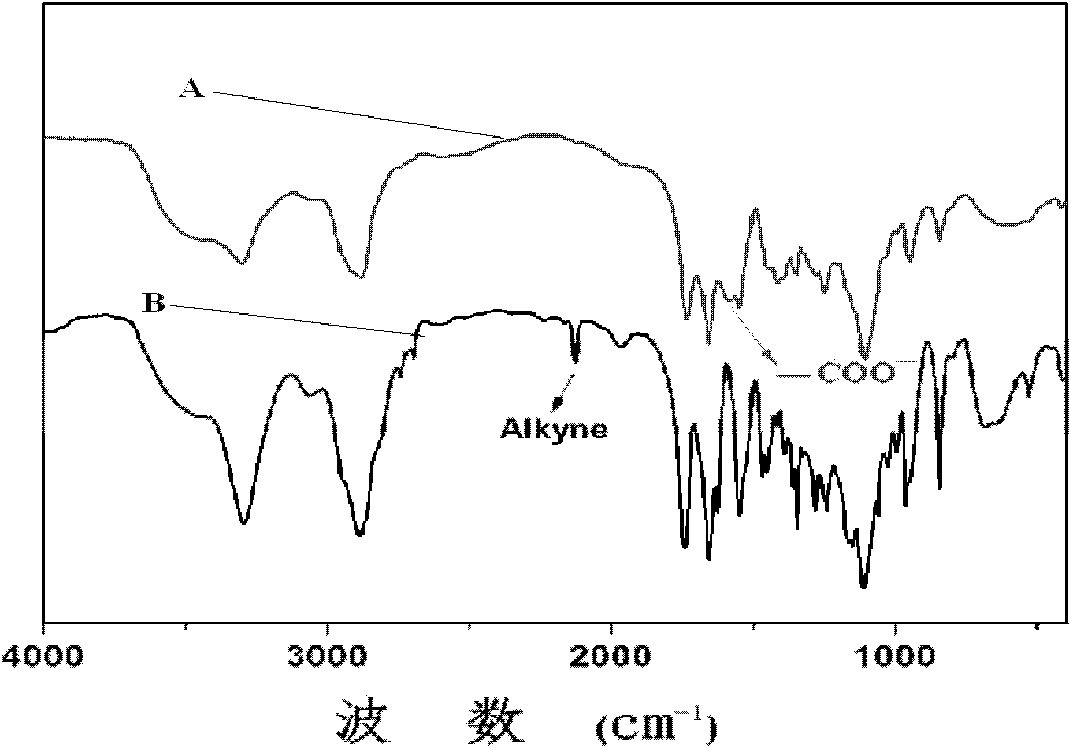
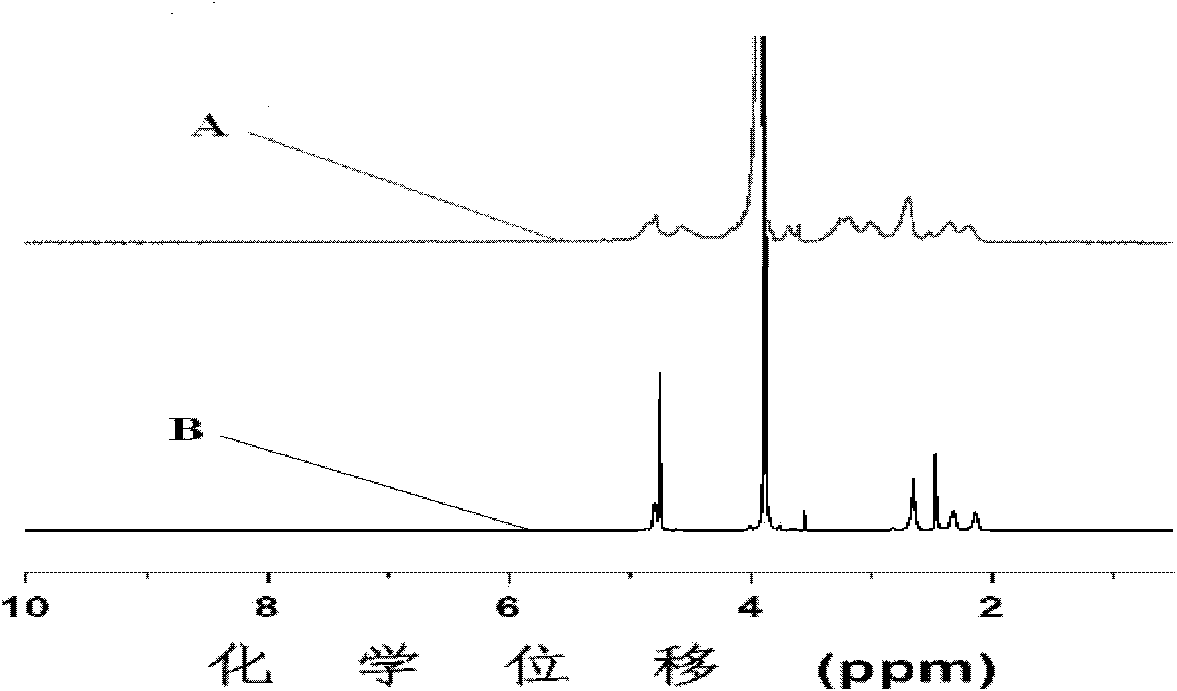
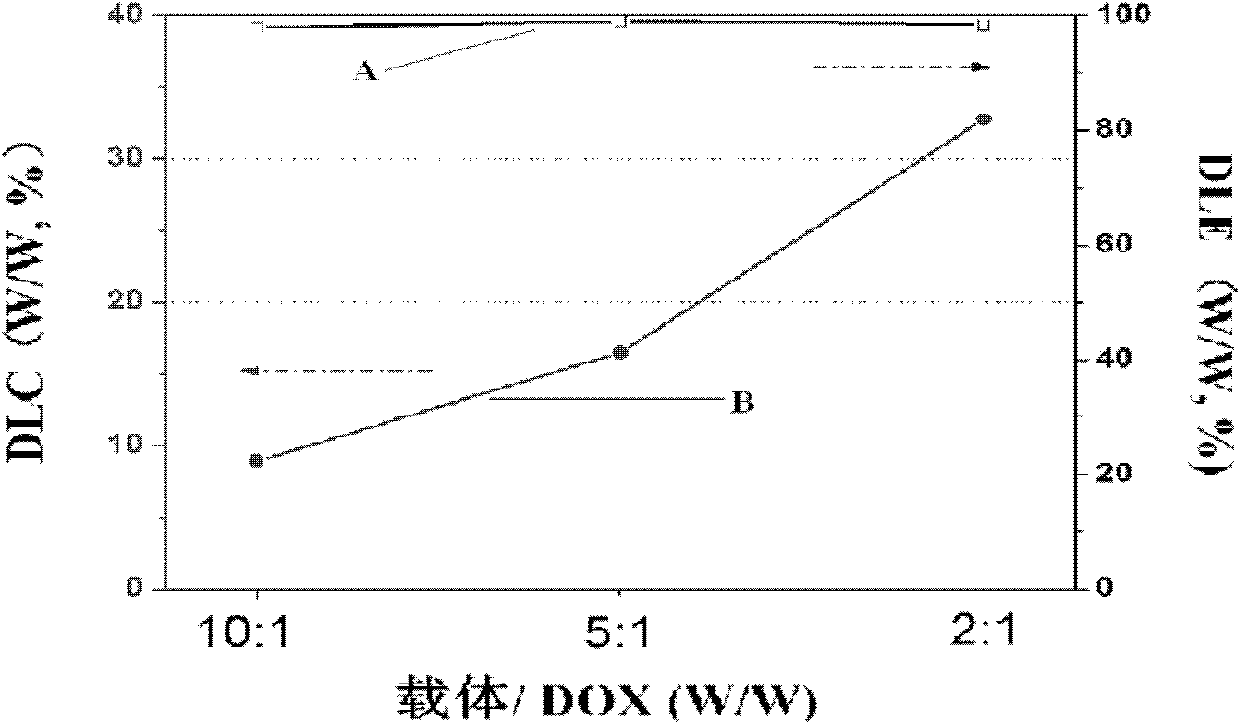
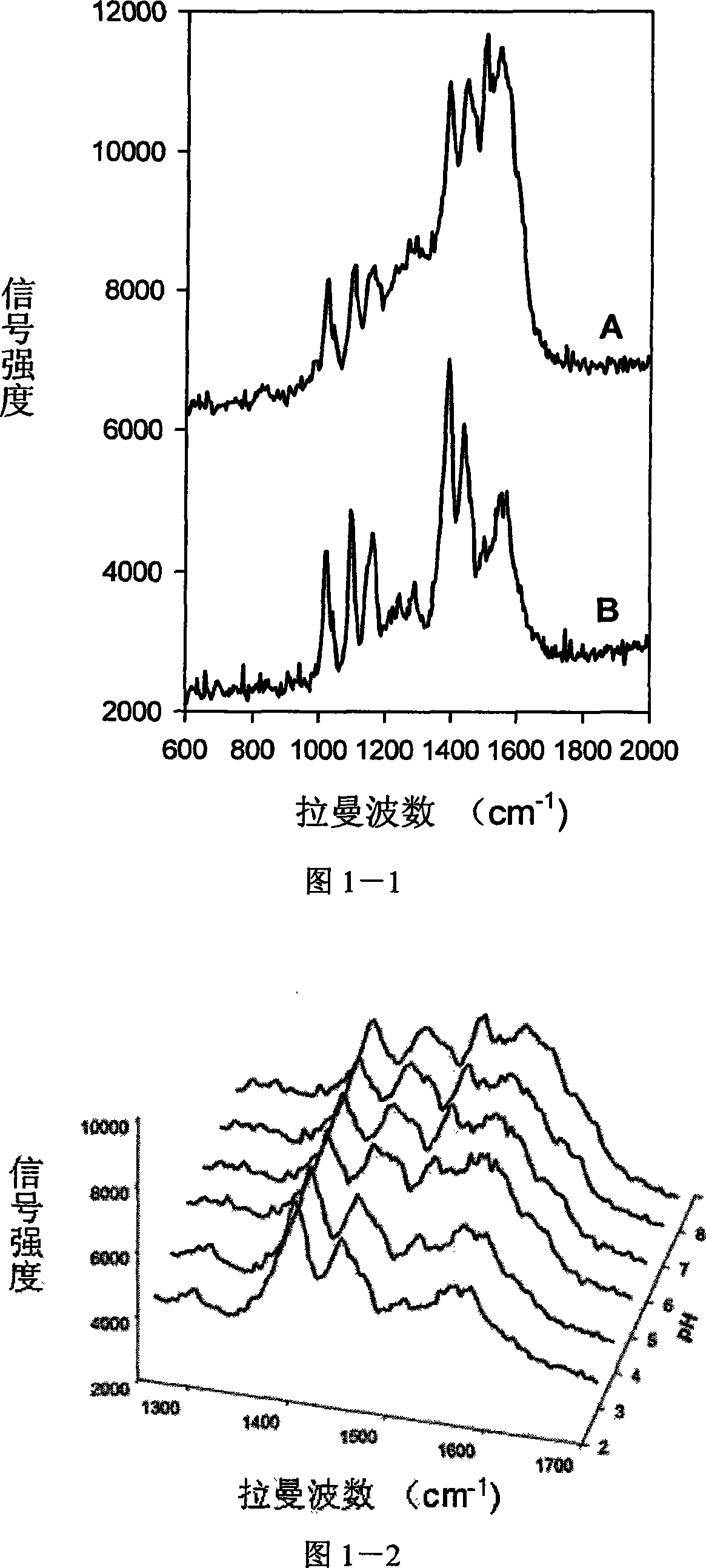
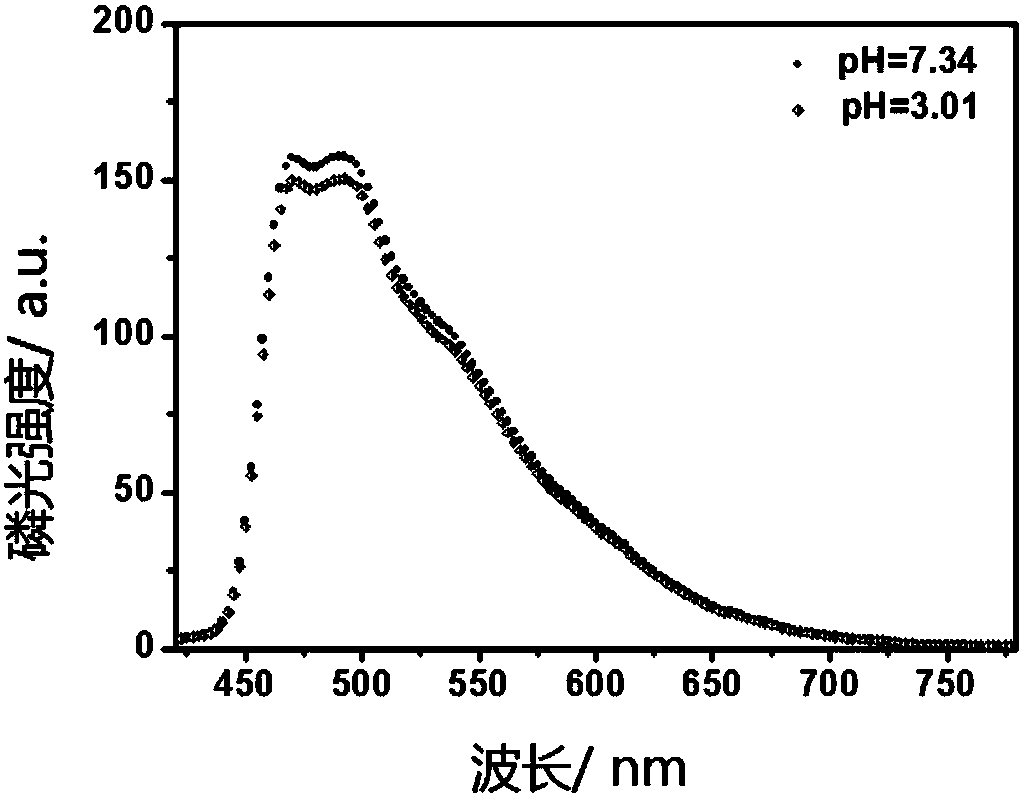
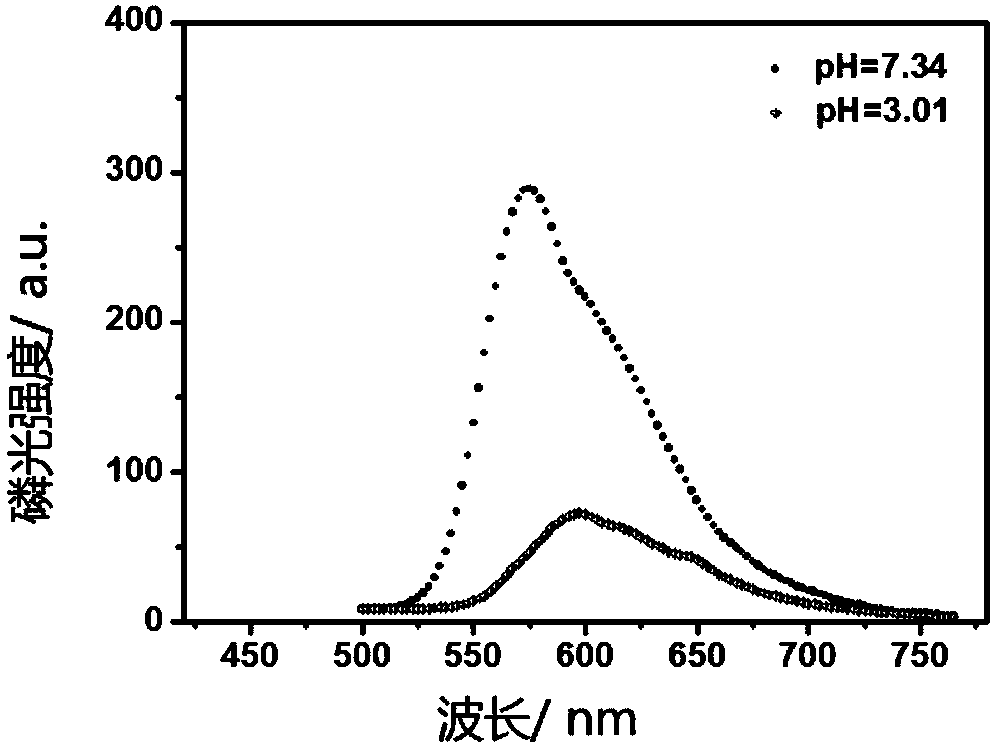
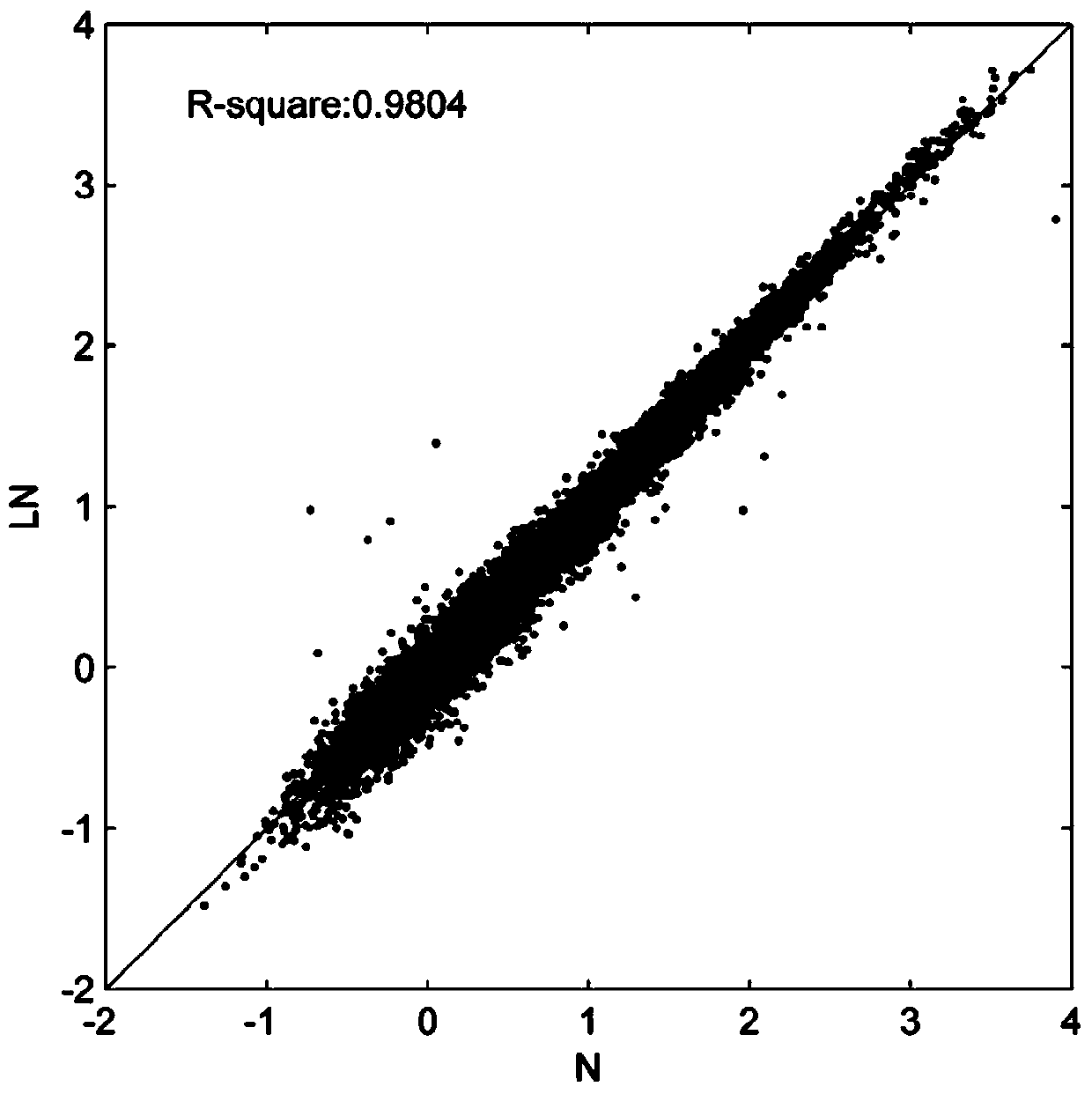
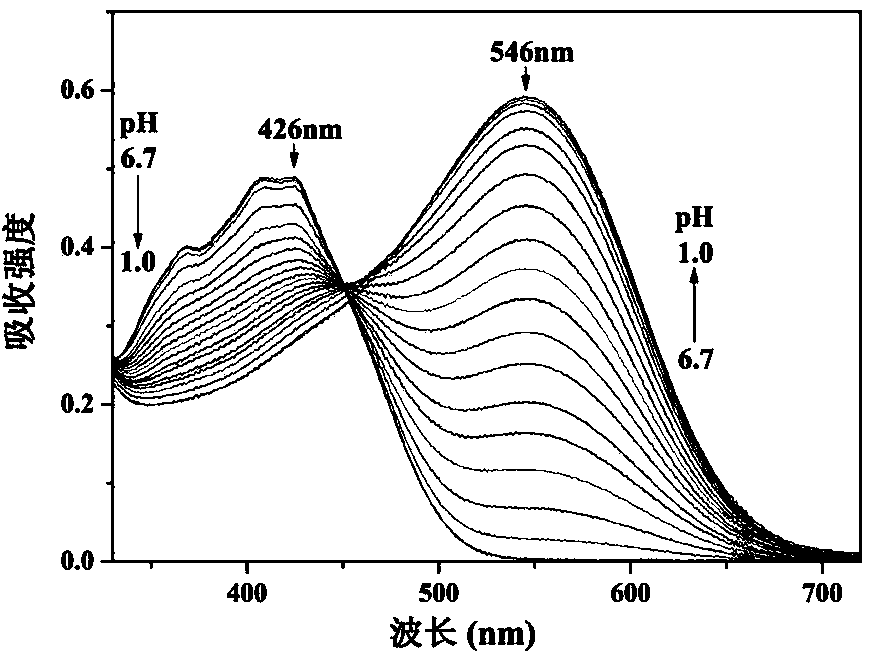
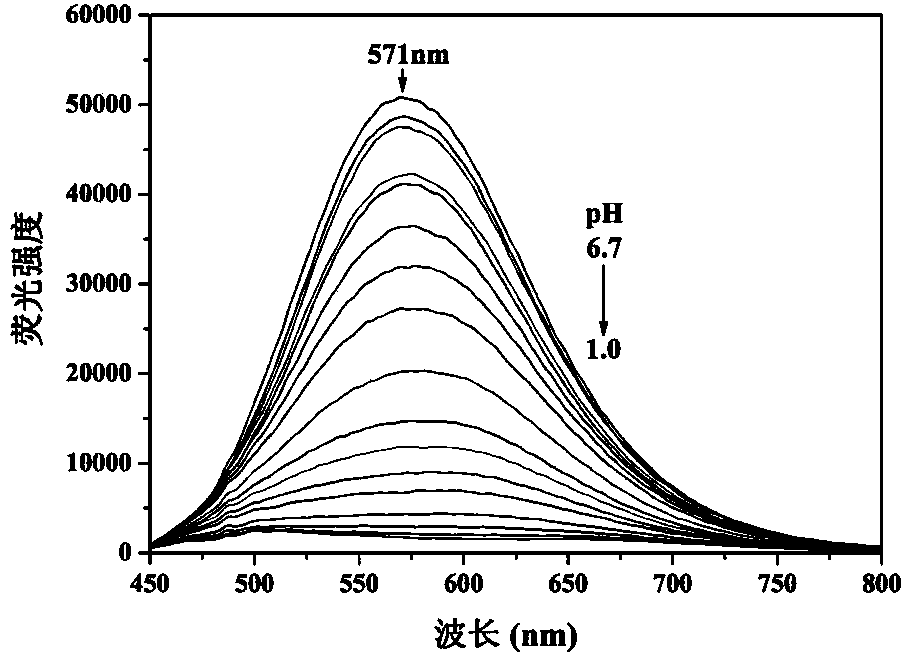
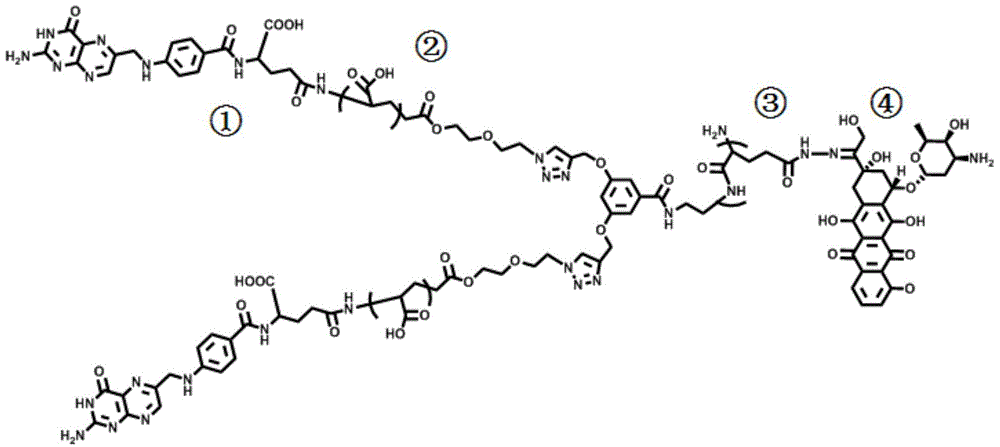
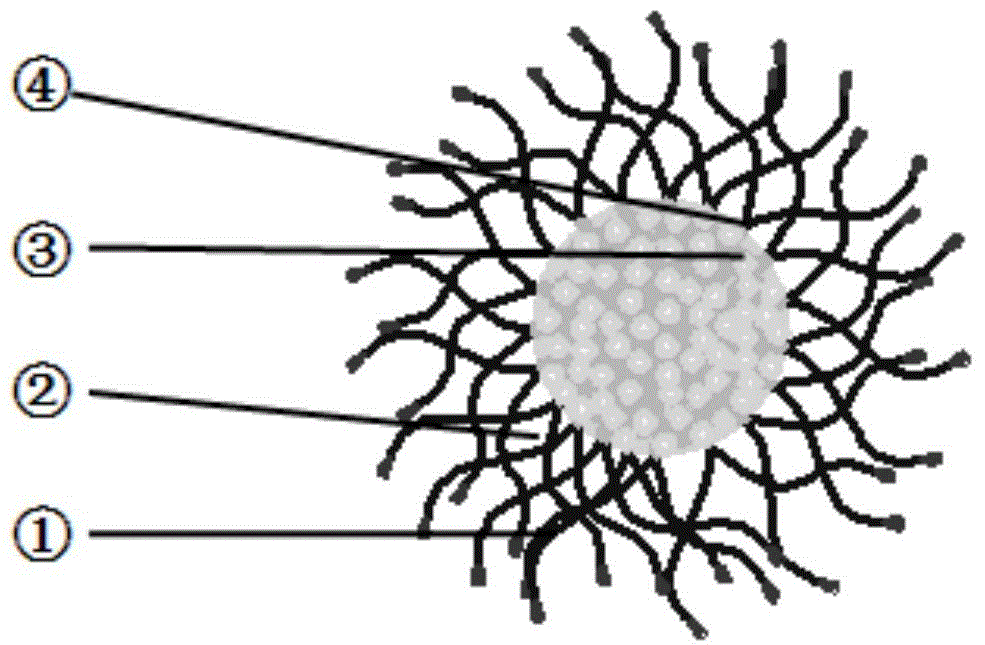
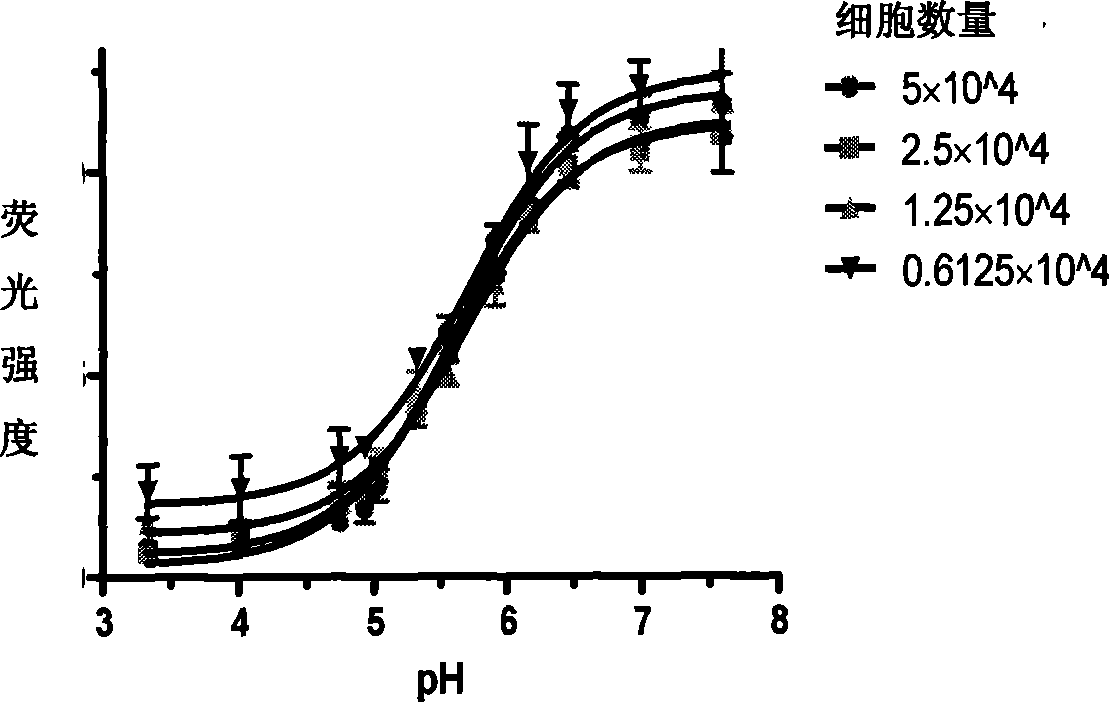
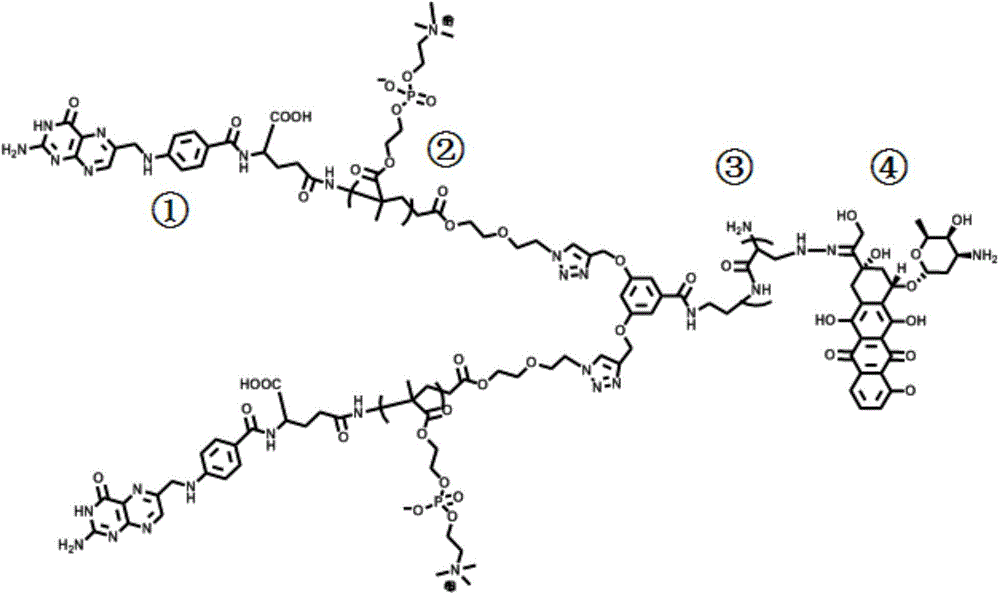
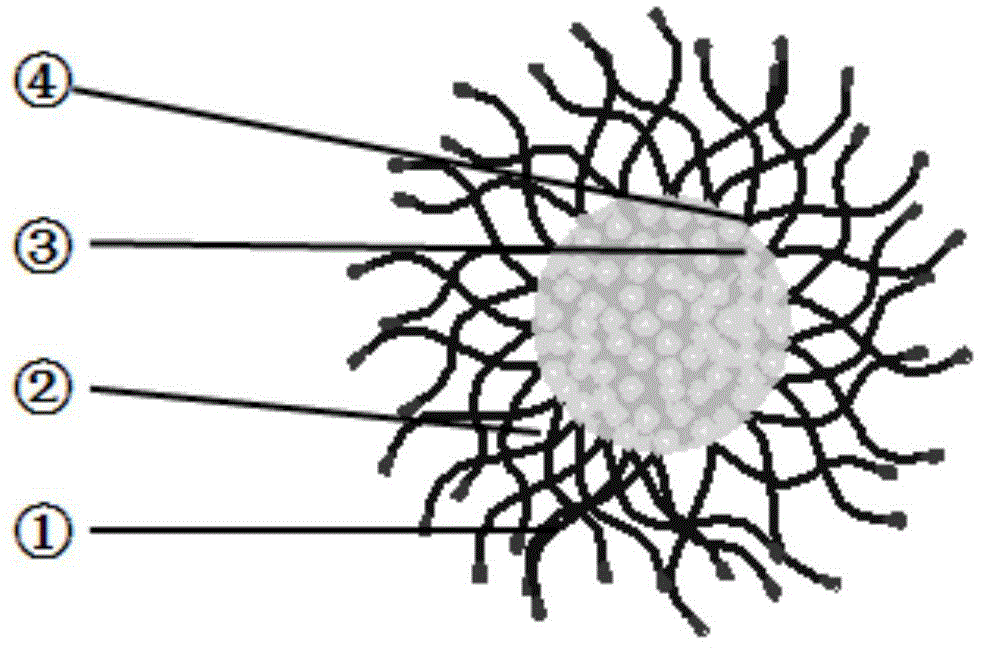
Patents
Literature
132 results about "Intracellular pH" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Intracellular pH (pHi) is the measure of the acidity or basicity (i.e., pH) of intracellular fluid. The pHi plays a critical role in membrane transport and other intracellular processes. In an environment with the improper pHi, biological cells may have compromised function. Therefore, pHi is closely regulated in order to ensure proper cellular function, controlled cell growth, and normal cellular processes. The mechanisms that regulate pHi are usually considered to be plasma membrane transporters of which two main types exist — those that are dependent and those that are independent of HCO⁻₃. Physiologically normal intracellular pH is most commonly between 7.0 and 7.4, though there is variability between tissues (e.g., mammalian skeletal muscle tends to have a pHi of 6.8-7.1).. There is also pH variation across different organelles, which can span from around 4.5 to 8.0. pHi can be measured in a number of different ways.
Methods for Analyzing Drug Response
InactiveUS20100099109A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingPhosphorylationOxidation-Reduction Agent
