Patents
Literature
37 results about "Microtitre plate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
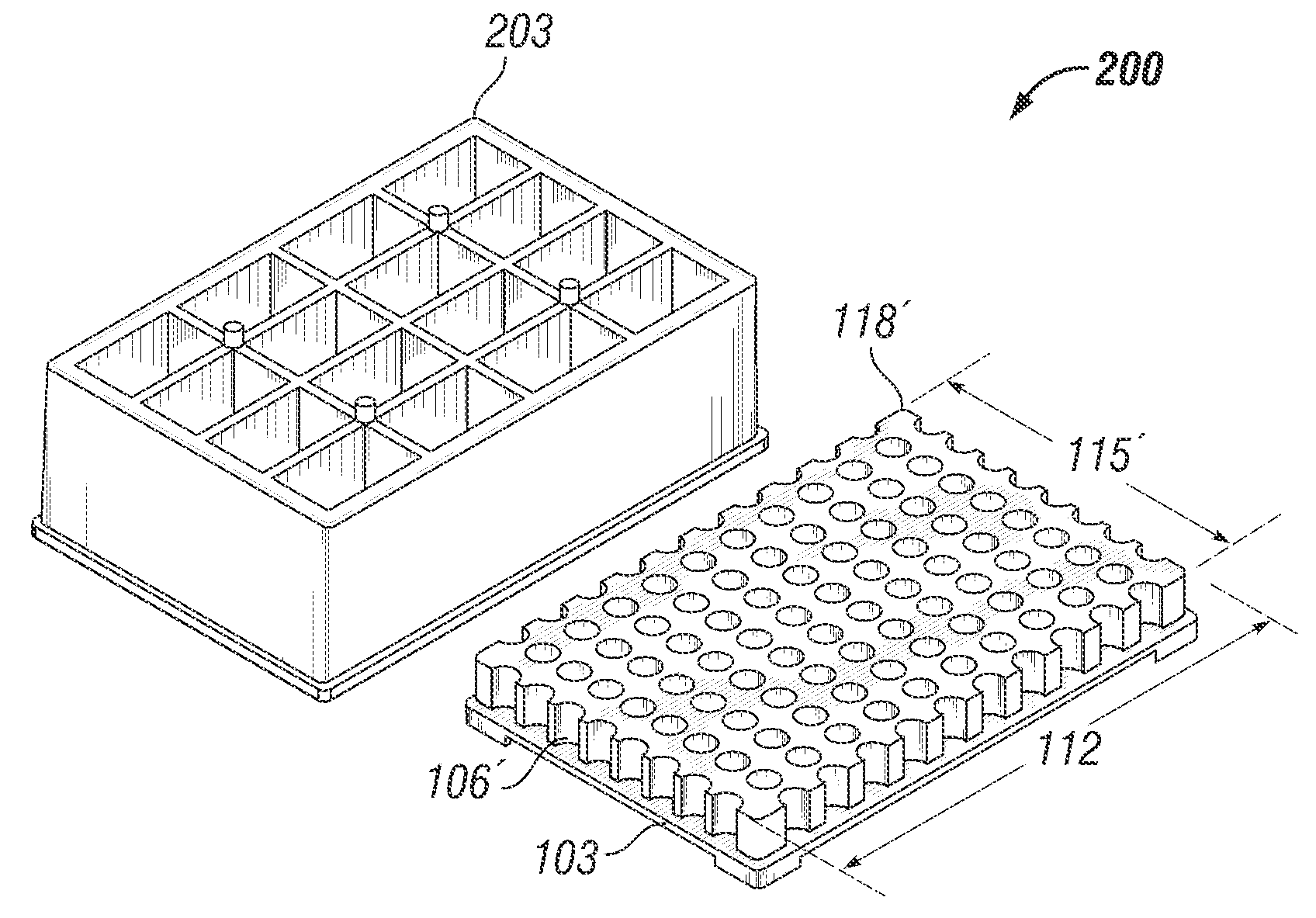
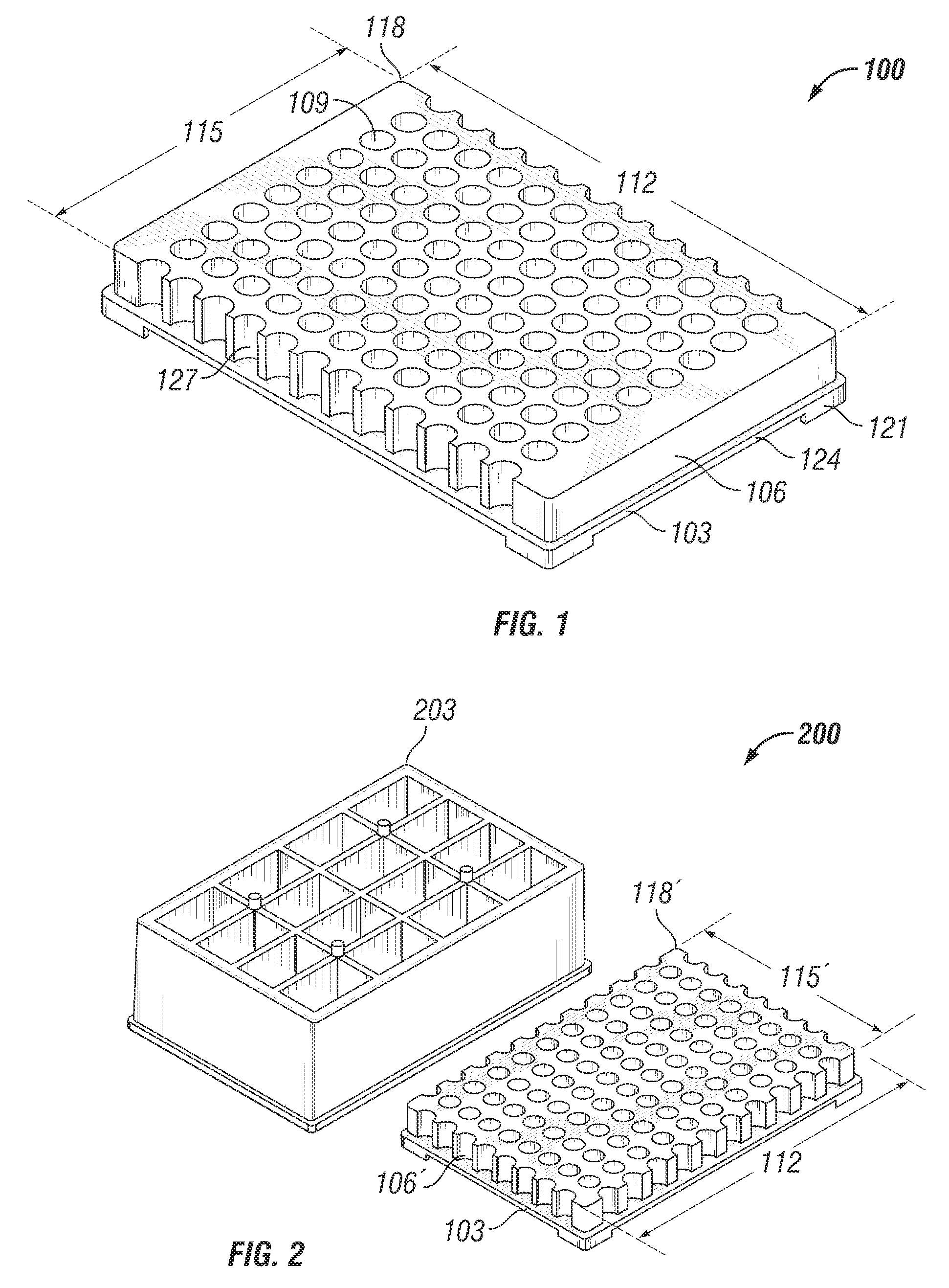
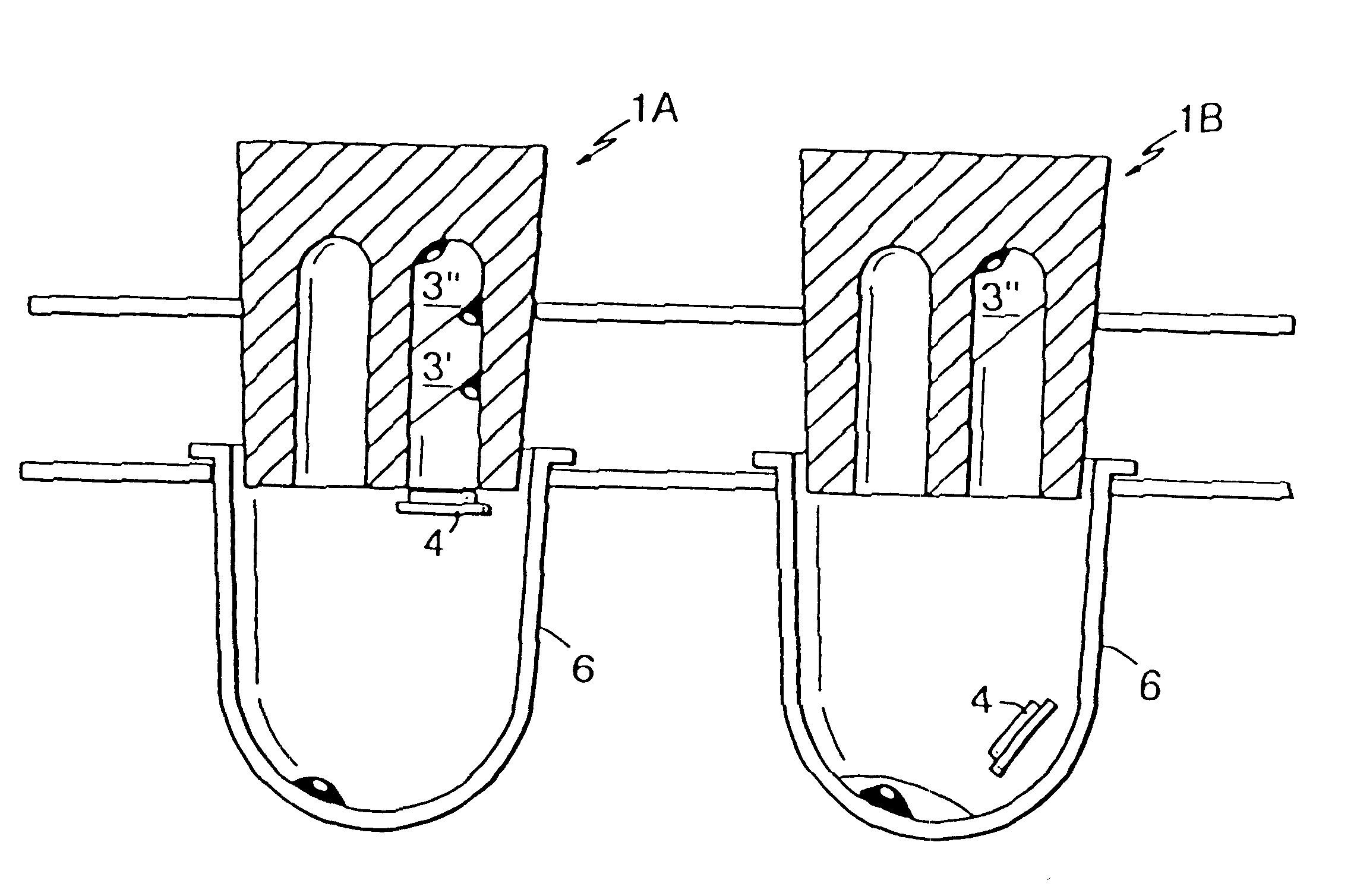
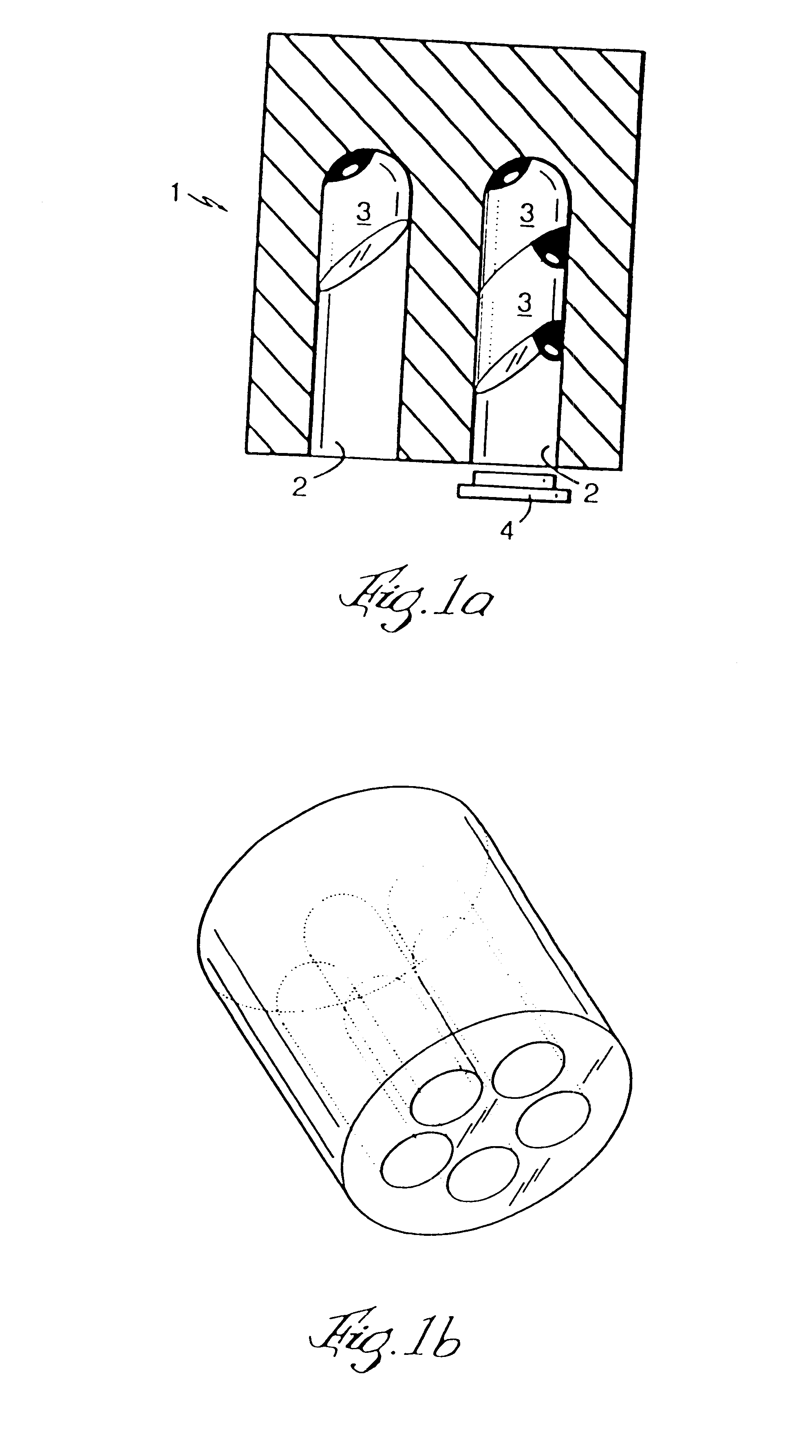
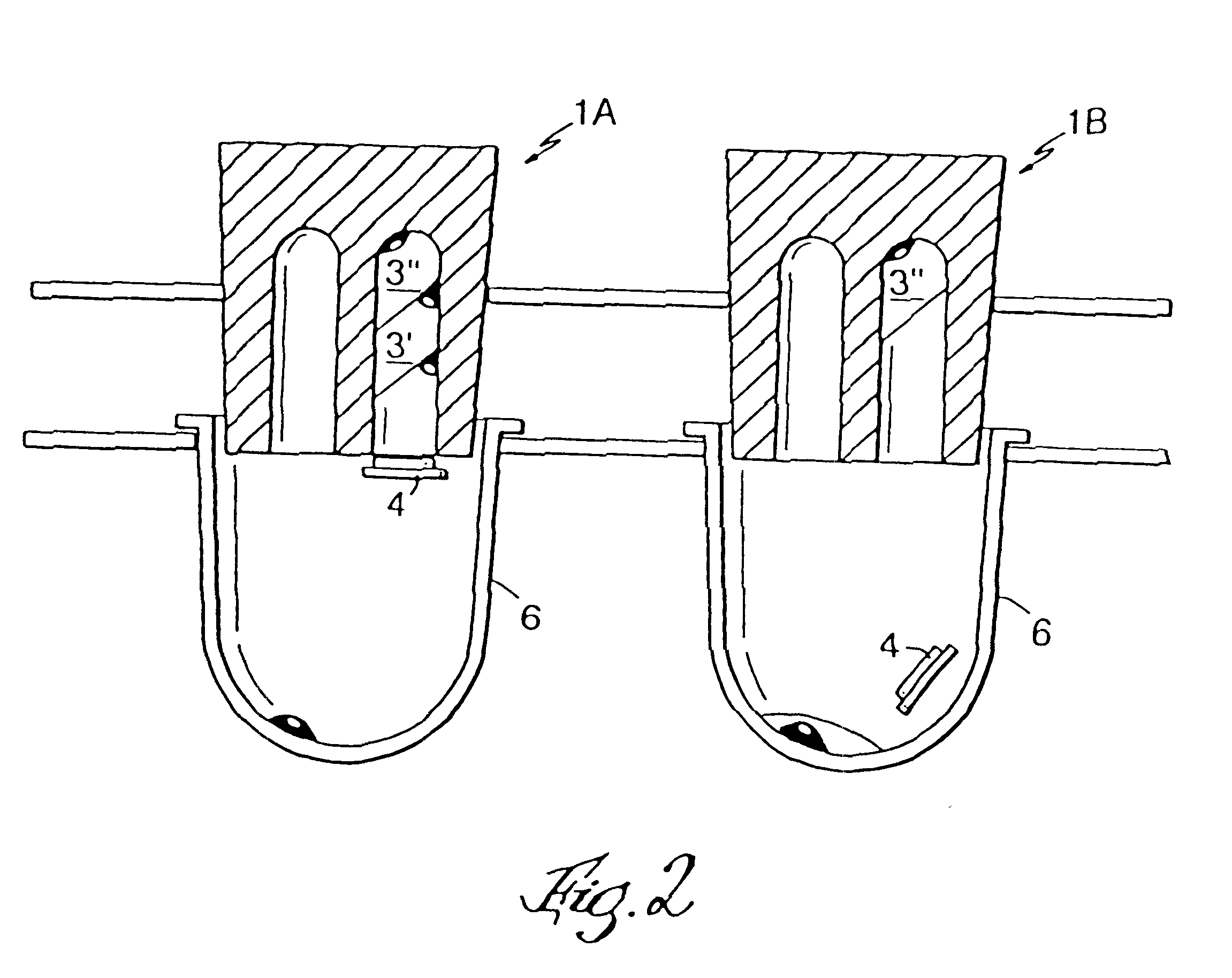
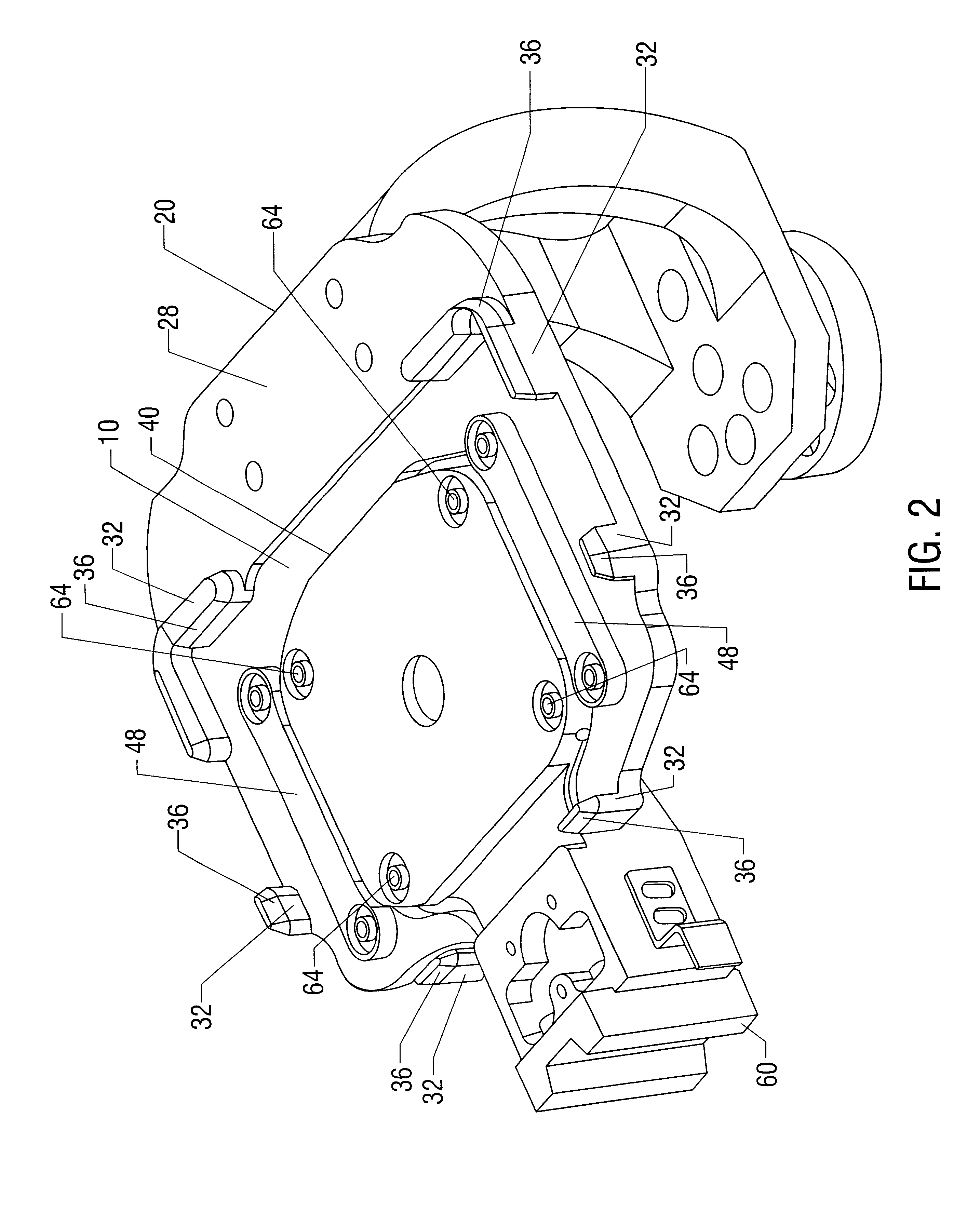
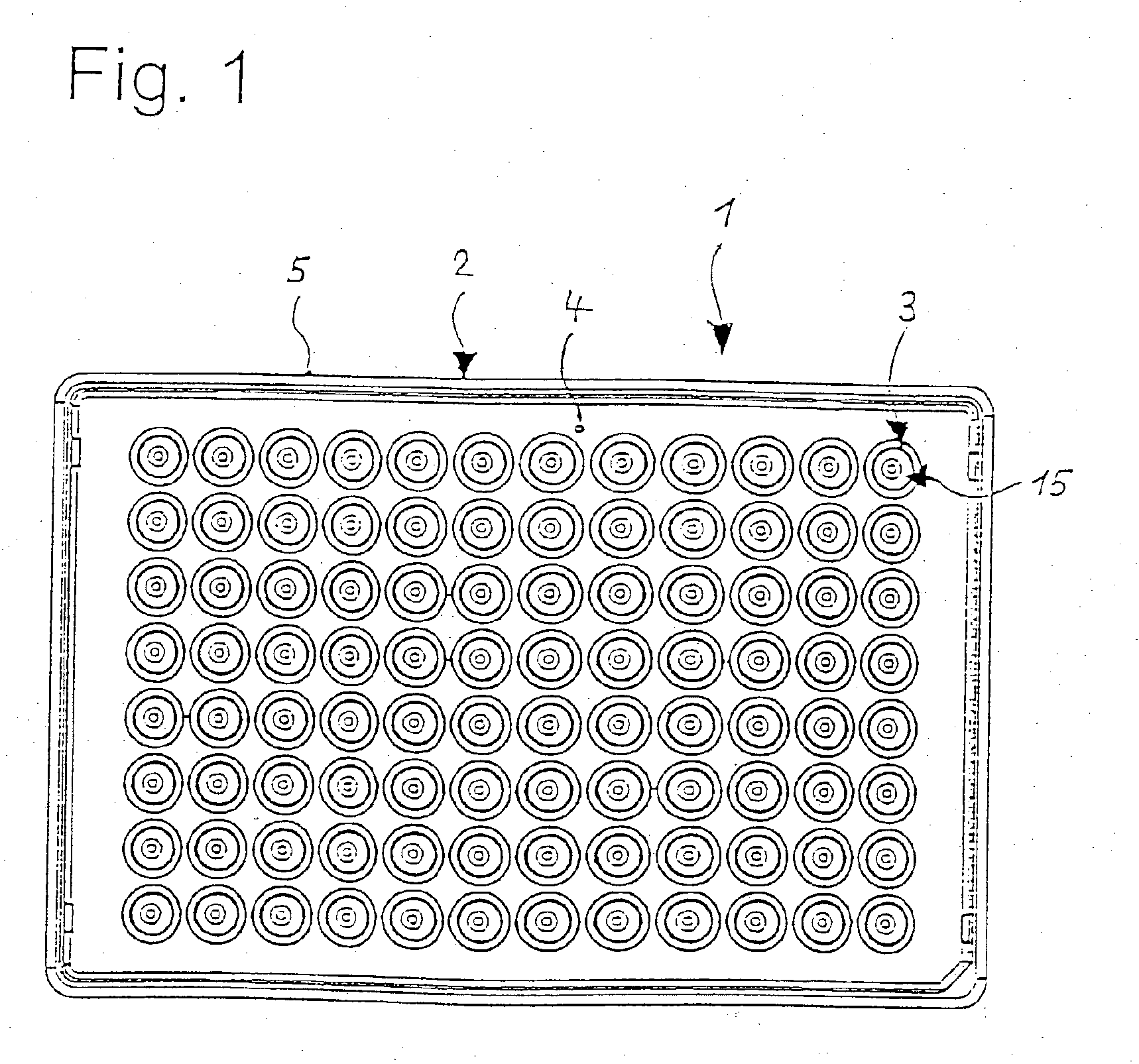
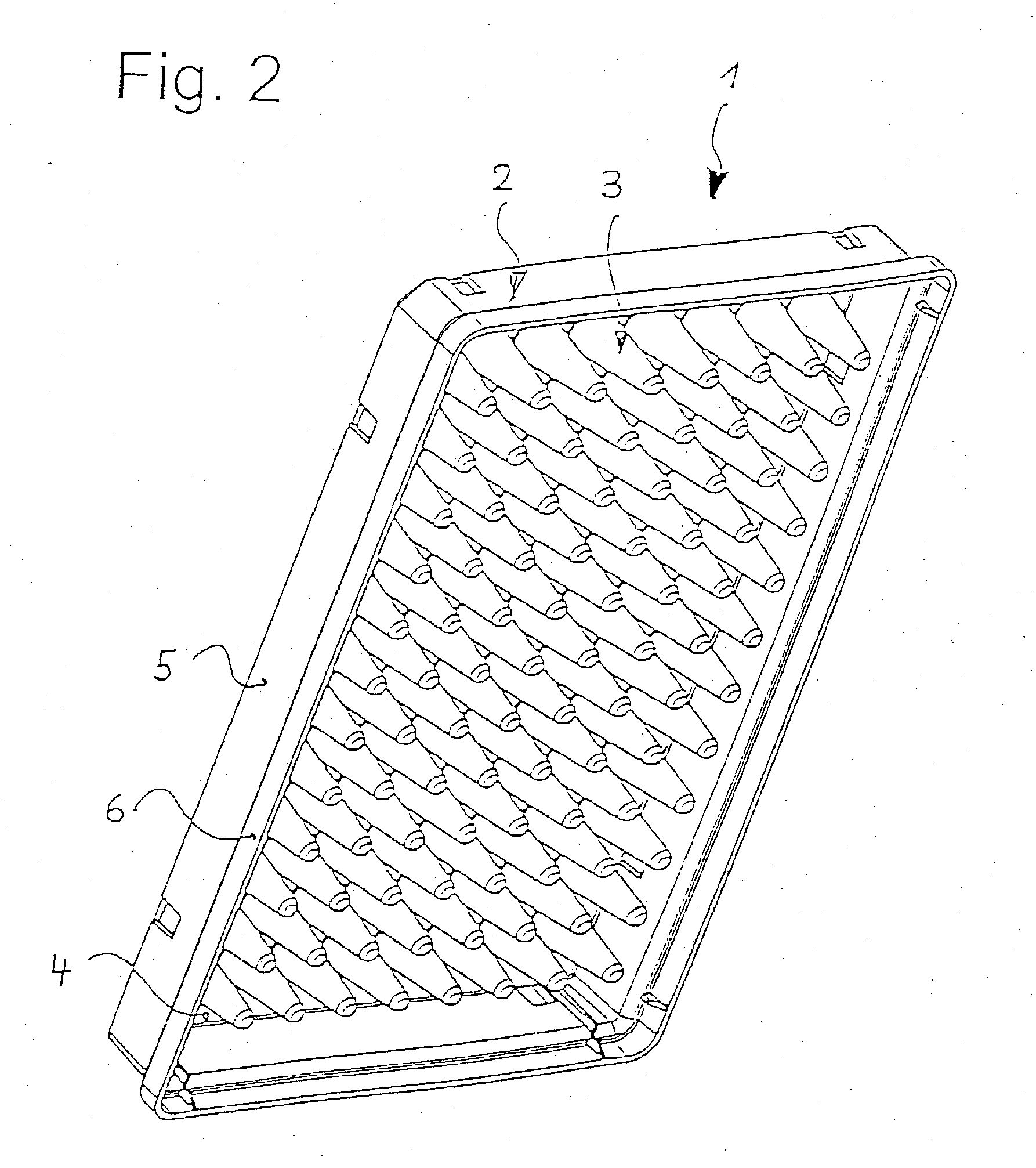
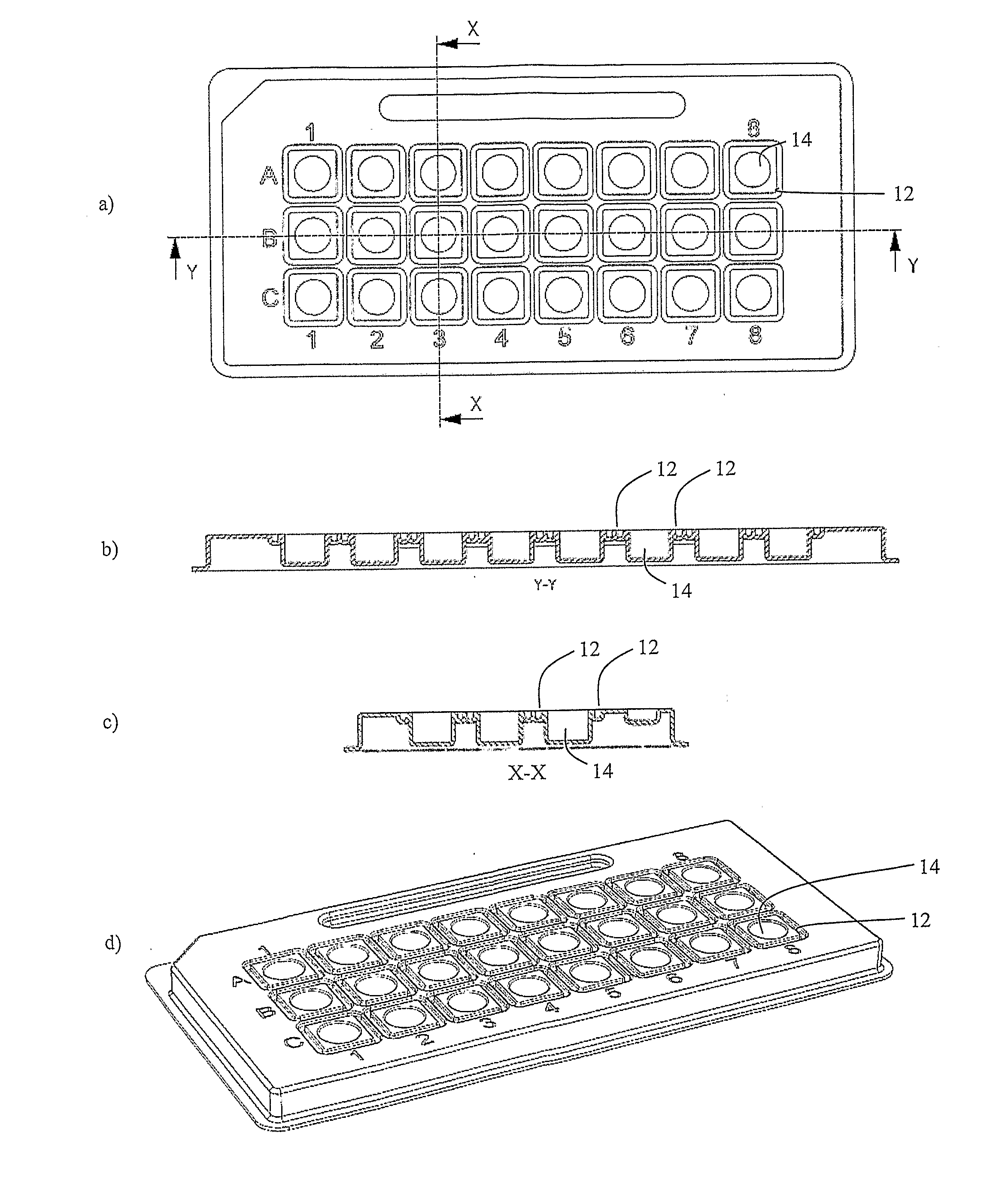
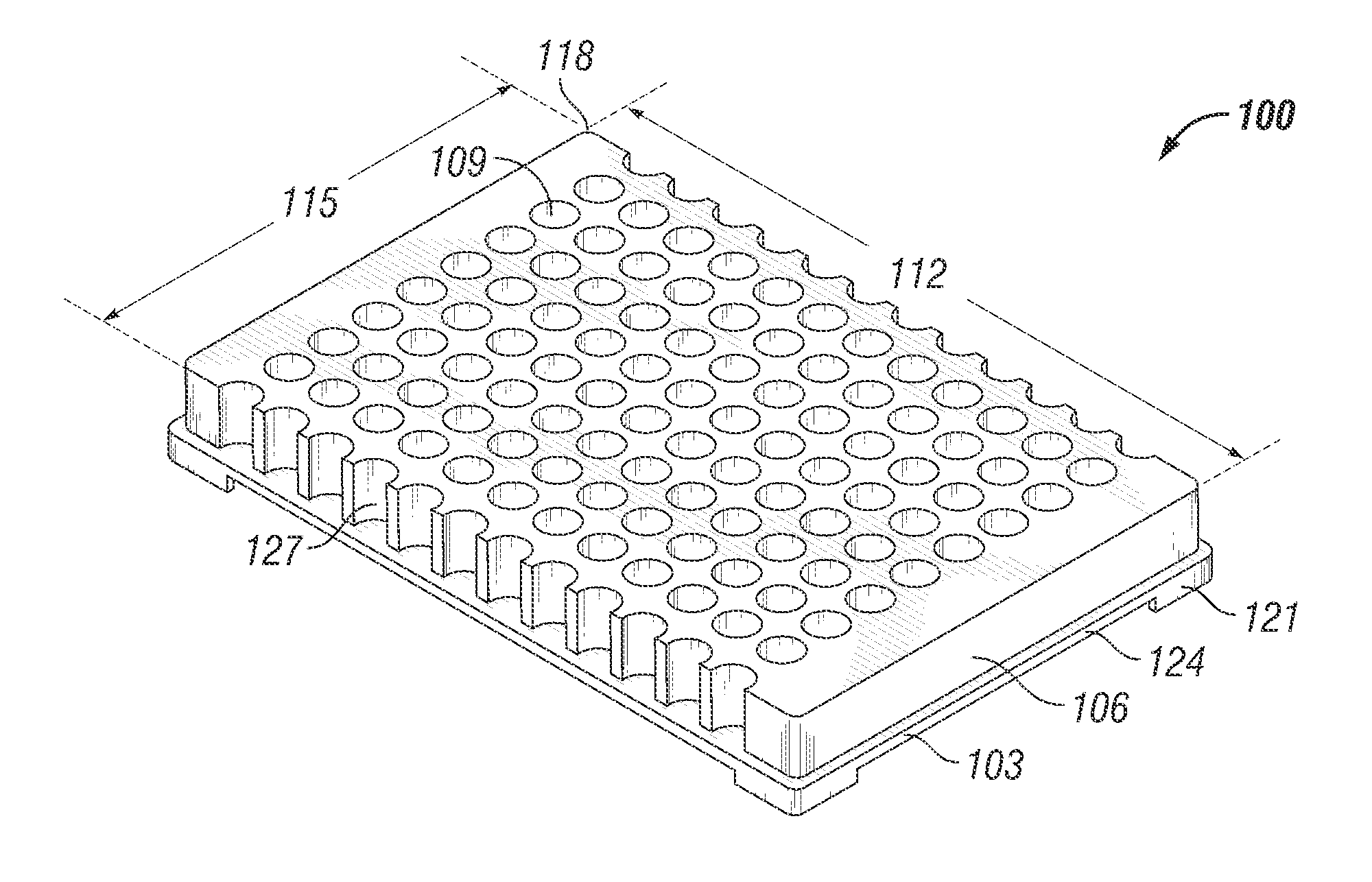
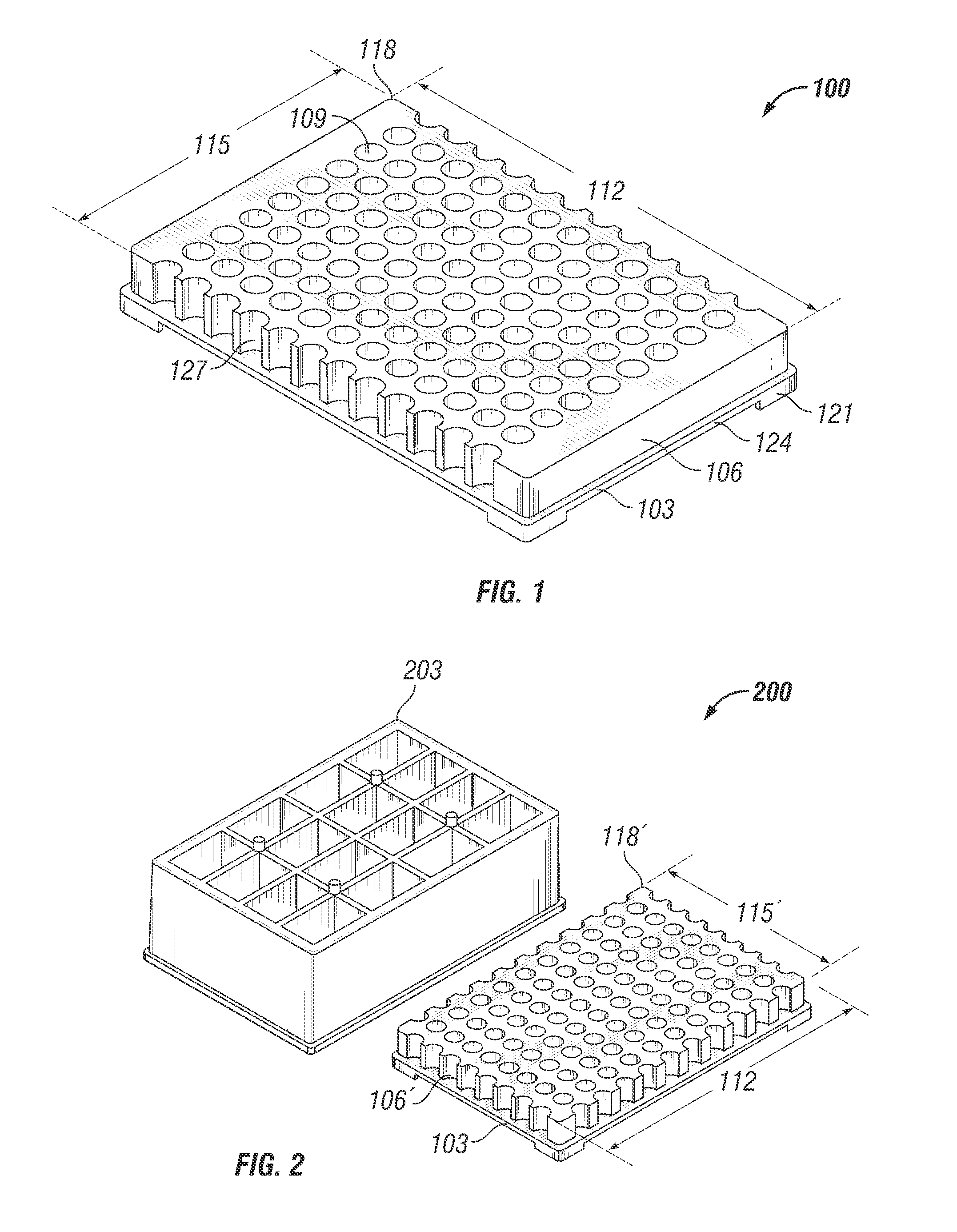
Microtitre plate with a relieved perimeter
ActiveUS7527769B2Chemical analysis using titrationLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringMechanical engineering
A microtitre plate having a relieved perimeter includes a plate defining a plurality of wells and the perimeter of the plate is horizontally relieved. Alternatively, a microtitre plate may include a base and a holding section extending from the base. The holding section defines a plurality of wells and the perimeter thereof being horizontally relieved.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Robot mounted barcode reader
A robotic arm-mounted laser barcode reader is provided. The robotic arm-mounted laser barcode reader may be used in the field of sample analysis to in increase the rate with which sample carriers such as microtitre plates may be interfaced with an automated system. The robotic arm-mounted laser barcode reader can read a bar code label affixed to a sample carrier immediately when the robotic arm grabs and manipulates a sample carrier, eliminating the step of presenting the sample carrier to a separate bar code reader to ensure proper tracking and / or inventorying of the sample carrier. The robotic arm-mounted laser barcode reader may also be used in other automated apparatuses that require tracking and / or inventorying.
