Patents
Literature
72 results about "Co incubation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
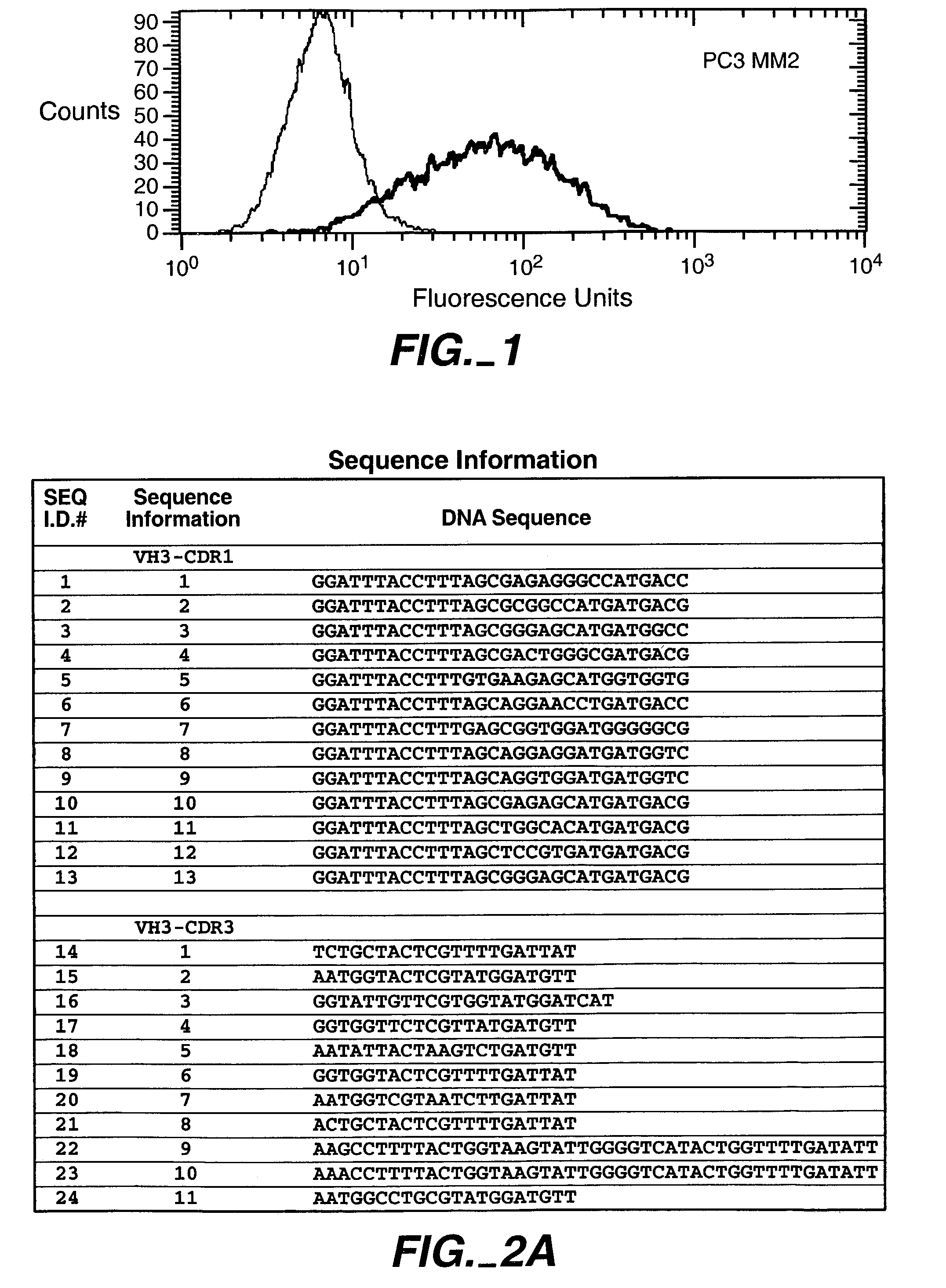
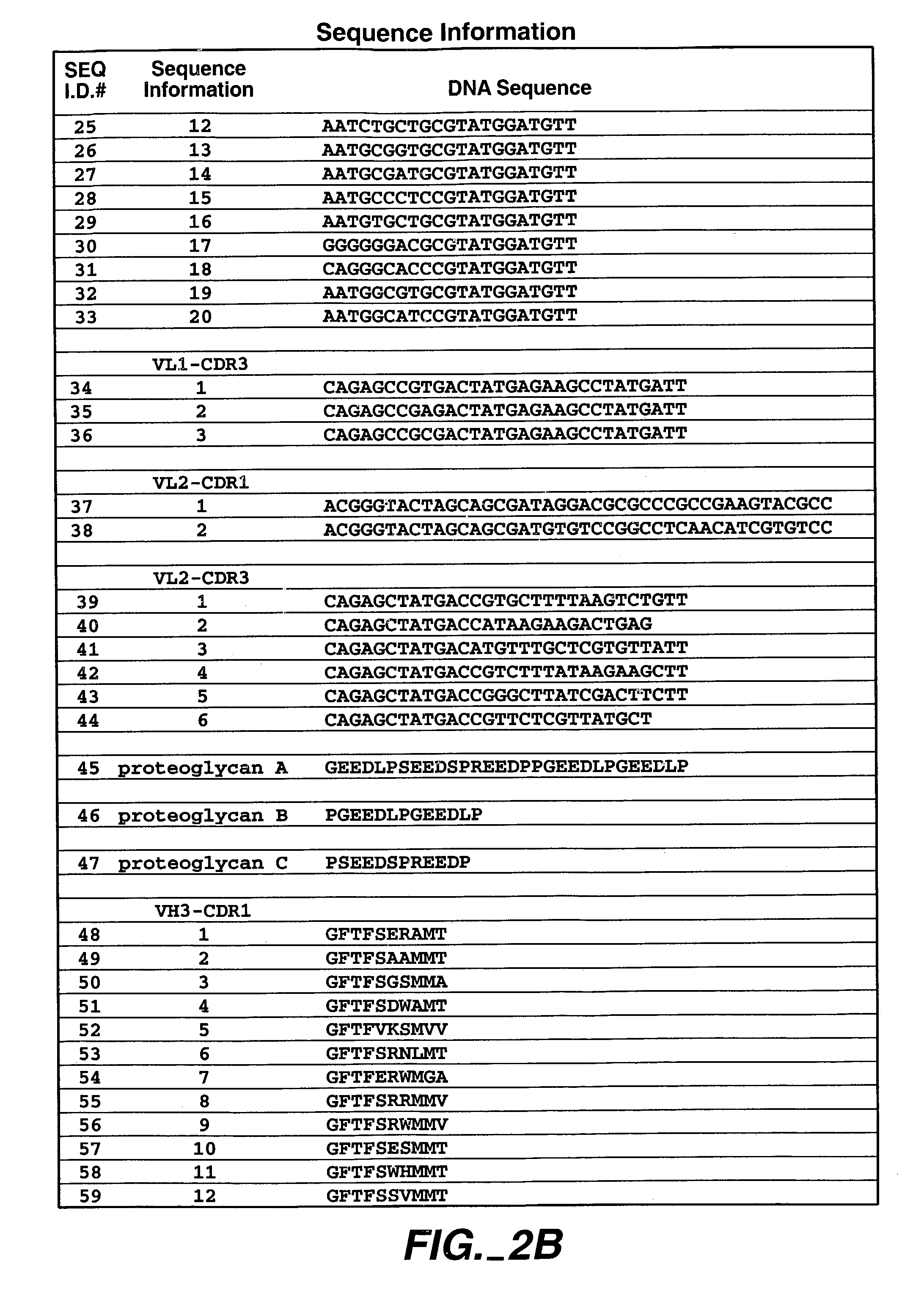
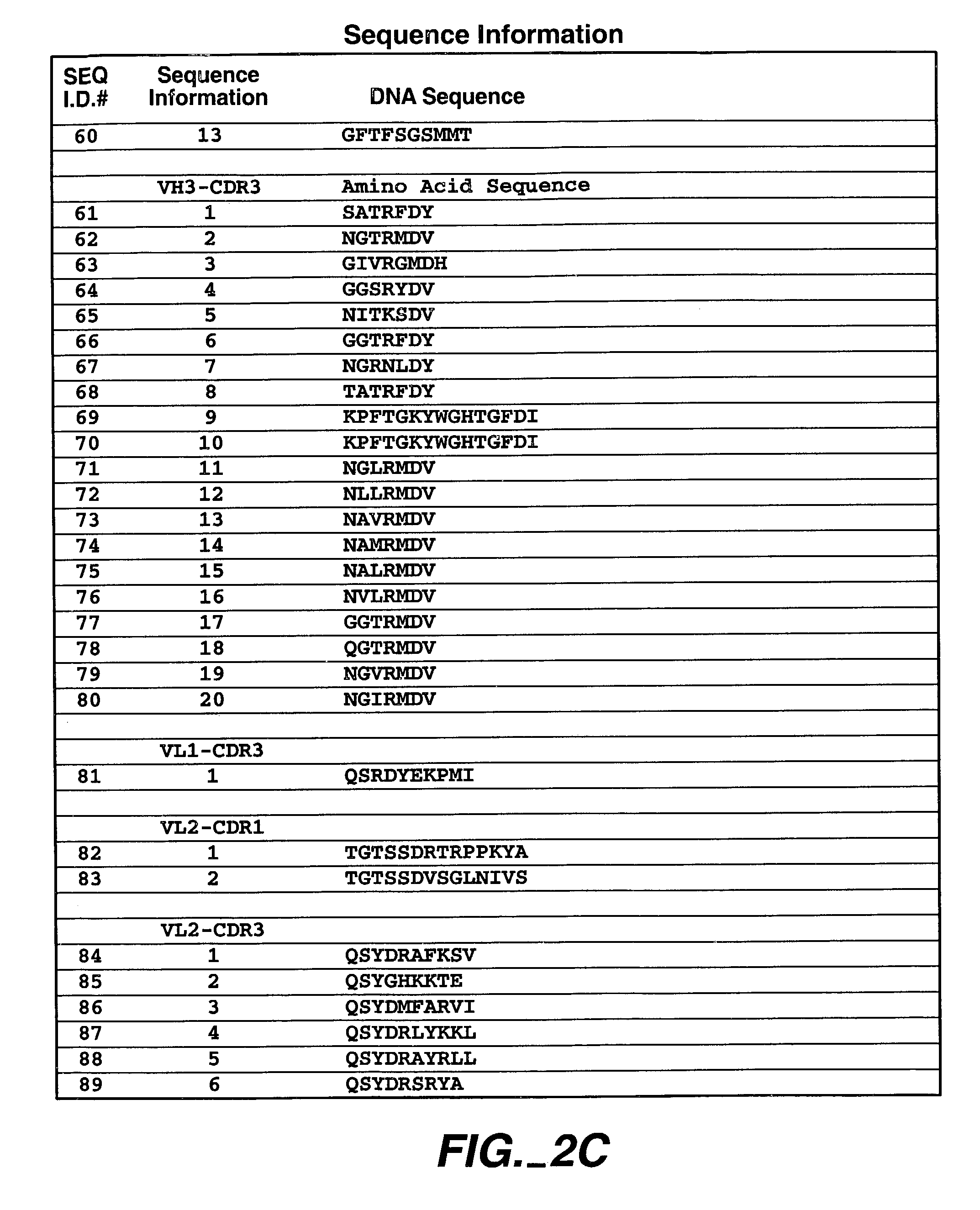
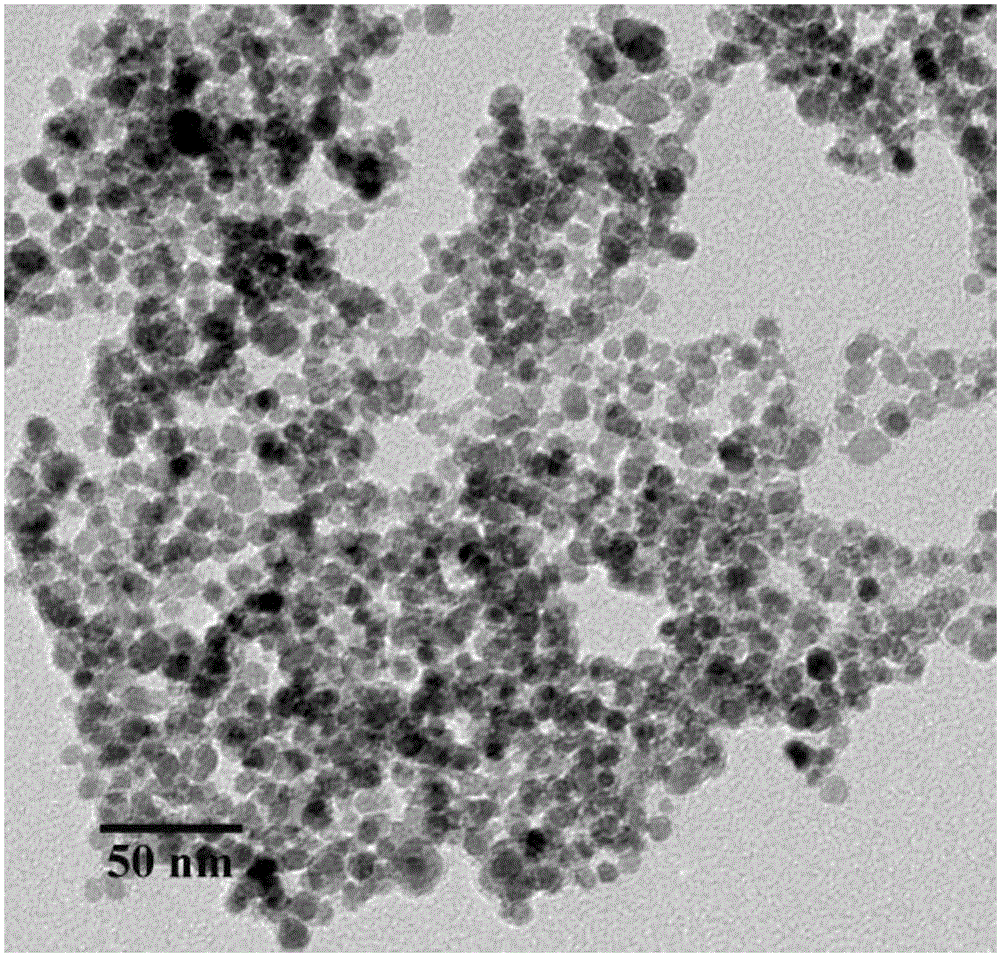
Human antibodies that have MN binding and cell adhesion-neutralizing activity
The invention is composed of monoclonal human MN antibodies or MN antibody fragments that target the GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeat within the proteoglycan domain. The proteoglycan domain of the MN cell surface protein contains four of these identical GEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 118) repeats. Binding to the desired epitope is verified by competition ELISA, where ELISA signal can be attenuated by co-incubation with a peptide containing this repeat (PGEEDLPGEEDLP (SEQ ID NO: 119)). This inhibition of binding can also be verified using Biacore assays, where binding of desired antibodies to immobilized MN or proteoglycan peptides can be inhibited by the peptide repeat. In addition to binding to the peptide repeat, human anti-MN antibodies can inhibit the cell adhesion of CGL-1 cells to MN coated plastic plates. Human anti-MN antibodies have been used to diagnose and quantify MN expression in cancer cells and tumors using FACS and immunohistochemical methods. An example is also provided where a human anti-MN IgG1 mediates tumor cell lysis though antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Therefore, these antibodies will be useful for the treatment of cancers in which MN is upregulated or can be useful for the diagnosis of cancers in which MN is upregulated.
Owner:BAYER HEALTHCARE LLC
Preparation method of magnetic biochar loaded photosynthetic bacteria material and sewage treatment method
ActiveCN106115938AHigh degradation activityPromote degradationBiological water/sewage treatmentPhosphateBiological activation
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment, and in particular to preparation method of magnetic biochar loaded photosynthetic bacteria material and a sewage treatment method. The preparation method comprises the steps of: preparing a magnetic nano iron oxide material by a chemical coprecipitation method, conducting activation and expansion culture on photosynthetic bacteria, loading the nano iron oxide particles on the surface of biological carbon material through a self-assembly method to form a magnetic biochar; and loading the photosynthetic bacteria on the surface of the magnetic biochar through a co-incubation method, so as to obtain the magnetic biochar loaded photosynthetic bacteria material. The magnetic biochar loaded photosynthetic bacteria material is co-incubated with sewage for a period of time, so as to realize degradation of COD, ammonia nitrogen and phosphate radical in the sewage. The invention employs the electrostatic binding of high specific surface of the nano magnetic iron oxide and the bacteria with charge on the surface to achieve immobilization of strains, and magnetic iron oxide material has activation on strain enzyme, thereby enhancing the degradation of COD, ammonia nitrogen and phosphate radical by microbes.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for culturing in-vitro fertilization embryo of oocyte collected from living cow or in vitro
The invention relates to a method for culturing an in-vitro fertilization embryo of an oocyte collected from a living cow or in vitro. The method comprises the following steps: collection and in-vitromaturation of the oocyte, wherein the oocyte can be collected in vitro or from the living cow; in-vitro fertilization, wherein mature COCs is cultured in a fertilization culture solution and then themature COCs and sperm suspension are subjected to co-incubation culture; and in-vitro culture of the embryo and cryopreservation in liquid nitrogen. The method has the excellent technical effect as shown in specification.
Owner:天津力牧生物科技有限公司
Preparation method, detection method and application of probe drug composition for determination of metabolic activity of cytochrome P450
InactiveCN102650620AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityComponent separationIn-vivo testing preparationsDrugs solutionMicroparticle
The invention relates to a preparation method, a detection method and application of a probe drug composition for determination of metabolic activity of cytochrome P450. The composition mainly comprises a preparation made with a specific probe with major isoforms of CYP450, i.e. CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4, as an active component. Cocktail probe drug solution is prepared, the probe drug composition is injected into an animal or liver microsomes for in vitro co-incubation, and the concentration of each probe drug is determined to assess the metabolic activity of the CYP1A2, CYP2C9, CYP2C19, CYP2D6, CYP2E1 and CYP3A4. In the early stage of research and development of new drugs, the effects of the drugs on the activity of each isoform of the cytochrome P450 are screened in a high-throughput way, and the interactions of the drugs can be predicted. In the stage of clinical research, the testing can be performed with the probe drug composition in an in-vivo probe method, and the effects of the drugs on the in-vivo metabolic activity of different isoforms of the human liver CYP450 can be examined.
