Patents
Literature
160 results about "Agar plate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
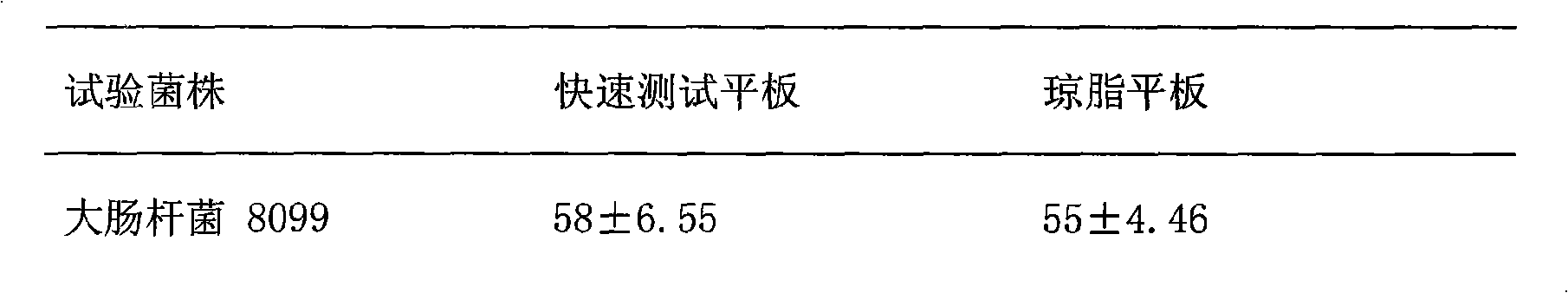
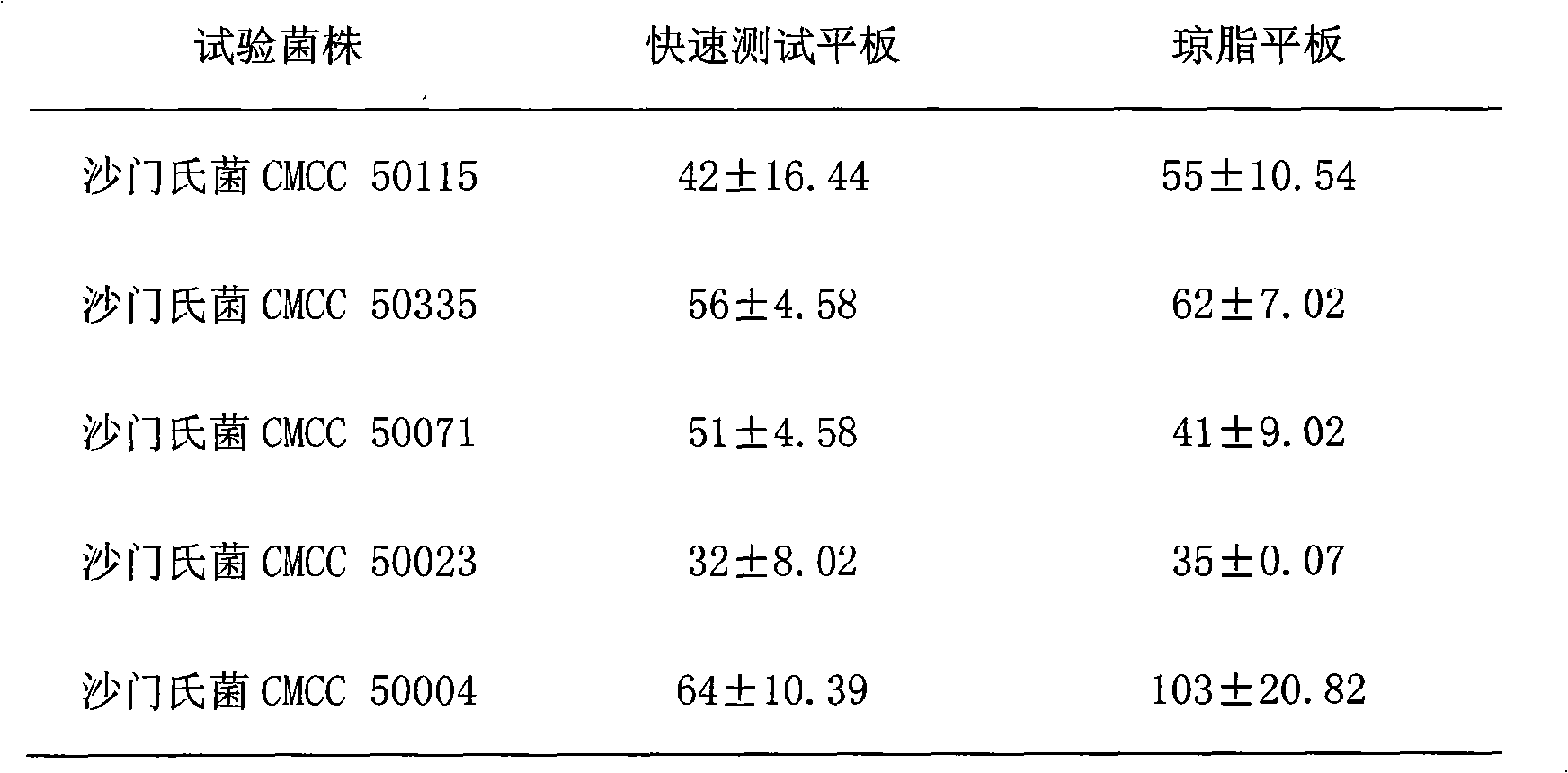
An agar plate is a Petri dish that contains agar as a solid growth medium plus nutrients, used to culture microorganisms. Sometimes selective compounds are added to influence growth, such as antibiotics.
A kind of enterococcus faecium and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103865846BTo promote metabolismPromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEcological environmentAnimal feces
The invention discloses enterococcus faecium and a preparation method thereof, relates to the field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to the enterococcus faecium and application thereof. A bacterium sample is acquired from the rumen of a slaughtered goat, subjected to directive breeding at the temperature of 32-42 DEG C under an anaerobic and photophobic condition, and separated and purified by use of a repeated divisional agar streak plate method so as to obtain enterococcus faecium L-01. The enterococcus faecium L-01 can be used as an animal microorganism fodder additive, has the effects of effectively inhibiting pathogenic bacterium in animal digestive tract, improving the micro-ecological environment of the digestive tract and enhancing the immunologic function of an animal body, can be used as a substitute product of antibiotics and can be used for effectively solving the existing serious situation.
Owner:江苏绿牧生态环保有限公司
Gene engineering bacterial strain used for producing phenazine-1-methanamide and its purpose
ActiveCN103642714AIncrease productionEffective biological controlBiocideBio-organic fraction processingBiotechnologyBacterial strain
The invention discloses a gene engineering bacterial strain used for producing phenazine-1-methanamide and its purpose; which is characterized in that knockout of psrA or rpeA gene in Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66(Pseudomonas chlororaphis HT66) CCTCC NO: M 2013467 genome is carried out. According to the invention, a strain of Pseudomonas chlororaphis is performed with seed culture, fermentation, extraction, concentration and crystallization to obtain phenazine-1-methanamide with purity of more than 96%. After the deletion of psrA and rpeA gene in the bacterium genome, the fermentation output of phenazine-1-methanamide can reach as high as 1800ppm. The agar plate bacteriostasis tests found that phenazine-1-methanamide has obvious inhibition effect on common plant pathogenic fungi such as Rhizoctonia solani, fusarium oxysporum, pythium wltmum and Stevia Septoria, has good stability and activity, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Preparation method and application of sea bdellovibrio bacteriovorus ecological preparation
InactiveCN101781627AGuaranteed lytic activityPromote lysisBiocideBacteriaNutrient brothCulture mediums
The invention provides a preparation method and application of a sea bdellovibrio bacteriovorus ecological preparation, and relates to a sea microbial ecological preparation and a preparation method of a bdellovibrio bacteriovorus preparation for mariculture. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing a host bacteria suspension; separating and purifying bdellovibrio bacteriovorus; and propagating and culturing bdellovibrio bacteriovorus. The preparation method is characterized in that after pseudomonas stutzeri is connected with an incline and is activated, adding physiological saline in a test tube to prepare the bacterial suspension; then propagating and culturing with nutrient bouillon; adding a flocculating agent in the obtained bacterial suspension; standing and precipitating after uniformly shaking; adding the physiological saline to obtain 1012 cfu / mL of host bacteria suspension; separating and purifying the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus of collected sea and bottom sediment samples with a double agar plate method; pouring culture media containing the host bacteria suspension and the collected samples into sea agar in the lower layer for culture after uniformly mixing; and adding the host bacteria and the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus obtained by separation into sterilized natural sea, and culturing until the concentration of the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus is 108 to 109 pfu / mL for future use.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
A Strain of Enterococcus Faecalis for Feed and Its Application
InactiveCN102277325AEnhanced inhibitory effectImprove the living environmentAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseOptimal growth
The invention discloses an Enterococcus faecalis strain SBD, of which the collection number is CGMCC No.4848. The strain is a Gram positive strain and is spherical according to observation with microscope, and the strain does not form spores; the strain can well grow on a Mann, Rogosa and Sharpe (MRS) agar plate and can grow into a round, smooth and raised bacterial colony like a grey white dew and with a diameter of 0.5 to 1 millimeter within 48 hours; and the strain can grow in a facultatively anaerobic environment, the growth temperature range is from 10 to 50 DEG C, the optimal growth temperature is 30 to 40 DEG C, and the growth pH value range is from 4 to 10 and the optimal pH value is 6.5. The bacterial preparation made by the strain is nontoxic and safe, can resist gastric juice and cholate, has a strong inhibition effect on various harmful bacteria and can be widely used in livestock breeding industry (by directly adding into daily ration or drinking water of animals) to increase the disease resistance in animals; and the preparation is expected to replace antibiotic for feed purpose and can obviously improve average weight of weaned piglets, reduce a feed-to-meat ratio and improve living environment of livestock and therefore has a bright prospect.
