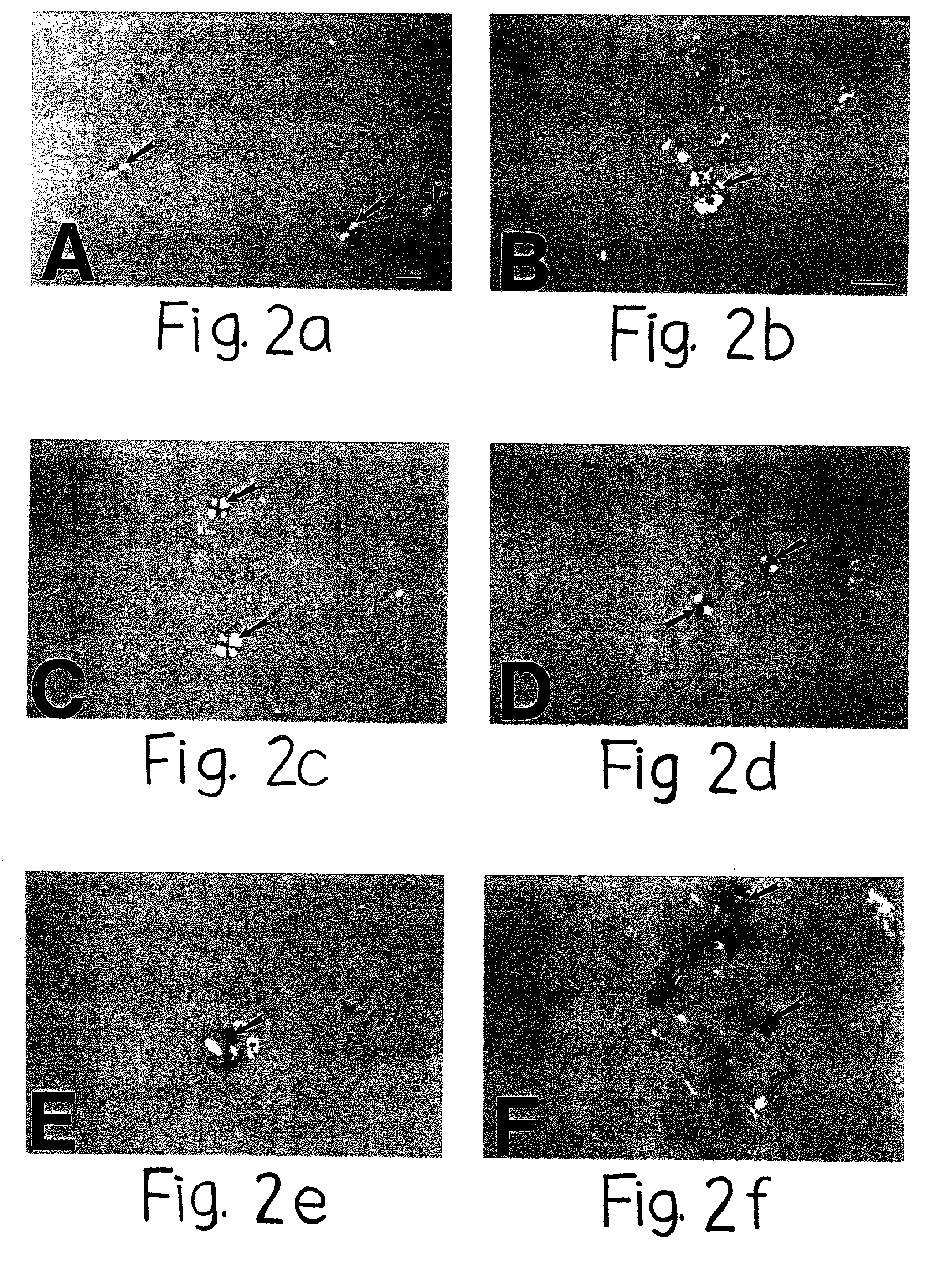
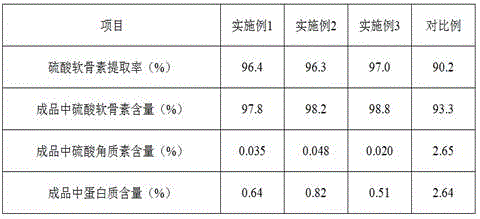
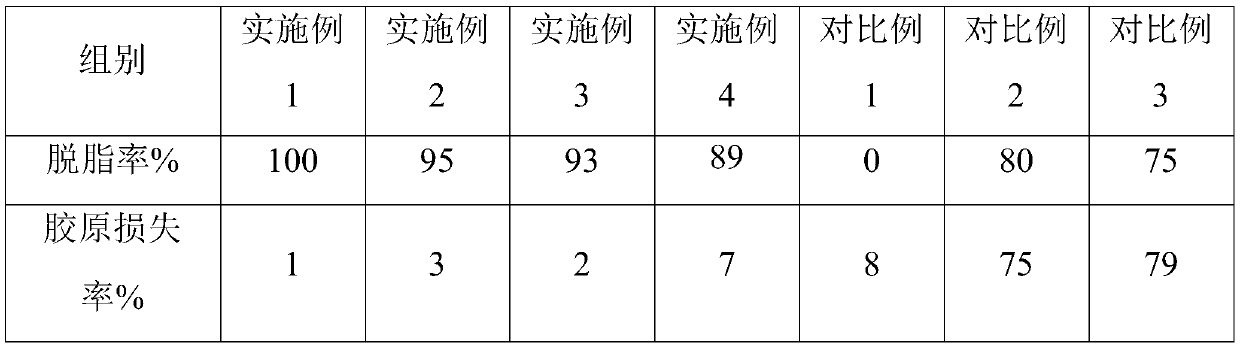
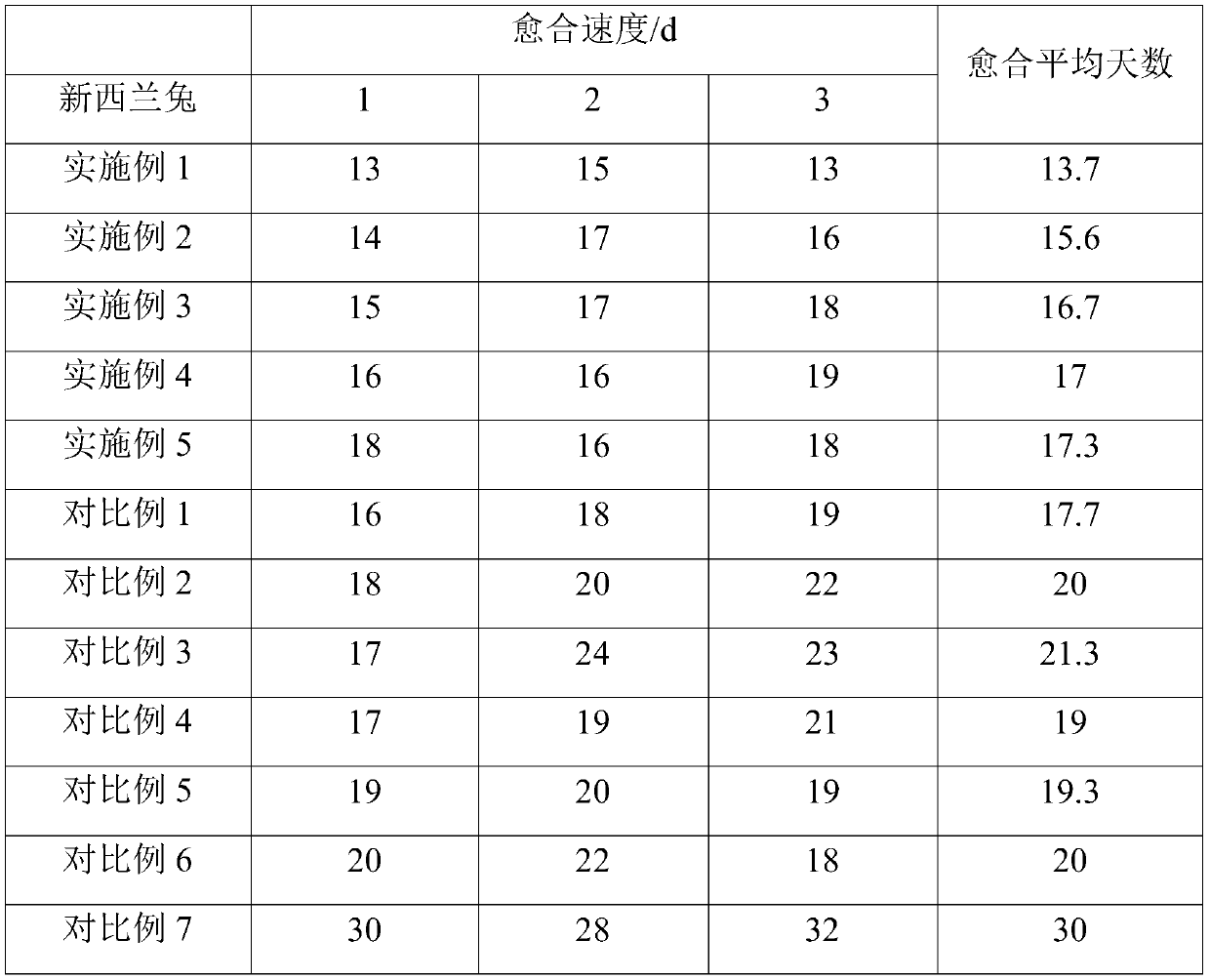
Patents
Literature
30 results about "Keratan sulfate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
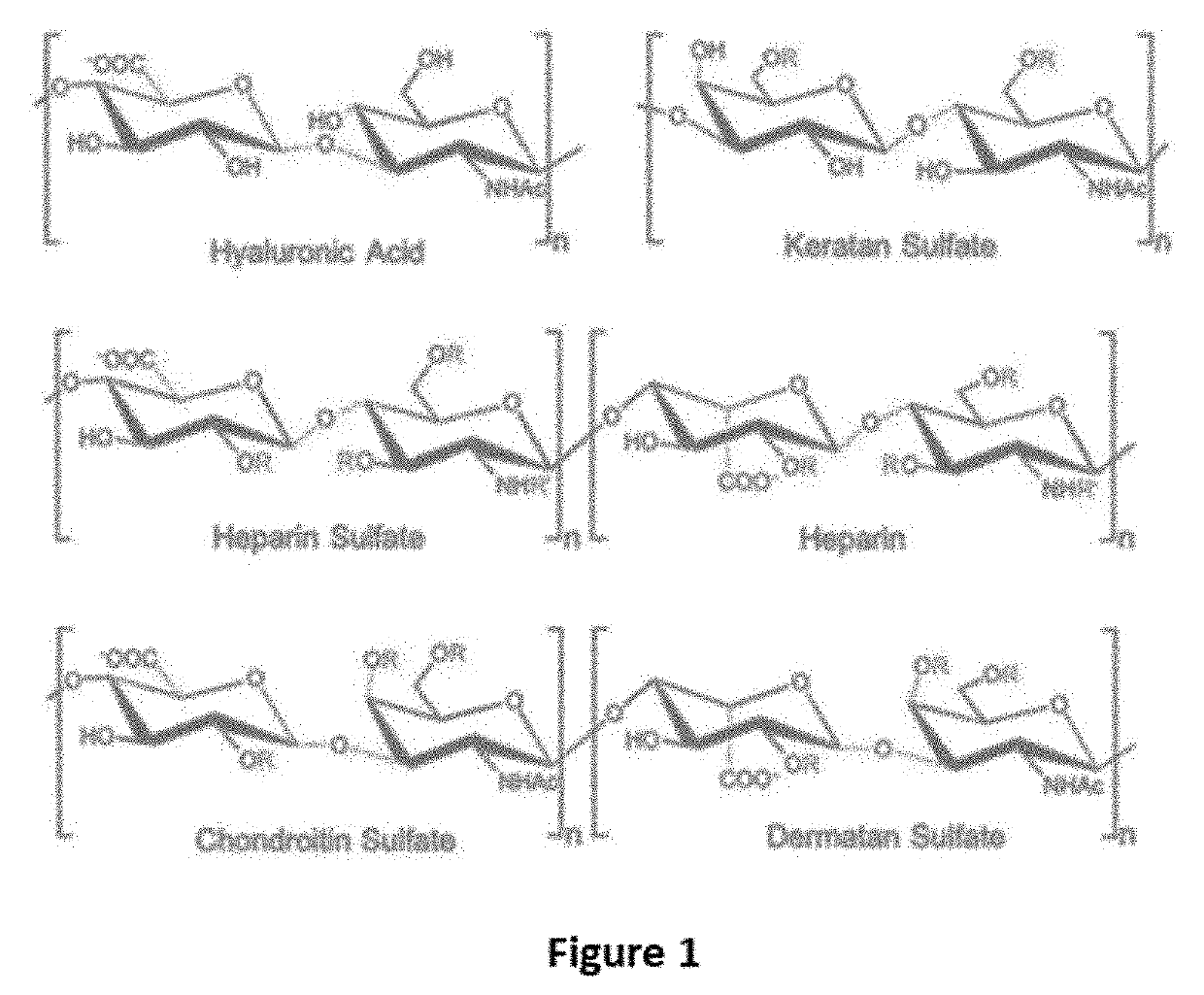
Keratan sulfate (KS), also called keratosulfate, is any of several sulfated glycosaminoglycans (structural carbohydrates) that have been found especially in the cornea, cartilage, and bone. It is also synthesized in the central nervous system where it participates both in development and in the glial scar formation following an injury. Keratan sulfates are large, highly hydrated molecules which in joints can act as a cushion to absorb mechanical shock.
Treating or preventing the early stages of degeneration of articular cartilage or subchondral bone in mammals using carprofen and derivatives
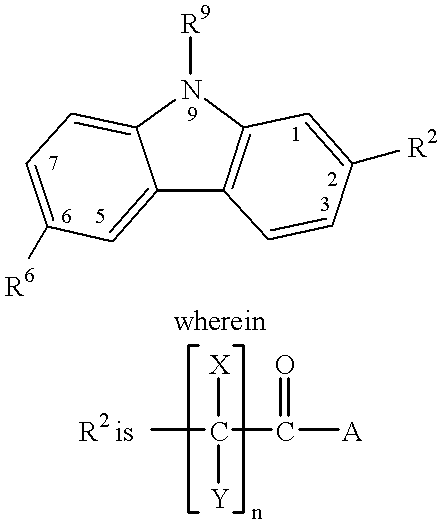
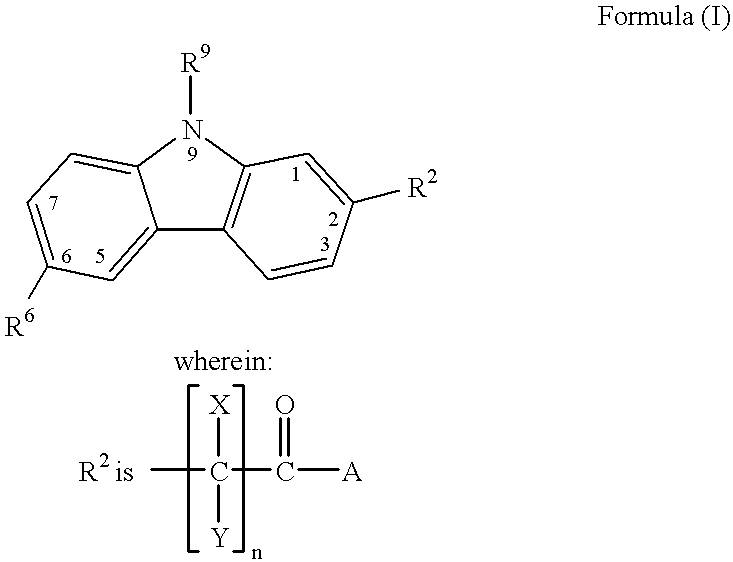
Treating or preventing the early stages of degeneration of articular cartilage or subchondral bone in the affected joint of a mammal is accomplished by administering a chondroprotective compound of Formula (I):where A is hydroxy, (C1-C4)alkoxy, amino, hydroxy-amino, mono-(C1-C2)alkylamino, di-(C1-C2)alkylamino; X and Y are independently H or (C1-C2)alkyl; and n is 1 or 2; R6 is halogen, (C1-C3)alkyl, trifluoromethyl, or nitro; R9 is H; (C1-C2)alkyl; phenyl or phenyl-(C1-C2)alkyl, where phenyl is optionally mono-substituted by fluoro or chloro; -C(=O)-R, where R is (C1-C2)alkyl or phenyl, optionally mono-substituted by fluoro or chloro; or -C(=O)-O-R', where R1 is (C1-C2)alkyl.This treatment ameliorates, diminishes, actively treats, reverses or prevents any injury, damage or loss of articular cartilage or subchondral bone subsequent to said early stage of said degeneration. Whether or not a mammal needs such treatment is determined by whether or not it exhibits a statistically significant deviation from normal standard values in synovial fluid or membrane from the affected joint, with respect to at least five of the following substances: increased interleukin-1 beta (IL-1beta); increased tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFalpha); increased ratio of IL-1beta to IL-1 receptor antagonist protein (IRAP); increased expression of p55 TNF receptors (p55 TNF-R); increased interleukin-6 (IL-6); increased leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF); decreased insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1); decreased transforming growth factor beta (TGFbeta); decreased platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); decreased basic fibroblast growth factor (b-FGF); increased keratan sulfate; increased stromelysin; increased ratio of stromelysin to tissue inhibitor of metalloproteases (TIMP); increased osteocalcin; increased alkaline phosphatase; increased cAMP responsive to hormone challenge; increased urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA); increased cartilage oligomeric matrix protein; and increased collagenase.
