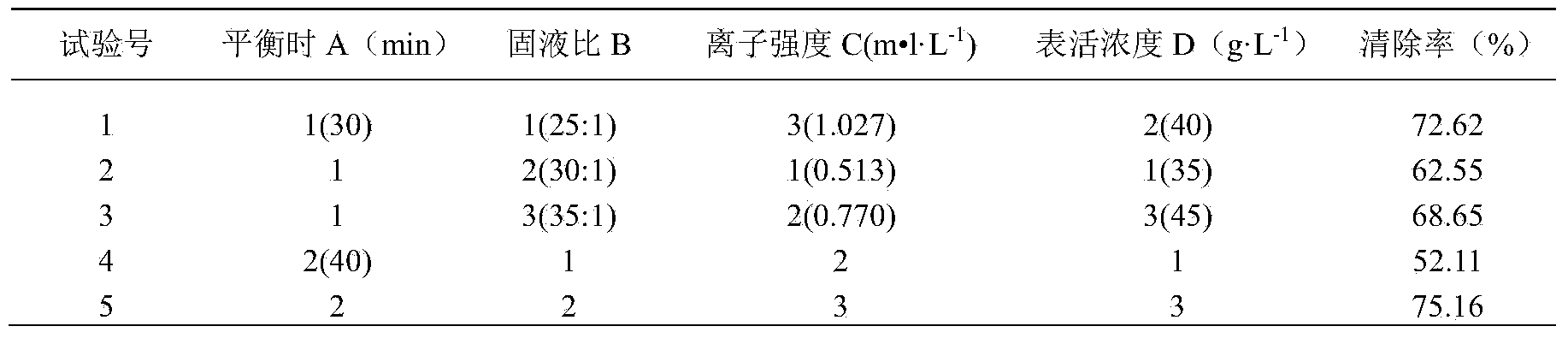
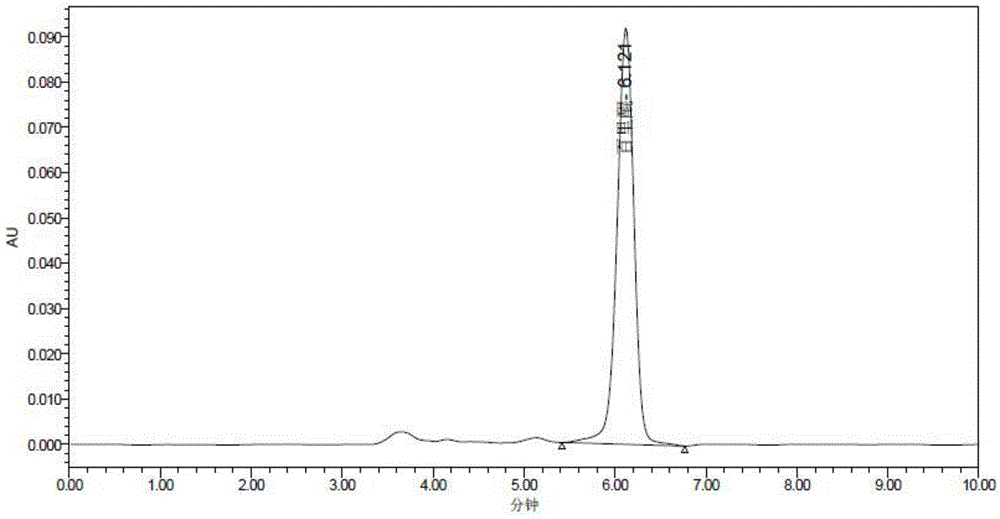
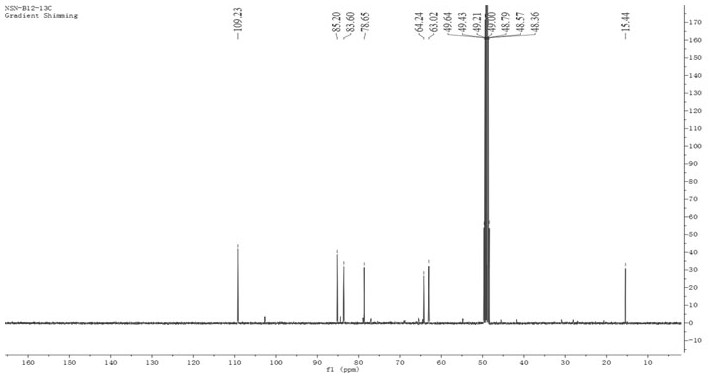
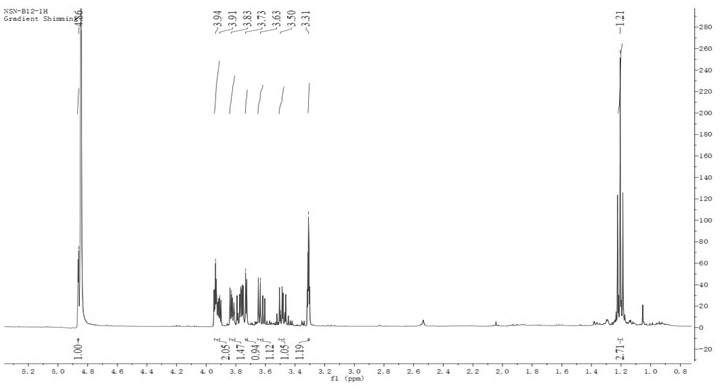
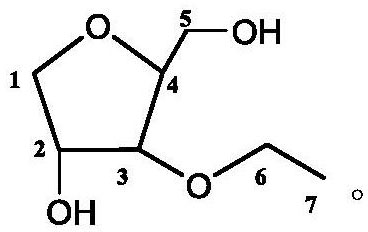
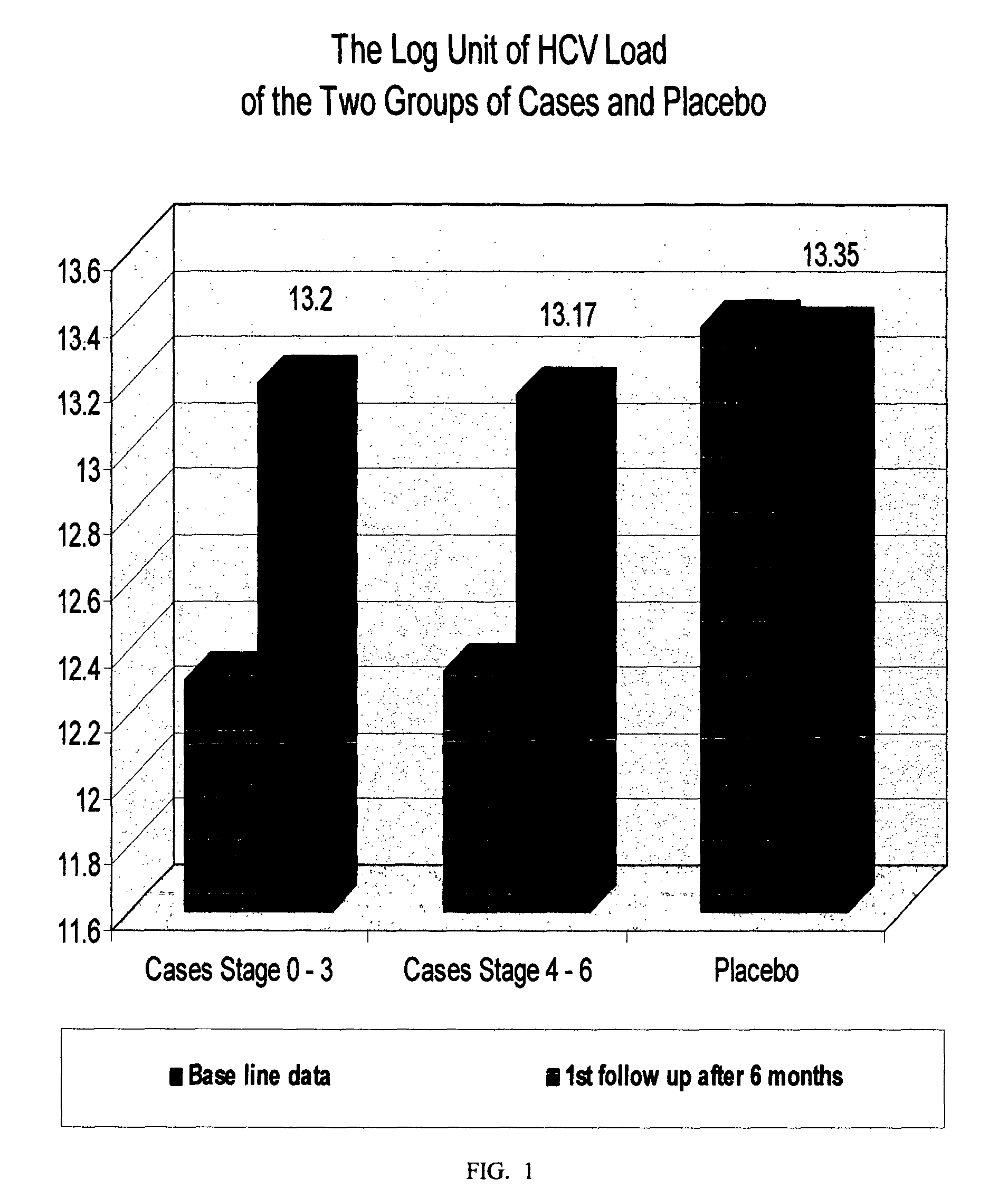
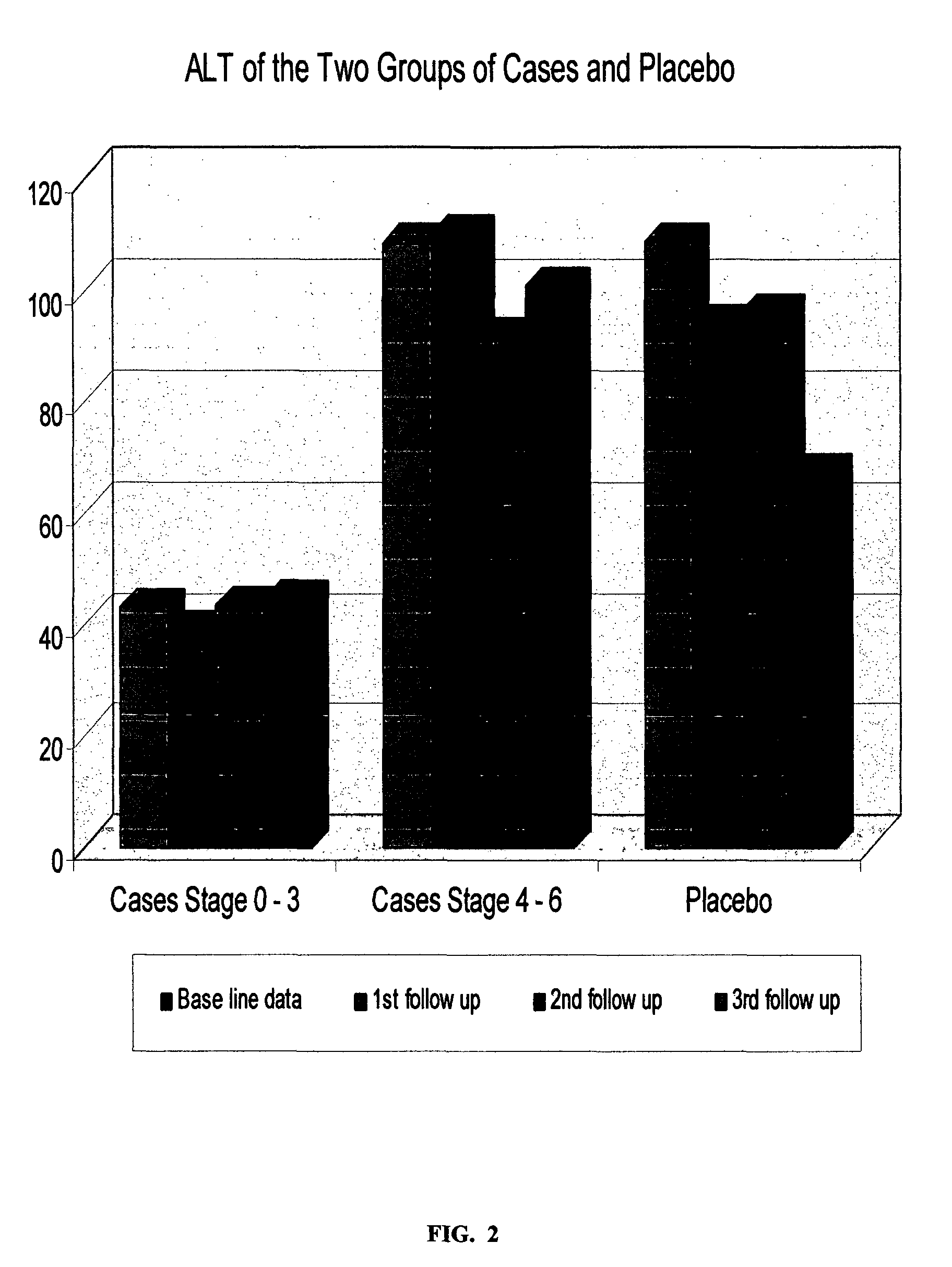
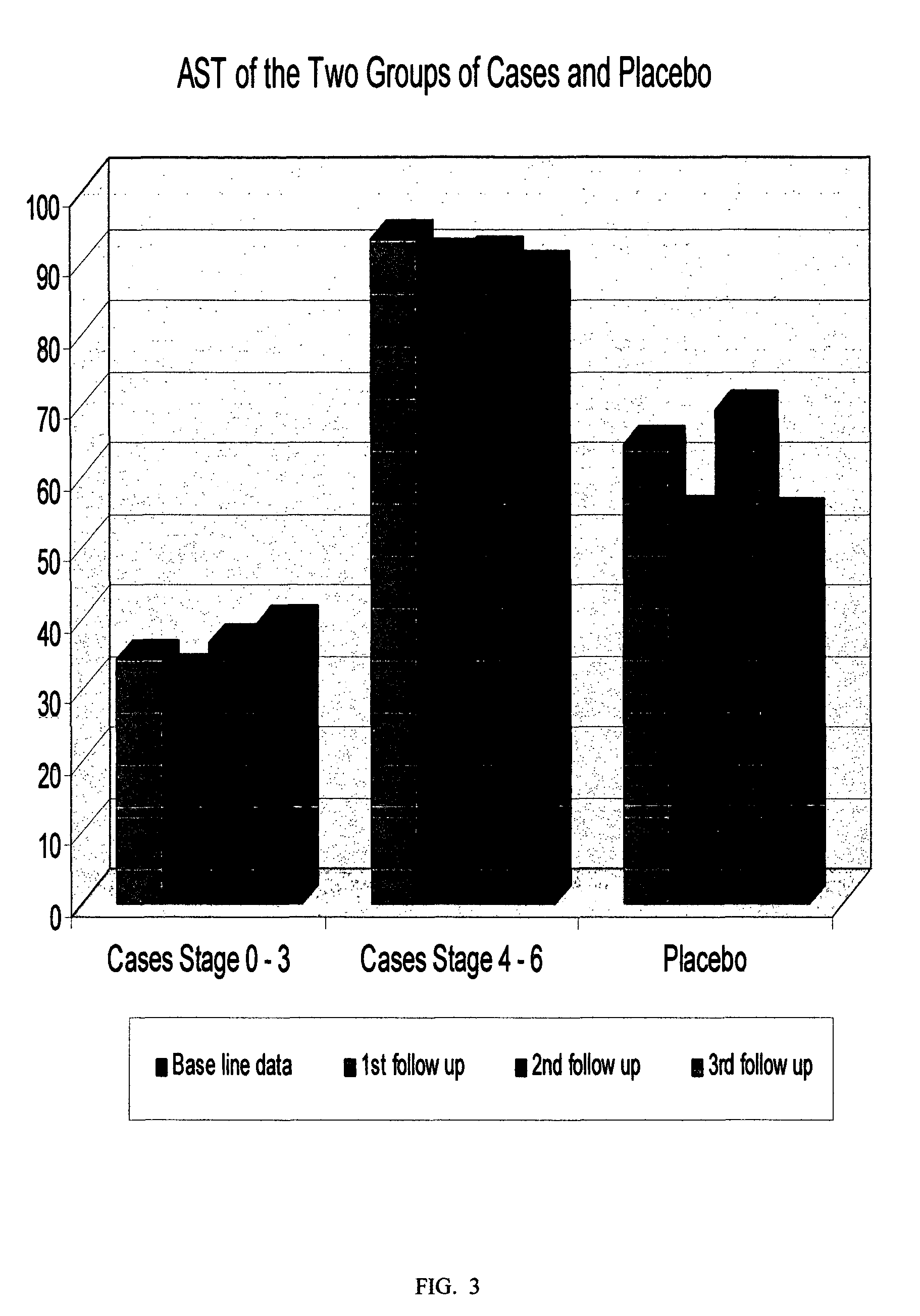
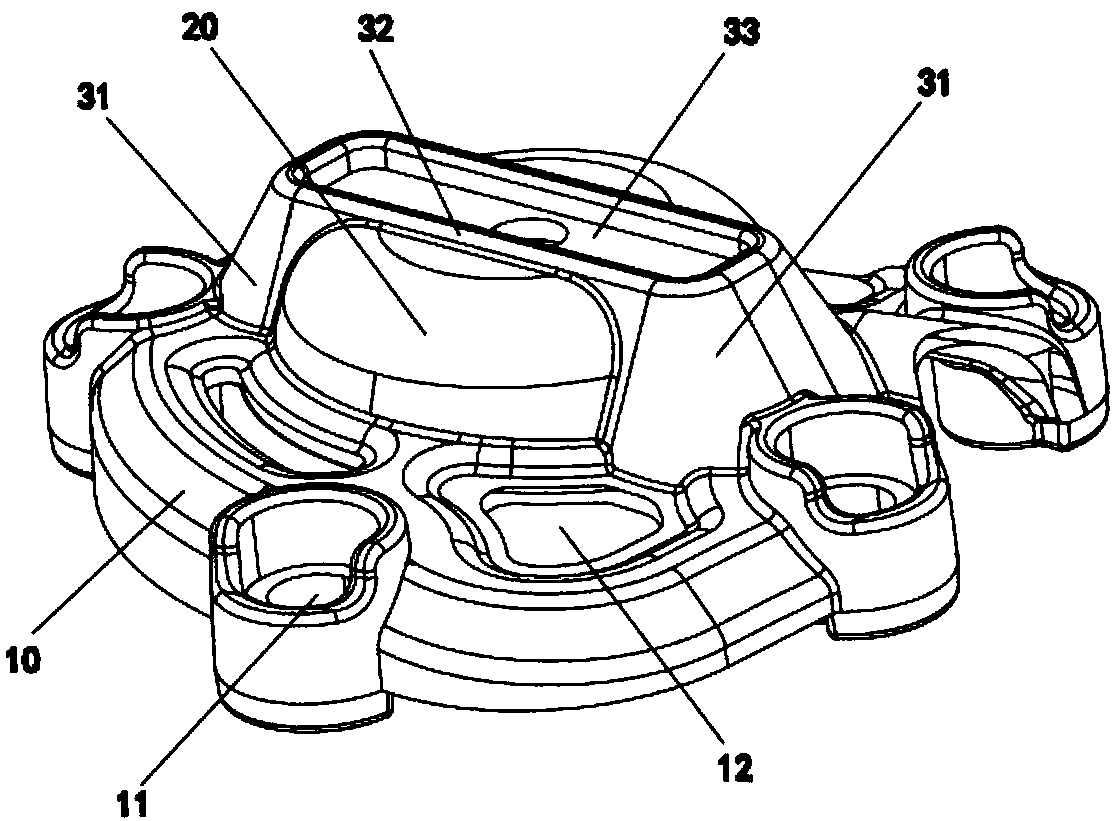
