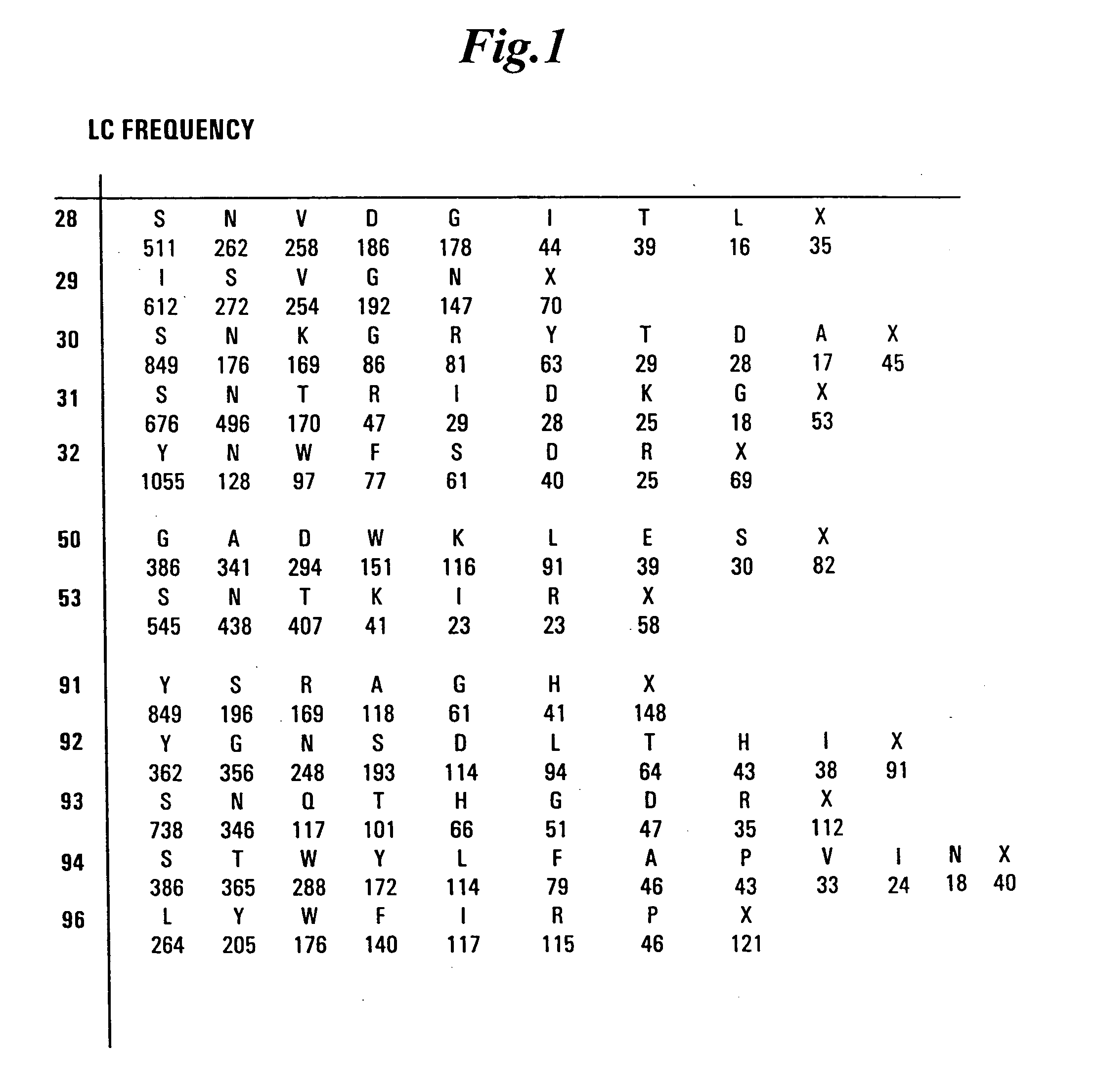
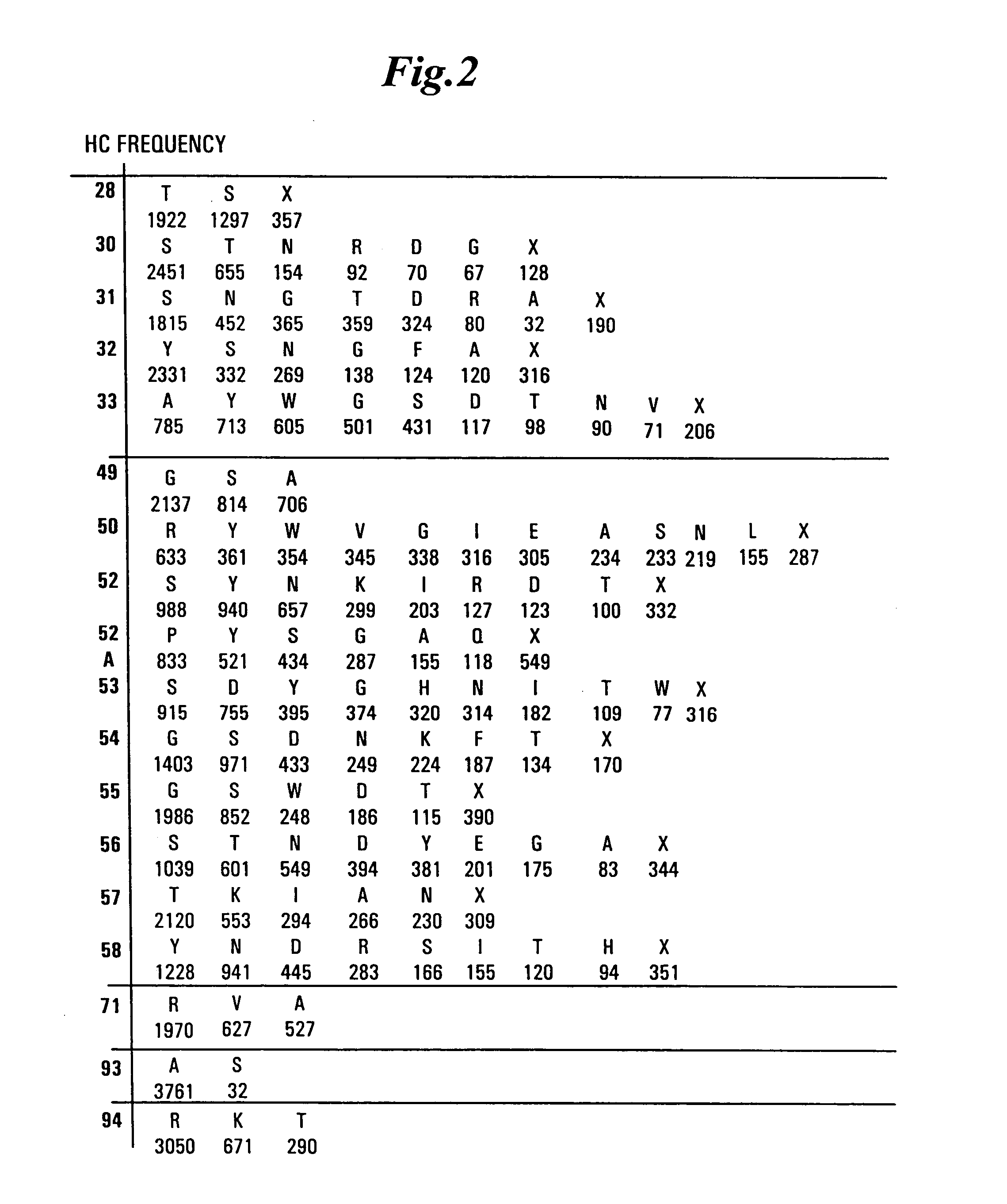
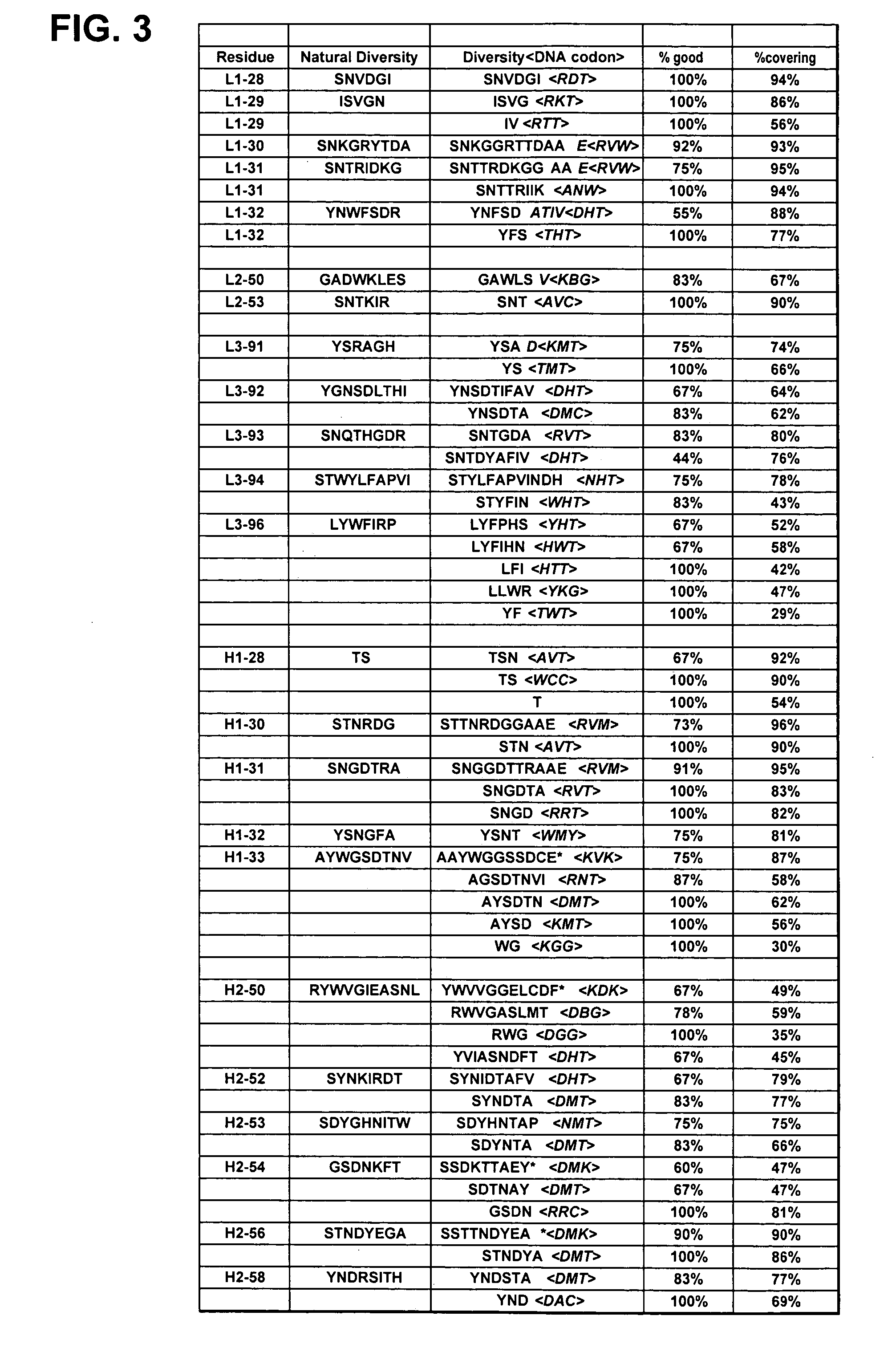
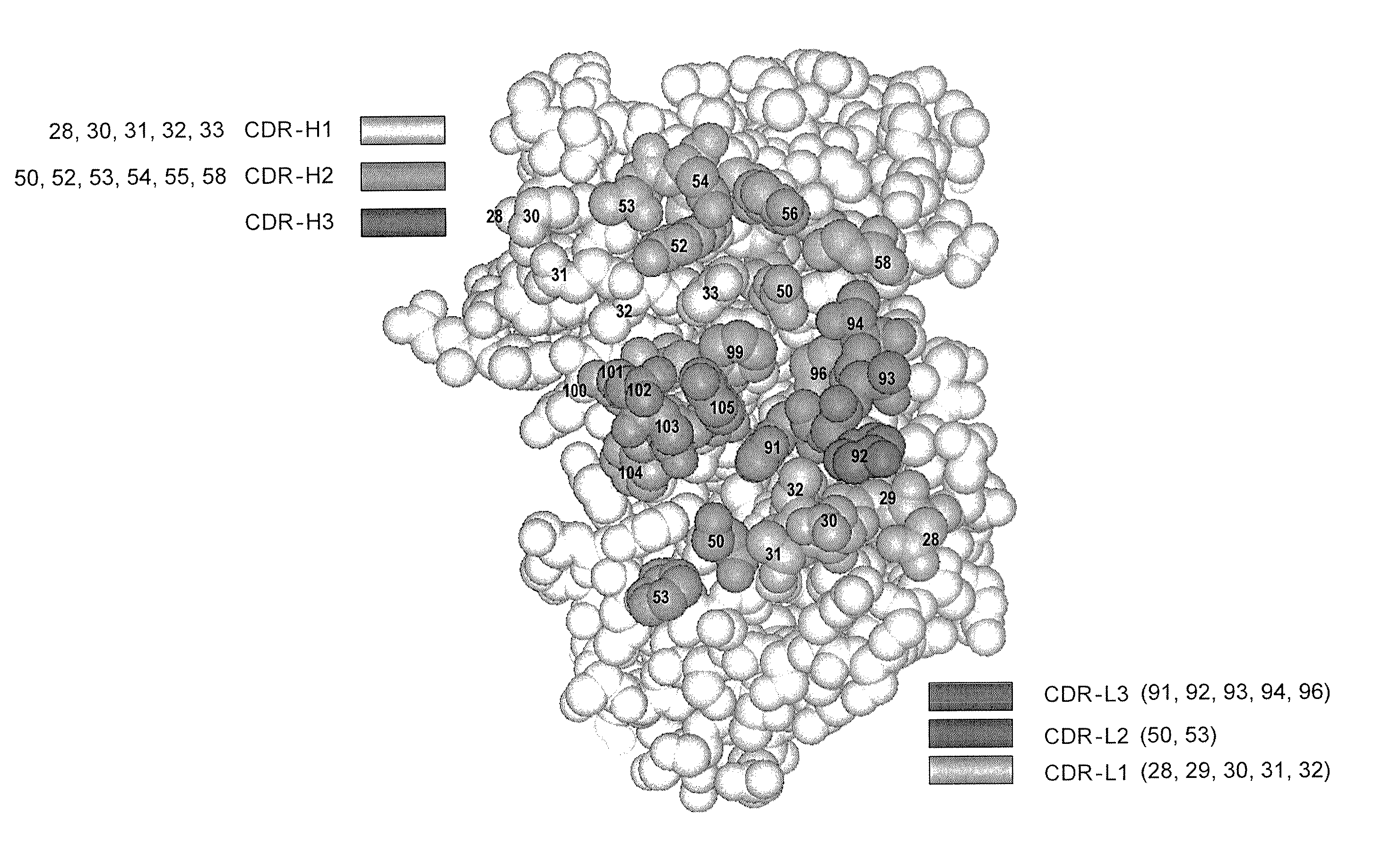
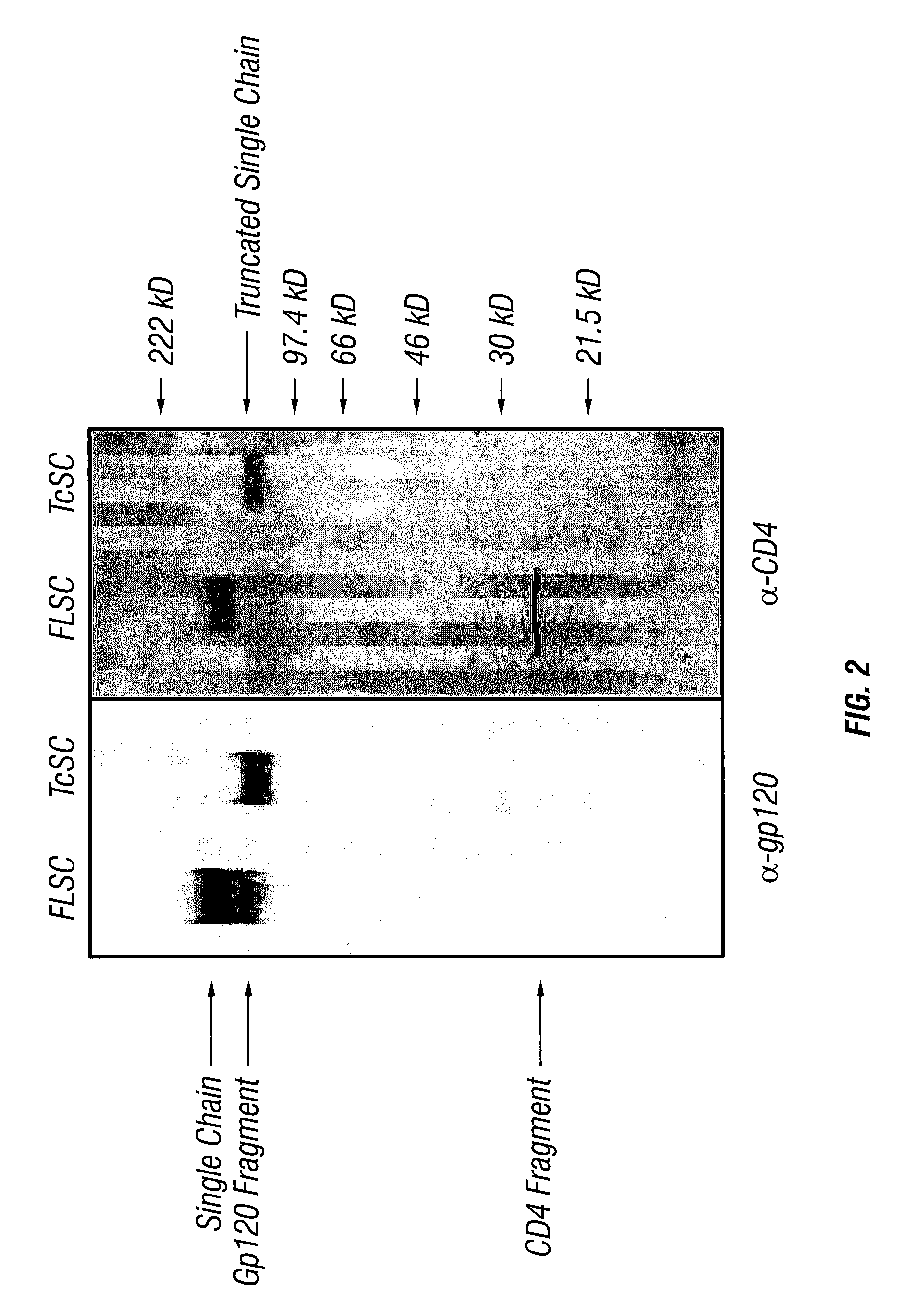
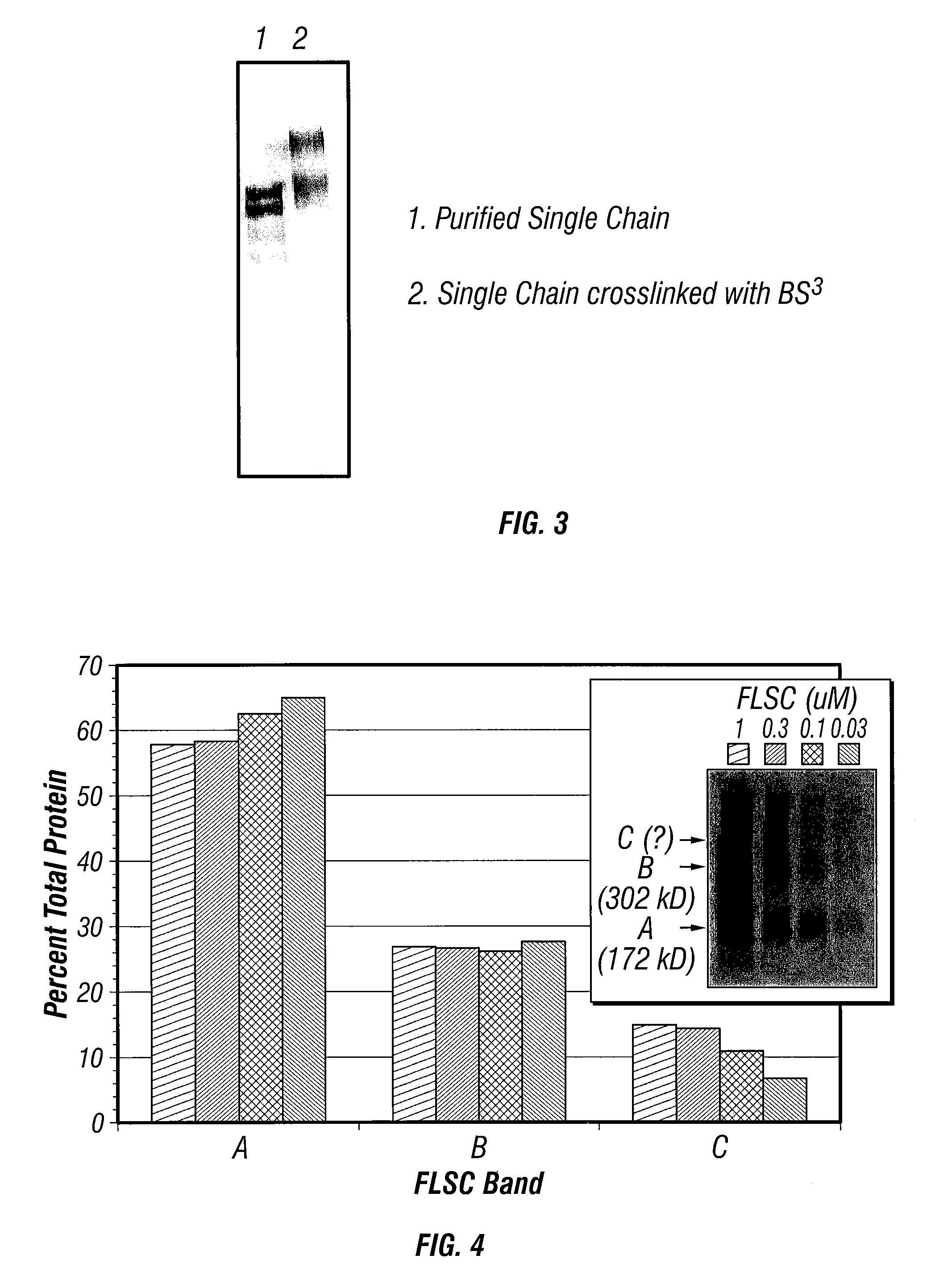
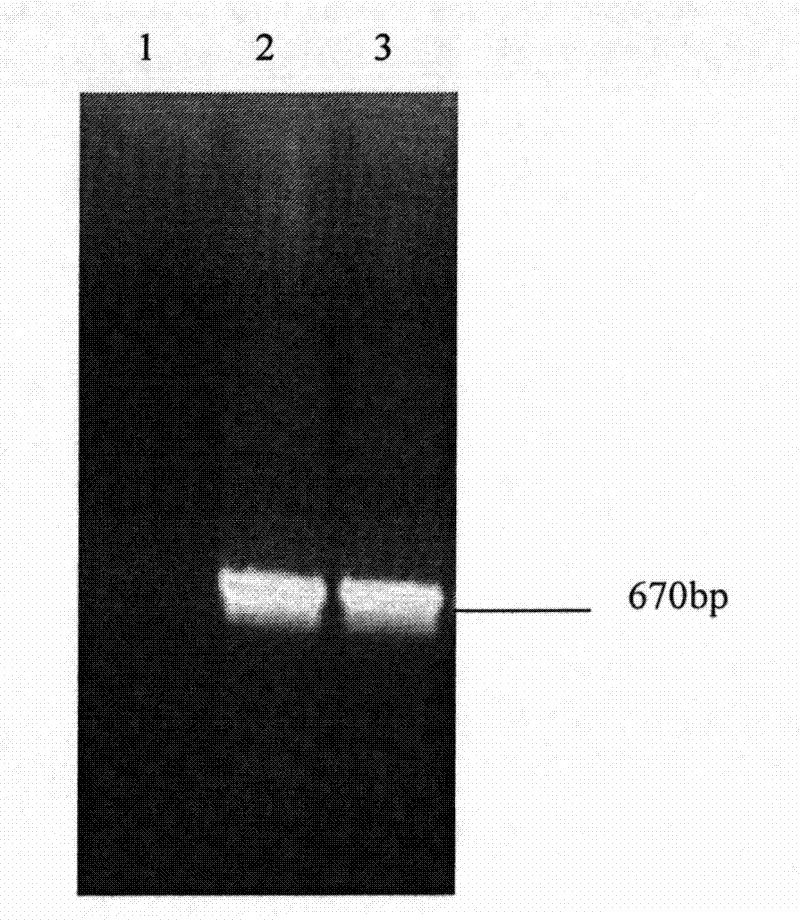
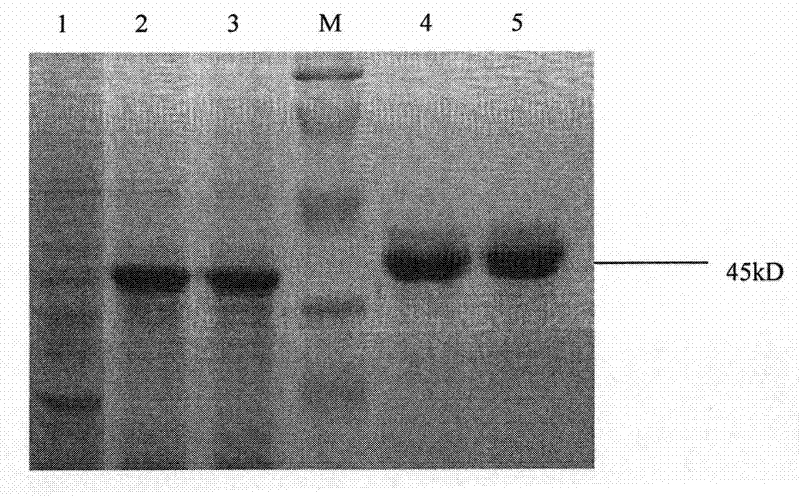
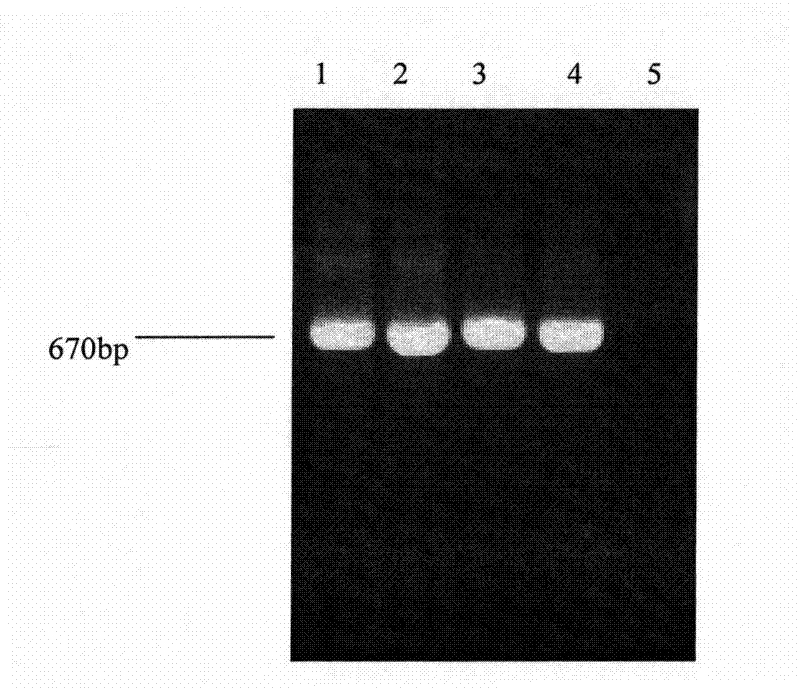
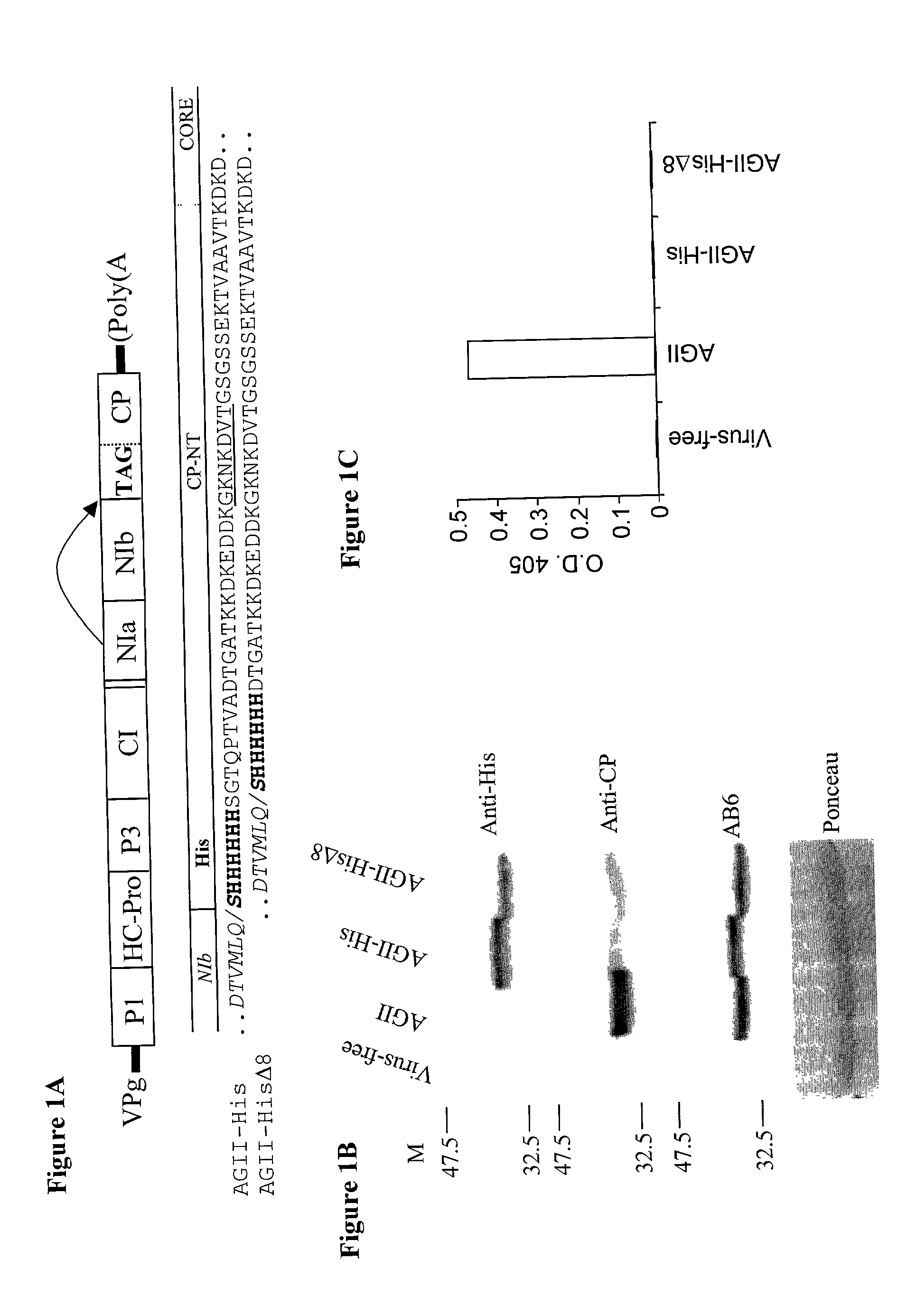
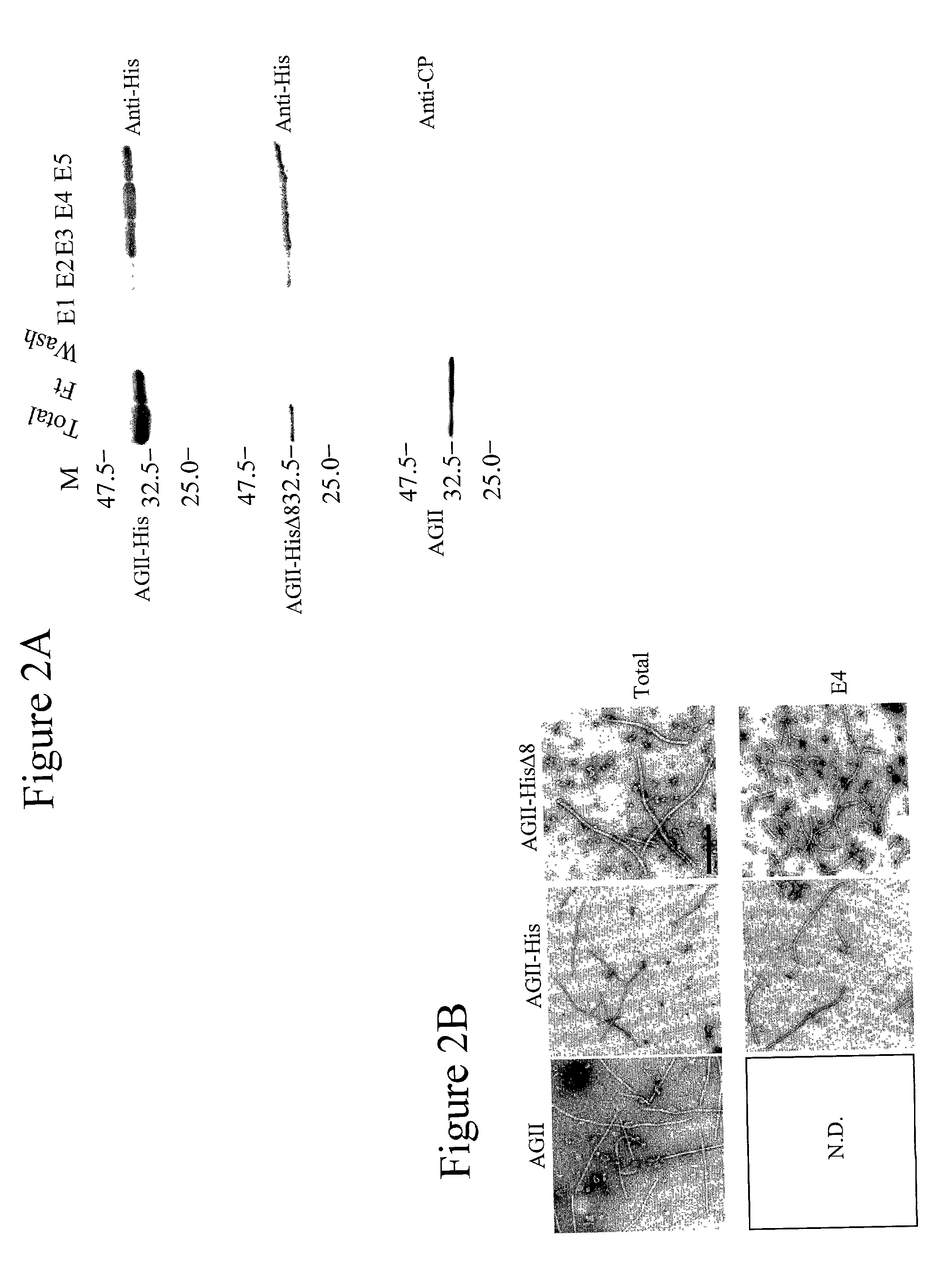