The present invention provides methods, instruments, reagents, kits and the biology involved in analyzing drug response. An embodiment of the present invention provides an approach for the characterization a plurality of pathways in single cells. This approach permits the rapid detection of heterogeneity in a complex cell population based on activation states of cellular molecules such as proteins, expression markers and other criteria, and the identification of cellular subsets that exhibit correlated changes in activation within the cell population. Some of these categories include redox potential, ITIM phosphorylation, intracellular pH and other categories allows for characterization of such pathways and cell populations. Also, the present analysis is useful for the analysis of the effect of compounds on potential target cells.
Owner:NODALITY
Monitoring intracellular proteins
InactiveUS20040137480A1Compound screeningApoptosis detectionProtein insertionBeta-galactosidase activity
Methods and compositions are provided for analyzing intracellular events employing fusion proteins comprising the small beta-galactosidase fragment fused to a protein of interest or fragment thereof. By expressing the fusion protein in a cellular host, one can determine the effect of various agents on the activity of the fusion protein, adding the large beta-galactosidase fragment to the fusion protein, either intracellularly or in a lysate and determining the activity of the formed beta-galactosidase using a substrate that forms a detectable product. In this manner, degradation, complex formation, RNAi inhibition or other situation that affects beta-galactosidase activity can be determined.