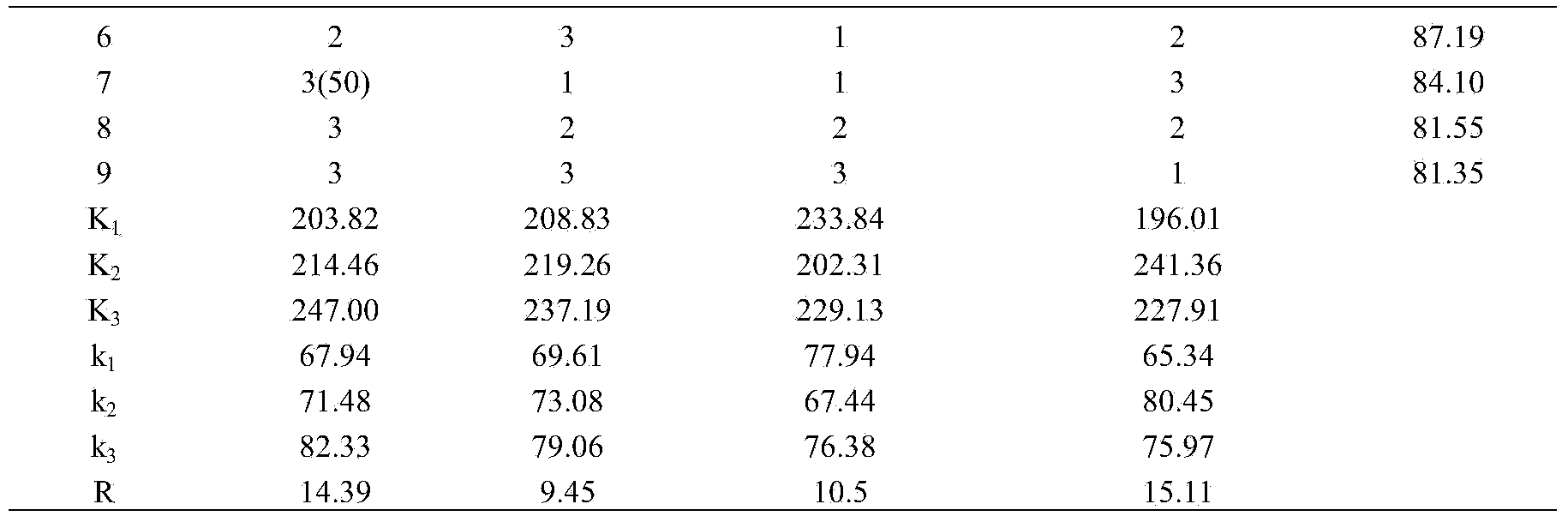Patents
Literature
33 results about "Nigella" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nigella is a genus of 18 species of annual plants in the family Ranunculaceae, native to southern Europe, north Africa, south and southwest Asia. Common names applied to members of this genus are nigella, devil-in-a-bush or love-in-a-mist.
