Virus like particles comprising target proteins fused to plant viral coat proteins
A capsid protein and plant virus technology, applied in the direction of viruses, viral peptides, drug combinations, etc., can solve the problem that viruses cannot be assembled
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
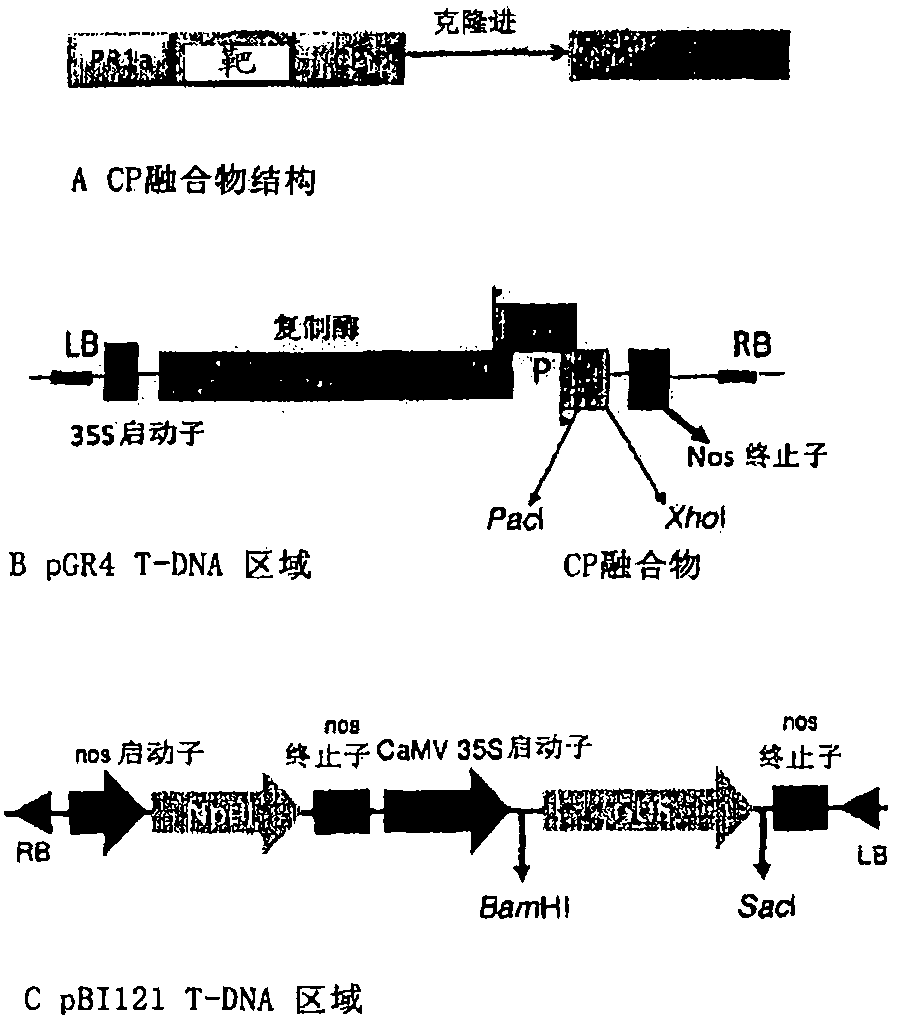
[0052] The construction of the heterologous vector expressing AIMV-CP fusion protein of embodiment 1
[0053] Target genes include different sex stages of malaria parasites, Plasmodium falciparum (Pfs25 (SEQ ID NO: 4), Pfs28 (SEQ ID NO: 5), and Pfs230 (SEQ ID NO: 49)), influenza virus Anwei strain blood Lectin (HA) globular domain (HA3A (SEQ ID NO: 6)), Influenza virus California strain HA globular domain (HA3C04 (SEQ ID NO: 7) and HA3C06 (SEQ ID NO: 8)), Influenza virus Indonesia strain HA The globular domain (HA3I (SEQ ID NO: 11)), the full-length HA of the Anhui strain (HAA or HAA1 (SEQ ID NO: 9)), and the full-length HA of the Indonesian strain (HAI or HAI1 (SEQ ID NO: 10)) are specific of cell surface proteins. Each target gene was cloned as an N-terminal fusion of an AIMV capsid protein (AIMV-CP, CP, or CPF), or an optimized AIMV capsid protein (CPO), using standard methods in molecular biology, wherein the optimized AIMV capsid The protein is encoded by a coding seque...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Example 2 Infiltration of Plants Using Expression Vectors Carrying Fusion Constructs
[0056] The expression vector produced in Example 1 was then introduced into Agrobacterium tumefaciens strain GV3101, and the resulting bacteria were grown overnight in minimal medium. The optical density of the culture was determined and the protein-expressing strain was mixed with the Agrobacterium strain expressing the silencing protein suppressor p19 in a 4:1 ratio to a final O.D. of 0.5. Agrobacterium solutions were introduced by manual infiltration into the aerial parts of 6-week-old, soil-grown N. benthamiana plants as previously described (Green et al., Biotechnol. J. 4:1-8, 2009).
[0057] Plant tissue samples were taken 3-7 days after infiltration to determine the expression level and solubility of the fusion protein. Samples were weighed and extracted in 3 volumes of extraction buffer (100 mM Na 2 HPO 4 , pH7.1; 2.5mM EDTA, pH8.0) to extract total soluble protein, extract...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Isolation and purification of virus-like particles
[0059] On the day of maximum expression, leaves were harvested and homogenized in 3 volumes of phosphate extraction buffer with 0.5% TritonX-100 in a blender. The homogenate was stirred at 4°C for 30 minutes and then centrifuged at 5,000 xg for 30 minutes. The supernatant was filtered through miracloth and centrifuged at 15,000 xg for 1 to 1.5 hours. The supernatant was pelleted with PEG and centrifuged again at 15,000 x g for 30 min. Pellets were resuspended in phosphate buffer and frozen at -20°C. After thawing, the suspension was centrifuged at 30,000 xg for 30 minutes. Protein concentrations were determined by examining aliquots of the suspension by SDS-PAGE. The suspension was centrifuged at 60,000 xg for 2 hours in a Ti70 rotor. The pellet was resuspended in phosphate buffer. The resulting suspension was analyzed using SDS-PAGE and Coomassie blue staining. Protein concentration is determined col...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com