Owner:VELOCITY11
Method for producing a grid structure, an optical element, an evanescence field sensor plate, microtitre plate and an optical communication engineering coupler as well as a device for monitoring a wavelength
InactiveUS6873764B2Improve accuracyLow effortCladded optical fibreMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorGratingPulsed DC
Owner:OERLIKON TRADING AG TRUEBBACH
Cartridge and system for storing and dispensing of reagents
InactiveUS6432694B1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTechnical standardReagent
Owner:ALPHAHELIX
Excitation and Imaging Optics for Fluorescence Detection
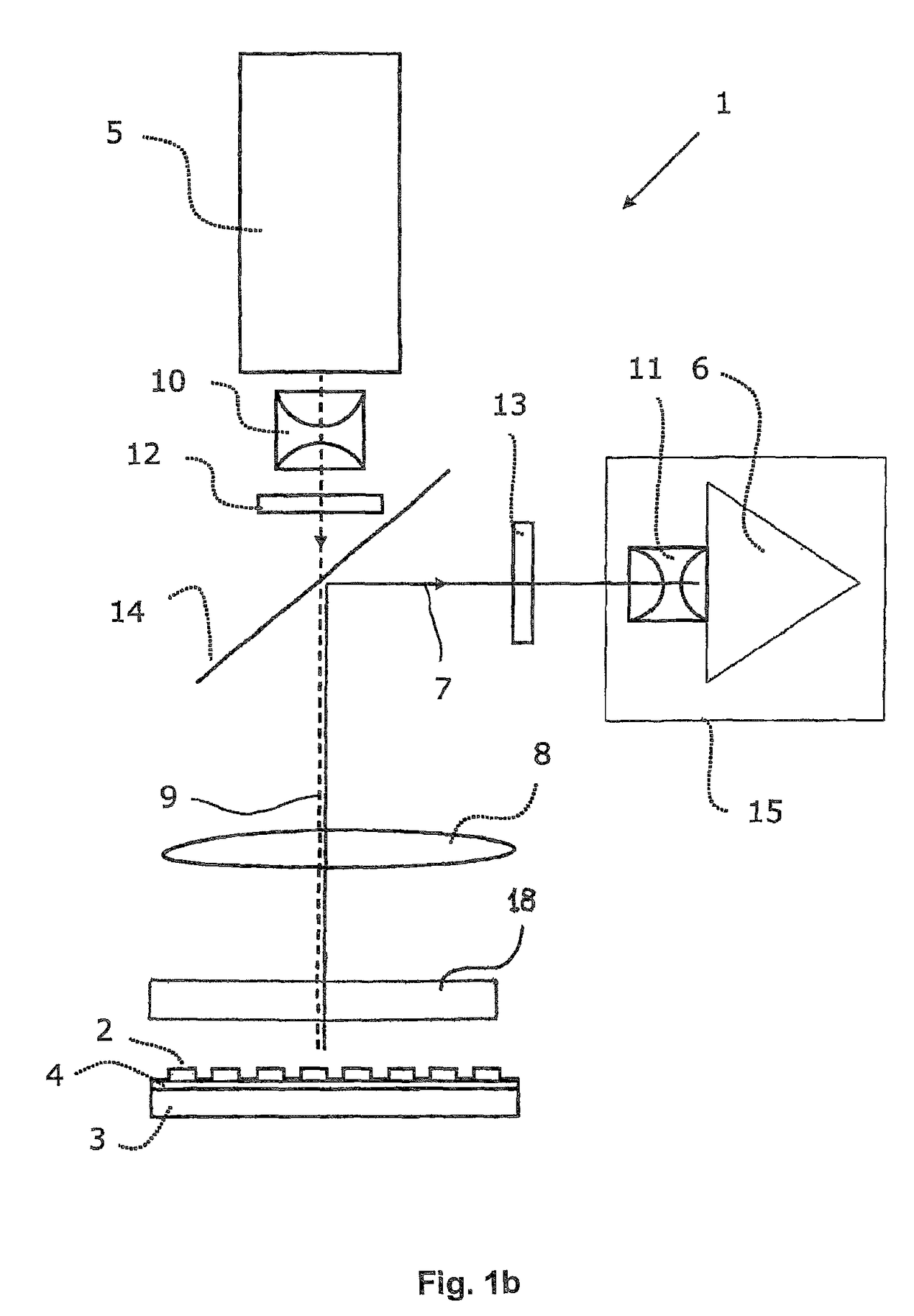
The invention concerns an optical instrument for imaging fluorescence signals from an arrangement of a plurality of individual detection sites, for example the wells of a microtitre plate. In order to improve the light yield of the fluorescence excitation with excitation light as well as the light yield of the detection of the fluorescence signals, an objective array is provided which is arranged in the beam path between the field lens and the detection sites and comprises a field lens array with field lens array elements and a pupil lens array with pupil lens array elements. In order to improve the channel separation and suppress interfering light the objective array can comprise a diaphragm array with in each case two diaphragm openings per detection site.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
Device and method for the determination of protein domain boundaries
InactiveUS6451591B1Improve throughputSuitable for automationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProteinase activityProtein structure
A method and device to assist in the determination of protein domain boundaries is described. In particular the device is designed to provide a high throughput of proteolytic digestion of proteins to identify domains and their boundaries, for use in protein structure determination, in a manner that is amenable to automation. Proteases are immobilized in a convenient format such as a microtitre plate and preferably arranged in a matrix thereby allowing for simultaneous degradation of a protein by a number of proteases at a number of concentrations.
Owner:AFFINIUM PHARMA
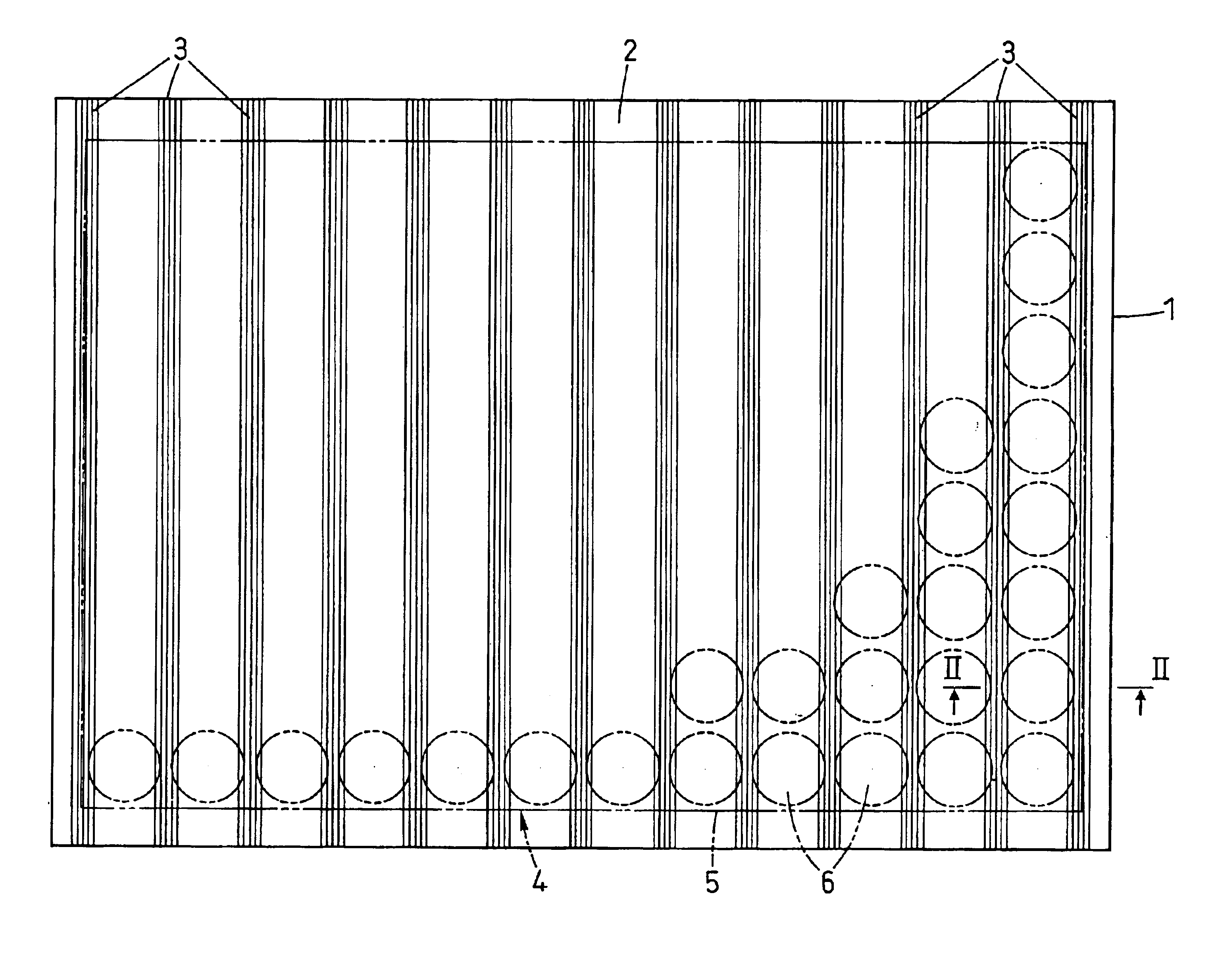
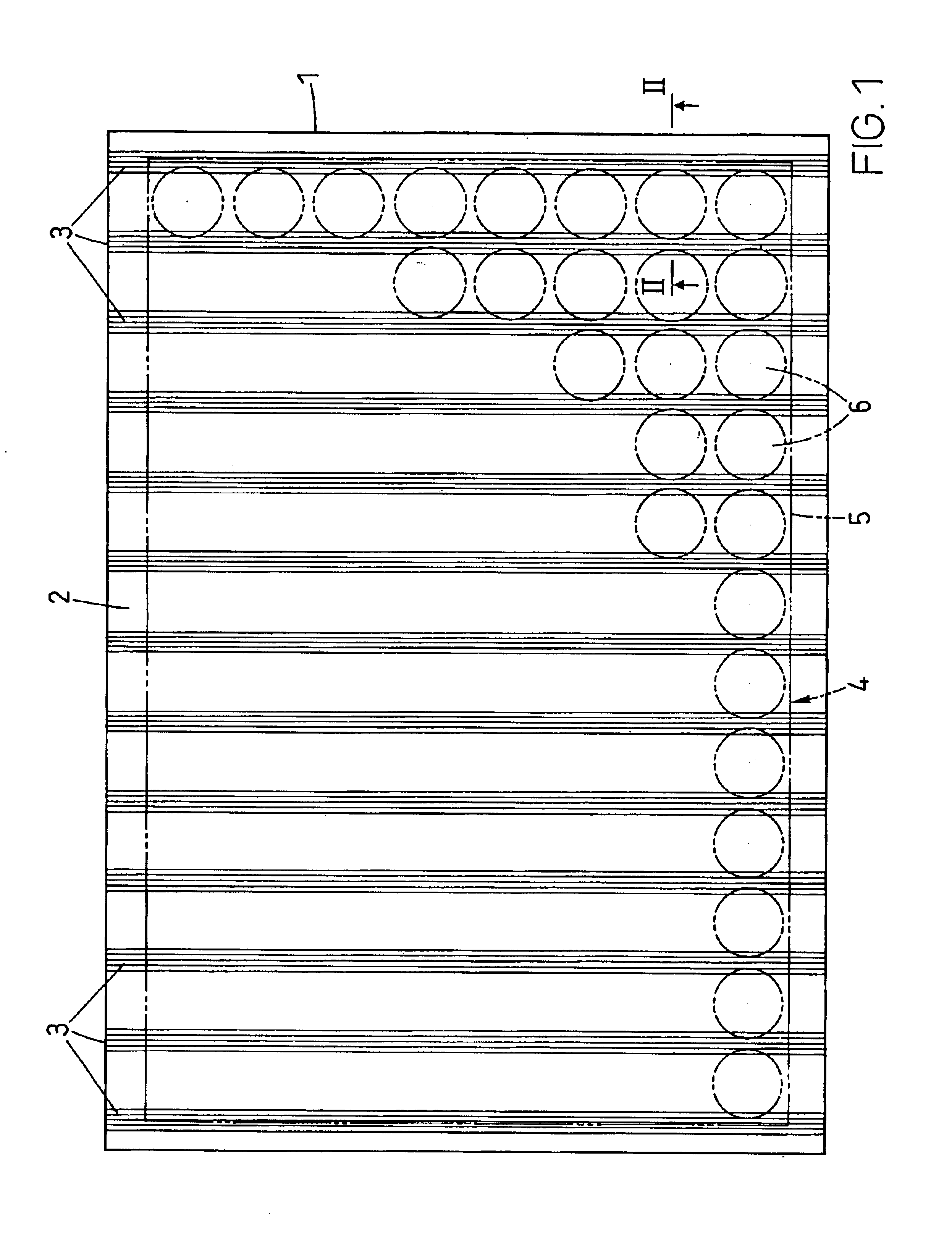
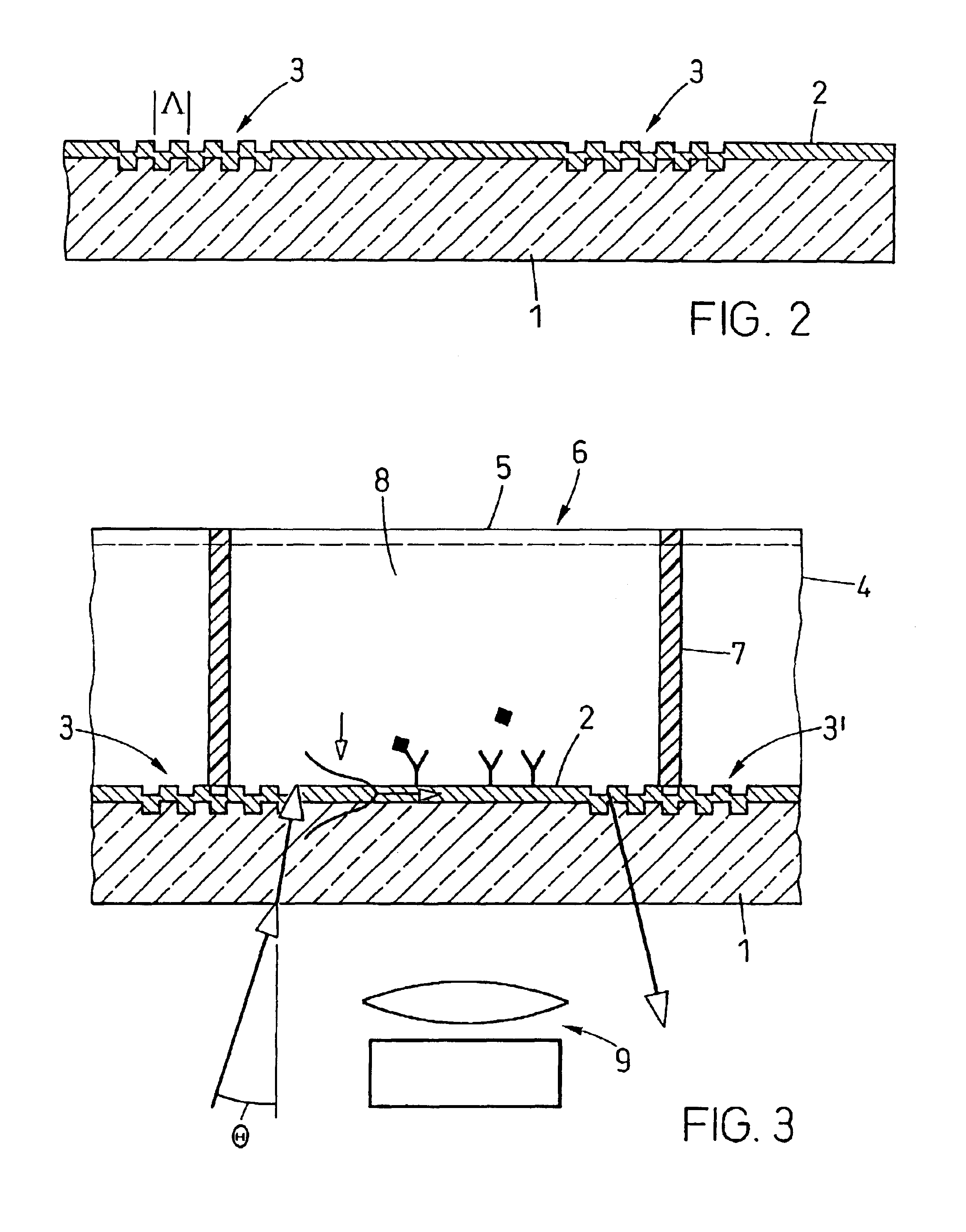
Waveguide plate and process for its production and microtitre plate
InactiveUS20060008206A1Good precisionEconomical and simpleMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorVacuum evaporation coatingGratingCoupling
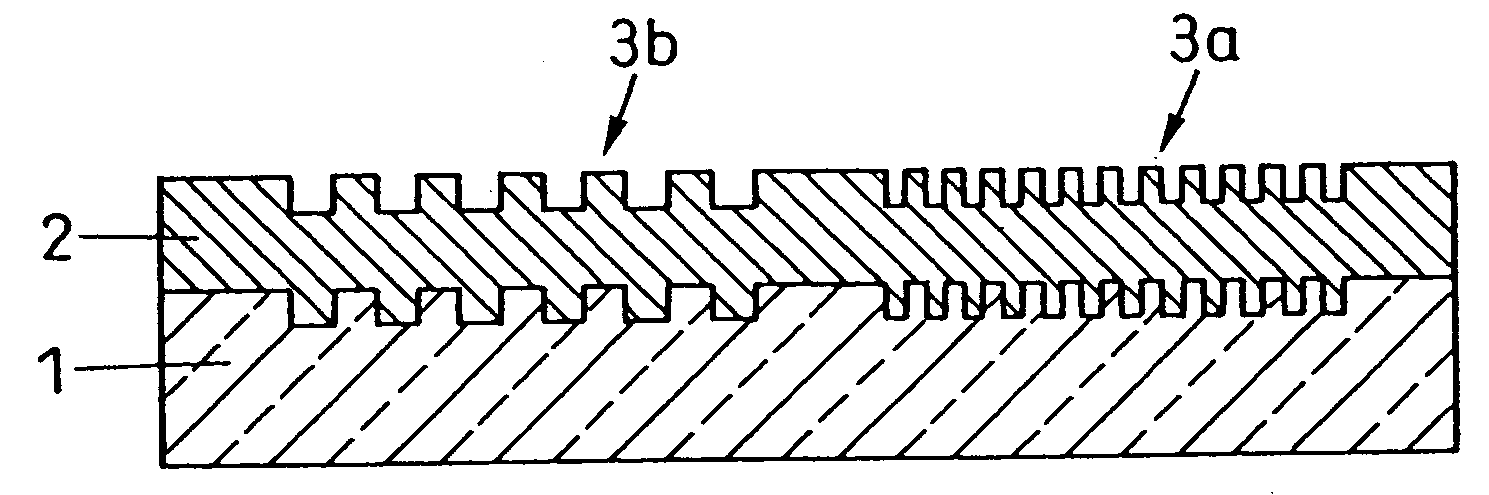
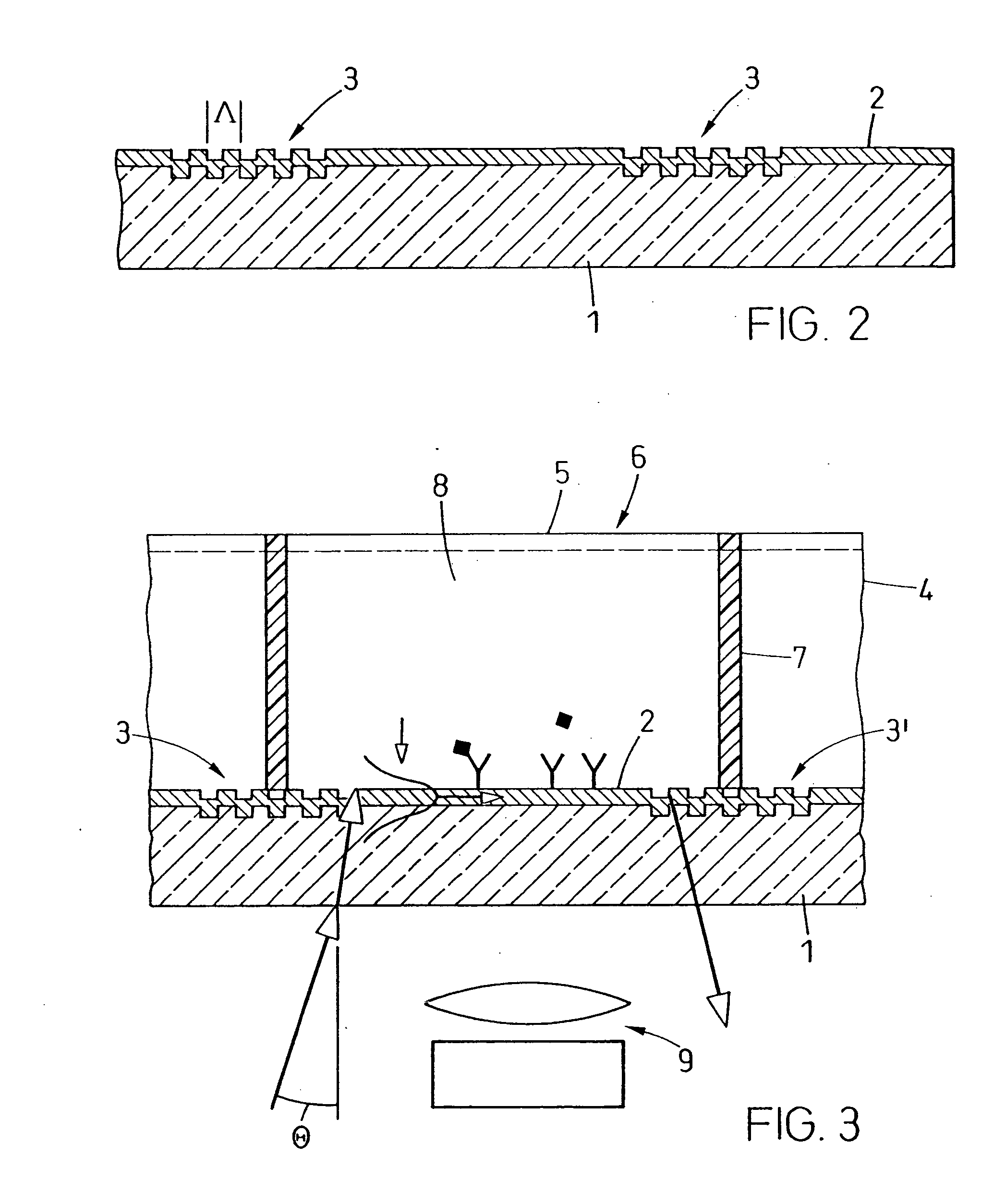
A waveguide plate and a process for making the waveguide plate with a plate-like glass substrate (1), carrying a waveguiding layer (2), with at least one coupling grating on the surface carrying said waveguiding layer (2), which coupling grating is formed as a grating of lines with a period between 150 nm and 1000 nm, the extension of said grating being at least 5 cm with lines parallel to one another, wherein the coupling angle (θ) varies by not more than 0.1° / cm along a line of said grating and wherein the absolute value of the deviation of the coupling angle (θ) on said waveguide plate, from a predefined desired value, does not exceed 0.5°. The deviation from the average value of the coupling angle does not exceed 0.3°, preferably not 0.15° on the whole waveguide plate. The waveguide plate is suitable as part of a sensor platform and of an arrangement of sample compartments for chemo-and bioanalytical investigations in order to produce a coupling grating formed as a line grating with a grating period between 100 nm and 2500 nm.
