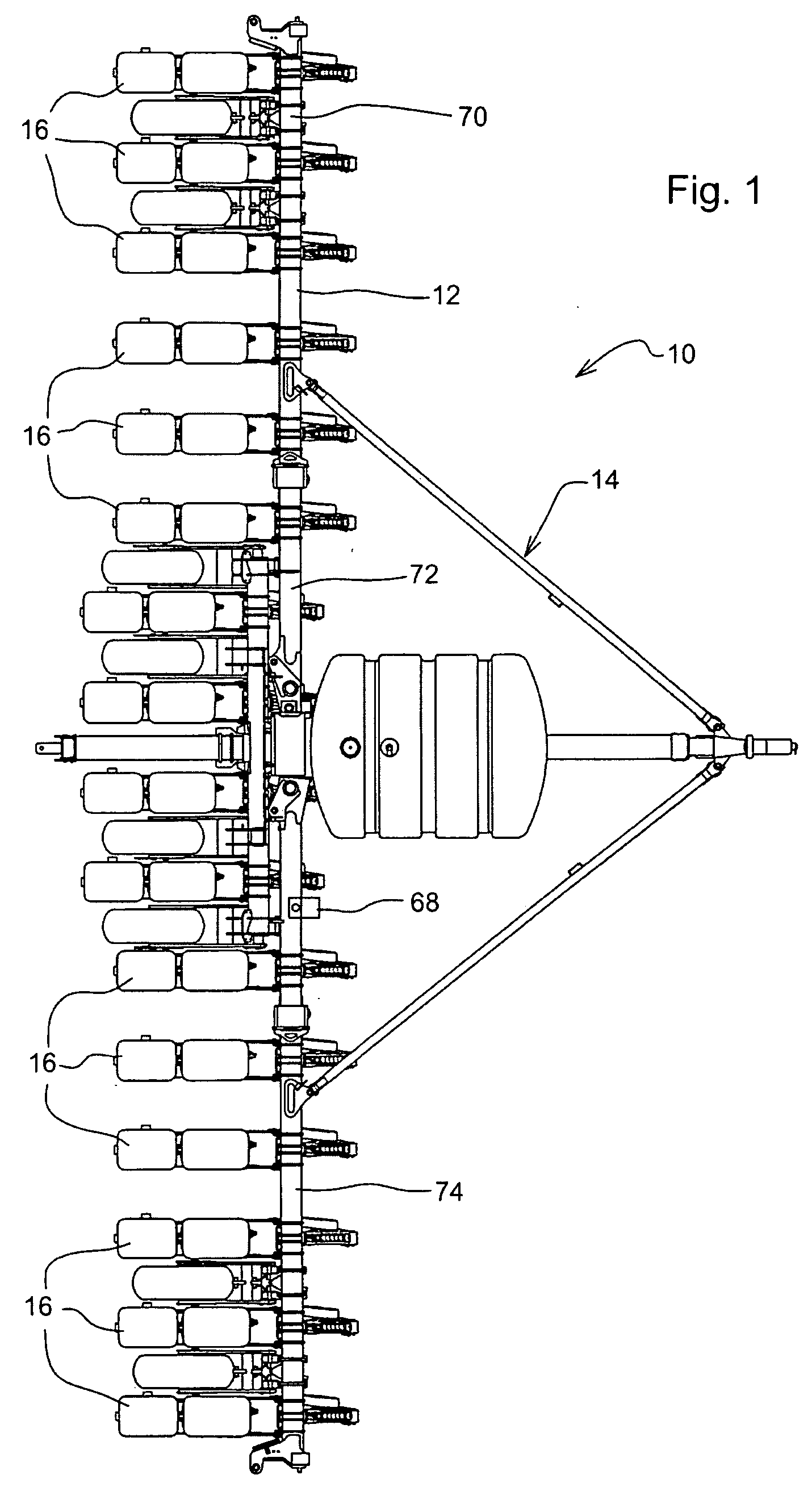
Sectional meter shut-off and agricultural implement having sectional meter shut-off
An assembly for selectively supplying particulate material to an air seeder, an agricultural implement able to selectively supply and dispense particulate material into the ground and a method of selectively dispensing particulate material into the ground are provided. The assembly has at least one supply receptacle for receiving particulate material from a source and a metering roller for supplying the material to an air seeder. The assembly is operative to selectively supply the material to the air seeder and prevent the material from being supplied to the air seeder. The implement can use the assembly to selectively supply particulate material to ground engaging openers where the particulate material will be dispensed into the ground. Particulate material can be selectively supplied to the implement when it is desired to have the particulate material dispensed into the ground and then prevented from being supplied to the implement when it is not desirable.