Owner:DISCOVERX INC
Method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein
PendingCN106754601ALarge domestic and foreign market demandImprove permeabilityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesExtracellularProtein target
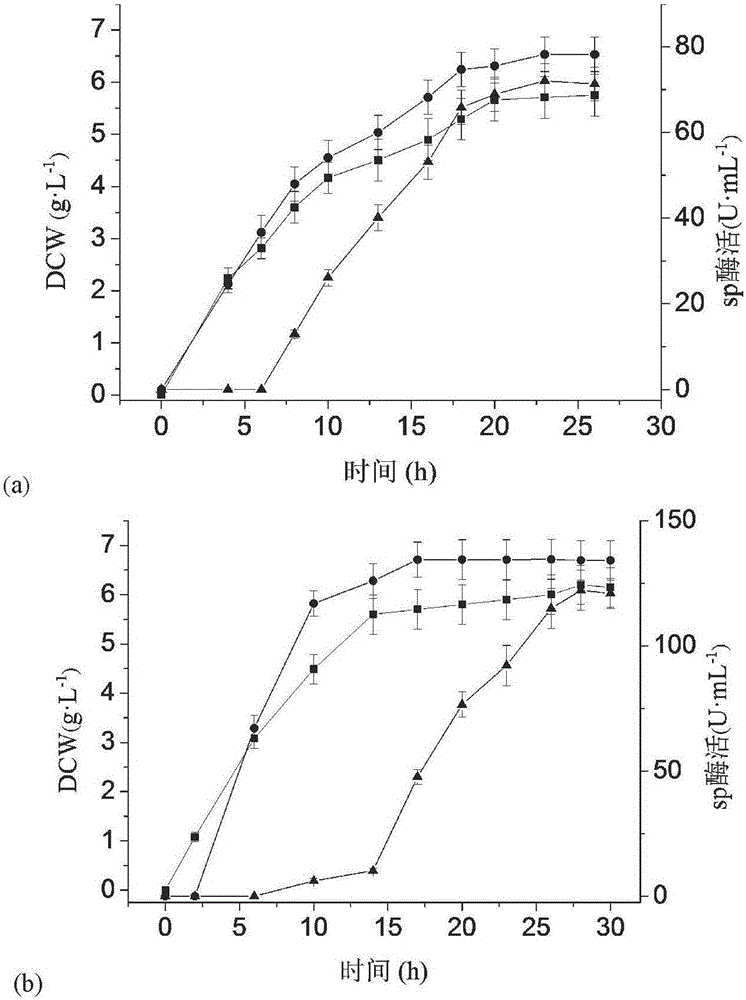
The invention discloses a method of using phospholipase C to extracellularly express intracellular protein and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. Through co-expression phospholipase C, intracellular positioning protein is released to the outsides of cells by means of nonspecific leaking, and high-performance phospholipase C and co-expression recombinant bacteria high in target protein extracellular enzyme activity are obtained by screening. Enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular sucrose phosporylase co-expressing sucrose phosphorylase and phospholipase C is 1445.1U mL-1, and enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria extracellular trehalase co-expressing trehalase and phospholipase C is 322.3U mL-1. The method can realize extracellular expression of intracellular positioning protein, improve production efficiency and simplify post-extraction process, has wide application value in food, cosmetics and pharmaceuticals industry and has great demand in market at home and abroad.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
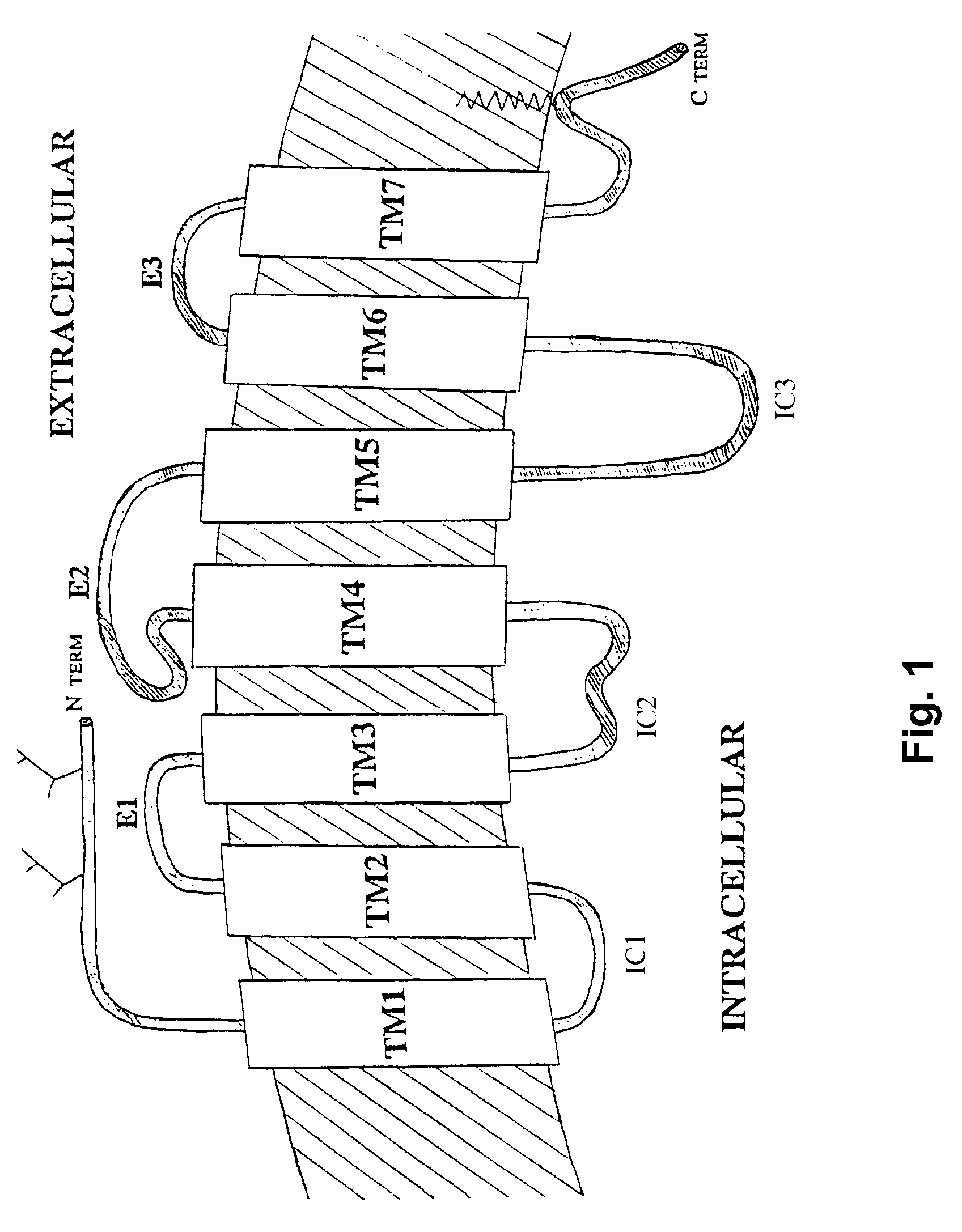
Method for obtaining G protein-coupled receptor (GPCR) diffraction-quality crystals employing a monoclonal antibody that binds to the third intracellular loop (IL3)
InactiveUS7947807B2Crystallization separationPeptide preparation methodsEpitopeG protein-coupled receptor
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Preparation method of metal coordination supermolecular nanogel
InactiveCN104151567AGood biocompatibilityPromote degradationAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryChemical treatmentPorphyrin
The invention provides a preparation method of metal coordination supermolecular nanogel. The metal coordination supermolecular nanogel is composed of natural polysaccharide, histidine and metalloporphyrin. The preparation method of the metal coordination supermolecular nanogel comprises the following steps: (1) grafting the histidine to the natural polysaccharide by use of an EDC / DMAP condensation reaction, thereby preparing the histidine-modified natural polysaccharide; and (2) preparing the metal coordination supermolecular nanogel under the metal coordination action of the metalloporphyrin and the histidine. The preparation method is simple and convenient in steps. The nanogel prepared by the method has tumor intracellular pH sensitivity, and excellent biocompatibility and biodegradability, can be taken as a carrier material for drug delivery and controlled release, and meanwhile, is capable of realizing tumor treatment by virtue of combined chemical treatment and photodynamic therapy.
Owner:NORTHEAST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Intrabodies
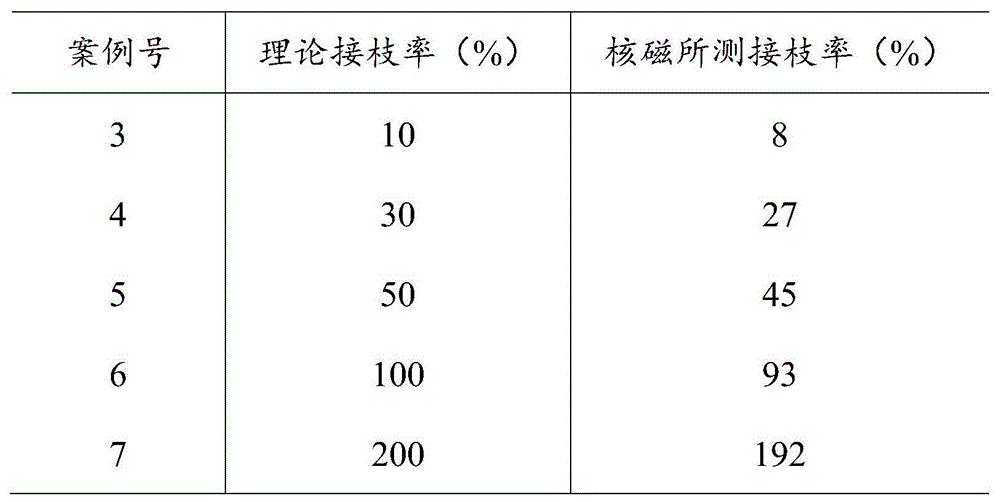
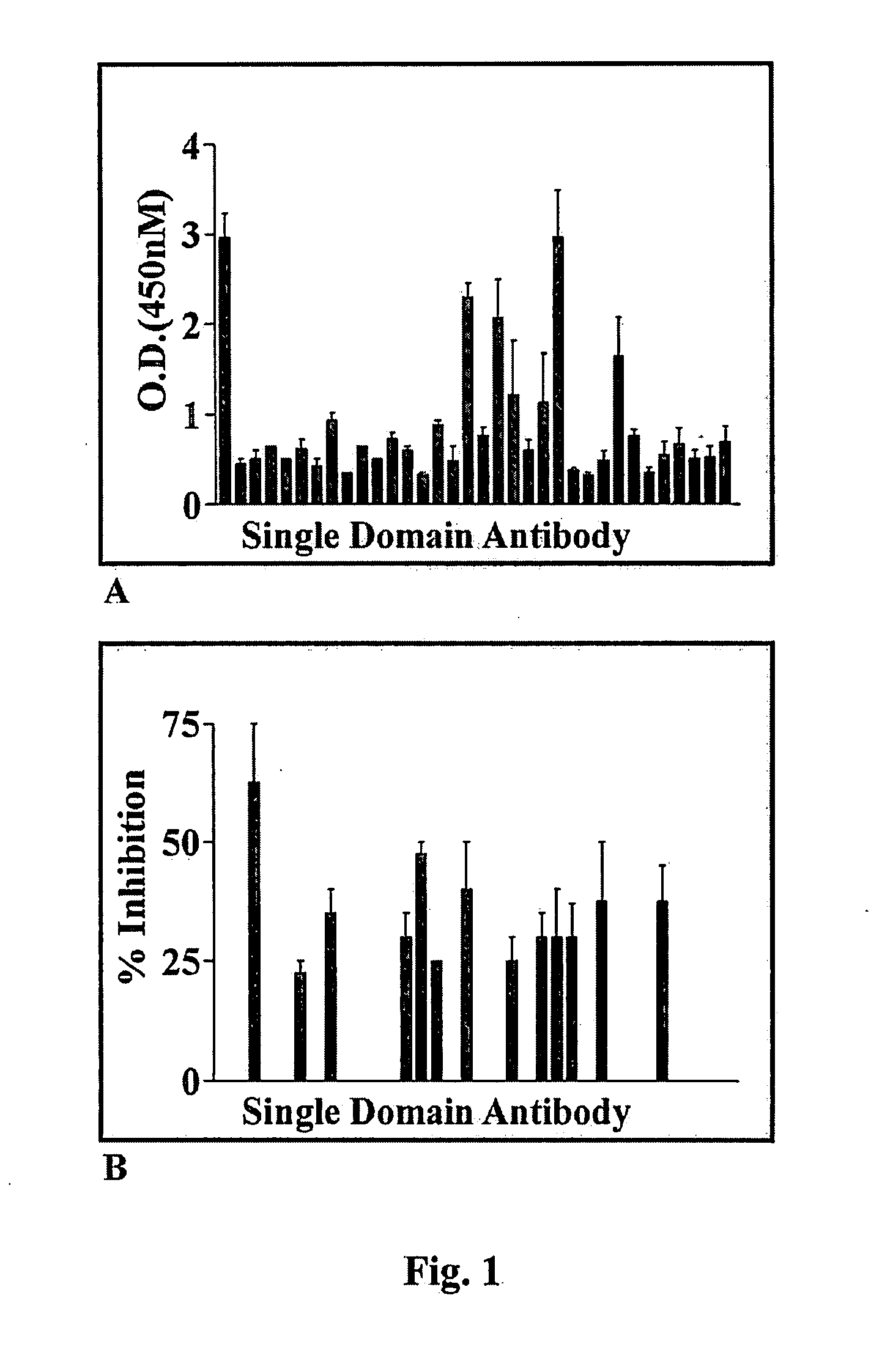
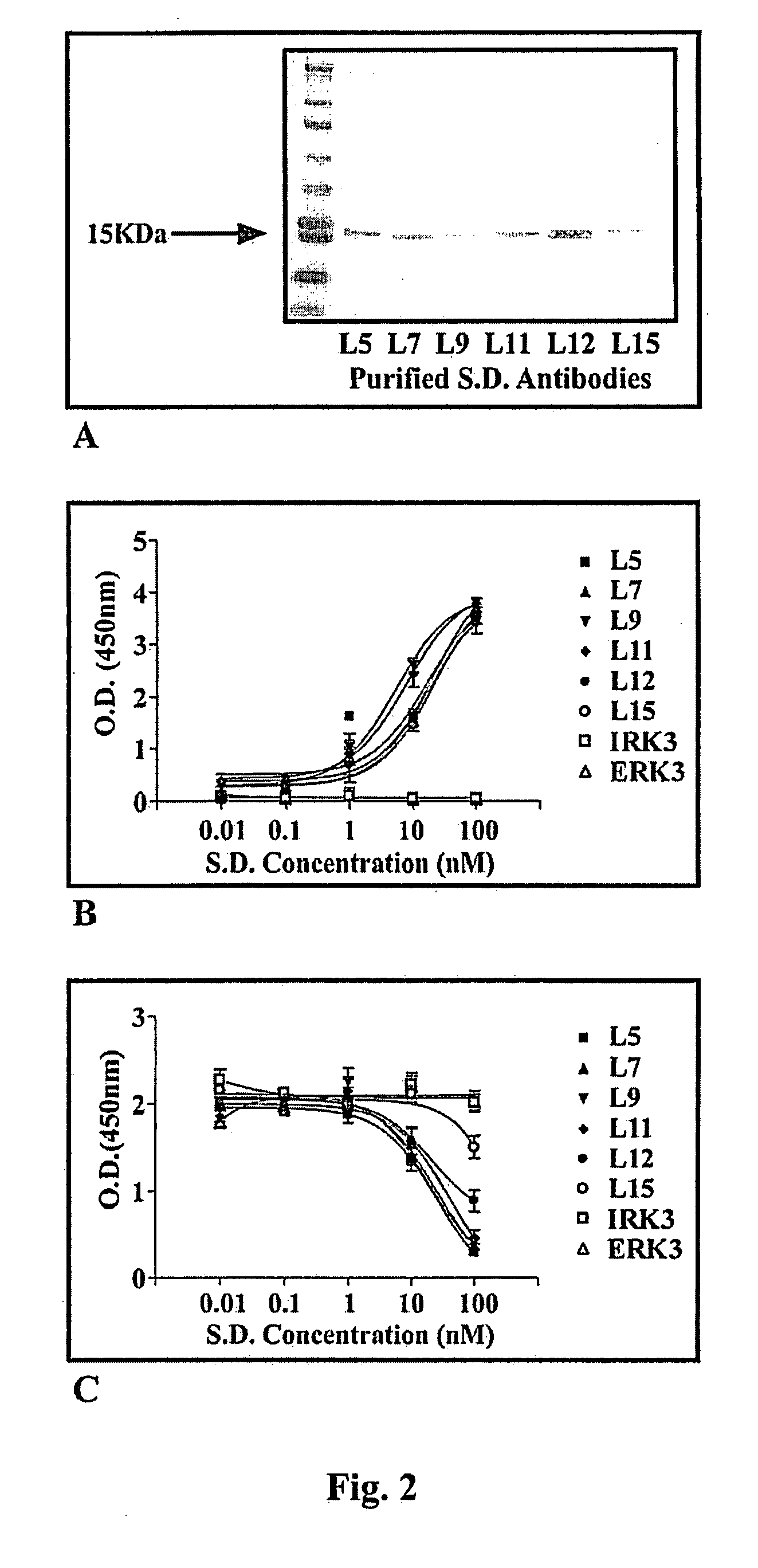
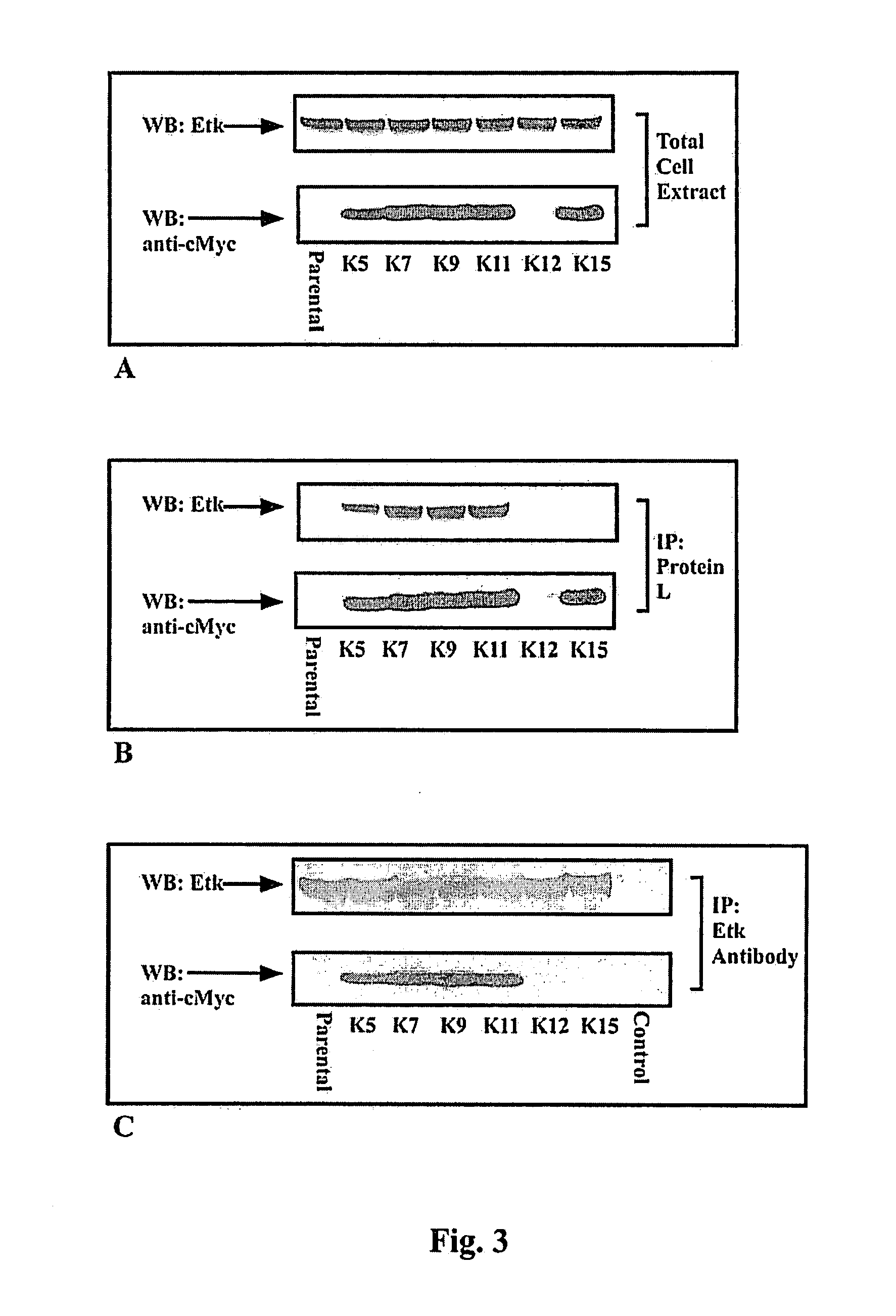
InactiveUS20100143371A1Inhibit enzyme activityInhibit transformationHeavy metal active ingredientsOrganic active ingredientsADAMTS ProteinsIntracellular pH
A single domain intrabody that binds to an intracellular protein or to an intracellular domain of an intracellular protein, such as Etk. Also provided is a method of inhibiting an intracellular enzyme, and treating a tumor in a patient by administering the intrabody or a nucleic acid expressing the inventive intrabody.
