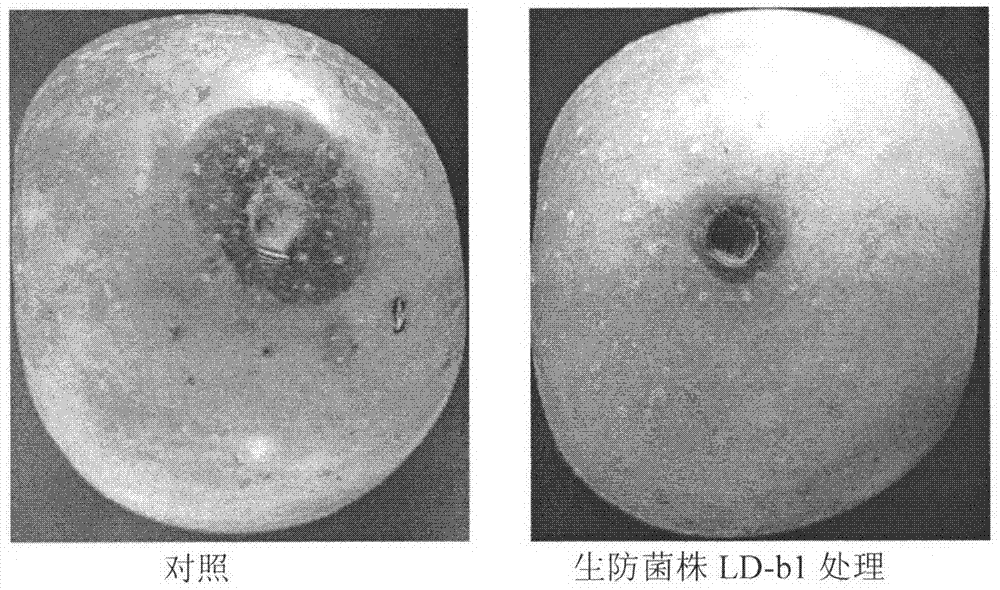
Fermentation process of Bacillus pumilus LD-b1 and its application in control of plant diseases
A technology for Bacillus pumilus and plant diseases, which can be used in applications, plant growth regulators, botanical equipment and methods, etc., and can solve problems such as difficulties in colonization
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
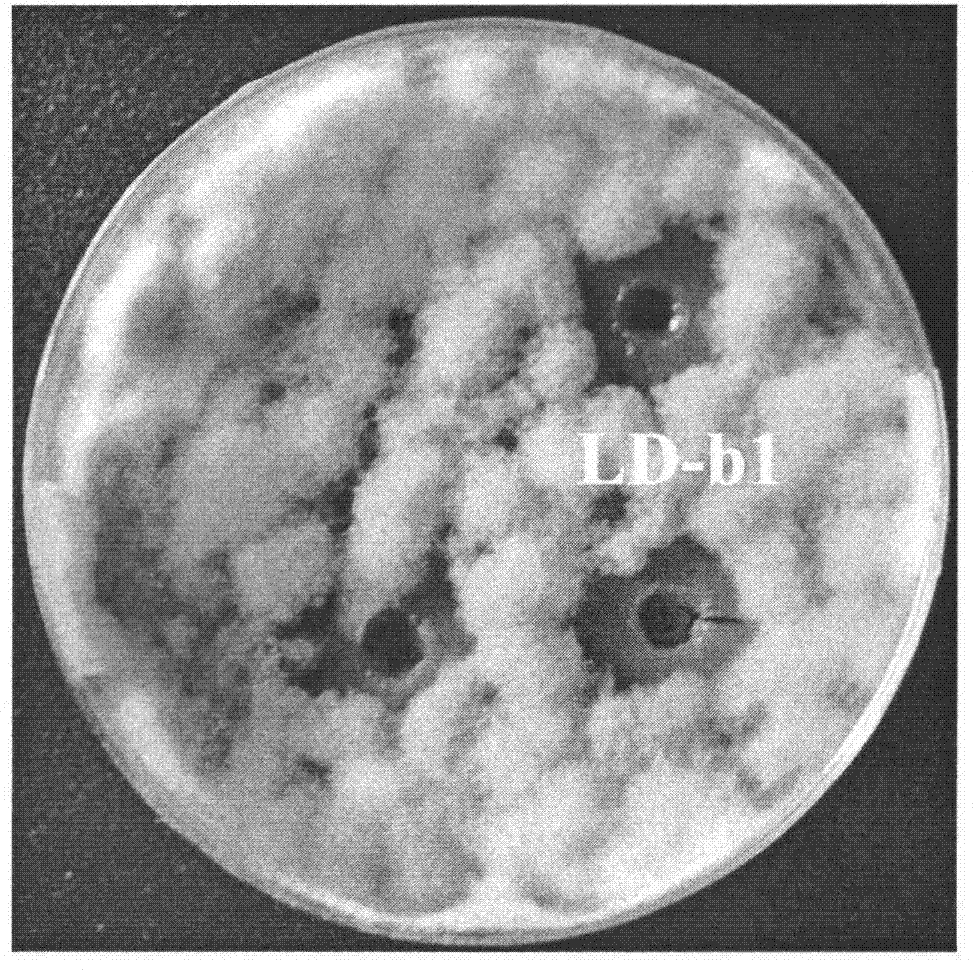
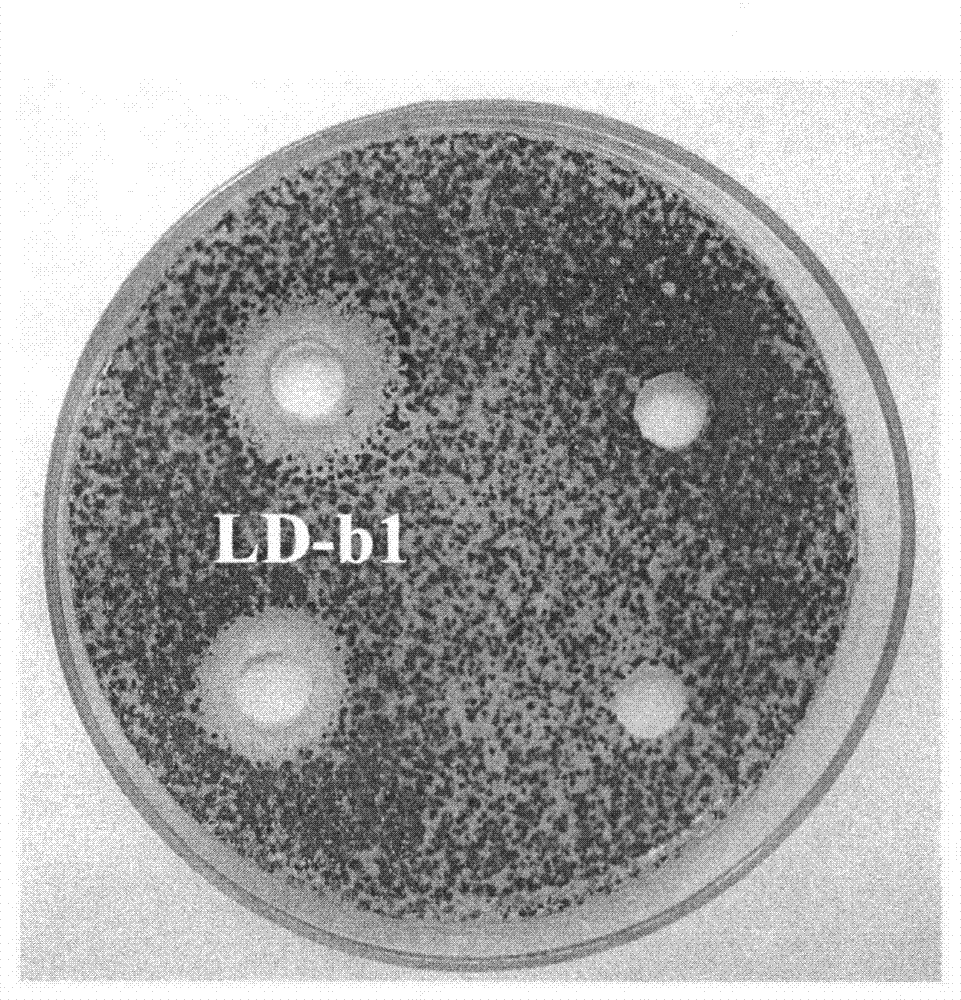
[0020] Isolation of Bacillus pumilus LD-b1
[0021] Take a section of the stem of fresh clouded gentian, rinse twice with sterile water, absorb the water with sterile filter paper; soak in 70% ethanol solution for 2 minutes, then soak with 0.1% mercury for 30 seconds, rinse with sterile water 3 times . Under aseptic conditions, peel off the outer skin with a blade and cut it into small sections of about 1 cm, place them on the surface of the screening medium, and incubate at 30°C for 4-8 days. After the bacteria grow on the plate, the plate is streaked and purified to obtain a pure culture of isolated bacterial strains.
Embodiment 2
[0023] Morphological characteristics of strain LD-b1
[0024] LD-b1 was cultured on a solid medium plate at 30°C for 1 day to form a milky white opaque colony. The colony was approximately round, with irregular edges, small protrusions in the middle, 0.6-1.1cm in diameter, and no pigment secretion; bacteria of strain LD-b1 The somatic cells are short rod-shaped, with a size of 0.5μ.m~0.6μm×1.5μm~2.1μm, Gram-positive, with spores.
[0025] Physiological and biochemical characteristics of strain LD-b1