Owner:TIANJIN MEDICAL UNIV
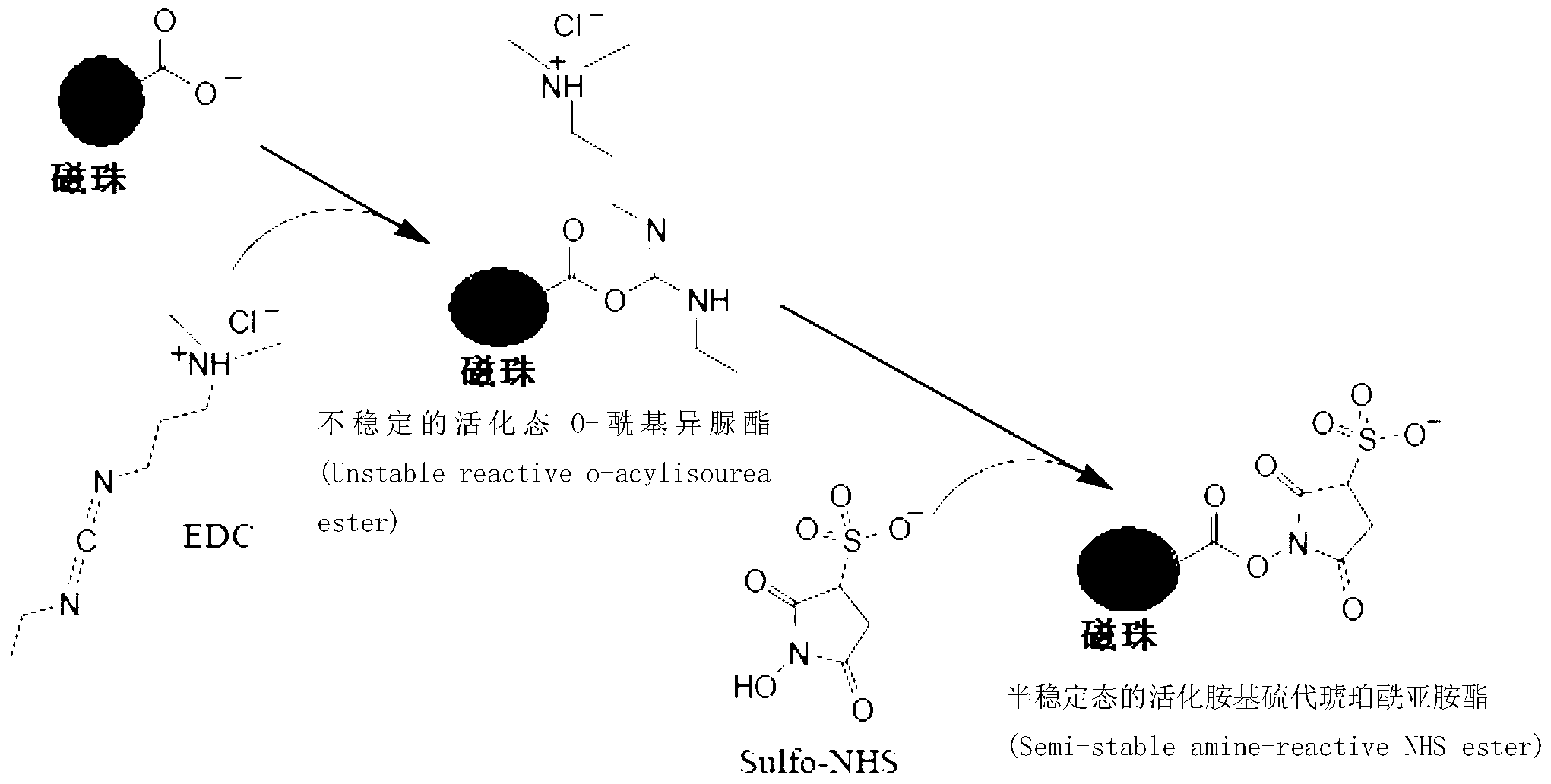
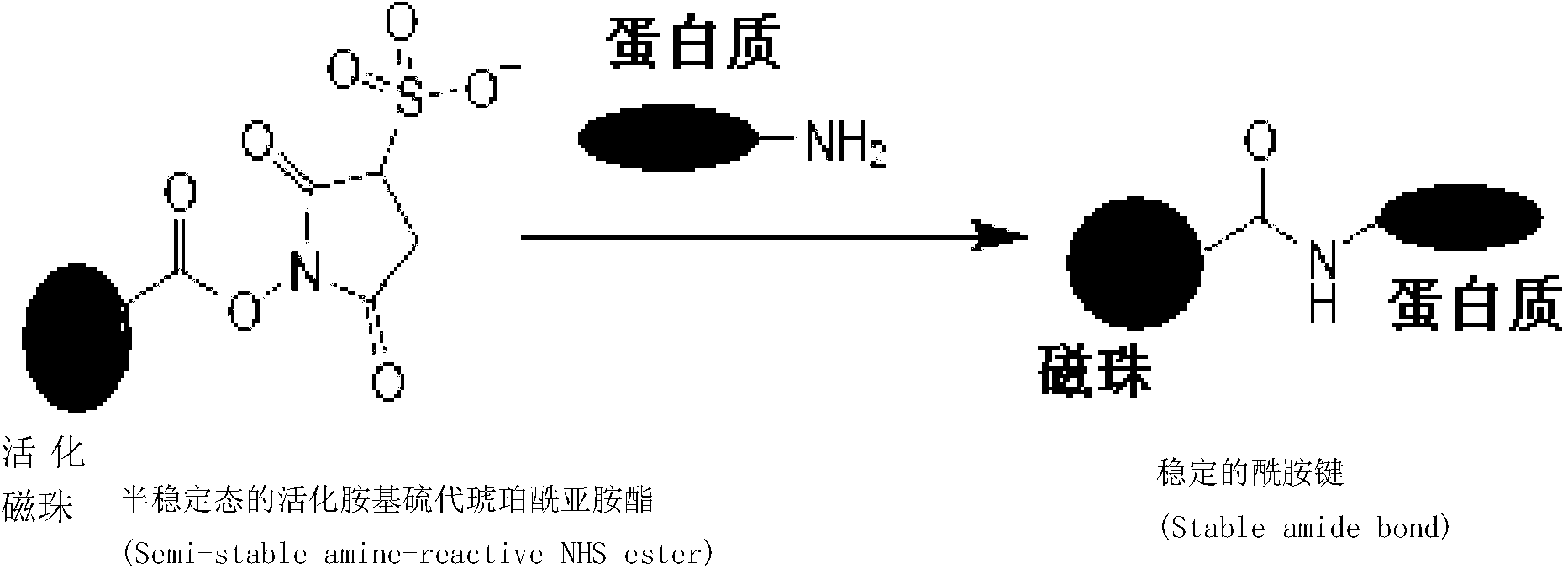
Protein covalent coupling method on surface of magnetic beads
InactiveCN103323603AImprove coupling efficiencyIncrease profitBiological testingProtein insertionMagnetic bead
The invention discloses a protein covalent coupling method on the surface of magnetic beads. The method comprises the steps that: (1) the magnetic beads and an activating agent are subjected to co-incubation, such that activated magnetic beads are obtained; (2) the activated beads are subjected to co-incubation with protein, such that magnetic beads coupled with the protein are obtained; (3) the magnetic beads coupled with the protein are treated by using a blocking solution, such that surface active sites are blocked; and (4) the magnetic beads obtained in the step (3) are subjected to simultaneous vibration and sieving, and the sieved magnetic beads are collected. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high protein coupling efficiency, good repeatability, and versatility. With the method, biological activities of protein coupled on the magnetic beads are not influenced. With the method provided by the invention, the obtained magnetic beads with covalently coupled protein can be used in fields such as immunoassay, biochemical detection, molecular detection, cell typing, and the like.
Owner:CAPITALBIO CORP +1
Method for detecting alkaline phosphatase activity by molybdenum disulfide quantum dot inner-filter effect fluorescence
ActiveCN108414482AAvoid pollutionReduce manufacturing costFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceNa k atpase activity
The invention belongs to the field of nano-particles, and particularly relates to a method for detecting alkaline phosphatase activity by molybdenum disulfide quantum dot inner-filter effect fluorescence. The method includes the steps: firstly, preparing fluorescent molybdenum disulfide quantum dots: taking molybdenum disulfide powder as a raw material, taking ethyl alcohol / water as a solvent, taking inorganic base as a stripping auxiliary and synthesizing the molybdenum disulfide quantum dots by an ultrasonic method; secondly, adding alkaline phosphatase solution into 4-nitrophenyl phosphatedisodium salt (PNNP) and magnesium sulfate alkaline buffer solution, and performing co-incubation; thirdly, adding the alkaline buffer solution into molybdenum disulfide quantum dot solution and performing further co-incubation; fourthly, building a standard work curve for detecting alkaline phosphatase; fifthly, acquiring the activity of the alkaline phosphatase in the solution to be detected according to a standard curve equation. The fluorescent molybdenum disulfide quantum dots have the advantages of stable performance, simple synthesis conditions, low price and the like, and are simple indetection process and high in selectivity and sensitivity when being used for detecting the alkaline phosphatase.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
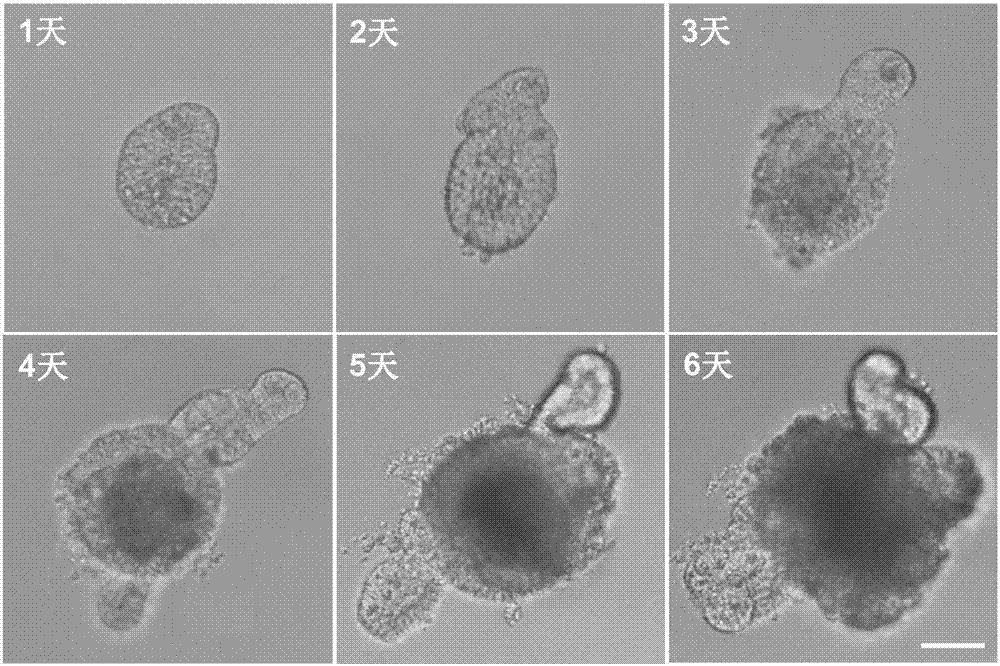
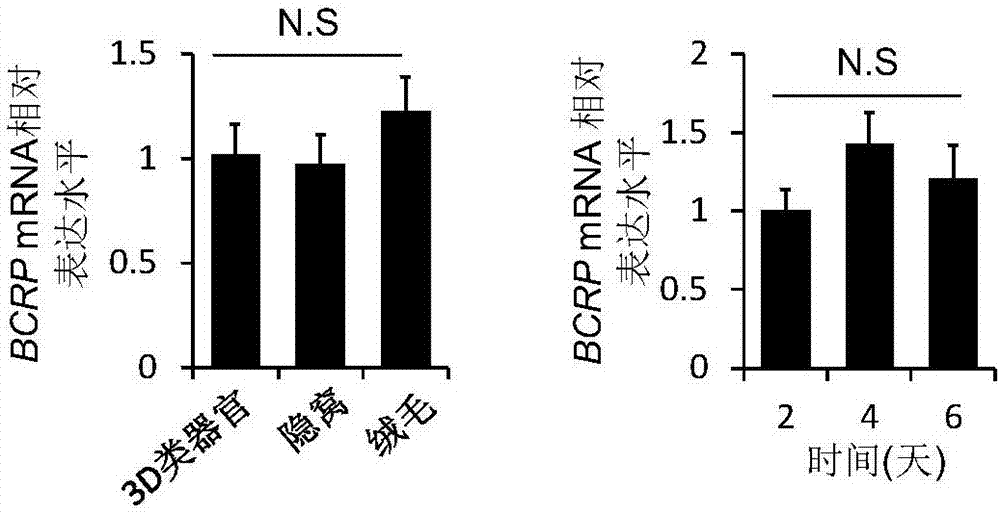
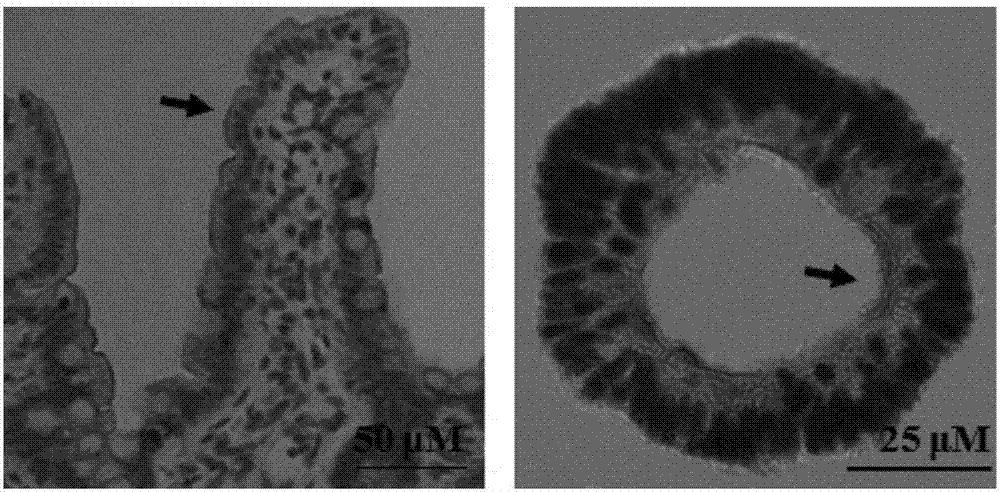
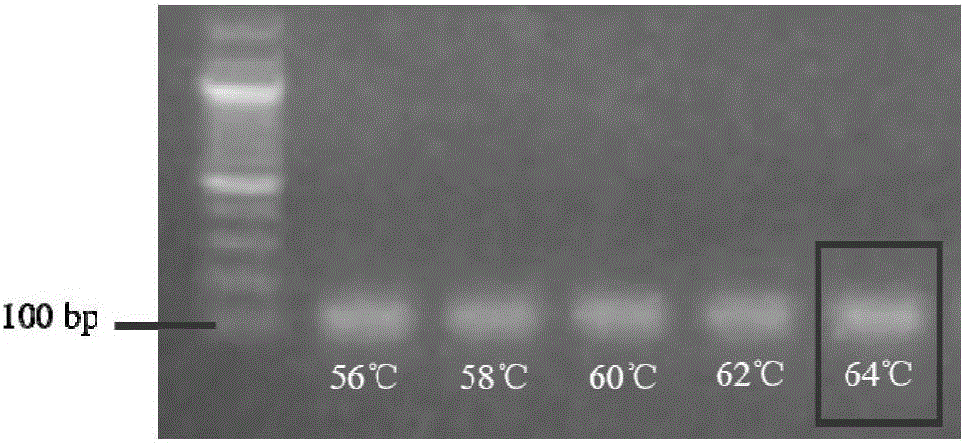
Method for building BCRP (breast cancer resistance proteins) mediated medicine transport models for research on 3D (three-dimensional) organs of small intestines and application
InactiveCN107012116ASimple and fast operationEfficient detectionGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementMatrigelFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for building medicine transport models for research on BCRP (breast cancer resistance proteins) mediation for 3D (three-dimensional) organs of the small intestines of mice. The method includes separating crypts from the small intestines of the mice by means of digestion, suspending the crypts in matrigel and then joining the crypts with cell culture plates and promoting differentiation of the crypts by the aid of ADMEM / F12 media with Respondin-1, m-noggin and m-EGF cell differentiation growth factors to form the 3D organs; carrying out morphologic observation and detecting the expression level of BCRP genes and proteins to verify the feasibility of model theories; carrying out research on the trans-membrane transport activity of BCRP in the 3D organs by the aid of fluorescent substrates Hoechst 33342 of the BCRP and inhibitors Ko143 or YHO-13177 of the fluorescent substrates by co-incubation processes. The method has the advantages that the medicine trans-cell-membrane transport in-vitro models for the research on the BCRP mediation for the 3D organs of the small intestines of the mice are built for the first time, and the method for building the models is easy and convenient to implement and high in detection efficiency and speed and can be widely applied to screening BCRP substrates and inhibitors in an in-vitro manner.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Microfluid system used for detecting circulating tumor cells (CTCs) of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma, and application thereof
The invention discloses a microfluid system used for detecting CTCs of the esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. The microfluid system is prepared through the following steps: 1, preparation of a microfluid pipeline system which is divided into two or more parallel microfluid channels from an inlet, wherein the microfluid channels are provided with a plurality of fishbone structures; 2, etching of a silicon nanowire substrate; 3, surface modification and biotin bio-functionalization of silicon nanowires; and 4, modification of the silicon nanowire substrate and assembling of a PDMS microfluid chip. In use of the system, cells of a to-be-detected sample and 200 [mu]L of a PBS solution of biotin-modified p-EpCAM and p-cKit are subjected to co-incubation for 1 h, and then a co-incubation product is injected into the microfluid system for detection. The microfluid system provided by the invention can recognize and bind to CTCs with extremely low content, and is applicable to traditional immunofluorescence dyeing; obtained detection results and phenotypic analysis results can be subjected to further specific release; so purification of CTCs is realized, and the purity of CTCs is improved so as to meet requirements of gene detection limits.
Owner:无锡准因生物科技有限公司
DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere and preparation and application of DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere and nucleic acid aptamer compound
ActiveCN109745567AHas a specific targeting functionEasy to prepareOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTumor targetAptamer
The invention belongs to the technical field of chemical and biochemical medicines, particularly relates to a DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere, a preparation method of the DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere and a nucleic acid aptamer compound and an application of the DNA fixed nano hydrogel microsphere as a tumor targeting preparation. The preparation method is simple, only a segment of single-stranded DNA is synthesized at one end of the nucleic acid aptamer as a connecting arm when the nucleic acid aptamer is synthesized, and the sequence of the DNA connecting arm and the DNA sequence on the surface of the nano material of the nano hydrogel microsphere can be complemented and paired. One or a plurality of nucleic acid can be matched and connected on the surface of the nano materialat one time by co-incubation in aqueous solution so as to obtain the drug delivery carrier with the specific targeting function. According to the method, one or more nucleic acid aptamers can be connected on the surface of the drug delivery carrier at one time in a base complementary pairing mode; the base complementary pairing can be carried out in aqueous solution; reaction conditions are mild and easy to control; and the preparation process is very simple.