Owner:PFIZER INC +1
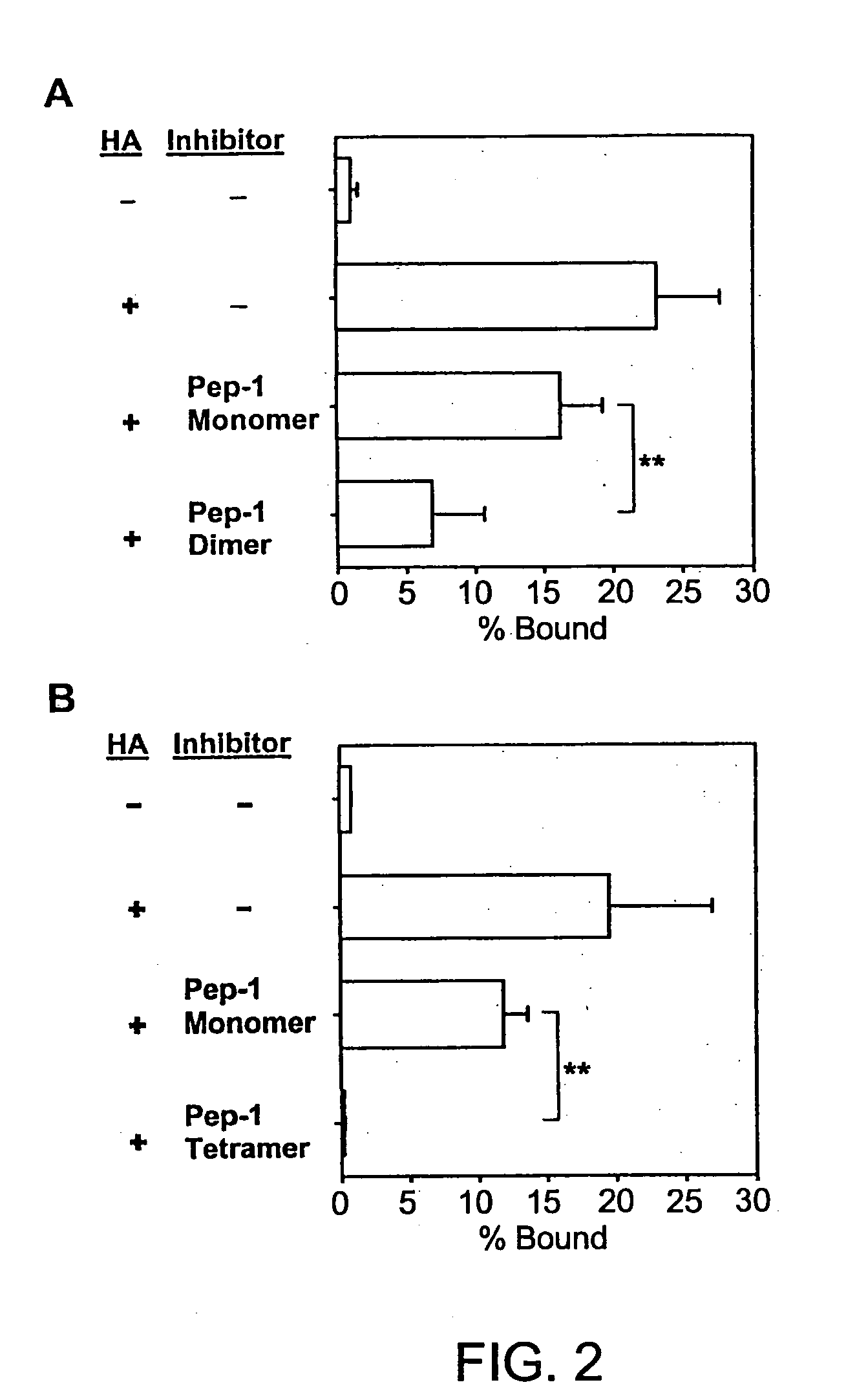
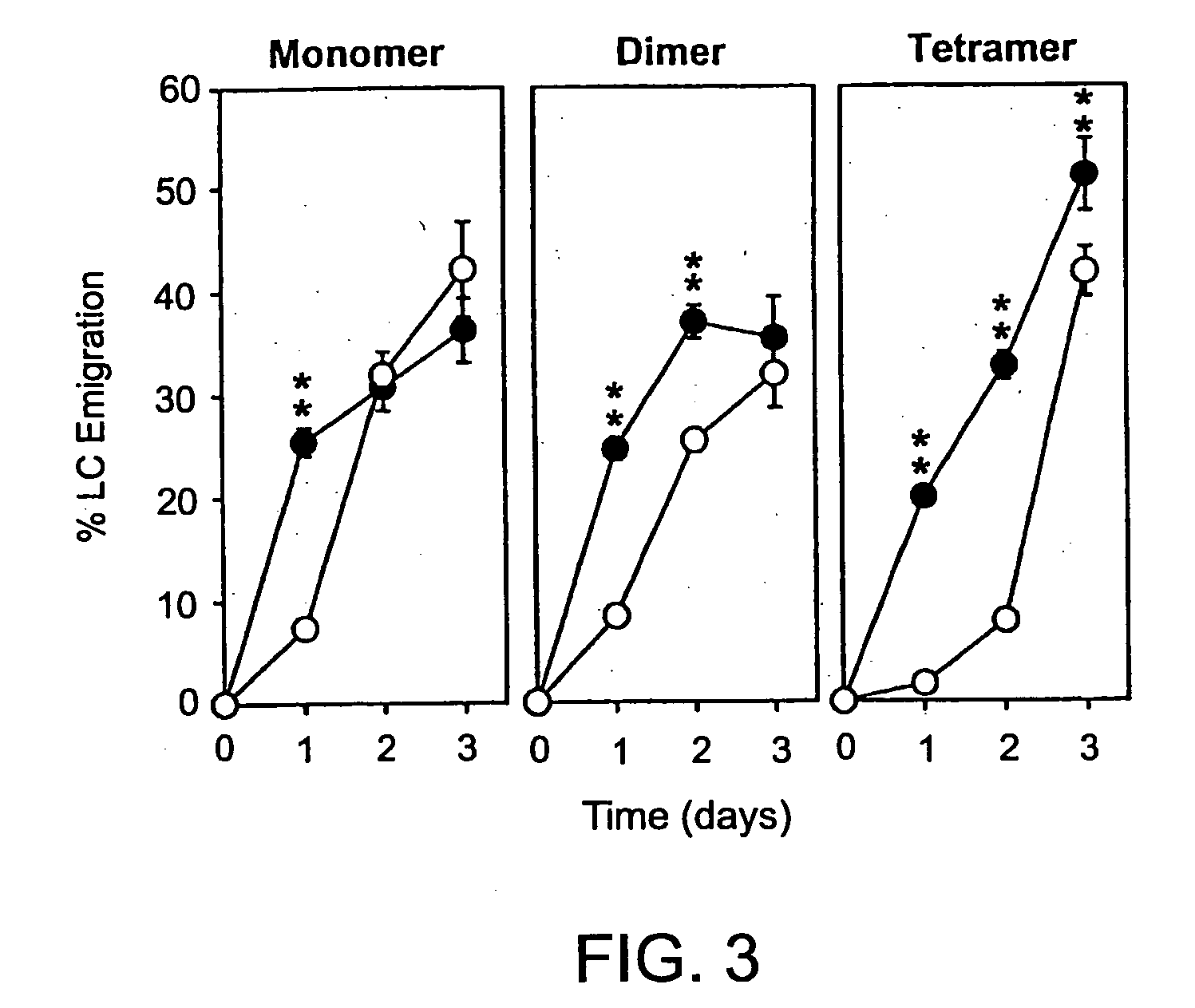
Inhibitors of glycosaminoglycans
InactiveUS20050159343A1Inhibit HA-dependent processInhibit tumorigensis and metastasisConnective tissue peptidesAntipyreticChondroitin Sulfate CAutoimmune condition
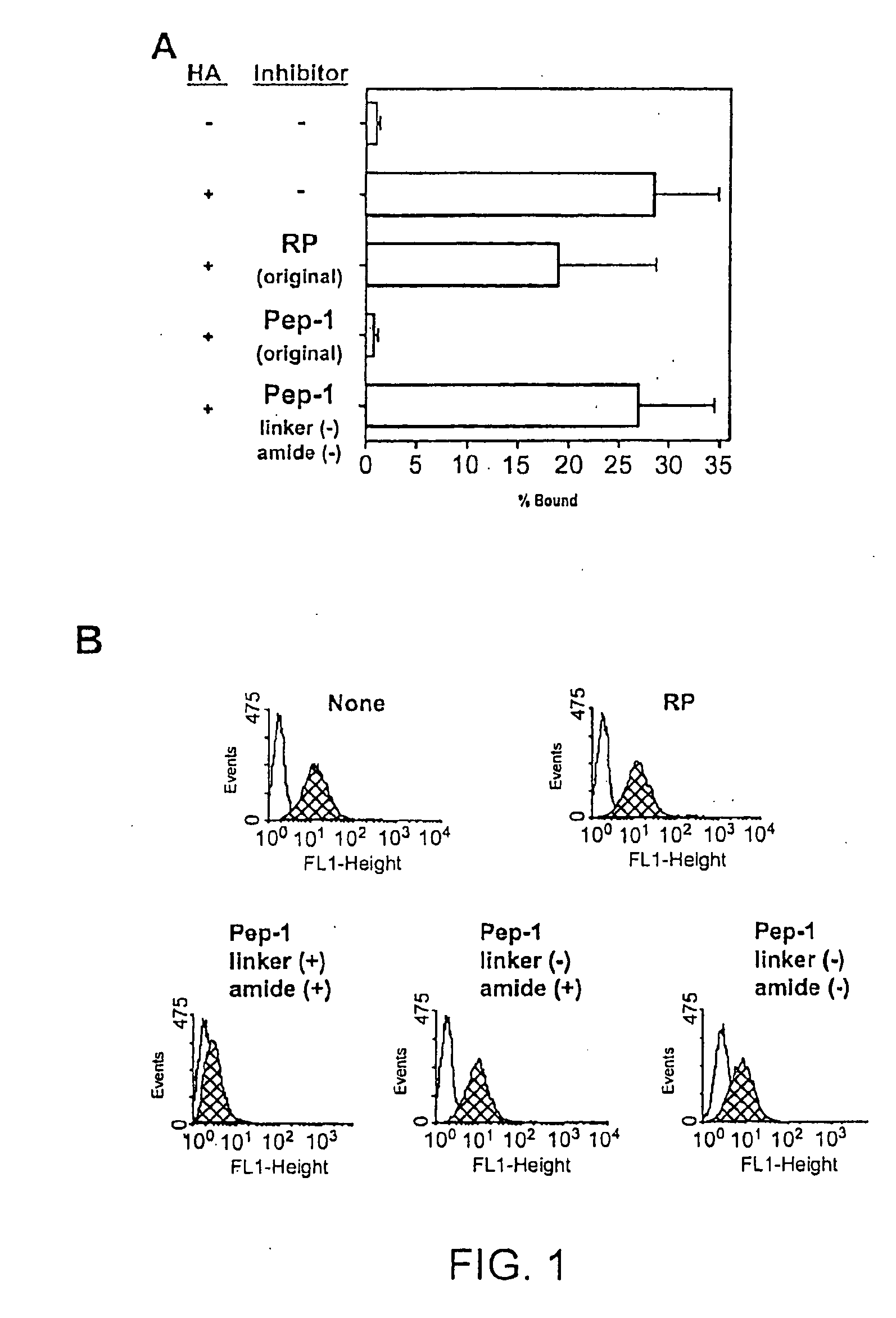
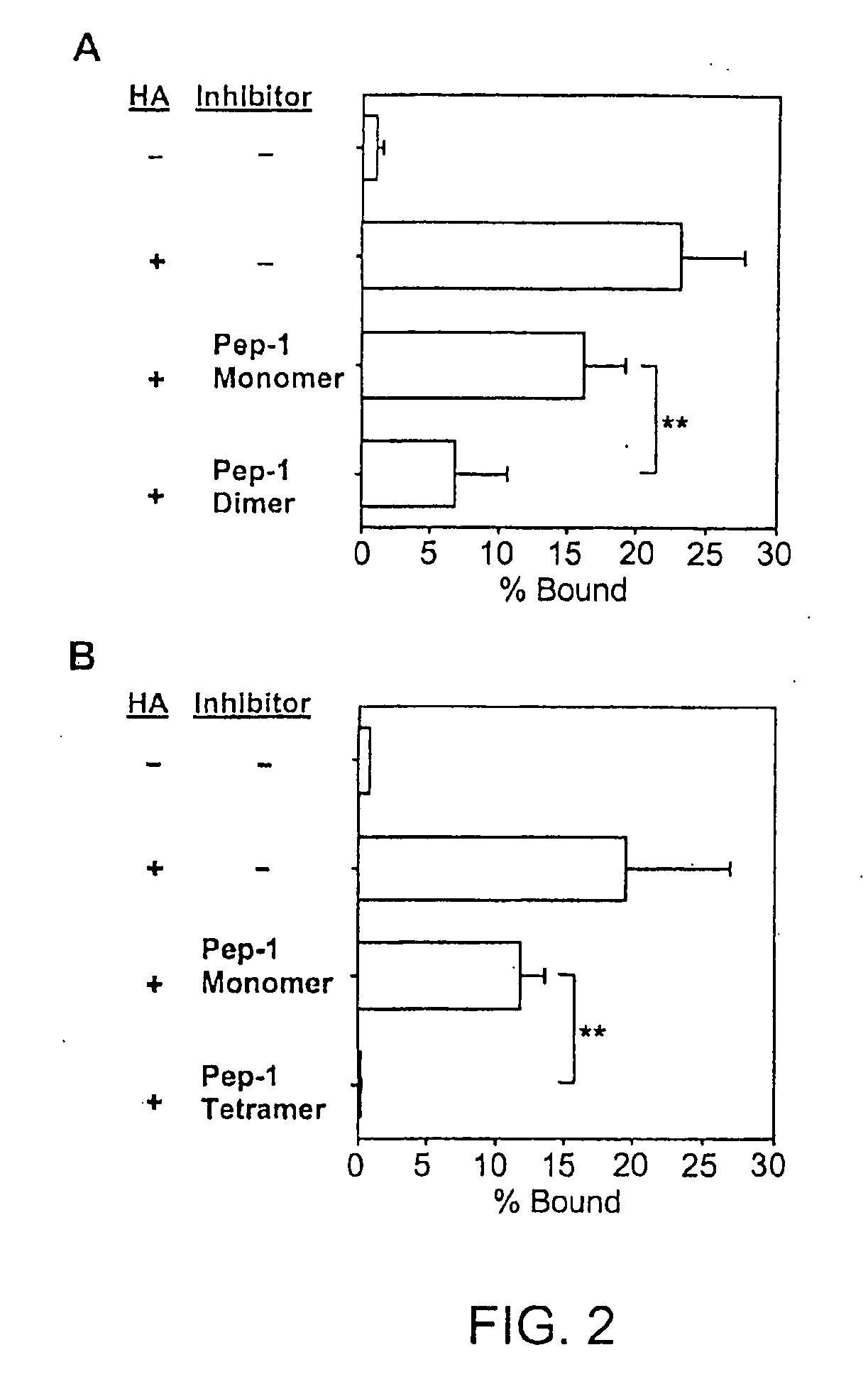
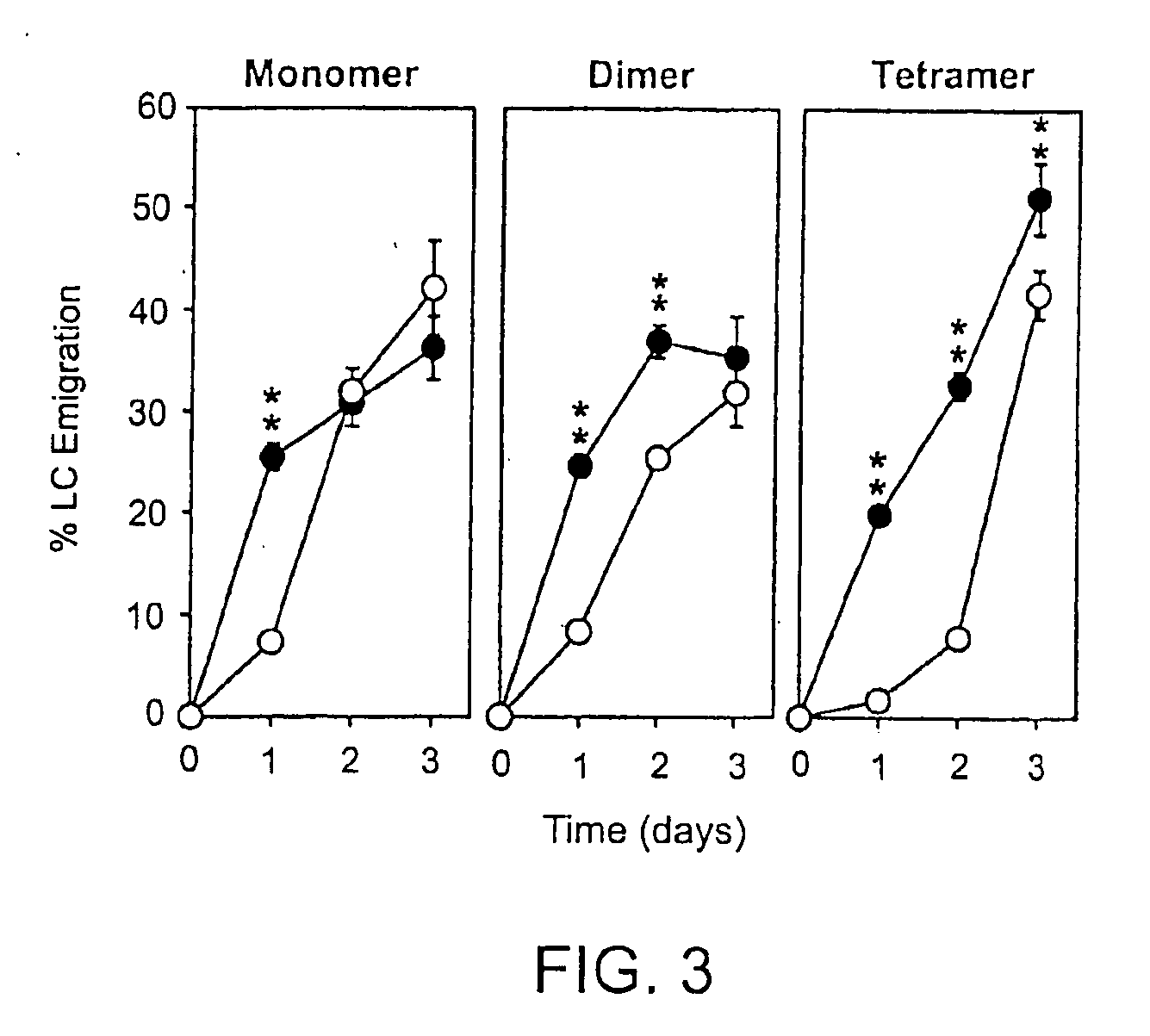
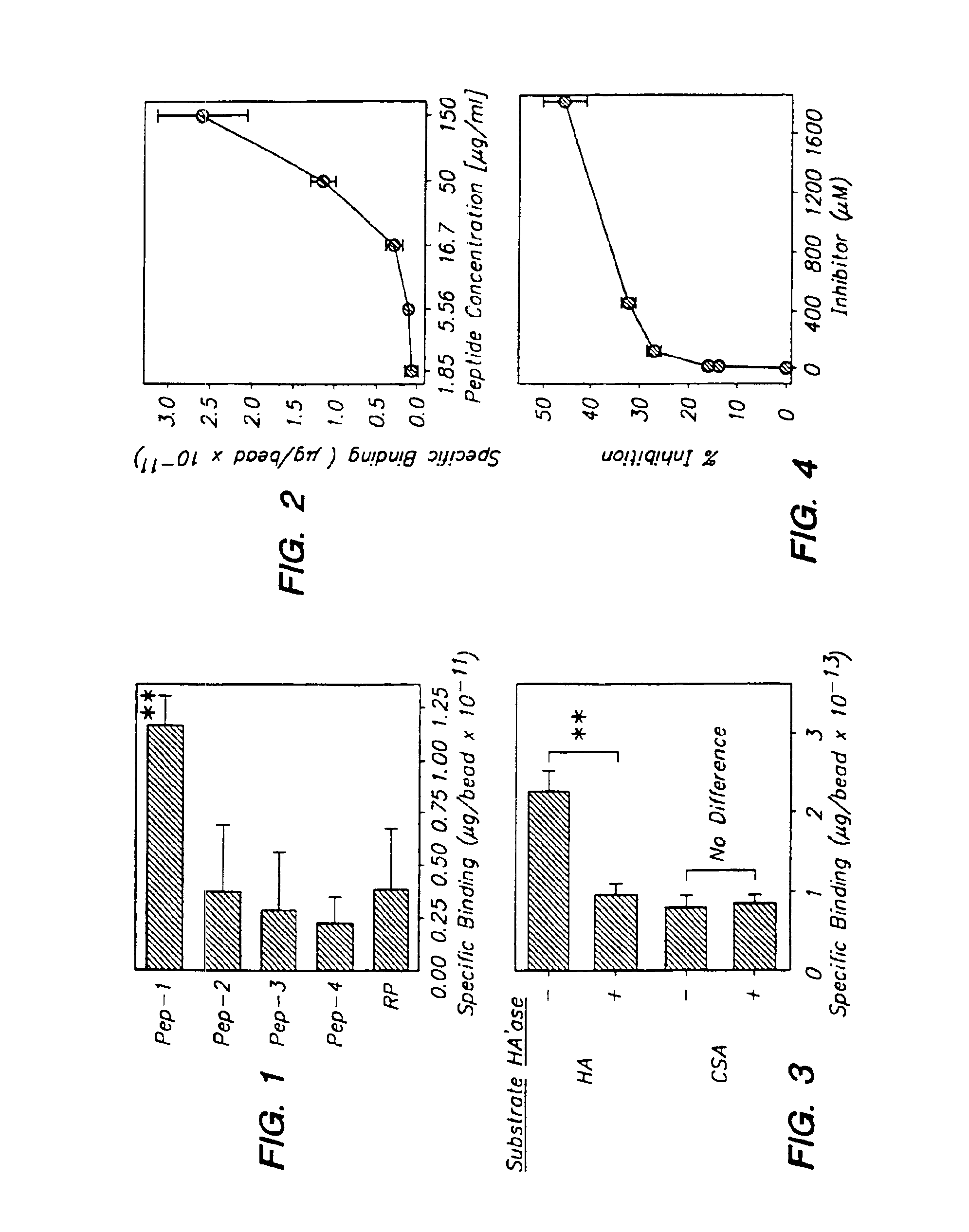
The present invention provides peptide derivatives with a specific affinity for glycosaminoglycan molecules. These peptide derivatives include multimers as well as chemically modified peptides and may be prepared by a variety of methods. The peptides of the invention have numerous functions, including but not limited to use as inhibitors of glycosaminoglycan-mediated signaling events and targeting agents. Peptides of the invention may be directed against any glycosaminoglycan, including hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate A, chondroitin sulfate C, dermatan sulfate, heparin, keratan sulfate, keratosulfate, chitin, chitosan 1, and chitosan 2. The peptide derivatives of the invention also have therapeutic uses in the treatment and prevention of diseases involving inflammatory diseases, cancer, and cancer metastasis, autoimmune diseases, etc.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Cross-linked polysaccharide drug carrier
InactiveUS6953784B2High biodegradation rateControl releasePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsCross-linkDextran
A carrier and a method for preparing it are provided for use in the delivery of therapeutic agents. A polysaccharide is reacted with an oxidizing agent to open sugar rings on the polysaccharide to form aldehyde groups. The aldehyde groups are reacted to form covalent oxime linkages with a second polysaccharide and each of the first and second polysaccharide is selected from the group consisting of hyaluronic acid, dextran, dextran sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, heparan, heparan sulfate and alginate.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Inhibitors of glycosaminoglycans
The present invention provides peptide derivatives with a specific affinity for glycosaminoglycan molecules. These peptide derivatives include multimers as well as chemically modified peptides and may be prepared by a variety of methods. The peptides of the invention have numerous functions, including but not limited to use as inhibitors of glycosaminoglycan-mediated signaling events and targeting agents. Peptides of the invention may be directed against any glycosaminoglycan, including hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate A, chondroitin sulfate C, dermatan sulfate, heparin, keratan sulfate, keratosulfate, chitin, chitosan 1, and chitosan 2. The peptide derivatives of the invention also have therapeutic uses in the treatment and prevention of diseases involving inflammatory diseases, cancer, and cancer metastasis, autoimmune diseases, etc.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compositions and methods for treating joints
Compositions and methods are provided for treating joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis and / or the pain associated therewith. The compositions and methods utilize a first component, namely hyaluraonic acid (“HA”), in combination with a lyophilized second component that is effective to at least temporarily reduce the viscosity of the HA. In an exemplary embodiment, the second component is one or more glycosaminoglycans (“GAG”), such as chondroitin sulfate (“CS”), including CS4 and / or CS6, dermatan sulfate, heparin, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate. The composition can optionally include other joint supplements, such as glucosamine (“GlcN”).
