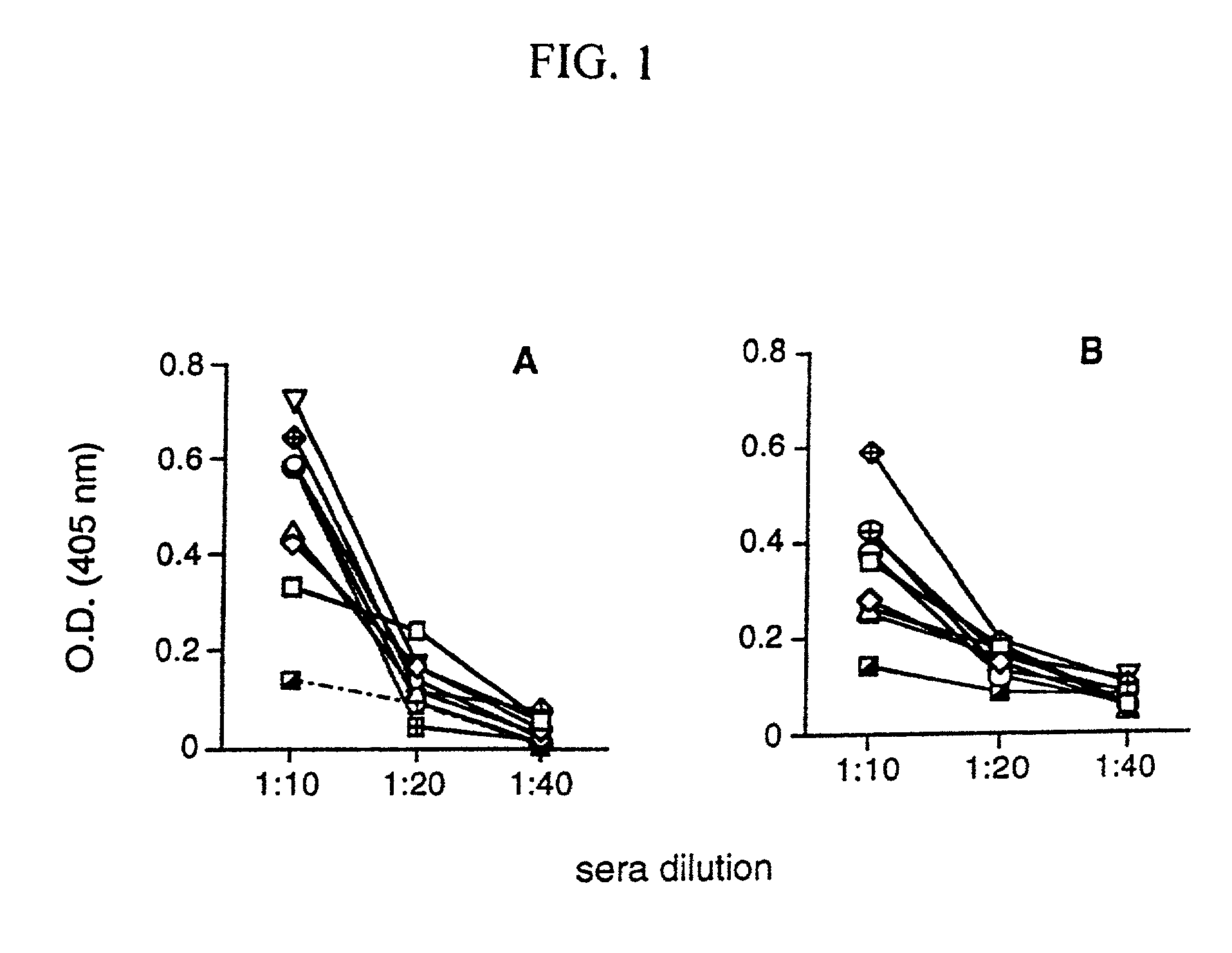
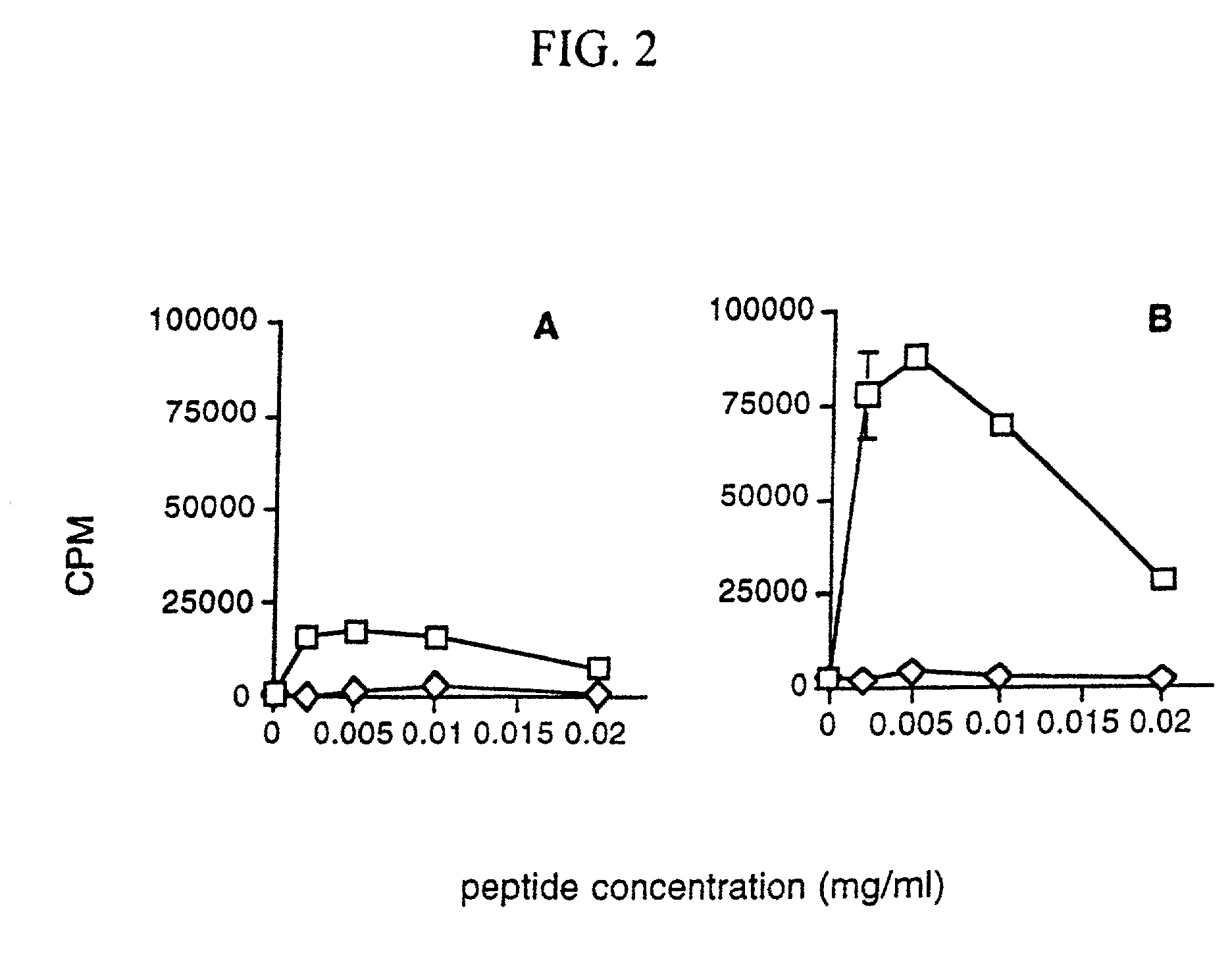
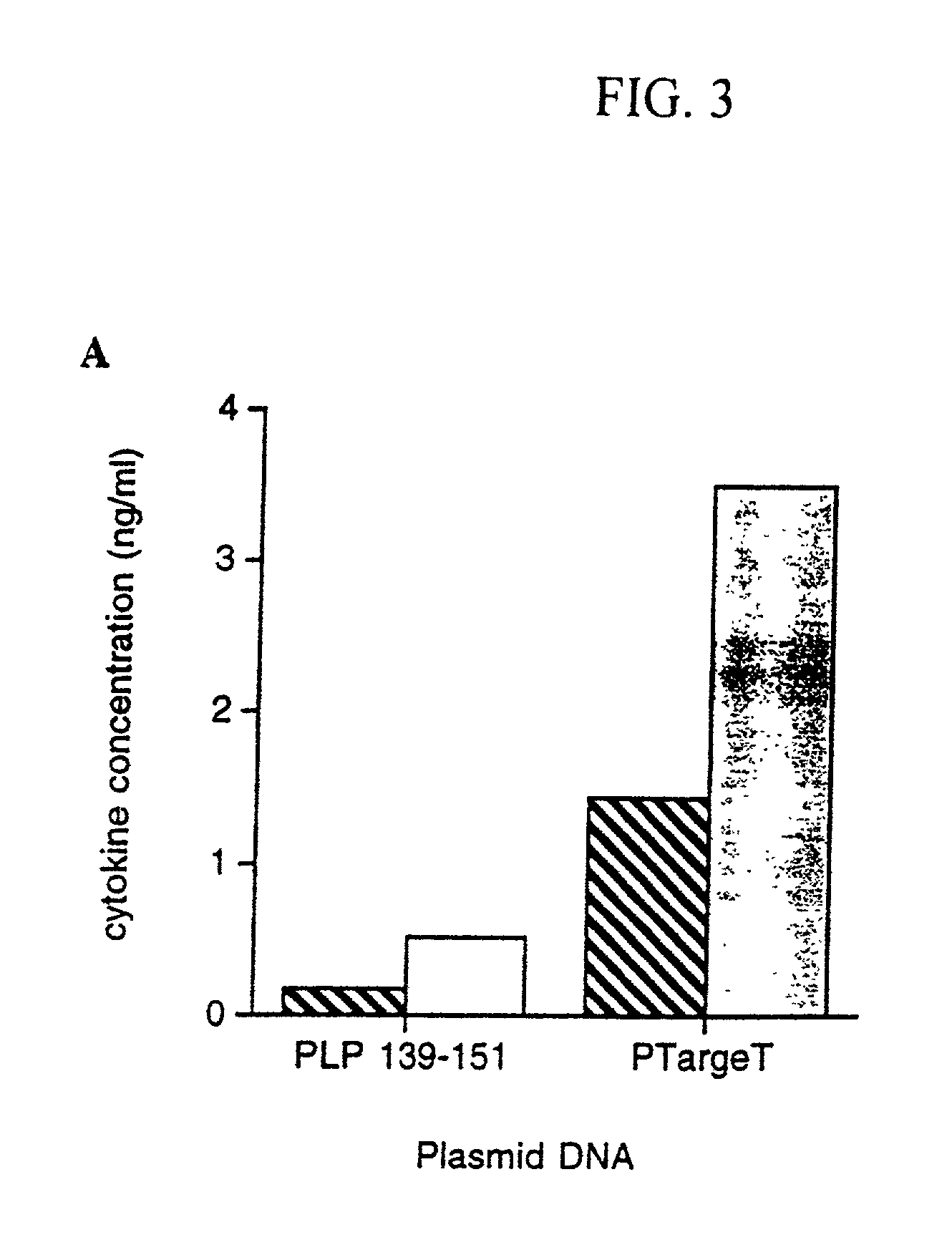
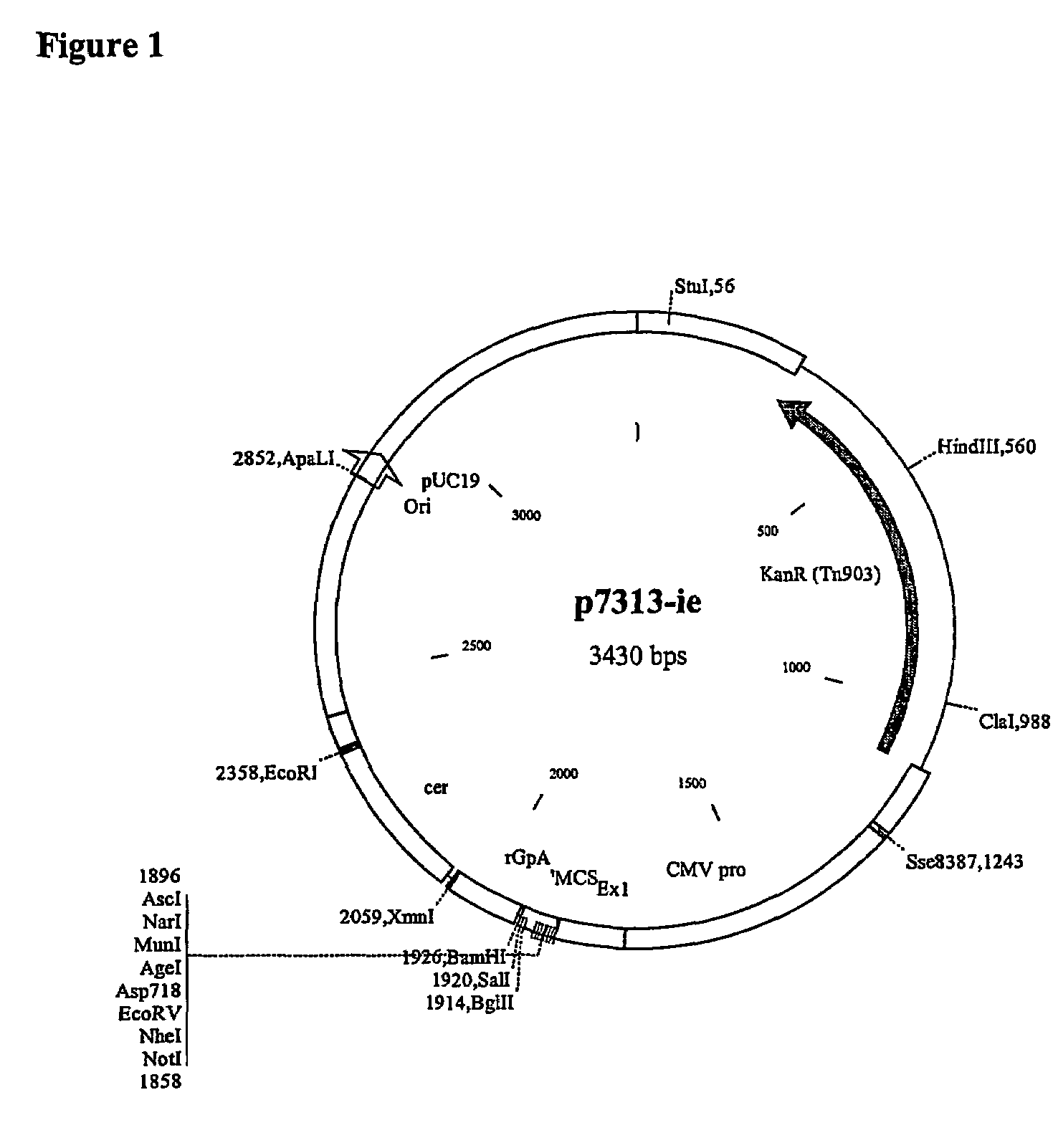
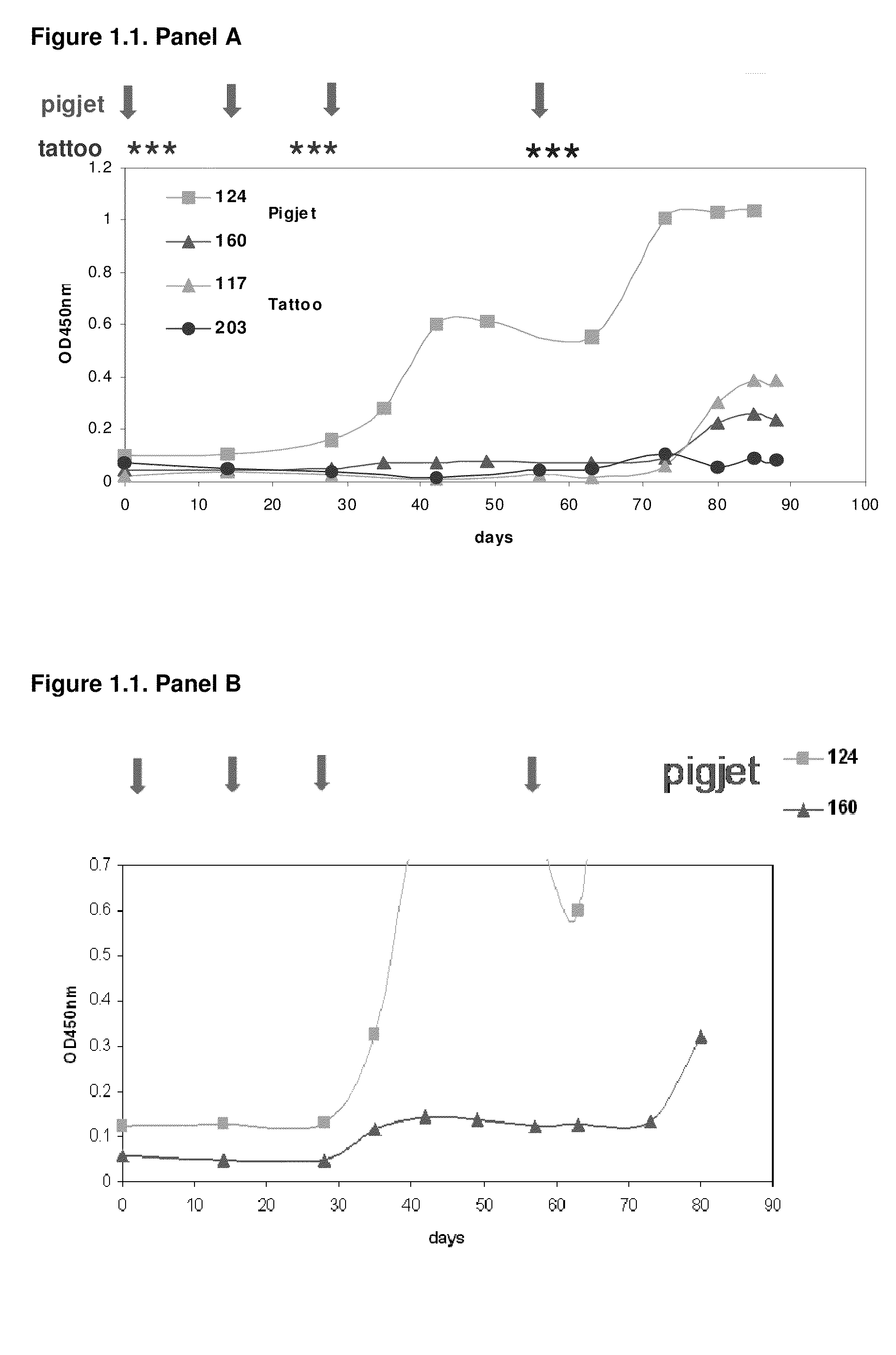
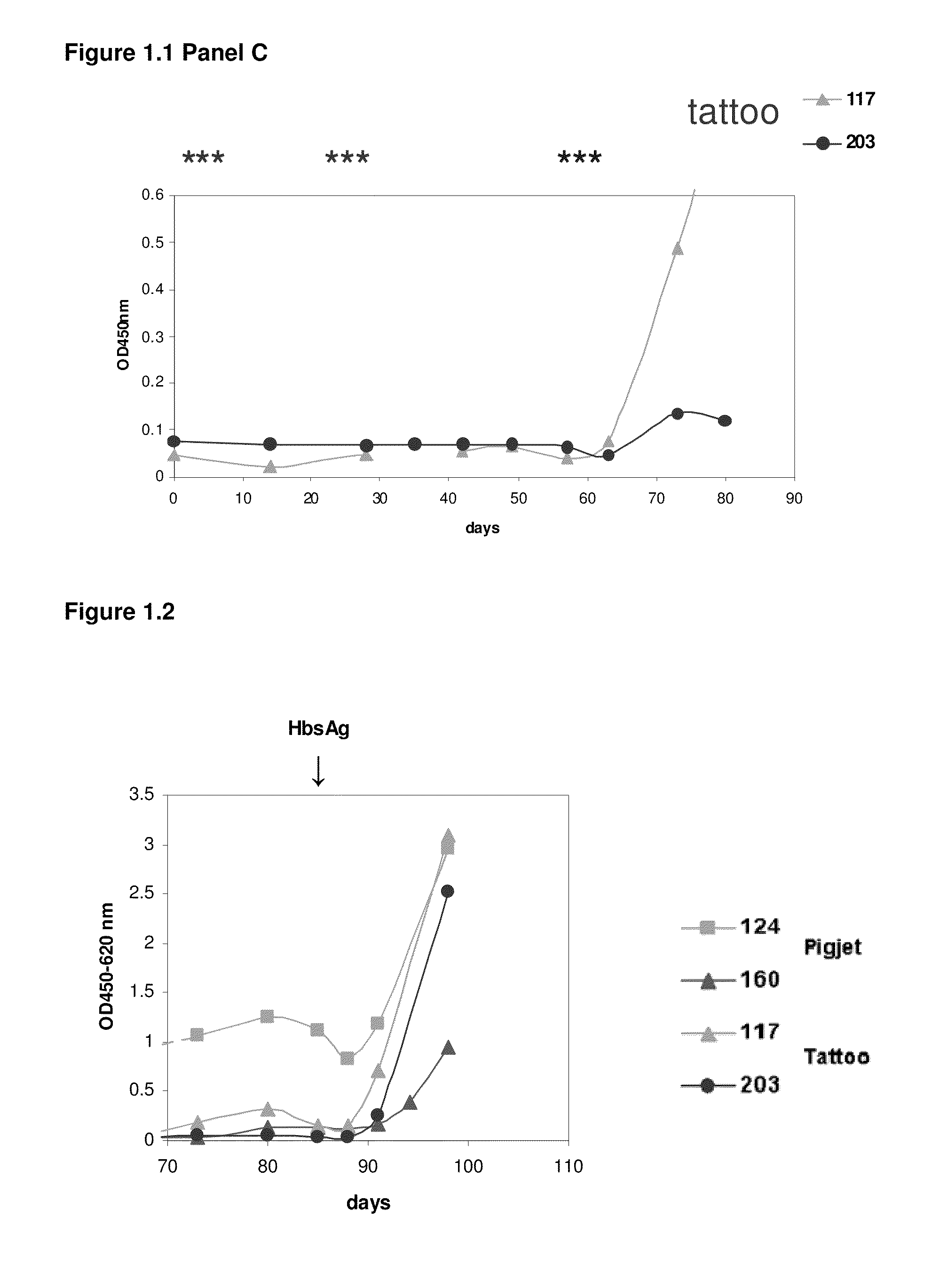
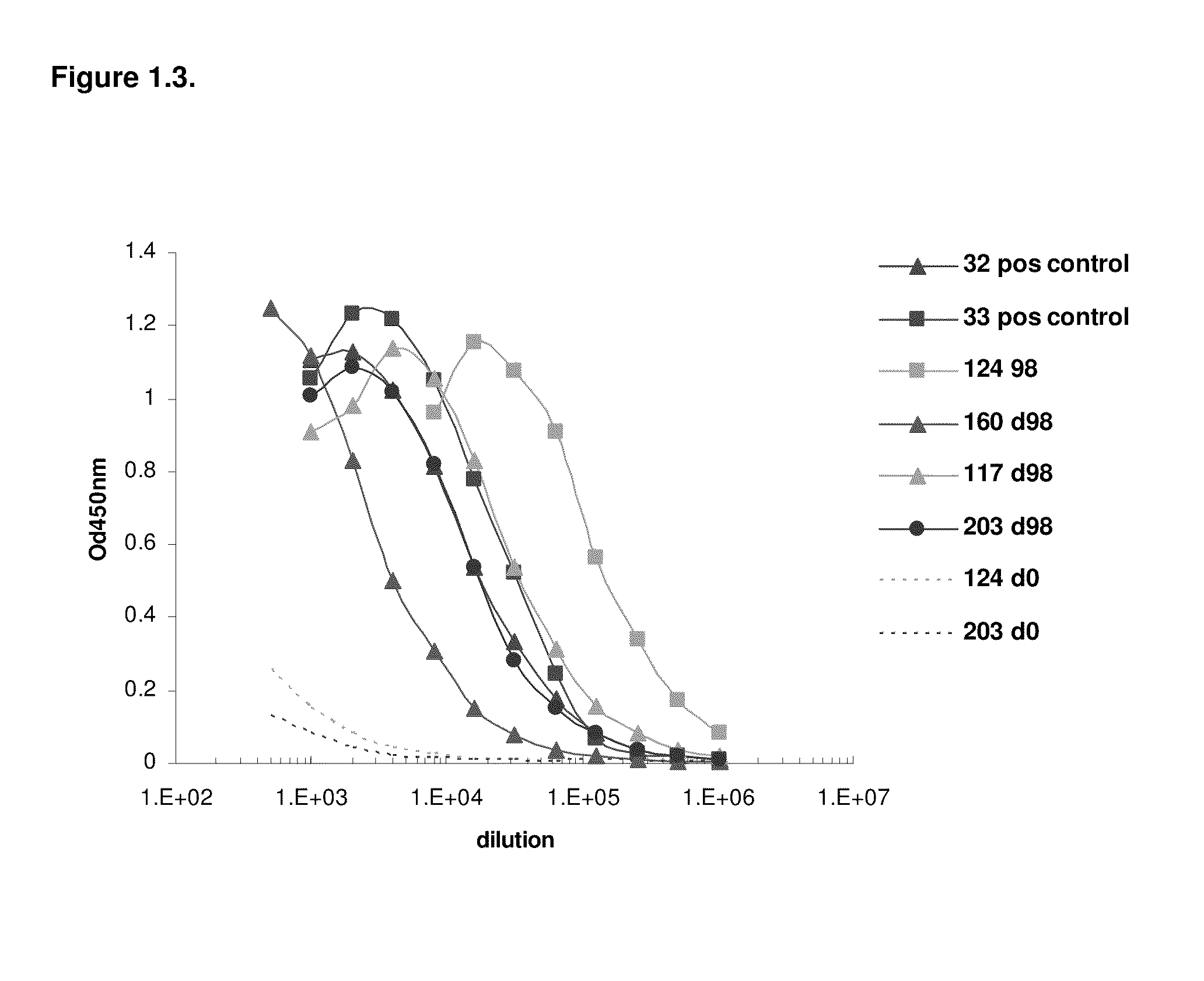
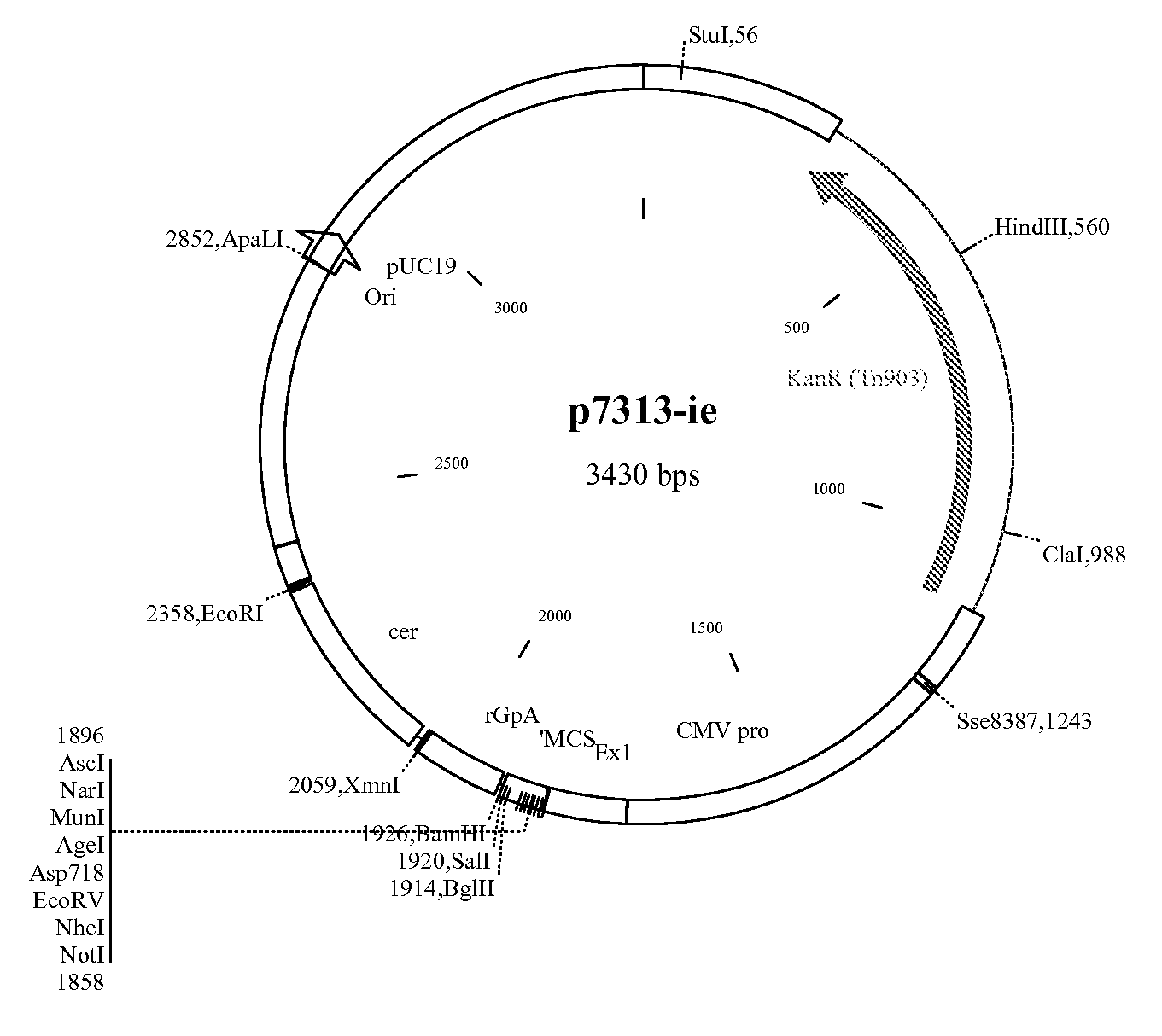
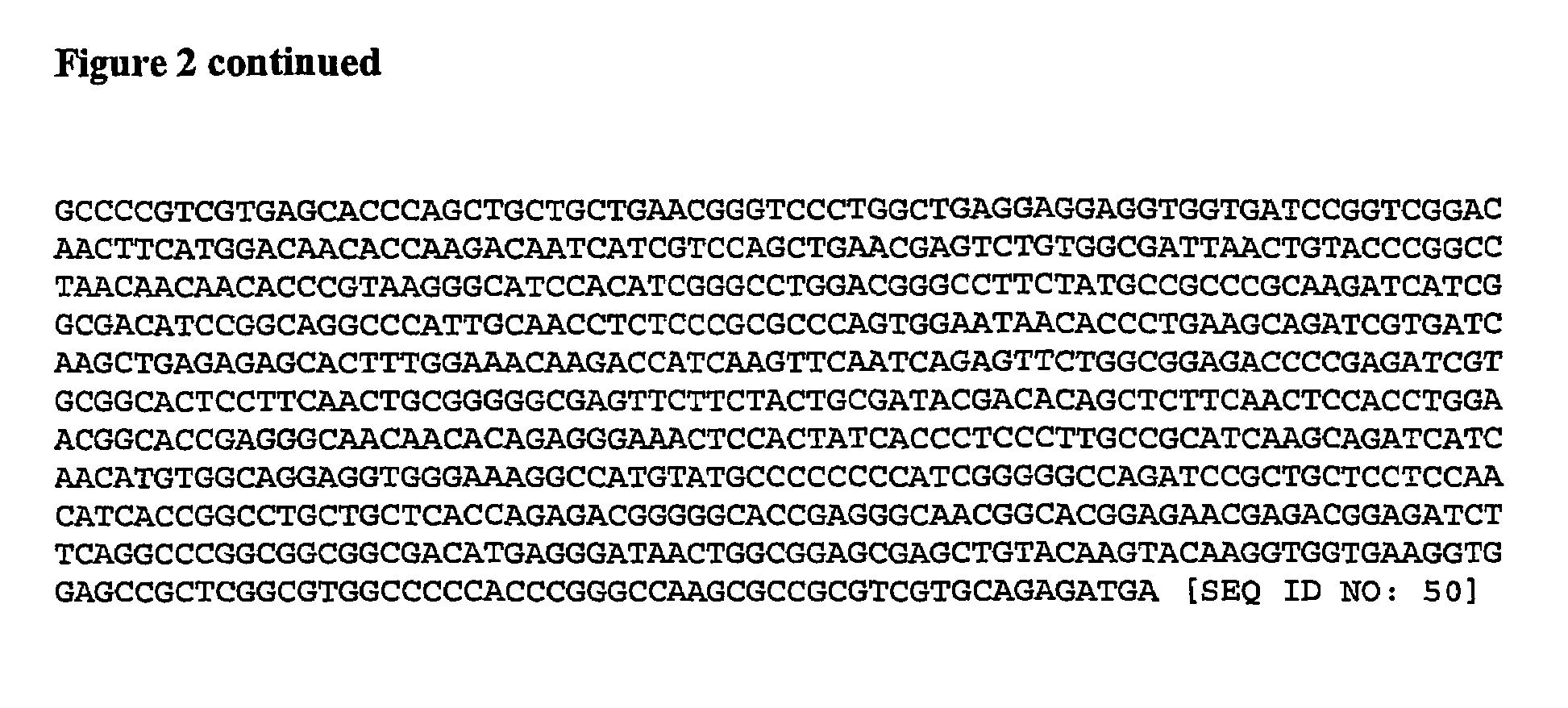Patents
Literature
41 results about "DNA vaccination" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting against disease by injection with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, producing a protective immunological response. DNA vaccines have potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.
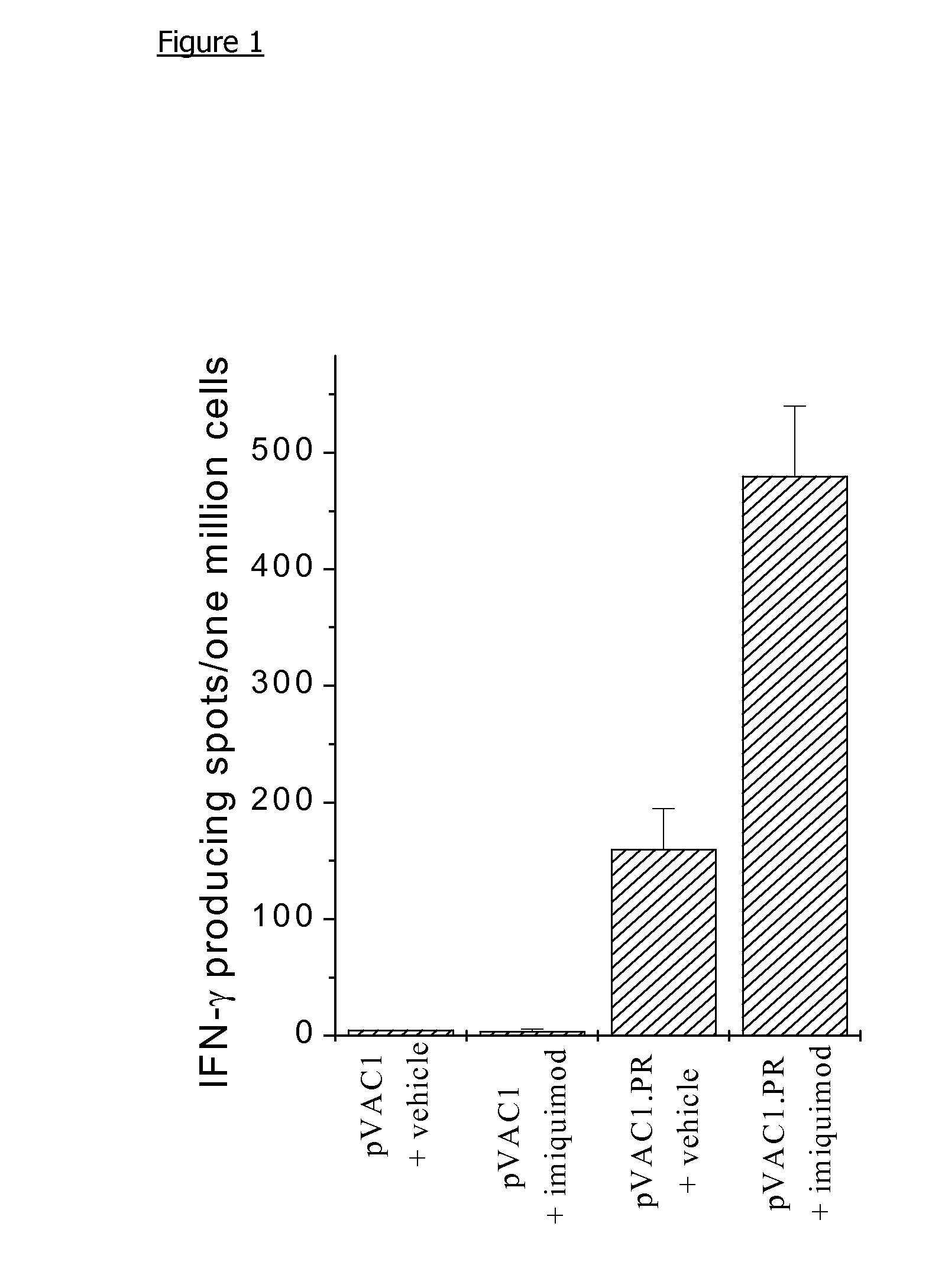
Immuno-modulating effects of chemokines in DNA vaccination
InactiveUS6569418B1Reduce in quantityEnhance immune responseGenetic material ingredientsImmunoglobulinsAntigenDNA vaccination
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAD BIOTECH INST
Immuno-modulating effects of chemokines in DNA vaccination
InactiveUS6919319B2Increase speedReduce in quantityBiocideGenetic material ingredientsDNA vaccinationAntigen
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
DNA vaccination for treatment of autoimmune disease