Owner:SHENYANG PHARMA UNIVERSITY
Method of utilizing aptamer molecular switch to detect aflatoxin B1
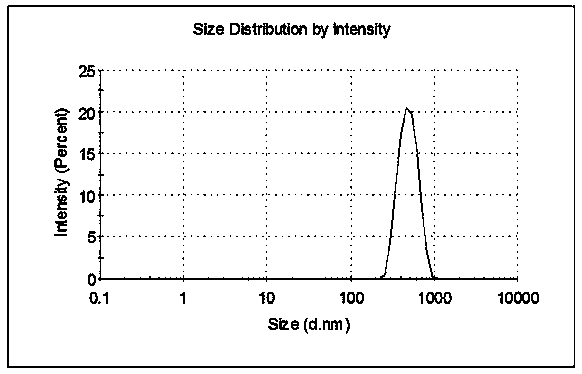
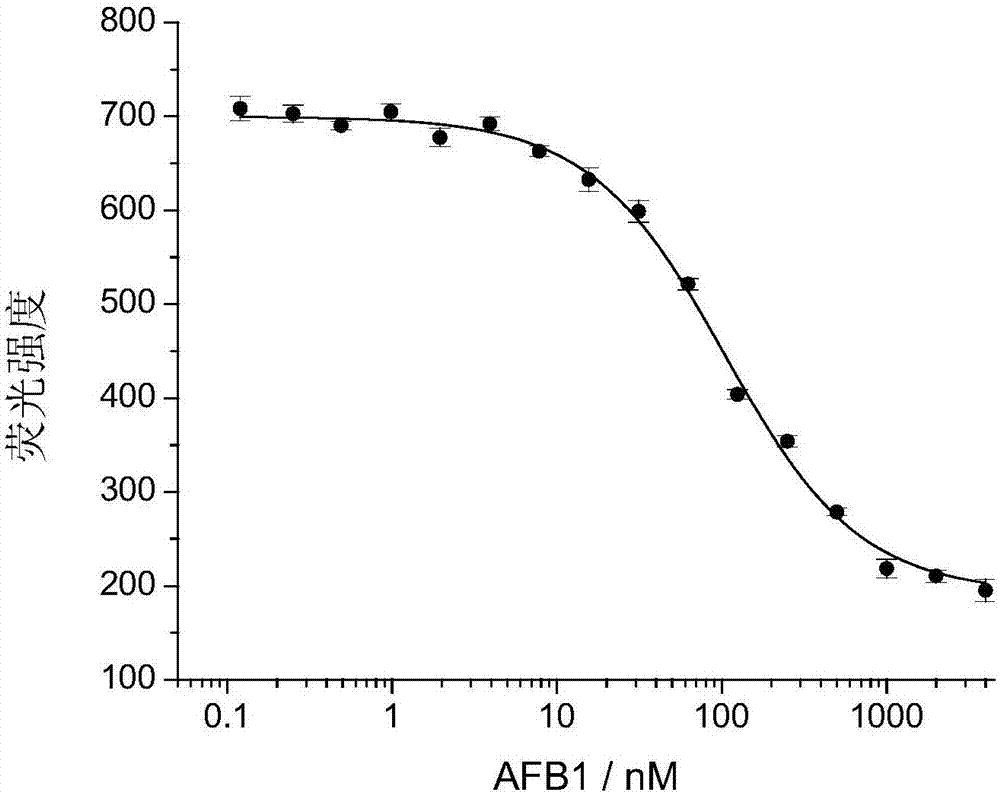
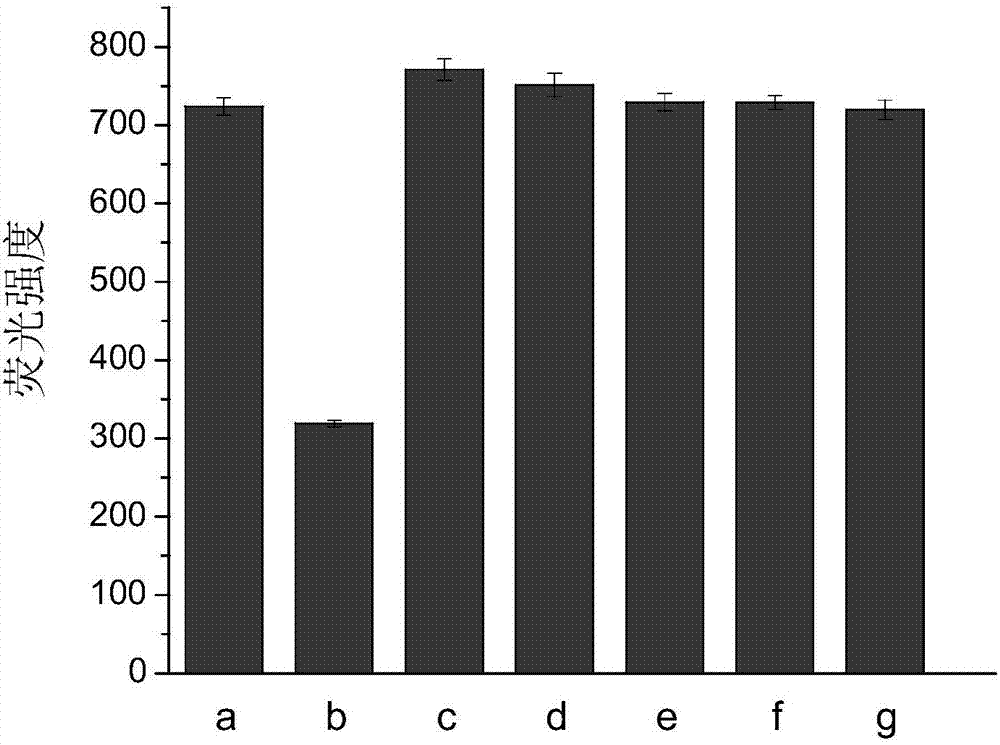
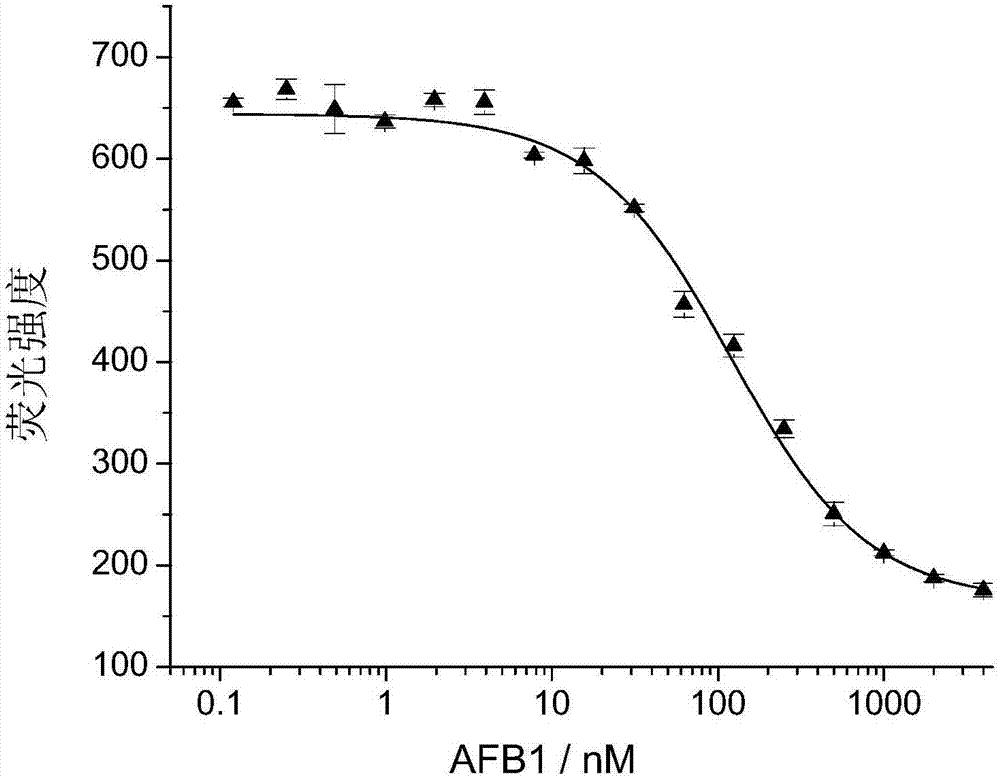
ActiveCN106916822AEasy to introduceRealize detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAptamerCo incubation
The invention discloses a method of utilizing an aptamer molecular switch to detect aflatoxin B1. At first, protection of an aptamer is claimed, and the sequence of the aptamer is represented by the sequence 1 in the sequence table. Then protection of a probe is claim. The probe is obtained by labeling a fluorescent group (FAM) on the 5' terminal of a single chain DNA molecule and labeling a quenching group (BHQ1) on the 3' terminal of the single chain DNA molecule. Protection of a method for detecting aflatoxin B1 is also claimed. The method comprises a step of co-incubating any one of abovementioned probes with a sample to be tested, and if the fluorescent strength is reduced after co-incubation, the sample contains aflatoxin B1. The method has the advantages that aptamer is taken as an affinity ligand and is used to detect aflatoxin B1, the advantages of aptamer can be fully exerted; the provided aptamer molecular switch can generate respond of fluorescence reduction, and the rapid and sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 is realized therefore.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for Determination of Minimum Inhibitory Concentration of Drugs
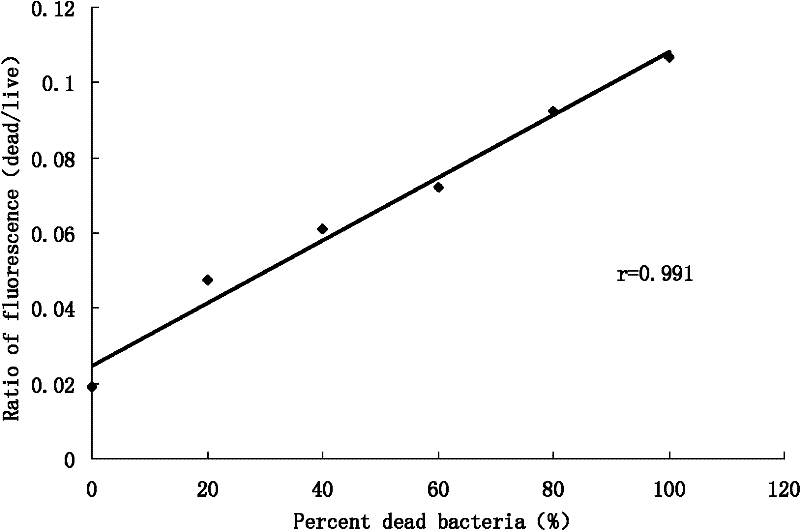
ActiveCN102288586AMIC value is accurateLow costFluorescence/phosphorescenceMinimum inhibitory concentrationConcentration gradient
The invention discloses a method capable of rapidly, simply, conveniently and quantitatively detecting minimal inhibitory concentration, and the method comprises the following steps of: in accordance with the standard of CLSI (Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute) (Version 2010), adding a fresh enterococcus suspension of a certain concentration into a sterile 96-well plate containing concentration gradient antibacterials for co-incubation; upon the ending of the 4-hour incubation, adding a fixed amount of fluorescent dyes SYTOX Green and DAPI (4,6-diamino-2-phenyl indole) to all the wells, protecting the wells from light for 15 minutes at room temperature, reading the fluorescent intensity of the two dyes in the wells by use of a fluorescent microplate reader respectively; after relevant background fluorescence is deducted, drawing a corresponding curve between bacterial fluorescence intensity ratio (Pdead / livel) and concentration of drug (CDrug), and determining the minimal concentration of drug corresponding to the moment the Pdead / livel is no longer fluctuated as the MIC (Minimal Inhibitory Concentration) of the antibiotic to the bacterium. The detection method provided by the invention has the characteristics of being simple, convenient, rapid and objective and being capable of performing mathematic statistics and analysis directly on detected data, becomes a new detection method for determining the minimal inhibitory concentration of antibacterials, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FRIENDSHIP HOSPITAL CAPITAL MEDICAL UNIV
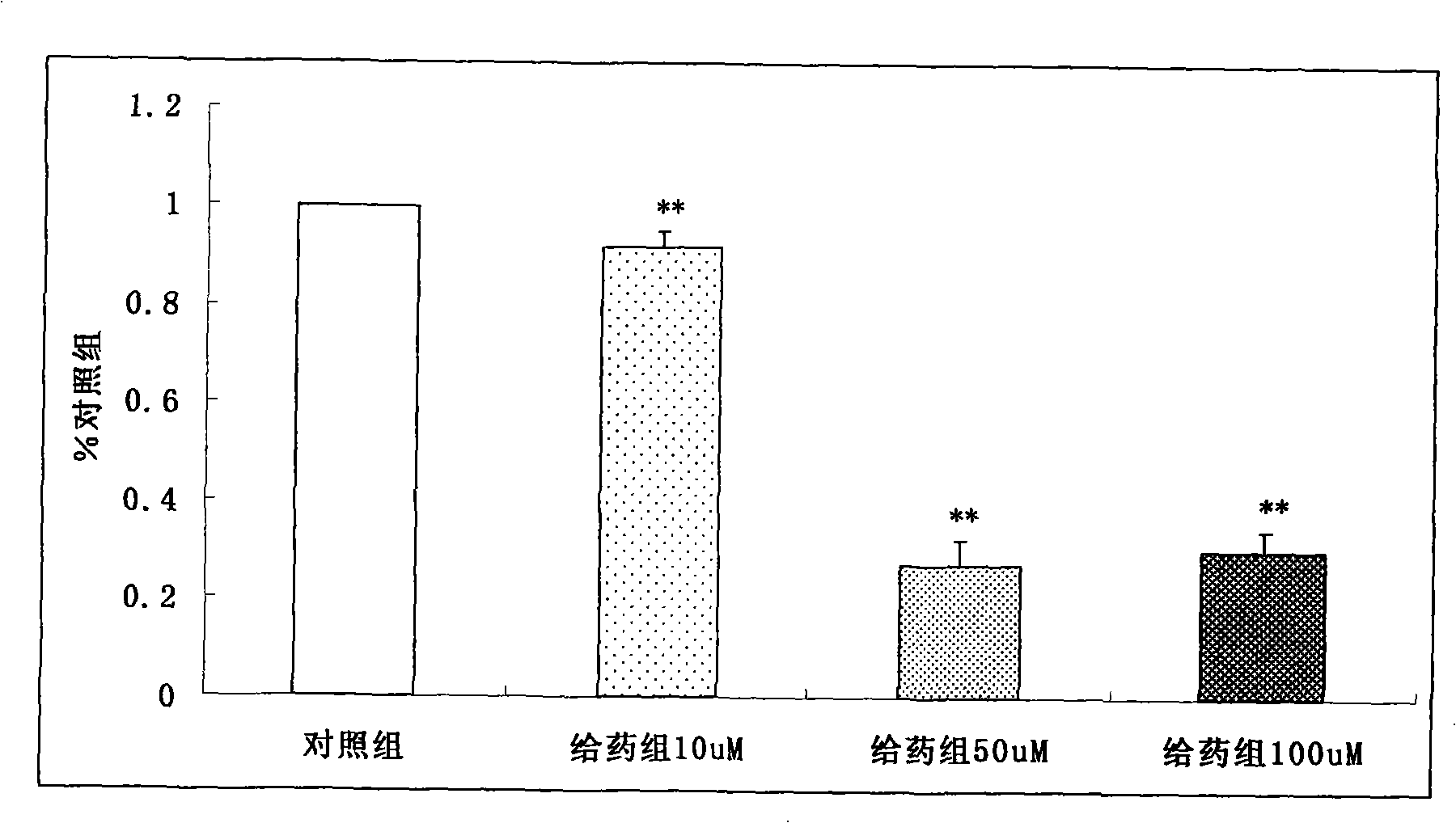
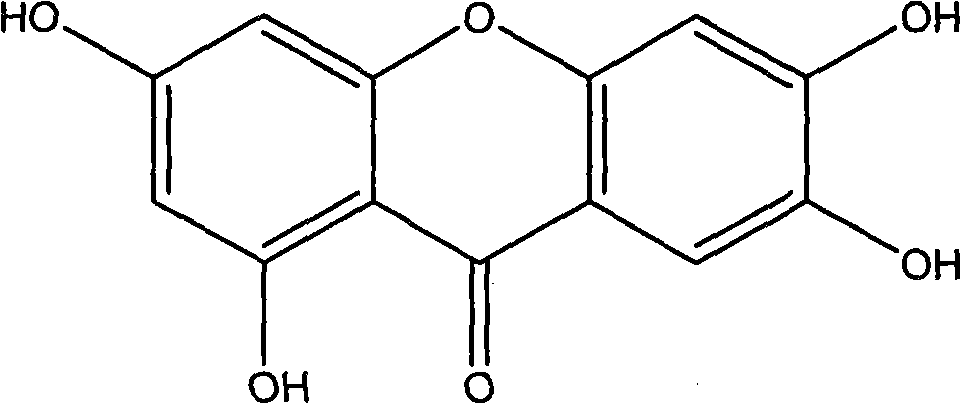
Application of mangiferin in treating type II diabetes and vitro trial model thereof
The invention relates to an application of norathyriol in treating type II diabetes, belonging to the technology field of biopharmaceuticals and molecular biology. After co-incubation of 293A cells and norathyriol for 24 hours, the expression level of uncoupling protein 2 (UCP2) coding gene in 293A cells is remarkably down-regulated. The invention discloses that the norathyriol can be used for inhibiting expression UCP2 gene in 293A cells and can be used for preparing drugs for preventing and treating type II diabetes; and proposes an in vitro test model for treating type II diabetes.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
In vitro formation of congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques to identify anti-plaque therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's and Prion diseases
InactiveUS20020168753A1Test effectivenessCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderCongo redNeuroglycan C
Co-incubation of an amyloid protein with sulfated macromolecules as a method for the formation of amyloid plaques. The amyloid protein may be the beta-amyloid protein or the prion protein or the like. Amyoid plaque formation in one embodiment proceeds in vitro and desireably produces amyloid plaques that stain with Congo red and demonstrate a maltese-cross pattern when viewed under polarized light. The method also produces amyloid plaques that demonstrate an "amyloid star" appearance when viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Sulfated macromolecules include a sulfated proteoglycan selected from the group consisting of perlecan, ~220 kilodalton heparan sulfate proteoglyean, glypican, cerebroglycan, aggrecan, synaptoglycan (SV2PG), syndecan, N-syndecan (also known as syndecan-3), syndecan-1, syndecan-4, neurocan, phosphacan, decorin, biglycan, versican, amphiglycan, lumican, PG-M, PG-M (3), agrin, betaglycan, claustrin, brevican, appican, epican, neuroglycan-C, and fragments thereof. Thw sulfated macromolecule may be a sulfated glycosaminoglycan selected from the group consisting of heparin, heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate, and fragments thereof. An in vivo assay is also presented for selecting a candidate therapeutic agent for inhibiting or disrupting amyloid plaque deposition or persistence. The assay includes a) pre-forming congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques in vitro following incubation of an amyloid protein and a selected sulfated macromolecule, b) using a first cannula and osmotic pump to continuously infuse for a selected duration the pre-formed congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques into a tissue or organ, c) changing the first cannulae and osmotic pump with a second cannulae and osmotic pump to administer the candidate therapeutic, and d) detecting the candidate therapeutic's ability to disrupt, reduce, or eliminate congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaque deposition / persistence in the tissue or organ.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