Owner:ONE PASS IMPLEMENTS
Dual configurable distribution nurse system
InactiveUS6883445B2Reliable constructionReduce manufacturing costFertiliser distributersCentrifugal wheel fertilisersEngineeringAirflow
A nurse receiver header for an agricultural planting implement is cooperable with a nurse mechanism that conveys seeds entrained in an air stream from a central hopper. A receiver is positioned at the planting mechanism to receive the seeds entrained in the air stream and accumulate a supply of seeds for utilization by the associated planting mechanism. The receiver header includes a plurality of legs and a rotatable baffle positioned internally at an uppermost position of at least one leg of the receiver header. The baffle is pivoted by an external lever that is positioned in the same orientation as the baffle to indicate the position of the baffle. The header can be placed in a closed configuration by positioning the baffle across the leg to be blocked. When in an open configuration, the baffle is positioned parallel to the leg and all of the legs of the header are open.
Owner:CNH IND CANADA
Directly Driven Seed Meter Hub Drive
A direct drive electric seed metering system is provided for use with a row crop planter or seed planter that intakes a volume of multiple seeds from a seed hopper, draws individual seeds from the volume of multiple seeds and discharges them into a seed furrow formed in an agricultural field. The direct drive electric seed metering system includes a meter assembly having a meter housing and a seek disk rotatably mounted concentrically in the housing for singulating the seeds. A direct drive mechanism is mounted to the meter assembly for interfacing and driving the seek disk at an angular velocity which corresponds to the travel velocity of the seed planter. A single seed planter can have multiple direct drive electric seed metering systems, and each of the multiple direct drive electric seed metering systems preferably has its own prime mover to effectuate driving the seek disk.
Owner:BLUE LEAF I P INC
System and Method for Prescriptive Seed Treatment
PendingUS20180192577A1Centrifugal wheel fertilisersFertilising methodsMultiple criteriaMedical prescription
An improved method for prescriptive seed treatment is provided. A location can be calculated where a combination of seed and one or more types and / or amounts of seed-applied substances will be planted. The combination is selected, based at least in part, on one or more conditions. The combination is generated prior to being planted. The method can further include selecting a type of seed and / or a type and / or amount of the one or more seed-applied substances to be applied. One or more applicators can apply the seed-applied substance(s) to the seed within a seed flow path during operation. A plurality of seed receptacles can contain different combinations of seed and / or seed-applied substances generated prior to being placed into the receptacles. The method could further include selecting a seed receptacle containing a selected combination, and delivering the selected combination from the selected seed receptacle to be planted by the planter.
