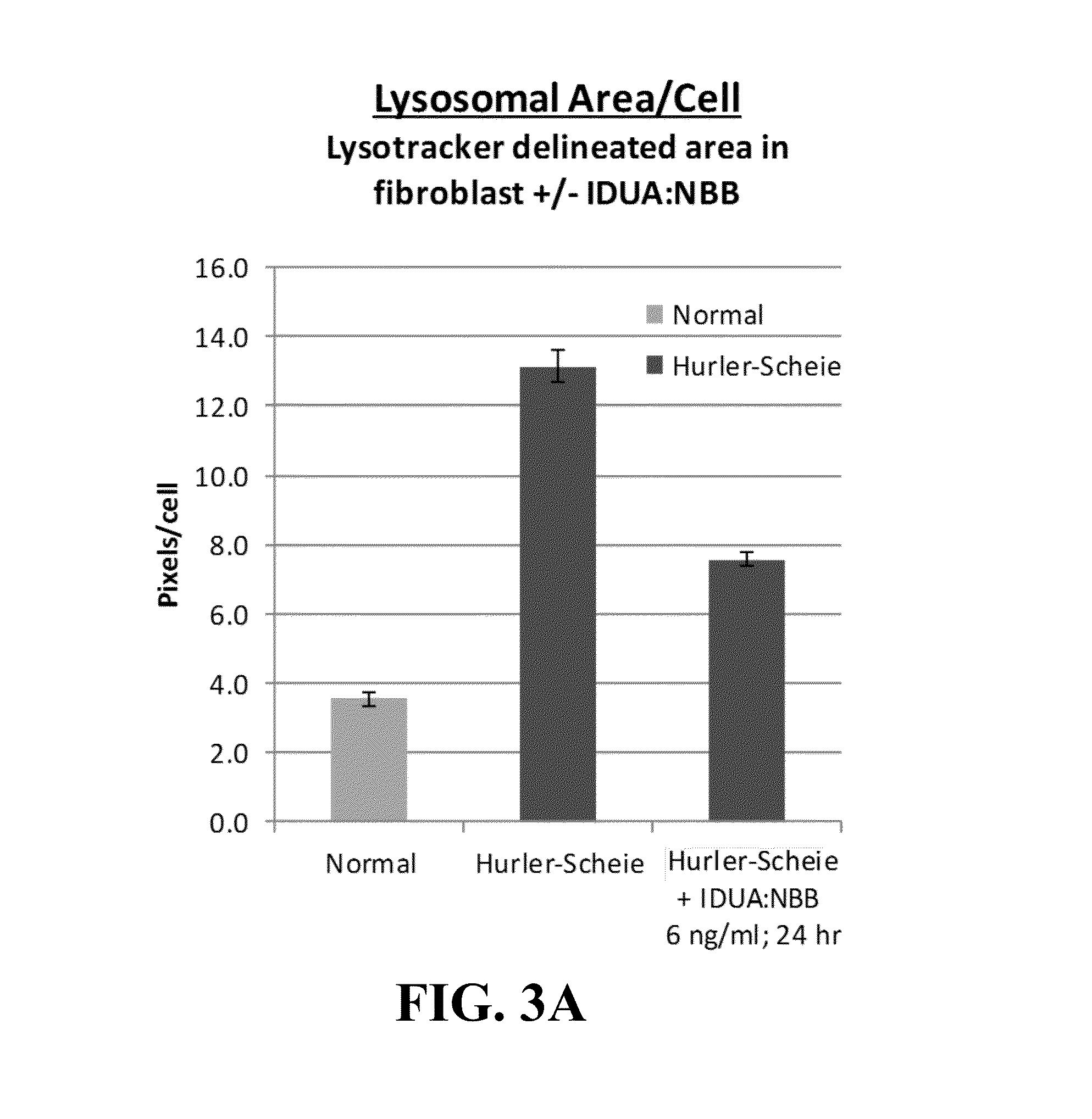
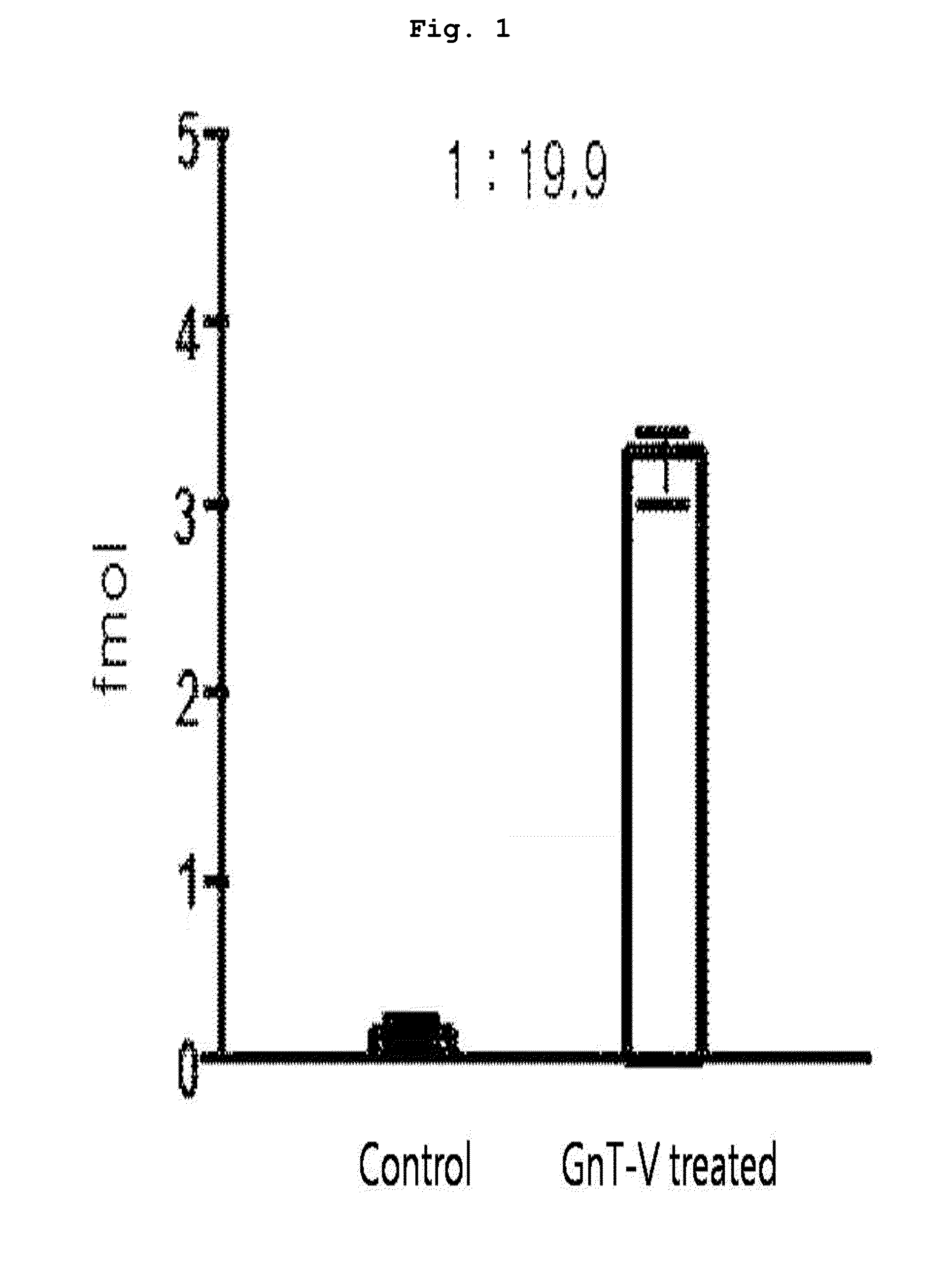
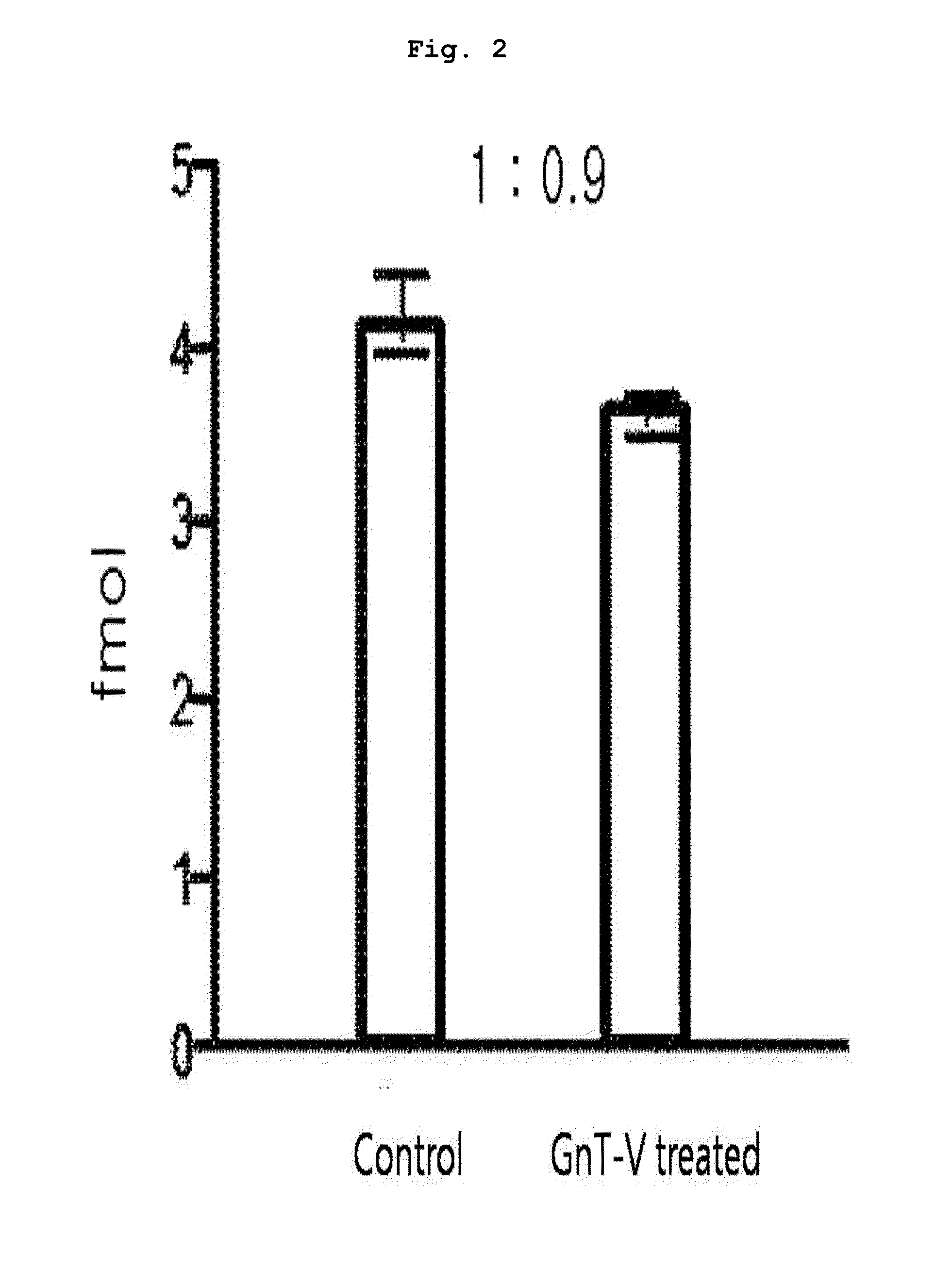
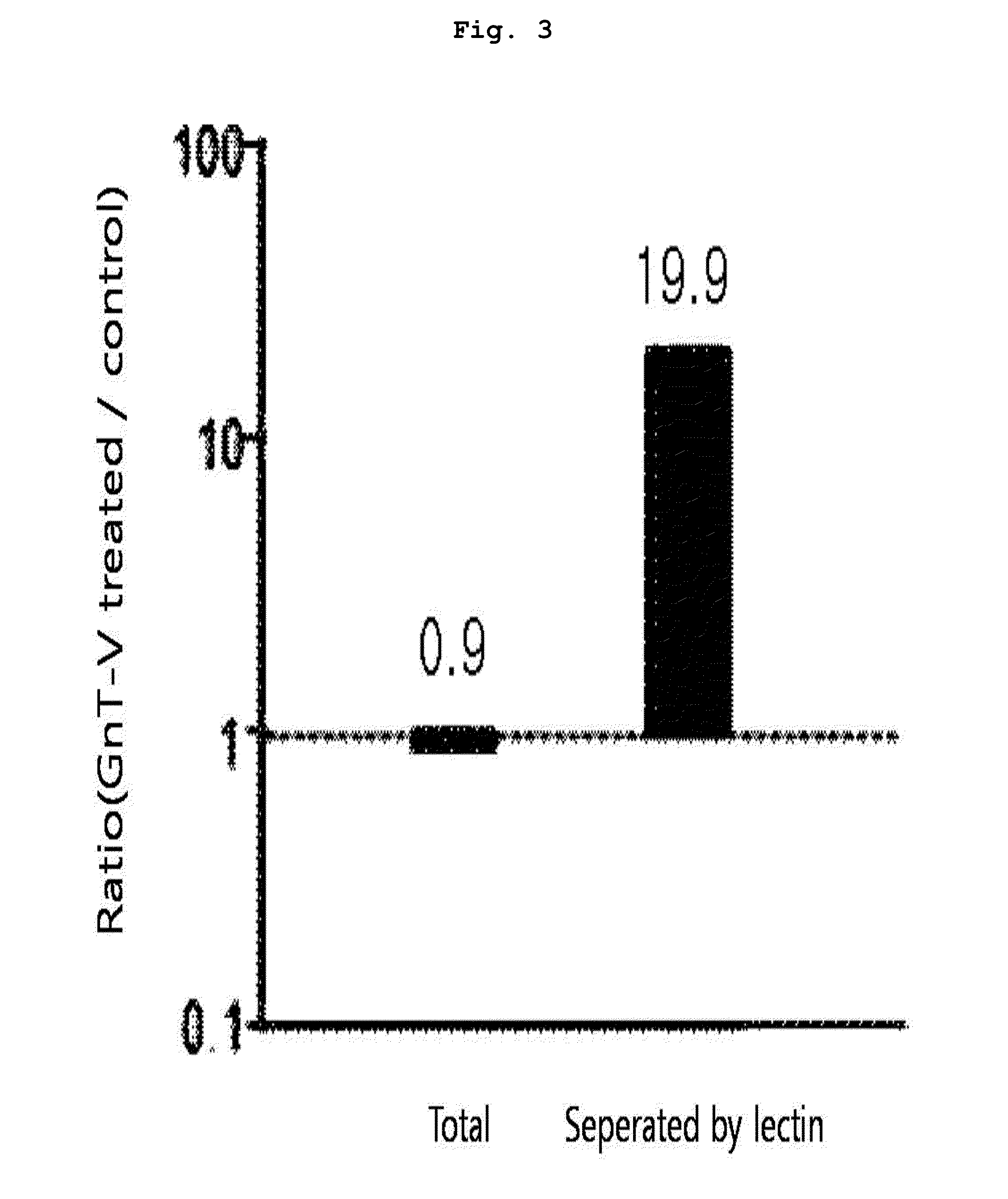
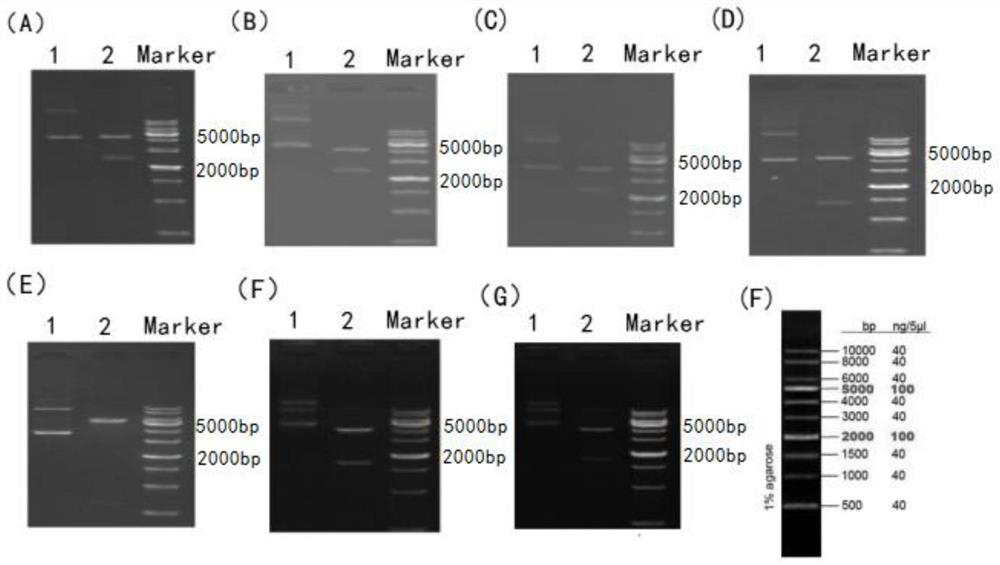
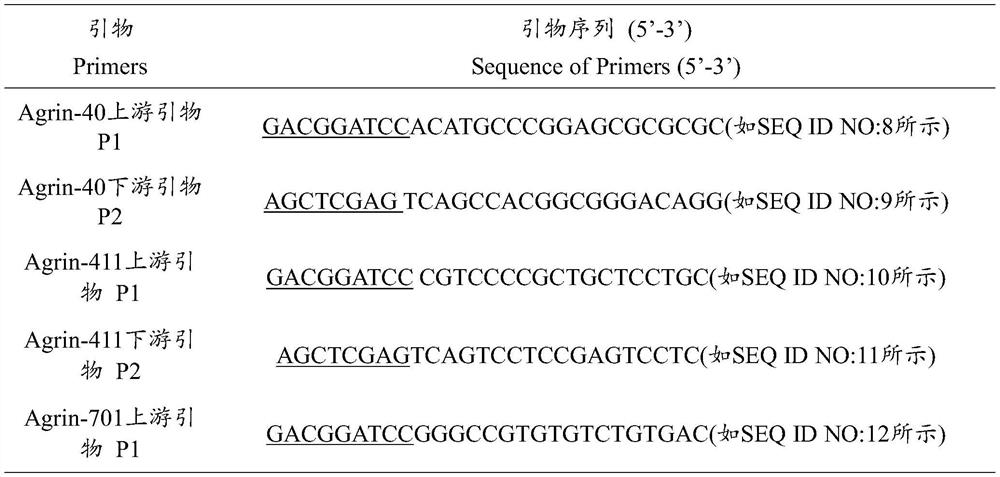
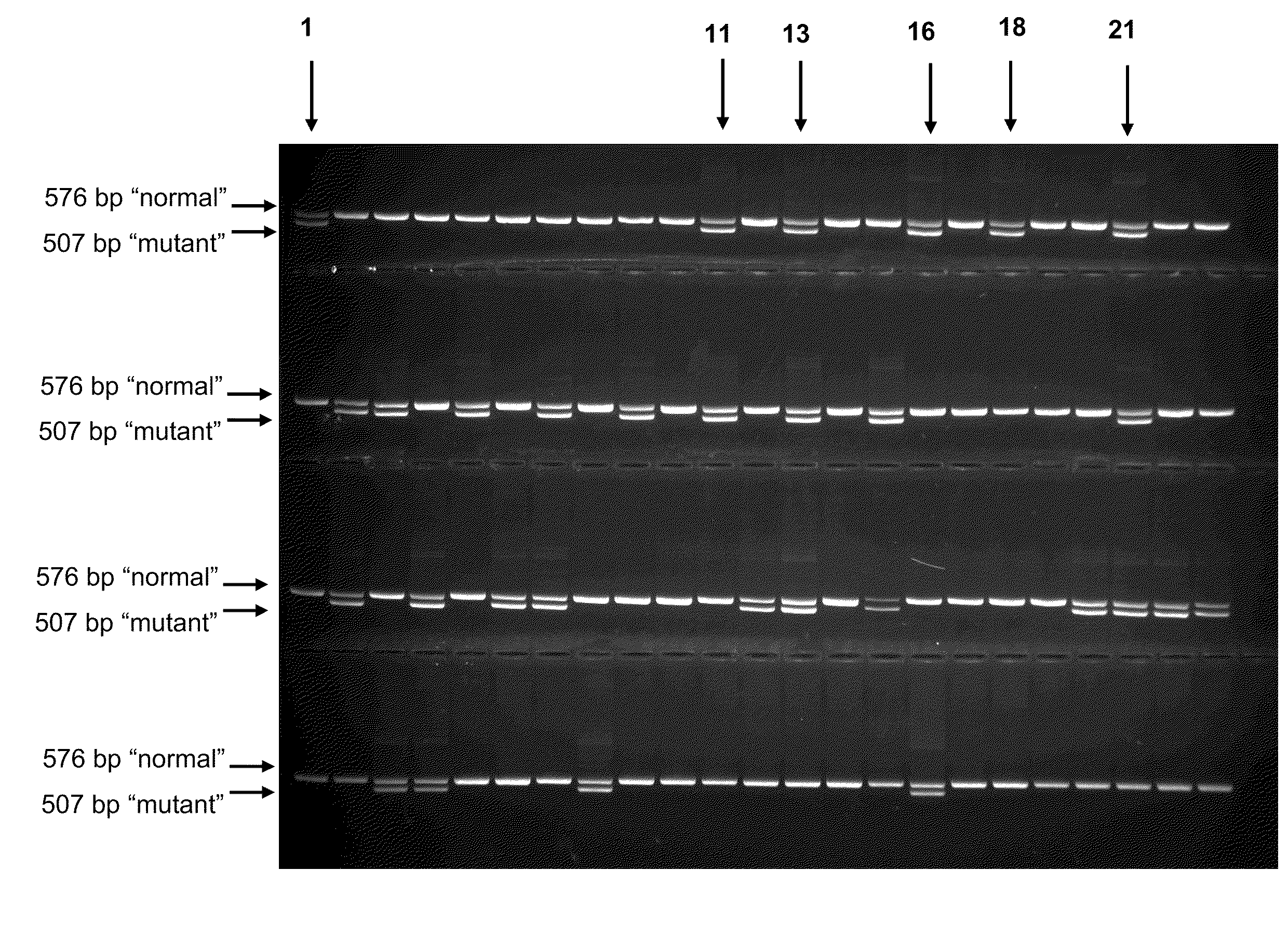
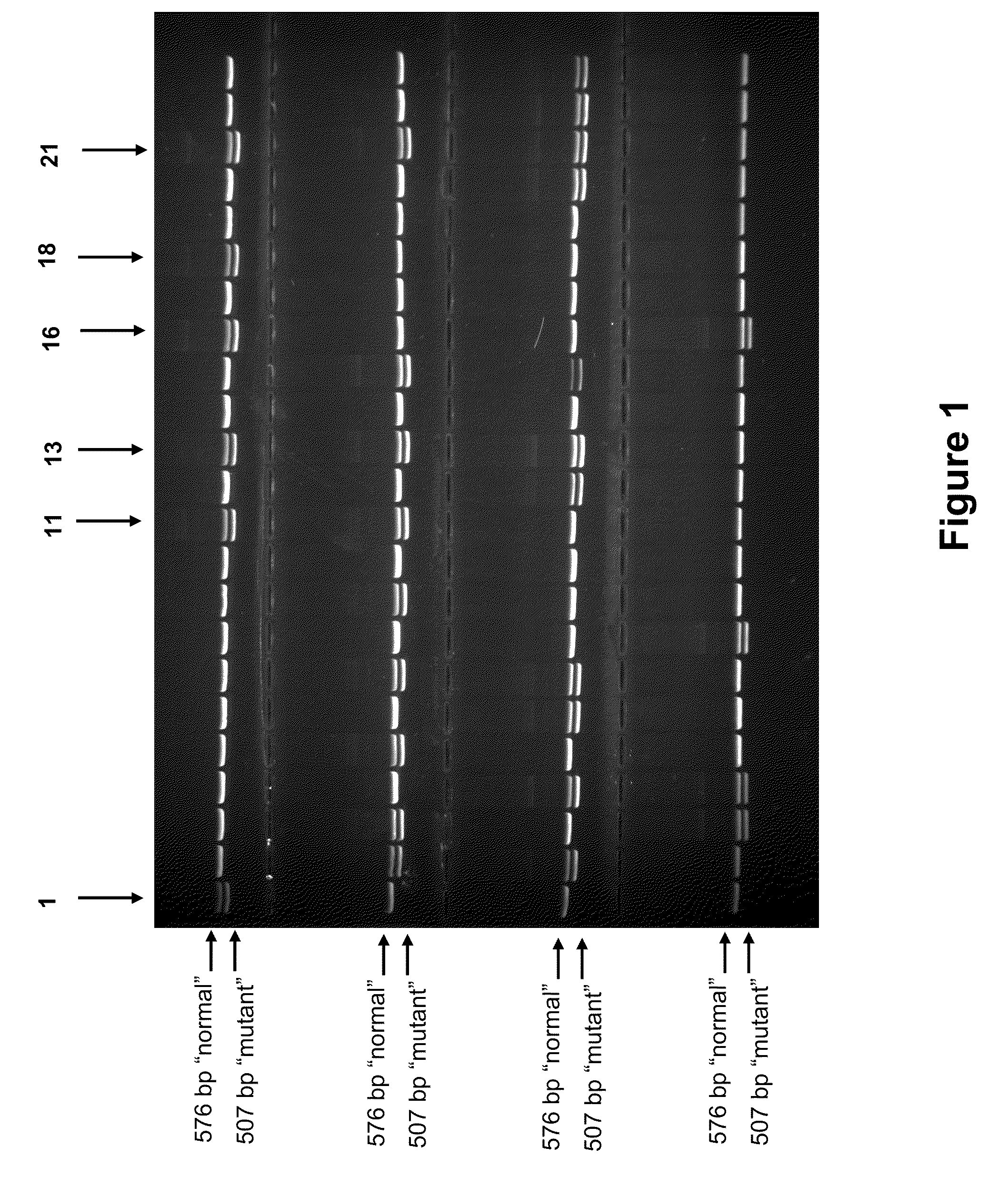
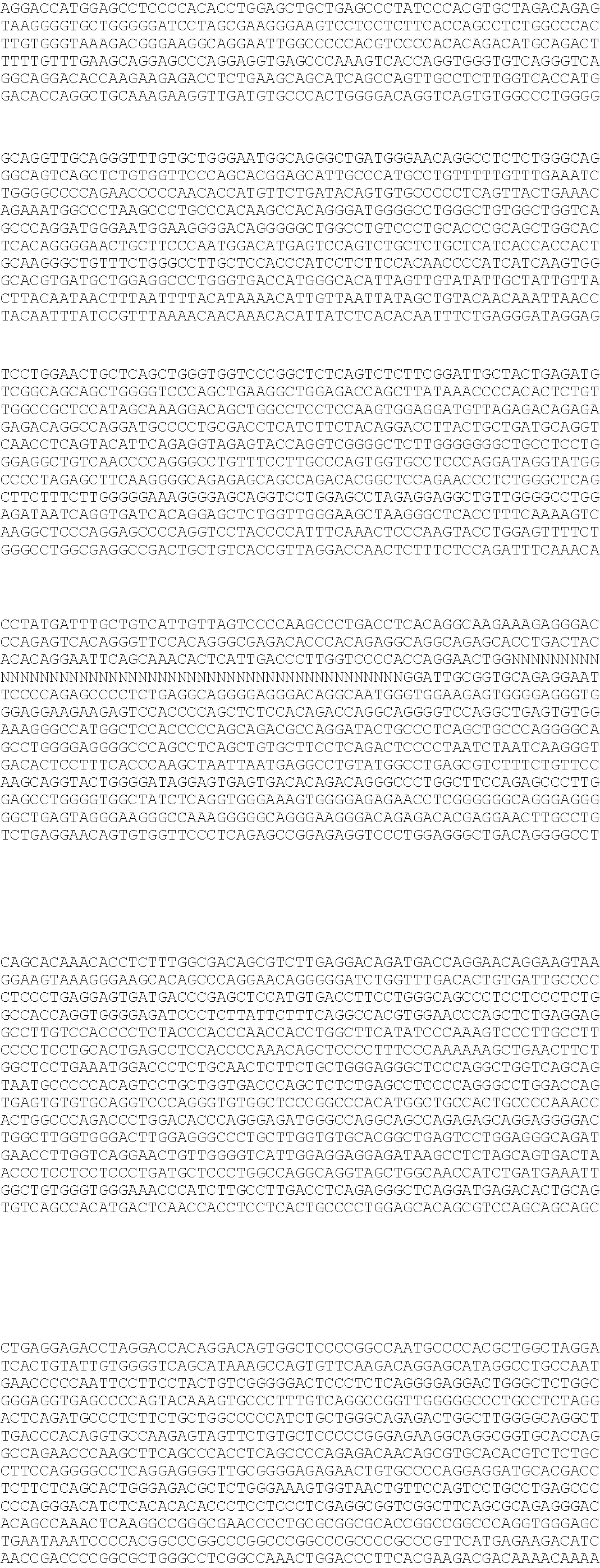Patents
Literature
32 results about "Agrin" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
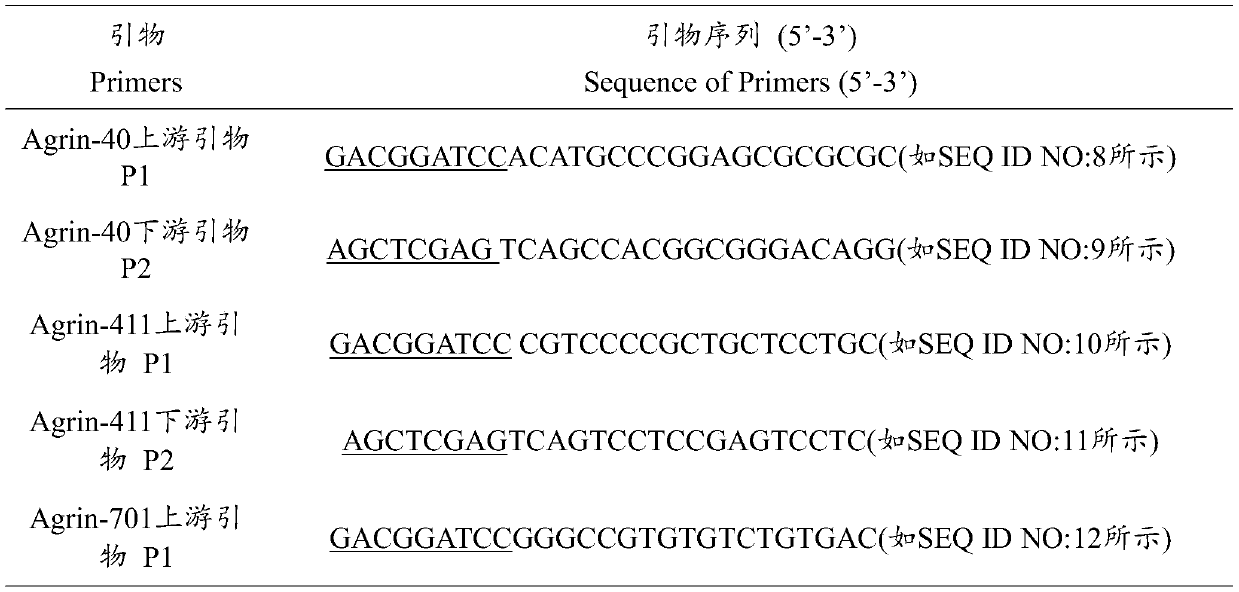
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Agrin is a large proteoglycan whose best-characterised role is in the development of the neuromuscular junction during embryogenesis. Agrin is named based on its involvement in the aggregation of acetylcholine receptors during synaptogenesis. In humans, this protein is encoded by the AGRN gene.
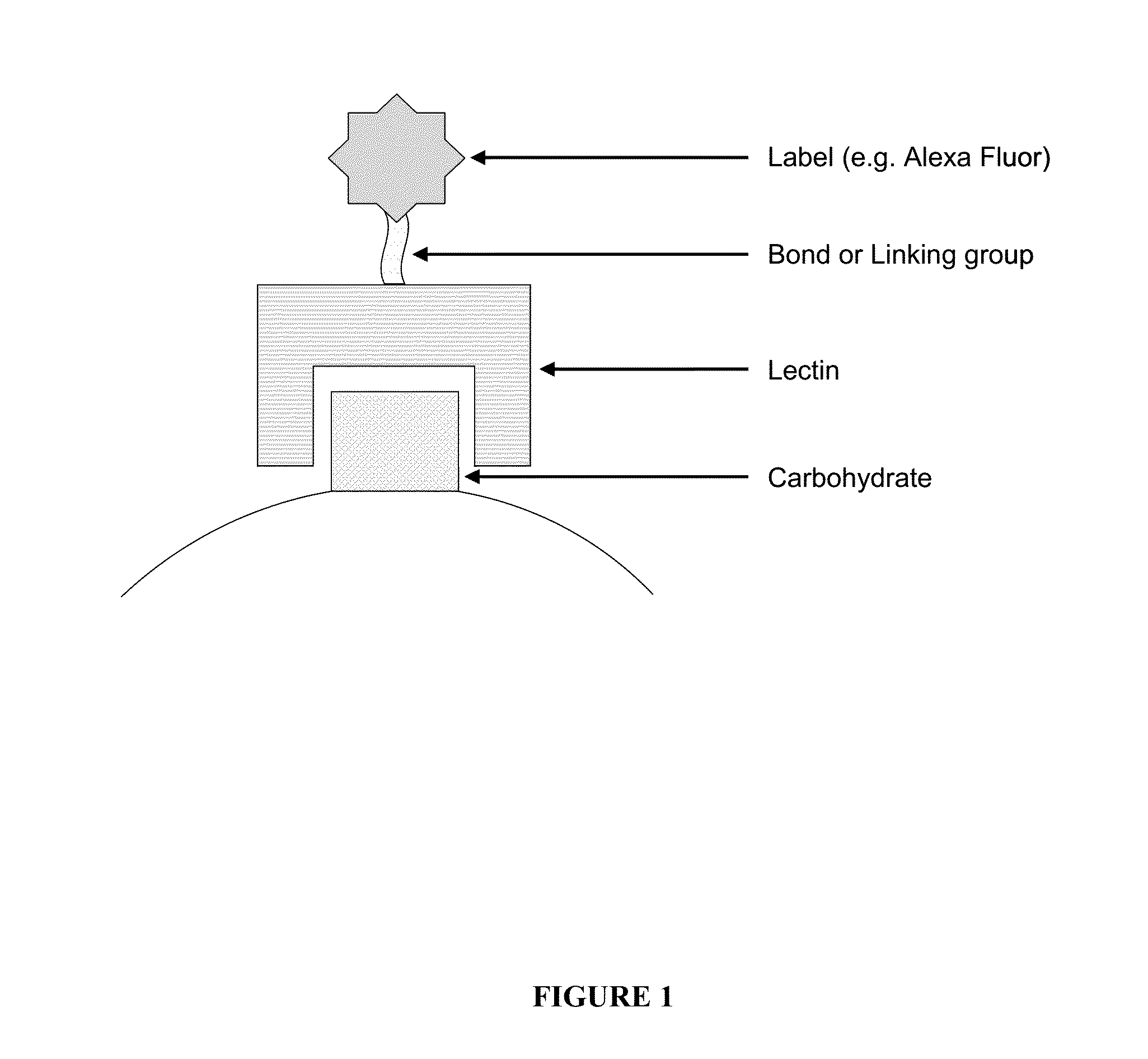