Owner:OERLIKON TRADING AG TRUEBBACH
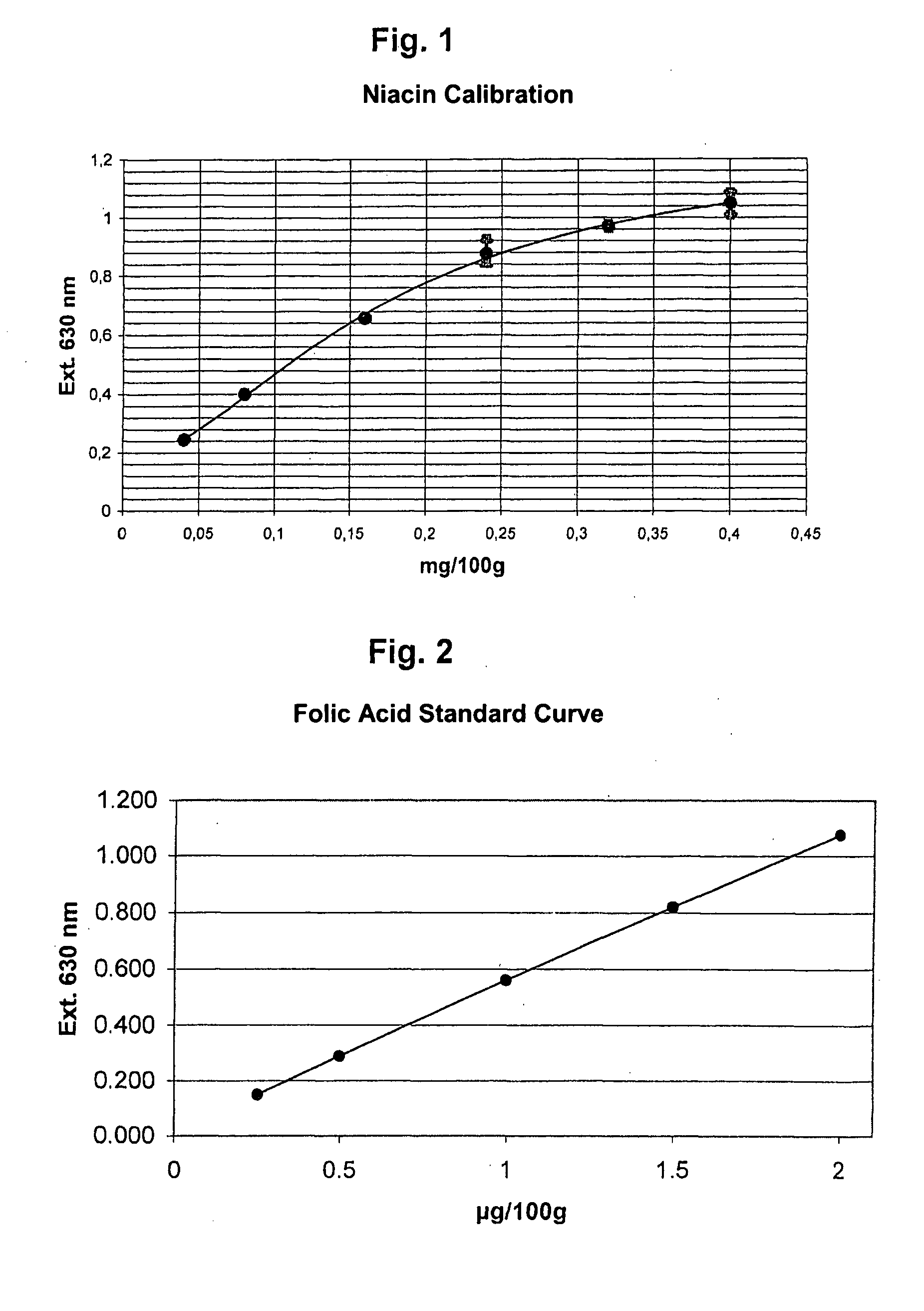
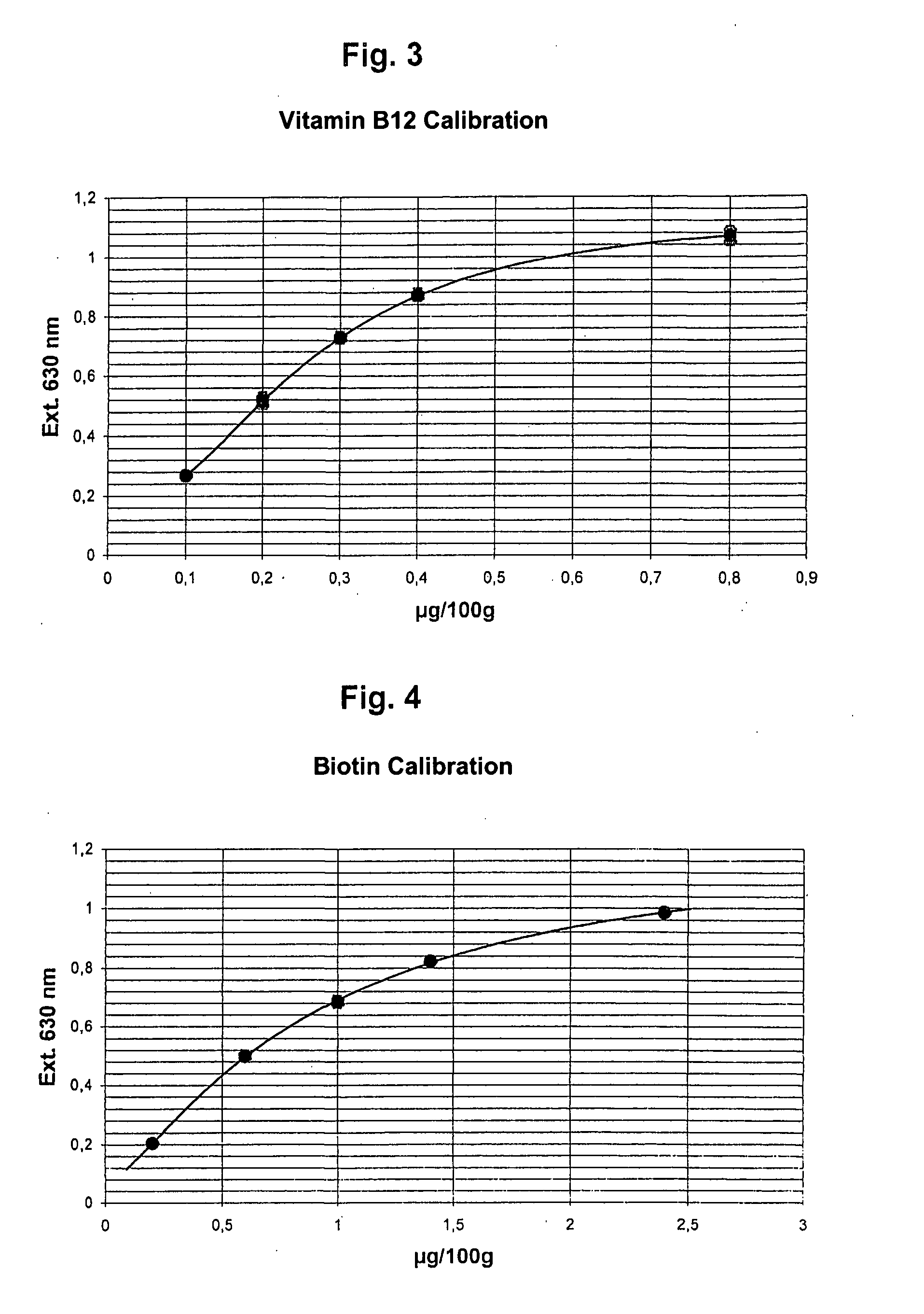
Method and Kit for the Microbiological Determination of Vitamins in Substance Mixtures
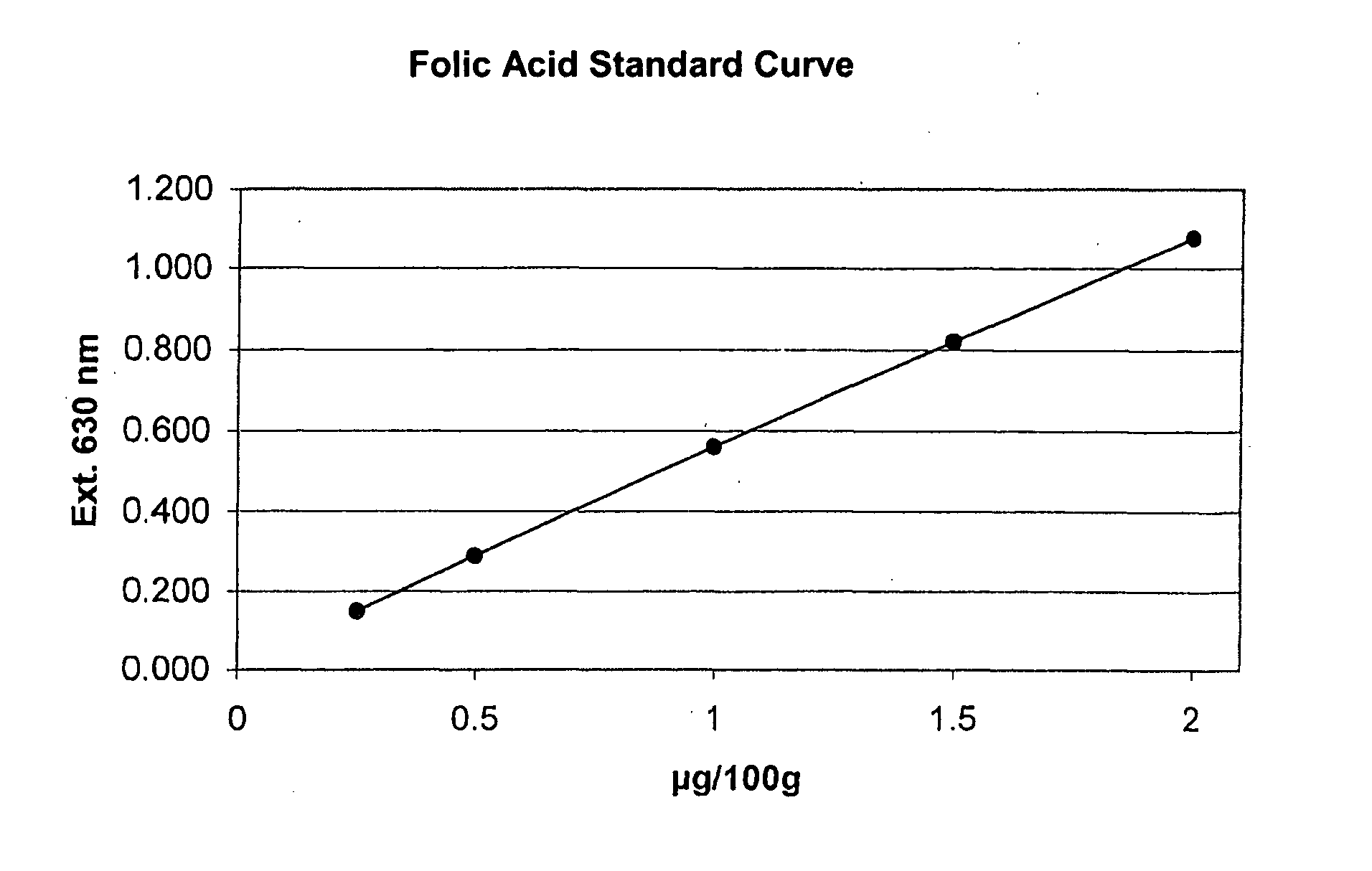
ActiveUS20080044846A1Measurement range is lessReduce riskBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismFreeze-drying
Method for the quantitative determination of vitamins, amino acids, or other substances necessary for life, in a substance mixture, whereby in the culture container, the cavities of a microtitration plate, in each case a predetermined number of vital cells of a suitable microorganism are prepared in a permanent manner. For this purpose, the cells are shock frozen at −80° C. and then freeze dried in a freezing solution containing 200 to 500 mM trehalose / sucrose. The freezing solution is preferably the test medium. The culture containers are preferably the wells of a microtitration plate.
Owner:IFP PRIVATES INSTITUT FUR PRODQUALITAT
Method and apparatus for shuttling microtitre plates
A shuttle apparatus for transferring sample carriers comprising a shuttle table having a mating section, the mating section allowing a sample carrier to be transferred between the shuttle table and a mating support structure. The shuttle table can optionally further comprise a mating section having a void section.
Owner:INCYTE PHARMA INC
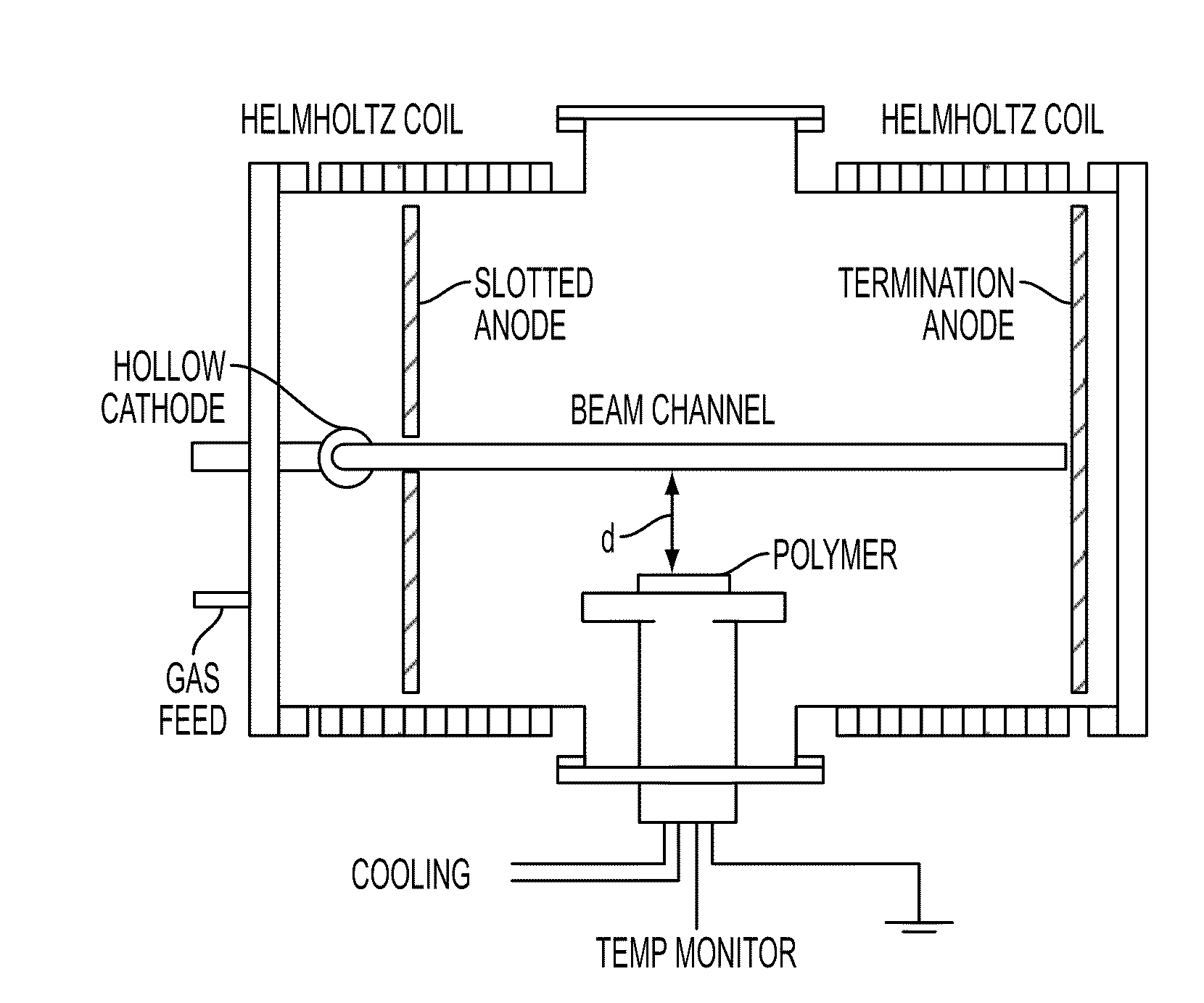
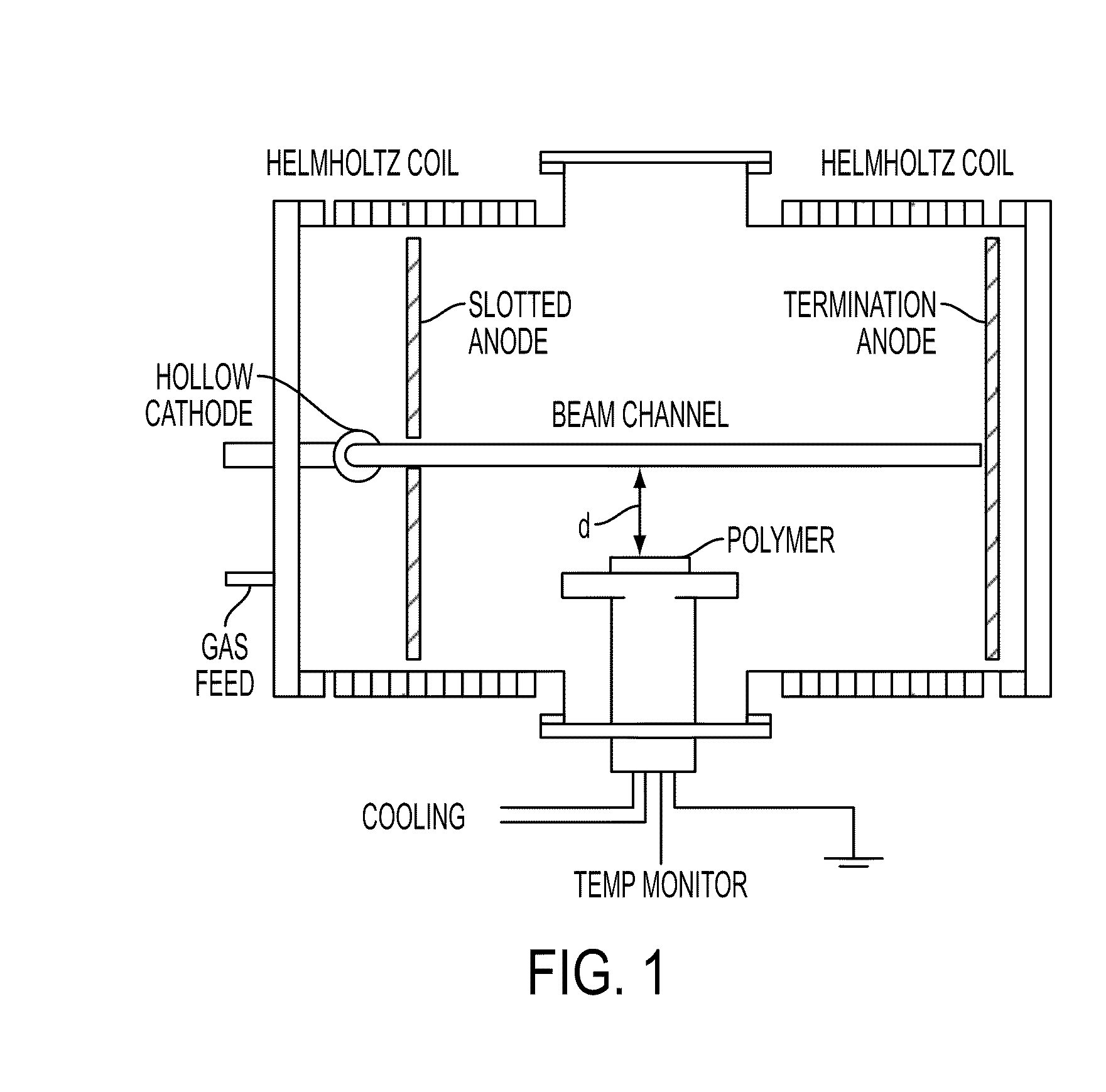
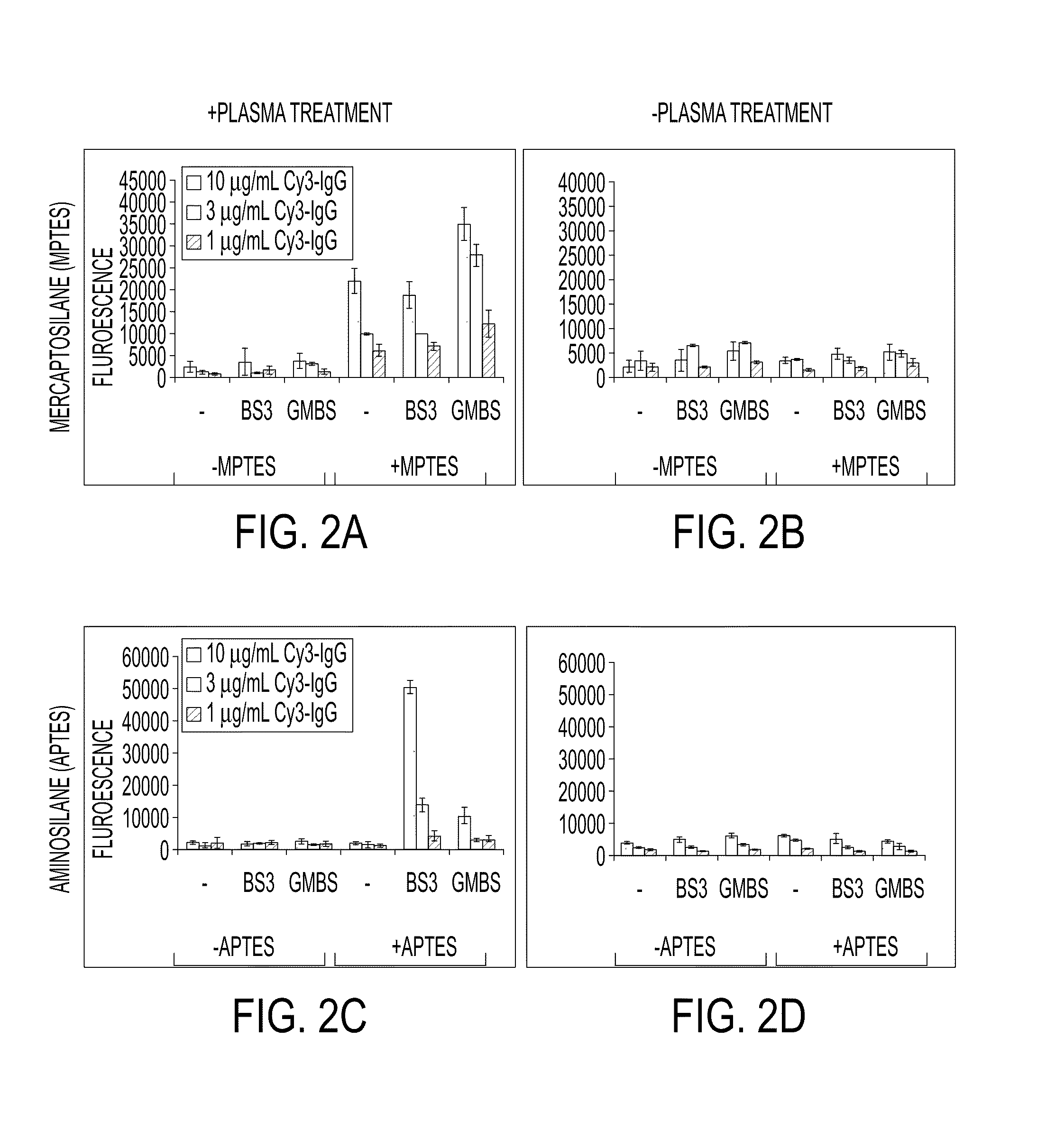
Processing microtitre plates for covalent immobilization chemistries
ActiveUS20110116992A1Sequential/parallel process reactionsPharmaceutical containersPolymeric surfaceOxygen
Disclosed herein is a method of: treating an organic polymer with an electron beam-generated plasma; exposing the treated polymer to air or an oxygen- and hydrogen-containing gas, generating hydroxyl groups on the surface of the polymer; reacting the surface with an organosilane compound having a chloro, fluoro, or alkoxy group and a functional or reactive group that is less reactive with the surface than the chloro, fluoro, or alkoxy group; and covalently immobilizing a biomolecule to the functional or reactive group or a reaction product thereof.
Owner:THE UNITED STATES OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SECRETARY OF THE NAVY
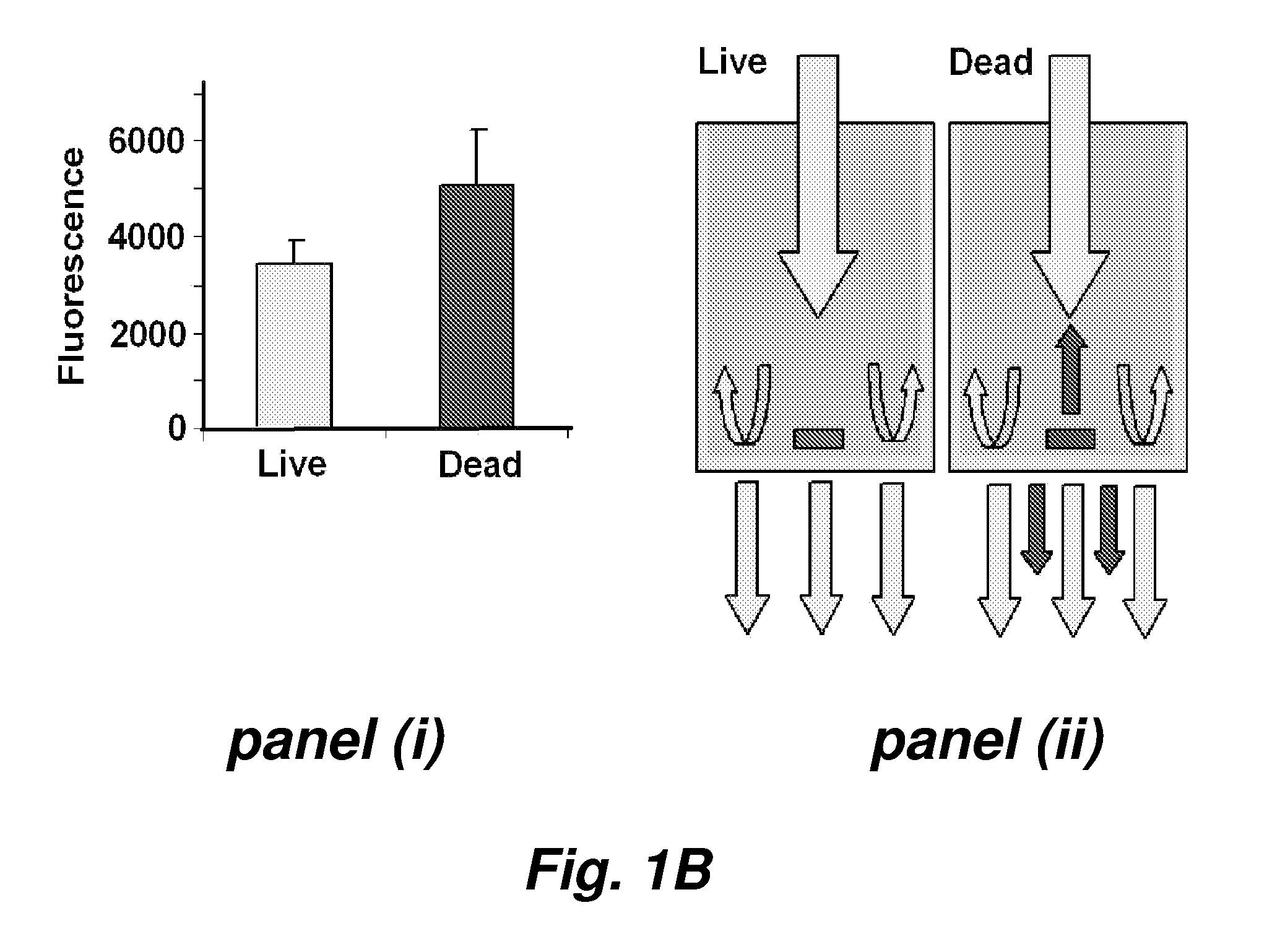
Automated method for high throughput screening of nematodes
InactiveUS20060191023A1Improve permeabilitySimple and quantitative single-step indicatorBiological testingAnimal husbandryHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAssay
This invention provides a high throughput survival assay, using uptake of a marker dye (e.g. a fluorescent dye) as a marker of death of a nematode. The assay permits high throughput screening of thousands of compounds possible. By the application of automated worm handling technology we are able to accurately dispense nematodes into 384 well microtitre plates, at rates many thousand of Limes faster than previously possible. In addition, we have automated the analysis of survival by the use of a fluorometric plate reader that quantitates the degree of fluorescence within each well.
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
Excitation and imaging optics for fluorescence detection
The invention concerns an optical instrument for imaging fluorescence signals from an arrangement of a plurality of individual detection sites, for example the wells of a microtitre plate. In order to improve the light yield of the fluorescence excitation with excitation light as well as the light yield of the detection of the fluorescence signals, an objective array is provided which is arranged in the beam path between the field lens and the detection sites and comprises a field lens array with field lens array elements and a pupil lens array with pupil lens array elements. In order to improve the channel separation and suppress interfering light the objective array can comprise a diaphragm array with in each case two diaphragm openings per detection site.
