Biological ink for 3D (Three Dimensional) printing and preparation method thereof
A bio-ink, 3D printing technology, applied in tissue regeneration, medical science, prosthesis, etc., can solve the problems of unsatisfactory biological activity, chemical residue, unsatisfactory effect, etc., to achieve individual targeting and immunogenicity Low, safe effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
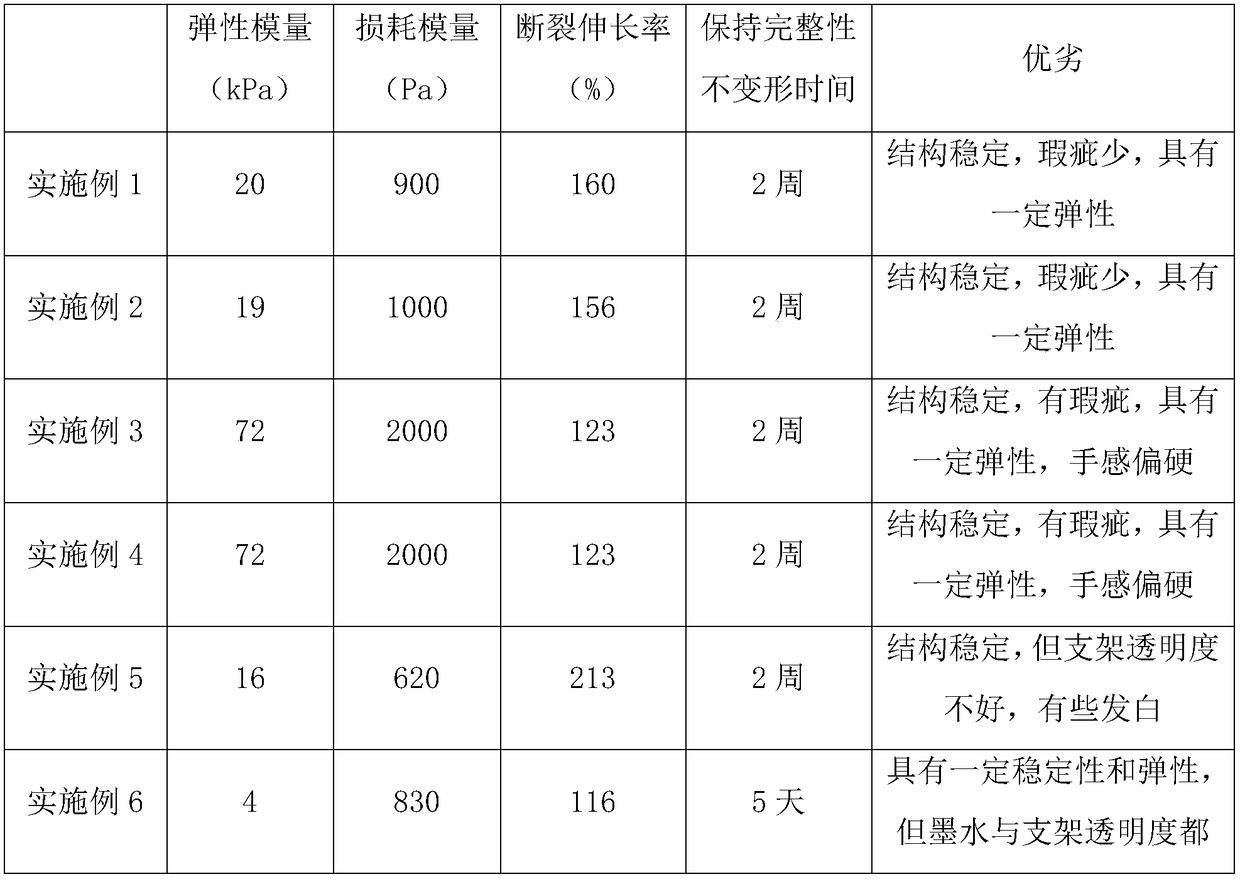
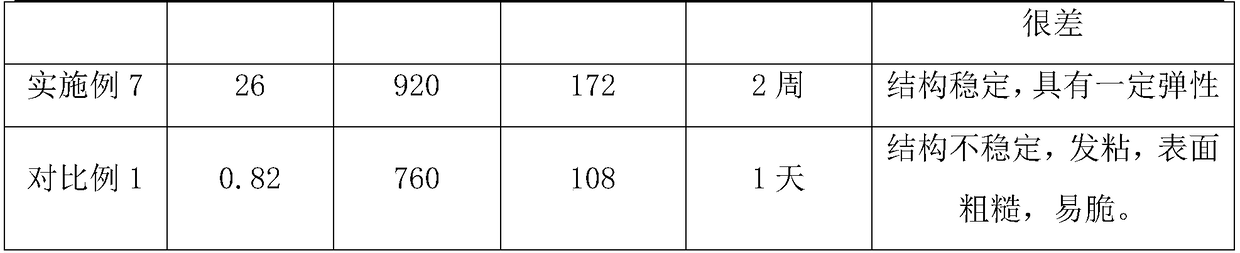
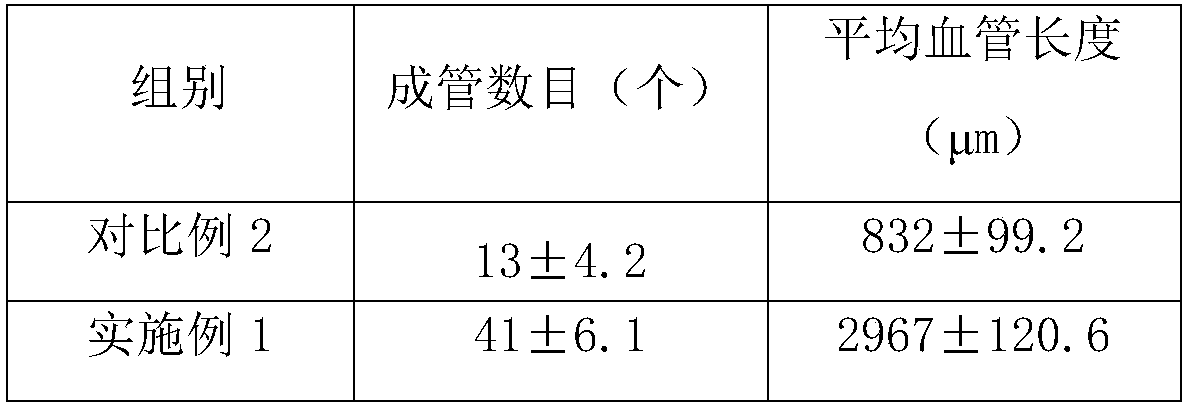
Embodiment 1
[0034] A kind of 3D printing biological ink, comprises the raw material of following mass percentage and is made of:
[0035] Extracellular Vesicle Suspension 10%
[0036] Pig dermal soft tissue derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder 5%
[0037] Hydrochloric acid 1%
[0038] Ultrapure water balance.
[0039] The 3D printing bio-ink is prepared according to the following method:
[0040] Mix pig dermis and soft tissue-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber micropowder, hydrochloric acid and ultrapure water, stir until completely dissolved, adjust the pH to 6.5 with sodium bicarbonate solution, add extracellular vesicle suspension, mix evenly, centrifuge, and bioink material.
[0041] 3D printing forming method, comprising the steps of:
[0042] (1) 3D bioprinting: use the 3D bioprinter to print the composite ink material from the ink injection cylinder at 15°C through the needle to the receiving platform at 8°C according to the established digital model, and store i...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A kind of 3D printing biological ink, comprises the raw material of following mass percentage and is made of:
[0046] Extracellular Vesicle Suspension 30%