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Modulators of polysaccharides and uses thereof
InactiveUS6923965B2Produced cost-effectivelyBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseChondroitin Sulfate C
The present invention provides peptides with a specific affinity for glycosaminoglycan molecules. These peptides may have any number of functions, including but not limited to use as inhibitors of glycosaminoglycan-mediated processes, enhancers of glycosaminoglycan-mediated processes, and as molecular probes to identify the presence of a specific glycosaminoglycan. Peptides of the invention may be directed against any glycosaminoglycan, including hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate A, chondroitin sulfate C, dermatan sulfate, heparin, keratan sulfate, keratosulfate, chitin, chitosan 1, and chitosan 2. These isolated peptides may have therapeutic uses in the treatment or prevention of diseases involving infection, inflammatory diseases, cancer, infections, etc. The peptides may also have other biological functions such as contraception.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Compositions and methods for treating joints
Compositions and methods are provided for treating joint conditions, such as osteoarthritis and / or the pain associated therewith. The compositions and methods utilize a first component, namely hyaluraonic acid (“HA”), in combination with a lyophilized second component that is effective to at least temporarily reduce the viscosity of the HA. In an exemplary embodiment, the second component is one or more glycosaminoglycans (“GAG”), such as chondroitin sulfate (“CS”), including CS4 and / or CS6, dermatan sulfate, heparin, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate. The composition can optionally include other joint supplements, such as glucosamine (“GlcN”)
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
In vitro formation of congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques to identify anti-plaque therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's and Prion diseases
InactiveUS20020168753A1Test effectivenessCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderCongo redNeuroglycan C
Co-incubation of an amyloid protein with sulfated macromolecules as a method for the formation of amyloid plaques. The amyloid protein may be the beta-amyloid protein or the prion protein or the like. Amyoid plaque formation in one embodiment proceeds in vitro and desireably produces amyloid plaques that stain with Congo red and demonstrate a maltese-cross pattern when viewed under polarized light. The method also produces amyloid plaques that demonstrate an "amyloid star" appearance when viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Sulfated macromolecules include a sulfated proteoglycan selected from the group consisting of perlecan, ~220 kilodalton heparan sulfate proteoglyean, glypican, cerebroglycan, aggrecan, synaptoglycan (SV2PG), syndecan, N-syndecan (also known as syndecan-3), syndecan-1, syndecan-4, neurocan, phosphacan, decorin, biglycan, versican, amphiglycan, lumican, PG-M, PG-M (3), agrin, betaglycan, claustrin, brevican, appican, epican, neuroglycan-C, and fragments thereof. Thw sulfated macromolecule may be a sulfated glycosaminoglycan selected from the group consisting of heparin, heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate, and fragments thereof. An in vivo assay is also presented for selecting a candidate therapeutic agent for inhibiting or disrupting amyloid plaque deposition or persistence. The assay includes a) pre-forming congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques in vitro following incubation of an amyloid protein and a selected sulfated macromolecule, b) using a first cannula and osmotic pump to continuously infuse for a selected duration the pre-formed congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques into a tissue or organ, c) changing the first cannulae and osmotic pump with a second cannulae and osmotic pump to administer the candidate therapeutic, and d) detecting the candidate therapeutic's ability to disrupt, reduce, or eliminate congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaque deposition / persistence in the tissue or organ.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Chondroitin sulfate/dermatan sulfate extraction method
InactiveCN105821097AOvercome the source's shortcomingsWide variety of sourcesFermentationDermatan sulfateHyaluronic acid
The invention discloses a chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate extraction method which comprises the following steps: drying the eggshell matrix and grinding to obtain eggshell matrix powder; separating and extracting total glycosaminoglycan from the eggshell matrix powder; and removing heparin / heparan sulfate, keratan sulfate and hyaluronic acid in the total glycosaminoglycan to obtain high-purity chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate.
Owner:刘长国
Method for removing keratan sulfate from chondroitin sulfate crude extract
ActiveCN105777938ABreaking covalent bondsEasy to separateDermatan sulfateElectrical resistivity and conductivity