A pro-inflammatory T cell response is specifically suppressed by the injection into a recipient of DNA encoding an autoantigen associated with autoimmune disease. The recipient may be further treating by co-vaccination with a DNA encoding a Th2 cytokine, particularly encoding IL4. In response to the vaccination, the proliferation of autoantigen-reactive T cells and the secretion of Th1 cytokines, including IL-2, IFN-γ and IL-15, are reduced.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Vaccine
InactiveUS7655235B2Reduce and prevent glycosylationGlycosylation can be reduced and preventedAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesDNA vaccinationHeterologous
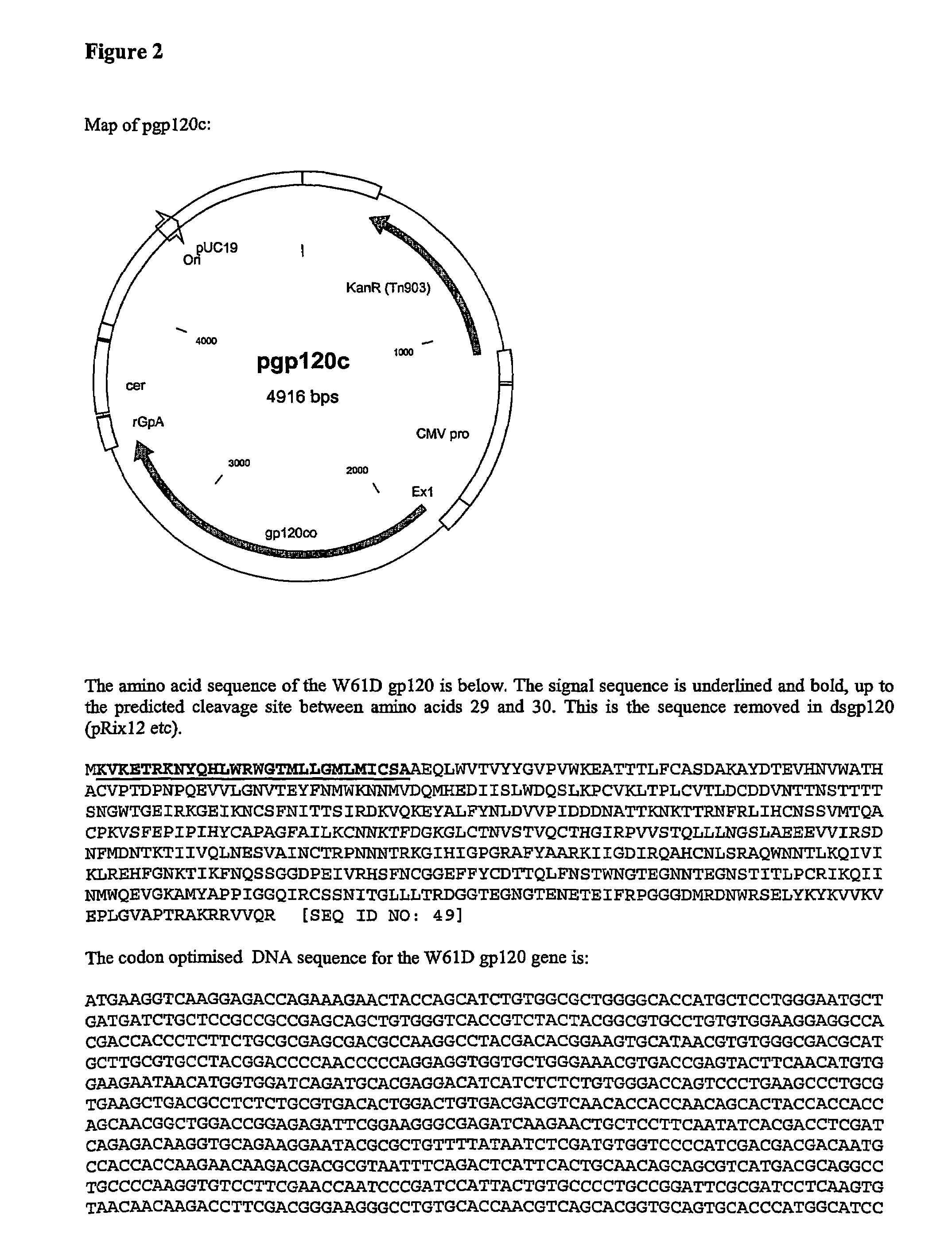
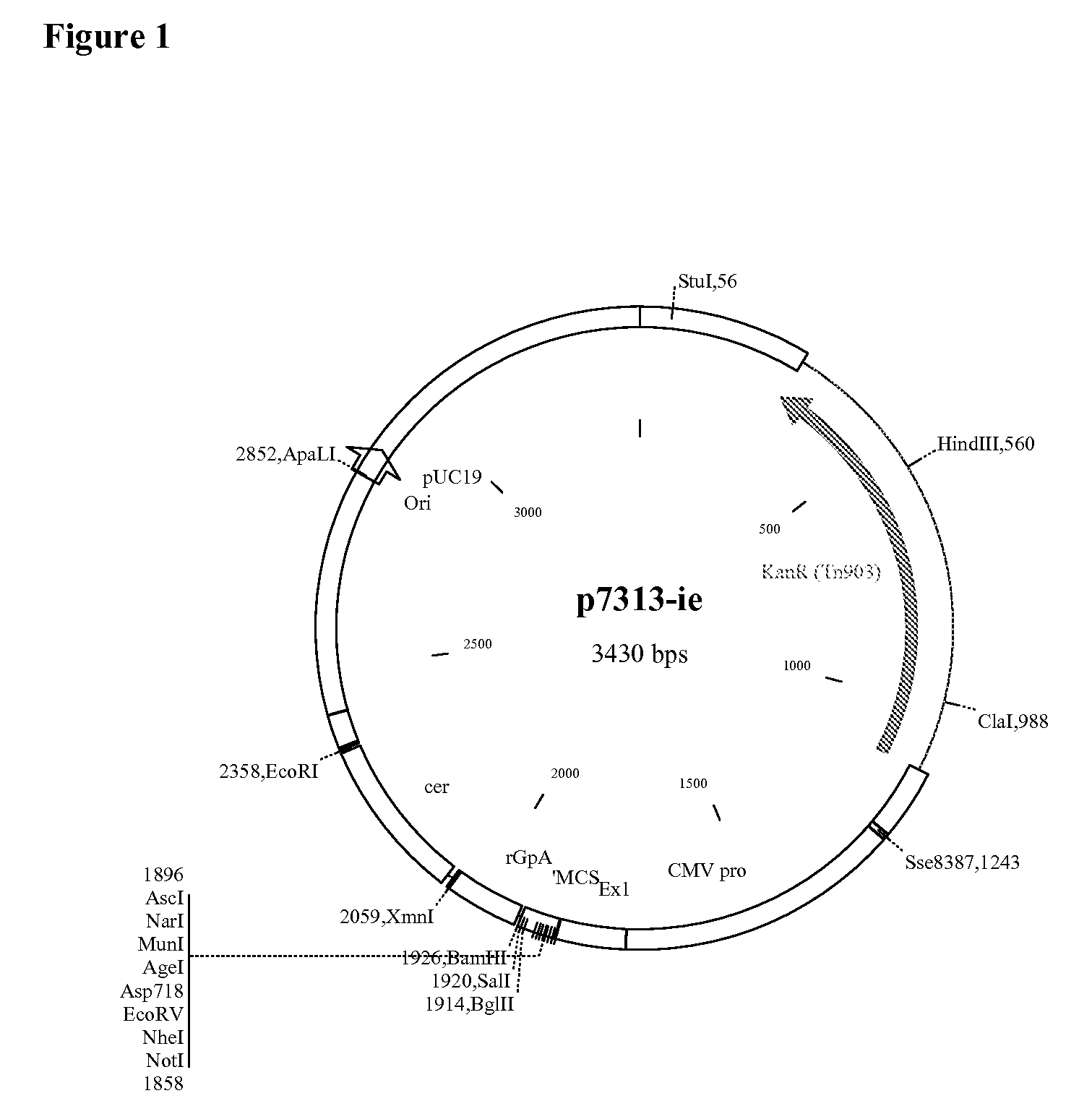
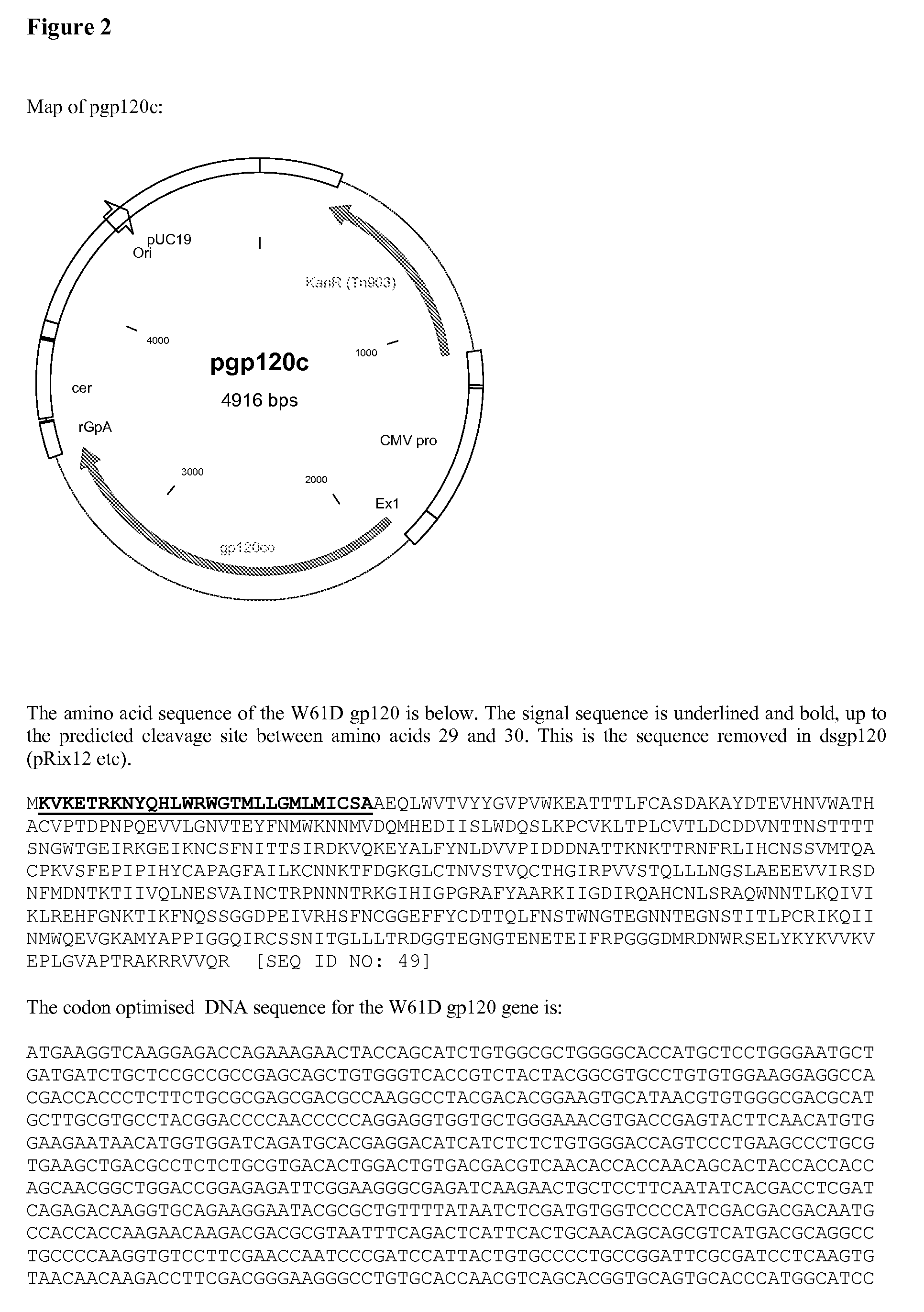
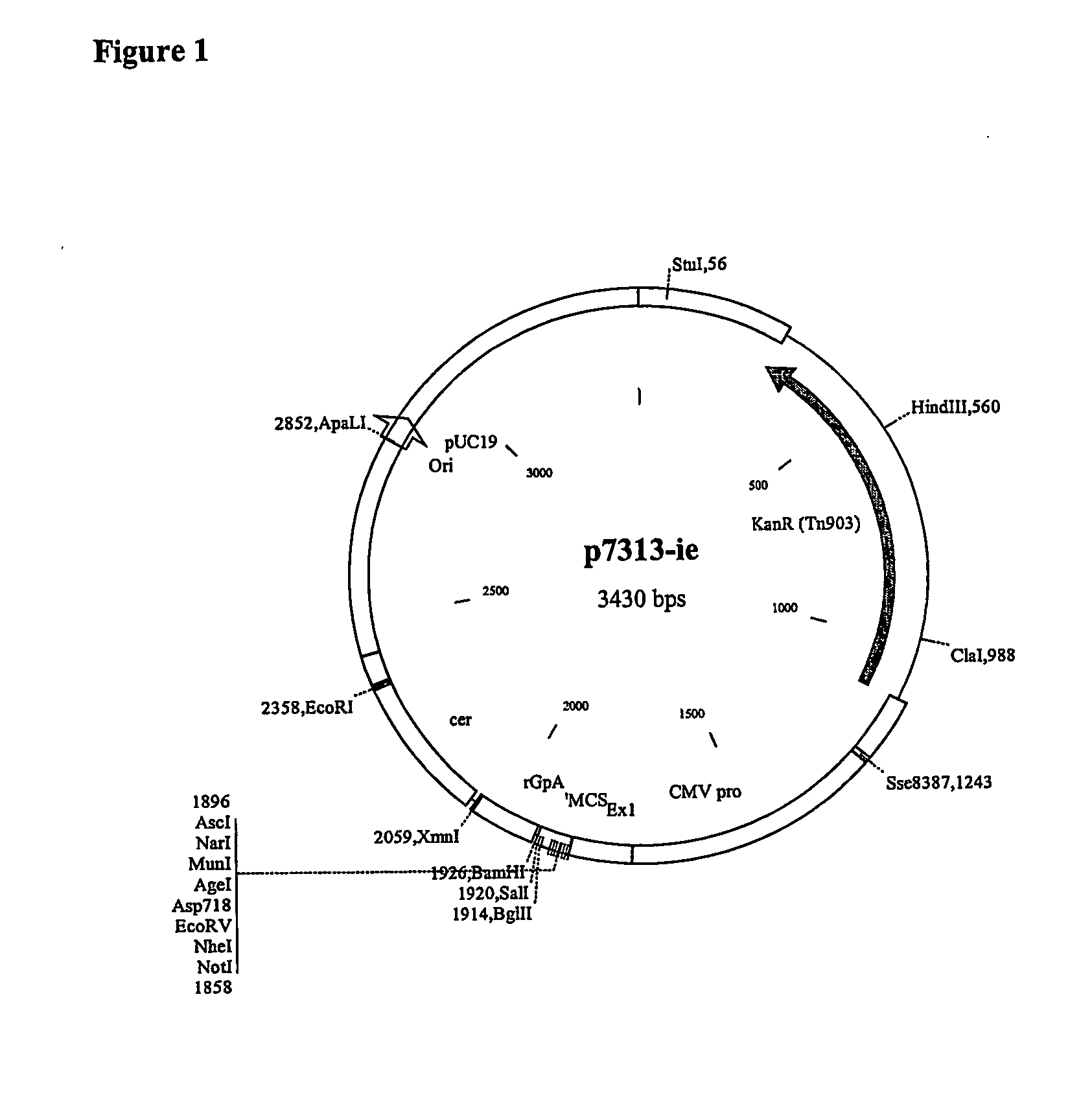
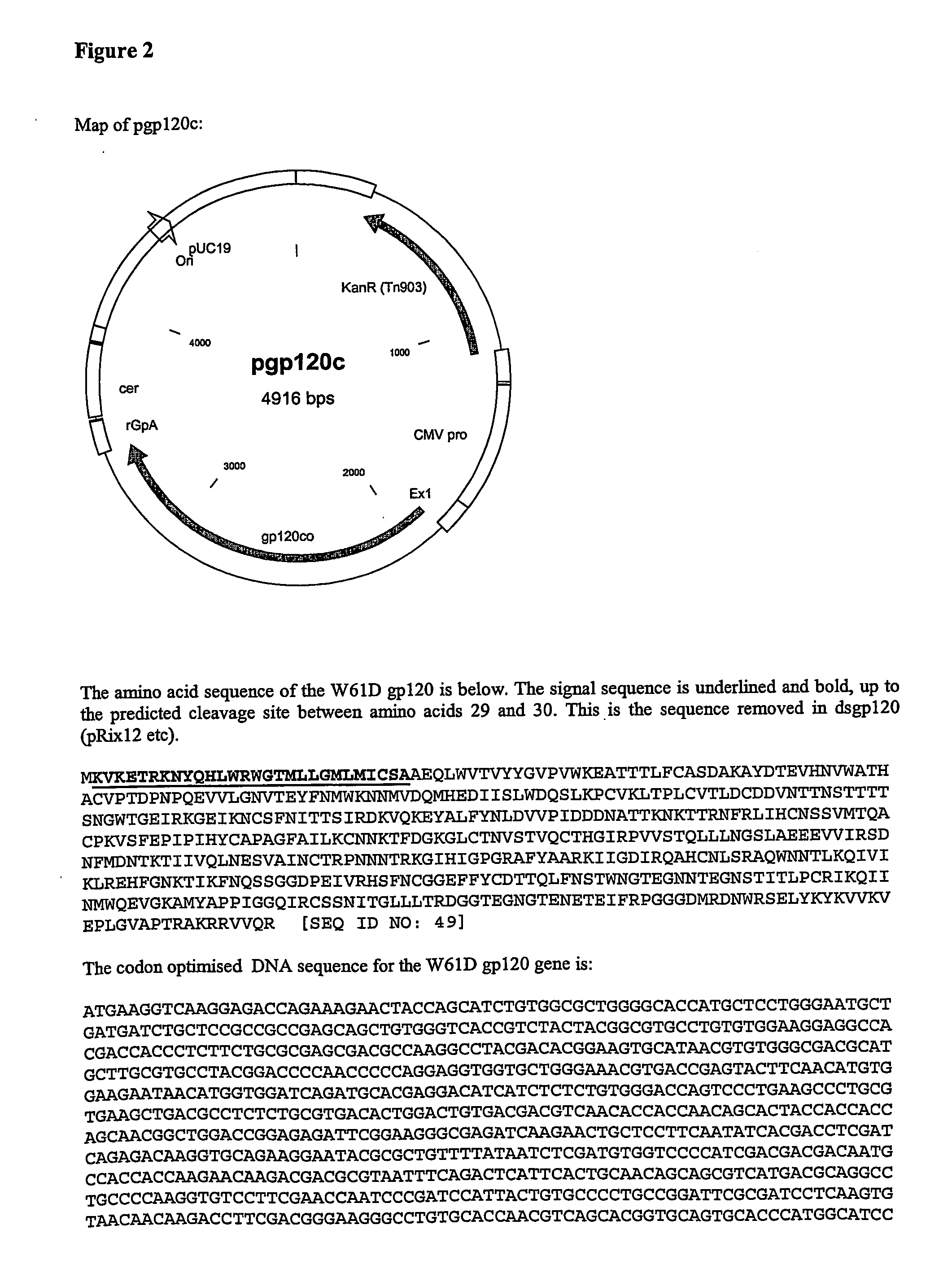
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative, which is non-glycosylated when expressed in a mammalian target cell, operably linked to a heterologous promoter. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule, such as gp120 or gp140 or gp160, lacks a functional secretion signal. It may be fused to additional HIV proteins such as Nef, Gag, RT or Tat.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LTD
Method of DNA vaccination
InactiveUS7074770B1Improve responseEnhance immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseBiocideAntigenDisease
A method of vaccinating a mammal against a disease state, comprising administrating to said mammal, within an appropriate vector, a nucleotide sequence encoding an antigenic peptide associated with the disease state; additionally administering to said mammal a compound which enhances both humoral and cellular immune responses initiated by the antigenic peptide, the compound being selected from the list contained herein, wherein the compound is preferably Tucaresol or a physiologically acceptable salt or ester thereof, where appropriate.
Owner:SMITHKLINE BECKMAN CORP
Method of transfection and compositions therefor
ActiveUS20100310595A1Antibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsDNA vaccinationToll-like receptor
The present invention relates to the targeted delivery of molecules to cells expressing toll-like receptors (TLRs). Aspects of the invention provide compounds comprising a positively charged group linked to a TLR ligand. These compounds are useful for in vitro and in vivo methods of transfection of TLR-expressing cells. Other aspects of the invention relate to the use of such compounds for repression of gene expression and DNA vaccination approaches.
