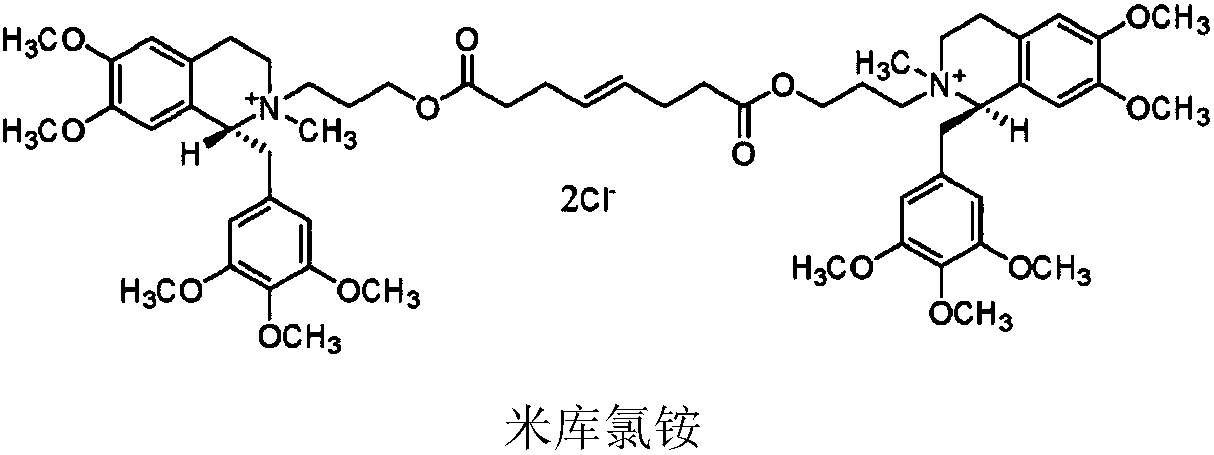
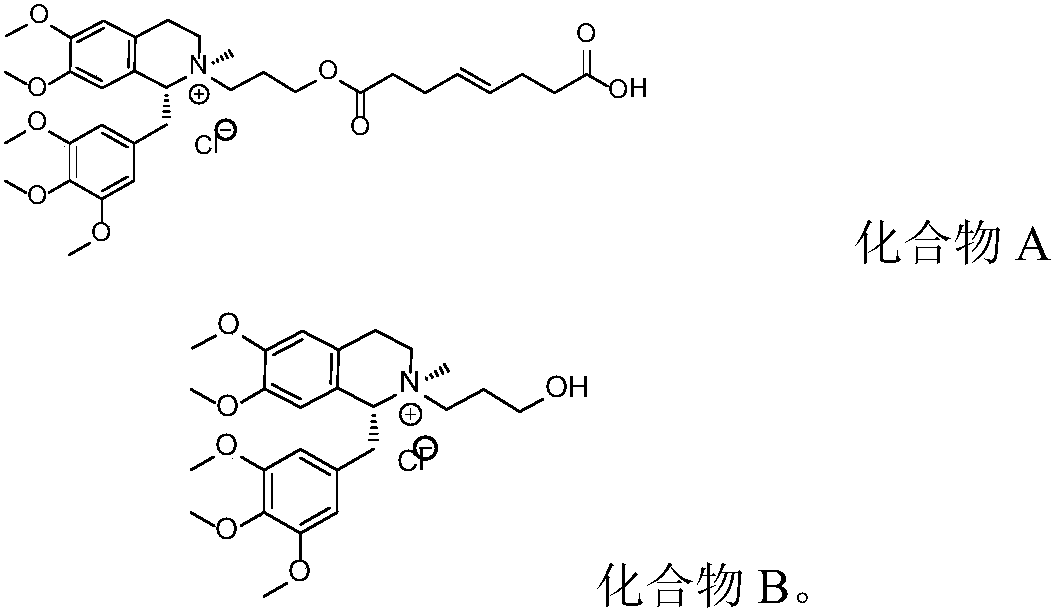
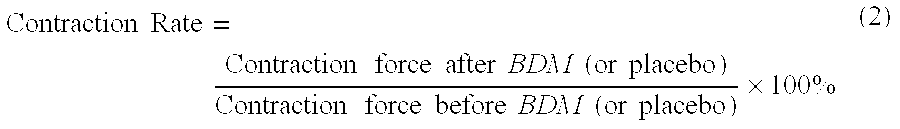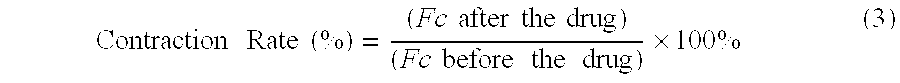Patents
Literature
113 results about "Muscle relaxant" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A muscle relaxant is a drug that affects skeletal muscle function and decreases the muscle tone. It may be used to alleviate symptoms such as muscle spasms, pain, and hyperreflexia. The term "muscle relaxant" is used to refer to two major therapeutic groups: neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics. Neuromuscular blockers act by interfering with transmission at the neuromuscular end plate and have no central nervous system (CNS) activity. They are often used during surgical procedures and in intensive care and emergency medicine to cause temporary paralysis. Spasmolytics, also known as "centrally acting" muscle relaxants, are used to alleviate musculoskeletal pain and spasms and to reduce spasticity in a variety of neurological conditions. While both neuromuscular blockers and spasmolytics are often grouped together as muscle relaxants, the term is commonly used to refer to spasmolytics only.
Pain relief lollipop compositions and methods
InactiveUS20090191257A1Without pain and invasivenessFast pain reliefOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderGabapentinOpioid Agonist
A pain relief lollipop comprises a candy matrix comprising (a) an opioid agonist, (b) an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist different from the opioid agonist, (c) gabapentin, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof, and, optionally, a muscle relaxant, sedative, anxiolytic, and / or antidepressant. A patient can self-administer small amounts of the pain relief drug as needed by simply licking or sucking on the lollipop in response to his subjective experience of pain.