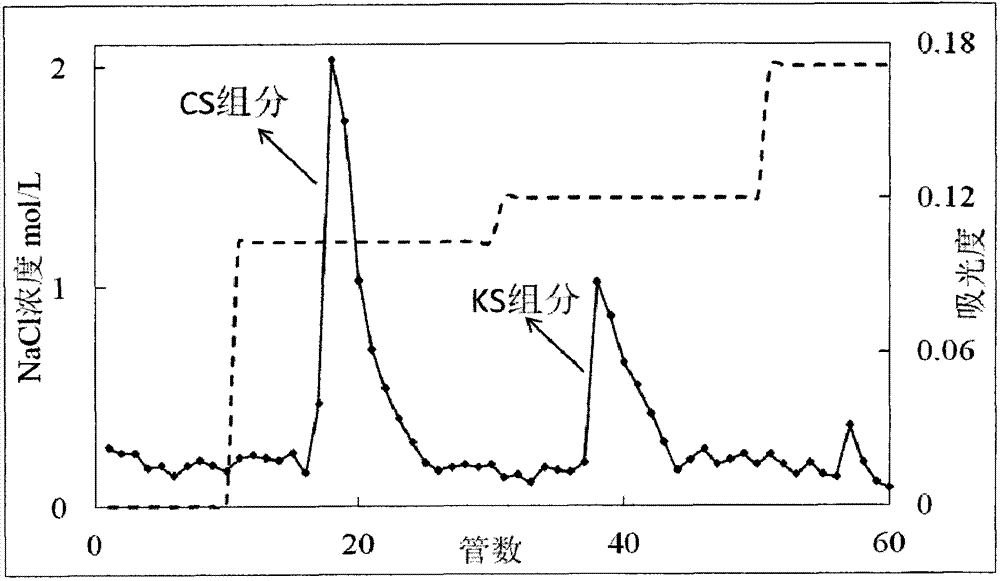
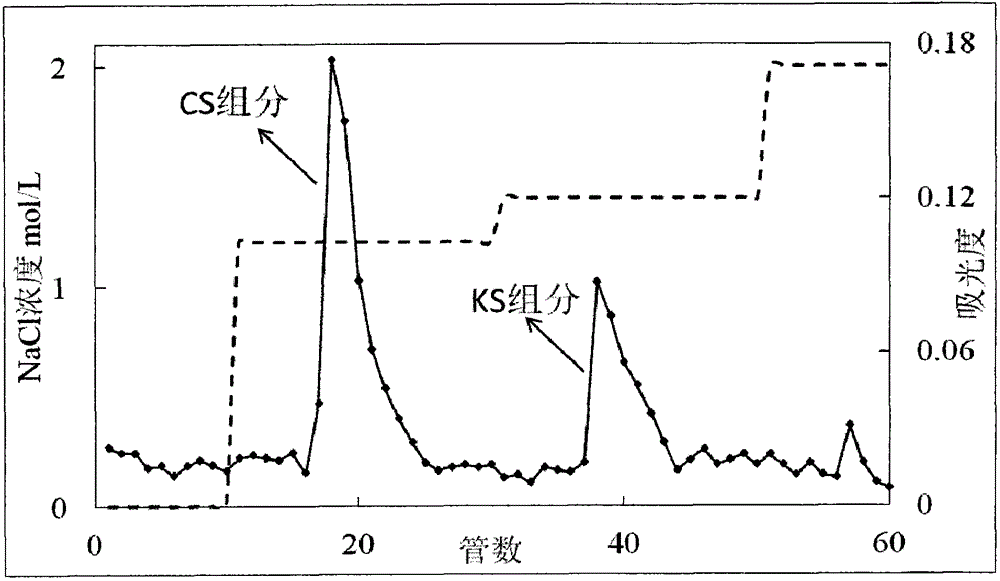
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a method for removing keratan sulfate from a chondroitin sulfate crude extract. The method comprises the following steps of adding a sodium hydroxide solution into a chondroitin sulfate crude extract for reaction; then adding hydrochloric acid to regulate the PH value, filtering to obtain a filtrate, and adding sodium chloride into the filtrate to regulate the electrical conductivity of the solution to be 45-48ms / cm; then adding an ethanol solution, controlling the flow velocity of the ethanol solution to be 10-15mL / (L.min), precipitating chondroitin sulfate, and filtering to obtain a precipitate; dehydrating and drying the precipitate obtain a chondroitin sulfate finished product. The method is easy in control over technological conditions, low in cost, simple in operation and low in experimental apparatus requirement, and can be used for thoroughly solving the problems that removal of the keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate is difficult and industrial production is difficult to realize.
Owner:RIZHAO LANSHAN BIOCHEM PROD
Composite decellularized dermal matrix biological dressing and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN109847088AImprove mechanical propertiesAvoid breakingAbsorbent padsBandagesCross-linkPhenyl Ethers
The invention provides composite dermal matrix biological dressing and a preparation method thereof. The composite decellularized dermal matrix biological dressing is prepared through the steps of mixing fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether with polyoxy ethylene nonyl phenyl ether and sodium dodecyl sulfate in an appropriate proportion, defatting skin, performing decellularizing treatment on skin through complex enzymes of Dispase and Trypsin-EDTA in an appropriate proportion, performing soaking in a mixed solution of carboxymethyl chitosan, hyaluronic acid, hydroxyethyl cellulose, calcium chloride and keratan sulfate, and performing a cross-linking reaction through oxidized sodium alginate. Based on high defatting rate, the characteristic of original skin collagen content is maintained, the united synergetic action of the carboxymethyl chitosan, the hyaluronic acid, the hydroxyethyl cellulose, the calcium chloride and the keratan sulfate is used for cooperation, and the composite decellularized dermal matrix biological dressing is prepared. The composite decellularized dermal matrix biological dressing has favorable efficacy of resisting bacteria and promoting healing, can concurrently have favorable mechanical properties, is easy to tile and apply on wound surfaces and is not liable to damage.
Owner:GUANGZHOU RAINHOME PHARM&TECH CO LTD
Method for extracting hyaluronic acid from eggshell membranes of poultry
The invention provides a method for extracting hyaluronic acid from eggshell membranes of poultry. The method includes steps: separating the eggshell membranes from calcified shells; drying and grinding the eggshell membranes; separating and extracting total glycosaminoglycan from the ground eggshell membranes; removing heparin / heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate from the total glycosaminoglycan, and separating the hyaluronic acid from chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate. By the method, high-purity hyaluronic acid can be separated out, direct extraction of the hyaluronic acid from the eggshell membranes of poultry is realized, extensive sources are available, and the obtained hyaluronic acid which is derived from natural tissues of animals is stable in molecular weight and free of endotoxin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
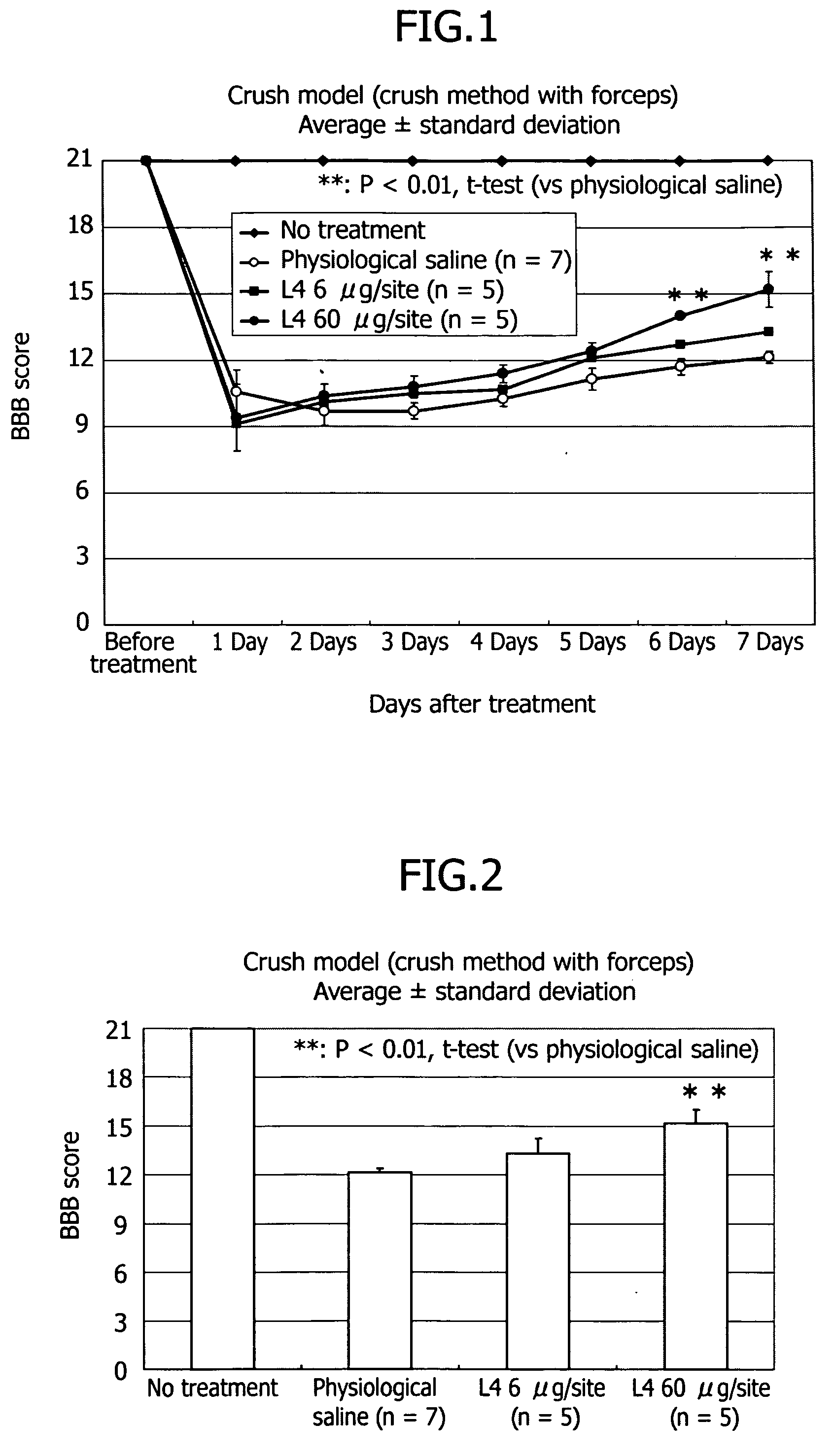
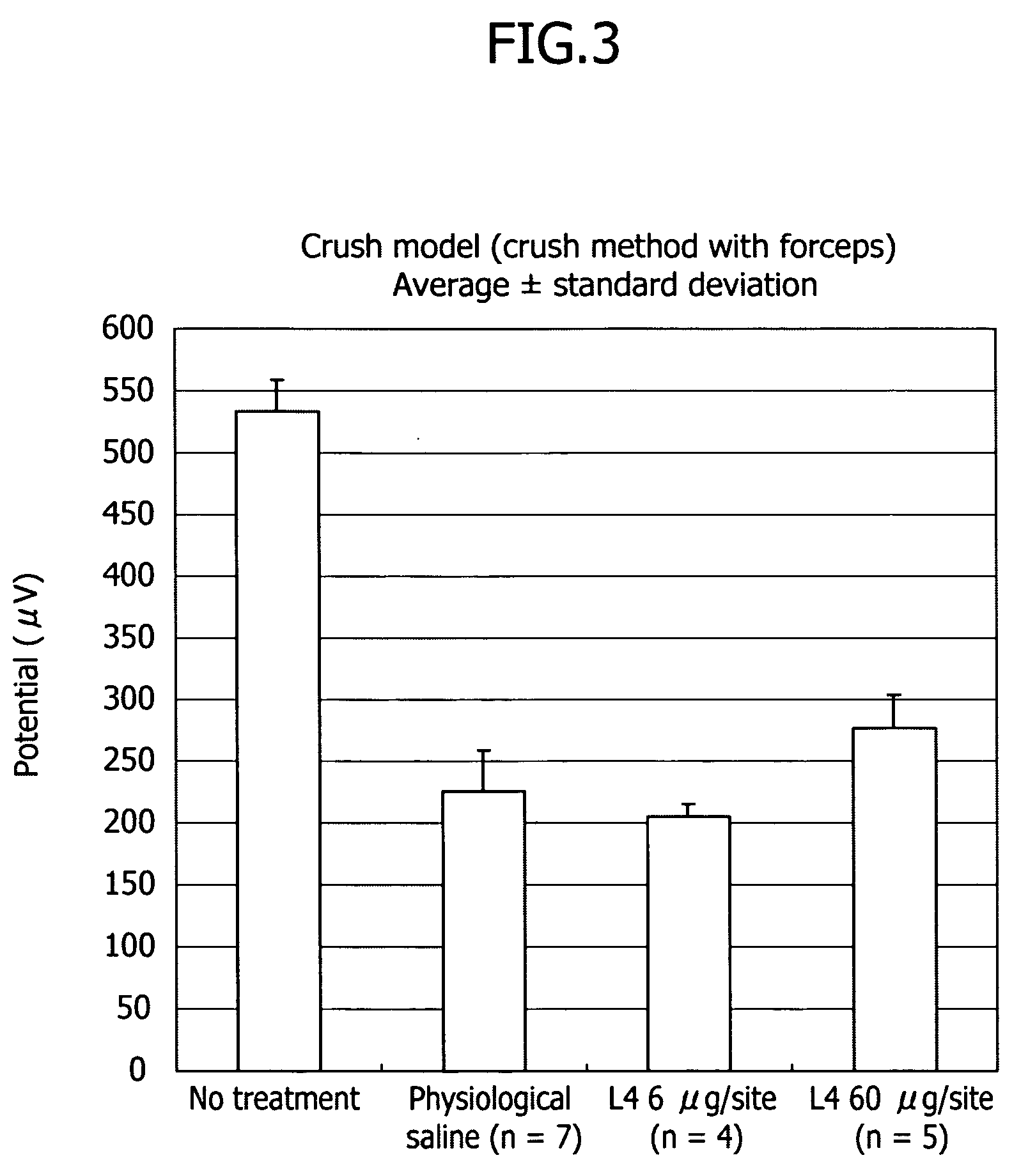
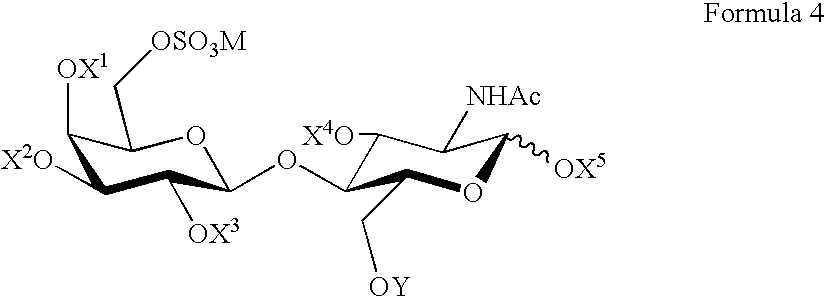
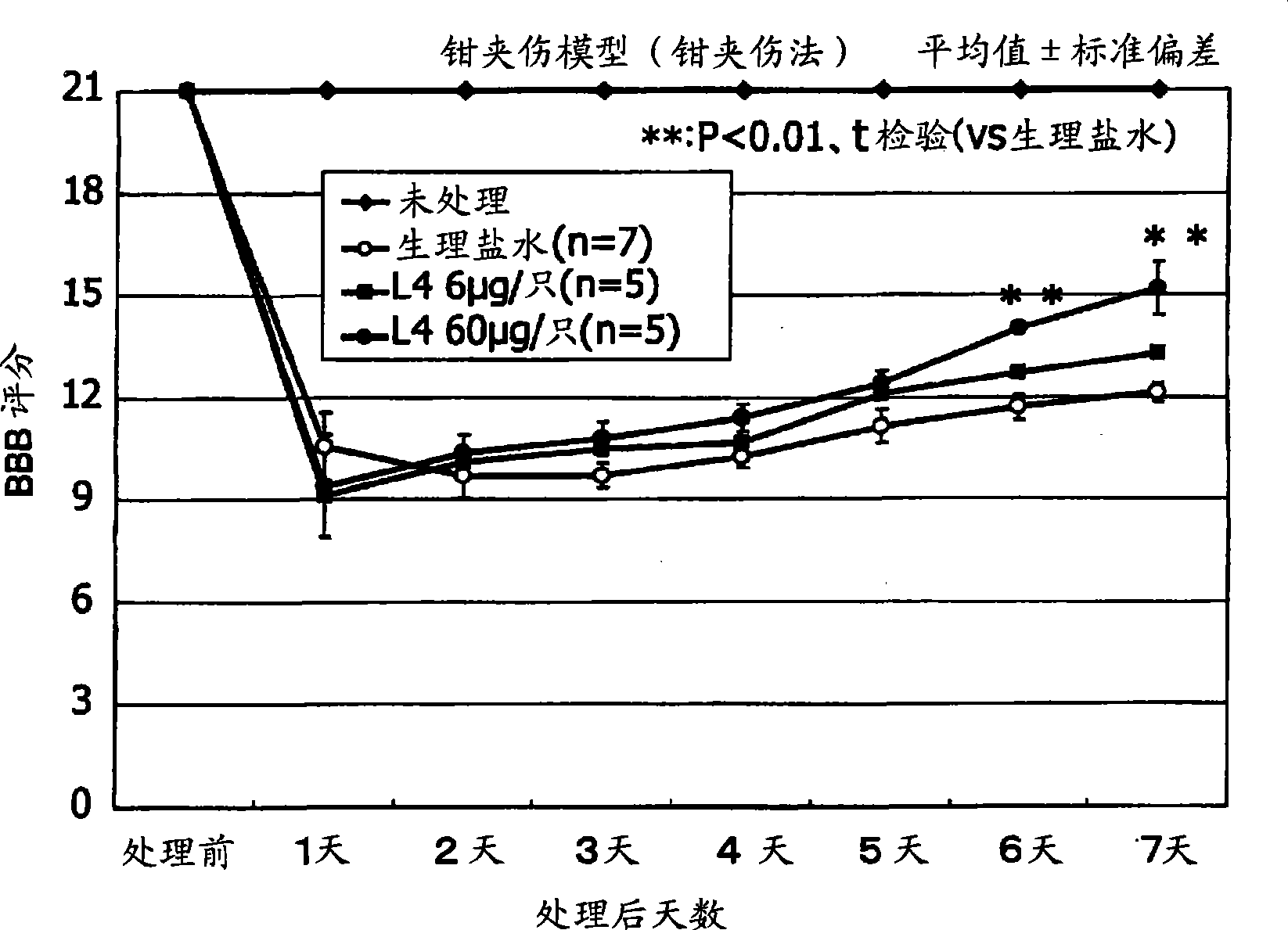
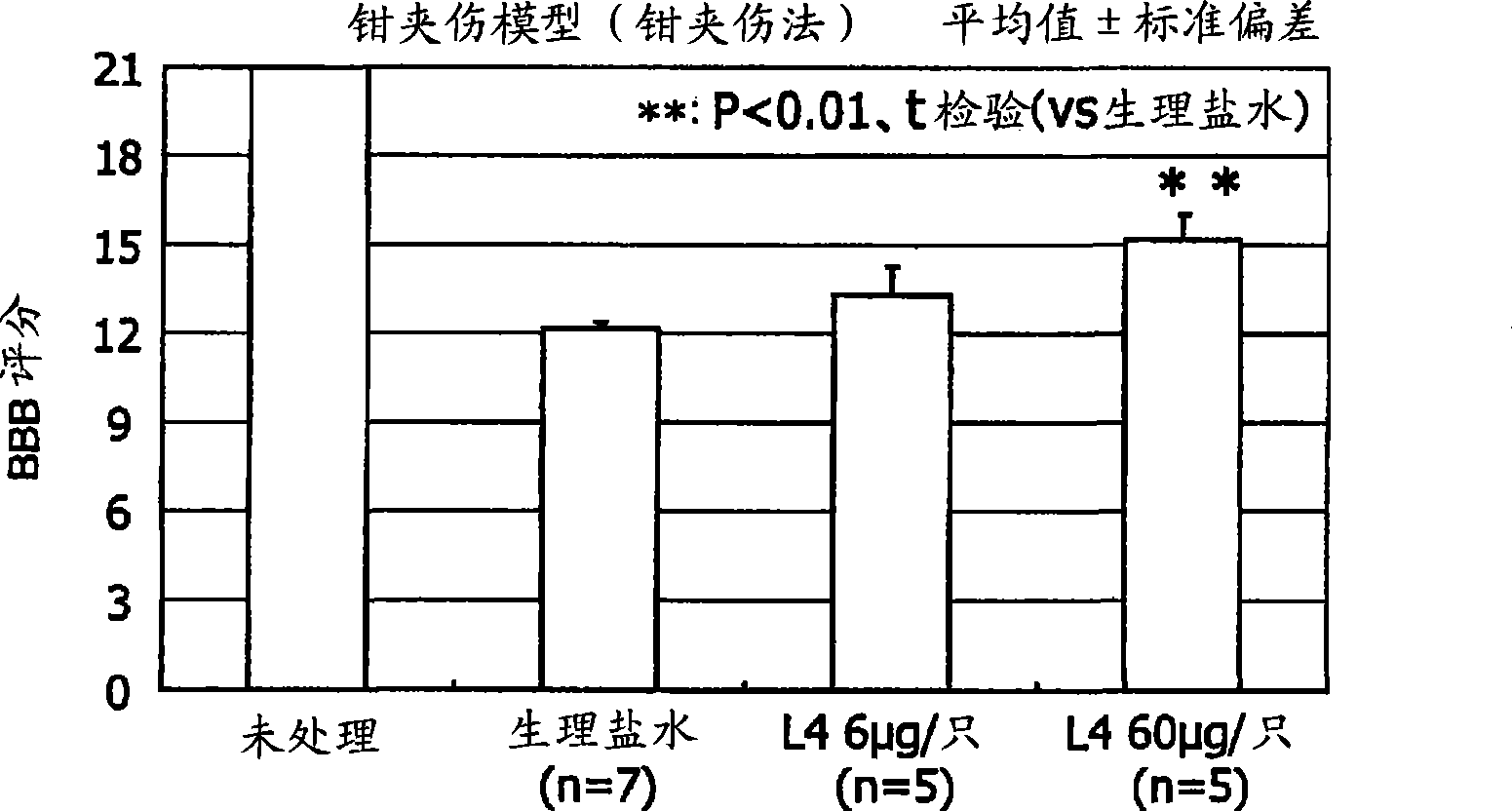
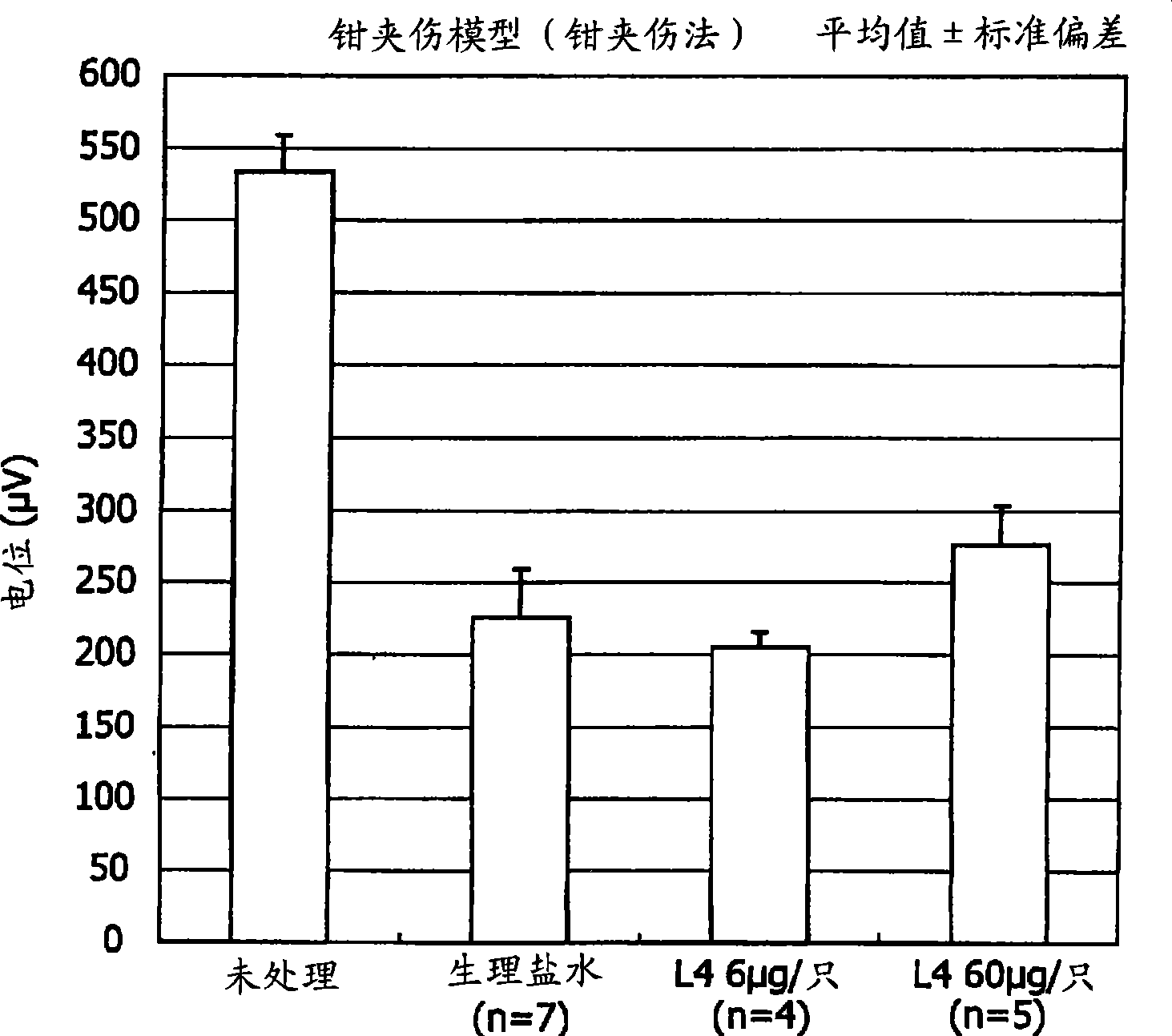
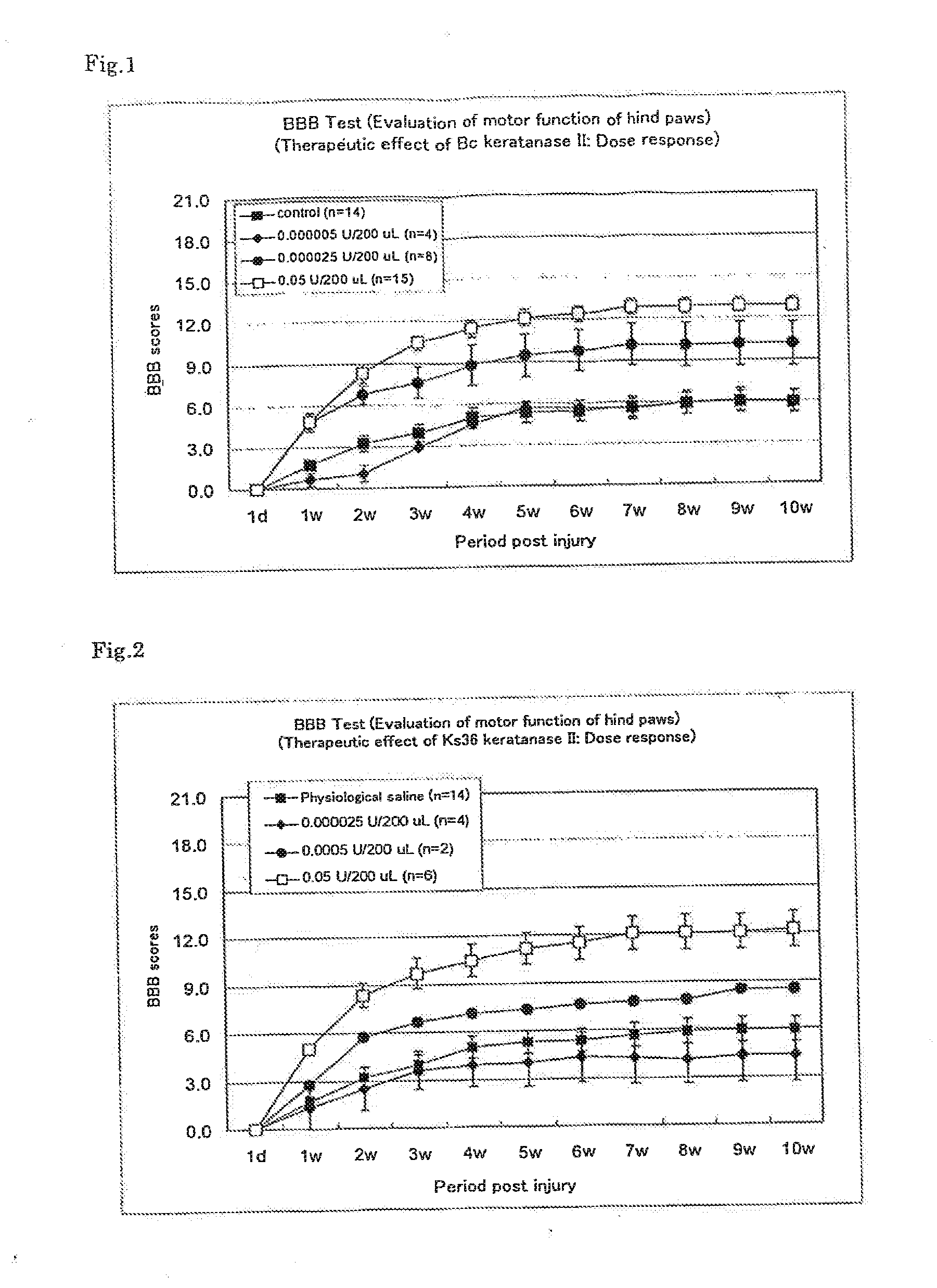
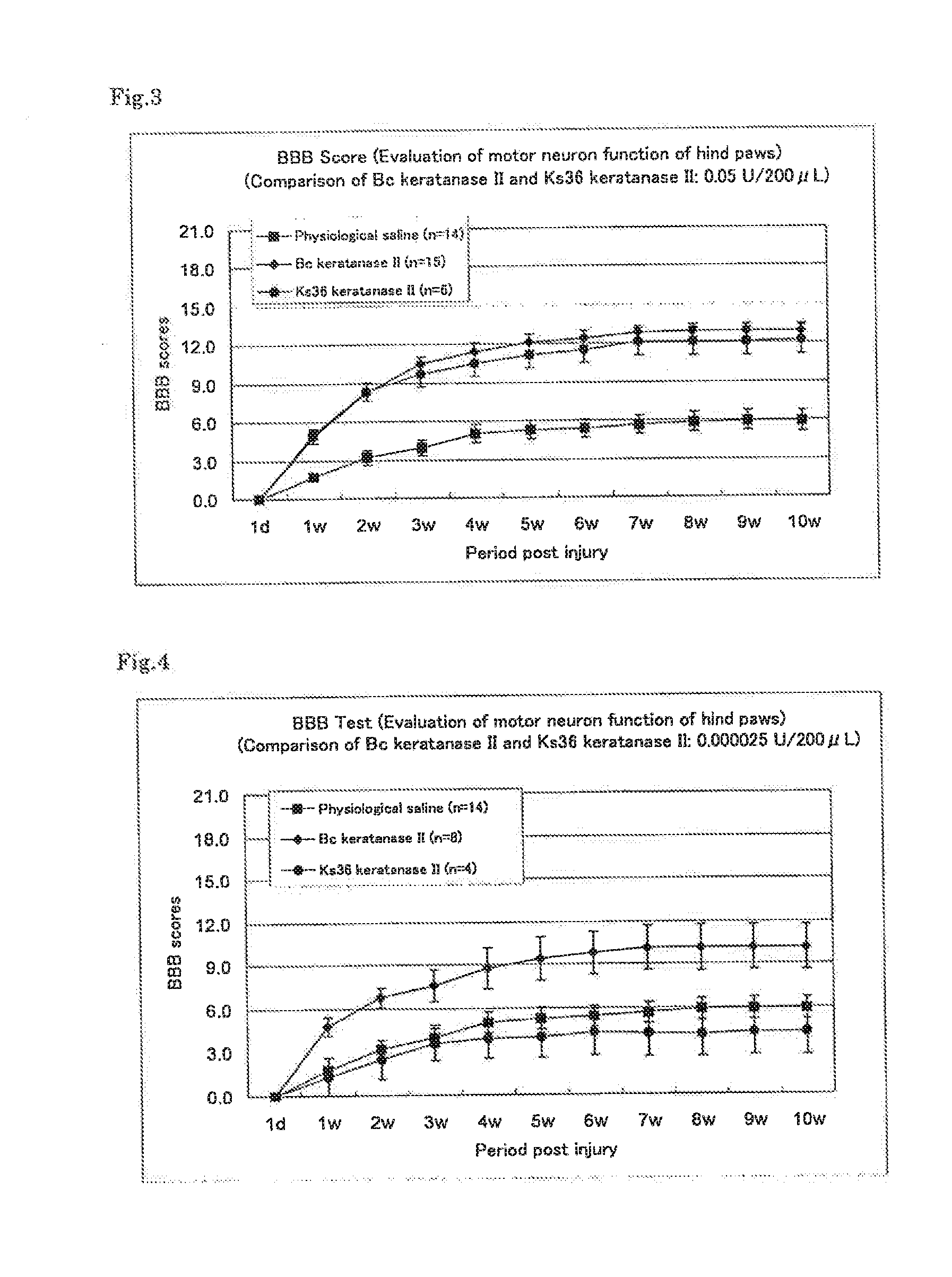
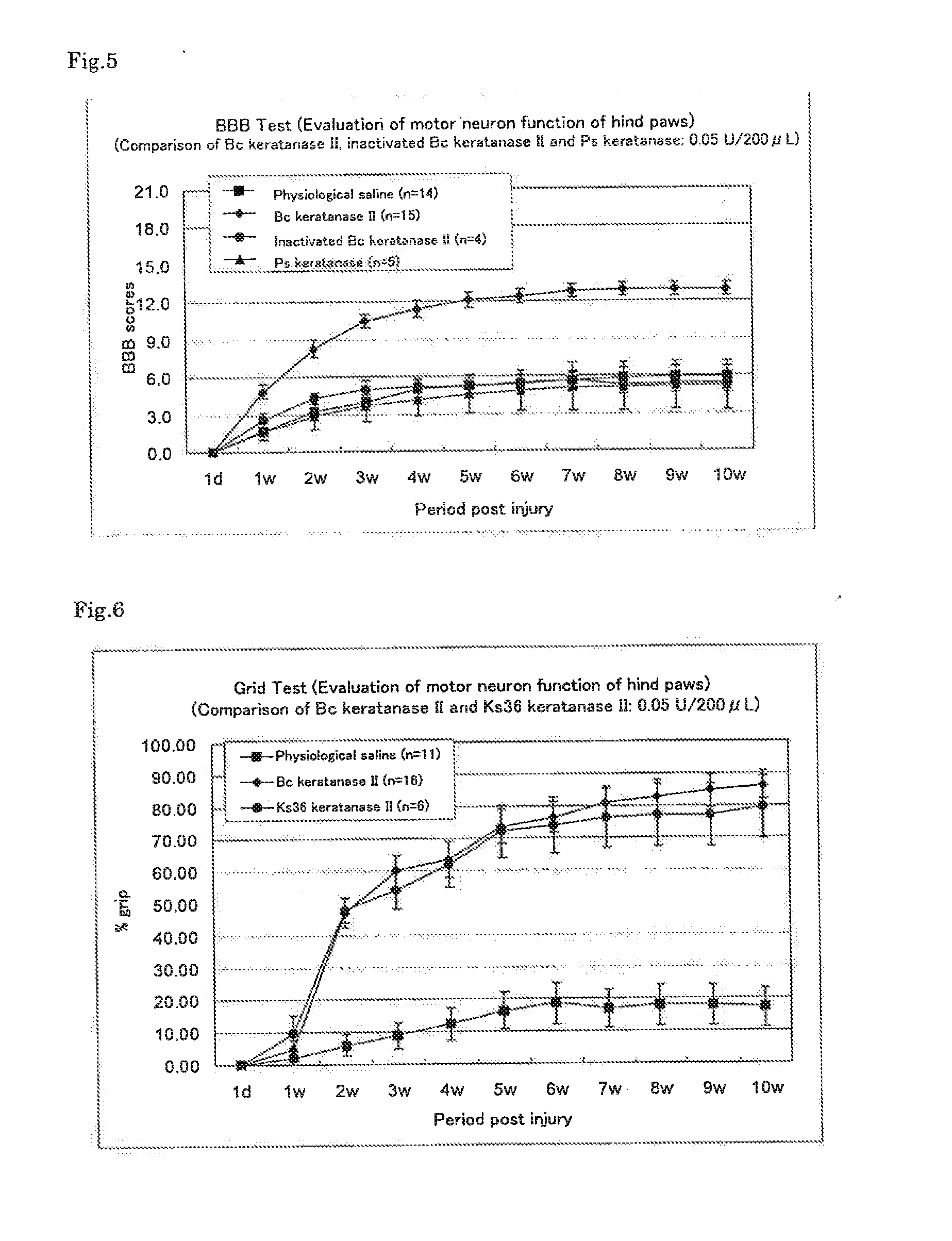
Therapeutic drug for traumatic neural disease (disorder) and/or motor function disorder
InactiveUS20070167399A1Improvement effect on motor function disorderBiocideOrganic active ingredientsMotor functionOligosaccharide
The object is to provide a therapeutic drug for traumatic neural disease (disorder) and / or motor function disorder, more particularly, a therapeutic drug for traumatic neural disease (disorder) and / or motor function disorder derived from spinal cord injury. A keratan sulfate oligosaccharide or a derivative thereof was found to have an effect of improving the traumatic neural disease (disorder) and / or motor function disorder derived from spinal cord injury and to be useful as the therapeutic drug for traumatic neural disease (disorder) and / or motor function disorder. That is, according to the present invention, there is provided a therapeutic drug for traumatic neural disease (disorder) and / or motor function disorder comprising an effective amount of the keratan sulfate oligosaccharide or the derivative thereof.
