Ribosome resistance mutagenesis breeding vancomycin production bacterial strain and application thereof
A technology for producing vancomycin and strains, applied in the direction of microorganisms, microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., which can solve problems such as time-consuming and labor-intensive
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
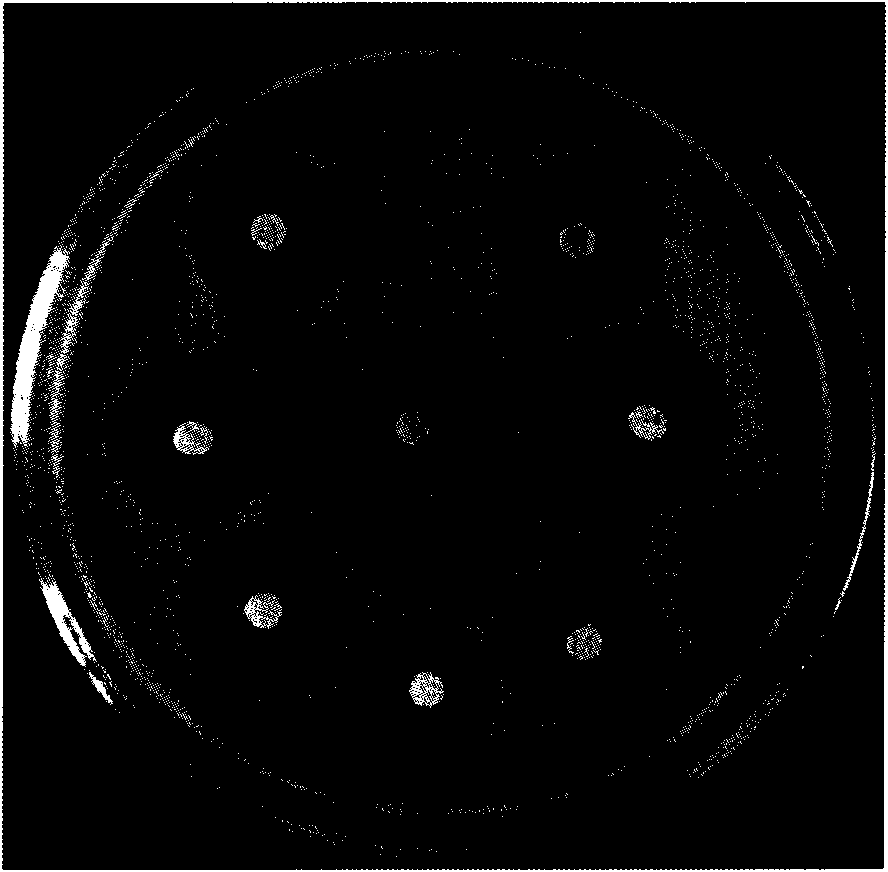
[0022] 1) Purchased from the American Culture Collection, numbered ATCC No.19795 The starting strain AO-1 of the vancomycin-producing bacteria was inoculated on Gao’s No. 1 agar medium plate and cultured at 28°C for 7 days. After the spores grew out, take an appropriate amount and use sterile water to make 10 4 mL -1 spore suspension. Spread 0.1 mL of the spore suspension on Gaoshi No. 1 agar medium plate containing 500, 1000 mg / L vancomycin and culture it at 28°C for 7 days, and randomly select 50 single colonies that grow out and inoculate it in Gaoshi No. 1 On the agar plate medium, cultivate at 28°C for 7 days, and measure the biological activity of the grown mutagenized strains by the agar block inhibition zone method, and select 12 mutagenized strains whose diameter of the inhibition zone is 2mm larger than that of the starting strain AO-1 (see figure 1 ).
[0023] 2) Inoculate the above 12 mutagenized strains into a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask equipped with 40mL liquid...