Owner:INNOVATIVE PHARMA
Cosmetic composition to accelerate repair of functional wrinkles
InactiveUS20070048245A1Reduce mechanical deformationInhibition of contractilityCosmetic preparationsBiocideWrinkle skinTraditional medicine
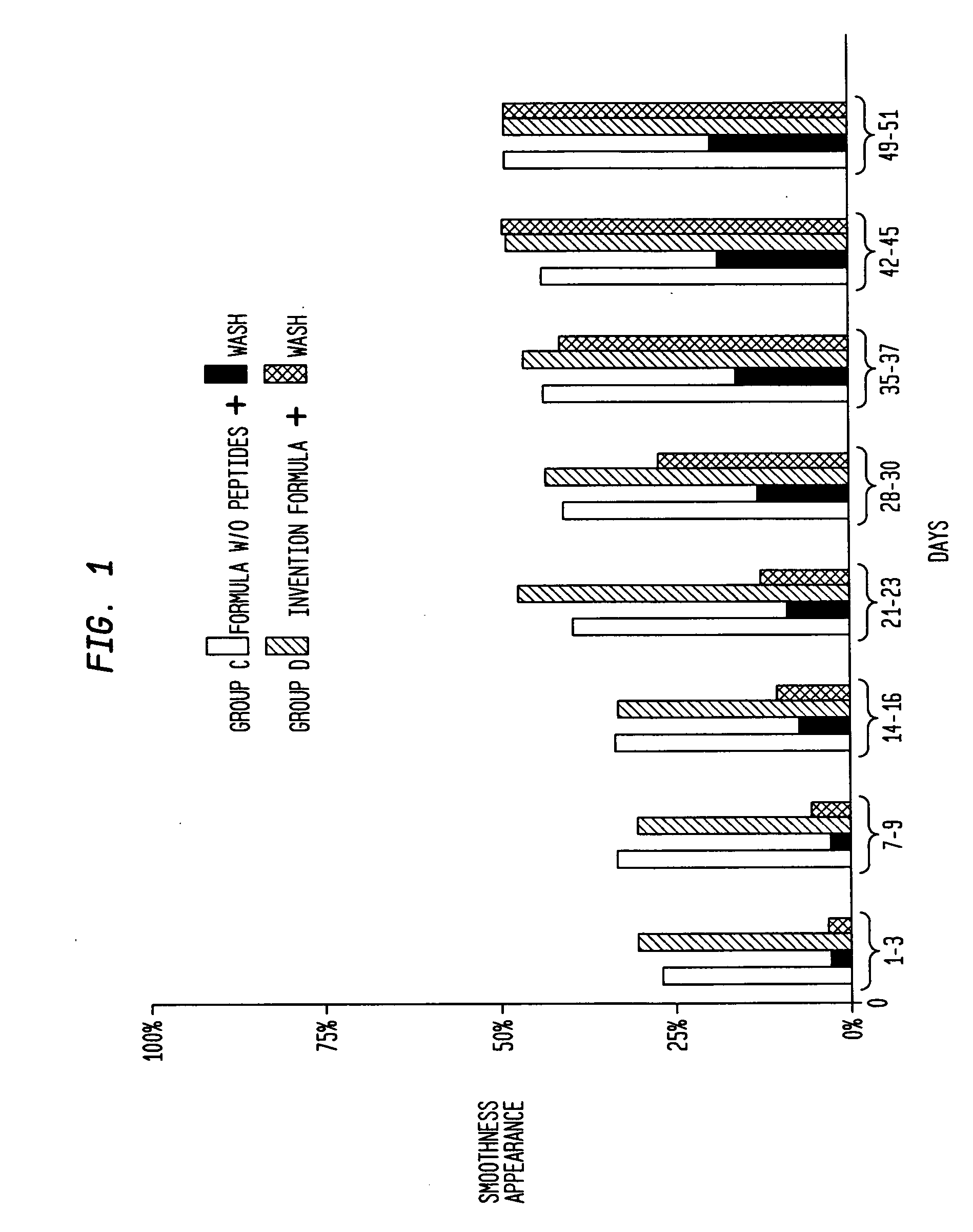
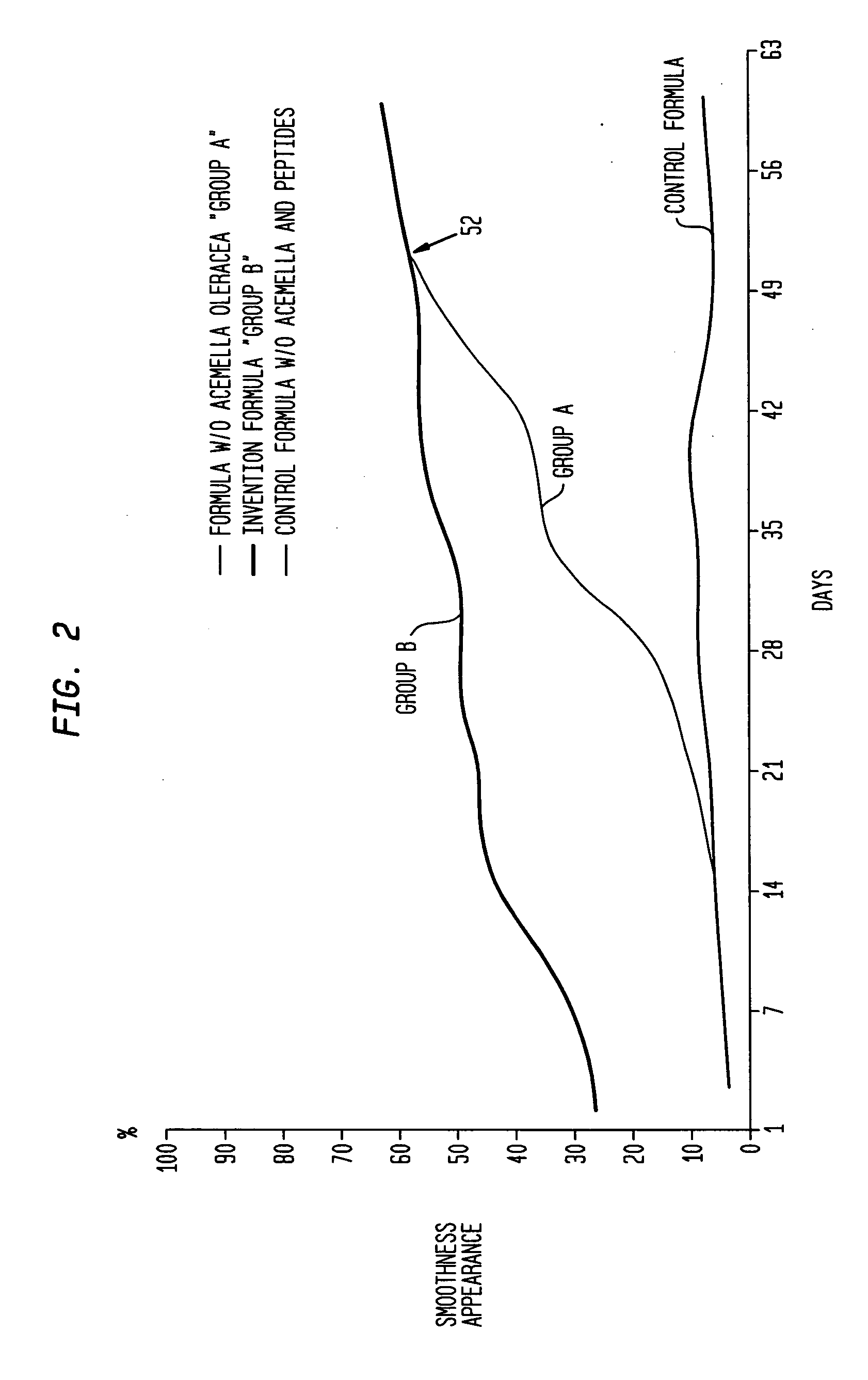
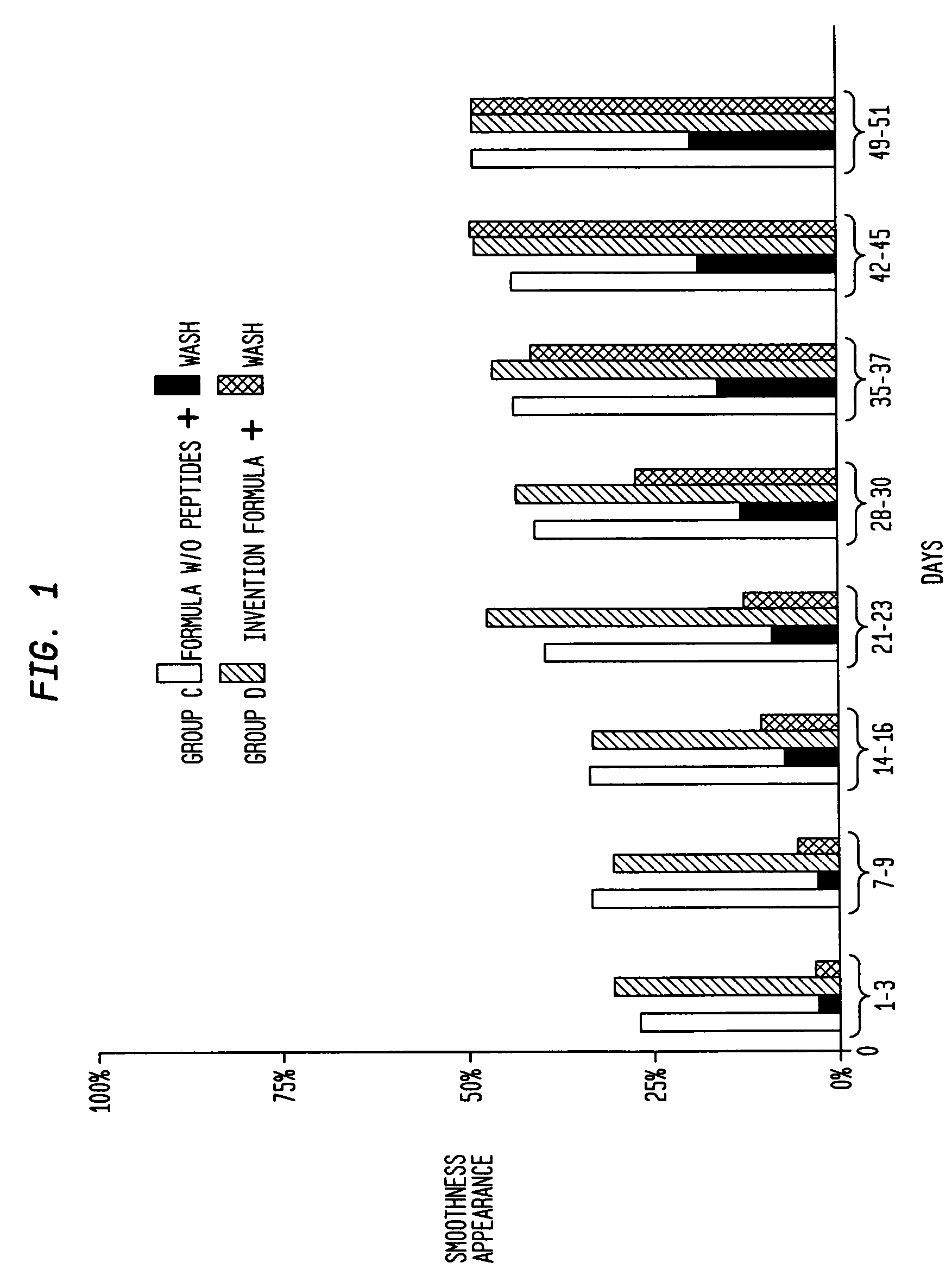
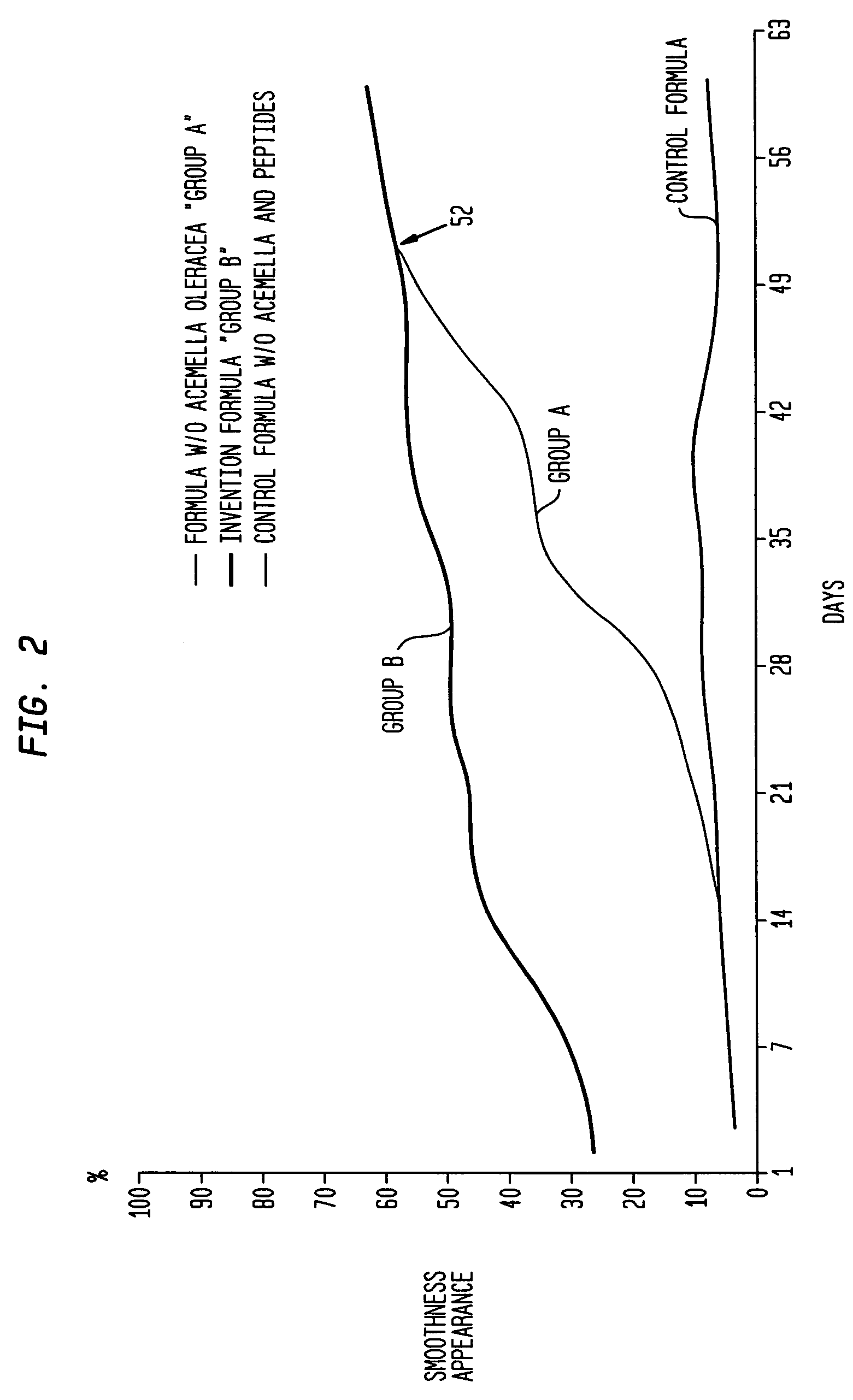
The present invention relates to a composition consisting of a combination of peptides that regenerate the dermal matrix and a rapid acting muscle relaxant derived from the extract of the plant, Acemella oleracea. By limiting cutaneous deformation caused by the contraction of facial muscles the extract increases the efficiency of the peptides in reducing expression lines.
Owner:BELFER COSMETICS
Composition and method for compounded therapy
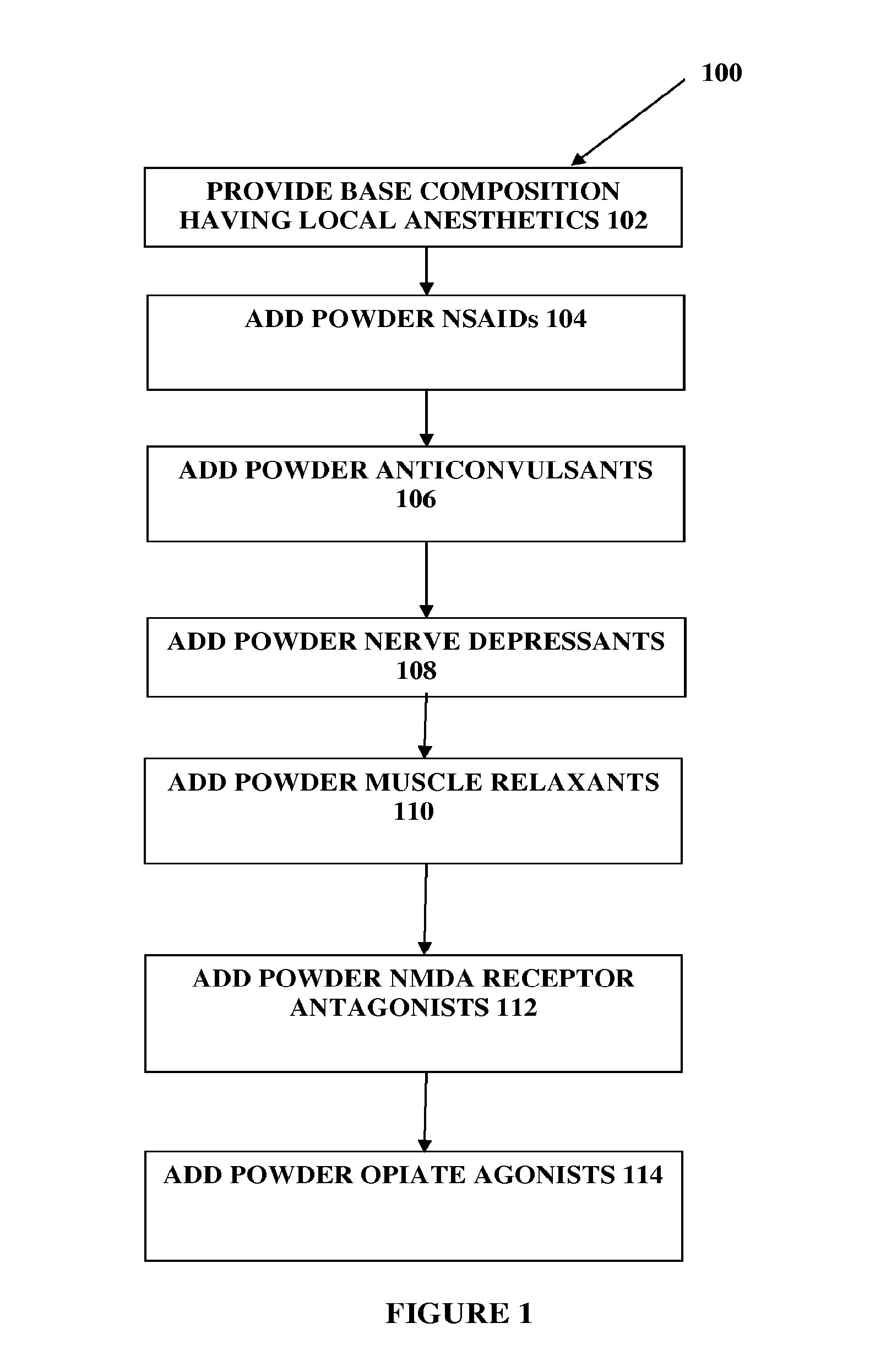
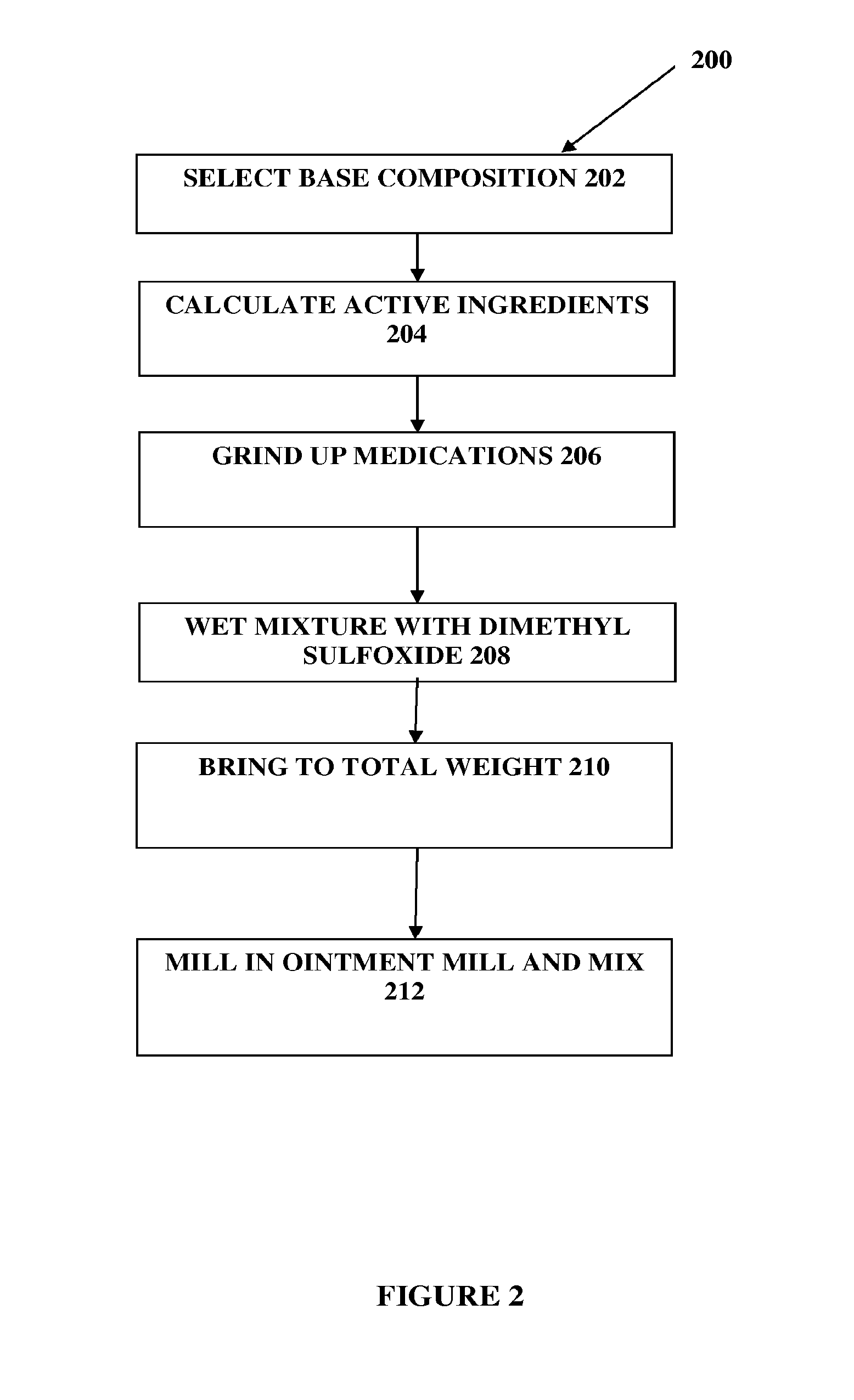
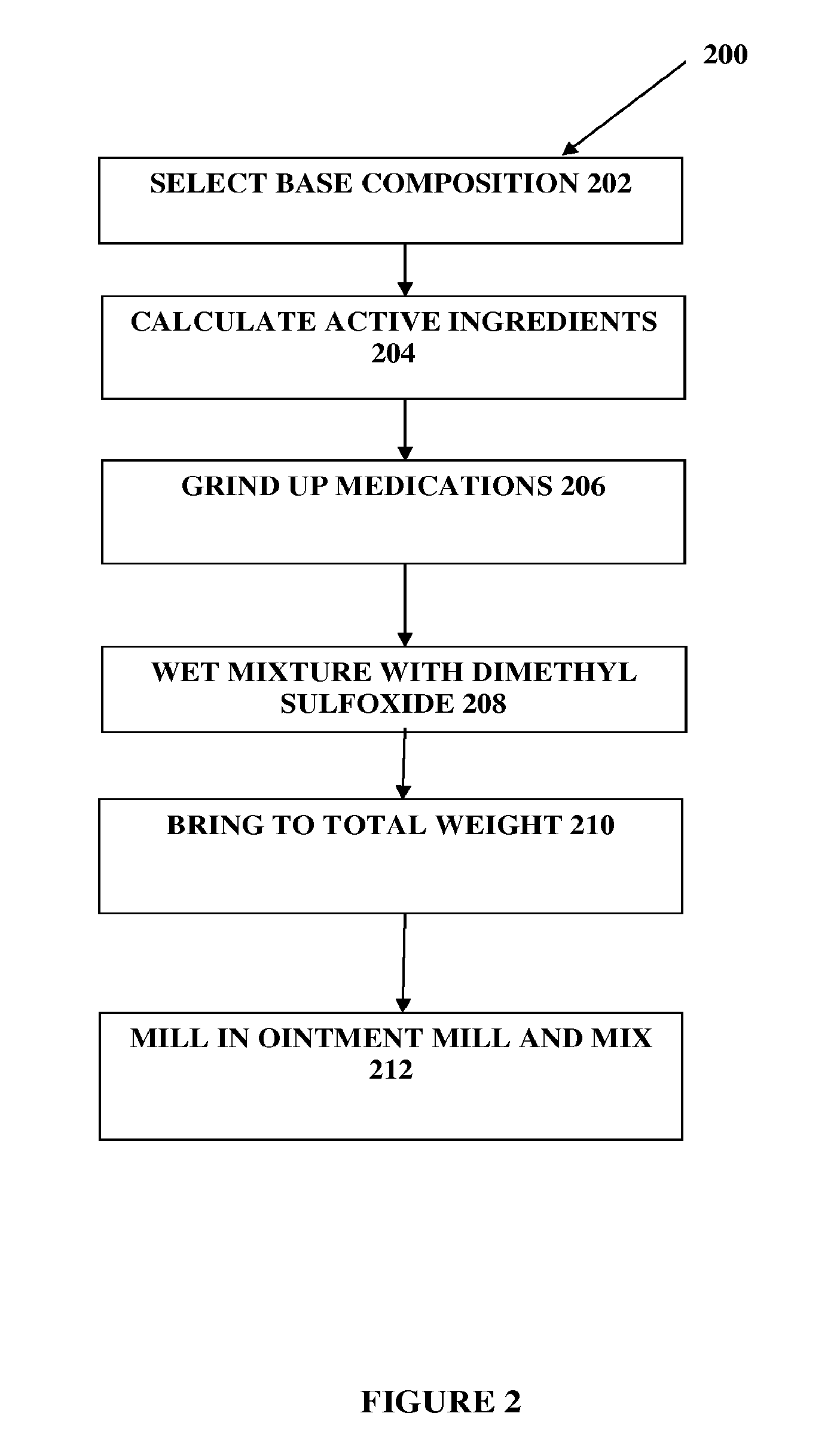
The present embodiments relate to topically delivered compounded medications. A transdermal cream may provide the effective topical administration of multiple medications simultaneously; may include low concentrations of local anesthetics, a NSAID, an anticonvulsant, and / or other active ingredients; and may include lidocaine, prilocaine, meloxicam, and lamotrigine and / or topiramate. Alternatively, the transdermal cream may include a lidocaine / prilocaine base cream to which is added a fine