Owner:GLYCOSCIENCE LAB INC
Purification and detection method for keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate
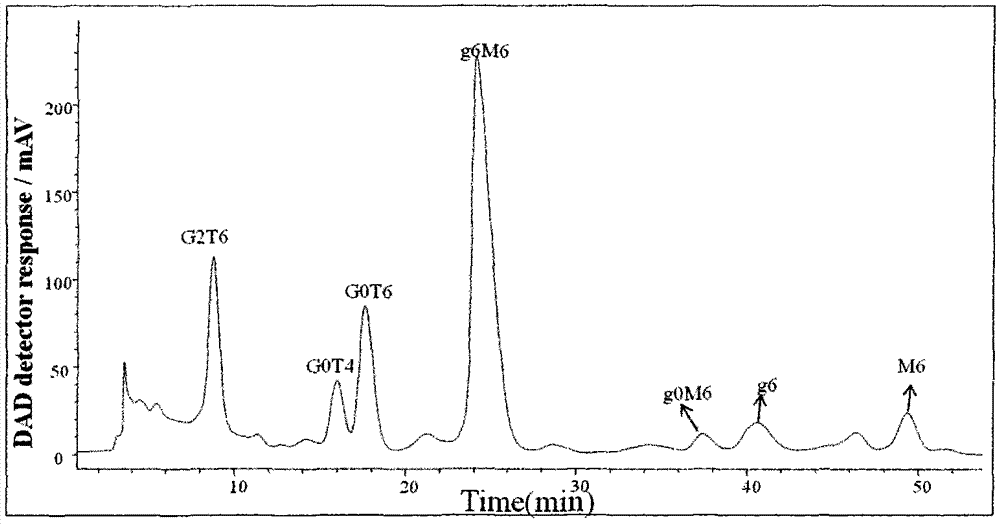
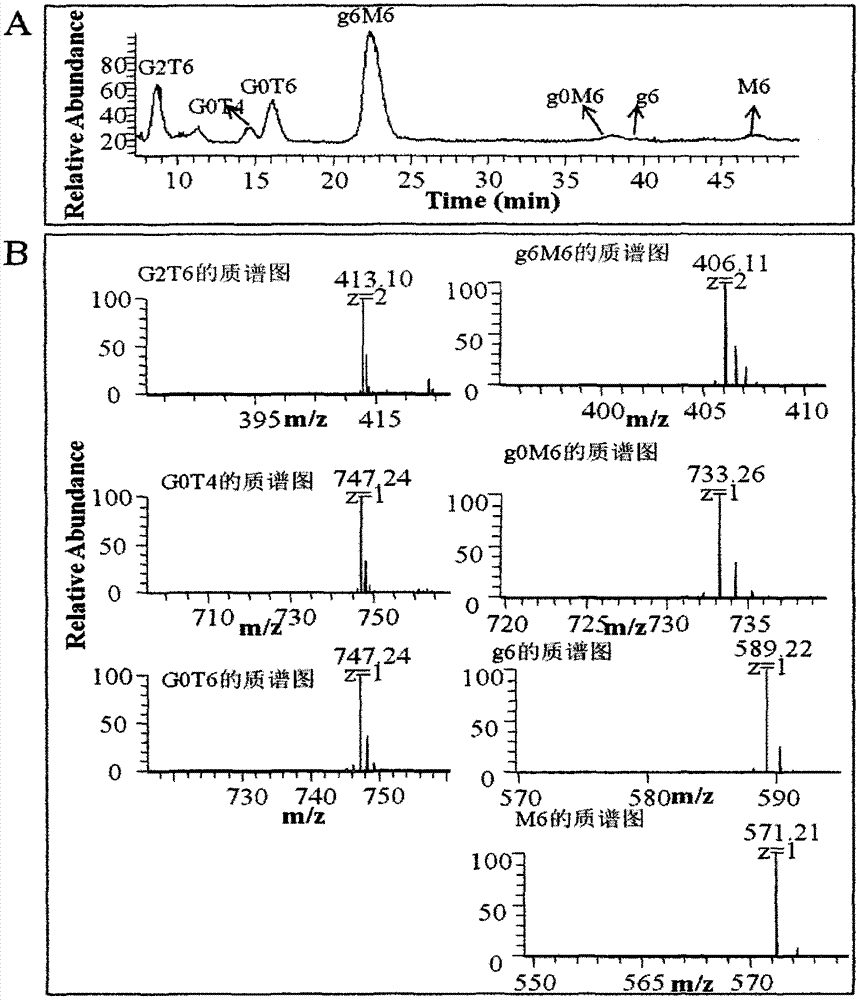
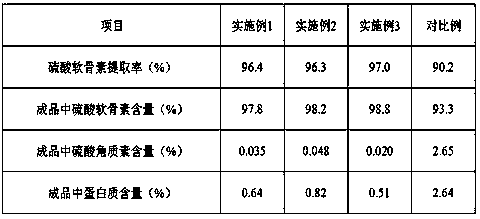
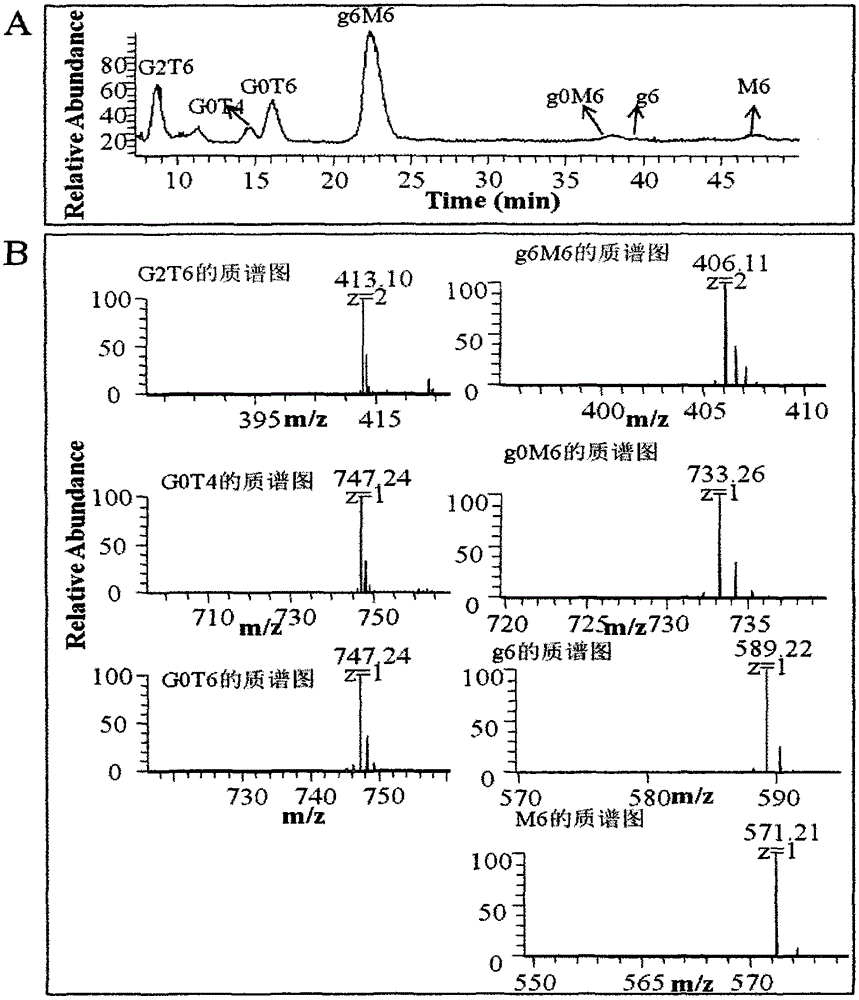
Belonging to the field of medicines, the invention relates to a purification and detection method for keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate. The method includes the steps of: (1) detecting the keratan sulfate in a chondroitin sulfate mixture; (2) separating and purifying the keratan sulphate in chondroitin sulfate; and (3) detecting the content of keratan sulfate. The method provided by the invention can degrade the glycosaminoglycan in the chondroitin sulfate mixture into disaccharide completely, can save all uronic acid structural information, and can accurately and totally obtain the structural information of chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate disaccharide. The trace keratan sulfate in the chondroitin sulfate mixture can be qualitative and quantitative. The chemical degradation conditions are mild, the cost is low, the operation is simple, and the requirements for experimental instruments are low. With a wide application range, the method is suitable for detection of keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate from any source. The detection needs short time, the sample consumption is small, the sensitivity is high, the analysis result has good repeatability, and the detection limit is ng level.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Anti-aging skin activating and caring liquid containing growth factors and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107648066AReduce harmIncrease elasticityCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsAdditive ingredientLotion
The present invention relates to an anti-aging and revitalizing skin care liquid containing growth factors and a preparation method thereof. 0.5-3 parts, recombinant human epidermal growth factor 0.00001-0.0005 parts, recombinant human basic fibroblast growth factor 0.00001-0.0005 parts, naringenin 0.05-1 part, N-acetylglucosamine 1-4 parts, preservative 0.01-1 part, 4-8 parts of glycerin, 1-3 parts of panthenol triacetate, 2-6 parts of keratan sulfate oligosaccharides and 50-70 parts of water. The composition of the skin care lotion provided by the invention is reasonably matched, scientifically proportioned, exerts a synergistic effect, and has outstanding moisturizing and anti-aging effects.
Owner:GUANGDONG COOWAY BIOTECH CO LTD
Therapeutic drug for traumatic neural disease (disorder) and/or motor function disorder
Provided is a therapeutic agent for traumatic neuropathy and / or movement disorder, particularly a therapeutic agent for traumatic neuropathy and / or movement disorder caused by spinal cord injury. It is found that a keratan sulfate oligosaccharide or a derivative thereof has an ameliorative effect on traumatic neuropathy and / or movement disorder caused by spinal cord injury and therefore is useful as a therapeutic agent for traumatic neuropathy and / or movement disorder. Thus, provided is a therapeutic agent for traumatic neuropathy and / or movement disorder, wherein the therapeutic agent comprises an effective amount of a keratan sulfate oligosaccharide or a derivative thereof.