Owner:DORMANTIS LTD
Microscope system and methods for intracellular studies
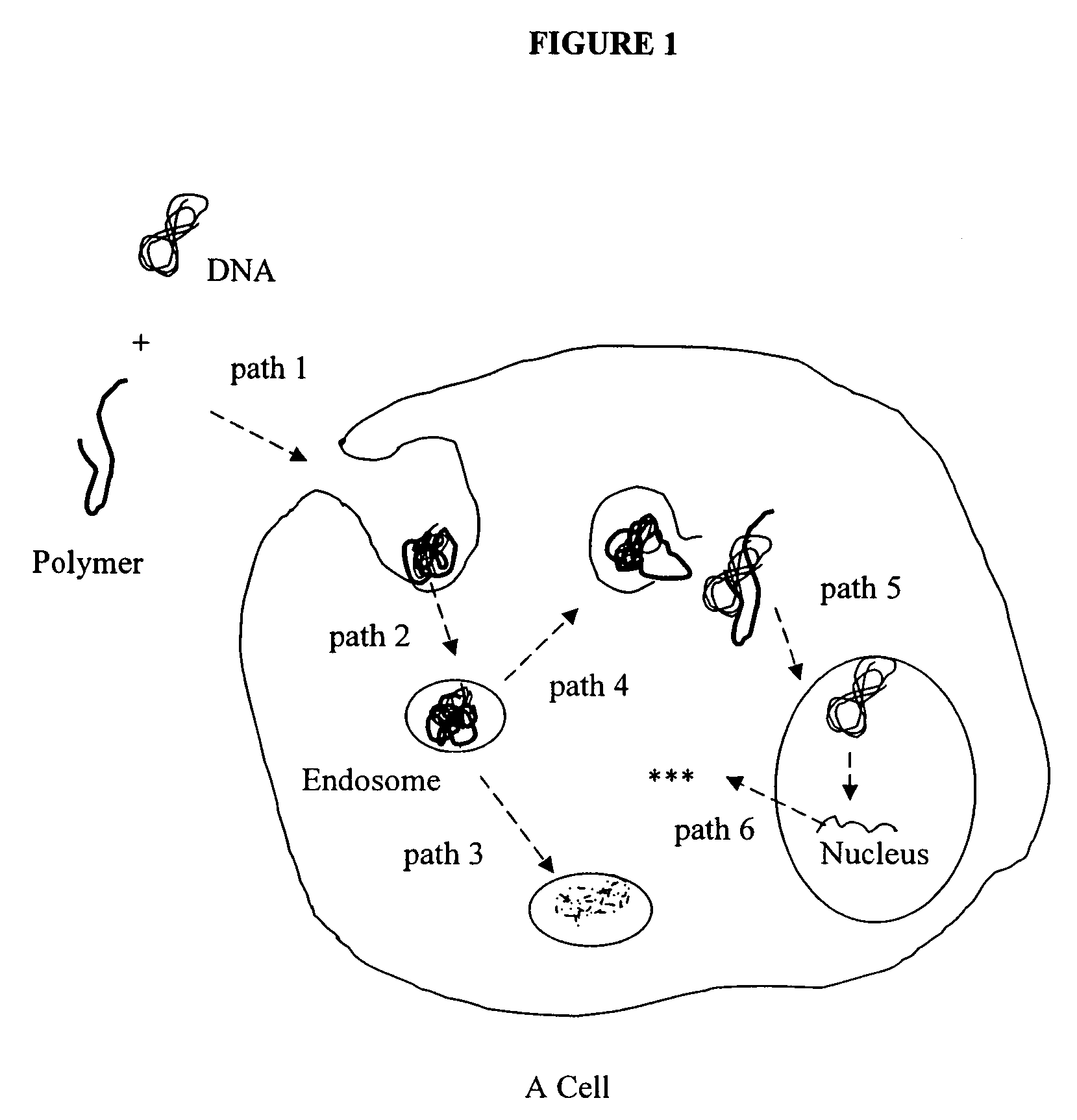
A microscope system, kit and method are described for observation of cellular activity in real time. The system is used to monitor cell transfection using a polynucleotide noncovalently attached to a carrier, The carrier labeled with a dye or fluorescent agent so that transport of complex can be monitored in real time. The polynucleotide includes both a gene of interest and a reporter gene. The reporter gene indicates successful expression of the gene of interest.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
Method for producing internal reference nano PH sensor and using for in-cell PH non-trauma monitoring
InactiveCN1609600AUniform sizeGood dispersionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceFluorescenceOil phase
The present invention aims at synthesizing one kind of nanometer pH sensor with embedded reference dye and sensitive dye and stable performance for non-invasive monitoring of dynamic pH variation inside cell. The preparation process includes mixing oil phase cyclohexane, surfactant Triton X-100 and co-surfactant n-hexanol and water as dispersive phase to obtain water-in-oil micro emulsion; adding mixed sensitive and reference dye liquid via stirring; adding ethyl acetate as sylylation reagent, TEOS and catalyst ammonia water to react, demulsifying with acetone, washing with absolute ethanol and super-purified water to obtain inner reference nanometer sensor with silicon shell. The inner reference nanometer sensor is used in non-invasive dynamic intracellular pH monitoring.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Viable cell mitochondria G-quadruplex targeted fluorescent probe and application thereof
ActiveCN110055054AGood biocompatibilitySimple ingredientsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCyanineBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses novel application of a cyanine dye to viable cell mitochondria G-quadruplex detection. The cyanine dye is a structural compound shown as a formula (I) or a stereoisomer of thecompound shown as the formula (I). A cyanine dye fluorescent probe has advantages of high biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, low molecular weight and low biological sample damages, and real-time observation of cell samples can be realized without being affected by pH values of cells.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Fluorescent probe and application thereof
ActiveCN108794425AGood biocompatibilitySimple ingredientsOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceCytotoxicityTe element
The invention discloses a fluorescent probe and application thereof. The fluorescent probe is provided with a structure shown as a formula I or a stereoisomer of the fluorescent probe, wherein R1 is hydrogen, alkyls of C1 to C6, phenyl or alkyl-substituted phenyl; R2 to R9 are independent hydrogen atoms, alkyls of C1 to C6, halogenated alkyls of C1 to C6 and alkoxys or hydrogen atoms of C1 to C6;R10 and R11 are independent sulfo or sulfo-substituted alkyls of C1 to C6; X1 and X2 are independent carbon, oxygen, sulfur, selenium or tellurium. The fluorescent probe has the specific advantages ofgood biocompatibility, low cytotoxicity, small damage to a biological sample and good photobleaching resistance; long-time effective observation of a cell sample can be realized without influence from a pH value of a cell.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
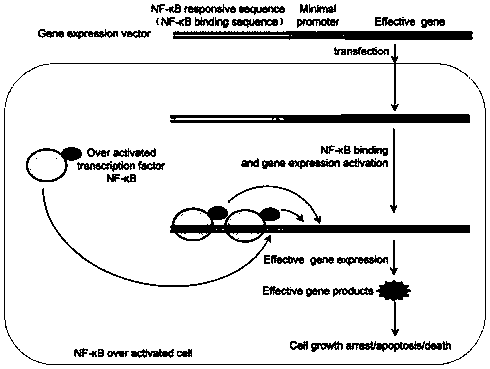
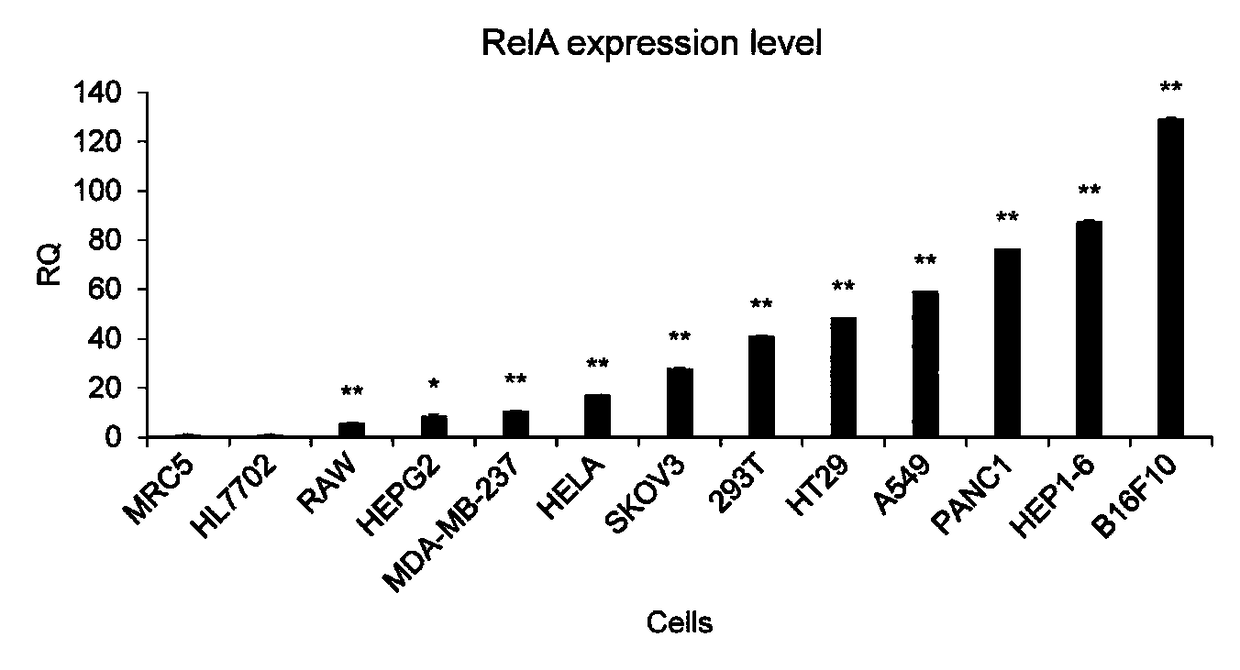
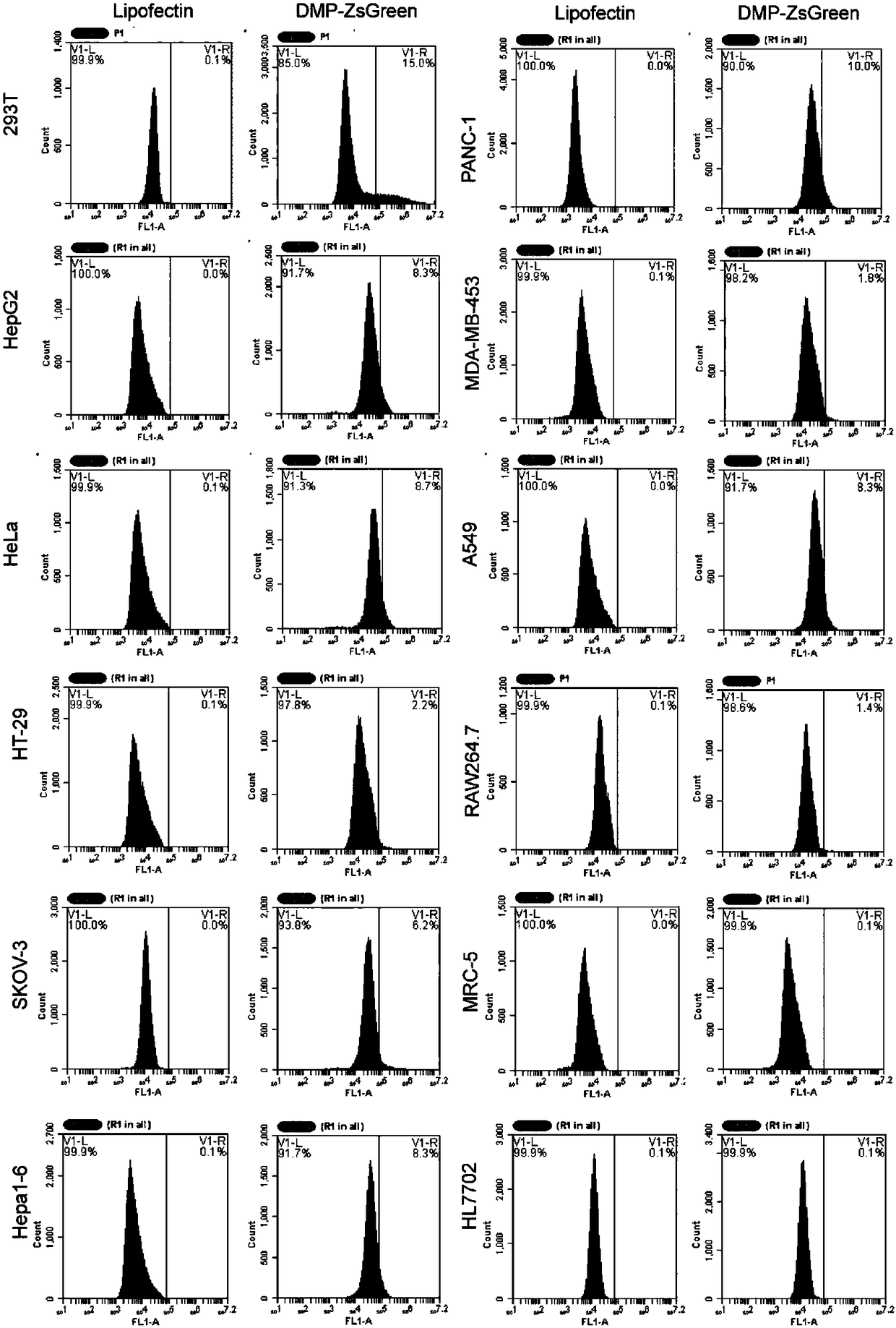
Gene expression based on intracellular NF-kappa B activity activation effect gene in NF-kappa B overactivated cells and application
InactiveCN108220336AExpress avoidanceImportant application valueOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseApoptosis
The invention discloses a NF-kappa B specifically activated gene expression vector and application thereof. A gene expression technique is implemented by the NF-kappa B specifically activated gene expression vector. The gene expression vector contains two elements, i.e., a regulatory gene-expressed promoter sequence and a promoter downstream effect gene coding sequence, wherein the promoter sequence consist of a section of NF-kappa B response sequence and a minimal promoter sequence. After the gene expression vector is introduced into NF-kappa B overactivated cells, an effect gene on the vector is expressed under the activation of a sequence-specific transcription factor NF-kappa B, and the effect gene generates influence on cell physiology, such as cell growth inhibition, apoptosis and death. The gene expression technique provided by the invention can be used for treating diseases related to NF-kappa B overactivation, such as inflammation and cancers. The gene expression vector constructed by the invention can be used in the preparation of gene therapy reagents and drugs for treating diseases related to NF-kappa B overactivation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Adriamycin nano-particles and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102552934AAvoid sudden releaseInhibition releaseOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyethylene glycolL glutamate