powder of one or more ground up medications to form a compounded medication. The compounded medication in powder form may be generated from grinding up tablets of NSAIDs, anticonvulsants, nerve depressants, antidepressants, muscle relaxants, NMDA receptor antagonists, opiate or opioid agonists, and / or other agents. The compounded medication in powder form may include meloxicam, lamotrigine, topiramate, other active ingredients, and DMSO or Sterile Water for Irrigation. In another aspect, the present embodiments relate to methods of compounding medications and transdermal creams or gels.
Owner:CMPD LICENSING
Synthetic method of bromamines muscle relaxant
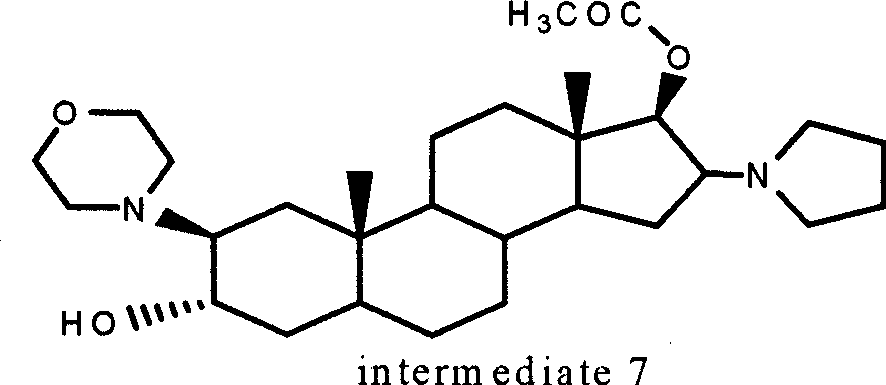
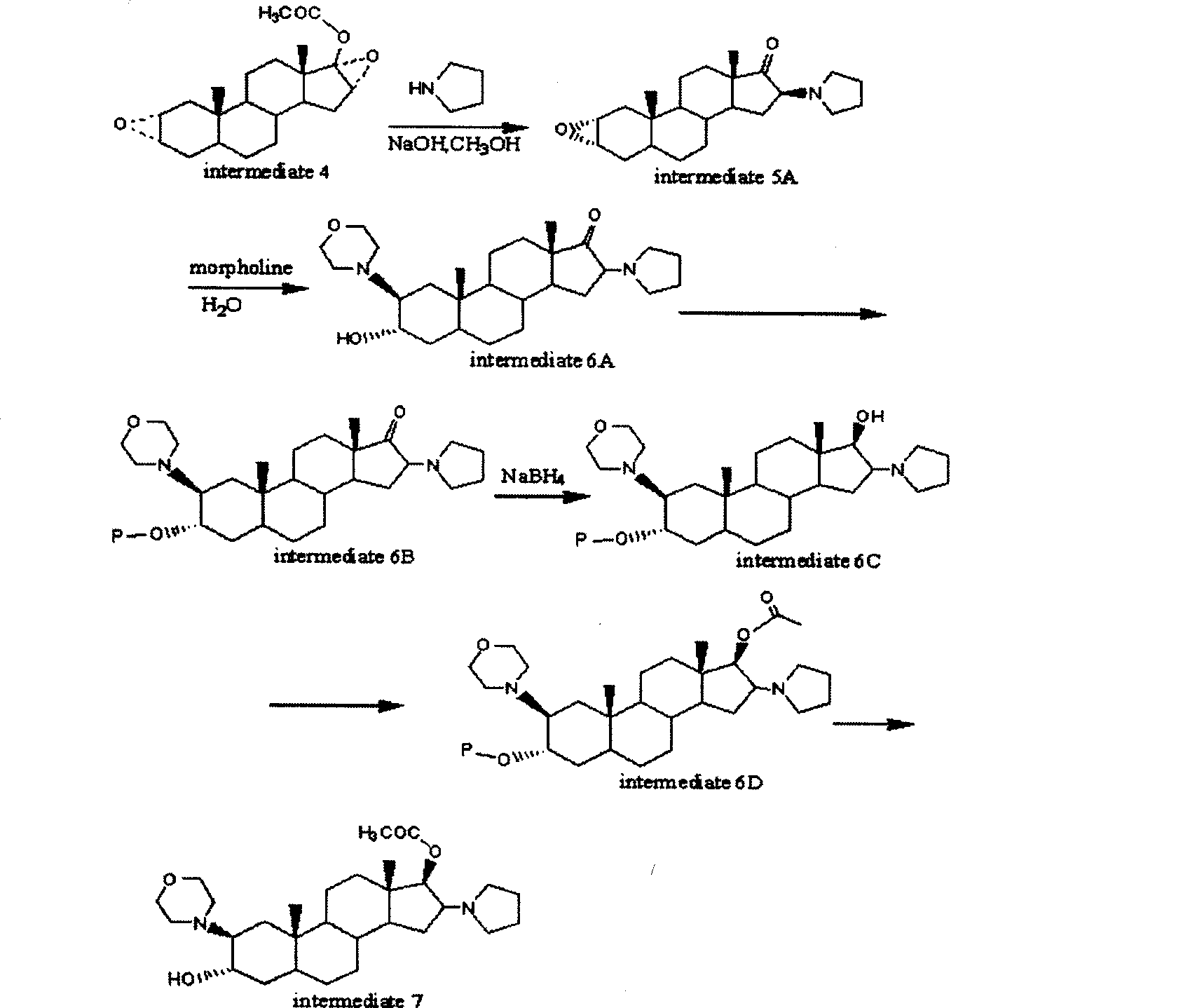
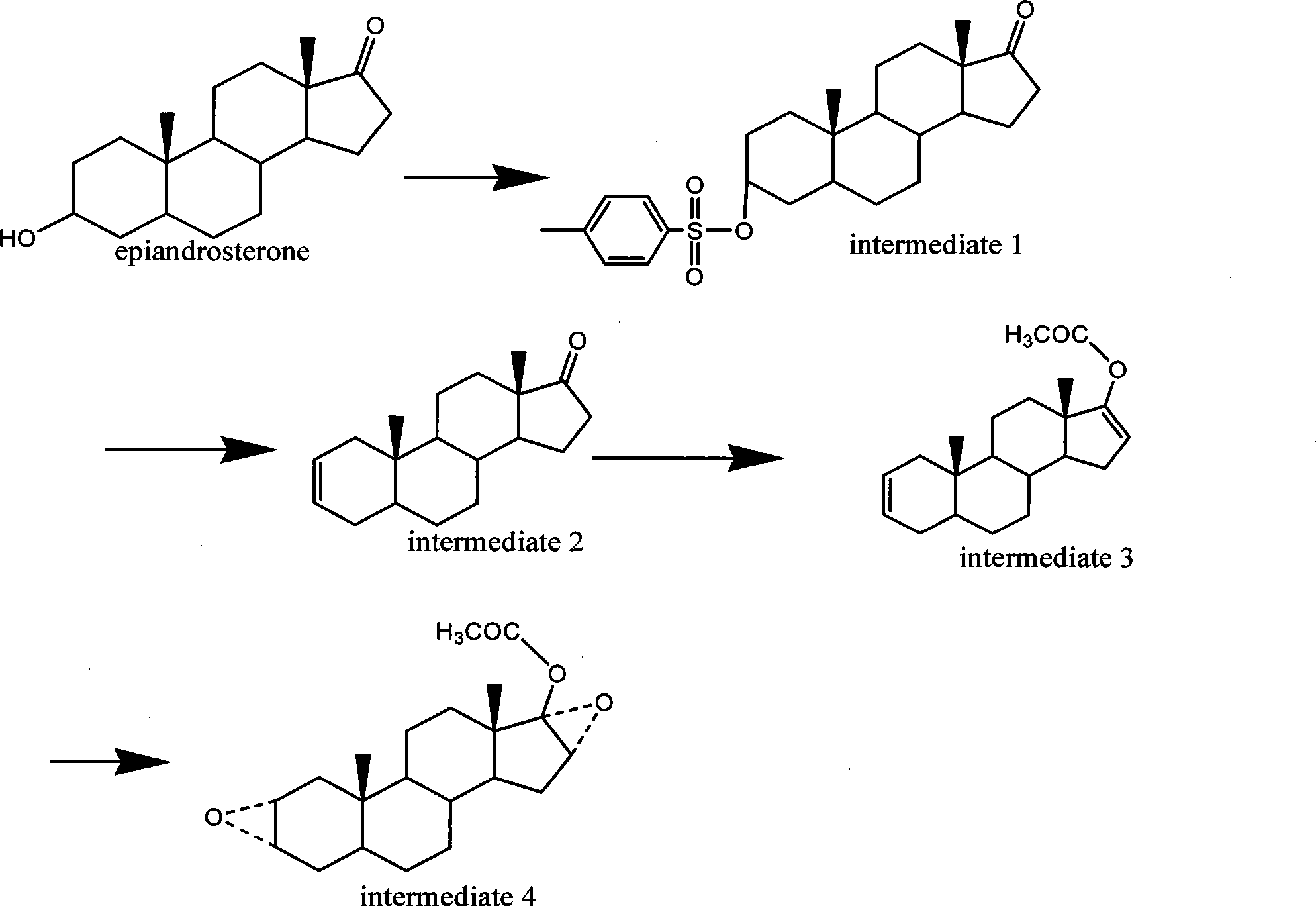
The invention provides a bromide type muscle relaxant, which mainly comprises a method for synthesizing rocuronium bromide, vecuronium bromide, pancuronium bromide and pipecuronium bromide , and is mainly characterized by adopting a ketene as an acylating agent during the process of transforming 5Alpha-androstane -2-alkene-17-alkone to 17-acetoxyl group-5Alpha- androstane-2, and 16-diene, adopting a stress kettle as a reactor when realizing the step of ring-opening and condensation of the 2 Alpha and 3 Alpha-epoxy compound, and adding a solid catalyst and a desiccant in the last step of operation of rocuronium bromide to greatly improve the reaction yield and the quality of products. The technology provided by the invention can shorten the synthesis time of the bromide type muscle relaxant, simplify the operation steps, improve the quality of products and reduce the production cost.