Owner:GLYCOSCIENCE LAB INC
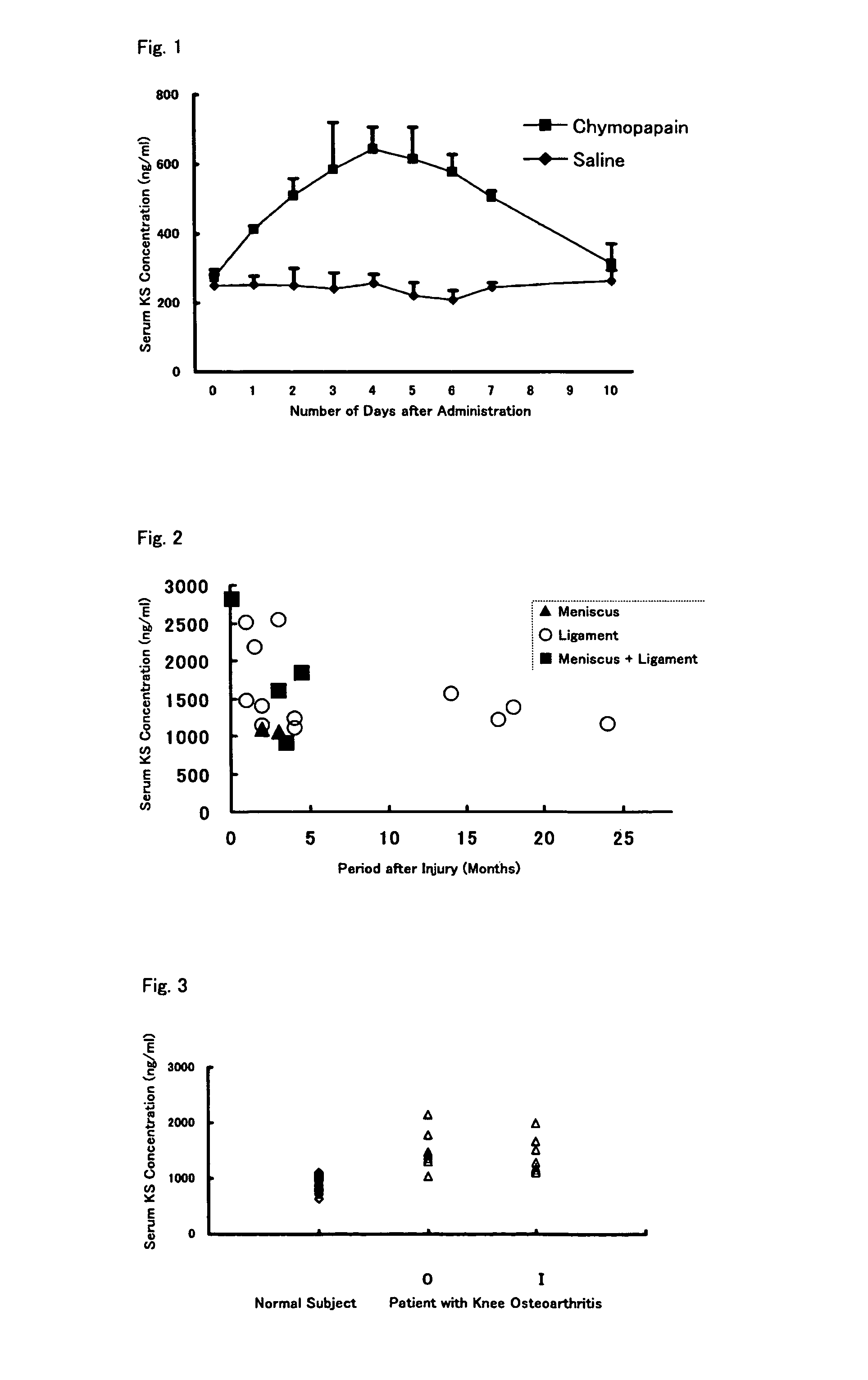
Method of detecting articular cartilage degeneration or damage
InactiveUS8557536B2Improve progressSymptoms improvedMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSacroiliac jointArticular cartilage
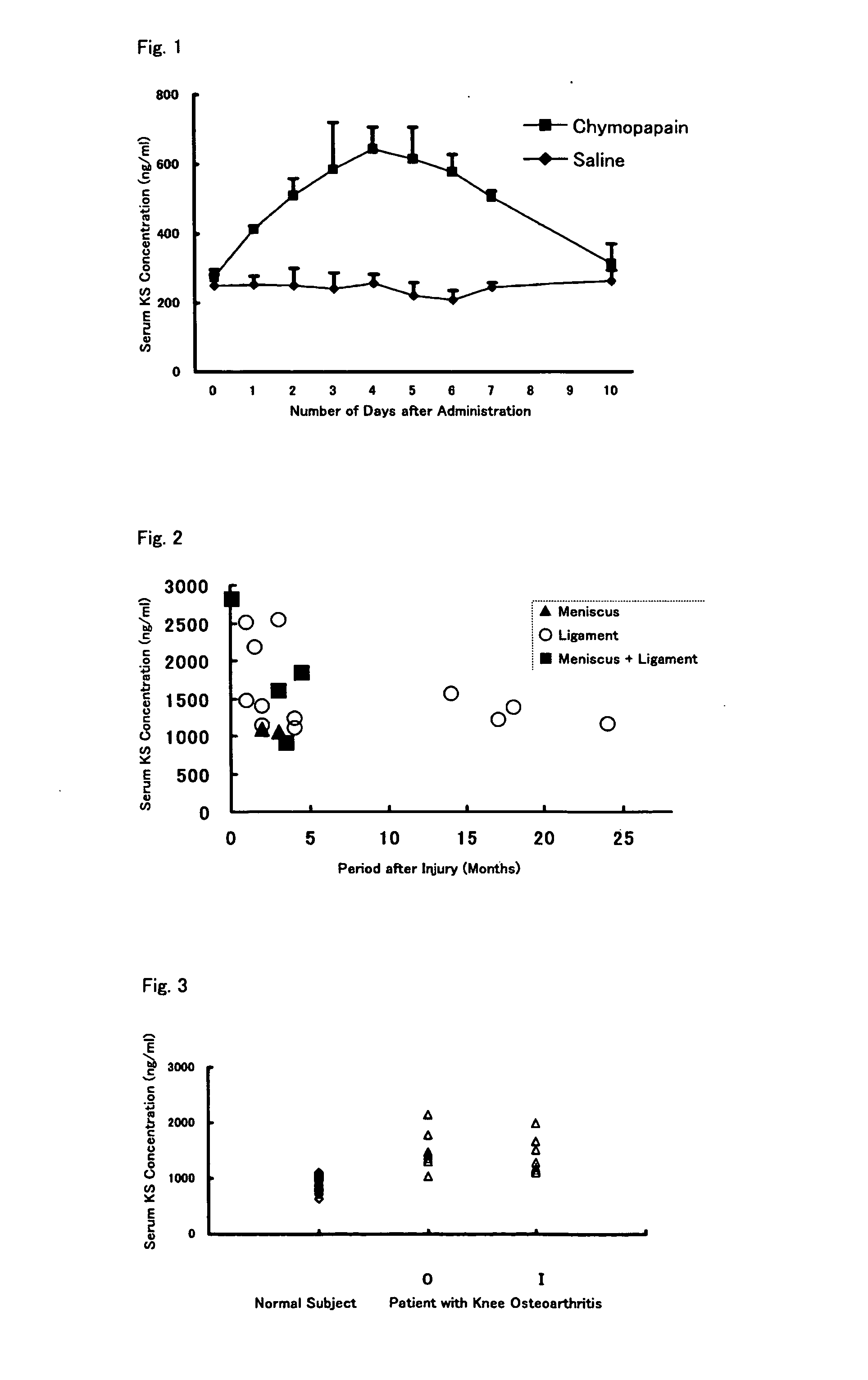
An object of the present invention is to provide a detection method capable of detecting articular cartilage degeneration or damage in which the abnormality cannot be detected in a radiograph in a simple method and with high accuracy, a method of evaluating the rate of progression of articular cartilage degeneration or damage, and the like.The present invention as a means for achieving the object provides a method of detecting articular cartilage degeneration or damage which cannot be detected in a radiograph, by using the concentration of keratan sulfate in a sample derived from blood as an index, and the like.Further, the present invention provides a method of evaluating the rate of progression of articular cartilage degeneration or damage by using the concentration of keratan sulfate in a sample derived from blood as an index, and the like.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Method and kit for detecting stem cell
Owner:FUJIFILM WAKO PURE CHEM CORP +1
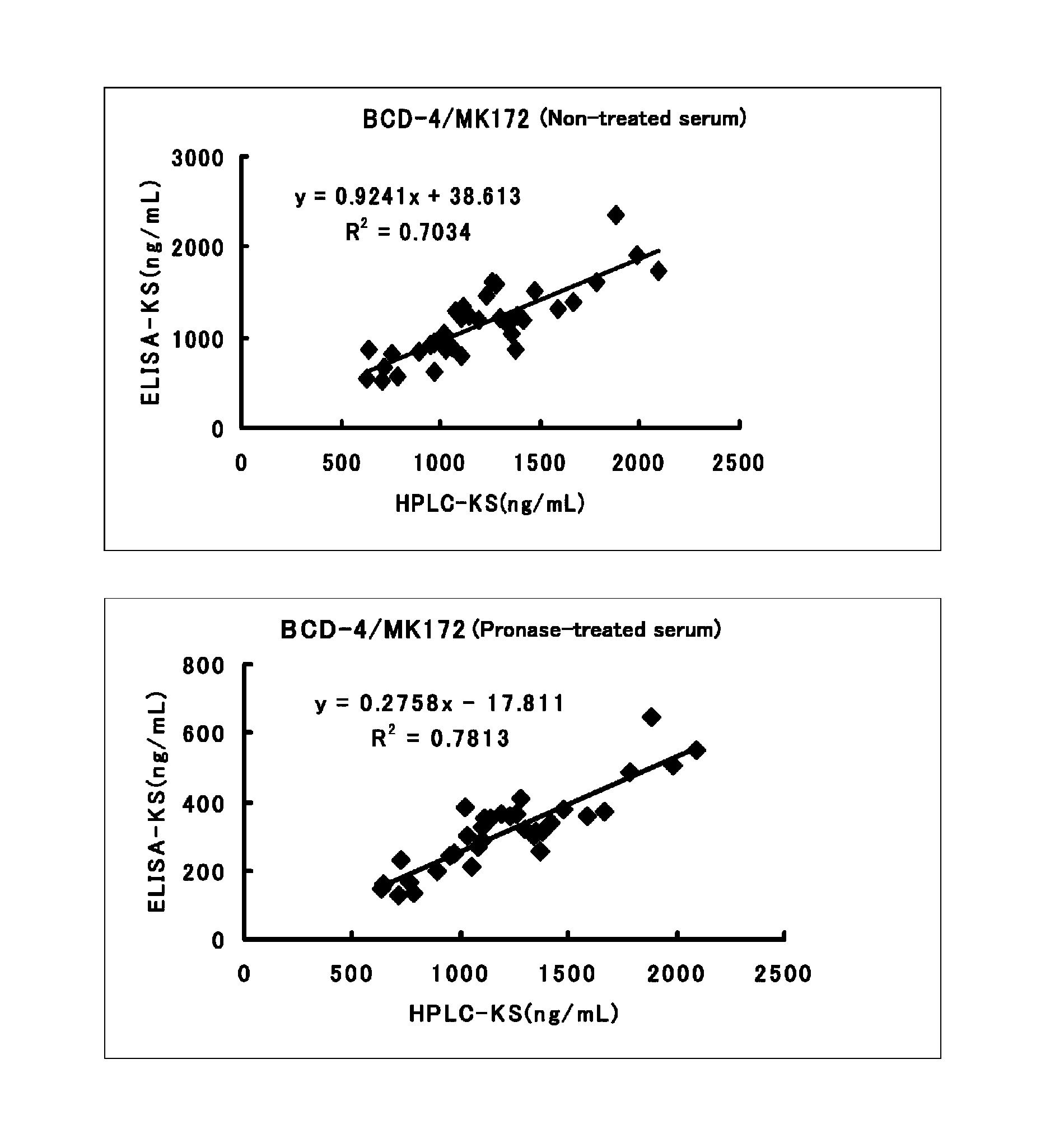
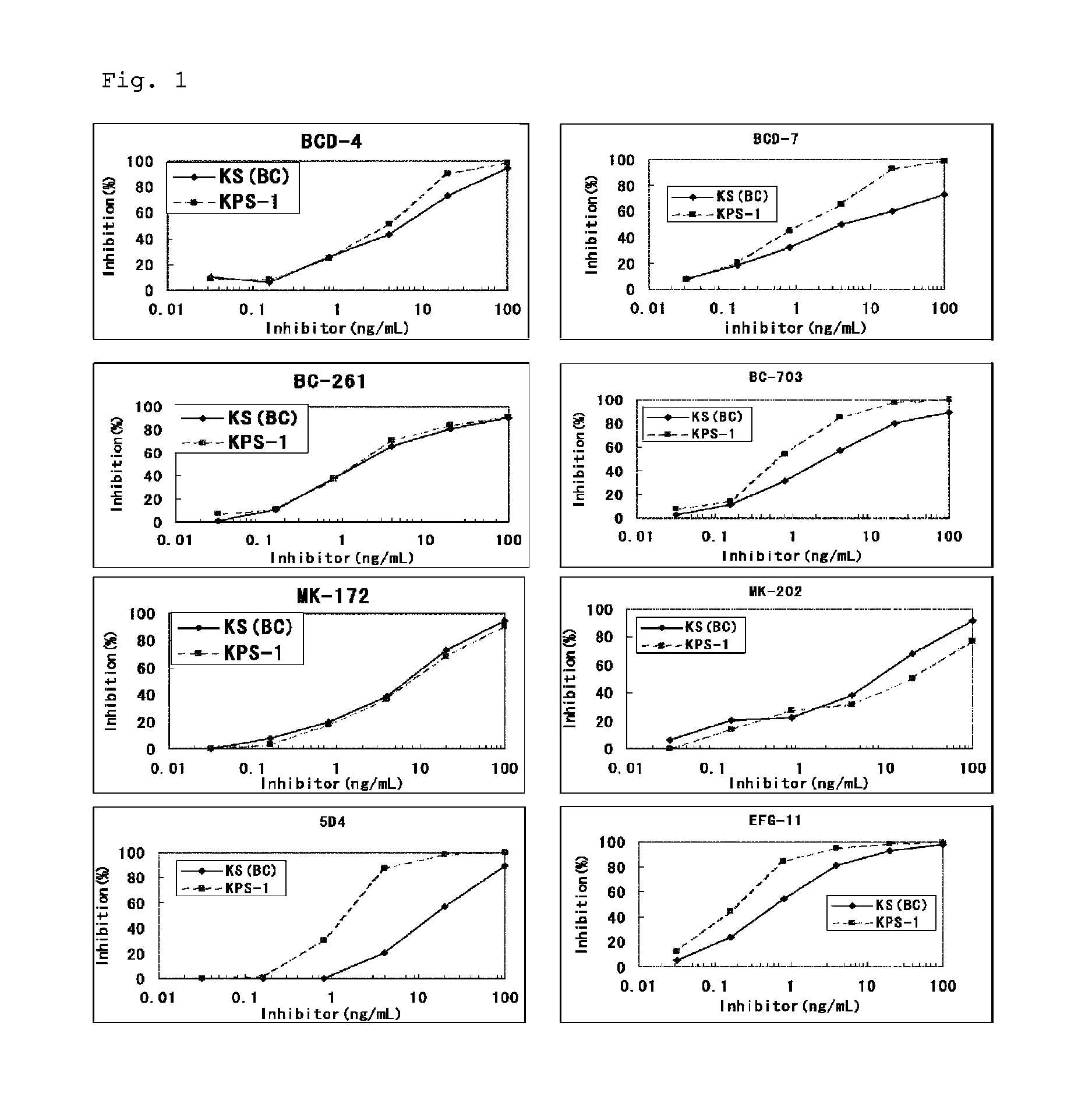
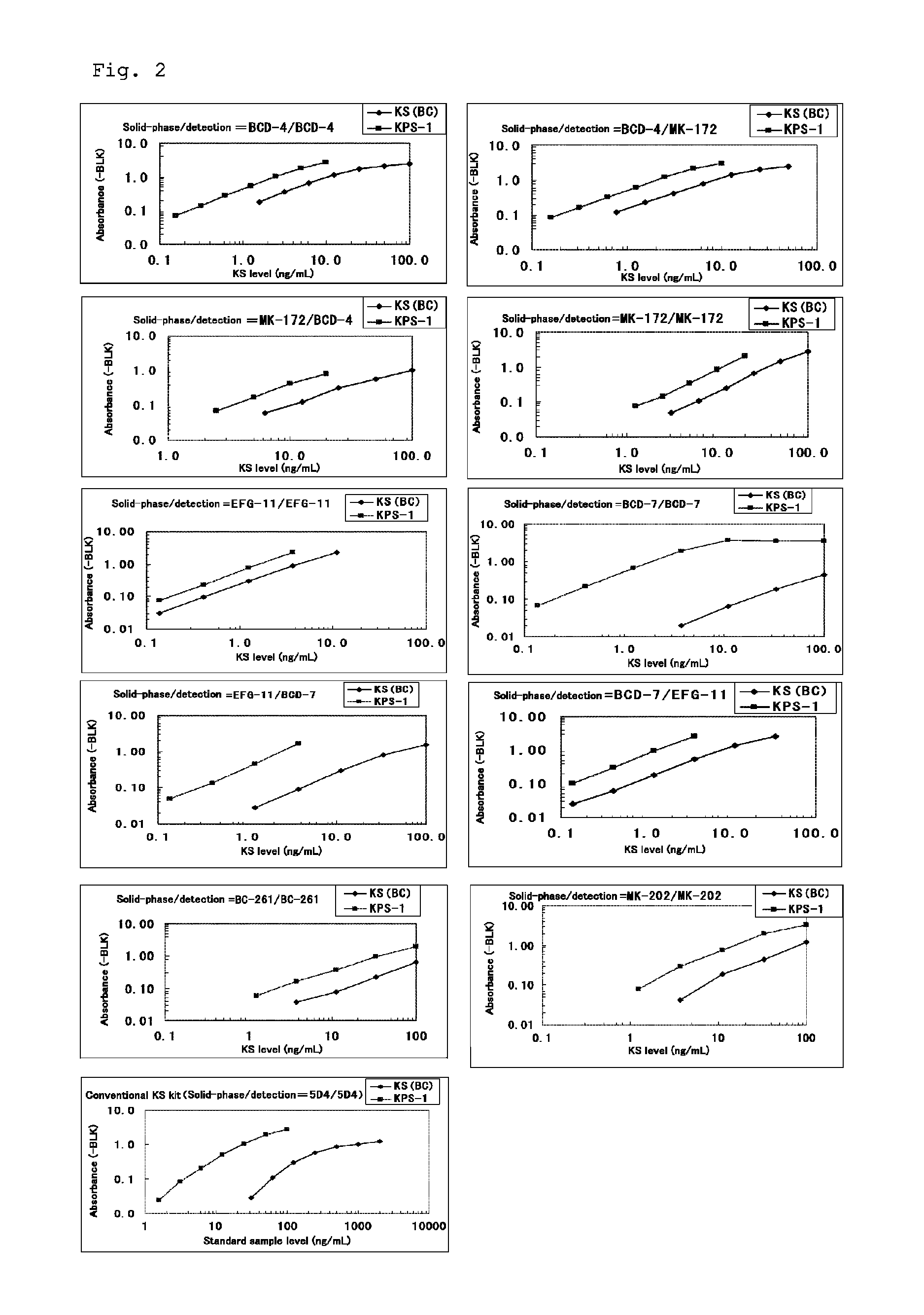
Method for assaying keratan sulfate, assay kit therefor and method for detecting joint disease by using the same
InactiveUS20110318759A1High sensitivityDifficult to determineImmunoglobulins against animals/humansDisease diagnosisDiseaseTreatment effect
The inventions provides a method for immunologically determining a keratan sulfate level which method includes bringing an anti-keratan sulfate monoclonal antibody into contact with a biological sample, the anti-keratan sulfate monoclonal antibody exhibiting a relative reaction specificity between keratan sulfate-I and keratan sulfate-II represented by IC50KS-I / KS-II of 0.4 to 5, to thereby provide a signal; and detecting keratan sulfate contained in the biological sample from the signal. On the basis of the method, the invention also provides a joint disease detection method and a method for assessing the effect of a remedy for a joint disease and a candidate substance therefor. Through these methods, a very small amount of keratan sulfate contained in a sample, can be determined. Particularly, these methods can determine, at high-sensitivity and high-specificity, the total keratan sulfate including keratan sulfate-I, which have been difficult to determine through a conventional technique. The methods also enables detect a joint disease and assess the effect of a remedy for a joint disease or a candidate substance therefor.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
A method for removing keratan sulfate from chondroitin sulfate crude extract
ActiveCN105777938BBreaking covalent bondsEasy to separateDermatan sulfateElectrical resistivity and conductivity
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology and particularly relates to a method for removing keratan sulfate from a chondroitin sulfate crude extract. The method comprises the following steps of adding a sodium hydroxide solution into a chondroitin sulfate crude extract for reaction; then adding hydrochloric acid to regulate the PH value, filtering to obtain a filtrate, and adding sodium chloride into the filtrate to regulate the electrical conductivity of the solution to be 45-48ms / cm; then adding an ethanol solution, controlling the flow velocity of the ethanol solution to be 10-15mL / (L.min), precipitating chondroitin sulfate, and filtering to obtain a precipitate; dehydrating and drying the precipitate obtain a chondroitin sulfate finished product. The method is easy in control over technological conditions, low in cost, simple in operation and low in experimental apparatus requirement, and can be used for thoroughly solving the problems that removal of the keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate is difficult and industrial production is difficult to realize.