The invention provides adriamycin nano-particles. The adriamycin nano-particles are prepared by compounding adriamycin and a block copolymer with a structure shown as a formula (I) or a formula (II) through electrostatic interaction. A preparation method for the adriamycin nano-particles comprises the following step of: electrostatically compounding the adriamycin and the block copolymer with thestructure shown as the formula (I) or the formula (II) in an aqueous medium to obtain the adriamycin nano-particles. In the aqueous medium, a poly(gamma-propargyl-L-glutamate-g-mercaptosuccinic acid)segment and a polyethylene glycol segment which are contained in the block copolymer wrap the adriamycin into cores of the nano-particles, so the adriamycin composite particles are high in stability.The nano-particles are expected to be gathered at tumor sites in blood circulation through an 'enhanced permeability and retention effect' so as to improve the targeting effect of the adriamycin on the tumor sites. Meanwhile, the electrostatic interaction between a carboxyl group of the block copolymer and an amino group of the adriamycin is easy to eliminate under the condition of low intracellular pH values, so that the intracellular release can be accelerated, and the medicinal effect can be improved.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
Preparation method of function surface strength laman scattering probe
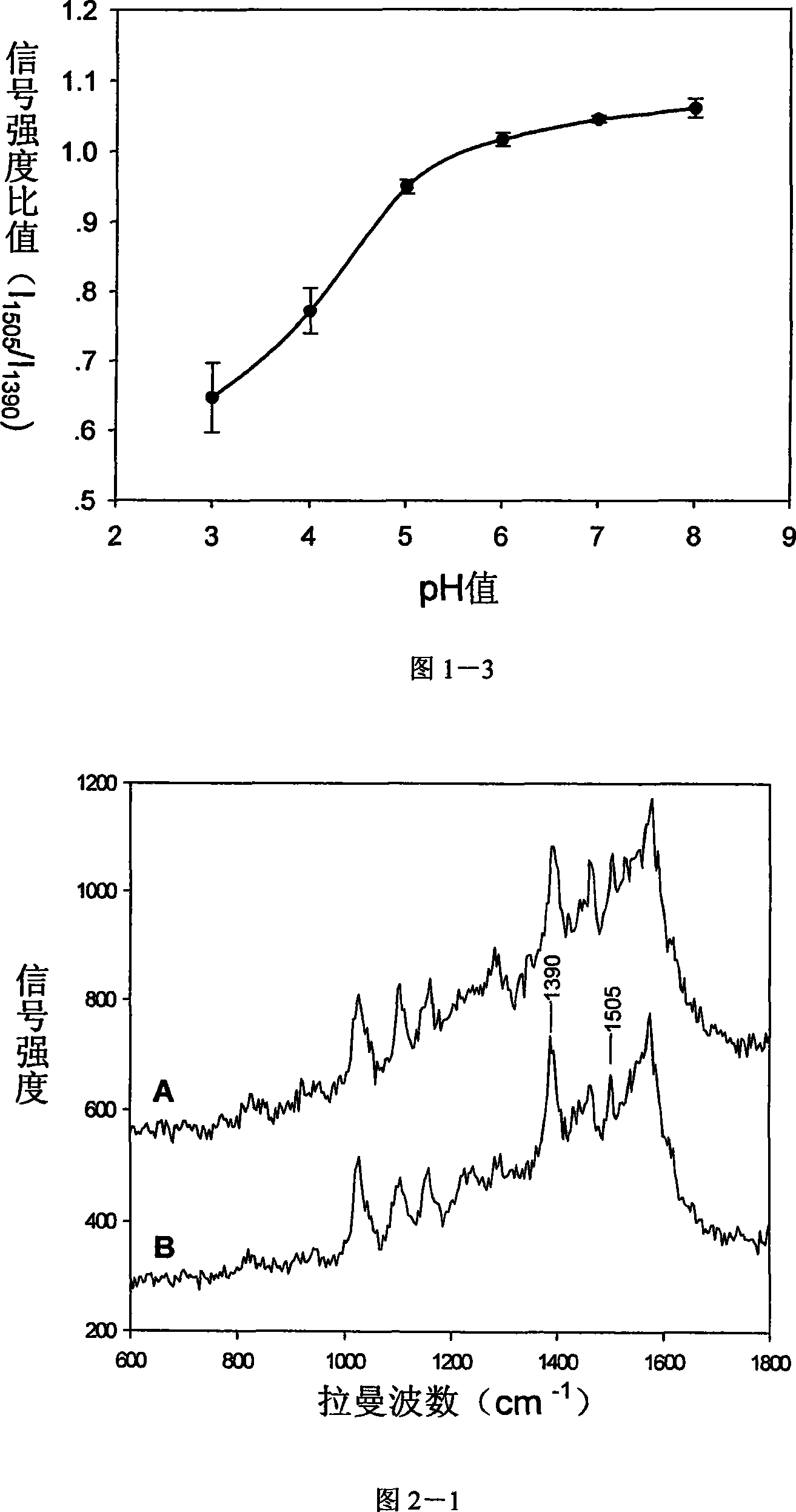
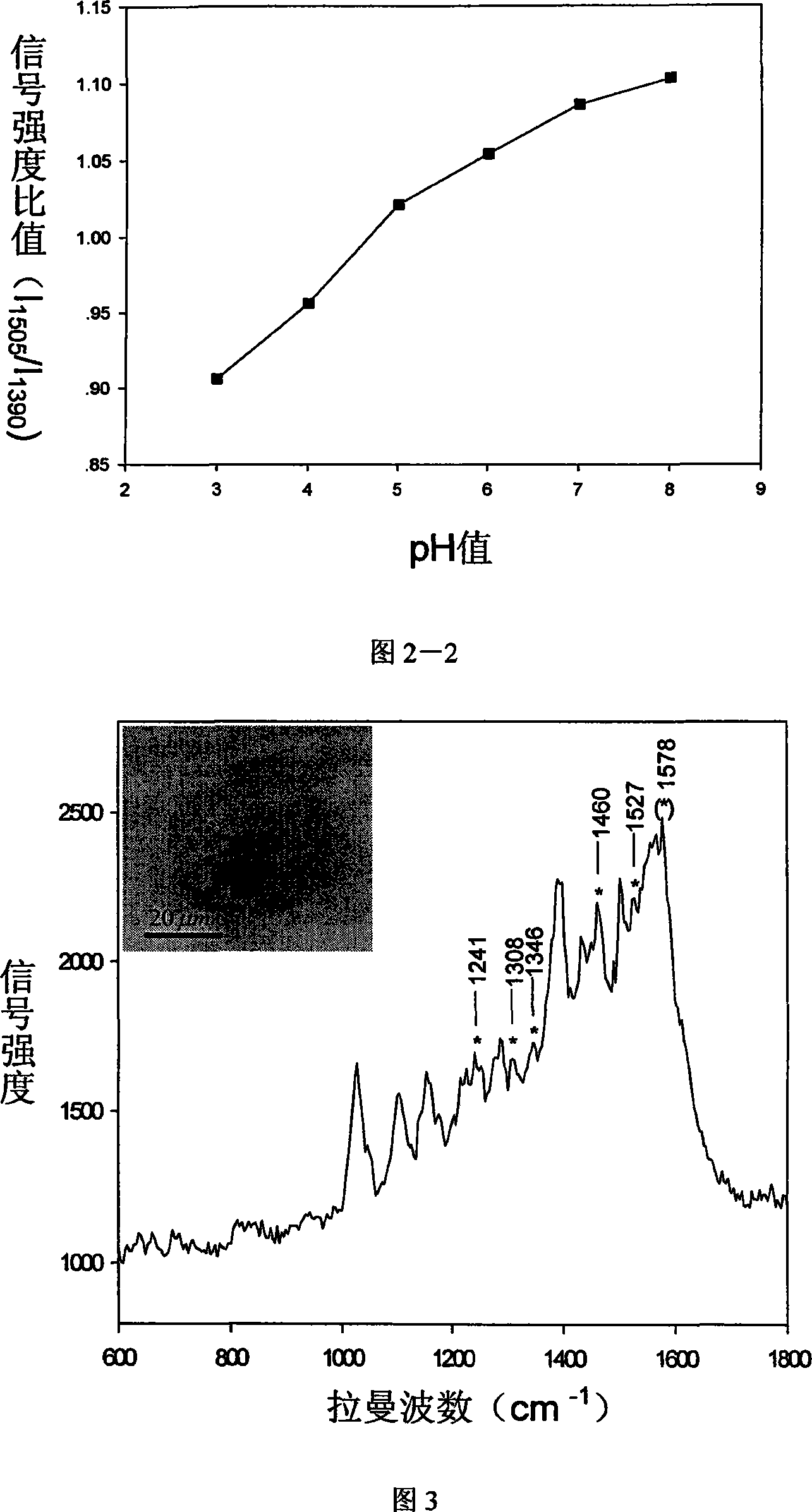
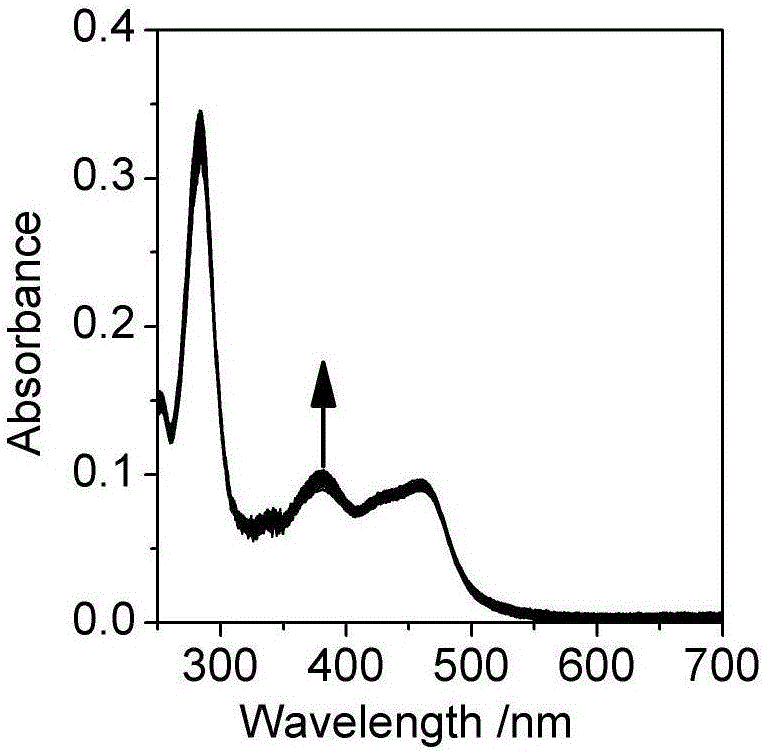
InactiveCN101089614AHigh sensitivityLow toxicityMicrobiological testing/measurementRaman scatteringWater solubleIntracellular pH
A method for preparing functional Roman scattering probe with intensified surface includes mixing 10-5 M of sensitive material using (-NH2) as PH sensitive group with silver glue solution in volume ratio of 3:1000-300:1000 uniformly then adding o.1M of sodium chloride solution in as per volume ratio of 3:1-10:1 for obtaining functional Roman scattering probe in size of 20-50nm with intensified surface.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Preparation method and application of physiological pH (potential of hydrogen) sensing dinuclear ruthenium complex
InactiveCN106366131AStable structureSoluble in waterRuthenium organic compoundsMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorBiological cellHydrogen
The invention discloses a preparation method of a dinuclear ruthenium complex and an application of the dinuclear ruthenium complex to pH (potential of hydrogen) sensing in water and cells. The complex is low in cytotoxicity, physiological pH response is realized by visible light excitation, biological cells can be sensed by phosphorescence according to a ratio, and pH change of the biological cells is detected in real time.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Application of near-infrared luminescent ruthenium complex to cell pH sensing
InactiveCN107118235AAvoid damageNon-cytotoxicRuthenium organic compoundsAnalysis by material excitationCytotoxicityNear infrared luminescence
The invention discloses application of a near-infrared luminescent ruthenium complex to cell staining and pH sensing in a probe cell. The complex has almost no cytotoxicity at the staining concentration, and can stain a cell nucleus and cytoplasm. Through change of near-infrared luminescence intensity of the cell along with pH, the pH in the cell can be detected by a flow cytometry and a microscopic imaging technology.
Owner:BEIJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Water-soluble phosphorescent polymer for detecting pH as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108218923ALow toxicityAvoid damageIndium organic compoundsFluorescence/phosphorescenceIridiumSolubility
The invention discloses a water-soluble phosphorescent polymer for detecting pH by a ratio method as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The polymer consists of two iridium complexes(Ir1, Ir2) and polyvinylpyrrolidone, wherein the Ir1 is a reference complex and does not respond to pH; the Ir2 can specifically respond to pH, and the luminous intensity of the Ir2 is weakened alongwith reduction of pH; and the polyvinylpyrrolidone gives high water solubility and biocompatibility to the polymer. The luminous intensity and the emitting life of the water-soluble phosphorescent polymer P disclosed by the invention are reduced along with reduction of pH, so that the pH of a cell is detected through confocal imaging; and the water-soluble phosphorescent polymer is a phosphorescent probe integrating excellent water solubility and biocompatibility and has important application prospect in aspects of biological imaging and sensing.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Method for complete cryopreservation and thawing of intracellular RNC (ribosome nascent-chain complex)
ActiveCN104186460AEfficient transportEffective cryopreservationDead animal preservationNormal growthCryopreservation
The invention discloses a method for complete cryopreservation and thawing of an RNC (intracellular ribosome nascent-chain complex). The method comprises the following steps: adding a translation elongation inhibitor into cell culture fluid in normal growth, cooling cells to the temperature of 0-4 DEG C after the translation elongation inhibitor effectively acts on the RNC and translation elongation is inhibited, cleaning the cells by using a PBS solution which is precooled to the temperature of 0-4 DEG C, adding the PBS solution into the cells, rapidly freezing in liquid nitrogen, preserving at an ultra-low temperature, thawing on ice, and extracting the RNC. According to the method, ribosome is effectively fixed by adopting the translation elongation inhibitor and is unlikely to dissociate, and the translation conditions in the cells are fixed. Moreover, the RNC is effectively cryopreserved for long-term storage and transport through a liquid nitrogen quick freezing method, and the extracted RNC after thawing is the same as the RNC extracted from fresh cells, so the limitation of time and space is broken through, and convenience is provided for research of the RNC and development of commercial service of the RNC.