[0047] Pig dermal soft tissue-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder 9%
[0048] Acetic acid 1%
[0049] Ultrapure water balance.
[0050] The 3D printing bio-ink is prepared according to the following method:
[0051] Mix pig dermis soft tissue-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber micropowder, acetic acid and ultrapure water, stir until completely dissolved, adjust the pH to 6.9 with sodium bicarbonate, add extracellular vesicle suspension, mix well, and centrifuge. bioink material.
[0052] 3D printing forming method, comprising the steps of:
[0053] 3D printing was carried out according to the 3D printing molding method of Example 1, and then washed with water and cross-linked to finalize the shape.
Embodiment 3
[0055] A kind of 3D printing biological ink, comprises the raw material of following mass percentage and is made of:
[0056] Extracellular vesicle suspension 20%;
[0057] Bovine dermis soft tissue-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder 15%;
[0058] Phosphoric acid 0.1%;
[0059] Ultrapure water balance.
[0060] The 3D printing bio-ink is prepared according to the following method:
[0061] Mix bovine soft tissue-derived extracellular matrix nanofiber powder, phosphoric acid and ultrapure water, stir until completely dissolved, adjust the pH to 6 with sodium phosphate, add extracellular vesicle suspension, mix well, and centrifuge to obtain bioink materials.
[0062] 3D printing forming method, comprising the steps of:
[0063] Carry out 3D printing according to the 3D printing molding method of Example 1, then wash with water, 0.5% (according to the amount of 3D printing bio-ink) glutaraldehyde cross-linking to set the shape.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com