In vitro formation of congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques to identify anti-plaque therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's and Prion diseases
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Three-dimensional graphene based proportional signal amplification aptasensor, preparation method and application thereof
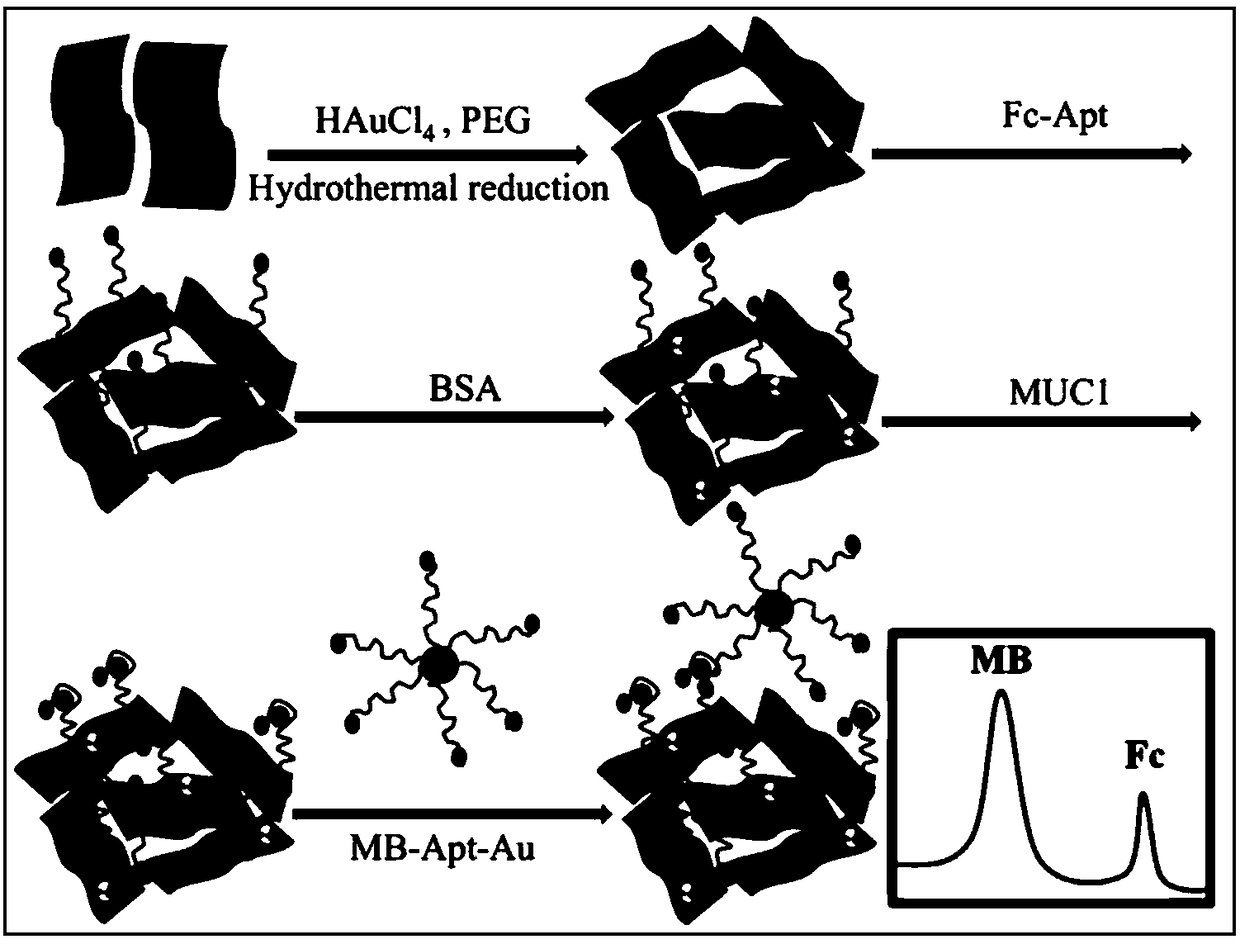
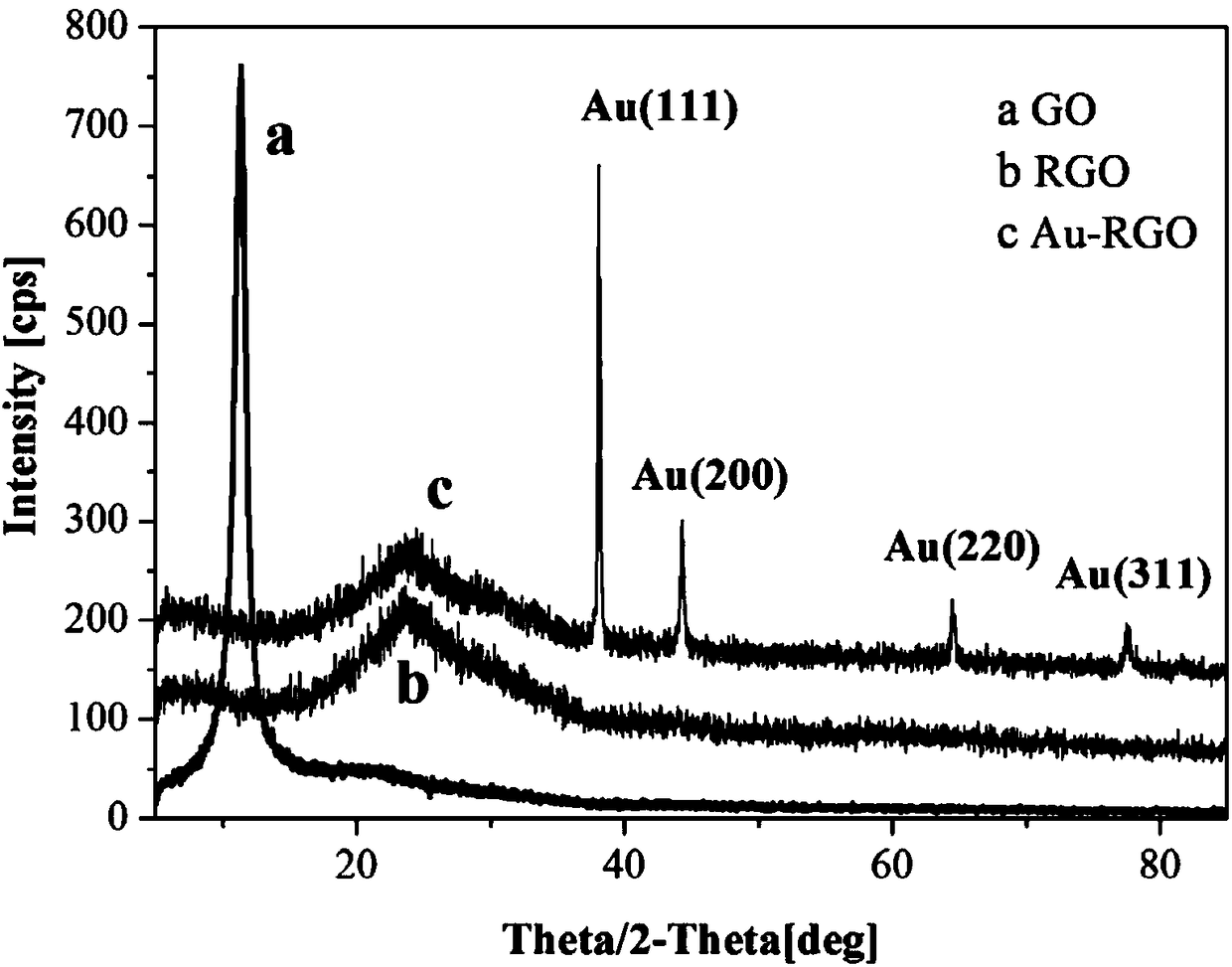
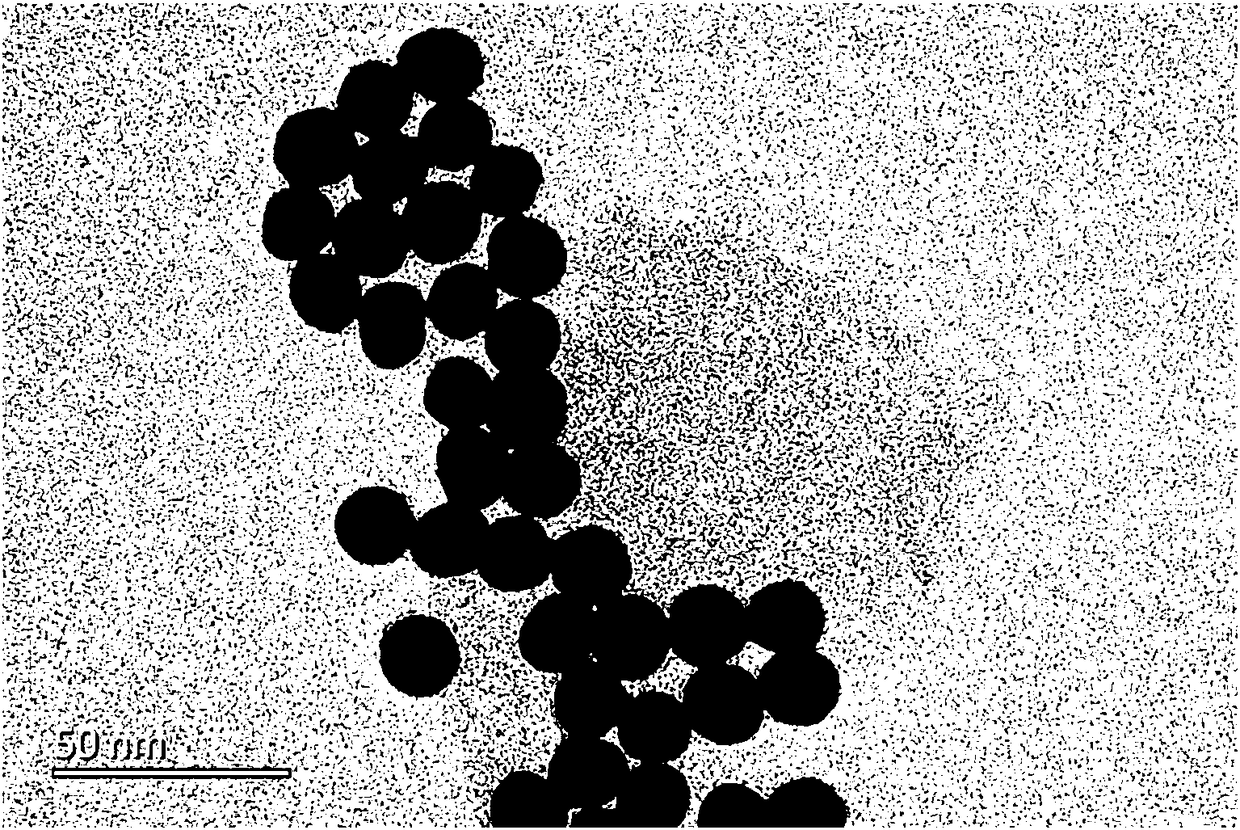
ActiveCN108490053ALarge specific surface areaImprove mechanical propertiesMaterial electrochemical variablesMethyl blueBovine serum albumin
The invention discloses a preparation method of a three-dimensional graphene based proportional signal amplification aptasensor. The method adopts a gold nano-three-dimensional graphene compound as the modified electrode substrate material, then grafts ferrocene-labeled mucin aptamer to gold nanoparticles on a three-dimensional graphene surface, and employs bovine serum albumin to close non-specific sites on a sensing interface, and when the ferrocene-labeled aptamer captures mucin to an electrode surface, a methyl blue labeled mucin aptamer-gold nano compound is employed for co-incubation, thus obtaining the aptasensor for electrochemical detection. According to the invention, the aptamer is employed to construct a sensing interface, and is conducive to enhancing the stability and selectivity of the sensor; at the same time, the two electroactive substances ferrocene and methyl blue are introduced into the sensing system to play an internal reference role and a signal amplification role respectively. The construction method of the proportional signal amplification aptasensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, good stability, simple method, high cost-effectiveness, etc.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Dimensional flow liquid phase array detection method of fusion protein in leukemia cells
ActiveCN102353793AEliminate errorsBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceFusion Protein ExpressionAntileukemic agent
The invention relates to a dimensional flow liquid phase array detection method of fusion protein in leukemia cells, characterized in that: a microballoon 1 fluorescently labeled by FITC or Alexa Fluor 488 coated by fusion protein capture antibody and a microballoon 2 fluorescently labeled by FITC or Alexa Fluor 488 with another conentration coated by fusion protein capture antibody form a dimensional flow liquid phase array for detecting fusion protein in leukemia cells, after the co-incubation of the microballoon 1, the microballoon 2 , the fusion protein, a reported antibody and / or a secondary antibody fluorescently labeled by PE, a flow cytometry is used for detecting the dimensional flow liquid phase array, and the fusion protein expression value is expressed as a ratio of the PE fluorescence intensity of the microballoon 1 to the PE fluorescence intensity of the microballoon 2. The method can be applied in the biomedicine research fields, such as leukemia pathology, molecular diagnosis, and discovery of anti-leukemic medicines. The method has the advantages of effective elimination of system error, rapidness, and accuracy.
Owner:山东济清科技服务有限公司
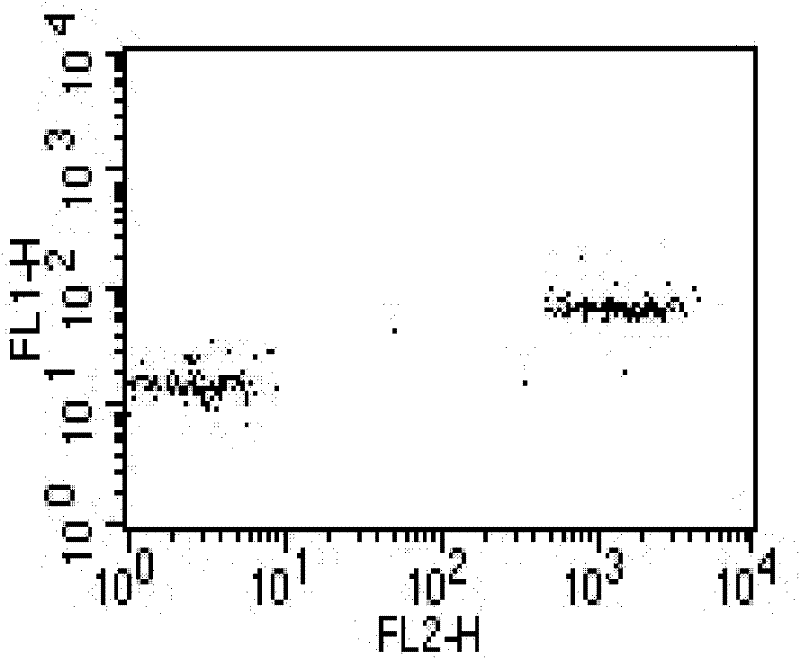
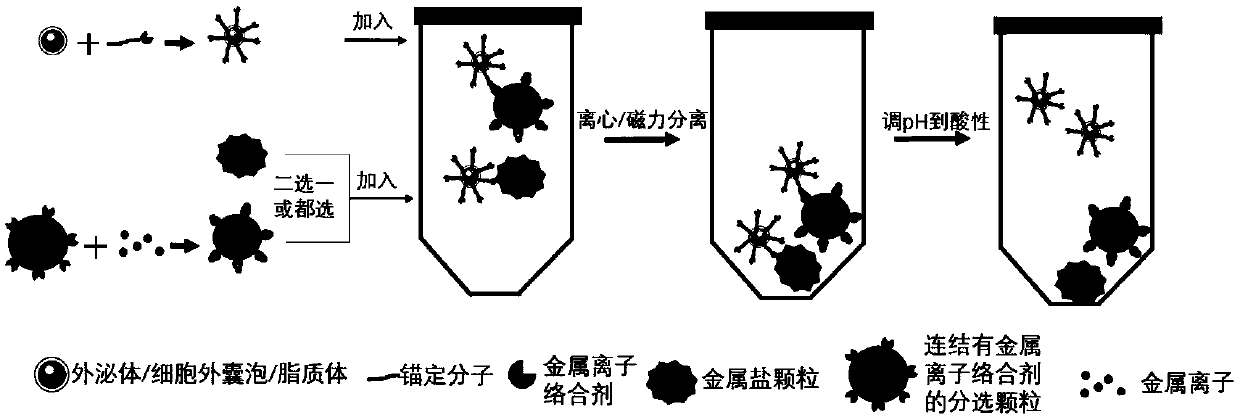
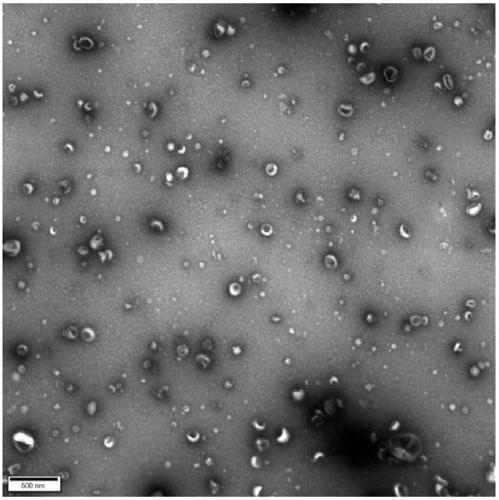
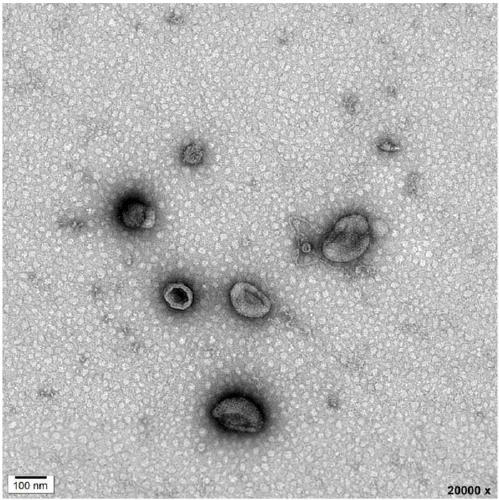
Method for separating extracellular vesicles based on metal ion complexing agent
InactiveCN109576207AEfficient separationEasy to operateCell dissociation methodsExtracellular vesicleChemical physics
The invention discloses a method for separating extracellular vesicles based on a metal ion complexing agent. The method comprises the steps of performing co-incubation by using an anchoring molecule-metal ion complexing agent molecular complex and liquid which is to be separated and contains the extracellular vesicles, and anchoring the molecular complex onto the extracellular vesicles; mixing sorted particles or salt particles of metal ions with the extracellular vesicles linked with the molecular complex, and incubating to enable the extracellular vesicles to be linked with the sorted particles (or the salt particles); separating, re-suspending a separated product, and adding an eluent to separate the extracellular vesicles from the sorted particles (or the salt particles); and separating out the sorted particles (or the salt particles) to obtain the separated extracellular vesicles remaining in a remaining solution. The method can realize the efficient separation of the extracellular vesicles, does not have special requirements for equipment, and is low in cost and wide in application scope; and exosome obtained by separation is high in purity, and a reagent added in a separating step does not affect the subsequent analysis or application.