Owner:武汉承启医学科技有限公司
Quantitative detection tracing method of intracellular HPA (hydroxyapatite) nano particles
ActiveCN103822906AAccurate dissolutionThere is no problem of limited use conditionsFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceRare earth
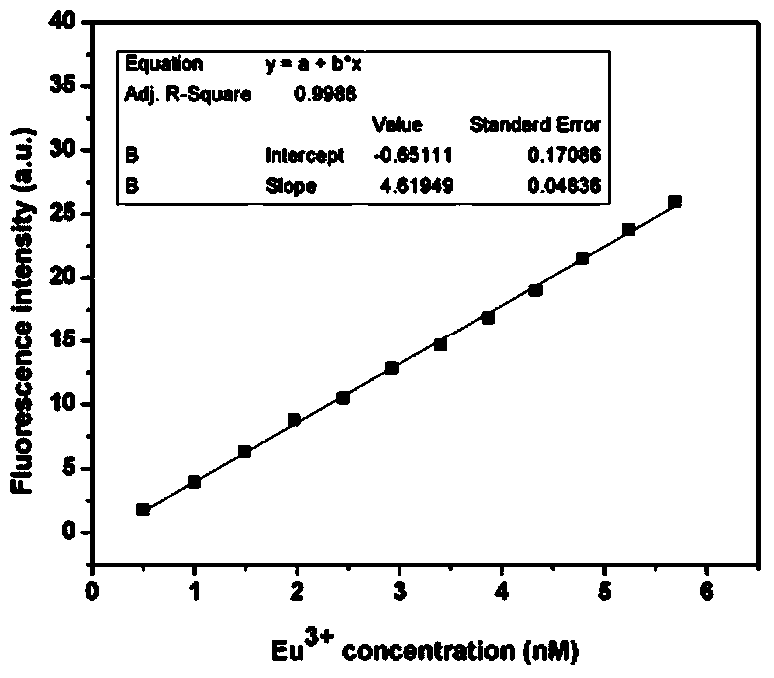
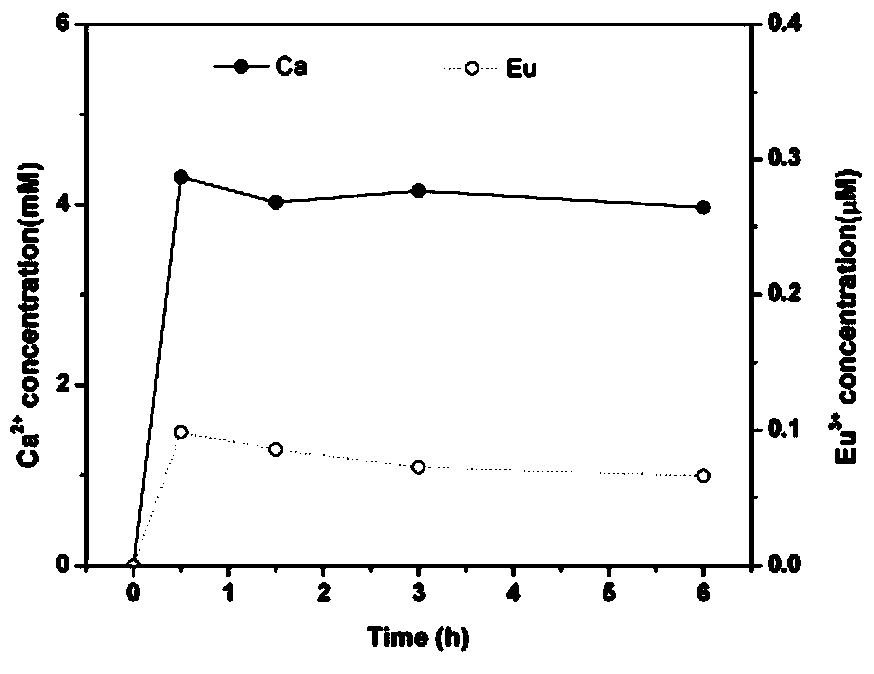
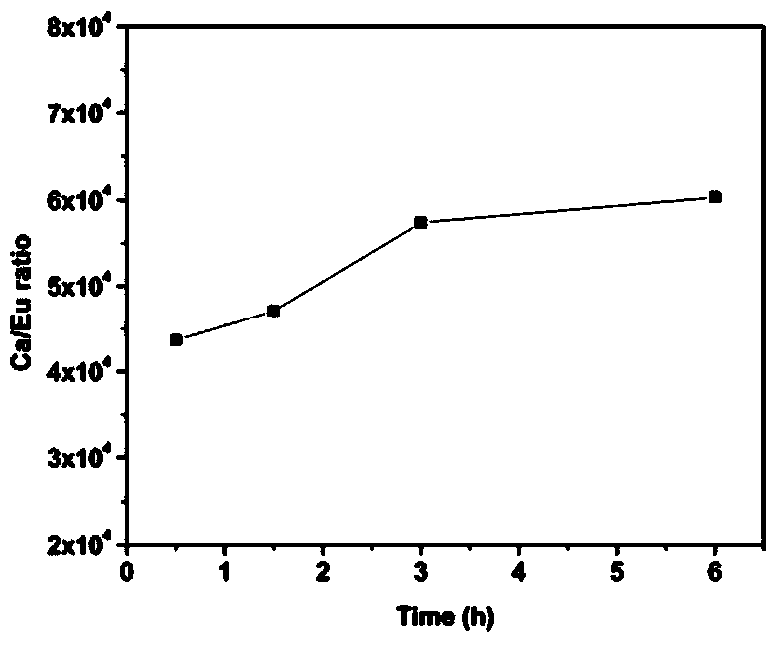
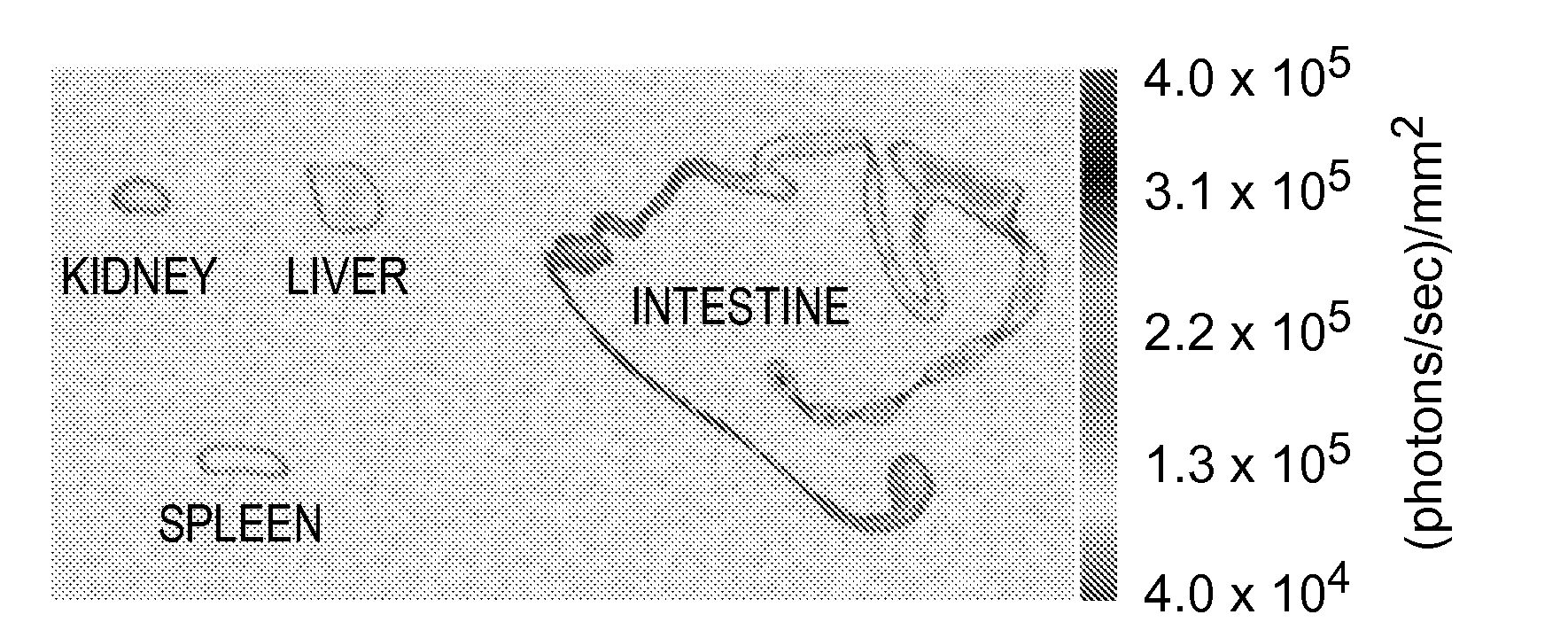
The invention relates to a rare earth fluorescent signal based quantitative detection method of HPA (hydroxyapatite) nano particles, and the quantitative detection method is characterized by comprising the following steps: 1) formulating a europium ion fluorescence-concentration standard curve; 2) establishing dissolution rate of calcium ions and europium ions in the HPA (hydroxyapatite) nano particles, and determining the accuracy of a fluorescence-concentration standard curve method; 3) quantitatively detecting intracellular HAP nano particles; and 4) tracing a dissolution course of the intracellular HAP nano particles. The main advantages of the quantitative detection method are that: 1) the quantitative detection method is good in biocompatibility, safe and reliable, and is free of radioactive labeling using condition limitation problems; 2) the quantitative detection method is low in the detection limit, the detection limit concentration can reach 0.5nM, and the sample needing amount is less; and 3) the quantitative detection method can more accurately shown dissolution of the intracellular HAP nano particles, and the compatibility of the dissolving out of the europium ions and the dissolution of the HAP nano particles is high.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
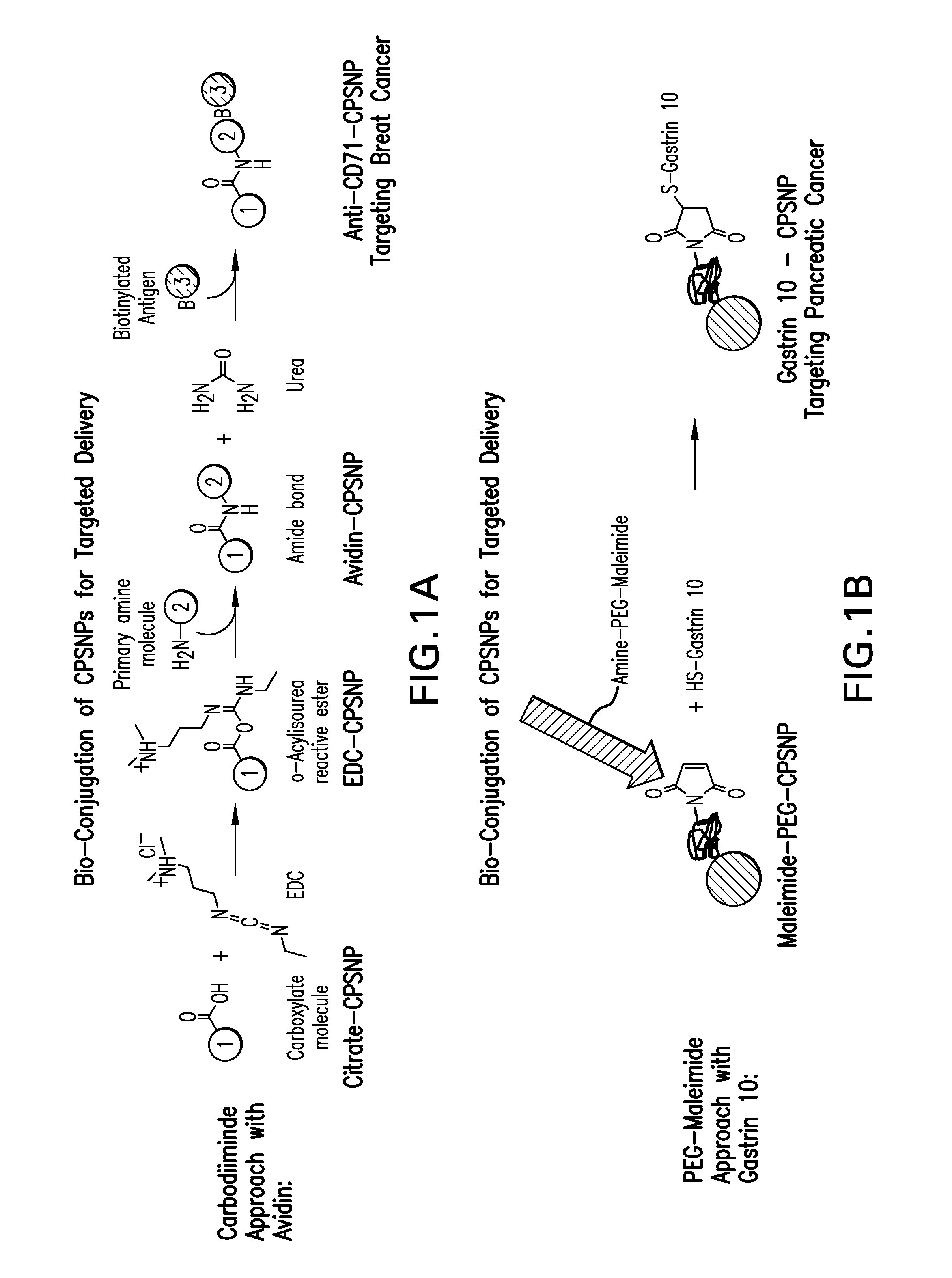
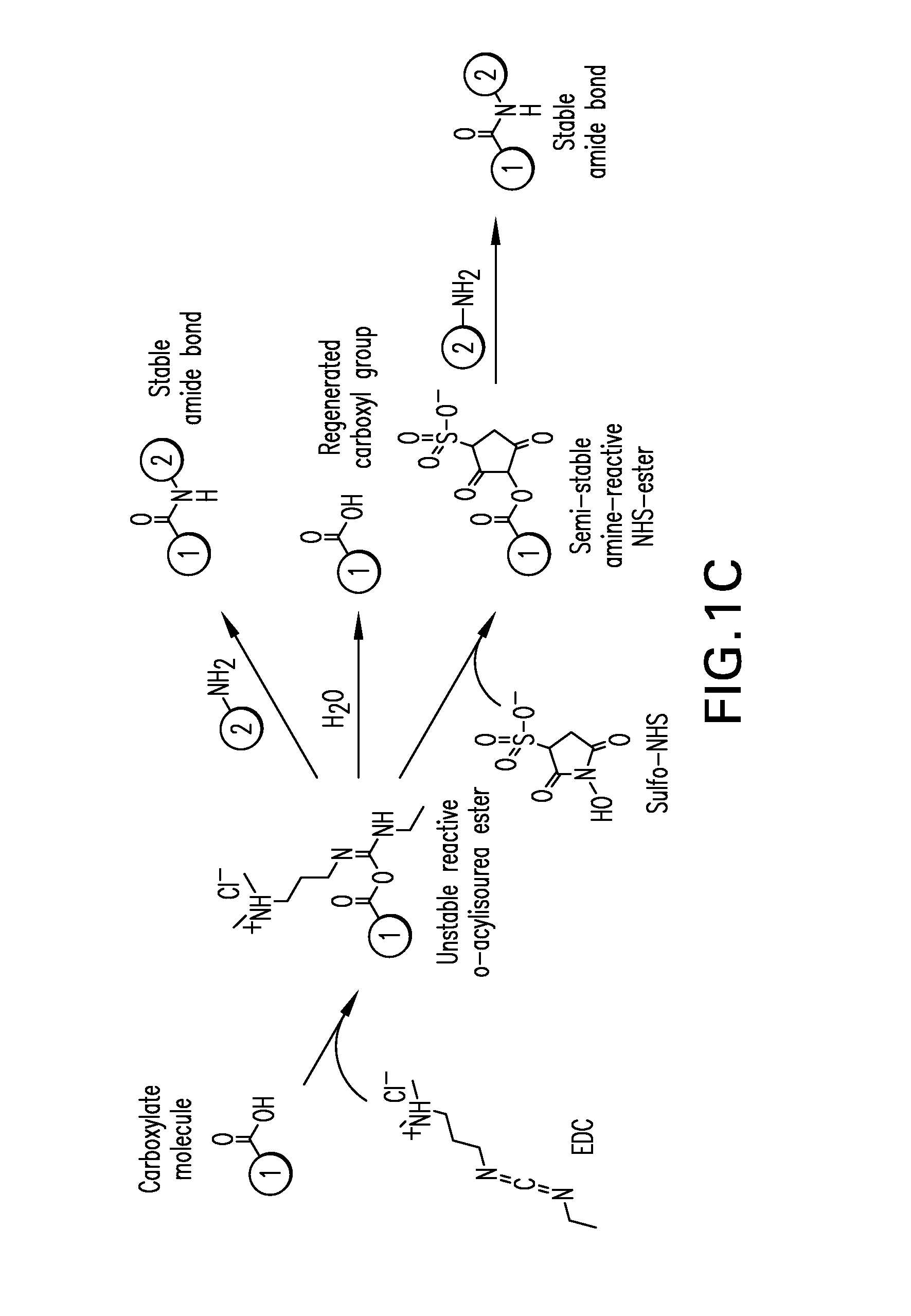
Bioconjugation of Calcium Phosphosilicate Nanoparticles For Selective Targeting of Cells In Vivo
ActiveUS20110129413A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPowder deliveryHigh concentrationWhole body
Non-aggregating resorbable calcium phosphosilicate nanoparticles (CPNPs) are bioconjugated to targeting molecules that are specific for particular cells. The CPNPs are stable particles at normal physiological pH. Chemotherapy and imaging agents may be integrally formed with the CPNPs so that they are compartmentalized within the CPNPs. In this manner, the agents are protected from interaction with the environment at normal physiological pH. However, once the CPNPs have been taken up, at intracellular pH, the CPNPs dissolve releasing the agent. Thus, chemotherapeutic or imaging agents are delivered to specific cells and permit the treatment and / or imaging of those cells. Use of the bioconjugated CPNPs both limits the amount of systemic exposure to the agent and delivers a higher concentration of the agent to the cell. The methods and principals of bioconjugating CPNPs are taught by examples of bioconjugation of targeting molecules for breast cancer, pancreatic cancer, and leukemia.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
Compositions and methods for cell killing
A method of generating a change in a cellular process of a target cell is disclosed. The method comprises contacting the target cell with a solid buffer, so as to alter an intracellular pH value in at least a portion of the cell, thereby generating the change in a cellular process of a target cell of a multicellular organism. The method may be used to kill either eukaryotic or prokaryotic cells. Pharmaceutical compositions and devices are also enclosed.
Owner:OPLON
Phenyl quinoline derivative iridium (III) complex based on piperidine or morpholine methylene substitution, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104910213AExcellent pH response propertiesRealize ratiometric detectionIndium organic compoundsSolid-state devicesIridiumMorpholine
The invention relates to a phenyl quinoline derivative iridium (III) complex based on piperidine or morpholine methylene substitution, and relates to the technical field of organic photoelectric materials. The complex is composed of a cyclometalated C^N bidentate ligand substituted by piperidine or morpholine through methylene connection, central metal iridium (III) ion and 2,2'-bipyridyl. The complex has a structural general formula as the following. According to the invention, a piperidine or morpholine methylene-substituted phenyl quinoline derivative C^N bidentate ligand is subjected to a reaction with iridium trichloride trihydrate, such that a iridium (III) chloro-bridged dimer with a corresponding ligand is obtained; the dimer is further subjected to a reaction with 2,2'-bipyridyl; and the complex is prepared through ion exchange. The iridium (III) complex provided by the invention has a good application prospect in the fields of intracellular pH value testing, imaging and marking.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Extremely acidic pH fluorescent probe, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN104017572ACell membrane penetration is goodThe synthesis steps are simpleOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBenzeneN dimethylformamide
The invention discloses an extremely acidic pH fluorescent probe, and a preparation method and application thereof. The pH fluorescent probe is constructed by using butadiene bridged indole or derivatives thereof and 3-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-alkyl-1H-indole on the basis of intramolecular charge transfer effect. The preparation method comprises the following steps: in an inert gas protective atmosphere, dissolving 2,3,3-trimethylindole or 1,1,2-trimethyl-1H-benzo[e]indole and 3-[3-(4-fluorophenyl)-1-alkyl-1H-indolyl-2-yl]-acraldehyde in N,N-dimethylformamide, adding KOH solid, stirring at room temperature, standing over night, concentrating under reduced pressure to obtain a crude product, and separating through a silica gel column to obtain the pure product. The probe has the advantages of lower pKa value, higher sensitivity for H<+>, favorable selectivity and large Stocks displacement. The probe has obvious color variation before and after combination with H<+>, and thus, can be conveniently identified by naked eyes. The probe can penetrate the cytomembrane, and is suitable for intracellular pH value detection and cell imaging.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
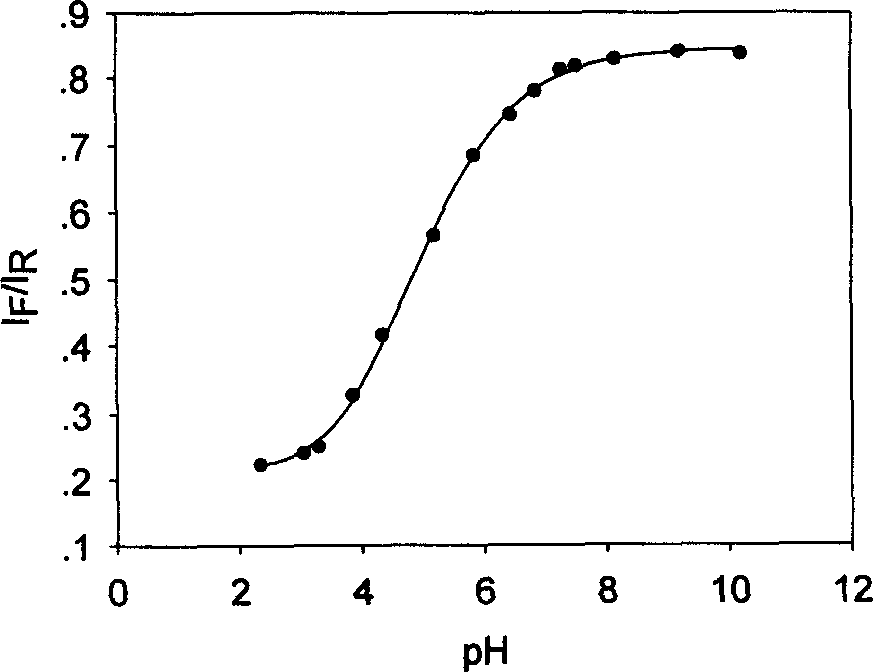
Intracellular pH value detection method
ActiveCN108535169ASimple and fast operationShort response timeIndividual particle analysisCell membraneIntracellular pH
The invention relates to the field of single cell detection, in particular to an intracellular pH value (pHi) detection method. The method comprises the following steps: (1) co-incubating to-be-detected cells with a cell membrane-permeable and pH-sensitive fluorescent dye, and putting the to-be-detected cells loaded with the fluorescent dye into a buffer solution in an air and temperature controldevice; with the assistance of a perfusion / drug delivery system, using a device capable of monitoring the fluorescence change of cells in real time to record the cell fluorescence intensity data corresponding to different treatments; (2) treating the cells with calibration solutions of different known pH values, establishing a standard curve of cell fluorescence intensity-cell pHi related data, and substituting cell fluorescence intensity data into the standard curve to obtain a single cell pHi. The method can monitor the change of pHi of single or multiple cells for a long time and in real time without damaging the cells, has good reproducibility, and is suitable for detecting the pH of cells of various sizes.
