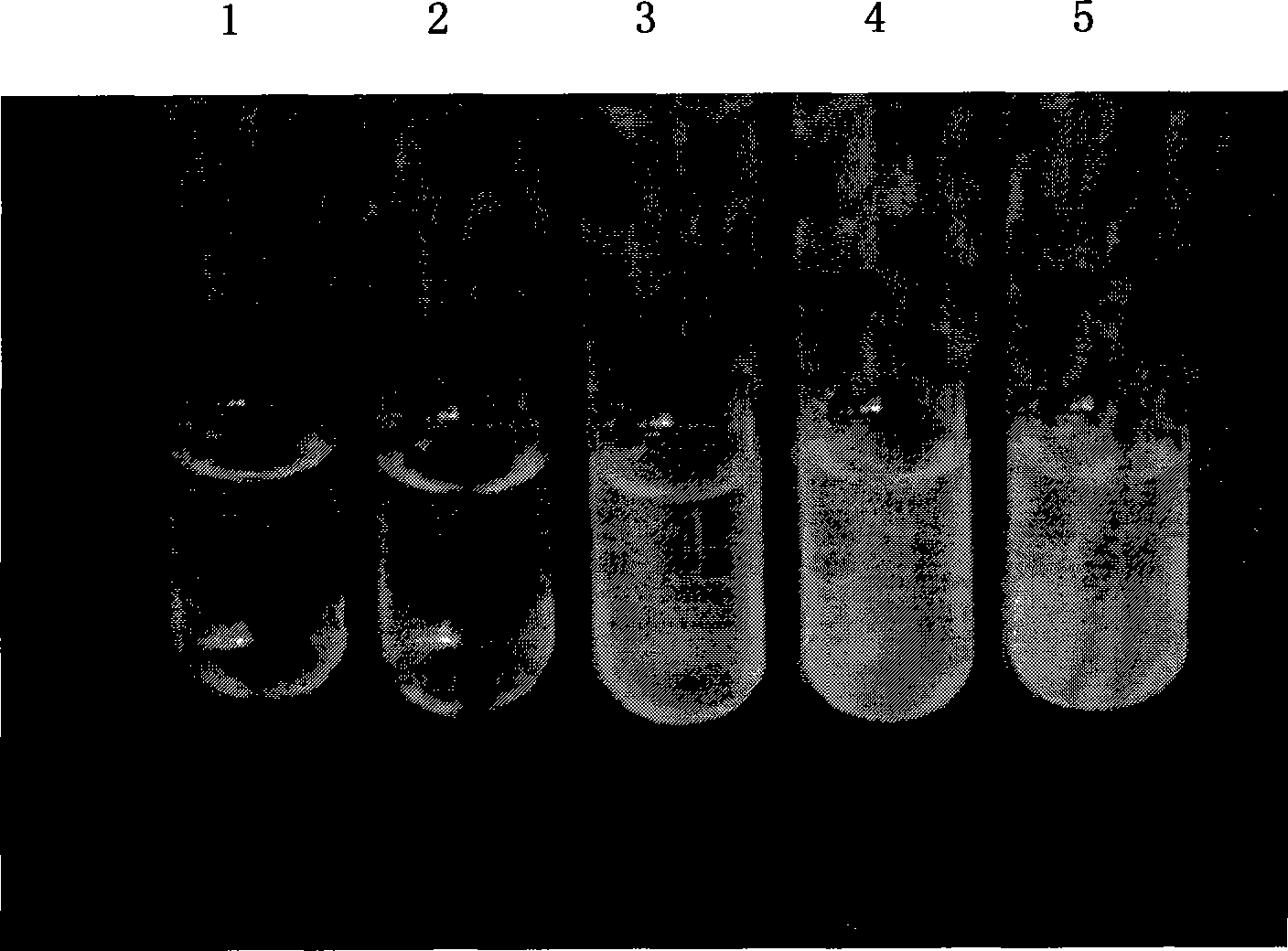Gene for improving plant salt tolerance and drought resistance and use thereof
A technology of drought resistance and salt tolerance, applied to the application of drought stress resistance, improving the field of plants to salt, can solve the problems of D.radiodurans and so on.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0048] Example 1 SEQ ID NO: 1 nucleotide sequence expression in Escherichia coli and analysis of salt tolerance and drought resistance performance
[0049] 1. Cloning of the nucleotide sequence SEQ ID NO: 1
[0050] The complete nucleotide sequence was amplified from D. radiodurans genomic DNA based on the published Deinococcus radiodurans genomic sequence involving a pair of PCR-specific primers.
[0051] 2. Construction of Escherichia coli expression vector and molecular verification
[0052] The above-mentioned cloned fragment was digested with NdeI and SacII double enzymes, connected with the vector pTtSacB containing the E.coli universal promoter groE, and replaced the SacB gene to generate an Escherichia coli expression vector of the gene. Transform E.coli JM109, smear it on LB solid medium containing Amp, pick white colonies, extract plasmids by alkali lysis method, screen different recombinants, digest with BglII and sequence verification, and obtain a strain expressi...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Embodiment 2 SEQ ID NO: artificial synthesis of 2 nucleotide sequence
[0056] According to the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1, firstly divide 7 segments into single-stranded oligonucleotide fragments with a length of 150-200bp and sticky ends according to the positive and secondary strand sequences respectively. Anneal the 7 complementary single-stranded oligonucleotide fragments in one-to-one correspondence between the positive strand and the auxiliary strand respectively to form 7 double-stranded oligonucleotide fragments with sticky ends. The mixed double-stranded oligonucleotide fragments are catalyzed by T4 DNA ligase and assembled into a complete gene. Both ends of the synthesized DNA fragment contain XbaI and SacI sites.
[0057] The above-mentioned artificially synthesized 5' and 3' end restriction sites are XbaI and SacI sites SEQ ID NO: 2, which are used for the construction of the following high salt tolerance and drought resistance gene plant expressi...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Example 3 Eukaryotic expression of the nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 2 in tobacco cells and identification of salt tolerance and drought resistance of transgenic plants
[0059] (1) Construction of expression vector containing target gene
[0060] According to the full-length coding sequence (SEQ ID NO: 2), design primers to amplify the complete coding reading frame, and introduce restriction endonuclease sites on the forward and reverse primers respectively (this can be determined by the vector selected), In order to construct the expression vector. Using the amplified product obtained in Example 1 as a template, after PCR amplification, the sequence cDNA was cloned into an intermediate vector (such as pBluescript), and further cloned into a binary expression vector (such as pBI121 and pCAMBIA2200). The expression vector identified under the premise was transformed into Agrobacterium, and the model plant Nicotiana tabacum was transformed by the leaf disc method. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com