Owner:RIZHAO LANSHAN BIOCHEM PROD
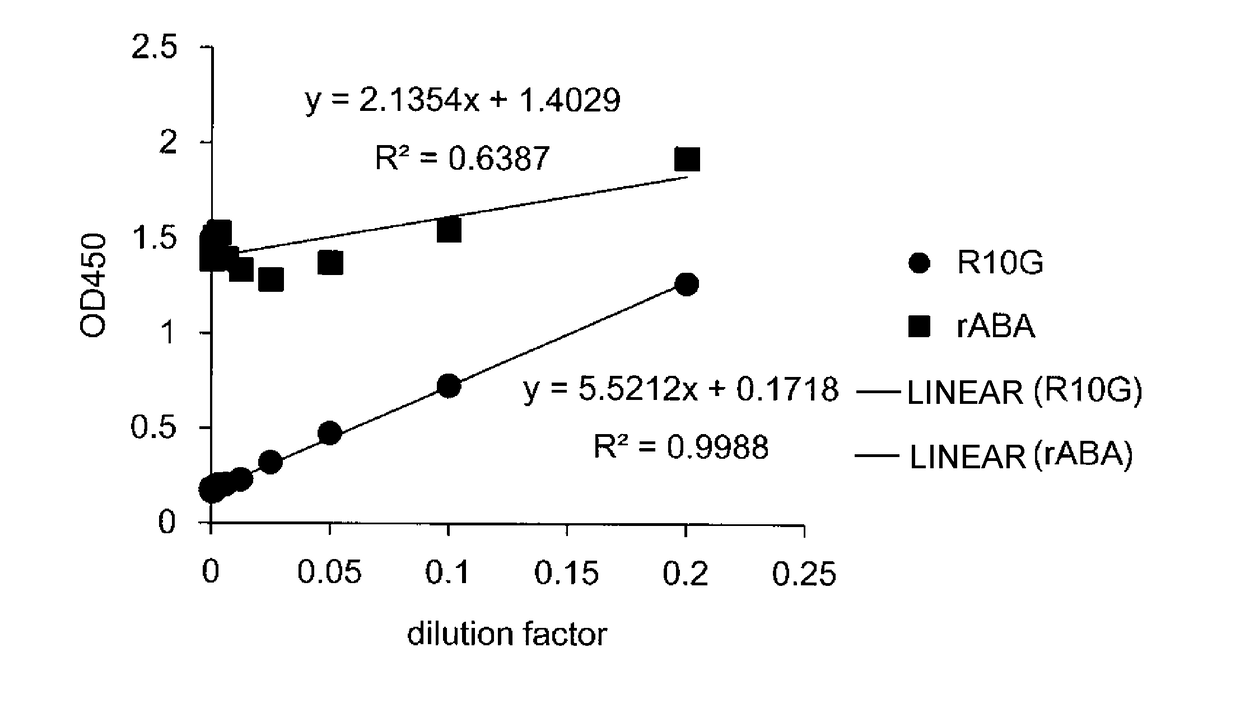
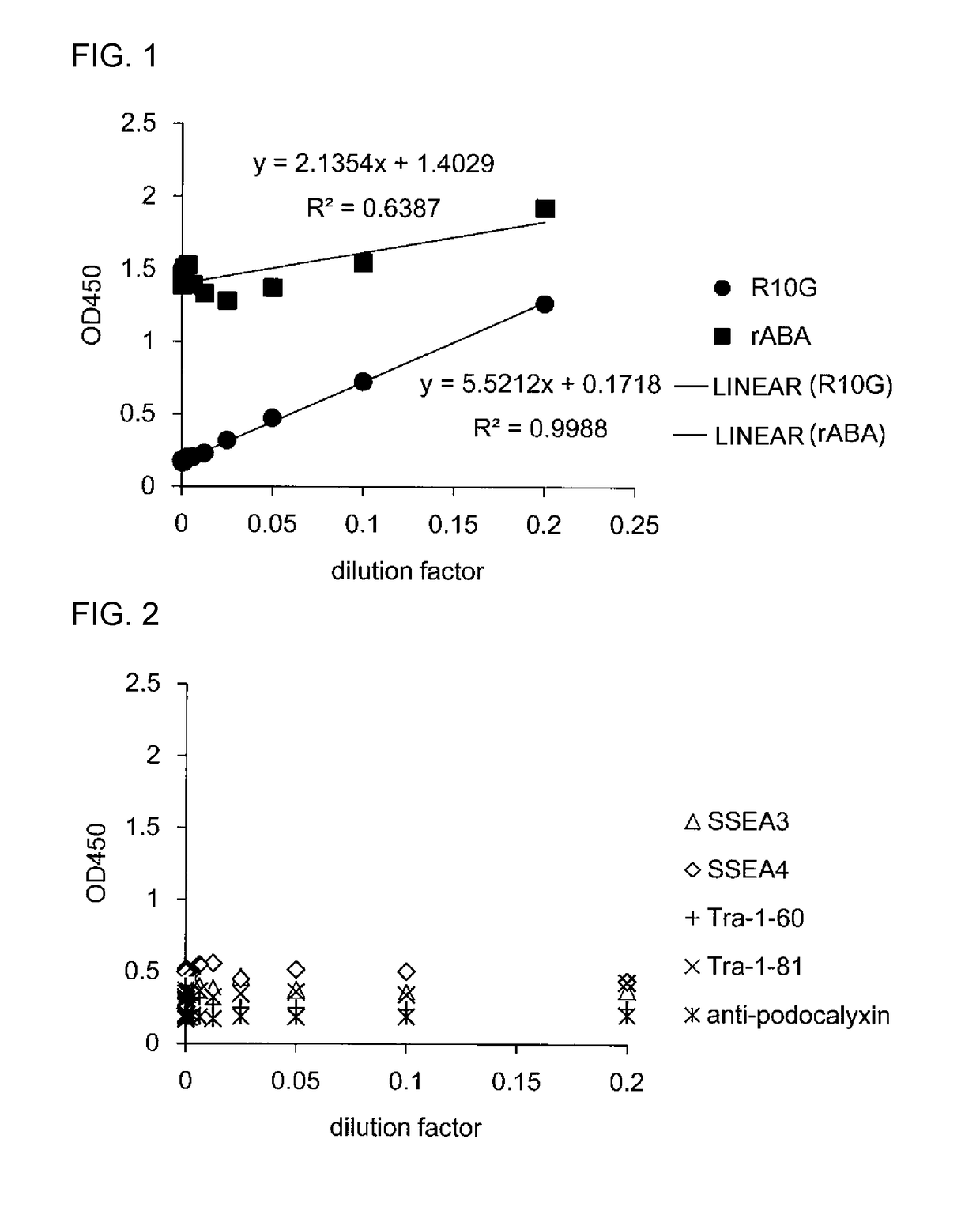
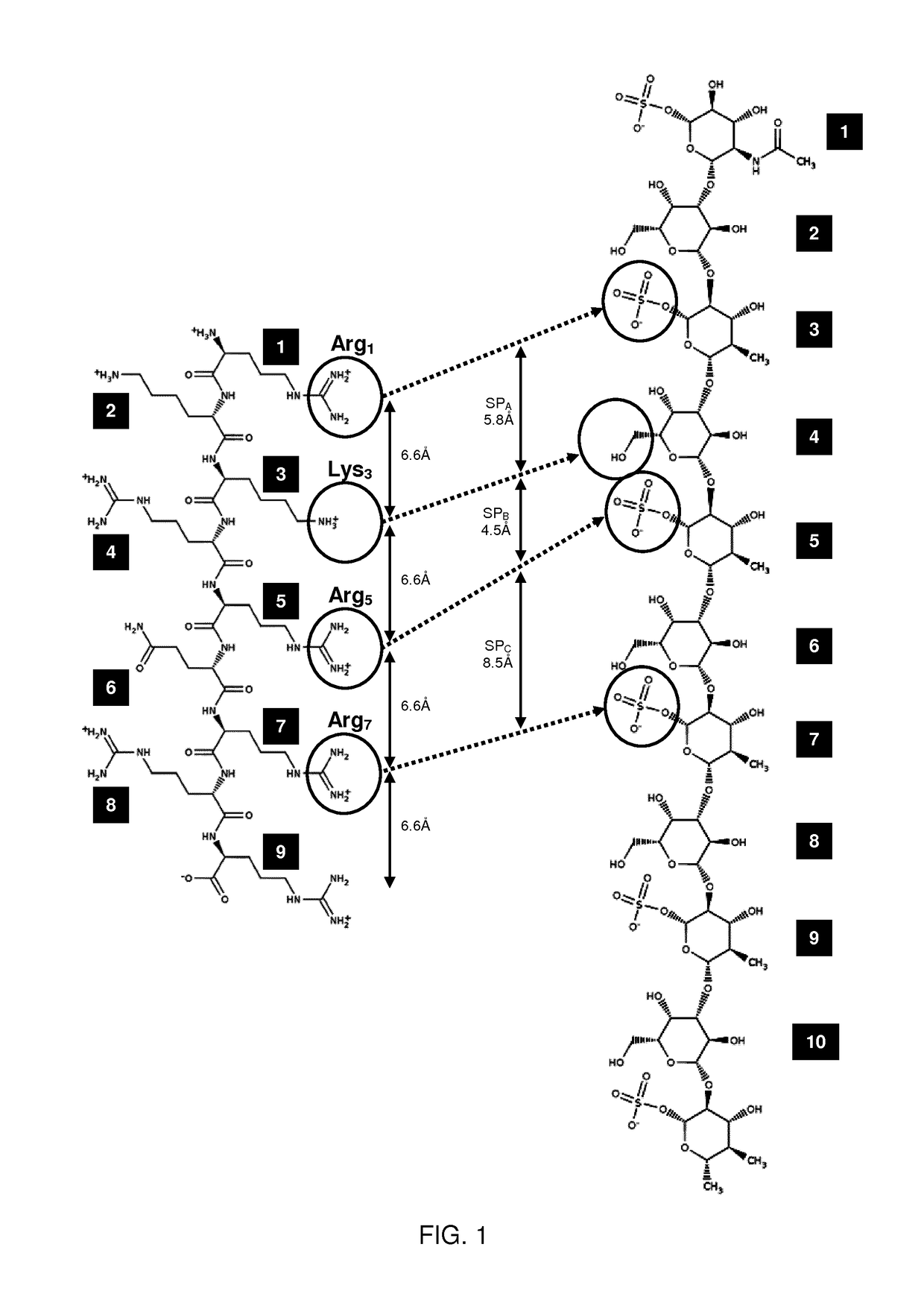
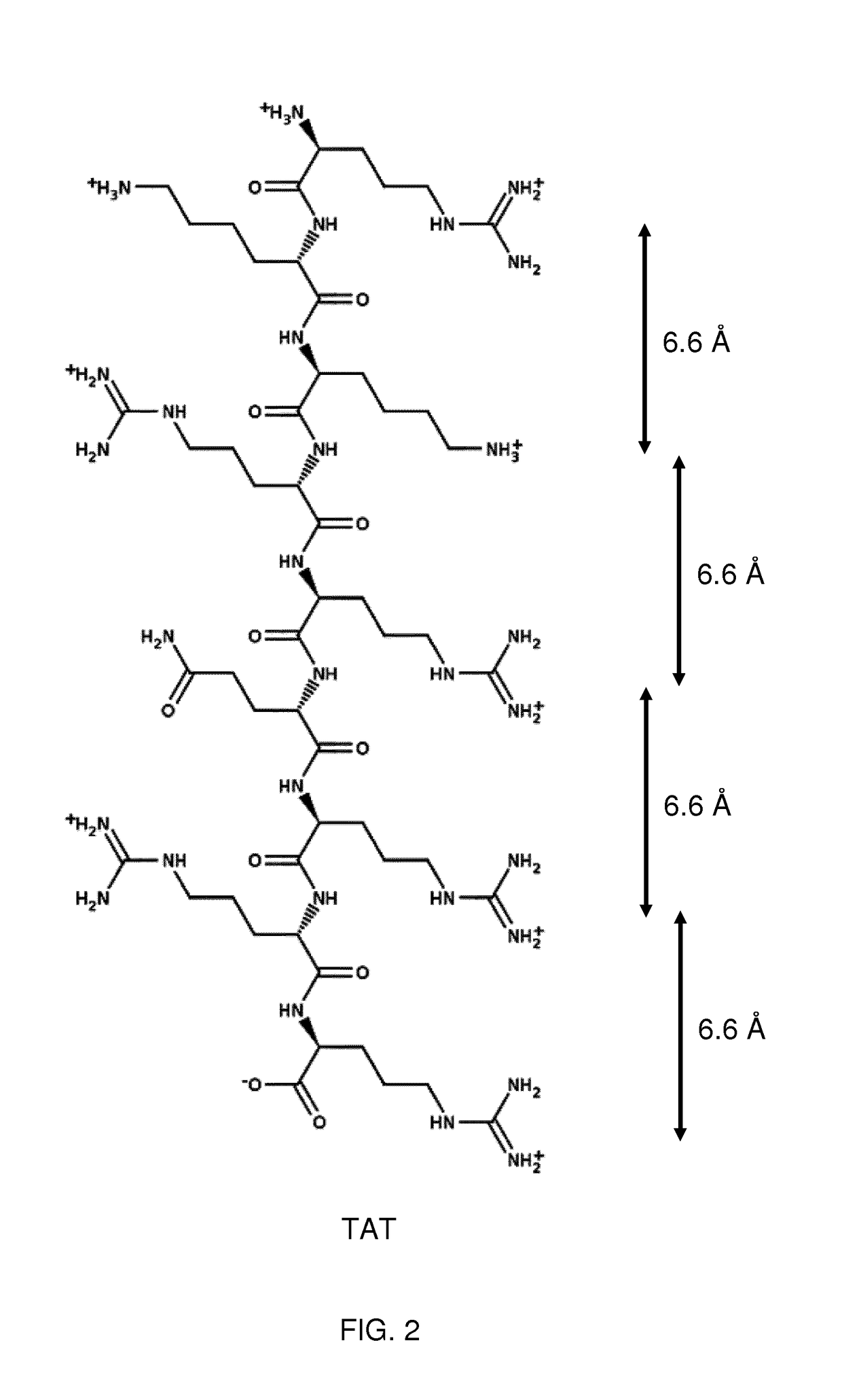
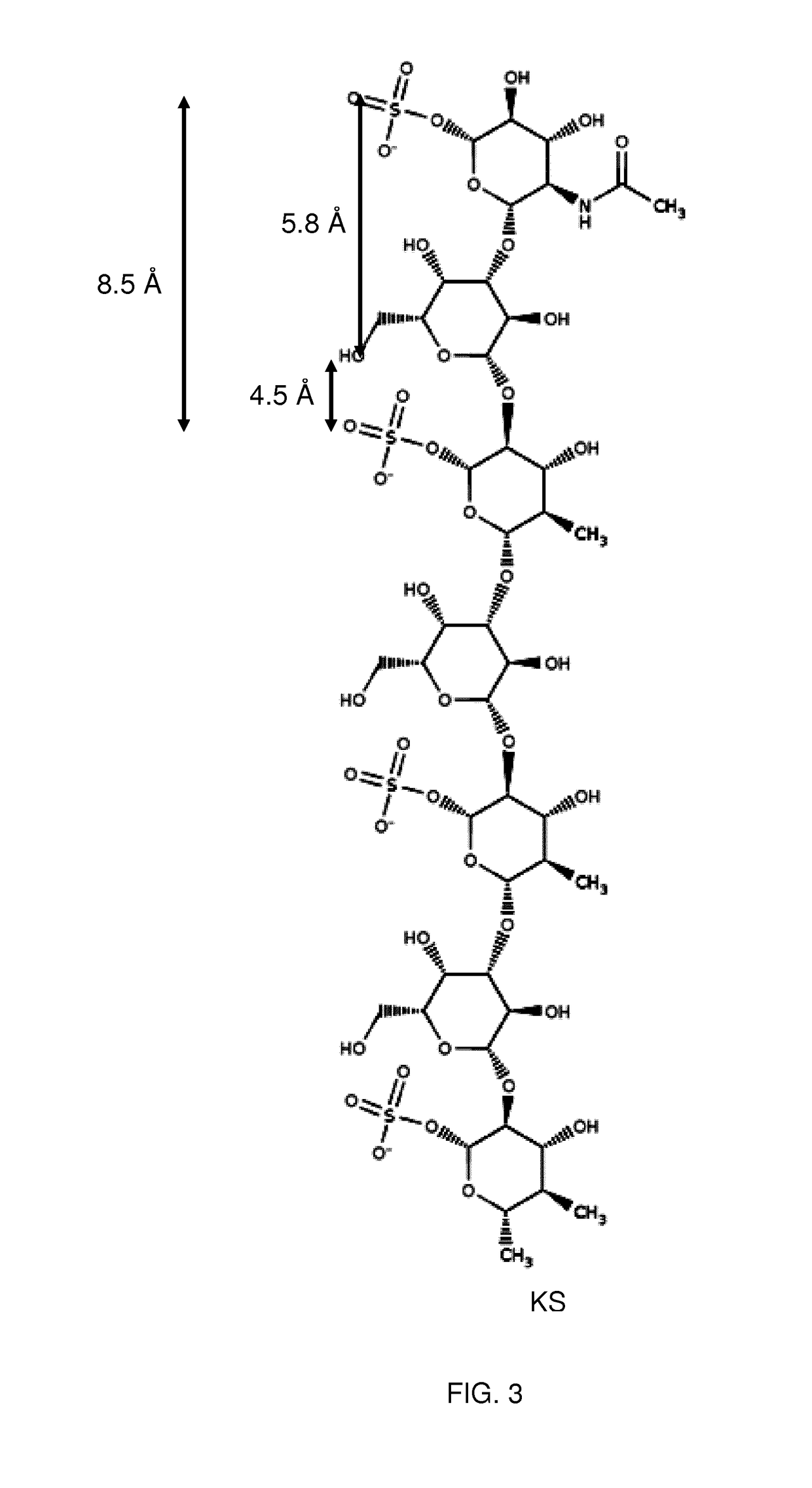
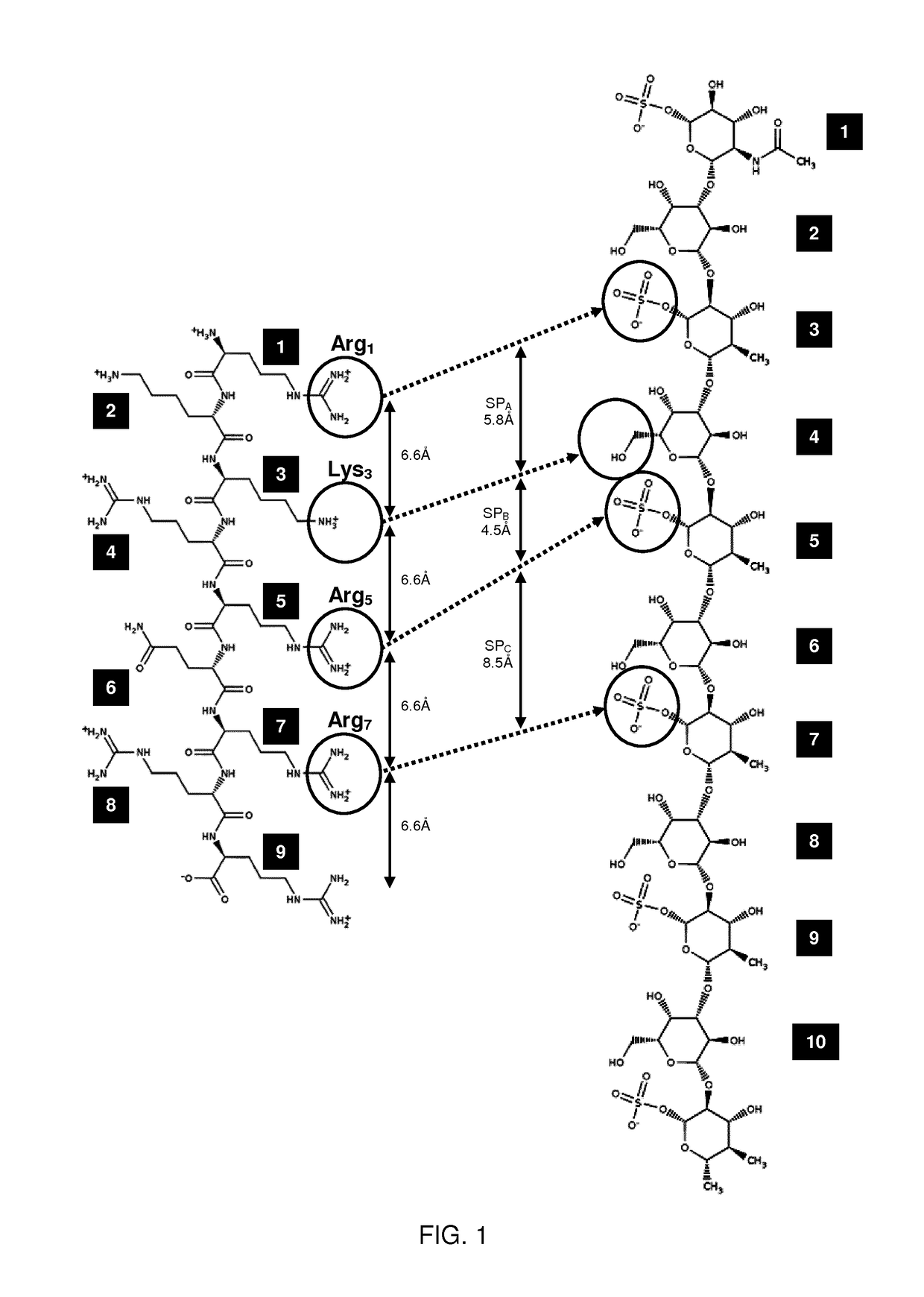
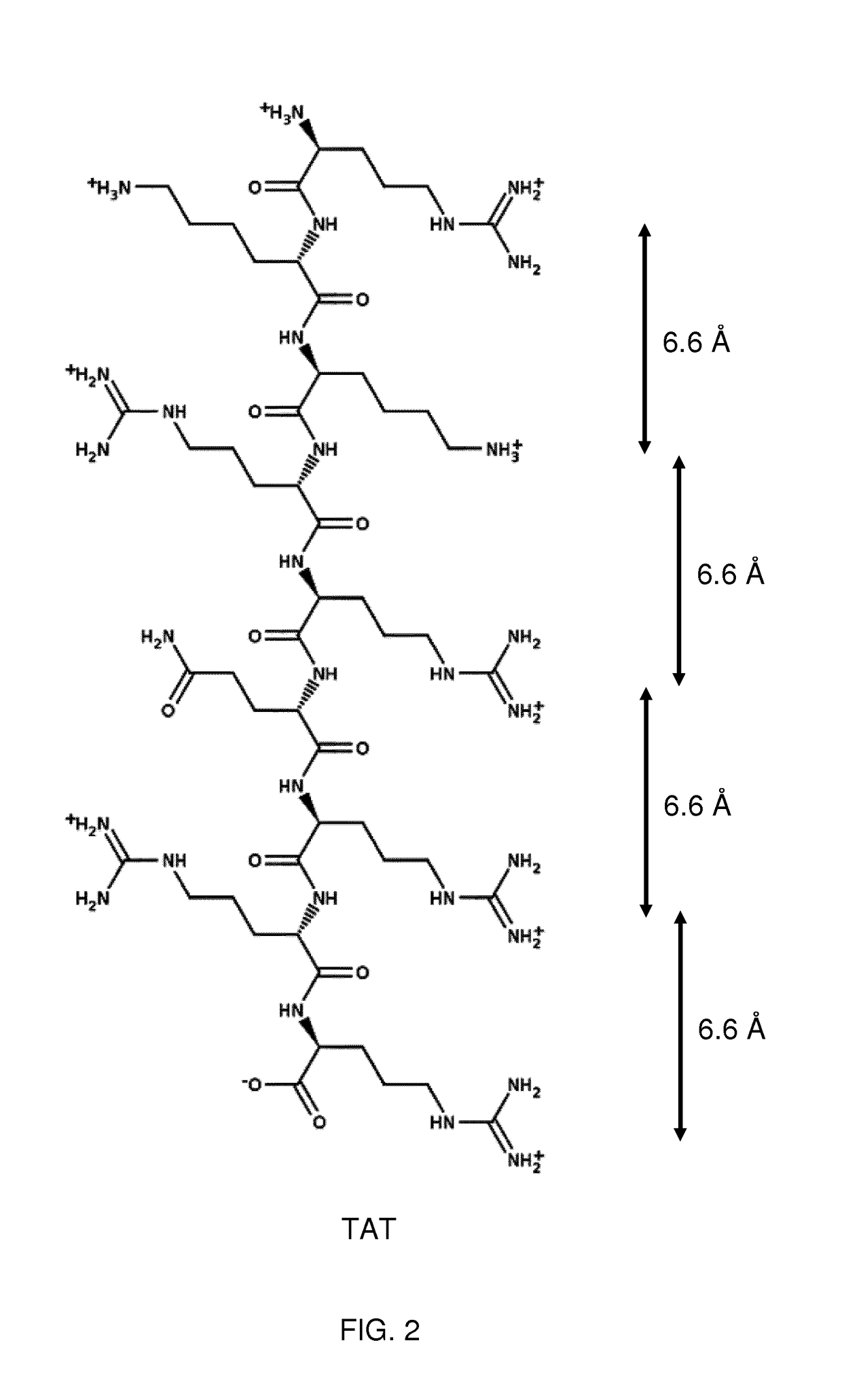
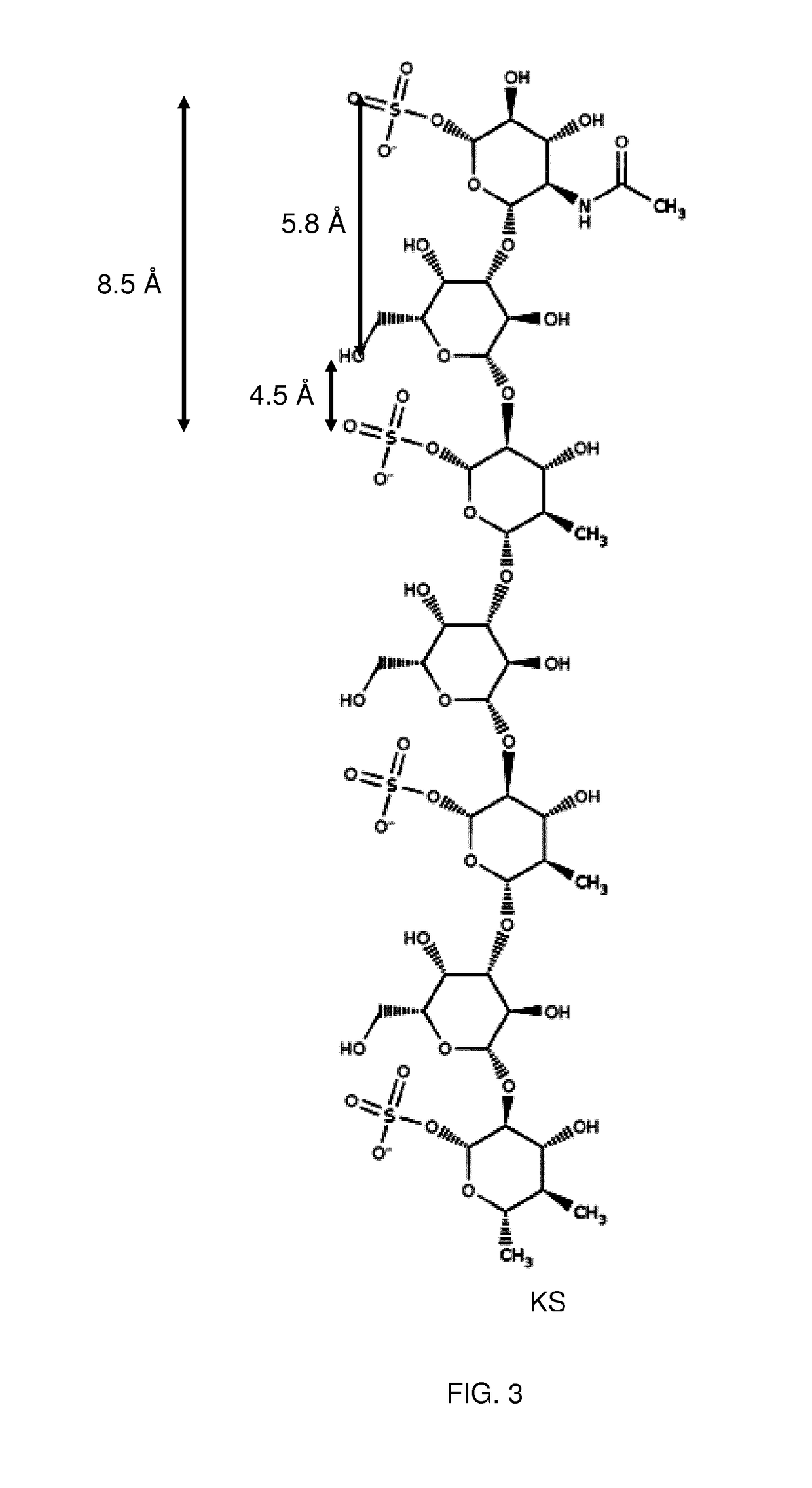
Keratan sulfate specific transporter molecules
ActiveUS10174078B2Senses disorderNervous disorderTransporter associated with antigen processingIn vivo
The present invention relates to isolated molecules, peptides, and polypeptides of specific consensus sequences or structures, and to compounds comprising or consisting of such molecules, peptides or polypeptides, that function as transporter moieties or compositions specifically recognizing the proteoglycan, keratan sulfate. The isolated molecules, peptides, polypeptides and compounds of the invention may be conjugated or otherwise linked to a biologically active moiety (BAM). Thus the BAM conjugates allow the specific targeting and delivery of the BAM, which may be, for example, a peptide, chemical entity or nucleic acid, into the cytoplasm and / or nuclei of keratan-sulfate expressing cells in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:PHI PHARMA
AGENT FOR DYSFUNCTION DUE TO NEUROPATHY AND Rho KINASE ACTIVATION INHIBITOR
An object of the present invention is to provide a substance which is able to be an active ingredient for the improvement of dysfunction caused by nerve damage. An improving agent for dysfunction due to nerve damage of the present invention as a means for resolution thereof is characterized in that it comprises an endo-β-N-acetylglucosaminidase type enzyme which hydrolyzes an N-acetylglucosamide bond in a keratan sulfate backbone as an active ingredient. When the improving agent of the present invention is administered, clinical improvement is achieved in motor neuron dysfunction and sensory neuron dysfunction such as neuropathic pain represented by a pain caused by allodynia and hyperalgesic reaction of the object to be treated.
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
Purification and detection method of keratan sulfate in a kind of chondroitin sulfate
Belonging to the field of medicines, the invention relates to a purification and detection method for keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate. The method includes the steps of: (1) detecting the keratan sulfate in a chondroitin sulfate mixture; (2) separating and purifying the keratan sulphate in chondroitin sulfate; and (3) detecting the content of keratan sulfate. The method provided by the invention can degrade the glycosaminoglycan in the chondroitin sulfate mixture into disaccharide completely, can save all uronic acid structural information, and can accurately and totally obtain the structural information of chondroitin sulfate and keratan sulfate disaccharide. The trace keratan sulfate in the chondroitin sulfate mixture can be qualitative and quantitative. The chemical degradation conditions are mild, the cost is low, the operation is simple, and the requirements for experimental instruments are low. With a wide application range, the method is suitable for detection of keratan sulfate in chondroitin sulfate from any source. The detection needs short time, the sample consumption is small, the sensitivity is high, the analysis result has good repeatability, and the detection limit is ng level.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method of detecting articular cartilage degeneration or damage
InactiveUS20110151492A1Improve progressSymptoms improvedMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisSacroiliac jointArticular cartilage
An object of the present invention is to provide a detection method capable of detecting articular cartilage degeneration or damage in which the abnormality cannot be detected in a radiograph in a simple method and with high accuracy, a method of evaluating the rate of progression of articular cartilage degeneration or damage, and the like.The present invention as a means for achieving the object provides a method of detecting articular cartilage degeneration or damage which cannot be detected in a radiograph, by using the concentration of keratan sulfate in a sample derived from blood as an index, and the like.Further, the present invention provides a method of evaluating the rate of progression of articular cartilage degeneration or damage by using the concentration of keratan sulfate in a sample derived from blood as an index, and the like.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Pharmaceutical composition
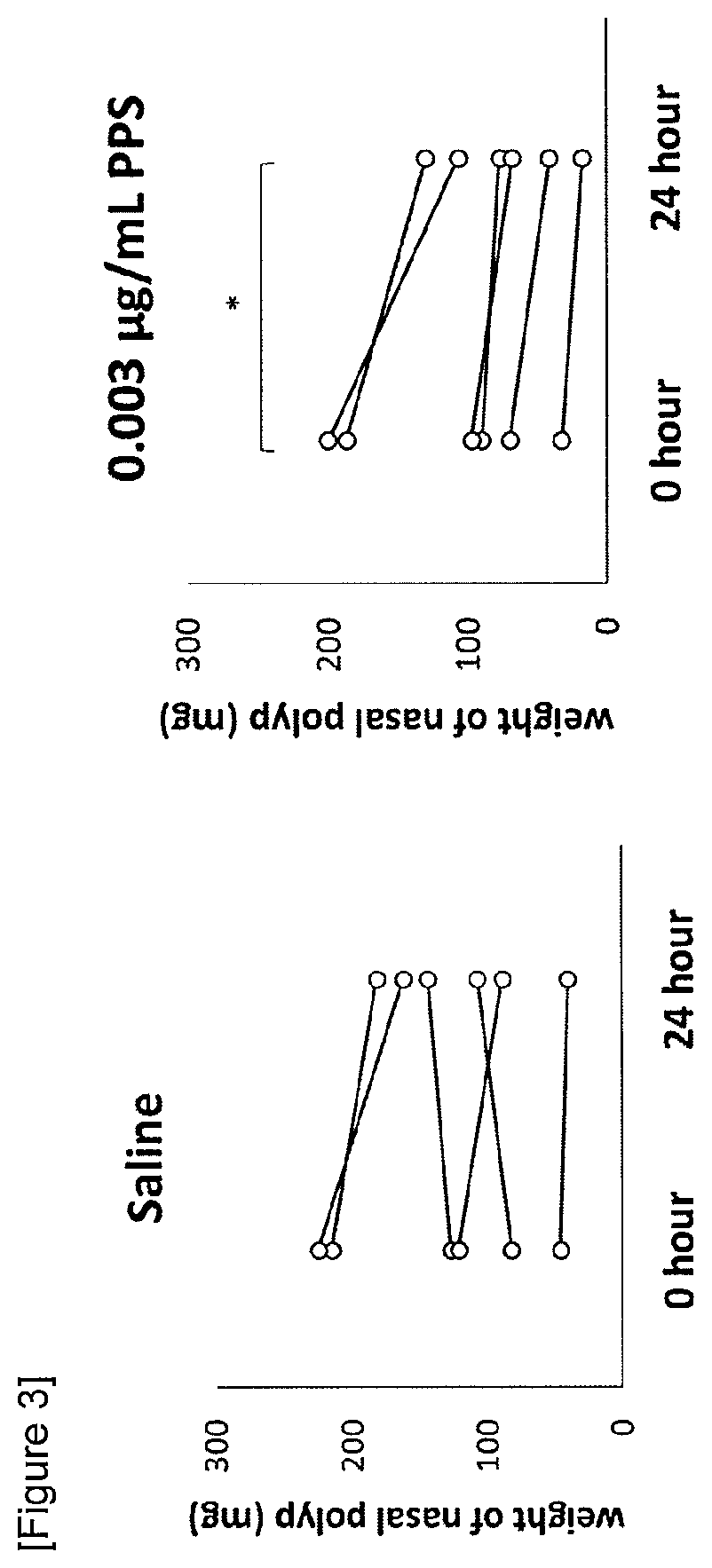
PendingUS20220347093A1Safe nasal polyps reducingOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENTDermatan sulfate
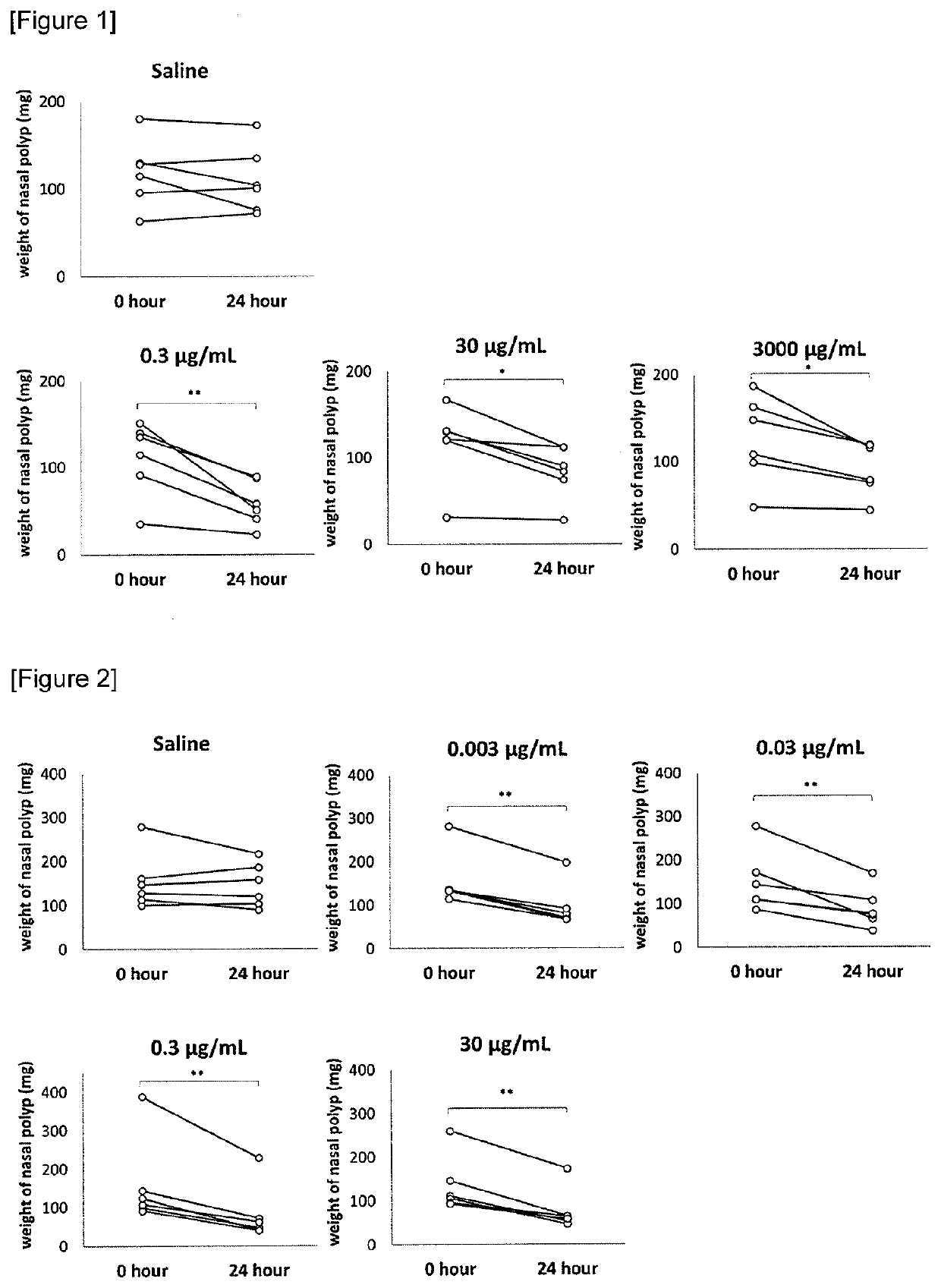
The present invention relates to a nasal polyps reducing agent containing a polysaccharide selected from a polysulfated chondroitin sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, heparan sulfate, dextran sulfate, pentosan polysulfate (PPS), chondroitin, glucomannan, inulin and xylo-oligosaccharide, or a salt thereof as an active ingredient, a pharmaceutical composition, a method for reducing nasal polyps or a method for preventing / treating nasal polyps. According to the present invention, it is possible to provide an effective and safe nasal polyps reducing agent.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF FUKUI +1