Anti-cigarette herbal formulation as an antidote to tobacco
InactiveUS20060137702A1Good effectControl is complicatedBiocideTobacco treatmentNicotiana tabacumCinnamomum zeylanicum
The present invention provides a novel nicotine free anticigarette herbal formulation as an anti-dote to the poisoning effects of tobacco products such as Cigarettes, Gutka, Pan masala and other similar tobacco related products. Formulation(s) comprises of sterilized dried plant powder / extracts together with the conventional additives to form the oral dosage forms, which include tablets, capsules, syrup and powders ready for suspension and mouth spray. The anti tobacco addiction herbal formulation comprises of Sesbania grandiflora, Catharanthus roseus, Ocimum sanctum, Myristica fragrans, Elettaria cardamomum, Carum copticum, Syzgium aromaticum, Cinnamomum tamala, Acorus calamus, Zingiber officinale, Piper nigrum, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Cuminum cyminum, Nigella sativum, Cinnamomum camphora, Piper longum Ocimum gratssimum and Hemidesmus indicus.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Anti-cigarette herbal formulation as an antidote to tobacco
InactiveUS7534454B2Control is complicatedEffective controlBiocideTobacco treatmentCinnamomum zeylanicumNicotiana tabacum
The present invention provides a novel nicotine free anticigarette herbal formulation as an anti-dote to the poisoning effects of tobacco products such as Cigarettes, Gutka, Pan masala and other similar tobacco related products. Formulation(s) comprises of sterilized dried plant powder / extracts together with the conventional additives to form the oral dosage forms, which include tablets, capsules, syrup and powders ready for suspension and mouth spray. The anti tobacco addiction herbal formulation comprises of Sesbania grandiflora, Catharanthus roseus, Ocimum sanctum, Myristica fragrans, Elettaria cardamomum, Carum copticum, Syzygium aromaticum, Cinnamomum tamala, Acorus calamus, Zingiber officinale, Piper nigrum, Cinnamomum zeylanicum, Cuminum cyminum, Nigella sativum, Cinnamomum camphora, Piper longum Ocimum gratissimum and Hemidesmus indicus.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
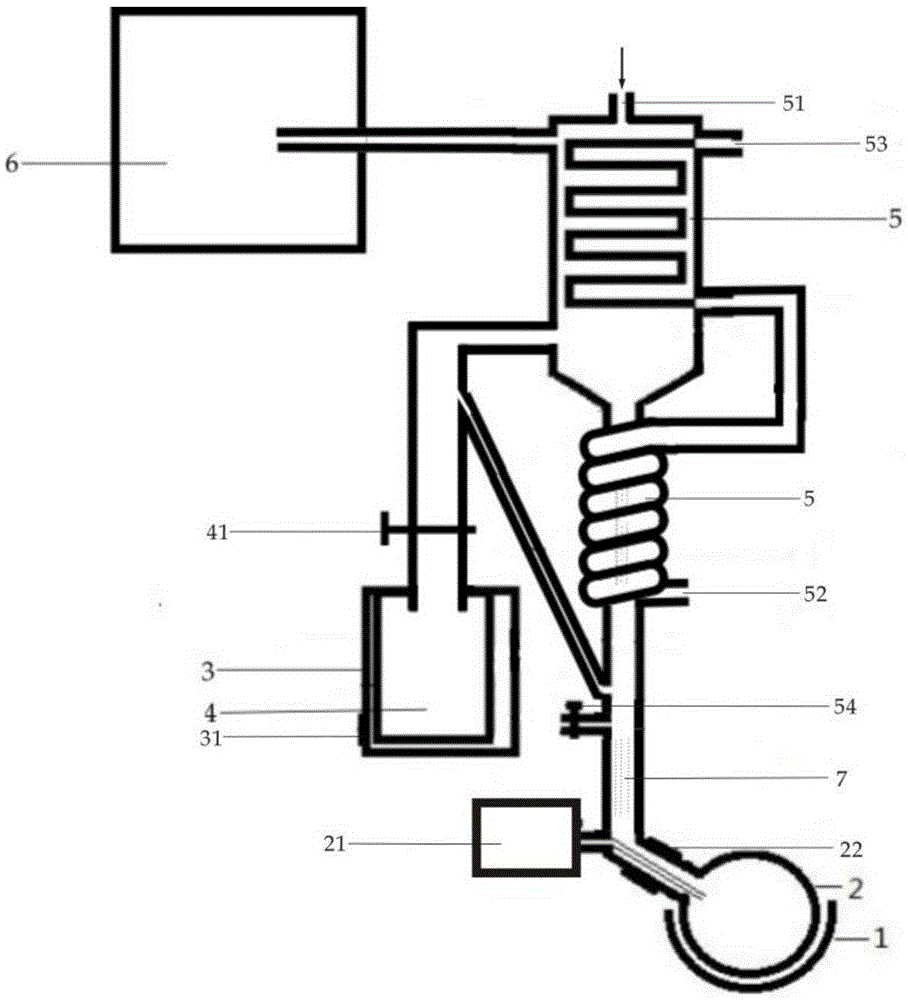
Method and device for extracting nigella plant seed volatile oil and application of volatile oil
The invention discloses a method and a device for extracting nigella plant seed volatile oil and an application of the volatile oil. The method comprises the following steps: extracting, namely extracting volatile oil from soaked ground materials under the microwave irradiation power of 400-700W and the pressure of 0.03-0.05MPa, vaporizing out the volatile oil along with water vapor and feeding into a condensation device; dissolving, namely washing and dissolving the condensed and refluxed volatile oil by an organic solvent; drying to remove water, namely removing water from the organic solvent in which the volatile oil is dissolved through an organic solvent drying water remover; recovering and separating, namely recovering the organic solvent by performing reduced-pressure rotary thin film evaporation on the dried organic solvent in which the volatile oil is dissolved at 28-32 DEG C, wherein the rest liquid is the nigella plant seed volatile oil. According to the method, the volatile oil is extracted by virtue of a microwave-assisted extraction method under the reduced-pressure condition, so that the extraction efficiency is remarkably improved. Meanwhile, the obtained volatile oil is better in aroma quality and suitable for spice and essence research.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Botanical drug compositions for treatments of liver and immunological disorders
InactiveUS20050058735A1Increase the number ofHigh activityBiocideUnknown materialsDiseaseAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to compositions comprising the botanicals from the Family Ranunculaceae, Subclass: Dicotyledonae; Crassinucelli, Superorder: Ranunculales. Examples of these botanicals include but are not limited to; Actaea, Anemone, Ranunculus, and Nigella, or extracts thereof, which are useful in treating liver diseases, particularly those with viral etiology. More specifically, the compositions of the present invention are derived from various botanicals or medicinal plants. The compositions of the invention have demonstrated outstanding efficacy for treatment of patients with hepatic disorders. Compositions of the present invention have also exhibited immunomodulatory activities. The preferred compositions contain the botanical ingredients in concentrations of not less than 20% w / v. The treatment can be therapeutic or prophylactic and may be administered orally, parenterally, as suppository or via nasal mucosa. The treatment may be delivered in a single dose, multi-doses or via a slow release mechanism.
Owner:AMBOTAN PHARMA
Oral preparation for treating vitiligo
The invention relates to an oral preparation for treating vitiligo, the preparation is prepared by the ana roots, cloves, dried ginger, aniseed, nigella seed, vegetable seedsf, west fruit, acid vine fruit, deworming Vernonia, psoralen, yellow myrobalan skin, belleric terminalia fruit, emblic leafflower fruit, and saffron. The clinical data indicate that 286 cases of patients is inspected and treated, after they takes the preparation 15-20 days, have obvious effect, the white spot area becomes red, continue taking 45 days, 92% of the patients return to normal local pigment, the pigment recovery area is more than 85%, after continued three courses of treatment, the disease will not relapse. The preparation is capable of regulating abnormal phlegm, promoting blood-circulation and removing blood stasis, catalyzing the synthesizing of melanin cell, having remarkable effect of treating vitiligo, short curative effect, high curability, is not liable to relapse, no toxic effect deputy to make up the lack of other drugs.
Owner:吐尔逊·乌甫尔 +1
Method for extracting antioxidant ingredient from nigella plant seeds based on cloud point extraction and application of antioxidant ingredient
ActiveCN103961282ASimple processMild extraction conditionsCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsWater bathsCloud point
The invention discloses a method for extracting an antioxidant ingredient from nigella plant seeds based on a cloud point extraction and application of the antioxidant ingredient. According to the method, degreased nigella plant seed powder is used as a raw material, and the method comprises the following steps: adding the seed powder into a surfactant solution, sufficiently and uniformly mixing, extracting by assistance of ultrasonic wave to obtain extract and extracted residues; adding an electrolyte into the extract to regulate the ion strength, heating in water bath to a certain temperature and balancing at a constant temperature; standing or centrifuging split phases into an aqueous solution layer and a surfactant enriched layer of the surfactant. The surfactant enriched layer can be treated in two ways respectively: one way is to directly dehydrate to obtain a surfactant mixture with anti-oxidation activity, which can be directly used in appropriate types of cosmetics; the other way is to separate and reclaim the surfactant by adopting a macroporous adsorption resin method, and an antioxidant active crude extract is obtained at the same time. The method is simple in process, does not need toxic or harmful organic solvents, is mild in extraction condition and good in maintenance of antioxidant activity of products, and is advantageous to sufficient utilization of nigella plant seed resource and development of natural antioxidant active cosmetics.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Compositions and methods for treating reproductive indicators symptomatic of male infertility
InactiveUS20190160126A1Promote reproductionGranular deliveryFood scienceCommiphora myrrha resinMale infertility
A nutraceutical composition containing (i) garden cress, (ii) nigella saliva, (iii) commiphora myrrha, and (iv) fenugreek for treating male infertility and a method of treating symptomatic reproductive indicators of male infertility such as sperm concentration, sperm count, and progressive sperm motility by administering an effective amount of the nutraceutical composition having an effective proportion of each constituent.
Owner:ALAFFARI OMAR SALEH
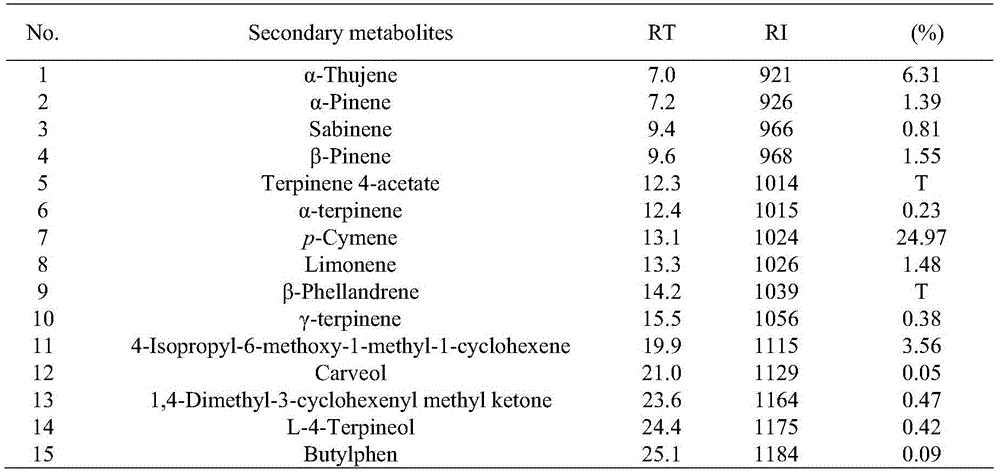
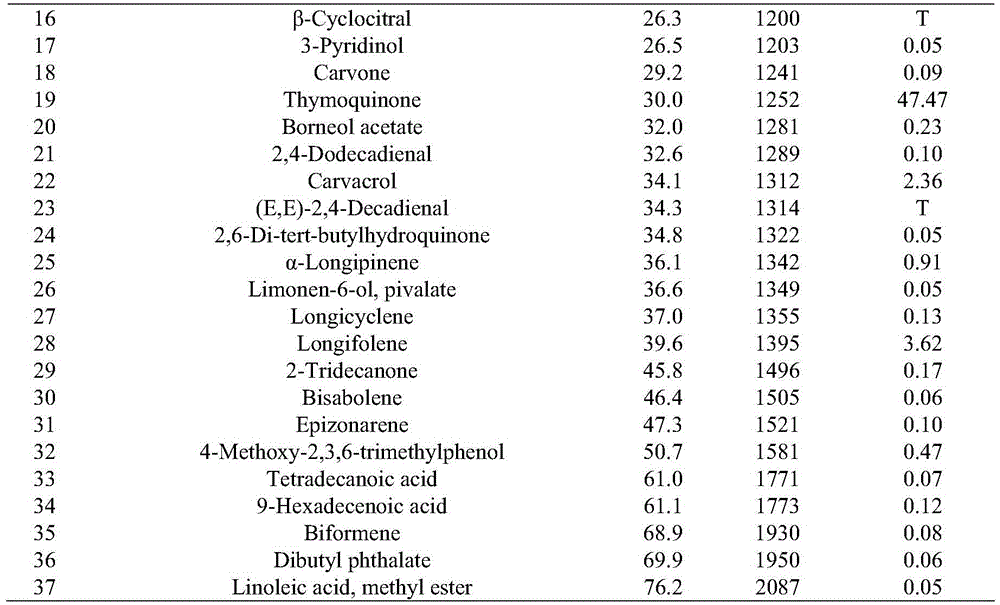
Process for extracting thymoquinone from nigella plant seeds
The invention discloses a method for extracting thymoquinone in nigella plant seeds on the basis of a microwave-assisted solvent extraction method and separating the thymoquinone in nigella plant seeds by virtue of silica gel column chromatography. The method comprises the following steps: extracting: weighing the crushed nigella plant seeds, adding absolute ethyl alcohol according to a certain ratio of material to liquor, extracting under the condition of the microwave irradiation power of 400-700W, filtering, thereby obtaining solid filter residues and thymoquinone extracting solution; repeatedly extracting the filter residues for 1-2 times according to the previous extraction step, and mixing the extracting solution; and separating and purifying: recycling the solvent from the extracting solution at a low temperature until the solution is dry, adding a proper amount of petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (9:1) solution for dissolving, totally transferring the dissolving solution to the top end of the pretreated silica gel chromatography column, eluting by using petroleum ether-ethyl acetate (8:2), collecting the eluent, performing vacuum concentration on the eluent, drying at a low temperature, thereby obtaining the thymoquinone.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Lactation-promoting sow feed and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107616337ADispelling wind and dehumidification is beneficialConducive to detoxificationFood processingAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceDregea sinensis
The invention provides lactation-promoting sow feed and a preparation method thereof. The formula of the feed is prepared from 20 to 40 parts of corn kernels, 5 to 25 parts of dried small shrimp powder, 10 to 30 parts of soybean meal, 12 to 28 parts of whey powder, 15 to 27 parts of spirulina, 9 to 21 parts of duckweed, 12 to 24 parts of nigella damascene, 8 to 24 parts of melodinus fusiformis leaf, 6 to 18 parts of dregea sinensis vine, 12 to 24 parts of primula cernua franch rhizome, 9 to 21 parts of stem of October clematis, 6 to 22 parts of helwingia japonica stem pith and 0.5 to 2 parts of probiotic bacteria. The preparation method of the feed comprises the following steps: (1) fermenting the corn kernels, the soybean meal and the whey powder; (2) reflowing and steaming the spirulina,the duckweed, the nigella damascene, the melodinus fusiformis leaves, the dregea sinensis vines, the primula cernua franch rhizomes, the stems of October clematis and the helwingia japonica stem pithby utilizing acetic acid; (3) mixing all the materials and carrying out secondary fermentation. The feed provided by the invention has the effects of clearing away heat and promoting lactation, dispelling wind and dampness, diminishing swelling and diminishing inflammation, enhancing the body constitution and the like.
