Quantitative detection tracing method of intracellular HPA (hydroxyapatite) nano particles
A nanoparticle, quantitative detection technology, used in material excitation analysis, fluorescence/phosphorescence, etc., can solve problems such as limited use conditions, inability to accurately react, and potential safety hazards of radioisotope labeling, achieving low detection limit, low sample volume, The effect of accurate response
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
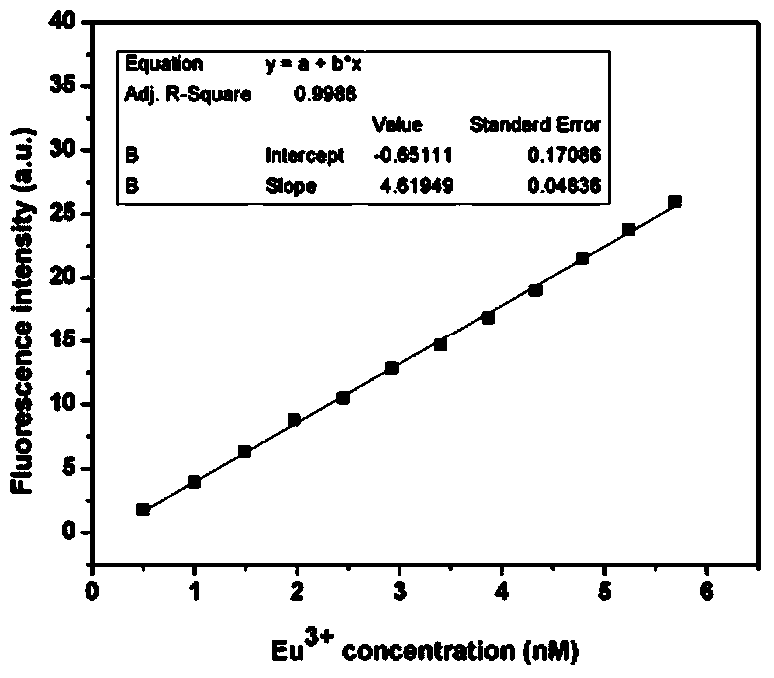
[0022] 1) Weigh 36.641 mg of europium trichloride hexahydrate and dissolve it in 100 mL of distilled water to obtain a concentration of 1 mM Eu 3+ For the ion storage solution, dilute the europium ion storage solution with fluorescence enhancement solution to form different concentrations of europium ion solutions (0.5, 0.99502, 1.48522, 1.97044, 2.45098, 2.92654, 3.39789, 3.86473, 4.32713, 4.78469, 5.23807, 5.68731nM). Fluorescence spectrophotometer, measuring the fluorescence emission intensity of europium ion solutions with different concentrations at excitation wavelengths of 340nm and 618nm, and obtaining the relationship between the fluorescence intensity y and the concentration x of europium ions by linear fitting ( figure 1 ), y=4.61949-0.65111x, R 2 = 0.9988. Eu 3+ The detection limit of ions is 0.5nM;
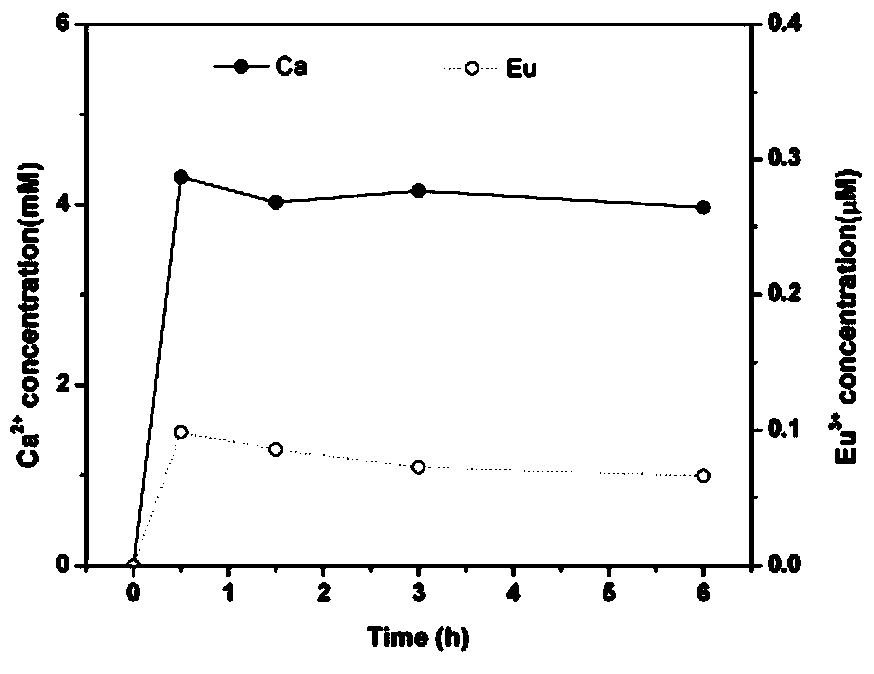
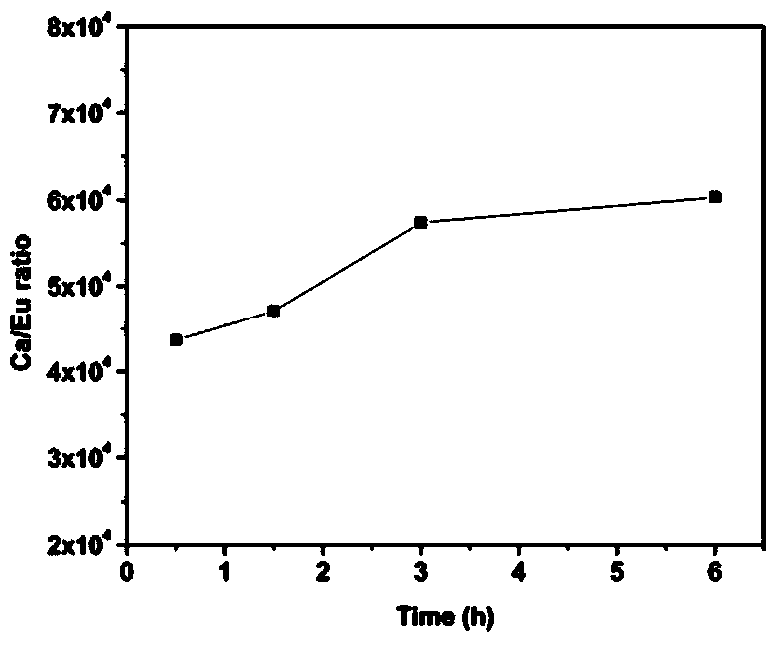
[0023] 2) Weigh 20 mg of 2% Eu-doped HAP nanoparticles and disperse them into 10 mL of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution with a pH value of 5.0. After inc...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com