[0026] The growth temperature range of strain LD-b1 is 8~50℃, pH range is 5.5~8.5, NaCl concentration range is 0~7%; the available carbon sources are: glucose, sucrose, lactose, aldose, xylose, galactose , Mannitol, N-acetyl-glucosamine, gluconate; can not use starch, dextrin, melibiose, rhamnose and sorbitol; strain LD-b1 contact enzyme, citrate utilization, casein Hydrolysis, esculin hydrolysis, VP is positive, oxidase, urease, H 2 S production, indole production, nitrate reduction,...
Embodiment 3
[0030] Fermentation production process of strain LD-b1
[0031] Slant medium (g / L): sucrose 10, peptone 2, beef extract 3, yeast extract 0.5, agar 15, pH 7.5, sterilized at 121°C for 30 min.
[0032] Seed medium (g / L): sucrose 15, peptone 5, yeast powder 0.2, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5, magnesium sulfate 0.05, sodium chloride 0.1, pH 7.5, sterilized at 121°C for 30 min.
[0033] Fermentation medium (g / L): sucrose 25, soybean meal 3, ammonium sulfate 2.5, yeast powder 0.2, diammonium phosphate 0.8, magnesium sulfate 0.05, ferrous sulfate 0.02, sodium chloride 0.1, pH 7.5, 121°C Sterilize for 30 minutes.
[0034] Streak the conserved strains and inoculate them on the solid slant medium, incubate at 30°C for 36 to 48 hours, wash the activated strains from the slant of the test tube with 5mL sterile water, and insert them into the seed culture medium. Liquid seed culture medium, the inoculated Erlenmeyer flask is placed on a rotary shaker, and cultured at 150r / min at 30°C for 24-...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com