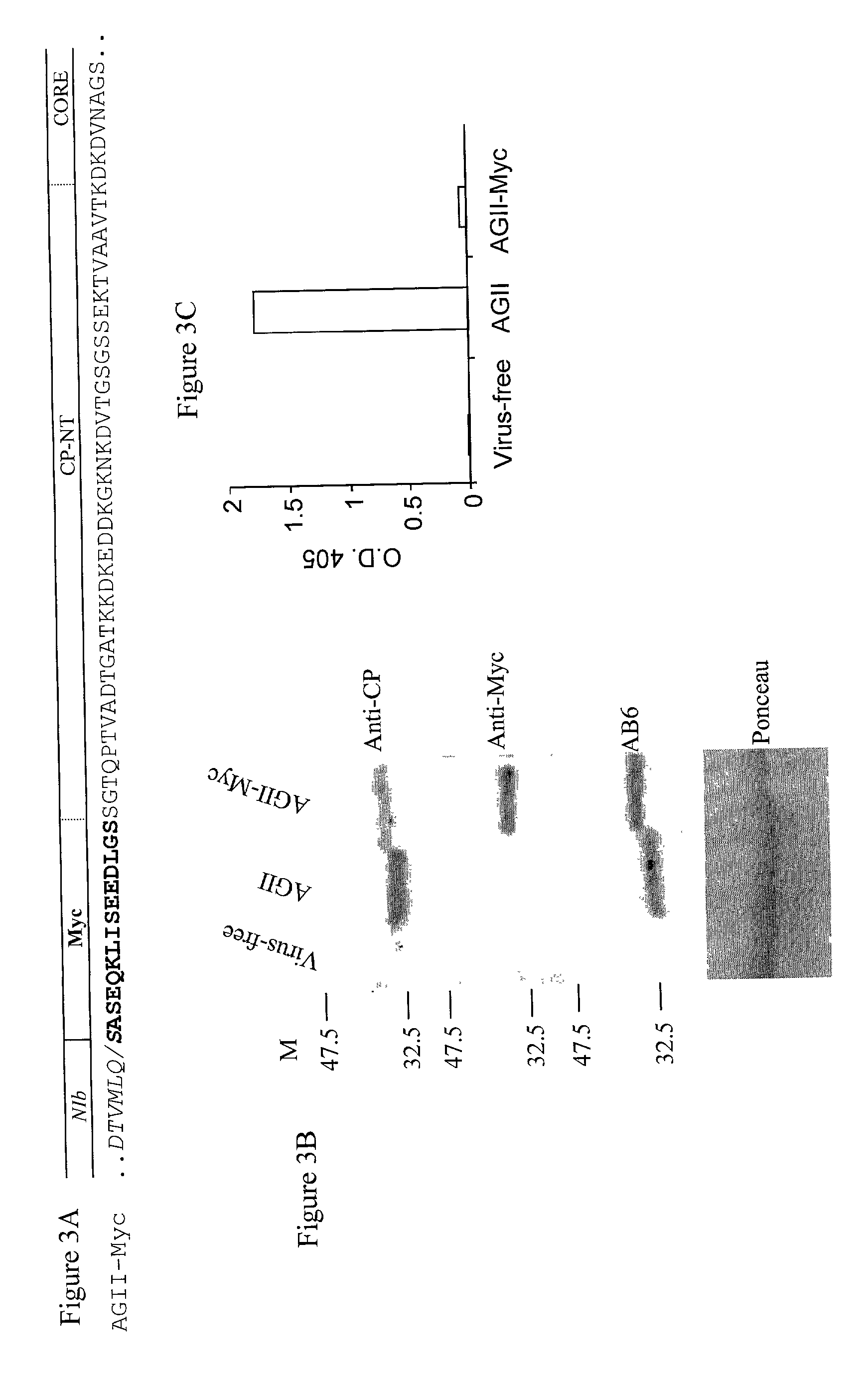
Patents
Literature
63 results about "Viral Coat Proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The protective protein coat of a virus, known as a viral capsid, covers the nucleic acid inside the virus and protects it while the virus inserts itself into the host. The capsid proteins help the virus attach to and penetrate into host cells in order to infect the host.