Owner:北京金泰得生物科技股份有限公司
Separating and screening method for saline-alkaline-resistant bacteria degrading petroleum hydrocarbon
InactiveCN104877930AImprove the quality of micro-ecological environmentNo secondary pollutionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementCulture fluidBacterial strain
The invention provides a method for separating and screening a saline-alkaline-resistant pure bacterial strain degrading petroleum hydrocarbon from oily soil. The method comprises the steps: firstly collecting soil polluted by salinized petroleum hydrocarbon from an oil field, adding the collecting soil according to an amount of 10% into an inorganic salt culture medium which takes crude oil as a unique carbon source, and carrying out enrichment culture in a constant temperature shaker; then inoculating a 10% enriching liquid into a fresh crude oil inorganic culture medium and continuously carrying out habituated culture under a same condition for 4-5 times, wherein the pH, salinity and crude oil content of the culture medium in the domestication process are gradually raised; after diluting the culture liquid after domestication in a gradient manner, coating the culture liquid to a LB-agar panel, after bacterial colonies grow, picking up single colonies in different shapes, and lineating and purifying and separating single bacteria; and finally, spreading the separated single bacteria to a crude oil inorganic salt-agar panel and detecting whether the bacterial colonies grow or not, if so, the bacterial strain is the bacteria degrading petroleum hydrocarbon; determining the petroleum hydrocarbon degradation rate of the single bacterial strain and carrying out 16Sr DNA molecular identification on the bacterial strain so as to determine the species relationship of the bacterial strain.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
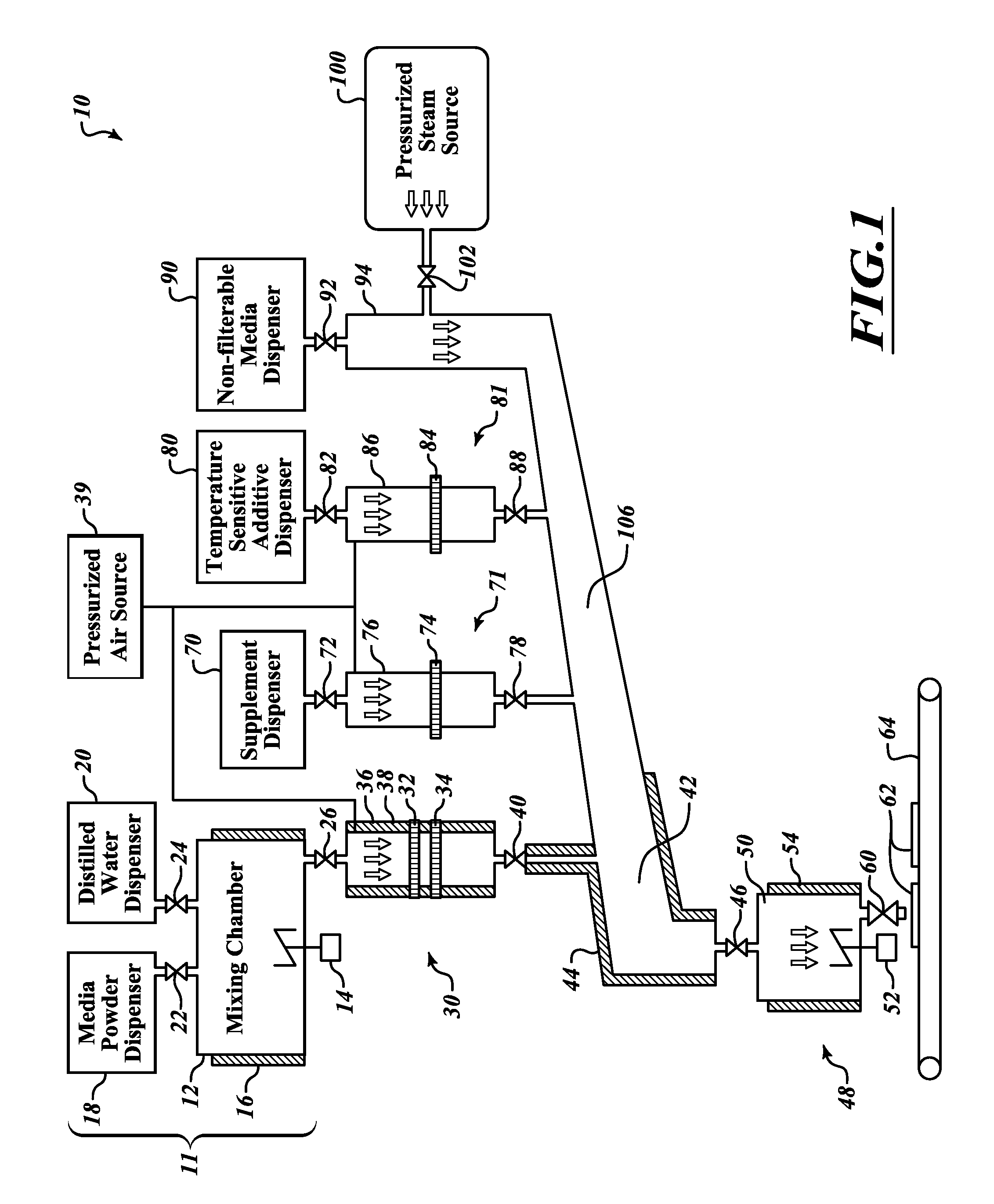
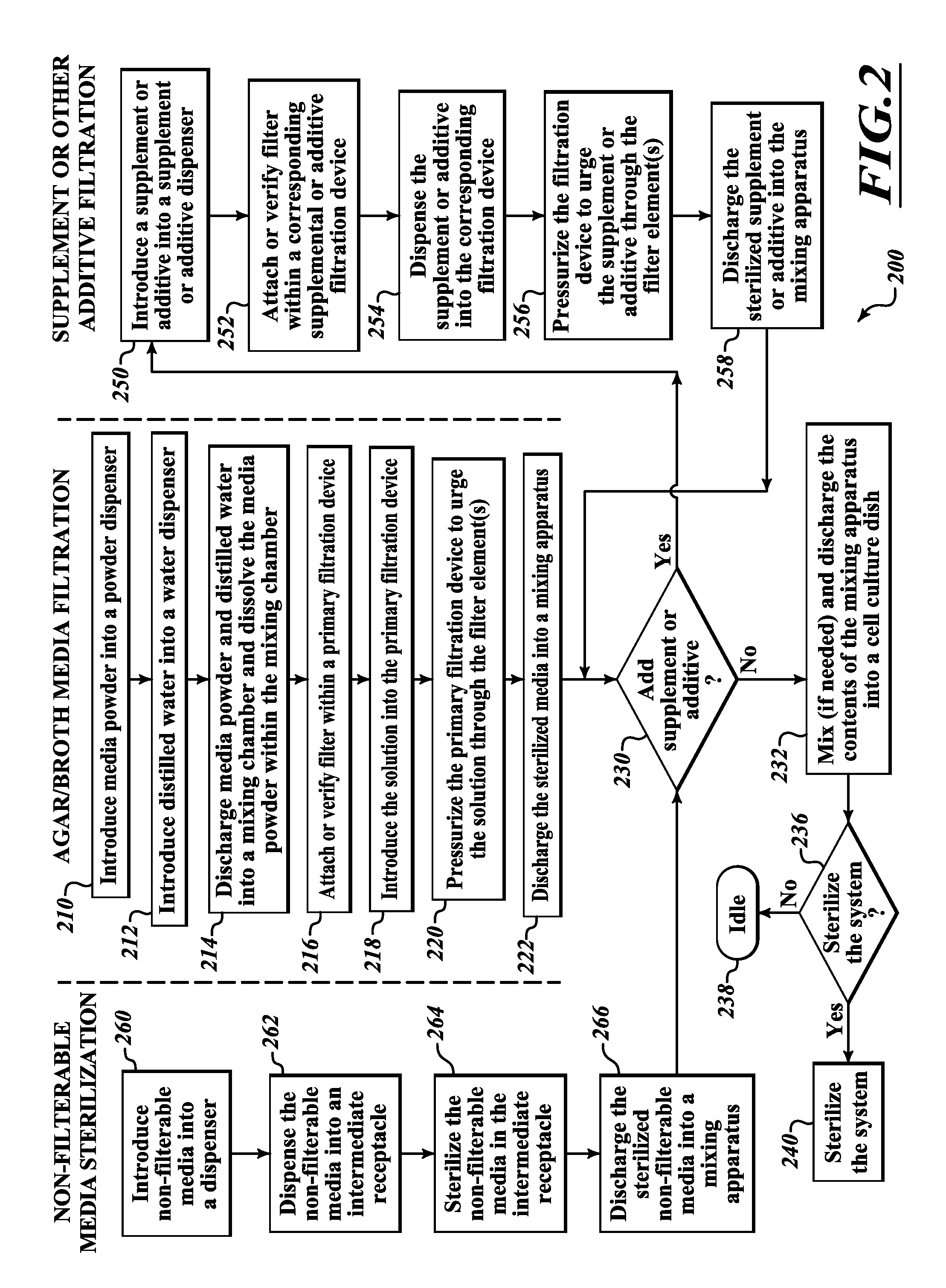
System and method for preparing cell culture dish media
InactiveUS20130102071A1Easy to adaptOpening closed containersBioreactor/fermenter combinationsMicroorganismFiltration
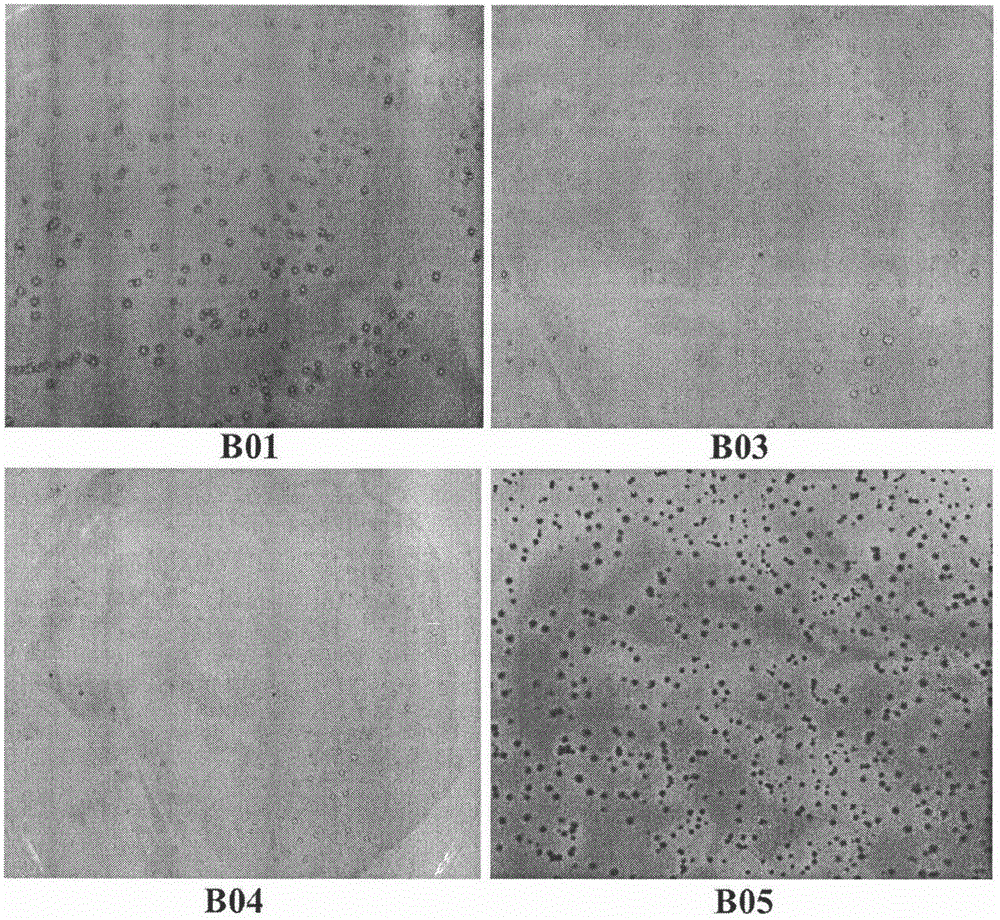
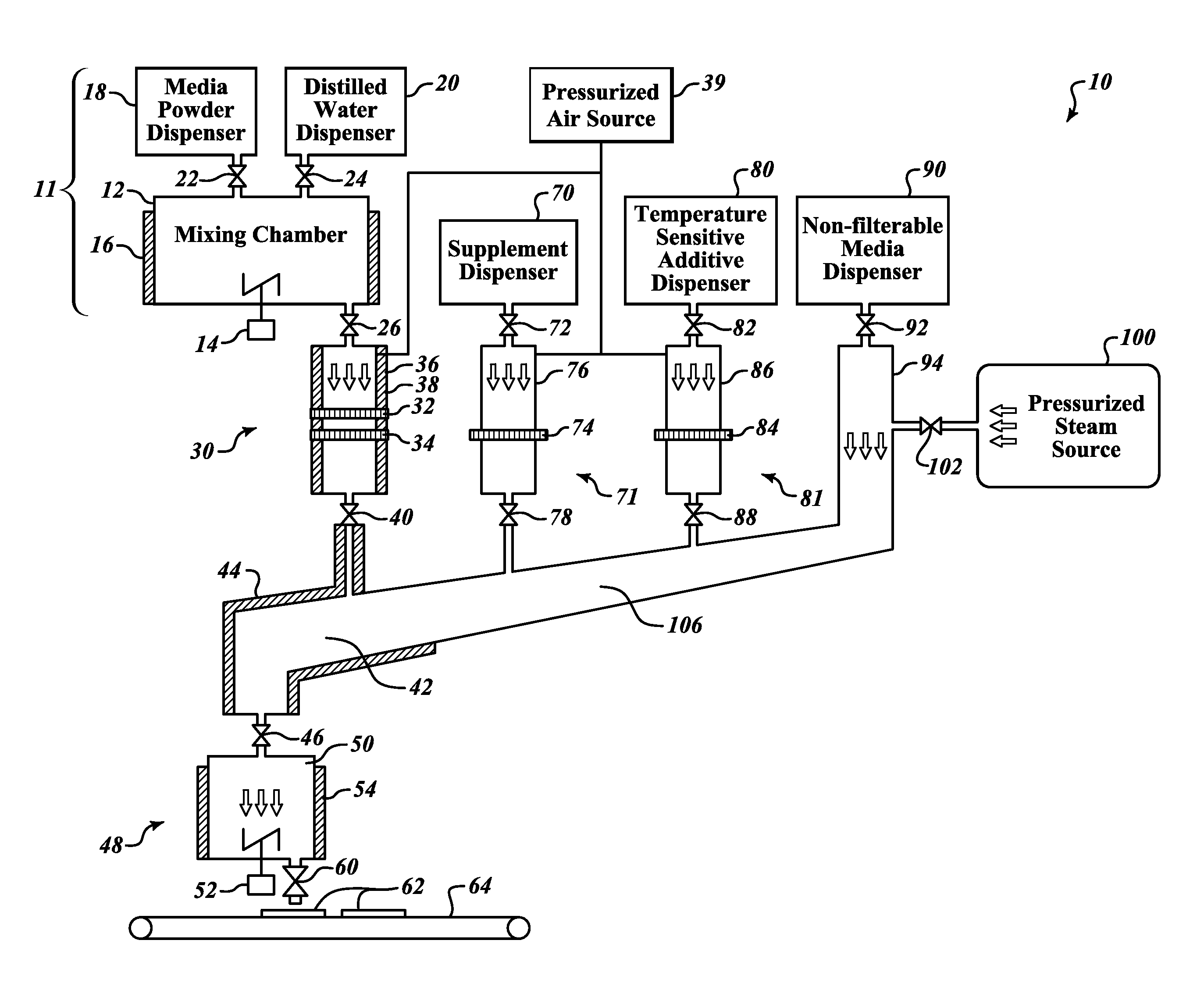
Systems for preparing cell culture dish media are provided which are well adapted for preparing cell culture media, supplements, additives and / or other ingredients in an efficient and versatile manner to form sterilized cell culture dish media having a variety of ingredients well adapted with respect to uniformity and nutritional content to culture microorganisms in a particularly effective manner. The systems include an array of filtration and steam sterilization devices to sterilize various types of media for selective combination of one or more of the types of media in a mixing chamber to form cell culture dishes (e.g., agar plates). Methods of preparing cell culture dish media and cell culture dishes are also provided.
Owner:TOKU E CO
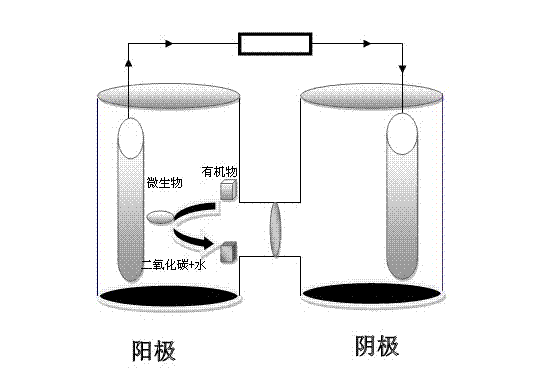
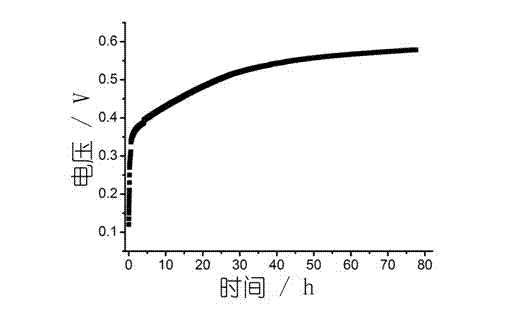
Bacillus cereus with electrogenesis characteristic and application thereof in microbiological fuel cell