Protein chip for detecting sugar chain abnormal IgA kidney disease
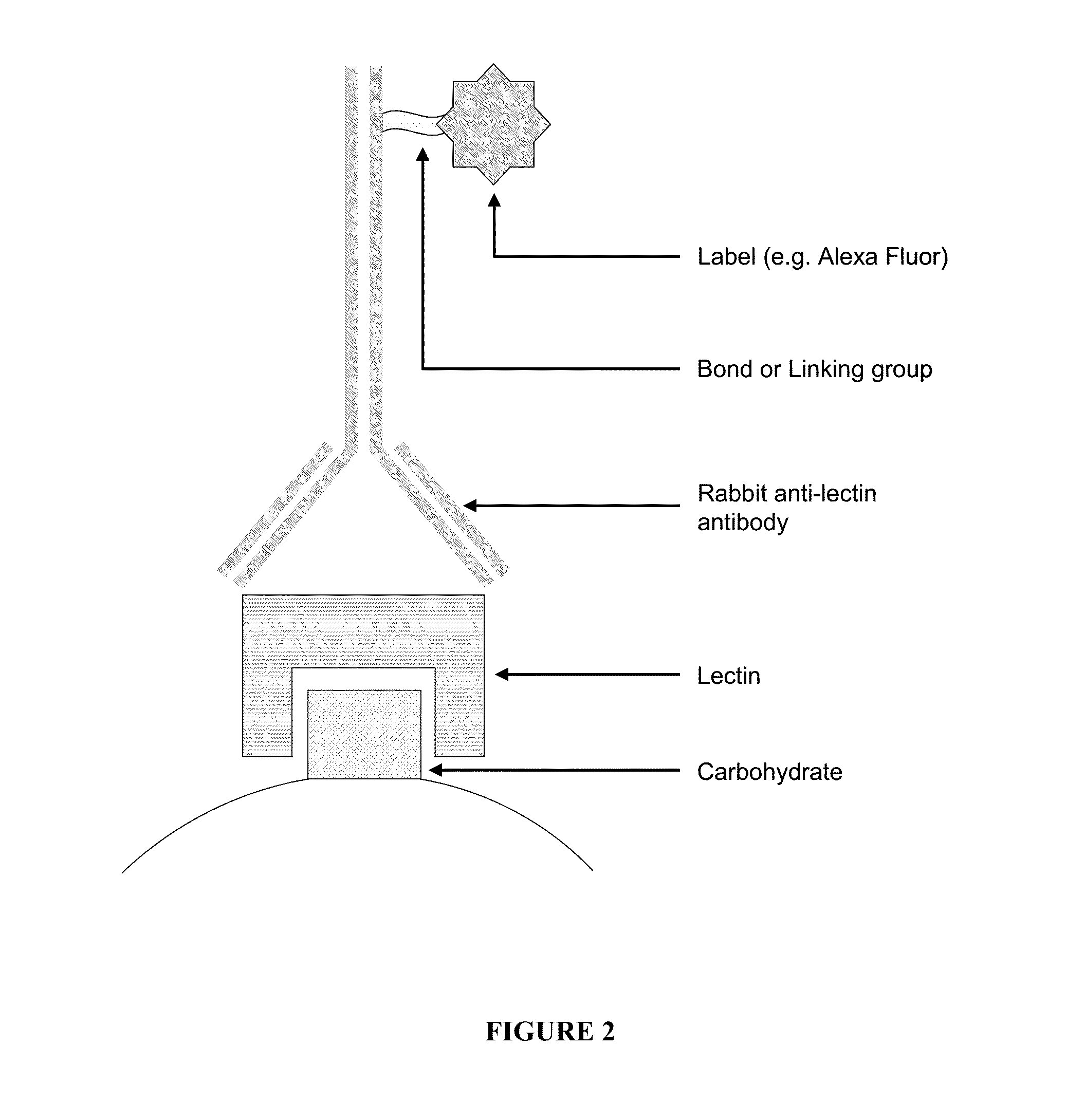
The invention relates to the field of protein chips, in particular to a protein chip for detecting a sugar chain abnormal IgA kidney disease. The protein chip is prepared by fixing lectin on a solid vector and using a marked second antibody to be combined with IgA in a detection sample, wherein the lectin is selected from snail lectin or vicia villosa lectin. The protein chip provided by the invention is specifically combined with special sugar chain protein by using the lectin so as to diagnose the disease, thereby providing a new way for the diagnose of the disease. The method is simple and practicable, the cost is low, the operation steps are simplified, the detection time is shortened, and the method is a novel method which is appropriate to generalize.