Owner:ENA RESPIRATORY PTY LTD
Method of transfection and compositions therefor
Owner:ENA RESPIRATORY PTY LTD
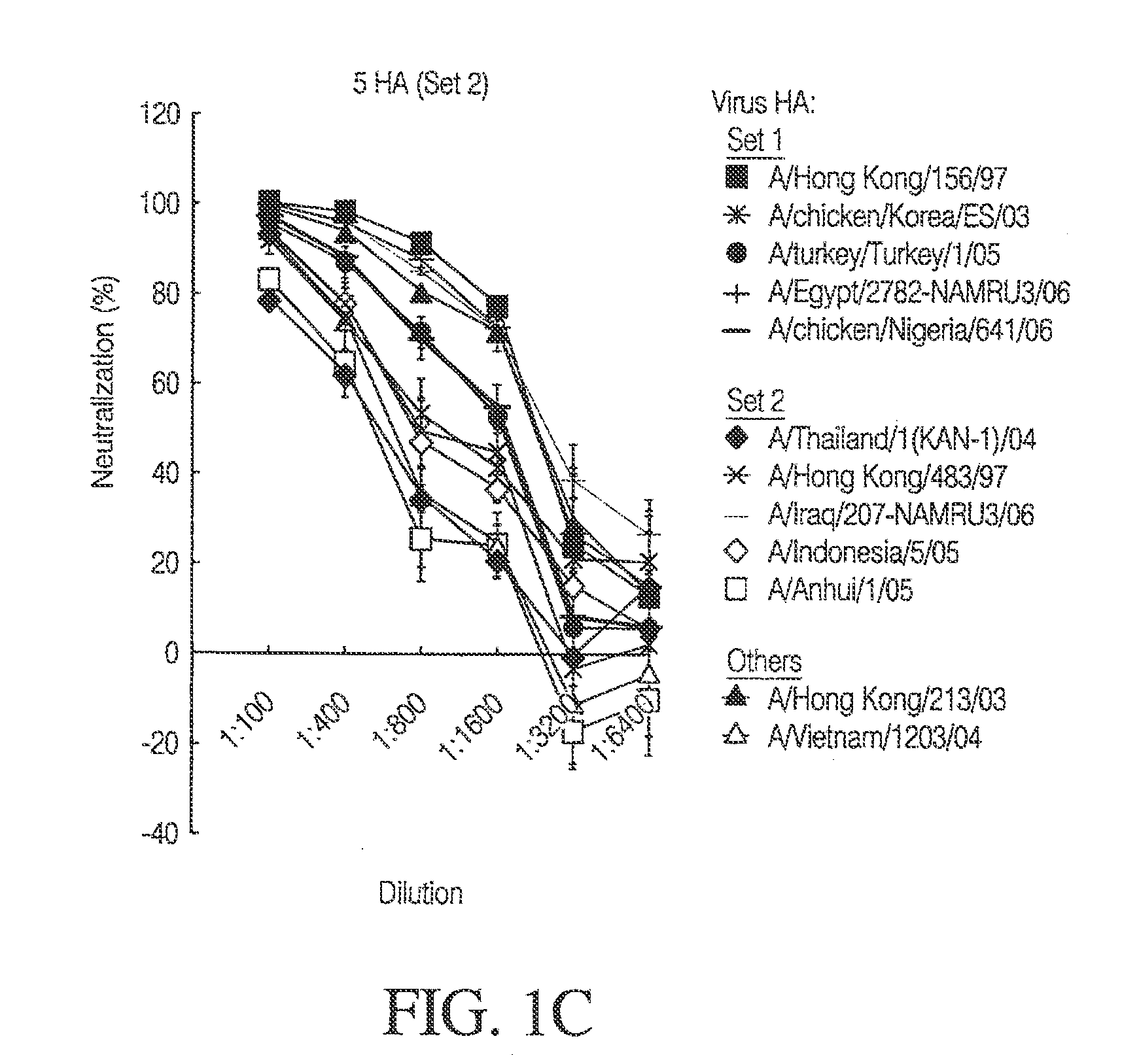
Influenza DNA vaccination and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20110171260A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsHeterologousDNA vaccination
The present invention relates to an influenza immunogen that includes one or more DNA constructs encoding at least two divergent influenza HAs, wherein each of such one or more DNA constructs encodes one or more of the at least two divergent influenza HAs. Such an immunogen, when administered to a subject, induces an immune response to a plurality of strains of influenza virus, wherein at least one strain of the plurality of strains does not encode any of the divergent influenza HAs encoded by the immunogen. The divergent influenza HAs can be swine influenza HAs or equine influenza HAs, such as influenza H1 HAs or influenza H3 HAs. The invention also relates to a method to use such an immunogen to induce such an immune response as well as to DNA constructs comprising such divergent influenza HAs. Such an immunogen can provide a heterologous as well as a homologous immune response. Such an immunogen can be used to induce an immune response against evolving influenza virus.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
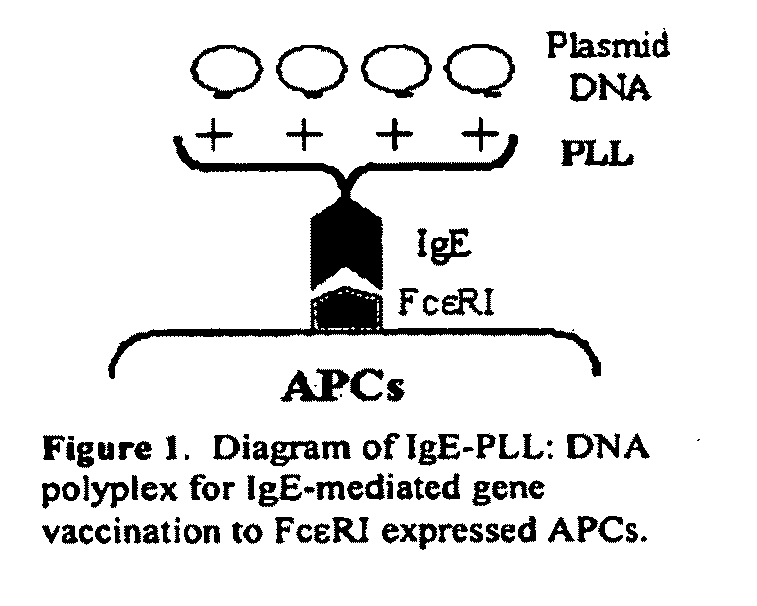
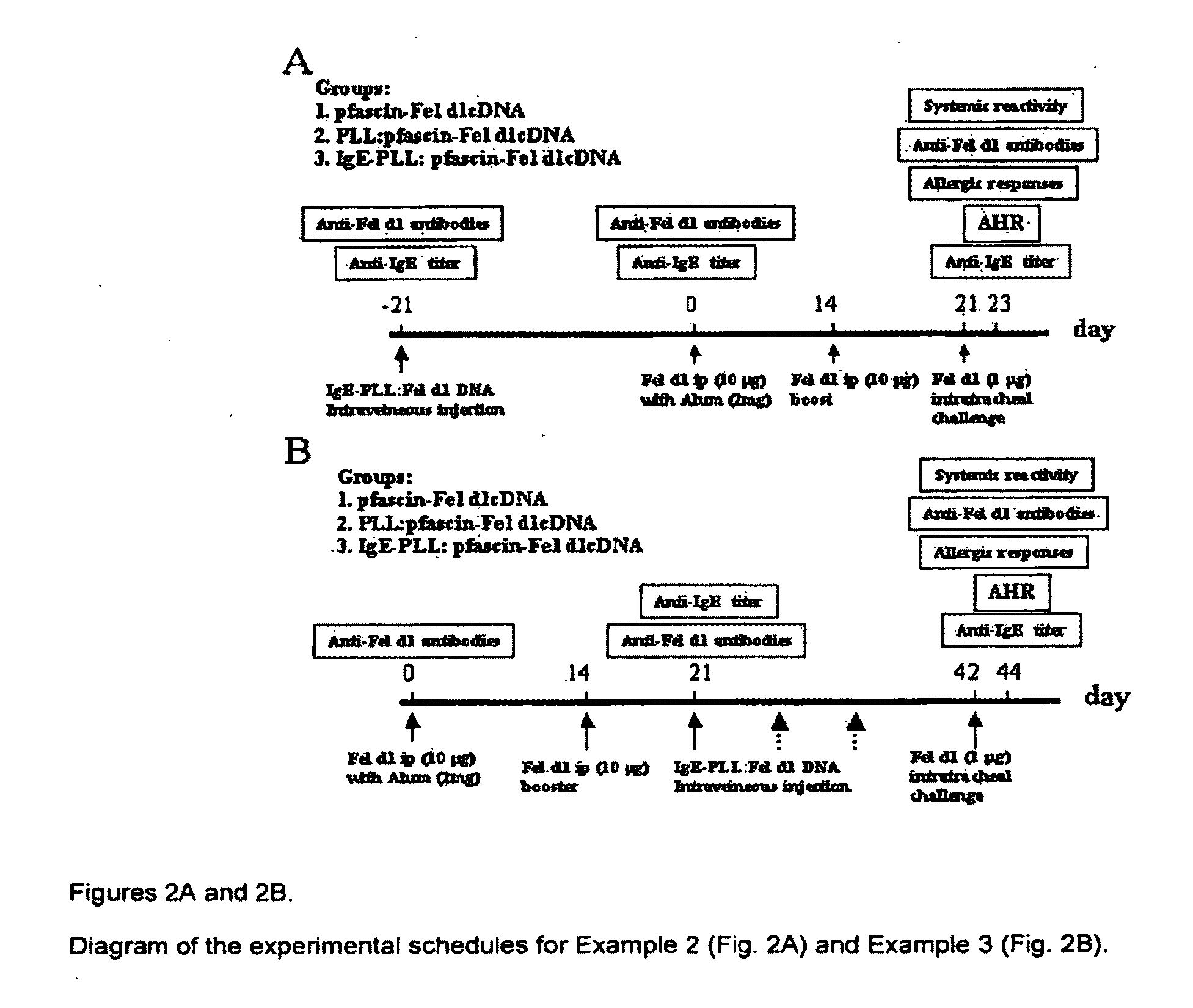
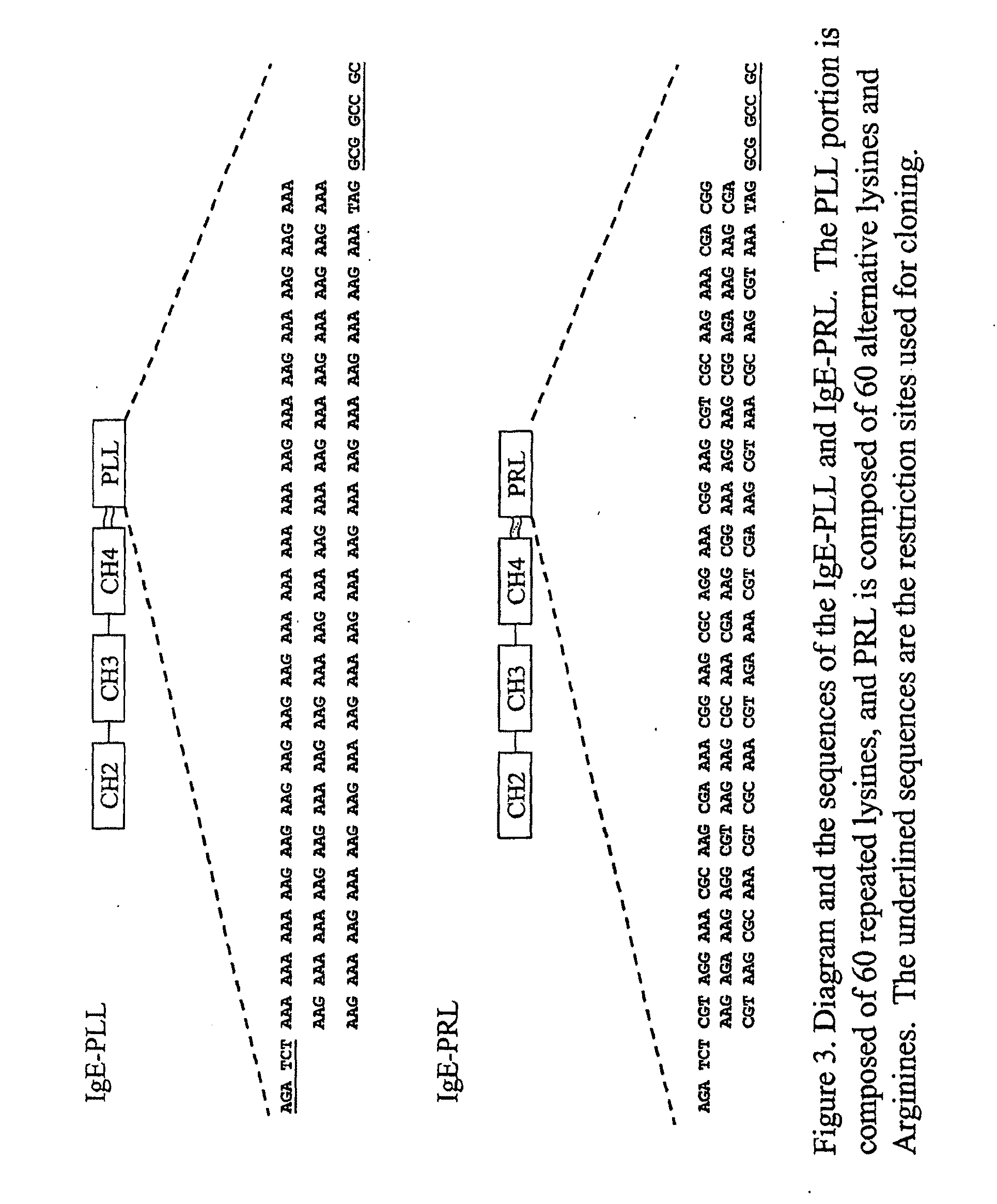
Ige directed DNA vaccination
InactiveUS20110020373A1Avoid symptomsFusion with DNA-binding domainAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDiseaseAntigen
This invention is directed to a novel approach for focusing and expressing DNA vaccinates in Antigen Presenting Cells (APCs) mediated through targeting IgE receptors (FcεRs) on APC and driving DNA expression through provision of an APC specific regulatory element This vaccine can be used in the prevention or treatment of allergic disease.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for generation of immunoglobulin sequences
ActiveUS20100173799A1Strong specificityAcceptable breadthLibrary screeningImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDNA vaccinationAntigen
The present invention relates to a method for generating immunoglobulin sequences against cell-associated antigens, more particularly, antigens that are membrane-anchored. The invention also provides immunoglobulin sequences obtainable by the method of the invention. Specifically, the present invention relates to the generation of immunoglobulin sequences by use of DNA vaccination. More specifically, the present invention relates to generation of immunoglobulin sequences in camelids, preferably directed against cell-associated antigens, in particular antigens with multiple transmembrane spanning domains, including GPCRs and ion channels, by DNA vaccination. Furthermore, the present invention relates to said immunoglobulin sequences against cell-associated antigens, more particularly, antigens that are membrane-anchored, such as e.g. GPCRs and ion channels, more preferably ion channels.
Owner:ABLYNX NV
Vaccine
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative fused to an additional HIV protein selected from a non-structural protein or capsid protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative thereof. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is gp120 and preferred fusions include one or more of HIV Nef, Gag, RT or Tat. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is non-glycosylated in mammalian cells.
Owner:GLAXO GRP LTD
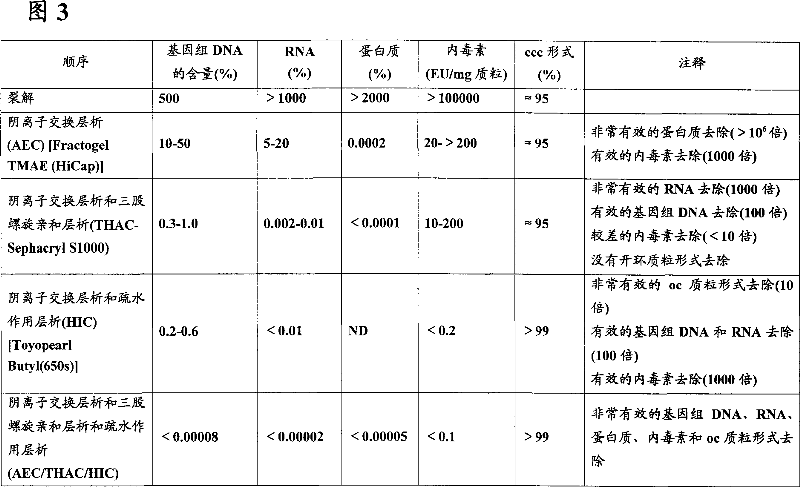
Method for purifying plasmid DNA
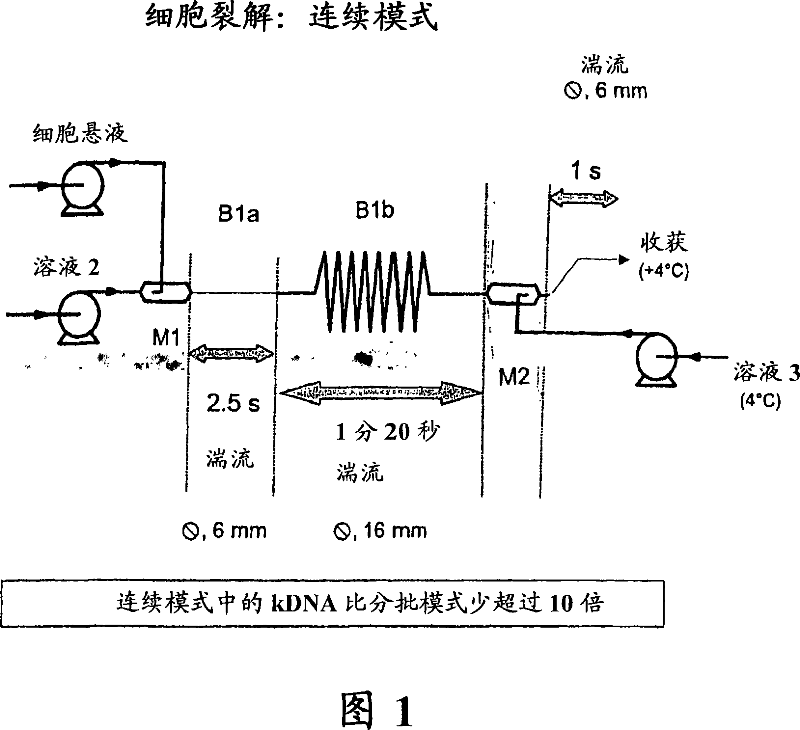
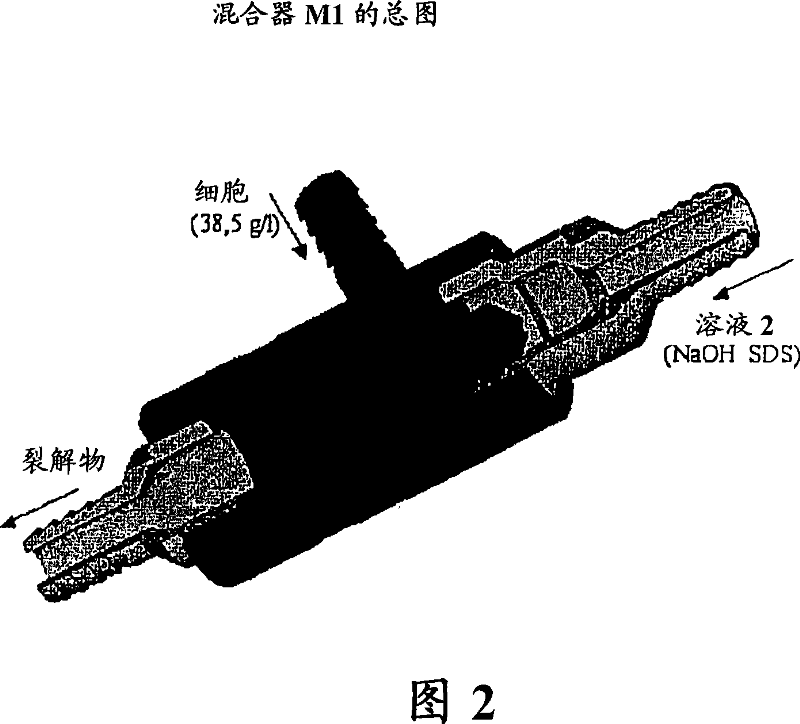
InactiveCN101040041AQuality improvementMicroorganism lysisVector-based foreign material introductionDNA vaccinationRoom temperature
The invention relates to plasmid DNA liquid formulations that are stable and stays un-degraded at +4 DEG C to room temperature for long periods of time, and are thus useful for storage of plasmid DNA that are used research, plasmid-based therapy, such as DNA vaccine and gene therapy. The present invention also relates to a method of preserving plasmid DNA in a stable form over time at +4 DEG C to room temperature. The present invention also relates to stable plasmid DNA liquid compositions for use in a method of treatment of the human or animal body by plasmid-based therapy, such as DNA vaccination or gene therapy.