The invention relates to a Bacillus cereus with electrogenesis characteristic, which is preserved in 'China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center' on 2011 July 12th, and the accession number is CGMCC No. 5055. The bacterial strain is identified as a Bacillus cereus bacterial strain, which has the following characteristics: a cell rod shaped thallus, a square end, short or long chains,a diameter of 0.4 to 0.6 micrometers, a bacterial length of 2.0 to 5.0 micrometers gram positivity, a large bacterium colony, rough, flat and irregular surface. On the plain agar plate, at a temperature of 37 DEG C for 24 hours cultivation, the Bacillus cereus can form a round or similar round, soft-texture, non-pigmented, lightly glossy, white bacterial colony (with a candle-like color) with a diameter of 5 to 7 millimeters, and can use a plurality of carbon sources and grow under anaerobic and aerobic conditions. A microbiological fuel cell produced by using the bacterial strain has higher electrogenesis capability and the Bacillus cereus can not only be directly used to produce electricity in microbiological fuel cell but also utilize sewage organic matter to produce electricity.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Culture device for white fly and tetranychid mite feeding experiment and method for conducting experiment using same
The invention discloses a culture device for a white fly and tetranychid mite feeding experiment and a method for conducting experiment using the same. The culture device comprises a culture dish and a sealing device covering the culture dish, wherein a water agar plate is arranged in the culture dish; the sealing device covering the culture dish is provided with multiple air holes; and the water agar comprises agar and water in a mass ratio of 1:50. When the culture device for the white fly and tetranychid mite feeding experiment is used to conduct experiment, the leave is separated and can be sheared into any shape without using the entire leave as the experimental material, thereby avoiding influence on the experiment caused by the limitation under space, temperature and humidity when the living plant or cut plant is used as the experimental material; and the experimental conditions are easy to control, and the operation is simple. Moreover, the problem of relatively large error between the repeated experiments for the same treatment caused by differences in height, size and strongness of the living plants or cut plants can be overcome.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU
Analytical method of components of fatty acid contained in listeria cells
InactiveCN101936960ABreaking the limits of taxonomyBreak the limitsComponent separationCytochemistryFatty acid
The invention relates to an analytical method of components of fatty acids contained in listeria cells, in particular to a method for carrying out bacteria classification by adopting a cell chemical analysis method, belonging to the technical field of biological engineering. The method mainly comprises the following steps of: rejuvenating listeria; respectively separating and purifying the listeria by using an OXA agar plate and a trypticase soy yeast extract agar plate; culturing the listeria of a single typical colony, and preparing into a bacterial suspension; carrying out inactivation processing by using formaldehyde; averagely filling the bacterial suspension processed by the formaldehyde into centrifuge tubes for washing; carrying out methyl esterification by using a mixed solution of hydrochloric acid and the formaldehyde; and carrying out GC-MS (Gas Chromatograph-Mass Spectrometer) analysis on the prepared fatty acids. The method can not only break through the limit of the traditional bacterial taxonomy and reduce the errors brought about by anthropic factors on the traditional morphological taxonomy, but also provide a strong and powerful tool for the classification and the identification of new strains and virus types; and in addition, the method can be used for identifying the listeria from other bacteria and foods.