Owner:INFLEXION POINT TECH LLC
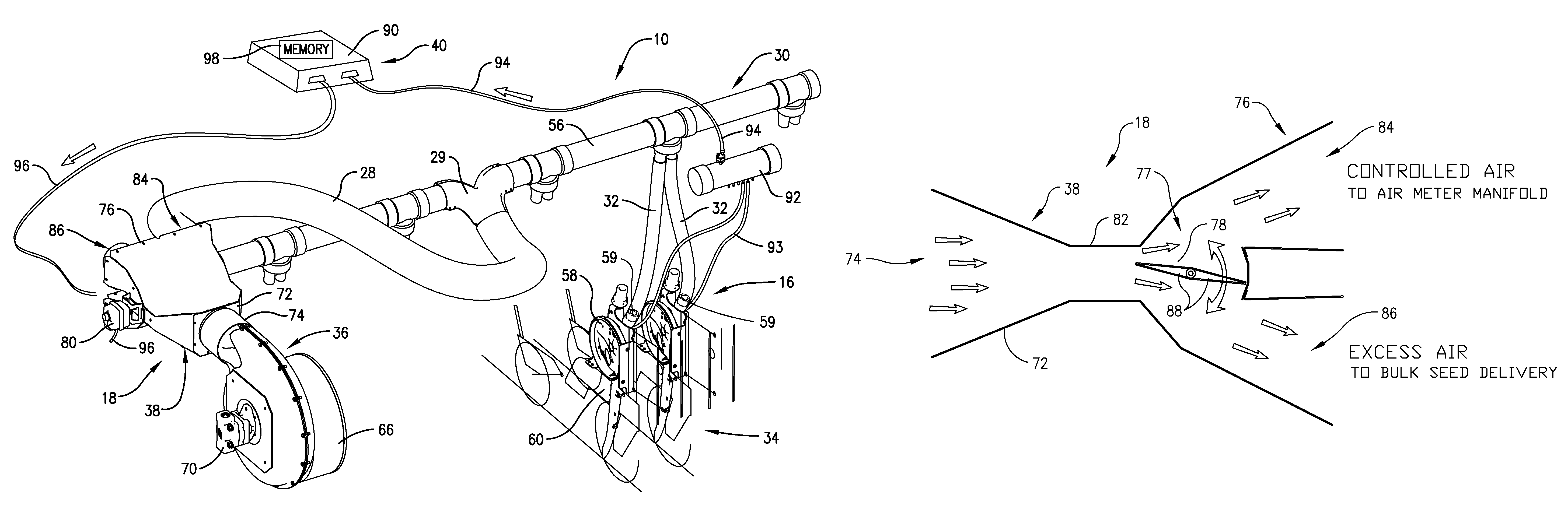
Air-assisted planting system having a single fan with pressure-responsive splitting of air streams for conveying and metering functions
To produce, monitor, and control a flow of air for a seed conveying system and a seed metering system, an air-assisted planting system includes an air handling system having a single air source and an air controller for maintaining a generally constant air pressure to the metering system. The air controller includes a plurality of sensors associated with and operable to monitor an air pressure through the metering system. Based on a sensed air pressure, a microprocessor of the air controller instructs