Owner:王加旺
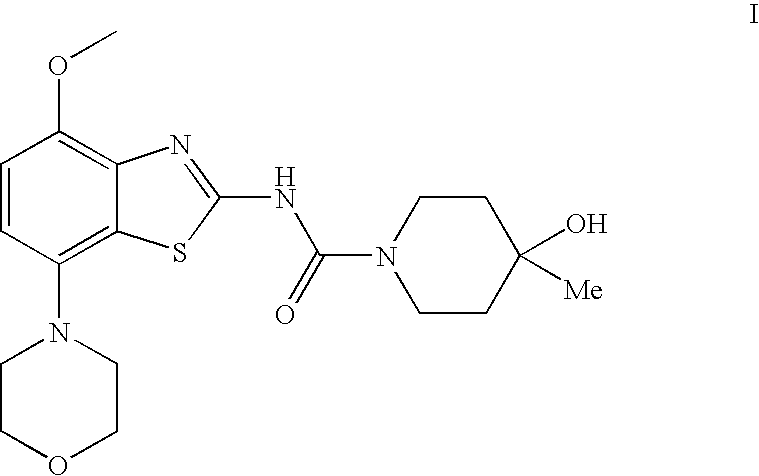
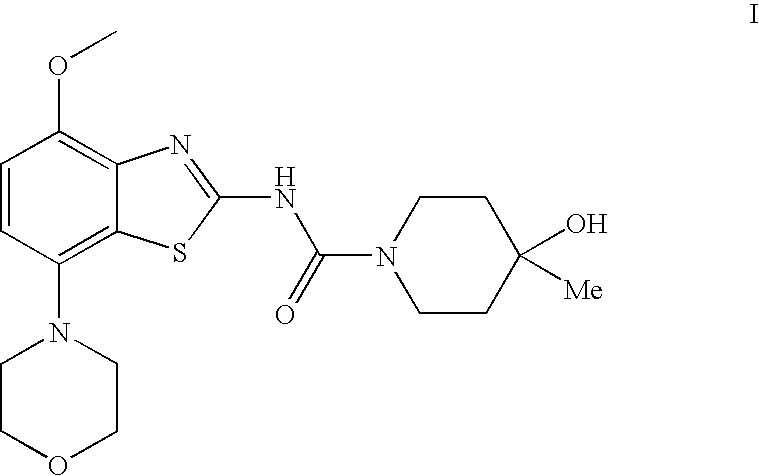
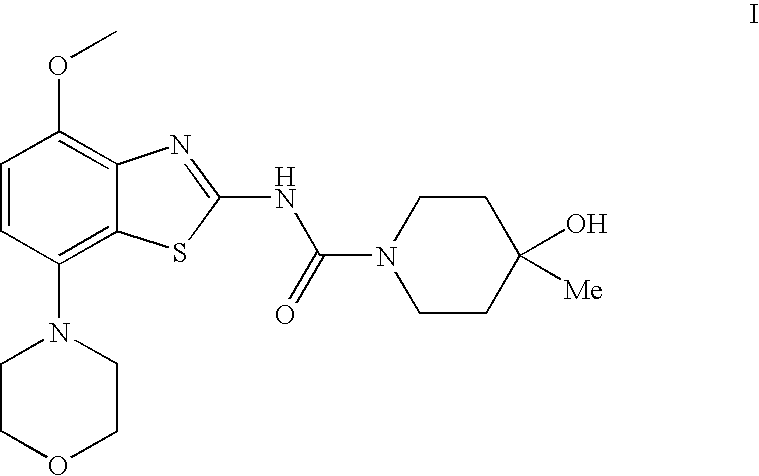
4-Hydroxy-4-methyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic acid (4-methoxy-7-morpholin-4-yl-benzothiazol-2-yl)-amide
ActiveUS20050261289A1High affinityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderSubstance abuserDisease cause
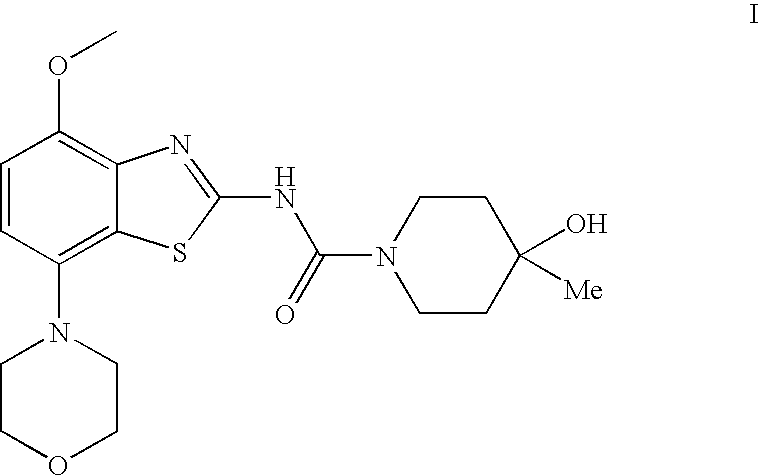
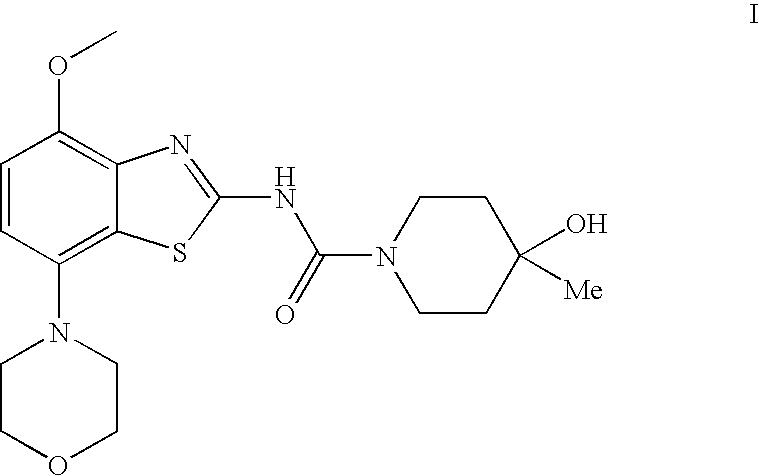
The present invention relates to the compound of formula which is 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic acid(4-methoxy-7-morpholin-4-yl-benzothiazol-2-yl)-amide, and to pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts thereof. It has been found that the compound is useful for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, neuroprotection, schizophrenia, anxiety, pain, respiration deficits, depression, ADHD (attention deficit hyper-activity disorder), drug addiction to amphetamines, cocaine, opioids, ethanol, nicotine, or cannabinoids, or for the treatment of asthma, allergic responses, hypoxia, ischemia, seizure, substance abuse, or for use as muscle relaxants, antipsychotics, antiepileptics, anticonvulsants and cardioprotective agents.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Compounded transdermal pain management
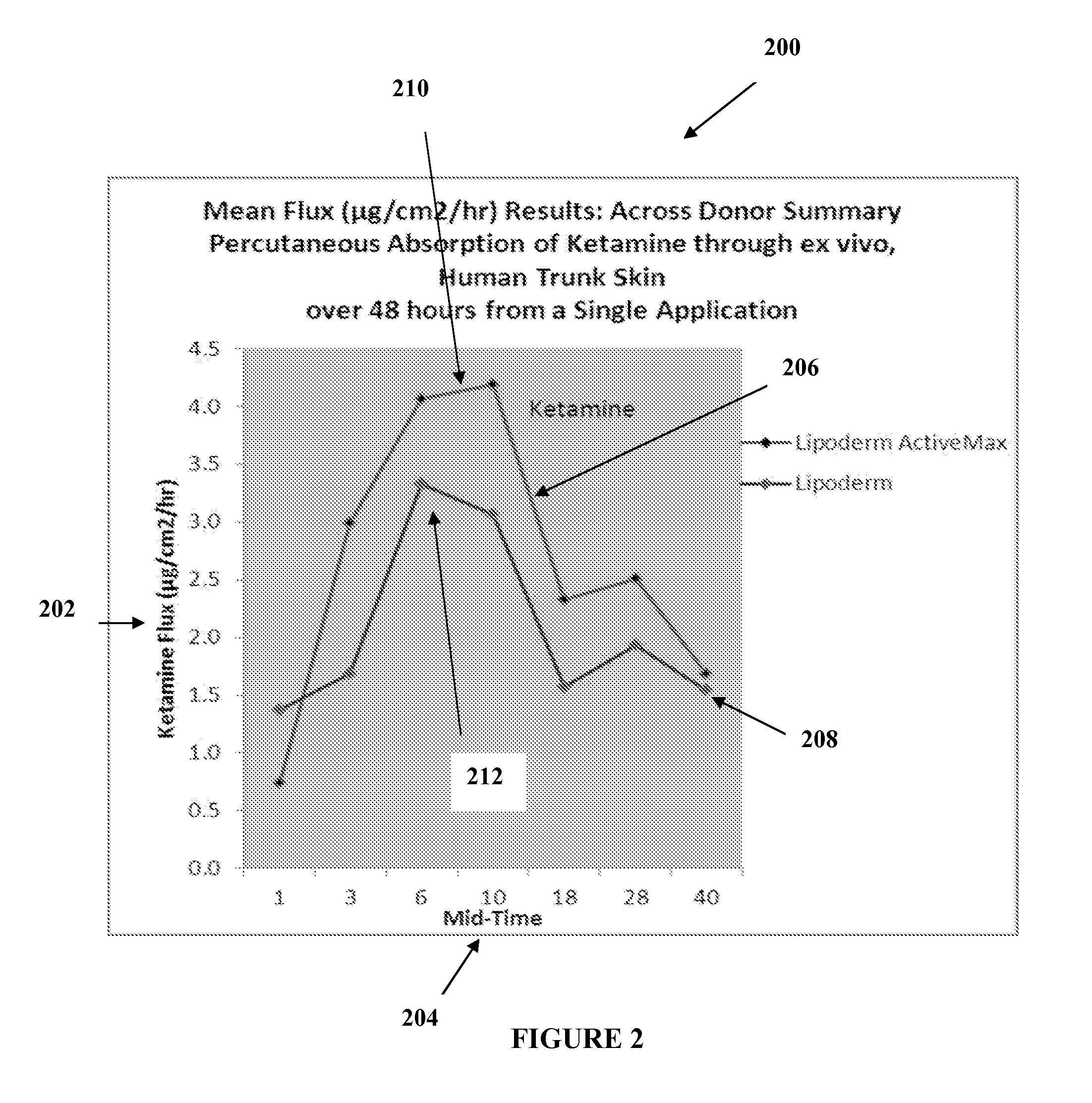
The present embodiments relate to topically delivered medication (compounded) for treatment of pain, inflammation, muscle fatigue, spasms, and / or other ailments. A transdermal cream may provide the effective topical administration of multiple medications simultaneously. The transdermal cream may include a salt load of approximately 30% or greater. The transdermal cream may include a unique base composition such that the transdermal cream may be able to remain stable and avoid degradation for six months or more and capable of effective delivery of active ingredient concentrations exceeding approximately 40% or more of the total formulation weight. The active ingredients may include a nerve depressant, NSAID, muscle relaxant, opiate agonist, local anesthetic, NMDA receptor antagonist, and a tricyclic antidepressant. In one embodiment, the transdermal cream may comprise ketamine HCL, gabapentin, clonidine HCL and baclofen. The transdermal cream may deliver an enhanced topical delivery flux of ketamine via a single transdermal application.