Owner:申特莱恩公司
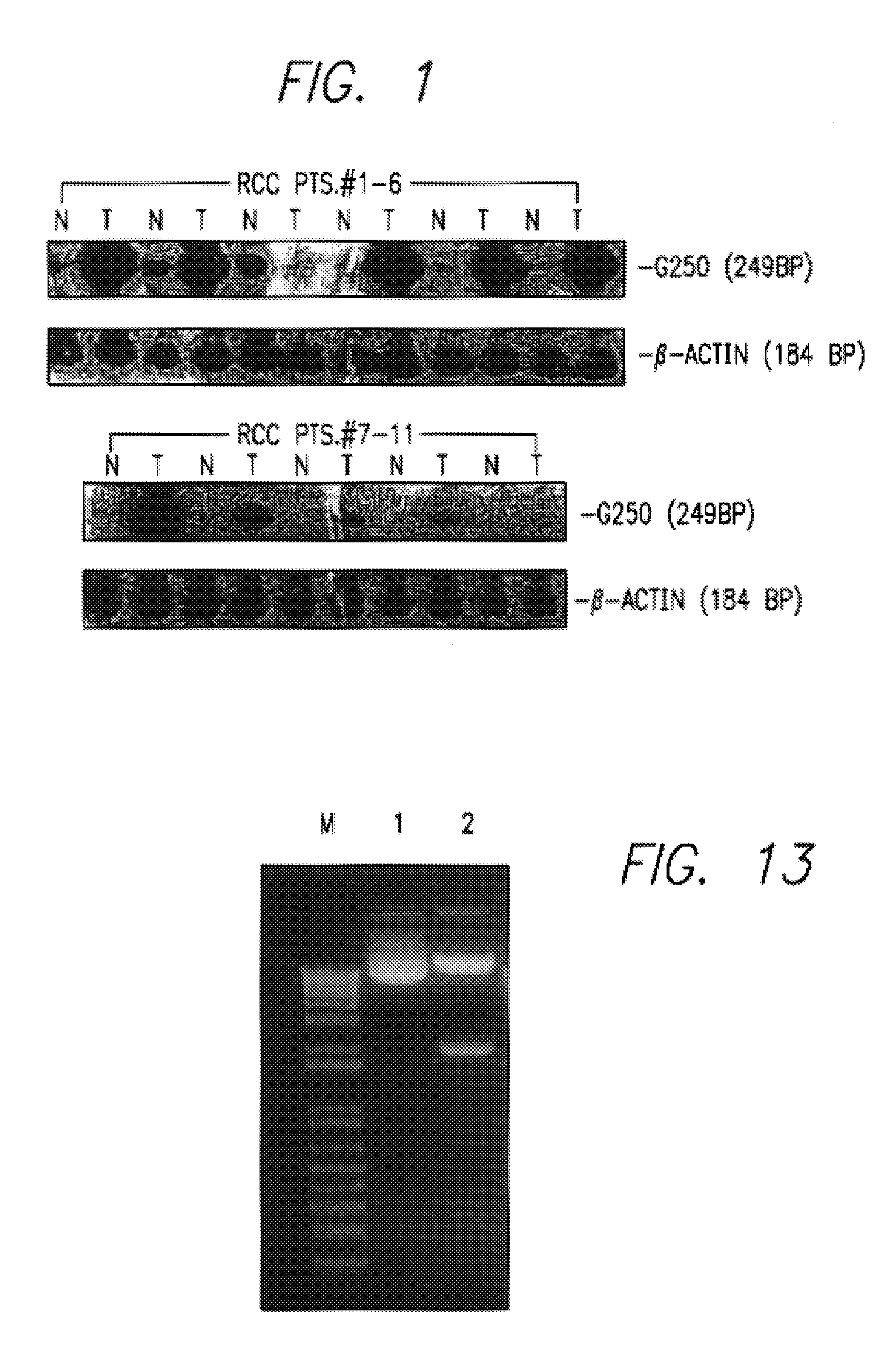
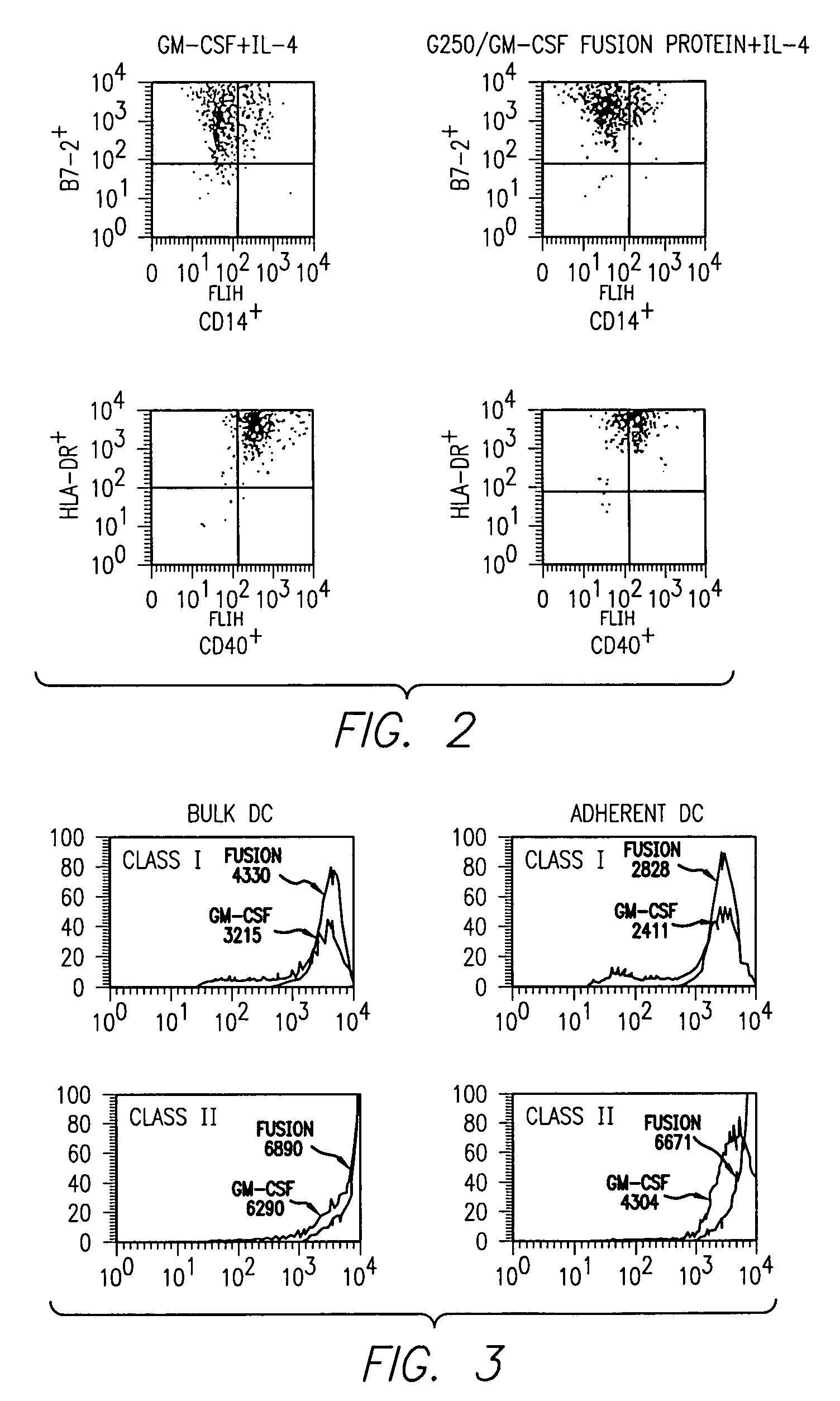
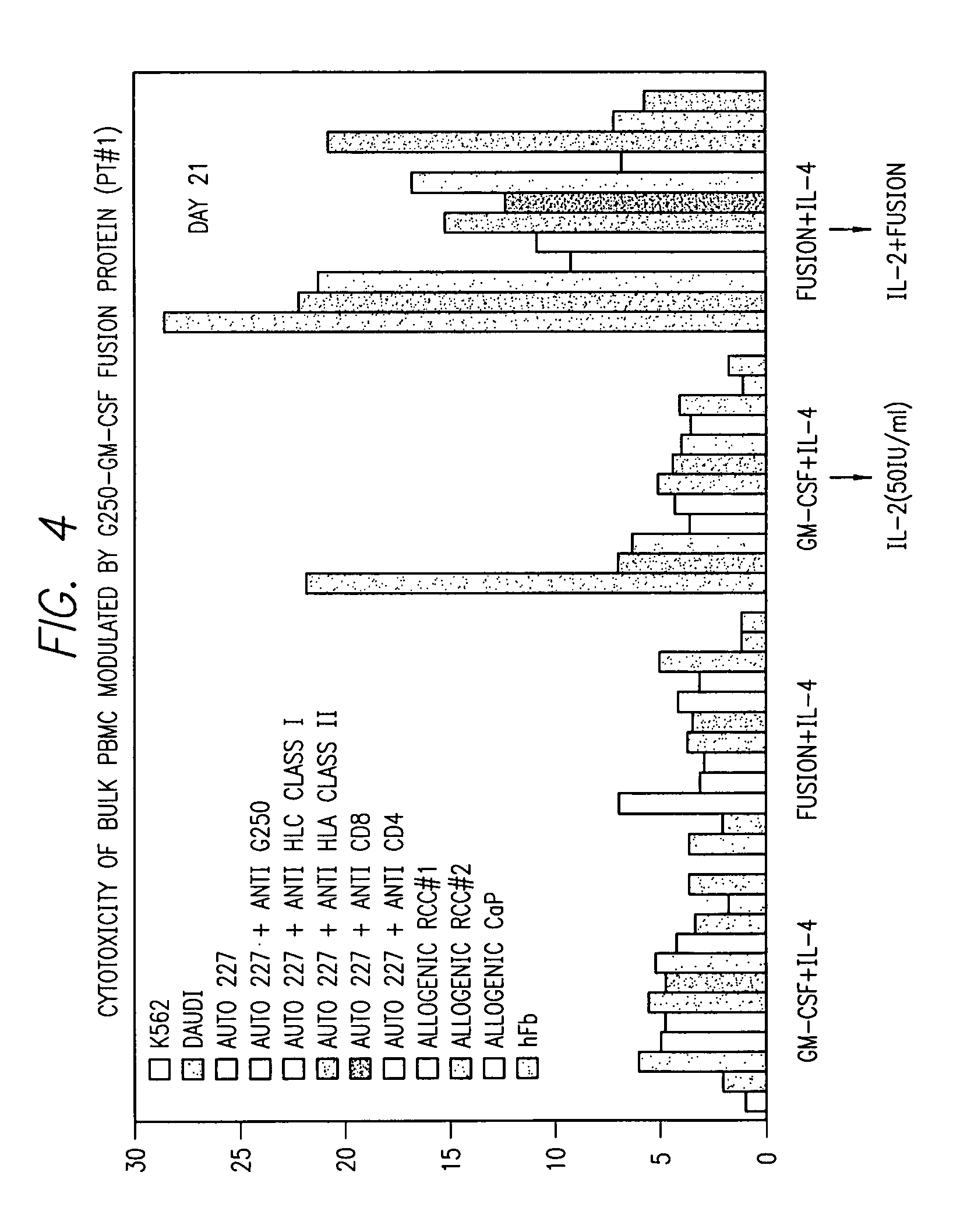
Kidney-specific tumor vaccine directed against kidney tumor antigen G-250
InactiveUS7572891B2Easy to addImprove stabilityPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismVaccinationImmunogenicity
This invention provides an anti-cancer immunogenic agent(s) (e.g. vaccines) that elicit an immune response specifically directed against renal cell cancers expressing a G250 antigenic marker. Preferred immunogenic agents comprise a chimeric molecule comprising a kidney cancer specific antigen (G250) attached to a granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF). The agents are useful in a wide variety of treatment modalities including, but not limited to protein vaccination, DNA vaccination, and adoptive immunotherapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Immuno-modulating effects of chemokines in DNA vaccination
InactiveUS7384641B2Increase speedReduce in quantityPeptide/protein ingredientsViral antigen ingredientsAntigenDNA vaccination
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND BIOTECH INST
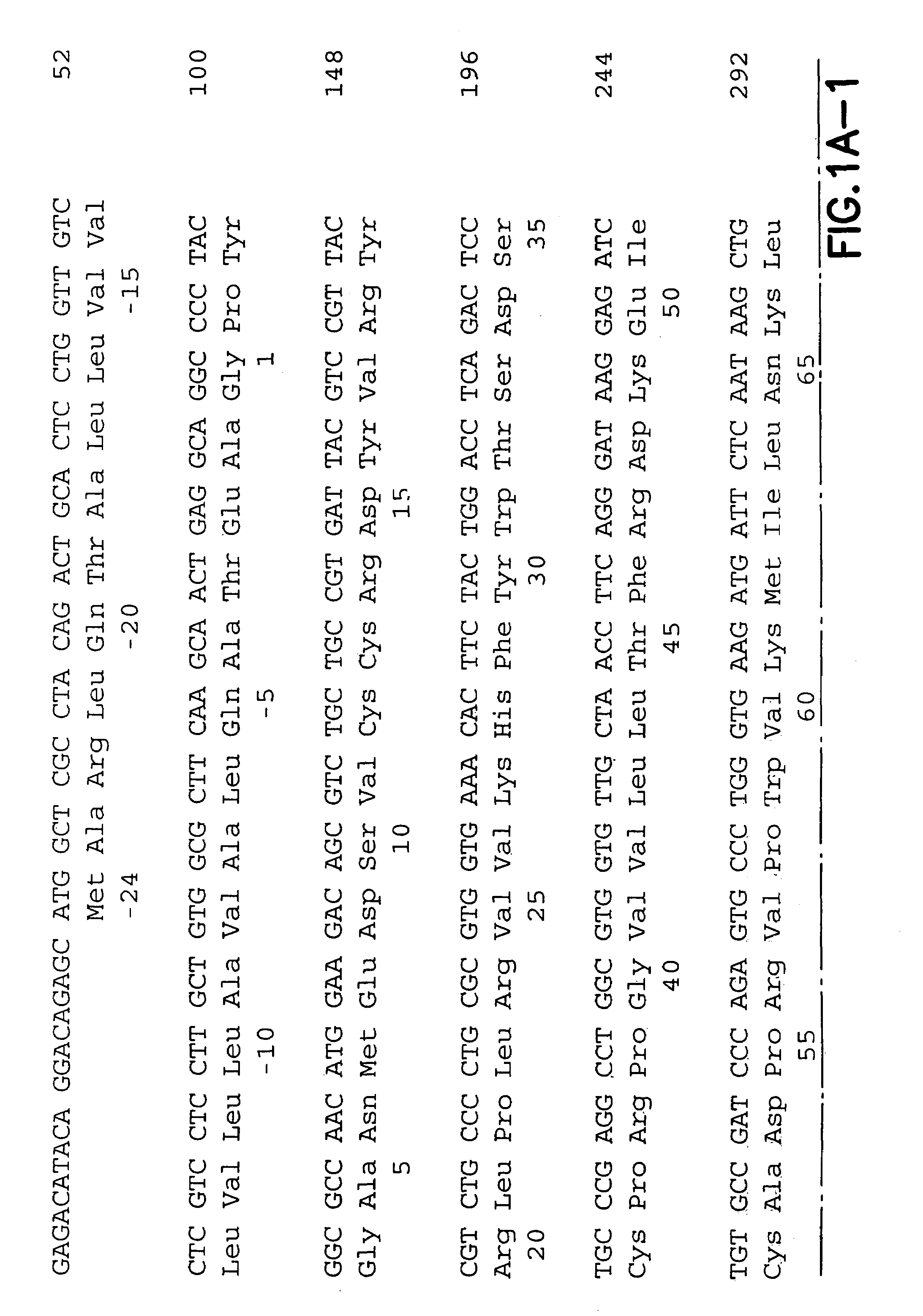
Chimeric lyssavirus nucleic acids and polypeptides
InactiveUS7235245B2Improve the level ofImprove protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseDNA vaccinationEpitope
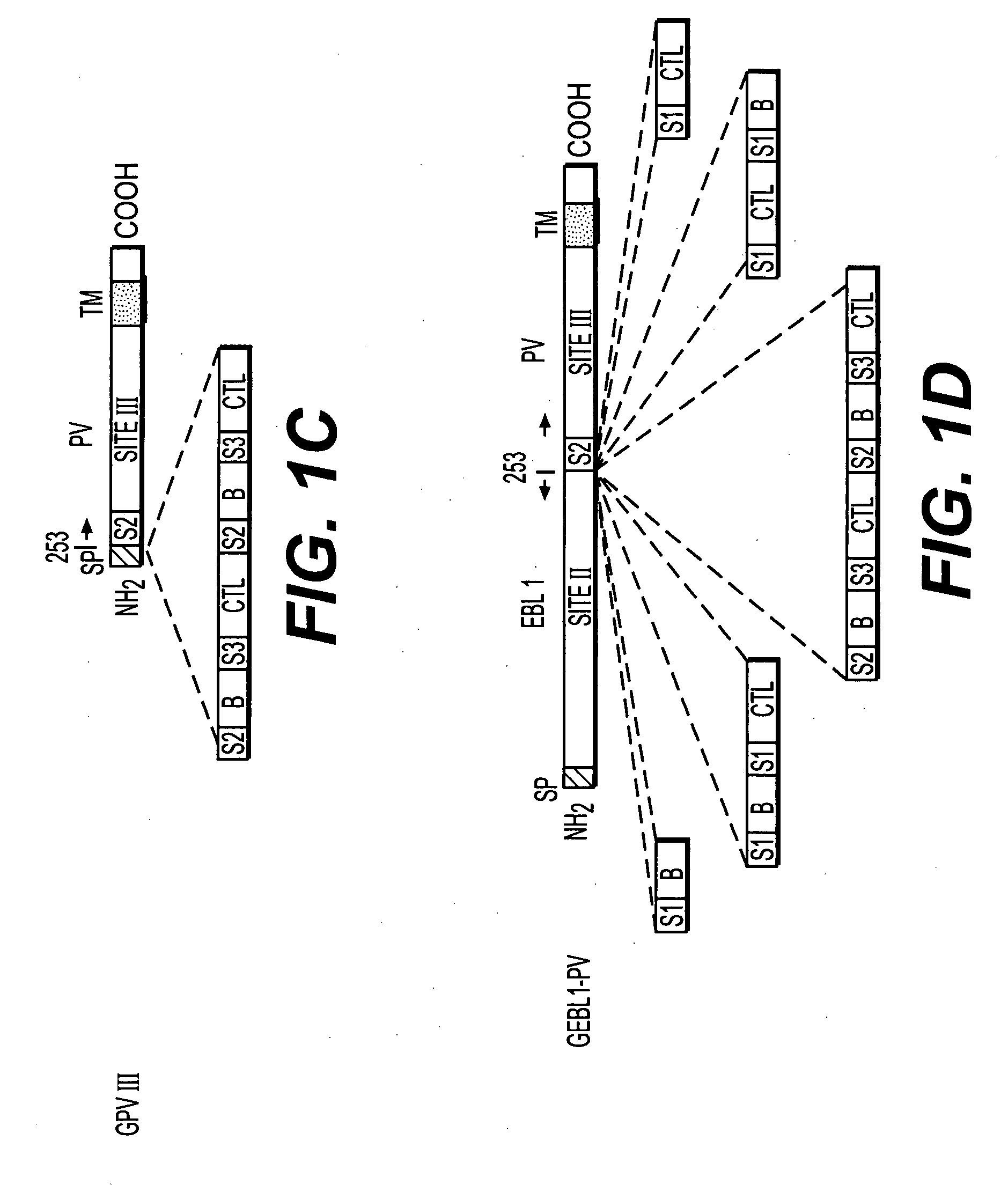
The present invention provides chimeric nucleic acids, preferably contained on an expression vector, that encode chimeric immunogenic polypeptides. The nucleic acids encode at least site III of a lyssavirus glycoprotein, which has been found to improve the immunogenicity of lyssavirus epitopes for protection from rabies. The chimeric nucleic acids and proteins can also contain antigenic determinants for epitopes other than those of lyssavirus. Thus, the invention provides chimeric nucleic acids and polypeptides that elicit a strong immune response to multiple antigens. Use of the methods of the present invention permits DNA vaccination without the need to supply multiple antigens on separate DNA molecules.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Vaccine
InactiveUS20070042977A1Reduce and prevent glycosylationGlycosylation can be reduced and preventedAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsDNA vaccinationHeterologous
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative, which is non-glycosylated when expressed in a mammalian target cell, operably linked to a heterologous promoter. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule, such as gp120 or gp140 or gp160, lacks a functional secretion signal. It may be fused to additional HIV proteins such as Nef, Gag, RT or Tat.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
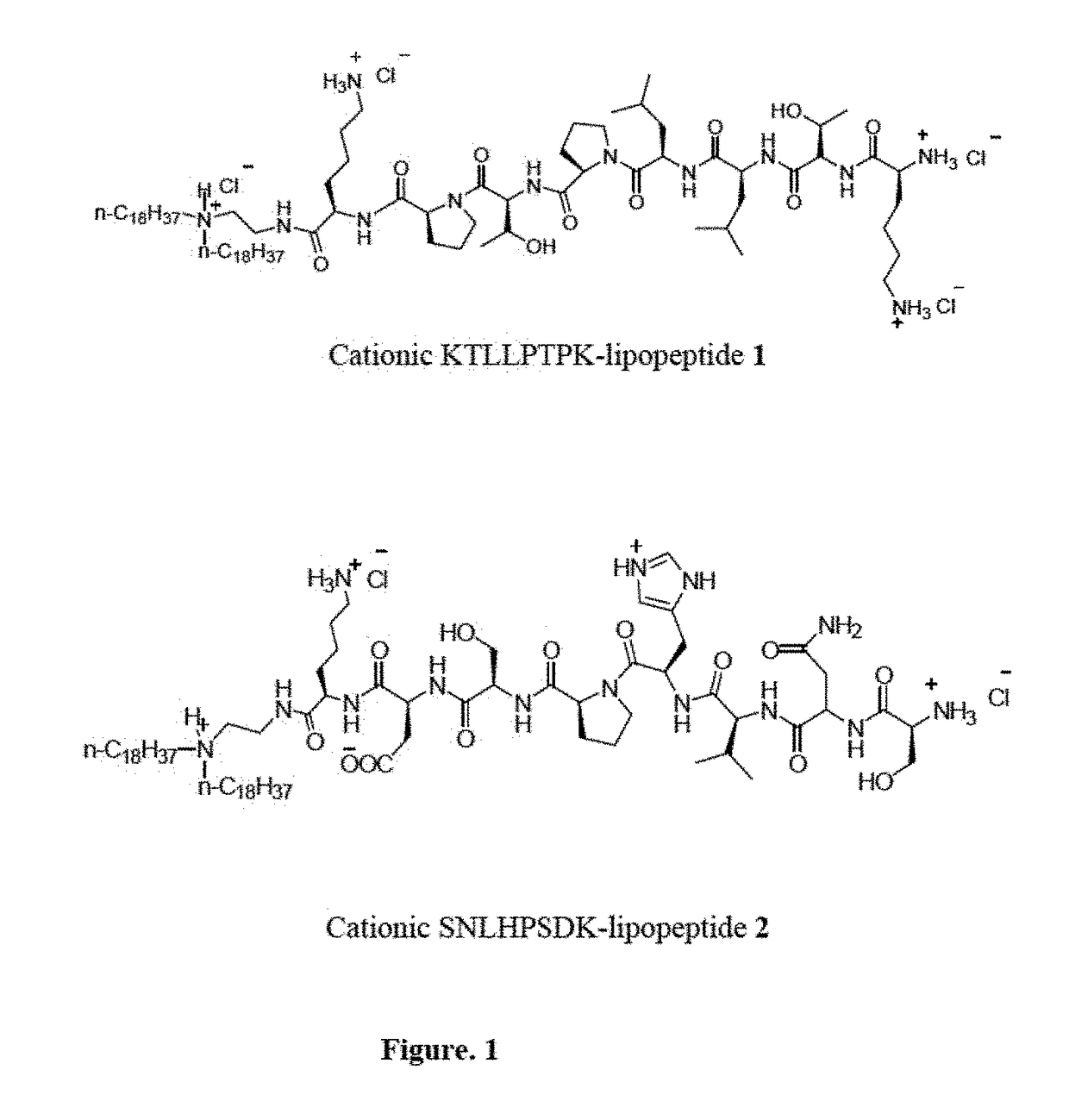
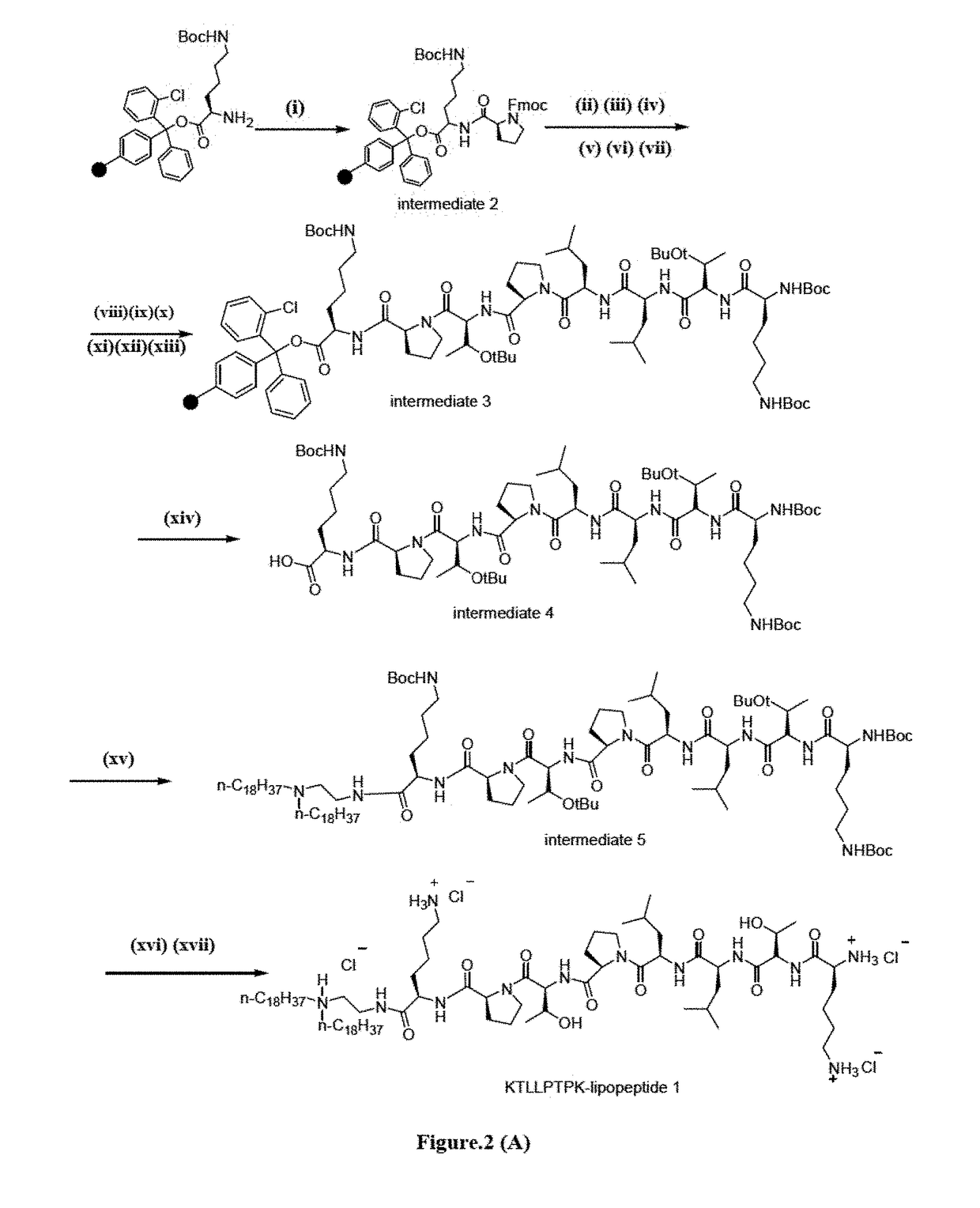
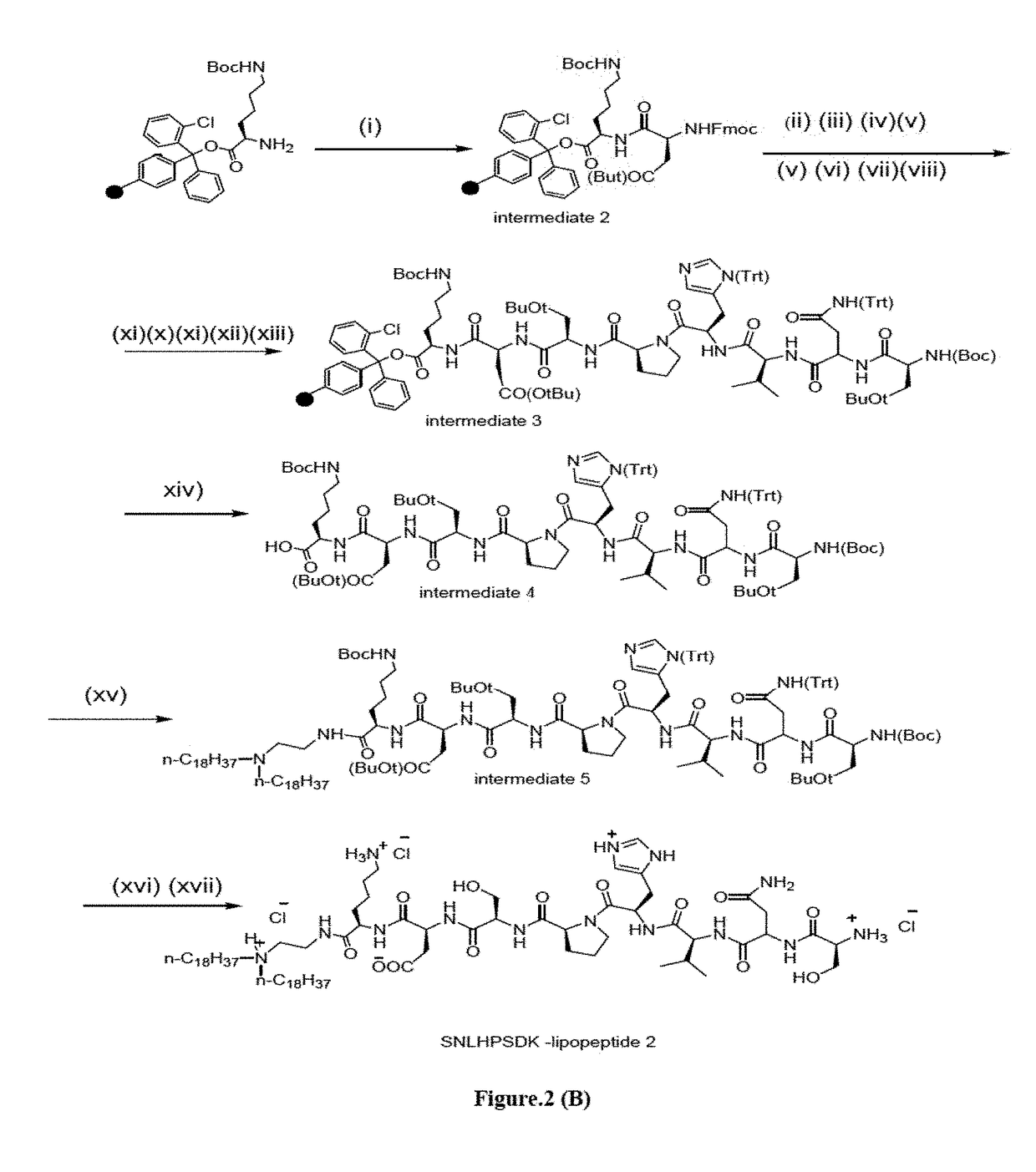
Method for regressing pancreatic tumor by a liposomal formulation along with DNA vaccines
The present invention discloses a Plectin-1 receptor targeting novel cationic KTLLPTPK-lipopeptide. The present invention further discloses a liposomal formulation comprising the cationic KTLLPTPK-lipopeptide, at least two co-lipids, therapeutic agents and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides a method for regressing established pancreatic tumors comprising administering therapeutically effective amount of the liposomal formulation with the therapeutic agents in combination with targeted genetic immunization (DNA vaccination) i.e. by immunizing mice with electrostatic complexes (direct in-vivo DC-targeting cationic liposomes) of DNA vaccines encoding mesothelin (p-CMV-MSLN).
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES +1
GENES OF IL-12p40 SUBUNIT MUTATED FOR IMPROVING THE ACTIVITY OF IL-12 AND USE THEREOF FOR DNA VACCINE ADJUVANT
InactiveUS20070269408A1Reduce secretionInhibition of activationVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsWhite blood cellMalaria