the air handling system to selectively divert the flow of air to the metering system on an as-needed basis to maintain the generally constant air pressure.
Owner:GREAT PLAINS MFG INC
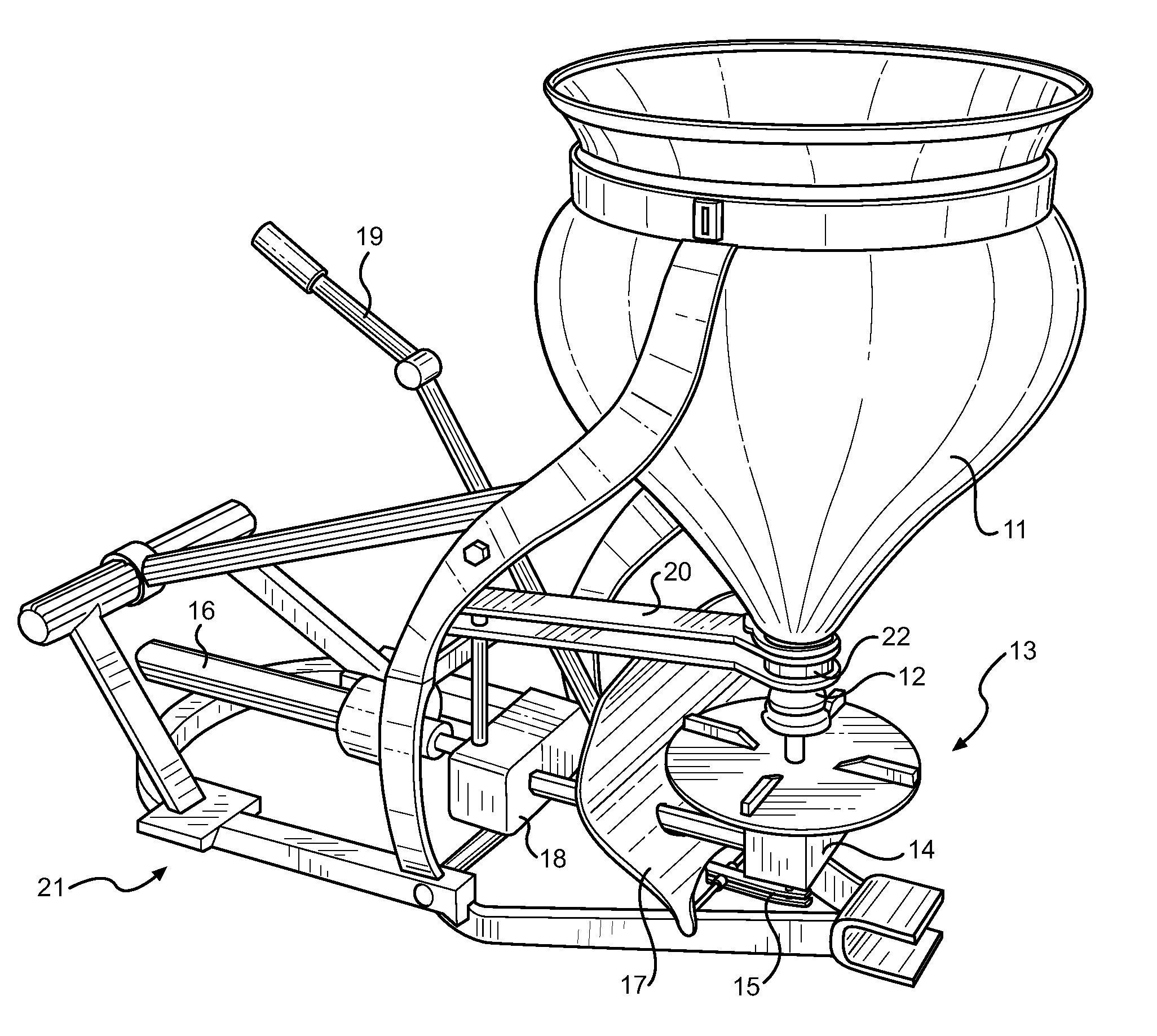
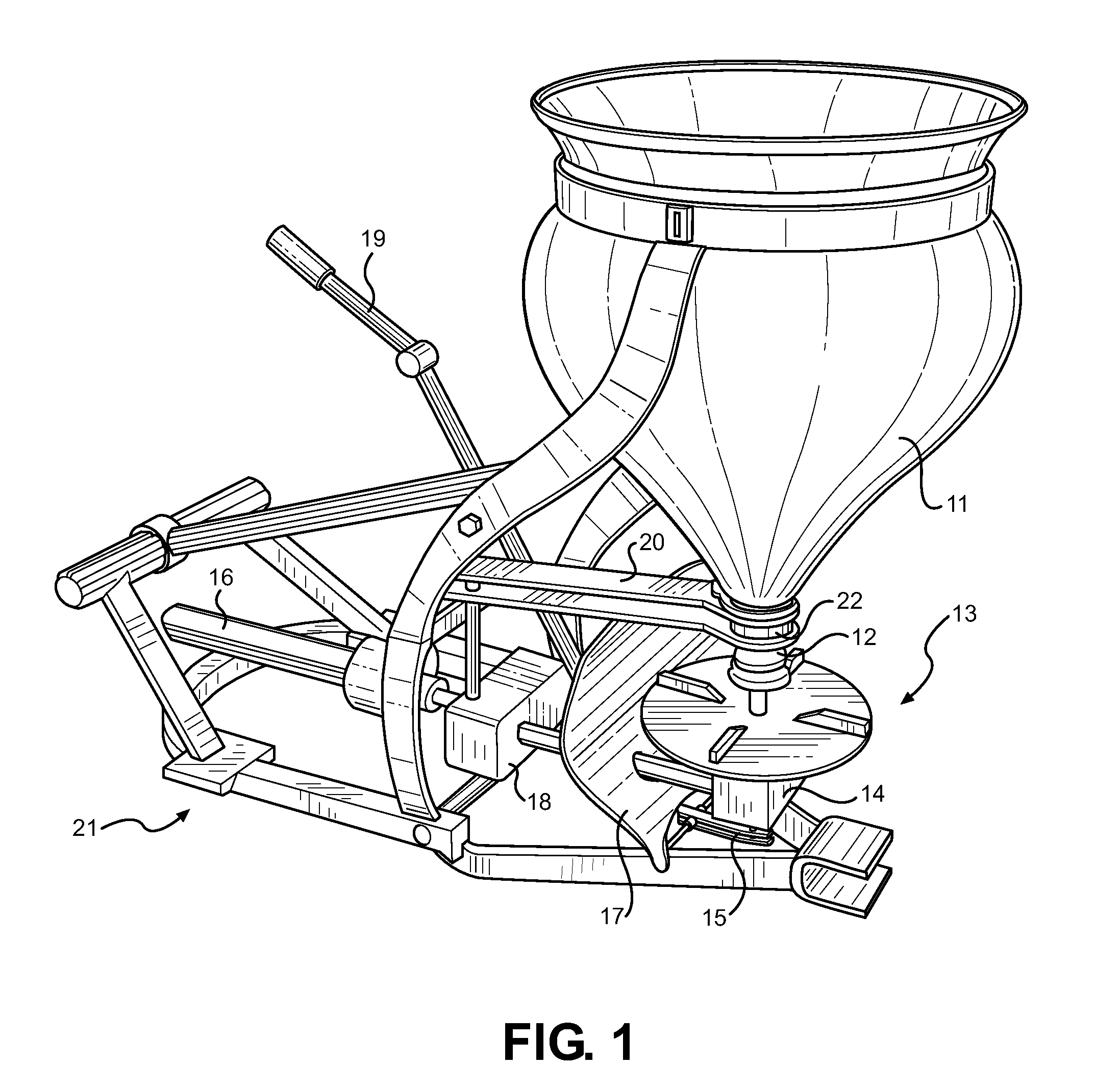
Free Flow Spreader Device
InactiveUS20110309170A1Uniform dispensingAccelerated settlementLiquid fertiliser distributionFertiliser distributersLiquid productImpeller
Disclosed is an improved means for spreading solid or liquid agricultural products, ideally suited for use with a tractor or similar vehicle with an external power takeoff shaft. For solid agricultural products, a specially designed hopper is used in conjunction with a cone-shaped, flow control stopper and an outlet agitator for providing a uniform delivery of product onto a rotating impeller. A plurality of gearboxes provide motive distribution of power for the hopper outlet agitation and impeller, while a user-accessible handle controls the control stopper height within the hopper outlet, and thus controlling the flow rate from the hopper. For liquid products, a cylindrical hopper is provided, along with a pump and a plurality of hoses for drawing or recycling the liquid product. A rear-mounted spray rail is provided for dispensing the liquid product, while an accessory connection is provided for a user to manually distribute the product with an attachable spray gun device.