Owner:上海睿昂基因科技股份有限公司 +1
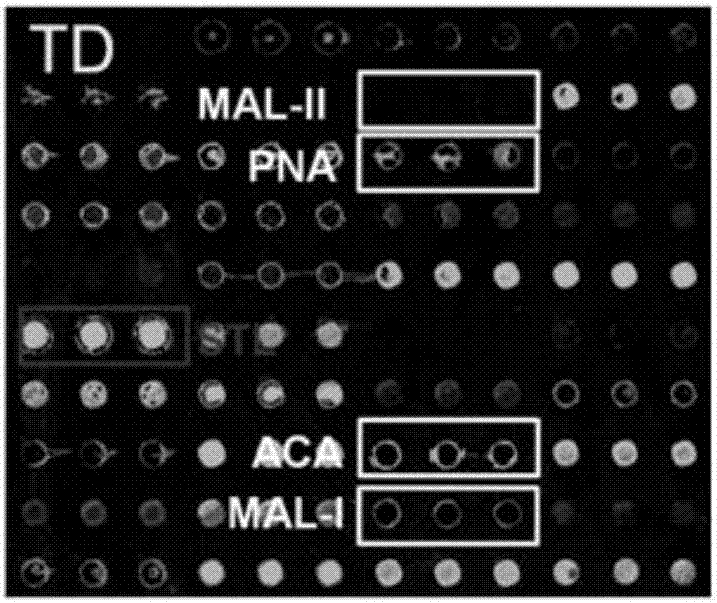
Lectin chip for detecting carbohydrate chain markers based on blood serum and commonly based on protein in blood serum and saliva as well as kit and application of lectin chip
InactiveCN105675893ARapid determination of specific bindingBiological testingSaliva sampleSalivary Proteins
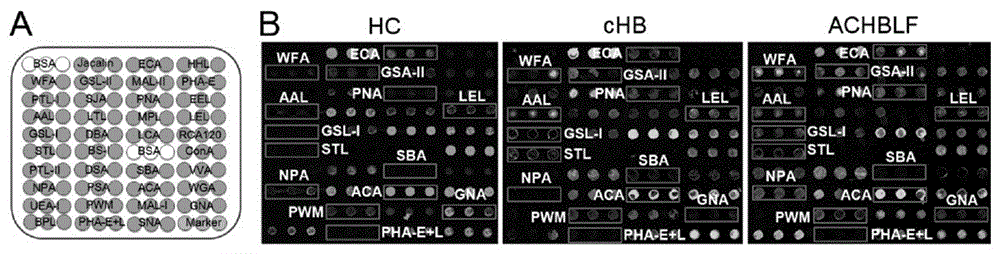
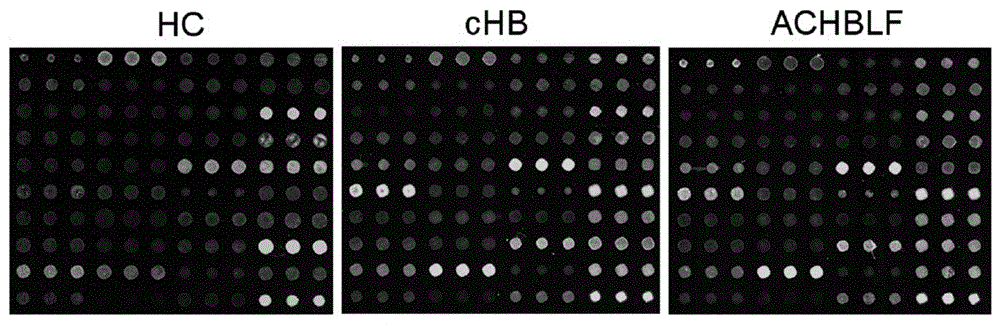
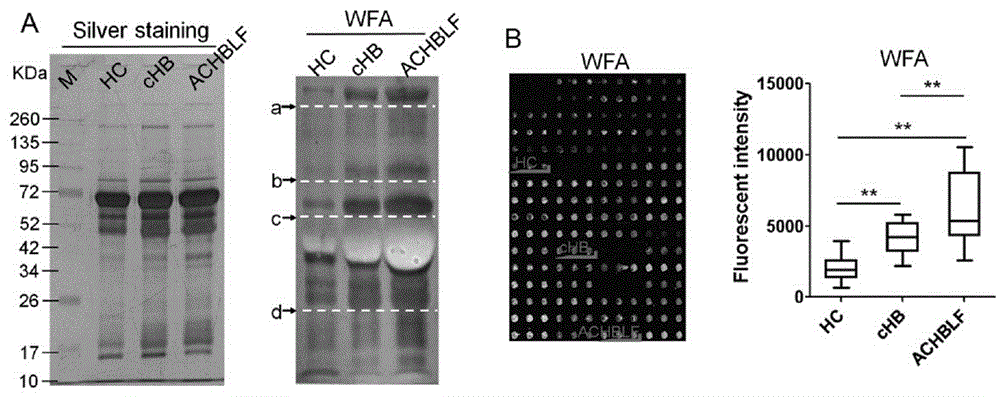
The invention provides a lectin chip for detecting carbohydrate chain markers based on protein in blood serum or saliva as well as a kit and application of the lectin chip, relates to the lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers in blood serum or saliva, and particularly relates to the lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers based on protein in blood serum and saliva as well as a kit and application of the lectin chip. The invention aims at providing a non-injury lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers by identifying protein in saliva or blood serum and a method thereof. The lectin chip for detecting the carbohydrate chain markers based on serum carbohydrate binding protein, provided by the invention, comprises a testing lectin probe set, wherein the testing lectin probe set at least comprises PTL-I, PNA, AAL, LTL, STL, BS-I, PTL-II, SBA, ACA, UEA-I, MAL-I and PHA-E+L. The lectin chip can be used for rapidly detecting a specific carbohydrate protein chain structure in blood serum and saliva samples, and rapidly judging the specific combination of carbohydrate chains in the samples, so as to determine whether corresponding people have hepatitis or not and determine whether people are ACHBLF patients or not.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
In vitro formation of congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques to identify anti-plaque therapeutics for the treatment of Alzheimer's and Prion diseases
InactiveUS20020168753A1Test effectivenessCompounds screening/testingNervous disorderCongo redNeuroglycan C
Co-incubation of an amyloid protein with sulfated macromolecules as a method for the formation of amyloid plaques. The amyloid protein may be the beta-amyloid protein or the prion protein or the like. Amyoid plaque formation in one embodiment proceeds in vitro and desireably produces amyloid plaques that stain with Congo red and demonstrate a maltese-cross pattern when viewed under polarized light. The method also produces amyloid plaques that demonstrate an "amyloid star" appearance when viewed by transmission electron microscopy. Sulfated macromolecules include a sulfated proteoglycan selected from the group consisting of perlecan, ~220 kilodalton heparan sulfate proteoglyean, glypican, cerebroglycan, aggrecan, synaptoglycan (SV2PG), syndecan, N-syndecan (also known as syndecan-3), syndecan-1, syndecan-4, neurocan, phosphacan, decorin, biglycan, versican, amphiglycan, lumican, PG-M, PG-M (3), agrin, betaglycan, claustrin, brevican, appican, epican, neuroglycan-C, and fragments thereof. Thw sulfated macromolecule may be a sulfated glycosaminoglycan selected from the group consisting of heparin, heparan sulfate, dermatan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, keratan sulfate, and fragments thereof. An in vivo assay is also presented for selecting a candidate therapeutic agent for inhibiting or disrupting amyloid plaque deposition or persistence. The assay includes a) pre-forming congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques in vitro following incubation of an amyloid protein and a selected sulfated macromolecule, b) using a first cannula and osmotic pump to continuously infuse for a selected duration the pre-formed congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaques into a tissue or organ, c) changing the first cannulae and osmotic pump with a second cannulae and osmotic pump to administer the candidate therapeutic, and d) detecting the candidate therapeutic's ability to disrupt, reduce, or eliminate congophilic maltese-cross amyloid plaque deposition / persistence in the tissue or organ.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Diagnostic composition for neurotransmission disorder diseases by utilizing agrin
InactiveCN103869078AFill studyFill a gap in the marketDisease diagnosisBiological testingEpitopeDisease
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and discloses a diagnostic composition for neurotransmission disorder diseases by utilizing agrin. The diagnostic composition comprises agrin or agrin mimic epitope. The composition can be used for diagnosing neurotransmission disorder diseases, and has an excellent effect and wide market prospects.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Amphioxus agglutinoid and expressed genes and application thereof
The invention relates to amphioxus agglutinoid and expressed genes and application thereof. An expressed gene nucleotide sequence of the amphioxus agglutinoid AmphiITLN239631 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. An amino acid sequence of the amphioxus agglutinoid AmphiITLN239631 is shown as SEQ ID NO.2. The amphioxus agglutinoid AmphiITLN239631 can be combined with polysaccharide to prepare a bacteria- polysaccharide- agglutinoid recognized chip and provides theory basis for quick identification and prevention treatment of mariculture diseases caused by bacterial infection.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
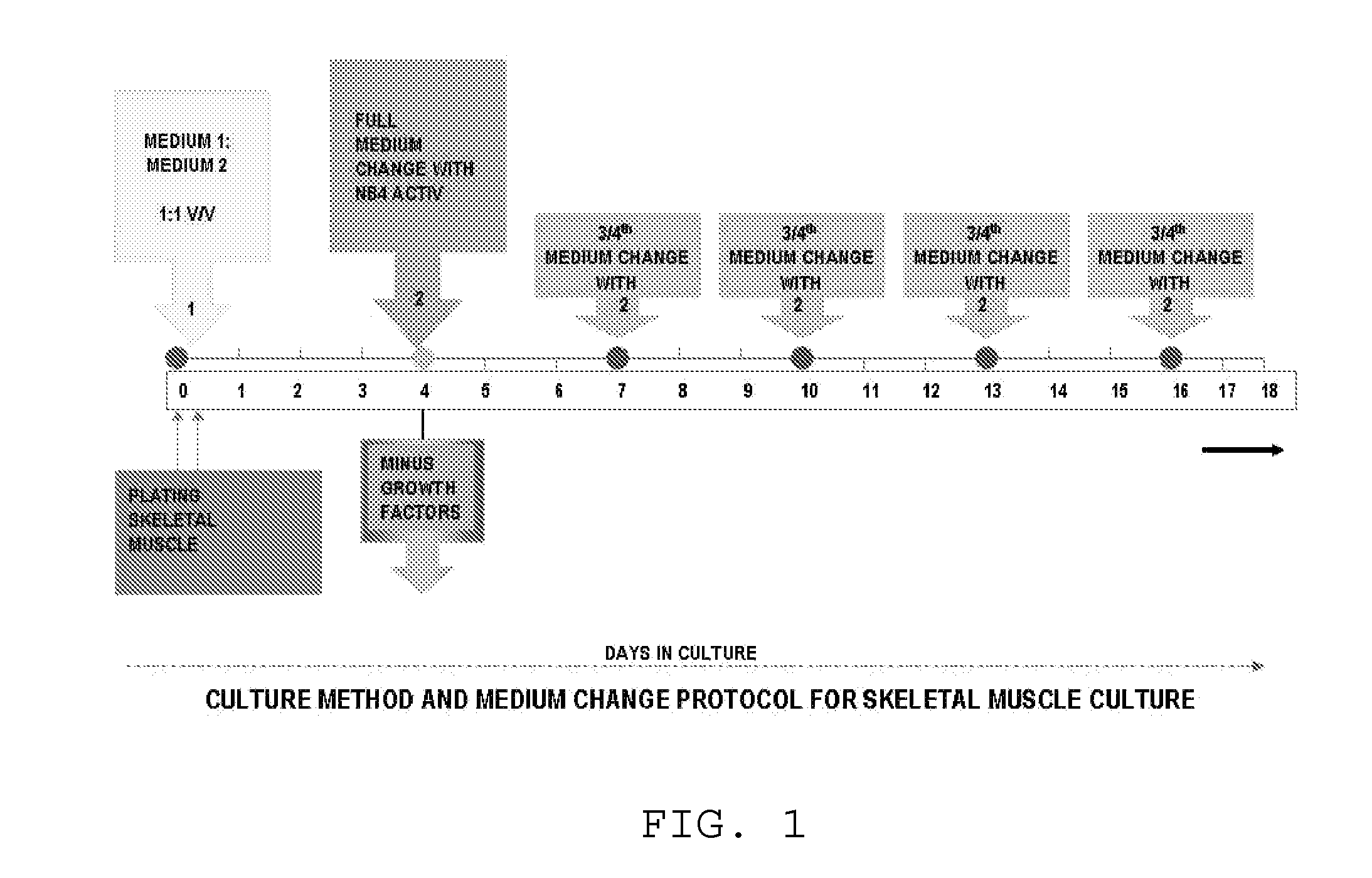
Method for culturing skeletal muscle for tissue engineering
ActiveUS9163216B1Small sizeReduce complexityCulture processNervous system cellsInsulin-like growth factorSerum free media
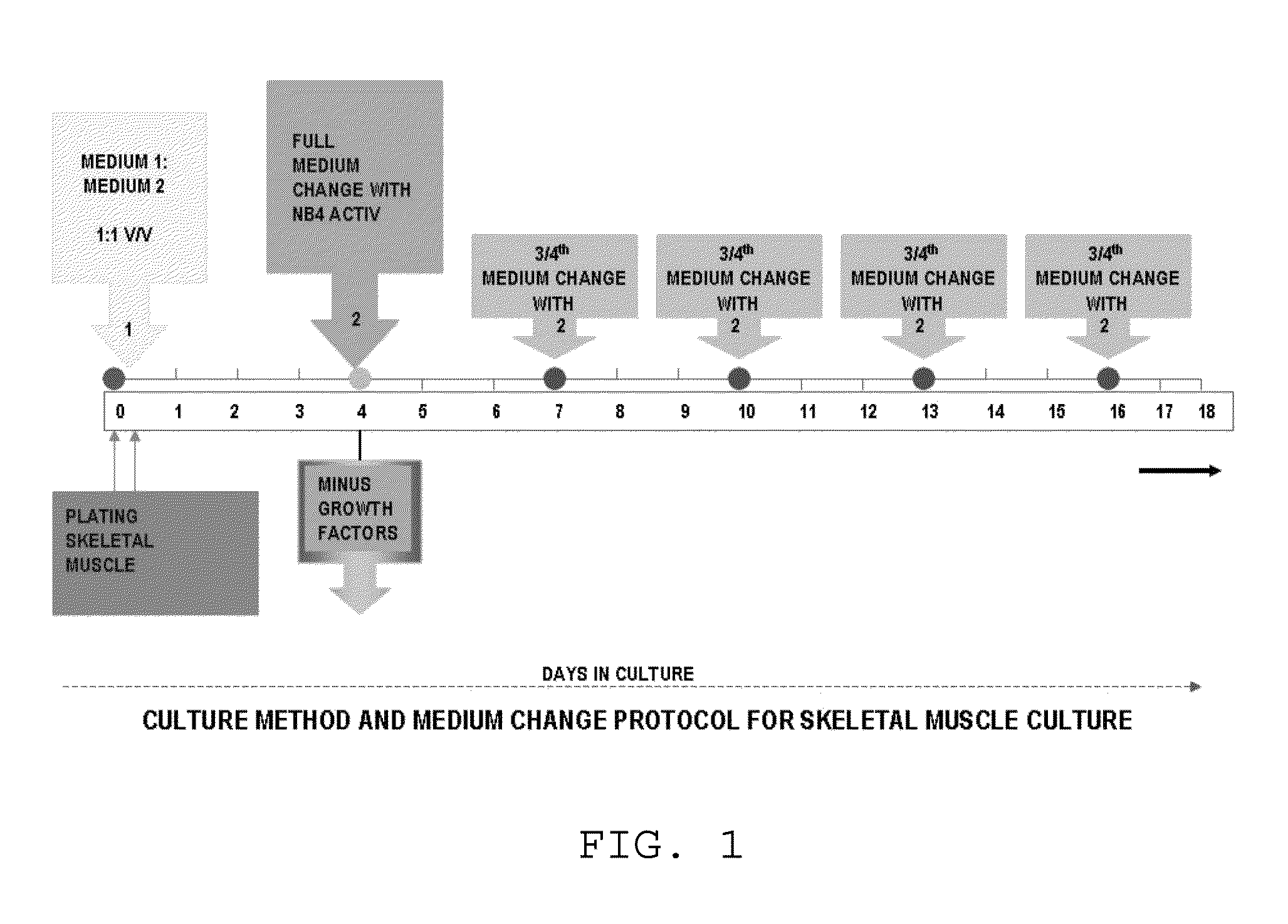
The invention provides a nutrient medium composition and associated methods for lengthening the useful life of a culture of muscle cells. Disclosed is a method of culturing mammalian muscle cells, including preparing one or more carriers coated with a covalently bonded monolayer of trimethoxy-silylpropyl-diethylenetriamine (DETA); verifying DETA monolayer formation by one or more associated optical parameters; suspending isolated fetal rat skeletal muscle cells in serum-free medium according to medium composition 1; plating the suspended cells onto the prepared carriers at a predetermined density; leaving the carriers undisturbed for cells to adhere to the DETA monolayer; covering the carriers with a mixture of medium 1 and medium 2; and incubating. A cell nutrient medium composition includes Neurobasal, an antibiotic-antimycotic composition, cholesterol, human TNF-alpha, PDGF BB, vasoactive intestinal peptides, insulin-like growth factor 1, NAP, r-Apolipoprotein E2, purified mouse Laminin, beta amyloid, human tenascin-C protein, rr-Sonic hedgehog Shh N-terminal, and rr-Agrin C terminal.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
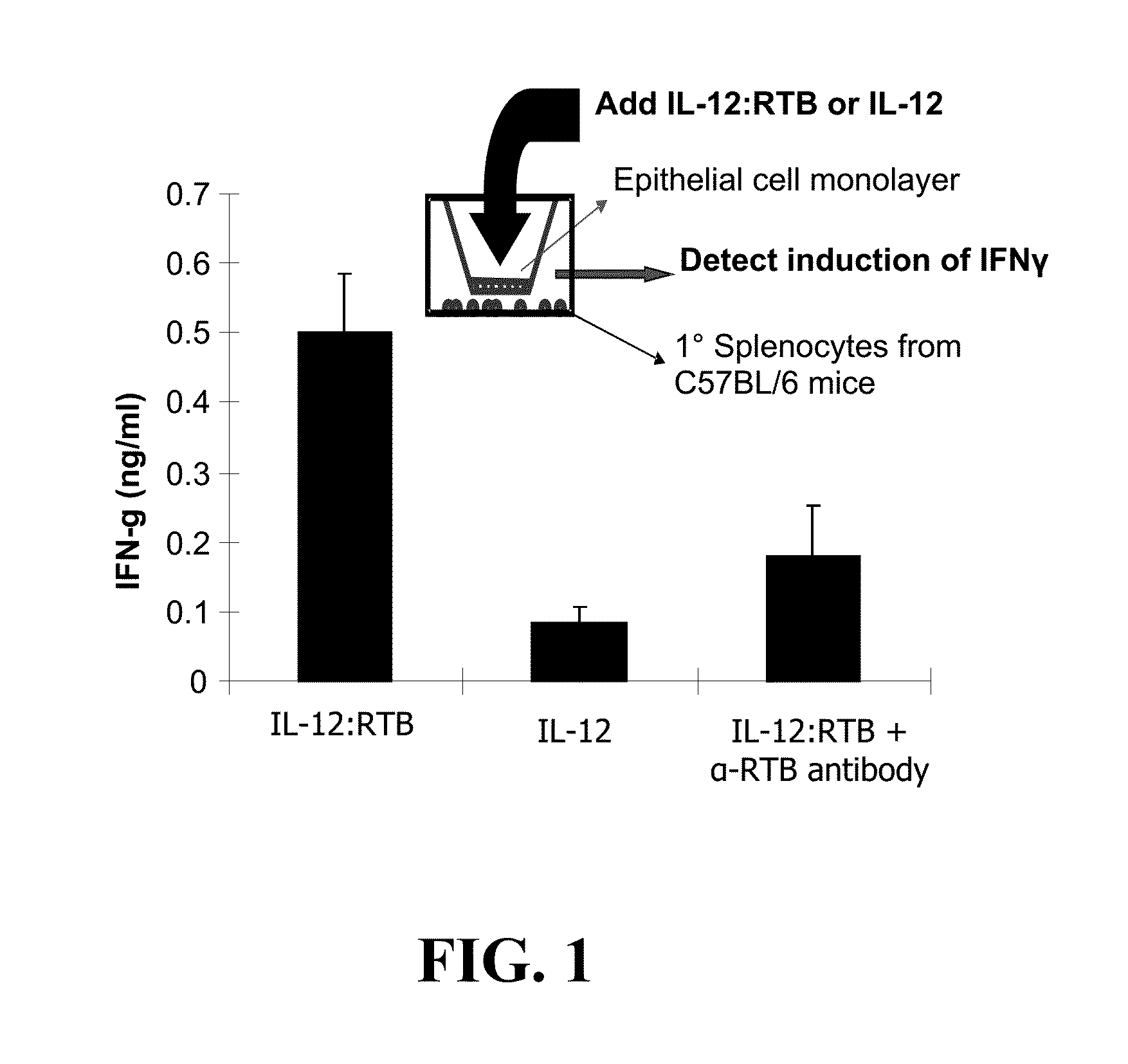
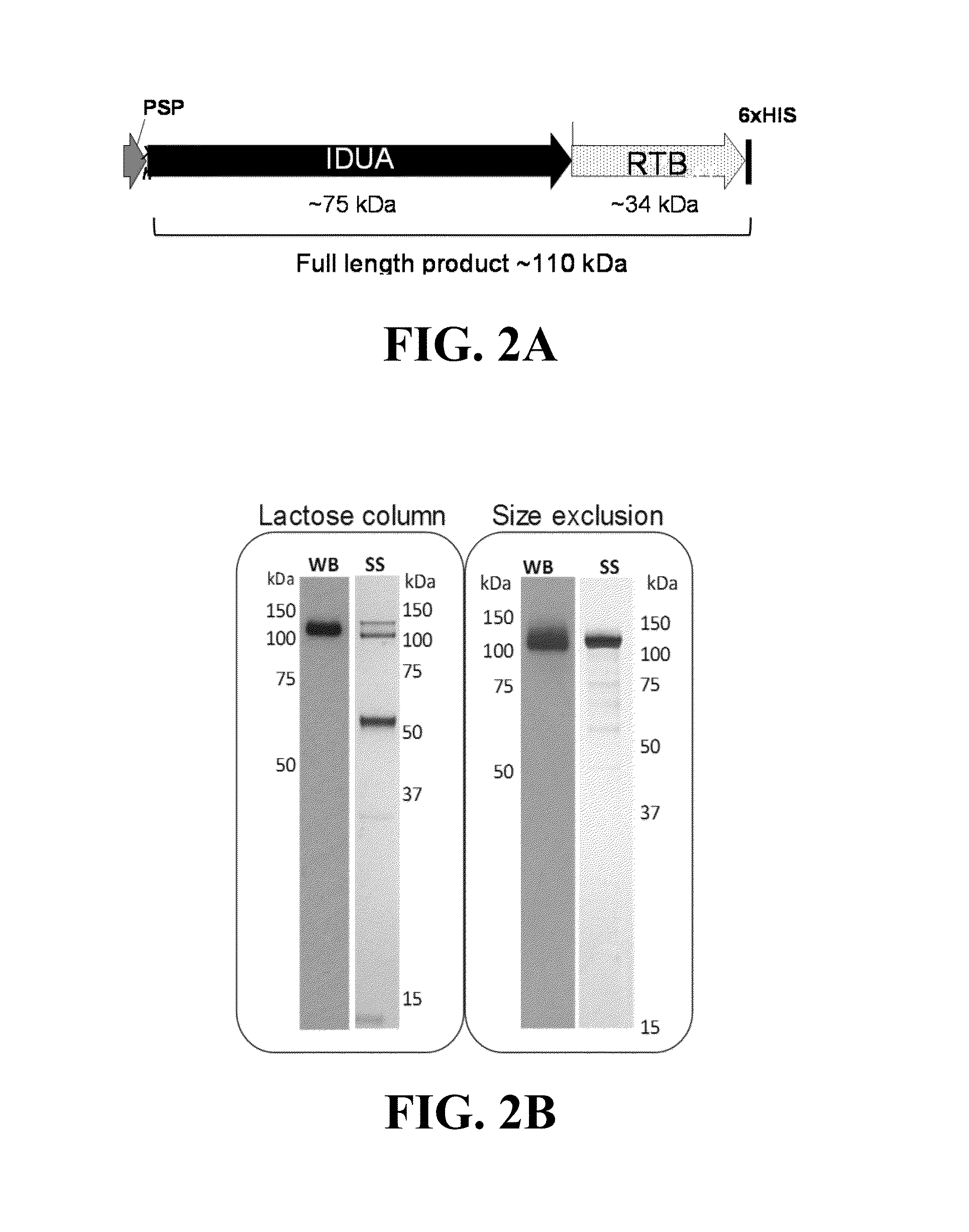
Plant lectins as carriers of associated drug substances into animal and human cells
InactiveUS20130323221A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderPlant LectinsDelivery vehicle
