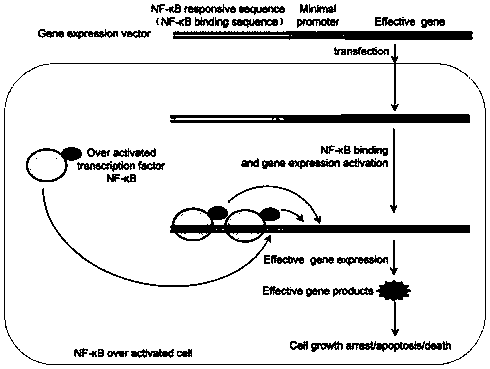
Gene expression based on intracellular NF-kappa B activity activation effect gene in NF-kappa B overactivated cells and application
A gene expression and effector gene technology, applied in the field of medical biology, can solve problems such as side effects, physiological process interference, and low specificity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
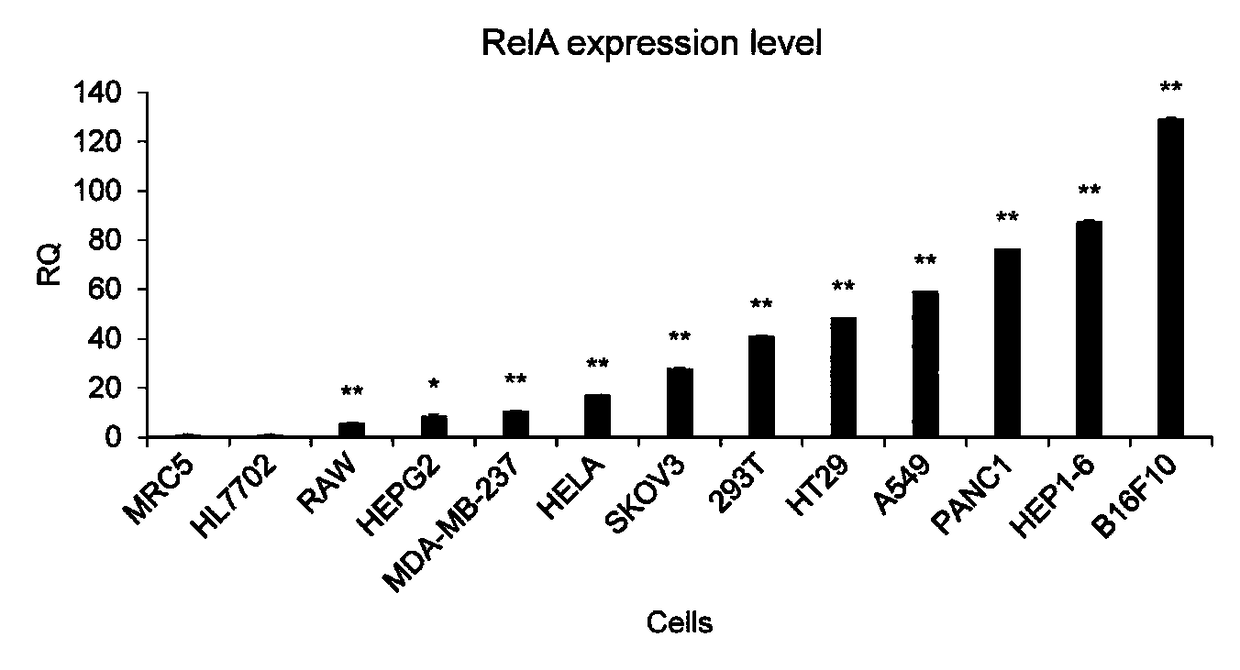
[0042] Example 1 Expression of NF-κB RelA in different cells
[0043] experimental method:
[0044] Cell culture: HEK-293T (human fetal kidney cells), HepG2 (human liver cancer cells), A549 (human lung cancer cells), HT-29 (human colon cancer cells), HeLa (human cervical cancer cells), SKOV3 (human ovarian cancer) Cells), PANC-1 (pancreatic cancer cells), MDA-MB-453 (human breast cancer), Hepa1-6 (mouse liver cancer cells), mouse macrophages (RAW264.7), mouse melanoma cells ( B16F10), HL7702 (human normal liver cells) and MRC5 (human embryonic fibroblasts) cell culture. Cell culture uses DEME (Hepa1-6, HEK-293T, HepG2, HeLa, PANC-1, MDA-MB-453, RAW264.7, B16F10, MRC-5) or RPMI 1640 medium (A549, HT-29, SKOV) -3, HL7702), 10% fetal bovine serum (HyClone), 100units / mL penicillin and 100μg / mL streptomycin culture; the culture environment contains 5%(v / v)CO 2 Incubate at 37°C in a humidified incubator. After the cells are recovered, they are seeded into a 24-well microtiter plate (1...
