Diagnostic composition for neurotransmission disorder diseases by utilizing agrin
A technology for neurotransmission disorders and diagnostic compositions, which can be used in disease diagnosis, biological testing, and biomaterial analysis. It can solve the problems of non-detection and achieve the effect of filling vacancies, good results, and broad market prospects.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
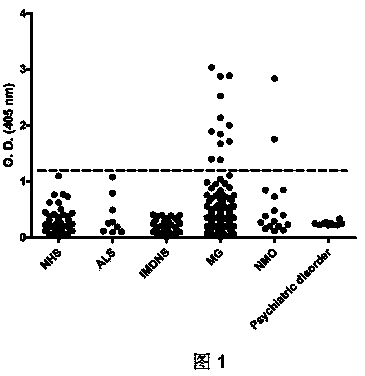
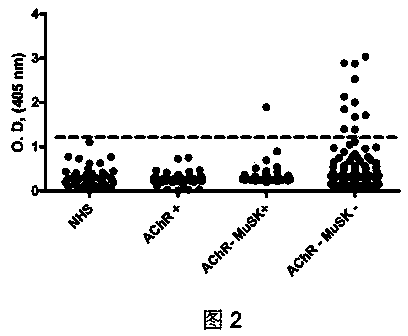
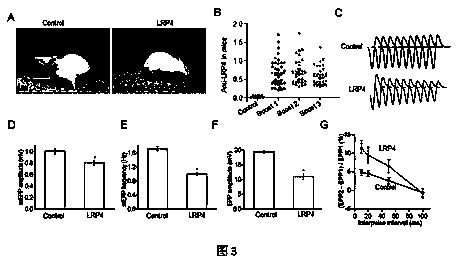
[0024] Example 1 LRP4 autoantibodies exist in the blood of patients with myasthenia gravis, which can induce myasthenia gravis
[0025] Myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disease, is a common neurosynaptic disease, affecting about 10-20 per 100,000 people. About 80% of patients have antibodies in their body that can bind to muscle acetylcholine receptors. These antibodies reduce the number of acetylcholine receptors or disable them, resulting in muscle weakness in neuromuscular transmission. Although most cases of myasthenia gravis are caused by autoantibodies that bind to acetylcholine receptors, about 20% of patients have undetectable antibodies to acetylcholine receptors. In 2001, about 4-50% of patients with negative acetylcholine receptor antibody could detect MuSK antibody. Immunization of rabbits with the extracellular region of MuSK can lead to myasthenia gravis and decrease in the number of acetylcholine receptors. Although a series of experiments demonstrated that an...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Autoantibodies from patients with myasthenia gravis bind to agrin
[0044] The sera of some patients with myasthenia gravis were negative for acetylcholine receptor antibody / MuSK antibody / LRP4 antibody, which may indicate the existence of new unknown autoantibodies. The present invention demonstrates the presence of antibodies to the agrin-containing protein in the sera of these patients. This example proves that among 93 patients with myasthenia gravis, 7 sera were positive for agglutinin antibodies (about 7-8%), while no positive for agglutinin antibodies was found in healthy people or other patient controls. This invention demonstrates that aggrin antibodies are a novel pathogen in patients with myasthenia gravis.
[0045] Experiments have proved that aggrin antibody serum can recognize aggrin, and can inhibit the phosphorylation of MuSK protein induced by aggrin, and can inhibit the aggregation of aggrin on acetylcholine receptors. This invention proves ...
Embodiment 3
[0054] Example 3 Preparation method and detection process of LRP4 autoantibody detection kit
[0055] Myasthenia gravis, an autoimmune disease, is a common neurosynaptic disease, affecting about 10-20 per 100,000 people. About 80% of patients have antibodies in their body that can bind to muscle acetylcholine receptors. These antibodies reduce the number of acetylcholine receptors or disable them, resulting in muscle weakness in neuromuscular transmission. In patients with negative acetylcholine receptor antibodies, MuSK antibodies can be detected in about 4-50% of patients. Although a series of experiments demonstrated that antibodies to acetylcholine receptors and MuSK caused myasthenia gravis, these antibodies were still undetectable in 10% of patients. This example describes the preparation method of the LRP4 autoantibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) detection kit, and the process of using the kit to detect LRP4 antibody in patients with double-negative acety...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com