Owner:WEEKS CHRISTOPHER
Special drive system that provides automatic application control of granular material
InactiveUS20120234934A1Wheel slippingSlow changeCentrifugal wheel fertilisersLiquid spraying apparatusElectricityAutomatic Generation Control
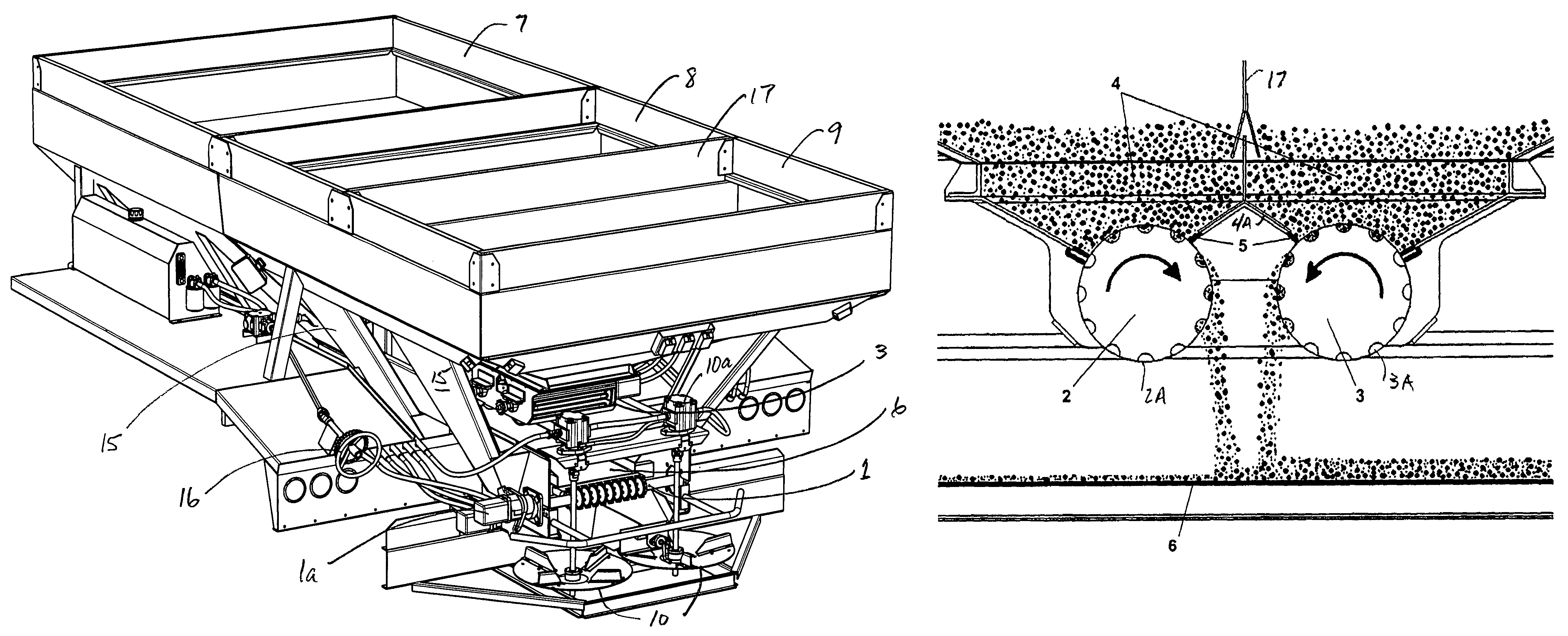
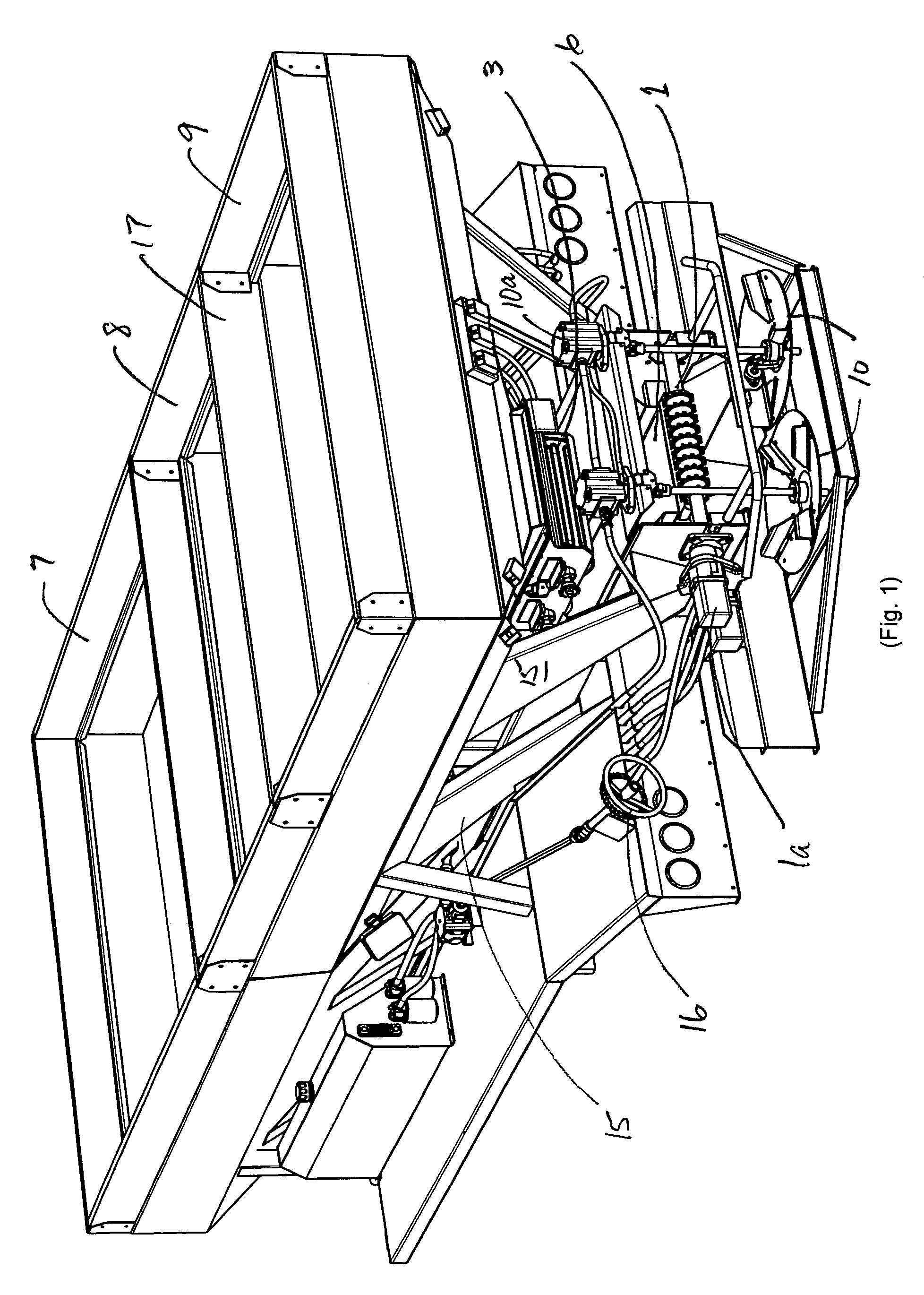
A special drive system that provides automatic and uniform application control of granular materials. It provides an automatic application control of a granular material from a granular material spreader and is comprised of (a) at least one electric motor for driving the conveyor and spinner at a speed, the said speed which determines a rate of discharge of the granular material; (b) a power source for the motor; (c) a means for controlling the power from the power source to the at least one motor; (d) a means for inputting a signal to the means for controlling the power; (e) a wiring harness with control and power electrical connectors; and (f) a means to mechanically mount the special drive system to the grain spreader wherein the result of the system is an accurately controlled rate of discharge and hence dispensing of the granular materials.