Owner:ROCHE MOLECULAR SYST INC
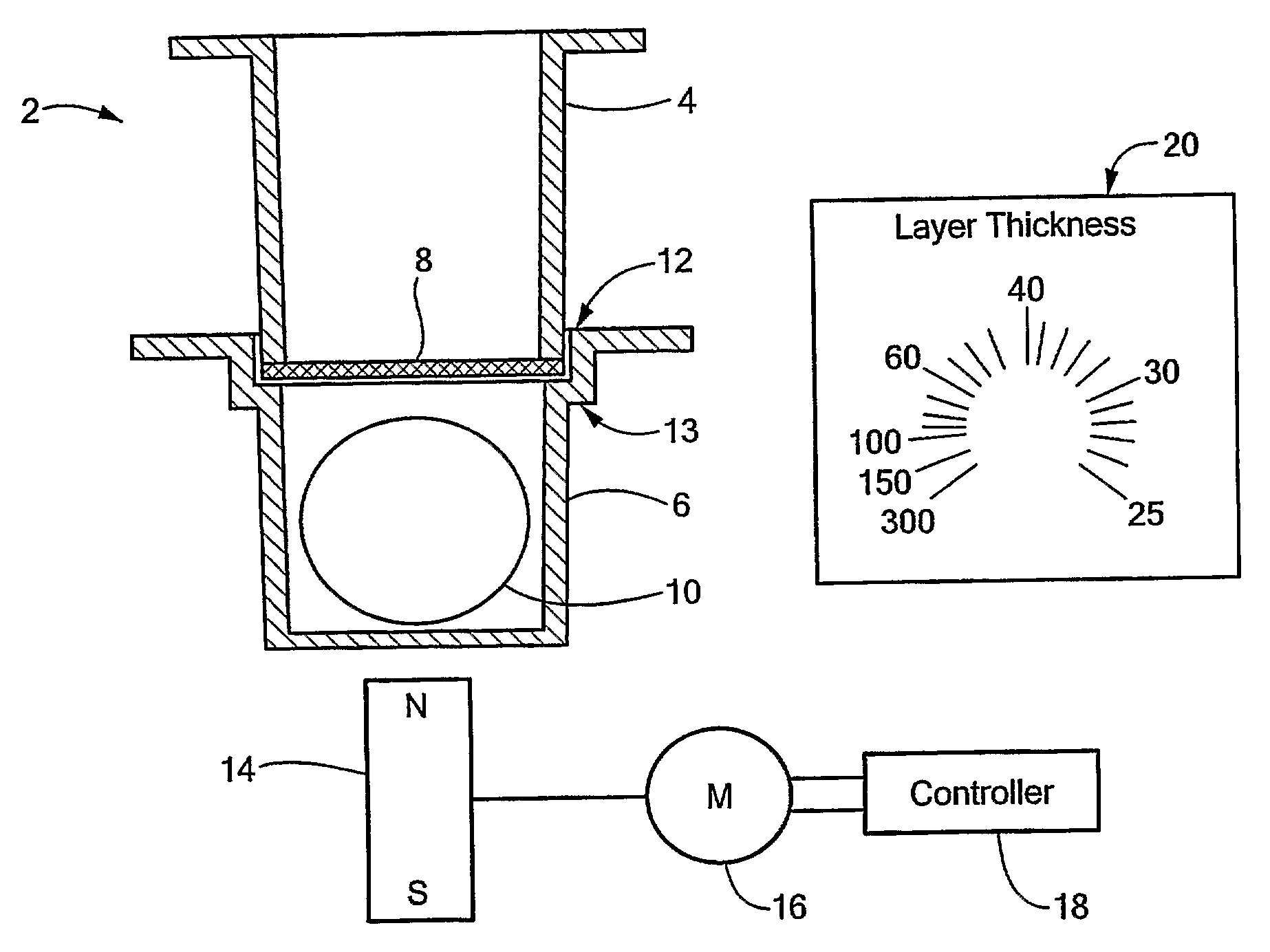
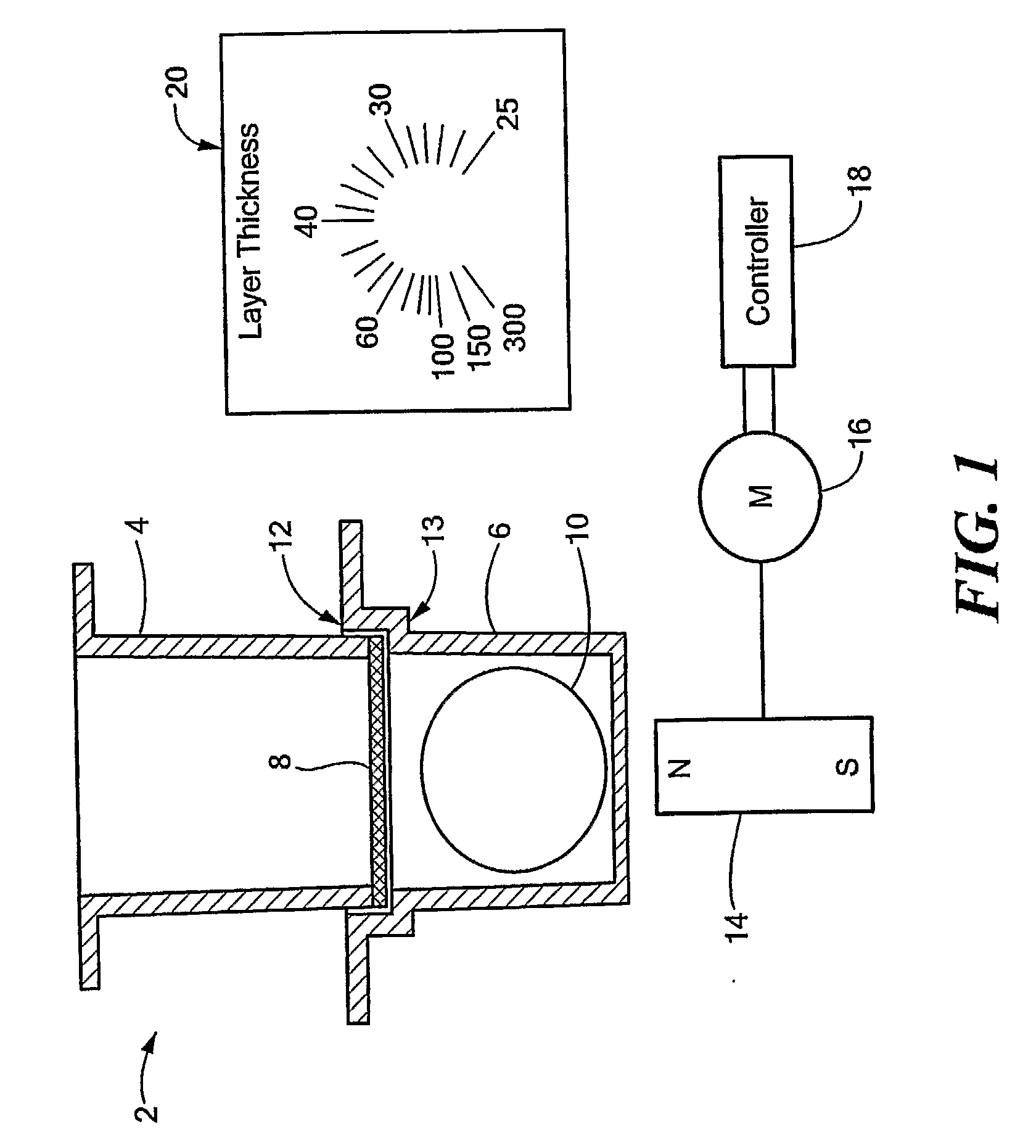
Permeation Device and Method for Reducing Aqueous Boundary Layer Thicknesses
ActiveUS20070251336A1Reduce thicknessReduced boundary layer thicknessSemi-permeable membranesWeather/light/corrosion resistanceRate limitingIntestinal structure
In many miniaturized high-throughput assays, effective stirring is difficult to achieve, and its consequences difficult to predict. Most microtitre plate-based in vitro assays of membrane permeability, such as Caco-2 and PAMPA, of sparingly soluble lipophilic test compounds in pharmaceutical research and development report permeability of water, and not of the intended membrane barrier. This is so because the aqueous boundary layer on both sides of the membrane barrier is rate limiting for these highly permeable molecules. The thickness of this water layer can be 1500-4000 μm in unstirred assays. Under in vivo conditions, however, the aqueous boundary layer is believed to be 30-100 μm thick in the intestine, and <1 μm at the blood-brain barrier. Using plate shakers to stir microtitre plates cannot lower the thickness of the water layer to match that found in vivo. We have discovered a high-throughput method and a simple, “robotics-friendly” device where individual-well stirring at speeds of about 600 rpm can lower the aqueous boundary layer thickness to <15 μm, which had not been previously achieved for plate-based permeability assays.
Owner:PION
Microtitration plate
InactiveUS20120129250A1Dimensionally stableIncrease injection pressureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:EPPENDORF SE
Synergistic composition useful as microbiological growth medium for rapid screening of phosphate accumulating microorganisms
InactiveUS20120028295A1Quick filterInvestment exemptionMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismAssay
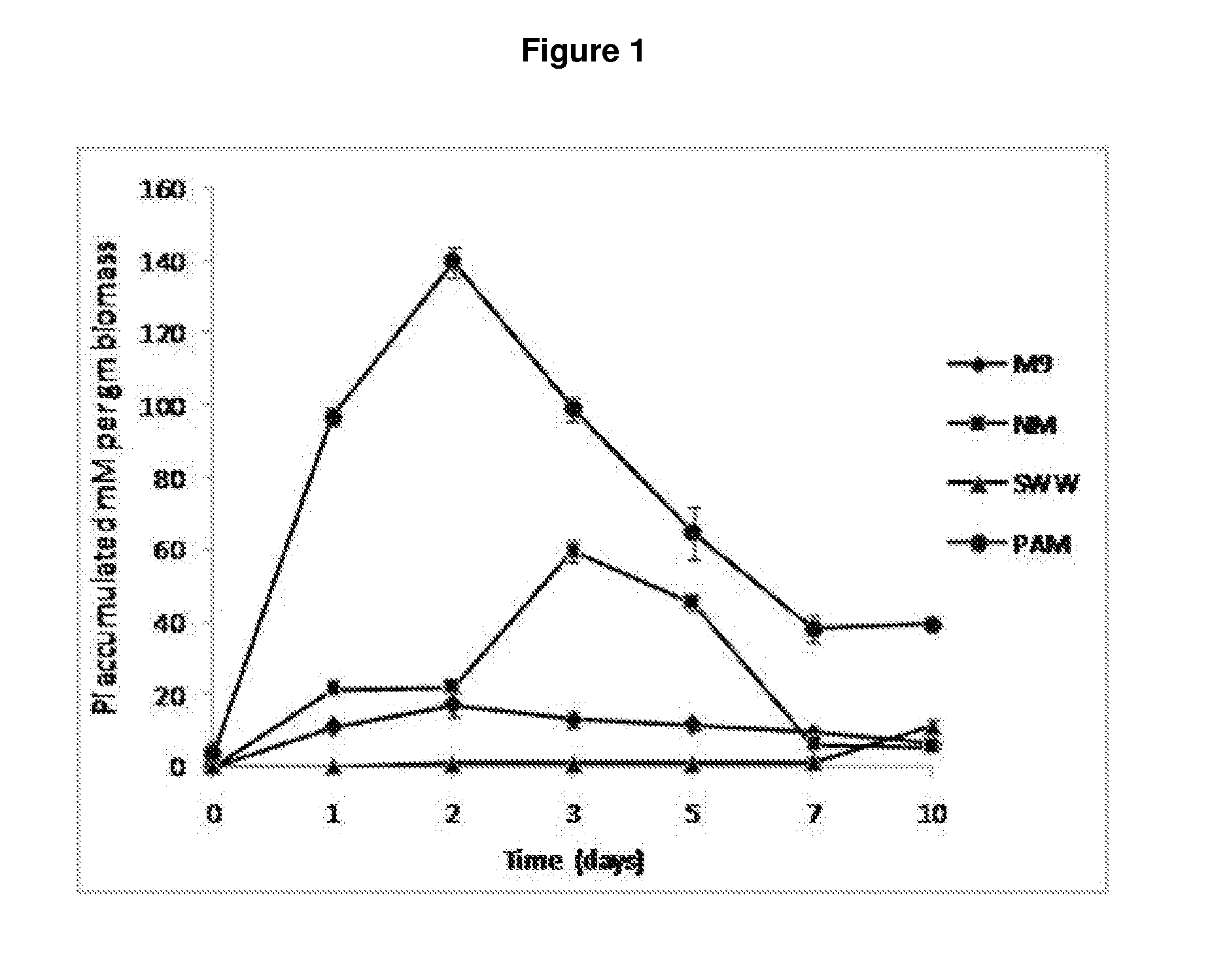
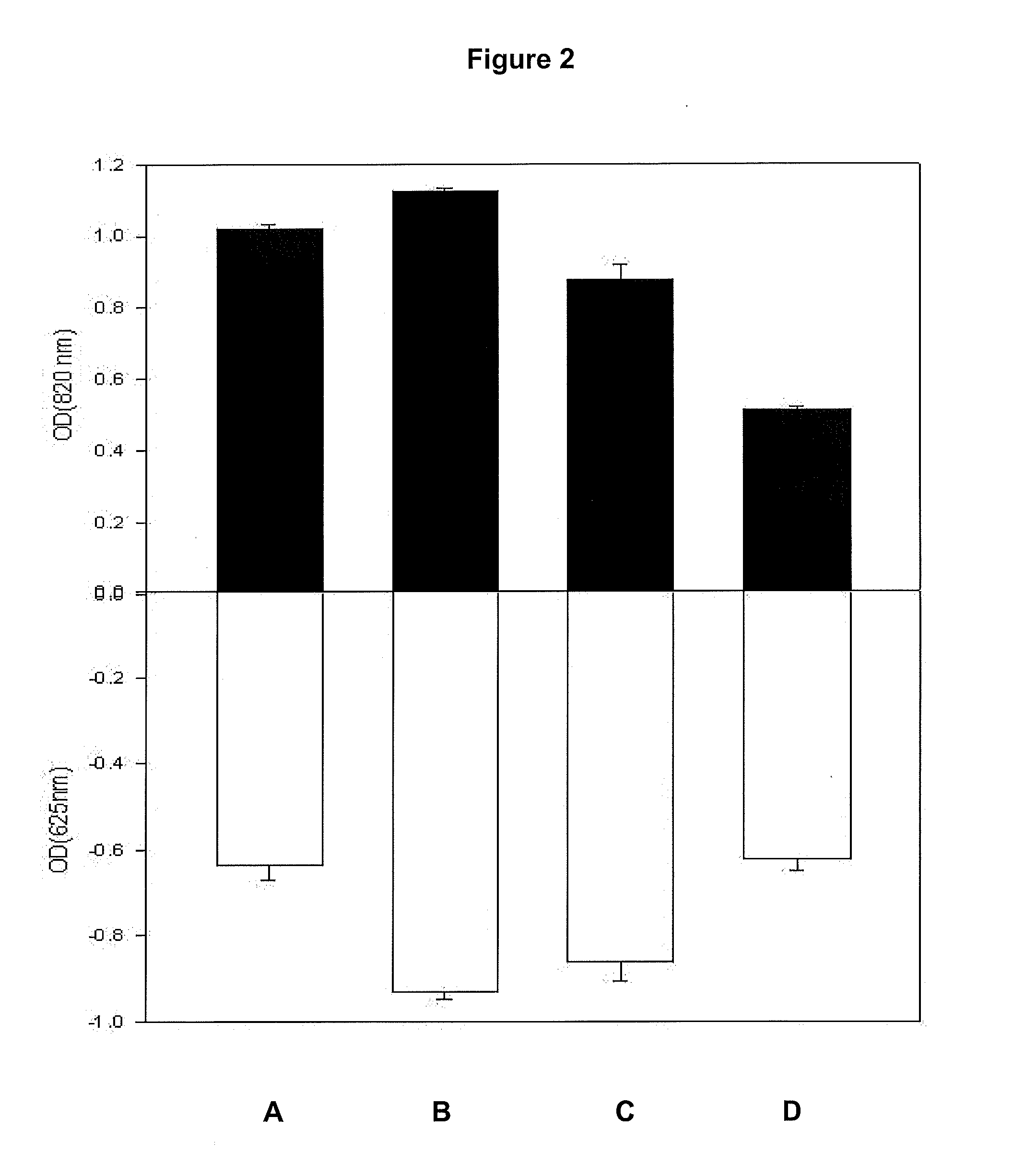
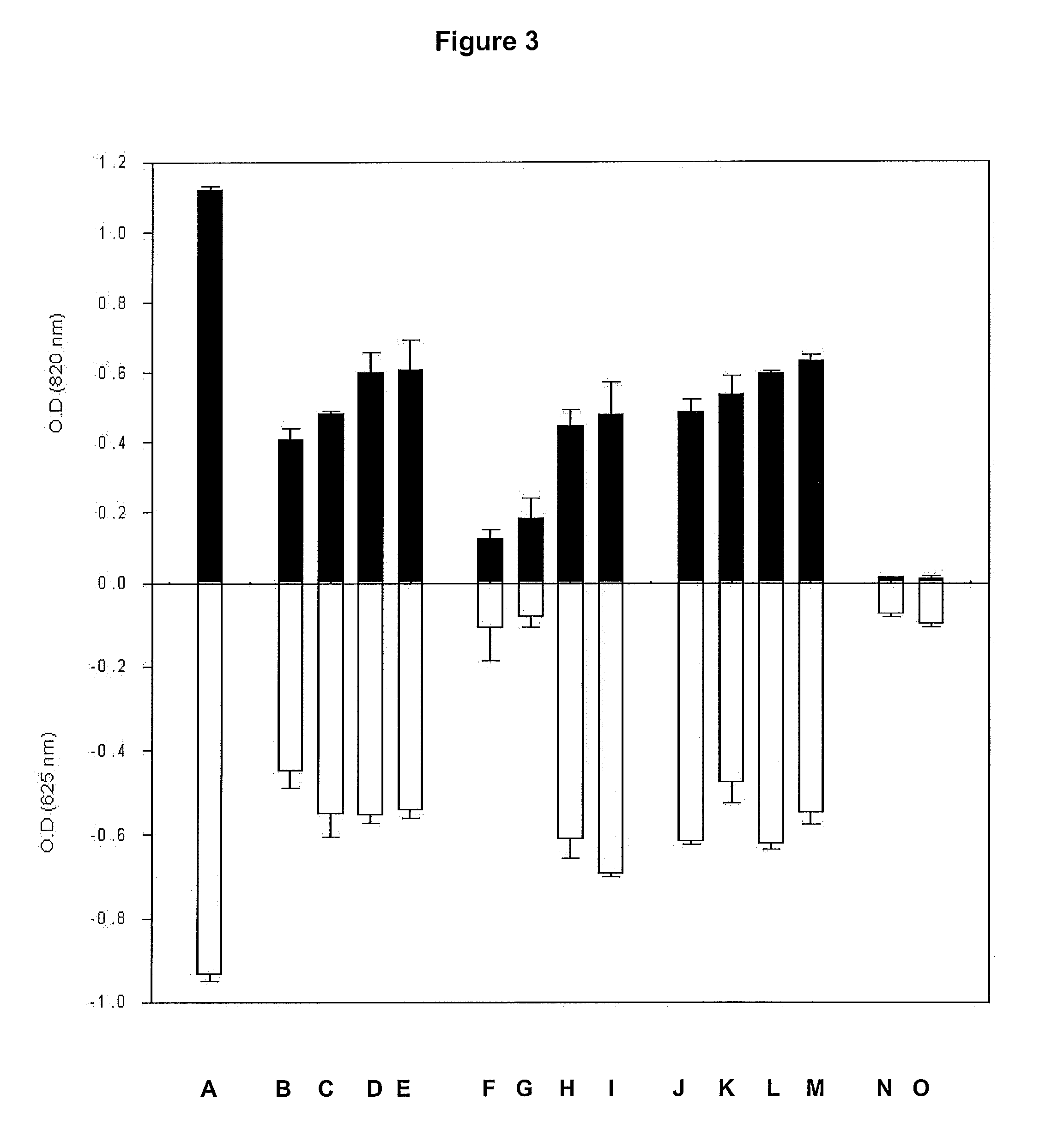
Screening isolates for phosphate accumulation by quantitative methods requires investment of time, labour and chemicals. There has been paucity of a medium and method for screening phosphate-accumulating microorganisms (PAOs) from the environment. Therefore, a new screening strategy is needed towards isolating effective PAOs in environments with diverse microbial populations and limited organic resources, where it is possible that PAOs are often out-competed by organisms capable of utilising available nutrients more rapidly. In view of these problems, a medium optimal for an efficient screening of P-accumulating microorganisms was developed, which is rapid and allows many PAOs to be screened. Thus, the present invention utilizes Toluidine Blue-O (TBO) a blue coloured dye, which decolorizes due drop in the concentration of phosphate in the medium, as an indicator to quickly evaluate the P-accumulating microorganisms based upon visual observations. Fast decolorization of the dye is an indicator of a superior phosphate accumulating microbe. Therefore, colorimetric reaction using PAM-TBO of the present work was further applied in a novel, extremely high-throughput manner to detect individual microbial isolates, growing on a PAM Petri plate. Adaptation of PAM-TBO assay in screening PAOs in environmental samples for microtitre plate assay enhanced the effectiveness of the assay system efficiently and effectively.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Droplet detection system
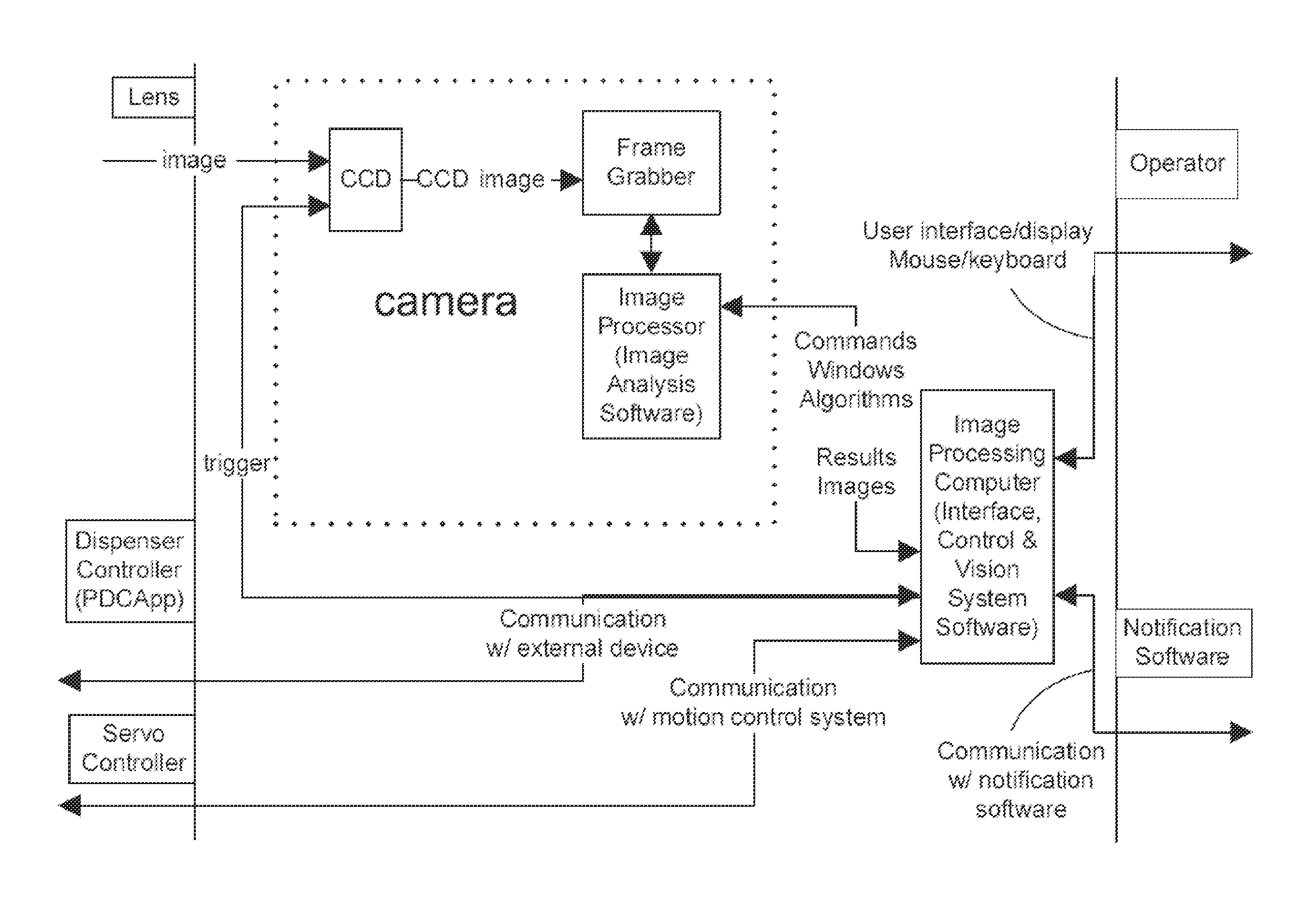
InactiveUS20080240542A1High of malfunctionHigh of materialCharacter and pattern recognitionTesting/calibration for volume meteringEngineeringImaging Feature
A system for a droplet detection device to monitor the dispensing operation in an ultra high throughput (uHTS) system. The system includes a microtitre plate with a defined number of wells and well walls, a dispenser for dispensing fluids into the wells, an illuminating sensor to extract image features from the wells and well walls, and a controller for analyzing the extracted image features to determine the presence or absence of the dispensing fluid on the wells and well walls.
Owner:KALYPSYS INC +1
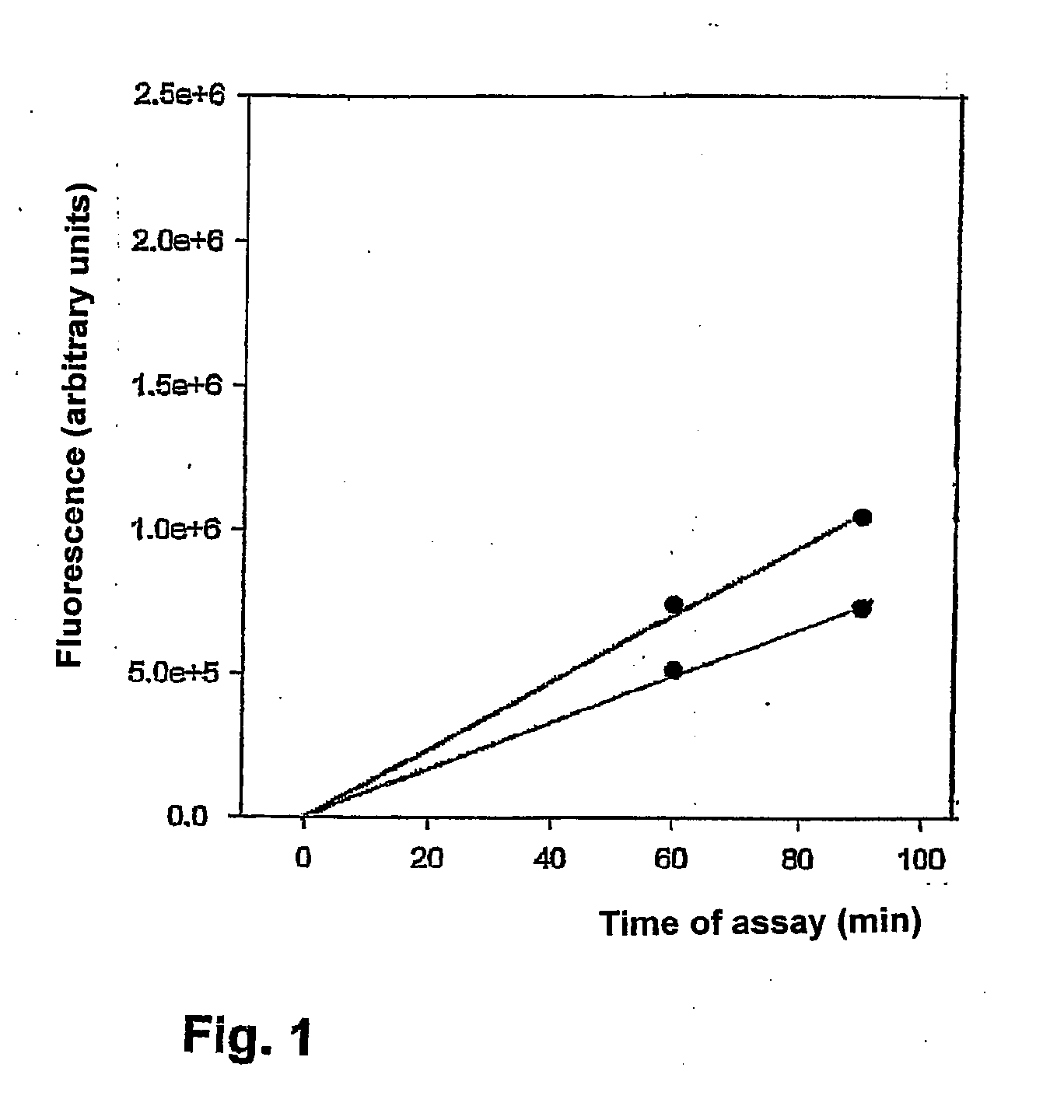
Measuring The Activity Of Proteases
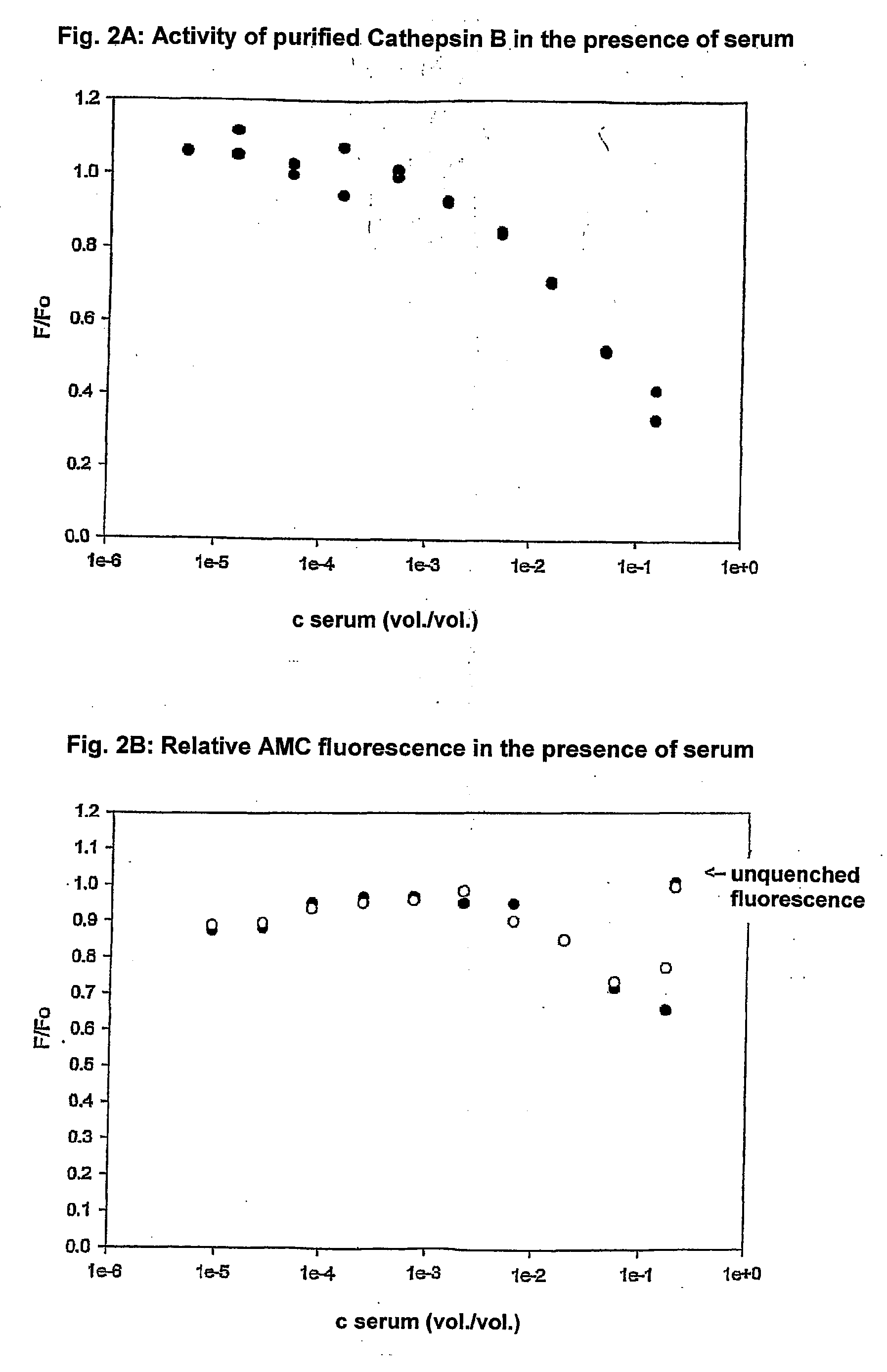
InactiveUS20100267054A1Sensitive measurementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsActivity measurementFluorogenic Substrate
A method and apparatuses for determining the total content of proteases by means of measuring their enzyme activity after previous deinhibition is disclosed. In biological samples, lysosomal proteases are completely (e.g. in blood serum) or partly (e.g. in tissue homogenates) inhibited. A method proposed for the deinhibition entails immersing a solid support material (e.g. nylon or nitrocellulose) as plastic strip to which is linked, covalently or by adsorption, an inhibitor-binding substance which binds the inhibitor corresponding to the protease more strongly than the protease in the sample for measurement. After the deinhibition has taken place, the plastic strip is removed from the liquid sample for measurement, and the sample for measurement is passed on for measurement of the enzyme activity. Fluorogenic substrates from which the fluorogen 7-amino-4-trifluoromethylcoumarin is eliminated proved to be particularly advantageous for the activity measurement. These substrates make it possible for the sensitivity on measurement in microtitre plates with a fluorescence reader to be at least 10 times higher compared with conventional AMC substrates in blood serum, and thus for the fluorimetric determination of such enzyme activities in blood serum to be efficient with this measuring arrangement which is widely used in clinical laboratories.