Owner:CMPD LICENSING
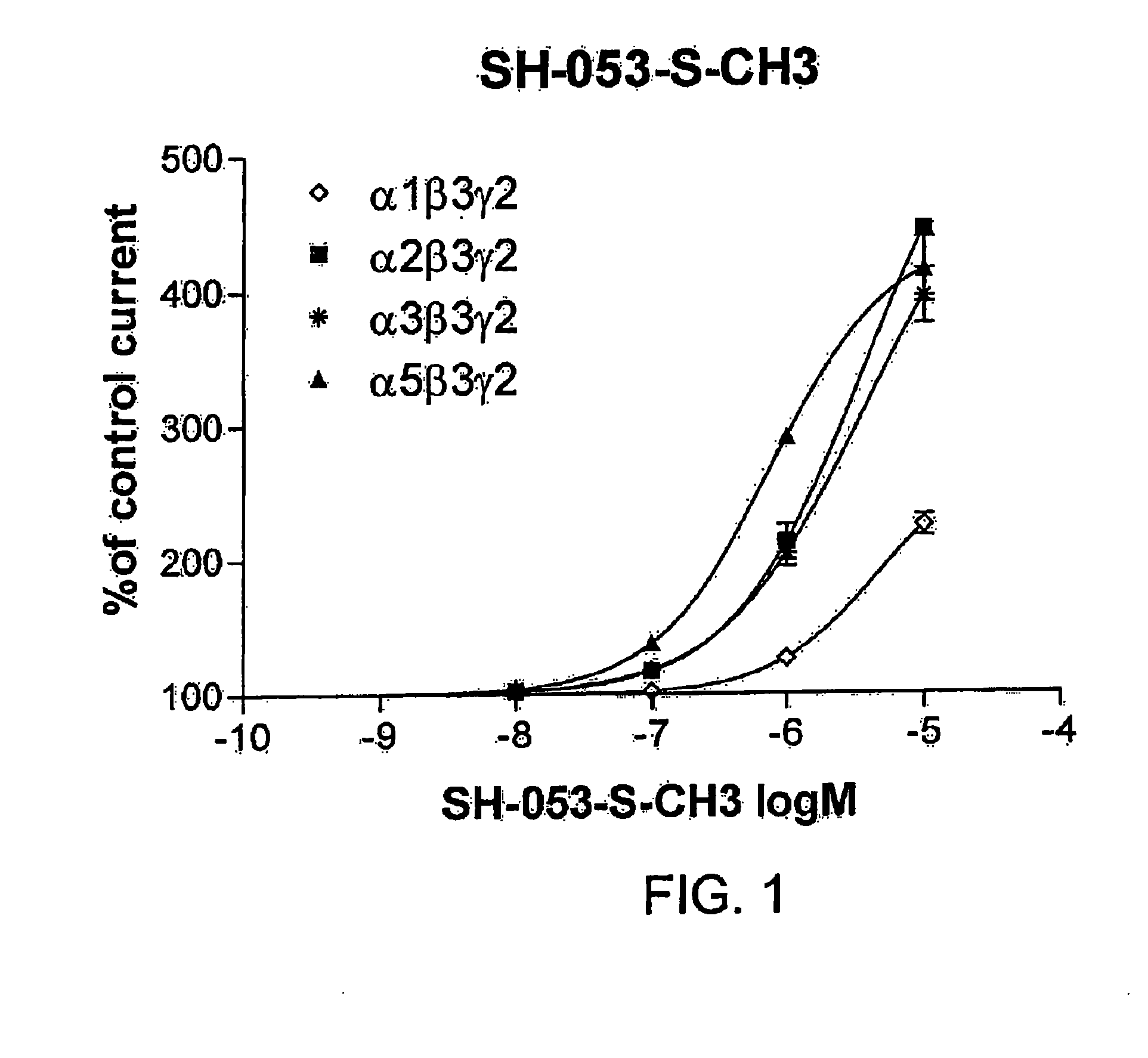
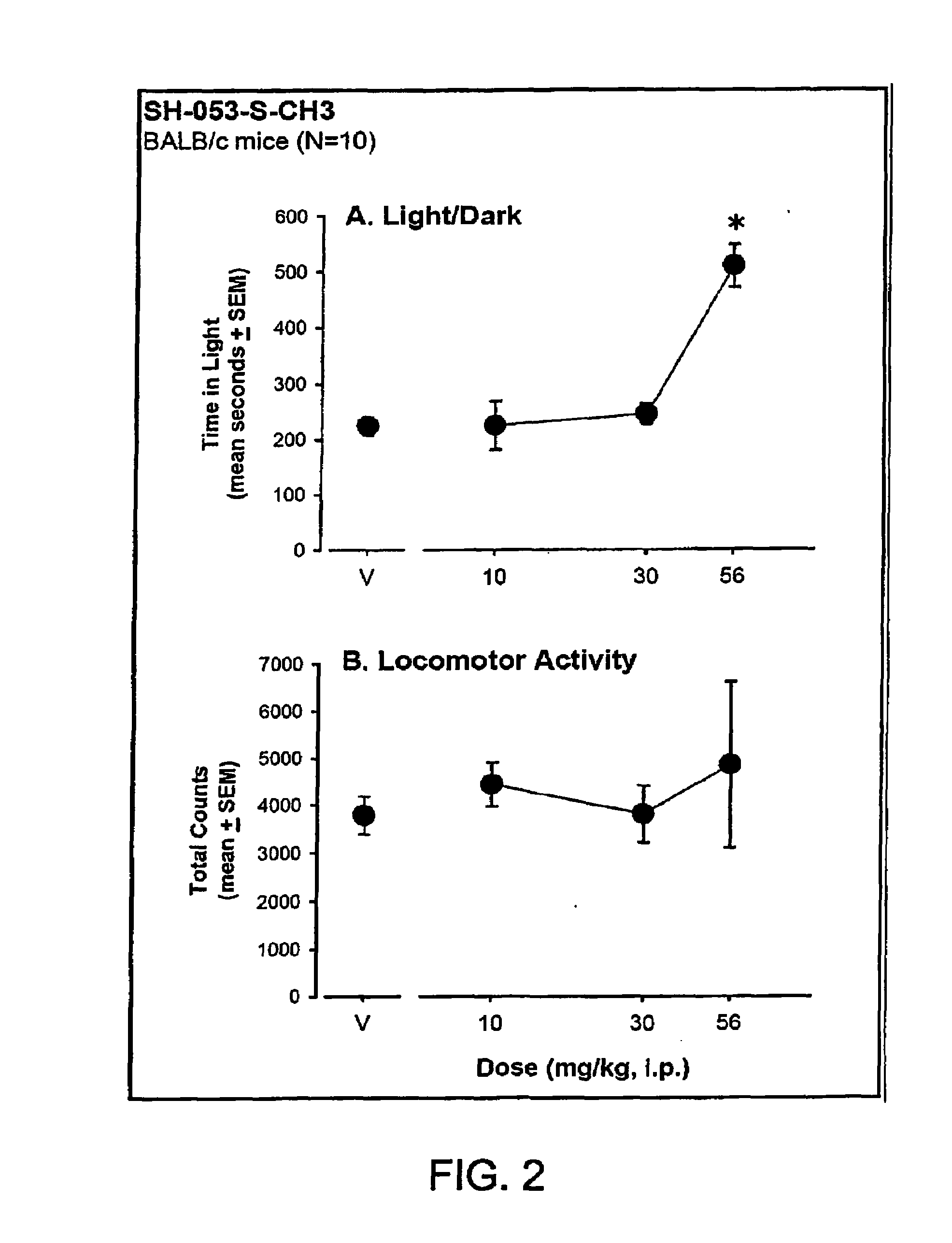
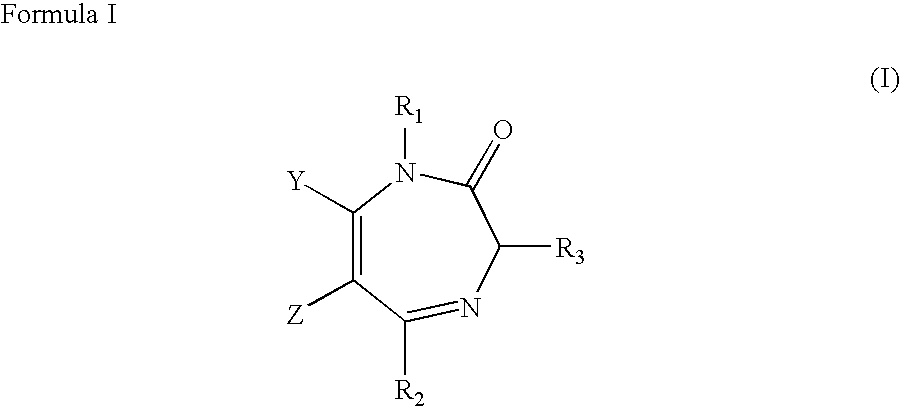
Stereospecific anxiolytic and anticonvulsant agents with reduced muscle-relaxant, sedative-hypnotic and ataxic effects
InactiveUS20060003995A1Reduce alcohol cravingReduce self administrationBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseBenzodiazepine
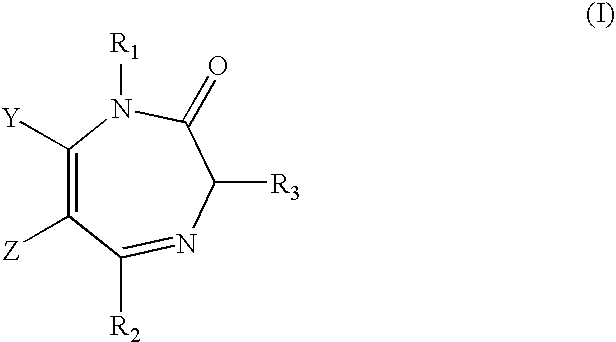
The present invention provides compositions and methods of using stereospecific benzodiazepine derivatives, their salts and prodrugs for the treatment of anxiolytic or convulsant disorders having the side effects of reduced alcohol craving in human alcoholics and a concomitant reduced sedative, hypnotic, muscle relaxant and ataxic side-effects. The invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of anxiolytic and convulsant disorders in subjects in need thereof, comprising a compound, prodrug or a salt having a chemical structure represented by any one of Formula I-XXI and a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier.
Owner:WISYS TECH FOUND
Cosmetic composition to accelerate repair of functional wrinkles
InactiveUS7566464B2Cut skinInhibit expressionCosmetic preparationsBiocideWrinkle skinMimetic Muscles
A composition consisting of a combination of peptides that regenerate the dermal matrix and a rapid acting muscle relaxant derived from the extract of the plant, Acmella oleracea. By limiting cutaneous deformation caused by the contraction of facial muscles the extract increases the efficiency of the peptides in reducing expression lines.
Owner:BELFER COSMETICS
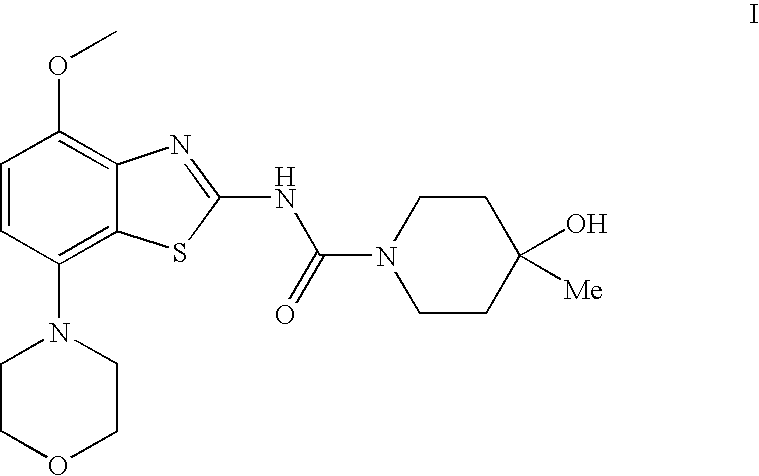
4-hydroxy-4-methyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic acid (4-methoxy-7-morpholin-4-yl-benzothiazol-2-yl)-amide
The present invention relates to the compound of formulawhich is 4-hydroxy-4-methyl-piperidine-1-carboxylic acid(4-methoxy-7-morpholin-4-yl-benzothiazol-2-yl)-amide, and to pharmaceutically acceptable acid addition salts thereof. It has been found that the compound is useful for the treatment or prevention of Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, Huntington's disease, neuroprotection, schizophrenia, anxiety, pain, respiration deficits, depression, ADHD (attention deficit hyper-activity disorder), drug addiction to amphetamines, cocaine, opioids, ethanol, nicotine, or cannabinoids, or for the treatment of asthma, allergic responses, hypoxia, ischemia, seizure, substance abuse, or for use as muscle relaxants, antipsychotics, antiepileptics, anticonvulsants and cardioprotective agents.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE INC
Phenylcarbamate compound and muscle relaxant containing the same
A novel phenylcarbamate compound and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same are provided. More specifically, a novel phenylcarbamate compound, a composition for muscle relaxation containing the phenylcarbamate compound as an active ingredient, and a method of muscle relaxation comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of the phenylcarbamate compound, are provided.