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
InactiveUS20050079574A1High-quality target binding characteristicGenerate efficientlyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsHeterologousIntravenous gammaglobulin
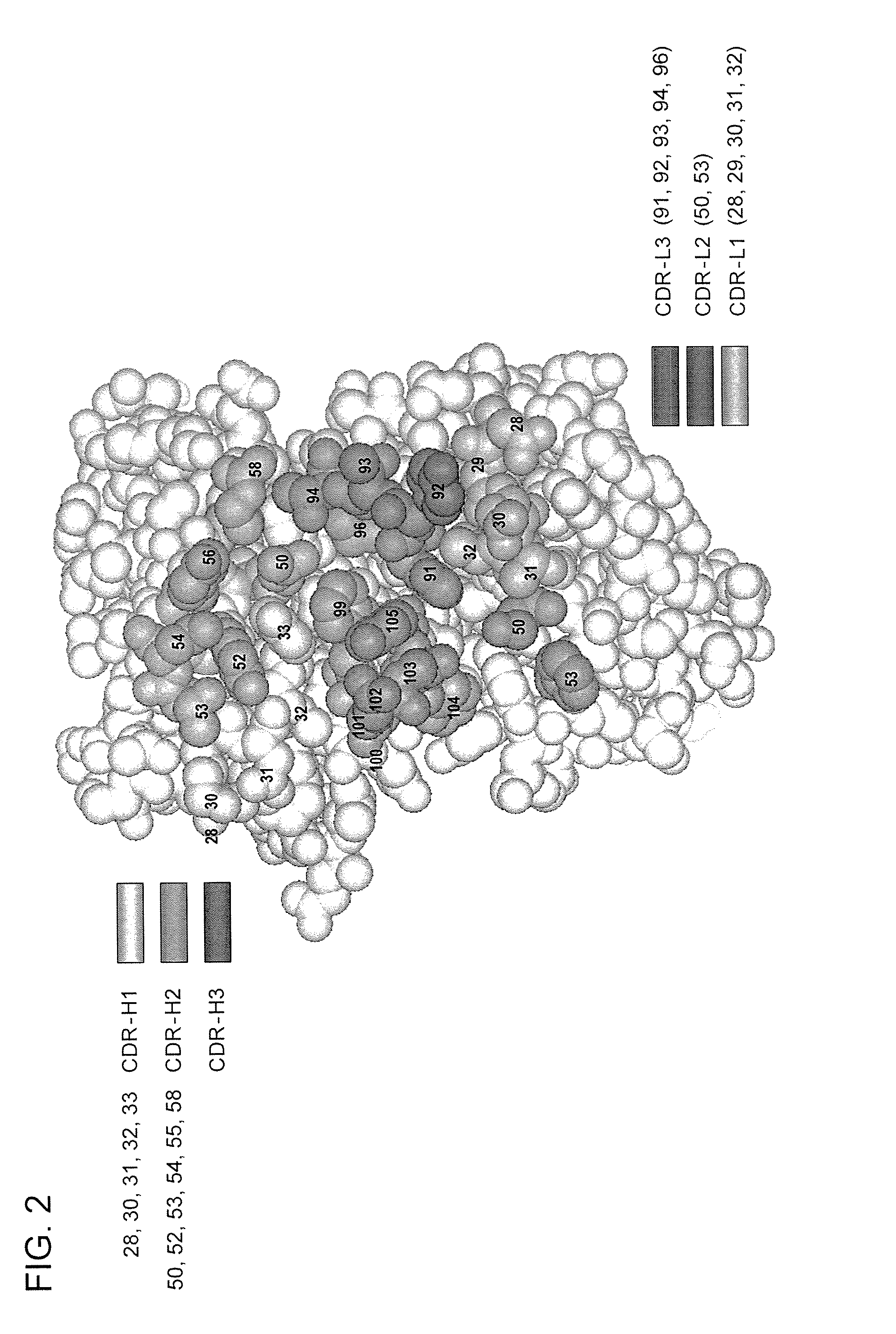
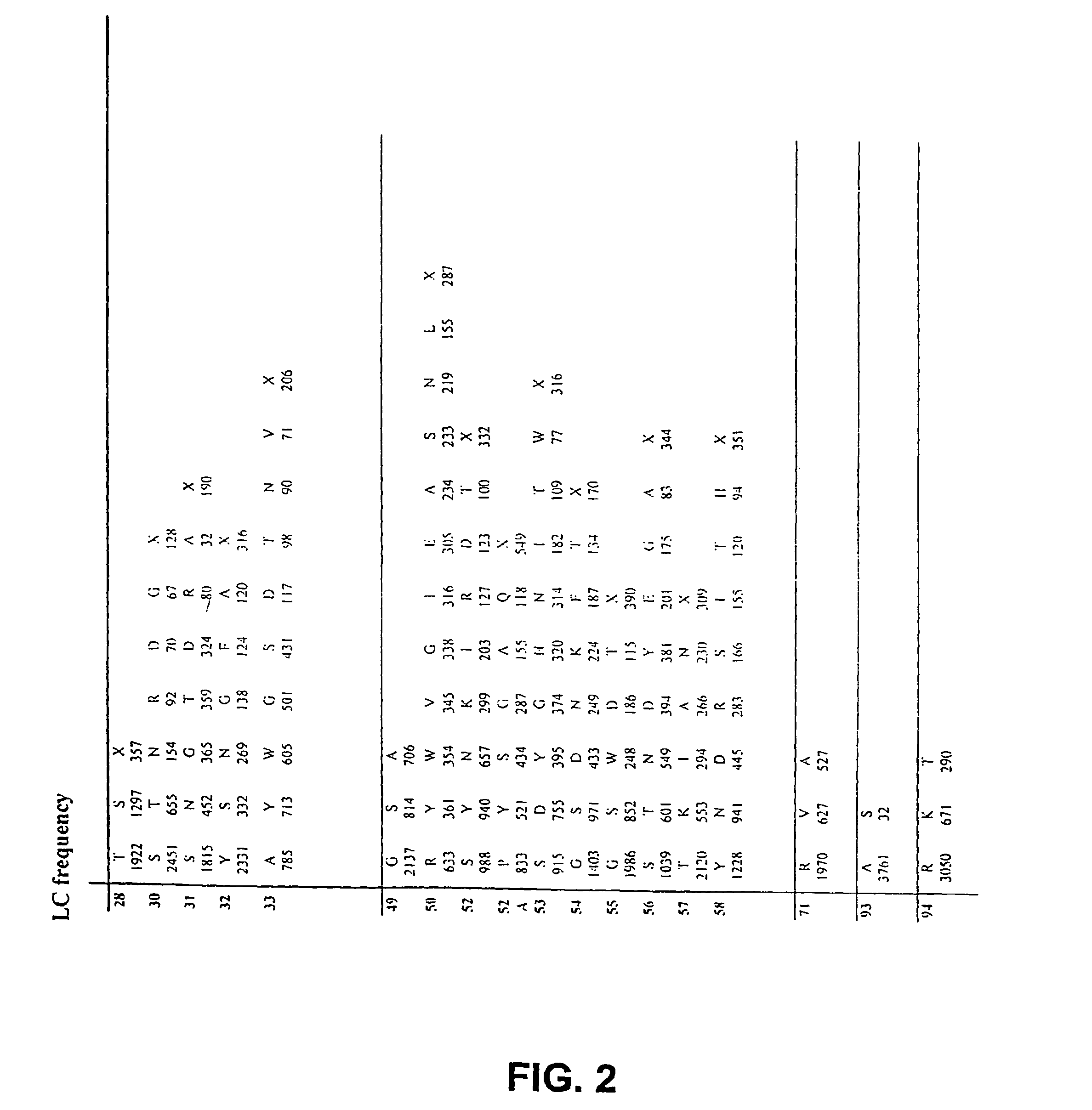
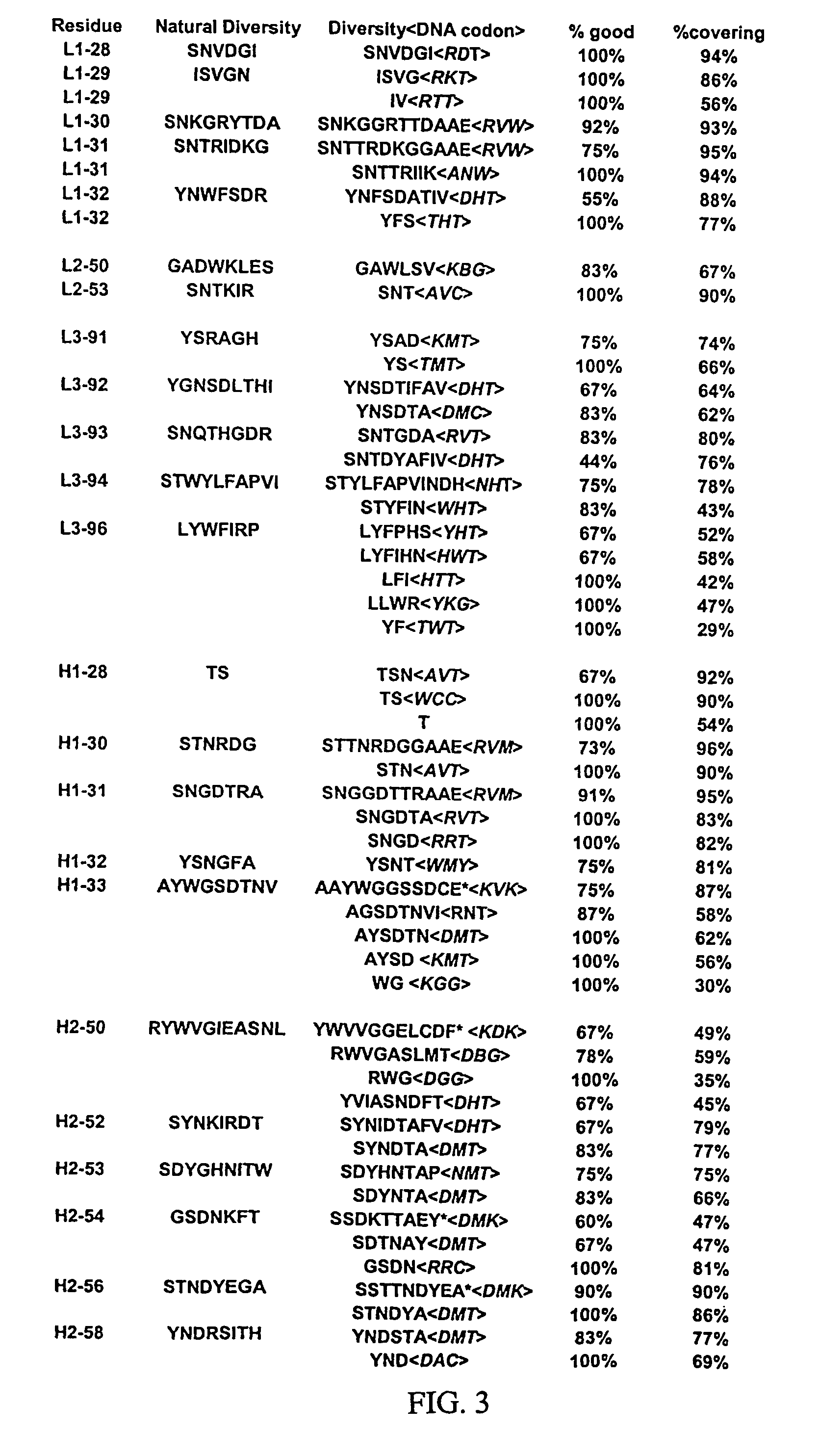
The invention provides immunoglobulin polypeptides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. In one embodiment, the polypeptide is a variable domain of a monobody and has a variant CDRH3 region. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Binding polypeptides with restricted diversity sequences
InactiveUS20070237764A1Small sizeHigh-quality target binding characteristicFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionHeterologousAntigen binding
The invention provides variant CDRs comprising highly restricted amino acid sequence diversity. These polypeptides provide a flexible and simple source of sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Synthetic antibody phage libraries
The invention provides comprising variant amino acids in CDRs of antibody variable domains. These polypeptides provide a source of great sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags, and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS7311920B1Sufficient amountMethod can be usedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
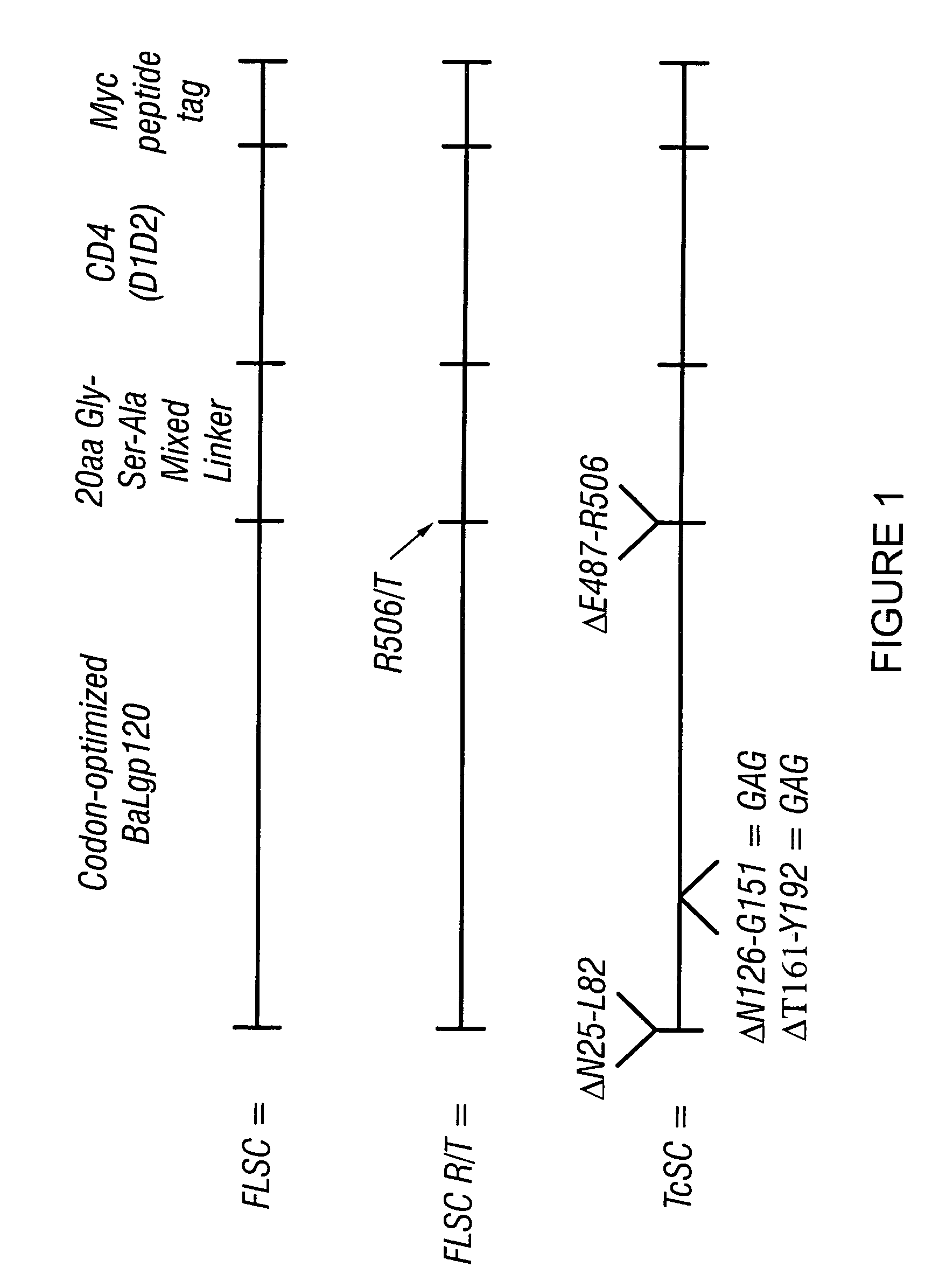
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can interact with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of co-receptor present on the cell, for example. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CCR5 and CXCR4 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND BIOTECH INST UNIV OF
Binding polypeptides with restricted diversity sequences
InactiveUS20050106667A1Small sizeHigh-quality target binding characteristicAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderHeterologousAntigen binding
The invention provides variant CDRs comprising highly restricted amino acid sequence diversity. These polypeptides provide a flexible and simple source of sequence diversity that can be used as a source for identifying novel antigen binding polypeptides. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. Libraries comprising a plurality of these polypeptides are also provided. In addition, methods of and compositions for generating and using these polypeptides and libraries are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Binding Polypeptides and Uses Thereof
ActiveUS20070202552A1Small sizeHigh-quality target binding characteristicAntipyreticAnalgesicsHeterologousAntigen Binding Fragment