Owner:INST OF SPECIAL ANIMAL & PLANT SCI OF CAAS
Preparation method of antitumor micelle containing adriamycin
InactiveCN104415010AHas a nanoscale structureReduce volumeOrganic active ingredientsNanomedicineFreeze-dryingRing-opening polymerization
The invention discloses a preparation method of an antitumor micelle containing adriamycin. The preparation method comprises the following steps: polymerizing acrylic acid by utilizing an atom transfer radical polymerization method, thus obtaining polyacrylic acid; modifying polyacrylic acid by utilizing folic acid molecules; polymerizing glutamic acid benzyl ester carboxylic acid anhydride by utilizing a ring opening polymerization method, thus obtaining polyglutamic acid benzyl ester; grafting adriamycin onto polyglutamic acid benzyl ester via hydrazone bonds; connecting polyacrylic acid with polyglutamic acid benzyl ester with bonds through click chemistry, thus obtaining block copolymers; after dissolving the block copolymers in tetrahydrofuran respectively, transferring the solutions into a dialysis bag, dialyzing the solutions with pure water, and filtering the dialysate with a filter membrane; freeze-drying the solutions after filtration, thus obtaining a drug loading micelle. The drug carrier micelle has a core / shell double-layer structure, wherein the outer layer is formed by hydrophilic polyacrylic acid, and the inner layer is a drug molecule coated layer. The material has the advantages that the material belongs to nanoparticles; the drug can achieve targeting delivery of cancer cells and pH-sensitive release in the cancer cells; the material has high drug loading capacity and good stability; the toxic and side effects of the drug on normal tissues and organs can be effectively reduced via the targeting function of the drug.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
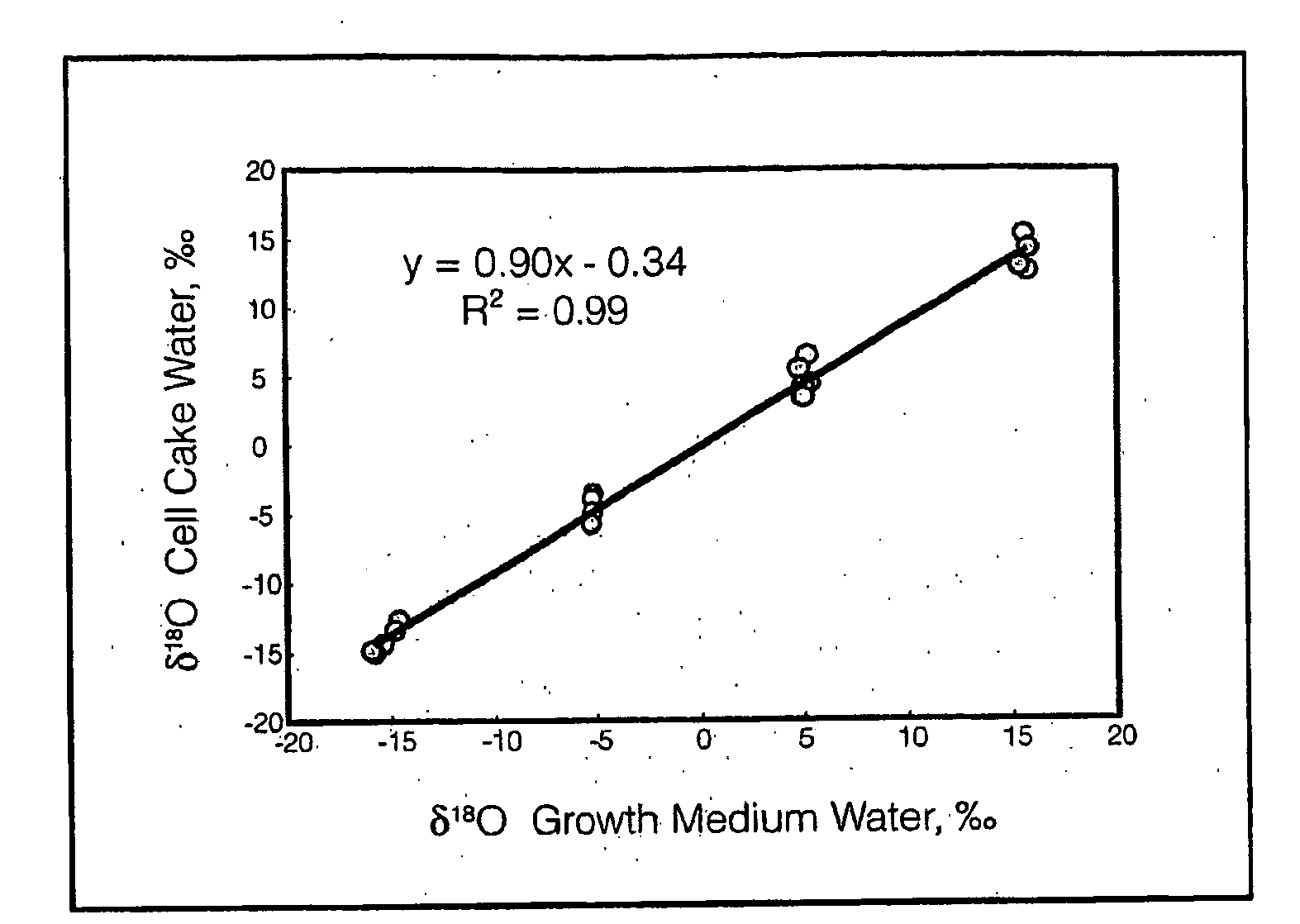
Isotope Detection and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20090305322A1Information can be usedMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisFiberEscherichia coli
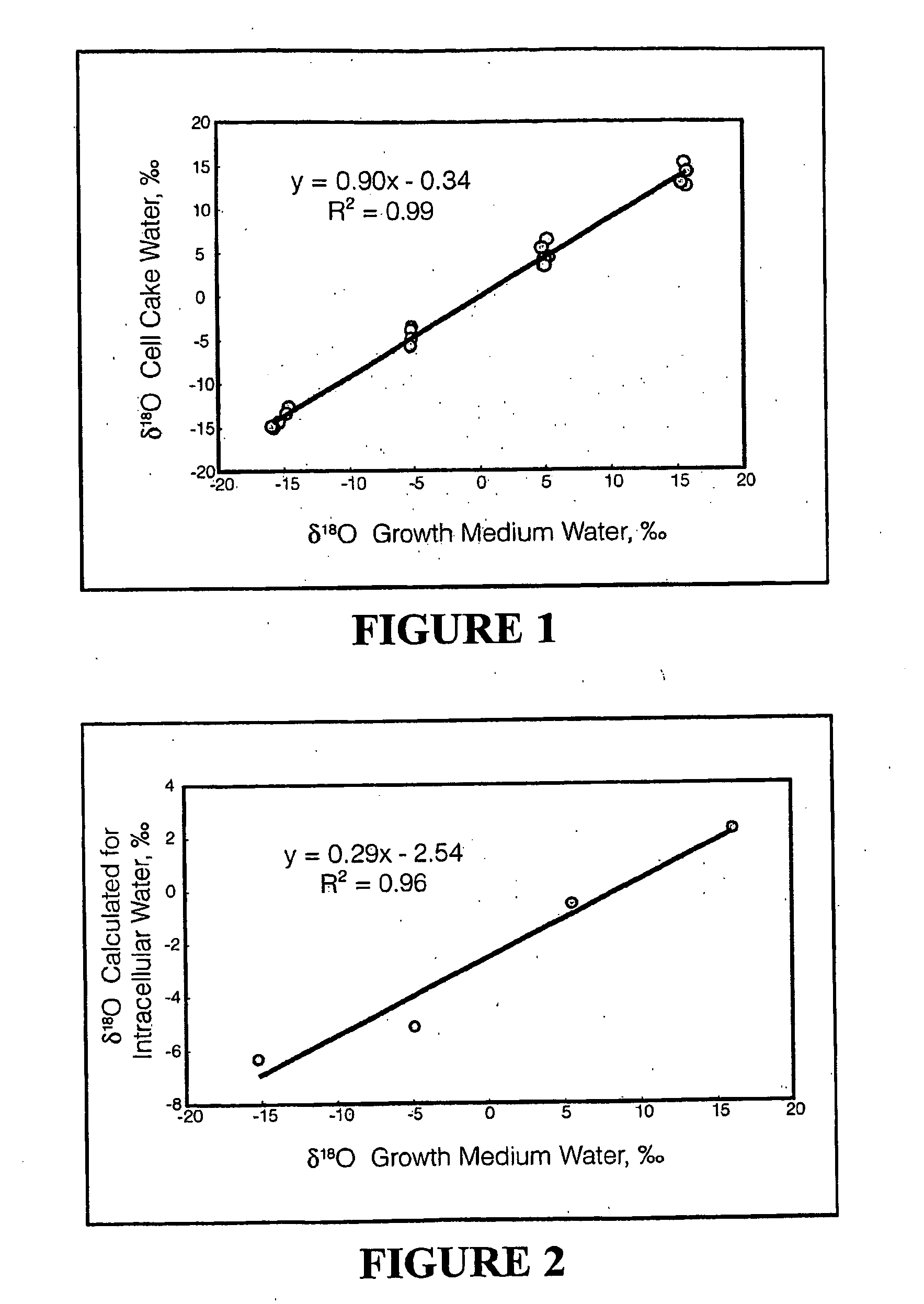
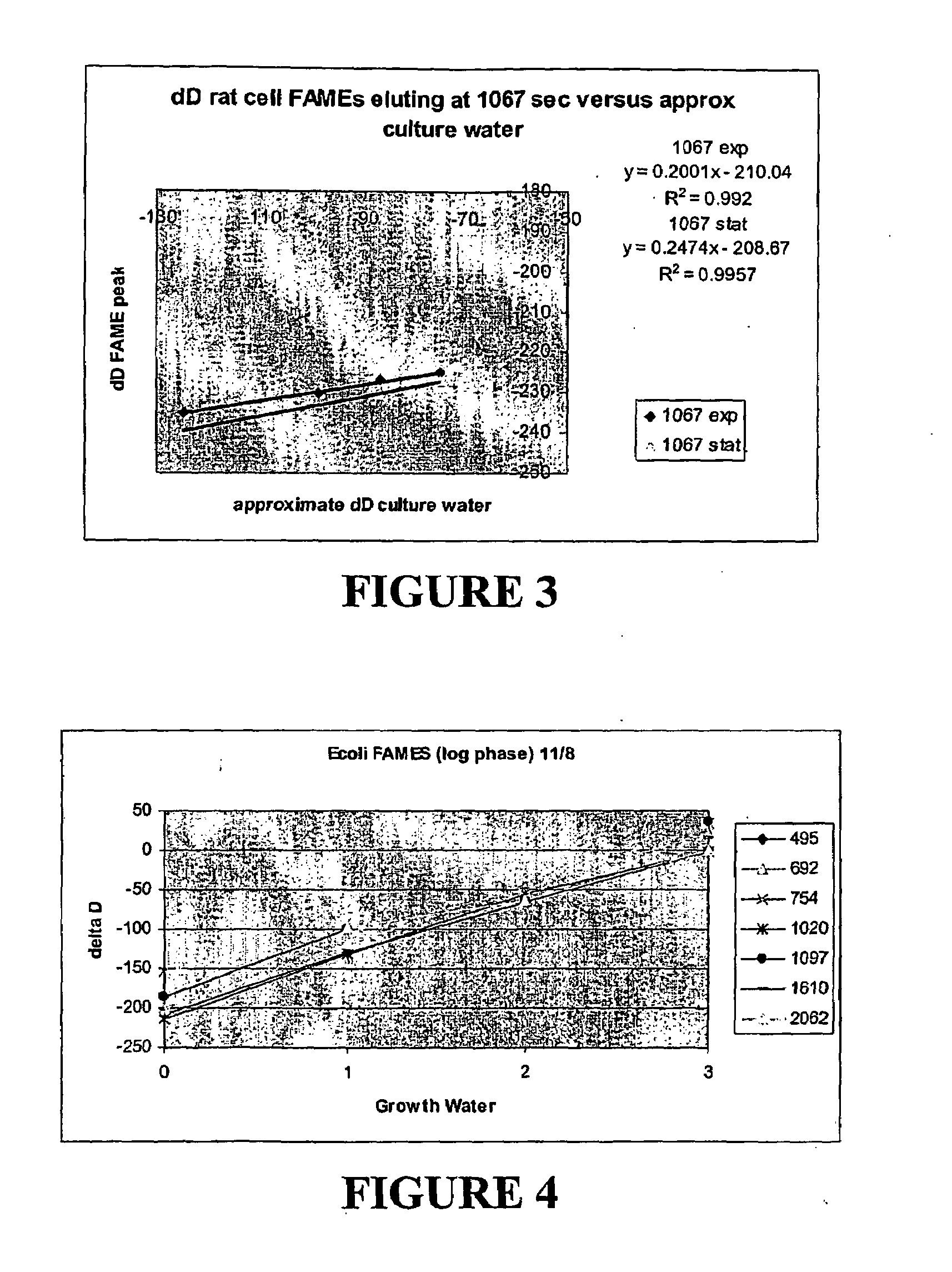
A method is disclosed for measuring the hydrogen and / or oxygen isotope ration of intracellular water in Escherichia coli cells and correlating the hydrogen and / or oxygen isotope ratio with the metabolic activity of the cell. A method is also disclosed for measuring the hydrogen and / or oxygen ratio of intracellular water via a probe, such as a fatty acid, and correlating the hydrogen and / or oxygen ratio with the metabolic activity of the cell. Methods for measuring the hydrogen and / or oxygen isotope ratio of water from eukaryotic organisms, such as cultured rat fibroblasts and whole mammals, and optionally relating the same to a metabolic rate, are also disclosed.