Owner:FOSHAN YINNUOWEI BIOTECH CO LTD
Method for extracting ethyl-alpha-D-furan arabinose from Nigella sativa seeds.
ActiveCN112409422AFast extraction and separationEffective extraction and separationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationBiotechnologyNIGELLA SATIVA SEED
The invention relates to a method for extracting and separating a compound ethyl-alpha-D-furan arabinose from a Nigella sativa seed, which comprises the following steps: selecting a dry Nigella sativaseed as a raw material, pulverizing, degreasing with petroleum ether, extracting with ethanol at room temperature, adding methanol into the extract, dissolving, stirring with silica gel, loading, eluting with dichloromethane and methanol to obtain seven components Fr1-Fr7, and continuously separating and purifying to obtain a compound pure product. The method disclosed by the invention is beneficial to better development and utilization of the medicinal plant, namely the Nigella sativa, and is beneficial to sustainable utilization of the plant; the extraction process is simple, the ethyl-alpha-D-furan arabinose compound monomer is easy to obtain, the solvent can be recycled, the extraction amount is large, and industrial production can be achieved.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Nigella saliniva seed polysaccharide and extraction method thereof, and application of Nigella saliniva seed polysaccharide in preparation of medicine for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus
ActiveCN111019010ASignificant effectNo side effectsOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderBacteroidesA lipoprotein
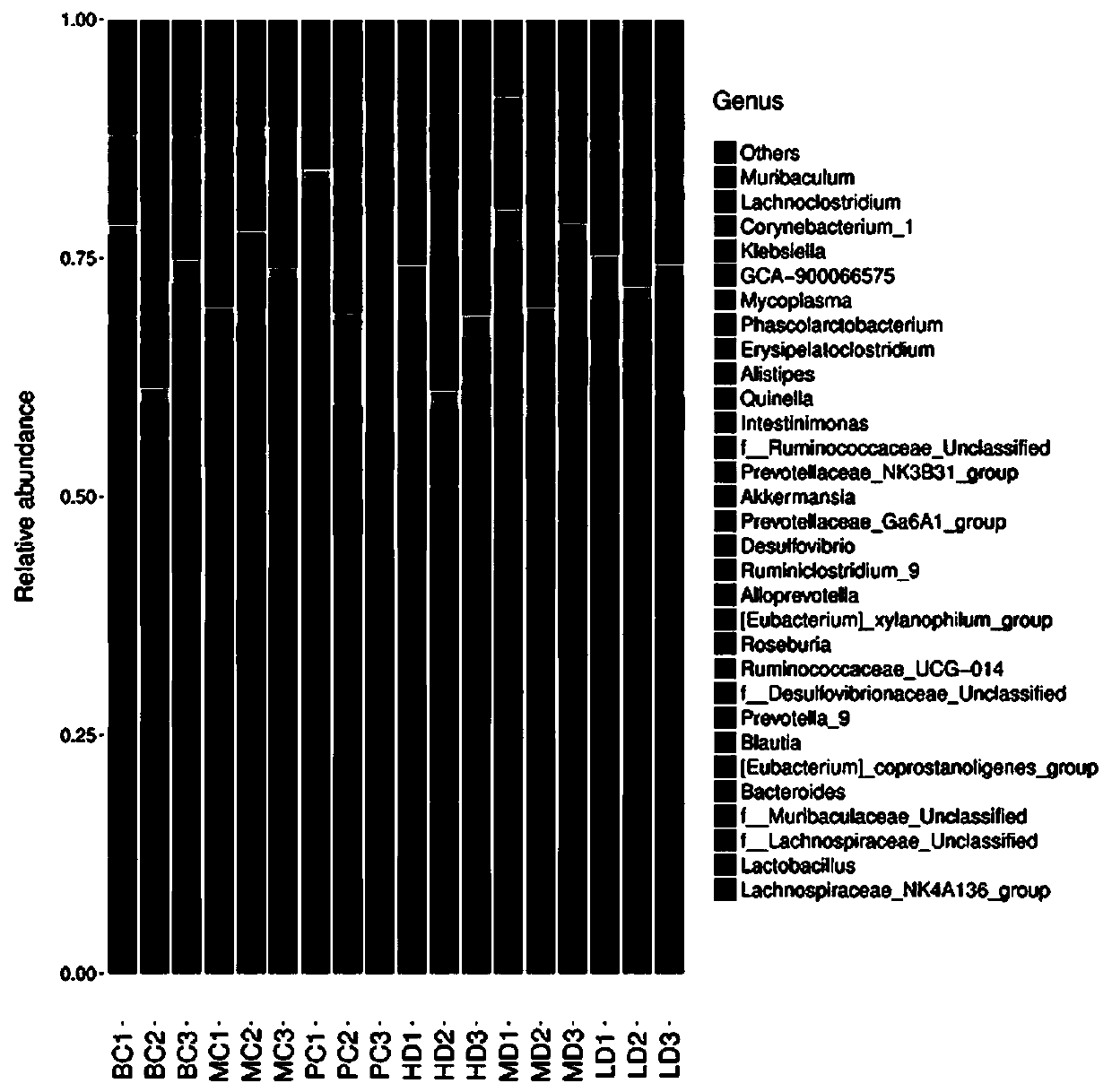
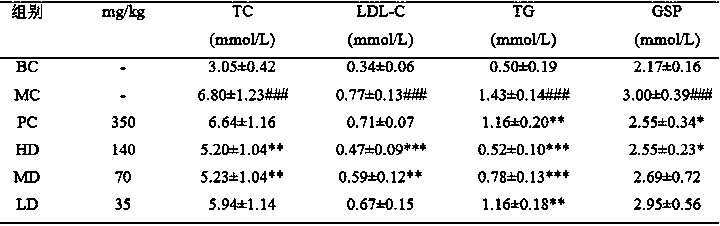
The invention discloses an extraction method for Nigella saliniva seed polysaccharide. The method comprises the following concrete steps of: decocting Nigella saliciva seeds with water, carrying out filtering, adding absolute ethyl alcohol into a filtrate until a final concentration is 70 + / -5 V%, carrying out standing, collecting a precipitate, removing protein by a Sevage method after water dissolution of the precipitate, taking a supernatant, adding absolute ethyl alcohol until a final concentration is 70 + / -5 V%, performing standing, washing a precipitate, and freeze-drying the washed precipitate to obtain the Nigella saliniva seed polysaccharide. Experiments show that the Nigella saliniva seed polysaccharide can significantly reduce the levels of FBG, glycated serum protein (GSP), triglyceride (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C), TNF-alpha, IL-6 and IL-1 beta of mice, and can significantly reduce the levels of FBG, glycated serum protein GSP,triglyceride TG, total cholesterol TC, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol LDL-C and increase the expression levels of insulin (INS), high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) and total antioxidantcapacity (T-AOC). The results of intestinal flora composition analysis show that the abundance of the f_Microbacterium_Unclassified bacterial genus and the Bacteroides genus in a model group is obviously reduced, and the Nigella saliniva seed polysaccharide remarkably increases the abundance of the f_Microbacterium_Unclassified bacterial genus and the Bacteroides genus, which indicates that the Nigella saliniva seed polysaccharide can improve the abnormal state of diabetic mice by regulating intestinal microbiota, and is an ideal medicine for treating type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
Xinjiang-Uygur-medicine nigella-sativa shampoo soap and production technology thereof
InactiveCN108467806AStrong convergenceOil controlCosmetic preparationsHair cosmeticsWrinkle skinAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a Xinjiang-Uygur-medicine nigella-sativa shampoo soap and a production technology thereof. The shampoo soap is prepared from nigella sativa seed oil, nigella-sativa plant ash,water, strong base, lavender essential oil and rosemary essential oil. The production technology includes the steps that 1, the nigella sativa seed oil is squeezed, a plant ash solution is prepared, and a base solution is prepared; 2, the plant ash solution and the strong base solution are mixed and added into the nigella sativa seed oil, and stirring and saponification are carried out; 3, the lavender essential oil and the rosemary essential oil are added, the saponified solution is poured into a mold, drying is carried out, and then demolding, cutting and packaging are carried out. The Xinjiang-Uygur-medicine nigella-sativa shampoo soap has the advantages that the shampoo soap has the effects of the three ingredients of the nigella sativa seed oil, the lavender essential oil and the rosemary essential oil, is capable of preventing alopecia, controlling the oil content, removing freckles, whitening the skin, removing wrinkles, tendering the skin and exciting hair regeneration, and isremarkable in hair growth and alopecia preventing effect; the odor is fragrant, hair is smooth and elegant after the shampoo soap is used, and light fragrances of the lavender essential oil and the rosemary essential oil are emitted; the making technology is scientific and simple, the working procedure is simple, and the cost is low.