The current invention involves the use of protein lectins produced by plants including the non-toxic carbohydrate binding subunits (B subunits) of plant “AB toxins” (PTB lectins) as delivery vehicles for mobilizing associated drug substances for delivery to animal and human cells. The resulting protein fusions or conjugates retain lectin carbohydrate specificity for binding to cells and cellular trafficking activity so as to deliver an associated drug compound to the site of disease manifestation. One embodiment of this invention concerns the ability of ricin toxin B subunit, as a model PTB lectin, to deliver enzyme replacement therapeutic drugs to cells of several organs of the body including the brain and central nervous system, eyes, ears, lungs, bone, heart, kidney, liver, and spleen for treating lysosomal diseases.
Owner:BIOSTRATEGIES LC
Purified renaturation method of L-aspartic acid oxidase inclusion bodies
InactiveCN106636024ASolve the problem of refoldingEasy to useNucleic acid vectorOxidoreductasesInclusion bodiesUltrafiltration
The invention provides a purified renaturation method of L-aspartic acid oxidase inclusion bodies. The purified renaturation method comprises the following steps that precipitates of the inclusion bodies are collected, and fully washed, denatured proteins are purified by a nickel column, the purified denatured proteins are diluted with a buffer solution D until the protein concentration is lower than 1mg / ml, and placed in a dialysis buffer solution, the dialysis temperature is kept at 4 DEG C, dialysis lasts for more than 12 hours, and supernatants are centrifugally collected. Finally, the supernatants are concentrated by an ultrafiltration tube, and then monomeric proteins and agrin are purified and separated by a molecular sieve to obtain homogeneous natural active proteins. The purified renaturation method of the L-aspartic acid oxidase inclusion bodies disclosed by the invention solves the problem of L-aspartic acid oxidase renaturation, purification and renaturation on the L-aspartic acid oxidase inclusion bodies are carried out with a convenient and fast method, the inclusion bodies are further rinsed and purified by the nickel column to obtain the denatured proteins with higher purity, denaturants are removed gradually through a one-step dialysis renaturation process, the proteins are folded to be protein molecules with activity, the renaturation efficiency of the proteins is not less than10%, and then the protein molecules are further dialyzed and purified by the molecular sieve to obtain high-purity enzymes with activity.
Owner:苏州埃德蒙生物技术有限公司
Method for raising alpha galactosidase activity
InactiveCN102242095AHigh activityAchieve contactMicroorganism based processesEnzymesCell wallAlpha-galactosidase activity
The invention provides a method for raising alpha galactosidase activity, which comprises the following steps: connecting an alpha galactosidase gene (Genbank number: X03102) with a N terminus of a saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall constituents alpha lectin sequence (Genbank number:M28164), then inserting a C terminus of downstream MFalphal1 signal peptide sequence (Genbank number:M17301) of a saccharomyces cerevisiae expression vector GAL1 promotor (Genbank number:AY428072), constructing an expression cassette, wherein the expression cassette is from the N terminus to the C terminus: the GAL1 promoter, a MF alpha1 signal peptide sequence, the alpha galactosidase gene, the alpha lectin sequence; converting a cerevisiae plasmid containing the expression cassette to the saccharomyces cerevisiae cell. The invention has the advantages that the alpha galactosidase is expressed out of an external surface of the saccharomyces cerevisiae cell wall so that a total contact of enzyme and an extracellular substrate can be realized, therefore the alpha galactosidase activity can be obviously improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Engineered lectin oligomers with antiviral activity
Engineered lectins and methods of using such reagents for both preventing and treating a broad array of viral infections are provided. The lectins of the invention are engineered in two ways, first through the enhancement of the natural mode of action of lectins against viruses through linked multimerization, and second through the creation of a new class of reagents, hereinafter referred to as a “lectibody” or “lectibodies”, that engage host immune function in addition to simply binding glycosylated viral proteins via the combination of a lectin and the Fc region of an antibody in order to drive Fc-mediated effector functions including ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity), increased half-life, complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC), and antibody-dependent cell-mediated phagocytosis (ADCP) in response to a lectin-mediated carbohydrate-binding event.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
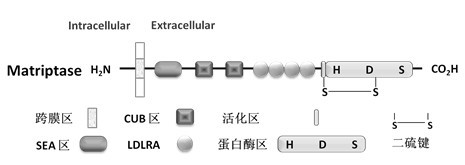
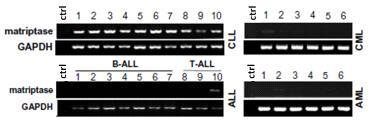
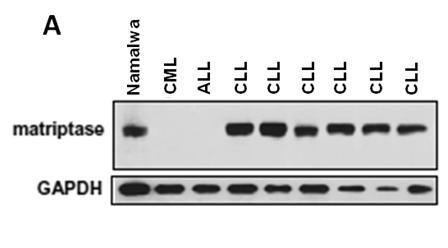
Application of Matriptase
The invention discloses an application of Matriptase. The Matriptase comprises a short intracellular segment, a transmembrane region, an SEA (sea urchin sperm protein, enteropeptidase, agrin domain) region, two CUB (Cls / Clr, urchin embryonic growth factor and bone morphogenetic protein-1) regions, four low density lipoprotein acceptor domains and a C-terminal trypsin-like protease region. The Matriptase is applied to diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocyte leukemia. By an experiment, bone marrows and peripheral blood specimens of normal people and leukemia sufferers are collected, and the detection result shows as follows: Matriptase mRNA and protein are highly expressed in the chronic lymphocyte leukemia sufferers, the expression level of Matriptase of the surface of lymphocyte can serve as a molecular marker for diagnosis of chronic lymphocyte leukemia, and the Matriptase can serve as a novel target for diagnosis and treatment of chronic lymphocyte leukemia.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
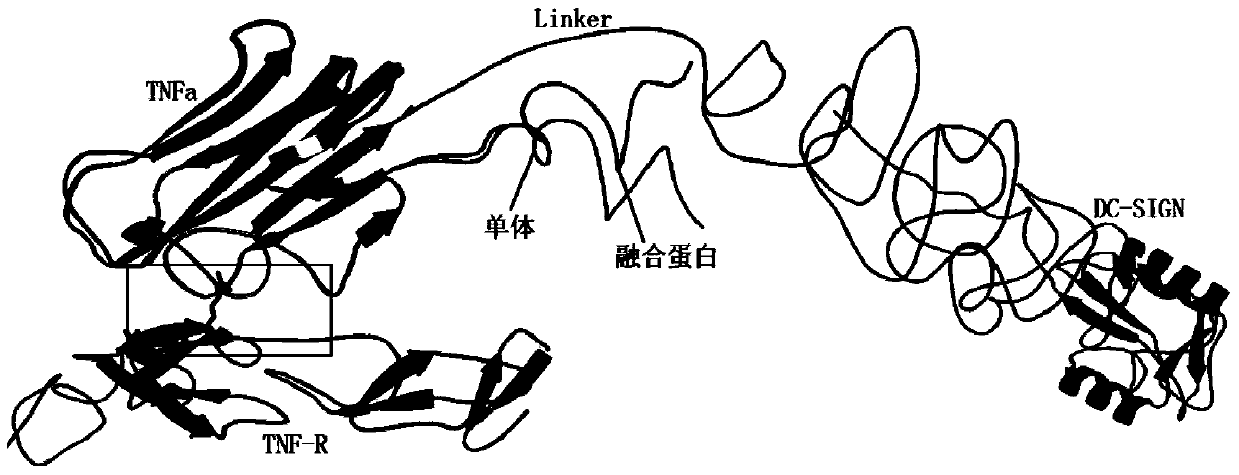
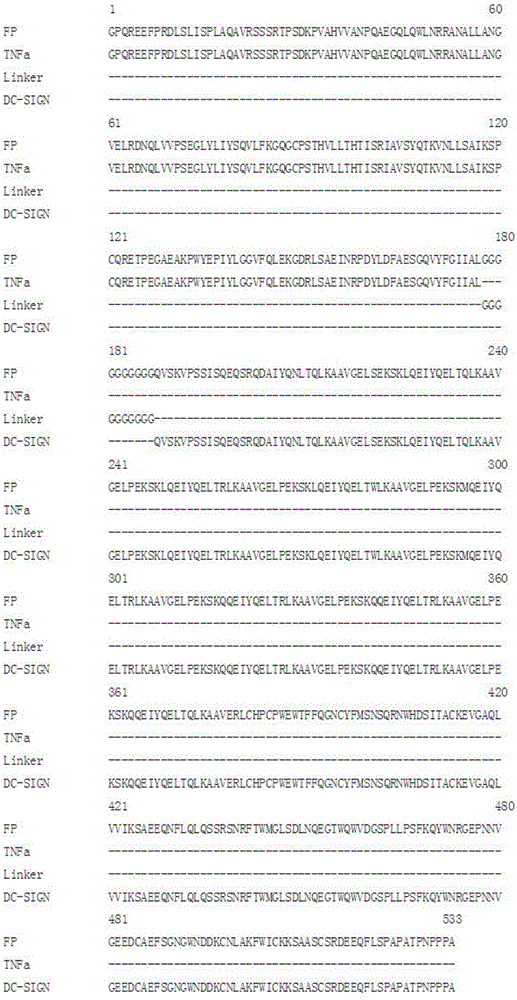
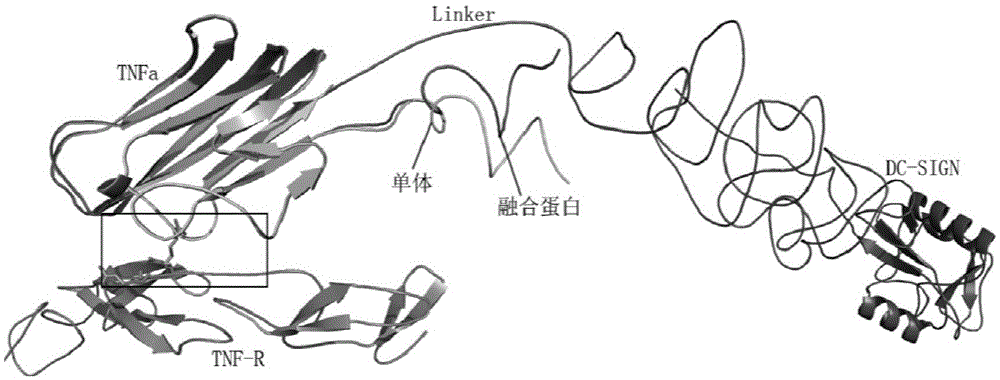
TNF alpha and DC-SIGN fusion protein and application thereof
ActiveCN103739714AImprove biological activityMake sure not to be killedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsApoptosisAdhesion factor
The invention relates to a TNF alpha and DC-SIGN fusion protein and an application thereof. In a traditional anti-tumor medicament or a treatment method, normal cells are easy to damage in the process of killing tumor cells. The targeting anti-tumor fusion protein provided by the invention comprises an identification functional domain and an action functional domain, as well as a connecting peptide for connecting the two functional domains. The identification functional domain is as follows: a lectin polypeptide with tumor cell surface sugar chain identification and combination functions-a DC surface specific intercellular adhesion factor 3 combined with non-integrin molecules (DC-SIGN, dendritic-cell-specific ICAM-3-grabbing nonintegrin) is positioned at a C terminal of the fusion protein; the action functional domain is as follows: a tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is positioned at an N terminal of the fusion protein; and the connecting peptide is a short peptide containing 8-25 amino acids. The fusion protein can utilize lectin and cancer cells to perform targeting combination, induce the apoptosis of the cancer cells through a ligand capable of promoting the apoptosis of the cells and simultaneously reduce the killing effect against normal tissues and cells.