Embodiment 2
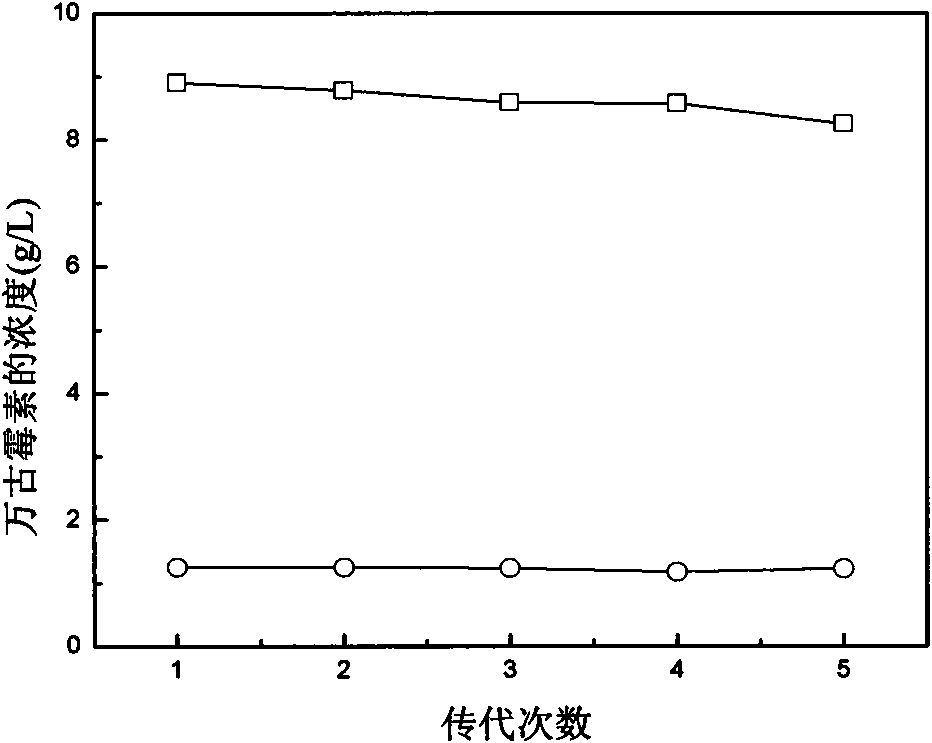
[0028] Take 0.1 mL of the spores of the starting strain with a concentration of 10,000 / mL and smear it on the mixed resistance Gowell No. 1 agar plate with a concentration of 500 mg / L of vancomycin and a concentration of 400 mg / L of streptomycin. -1 spores were diluted into different concentration gradients and spread on ordinary Goose No. 1 agar plates as a control, and cultured at 28°C for 7 days to obtain several mutant strains. The difference in the growth of the grown strains is as follows Figure 4 and shown in Table 1.
[0029] Table 1 Comparison of colony morphological differences between the vancomycin production strain and the starting strain AO-1
[0030] Strain characteristics
Embodiment 3
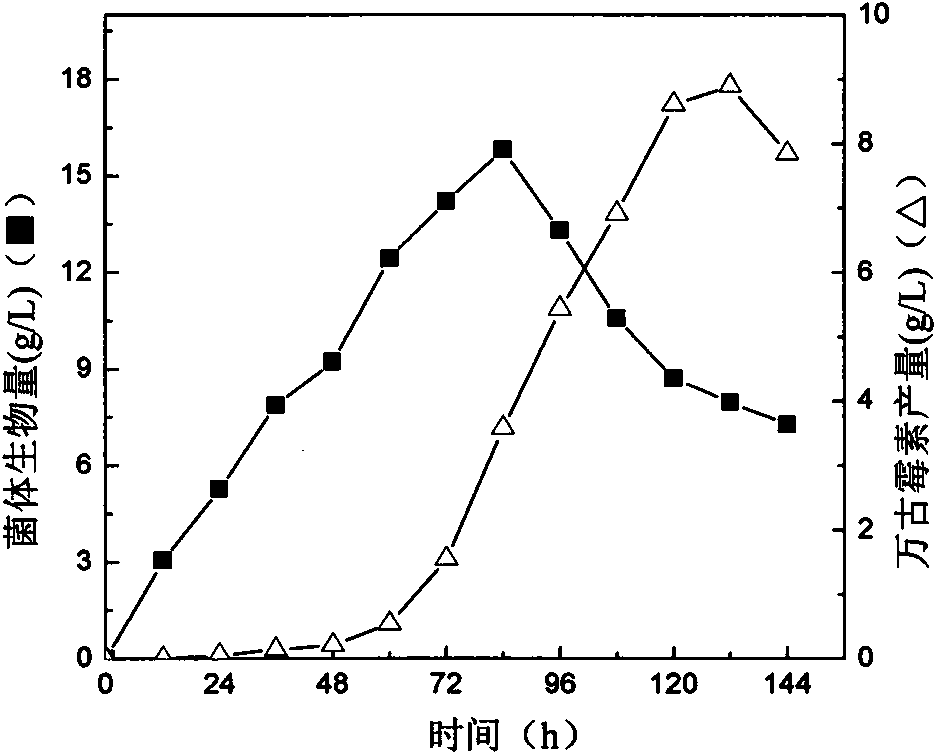
[0032] Insert the vancomycin production strain obtained in Example 1 into the liquid seed medium (the liquid fermented seed medium consists of (g / L): yeast powder 5, malt extract 4, peptone 13, glucose 17, pH 6.8; Liquid volume 40 / 250mL), at 28°C, 200rpm cultured for 48 hours, then transferred to shake flask fermentation medium (liquid fermentation medium composition (g / L): dextrin 100-150, potato protein 15-25, soybean powder 15~25, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.1~0.5, antifoaming agent 1~3, sodium chloride 1.2~1.6, pH 6.8~7.2, liquid volume 40 / 250mL), cultivated at 28°C, 200rpm for 120h, passed HPLC Determination of vancomycin content in fermentation broth. According to the chromatographic conditions provided in Example 1, the yield of vancomycin in the fermentation broth was measured to be 8.5 g / L. Its production curve see image 3 .
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com