Owner:贺川江
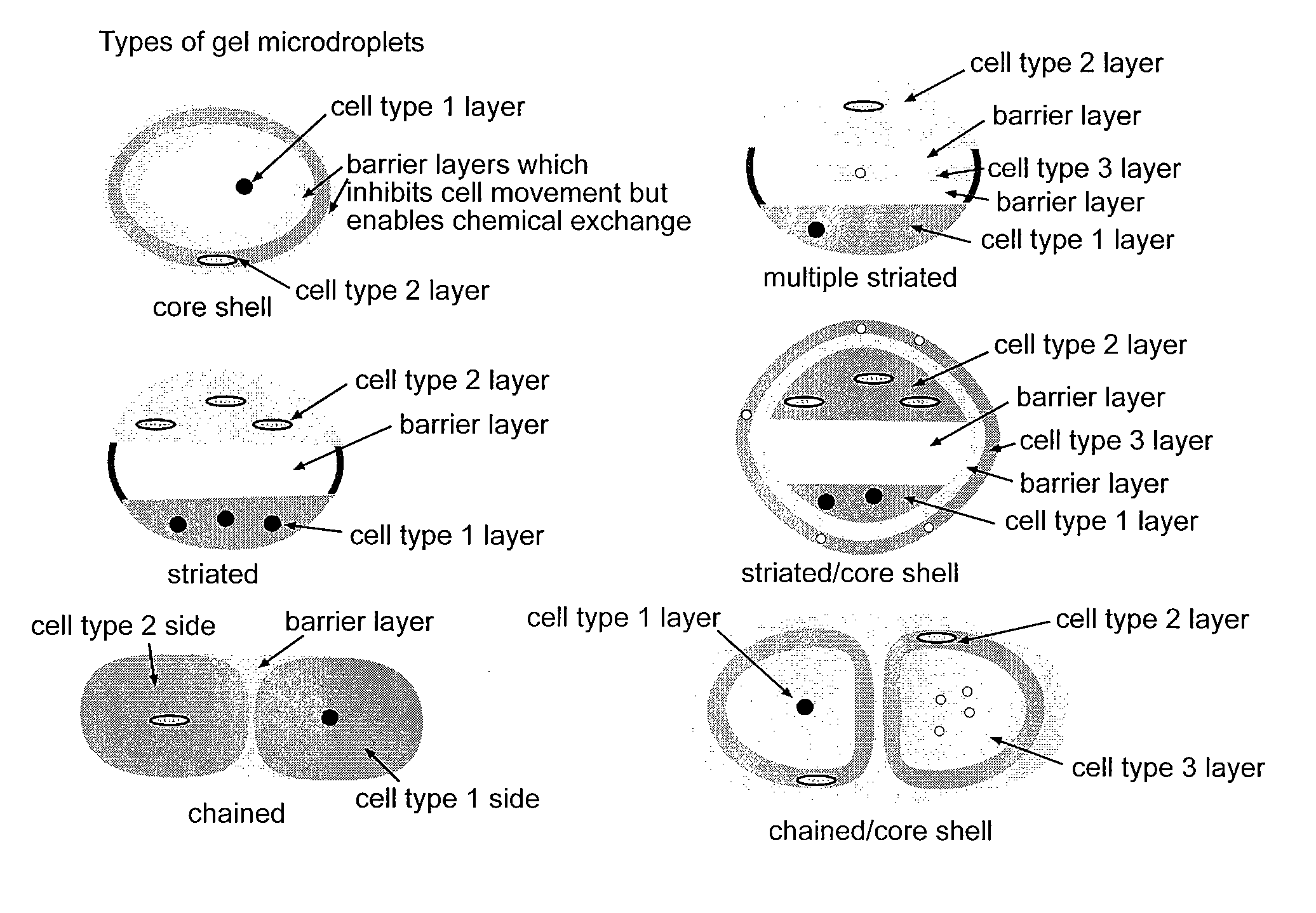
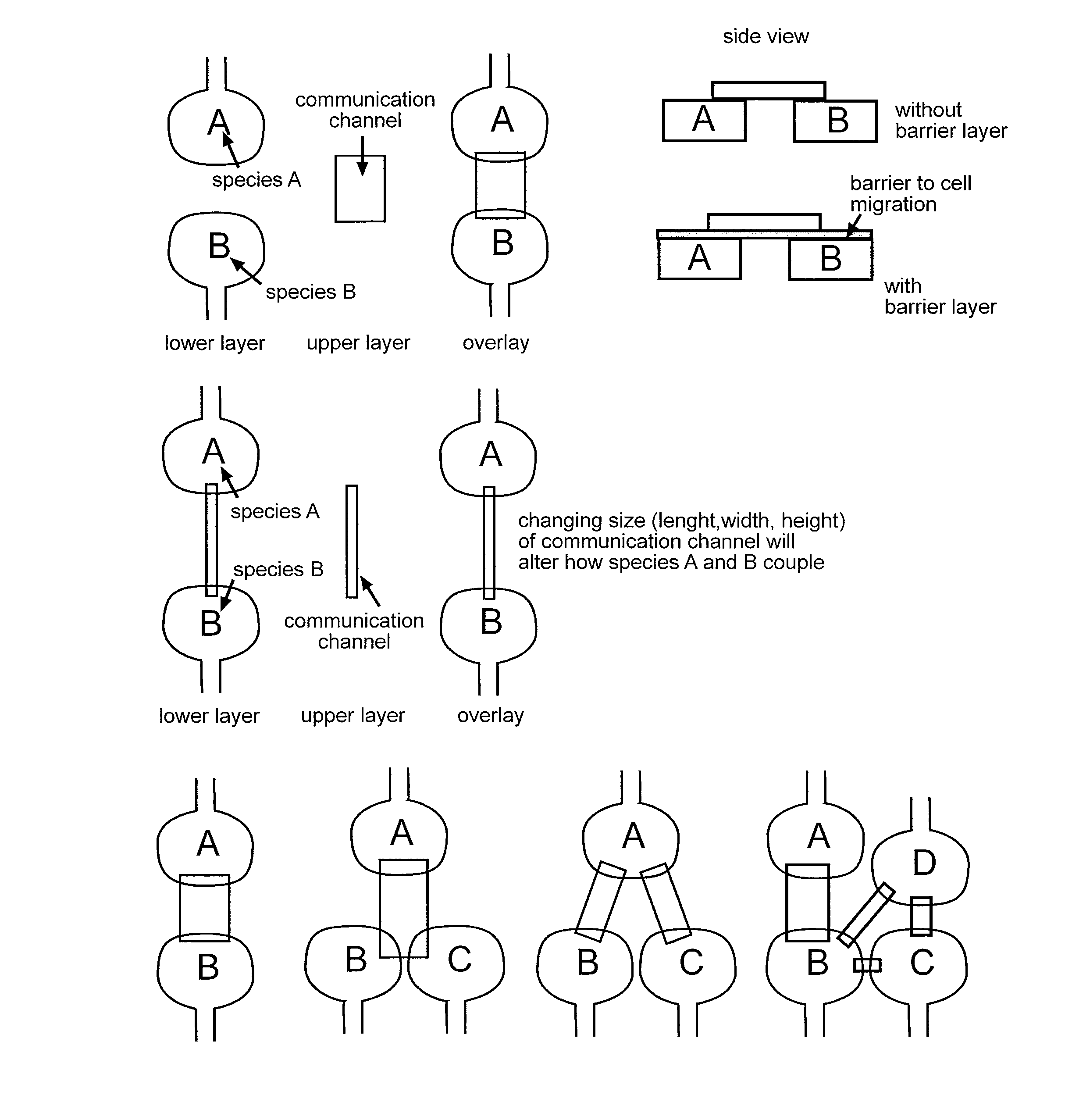
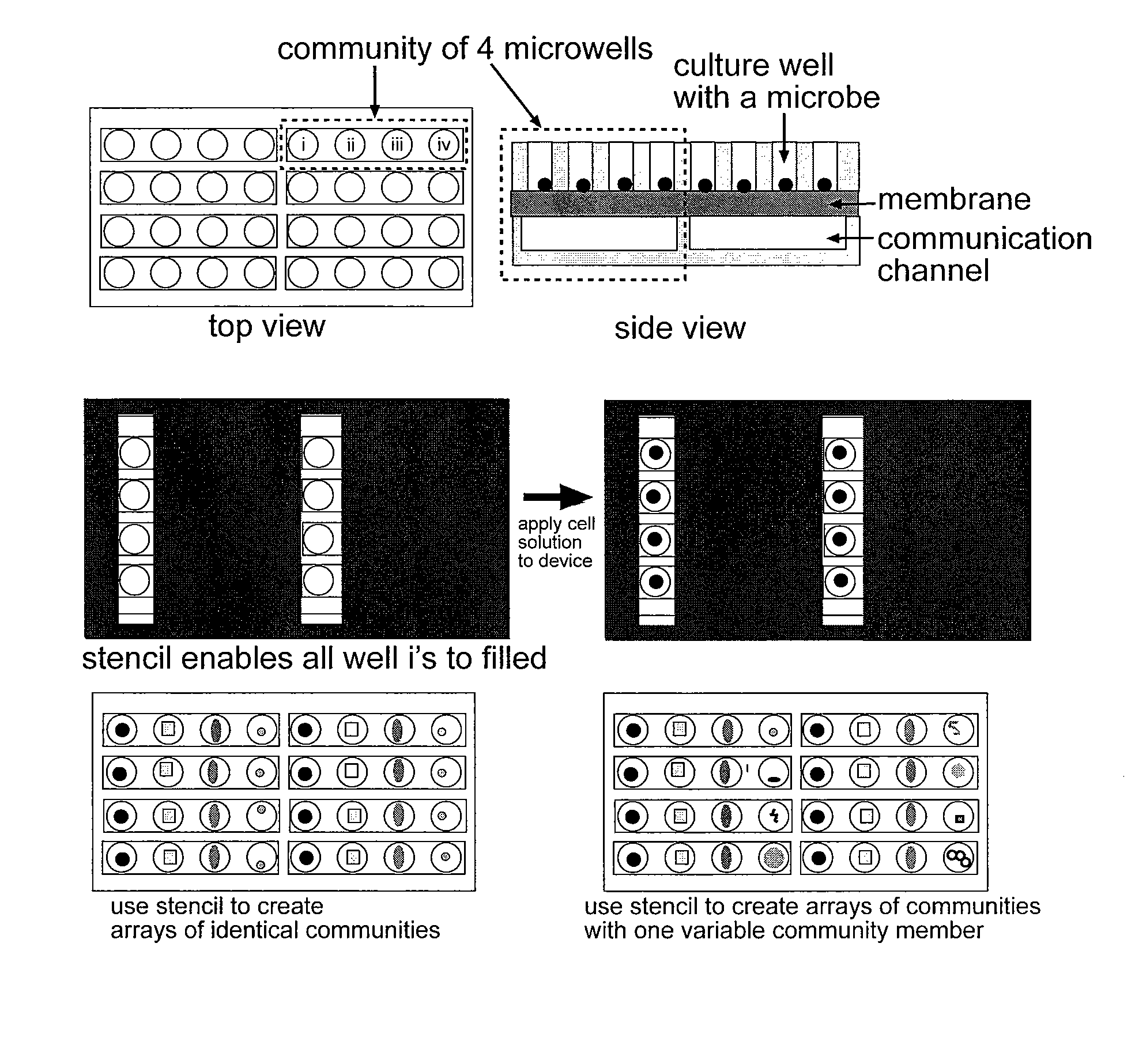
Co-incubating confined microbial communities
ActiveUS20100317085A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroorganismCo incubation
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
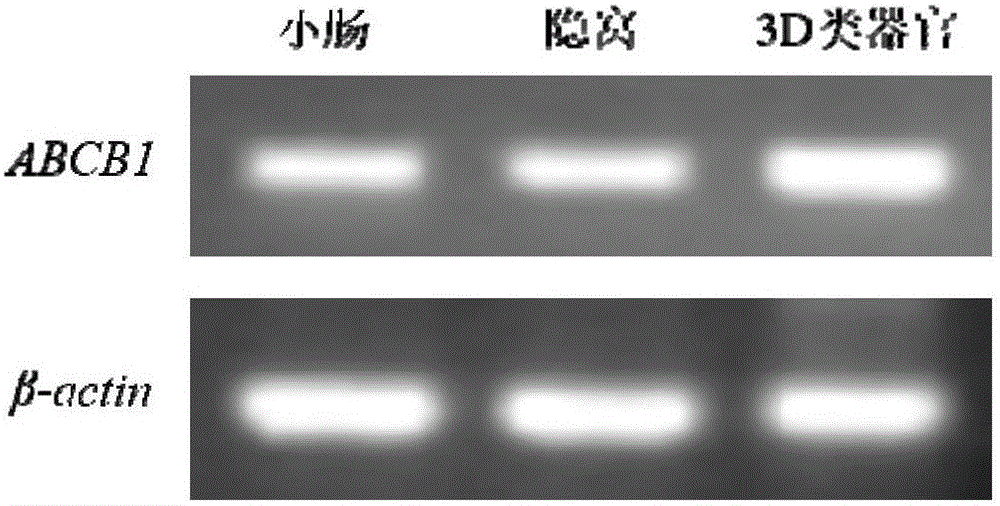
Method for building P-glycoprotein research models based on human small intestine 3D (three-dimensional) organoid and application of P-glycoprotein research models based on human small intestine 3D organoid
ActiveCN105950539AEfficient methodFast wayGastrointestinal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsMatrigel
The invention discloses a method for building P-glycoprotein (P-gp) research models based on human small intestine 3D (three-dimensional) organoid. The method includes inoculating human small intestine crypts in matrigel at first, adding ADMEM / F12 culture media with specific growth factors into the matrigel and cultivating the human small intestine crypts to form 3D organoids; carrying out morphological observation and detecting expression of P-gp from mRNA [messenger RNA (ribonucleic acid)] and protein level; researching influence of Verapamil and Mitotane on Rh123 transportation by the aid of a co-incubation process by Rhodamine 123 (Rh123) which is used as a substrate. The method has the advantages that the P-glycoprotein research models based on human small intestine 3D organoid can be applied to P-gp-mediated medicine transport research and also can be widely applied to in-vitro high-throughput screening on P-gp inhibitors, and the method is high in efficiency and speed.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting aflatoxin B1 by enzyme-labeled aptamer
ActiveCN107192816AQuick analysisRapid analysisColor/spectral properties measurementsBiotin-streptavidin complexStreptavidin
The invention discloses a method for detecting aflatoxin B1 by enzyme-labeled aptamer. The method sequentially includes the steps: (1) taking a coated microporous plate, adding a sample to be detected and a specific probe for co-incubation and then washing the microporous plate; (2) detecting the aflatoxin B1 by detecting corresponding signals of the specific probe. The coated microporous plate is a microporous plate coated with aflatoxin B1-BSA conjugates, the specific probe is a compound of a first element and a second element, the first element is a substance obtained by connecting biotin to the tail end of the aptamer specifically combined with the aflatoxin B1 by the aid of triethylene glycol serving as a connecting arm, and the second element is horseradish peroxidase-labeled streptavidin. The enzyme-linked aptamer analysis method has the advantages of simplicity, rapidness and high sensitivity, a plurality of samples can be rapidly analyzed, a detection kit can be made, and the method has a great application prospect in AFB1 analysis detection.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for preparing endothelial progenitor cell capturing bracket for gene modification and regulation
InactiveCN101695587AInhibition of differentiationPrevent proliferationSurgeryCoatingsPercent Diameter StenosisGene Modification
The invention provides a method for preparing an endothelial progenitor cell capturing bracket for gene modification and regulation, which comprises the following steps: 1, preprocessing a bare bracket; 2, preparing an endothelial progenitor cell antibody bracket; 3, combining Caspase genes and specific promoter gene segments differentiated from smooth muscle cells in a gene recombination way and then combining the composition of the Caspase genes and the specific promoter gene segments and eukaryotic expression vectors pEGFPC2 or pcDNA3.1 in the gene recombination way to obtain fusion genes; and 4, dissolving the fusion genes obtained in the step 3 in de-ionized water solution to obtain solution of which the concentration of the fusion genes is 10 to 100 mg / ml, placing the endothelial progenitor cell antibody bracket obtained in the step 2 into the solution for co-incubation at 4 DEG C for 12 minutes, taking the endothelial progenitor cell antibody bracket out, naturally airing the endothelial progenitor cell antibody bracket in a super clean bench for 2 to 6 hours and storing the endothelial progenitor cell antibody bracket at 4 DEG C. The method has the advantages of dual functions of resisting restenosis and protecting endothelial repair.