Owner:ZONHON BIOPHARMA INST
Plant lectins as carriers of associated drug substances into animal and human cells
ActiveUS20160083707A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifNervous disorderPlant LectinsLysosome
The current invention involves the use of protein lectins produced by plants including the non-toxic carbohydrate binding subunits (B subunits) of plant “AB toxins” (PTB lectins) as delivery vehicles for mobilizing associated drug substances for delivery to animal and human cells. The resulting protein fusions or conjugates retain lectin carbohydrate specificity for binding to cells and cellular trafficking activity so as to deliver an associated drug compound to the site of disease manifestation. One embodiment of this invention concerns the ability of ricin toxin B subunit, as a model PTB lectin, to deliver enzyme replacement therapeutic drugs to cells of several organs of the body including the brain and central nervous system, eyes, ears, lungs, bone, heart, kidney, liver, and spleen for treating lysosomal diseases.
Owner:BIOSTRATEGIES LC
Cancer diagnosis marker using the aberrant glycosylation of a protein
InactiveUS8580491B2Component separationMicrobiological testing/measurementCancers diagnosisAberrant glycosylation
The present invention relates to a method for diagnosing cancer using information on the aberrant glycosylation of a glycoprotein. More precisely, the present invention relates to a cancer diagnosis peptide marker, which is screened by: a step of separating, using a lectin, a glycoprotein which is aberrantly glycosylated in accordance with the occurrence of cancer; and a step of selecting a hydrolyzed peptide marker derived from the aberrantly glycosylated glycoprotein by observing the quantitative changes in the separated glycoprotein. The present invention also relates to a method for diagnosing cancer using the peptide marker as an agent.
Owner:KOREA BASIC SCI INST
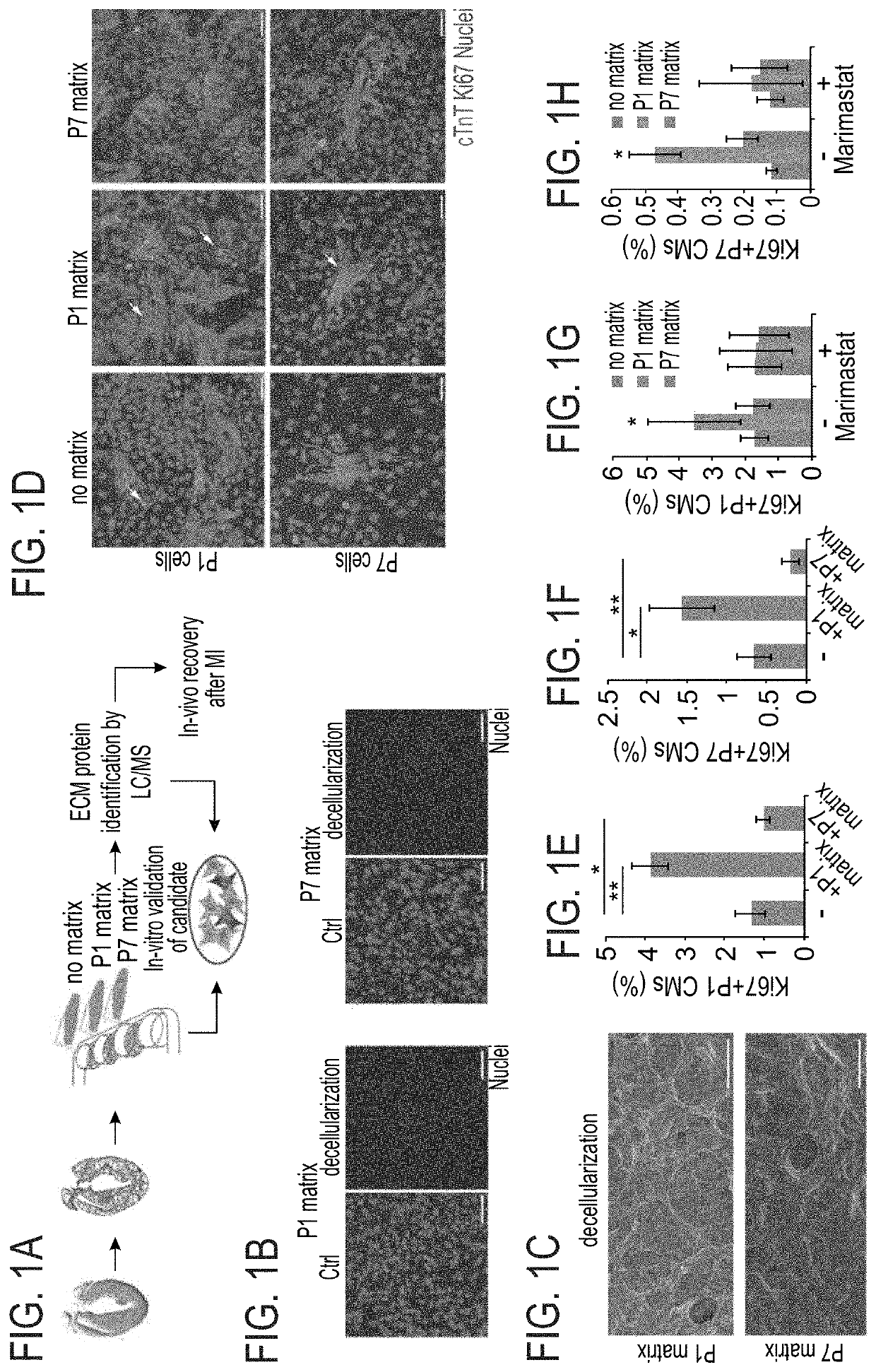
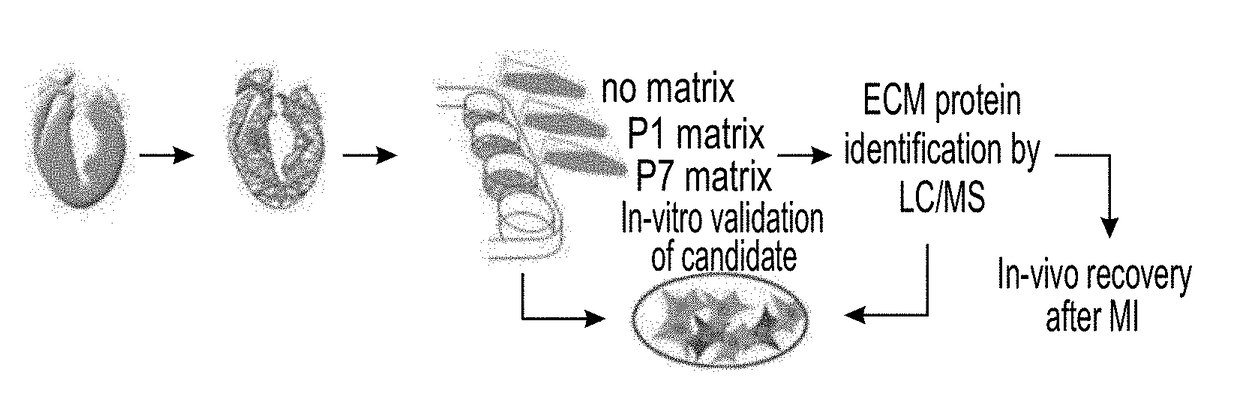
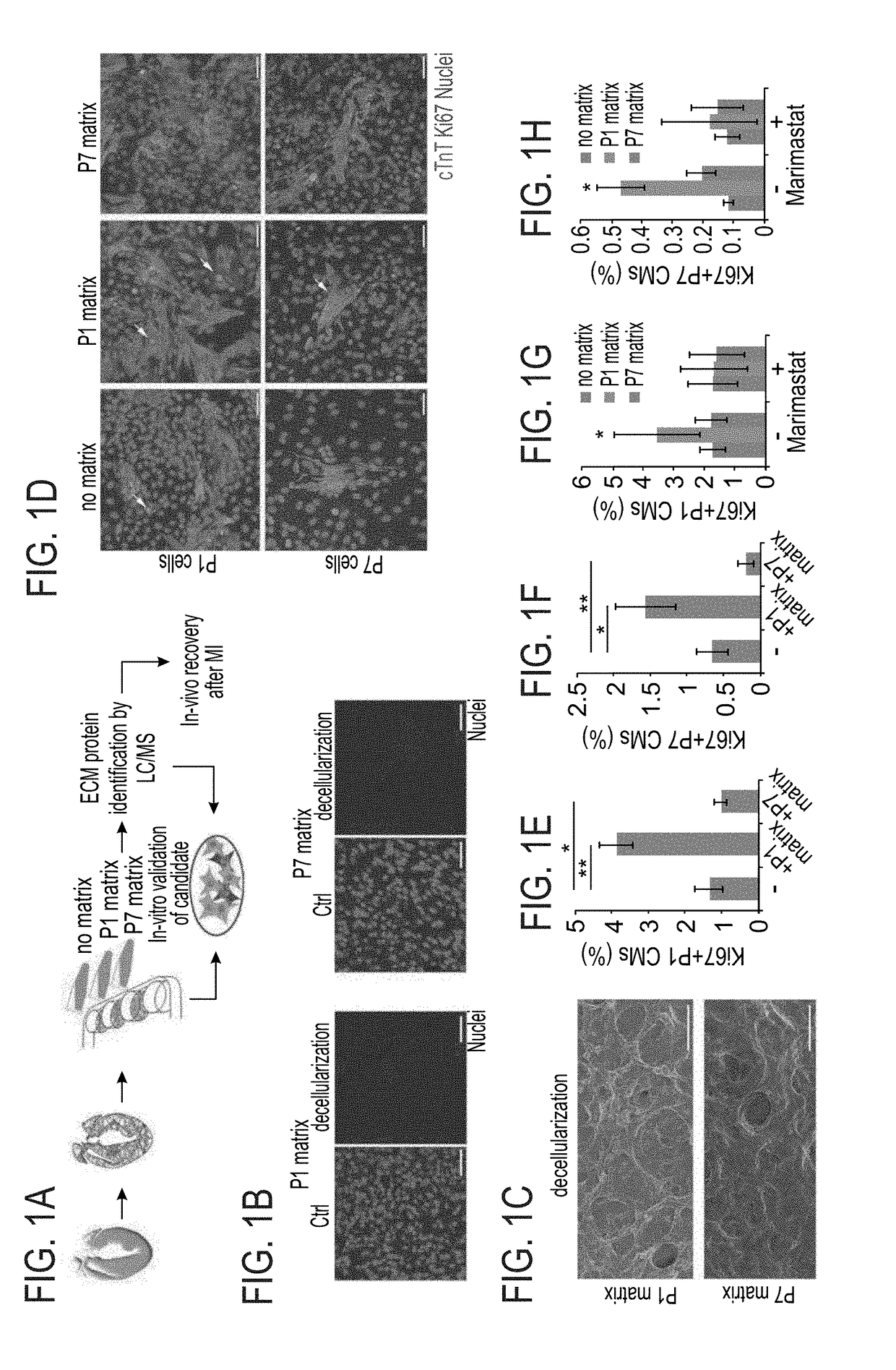
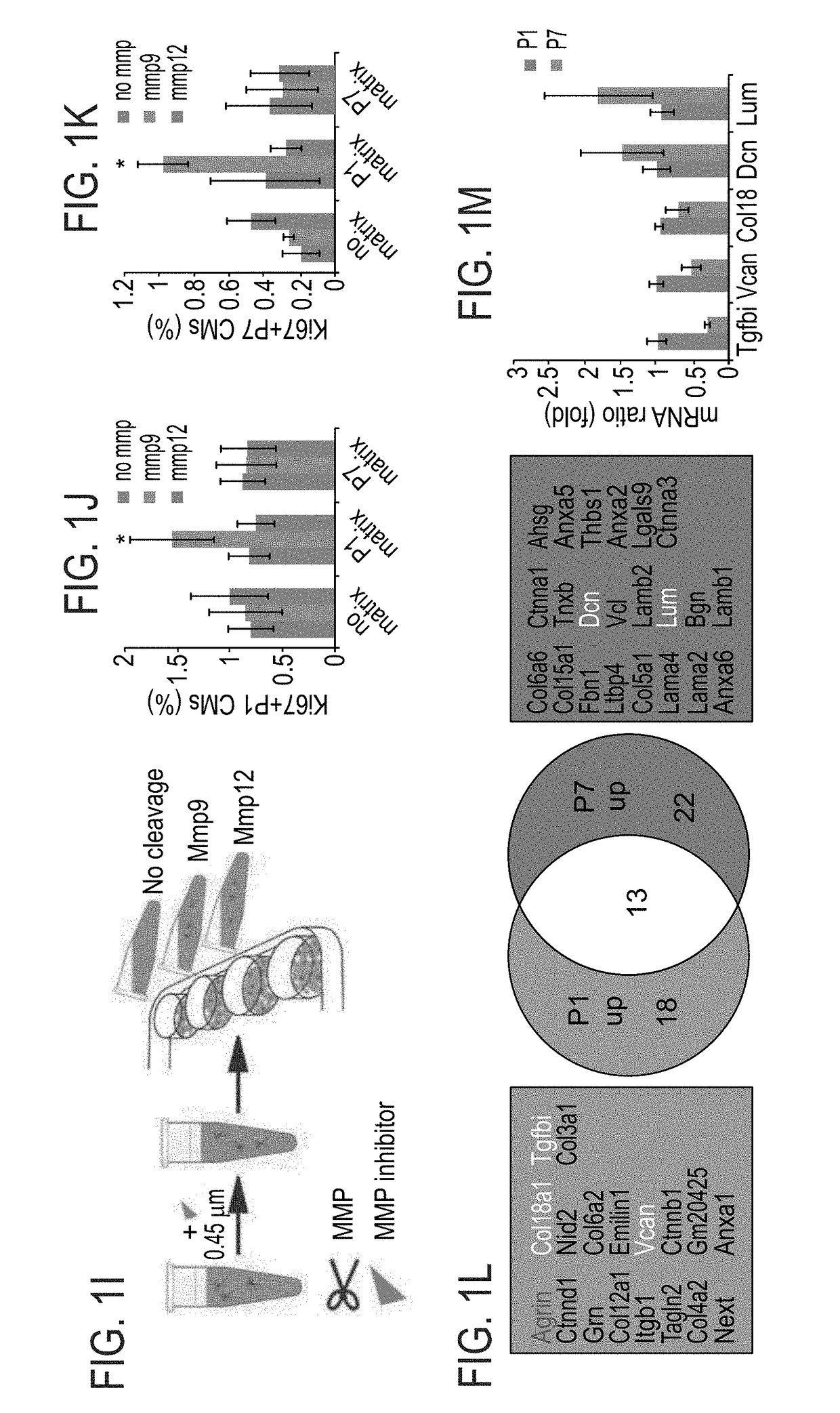
Method of inducing cardiomyocytes proliferation and treating heart diseases
ActiveUS10589132B2Induces proliferation of cardiomyocytesPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsHeart Muscle CellCardiac myocyte proliferation
An Agrin peptide which induces proliferation of cardiomyocytes for treating a heart disease is provided.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
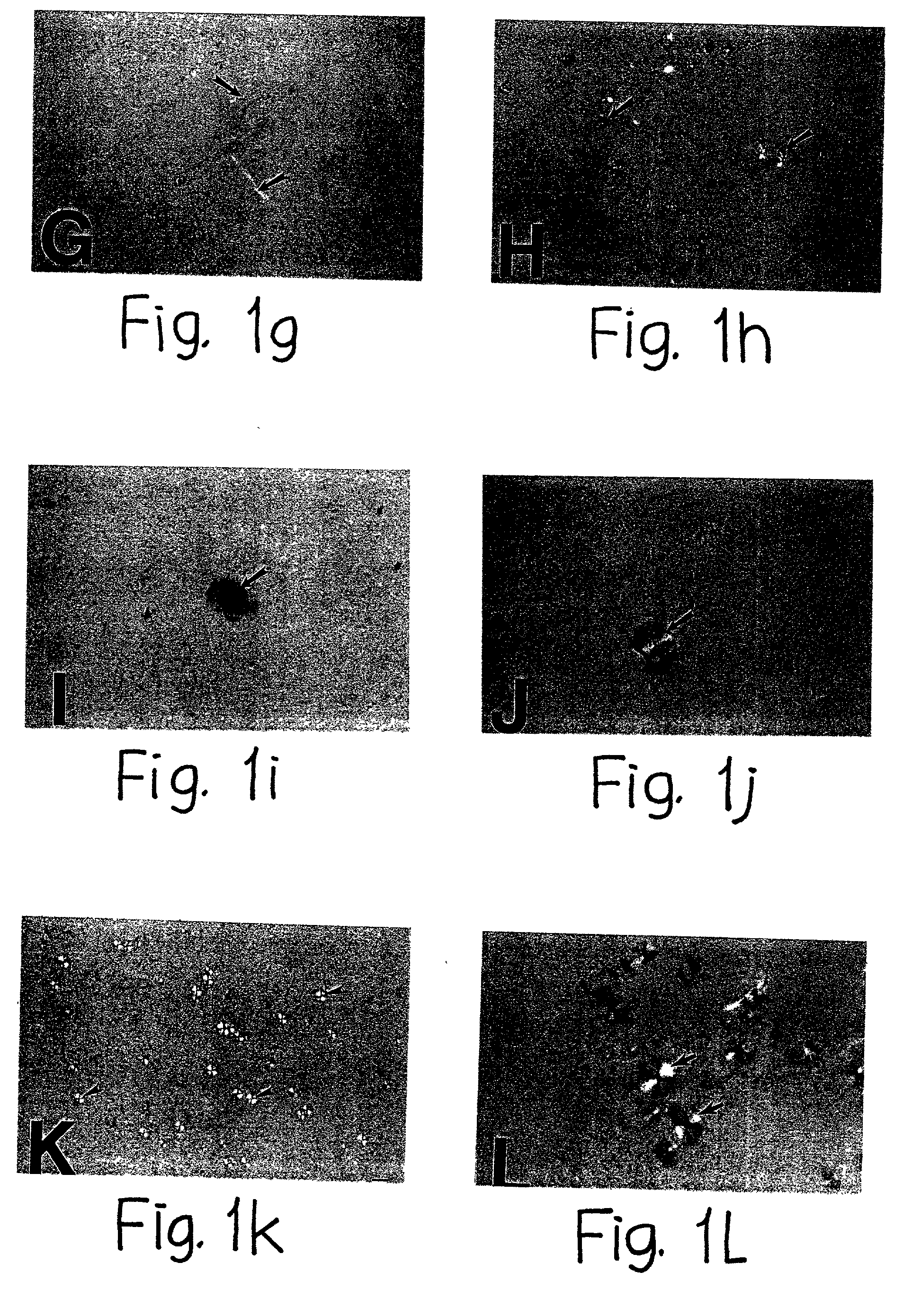
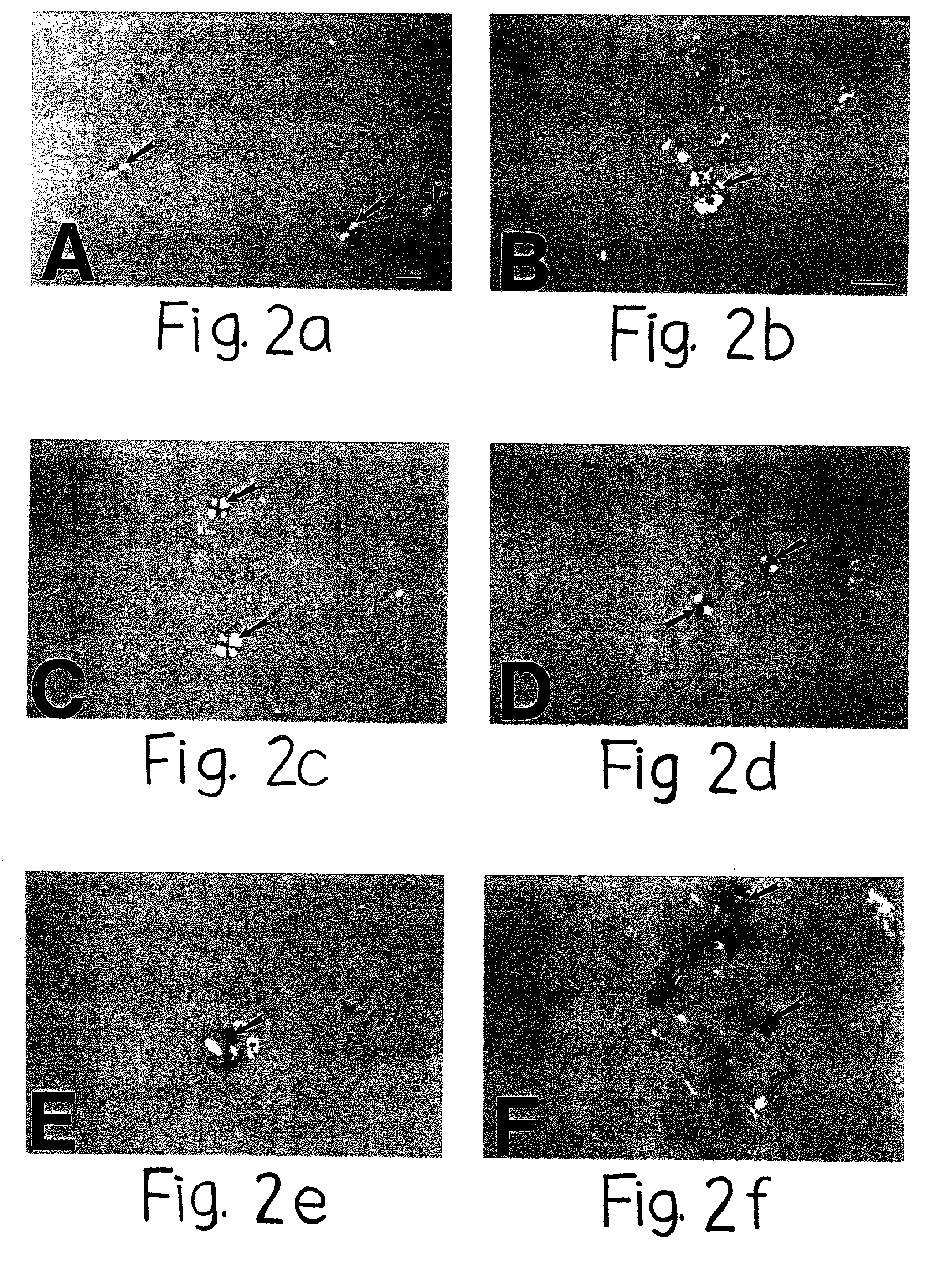
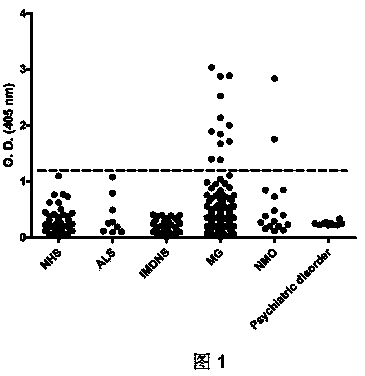
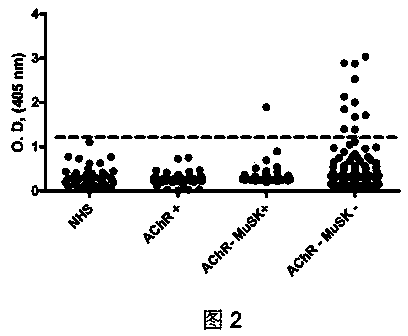
Human Agrin antigen and human Agrin antibody detecting kits and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveCN109734790AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityBiological testingAnimals/human peptidesSerum igeAntigen
The invention provides human Agrin antigen and ELISA detecting kits and a preparing method and application thereof. Human Agrin antigens have the amino acid sequences shown in SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4, SEQ ID NO:5, SEQ ID NO:6 and SEQ ID NO:7. The invention further provides the seven detecting kits with the seven human Agrin antigens respectively and the detecting kit with the seven human Agrin antigens simultaneously. The human Agrin detecting kit detects Agrin antibodies in human serum, is high in specificity, reaction sensitivity and flux and low in cost, can diagnose yasthenia gravis symptoms and is suitable for large-scale application and popularization.
Owner:WUHAN EASYDIAGNOSIS BIOMEDICINE
Method of inducing cardiomyocytes proliferation and treating heart diseases
