Exosomes comprising RNA therapeutics
An exosome, therapeutic technology, applied in retro RNA viruses, DNA/RNA fragments, fusions with RNA binding domains, etc., can solve problems such as adverse immune reactions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
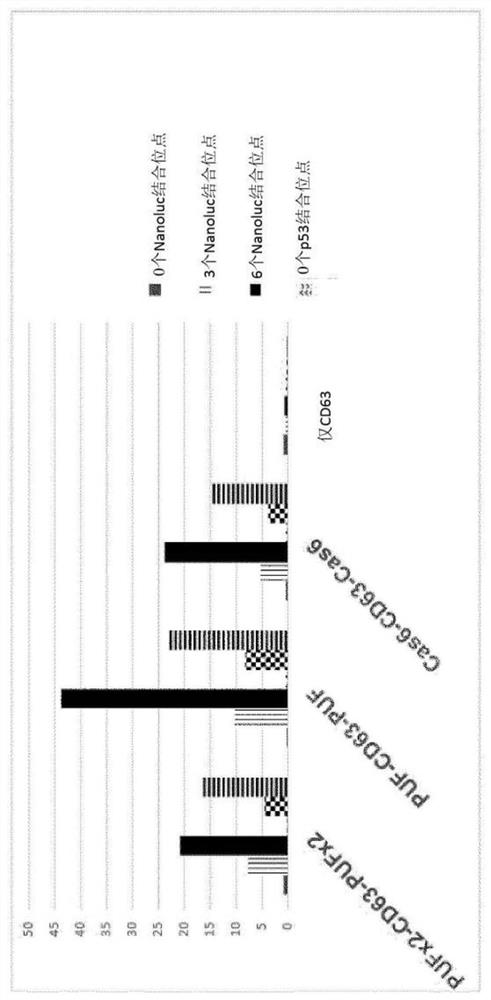
[0074] Example 1. Bone marrow-derived MSCs were cultured in conventional tissue culture flasks, and PEI transfection was used for transient transfection to achieve the loading and expression of mRNA cargo molecules and fusion polypeptide constructs. figure 2 The loading in EVs of mRNA cargo molecules encoding NanoLuc (RTM) and p21 obtained from BM-MSC is shown. Loading was achieved using a fusion polypeptide construct containing CD63 as an exosomal polypeptide and PUF or Cas6 as an NA binding domain. The experiment also included different numbers of binding sites for NA binding domains, namely 0, 3 and 6 binding sites, which were inserted into different positions on the 3'and / or 5'sides of the coding region.
[0075] MSC-EV was purified using a sequential combination of TFF and SEC. Only the expression of the exosomal polypeptide CD63 does not cause any mRNA to be loaded into the EV ( figure 2 The right column of the middle figure). Expression of PUF-containing fusion polypept...
example 2
[0076] Example 2. Silencing of in vitro gene expression in target cells (HEK293 cells) under EV-mediated delivery of shRNA targeting huntingtin. Lentiviral transduction was used to transduce amniotic membrane cells cultured in a shaking incubator to secrete EVs containing shRNA and fusion polypeptide constructs containing PUF or Cas6 as NA binding domains, and CD63 or CD81 binds as an EV polypeptide. The EV was purified from the supernatant using ultracentrifugation. image 3 The Y-axis shows how the huntingtin protein expression level decreases as the number of binding sites in the NA cargo molecule increases. Loading anti-huntingtin shRNA with a PUF-CD63-PUF fusion polypeptide will result in approximately 80% knockout .
example 3
[0077] Example 3. After HEK EV-mediated delivery of NanoLuc (RTM) mRN, NanoLuc (RTM) is used as a reporter gene to express in target Huh7 cells. HEK293T cells were stably transduced to express various fusion polypeptide constructs to load the reporter gene NanoLuc (RTM) mRNA cargo into the EV. The NanoLuc(RTM) mRNA cargo molecule is engineered to contain 0, 3 or 6 binding sites of the NA binding domain. The NA binding domain comprises a fusion polypeptide construct, in which case the fusion polypeptide construct is PUFx2-CD63-PUFx2 (two PUF NA-binding peptides are inserted into the N and C ends of the exosomal polypeptide CD63), PUF-CD63-PUF and Cas6-CD9-Cas6 ( Figure 4 ).
[0078] After purification of HEK-derived EVs based on TFF with bead-eluted LC, the EVs are added to HEK cells at the optimal concentration. For this assay, the optimal concentration is in each well of a 6-well plate of Huh7 target cells. 10 7 EV. Figure 4 The Y axis of shows the relative light (luminescenc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com