Method for the treatment of pompe disease using 1-deoxynojirimycin and derivatives
A technology of deoxynojirimycin and its derivatives, which can be used in gene therapy, pharmaceutical formulations, genetic material components, etc., and can solve problems such as side effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0240] Example 1: Synthesis of DNJ and derivatives
[0241] Tetra-O-benzyl-1-deoxynojirimycin [General imino sugar preparation method-1]
[0242]
[0243] DMSO (4.4ml, 0.124mol) in anhydrous CH 2 Cl 2 The solution (75 mL) was placed under an argon atmosphere and cooled to -78 °C. Keeping the temperature at -78 °C, slowly add trifluoroacetic anhydride (6.1 ml, 0.088 mol) in anhydrous CH 2 Cl 2 solution (50 mL). After the addition was complete, the reaction was stirred for an additional 30 minutes and 2,3,4,6-tetra-O-benzylsorbitol (5.4 g, 10 mmol) was added dropwise in CH 2 Cl 2 solution. The reaction was stirred at -78 °C for 90 minutes, then triethylamine (11.2 ml, 0.08 mol) in CH 2 Cl 2 (50 mL) solution to quench the reaction. The reaction was warmed to 0 °C, then concentrated using a rotovap. Dilute the residue with MeOH (75 mL), add 2M NH 3 MeOH (10.0ml, 20.0mmol) solution, followed by formic acid (0.77mL, 20.0mmol), Molecular sieve, add NaCNBH at the en...
Embodiment 2
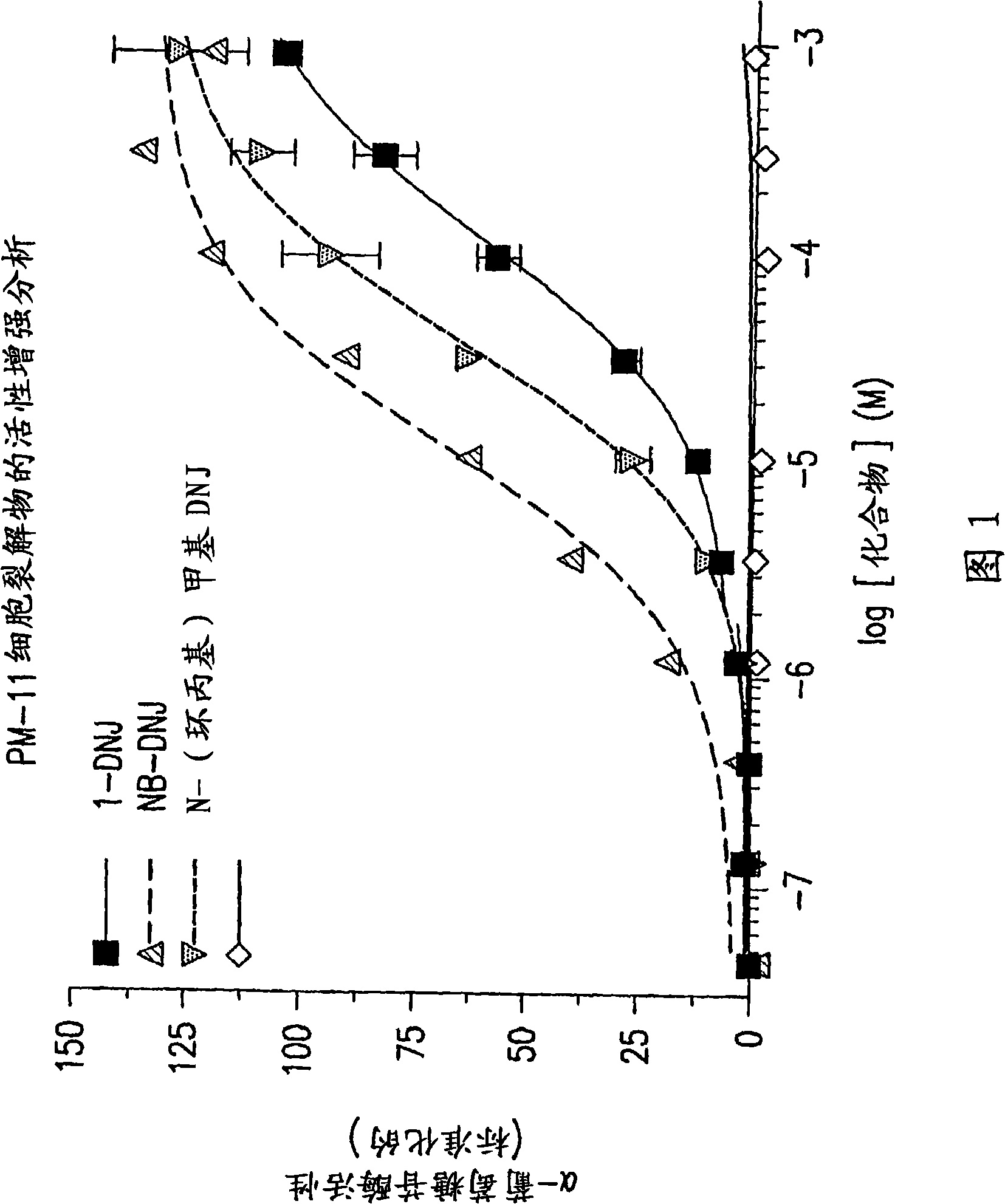
[0325] Example 2: Increasing Gaa with DNJ and DNJ derivatives
[0326] Experiments described below demonstrate that DNJ and the DNJ derivative N-butyl-DNJ, a known inhibitor of enzymes involved in glycolipid synthesis, can also bind Gaa and increase the activity of mutant Gaa without inhibiting glycolipid synthesis.