Owner:上海中山医疗科技发展有限公司 +1
HPV (human papillomavirus) peptide/DC (dendritic cell) mixed vaccine and preparation thereof
InactiveCN102008721APromote maturityImprove the level ofViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsAdjuvantHuman papillomavirus
The invention provides an HPV (human papillomavirus) peptide / DC (dendritic cell) mixed vaccine prepared in the presence of a TLR (toll-like receptor) agonist. The mixed vaccine comprises one part of HPV11E77-15, one part of mouse bone marrow-derived dendritic cells which are cultured in vitro and one part of TLR9 agonist as an adjuvant, wherein the dendritic cells are extracted from mouse bone marrow and further cultured in vitro, the co-incubation with one section of HPV11E7CTL (cytotoxic T lymphocyte) epitope peptide with strongest immunogenicity is firstly carried out, the co-incubation with the TLR ligand CpG and the like is further respectively carried out for promoting the maturation of the DC, the degree of maturation can be confirmed by detecting the change of a marker on the surface of the DC after incubation, and the DC vaccine which is simulated to mature can be used for immunizing mice. The TLR ligand and the HPV11E7 peptide are utilized jointly to promote the degree of maturation of the DC, the level of TNF-alpha (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) and IFN-gamma (immunoreactive fibronectin-gamma) of factors of secretory cells of T cells can be particularly improved after combination of the CpG, and the HPV peptide / DC mixed vaccine can be used for preventing and treating genital warts and cervical cancer.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for measuring 25-hydroxyvitamin D
ActiveCN109188003AMeet the requirements of detection accuracyBiological testingBiotin-streptavidin complexBlood plasma
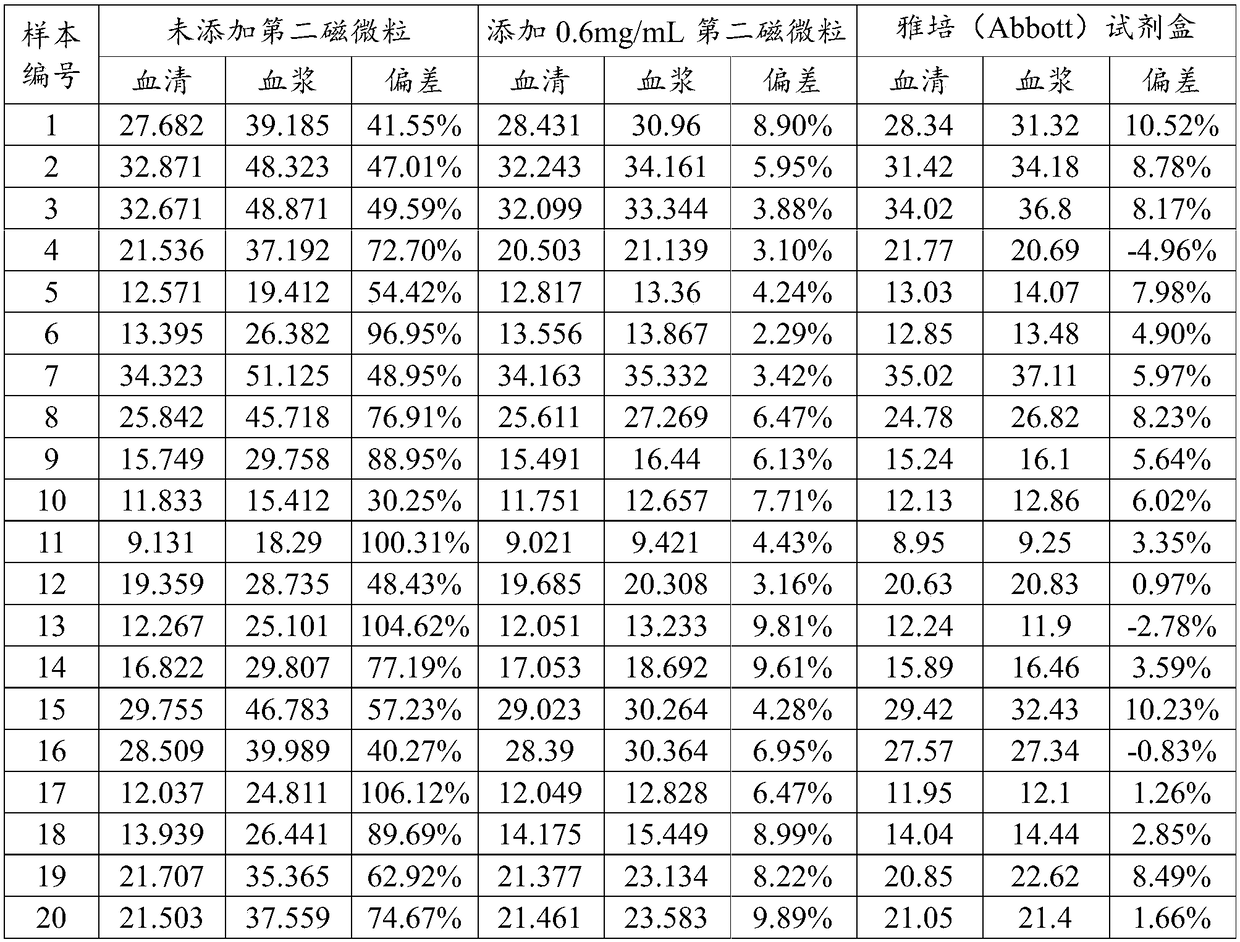
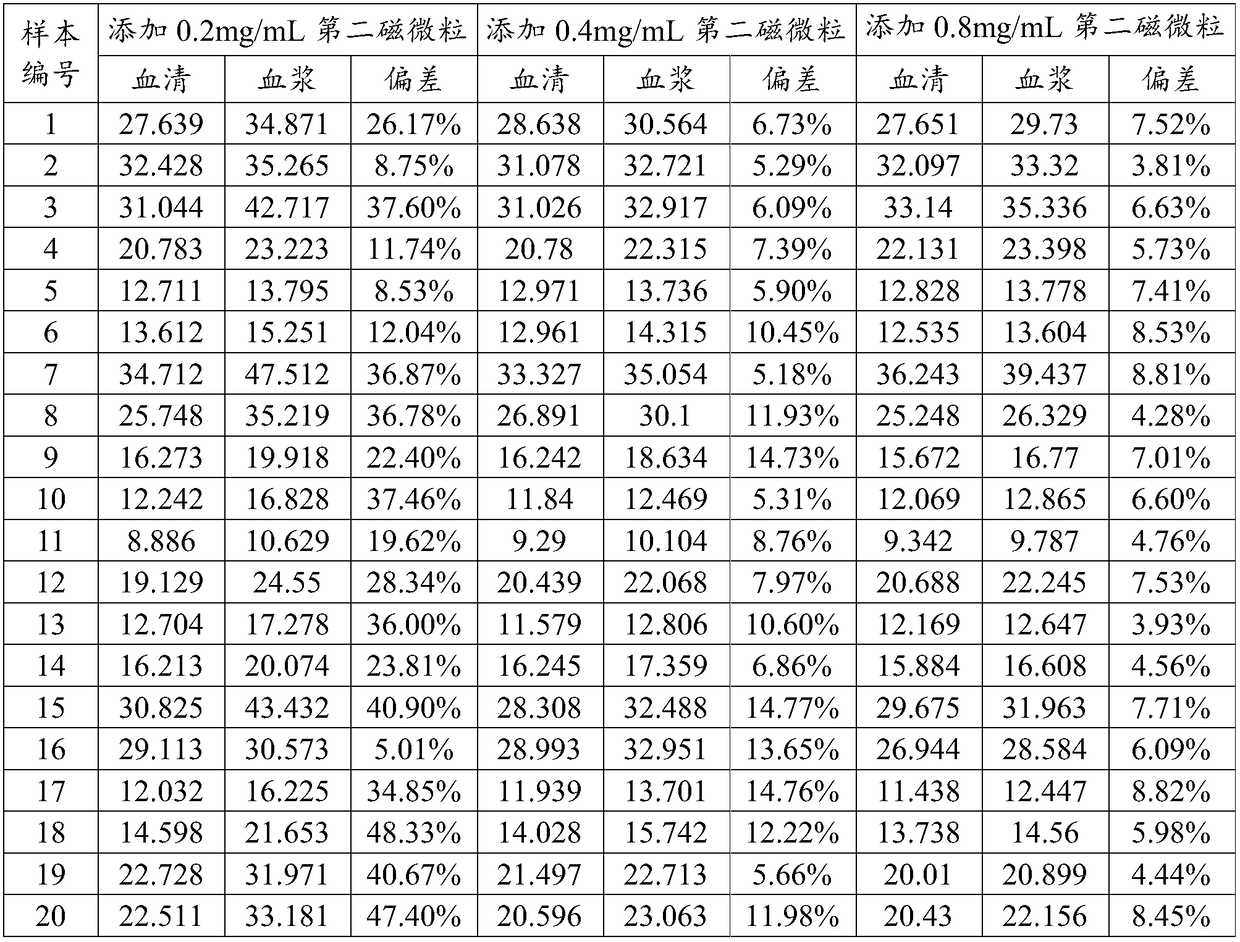
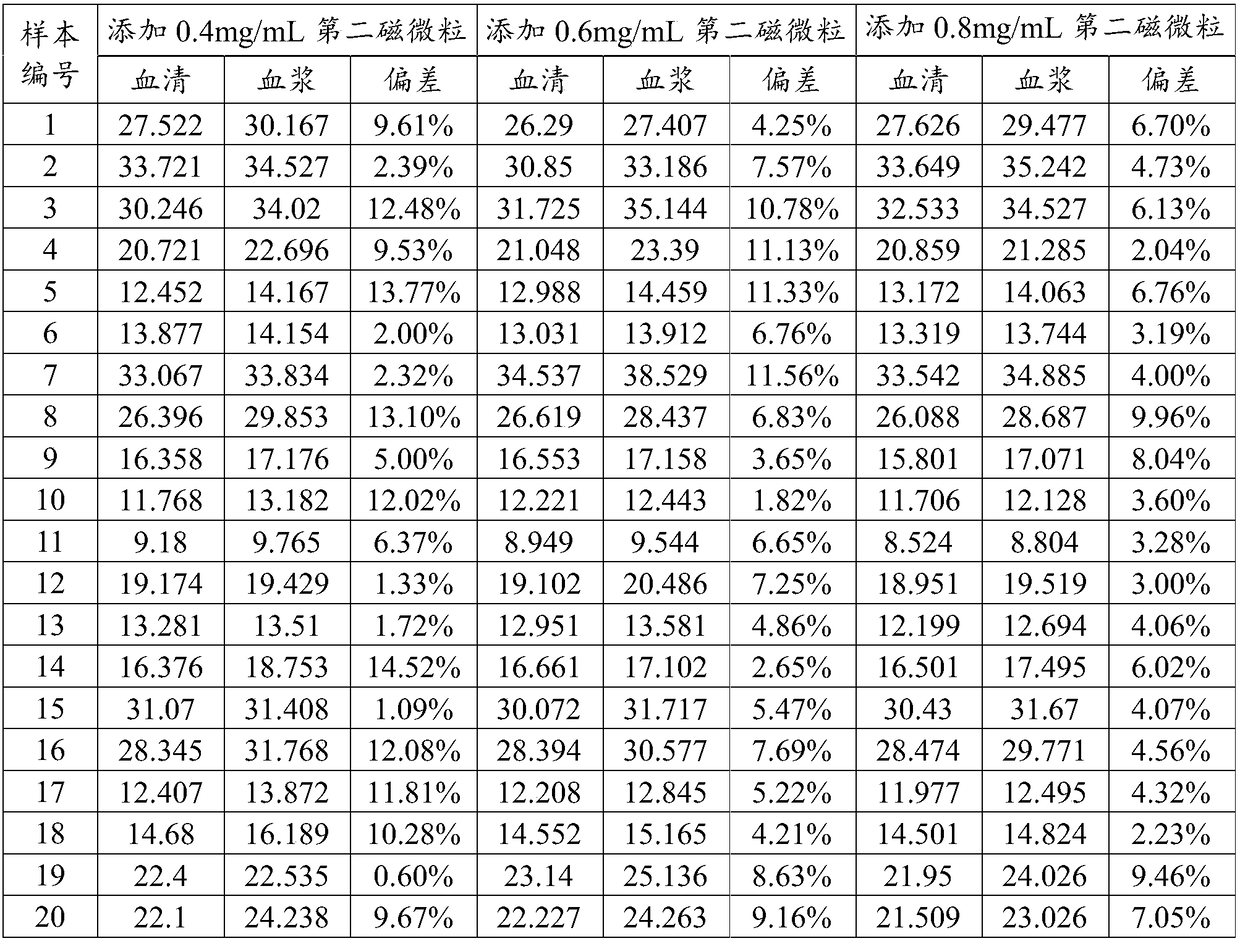
The present application discloses a method for measuring 25-hydroxyvitamin D. The method comprises the following steps: using a first reagent and a second reagent to co-incubate with a biological sample, wherein the first reagent comprises a first magnetic micro particle and a second magnetic micro particle in an acidic buffer solution, wherein the first magnetic micro particle is coated with a streptavidin magnetic micro particle; the second magnetic micro particle is the magnetic micro particle different from the first magnetic micro particle; the second reagent comprises a 25-hydroxyvitaminD antibody marker; further adding a third reagent comprising biotinylated 25-hydroxyvitamin D for co-incubation; separating the magnetic micro particles; adding a luminescent substrate and detectingthe luminescence intensity. The method of the present invention is simultaneously applicable to detection of 25-hydroxyvitamin D in serum and plasma samples without the need of additional sample processing reagents and additional sample processing steps as well.
Owner:SICHUAN MACCURA BIOTECH CO LTD
Lipidosome medicine carrying method
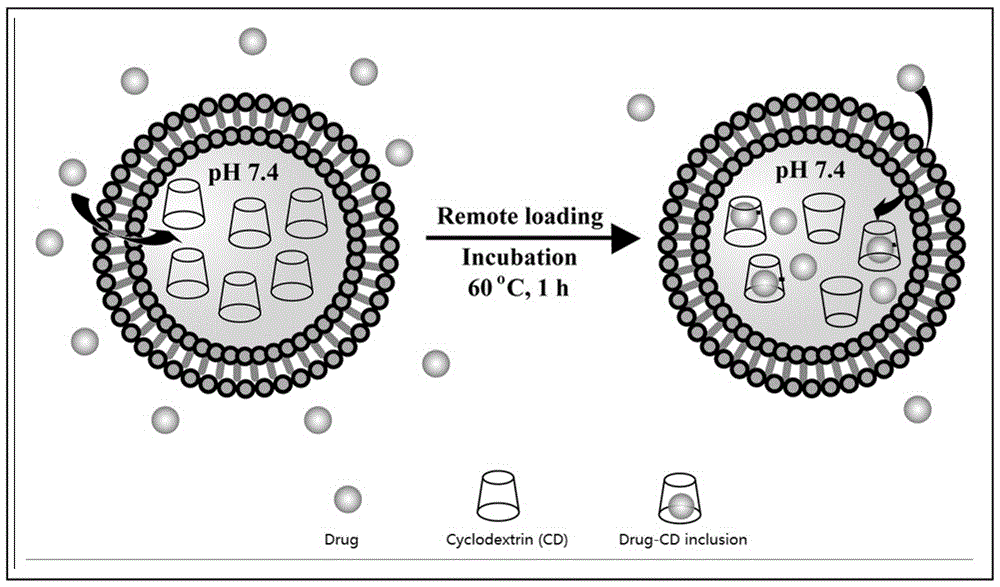
InactiveCN105943502AImprove stabilityStability is good for maintainingPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLiposomal deliveryMass ratioCo incubation
The invention relates to a lipidosome medicine carrying method. The method comprises the steps of 1, preparing cyclodextrin-encapsulated blank lipidosome, wherein the cyclodextrin-encapsulated blank lipidosome is lipidosome in which medicine to be encapsulated is not encapsulated but cyclodextrin is encapsulated, and the mass ratio of cyclodextrin to a lipidosome membrane material is 1:(5-15); 2, removing free cyclodextrin; 3, obtaining medicine-carrying lipidosome after co-incubation of the medicine to be encapsulated and the cyclodextrin-encapsulated blank lipidosome. The method has all the advantages of an ion gradient method, and also has the advantages that application range is wide, and limitation of medicine dissociation or complexing property is avoided; stability is high, and the pH of solution is neutral, so that the stability of components easy to hydrolyze such as phospholipid can be maintained; cyclodextrin is a polysaccharide compound, and integrity of a phospholipid membrane during freeze-drying can be maintained easily.
Owner:ANHUI MEDICAL UNIV
Method for promoting sheep in-vitro embryo development by using follistatin
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering, and relates to a method for promoting sheep in-vitro embryo development by using follistatin, which comprises the following steps: (1) acquiring a slaughtered sheep ovary; (2) extracting follicles for later use; (3) culturing selected oocytes in a CO2 incubator, and adding into in-vitro fertilization solution drops; (4) adding the in-vitro fertilization drops, and carrying out co-incubation with the oocytes; (5) taking out the early embryo, transferring into a 10 mu g / L follistatin in-vitro culture solution, washing 3-4 times, and culturing for 24-26 hours; and (6) taking out the embryo, washing with the in-vitro culture solution, calculating the merogenesis rate, and calculating the blastula rate after culturing for 144-168 hours. By using the follistatin to treat the early embryo subjected to sheep oocyte in-vitro fertilization, the method can obviously enhance the in-vitro embryo development blastula rate.