Owner:HUBEI INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT
Single spore isolation and purification method of verticillium dahliae
InactiveCN105002097AGuaranteed purityEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesPurification methodsLiquid medium
The invention relates to a single spore isolation and purification method of verticillium dahliae. The method mainly comprises the following steps: an agar medium cylinder is taken from a water agar plate by the use of a glass capillary with diameter being 1mm and is picked onto a sterilized glass slide with a sterilization needle; a verticillium dahliae strain is activated in a PDA solid medium and the activated strain is cultured in a Czapek-Dox liquid medium; spore concentration is counted under a microscope; and the spore concentration is adjusted to 102-106 cfu to prepare a spore suspension; 1 microlitre of the spore suspension is sucked up and dripped onto the surface of the water agar cylinder on the glass slide; the glass slide is moved into a culture dish for constant temperature incubation at 25 DEG C; the glass slide is detected under the microscope, and the cylinder containing a single conidiospore which has germinated germ tubes is transferred onto a PDA plate to be cultured at 25 DEG C so as to finish single spore isolation. The method is simple to operate, can be implemented by general operation staff and is suitable for mass separation. By the method, separation success rate is high. The method is also suitable for production of other fungi of microconidia.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method of separating screening heterotrophic nitration bacteria
InactiveCN1786184AReduce distractionsSimplify the experimental operation processBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismLiquid medium
The invention relates to a method of separating and scalping heterotrophy nitrobacteria. Its making steps are preparing beef extract-peptone liquid medium; heating sterilization after adding agar; condensing into flat solid medium; coating mixed microorganism flora to beef extract-peptone flat; setting in incubator at 30 centigrade degree to culture for 7-10 days; selecting mono bacteria to fall on the extract-peptone flat line to purify to from pure bacteria; inoculating the pure bacteria lawn to ammonia oxidation ability identification culture solution; dipping gelisi reagent into the culture solution to do nitration activity identification. The upper steps can separate heterotrophy nitrobacteria from the mixed microorganism series. So the invention is exact and reliable.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Yellow bacillus and its snail killing agent
InactiveCN1597930AStrong molluscicidal effectNo pollution in the processBiocideBacteriaOncomelaniaSide effect
The invention relates to a Xanthobacter and its snail killer. A snail bacterium, namely Xanthobacter autotrophicus is a Xanthobacter autotrophicus II whose collection unit. It uses beef peptone agar plate or slope culture medium to separate bacterial strains, obtains snail-killing Xanthobacter autotrophicus solution (a hundred million grades / ml) by bottle-shaking fermentation process; and the application of Xanthobacter autotrophicus as a snail killer is that: making ultrasonic processing on the Xanthobacter autotrophicus solution and plant material forming agent, then mixing them to prepare a novel biological snail killer, which has the characters: (1) quickly killing the snail, and effectively preventing the snails from climbing up to flee; (2) harmless to non-target living things and fish, fast to naturally degrade and no pollution; (3) no toxic and side effect, and time of maintaining snail-killing pesticide effect 15 days long; (4) convenient to store, transport and use; etc.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
Cold water coagulable culture medium coagulator and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101570730ANot easy to decomposeHigh strengthBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganismLocust bean gum
