Detection of haematopoietic stem cells and progeny and uses thereof
a technology applied in the field of haematopoietic stem cells and progeny detection, can solve the problems of not being able to define the spatial distribution of hemopoietic stem cells (hsc) within the bm, and may take many weeks or months for natural recovery of such hpc cells to their normal levels
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
HA Expression on Murine Hemopoietic Cells
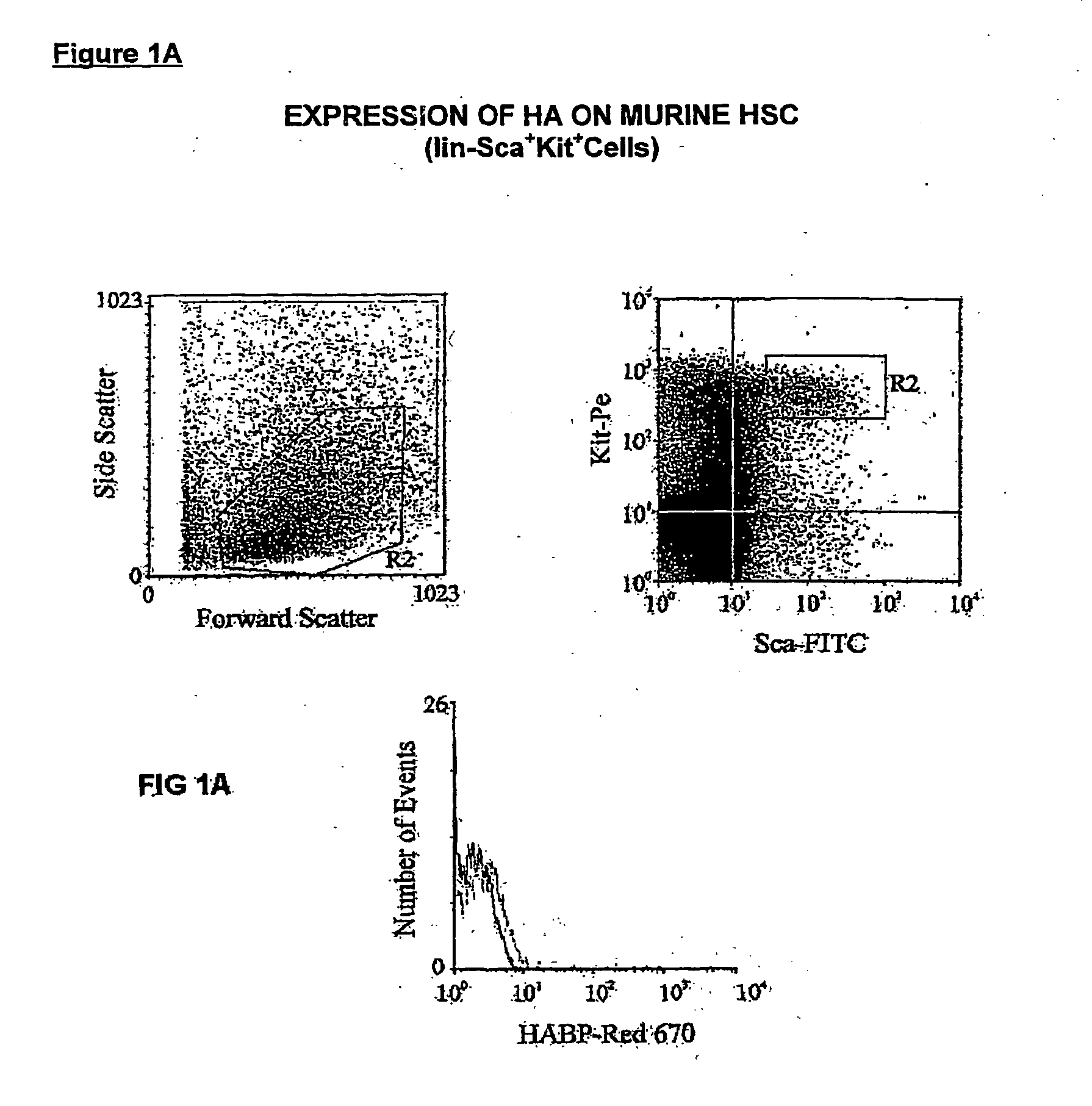
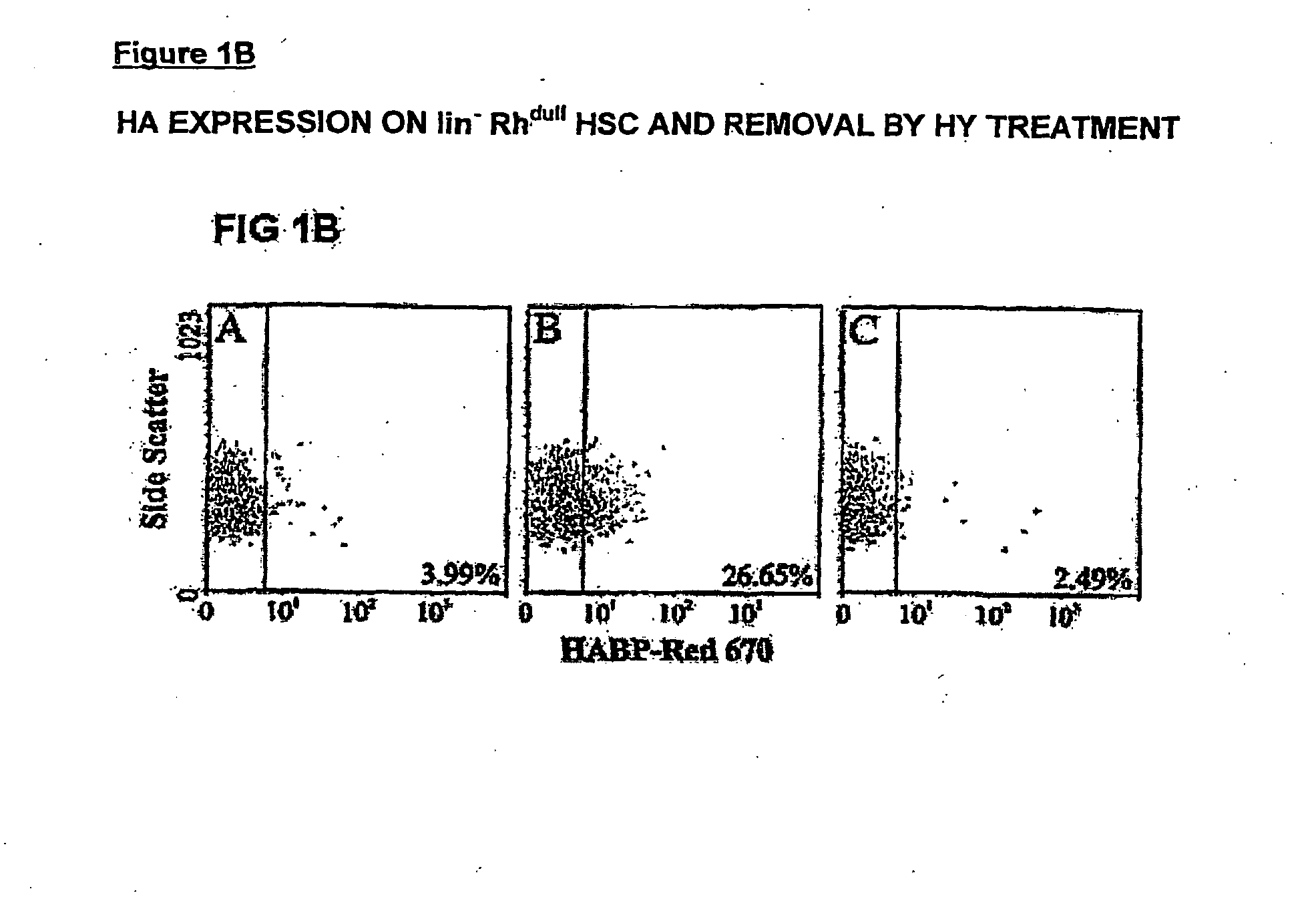
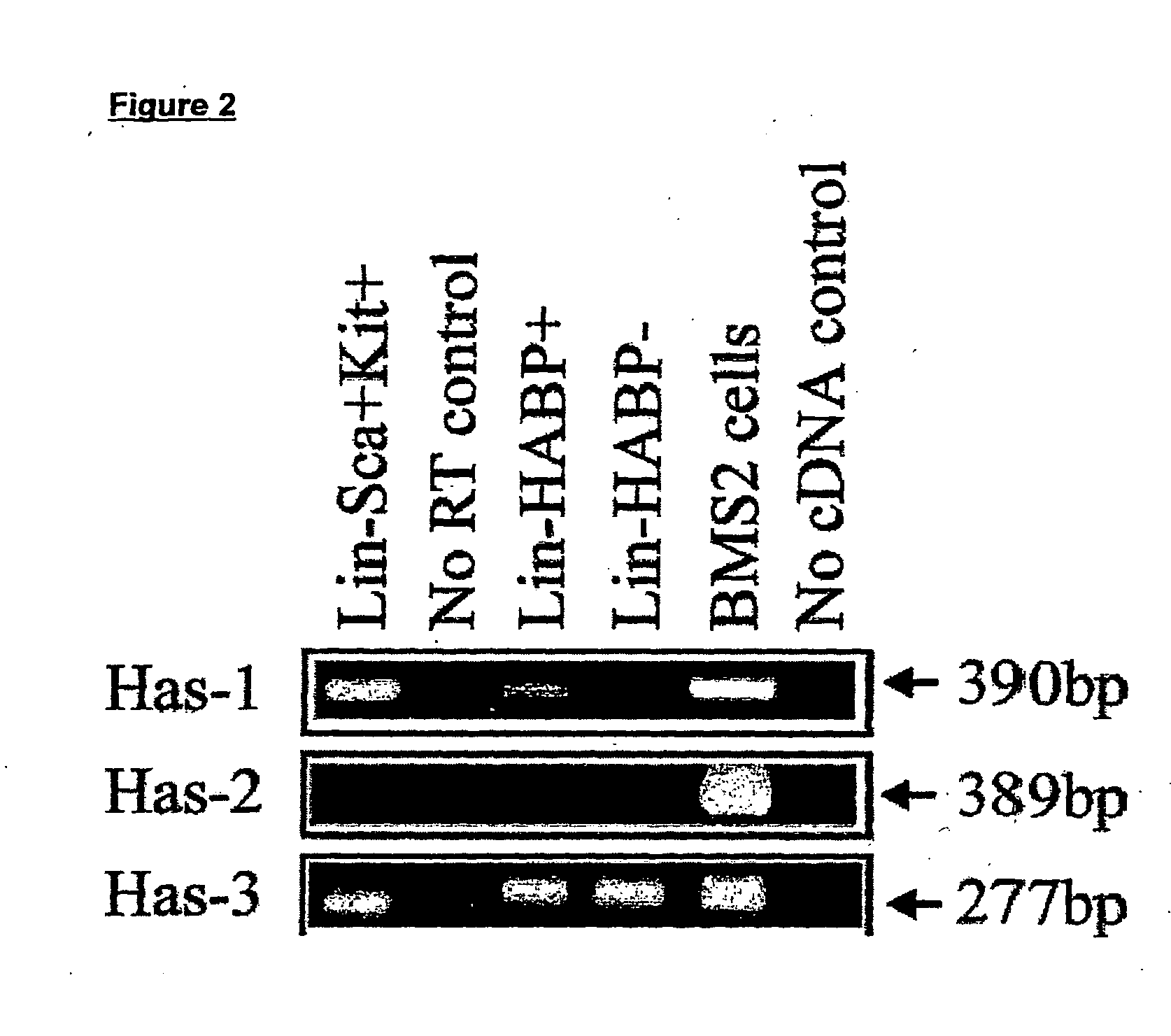
[0242] Expression of HA was demonstrated by flow cytometric analysis through the binding of a biotinylated form of hyaluronic acid binding protein (HABP), which demonstrates absolute specificity for HA (4). Using this approach, HABP binding was detected on two murine sub-populations enriched for HSC: Lin−Sca+Kit+(FIG. 1a) and Lin−Rhdull and was completely eliminated by prior treatment of the cells with the enzyme hyaluronidase (HY) (FIG. 1b). In addition, a similar proportion of Lin− Rh123dull cells isolated from CD44− / − mice (2) exhibited binding of HABP (25.0% compared to 26.5%), demonstrating that HA detected on the cell surface is not due to the binding of exogenous