Owner:BIO PHARM SOLUTIONS
Α-conotoxin peptides
InactiveUS6855805B2Quick effectPromote recoverySugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsMedicineMuscle relaxant
The invention relates to relatively short peptides (termed α-conotoxins herein), about 10-25 residues in length, which are naturally available in minute amounts in the venom of the cone snails or analogous to the naturally available peptides, and which preferably include two disulfide bonds. The α-conotoxins, as described herein, are useful for as neuromuscular blocking agents, such as muscle relaxants.
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND +1
Process for providing a temperature-stable muscle relaxant on the basis of the neurotoxic component of botulinum toxin in a solid form
The present invention relates to a method for providing a muscle relaxant at temperatures above 20° C., wherein said muscle relaxant is a solid dry composition comprising the neurotoxic component of botulinum toxin free of complexing proteins.
Owner:MERZ PHARMA GMBH & CO KGAA
Pharmaceutical formulation containing muscle relaxant and COX-II inhibitor
InactiveUS20050100594A1Minimize side effectsMaintain curative effectBiocidePill deliveryCyclooxygenaseSkeletal muscle
Disclosed is an extended release pharmaceutical formulation comprising a muscle relaxant drug, such as tizanidine, in combination with a cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor, such as valdecoxib. The formulations are useful in the treatment and management of painful inflammatory conditions associated with, for example, skeletal muscle spasms.
Owner:GLENMARK PHARMACEUTICALS LIMITED
Design of comprehensive extraction process for barberry plant resources
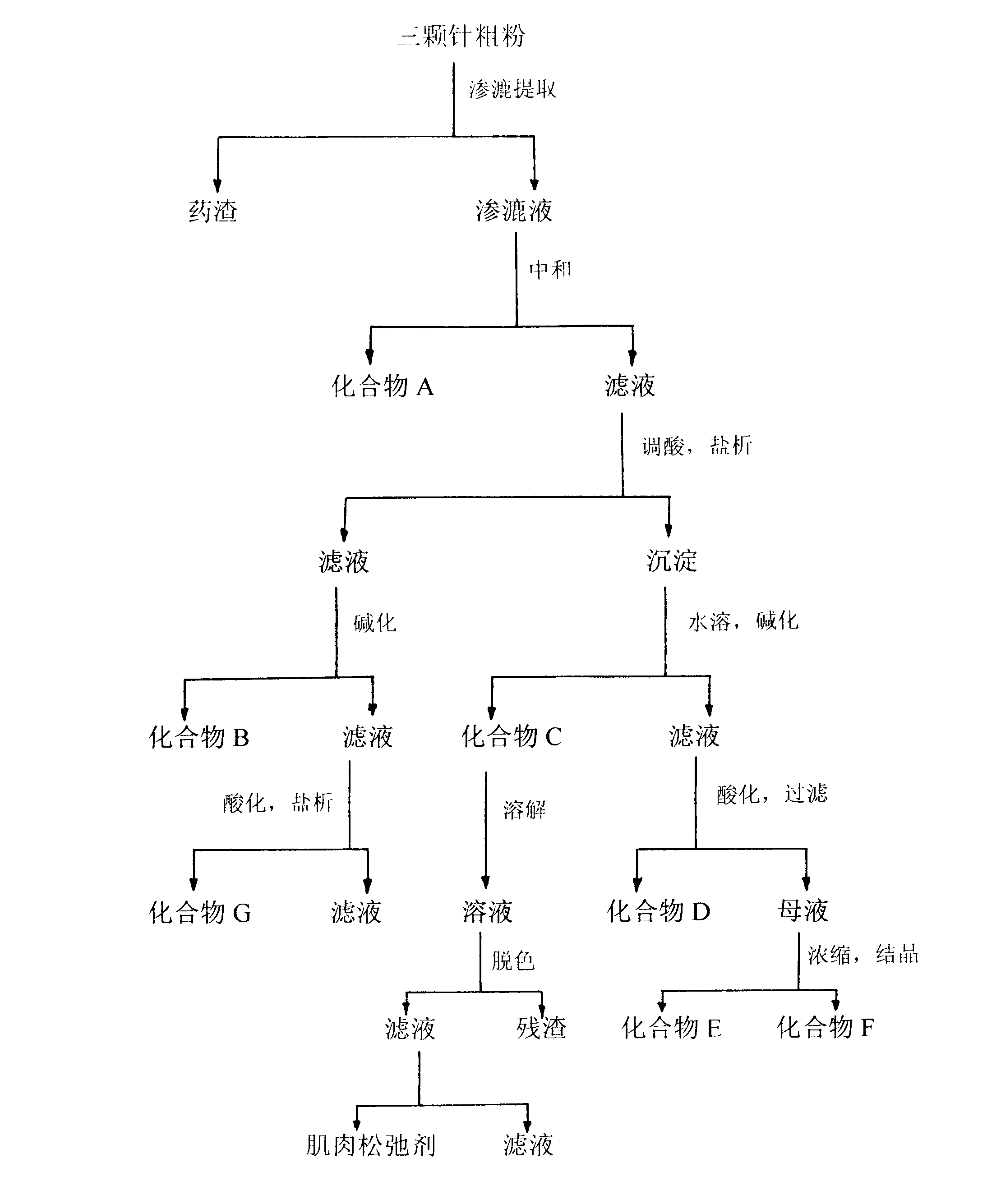
The invention discloses a design of a comprehensive extraction process for barberry plant resources. Berbamine hydrochloride, jatrorrhizine hydrochloride, palmatine hydrochloride and a muscle relaxant are synchronously, efficiently and comprehensively extracted while berberine hydrochloride is extracted, and berbamine is used as a raw material for synthesizing an analgesic drug. Therefore, the barberry plant resources are fully utilized, the added medicinal value is increased, and the comprehensive utilization rate of medicinal barberry is increased. For a traditional Chinese medicine, one medicinal part is often utilized only and other parts are discarded. Various components in the barberry are synchronously extracted and comprehensively utilized, so that the economic value of the barberry is greatly increased.
Owner:李玉山
Composition and method for compounded therapy
Owner:CMPD LICENSING
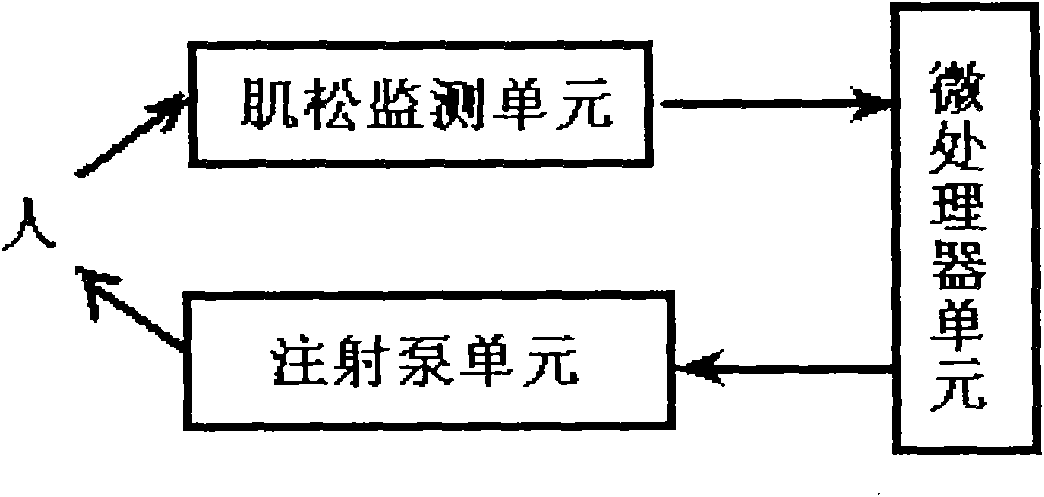
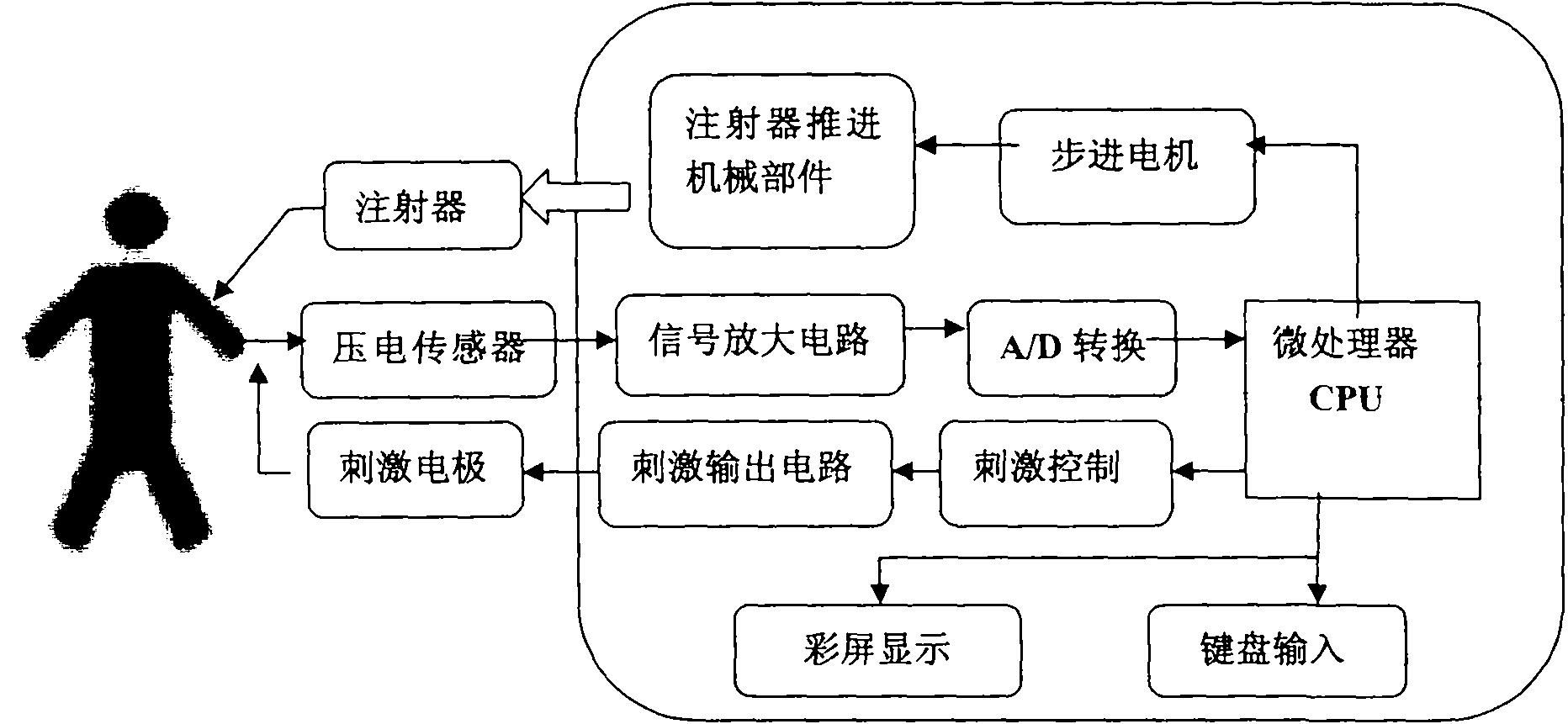
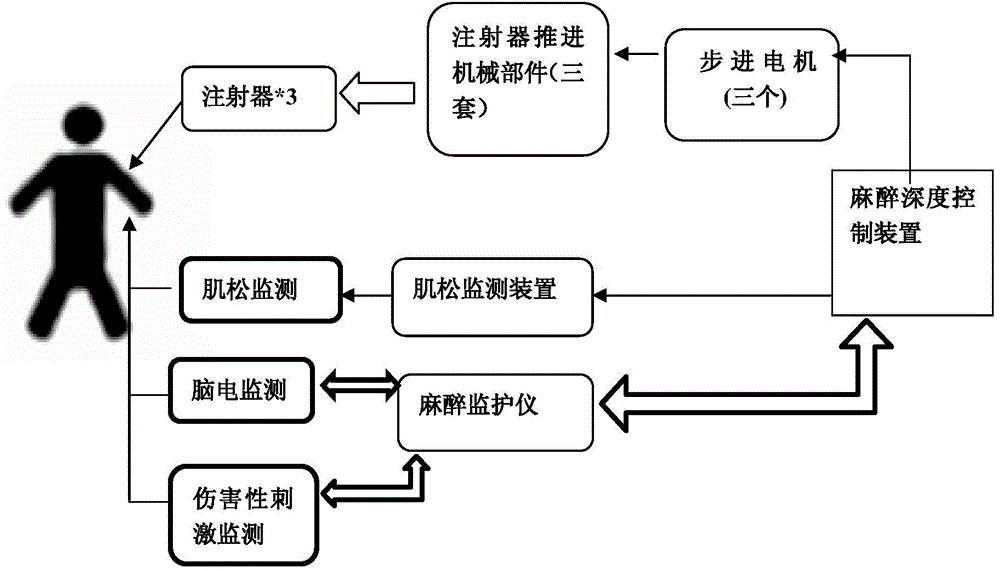
Closed loop muscle relaxation iatrical effect monitoring and injecting method and closed loop muscle relaxation injecting device
InactiveCN101816576AReal-time monitoring of muscle relaxationAutomatic drug deliverySurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsHuman bodyClosed loop
The invention discloses a closed loop muscle relaxation iatrical effect monitoring and injecting method and a closed loop muscle relaxation injecting device. The method comprises the specific steps of: acquiring muscle myoelectricity feedback actions of a patient through an independently developed muscle relaxation monitoring piezoelectric inductor and operating to obtain a muscle relaxation monitoring data TOF (turnover of frequency) value; and controlling a stepper motor to operate at a specified speed so as to push an injector to administrate medicine at a set speed by using the TOF value as a feedback data base and by a microprocessor by combining a built-in muscle relaxation administration method. The scheme can monitor the muscle relaxation state of a patient in real time, objectively reflect the true iatrical effect condition of the muscle relaxant in the human body and display the TOF value of a muscle relaxation feedback value, and meanwhile, an injection system can automatically administrate the muscle relaxant in the whole course according to the TOF value. Moreover, artificial interventions are not needed, and the automatic administrated dosage and the method are obtained through a large quantity of population parameters. The invention ends the times of fuzzy muscle relaxant administration and can scientifically improve the controllability of the muscle relaxant, avoid medicine deficiency or excess and improve the operation quality.