The invention discloses a cold water coagulable culture medium coagulator and a preparation method thereof. The culture medium coagulator is mainly prepared from the following raw materials by weight portion: 1 portion of xanthan gum and 0.5 to 1.5 portions of guar gum which are mixed together; 1 portion of polyacrylate sodium and 7 to 10 portions of locust bean gum which are mixed together, wherein the mass ratio of the mixture of the xanthan gum and the guar gum to the mixture of the polyacrylate sodium and the locust bean gum is 7-9:1. The cold water coagulable culture medium coagulator can be dissolved and coagulated in cold water, has good water absorption, short reaction time and high gel strength and viscosity, is suitable for the growth of most microbes, and can form gel. The gel can be used as the coagulator for a microbe culture medium, thus the cold water coagulable culture medium coagulator avoids the defects that the prior agar culture medium needs heating and consumes more time for cooling, and an agar plate is easy to dehydrate and check.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Analysis of microbes by maldi mass spectrometry
ActiveUS20150136972A1Increase stickinessImprove transfer rateParticle spectrometer methodsIon sources/gunsDesorptionMass Spectrometry-Mass Spectrometry
The invention relates to methods for the mass spectrometric analysis of microbes, in particular to a transfer method of microbes that are required to be identified from agar plates onto mass spectrometric sample supports and their preparation for ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). Microbes from microcolonies which have grown on the agar plates after a culture time of only six to eight hours are transferred with a high transfer yield onto contact surfaces of suitable size by direct contact and cell disrupted on the contact surface; the released proteins are prepared with matrix material on the contact surface as MALDI samples. The ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption also takes place on the contact surface.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Korean pseudomonas and application thereof
InactiveCN105586303APromote degradationPhosphorus dissolving ability is strongBiocideBacteriaMicrobial agentRoot rot
The invention provides a Korean pseudomonas and application thereof. The Korean pseudomonas is identified as Korean pseudomonas CJ-361, and the preservation number is CGMCC NO.12122. The Korean pseudomonas CJ-361 is obtained through separation from radix pseudostellariae rhizosphere soil by adopting a pseudomonas selectivity culture medium, an antagonistic experiment is performed on fusarium oxysporum and fusarium moniliforme separated to the radix pseudostellariae root lesion portion through an agar plate opposite culture method, and it is found that the Korean pseudomonas has the strong antagonism on the fusarium oxysporum and the fusarium moniliforme. Meanwhile, the invention provides the optimum culture medium for antagonistic bacterium growth, the optimum formula is 1 / 4LB+1 / 20MS (containing no ferric salt)+0.1 wt% brown sugar, and the fermented liquor has the obvious antagonistic effect. The antagonistic strain and the microbial agent thereof can effectively prevent and treat radix pseudostellariae root rot diseases, and the environment-friendly, ecological and safe biological prevention and control potential strain is provided for overcoming or relieving replantation diseases of radix pseudostellariae.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Fermentation process of Bacillus pumilus LD-b1 and its application in control of plant diseases
InactiveCN102965299ASignificantly inhibited the growthGrowth inhibitionBiocideBacteriaFungal endophyteBatch fermentation
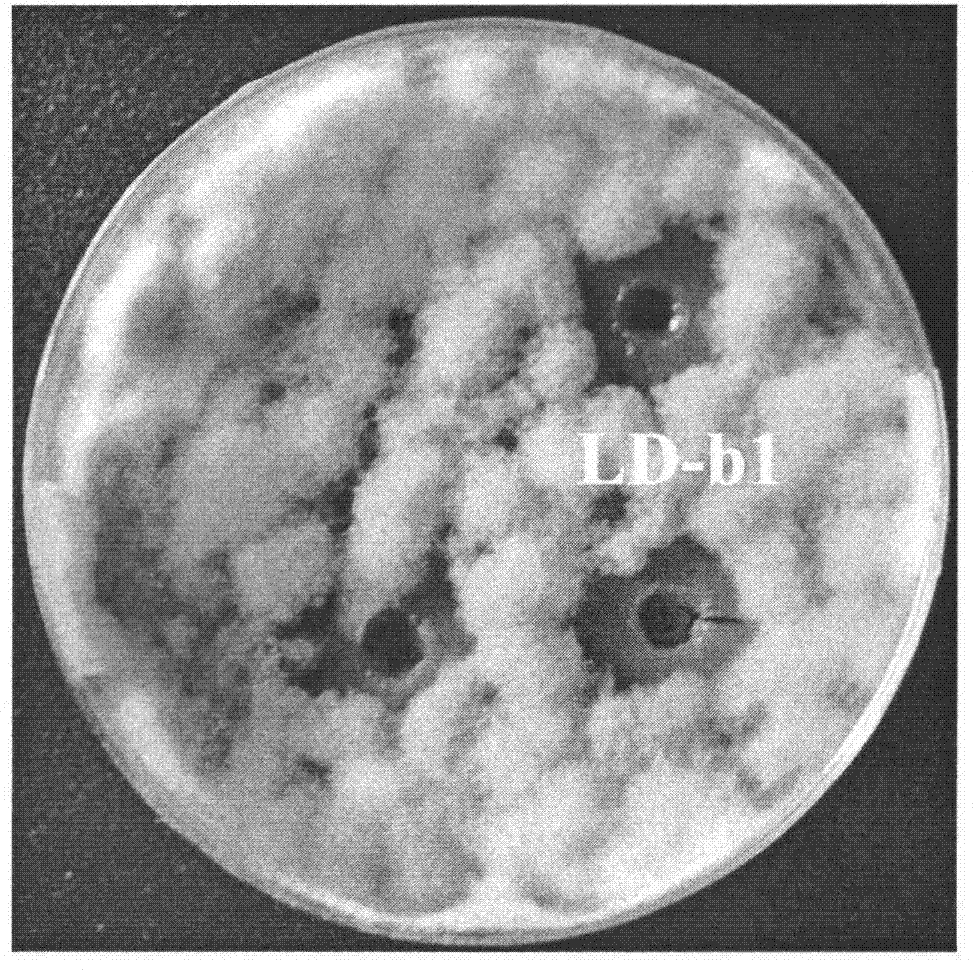
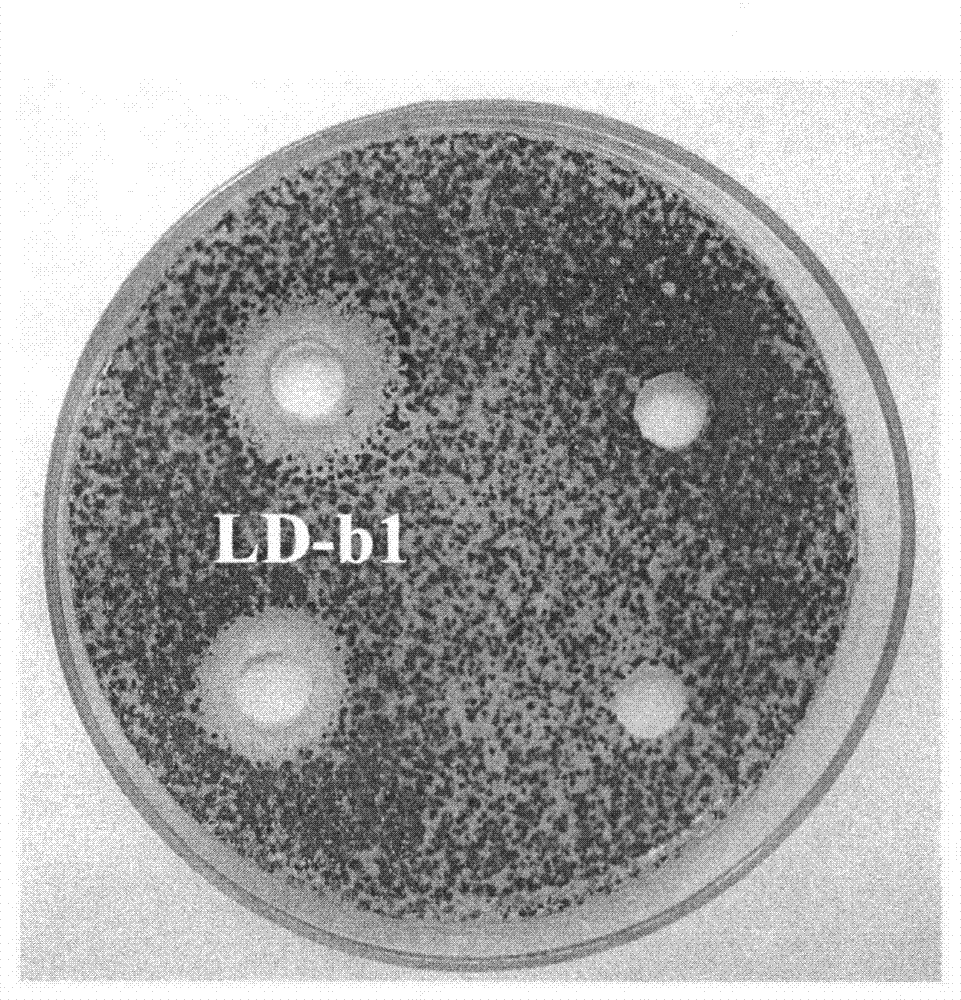
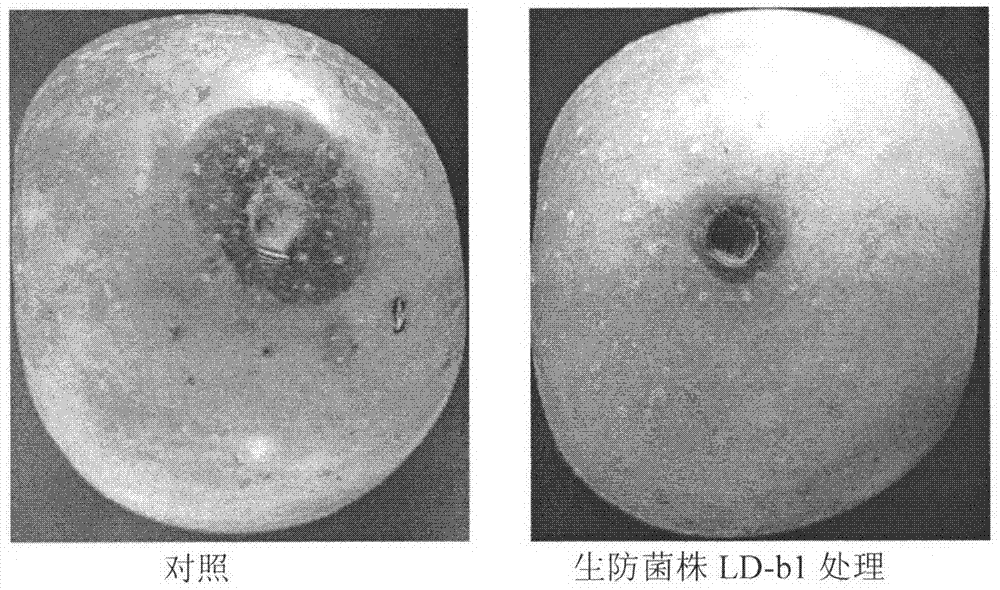