Owner:新疆畜牧科学院生物技术研究所
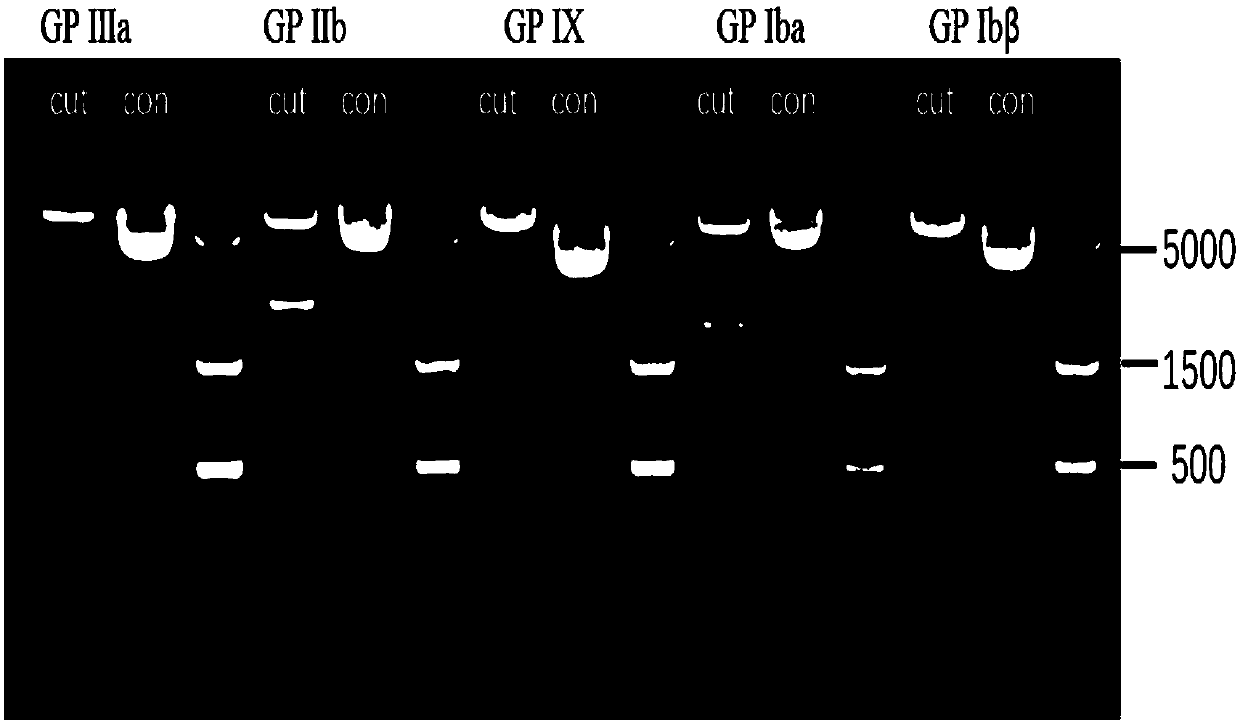
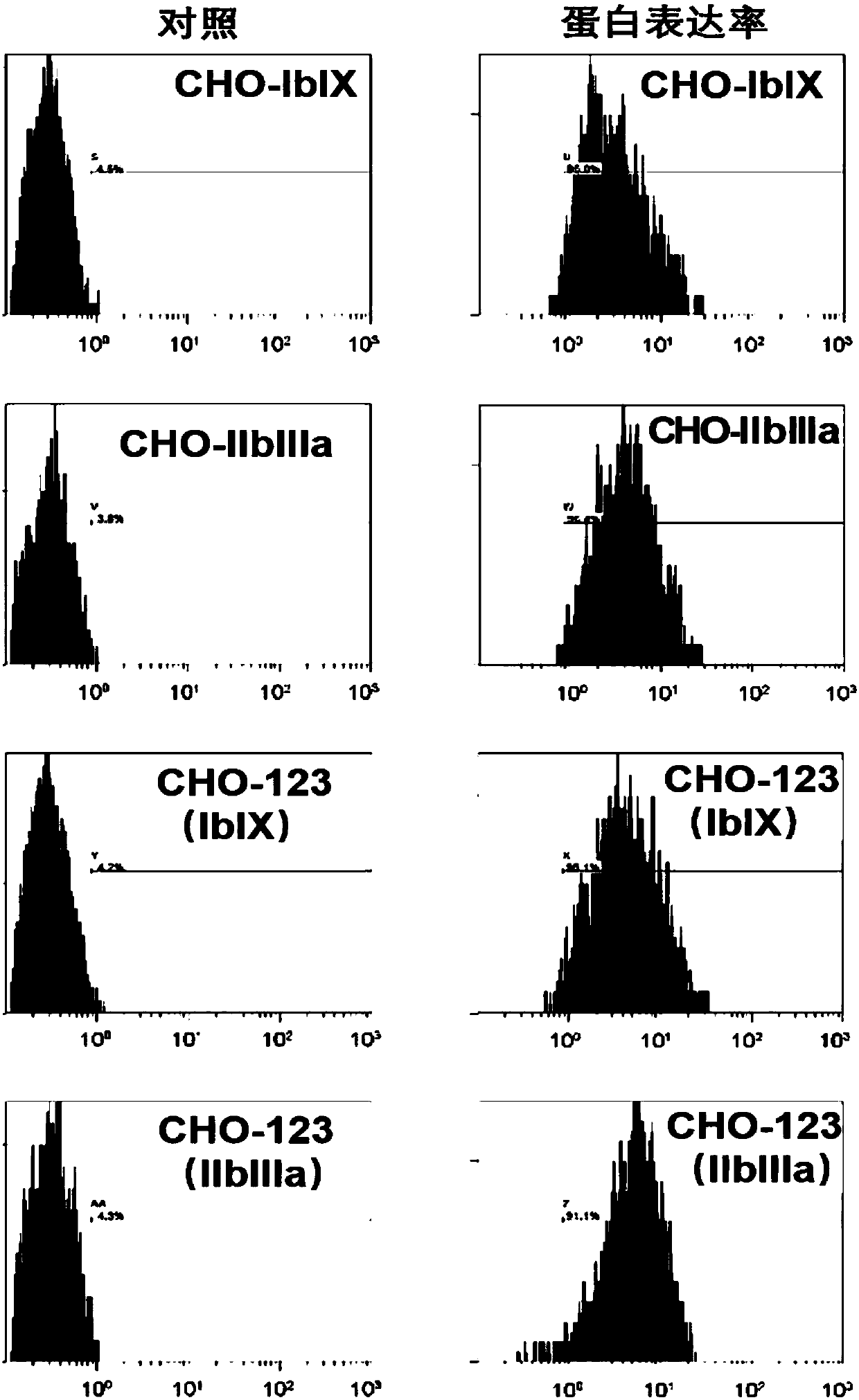
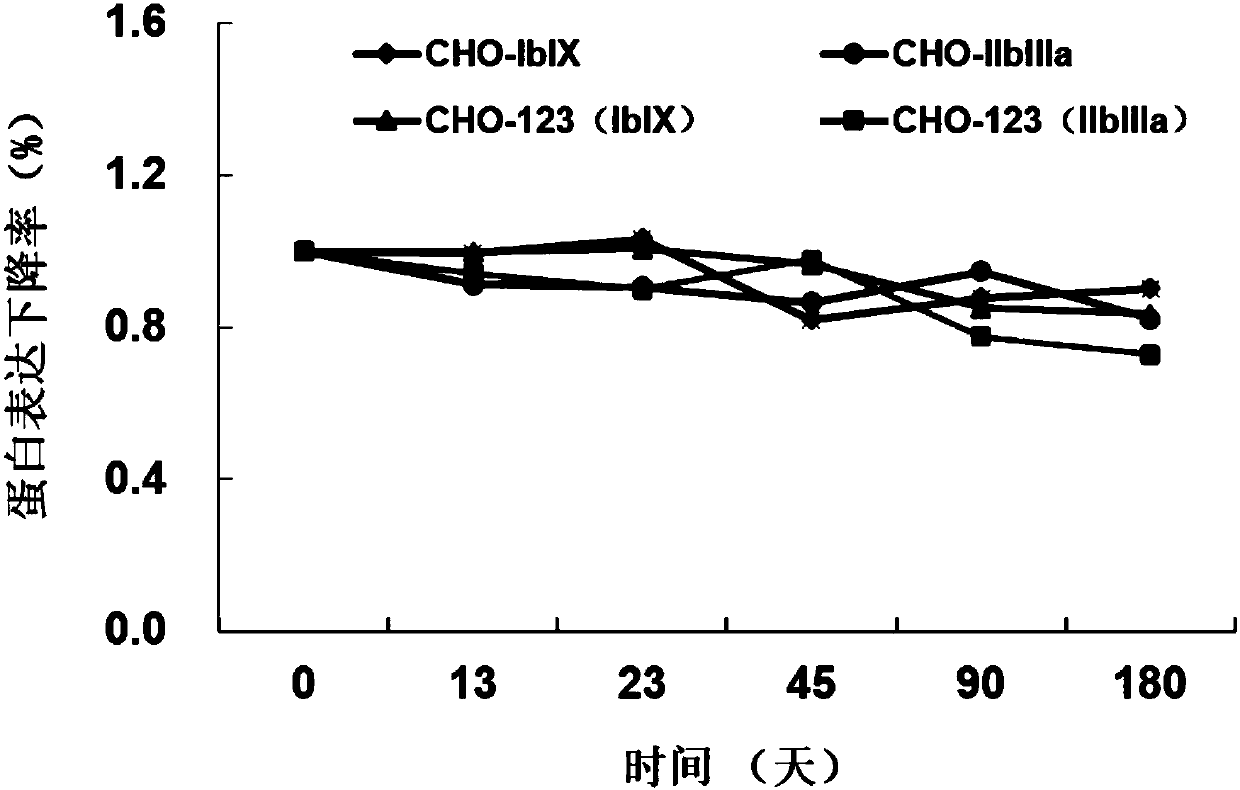
Reagent for detecting anti-platelet surface receptor-specific autoantibodies and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107727843ALow resolution sensitivitySolve operational problemsDisease diagnosisBiological testingHuman plateletFluorescence microscope
The invention discloses a reagent for detecting anti-platelet surface receptor-specific autoantibodies and a preparation method and application thereof. The reagent has high specificity and sensitivity. The method comprises expressing a human platelet-specific receptor membrane glycoprotein GP Ib-IX and / or GP IIb / IIIa receptor through CHO cells, carrying out co-incubation on the specific membraneglycoprotein receptor expression-positive CHO cells and serum to be detected and adding a fluorescein-labeled anti-human immunoglobulin polyclonal antibody (secondary antibody) for bonding. If there is an anti-platelet receptor-specific antibody in serum or plasma, the CHO-membrane glycoprotein specific antibody-fluorescein-labeled anti-human immunoglobulin polyclonal antibody complex structure isformed, has high CHO cell fluorescence intensity and can be used for flow cytometry or fluorescence microscope examination. The method is easy to operate, has enough specific membrane glycoprotein expression positive CHO cell sources, high specificity and sensitivity and high diagnosis efficiency and can be used for basic research and clinical examination.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
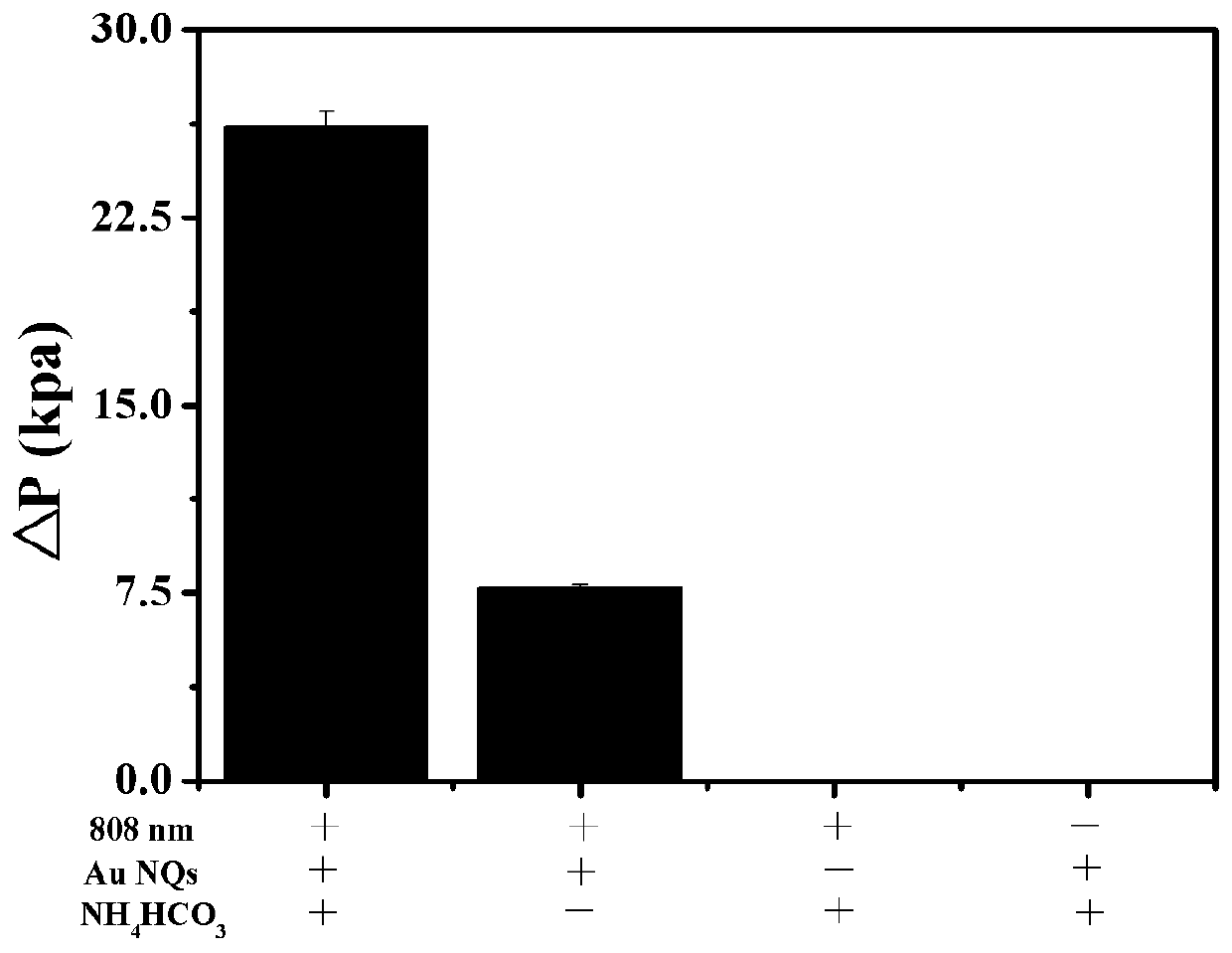
Method for tumor cell detection through porous gold nanospheres
ActiveCN109738417AEasy-to-control interface modificationGood biocompatibilityAnalysis by thermal excitationIndividual particle analysisAbnormal tissue growthBiocompatibility Testing
The invention belongs to the field of tumor cytology, and discloses a method for tumor cell detection through porous gold nanospheres. The method comprises the following steps: (1) preparing the porous gold nanospheres; (2) carrying out co-incubation on the porous gold nanospheres and a sulfydryl-modified aptamer to prepare functionalized porous gold nanospheres; (3) binding the functionalized porous gold nanospheres with sample cells, and removing the unbound porous gold nanospheres, so that a cell sample to be detected is obtained; and (4) adding a bicarbonate solution into the cell sample to be detected, and carrying out illumination under a 808nm laser. The method for the tumor cell detection through the porous gold nanospheres has the advantages that the operation is simple, and the detection cost is low; and the adopted porous gold nanospheres can be simply prepared, achieve high light and heat stability and high biocompatibility, and can produce a high temperature under the illumination of the 808nm laser for thermal decomposition of bicarbonate, so that air pressure changes in a reaction system can be monitored to distinguish tumor cells from normal cells.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
T cell vaccine constructed by secretory component of gene engineering-based aAPC (artificial Antigen Presenting Cell) as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108607094AImmune protective responseDevelopment impactViral antigen ingredientsAntiviralsHuman immunodeficiencyElectron
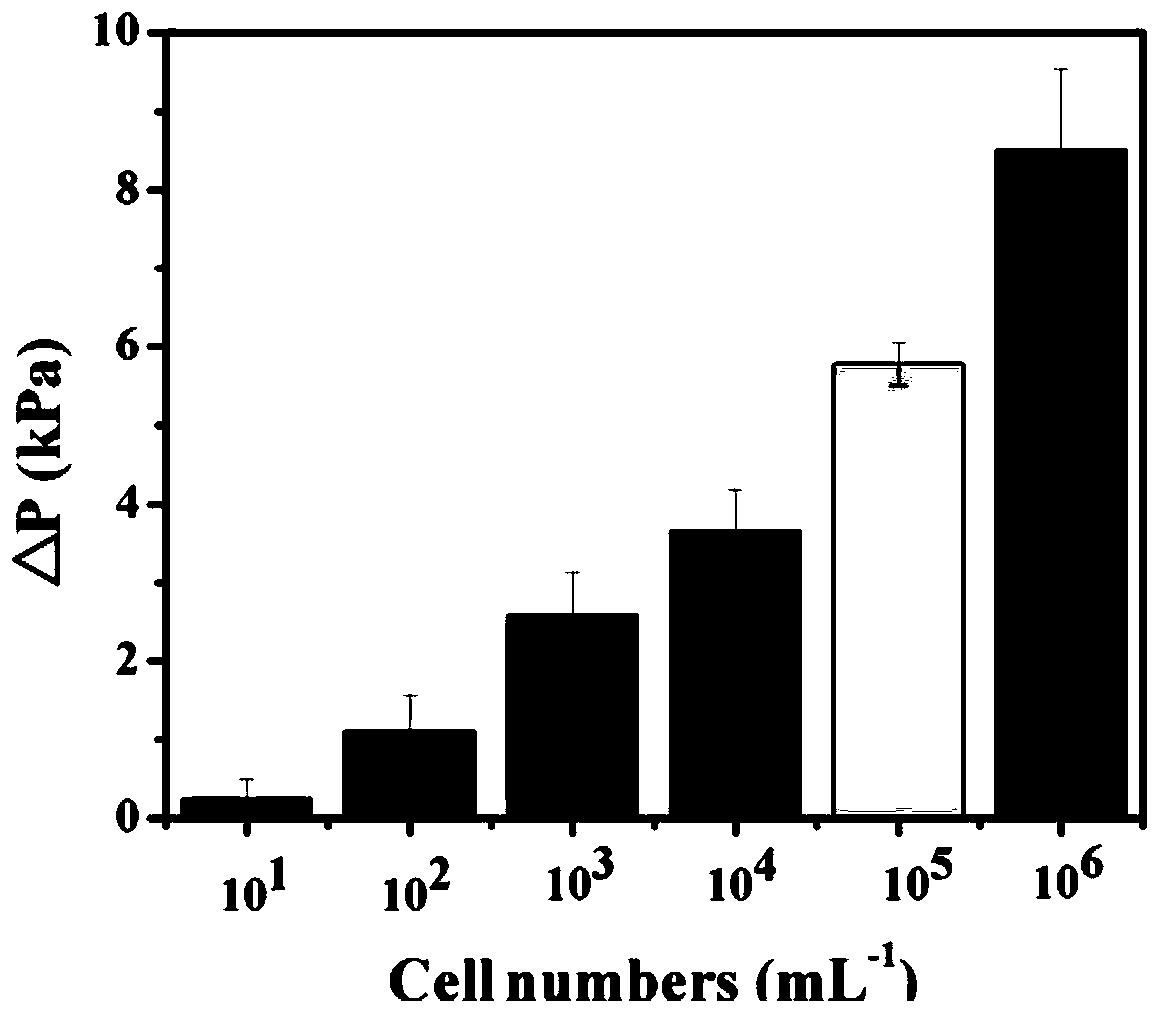
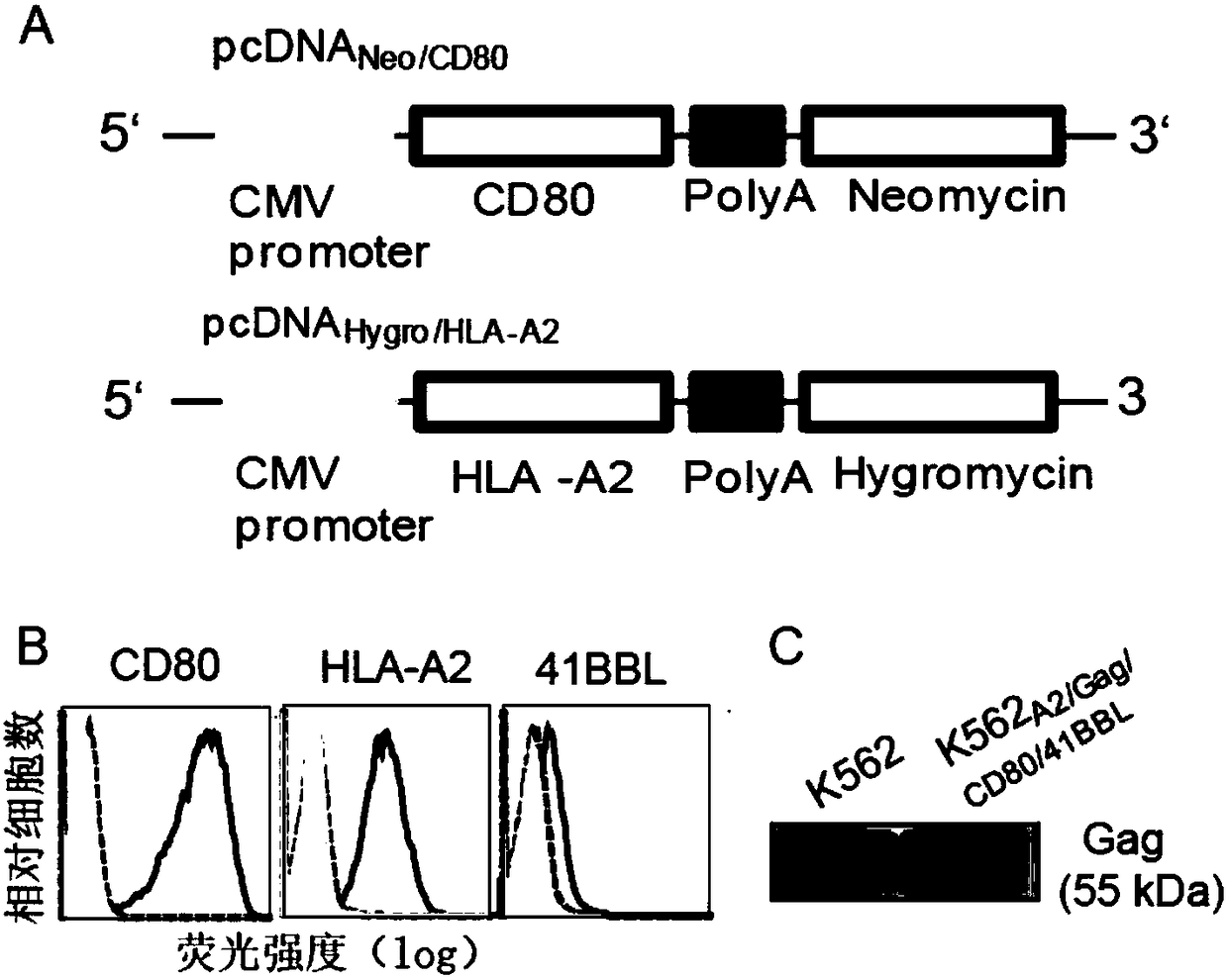
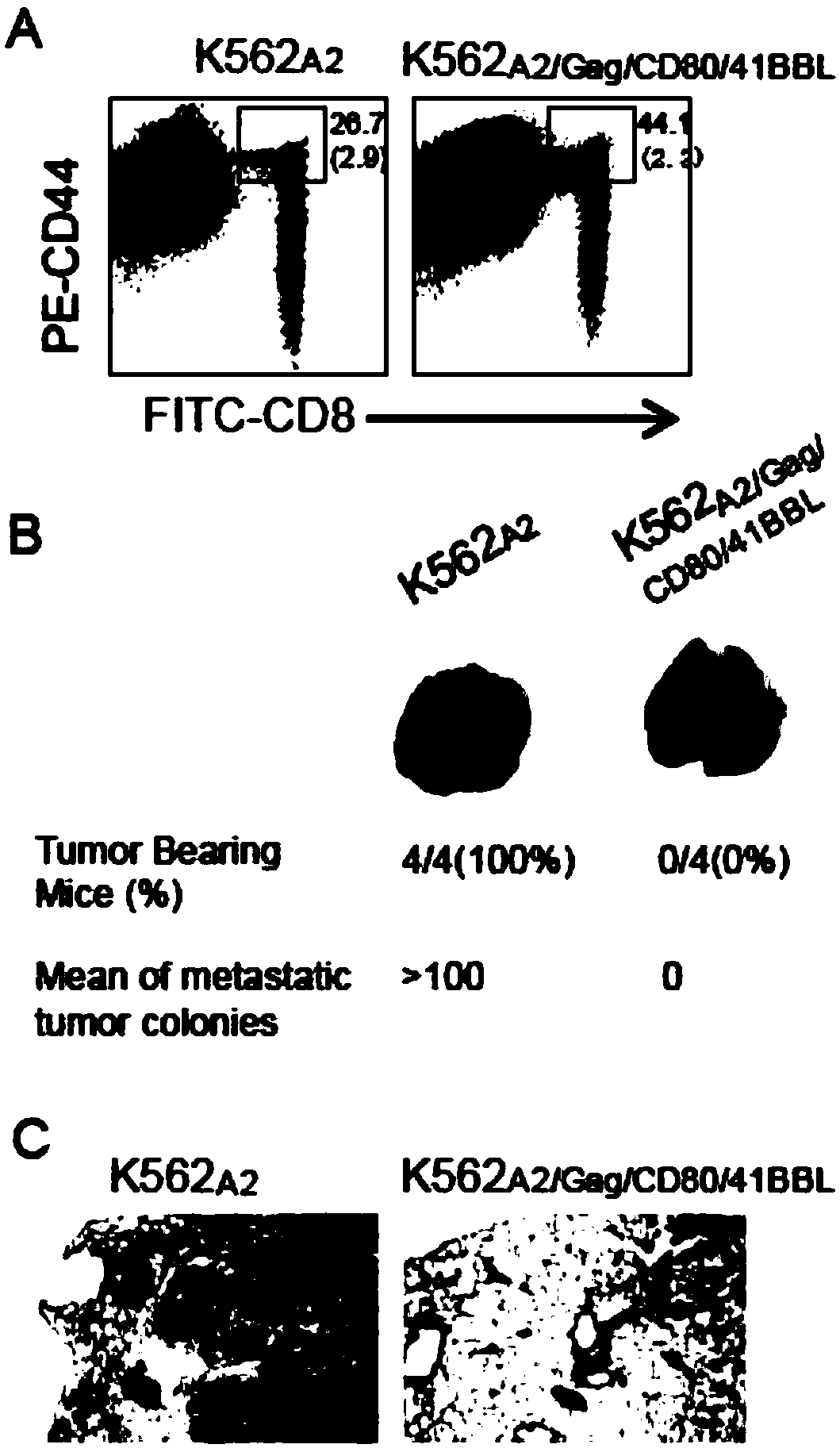
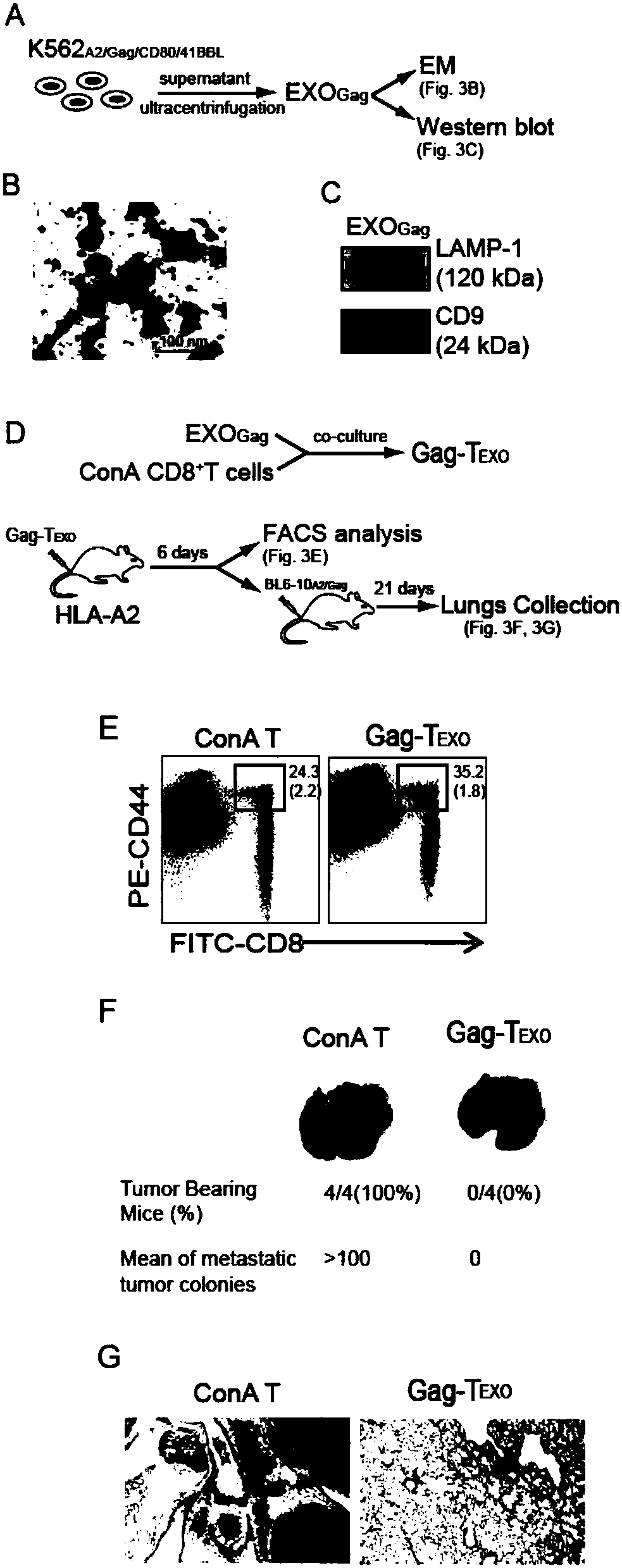