[0327] method
[0328] Cell culture and seeding: Cell lines of PM11 (P545L), PM8 and PM12 (both cleavage defects), fibroblasts were used for enhancement experiments. These cells were fibroblasts isolated from patients with Pompe disease. Seed cells at approximately 5000 cells per well in 180 μL medium in sterile black clear bottom 96-well Costar plates and store in 5% CO 2 , Incubate at 37°C for about 3-6 hours. The medium consisted of DMEM containing 10% FBS and 1% penicillin / streptomycin.
[0329] Drug Treatment All test compounds were dissolved in 1:1 DMSO:H at a stock concentration of 100 mM 2 O middle. Perform serial dilutions of cells with another s...
Embodiment 3
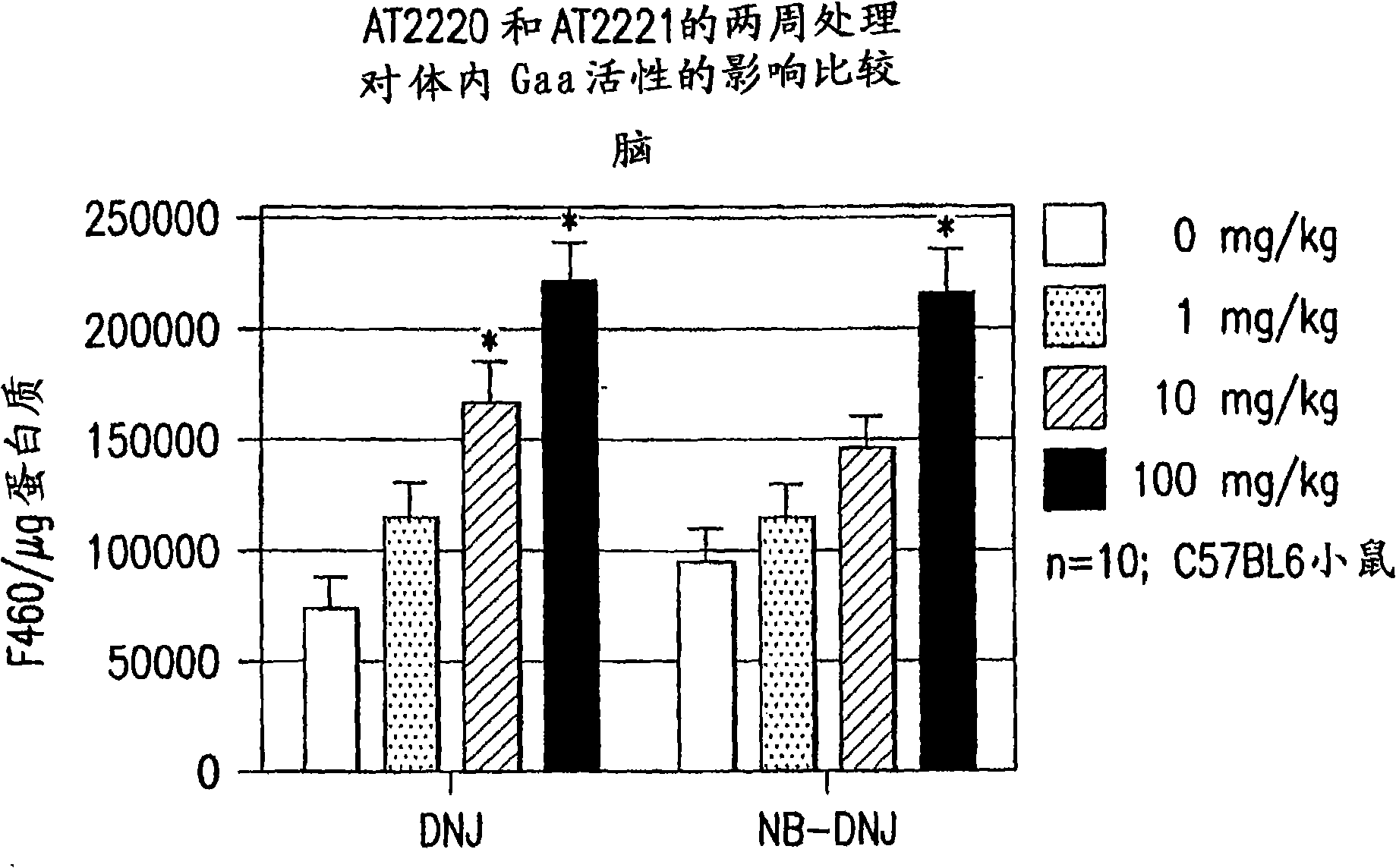
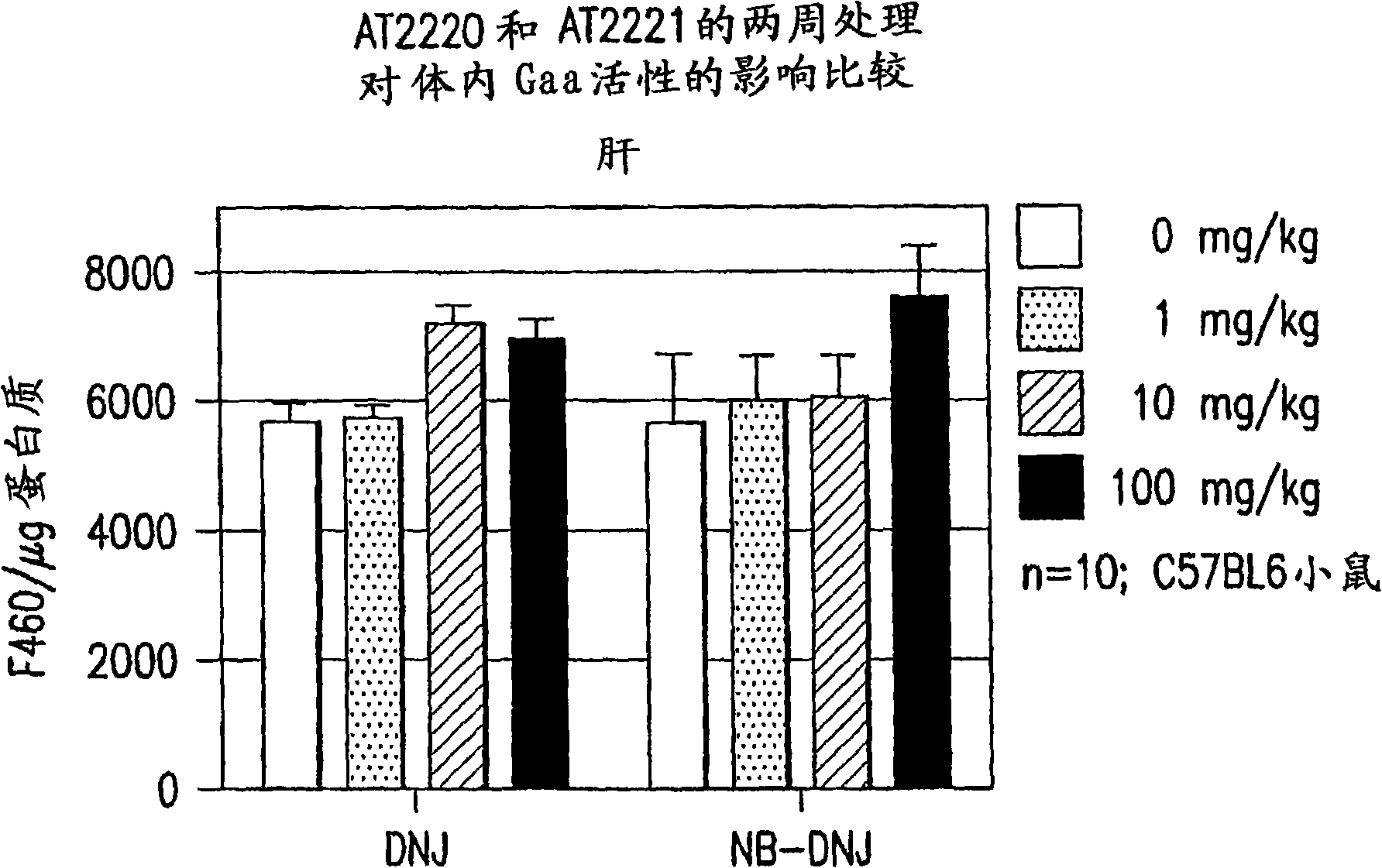
[0352] Example 3: In Vivo Gaa Activity Treated with DNJ and DNJ Derivatives
[0353] Drug Administration This example provides information on the effects of DNJ derivatives in mice. Mice were administered DNJ derivative test compound at 0, 1 mg / kg / day, 10 mg / kg / day and 100 mg / kg / day; organs and plasma were collected 2 and 4 weeks after the start of the study. Twenty male C57BL6 (25 g) mice per group were used. Medications are provided in drinking water, so water consumption is monitored daily.
[0354] In the control group (0 mg / kg / day), mice were dosed daily in drinking water (no drug) and divided into two groups. Ten animals were sacrificed two weeks after treatment, blood was collected from the descending aorta or great vein, tissue harvested and necropsy performed. The remaining 10 animals were sacrificed 4 weeks after treatment and subjected to the same evaluation.
[0355] In the first test group, 20 mice were dosed daily with a target of 1 mg / kg-day in the drinkin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com