Belonging to the technical field of biological pesticides, the invention provides a Gentiana nubigena endophyte applicable to biological control of plant diseases and its fermentation process. The strain involved in the invention is Bacillus pumilus LD-b1, which is preserved in the General microbiological center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms on May 14, 2012, and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.6112. Mixed strain agar plate punching method experiments show that the strain LD-b1 can inhibit the growth of a plurality of plant disease fungi. LD-b1 can substantially inhibit Valsa mali from eroding apple fruits. In greenhouse pot experiments, the LD-b1 can achieve a cucumber Mycosphaerella arachidicola control effect of 81.2%. The fermentation process consists of: culturing LD-b1 in a seed tank for 24h to a logarithmic growth phase, inoculating 5% of the LD-b1 into a production tank according to an inoculation amount, controlling the initial pH at 7.5 and the fermentation temperature at 30DEG C, maintaining dissolved oxygen over 5%, and performing fed-batch fermentation for 68h, thus obtaining a bacterial amount over 10<10>cfu / mL. With the advantages of fast growth and wide antibacterial spectrum, the strain LD-b1 has good application prospects in biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
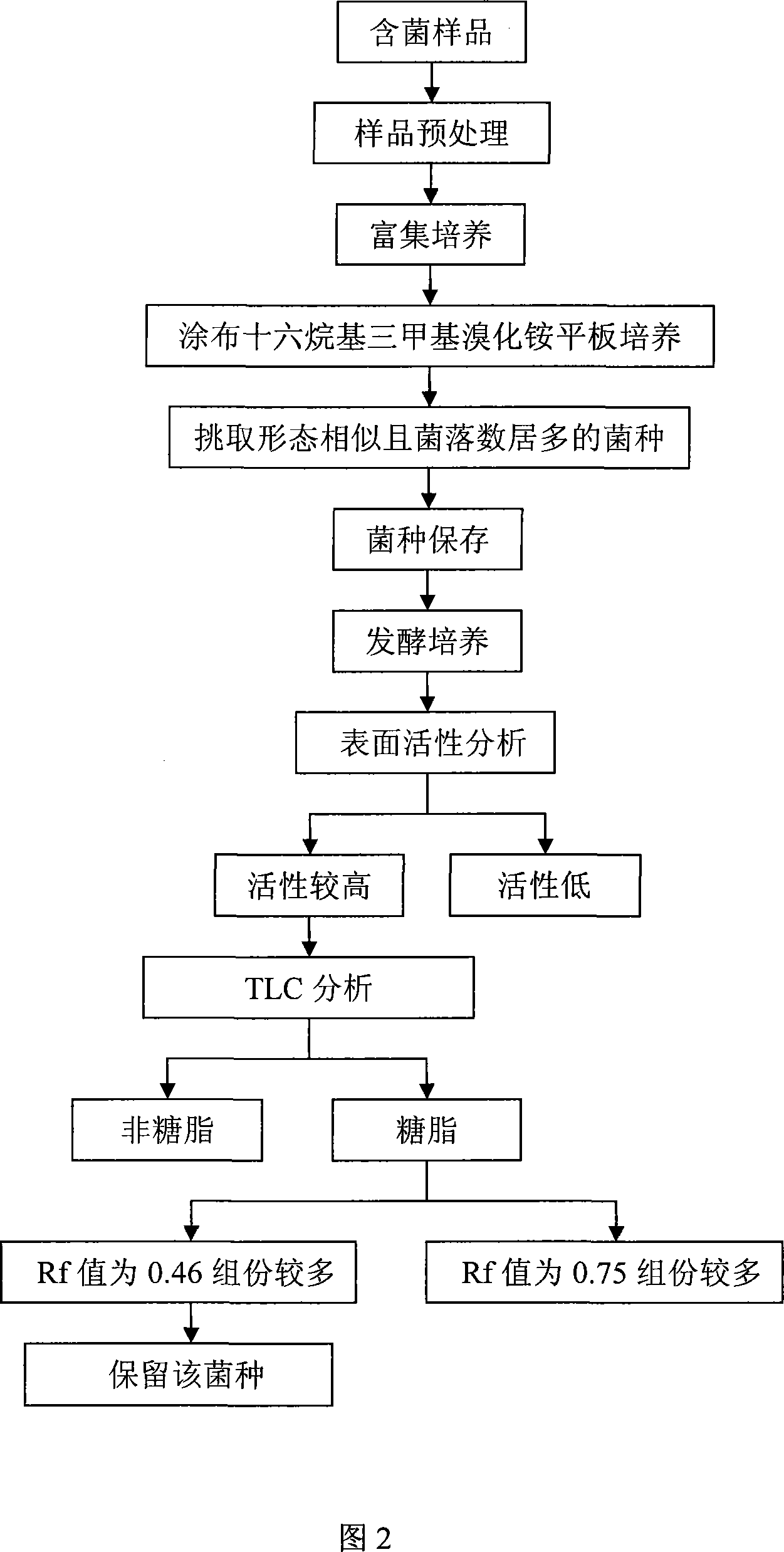
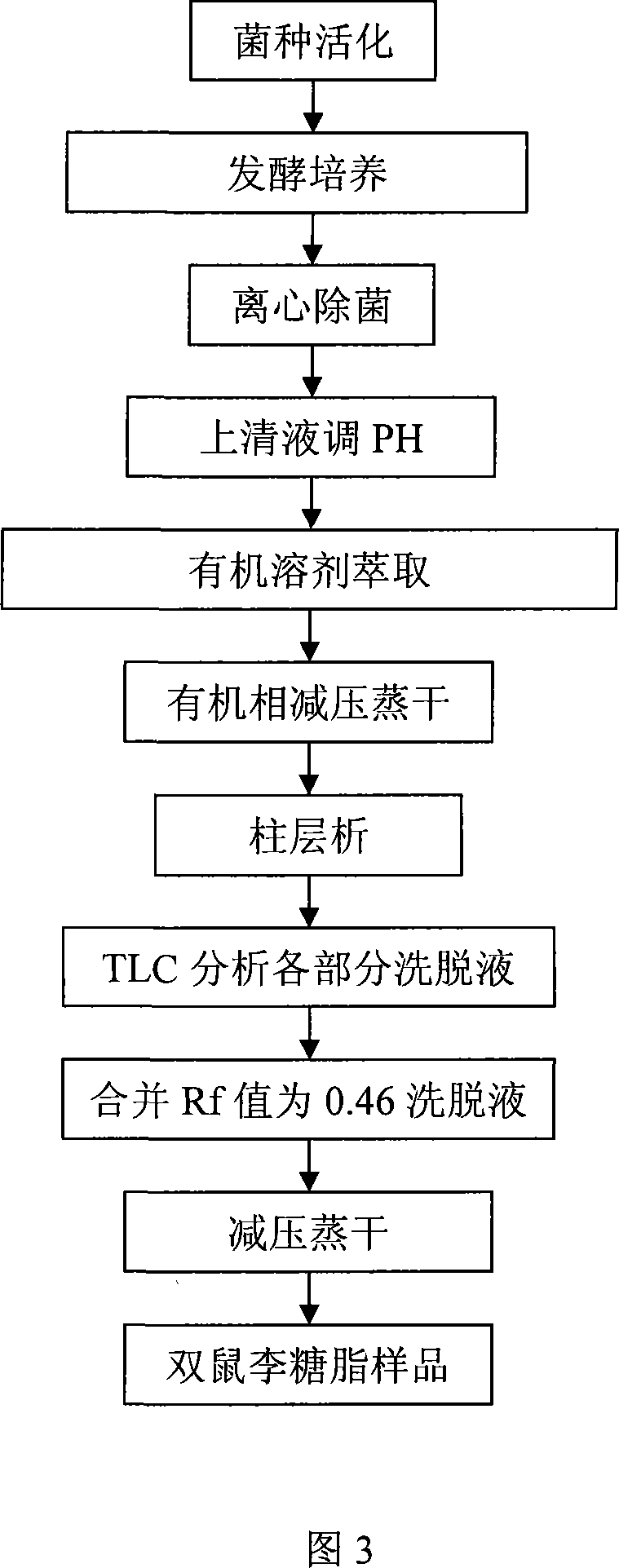
Method for sifting and producing generation agent of dual-rhamnolipid
InactiveCN101173210APromote growthHigh selectivityComponent separationMicroorganismsChromatographic separationVegetable oil
The invention discloses a method for screening and preparing culture seed for dirhamnolipids, which comprises the following steps: choosing the soil sample polluted by grease chronically as the strain source in strain screening; adopting vegetable oil as the liquid culture medium of single carbon source, and coating with the vegetable oil on the hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide agar plate with stronger selectivity after enrichment; then selecting suspect strain depending on the morphology and growth vigour of the bacterial colony; testing the surfactivity of the strain under primary screening after fermentation culture; analyzing the fermentation broth of the strain with high activity directly with TLC method; then selecting the strain with high dirhamnolipids productivity; extracting the rhamnolipids from the strain fermentation broth under screening with extraction method; obtaining purer dirhamnolipids with column chromatographic separation method. The invention overcomes the disadvantage that the strain is screened only based on the total output of rhamnolipids, and the strain with high dirhamnolipids output is obtained difficultly in the prior screening method, and has the advantages of high accuracy, high rhamnolipids output of the screened strain, more particularly higher dirhamnolipids output, and simple preparation technology.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Rhodo streptomycete and its spirillicide
The present invention relates to a Streptomyces violaceoruber and its molluscicides, wherein said Streptomyces violaceoruber is Streptomyces violaceoruber I which is preserved at China typical culture preservation center (CCTCC) with a preservation identification serial number of M203102 and a preservation date at 20030803. The bacterial strain is separated and activated by adopting Gao synthesized number 1 vegetable gelatine flat plate or inclined surface culture medium, and the Streptomyces violaceoruber bacterium solution with molluscidal functions is then cultured through fermentation by using a swing bottle; the Streptomyces violaceoruber bacterium solution and the plant pelleting additive are mixed to constitute a molluscicide. The Streptomyces violaceoruber in accordance with the present invention possesses stronger molluscidal effect, and the molluscicide formulated by the Streptomyces violaceoruber bacterium solution and plant pelleting additive possesses the following advantages: 1, without toxic and side effects and pollutions for the environment, it can be naturally degraded rapidly; 2, without toxic and side effects for persons and animals, it can maintain a long molluscidal time (longer than 15 days); 3, it is convenient to store, convey and use; 4, it has more improved molluscidal effect than pure bacterium solution and pure bacterium powder, with reduced drug amount; 5, relative pure plant powder, it has improved medical effects and prolonged time for maintaining the medical effects.