Owner:PAPST MOTOREN GMBH & CO KG
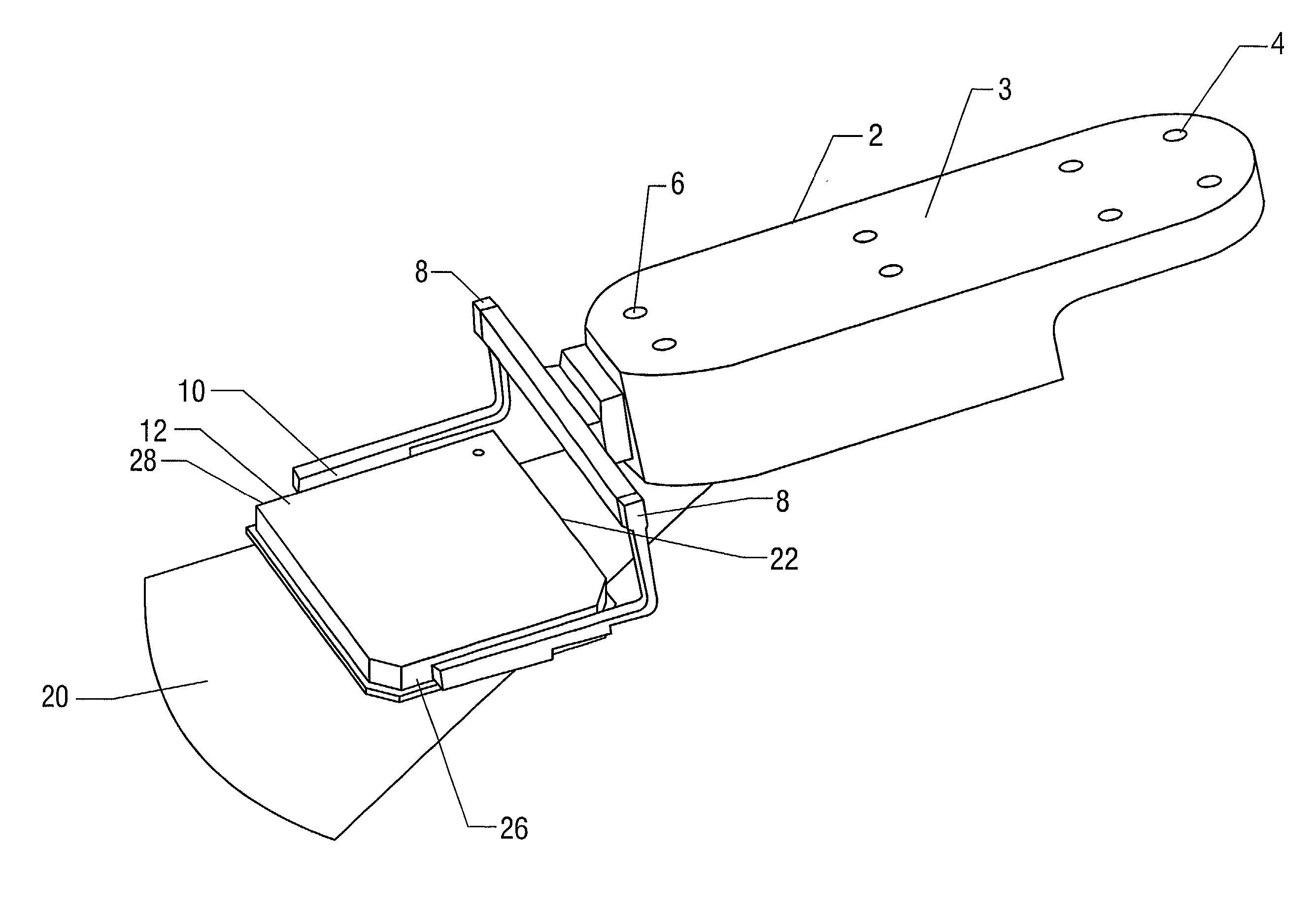
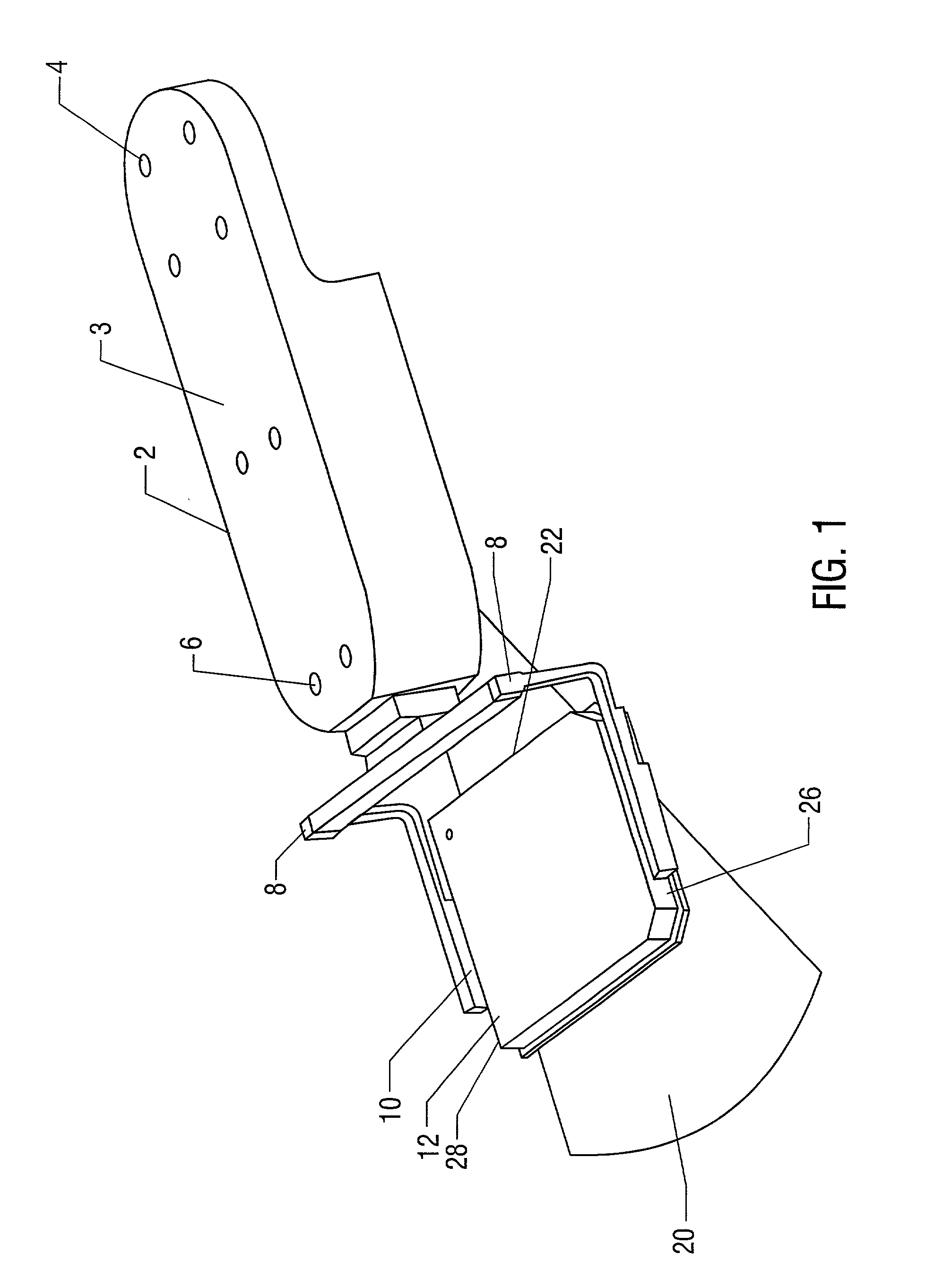
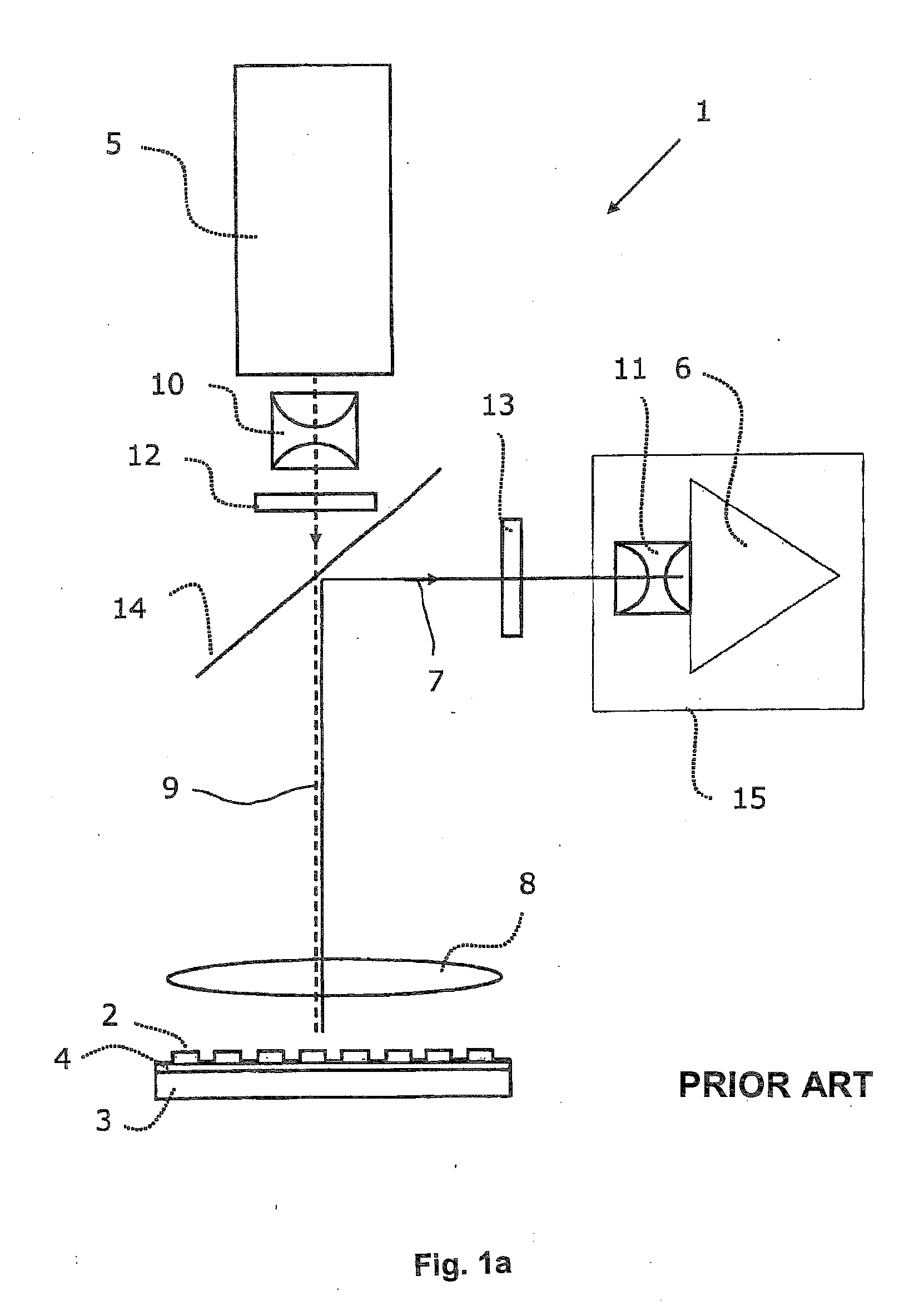
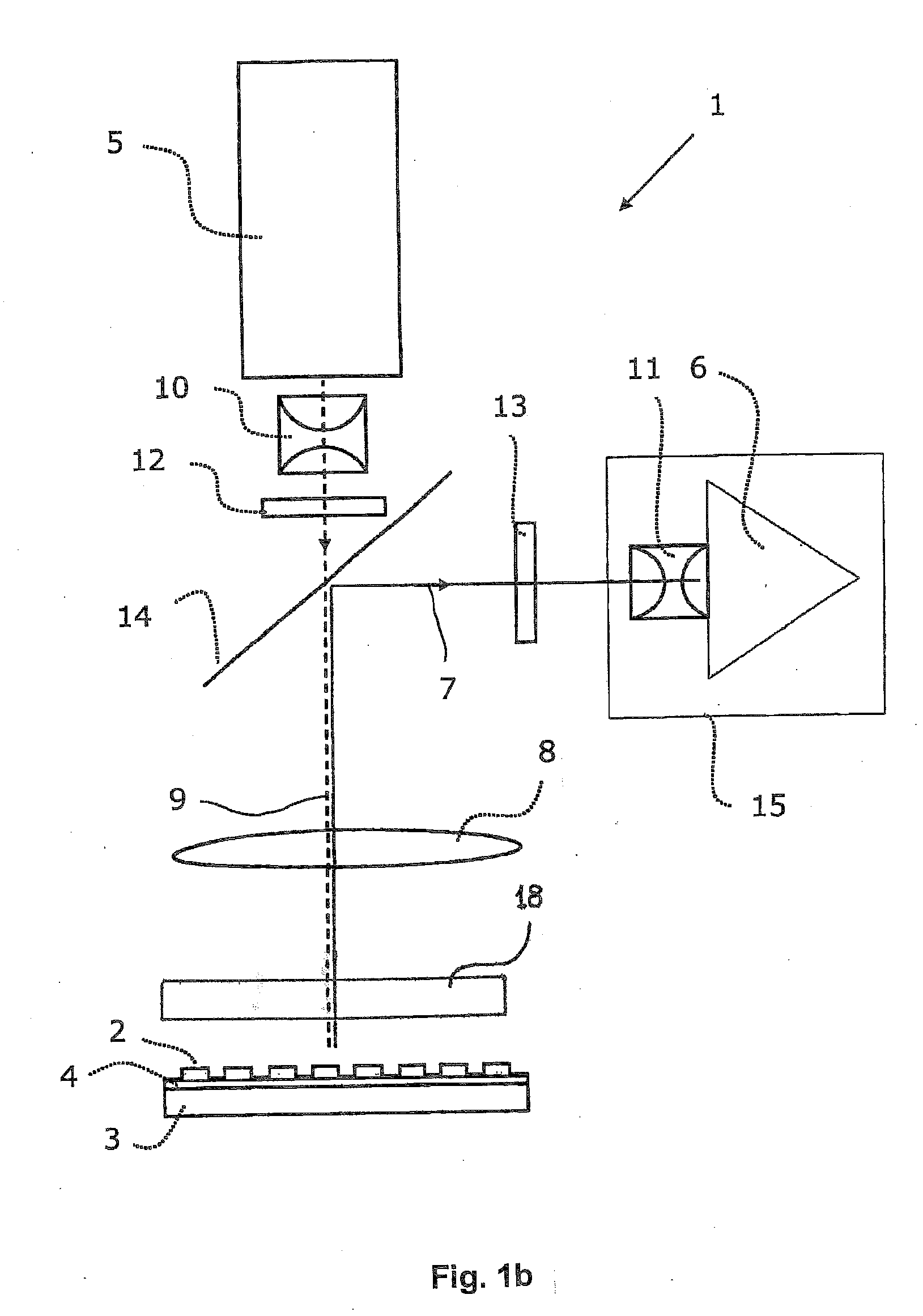
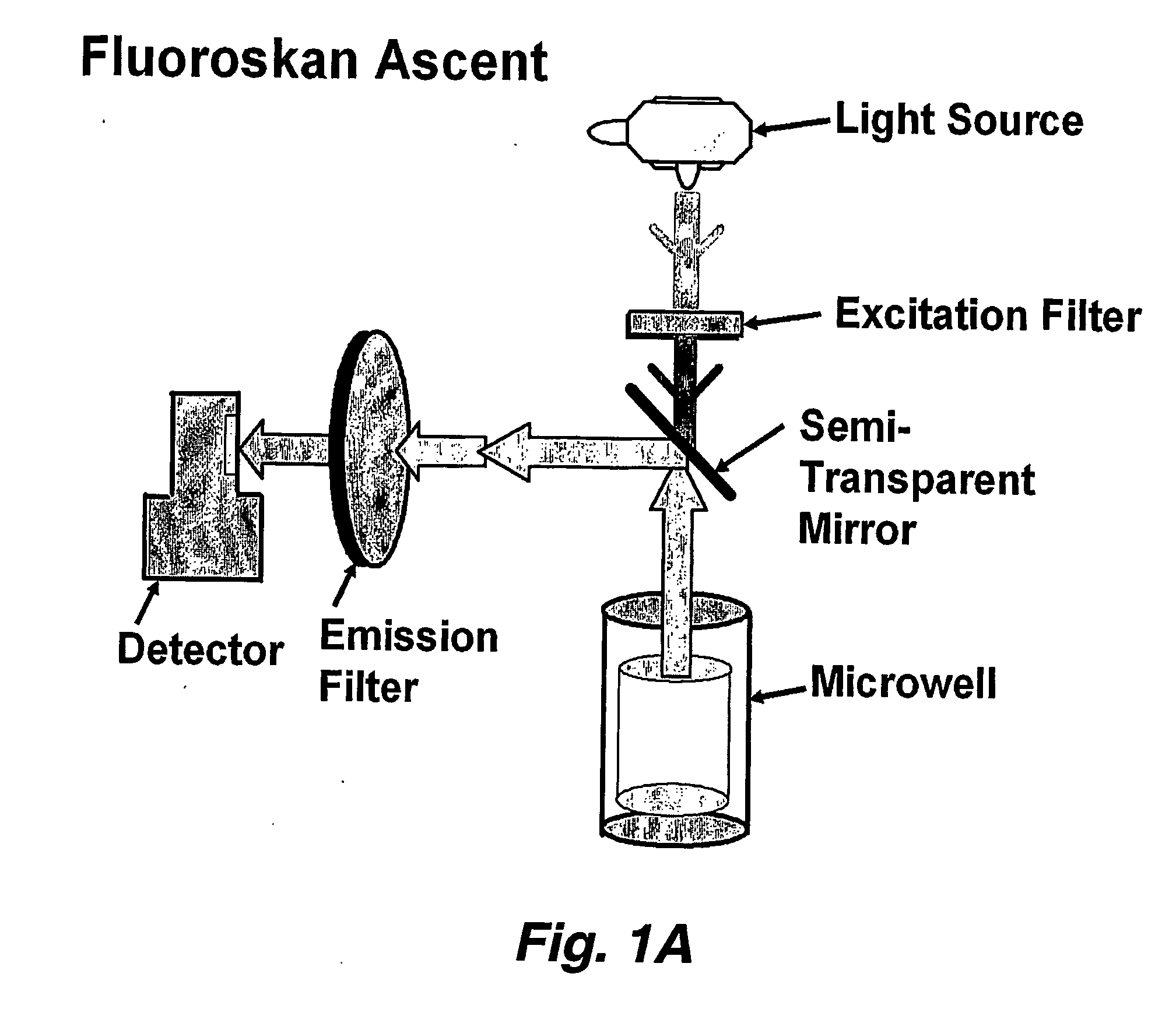
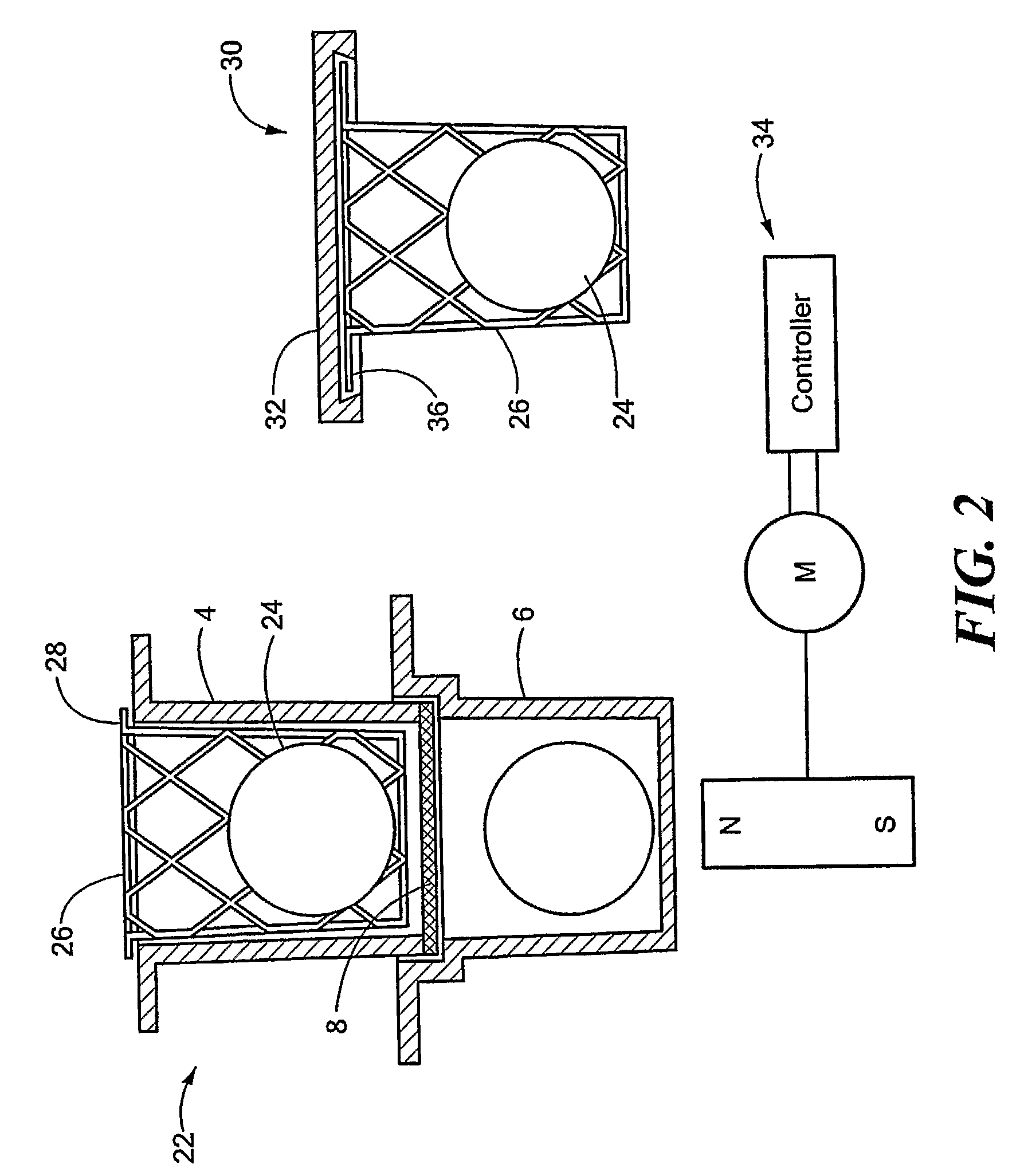
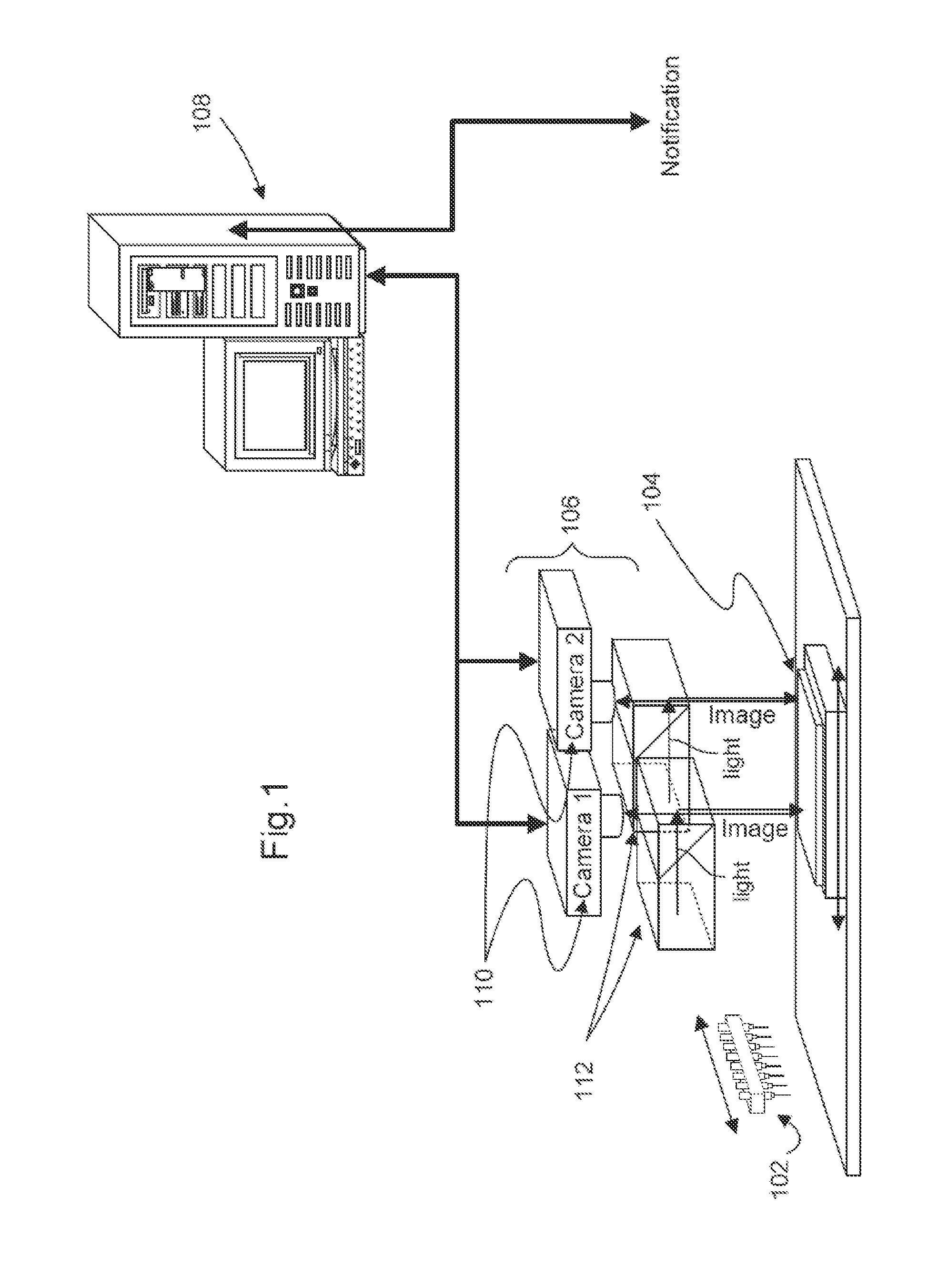
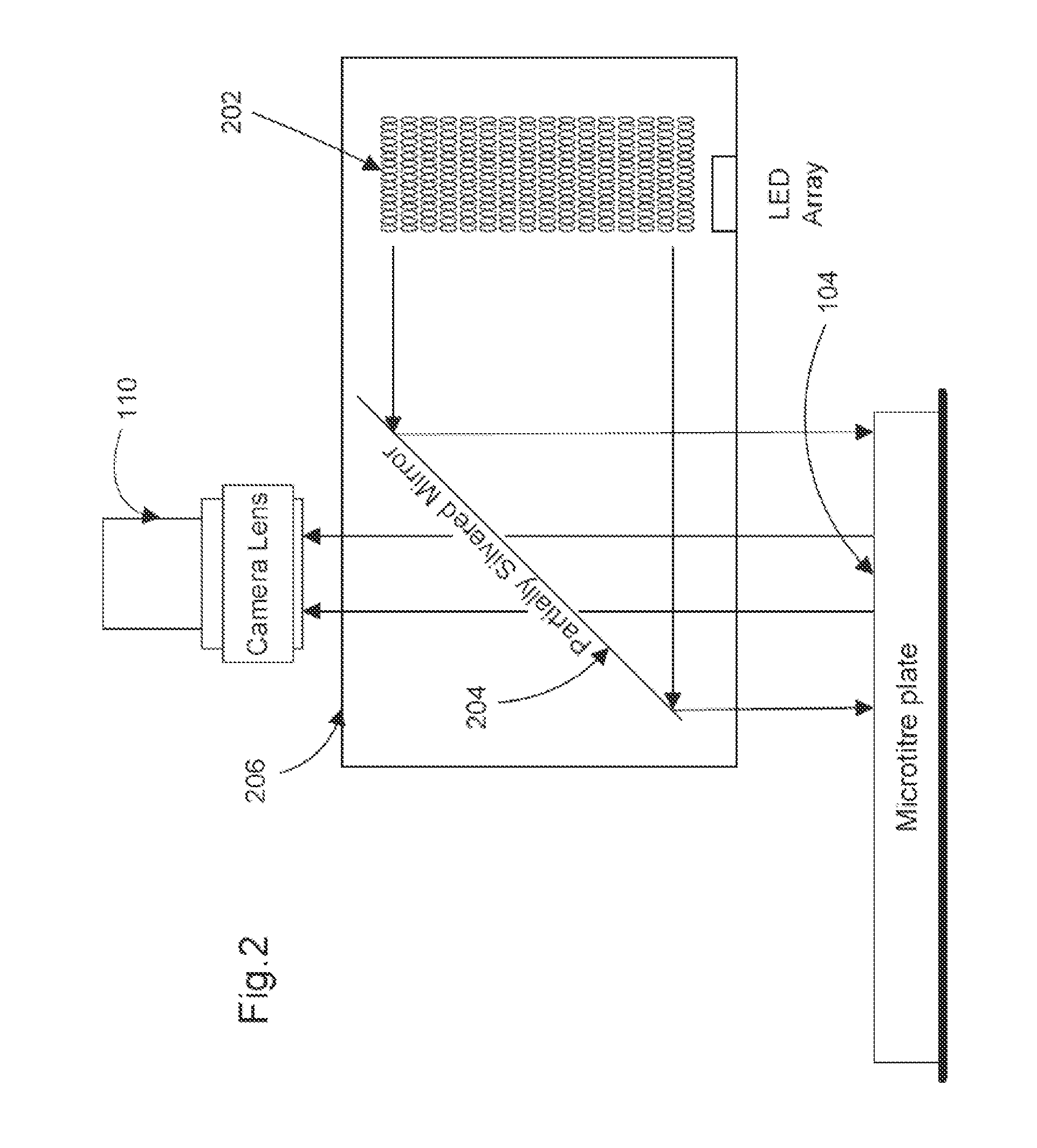
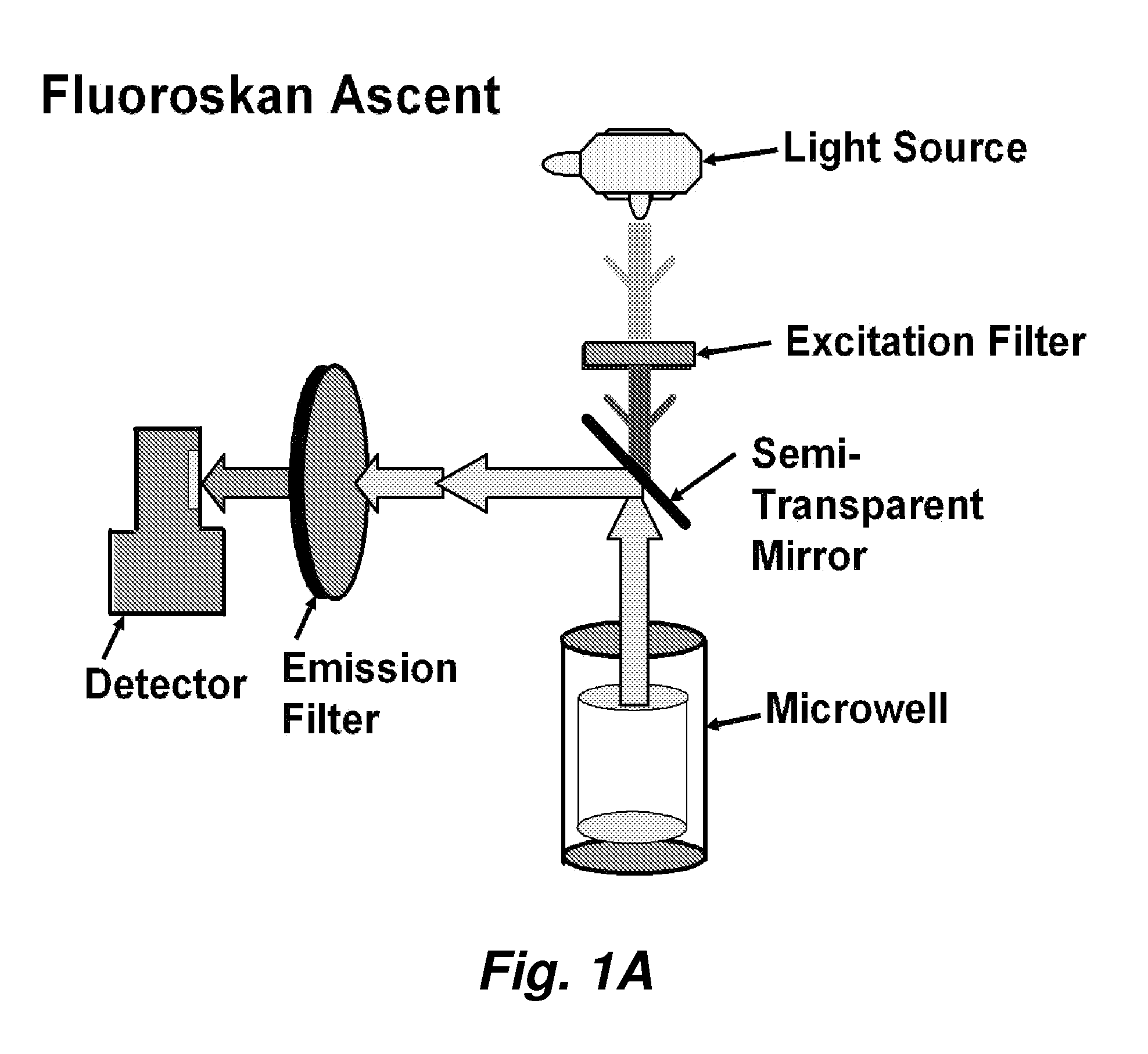
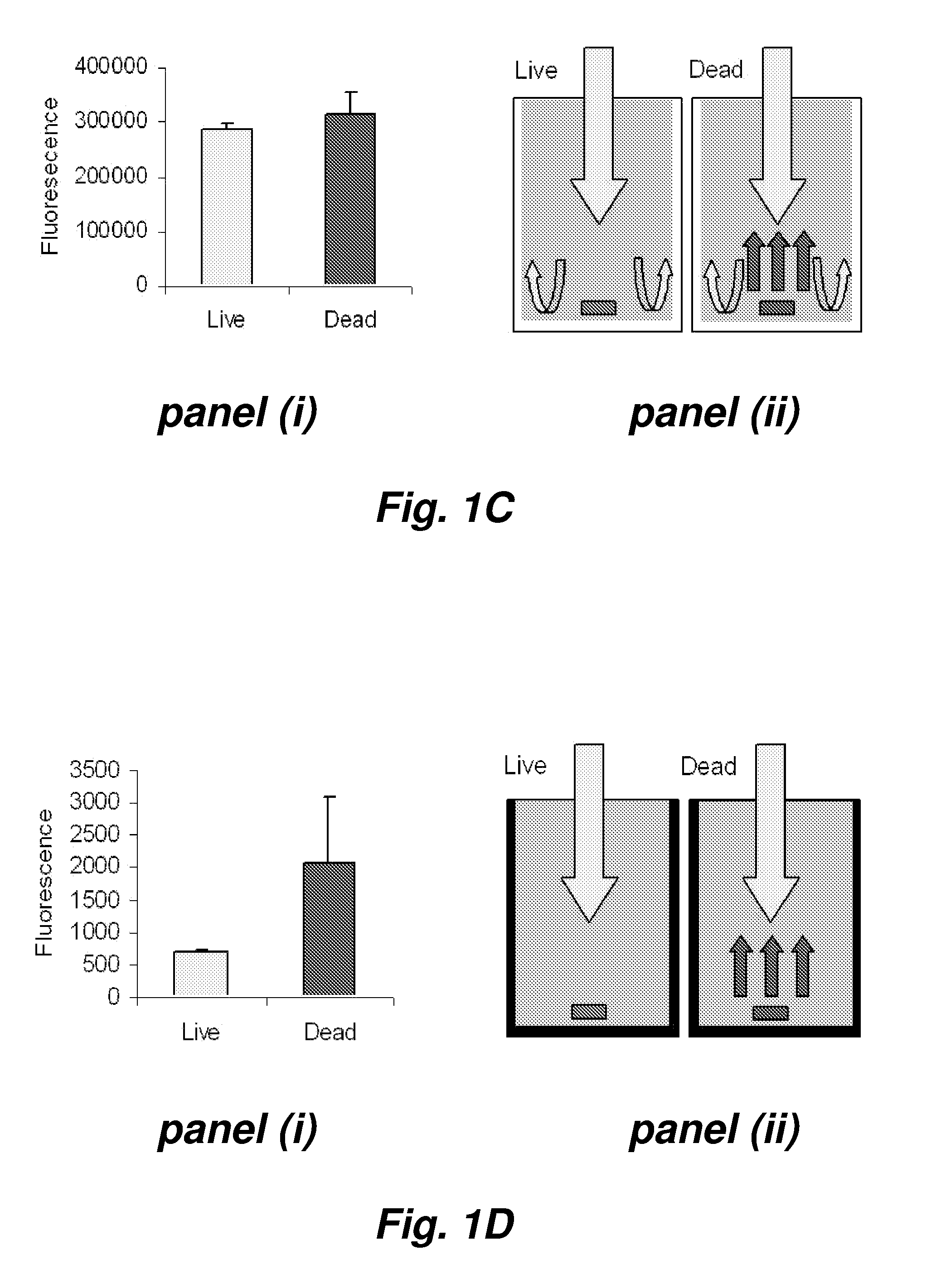
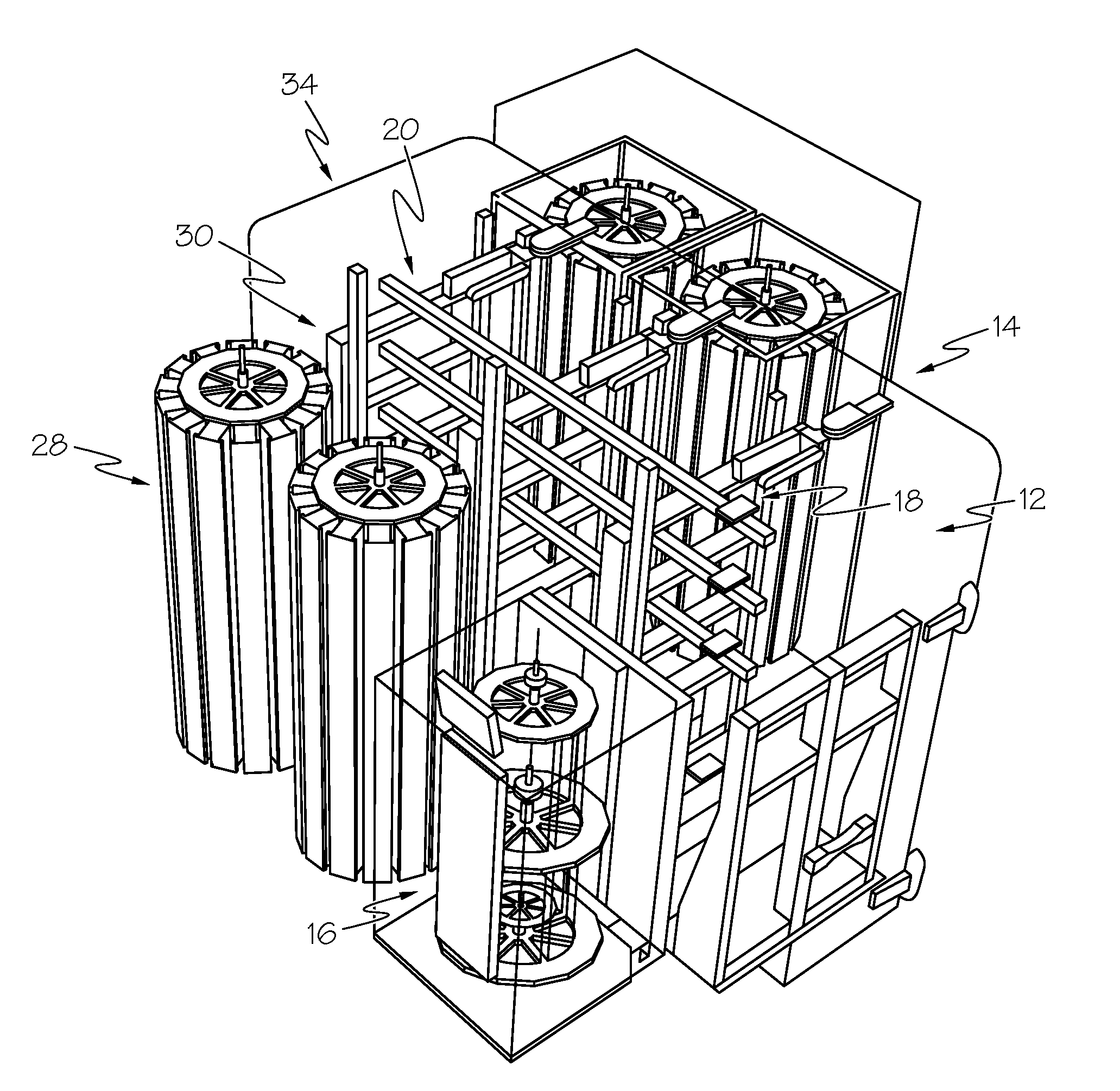
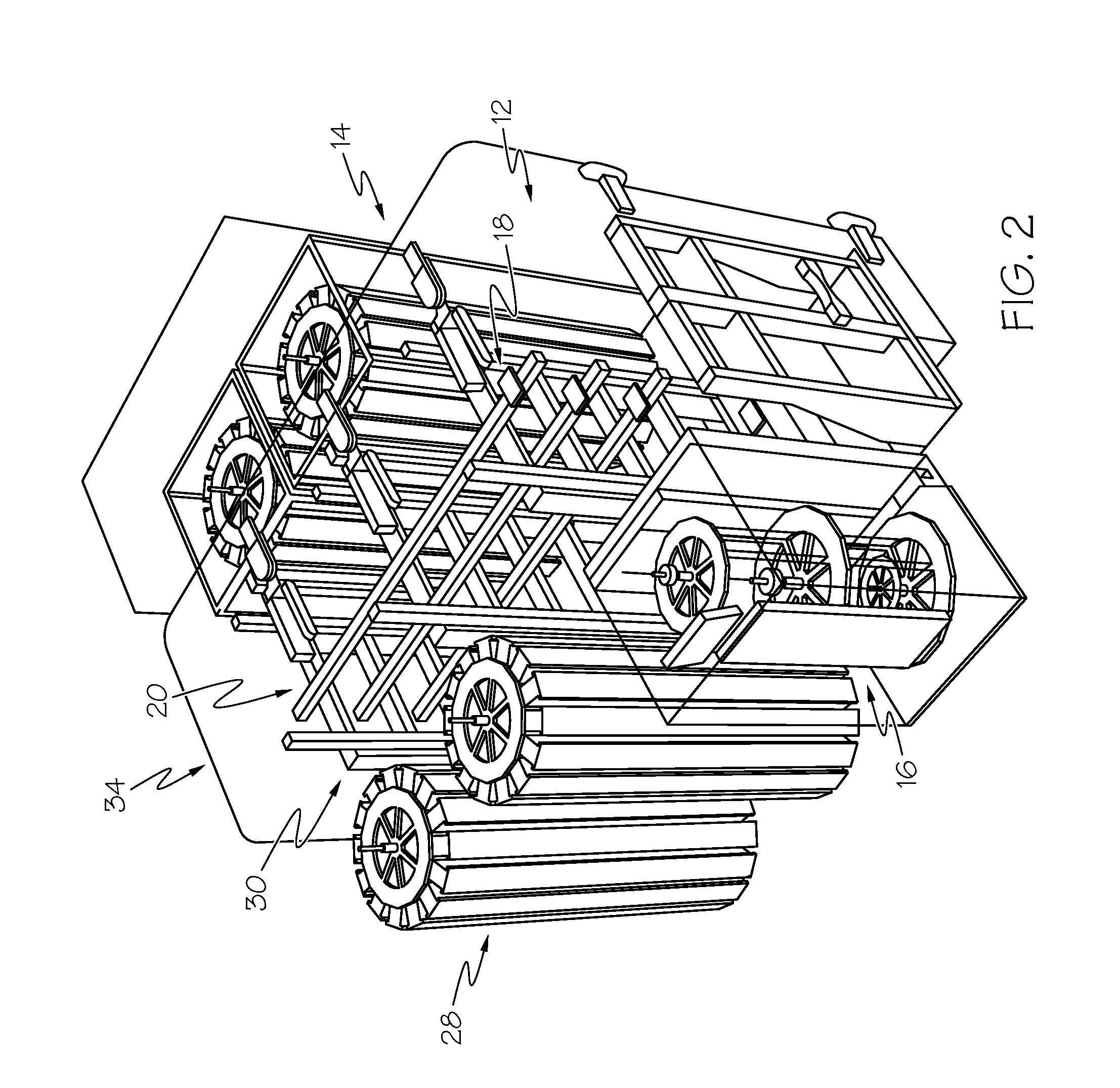
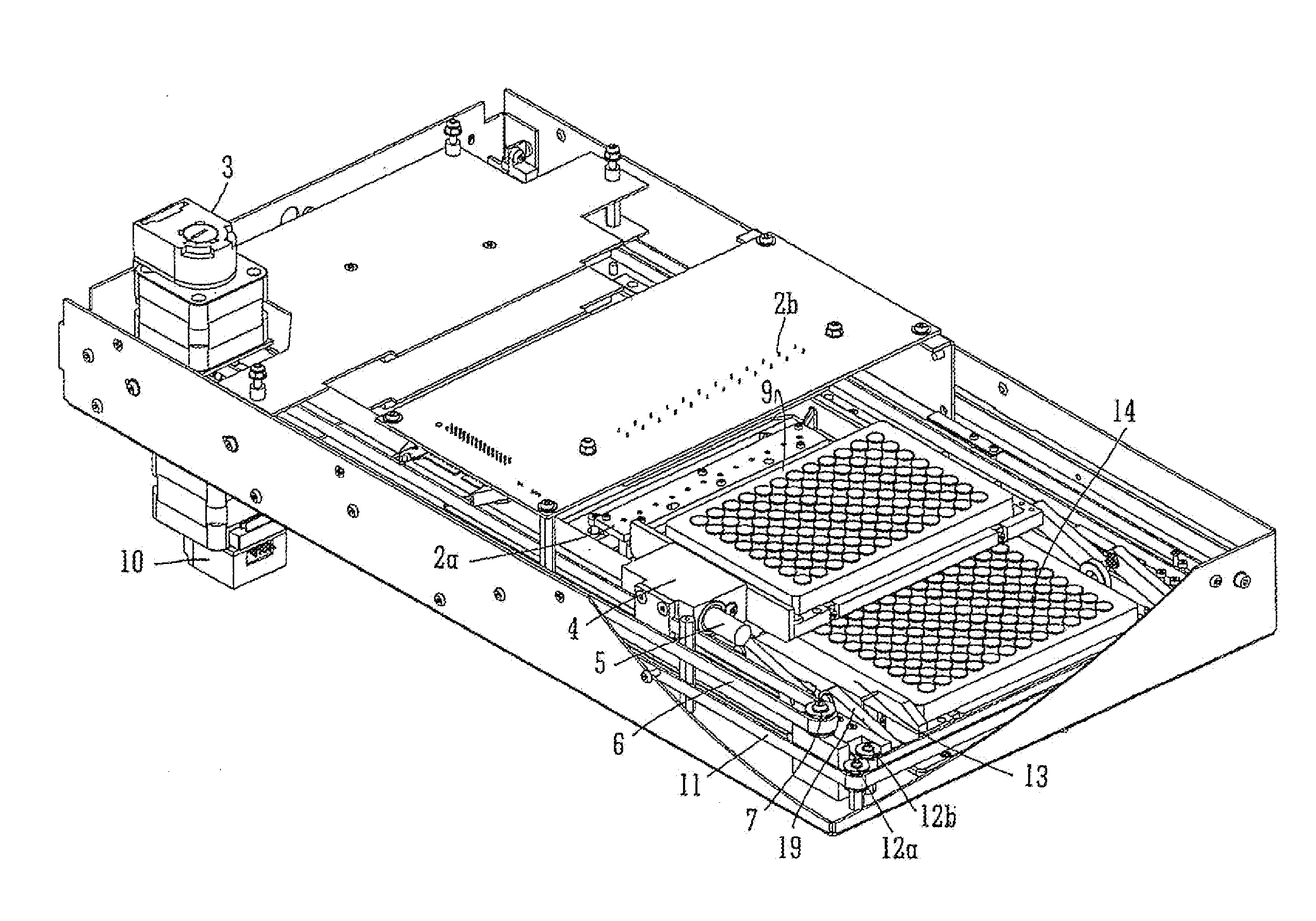
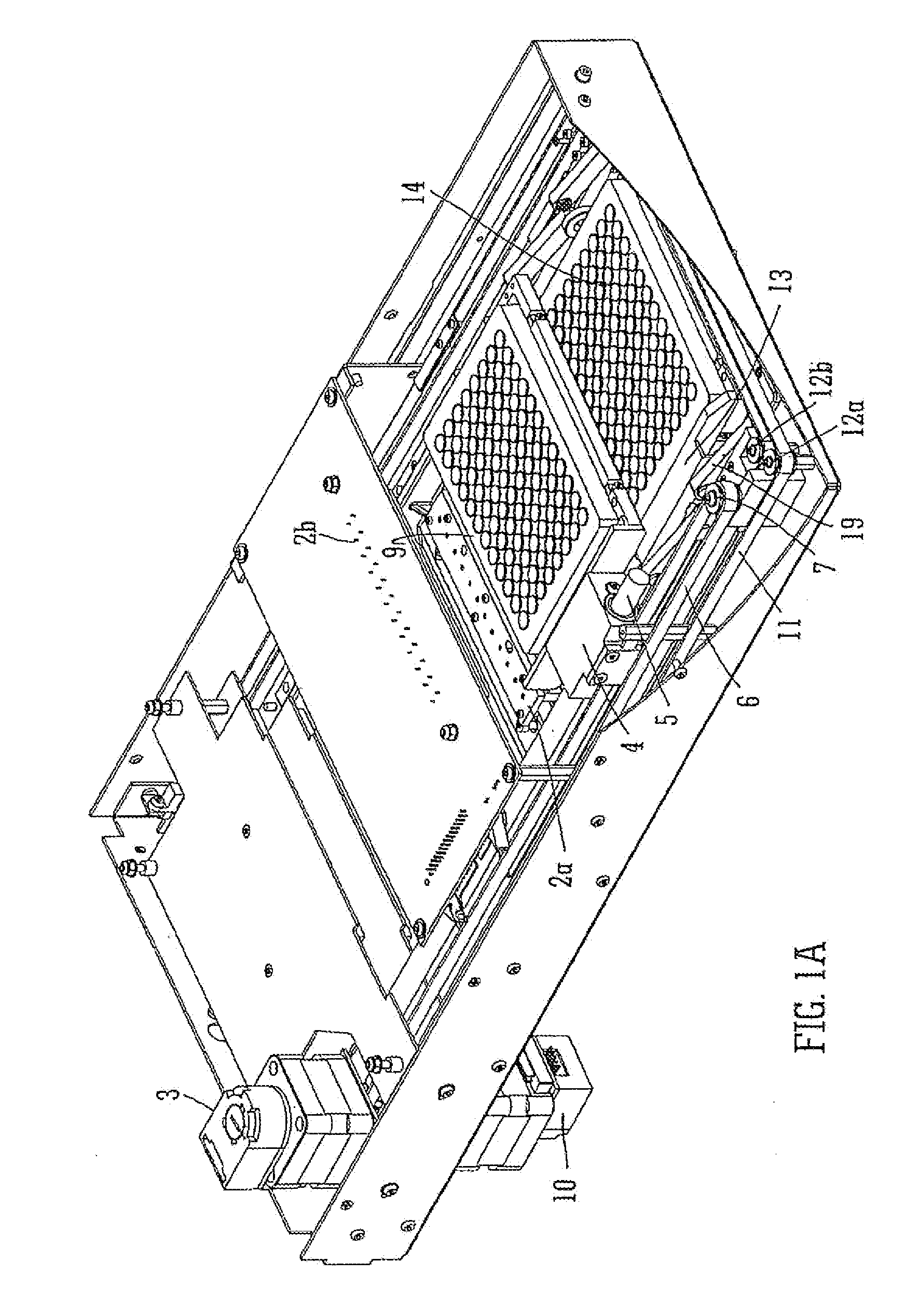
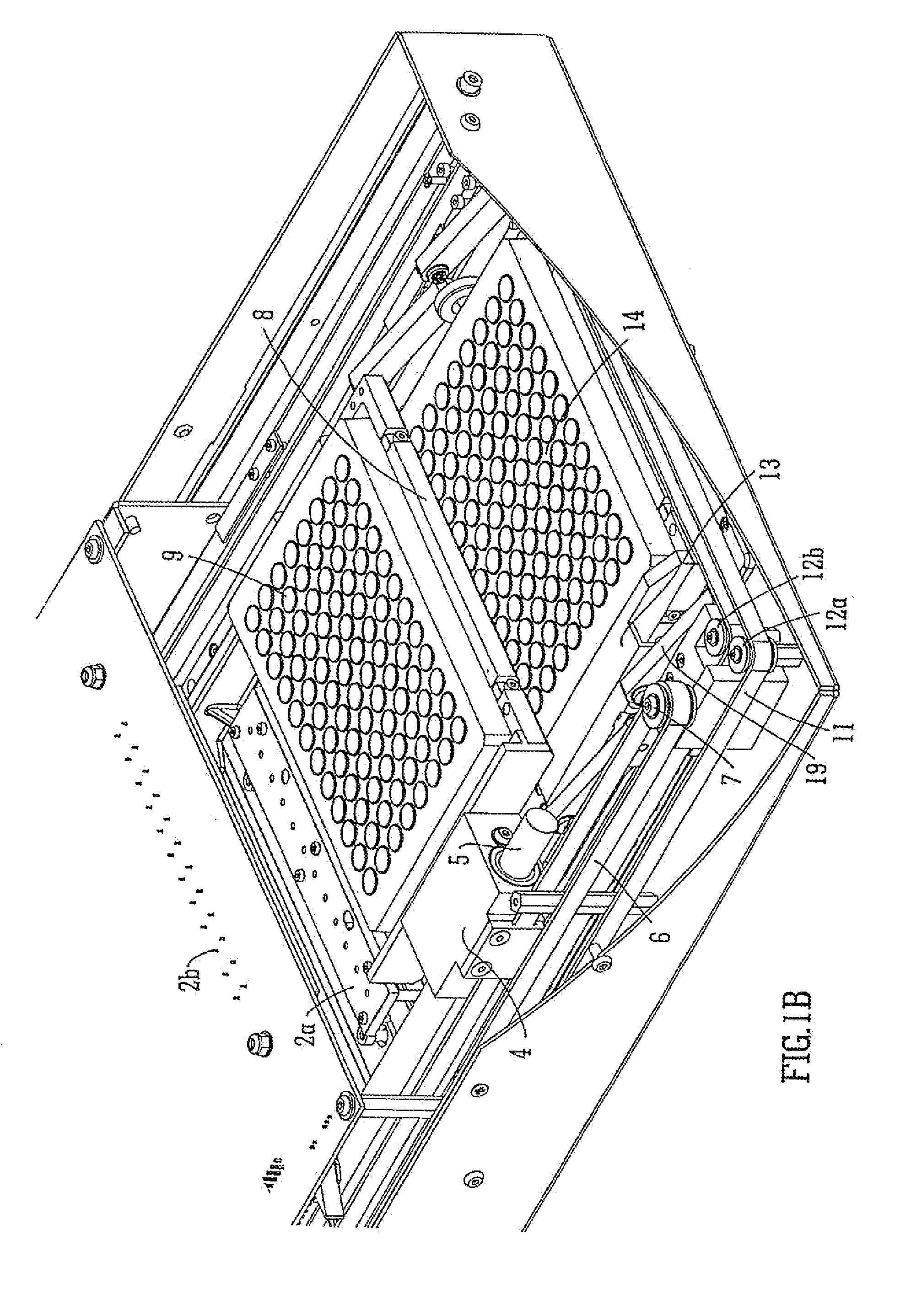
Fluorescence microtitre plate reader
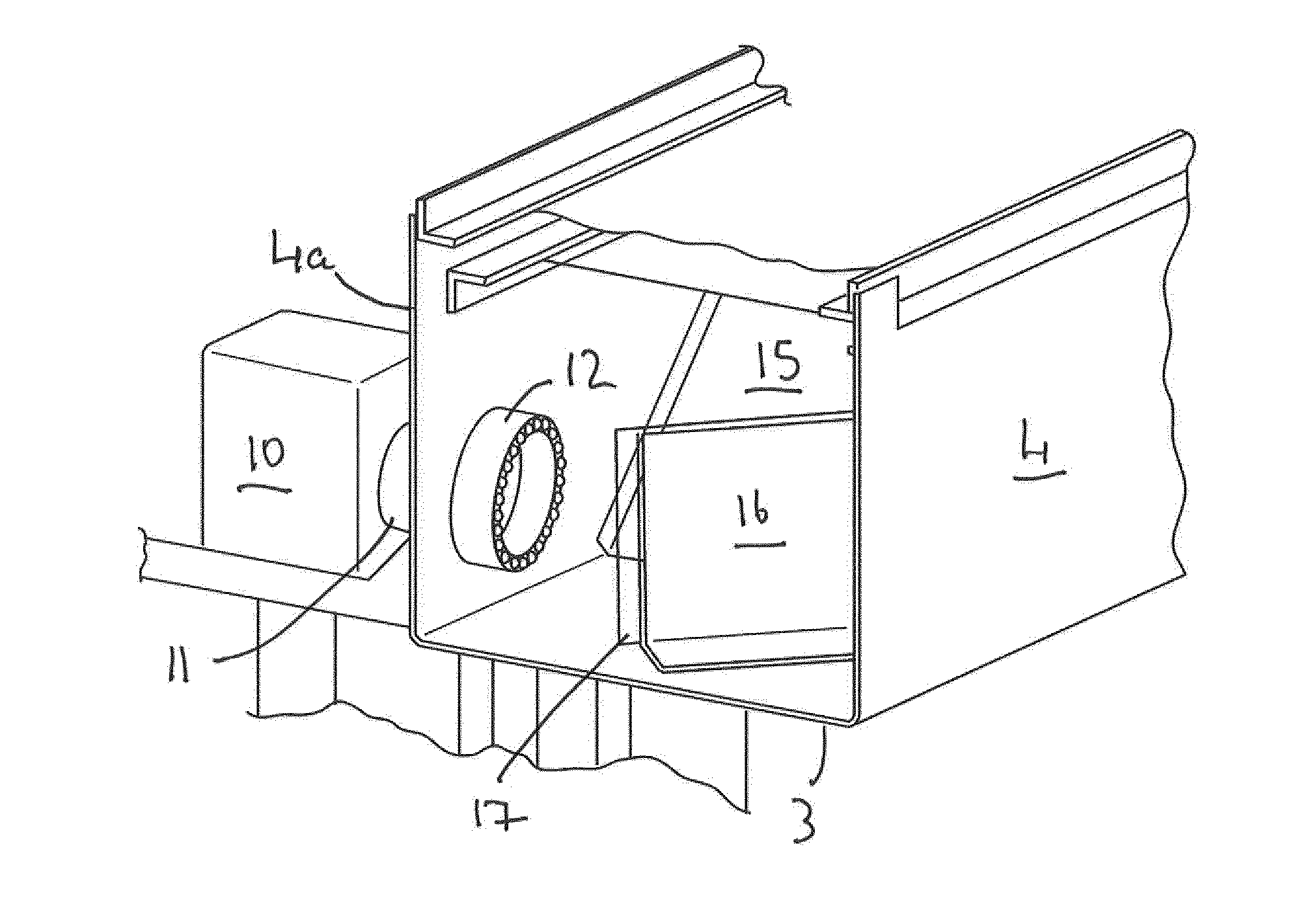
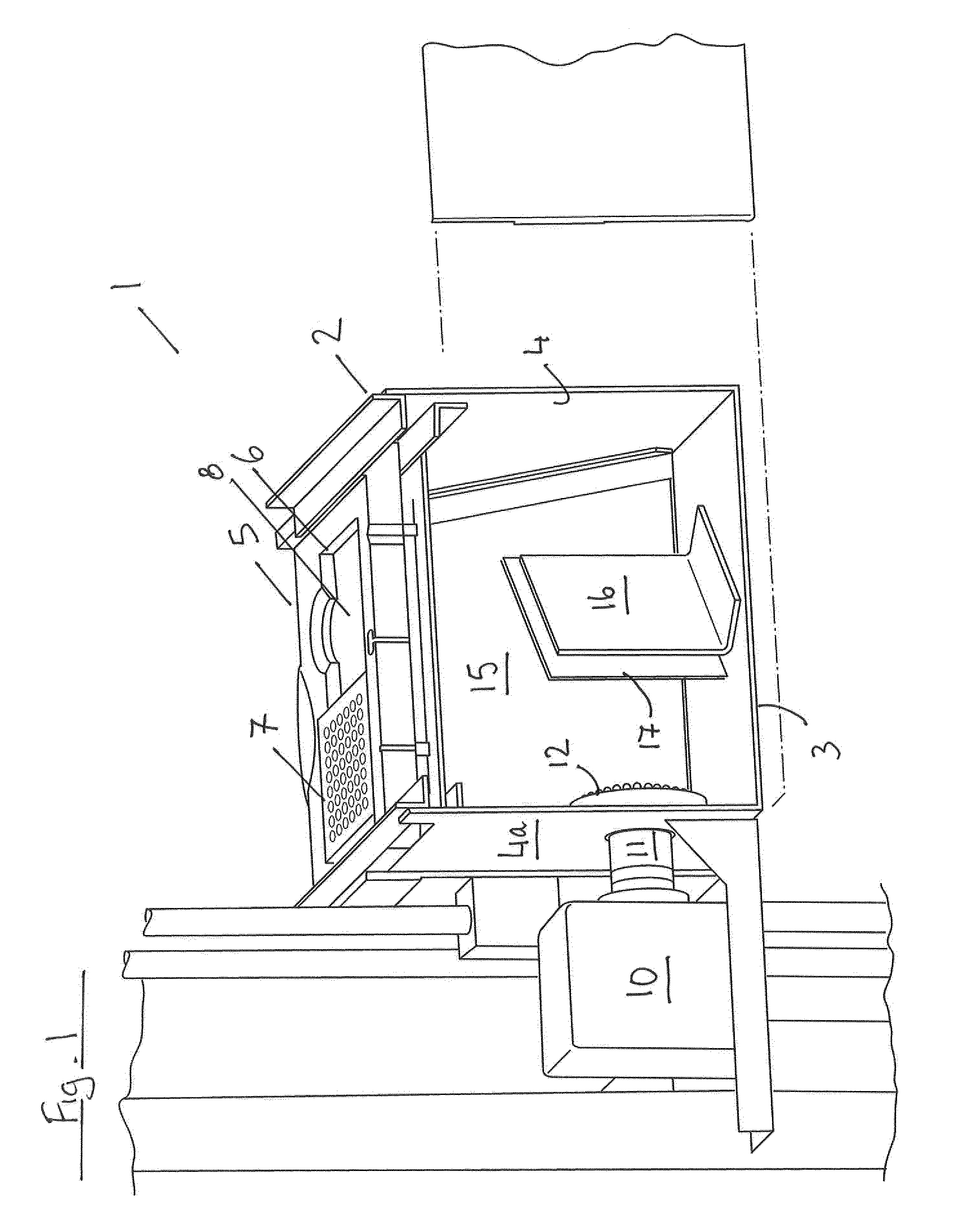
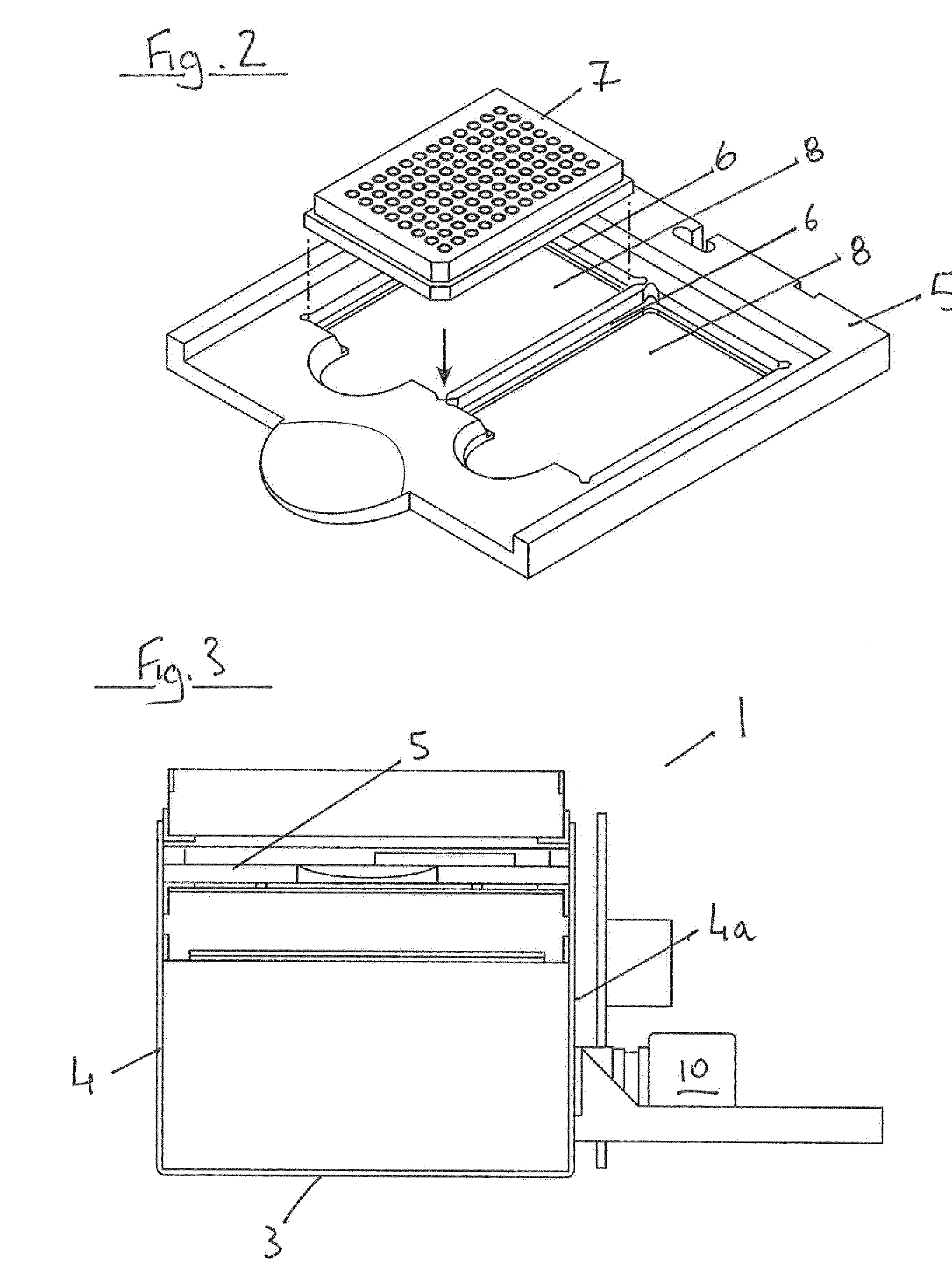
InactiveUS20150060698A1Cancel noiseReduce the impactBeam/ray focussing/reflecting arrangementsPhotometryCamera lensEngineering
A fluorescence microtitre plate reader comprises a plate reader body (2) having a base (3), top (5) and sidewalls (4), the top of the plate reader comprising at least one seat (6) dimensioned for receipt of a microtitre plate (7), the at least one seat defining an aperture (8) in the top of the plate that substantially corresponds to a base of the plate. The plate reader also includes means for illuminating wells of a microtitre plate with light from beneath the plate having an excitation wavelength, and a camera (10) and lens (11) assembly for capturing light emitted by the wells of the microtitre plate and generating a digital image, in which regions of light intensity of the image correspond to wells of the microtitre plate. An optical system is disposed within the plate reader body for expanding the distance to image plane of light, the optical system comprising a first mirror (15) disposed to receive light from the wells of the microtitre plate and reflect the light to second mirror (16) which is disposed to reflect incident light to the camera lens. The means for illumining the wells of the microtitre plate comprises a ring light (12) that embraces the camera and lens assembly.