Owner:伊犁缔花集香草文化科技有限公司
A method for separating and extracting phenolic glycosides from nigella sativa seeds
ActiveCN112300230BConducive to sustainable usePromote development and utilizationSugar derivativesSugar derivatives preparationBiotechnologyNIGELLA SATIVA SEED
The present invention relates to a Nigella sativa Method for separating and extracting phenolic glycosides from seeds: drying Nigella sativa After the seeds are crushed, degrease with petroleum ether, extract with 60-80% ethanol, recover the solvent under reduced pressure, and obtain the extract extract; Eluted to obtain 7 components Fr1-Fr7; 3) The fourth component Fr4 was separated by silica gel column chromatography to obtain 5 components 4-1~4-5; 4) Component 4-3 was separated by gel column Chromatography, silica gel column chromatography separation, obtain 3,5 dihydroxyphenethyl alcohol-3- O - β ‑Pyranoside; Component 4‑2 was separated by reverse phase column chromatography and Sephadex LH‑20 dextran gel column chromatography to obtain broadbactin C. The extraction process of the invention is simple, the product is easy to obtain, the solvent can be recycled, the extraction amount is large, and industrial production is possible.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY
A kind of oleanane type triterpene saponin and its extraction and separation method and application
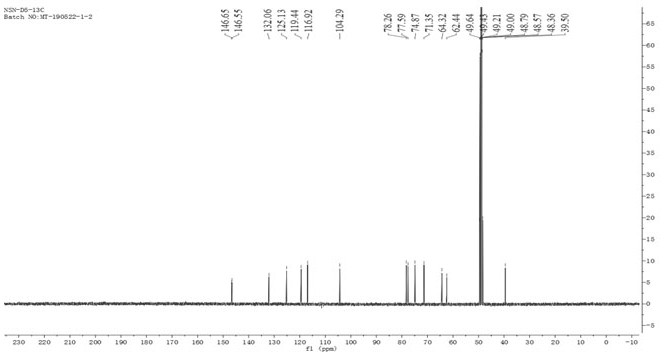
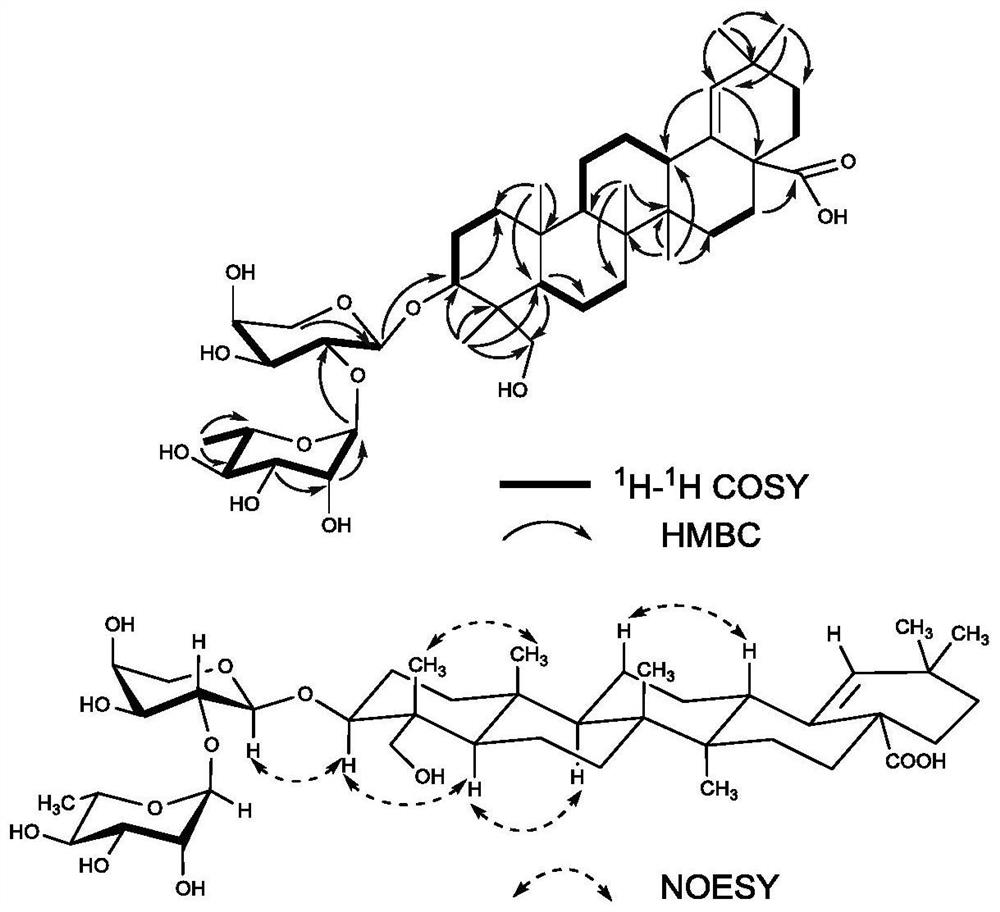
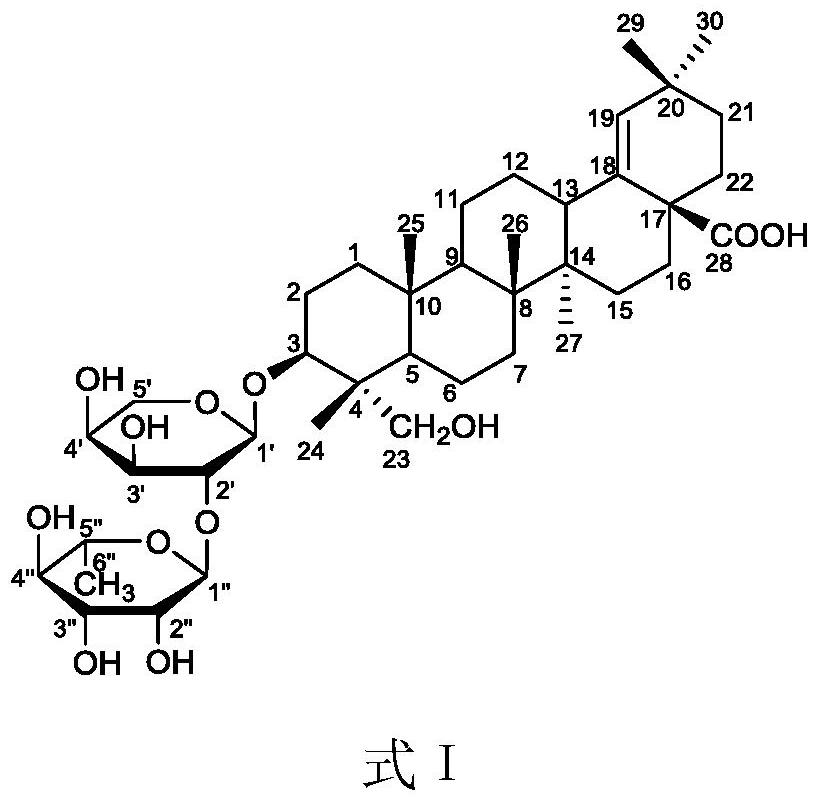
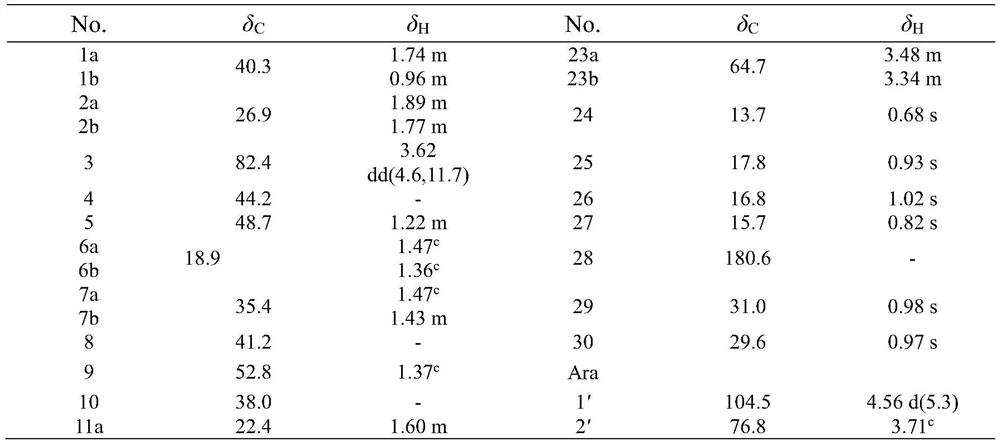
ActiveCN109912680BNovel structureLow toxicityOrganic active ingredientsSteroidsNigella glanduliferaTriterpenoid saponin
The invention discloses an oleanane-type triterpene saponin and its extraction and separation method and its application. It is confirmed by spectral technology that the oleanane-type triterpene saponin is a new kind isolated from Nigella nigella for the first time. compound. The invention discloses a method for extracting and separating the above-mentioned oleanane-type triterpene saponins from Nigella nigellae. The total saponins are obtained after preliminary extraction and separation by 70% ethanol, and the total saponins are obtained after passing through a silica gel chromatographic column. The crude triterpene saponins were separated and purified by Sephadex LH‑20 gel column and high performance liquid chromatography, and the target compound NGTS was successfully separated. The present invention also discloses for the first time that the above-mentioned oleanane-type triterpene saponins have anti-tumor effects, and in vitro anti-tumor experiments have found that the compounds have obvious inhibitory effects on gastric cancer cells and glioma cells, indicating that they can be further used as new anti-tumor compounds. Drug research and development.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Oral preparation for treating vitiligo
The invention relates to an oral preparation for treating vitiligo, the preparation is prepared by the ana roots, cloves, dried ginger, aniseed, nigella seed, vegetable seedsf, west fruit, acid vine fruit, deworming Vernonia, psoralen, yellow myrobalan skin, belleric terminalia fruit, emblic leafflower fruit, and saffron. The clinical data indicate that 286 cases of patients is inspected and treated, after they takes the preparation 15-20 days, have obvious effect, the white spot area becomes red, continue taking 45 days, 92% of the patients return to normal local pigment, the pigment recoveryarea is more than 85%, after continued three courses of treatment, the disease will not relapse. The preparation is capable of regulating abnormal phlegm, promoting blood-circulation and removing blood stasis, catalyzing the synthesizing of melanin cell, having remarkable effect of treating vitiligo, short curative effect, high curability, is not liable to relapse, no toxic effect deputy to makeup the lack of other drugs.
Owner:吐尔逊·乌甫尔 +1
A Minjiang Lily wrky transcription factor gene lrwrky2 and its application
ActiveCN110818783BIncrease resistanceReduce usagePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
The invention discloses a Minjiang lily WRKY transcription factor gene LrWRKY2 , whose nucleotide sequence is as described in SEQ ID NO: 1, and encodes a protein with an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 2, which is confirmed by functional genomics-related technical research in the present invention LrWRKY2 The gene has the function of improving the antifungal effect of the plant, and the antifungal effect of the present invention LrWRKY2 The gene is constructed on a plant expression vector and transferred to tobacco for overexpression. The transgenic tobacco plants have a strong ability to resist fungal infection. The experimental results show that the overexpression LrWRKY2 The transgenic tobacco has a high level of resistance to the infection of Nigeria oryzae, Fusarium solani, Fusarium verticillium, Vitis vinifera, and Alternaria ginseng.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
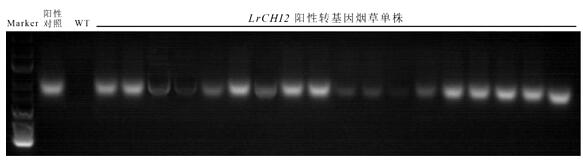
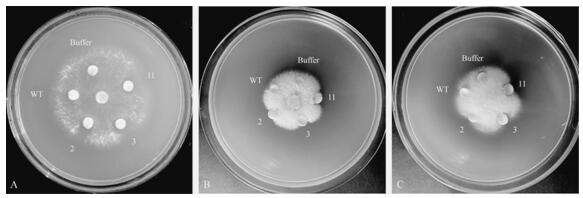
A kind of Minjiang lily chitinase gene lrchi2 and its application
ActiveCN112359049BIncrease resistanceReduce usageFermentationGlycosylasesBiotechnologyNicotiana tabacum
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Honey peach sports drink
InactiveCN105961962ARetain natural flavorRetain nutrientsNatural extract food ingredientsFood ingredient as mouthfeel improving agentPolygonum fagopyrumCoix
The invention discloses a honey peach sports drink, which is prepared from the following raw materials (by weight): 80-90 parts of fructose corn syrup, 24-25 parts of white granulated sugar, 12-15 parts of honey, 10-15 parts of compound juice, 0.6-0.8 part of salt, 0.1-0.2 part of a multi-vitamin preparation, 1-3 parts of lemon peel, 1-3 parts of pitaya peel, 1-2 parts of rose, 1-3 parts of honeysuckle flower, 1-2 parts of Gynura divaricata (Linn.) DC., a proper amount of water, 2-3 parts of coix seeds, 4-6 parts of sorghum rice, 1-3 parts of tartary buckwheat, 1-2 parts of male flowers of eucommia ulmoides oliv, 1.2-2 parts of Thelenota ananas, 1-3 parts of Angelica keiskei koidzmi and 1-2 parts of Nigella damascene.
Owner:安徽大吉象食品科技有限公司
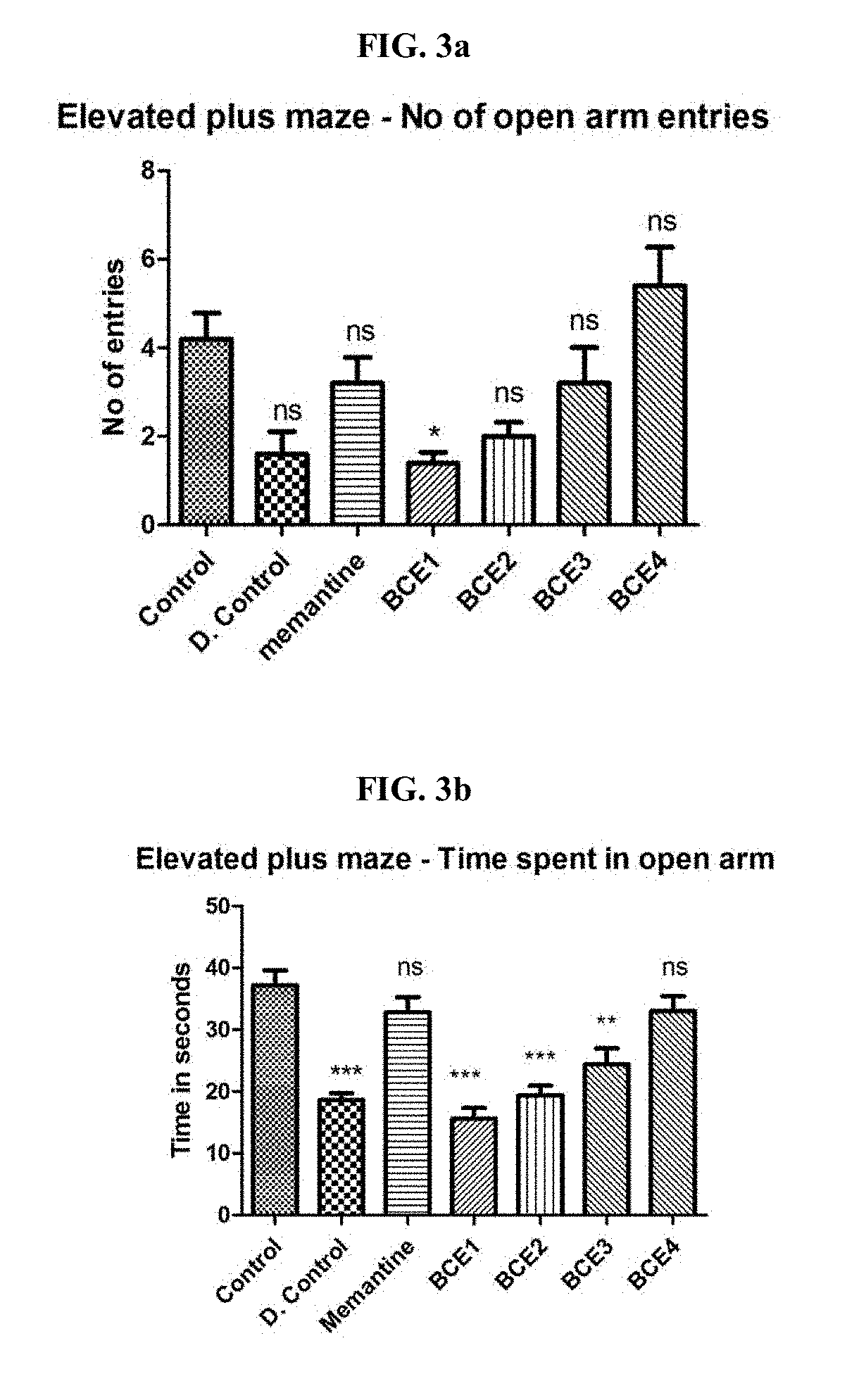
Composition of nigella sativaseeds to treat anxiety, stress and sleep disorders with significant memory enhancement properties and a process for producing the same
ActiveUS10485837B2Good effectEnhance memoryOrganic active ingredientsPlant ingredientsMedicineNigella
The present invention relates to novel black cumin extract compositions and a green process for making the composition. The black cumin extract composition of the invention can be used to treat anxiety, sleep and stress disorders along with significant effect on memory enhancement. The composition is available in oil and powder forms.