Owner:GUANGXI VERYARK TECH
Methods of treating involuntary facial spasms and facial wrinkles
InactiveUS20060093597A1Inhibition releaseReduce healingAntibacterial agentsBiocideWrinkle skinClinical settings
The invention describes antibiotics, muscle relaxants and plant extracts that have neuromuscular blockade effects as well as methods of use thereof. These compounds can be used in the same clinical settings as botulinum toxin and may be used topically, thereby providing an advantage over botulinum toxin in terms of application and ease of use. The compounds can be used in pharmaceutical compositions for the treatment of involuntary muscle spasms and neuropathic pain and in cosmetic compositions for the treatment of facial wrinkles. Also provided are kits useful for therapeutic and / or cosmetic applications.
Owner:JUVENTUS BIOSCI
Pharmaceutical compositions containing alpha3beta4 nicotinic receptor antagonists and methods of their use
InactiveUS20030199496A1Relief the painIncreased dopamineBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAntiepileptic drugAmphetamine use
A pharmaceutical composition comprising an .alpha.3.beta.4 nicotinic receptor antagonist effective to diminish the brain-derived feeling of pleasure due to increased dopamine in the pleasure-reward center of the brain typically associated with administration of an opioid agonist analgesic, a muscle relaxant, an anti-seizure medication, an anxiolytic drug, an amphetamine, a central nervous system stimulant, a tetrahydrocannabinol or that associated with an otherwise pleasurable or self-reinforcing behavior.
Owner:SIMON DAVID LEW
Skin Penetration Composition
InactiveUS20120034320A1Avoid systemic side effectsDecreasing nerve painAntibacterial agentsBiocideAntidoteAntioxidant
The present invention comprises an all-natural composition of matter and methods of delivering nutrients, medicines, pain relievers, antioxidants, antidotes, antibiotics and various active ingredients and supplements directly to the affected area of the body. The all-natural carrier composition consists essentially of the combination of a natural oil, water, salt(s), natural emulsifier, natural sugar(s), plant extracts, natural acid(s), starch and natural flavor(s). The active substances that are mixed with the all-natural carrier composition, include, but are not limited to, drugs, vitamins, minerals, antibiotics anti fungal agents, antioxidants, diuretics, allergy medicines, anti-inflammatory agents, muscle relaxers, pain reducers, diabetic drugs, neuropathy drugs, chemotherapy agents, arthritis drugs, lotions for eczema, shingles, psoriasis, skin rash; herbal medicines, erectile dysfunction drugs, hormones, cholesterol drugs, essential fatty acids, and the like. The all-natural carrier composition facilitates the penetration of active substances into the dermal layer of the skin.
Owner:DOMINION RESOURCES UNLTD
Stereospecific anxiolytic and anticonvulsant agents with reduced muscle-relaxant, sedative-hypnotic and ataxic effects
InactiveUS20100004226A1Reduce managementReducing anxiety and convulsant disorderBiocideNervous disorderDiseaseChemical structure
The present invention provides compositions and methods of using stereospecific benzodiazepine derivatives, their salts and prodrugs for the treatment of anxiolytic or convulsant disorders having the side effects of reduced alcohol craving in human alcoholics and a concomitant reduced sedative, hypnotic, muscle relaxant and ataxic side-effects. The invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of anxiolytic and convulsant disorders in subjects in need thereof, comprising a compound, prodrug or a salt having a chemical structure represented by any one of Formula I-IV, VI-XI, XV-XVIII and XX-XXI and a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier.
Owner:COOK JAMES M +4
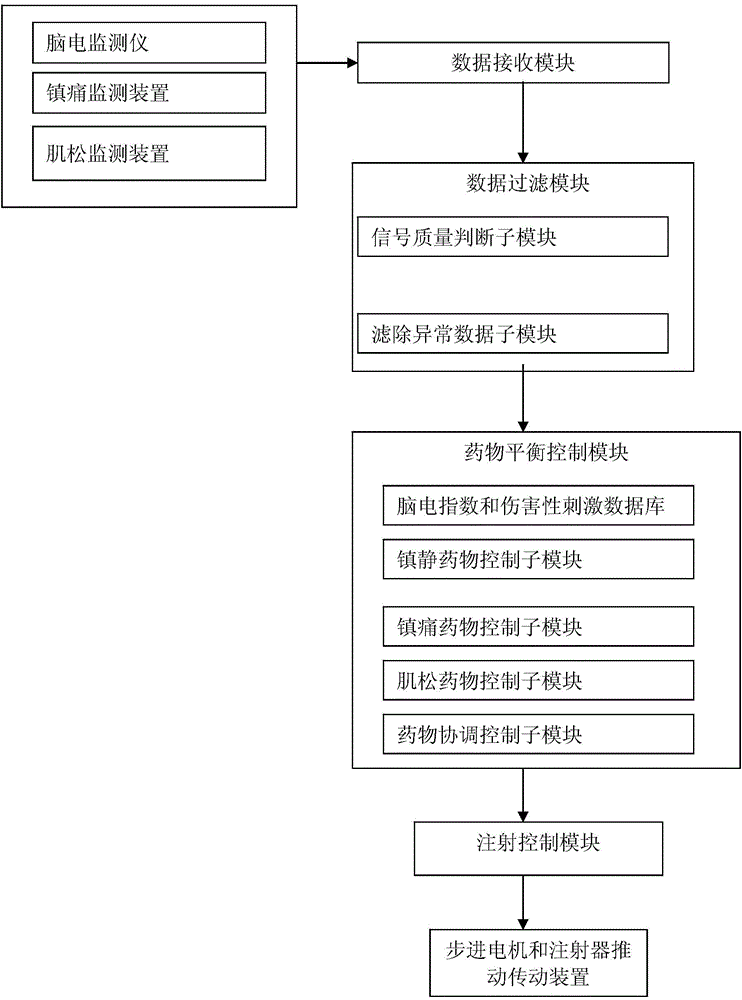
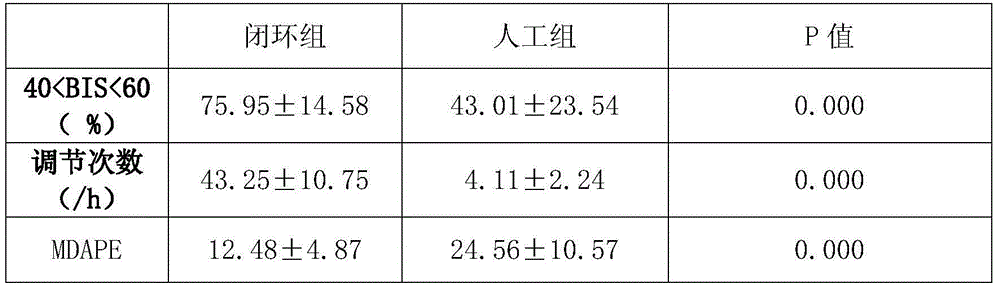
Anaesthetic balance control device and control method
ActiveCN103908249AAddressing Individual DifferencesEasy to controlAutomatic syringesDiagnostic recording/measuringBispectral Index MonitorNociceptive Stimulus
The invention aims at providing an anaesthetic balance control device. The device comprises a data filter module and a drug balance control module. Pre-stored electrocerebral indexes, noxious stimulation data drug usage data are divided into electrocerebral index-sedative data and noxious stimulation data-sedative data. Corresponding drug target control indexes are selected according to electrocerebral index and noxious stimulation data changes in certain period, threshold values are preset, and injection of muscle relaxants are increased or stopped based on the set threshold values. Meanwhile, bispectral index, noxious stimulation data, neuromuscular retarding depth data change tendency slope and the like can be analyzed dynamically, and transverse balance adjusting control is performed on three signals. The invention further provides a work method of the device. According to the device and the method, the problem the imbalanced usage of three drugs is solved, effects of individual differences are prevented, the safety during anesthesia is guaranteed to the largest extent, and good social values and application prospects are provided.
Owner:GUANGXI VERYARK TECH
Anxiolytic agents with reduced sedative and ataxic effects
ActiveUS7119196B2Less side effectsMedication convenienceBiocideNervous disorderBenzodiazepineMuscle relaxant
Orally active benzodiazepine derivatives and their salts are disclosed. These compounds and their salts have anxiolytic and anticonvulsant activity with reduced sedative / hypnotic / muscle relaxant / ataxic effects.
Owner:WISYS TECH FOUND
Bio-energy muscle relaxants
Human muscle tissues involve striated and smooth muscles. Each muscle tissue possesses its own special function. Differences of physiology functions among the muscle tissues are mainly determined by their various initiation and signal transmission systems, defined as the pre-muscle molecular motor mechanism, or initiating and regulating mechanism. The current medications, drugs, and therapies for diseases and symptoms related abnormal increased muscle tone or excessive muscle contraction are aimed just at the pre-muscle molecular motor mechanisms, whereas without directly intending to effect on the muscle molecular motor mechanism i.e. the contractile apparatus mechanism at all, which, however, is in common for all kinds of muscle tissues. The muscle molecular motor mechanism mainly involves recycling of actin-myosin filament cross-bridge formation and sliding movement. In the process, bio-energy provided by ATP hydrolysis is necessarily required. Therefore, abnormal increased muscle tone or excessive contraction of muscle tissues under diseased conditions may be modified by inhibition of the muscle molecular motor with the actin-myosin ATPase inhibitor, which blocks hydrolysis of ATP, then reduces release of bio-energy for the muscle contraction.Our studies in vitro and in vivo have demonstrated that BDM, an ATPase inhibitor, thereby, its analogues, derivatives, and other chemicals possessing similar effect on ATPase may be used as bio-energy muscle relaxants (general muscle relaxants).
Owner:YISHENG ZHANG CHONGGANG WANG & PEI WANG
Phenylcarbamate compound and muscle relaxant containing the same
A novel phenylcarbamate compound and a pharmaceutical composition containing the same are provided. More specifically, a novel phenylcarbamate compound, a composition for muscle relaxation containing the phenylcarbamate compound as an active ingredient, and a method of muscle relaxation comprising administering a therapeutically effective amount of the phenylcarbamate compound, are provided.
Owner:BIO PHARM SOLUTIONS
Nimesulide and muscle relaxant combinations thereof
InactiveUS20110053877A1Increased percutaneous penetration rateAvoid skin irritationBiocideAntipyreticThiocolchicineThiocolchicoside
A topical pharmaceutical formulation made up of nimesulide or a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative of nimesulide, together with thiocolchicoside or a pharmaceutically acceptable derivative of thiocolchicoside. The present invention more particularly relates to pharmaceutical combinations of nimesulide and thiocolchicoside, in the form of topical gels, ointments, cream, sprays, or lotions with anti-inflammatory, analgesic, and myorelaxant activities.
Owner:SANOVEL ILAC SANAYI & TICARET ANONIM SIRKETI
Non-depolarizing muscle relaxant composition as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN108926564AGood storage stabilityPromote recoveryOrganic active ingredientsMuscular disorderSide effectCompound c
The invention discloses a mivacurium chloride composition as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The mivacurium chloride composition consists of mivacurium chloride, a compound A,a compound B as well as an optional compound C and an optional compound D, wherein in terms of total weight of the mivacurium chloride composition, the compound A accounts for 0.001-0.15wt%, preferably 0.001-0.13wt%, and more preferably 0.001-0.1wt%; and the compound B accounts for 0.001-0.15wt%, preferably 0.006-0.15wt%, and more preferably 0.01-0.15wt%. The mivacurium chloride composition provided by the invention is good in stability in long-term preservation, relatively low in histamine release action and low in toxic and side effects.