HA to its major receptor CD44 (19) but due to de-novo synthesis by primitive hemopoietic cells themselves. Importantly, RT-PCR analysis demonstrated that Lin−Sca+Kit+, Lin−HABP+ but not HABP− cells express Has-1, Has-2 and Has-3 (FIG. 2a+b).
example 2
HA Expression of Human HPC
[0243] The expression of HA by primitive BM cells is not a unique feature of the mouse but is also a characteristic of human hemopoietic progenitors. FACS analysis of human umbilical cord blood (CB) (FIG. 3) using CD34, CD38 and HABP showed putative Human HSC synthesise HA. Interestingly, there was a significant decrease in the level of HA expression in correlation with a maturing cell phenotype, with no HA expression detected on CD34−CD38+ cells. In accord with data in the mouse, isolated human CD34+ and Lin−HA+ cells but not Lin−HA− also express HAS1, HAS2 and HAS3 (FIG. 4). Collectively these data demonstrate that HA is synthesized by and expressed on murine and human hemopoietic populations enriched for HSC.
[0244] However, repopulating HSC represent only a minor proportion of Lin−Rh123dull cells (5). In order to examine whether HSC were contained within the HABP+ subpopulation, FACS was used to isolate Lin−HABP+ and Lin−HABP−, and Lin− Sca+HABP+ and L...
example 3
The Potential Role of HA as a Negative Regulator of HSC Proliferation
[0248] In vitro stroma-free, cytokine-dependent cultures demonstrated that the ligation of HA by a the surrogate soluble ligand HABP results in a profound suppression of both murine and human HSC proliferation while stimulated by a potent combination of early acting hemopoietic growth factors. Both murine and putative human HSC (Lin−Sca+Kit+ and Lin−CD34+CD38− cells respectively) were cultured in serum free conditions in the presence of multiple cytokines consisting of either SCF (75ng / ml), IL-11, FLT3 Ligand and IL-6 (all 100 ng / ml) or G-CSF, SCF, FLT3 Ligand, MGDF (all 100 ng / ml), Il-6 and IL-3 (both 10 ng / ml) for murine and human HSC respectively, and various concentrations of HABP. As shown in FIG. 5 this resulted in a significant inhibition of cell proliferation corresponding to the presence of increasing concentrations of HABP. This unexpected data shows a marked growth inhibitory effect of HA on hemopoiesis...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| fluorescent | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| colorimetric assays | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| adhesion | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com