Owner:AKAY FLAVOURS & AROMATICS PVT
A method, device and application for extracting volatile oil from seeds of Nigella species
The invention discloses a method and a device for extracting nigella plant seed volatile oil and an application of the volatile oil. The method comprises the following steps: extracting, namely extracting volatile oil from soaked ground materials under the microwave irradiation power of 400-700W and the pressure of 0.03-0.05MPa, vaporizing out the volatile oil along with water vapor and feeding into a condensation device; dissolving, namely washing and dissolving the condensed and refluxed volatile oil by an organic solvent; drying to remove water, namely removing water from the organic solvent in which the volatile oil is dissolved through an organic solvent drying water remover; recovering and separating, namely recovering the organic solvent by performing reduced-pressure rotary thin film evaporation on the dried organic solvent in which the volatile oil is dissolved at 28-32 DEG C, wherein the rest liquid is the nigella plant seed volatile oil. According to the method, the volatile oil is extracted by virtue of a microwave-assisted extraction method under the reduced-pressure condition, so that the extraction efficiency is remarkably improved. Meanwhile, the obtained volatile oil is better in aroma quality and suitable for spice and essence research.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Botanical drug compositions for treatments of liver and immunological disorders
InactiveUS7744929B2Reduce productionOutstanding efficacyBiocideAnimal repellantsDiseaseAdditive ingredient
The present invention relates to compositions comprising the botanicals from the Family Ranunculaceae, Subclass: Dicotyledonae; Crassinucelli, Superorder: Ranunculales. Examples of these botanicals include but are not limited to; Actaea, Anemone, Ranunculus, and Nigella, or extracts thereof, which are useful in treating liver diseases, particularly those with viral etiology. More specifically, the compositions of the present invention are derived from various botanicals or medicinal plants. The compositions of the invention have demonstrated outstanding efficacy for treatment of patients with hepatic disorders. Compositions of the present invention have also exhibited immunomodulatory activities. The preferred compositions contain the botanical ingredients in concentrations of not less than 20% w / v. The treatment can be therapeutic or prophylactic and may be administered orally, parenterally, as suppository or via nasal mucosa. The treatment may be delivered in a single dose, multi-doses or via a slow release mechanism.
Owner:AMBOTAN PHARMA
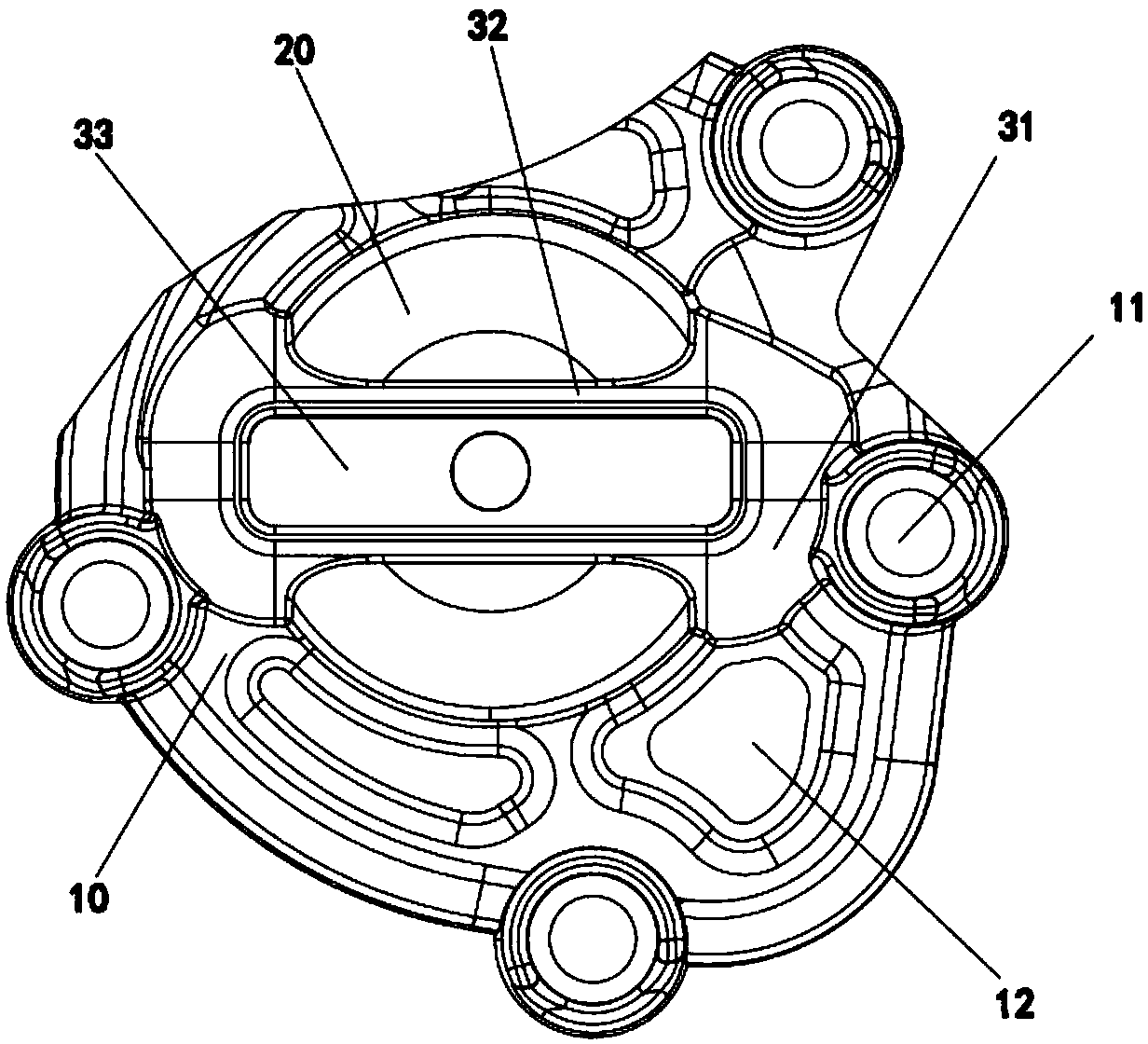
Engine protecting cover
InactiveCN107686656AImprove structural strengthImprove wear resistanceMachines/enginesEngine componentsGlass fiberNigella
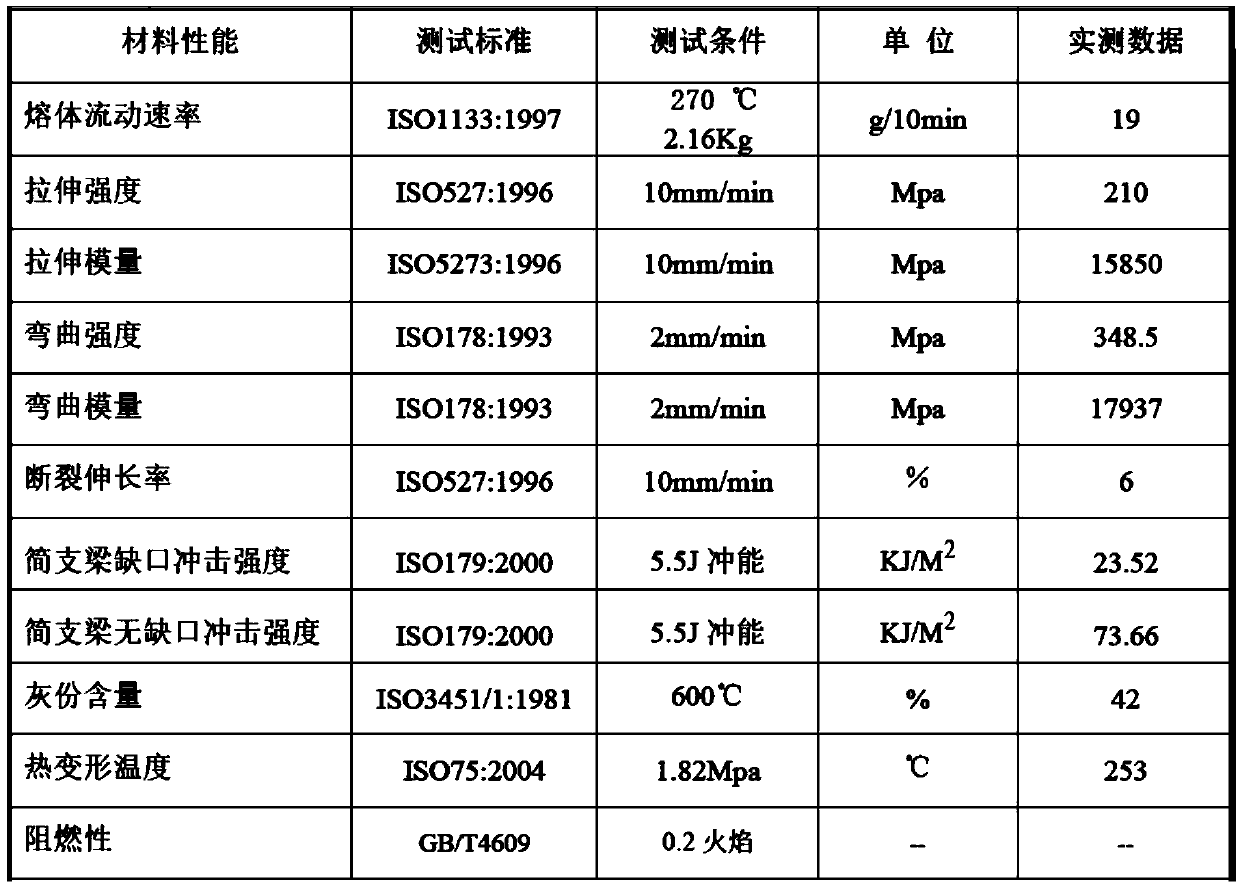
The invention discloses an engine protecting cover, which comprises a bottom plate. A cover body protruded outwards and used for covering on an engine is arranged in the middle of the bottom plate; aplurality of installation holes for installing and fixing the bottom plate are formed in the periphery of the bottom plate; the bottom plate and the cover body are prepared from the following materials in parts by proportion: 45 to 55 parts of PA66, 30 to 50 parts of glass fiber, 6 to 10 parts of flexibilizer, 0.1 to 1 part of lubricating agent, 0.1 to 1 part of phase solvent, 0.1 to 1 part of antioxygen, 0.1 to 1 part of antiaging agent, and 0.1 to 2 parts of nigella. The protecting cover provided by the invention has better structure strength and wear resistance.