The invention provides antibodies or antigen binding fragments thereof to DR5 and HER-2. The antibodies and / or antigen binding fragments thereof comprise variant CDRs comprising highly restricted amino acid sequence diversity. The invention also provides these polypeptides as fusion polypeptides to heterologous polypeptides such as at least a portion of phage or viral coat proteins, tags and linkers. In addition, compositions and methods of use for treatment of cancer and immune related conditions are provided.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS6908612B2Raise the potentialAvoid virus infectionOrganic active ingredientsFungiImmunodeficiency virusHerpes simplex virus DNA
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can inter-act with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of a co-receptor present on the cell. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CD4 D1D2 and CD4M9 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF BIOTECH INST
Phage display
The transformation yield of electroporation is increased by using higher DNA concentrations and DNA affinity purification. Fusion proteins of a viral coat protein variant and a heterologous polypeptide are useful in phage display systems.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Viral vectors having tissue tropism for T-lymphocytes, B- and mast cells
InactiveUS7332337B2Reduce infectionReduced and increased CTL responseBiocideVectorsMast cellViral nucleic acid
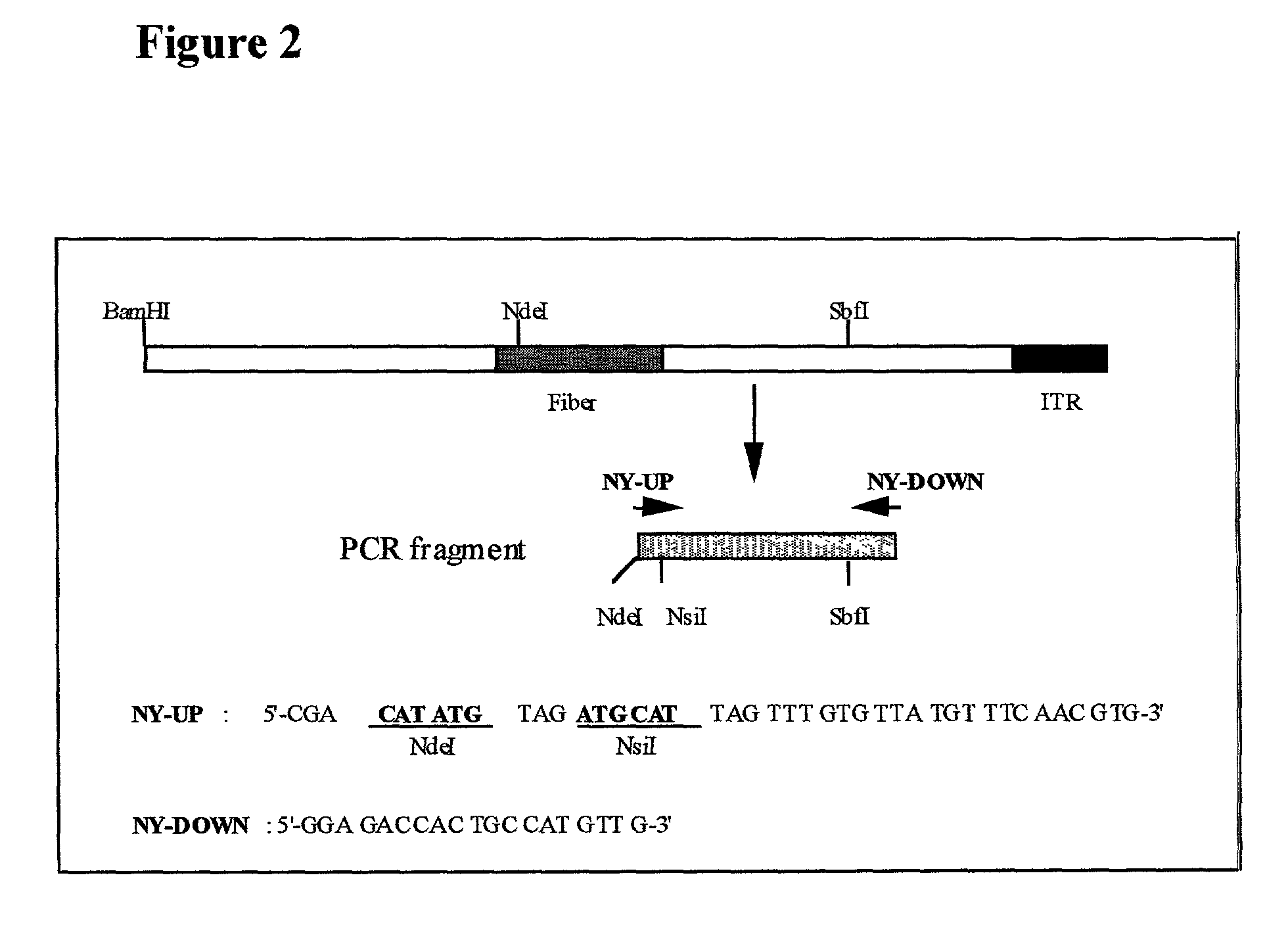
The present invention relates to methods of introducing an expressible non-viral nucleic acid sequence into a T lymphocyte cell, a B-cell, or a mast cell, comprising contacting the cell with a viral particle containing a modified viral coat proteins containing adenoviral amino acid sequence from an adenoviral serotype Ad35 or Ad51 fiber protein, arrays of subpopulations of cells made by such methods, and a method for a ex vivo transduction of a population of cells.
Owner:GALAPAGOS GENOMICS
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can inter-act with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of a co-receptor present on the cell. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CD4 D1D2 and CD4M9 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF BIOTECH INST
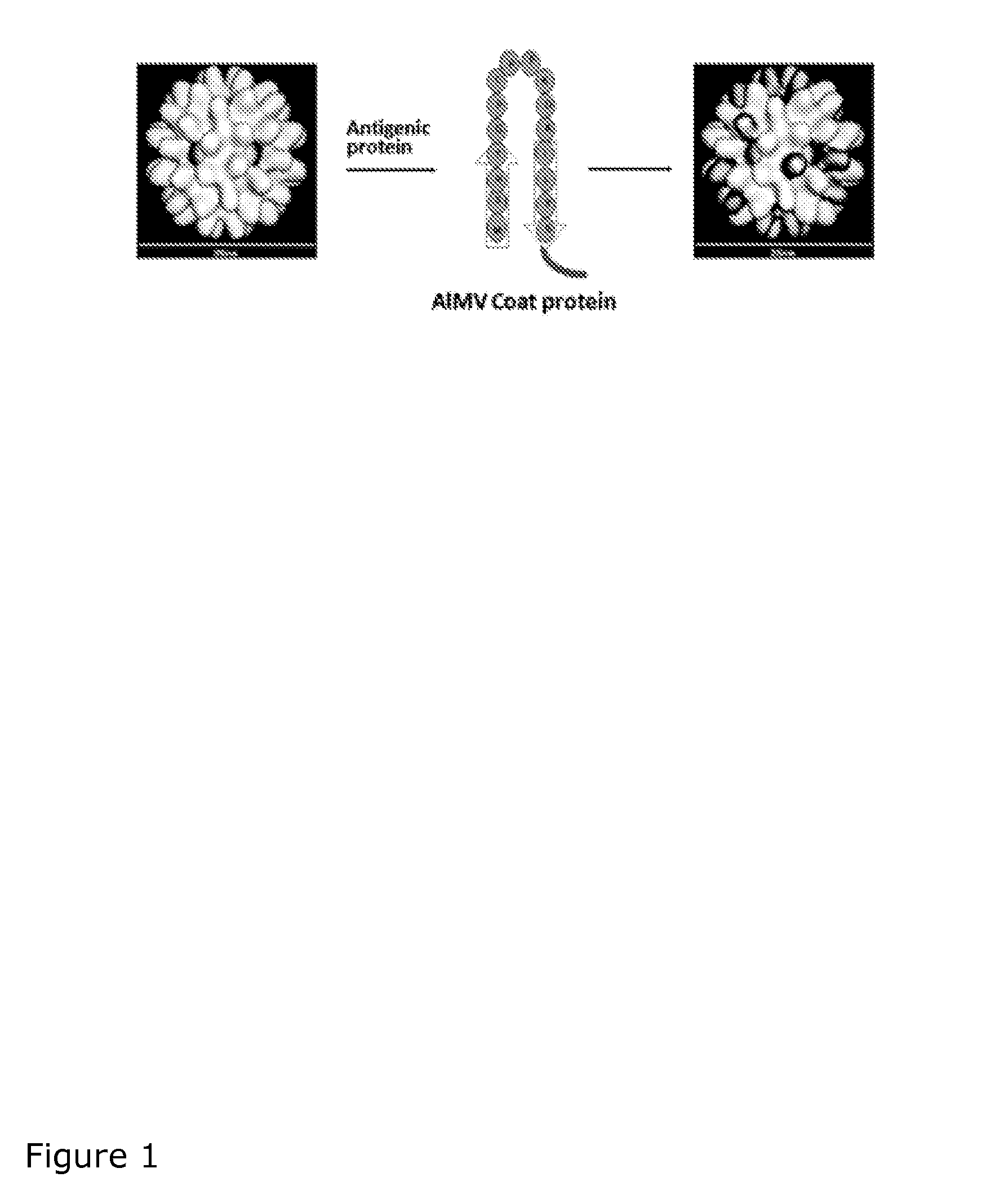
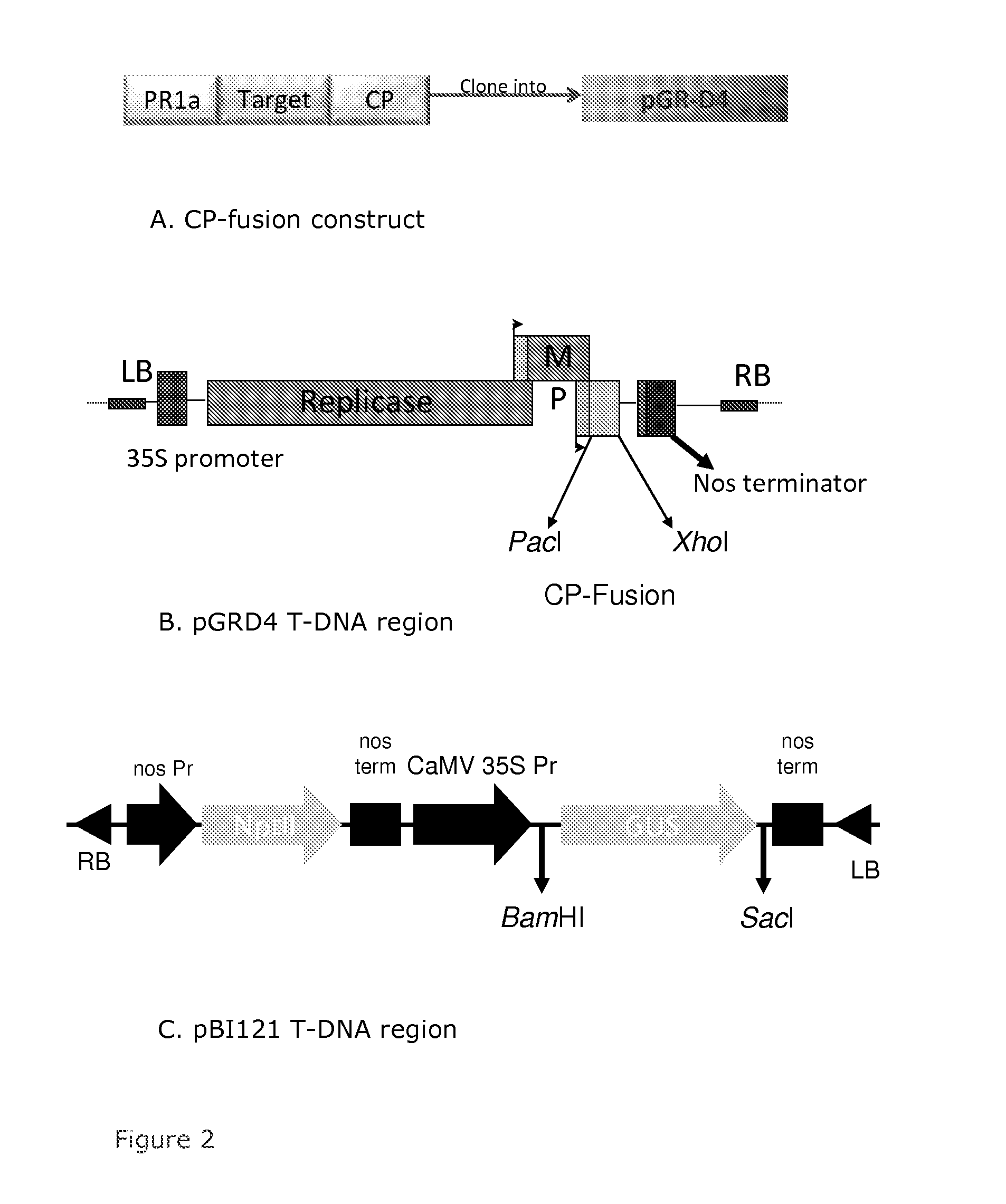
Virus like particles comprising target proteins fused to plant viral coat proteins
InactiveUS20120219579A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseSsRNA viruses positive-senseProtein targetPlant virus
Virus like particles comprising a fusion protein and substantially free of nucleic acid, wherein the fusion protein comprises a plant viral coat protein and a target protein, are provided. Immunogenic compositions comprising the virus like particles can be administered to subjects to induce protective immune responses in the subjects. Methods of producing the virus like particles are also provided.