ActiveUS20180318612A1Induced proliferationInduces proliferation of cardiomyocytesPeptide/protein ingredientsSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCardiac muscleHeart disease
An Agrin peptide which induces proliferation of cardiomyocytes for treating a heart disease is provided.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Method for culturing skeletal muscle for tissue engineering
ActiveUS20160068812A1Small sizeReduce complexityCulture processNervous system cellsSerum free mediaInsulin-like growth factor
The invention provides a nutrient medium composition and associated methods for lengthening the useful life of a culture of muscle cells. Disclosed is a method of culturing mammalian muscle cells, including preparing one or more carriers coated with a covalently bonded monolayer of trimethoxy-silylpropyl-diethylenetriamine (DETA); verifying DETA monolayer formation by one or more associated optical parameters; suspending isolated fetal rat skeletal muscle cells in serum-free medium according to medium composition 1; plating the suspended cells onto the prepared carriers at a predetermined density; leaving the carriers undisturbed for cells to adhere to the DETA monolayer; covering the carriers with a mixture of medium 1 and medium 2; and incubating. A cell nutrient medium composition includes Neurobasal, an antibiotic-antimycotic composition, cholesterol, human TNF-alpha, PDGF BB, vasoactive intestinal peptides, insulin-like growth factor 1, NAP, r-Apolipoprotein E2, purified mouse Laminin, beta amyloid, human tenascin-C protein, rr-Sonic hedgehog Shh N-terminal, and rr-Agrin C terminal.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Compositions and methods for detecting oral neoplasm
Methods and kits for assessing the presence of, and for detecting cancer, notably oral cancer, are disclosed. Such methods and kits use one or more lectins operably linked to a fluorophore, wherein the lectin binds differentially to cancerous and non-cancerous tissues, and wherein the fluorophore facilitates visualizing the differential binding. The lectins are applied to the oral mucosa of a subject, the fluorophore is exposed to light, and cancerous regions of the mucosa are visualized. In certain embodiments, the lectin specifically binds to one or more of a β-galactoside, an α- or β-N-acetylglucosamine, or a sialic acid moiety.
Owner:VSL ACQUISITION LLC
Fusion protein of tnfα and dc-sign and its application
ActiveCN103739714BImprove biological activityMake sure not to be killedPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsApoptosisAdhesion factor
The present invention relates to the fusion protein of TNFα and DC-SIGN and its application. Traditional anti-tumor drugs or treatment methods tend to cause damage to normal cells in the process of killing tumor cells. The targeted anti-tumor fusion protein of the present invention consists of a recognition functional domain, an action functional domain, and a connecting peptide connecting the two functional domains. The recognition functional domain is a lectin polypeptide with the function of recognizing and binding sugar chains on the surface of tumor cells-specific intercellular adhesion factor 3 on the surface of DCs binding to non-integrin molecules (DC-SIGN, dendritic-cell-specific? ICAM- 3-grabbing? nonintegrin), located at the C-terminus of the fusion protein; the functional domain is tumor necrosis factor (TNF), located at the N-terminus of the fusion protein; the connecting peptide is a short peptide containing 8-25 amino acids. The fusion protein can use lectin to carry out targeted combination with cancer cells, induce apoptosis of cancer cells through pro-apoptotic ligands, and at the same time reduce the killing effect on normal tissues and cells.