The present invention relates to the IL-12p40 subunit mutant gene which can produce IL-12 (interleukin 12) of human and mouse origin with high activity, the expression vector including above mutant gene and the use of them to DNA vaccine adjuvant. Particularly, it relates to IL-12p40 mutant gene which inhibits the secretion of IL-12p40 but normally secretes active IL-12p70 by making mutation at Asn-222 (human) or Asn-220 (mouse) amino acid of IL-12p40, which acts as a competitive inhibitor of active form of IL-12, IL-12p70. Therefore, the IL-12p40 mutant gene of the present invention can be useful for DNA vaccination and gene therapy against various diseases, for example, AIDS, hepatitis C or hepatitis B, cancer, influenza, tuberculosis and malaria, which essentially require cellular immune responses for their therapy.
Owner:GENEXINE INC
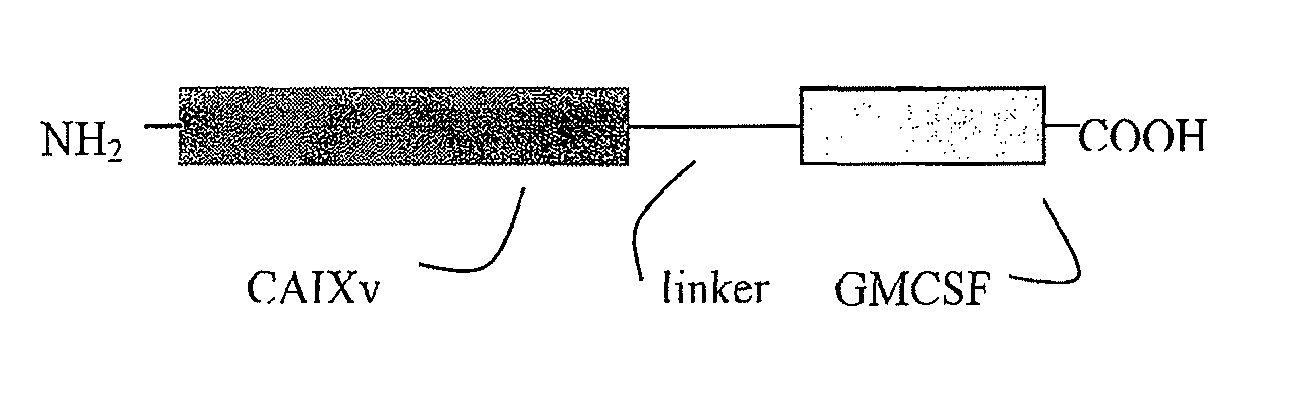
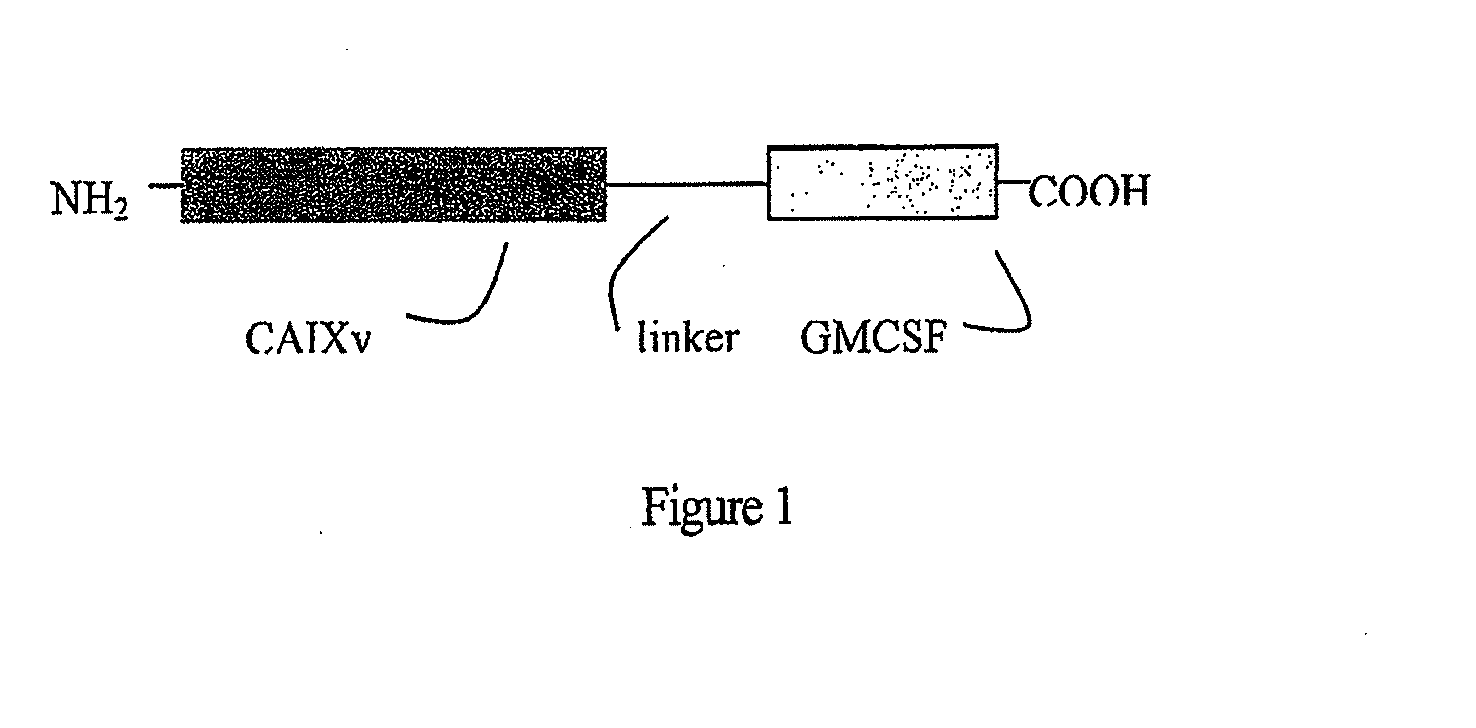
Fusion molecule based on novel TAA variant
This invention provides novel carbonic anhydrase (CAIX) nucleic acid and peptide sequences, as well as related methods and compositions, including anti-cancer immunogenic agent(s) (e.g. vaccines and chimeric molecules) that elicit an immune response specifically directed against cancer cells expressing a CAIX antigenic marker. The novel CAIX variant and related compositions are useful in a wide variety of treatment modalities including, but not limited to protein vaccination, DNA vaccination, and adoptive immunotherapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Synthetic gene
InactiveUS20090274726A1Enhance immune responseImprove responsivenessAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderDiseaseNucleotide
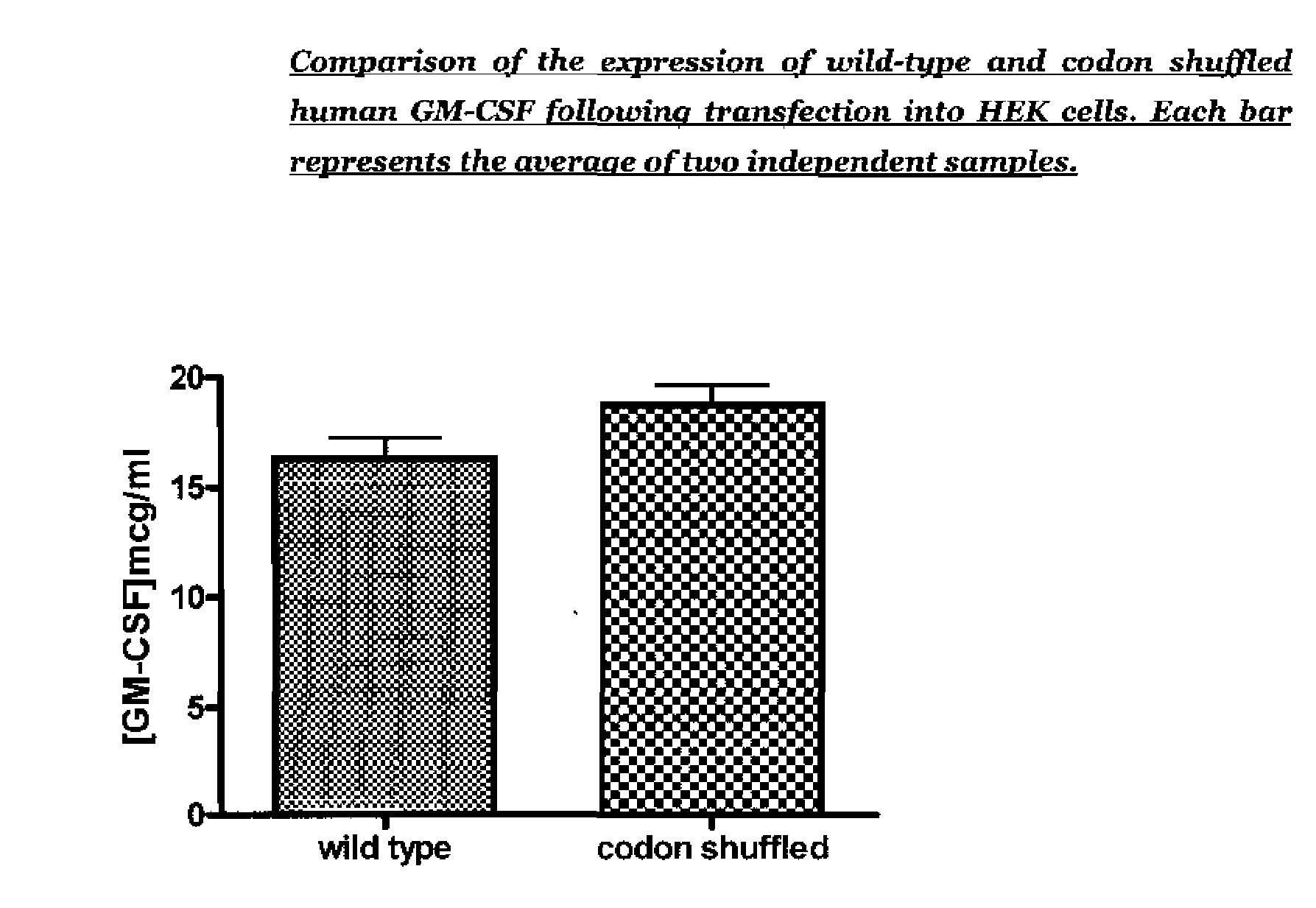
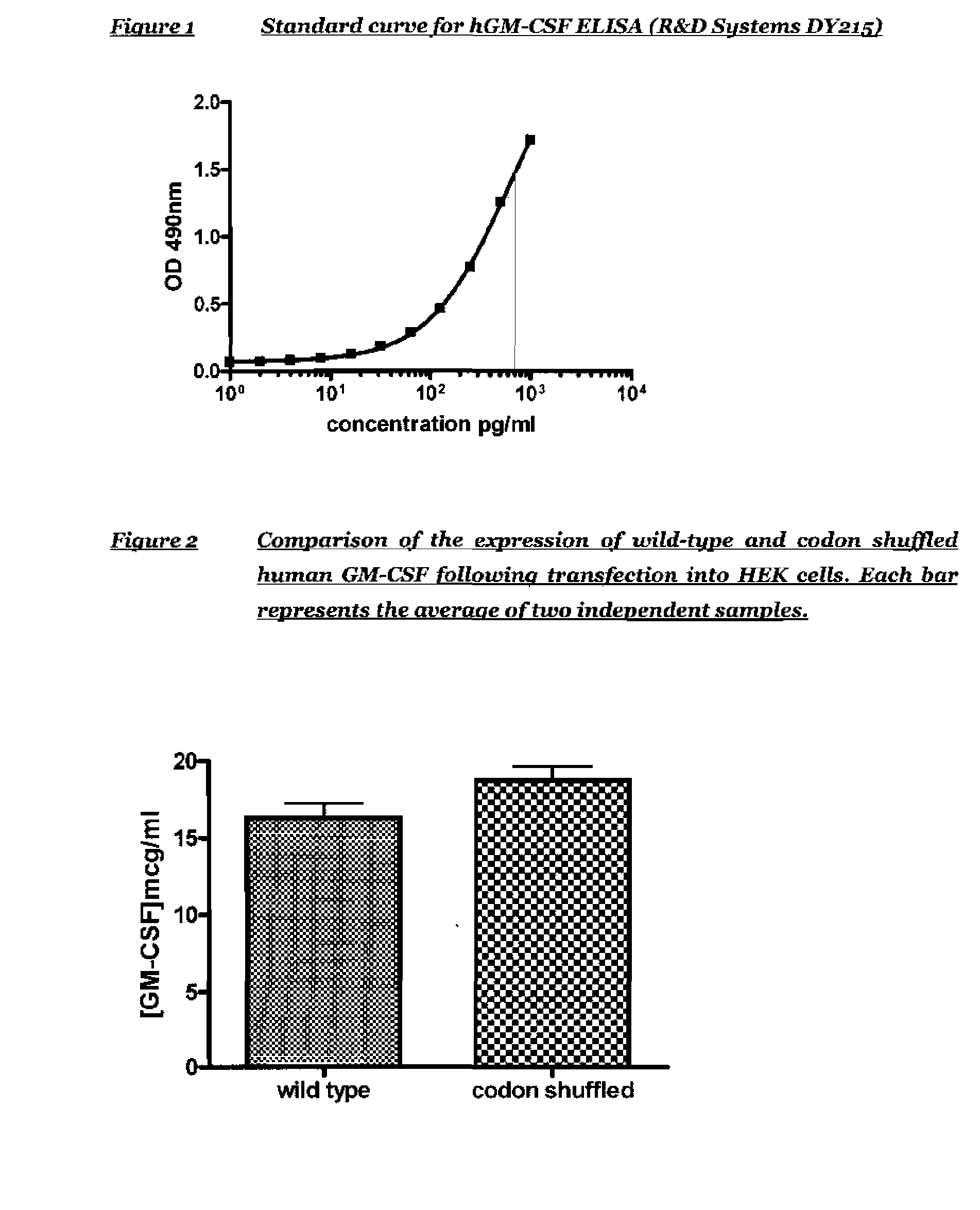
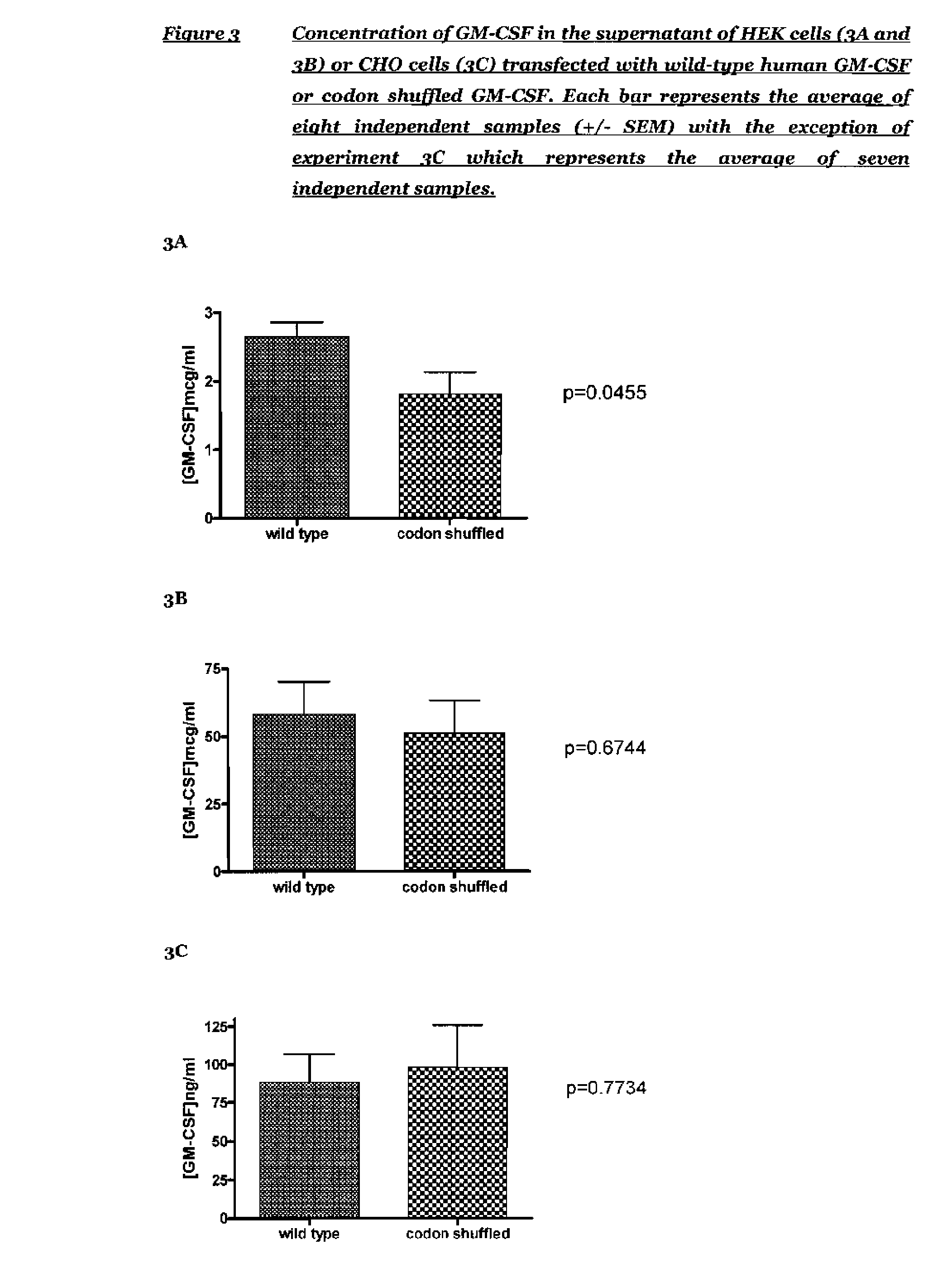
The present invention relates to synthetic genes, processes for designing said synthetic genes and their uses in gene therapy and improved DNA vaccination. The novel synthetic genes and processes are codon shuffled so that they have reduced homology relative to a naturally occurring gene encoding the same protein without altering the overall codon usage frequency of the gene. In particular the present invention relates to improved polynucleotides and methods for the treatment or prevention of disease comprising codon-shuffled GM-CSF nucleic acid sequences. Nucleic acid vaccines of the present invention may comprise a combination of a nucleotide sequence encoding codon-shuffled GM-CSF, a nucleotide encoding an antigen against which it is desired to raise an immune response and a toll-like receptor (TLR) agonist.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
Preparation method of anti-human Nogo-66 receptor protein vaccine and application thereof
InactiveCN101288771APromote regenerationPromote functional recoveryNervous disorderAntibody ingredientsEscherichia coliEukaryotic plasmids
The invention provides a method for preparing antihuman Nogo-66 receptor protein vaccine. An hNgR gene in full size is obtained by the PCR amplification from human neurobalstoma (SK-N-SH) cDNA. The amplified segment is inserted in a cloning vector and is sub-cloned to an expression vector pET28a (+) containing six His labels to obtain a recombinant expression plasmid pET28a-NgR. The recombinant plasmid is transformed into a coli expression strain BL21 (DE3) for the induced expression to obtain hNgR protein. By closing the effect of NgR and blocking the effect of inhibitory factor, the NgR protein vaccine can promote the regeneration of neurons axon after the spinal cord injury, can reduce the tissue necrosis in a damage zone, can promote the functional recovery of the injured spinal cord and express that the NgR protein vaccine is provided with a potential value for treating the spinal cord injury. The defect that exogenous biological agent can be easily eliminated by an autoimmune system is avoided. In addition, the characters that the cellular immunity is mainly induced after the DNA vaccination of NgR and only few individuals can induce humoral immunity are overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAOTONG UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Chimeric lyssavirus nucleic acids and polypeptides