Owner:FRAUNHOFER USA
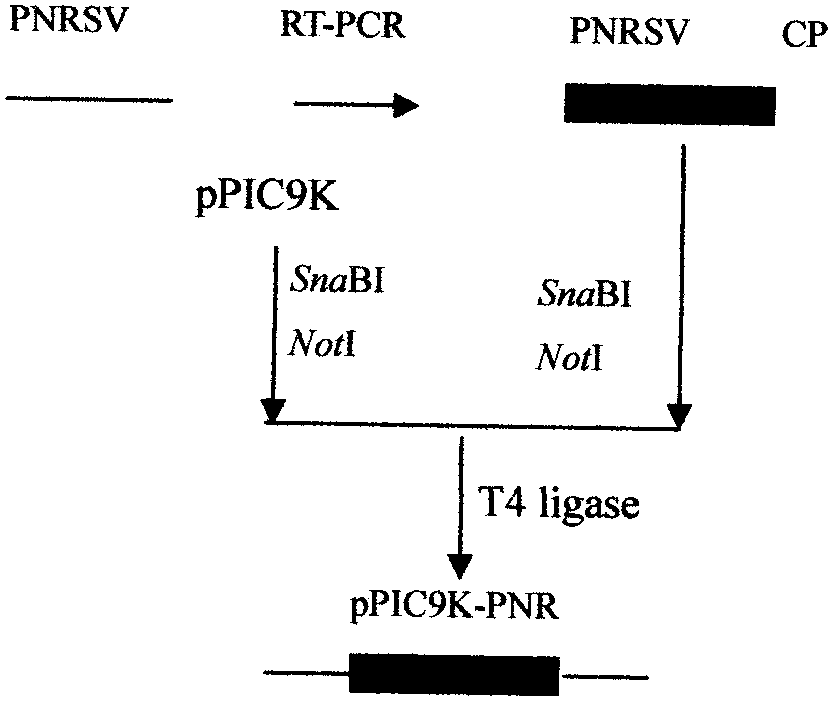
Expression process of coat protein gene of prunus necrotic ring spot virus (PNRSV), antiserum and kit
ActiveCN103045635AAvoid the danger of escapeGuaranteed supplySerum immunoglobulinsMicroorganism based processesPichia pastorisSequence analysis
The invention discloses an expression process of a coat protein gene of prunus necrotic ring spot virus (PNRSV), an antiserum and a kit. The expression method comprises the following steps of: extracting a ribose nucleic acid (RNA) of the PNRSV in an affected material; adopting a transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) amplification process to clone the coat protein gene of the PNRSV; connecting the obtained coat protein gene to a pGEM-T vector, obtaining a pGEM-T-PNRSV recombinant vector, and using sequence analysis to determine the sequence accuracy of the coat protein gene of the PNRSV; building an eukaryotic expression vector of the coat protein gene of the PNRSV; transforming a pichia pastoris GS115 strain, and inducing a pichia pastoris expression coat protein; and using Western-blot to detect the size accuracy of an expression proteine. The invention aims to provide the process for using the pichia pastoris to express the PNRSV coat protein gene, the antiserum, and a PNRSV ELISA detection kit.
Owner:ZHONGSHAN BGH BIOTECH CO LTD
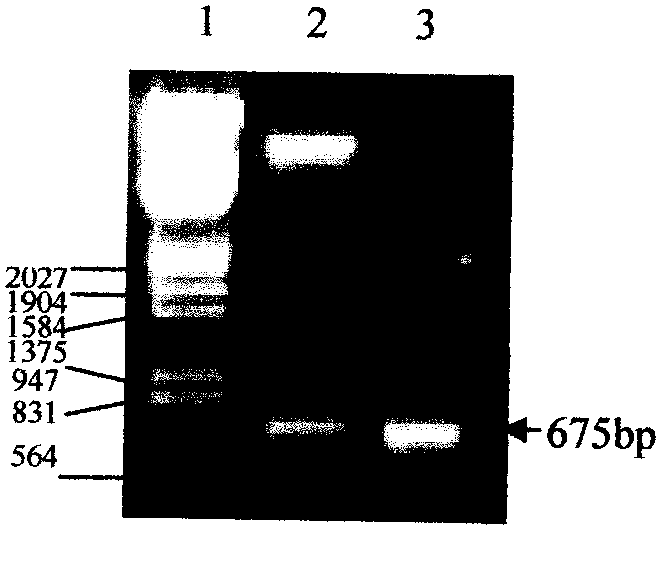
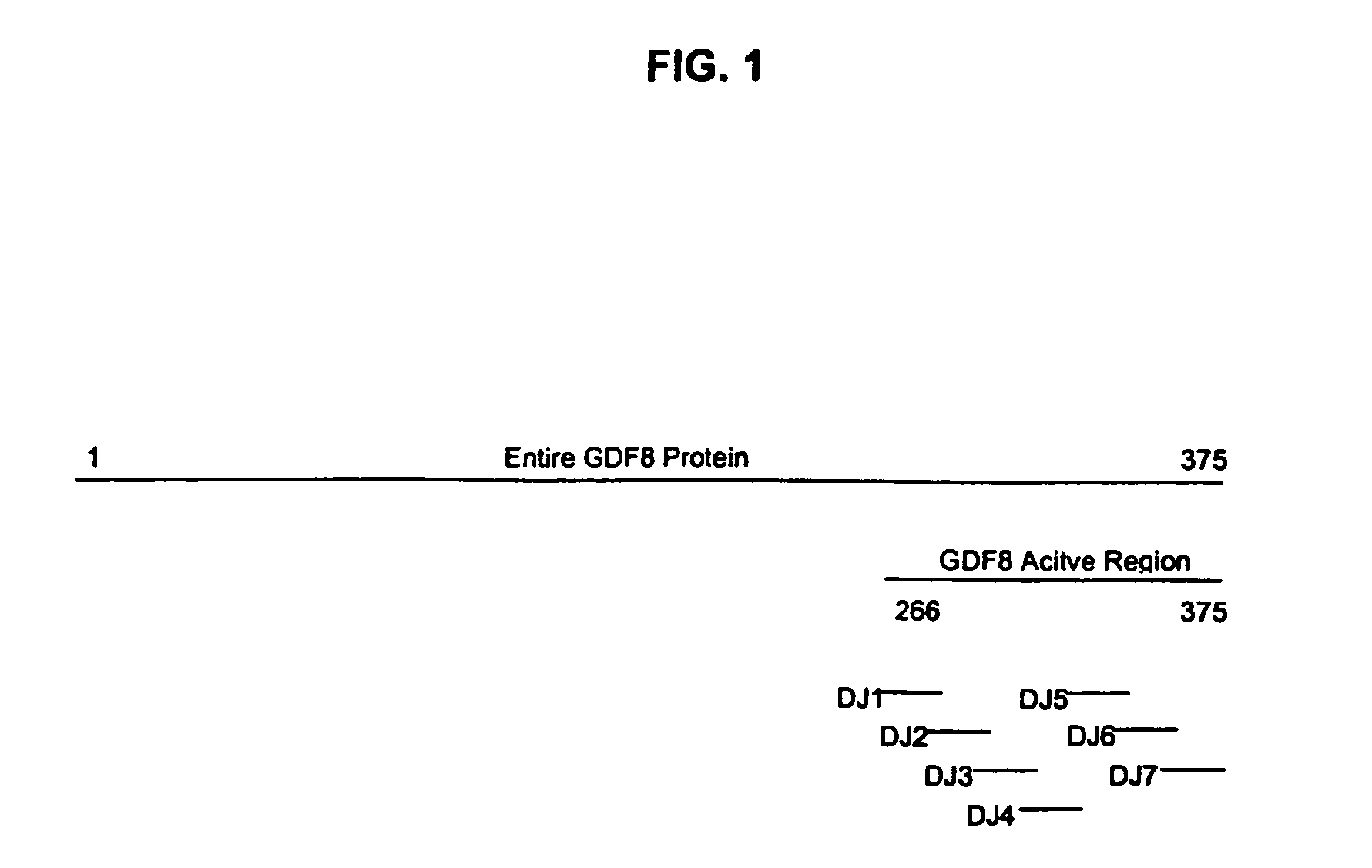
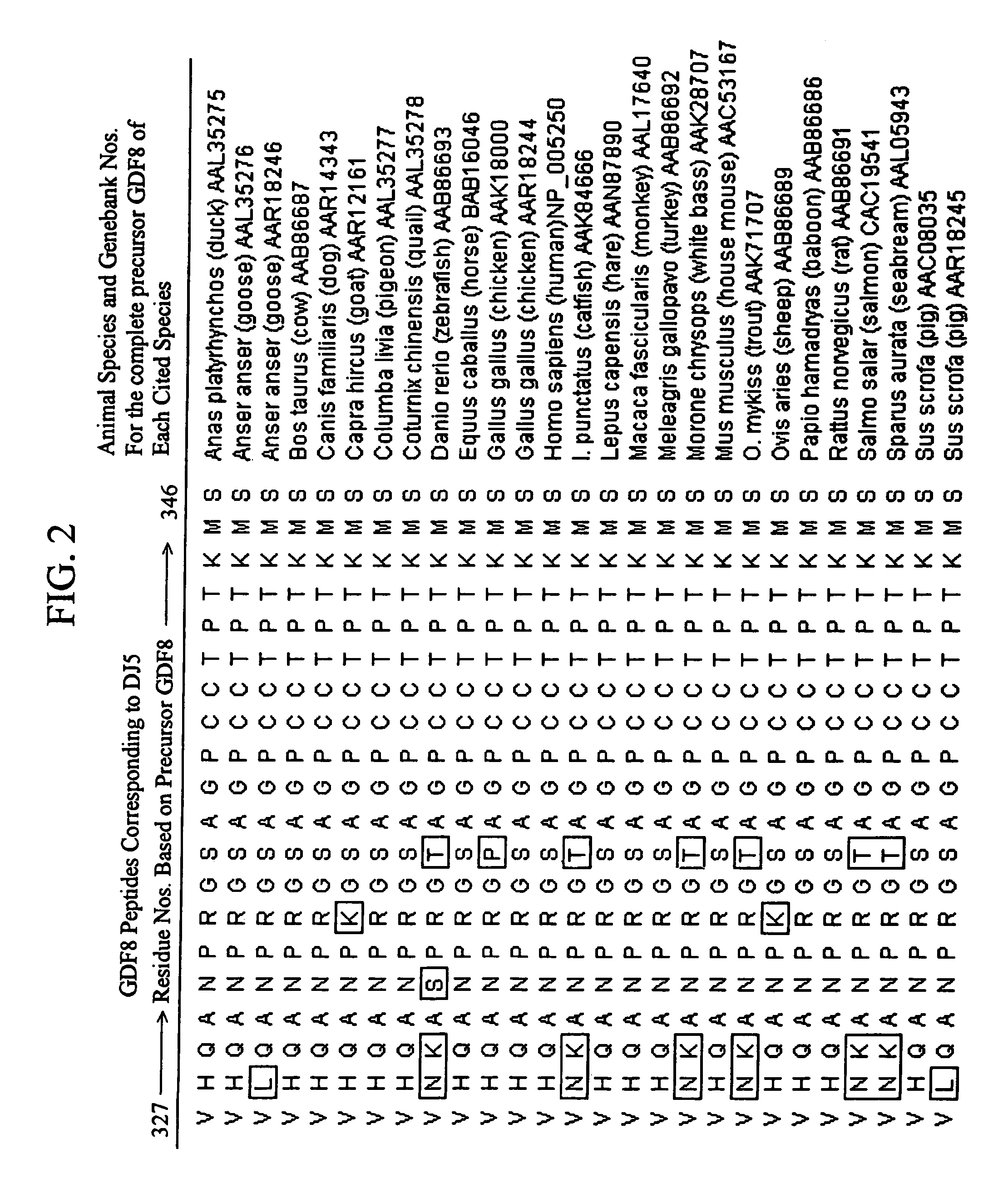
Plant virus coat fusion proteins with GDF8 epitopes and vaccines thereof
Owner:SCHERING PLOUGH ANIMAL HEALTH +1
Self assembling amphiphilic polymers as antiviral agents
InactiveUS20100008938A1Inherent propertyStrong antiviral activityOrganic active ingredientsNanostructure manufactureBiodegradable copolymersBackbone chain
There are provided amphiphilic biodegradable copolymers comprising a hydrophilic backbone with pendant aliphatic groups as the hydrophobic component. The polymers form nanoscale molecular aggregates in aqueous environments, which have hydrophobic interiors that are capable of solubilizing insoluble organic compounds and disrupting viral coat proteins. The polymers optionally feature reactive functional groups that provide attachment points for antibodies, ligands, and other targeting moieties which mediate adherence of the aggregate to a viral target.
Owner:ALLEXCEL INC
Gene recombinant vaccine for preventing enterovirus 71 infection and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a gene recombinant vaccine for preventing enterovirus 71 (EV71) infection and a preparation method thereof. The inflection comprises multiple diseases related with the nervous system such as hand-foot-and-mouth disease, paralytic diseases of sterile meningitis, cephalitis and poliomyelitis and the like. Escherichia coli labile enterotoxin B subunit (LTB) is used as an immunological enhancement adjuvant, two fragments of linear neutralizing epitope SP55 and SP70 in EV71 virus coat protein VP1 are used as antigens, prokaryotic expression plasmids of LTB-SP55-SP70 fusion genes are constructed by using gene engineering technology, the plasmids are expressed in escherichia coli, and a recombinant expression product is purified for preparing the EV71 virus gene engineering vaccine.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所 +1
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS8183354B2Raise the potentialAvoid virus infectionCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can inter-act with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occn-panty of co-receptor present on the cell, for example. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CCR5 and CXCR4 sequences.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Expression of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene and preparation method for antibody of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene
InactiveCN101748136AIncrease contentHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesBALB/cDisease
The invention discloses an expression of cymbidium mosaic virus (Cymbidium Mosaic Virus, CymMV) coat protein gene and a preparation method for antibody of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene. A prokaryotic expression system is used for expressing the coat protein of the cymbidium mosaic virus, and the cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene immune rabbit, the BALB / C mouse are used for preparing the polyclonal anti-serum; and the hybridoma technique is used for preparing the monoclonal antibody, and the prepared antibody is used for establishing the immune capture RT-PCR and ELISA method for detecting the high specificity, sensitivity and accuracy of CymMV. The invention provides technical support for the diagnosis of the virus, disease-resistance breeding and cultivation of virus-free seedlings. The expression of cymbidium mosaic virus coat protein gene and the preparation method for its antibody provided by the invention provides material base and technical support for rapid detection and diagnosis of the cymbidium mosaic virus, typing and the study on molecular biology, and lays the foundations for prevention and treatment of cymbidium mosaic virus disease.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Vectors for expressing heterologous peptides at the amino-terminus of potyvirus coat protein, methods for use thereof, plants infected with same and methods of vaccination using same
A recombinant vector for expressing a heterologous peptide at the amino-terminus of a potyvirus coat protein. The vector includes sufficient potyvirus nucleic acid sequence to permit viral replication and spread within a plant infected by the vector. The vector further includes a heterologous nucleic acid sequence inserted at the amino-terminus of the potyvirus coat protein. Further disclosed are methods for transiently expressing the heterologous protein in a plant using the vector and plants transiently expressing the vector. Additionally, methods for vaccination which employ the vector to express an antigenic determinant in a plant are disclosed.