The invention discloses a secretory component vesica of a gene engineering-based aAPC (artificial Antigen Presenting Cell), as well as preparation and application of a T cell vaccine constructed by anexosome. By transfecting two kinds of eukaryotic expression plasmids of pcDNAHLA-A2 and pcDNACD80 and infecting two kinds of recombinant adenovirus carriers of AdVGag and AdV41BBL, a gene engineering-based K562A2 / Gag / CD80 / 41BBLaAPC is constructed; then exosomes are purified in K562A2 / Gag / CD80 / 41BBL culture supernatant through a differential superspeed centrifugal method, and electron microscopingand immunoblotting analysis can be carried out, wherein the exosomes are in co-incubation with nonspecific T cells of Con-A stimulated HLA-A2 transgenic mice through incubating, so that Gag-Texo vaccine having HLA-A-A2 limitation and Gag specificity is constructed. According to the secretory component vesica disclosed by the invention, the aAPCK562A2 / Gag / CD80 / 41BBL vesica in unlimited source andcontinuous growth is used for replacing a DC vesica in limited source and is used for preparing an HIV-1 (Human Immunodeficiency Viru I) Gag specific T cell vaccine. A novel method for preparing the Tcell vaccine by using the gene engineering-based aAPC has important influence on development of clinic therapeutic vaccines for a patient suffering HIV-1.
Owner:项雯华
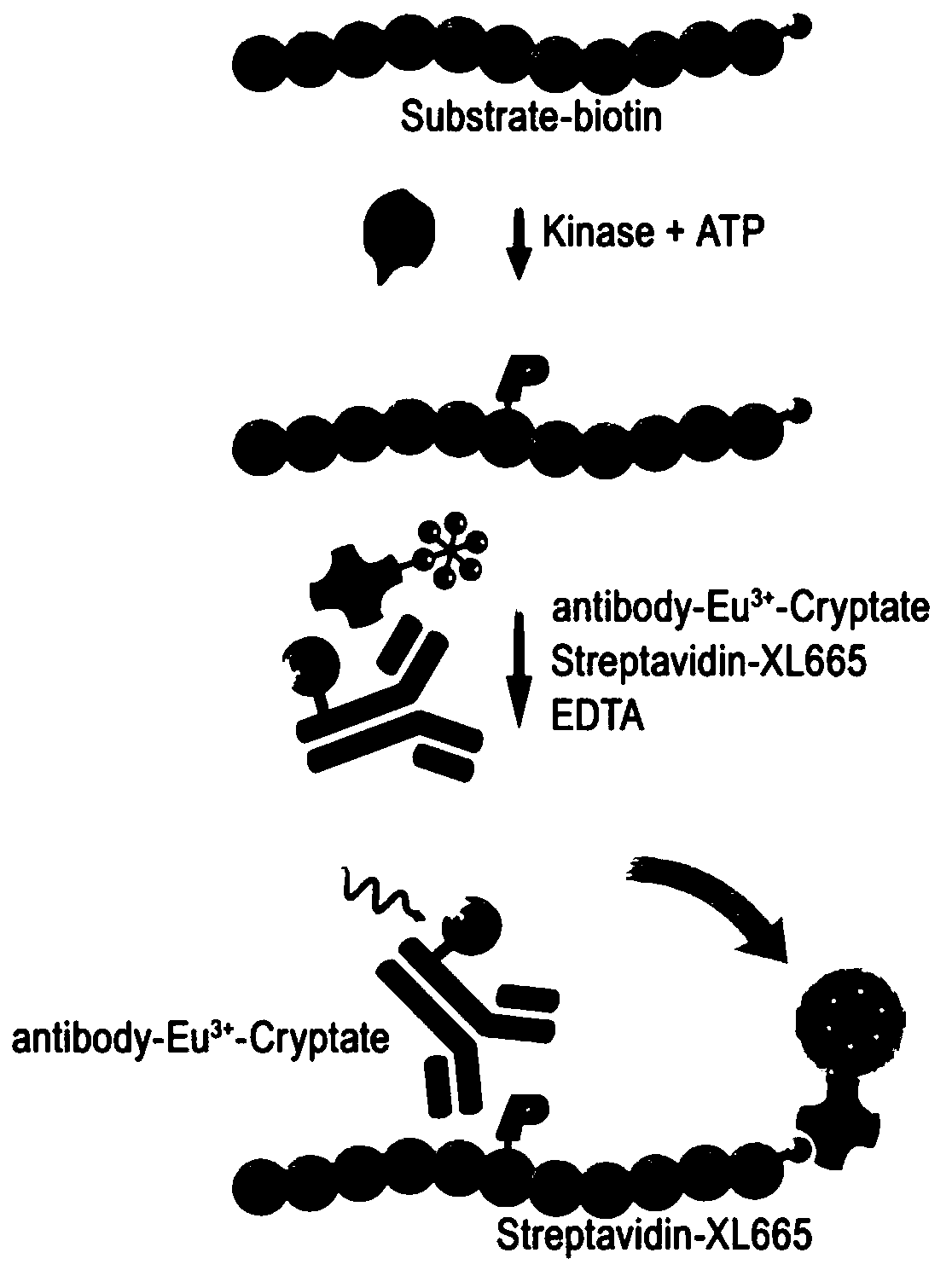
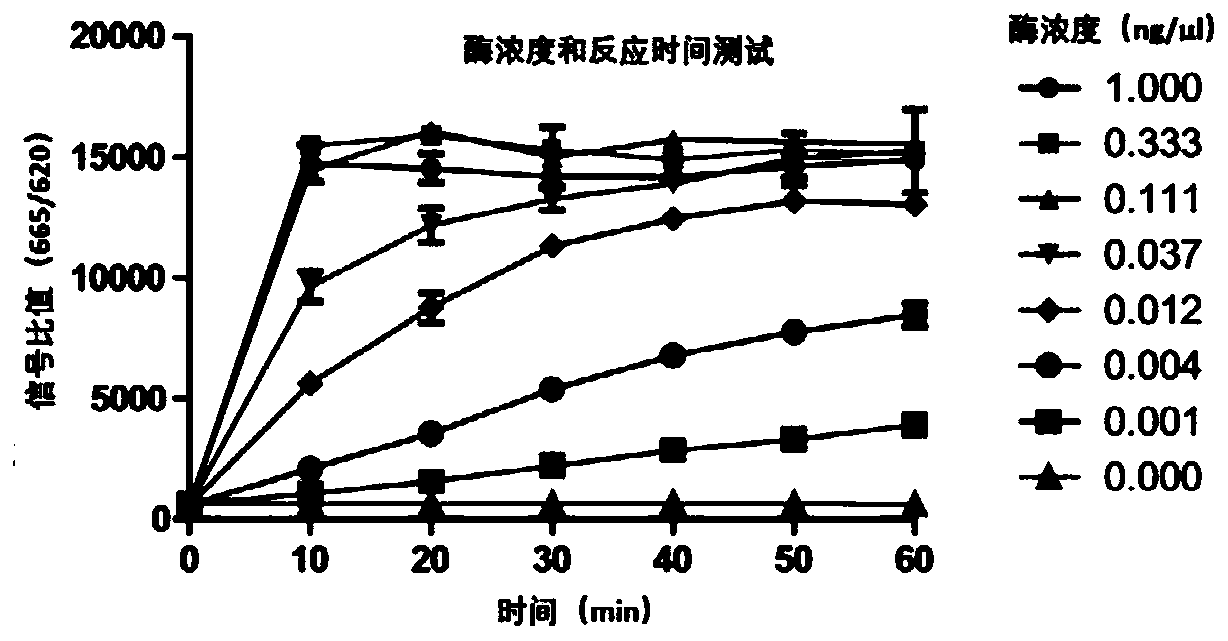
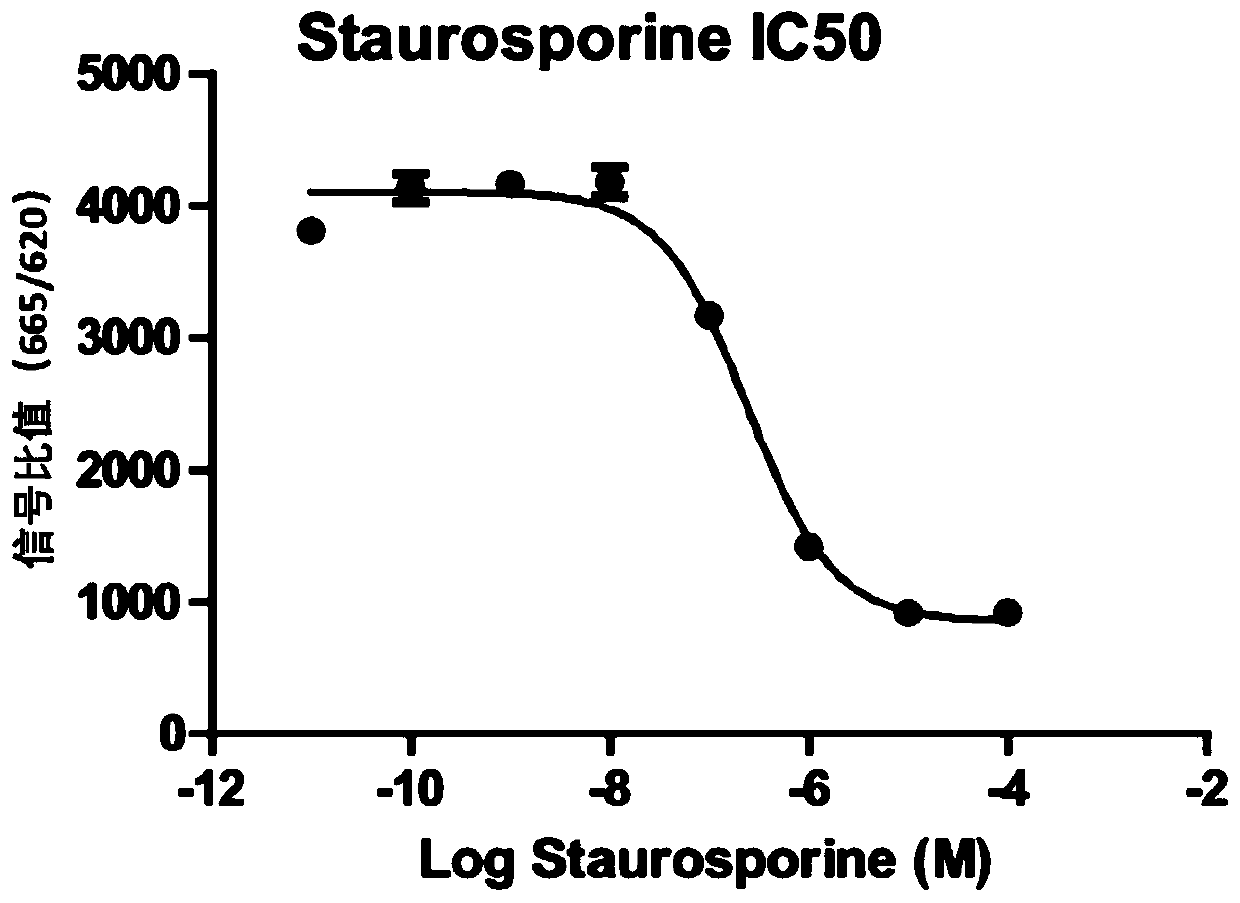
Method for screening kinase inhibitor by utilizing HTRF one-step method
InactiveCN109813915AEnables high-throughput screeningEconomical and Reliable Screening ResultsBiological testingFluorescence/phosphorescenceBiotin-streptavidin complexPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a method for screening a kinase inhibitor by utilizing an HTRF one-step method, and belongs to the field of inhibitor screening methods. The method for screening the kinase inhibitor by utilizing the HTRF one-step method comprises the following steps: sequentially adding a compound to be detected, a kinase, a substrate and ATP into a microporous plate for co-incubation; sequentially adding an antibody coupled with a recognition substrate phosphorylation site of Donor and streptavidin coupled with biotin on a recognition substrate of Acceptor into the microporous plate;incubating at room temperature, and detecting fluorescence by using an enzyme marker reading, wherein the ratio of 665nm / 620nm is original data; according to the method, screening the kinase inhibitor at the biochemical level can be achieved, and constructing cells is not needed, and the method is more direct and quicker.
Owner:浠思(上海)生物技术有限公司
Attenuated salmonella typhimurium mediated eukaryocyte plasmid transfection method
InactiveCN106591365ALow costGreat toxic effectNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionBacteroidesPenicillin
The invention provides an attenuated salmonella typhimurium mediated eukaryocyte plasmid transfection method. According to the transfection method, based on an intracellular invasion characteristic of the attenuated salmonella typhimurium, recombinant plasmids are carried to enter eukaryocytes to realize specific protein expression. Specifically, recombinant eukaryotic expression plasmids are introduced into an attenuated salmonella typhimurium VNP20009 strain in an electric shock transformation way; then recombinant bacteria and the eukaryocytes are cultured in a co-incubation manner; and finally, the attenuated salmonella typhimurium inside and outside cells is killed by a serum culture medium containing penicillin and streptomycin, and the recombinant plasmids are released to the eukaryocytes to realize the specific protein expression. Compared with conventional calcium sulfate transfection, liposome transfection and electro-transformation, the transfection method disclosed by the invention takes viable bacteria as a bearing host of specific plasmids, so that a larger number of target vectors can be obtained by only conventional culture; and in addition, the plasmid transfection operating steps are simplified, the cost is lowered, and the transfection efficiency and the cytotoxicity are comprehensively better than those in the conventional transfection method.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com