Antidote for Chondroitinase
InactiveUS20190249166A1Inhibitory activityChemical treatment enzyme inactivationChemical synthesisChondroitinase activity
The present invention provides a method for inhibiting chondroitinase activity in a substrate by introducing a non-substrate glycosaminoglycan (GAG) to the substrate containing the chondroitinase. The non-substrate GAG is undegradable by chondroitinase. The GAG may be administered as a single dose or in multiple doses. The chondroitinase may be Chondroitinase B, Chondroitinase C, Chondroitinase AC, or Chondroitinase ABC. The substrate may be one or more of dermatan sulfate, hyaluronic acid, chondroitin sulfate, or derivatives thereof. The non-substrate GAG may be from naturally unbranched homo-polysaccharide, unnaturally branched GAG, or a hybrid GAG molecule fused of two or three GAG chains, being produced by chemical synthesis or enzymatic reaction. The non-substrate GAG may be heparin, heparan sulfate, and keratan sulfate. The non-substrate GAG may bind to the active residue of the chondroitinase when being introduced to the substrate such that the chondroitinase is no longer enzymatically active.
Owner:WONG BING LOU
Extraction method of hyaluronic acid in poultry eggshell membrane
The invention provides a method for extracting hyaluronic acid from eggshell membranes of poultry. The method includes steps: separating the eggshell membranes from calcified shells; drying and grinding the eggshell membranes; separating and extracting total glycosaminoglycan from the ground eggshell membranes; removing heparin / heparan sulfate and keratan sulfate from the total glycosaminoglycan, and separating the hyaluronic acid from chondroitin sulfate / dermatan sulfate. By the method, high-purity hyaluronic acid can be separated out, direct extraction of the hyaluronic acid from the eggshell membranes of poultry is realized, extensive sources are available, and the obtained hyaluronic acid which is derived from natural tissues of animals is stable in molecular weight and free of endotoxin.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Keratan sulfate specific transporter molecules
ActiveUS20170114094A1Improve in vivo stabilitySenses disorderNervous disorderIn vivoTranslocator protein
The present invention relates to isolated molecules, peptides, and polypeptides of specific consensus sequences or structures, and to compounds comprising or consisting of such molecules, peptides or polypeptides, that function as transporter moieties or compositions specifically recognizing the proteoglycan, keratan sulfate. The isolated molecules, peptides, polypeptides and compounds of the invention may be conjugated or otherwise linked to a biologically active moiety (BAM). Thus the BAM conjugates allow the specific targeting and delivery of the BAM, which may be, for example, a peptide, chemical entity or nucleic acid, into the cytoplasm and / or nuclei of keratan-sulfate expressing cells in vitro and in vivo.
Owner:PHI PHARMA
Method for assaying keratan sulfate, assay kit therefor and method for detecting joint disease by using the same
InactiveUS8822229B2High sensitivityDifficult to determineBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMonoclonal antibodyTherapeutic effect
The inventions provides a method for immunologically determining a keratan sulfate level which method includes bringing an anti-keratan sulfate monoclonal antibody into contact with a biological sample, the anti-keratan sulfate monoclonal antibody exhibiting a relative reaction specificity between keratan sulfate-I and keratan sulfate-II represented by IC50KS-I / KS-II of 0.4 to 5, to thereby provide a signal; and detecting keratan sulfate contained in the biological sample from the signal. On the basis of the method, the invention also provides a joint disease detection method and a method for assessing the effect of a remedy for a joint disease and a candidate substance therefor. Through these methods, a very small amount of keratan sulfate contained in a sample, can be determined. Particularly, these methods can determine, at high-sensitivity and high-specificity, the total keratan sulfate including keratan sulfate-I, which have been difficult to determine through a conventional technique. The methods also enables detect a joint disease and assess the effect of a remedy for a joint disease or a candidate substance therefor.
Owner:SEIKAGAKU KOGYO CO LTD
Extraction method of keratan sulfate in egg white
The invention discloses an extraction method for keratin sulfate in egg white.The extraction method comprises the steps that the egg white is acquired; total glycosaminoglycan is separated and extracted from the egg white; heparin or heparan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate or dermatan sulfate and hyaluronic acid in the total glycosaminoglycan are removed, and then the high-purity keratin sulfate is obtained.
Owner:刘长国
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com