InactiveUS20080206282A1Improve the level ofImprove protectionSsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseDNA vaccinationEpitope
The present invention provides chimeric nucleic acids, preferably contained on an expression vector, that encode chimeric immunogenic polypeptides. The nucleic acids encode at least site III of a lyssavirus glycoprotein, which has been found to improve the immunogenicity of lyssavirus epitopes for protection from rabies. The chimeric nucleic acids and proteins can also contain antigenic determinants for epitopes other than those of lyssavirus. Thus, the invention provides chimeric nucleic acids and polypeptides that elicit a strong immune response to multiple antigens. Use of the methods of the present invention permits DNA vaccination without the need to supply multiple antigens on separate DNA molecules.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Vaccine
InactiveUS20060142221A1Reduce removalReduce and prevent glycosylationAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsGenetic material ingredientsDNA vaccinationHIV Proteins
The invention relates to polynucleotides for DNA vaccination which polynucleotides encode an HIV envelope protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative fused to an additional HIV protein selected from a non-structural protein or capsid protein or fragment or immunogenic derivative thereof. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is gp120 and preferred fusions include one or more of HIV Nef, Gag, RT or Tat. Preferably the HIV envelope molecule is non-glycosylated in mammalian cells.
Owner:GLAXO GROUP LTD
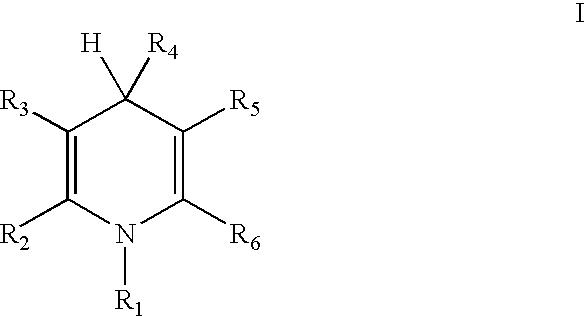
Cationic amphiphilic 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives useful for delivery of nucleotide containing compounds
InactiveUS20030064954A1Safe and efficientHigh transfection efficiencyBiocideOrganic chemistryDNA vaccinationDihydropyridine
The present invention discloses amphiphilic 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives useful for the preparation of a composition for delivering nucleotide containing compounds into a target cell and / or its nucleus. Said composition comprises 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives having a good DNA condensing capacity and capability of self-association. Also disclosed are composition comprising said derivatives complexed with nucleotide containing compounds as well methods for the producing of said complexes. The invention is also related to the use of said 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives for manufacturing systems for delivering nucleotide containing compounds useful in gene therapy and DNA vaccination.
Owner:SPONDULI SERVICES
Use of immidazoquinolinamines as adjuvants in DNA vaccination
InactiveUS20110002953A1Enhance immune responseOrganic chemistryGenetic material ingredientsDNA vaccinationAdjuvant
The present invention relates to the use of a 1H-imidazo[4,5-c]quinolin-4-amine derivative as an adjuvant for use with nucleic acid vaccination.
Owner:THOMSEN LINDY LOUISE +2
Immunomodulatory peptides derived from heat shock proteins and uses thereof
InactiveUS7301005B2Modulate immune responseReduction and inhibition of inflammatory responseFungiBacteriaArthritisT cell
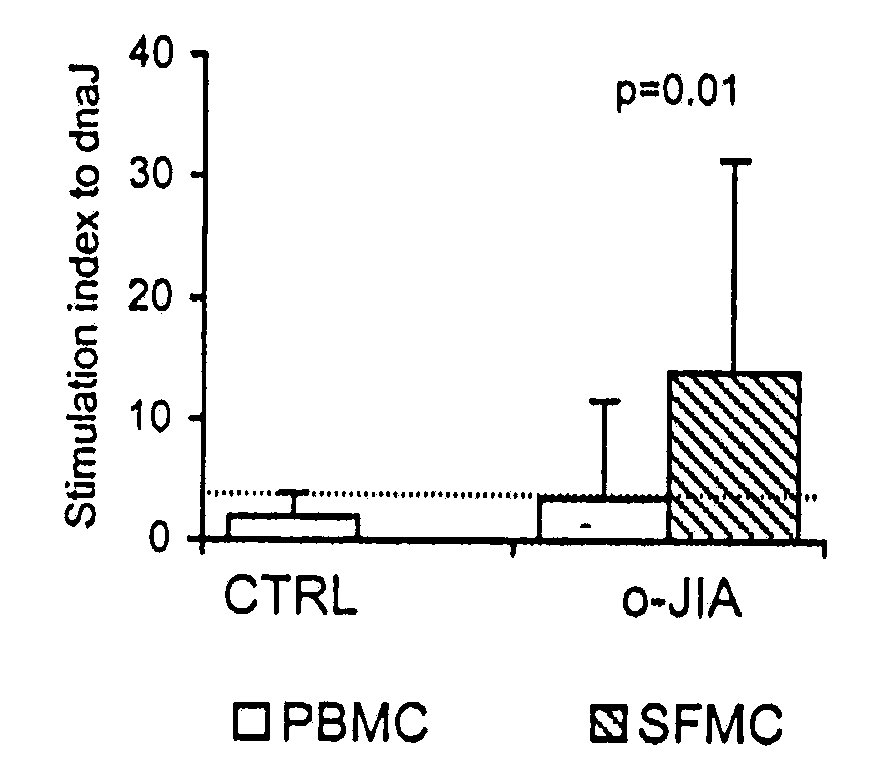
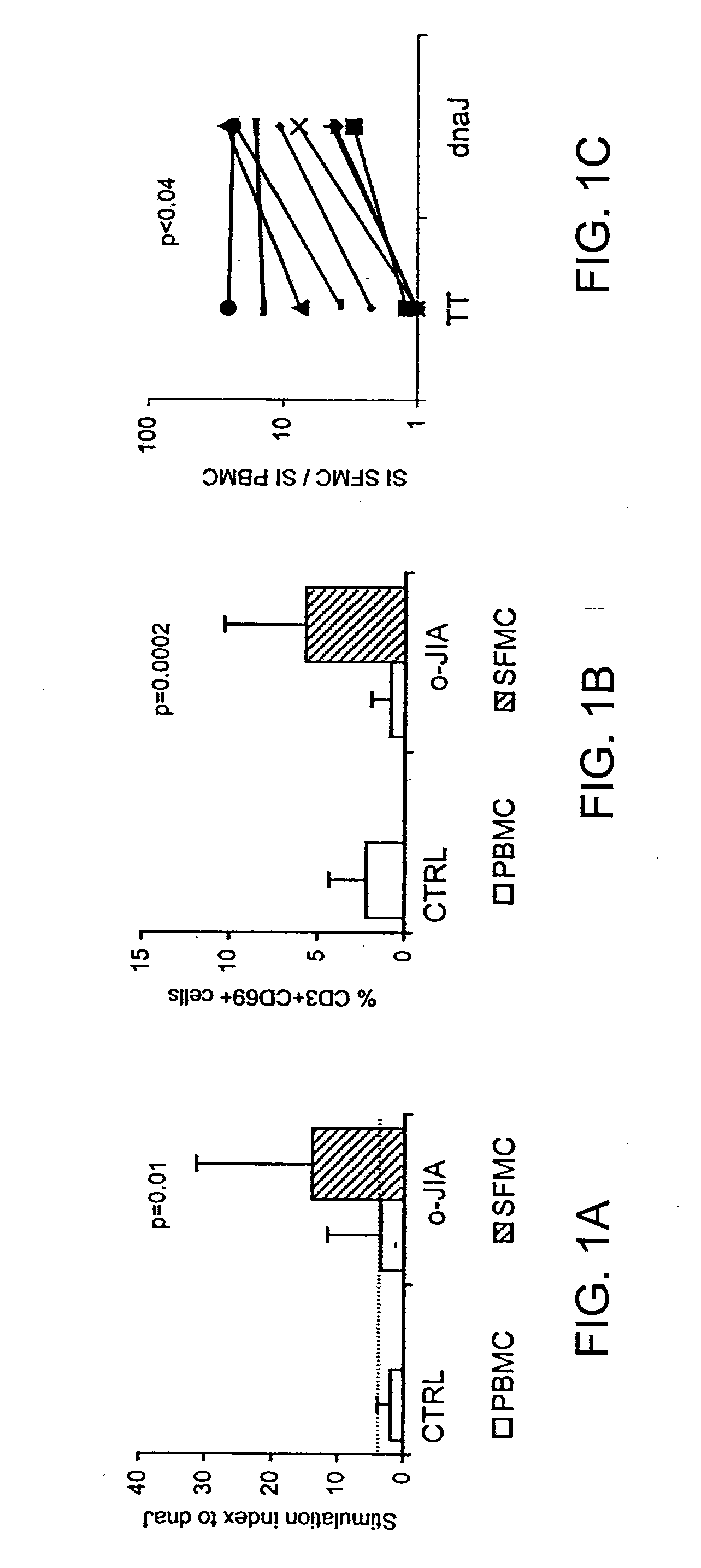
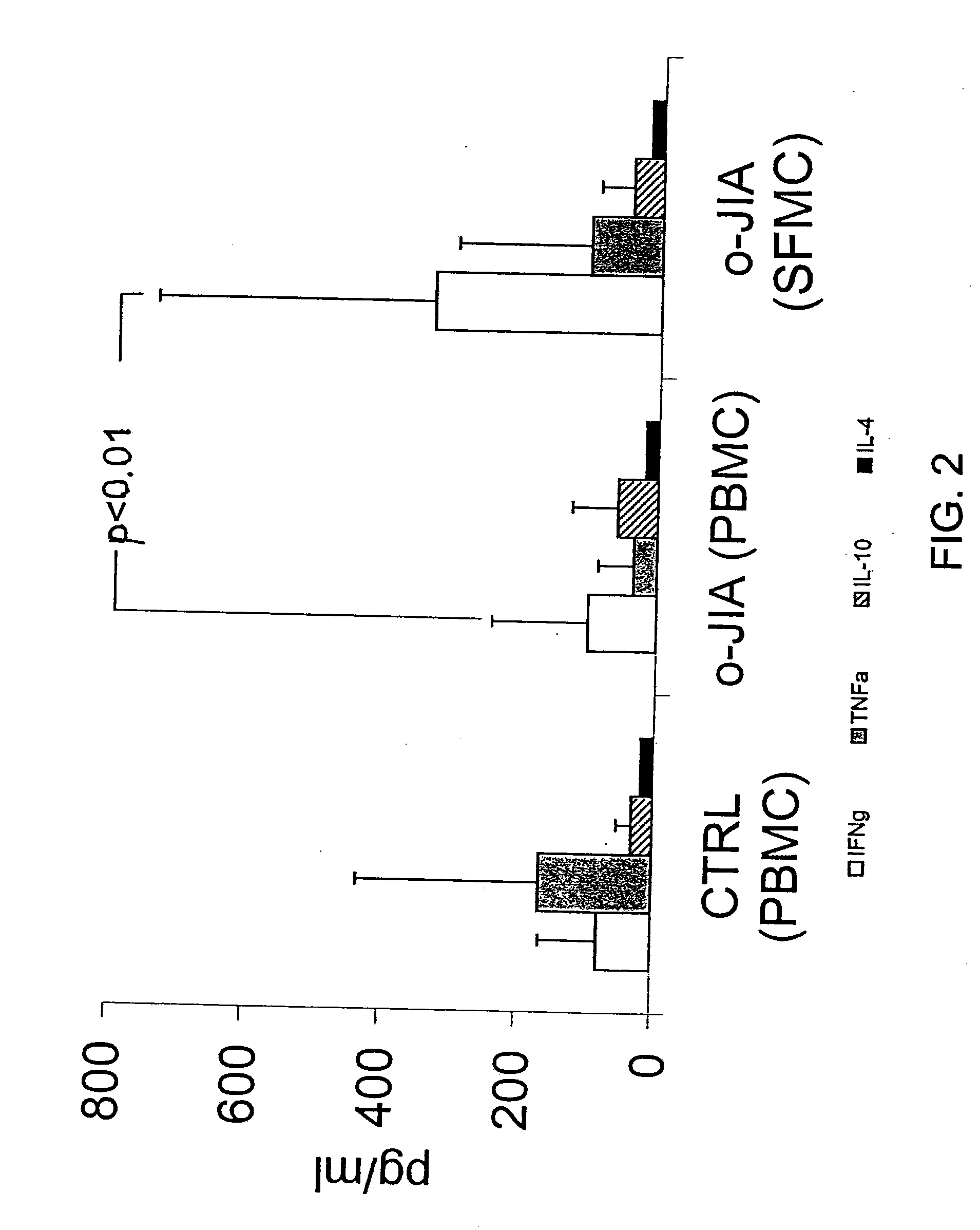
A method of modulating an immune response in a subject is disclosed. The invention is based on the discovery that an effective therapeutic strategy for ameliorating the inflammation-related symptoms of an immune-mediated disease, such as arthritis, can be achieved by modulation of the underlying immune response itself, rather than by merely addressing the resulting inflammation. This strategy can be used to regulate the inflammatory response and is applicable to a variety of contexts in which immune modulation is desired, such as mucosal tolerization, DNA vaccination, anergy induction, active immunization, and ex vivo modulation of antigen-specific T cells. In one embodiment, the method comprises administering to the subject a bacterial dnaJ peptide or a human homolog or a non-homologous human isoform thereof.