Owner:HUBEI UNIV
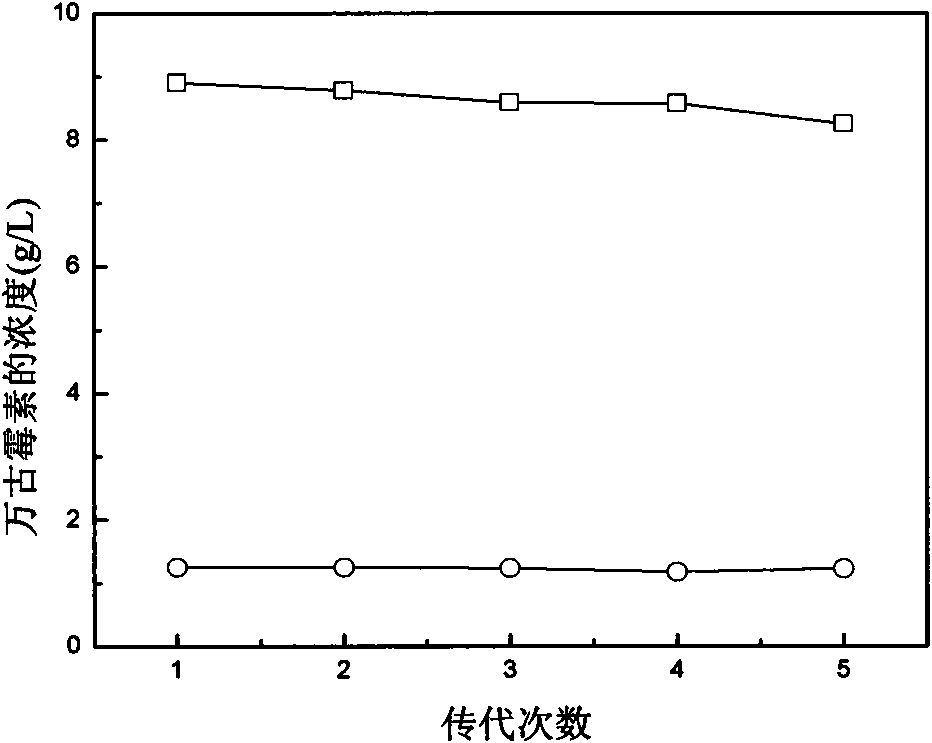
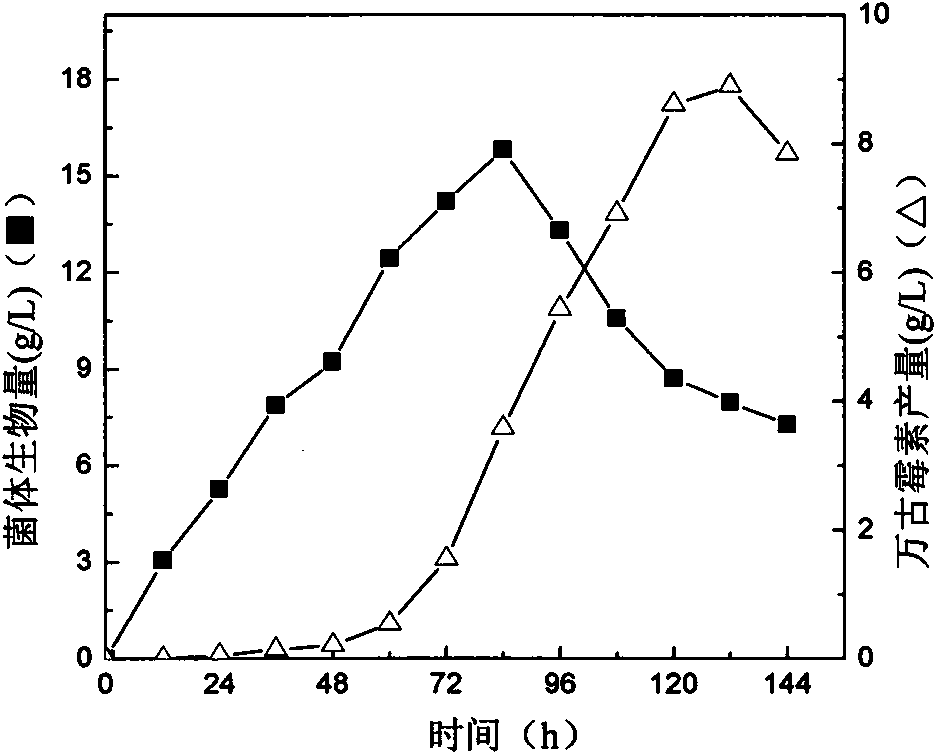
Ribosome resistance mutagenesis breeding vancomycin production bacterial strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101608209AIncrease productionGood yield stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesInhibition zoneHplc method
The invention provides ribosome resistance mutagenesis breeding vancomycin production bacterial strain and an application thereof, specifically the mutagenesis breeding method of mutagenesis bacterial strain of Amycolatopsis orientalis and the application thereof in preparing vancomycin, relating to breeding of microorganism. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating the Amycolatopsis orientalis to Gause-1 agar culture medium panel to be cultured; taking out spore and using sterile water to prepare spore suspension and coating the spore suspension in Gause-1 agar culture medium panel featuring mixing resistance of vancomycin and streptomycin to be cultured; randomly selecting produced single bacterial colony and streak-inoculating the single bacterial colony to the Gause-1 agar culture medium panel to be cultured, carrying out biological activity determination on produced mutagenesis bacterial strain; selecting mutagenesis bacterial strain with inhibition zone diameter thereof being 2mm larger than the inhibition zone diameter of original strain and inoculating the mutagenesis bacterial strain to liquid fermentation medium to be cultured; determining the content of vancomycin in fermentation liquor by HPLC method to verify the obtained vancomycin mutagenesis bacterial strain; subjecting the obtained vancomycin mutagenesis bacterial strain to 5 times of continuous passage stability inspection to obtain the vancomycin production bacterial strain.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Bacilluscereus and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacilluscereus (Bacilluscereus1205) and an application thereof. The morphological characteristics are as follows: the 1205 bacterial strain is cultivated on an ordinary agar plate culture medium at 37 DEG C for 36 hours, the bacterial colony is nearly round, grey white, non-transparent and as large as 3-7mm, the edge is irregular and expanded, the surface is rough, granulated and is like ground glass or wax, no pigment is secreted; the bacilluscereus is a gram positive bacteria, rod-shaped, 1.0-1.3*3.0-5.0 micrometer, chaining and moveable; the spore is ellipse, terminal or secondary terminal and unclearly expanded; and the bacilluscereus can endure the cultivation of 7% NaCl. The bacilluscereus has the characteristics of strong stress resistance, simple nutritional requirement, stabilization, easy colonization, stability to light and ultraviolet, low cost, long storage period, is easy to apply and realize industrialization, and has a certain growth promoting effect on tobaccos.
Owner:BIJIE COMPANY OF GUIZHOU TOBACCO +1
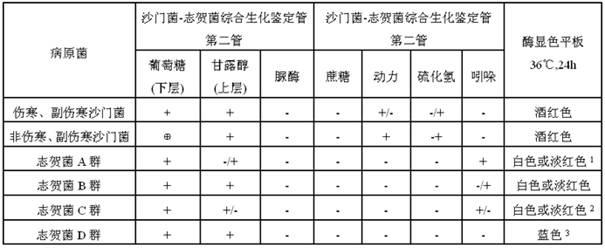
Kit for synchronously separating and identifying salmonella and shigella as well as preparation and application
InactiveCN102031281AImprove timelinessImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesBiotechnologyColony morphology
The invention relates to a method for synchronously separating and identifying salmonella and shigella in enteric pathogenic bacteria, which mainly solves the technical problems of high detection-missing rate, complicated identification step, high cost and unintuitive screening result in the existing method for separating the salmonella and the shigella. The kit comprises: 1) a TSB (Trypticase Soy Broth) serving as an universal-type non-selective proliferous liquid; 2) a 10-folds concentrated TSB serving as a 10-folds concentrated universal-type non-selective proliferous liquid; 3) a selenite brilliant green-sulfanilamide proliferous liquid serving as a salmonella proliferous liquid; 4) a shigella proliferous liquid; 5) a xylose lysine deoxycholate agar plate; 6) a salmonella chromogenic agar plate; 7) a salmonella-shigella comprehensive biochemical identification tube comprising a first test tube and a second test tube; 8) a hydrogen sulphide filter paper strip; and 9) an indole filter paper strip. In the invention, typical colonial morphology corresponding to the growth of a selective isolation medium, simple biochemistry and reaction combination test of a specific enzyme and a substrate are adopted to identify two kinds of enteric pathogenic bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Analysis of microbes by MALDI mass spectrometry
ActiveUS9171709B2Increase stickinessImprove transfer rateComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionDirect touchDesorption
The invention relates to methods for the mass spectrometric analysis of microbes, in particular to a transfer method of microbes that are required to be identified from agar plates onto mass spectrometric sample supports and their preparation for ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption (MALDI). Microbes from microcolonies which have grown on the agar plates after a culture time of only six to eight hours are transferred with a high transfer yield onto contact surfaces of suitable size by direct contact and cell disrupted on the contact surface; the released proteins are prepared with matrix material on the contact surface as MALDI samples. The ionization by matrix-assisted laser desorption also takes place on the contact surface.
Owner:BRUKER DALTONIK GMBH & CO KG
Kit for separating and identifying campylobacter rectus as well as preparation and application for kit
InactiveCN102816831AValid identificationEasy to identifyMicrobiological testing/measurementAgainst vector-borne diseasesCulture mediumsCampylobacter jejuni
The invention relates to a kit for separating and identifying campylobacter rectus as well as a preparation and an application for the kit, and mainly solves technical problems of high omission factor, complex identifying steps, higher cost and insufficiently visualized screened results in the existing method for separating the campylobacter rectus, such as campylobacter jejuni and non campylobacter jejuni. The kit for separating and identifying the campylobacter rectus has the technical scheme that: the kit comprises a selective enrichment broth I, a selective enrichment broth II, an improved Karmali agar plate, a Columbia blood plate, a microaerophilic gas generation bag, a gram staining solution, an oxidase reagent, a hippuric acid paper sheet and a hippuric acid enzyme reaction reagent. The campylobacter jejuni or non campylobacter jejuni is identified through a reaction combination test of a substrate and a typical colonial morphologic, simple biochemical and specific enzyme of the campylobacter rectus correspondingly grown in a culture medium for selective separation.
Owner:SHANGHAI MUNICIPAL CENT FOR DISEASE CONTROL & PREVENTION
Method and kit for identifying Vibrio harveyi quickly by means of strong vibrio harveyi phage
InactiveCN107988312AAccurate identificationSuitable for initial screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBacteriophageMicrobiology
The invention provides a method and a kit for identifying Vibrio harveyi quickly by means of strong vibrio harveyi phage and belongs to the technical field of identification of cultures of Vibrio harveyi. The method comprises the following steps: 1) coating 10<7>-10<9>cfu / mL to-be-detected culture to a LB agar plate, leaving the LB agar plate to stand for 15-20min to obtain a to-be-detected plate;2) dropwise adding a strong vibrio harveyi phage mixed liquid to the to-be-detected plate to obtain an identification system; and 3) leaving the identification system obtained in the step 2) to standfor 8-16h at 28-35 DEG C, observing whether bacteriophage plaques appear or not in the identification system, and identifying the to-be-detected culture as the Vibrio harveyi. The method is low in cost and time- and labor-saving, the time needed is only 16-18h, and the method is particularly suitable for initially screening a lot of Vibrio harveyi.