Owner:SICHUAN CREDIT PHARMA
Stereospecific anxiolytic and anticonvulsant agents with reduced muscle-relaxant, sedative-hypnotic and ataxic effects
InactiveUS7618958B2Reduce managementReducing anxiety and convulsant disorderBiocideNervous disorderChemical structureDisease
The present invention provides compositions and methods of using stereospecific benzodiazepine derivatives, their salts and prodrugs for the treatment of anxiolytic or convulsant disorders having the side effects of reduced alcohol craving in human alcoholics and a concomitant reduced sedative, hypnotic, muscle relaxant and ataxic side-effects. The invention further provides pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of anxiolytic and convulsant disorders in subjects in need thereof, comprising a compound, prodrug or a salt having a chemical structure represented by any one of Formula I-XXI and a pharmaceutically-acceptable carrier.
Owner:WISYS TECH FOUND
Flurbiprofen and muscle relaxant combinations
This invention is a novel pharmaceutical composition comprising flurbiprofen or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt thereof in combination with an α-2 adrenergic receptor agonist or a gamma-aminobutiric acid receptor agonist with anti-inflammatory, analgesic and myorelaxant activity.
Owner:SANOVEL ILAC SANAYI & TICARET ANONIM SIRKETI
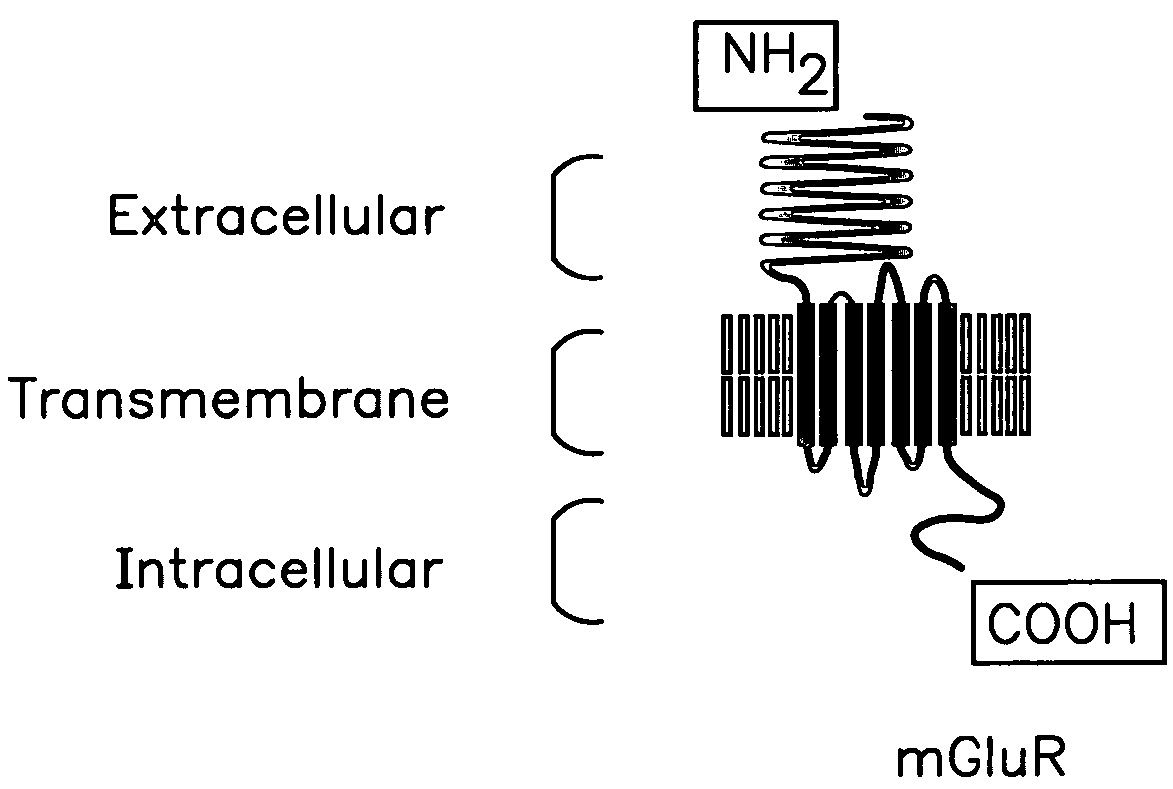
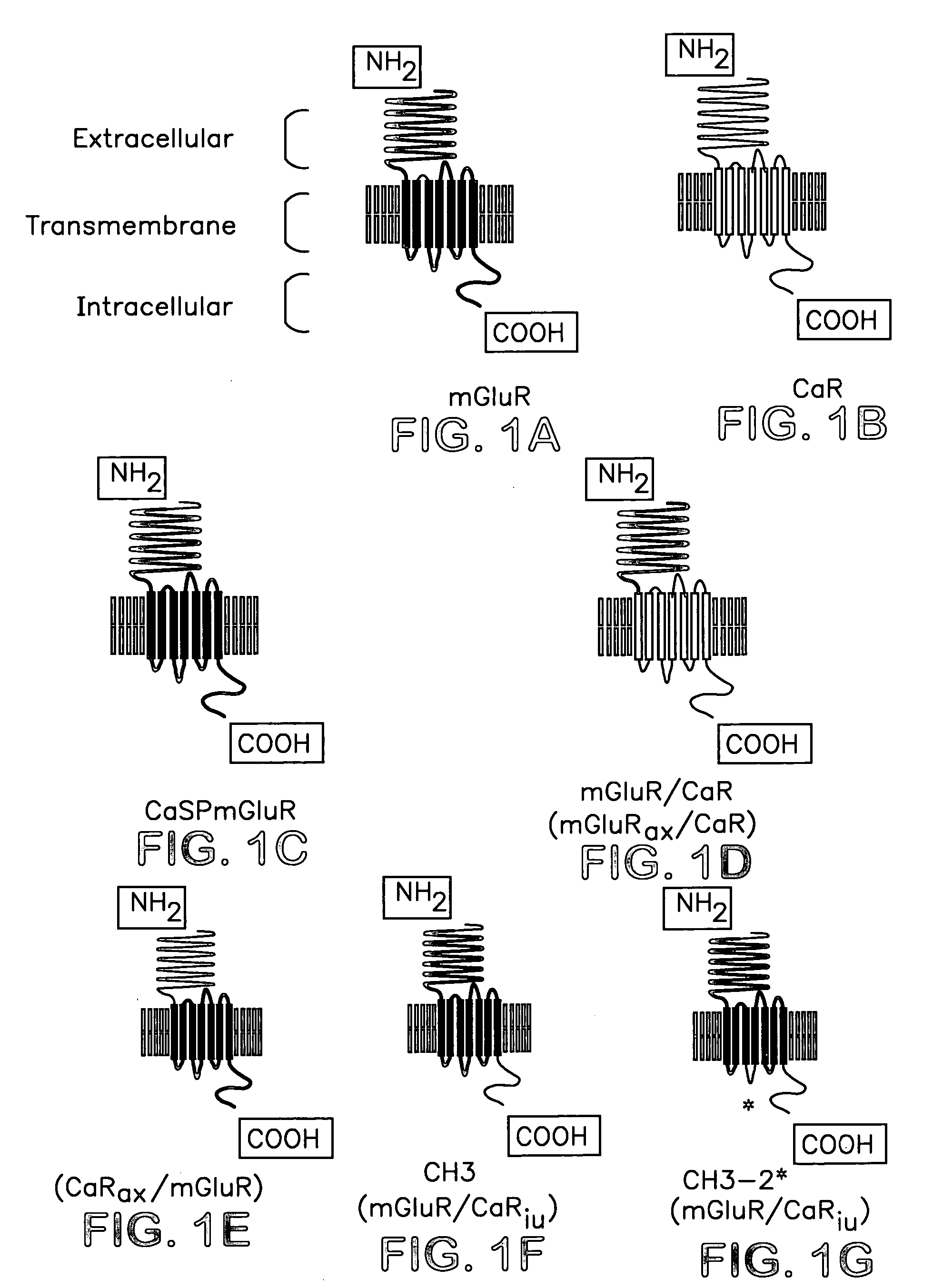
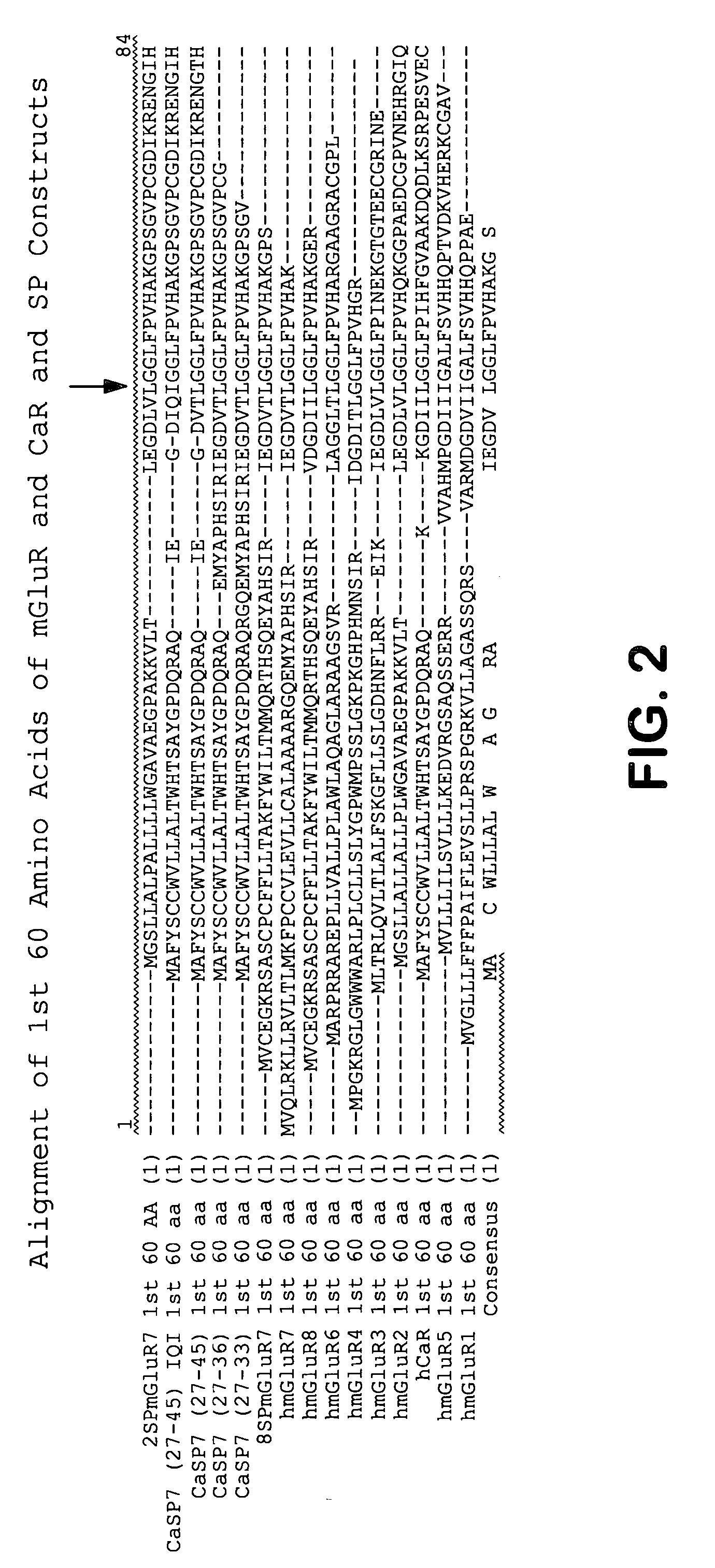
Chimeric metabotropic glutamate receptors and uses thereof
InactiveUS20050186658A1High expressionImprove the level ofPeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMuscle relaxantAnalgesic effect
The present invention provides chimeric receptors that include an extracellular domain from a metabotropic glutamate receptor and a non-native signal peptide, e.g., a calcium receptor signal peptide. The invention also includes methods of preparing such chimeric receptors, and methods of using such receptors to identify and characterize compounds which modulate the activity of metabotropic glutamate receptors. The invention also relates to compounds and methods for modulating metabotropic glutamate receptor activity and binding to metabotropic glutamate receptors. Modulation of metabotropic glutamate receptor activity can be used for different purposes such as treating neurological disorders and diseases, inducing an analgesic effect, cognition enhancement, and inducing a muscle-relaxant effect.
Owner:ASTRAZENECA AB
Composition and method for vaginal therapy
InactiveUS20150306063A1Reduces and eliminates painBiocidePharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineActive agent
Provided are a composition and method for vaginal therapy. The composition includes a delivery compound and a pharmaceutically active agent dispersed in the delivery compound. The pharmaceutically active agent includes a centrally acting muscle relaxant. The method for vaginal therapy includes preparing a composition including a pharmaceutically active agent dispersed in a delivery compound, and administering the composition intravaginally. The pharmaceutically active agent includes a muscle relaxant. Another method includes administering the composition extravaginally and then administering the composition intravaginally.
Owner:MCGINNIS DIANE +3
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com