Owner:ZONHON BIOPHARMA INST
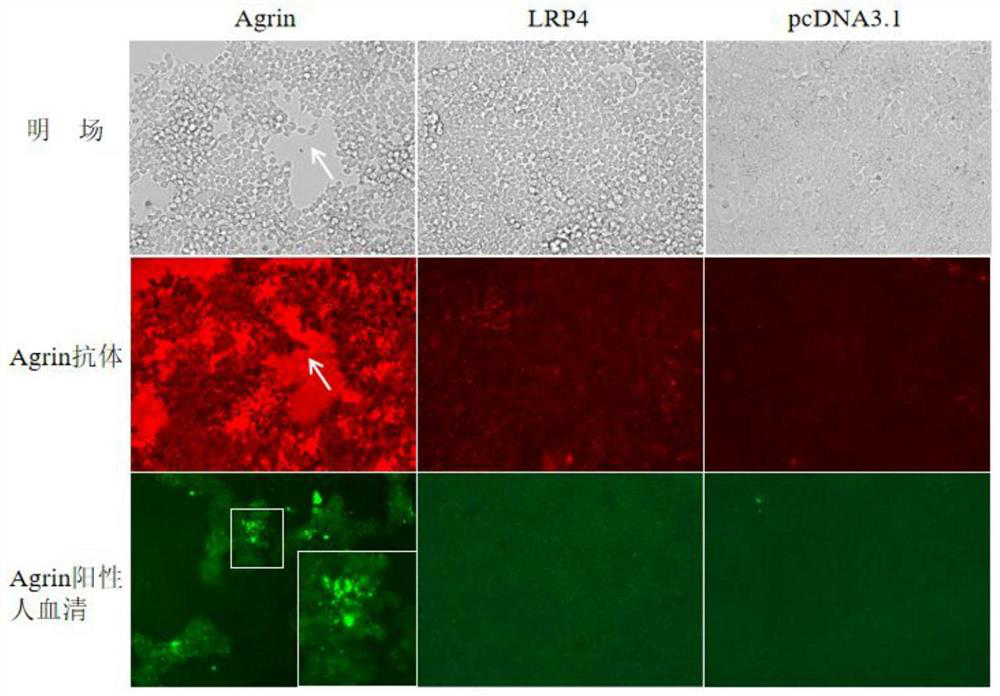
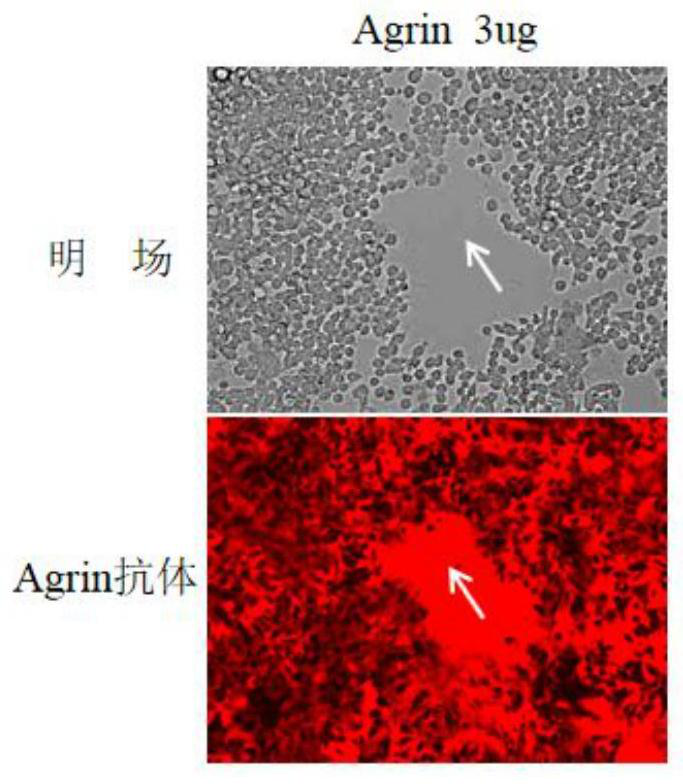
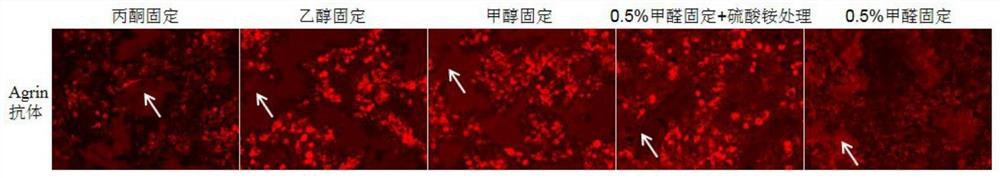
Reagent and method for improving quality of Agrin protein immunofluorescence flaking and application
ActiveCN114480498AImprove poor qualityGrowth inhibitionCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunofluorescenceCell membrane
Owner:SHAANXI MYBIOTECH CO LTD
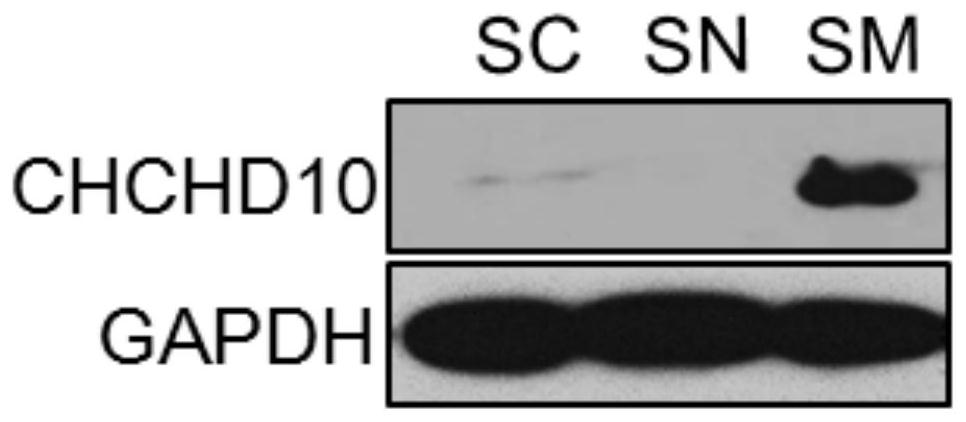
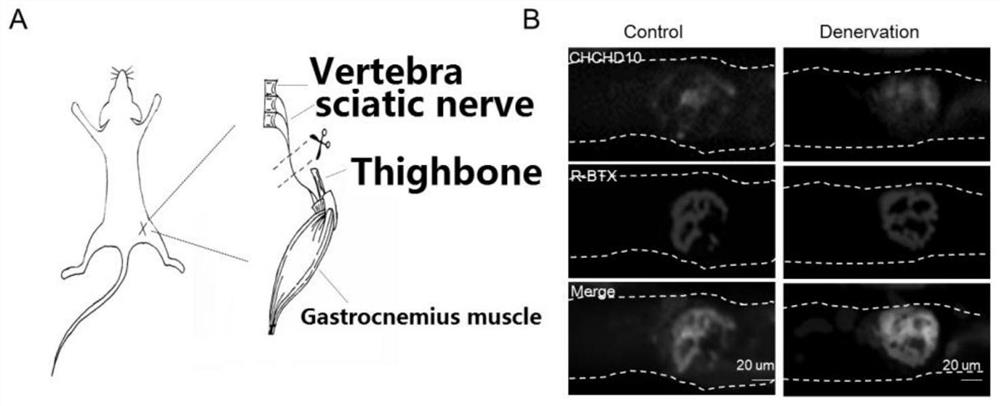
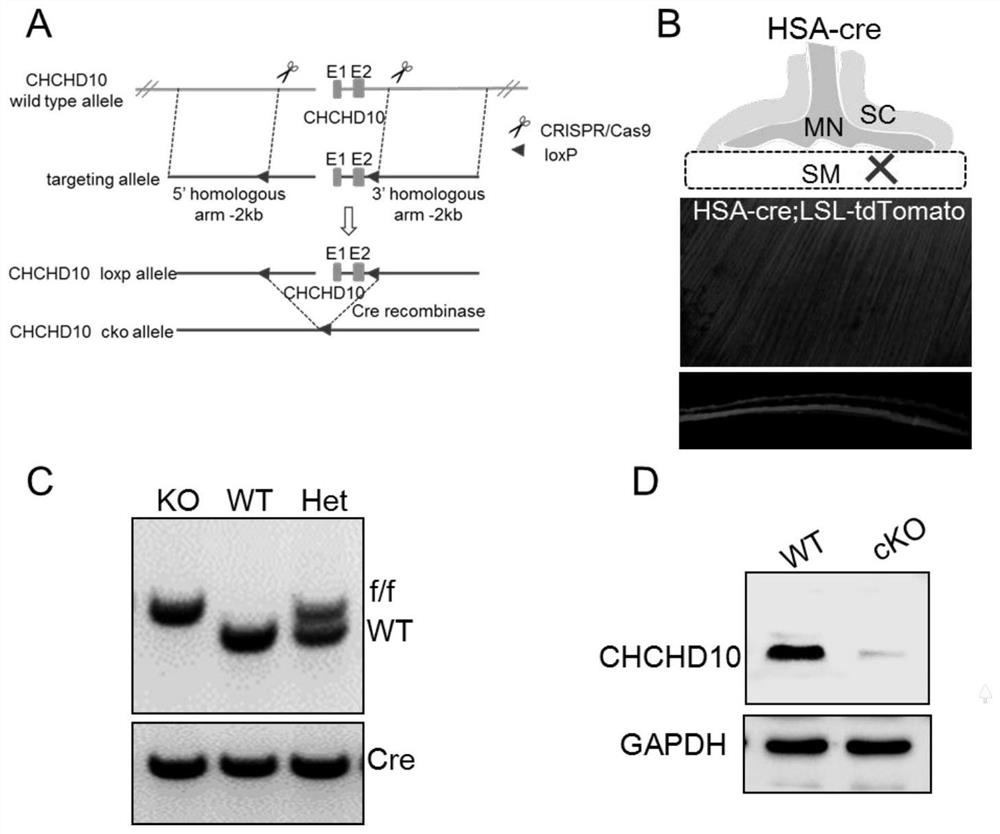
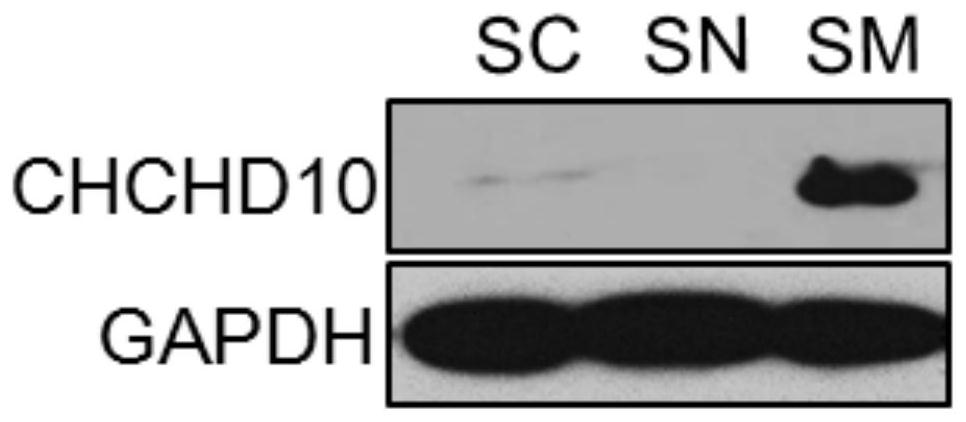
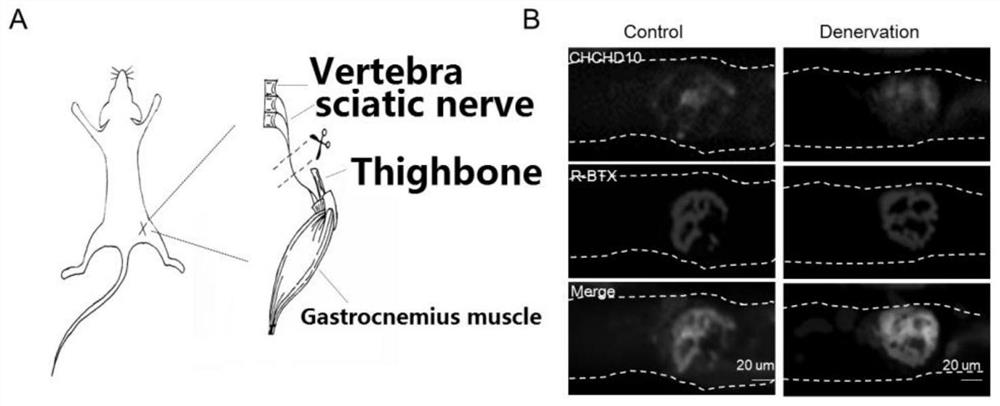
Application of chchd10 in promoting achr subunit gene expression and maintaining nmj stability
ActiveCN111948401BPromote aggregationImprove bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseImmunoprecipitation
The invention discloses the application of CHCHD10 in promoting AChR subunit gene expression and maintaining NMJ stability. The present invention explores the regulatory effect of CHCHD10 on NMJ homeostasis in skeletal muscle through immunohistochemistry, electrophysiology, electron microscopy and behavioral experimental techniques; silencing or knocking out the CHCHD10 gene can cause a decrease in the ATP level of cells or tissues, suggesting that ATP The production depends on the expression of CHCHD10; it is further confirmed that ATP can promote the aggregation of AChR induced by Agrin; through chromatin immunoprecipitation experiments, ATP can promote the combination of transcription factor GABPα and the promoter of AChR subunit gene; this suggests that ATP through Promote the expression of AChR subunit genes, and then promote the aggregation of AChR induced by Agrin, so as to maintain the normal function of NMJ; the present invention suggests that targeting NMJ may be an important means for early treatment and intervention of ALS and other neuromuscular diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
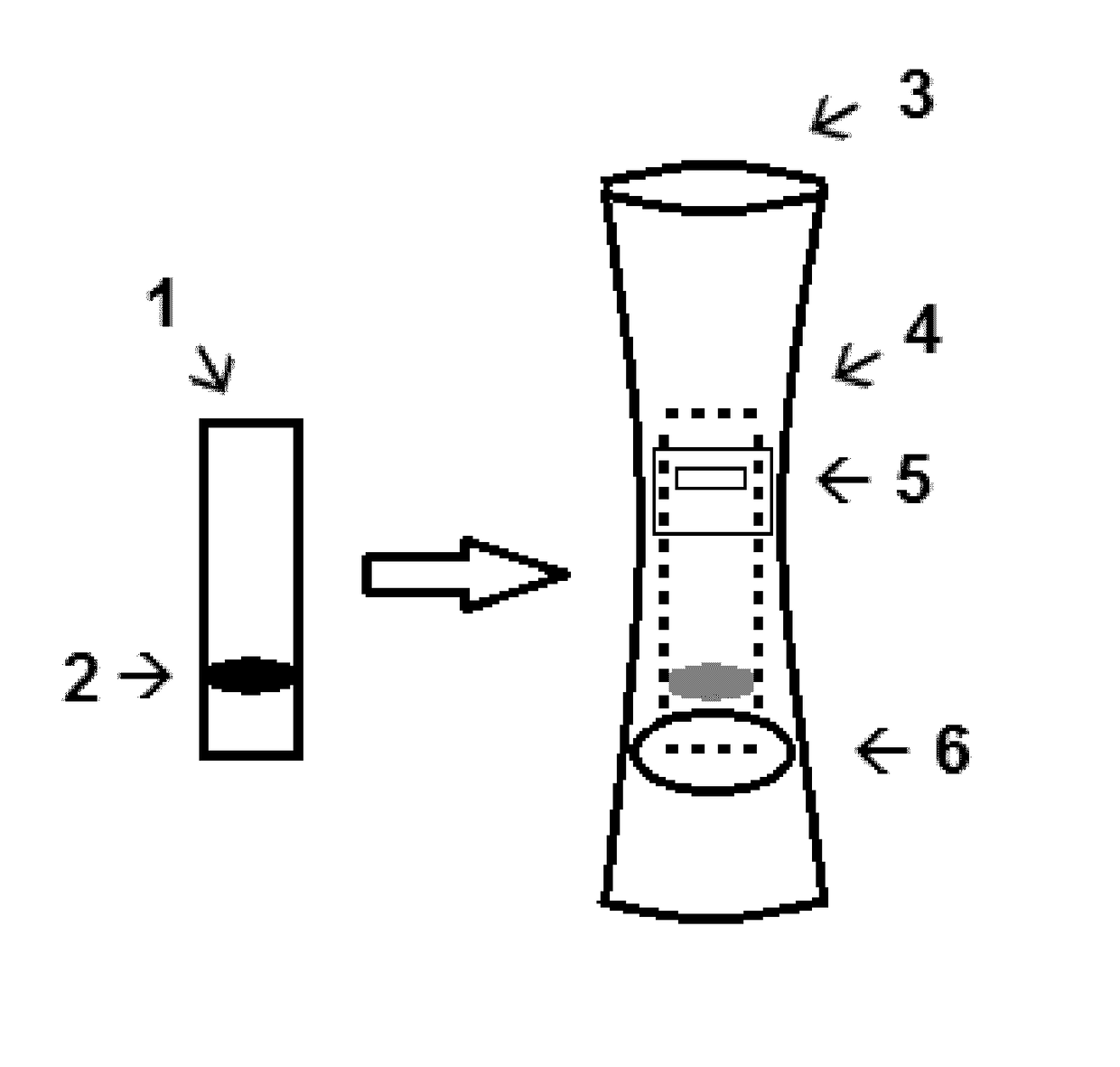
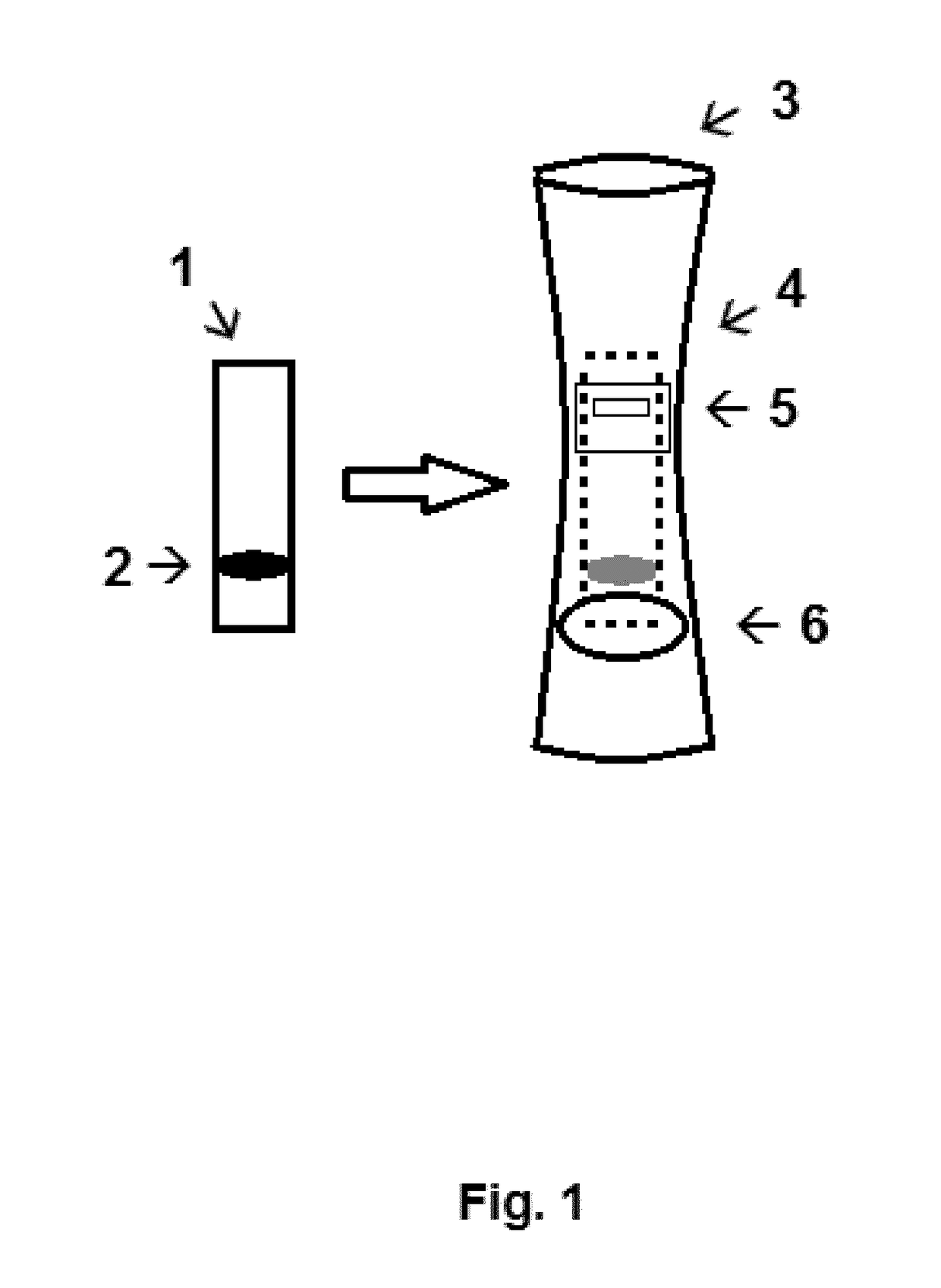
Kit-of-parts to identify mother's milk missing fucosyltransferase-2 dependent glycans and feeding doses with said glycans
Described is a matrix to identify mother's milk missing fucosyltransferase-2 (FUT2) dependent glycans which comprise a line of a glycan binding protein such as a lectin or antibody suitable to bind 2′fucosyl-glycans and a line of a positive control to bind a mother's milk protein. For instance, this matrix is porous and allows for transport by capillary force of compounds of mother's milk such as glycoproteins. Especially, the glycan binding protein is the plant lectin from Ulex europaeus. A diagnostic kit comprising one or more of such matrices and a device suitable to receive such a matrix provided with a milk application window and a read-out window has been described as well. Finally a kit-of-parts comprising such a diagnostic kit and one or more feeding doses of 2′fucosyl-glycans has been disclosed.
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
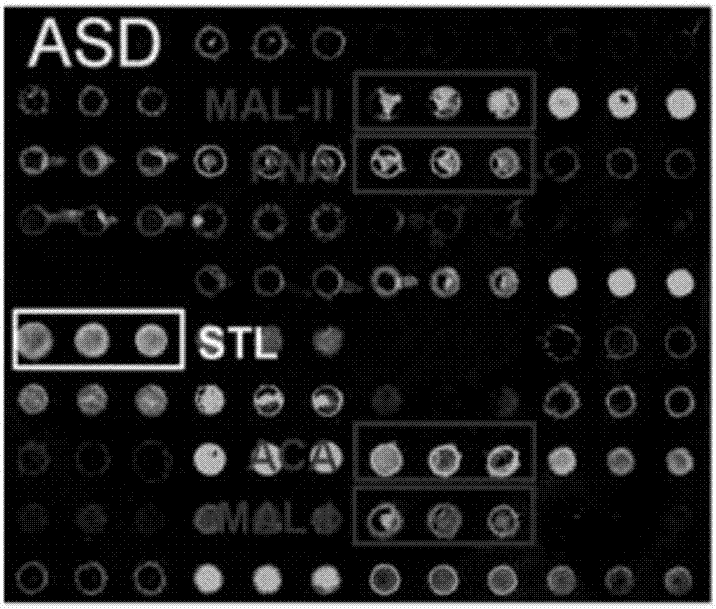
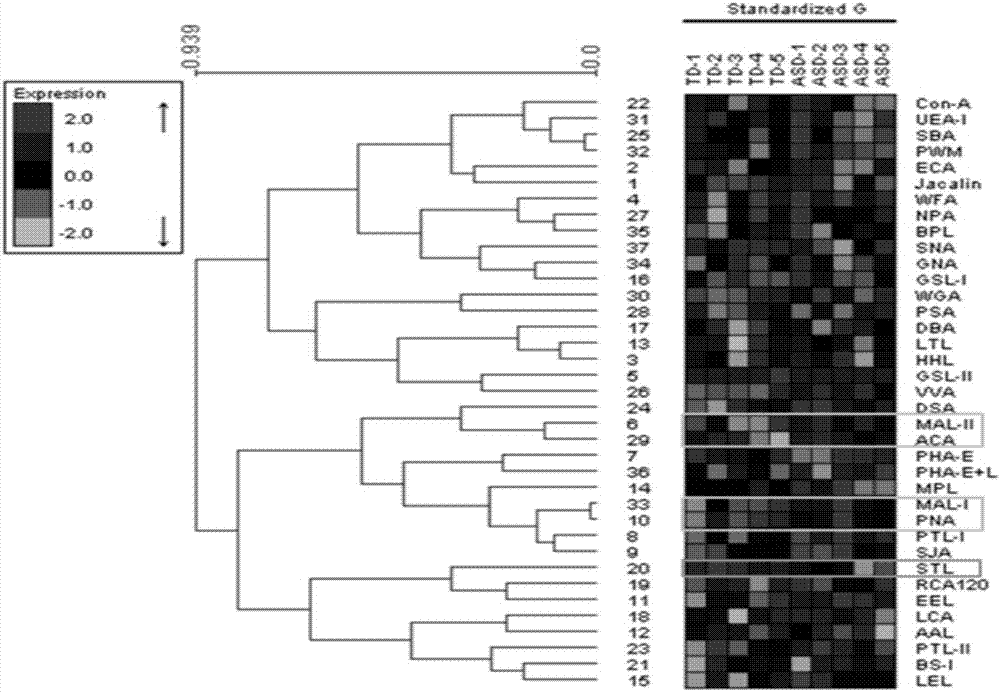
Application of a serum glycoprotein marker for autism
The invention discloses use of an autism seroglycoid marker. High-expression Apolipoprotein D (APOD) in ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorders) serum is simultaneously verified in agglutinin chip combined protein mass spectrometry forward verification and agglutinin / sugar-antibody chip reverse verification manners, and the APOD can serve as a seroglycoid marker for autism diagnosis, According to the use, vacancies in biochemical diagnosis on autism are made up.