Owner:VIROGENE LTD
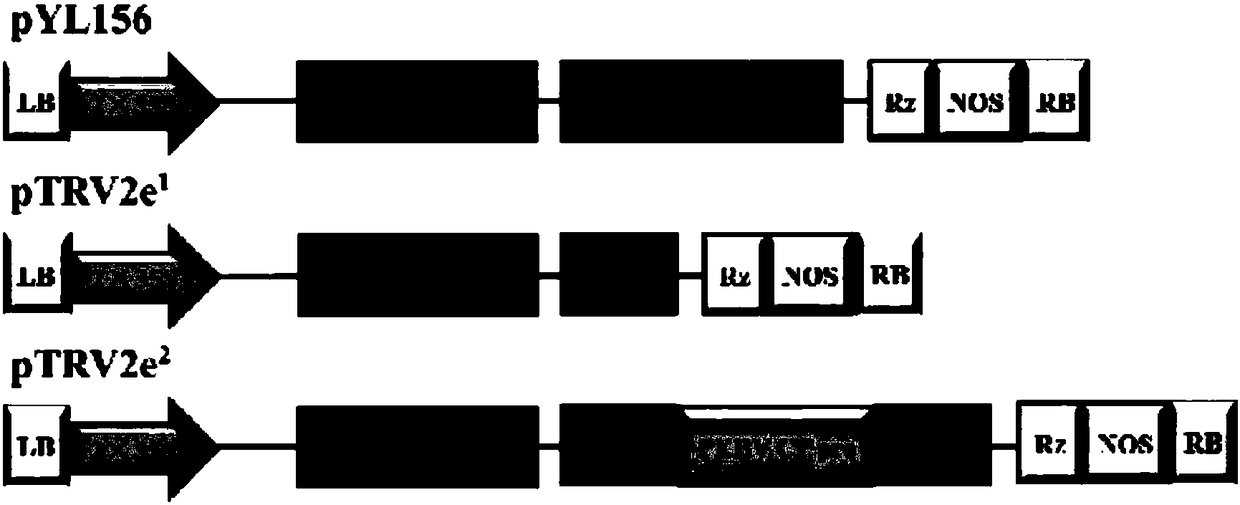
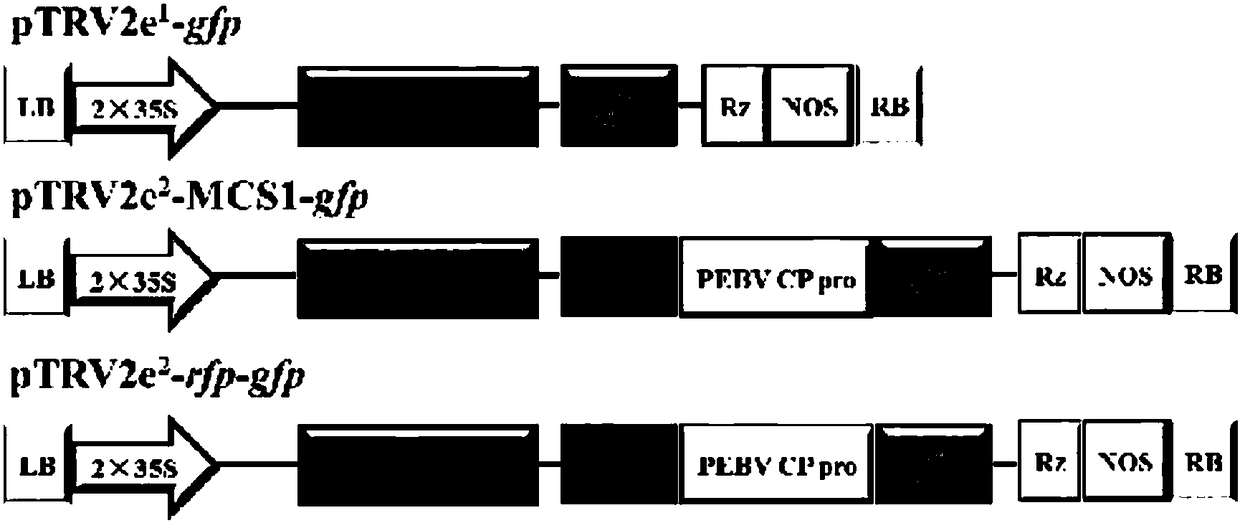
Construction method for simultaneously expressing two foreign protein vectors TRVe2 and application
The invention discloses a construction method for simultaneously expressing two foreign protein vectors TRVe2. The construction method comprises the following steps: cloning pYL156 by agrobacterium infection of genome RNA2 of TRV as a material, constructing a vector containing 2b gene promoter and pea early-browning virus coat protein gene promoter sequences of TRV, and driving expressions of foreign genes in nicotiana benthamiana by virtue of genome promoters of the two plant viruses. The plant virus TRV2e2 capable of simultaneously expressing two non-fusion-proteins is first reported internationally; the virus does not cause any obvious symptoms in the nicotiana benthamiana, carries two foreign genes to systematically expand to the whole plant and is capable of expressing two foreign proteins in the same cell.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SCI-TECH UNIV +1
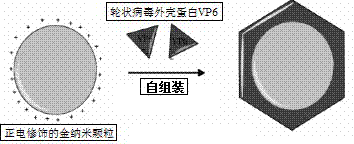
Building method for medicament transportation or radiography carrier containing coat protein and inorganic nanoparticles
InactiveCN102886048AGood biocompatibilityImprove circulation time in the bodyMacromolecular non-active ingredientsIn-vivo testing preparationsElectricityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a building method for a medicament transportation or radiography carrier containing coat protein and inorganic nanoparticles, comprising the following steps of: firstly, carrying out positive electricity modification on the surfaces of inorganic nanoparticles; and inducing viral protein to be assembled per se around the positive electricity-modified nanoparticles. According to the building method, the viral protein is induced to be assembled per se by the nanoparticles of which the surfaces are modified by the positive electricity, so that the nanoparticles of which the outer surfaces are coated with the coat protein can be obtained, and the biocompatibility, the stability in the blood, the cycle time in vivo of the nanoparticles and the like can be improved due to the modification of the viral protein, and therefore, the building method is more suitable for use in vivo; and the natural assemble mode of the viral protein can be changed due to the nanoparticles, so that a novel strategy can be found for the fundamental research, the vaccine development and the like of the virus.
Owner:苏州百拓生物技术服务有限公司
Method of enhancing virus-resistance in plants and producing virus-immune plants
InactiveUS20040068764A1Lower Level RequirementsDelayed and reduced spreadSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleotide
The present invention provides a method of enhancing resistance of plants to one or multiple viruses, comprising introducing to a plant cell, and preferably expressing therein, a nucleotide sequence encoding a virus-encoded polypeptide. The present invention provides a method of enhancing the proportion of virus-resistant or virus-immune lines obtained from a single transformation experiment comprising introducing to a plant cell, a nucleotide sequence encoding a virus-encoded polypeptide operably in connection with a strong promoter sequence. The present invention provides novel gene sequences encoding the coat proteins of a virus and novel dysfunctional replicase sequences as well as gene constructs comprising same, in particular binary vector constructs suitable for introducing into plants and expressing the genes therein. The present invention provides and methods using same to enhance viral resistance in plants. The present invention provides novel methods of testing transgenic plants for the presence of a transgene.
Owner:DAIRY AUSTRALIA +2
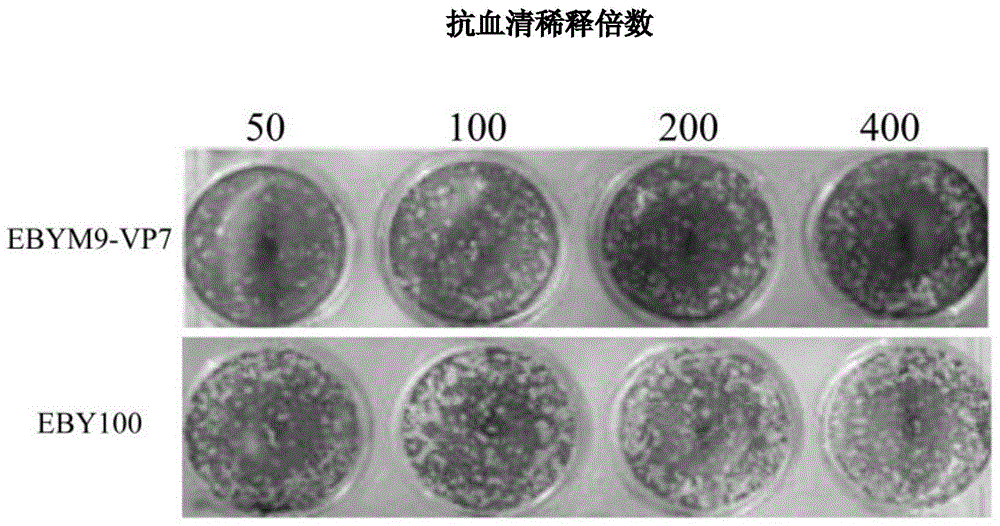
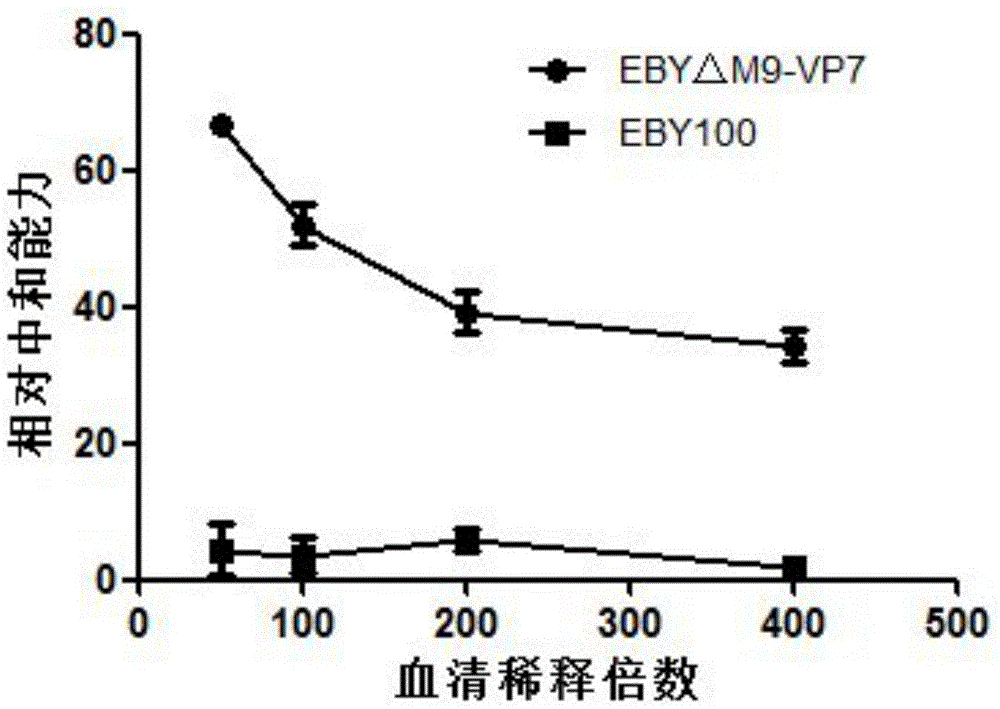
Grass carp hemorrhage vaccine prepared through yeast display and preparation method of grass carp hemorrhage vaccine
InactiveCN105879022AAvoid efficiencyAvoid attenuationFungiViral antigen ingredientsSurface displayYeast display
