Degradable open-cell porous zinc/zinc alloy biomaterial and preparation method thereof
A biomaterial and zinc alloy technology, applied in the field of degradable open-pore porous zinc and zinc alloy biomaterials and their preparation, to achieve the effects of controllable size, convenient operation, and excellent biocompatibility
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
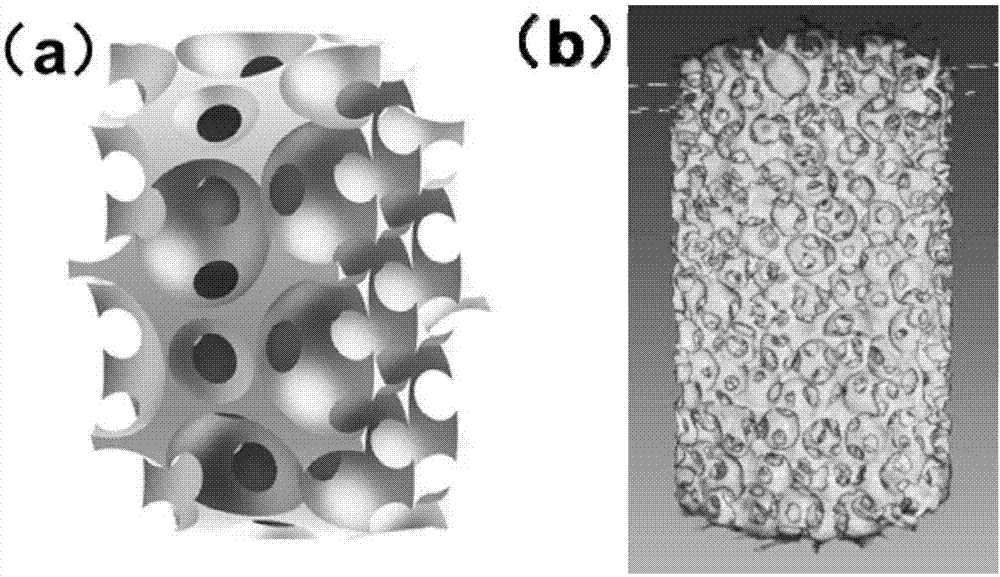
[0031] This example relates to a degradable open-pore porous zinc alloy used for bone tissue engineering scaffolds, with a diameter of 55 mm, a height of 50 mm, a spherical pore shape, and a pore diameter of 500-600 μm. The number of interconnected pores contained in the inner wall of a single cavity is 5 to 10, the diameter of the connected pores is 150 μm, and the porosity is 90%. Its structure is as figure 1 As shown, (a) is a schematic diagram of the three-dimensional structure of degradable open-pore porous zinc and zinc alloy bone tissue engineering scaffolds, which accurately reflects the pore characteristics described in the present invention, for example, spherical pore type and interconnected pores The hole type and their distribution characteristics; (b) The picture is the corresponding physical map, from which we can see the spherical hole type and the hole type of the connected holes distributed on the hole wall and their distribution characteristics and schematic...
Embodiment 2
[0037] This embodiment relates to a degradable open-pore porous zinc alloy used for bone tissue engineering scaffolds, with a diameter of 100mm, a height of 100mm, a cubic shape, a pore diameter of 900-1000μm, and the number of interconnected pores contained in the inner wall of a single cavity There are 3 to 5 connected pores, the diameter of the connected pores is 400 μm, and the porosity is 85%.
[0038] This embodiment relates to the aforementioned method for preparing a degradable open-pore porous zinc alloy for bone tissue engineering scaffolds, the method comprising the following steps:
[0039] Step 1, put the cubic sodium chloride crystal particles with a size of 900-1000 μm into a mold with an inner diameter of 100 mm and a height of 100 mm and sinter at a constant temperature of 790 ° C for 24 hours, and then cool with the furnace to obtain an open-pore porous sodium chloride prefabricated body with a certain strength ;
[0040] Step 2, pouring the Zn-3wt%Mg alloy ...
Embodiment 3
[0043] This example relates to a degradable open-pore porous zinc used for bone tissue engineering scaffolds, with a diameter of 200 mm and a height of 200 mm. The pore type is irregular and the pore diameter is 700-750 μm. 3 to 4 pieces, the diameter of the connected pores is 250 μm, and the porosity is 70%.
[0044] This embodiment relates to the preparation method of the aforementioned degradable open-pore porous zinc for bone tissue engineering scaffold, the method comprising the following steps:
[0045] Step 1, put irregular sodium chloride crystal particles with a size of 700-750 μm into a mold with an inner diameter of 200 mm and a height of 200 mm, sinter at a constant temperature of 700 ° C for 10 hours, and cool with the furnace to obtain an open-pore porous sodium chloride prefabricated with a certain strength body;
[0046] Step 2, pouring pure zinc metal melt into the mold cavity with open porous sodium chloride prefabricated body, and carrying out pressure seep...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com