Owner:珠海市辉环机动车零部件有限公司
The application of Nigella sativa extract as a drug for the preparation of adjuvant arthritis
ActiveCN107362208BGood treatment effectImprove securitySkeletal disorderRespiratory disorderDiseaseDexamethasone
Owner:中国人民解放军新疆军区药品仪器检验所
A kind of tipping paper base paper with heat-clearing and alcohol-relieving functions and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104005254BHas health benefitsLarge adsorption capacityCoatings with pigmentsPulp beating methodsFiberAlcohol poisonings
The invention discloses a tipping paper base paper with functions of clearing away heat and relieving alcohol, which is characterized in that it is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 3-4 parts by weight of ashweed, 1-2 parts of nigella seed oil, and 41 parts by weight of pomegranate pulp -46, cork pulp 52-55, pterygium 2-4, mannitol 1-1.5, Hovenia dulcis 1-2, taurine 0.5-0.7, activated clay 3-4, iron oxide yellow 1-2, Carboresin 2-3, Ammonium Bicarbonate 1-1.6, Calcium Peroxide 2-2.5, Calcium Propionate 1-2, Auxiliary 1-2, appropriate amount of water; the present invention adds Pterocephala clearing heat and detoxifying, Hovenia dulcis Alcohol poisoning, the production of tipping paper base paper has certain health effects, suitable for social use, adding additives, not only can increase the amount of tar adsorption, but also has a natural fragrance, fresh and pleasant, reducing bad breath, and the fiber distribution of the product of the present invention Uniform, small fluctuations in thickness, tightness, air permeability and other indicators, easy to print.
Owner:CHUZHOU CIGARETTE MATERIALS FACTORY
A kind of mascara and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106963673BImprove use valueFully extractedCosmetic preparationsMake-upBiotechnologyCellulose
The invention discloses a mascara and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of cosmetic preparation. The main raw materials of the mascara include: laurocapram, glyceryl monostearate, β-glucan, modified hydroxyethyl cellulose, lecithin, propolis, concentrated watermelon peel juice, actin, beet Alkali, multivitamin, black seed, lovage and mulberry. The raw materials of the invention have mutual synergistic effect, are rich in nutrition, good in absorbability, have good biological activity, can effectively promote the rapid growth of eyelashes, have good antiseptic performance, and are worthy of popularization and application.
Owner:玉林祺钟商贸有限公司
Skin bacteriostatic cream and preparation method thereof
The invention provides skin bacteriostatic cream and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: dissolving: dissolving beeswax in a water bath kettle at the temperature of 60 DEG C for later use; stirring the vegetable oil: pouring olive fruit oil, sesame oil, cultivated nigella nigra seed oil, clove essential oil, lithospermum oil, sea buckthorn fruit oil, pistachio oil, walnut oil, pomegranate seed oil and shea butter into an interlayer stirring pot with a heating function, heating to 40 to 50 DEG C while stirring, stirring for 6 to 8 hours, and keeping the temperature and standing for 2 hours; stirring the mixture: pouring the dissolved beeswax into an interlayer stirring pot, continuously stirring for 2H, reducing the temperature to 35 DEG C, slowly adding parachlorometaxylenol, and uniformly stirring; and filtering and filling: filtering the fully stirred mixture, and filling to obtain a finished product. The skin antibacterial cream is very suitable for the skin of people living in dry climate in Xinjiang due to high oil content, is rich in vitamin E grease, not only nourishes the skin, but also forms a layer of protective film on the skin, shrinks, moistens, inhibits bacteria and relieves itching.
Owner:新疆埃芙卢兹生物科技有限公司
Cod pastry capable of promoting production of body fluid to quench thirst
InactiveCN106235001AFull of nutritionIncrease elasticityLactobacillusNatural extract food ingredientsThirstSweet flavor
The invention provides a cod pastry capable of promoting production of body fluid to quench thirst. The cod pastry is prepared from the following raw materials by weight: 80 to 90 parts of cod, 3 to 5 parts of Lactobacillus casei, 2 to 3 parts of salt, 2 to 3 parts of glucose, 0.01 to 0.02 part of sodium selenite, 20 to 25 parts of trotters, 5 to 6 parts of sweet osmanthus, 4 to 5 parts of white vinegar, 5 to 6 parts of yellow rice wine, 30 to 35 parts of pumpkin, 1 to 2 parts of rice juice, 0.01 to 0.02 part of nigella oil. According to the invention, the cod is subjected to selenium-rich fermentation by Lactobacillus casei, so fish protein is slowly acidified by organic acid to form a gel structure, and thus, the cod flesh has improved elasticity and hardness and enhanced color and flavor, is rich in organic selenium and exerts health-care effect; the cod pastry prepared through combination of the cod flesh, brown sugar, fruit vinegar and the like has fragrant and sweet flavor; to increase the content of dietary fiber of the cod pastry, lemon pomace dietary fiber is increased, so waste of lemon pomace is prevented; and soup prepared from the sweet osmanthus and trotter is added to improve nutrients of the cod pastry.
Owner:合肥市香口福工贸有限公司
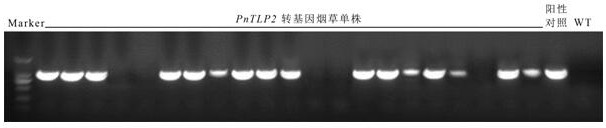
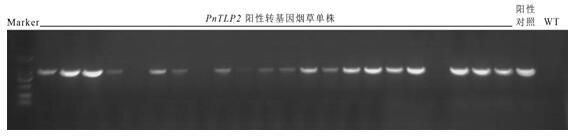
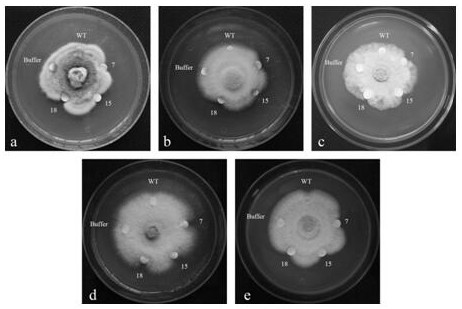
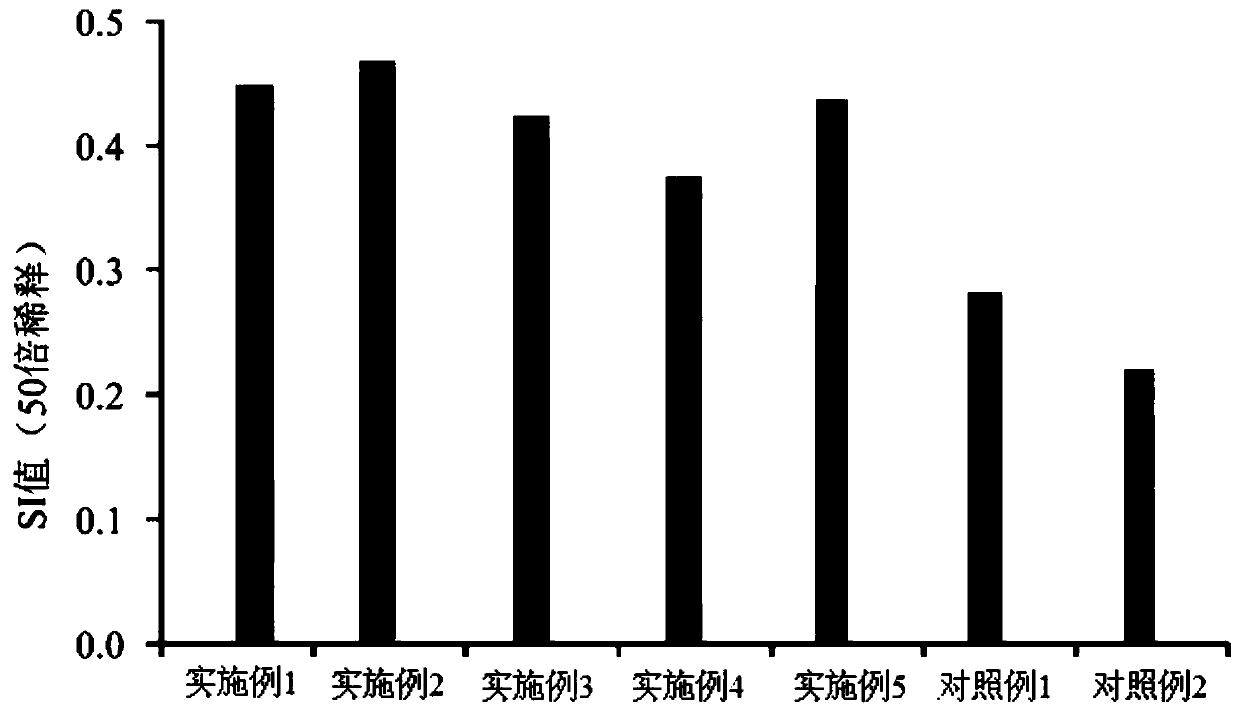
A kind of notoginseng sweet protein gene pntlp2 and its application
ActiveCN109295068BIncreased fungal resistanceIncrease resistancePlant peptidesFermentationBiotechnologyAntifungal
The invention discloses a notoginseng sweet protein gene PnTLP2 , its nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO: 1, encoding the sweet protein of amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO: 2; PnTLP2 The gene has the function of improving the anti-fungal effect of the plant, and the anti-fungal effect of the present invention PnTLP2 The gene was constructed on a plant expression vector and transferred to tobacco for overexpression. As a result, the transgenic tobacco plants had strong antifungal activity in vitro, and the overexpression PnTLP2 The transgenic tobacco has a significant inhibitory effect on the growth of five plant pathogenic fungi, including Fusarium oxysporum, Fusarium solani, Alternaria ginseng, Sclerotinia and Nigeroryza sativa.
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Antrodia camphorata fermented product and preparation method thereof
The invention provides an Antrodia fermented product and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps that (1) Antrodia is soaked in water, extracted, crushed and subjected to mashing, and mash is obtained; (2) after culture medium components are added into the mash, leuconostoc mesenteroides are added to carry out first fermentation, and first fermentation liquor is obtained; (3) pectinase is added into fruit and vegetable liquid with the pH value being 4.5-6 to carry out enzymolysis, and zymolytic fruit and vegetable liquid is obtained; (4) after culture medium components are added into the zymolytic fruit and vegetable liquid, compound lactic acid bacteria are added to carry out second fermentation, and second fermentation liquor is obtained; (5) after culture medium components are added into the second fermentation liquor, compound microzyme is added to carry out third fermentation, and third fermentation liquor is obtained; (6) the first fermentation liquor and the third fermentation liquor are evenly mixed and then centrifuged, and the Antrodia fermented product is obtained after homogenization and sterilization are carried out on centrifuged supernate. The Antrodia fermented product is good in taste and unique in flavor, has good immune adjustment and oxidation resistance functions, and is suitable for the crowd.