Embodiment 2
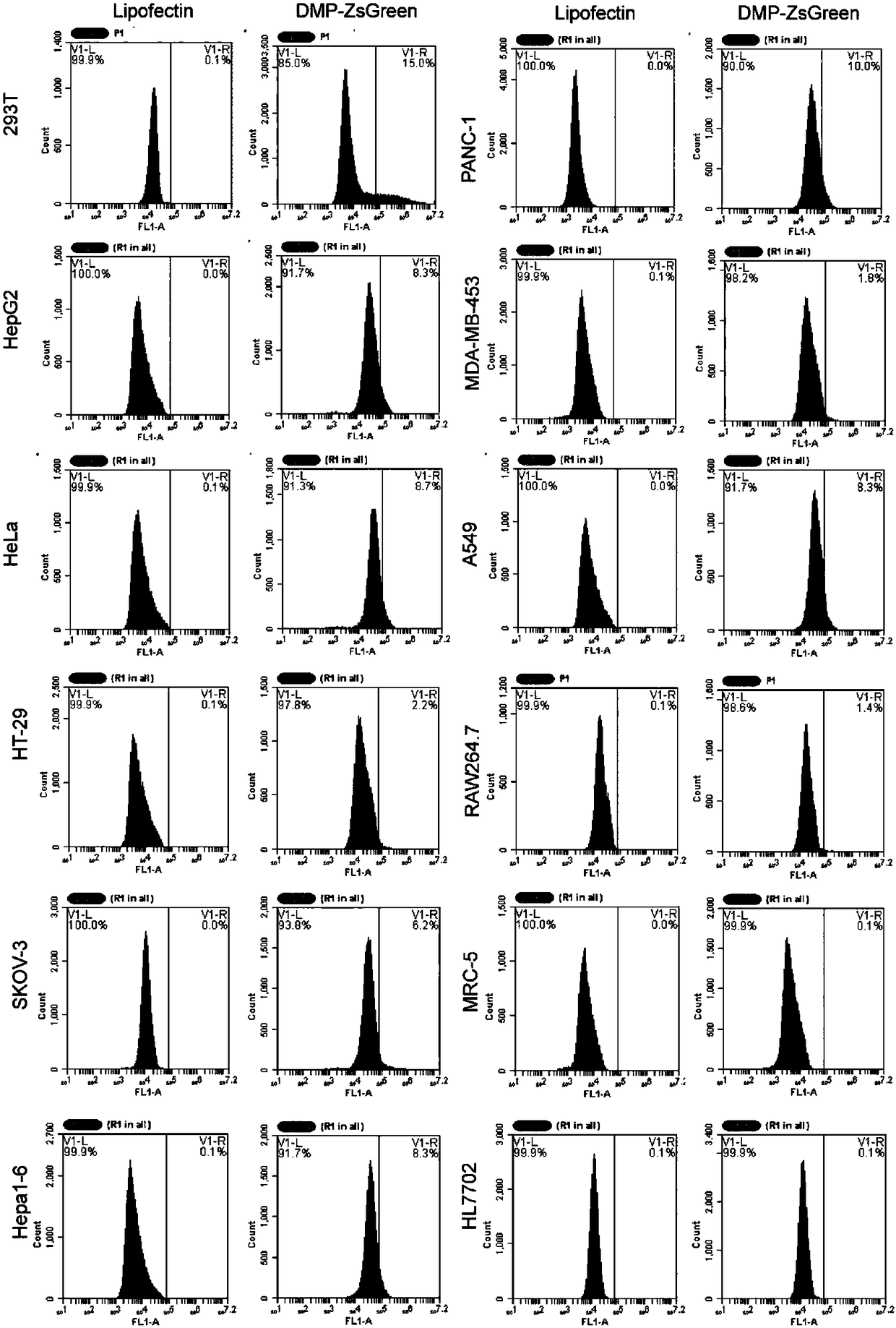
[0048] Example 2 DMP-zsGreen (intracellular expression of effector gene)
[0049] experimental method:
[0050] Vector construction: construct an expression vector DMP-zsGreen; this vector contains the DMP sequence and the coding sequence of the green fluorescent protein zsGreen that can be expressed in cells under its control. Among them, DMP contains NF-κB response sequence (5'- GGGAAT TTC CGG GGA CTT TCC GGG AAT TTC CGG GGA CTT TCC GGG AAT TTC C-3', SEQ ID NO.1) and minimal promoter sequence (5'-TAG AGG GTATAT AAT GGA AGC TCG ACT TCC AG-3', SEQ ID NO. 3).
[0051] Cell culture: HEK-293T (human fetal kidney cells), HepG2 (human liver cancer cells), A549 (human lung cancer cells), HT-29 (human colon cancer cells), HeLa (human cervical cancer cells), SKOV3 (human ovarian cancer) Cells), PANC-1 (pancreatic cancer cells), MDA-MB-453 (human breast cancer), Hepa1-6 (mouse liver cancer cells), mouse macrophages (RAW264.7), HL7702 (human normal liver cells) ) And MRC5 (human embryonic f...
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 DMP-Display-SBP (effect gene cell surface display expression)
[0058] experimental method:
[0059] Vector construction: construct an expression vector DMP-Display-SBP; this vector contains DMP sequence and the coding sequence for cell expression display streptavidin binding peptide (SBP). The DMP contains the NF-κB response sequence (5'-GGG AAT TTC CGGGGACTT TCC GGG AAT TTC CGG GGACTT TCC GGG AAT TTC C-3', SEQ ID NO. 1) and the minimal promoter sequence (5'-TAG AGG GTATAT AAT GGAAGC TCG ACT TCC AG-3', SEQ ID NO. 3). The SBP coding sequence is: ATG GAC GAG AAG ACC ACC GGG TGG CGG GGC GGC CAC GTT GTG GAG GGT CTCGCT GGC GAG CTG GAG CAG CTC AGG GCC CGC TTG GAG CAC CAT CCC CAG GGG CAACGCGAG CCT ATC GAT TAA (SEQ ID NO.4) . The expressed skeleton sequence is cloned from the vector pDisplay TM (Invitrogen); pDisplay TM The protein or polypeptide to be displayed on the cell membrane surface is fused to the N-terminus of the rat Igκ-chain leader sequence, which can ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com