Owner:ALBANI SALVATORE +3
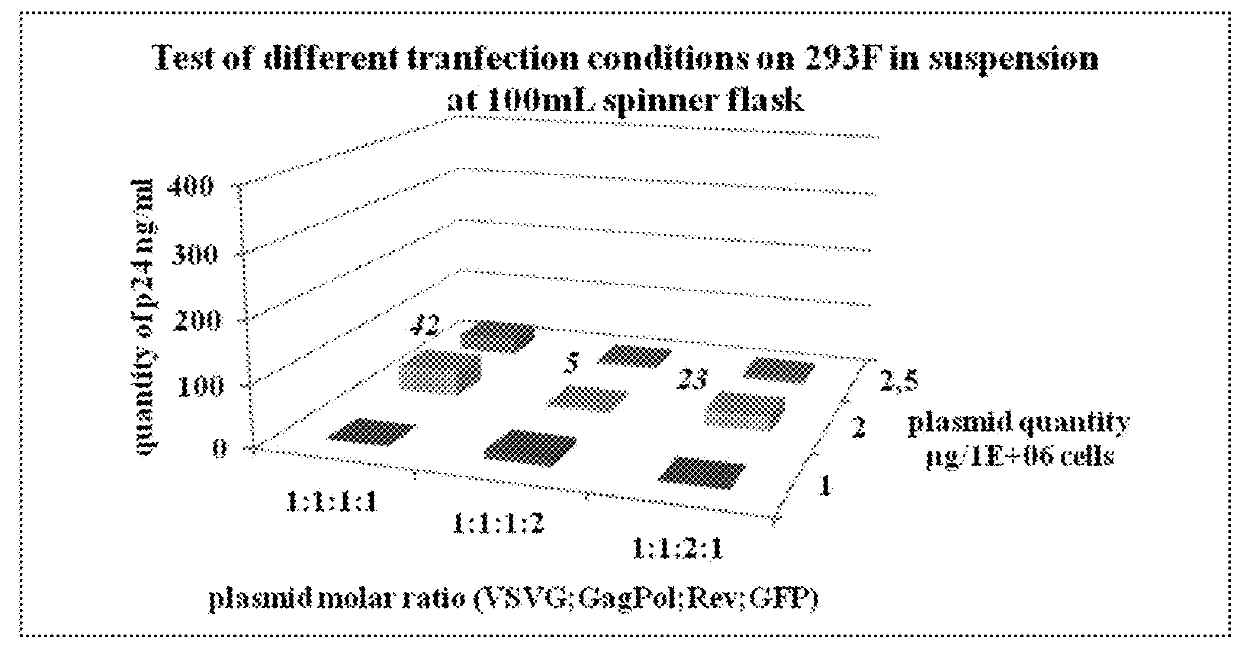
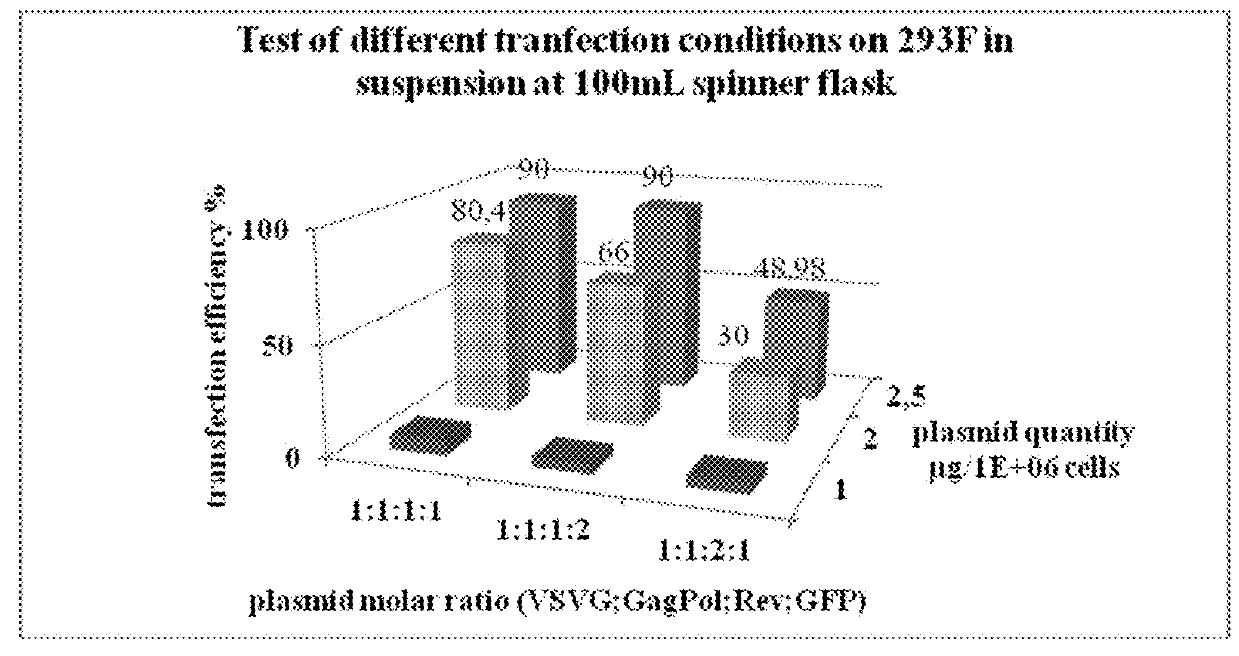
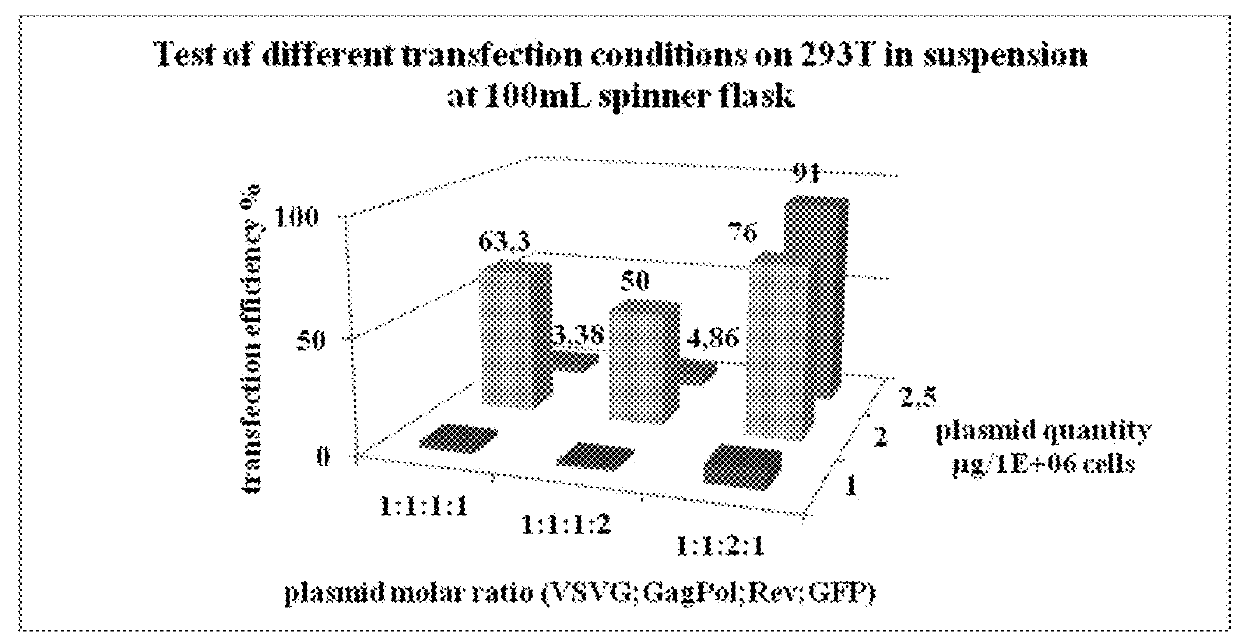
Scalable lentiviral vector production system compatible with industrial pharmaceutical applications
InactiveUS20190211360A1Improve the level ofHigh scaleRecovery/purificationVector-based foreign material introductionDNA vaccinationClinical trial
The present invention relates to the industrialization of the production of recombinant lentiviral vectors in order to manufacture sufficient materials for therapeutic applications such as gene therapy and / or DNA vaccination, for use in clinical trials and / or commercial use.
Owner:GENETHON
Fusion molecule based on novel taa variant
ActiveUS20130230483A1Peptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsDNA vaccinationCancer cell
This invention provides novel carbonic anhydrase (CAIX) nucleic acid and peptide sequences, as well as related methods and compositions, including anti-cancer immunogenic agent(s) (e.g. vaccines and chimeric molecules) that elicit an immune response specifically directed against cancer cells expressing a CAIX antigenic marker. The novel CAIX variant and related compositions are useful in a wide variety of treatment modalities including, but not limited to protein vaccination, DNA vaccination, adoptive immunotherapy.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
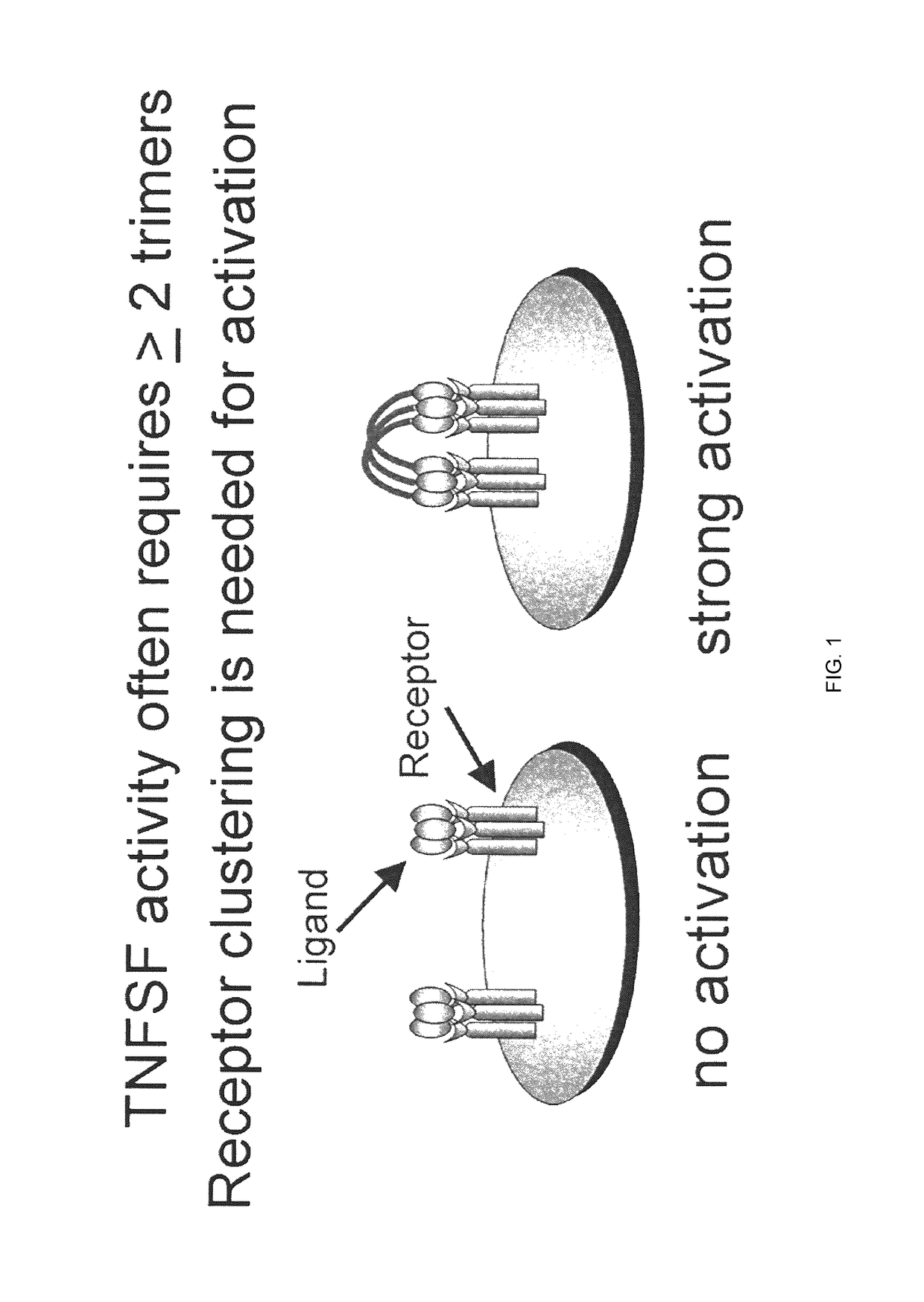
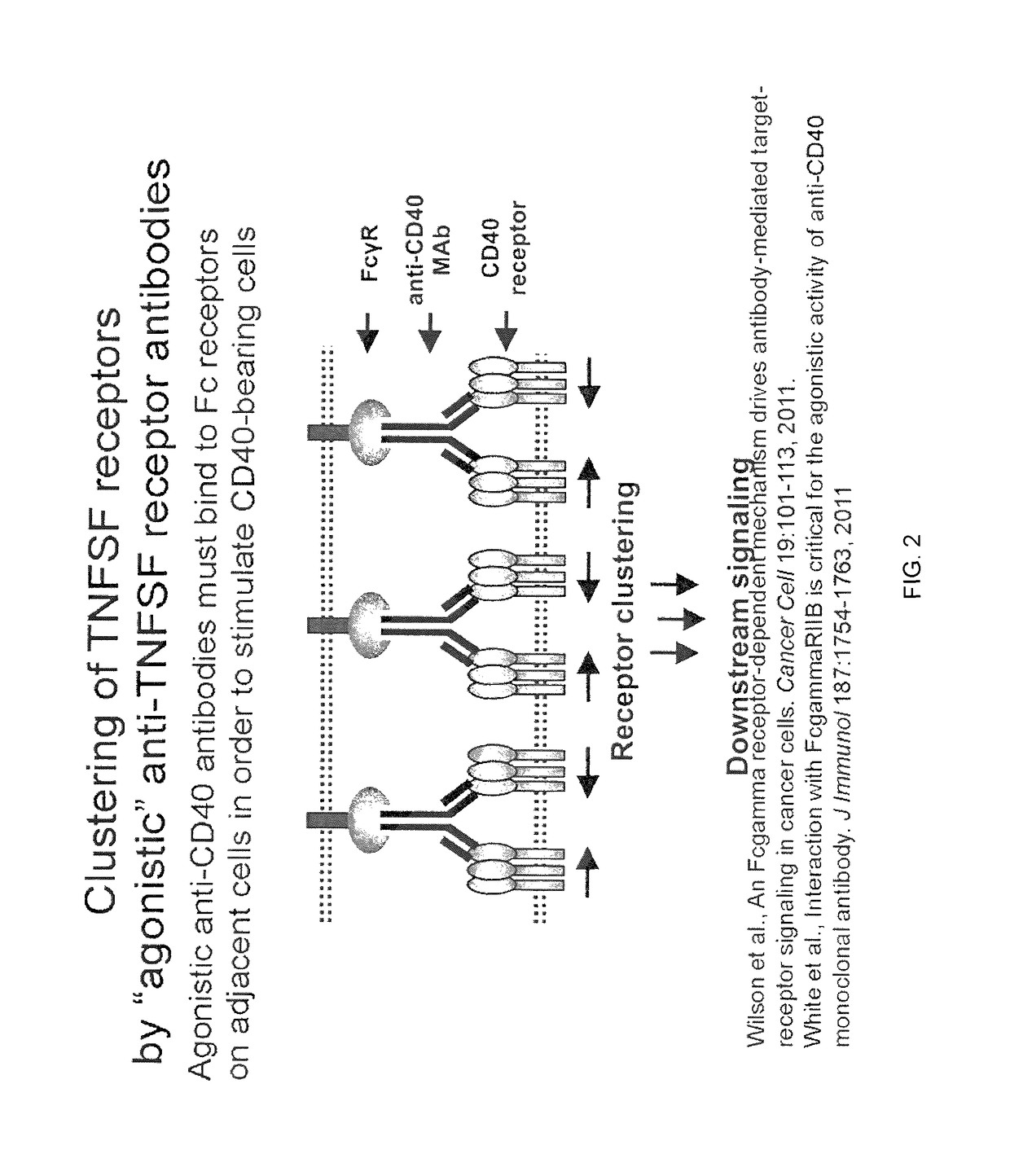
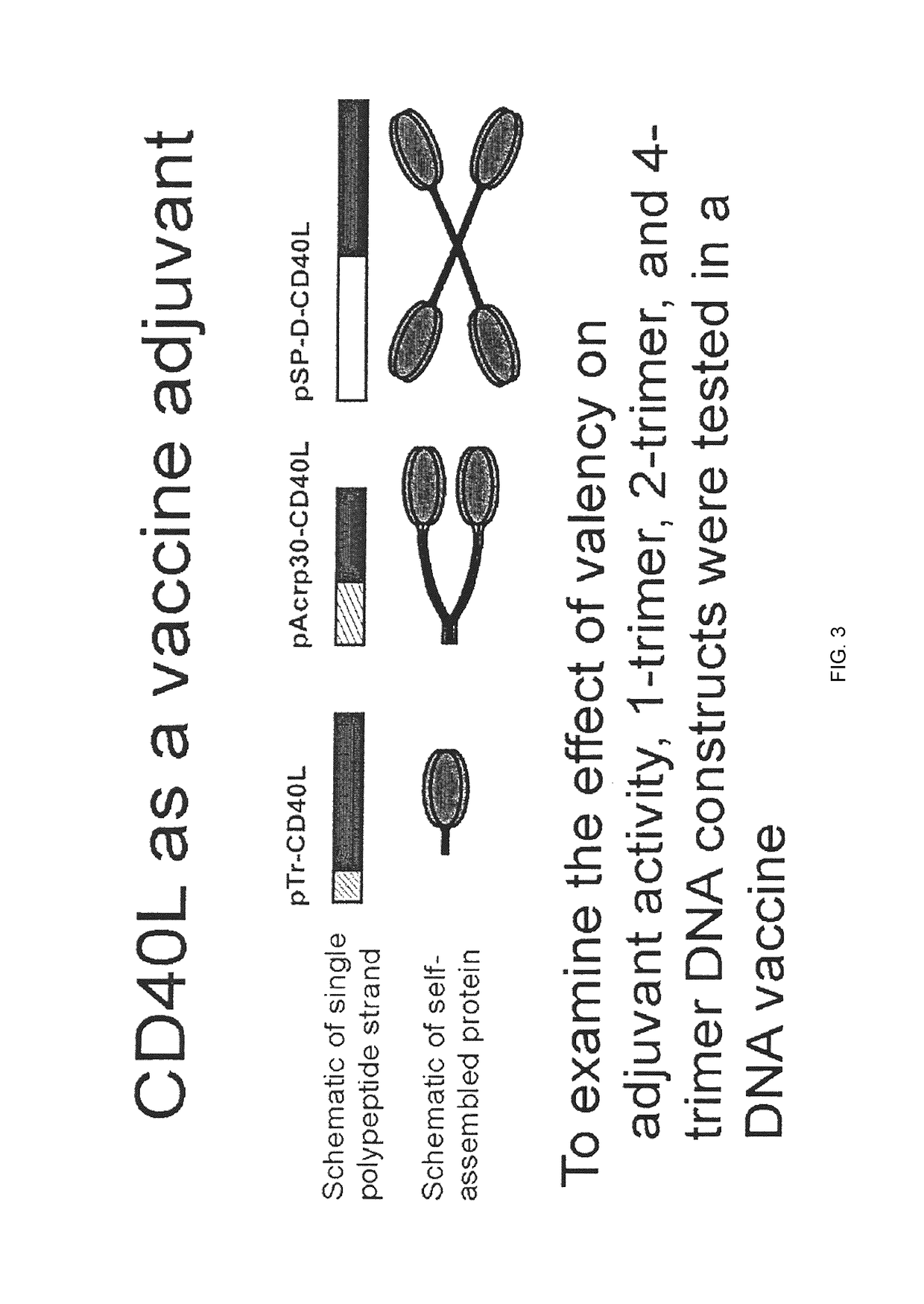
Composition comprised of antigen linked to a TNF superfamily ligand
The invention provides fusion proteins comprising antigens of infectious disease agents and cancer cells linked to multiple-trimer forms of TNF SuperFamily (TNFSF) ligands. The TNFSFs serve as vaccine adjuvants for increasing the immune response to the antigens. In particular, a fusion polypeptide strand that self-assembles inside cells into a multiple-trimer form of CD40 ligand (CD40L, TNFSF5) is provided. Other similar fusion proteins are also disclosed. The fusion proteins can be delivered to a host as isolated proteins, as nucleic acids used directly in DNA vaccination or carried and expressed by a viral vector such as adenovirus. In addition to use as a vaccine to prevent or ameliorate disease caused by an infectious agent, compositions of the invention may be used for the treatment of ongoing infection or for cancer immunotherapy.
Owner:UNIV OF MIAMI
Immunomodulatory Peptides Derived from Heat Shock Proteins and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080187550A1Improve inflammation symptomsRegulate immune responseFungiBacteriaHeat shockDNA vaccination
A method of modulating an immune response in a subject is disclosed. The invention is based on the discovery that an effective therapeutic strategy for ameliorating the inflammation-related symptoms of an immune-mediated disease, such as arthritis, can be achieved by modulation of the underlying immune response itself, rather than by merely addressing the resulting inflammation. This strategy can be used to regulate the inflammatory response and is applicable to a variety of contexts in which immune modulation is desired, such as mucosal tolerization, DNA vaccination, anergy induction, active immunization, and ex vivo modulation of antigen-specific T cells. In one embodiment, the method comprises administering to the subject a bacterial dnaJ peptide or a human homolog or a non-homologous human isoform thereof.
Owner:ALBANI SALVATORE +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com