Owner:CHINA NAT RES INST OF FOOD & FERMENTATION IND CO LTD
Herbal composition for increasing fertility in men and a method of synthesizing the same
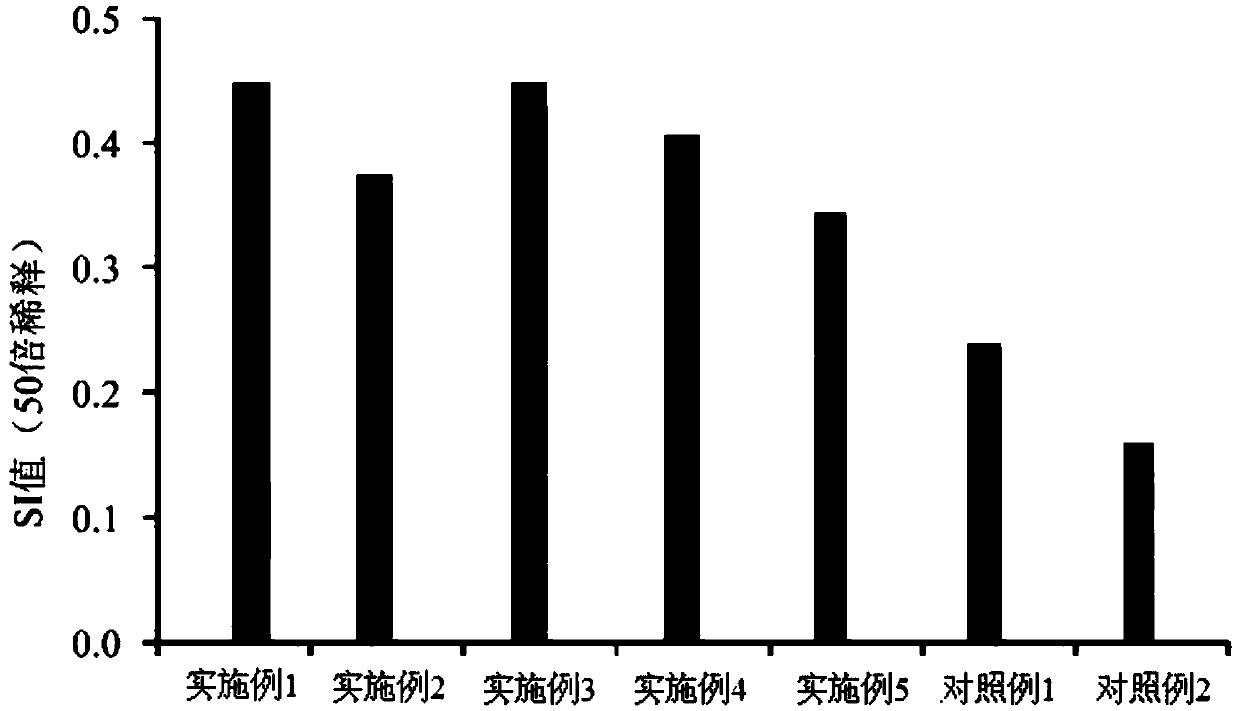
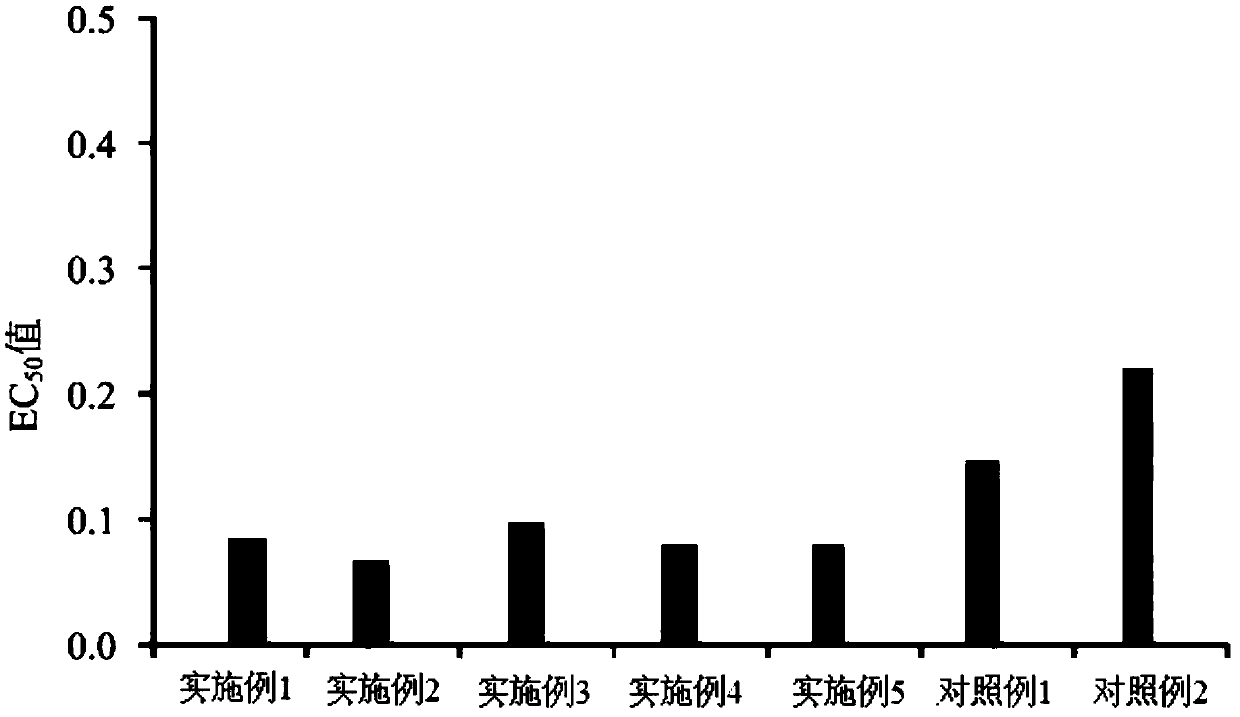
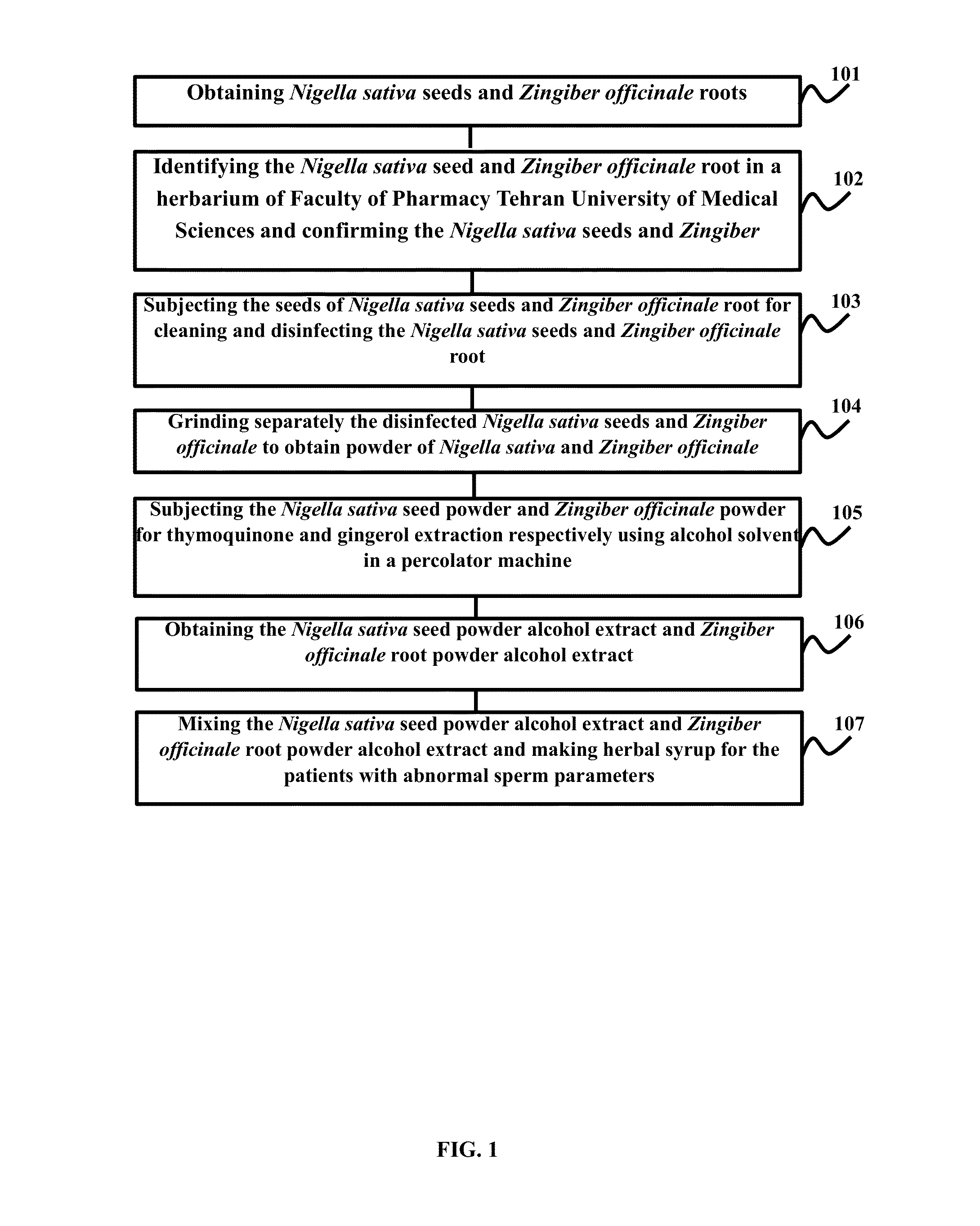
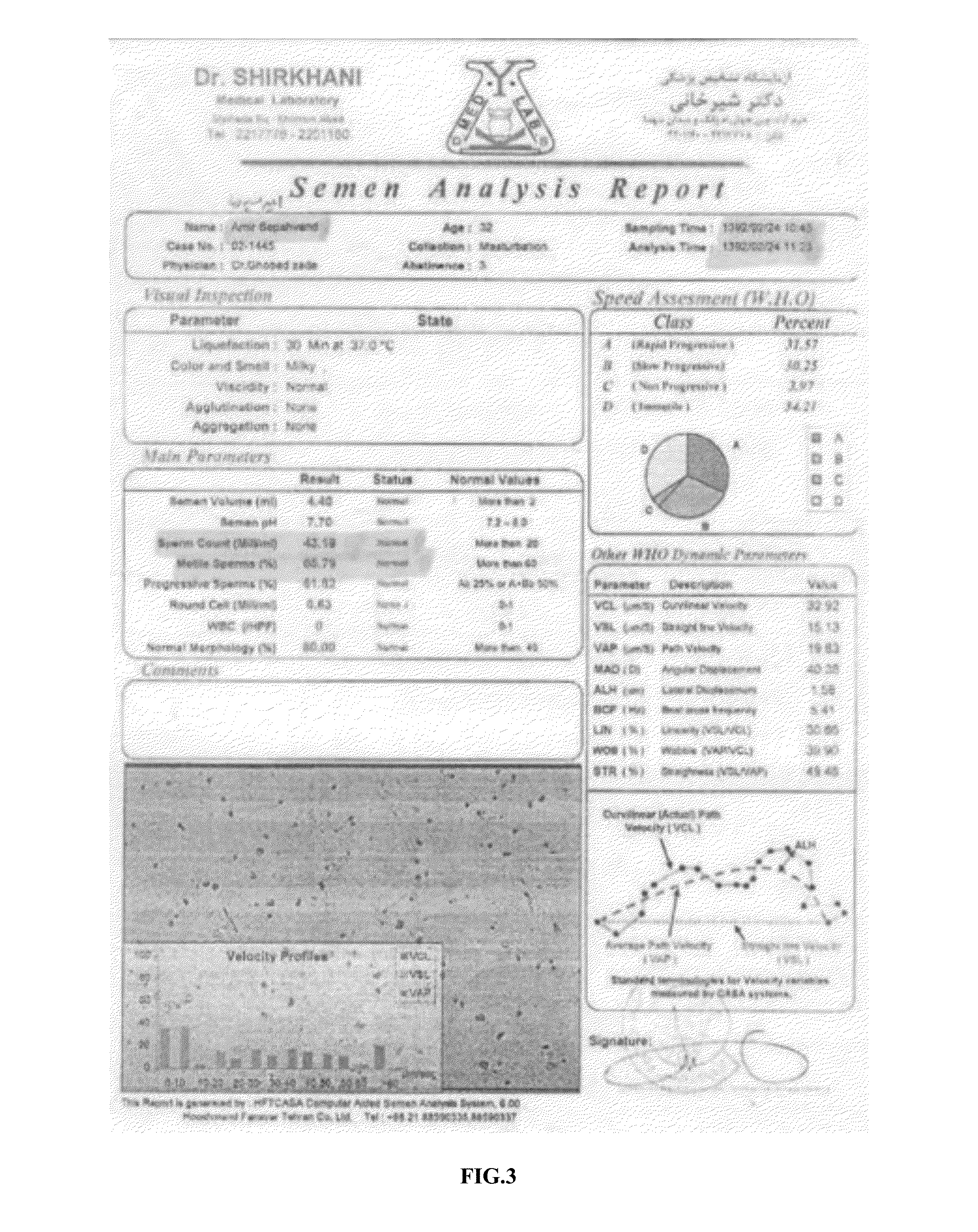
InactiveUS20160158306A1Improving male fertilityIncrease sperm countBiocideDispersion deliveryIncreased fertilityNigella
The embodiments of the present invention provide herbal syrup comprising Nigella sativa (Nigella) seed extract and Zingiber officinale (ginger) root extract. The Nigella seeds and ginger roots are identified in a herbarium and confirmed. The Nigella seeds and ginger roots are cleaned and disinfected. After disinfection the Nigella seeds and ginger roots are grinded separately to obtain powder. The powders of Nigella seed and ginger root are treated in a percolator machine to extract thymoquinone and gingerol. The Nigella seed extract and ginger extract are mixed and herbal syrup is made for the patients with abnormal sperm parameters. The dosage of the herbal syrup is 7 ml. The syrup is administered daily during breakfast for 4 months. The sperm count increases gradually from 15 million / ml, 43 million / ml, 89 million / ml and 120 million / ml after four month of administration.
Owner:SEPAHVAND FARIBA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com