Owner:SCORE MICHAEL D +1
Integrated low k dielectrics and etch stops
InactiveUS20020074309A1Vacuum gauge using ionisation effectsDecorative surface effectsHydrogenFluorocarbon
A method of depositing and etching dielectric layers having low dielectric constants and etch rates that vary by at least 3:1 for formation of horizontal interconnects. The amount of carbon or hydrogen in the dielectric layer is varied by changes in deposition conditions to provide low k dielectric layers that can replace etch stop layers or conventional dielectric layers in damascene applications. A dual damascene structure having two or more dielectric layers with dielectric constants lower than about 4 can be deposited in a single reactor and then etched to form vertical and horizontal interconnects by varying the concentration of a carbon:oxygen gas such as carbon monoxide. The etch gases for forming vertical interconnects preferably comprises CO and a fluorocarbon, and CO is preferably excluded from etch gases for forming horizontal interconnects.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
Air-assisted planting system having a single fan with pressure-responsive splitting of air streams for conveying and metering functions
ActiveUS20100313801A1Decrease in RPMIncrease air pressureAnalogue computers for trafficFertiliser distributersAir treatmentHandling system
To produce, monitor, and control a flow of air for a seed conveying system and a seed metering system, an air-assisted planting system includes an air handling system having a single air source and an air controller for maintaining a generally constant air pressure to the metering system. The air controller includes a plurality of sensors associated with and operable to monitor an air pressure through the metering system. Based on a sensed air pressure, a microprocessor of the air controller instructs the air handling system to selectively divert the flow of air to the metering system on an as-needed basis to maintain the generally constant air pressure.
Owner:GREAT PLAINS MFG INC
Pressure Sensing System For A Planter
A pressure sensing system for a seeding machine such as a planter to measure the down force on a planter row unit uses a wireless pressure sensor embedded in a load carrying wheel of the row unit. In a preferred embodiment, the pressure sensor is a passive piezoelectric pressure sensor that is a transmitter only, transmitting both pressure and RFID the information that identifies the particular sensor. Multiple sensors may be employed in each wheel and sensors may be employed in more than one wheel of the row unit, such as the gauge wheels on opposite sides of the trench opening disks. The sensors may be made of a PVDF, a known piezoelectric material. A wireless receiver is located on the planter frame or could be located elsewhere to receive the signals from the pressure sensor. A controller determines from the signal, any change in down force and commands the change to a down force generator on the row unit.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Dual mode spreader
InactiveUS6945481B2Accurate identificationFertiliser distributersManure distributersImpellerDual mode
A dual mode spreader for broadcast spreading and drop spreading material comprising a hopper to hold a supply of spreadable material, first and second discharge openings located within the hopper for which spreadable material can flow therethrough, an impeller mounted in a position below the hopper for rotational movement about an upright axis, wherein the first discharge opening leads to impeller to enable the spreadable material in the hopper to exit therefrom onto the impeller to be distributed in a path outwardly therefrom onto the surface to be treated; and a diffuser defining an inlet opening and an outlet opening, wherein the second discharge opening is in communication with the inlet opening to enable the spreadable material in the hopper to enter the diffuser and exit therefrom through the outlet opening to be distributed in a path downwardly therefrom onto the surface to be treated.
Owner:USG STAMFORD BRANCH +1
Twin spinner spreading apparatus
ActiveUS7044408B2Efficient disseminationFertiliser distributersSowingElectrical and Electronics engineeringChassis
Owner:TORO CO THE
Pheumatic delivery system for application implement using multiple metering devices
ActiveUS20160095276A1Minimize complicationsLess-prone to adverse impactFertiliser distributersManure distributersParticulatesInductor
A pneumatic delivery system for particulate agricultural products includes one or more compartment for containing and supplying one or more particulate product. An inductor assembly separately receives and fluidizes the particulate products and conveys the fluidized products to a metering assembly. The metering assembly separately meters each of the product flows and transfers the metered flows to one or more delivery units for applying the products. The pneumatic delivery system can be used on various implements, including planters and applicators for applying seeds, fertilizer, pesticides and other products.
Owner:CNH IND CANADA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com