The invention discloses a grass carp hemorrhage vaccine prepared by adopting a yeast surface display technology, relating to the preparation of genetic engineering vaccines. The grass carp hemorrhage vaccine is prepared in a manner that GCRV-VP7 protein is displayed on the surface of brewer's yeast cells EBY100 delta Mnn9 with glycosylated genes knocked out. The brewer's yeast is an expression system of eukaryon, the galactosylated modification is carried out on the virus coat protein expressed by the brewer's yeast, and then an immune system of the grass carp is induced to generate virus-neutralizing antibodies. The grass carp hemorrhage vaccine has the advantages that a used yeast strain EBY100 delta Mnn9 with glycosylation deficiency can effectively remove the super glycosylation of the protein on the surface of the yeast, and thus the problem that the GCRV-VP7 antigen is covered, consequently, the vaccine efficiency loss and decrease are caused, is solved; the yeast cells are easy to culture and low in preparation cost, and thus the grass carp hemorrhage vaccines can be prepared in large scale at low cost.
Owner:INST OF AQUATIC LIFE ACAD SINICA +1
Nolvac viral coat protein with recombinant rod virus expression and its preparation
InactiveCN1778812ANo danger of spreading poisonStrong specificityViral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesAntigenOpen reading frame
Owner:NATIONAL MARINE ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING CENTRE +1
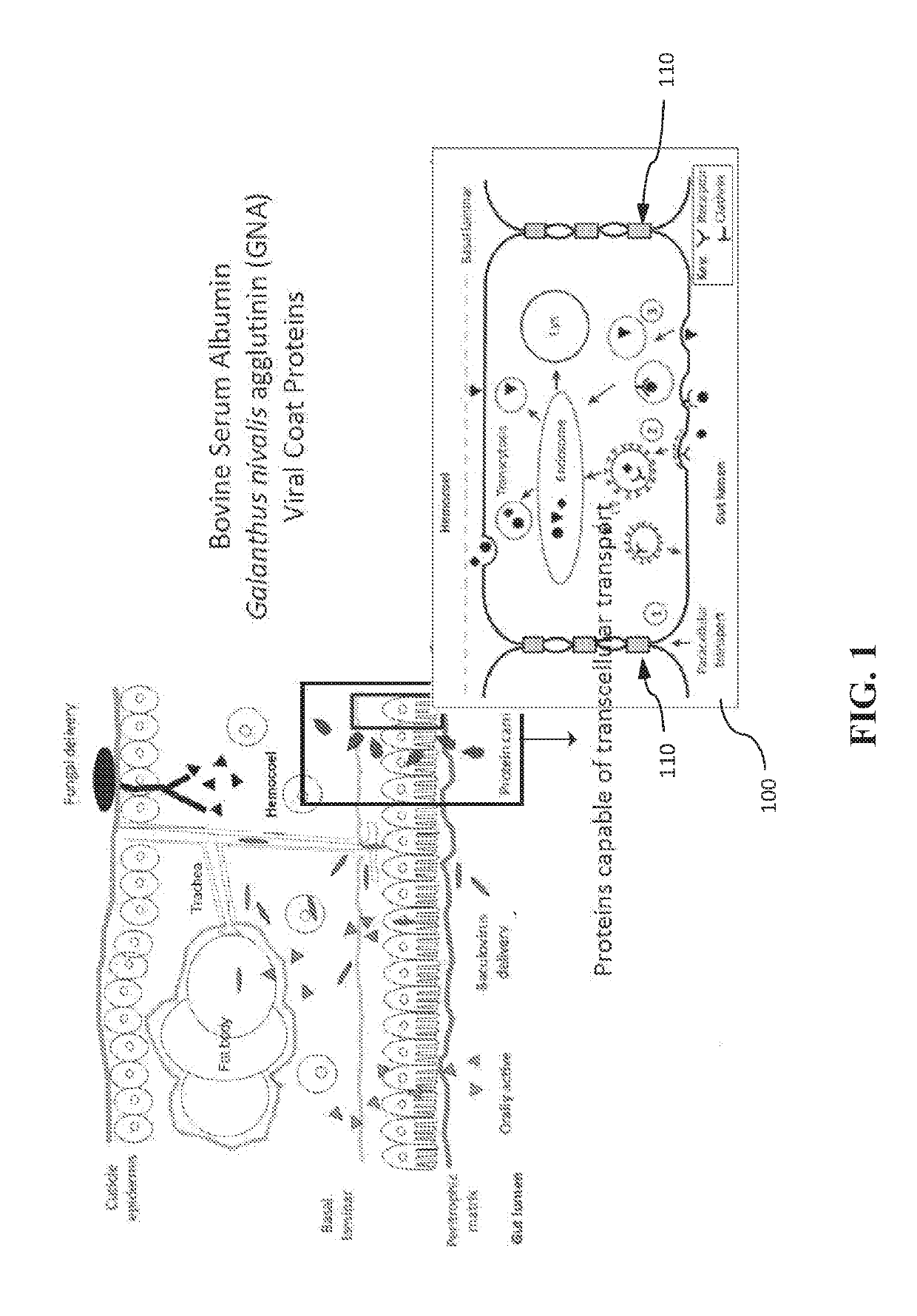
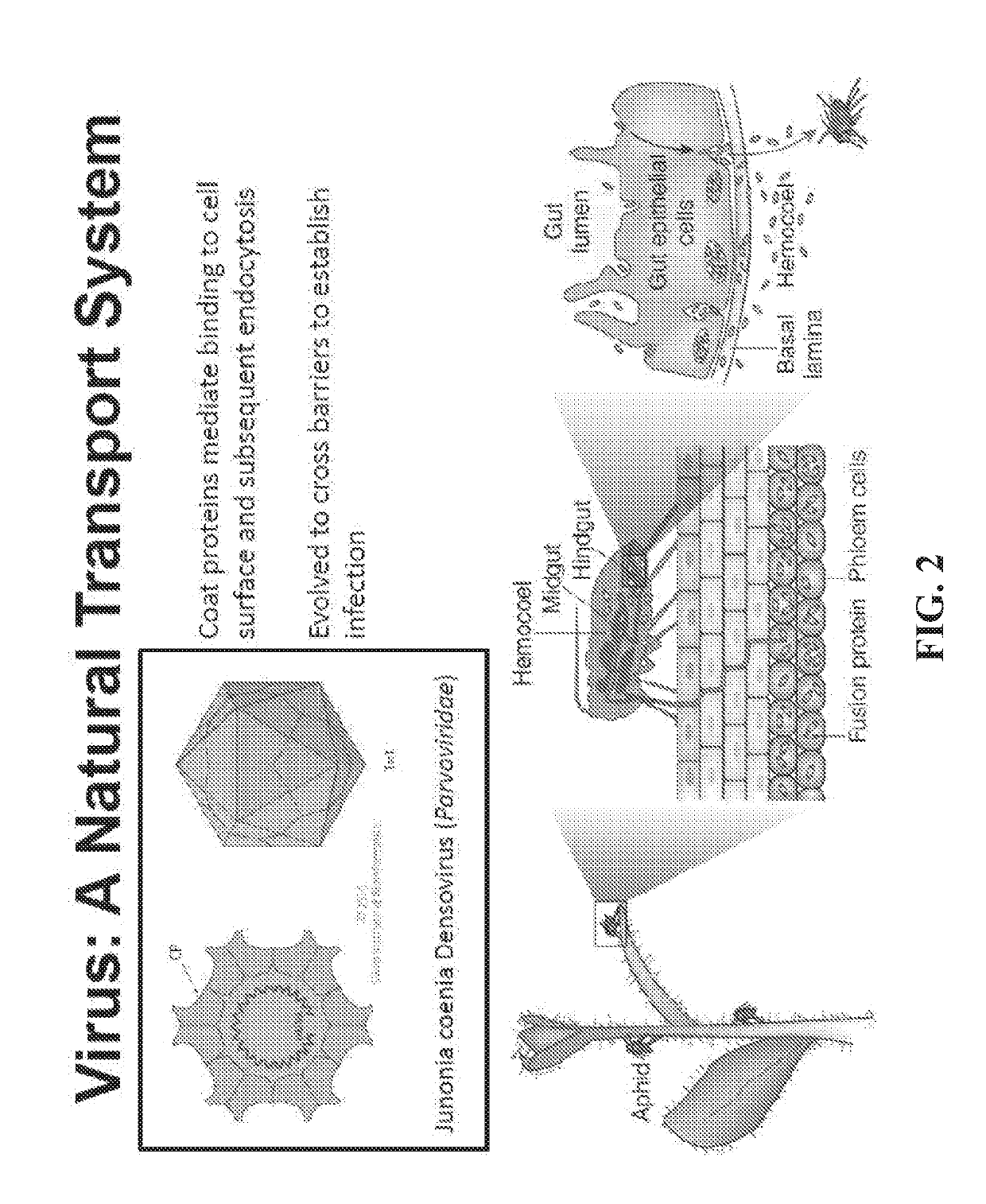
Insect toxin delivery mediated by a densovirus coat protein
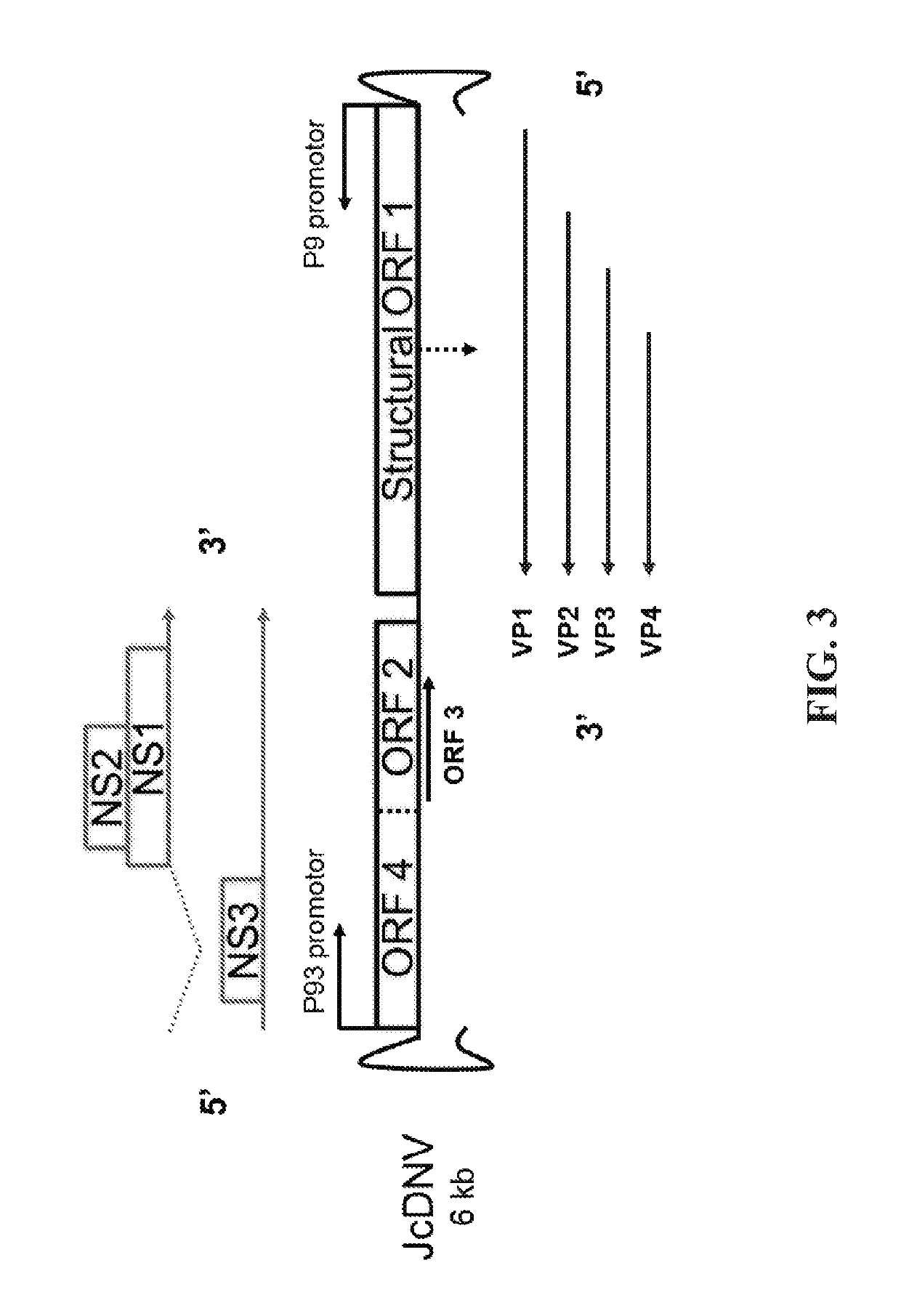
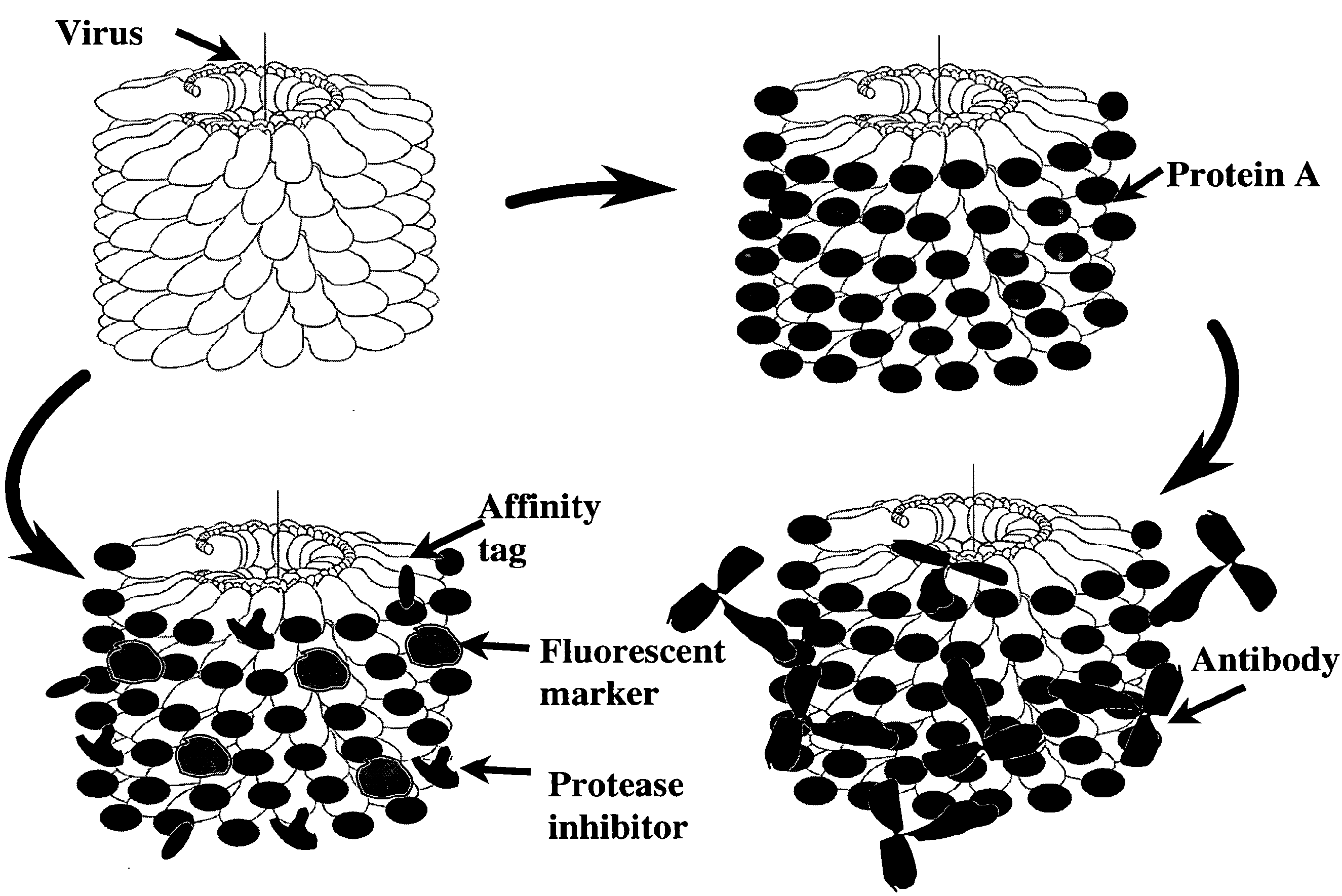
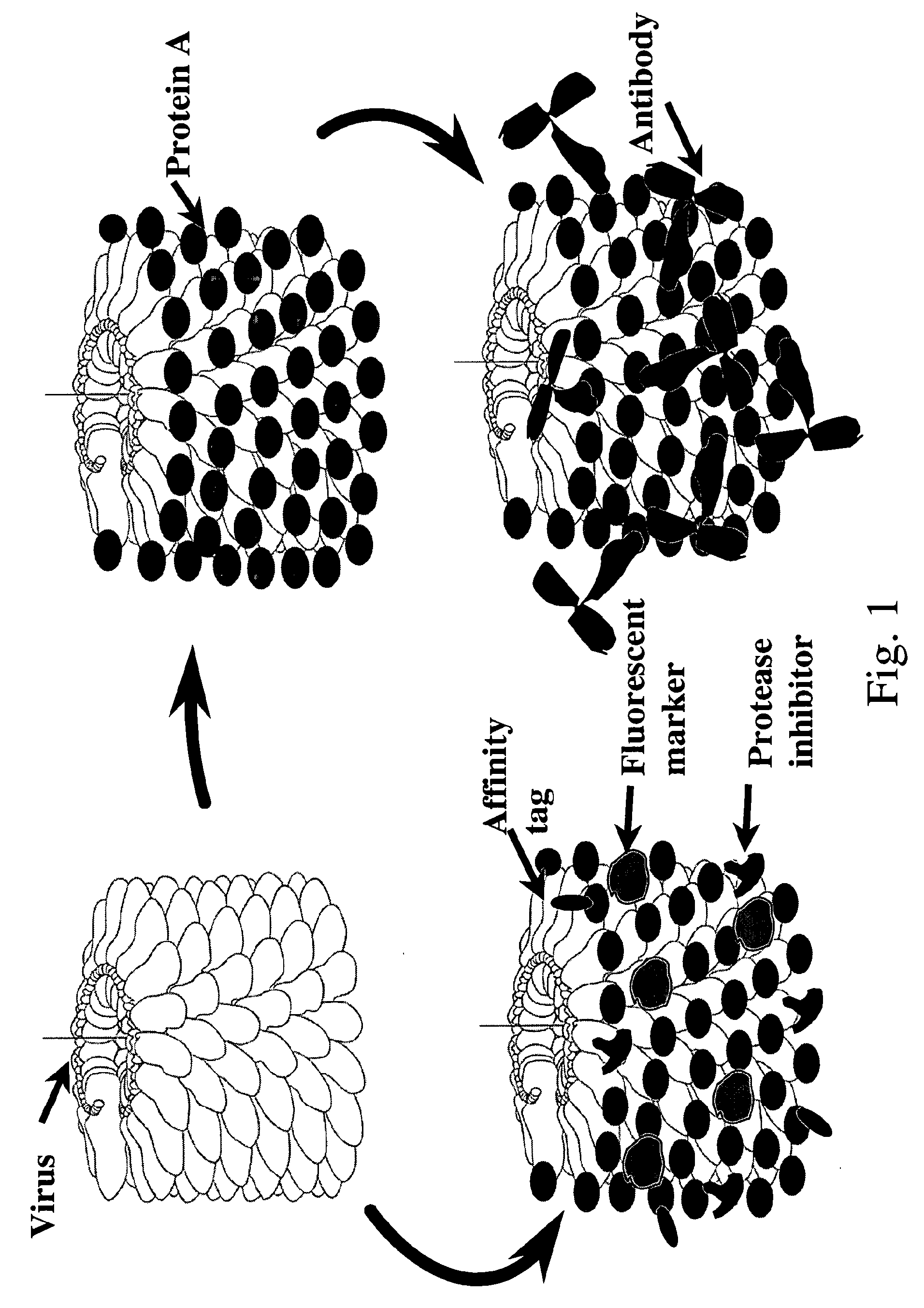
A coat protein of Junonia coenia densovirus (JcDNV) is used to deliver attached peptide insect toxin across the gut epithelium of a fall armyworm, Spodoptera frugiperda. A fusion protein comprising VP4 attached to an insect toxin via a peptide linker is developed. A composition comprising a JcDNV coat protein attached to an insect toxin via a peptide linker can be used for insect pest control.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC +1
Fast detection method for detecting Actinidia chlorotic ringspot-associated virus (AcCRAV) on basis of RT-LAMP-LFD
ActiveCN110295255AQuick checkReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDiseaseActinidia
The invention discloses primers for detecting Actinidia chlorotic ringspot-associated virus (AcCRAV) on the basis of RT-LAMP-LFD and a detection method. The primers include inner primers FIP and BIP and outer primers F3 and B3. The detection method comprises the following steps of S1, extracting RNA of a to-be-detected sample of kiwifruits; S2, reversely transcribing the RNA of the to-be-detectedextracted sample of the kiwifruits into cDNA; S3, taking the cDNA of the to-be-detected sample of the kiwifruits as a template to carry out isothermal amplification; S4, detecting an isothermal amplification subject obtained in step S3 through an LFD test paper strip, and judging whether or not the to-be-detected sample of the kiwifruits contains Actinidia chlorotic ringspot-associated virus. According to the method, the LAMP primers are designed according to the nucleotide sequence of the coat protein of Actinidia chlorotic ringspot-associated virus, so that fast detection of Actinidia chlorotic ringspot-associated virus is realized, whether or not the virus is contained in a kiwifruit plant or a tissue culture seedling can be fast identified, the purposes of detection, monitoring, prewarning and implementation of targeted measures are achieved, and the loss caused by diseases is reduced.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Microbial protein expression system utilizing plant viral coat protein
InactiveUS20070141698A1Fusions for enhanced expression stability/foldingFermentationCymbidium mosaic virusEscherichia coli
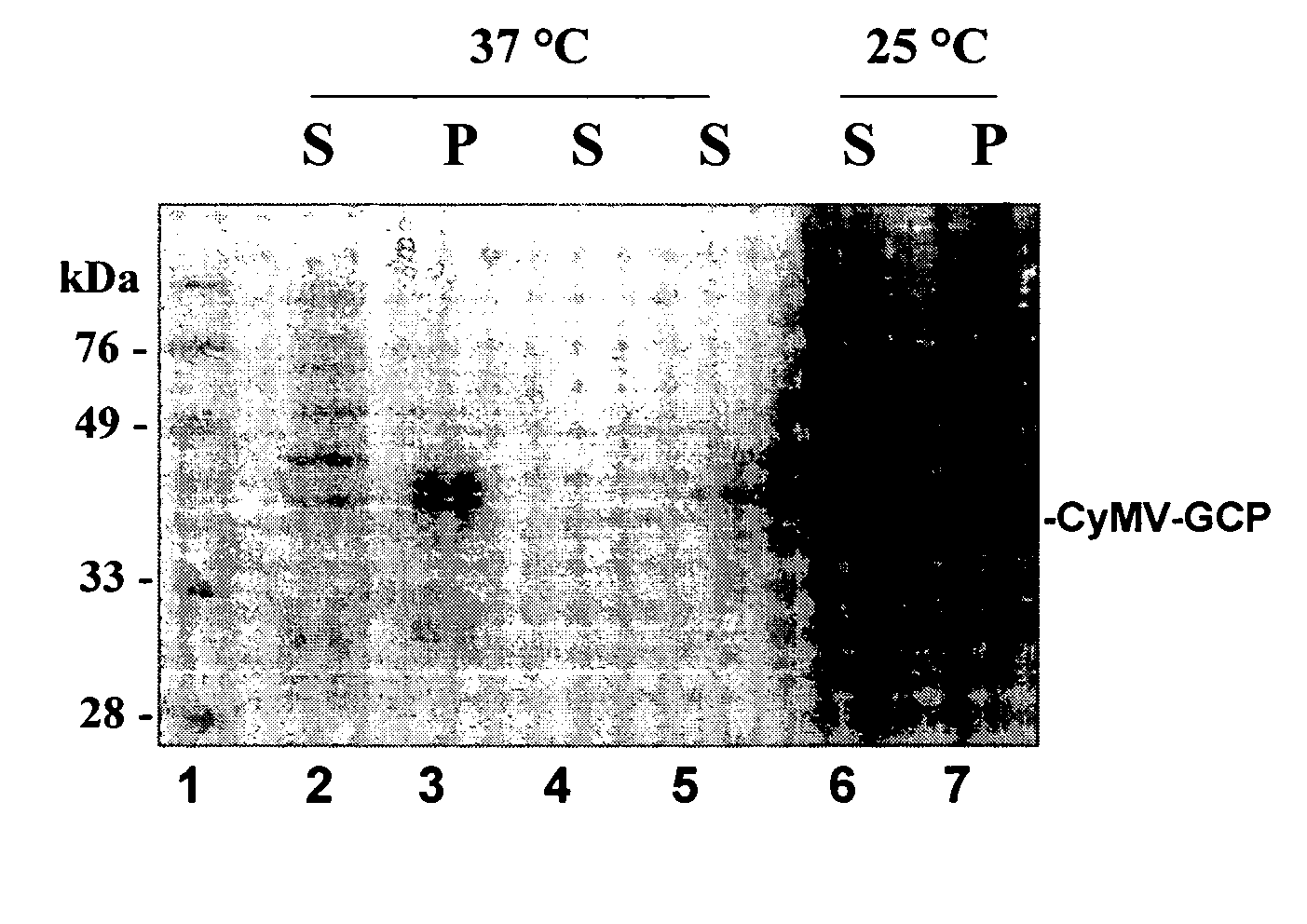
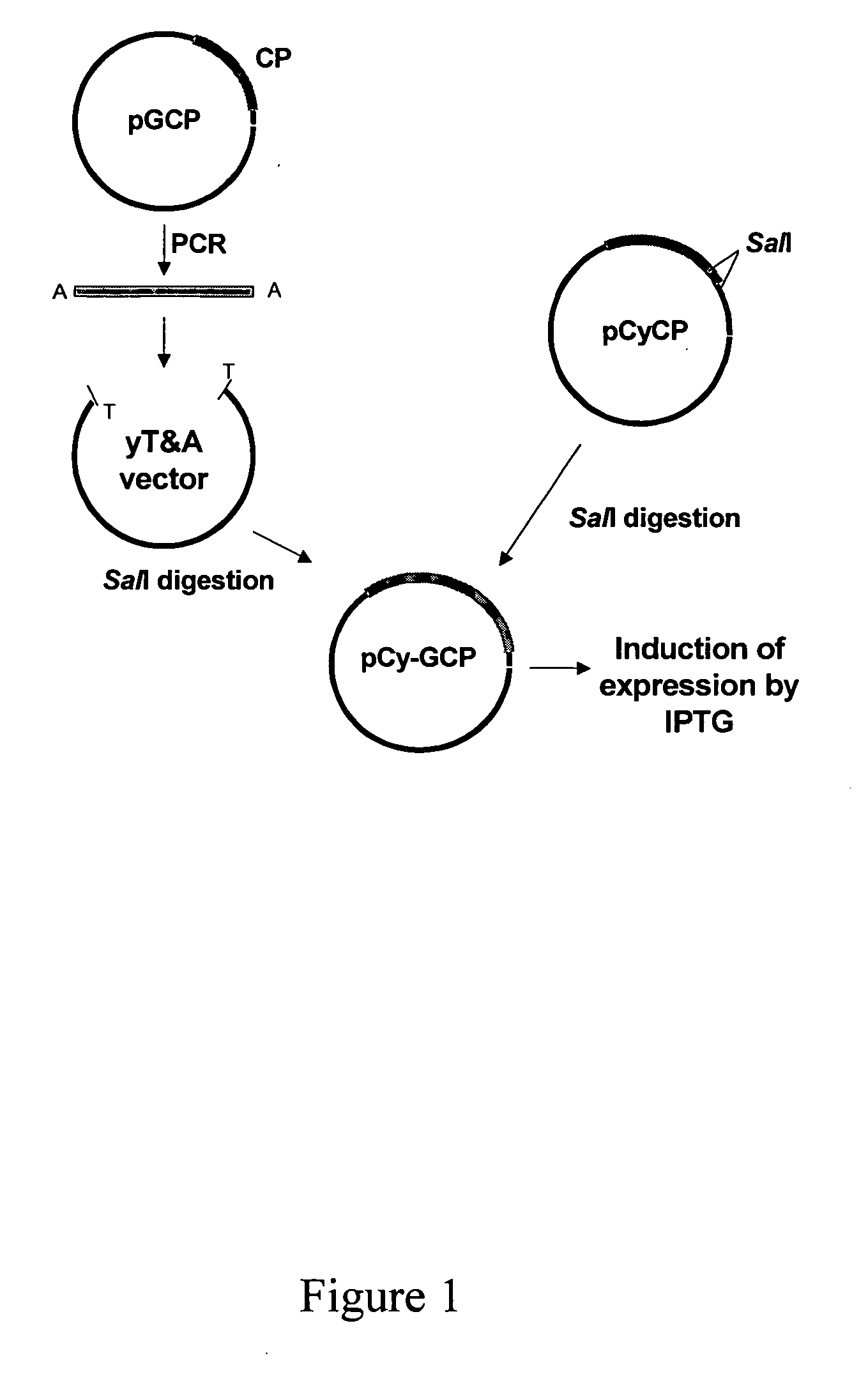
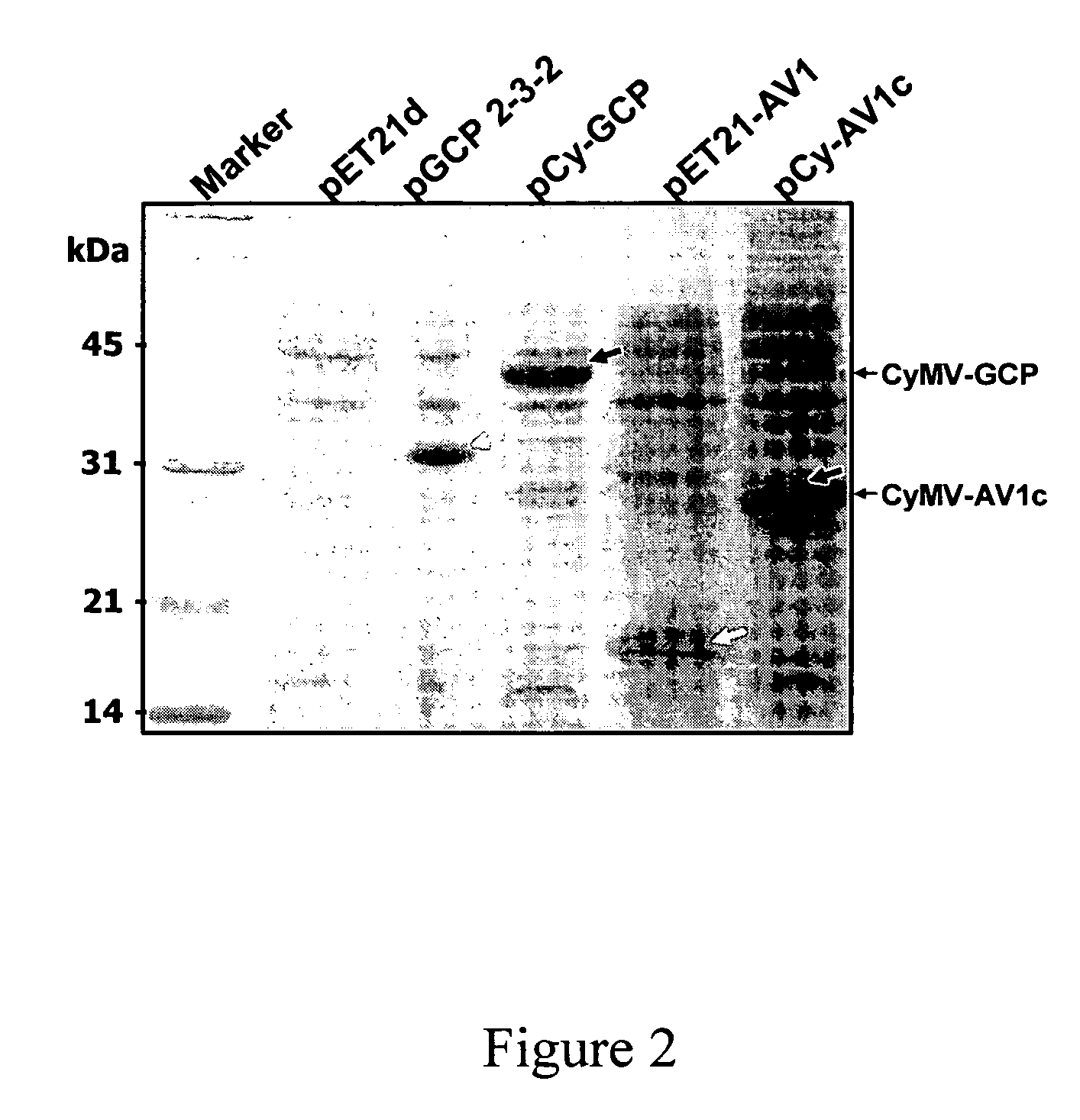
The present invention relates to an efficient microbial protein production system. A target protein is expressed as a portion of a fusion protein with the coat protein of Cymbidium mosaic virus (CyMV) in E. coli. Accordingly, the present invention provides nucleic acid expression vectors comprising a sequence encoding a protein of interest fused to CyMV coat protein, as well as methods of utilizing such vectors to produce the protein of interest.