Owner:OCULER
Thermocycler and lifting element
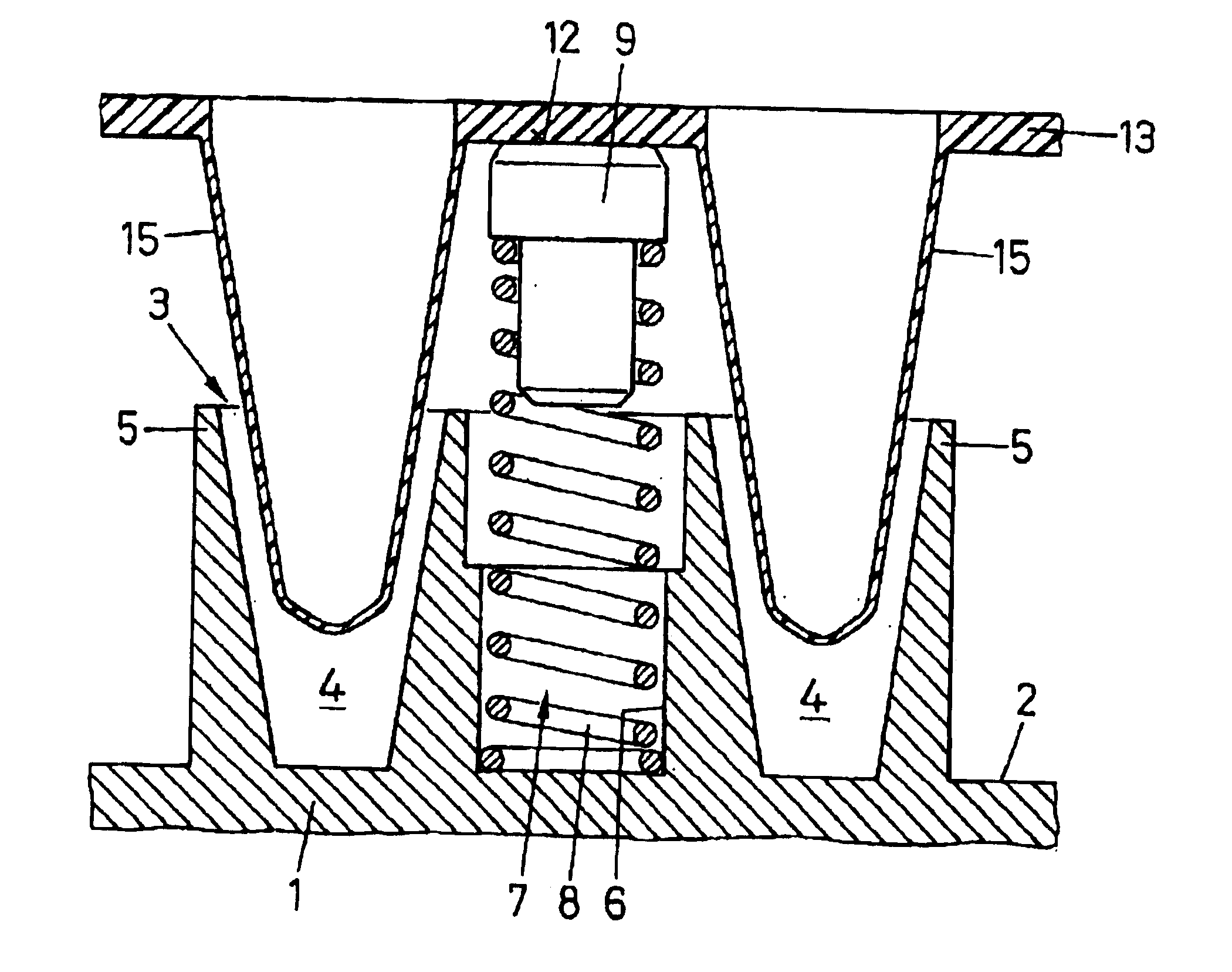
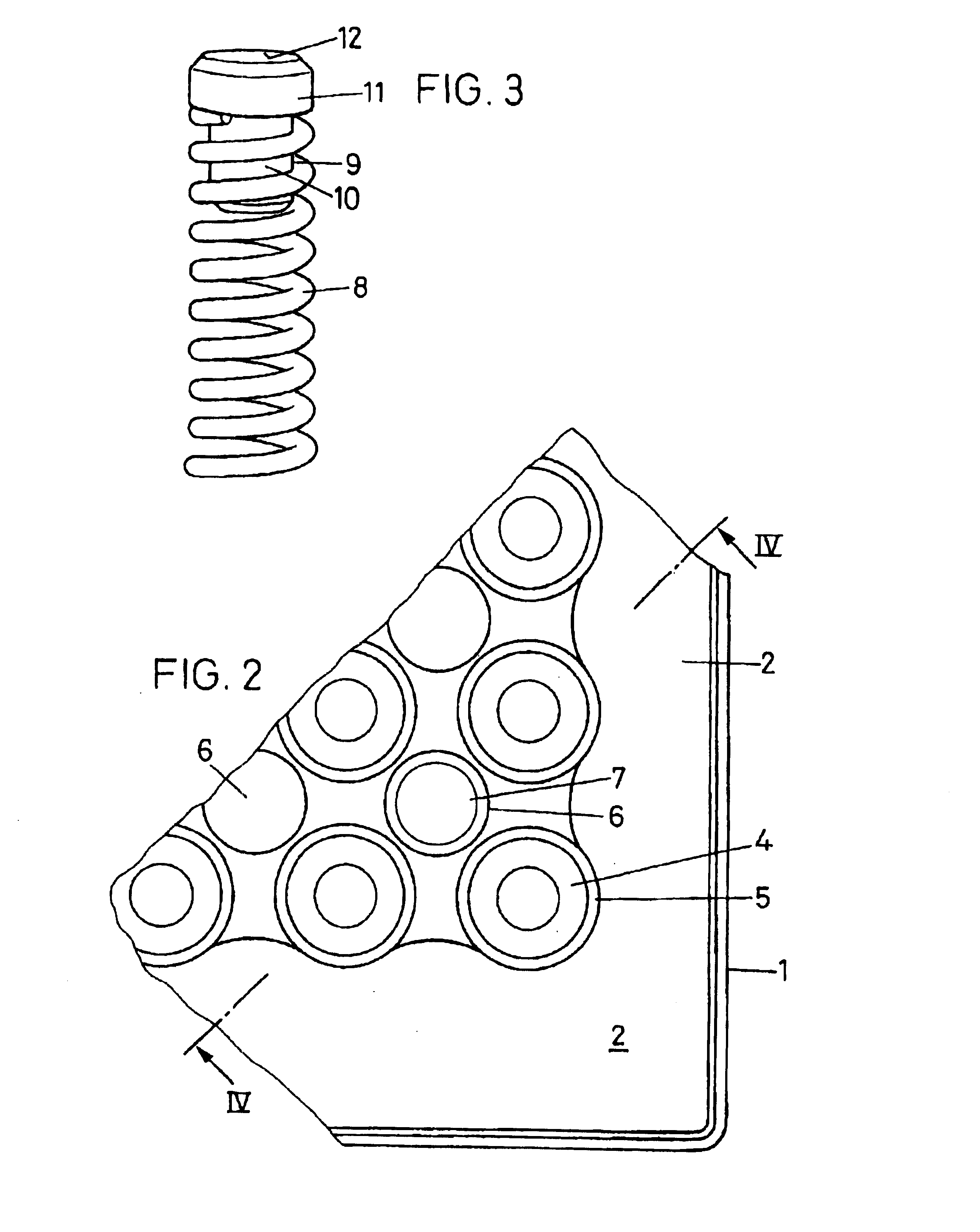
InactiveUSRE39566E1Facilitate manual removalGood removal effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsHeating or cooling apparatusCoil springEngineering
Some of the blind holes (6) between indentations (4) of a heating surface (3) contain lifting elements (7) which, after opening of a cover, release a microtitre plate (13) from the heating surface (3) and raise said microtitre plate about 2 to 3 mm, so that it can be removed without application of force. Each lifting element (7) consists of a coil spring (8) and a contact pin (9) made of, for example, PEEK which is inserted into said coil spring and presses with a round flat abutting surface (12) against the lower surface of the microtitre plate (13). The spring constant of the lifting element (7) is about 6 N / mm.
Owner:APPLERA
Method for the detection of a pathogenic form of a prion protein
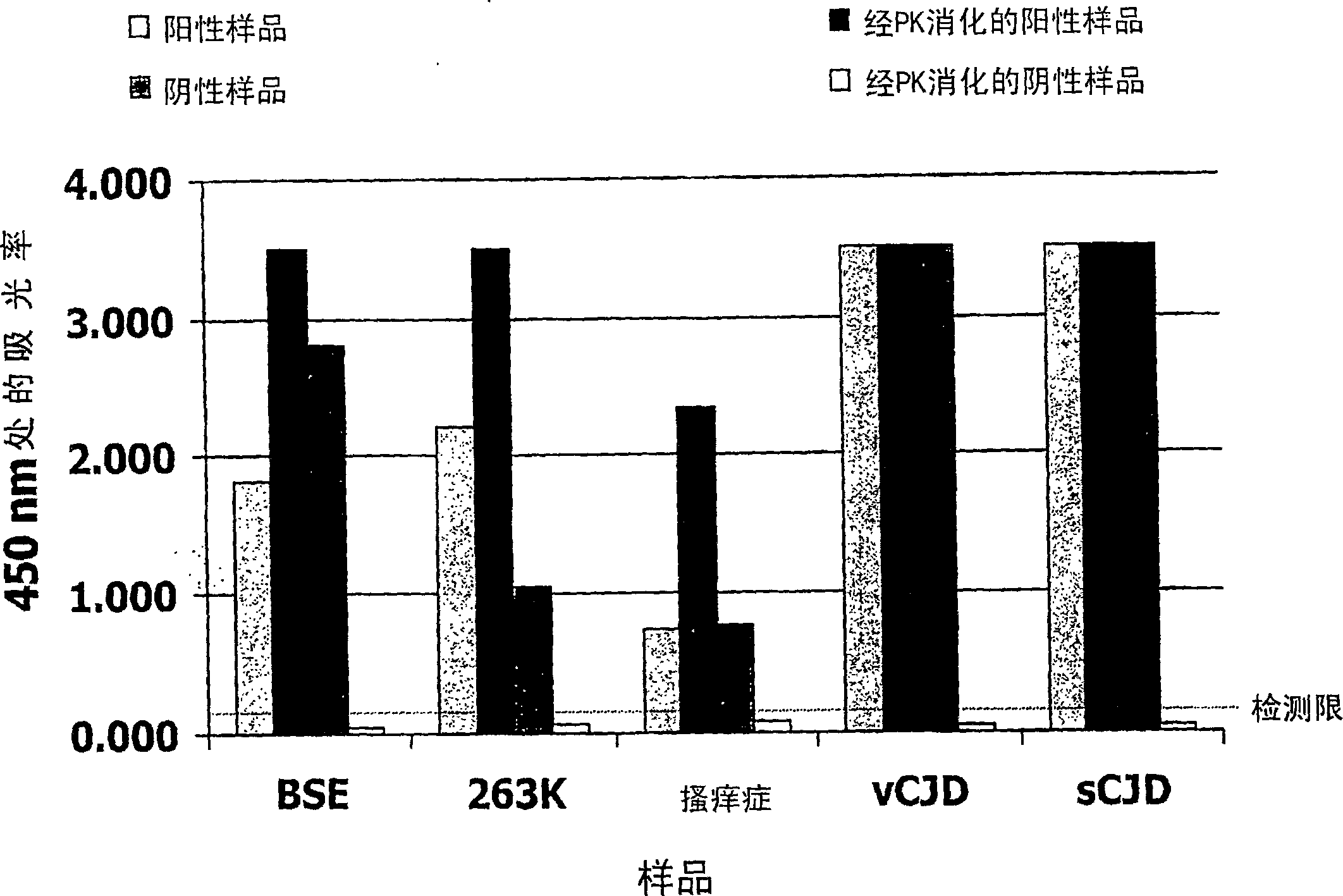
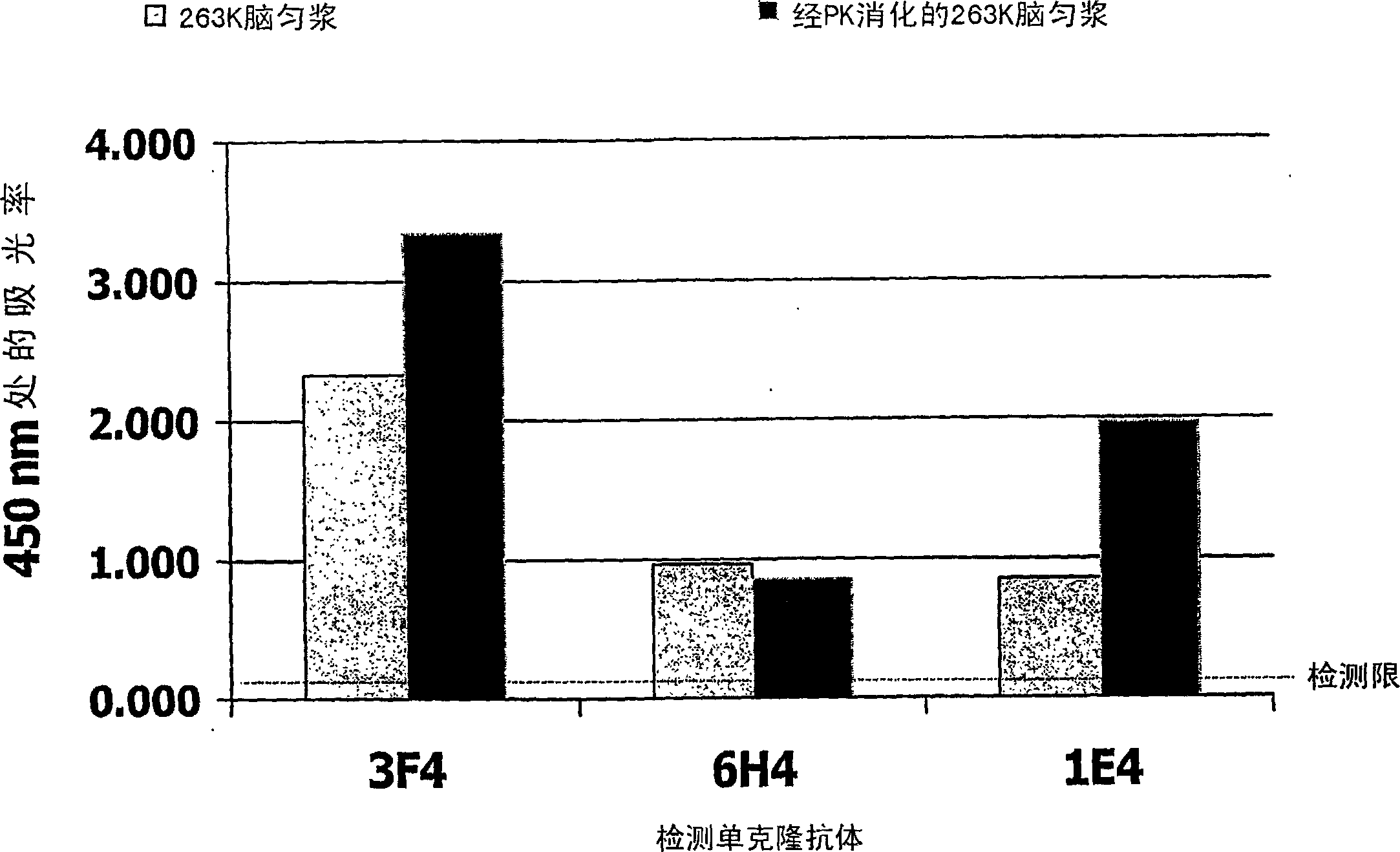
InactiveCN1820202AMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisEnzymatic digestionNitrocellulose
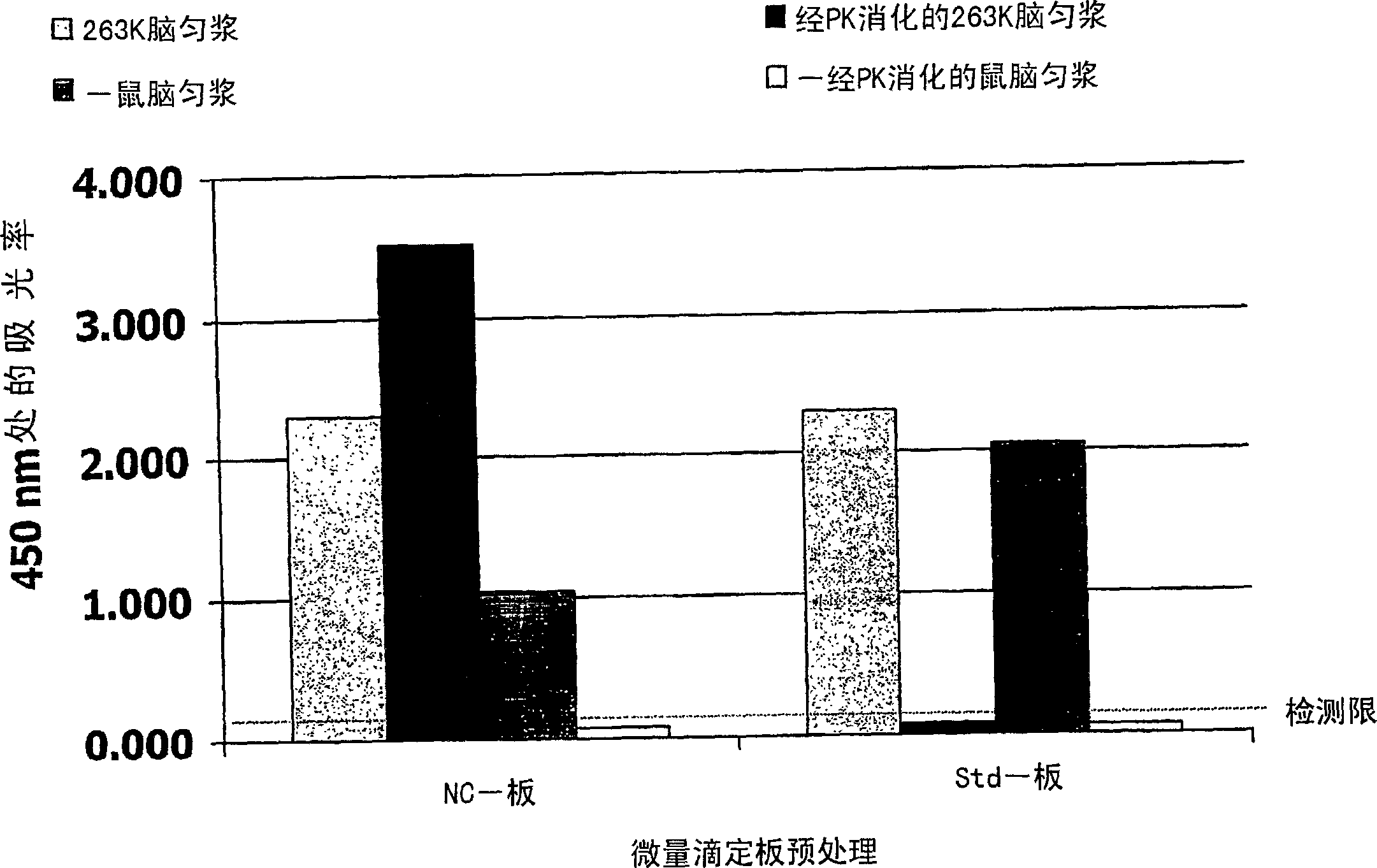
Method for the detection of a pathogenic form of a prion protein in a sample, comprising providing a container, pretreating the container to deposit on a surface of the container a coating of a cellulose derivative capable of favoring the binding of pathogenic prion protein to said container surface over the binding of cellular prion protein, incubating the sample in said container to bind any pathogenic prion protein present in the sample to said container surface, labelling the thus immobilized pathogenic prion protein, if present, with an appropriate labelling agent using an anti-prion antibody capable of binding to pathogenic prion protein and detecting the presence of labelling agent attached to the container surface. Coating a surface of a microtitre plate well with nitrocellulose allows to perform an ELISA for quantification of pathogenic prions in a suspected sample, especially after enzymatic digestion of the sample with an enzyme like proteinase K, by enhancing binding of pathogenic prions and / or reducing binding of cellular (non-pathogenic) prions.
Owner:桑昆血液供给基金会
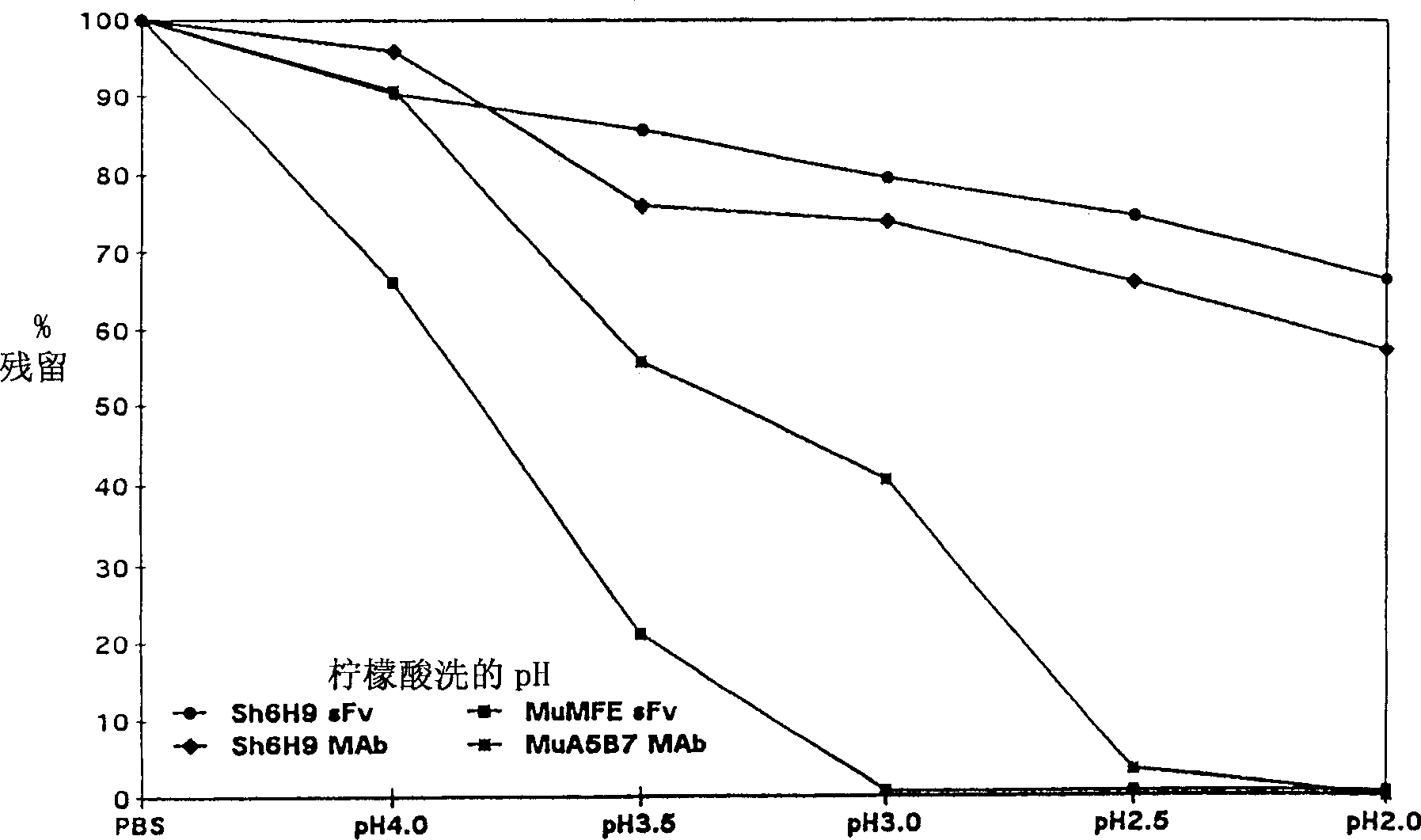
High-affinity antibodies
InactiveCN1315966AImprove targetingImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody ingredientsMonoclonal antibodyHigh affinity antibody
High-affinity monoclonal antibodies, wherein the affinity is characterised by: (i) incubating first and second samples of the antibody in antigen-coated microtitre plate wells at a concentration chosen to be within the linear part of a standard curve at pH 7.2 for 1 hour at 37 DEG C; (ii) removing unbound antibody from both samples; (iii) incubating the first sample with PBS at pH 7.2 for 1 hour at 37 DEG C, and reducing the pH of the second sample to pH 3 or below and incubating for 1 hour at 37 DEG C; (iv) removing unbound antibody from both samples; (v) incubating both samples with anti-antibody alkaline phosphatase-conjugate for 1 hour at 37 DEG C; (vi) removing unbound conjugate from both samples; and (vii) adding PNPP substrate to the samples, measuring the absorbance of the samples at 405 nm, and determining the amount of antibody bound to antigen, wherein the amount bound in the second sample is > 50 % of that of the first sample.