Owner:HEGG ERIC L +3
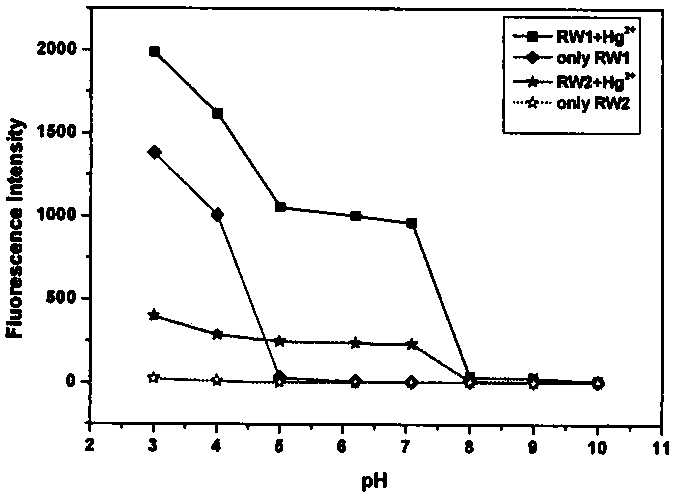
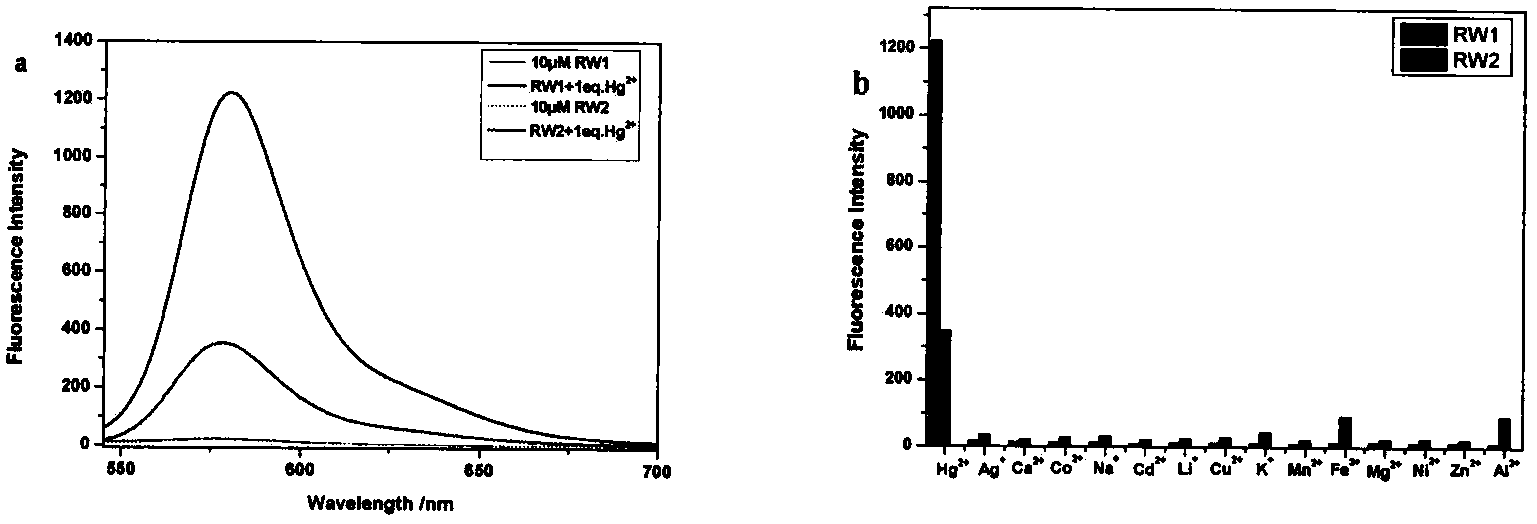
Fluorescent probe for intracellular Hg<2+> detection by using oxygen atoms as combination sites
InactiveCN104277826ALow absorbanceLow fluorescence quantum yieldOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBinding siteOxygen
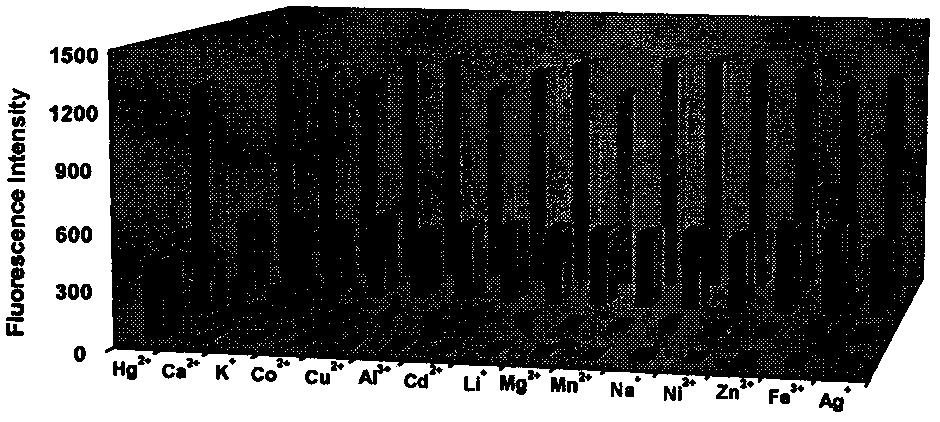
The invention relates to a fluorescent probe for intracellular Hg<2+> detection by using oxygen atoms as combination sites. The invention relates to an Hg<2+> fluorescent molecular probe in the field of fine chemical engineering. The probe is prepared by reacting rhodamine fluorescent dyes with amino acids and phthalic anhydride. The excitation and emission wavelengths are in the visible light region. The pH value is 5-8, the probe has favorable selectivity for Hg<2+>, the detection can not be influenced by Mg<2+>, Mn<2+>, Fe<3+>, Ca<2+>, Zn<2+>, Ag<+> and other metallic ions, and the probe can detect Hg<2+> with micromole concentration. The cell imaging experiment indicates that the probe has favorable permeability for HL-7702 cells and various other cells or tissues, has no toxic or side effect on the cells and is especially suitable for detecting intracellular Hg<2+> concentration changes and distribution.
Owner:TIANJIN POLYTECHNIC UNIV
Intracellular protein detection method by flow cytometry
ActiveCN102520188ARealize qualitative detectionEfficient detectionBiological testingSilica nanoparticlesFluorescein
The invention belongs to the field of flow cytometry technology, and specifically relates to an intracellular protein detection method by the use of flow cytometry. The method comprises the following steps of: connecting an amino or carboxy functional group on the surface of 100-120nm silica nanoparticle with an amino group of an antibody against the intracellular protein to be detected by the use of covalent bonds, incubating the silica nanoparticle together with intracellular proteins obtained by ultrasonic and other methods, adding another differently sourced antibody which targeted the same intracellular protein to be detected and carrying out incubating, then incubating with a fluorescein labeled second antibody to form a silica nanoparticle-antibody-intracellular protein-antibody-fluorescein labeled second antibody compound, and finally carrying out qualitative detection on the compound by using flow cytometry. According to the invention, after binding to the antibody against the intracellular protein to be detected, the silica nanoparticle has initiative targeting ability and can target various different intracellular proteins.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
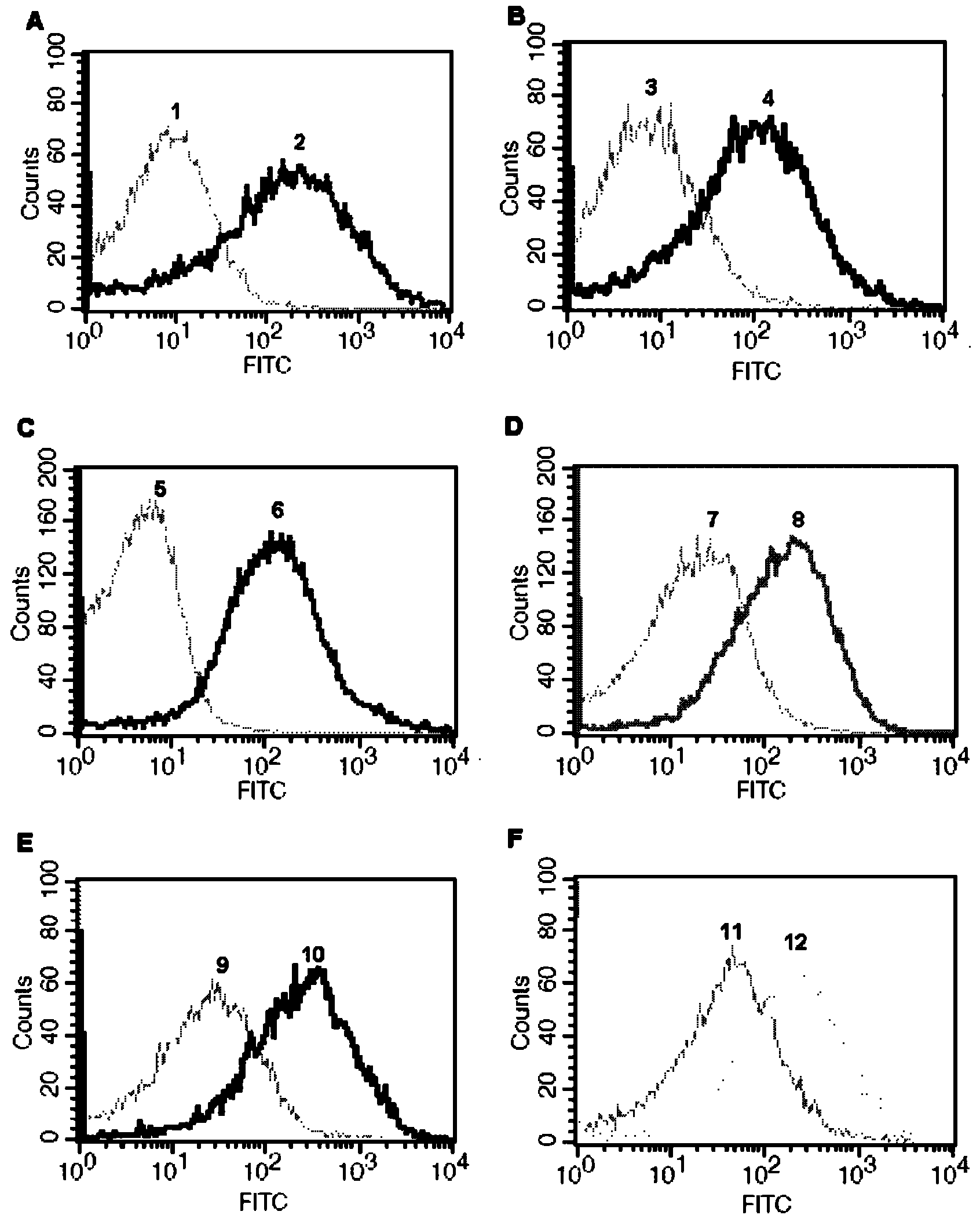
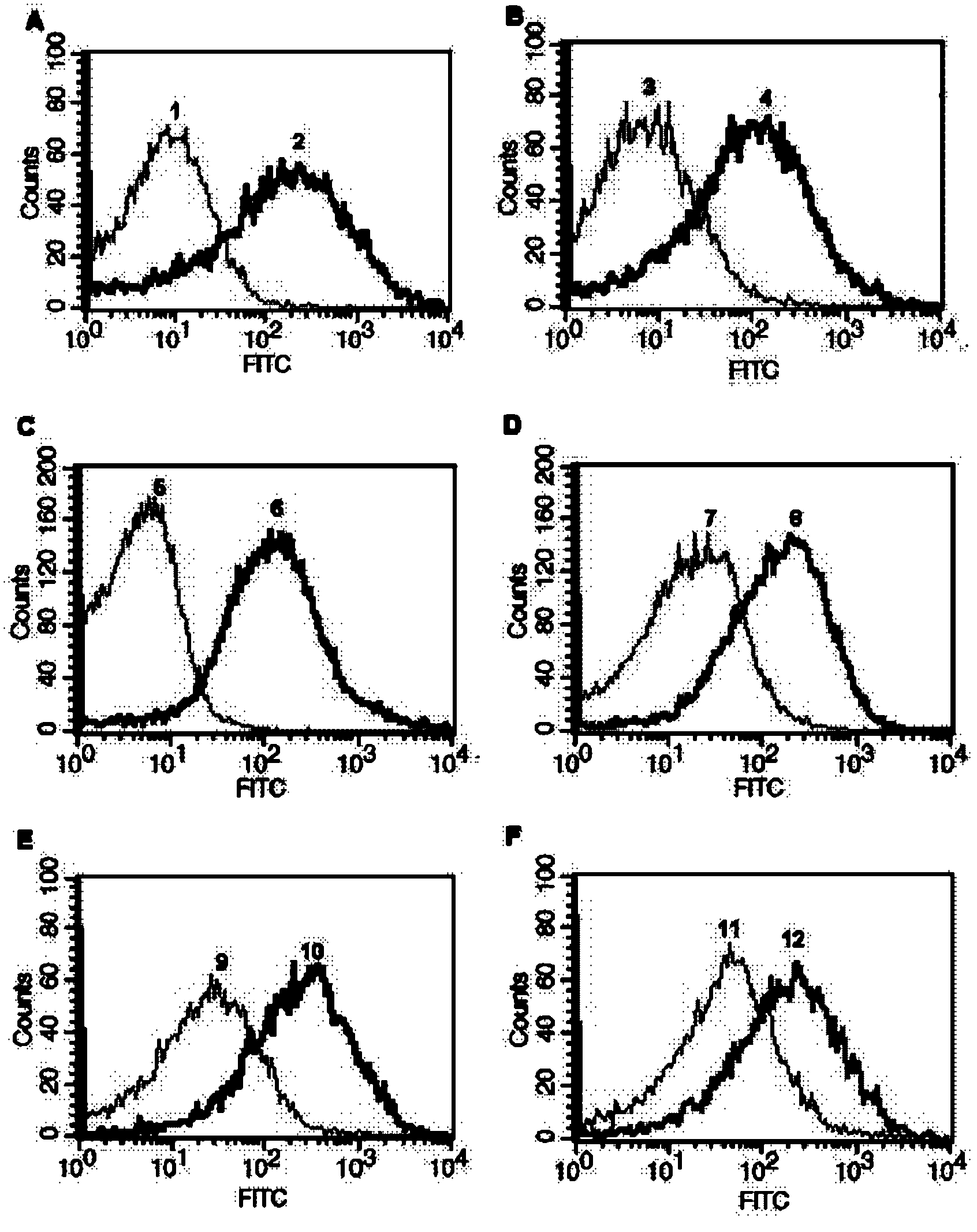
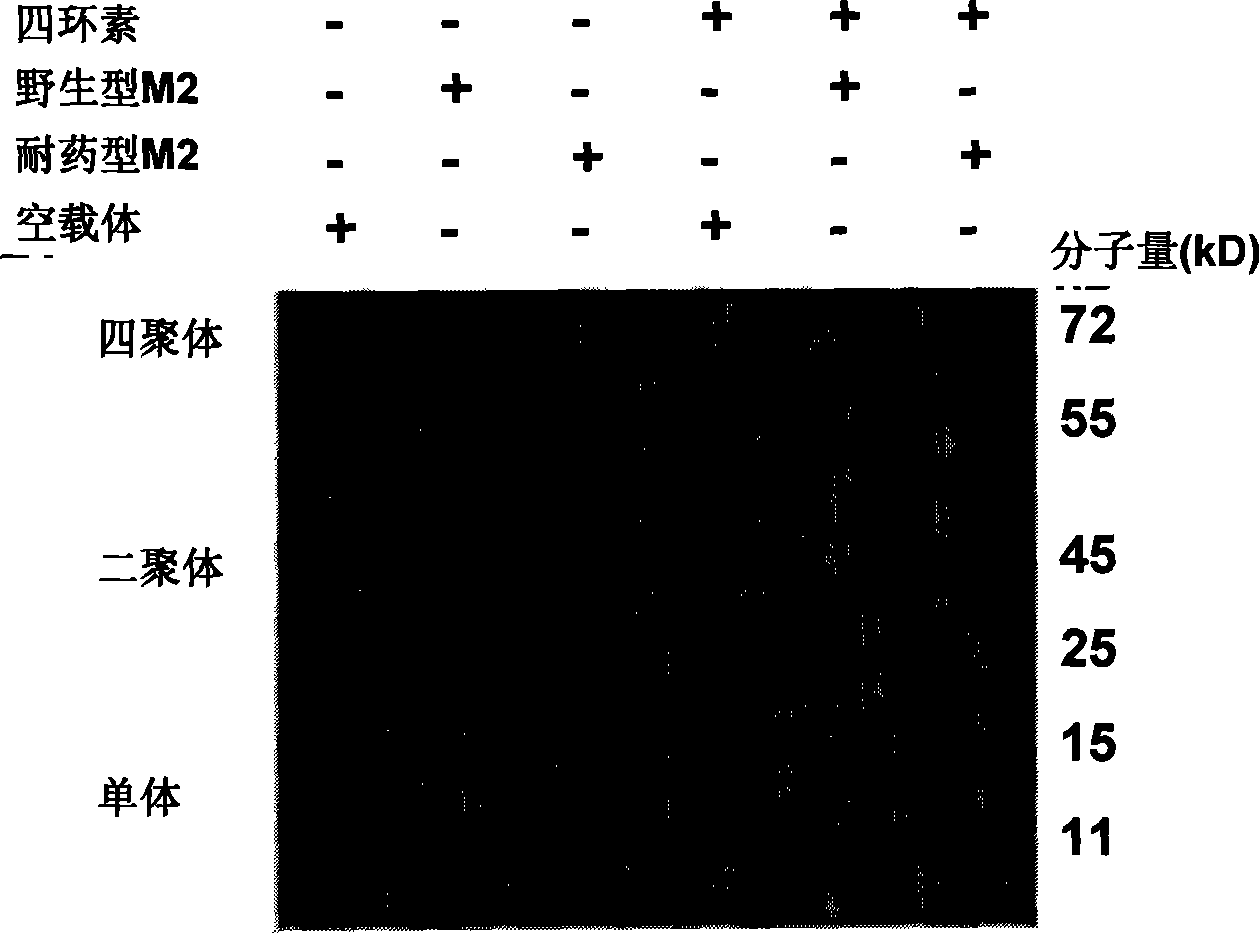
Fluorescent cell model for screening M2 ion channel blocker for influenza virus and application method thereof
InactiveCN101519648ASuitable for high throughputMechanism of drug action is clearMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceHigh fluxMechanism of action
The invention provides a fluorescent cell model for screening an M2 ion channel blocker for influenza virus, and the cell model is a cell containing pH sensitive fluorescent materials. Meanwhile, the invention also provides a method for screening the M2 ion channel blocker for the influenza virus by the cell model, which is to detect the change of fluorescent values in the cell model under the condition of an acidic buffer. The invention has the advantages that the H+ flowing condition through the M2 ion channel is directly reflected by detecting the change of the fluorescent values reflecting pH in the cell; and the M2 ion channel blocker screening method established by the cell model has definite mechanism of drug action, is simple and convenient, quick and direct, and is suitable for high-flux accurate screening of the M2 ion channel blocker.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Self-assembled targeted nanometer drug carrier micelles
InactiveCN104415339AHas a nanoscale structureMicelles are smallOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsFreeze-dryingRing-opening polymerization
The present invention discloses self-assembled targeted nanometer drug carrier micelles. The self-assembled targeted nanometer drug carrier micelle preparation method comprises: adopting an atom transfer radical polymerization method to polymerize phosphatidyl choline to obtain poly phosphatidyl choline; modifying the poly phosphatidyl choline with folic acid molecules; adopting a ring-opening polymerization method to polymerize S-benzyl-L-cysteine carboxylic anhydride to obtain poly S-benzyl-L-cysteine; grafting adriamycin on the poly S-benzyl-L-cysteine through a hydrazone bond; bonding the poly phosphatidyl choline and the poly S-benzyl-L-cysteine through a click chemistry method to obtain a block copolymer; respectively dissolving the block polymer in tetrahydrofuran, transferring into a dialysis bag, carrying out dialysis with purified water, and filtering the dialyzed solution with a filtration membrane; and carrying out freeze-drying on the filtered solution to obtain the drug-loaded micelles, wherein the drug carrier micelles have a core-shell double-layer structure, the outer layer is the hydrophilic poly phosphatidyl choline, and the inner layer is the drug molecule wrapping layer. According to the present invention, the material has the following advantages that: the material belongs to the nanoparticles; the targeted drug delivery on the cancer cells and the pH-sensitive drug release in the cancer cells can be achieved; the drug loading is high; the stability is good; and with the targeting function, the toxic-side effect of the drug on the normal tissues and organs can be effectively reduced.
Owner:CHENGDU LVKE HUATONG TECH
Ion flux in biological processes, and methods related thereto
InactiveUS20080131920A1Easy to identifyAvoid difficult choicesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingIntracellular pHMembrane potential
The present invention provides methods for promoting dedifferentiation and / or regeneration by modulating membrane potential and / or intracellular pH in non-naturally regenerating cells.
Owner:THE FORSYTH INST
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com