Owner:XIAMEN CANCO BIOTECH CO LTD
Separation method of melon powdery mildew
InactiveCN102994440ANormal germinationAvoid breakingMicroorganism based processesSpore processesBiotechnologySporeling
The invention discloses a monospore separation method of a melon powdery mildew. The method comprises the following steps: collecting a diseased melon leaf; brushing old spores from the surface of the diseased melon leaf by using a sterilizing brush; maintaining the diseased melon leaf under the condition of heat and moisture preservation so as to be bred into new spores; blowing the new cultured conidiospores onto a water agar plate through an ear washing bulb; utilizing a specific picking needle to pick out a single conidiospore under an anatomical lens; inoculating the single conidiospore on the leaf disc of the sterilized diseased melon or cucumber product; horizontally putting the leaf disc in a culture dish containing a mannitol culture medium; placing the leaf disc in an illumination incubator after overlaying a culture dish cover; and culturing the leaf disc for 7 days, thereby obtaining a purified melon powdery mildew bacteria colony. According to the invention, the single conidiospore is picked out by using the specific picking needle and is germinated normally under the action of suitable culturing medium and under the condition of suitable culturing condition, so that the separated melon powdery mildew has a pure pathogen and is free of microspecies cross infection. Therefore, the accuracy and the reliability of a subsequent research result are ensured. As a result, the prepared melon powdery mildew has an important practical value.
Owner:XINJIANG AGRI SCI ACAD CANTALOUPE RES CENT
Yeast strain of beer and application thereof
InactiveCN101665772AHigh positive mutation rateIncrease mutagenic effectFungiBeer fermentationBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The invention discloses a yeast strain of beer and the application thereof in the aspect of beer fermentation. The strain of the beer-brewing yeast (saccharomyces cerevisiae) provided by the inventionis preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.3217. The selecting and breeding method of the strain comprises the following steps: activating the original starting strain, injecting ions for mutation, mutating by laser, primarily sieving by using wort and agar flat plate culturing medium, sieving again by using a fermentationbung, testing genetic stability, and performing a pilot-scale test. The yeast strain of beer is an excellent yeast strain of beer and has a potential suitable for large production of beer breweries.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
Method for detecting total number of bacterial colonies in activated lactobacillus drink
InactiveCN101717813AAccurate detectionEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBacilliPollution
The invention relates to a method for detecting the total number of bacterial colonies in an activated lactobacillus drink, relating to a microorganism detecting method. The method comprises the following steps of: filtering diluent of the activated lactobacillus drink with a filter membrane, flushing the filter membrane with physiological saline, pasting the flushed filter membrane on a TTC nutrient agaragar tablet with the filtering face facing upwards, converting the nutrient agaragar tablet and culturing at 37 DEG C, and counting after culturing for 48+ / -2h. By adopting the method, the total number of pollution bacterial colonies in the activated lactobacillus drink can be accurately, simply and quickly detected so as to provide an effective method for detecting the sanitation quality of the of the activated lactobacillus drink.
Owner:GUANGDONG HUANKAI MICROBIAL SCI & TECH
Method for counting effective viable bacterium content of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus powder
ActiveCN102352405AOvercoming the inability to distinguish dead bacteriaOvercoming activityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesNutrient brothDirect observation
The invention provides a method for counting the effective viable bacterium content of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus powder, which comprises the following steps: appropriately diluting a sample to be detected, so that Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus in the sample to be detected is sufficiently dispersed into individual cells; then, carrying out incubation culture in an aseptic nutrient broth diluted by 10 times to promote growth and propagation, thus forming a megascopic turbid liquid; further determining that a large amount of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus is contained in the turbid liquid having the maximum dilution through plaque detection; and finally, determining the total amount of effective viable bacteria in the sample to be detected. Compared with a microscopic direct observation method anda dilution-by-tap-water double-layer agar plate method, the method provided by the invention is more accurate, and overcomes the defects that detection is inaccurate due to dilution in the dilution-by-tap-water double-layer agar plate method and killed bacteria and viable bacteria can not be distinguished in the microscopic direct observation method.
Owner:绿奥环保科技(上海)有限公司
Puncher for countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis agar plate
InactiveCN105382881AImprove efficiencyPunch neatlyMetal working apparatusPunchingImmunoelectrophoresis
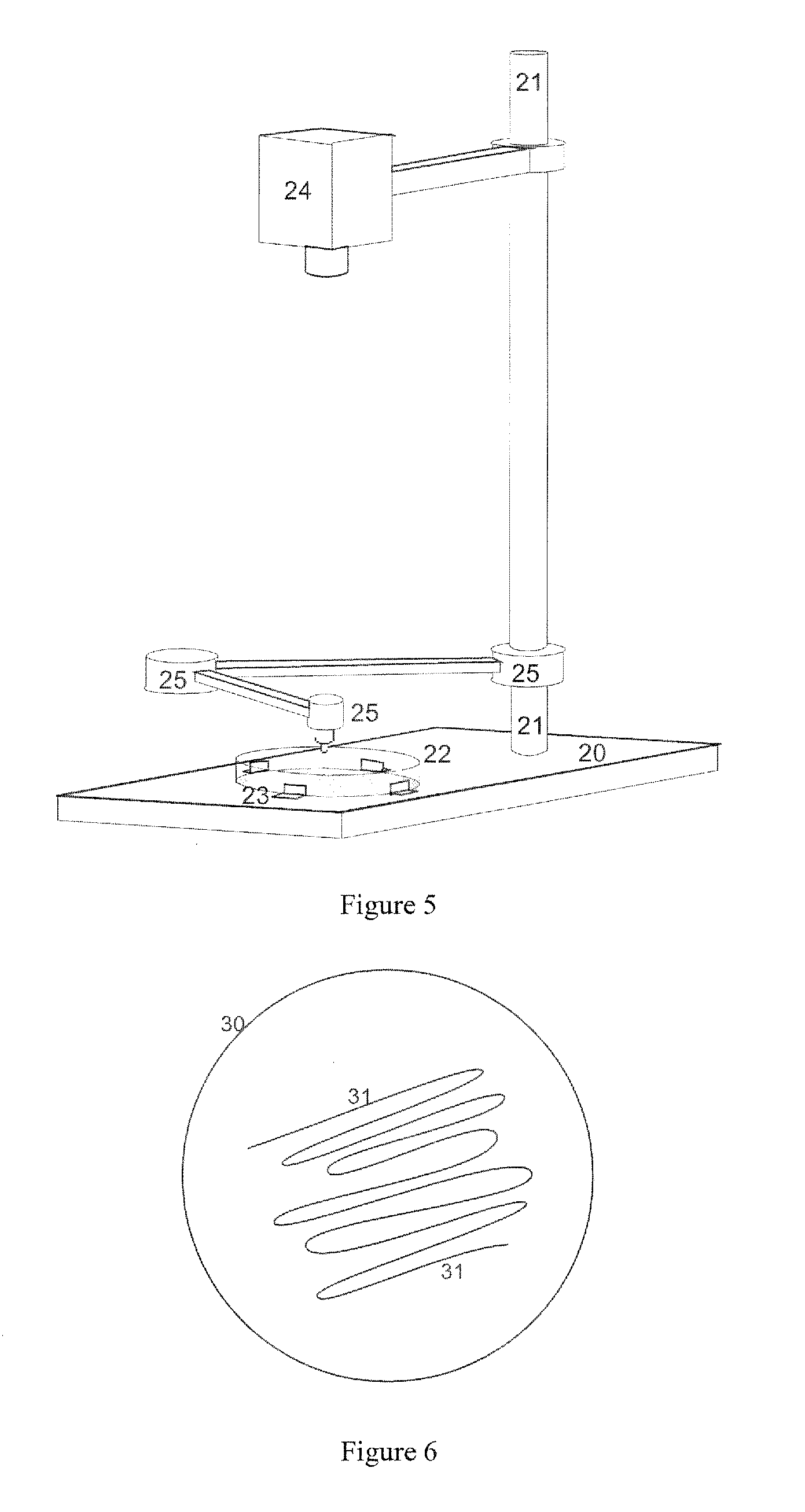
The invention discloses a puncher for a countercurrent immunoelectrophoresis agar plate. The puncher comprises a punching tube, a fixing plate, a fixing plate frame, a handle and a negative-pressure barrel, wherein the punching tube is communicated with the negative-pressure barrel through a hose; the inner side of the opposite side of the fixing plate frame is provided with a slide path; the two ends of the fixing plate can be arranged in the slide path in a sliding mode; at least one end of the fixing plate is provided with a stirring block; the stirring block is positioned at the outer side of the fixing plate frame; a slide slot for allowing the stirring block to slide is formed in the fixing plate frame; a displacement sensor is arranged in the slide path; and a displacement display screen is arranged on the fixing plate frame or the handle. The puncher can be used for punching a plurality of holes in the agar agarose gel plate once and can automatically suck out agar in the holes, so that the whole operation can be completed by only one hand, and therefore, the puncher is efficient and convenient.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Evaluation method for disinfection effect of disinfectant
InactiveCN102321728ASolve application problemsThe disinfection effect is simple and convenientMicrobiological testing/measurementDisinfectantThermostat
The invention provides an evaluation method for a disinfection effect of a disinfectant with a bacteria test sheet. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparing and grouping samples to be tested; (2) disinfecting: uniformly mixing the samples to be tested and diluted disinfectant and disinfecting; (3) inoculating: inoculating the samples to be tested and the disinfected samples on a total bacterial colony number test sheet; (4) culturing: packaging the bacterial colony test sheet on which the samples are inoculated into a sealed bag and placing in a thermostat of 37 DEG C to culture for 24-48 hours; and (5) observing a result: counting the bacteria number on each test sheet and calculating sterilization rate of each disinfectant. The evaluation method for the disinfection effect of the disinfectant with the bacteria test sheet is simple and convenient, has high accuracy and is an effective method which can substitute the conventional agar plate sterilization rate evaluation method.
Owner:LUOYANG HUIZHONG ANIMAL MEDICINE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com