Owner:KS BIOMEDIX LTD
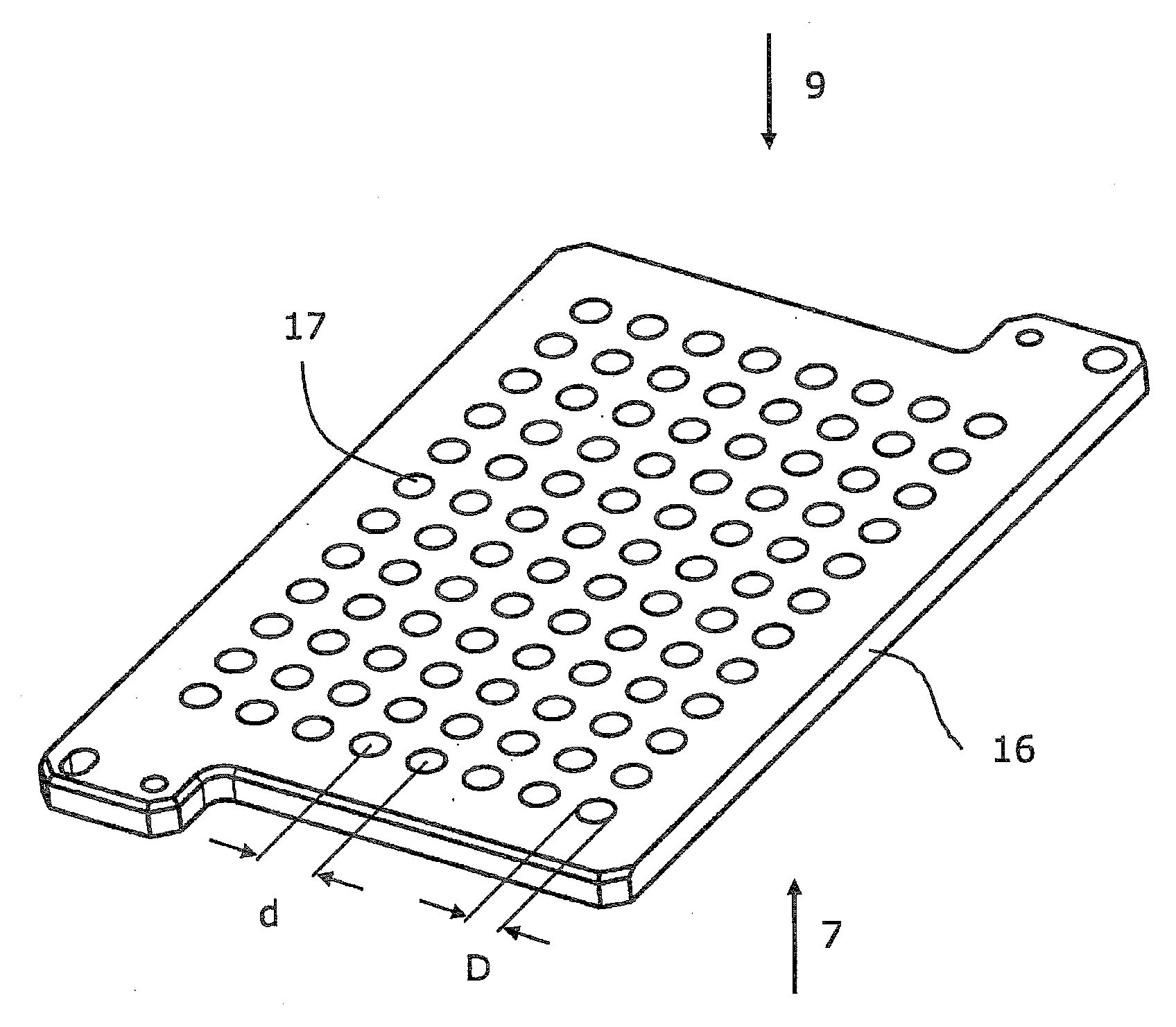
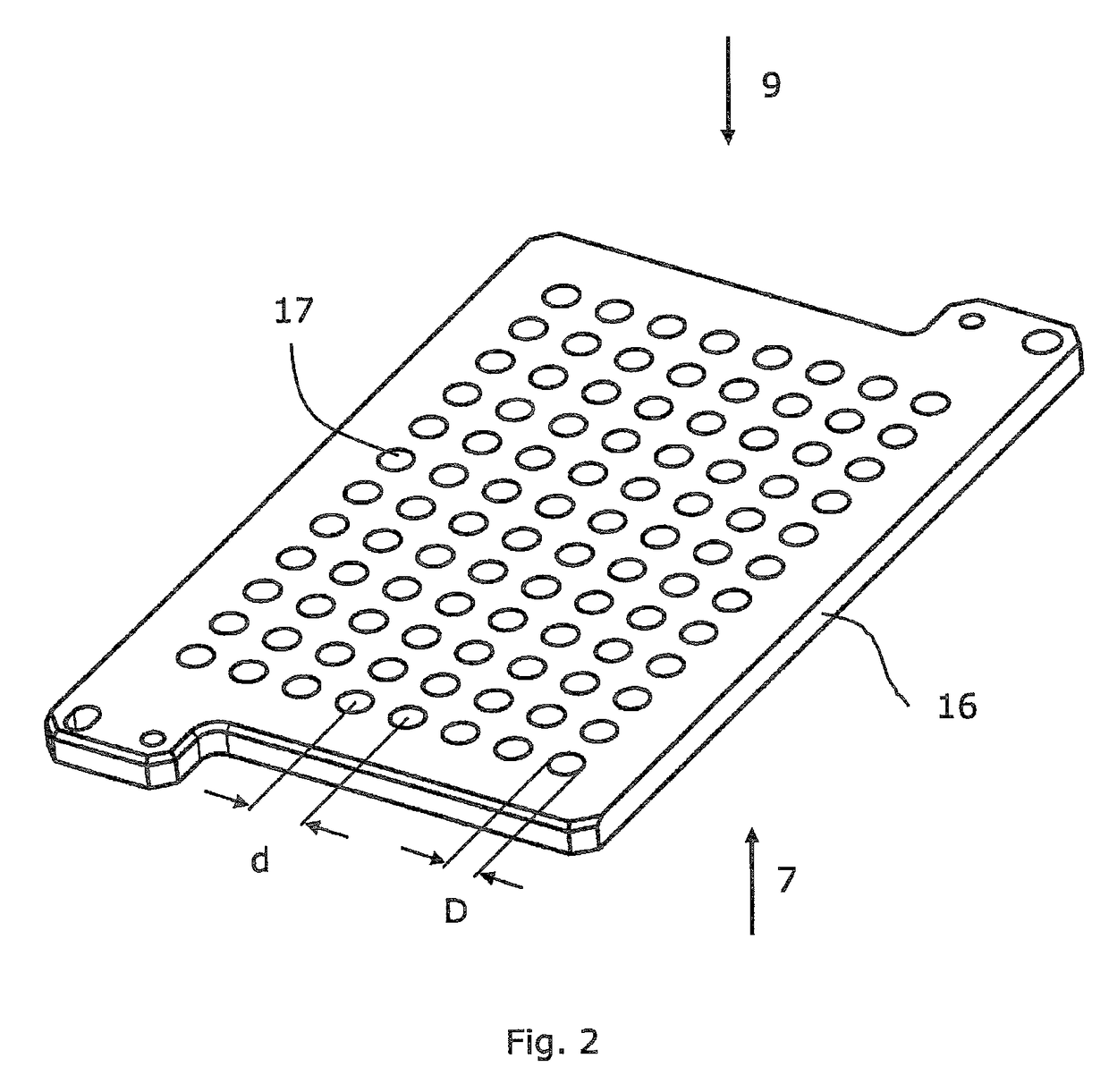
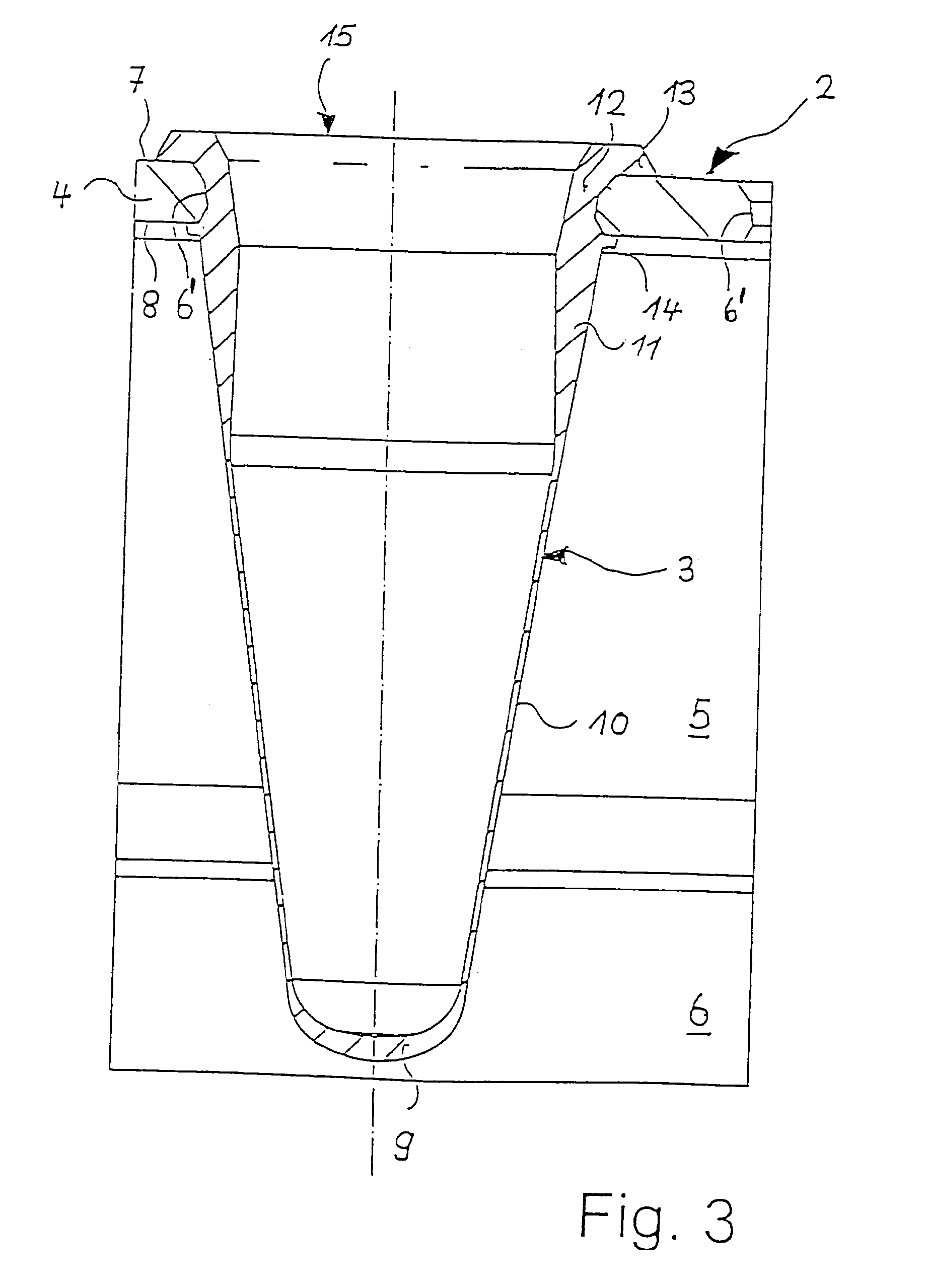
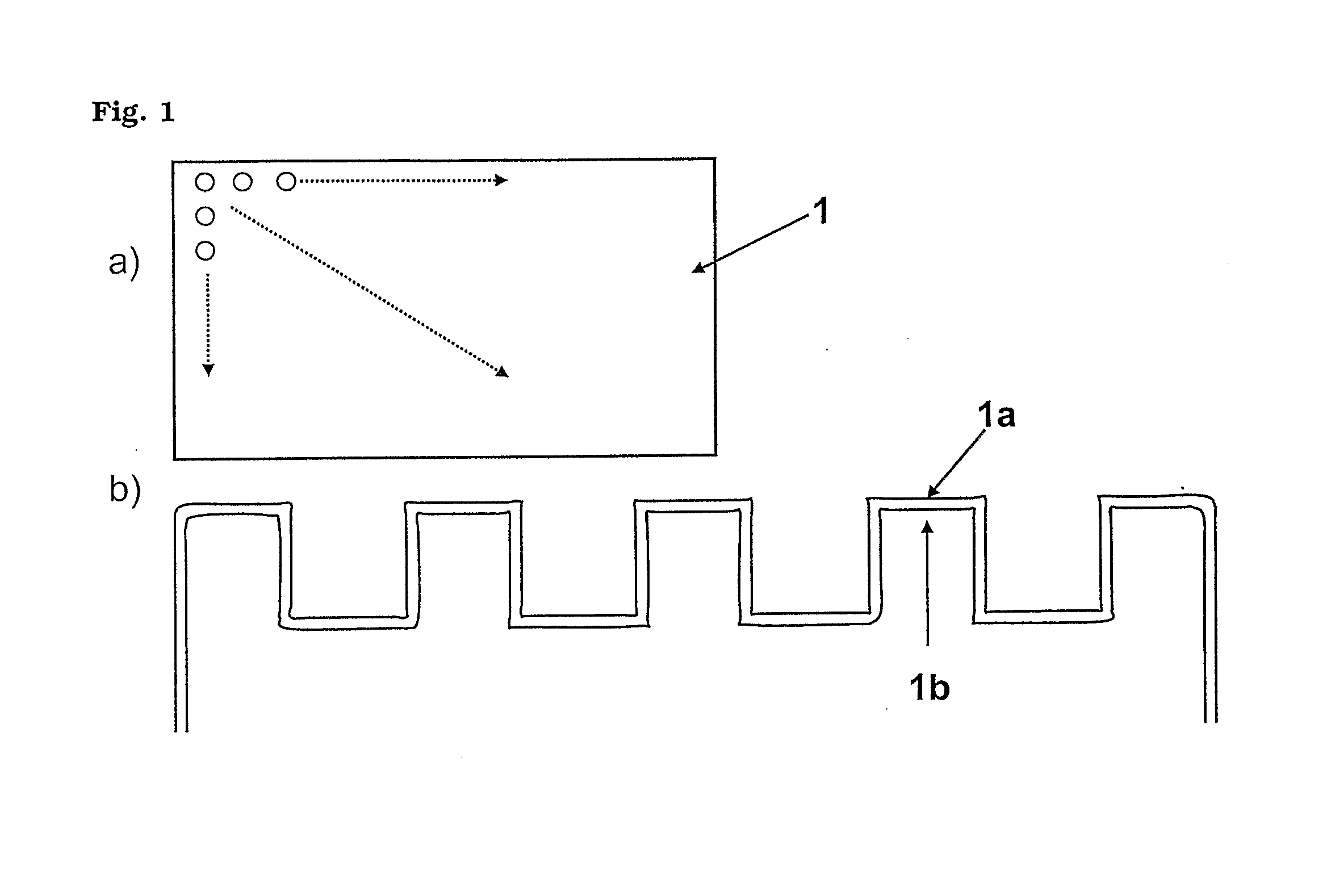
Microtitre plate
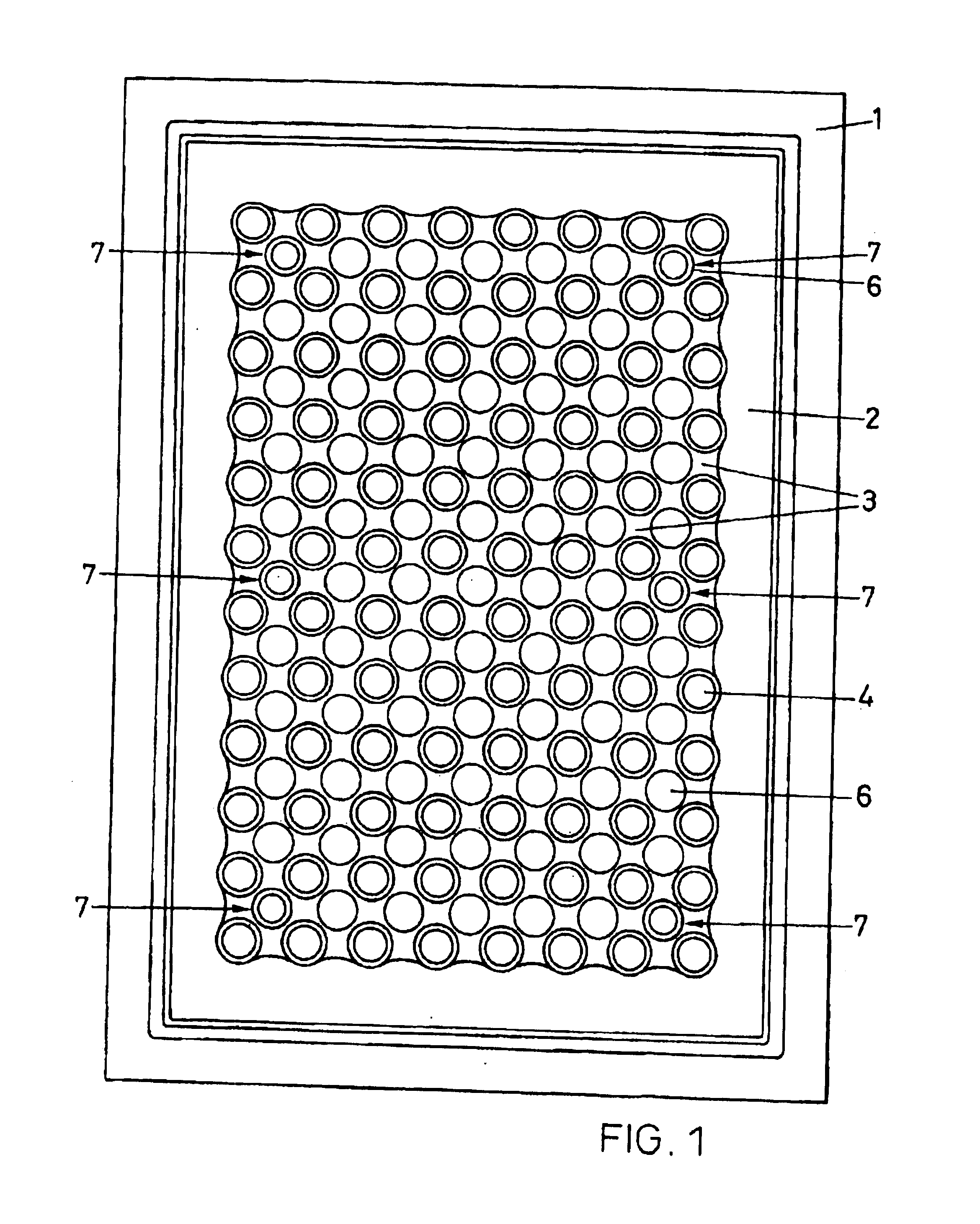
InactiveUS20110003717A1Easy to measureReduced optical cross-talkLaboratory glasswaresLibraries apparatusAcousticsRidge
A microtitre plate with wells having transparent bottoms, wherein the microtitre plate includes at least one physical deformation between at least two adjacent wells. The physical deformations may have the shape of e.g. a channel, a ridge, a hole, a slit or a step.
Owner:QIAGEN INSTR
Automated method for high throughtout screening of nematodes
InactiveUS20080267880A1Rapid and objective score of survivalSimple and quantitative single-step indicatorBiological testingIn-vivo testing preparationsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsAssay
This invention provides a high throughput survival assay, using uptake of a marker dye (e.g. a fluorescent dye) as a marker of death of a nematode. The assay permits high throughput screening of thousands of compounds possible. By the application of automated worm handling technology we are able to accurately dispense nematodes into 384 well microtitre plates, at rates many thousand of times faster than previously possible. In addition, we have automated the analysis of survival by the use of a fluorometric plate reader that quantitates the degree of fluorescence within each well.
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
Modular sample storage system
Various embodiments include a sample storage system having: a transport module; a storage module coupled with the transport module on at least one side of the transport module, the storage module for storing a plurality of specimen tubes or microtitre plates; a tube selector module coupled to an end of the transport module for selecting at least one of the plurality of specimen tubes or microtitre plates; and an input / output (I / O) module coupled with the transport module on a side of the transport module, wherein the transport module is configured to modularly couple with at least one additional storage module for storing a plurality of specimen tubes or microtitre plates.
Owner:HIGHRES BIOSOLUTIONS INC
Method for detecting bacterial drug resistance in aquaculture
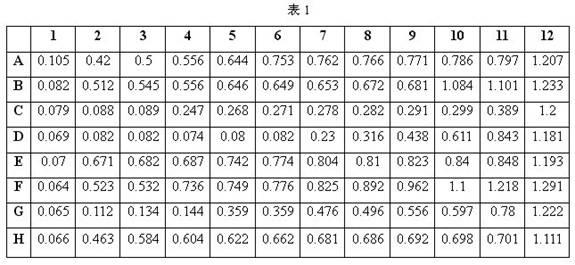
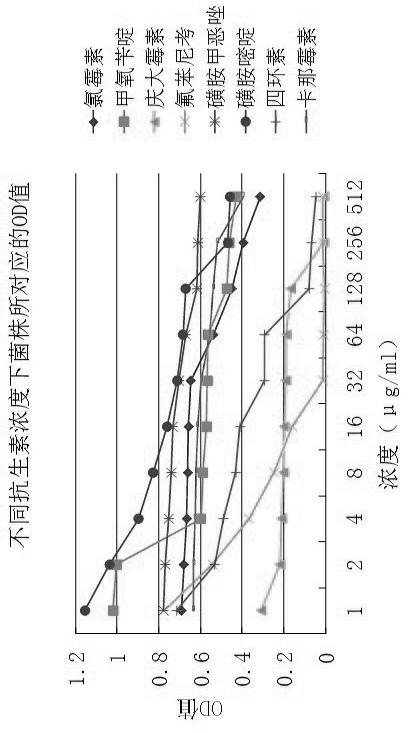
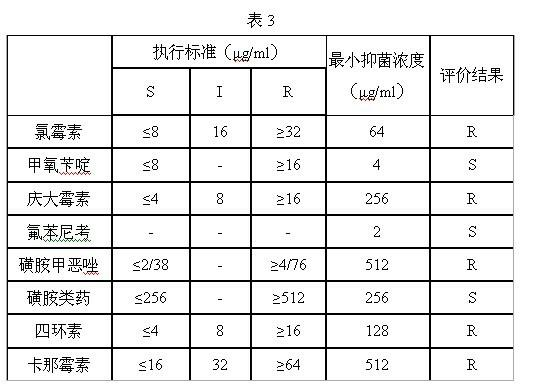
InactiveCN102676629AReduce dosagePracticalMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyInhibition zone
The invention discloses a method for detecting bacterial drug resistance in aquaculture, which comprises the following steps: (1) an antibacterial drug stock solution is prepared; (2) a bacterial liquid is prepared; (3) an antibiotic working solution is prepared from the antibacterial drug stock solution obtained in step (1); (4) a 96-well microtitration plate is placed in an incubator for incubation; and (5) data are read through a microplate reader for analysis. The method applies to bacterial drug resistance detections in aquaculture and other areas. In combination of the specification of the 96-well microtitration plate (8 multiply 12) and the drug concentration scope required by CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute), 8 categories of antibiotic drugs and 10 concentration gradients are selected for detection. When the method is in use, no flat plate is required, the steps of configuring a large amount of culture mediums, manufacturing drug sensitive paper scraps and measuring the inhibition zone are spared, and a small quantity of culture solutions is required. The method has the advantages of strong practicability, convenience, accuracy and stability in results, good repeatability and high sensitivity.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV +1
Device and method for the determination of protein domain boundaries
InactiveUS20030104509A1Improve throughputBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProtein structureEngineering
A method and device to assist in the determination of protein domain boundaries is described. In particular the device is designed to provide a high throughput of proteolytic digestion of proteins to identify domains and their boundaries, for use in protein structure determination, in a manner that is amenable to automation. Proteases are immobilized in a convenient format such as a microtitre plate and preferably arranged in a matrix thereby allowing for simultaneous degradation of a protein by a number of proteases at a number of concentrations.
Owner:AFFINIUM PHARMA
Methods and systems for adding a reagent to an analyte in a gel
The present invention relates to methods and systems for adding a reagent to an analyte in a gel. The invention further provides methods and systems for transferring liquid analyte reagent mixtures from a gel to a second vessel, such as a microtitre plate. The invention is useful in the manipulation of biological molecules such as nucleic acids, carbohydrates, proteins and peptides. In particular, the invention has utility for manipulating proteins and peptides in isoelectric focusing gels.
Owner:GE HEALTHCARE BIO SCI CORP
Microtitre plate with a relieved perimeter
ActiveUS20070025885A1Chemical analysis using titrationLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringMechanical engineering
A microtitre plate having a relieved perimeter includes a plate defining a plurality of wells and the perimeter of the plate is horizontally relieved. Alternatively, a microtitre plate may include a base and a holding section extending from the base. The holding section defines a plurality of wells and the perimeter thereof being horizontally relieved.
Owner:CAPLIPER LIFE SCI INC
Automated Immunoassay Apparatus
InactiveUS20110268629A1Chemical analysis using titrationLaboratory glasswaresEngineeringMicrotitre plate
An automated immunoassay apparatus is disclosed comprising a single optical reading device for reading two microtitre plates. A first microtitre plate is loaded into an upper plate holder which is linearly translated at a fixed height. A second microtitre plate is loaded into a lower plate holder. The lower plate, holder runs along a contoured track which varies the vertical height of the second microtitre plate.
Owner:DYNEX TECH
Method Of Determining A Compositional Or Functional Characteristic Of A Cell Culture Media
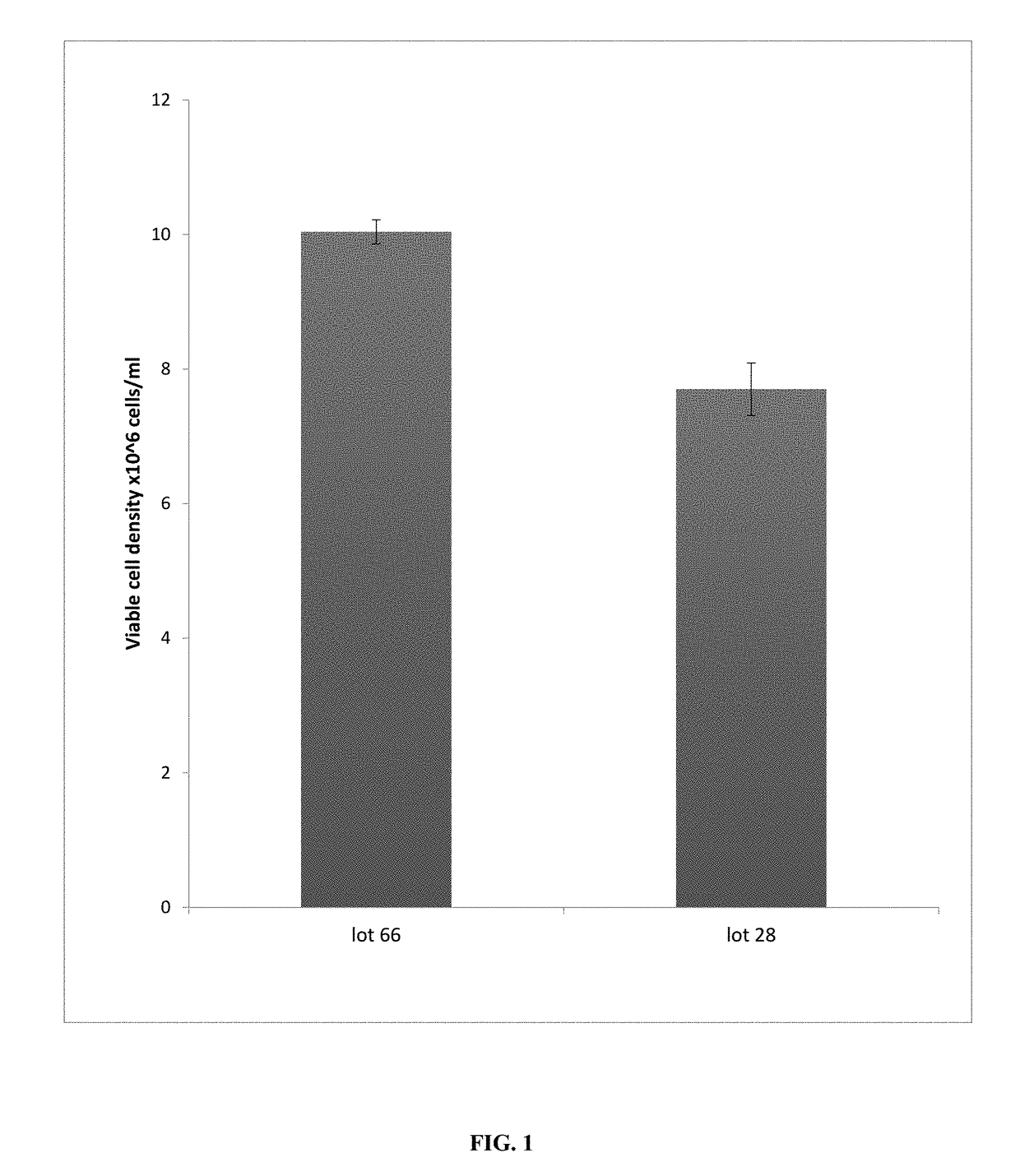
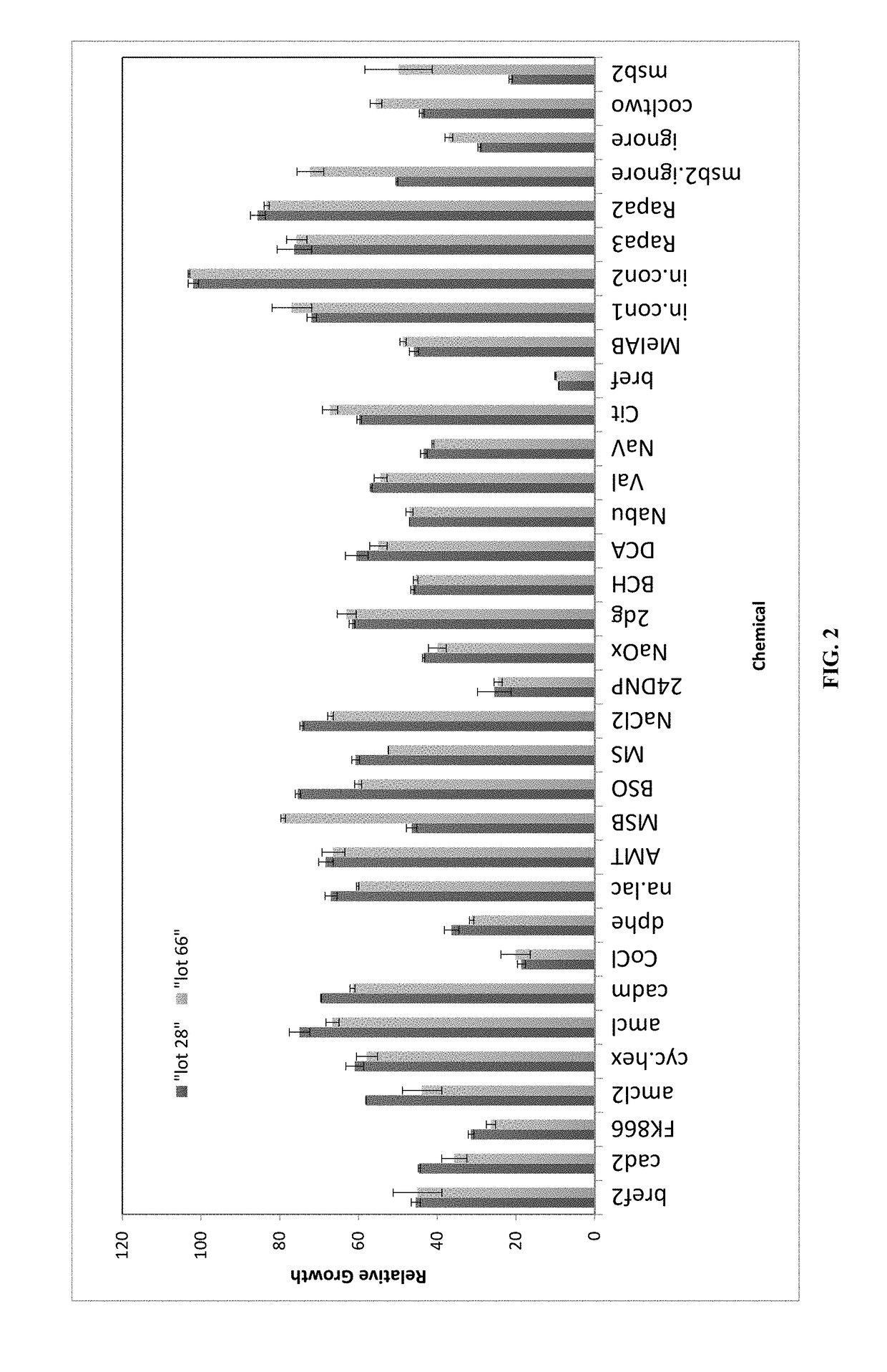
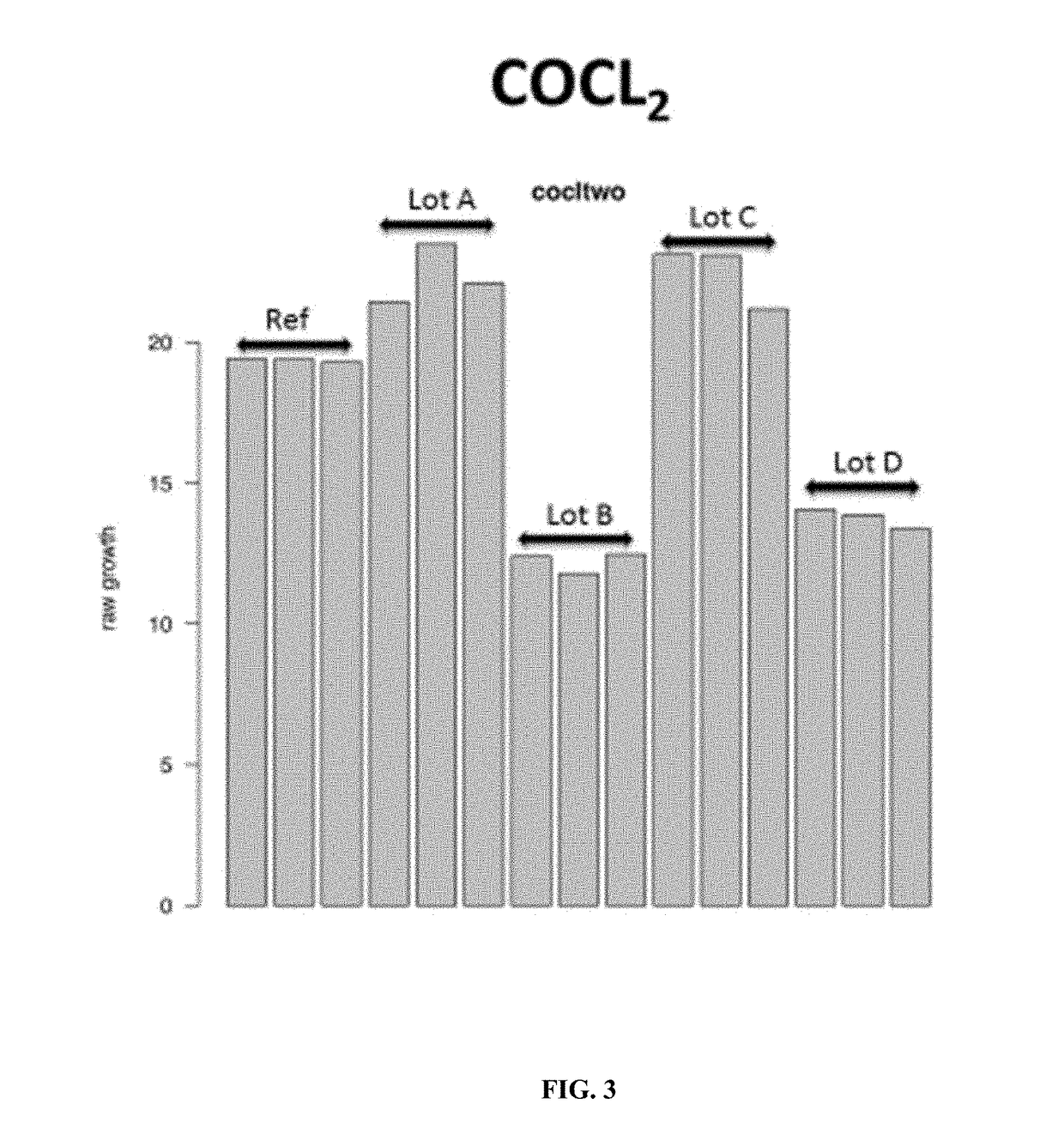
ActiveUS20180282779A1Improve performanceLess expensiveMicrobiological testing/measurementCell culture mediaCell culture mediaStressor
A method of determining variation between a query cell culture media and a reference cell culture media is provided. The method comprises the steps of incubating a reference cell with an aliquot of the query culture media and at least three chemical cell stressors in wells of a microtitre plate and determining an environmental response of the reference cell in the presence of the query cell culture media and each of the plurality of chemical cell stressors. A query cell culture media specific environmental response fingerprint is generated comprising the plurality of chemical cell stressor specific environmental responses. The query cell culture media-specific environmental response fingerprint is compared with a reference media-specific environmental response fingerprints corresponding to a reference cell culture media and generated using the reference cell. Variation between the query cell culture media and the reference cell culture media is then determined based on the level of correlation between the query cell culture media-specific environmental response fingerprint and the reference media-specific environmental response fingerprints.
Owner:VALITACELL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com