Owner:广东侨都汇医疗科技有限公司
Screening for arthrogryposis multiplex in bovines
Owner:AGRIGENOMICS
Human agrin antigen, human agrin antibody detection kit, preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109734790BStrong specificityHigh sensitivityBiological testingAnimals/human peptidesMyasthenia gravisAntigen testing
The invention provides human Agrin antigen, ELISA detection kit, preparation method and application thereof. The human Agrin antigens include those shown in SEQ ID NO:1, SEQ ID NO:2, SEQ ID NO:3, SEQ ID NO:4, SEQ ID NO:5, SEQ ID NO:6 and SEQ ID NO:7 The amino acid sequence also provides seven detection kits containing the above seven human Agrin antigens, and one detection kit simultaneously containing the above seven human Agrin antigens. The human Agrin detection kit detects the Agrin antibody in human serum, has strong specificity, high reaction sensitivity, high throughput and low cost, can diagnose myasthenia gravis, and is suitable for large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:WUHAN EASYDIAGNOSIS BIOMEDICINE
Screening for Arthrogryposis Multiplex in Bovines
InactiveUS20110151440A1Operation and useSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementISG15ISG15 ubiquitin-like modifier
Provided are methods, materials and kits for analyzing DNA samples from bovine to determine whether the animal is a recessive carrier of a genetic mutation that is associated with arthrogryposis multiplex (AM). DNA-containing samples are analyzed by genetic testing to determine whether or not a deletion mutation is present in one of the alleles that are responsible for the AM genetic mutation. In an aspect the deletion encompasses the entirety of the ISG15 ubiquitin-like modifier (ISG15) gene. In an aspect the deletion further encompasses one or both of the 5′ regulatory region of the hairy and enhancer split 4 (HES4) and of the agrin (AGRN) gene and of the first two exons of the AGRN gene.
Owner:AGRIGENOMICS
Application of CHCHHD10 in promoting AChR subunit gene expression and maintaining NMJ stability.
ActiveCN111948401APromote aggregationImprove bindingMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisDiseaseImmunoprecipitation
The invention discloses an application of CHCHHD10 in promoting AChR subunit gene expression and maintaining NMJ stability. According to the invention, the regulation effect of CHCHD10 in skeletal muscle on NMJ steady state is explored through experimental technical means such as immunohistochemistry, electrophysiology, electron microscopy, behavioristics and the like; the ATP level of cells or tissues can be reduced by silencing or knocking out the CHCHD10 gene, and the generation of ATP is prompted to depend on the expression of CHCHD10; the fact that ATP can promote AChR aggregation inducedby Agrin is further proved; a chromatin immunoprecipitation experiment shows that ATP can promote the combination of a transcription factor GABP alpha and a promoter of an AChR subunit gene; the ATPis prompted to promote AChR aggregation induced by Agrin by promoting AChR subunit gene expression, so that the normal function of the NMJ is maintained; the invention suggests that targeting NMJ maybe an important means for early treatment and intervention of ALS and other neuromuscular diseases.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for the production of hybridoma cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies capable to specifically binding to a human c44-fragment of agrin
InactiveUS20130344593A1Good immune effectImprove immunityAnimal cellsNervous disorderWild typeAntibody-Producing Cells
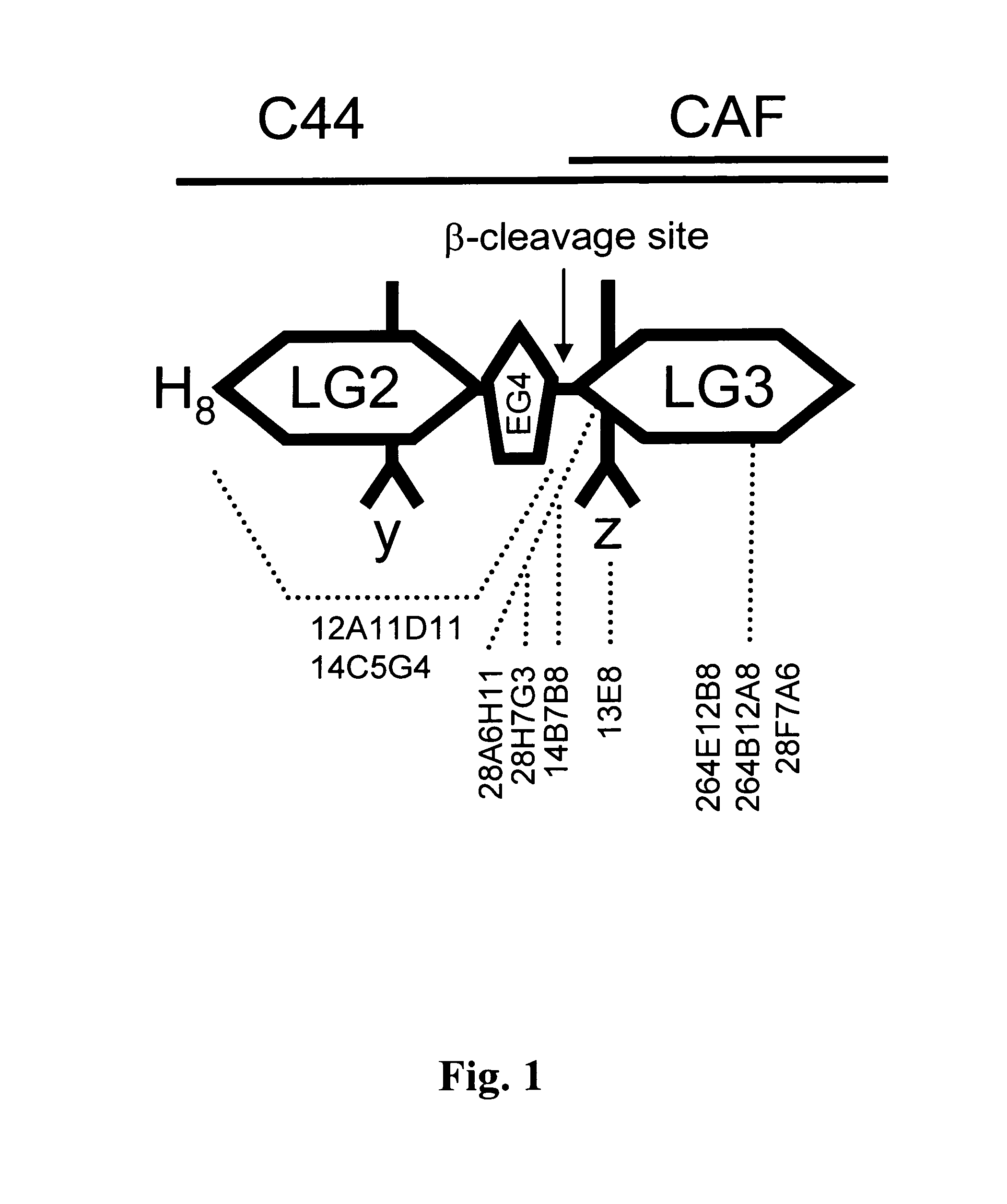
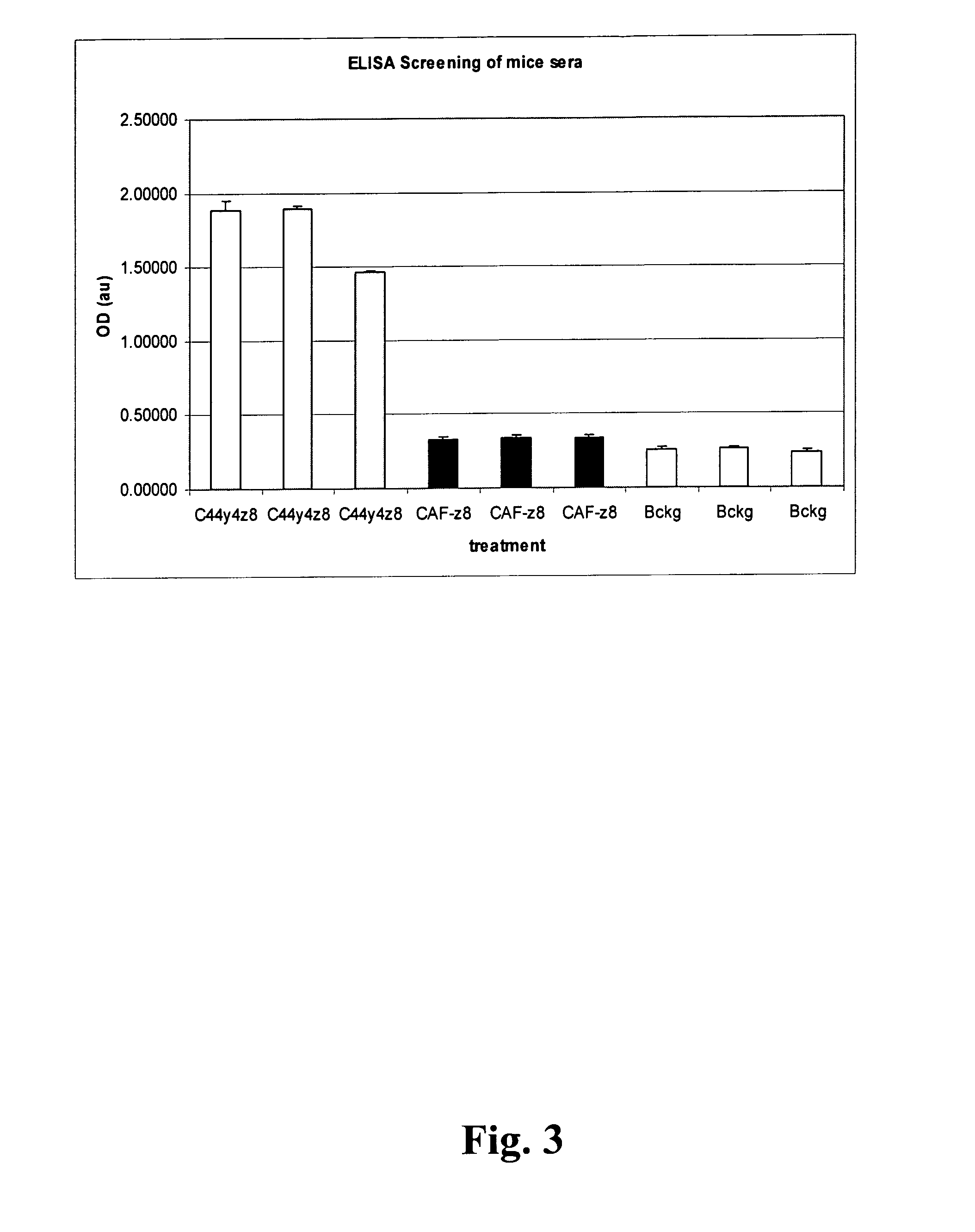
A method for the production of a hybridoma cell lines producing monoclonal antibodies capable to specifically binding to a human C44-fragment of agrin, comprising administering to wild-type-mice an immunizing amount of C44y≧4-fragment of agrin, isolating antibody producing cells from the immunized mice, fusing them with a myeloma cell line, growing the fused cells in a selection medium, screening the antibodies in the supernatants of hybridoma cells for binding to C44-fragment of agrin and isolating the hybridoma cells producing the desired monoclonal antibodies
Owner:NEUROTUNE AG
Treatment of an ischemic heart disease
PendingUS20200306343A1Peptide/protein ingredientsCardiovascular disorderCoronary arteriesIschemic Heart Diseases
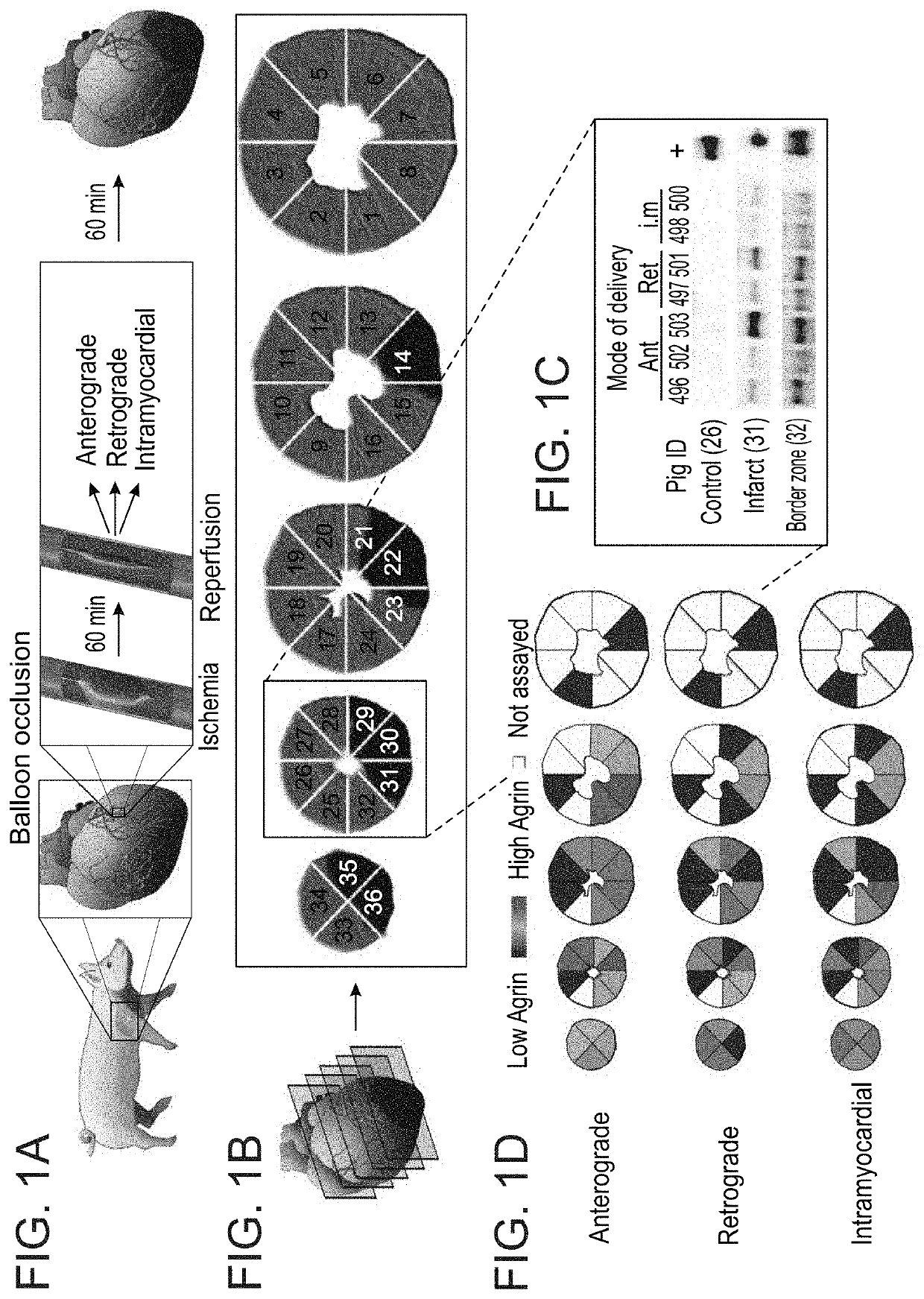
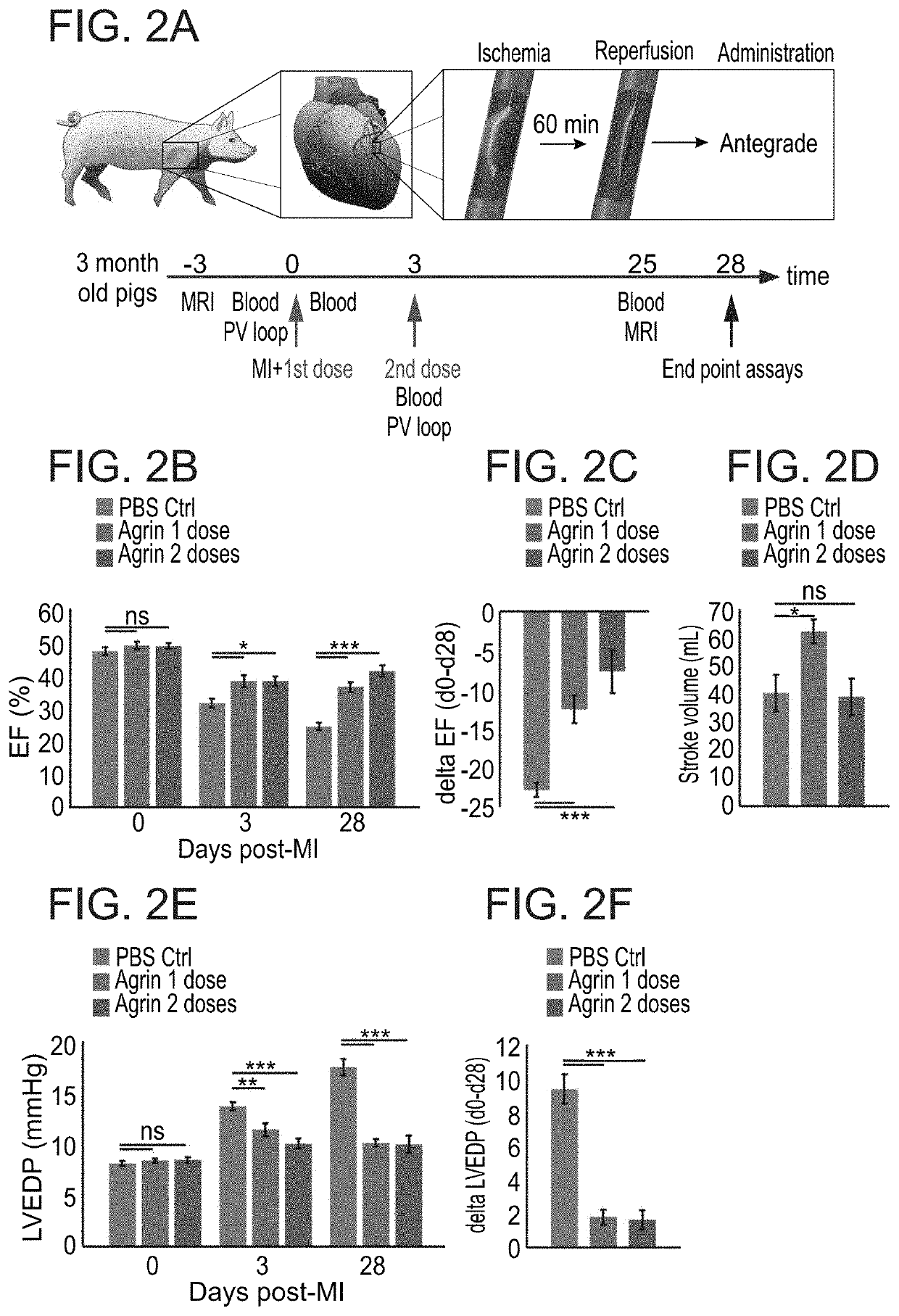
A method of treating an ischemic heart disease in a subject in need thereof is provided. The method comprises administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of Agrin in an anterograde intracoronary manner, thereby treating the ischemic heart disease in the subject.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com