Owner:BUREAU ANIMAL & PLANT HEALTH INSPECTION & QUARANTINE COUNCIL AGRI EXECUTIVE YUAN
Kit for rapidly detecting banana streak virus (BSV) by isothermal gene amplification and use method of kit
InactiveCN102703605AStrong specificitySimple extraction methodMicrobiological testing/measurementRNA extractionPositive control
The invention relates to a kit for rapidly detecting a banana streak virus (BSV) by isothermal gene amplification. Reagents of the kit include a primer mixed solution, a Bst DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase with the concentration of 8U / Mu l, a 8U reverse transcriptase, an RNA extract, a reaction buffer solution, a nucleic acid dye, a positive control reagent and a negative control reagent, wherein the primer mixed solution consists of two pairs of primers; the RNA extract contains 100mM of Tris-HCL (pH 7.4), 1M of KCl, 10mM of EDTA and 2% (w / v) of PVPP; the reaction buffer solution contains 10mM of dNTP, a 10*ThermoPol reaction buffer solution, 150mM of MgSO4 and 5mM of betaine which are at a ratio of 8:5:2:10; the positive control reagent is a cDNA containing BSV coat protein; and the negative control reagent is 100mM of Tris-HCL (pH 8.0) and 50mM of EDTA. The invention also relates to a use method of the kit. By extraction of nucleic acid of the BSV from a sample and isothermal gene amplification with the kit, the color of the reaction solution is finally judged through naked eyes, so that the high-specificity, rapid, high-sensitivity, simple and convenient molecular detection on the BSV is achieved.
Owner:ENVIRONMENT & PLANT PROTECTION INST CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Barley yellow dwarf virus interference virogene expression vector and its construction method and application
InactiveCN101215572AMake up for the vacancyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBarley yellow mosaic virusRestriction site
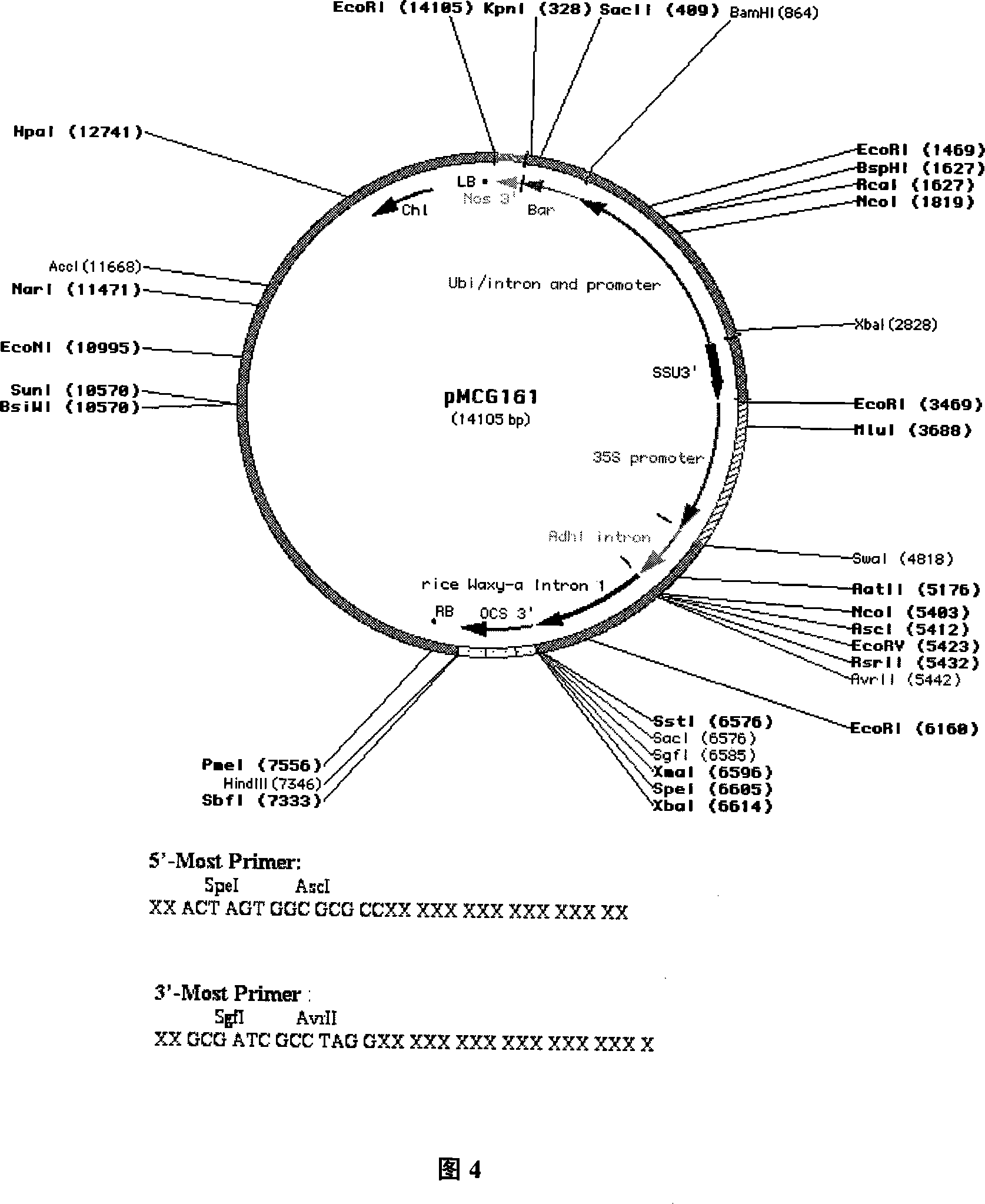
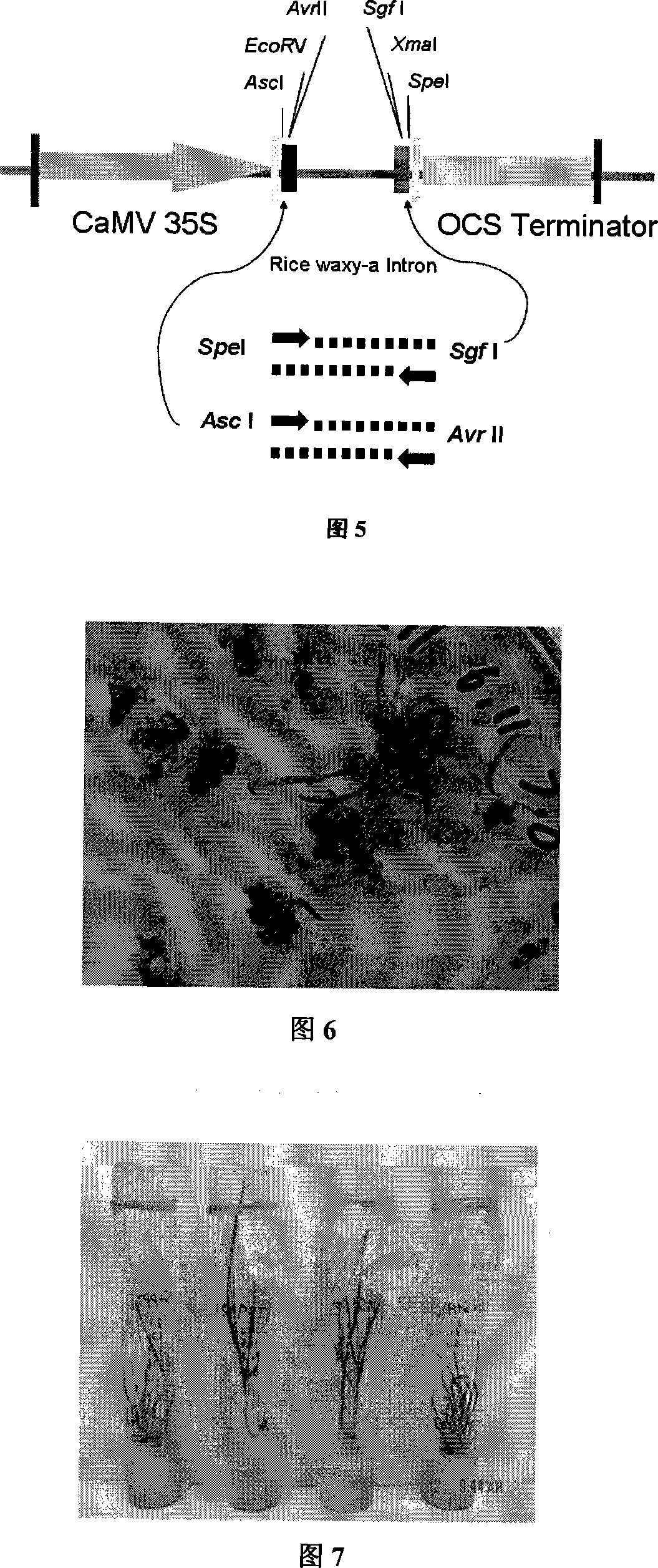
The invention relates to 'an expression vector of interfering viruses of barley yellow dwart viruses, a constructing method, and the application' and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. The invention provides the expressing vector of interfering viruses of barley yellow dwart viruses which is characterized in that a skeleton carrier which is adopted is pMCG161, a sense strand of a coat protein gene of the barley yellow dwart viruses is inserted between two restriction sites of AscI and AvrII which are on the upstream portion of the pMCG161, and an antisense strand of the coat protein gene of the barley yellow dwart viruses is inserted between two restriction sites of SpeI and SgfI which are on the downstream portion of the pMCG161. The expression vector of interfering viruses of barley yellow dwart viruses GAV which is constructed by the invention is transferred into wheat through particle bombardment to obtain a transgene wheat variety which has resistance to the barley yellow dwart viruses GAV. The invention provides a breeding way with high efficiency and a new strategy.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Plant viral particles comprising a plurality of fusion proteins consisting of a plant viral coat protein, a peptide linker and a recombinant protein and use of such plant viral particles for protein purification
InactiveUS20090062514A1Reduce the amount of solutionImprove mechanical propertiesSsRNA viruses positive-senseSugar derivativesPlant virusVirus-like particle
A process of purifying a protein of interest using viral particles or virus-like particles comprising a plurality of fusion protein molecules, said fusion protein comprising the following fusion protein domains: (i) a plant viral coat protein, (ii) a recombinant protein, and (iii) optionally a peptide linker linking said plant viral coat protein and said recombinant protein, wherein formation of said viral particle does not require free viral coat protein.
Owner:ICON GENETICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com