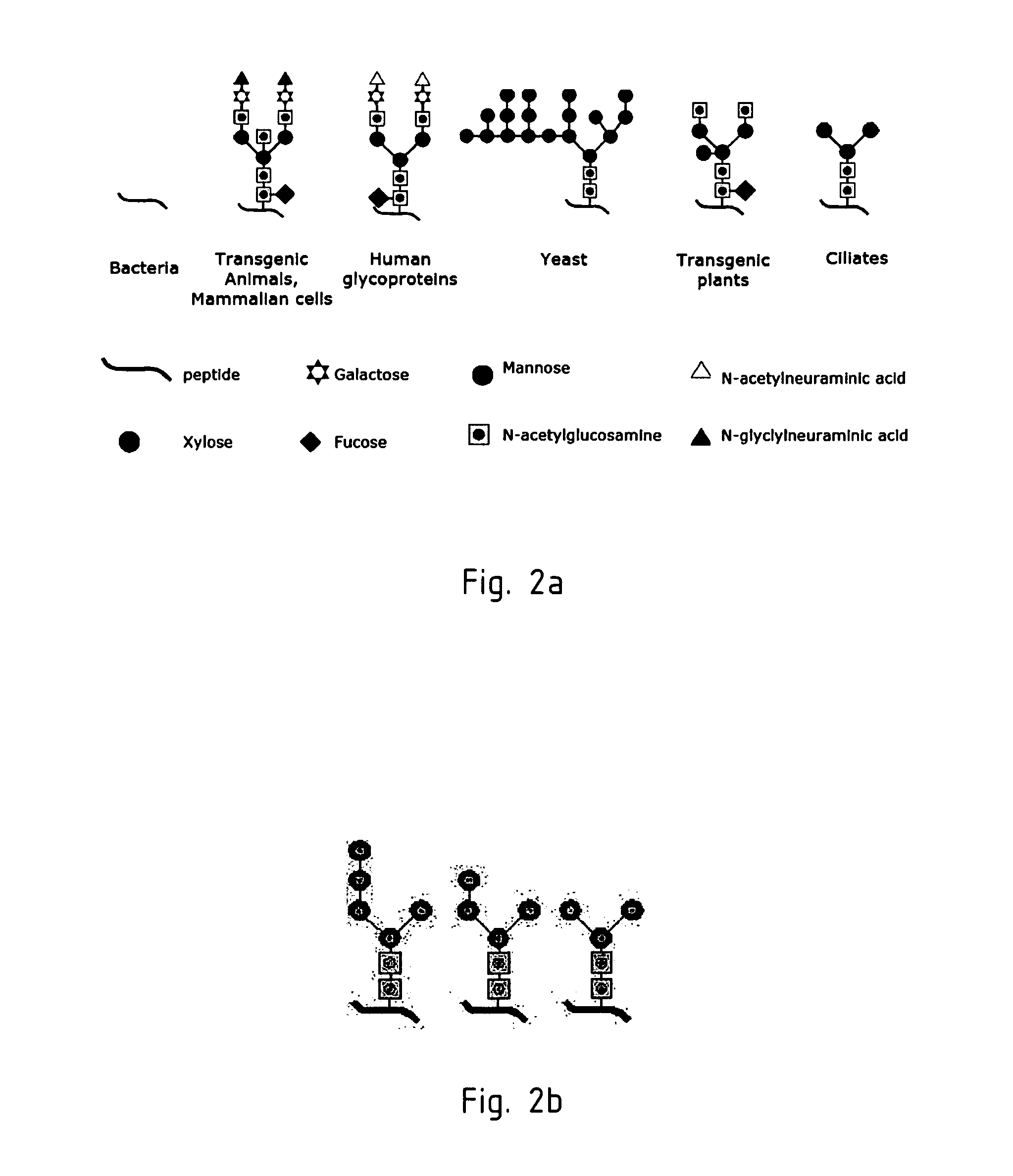
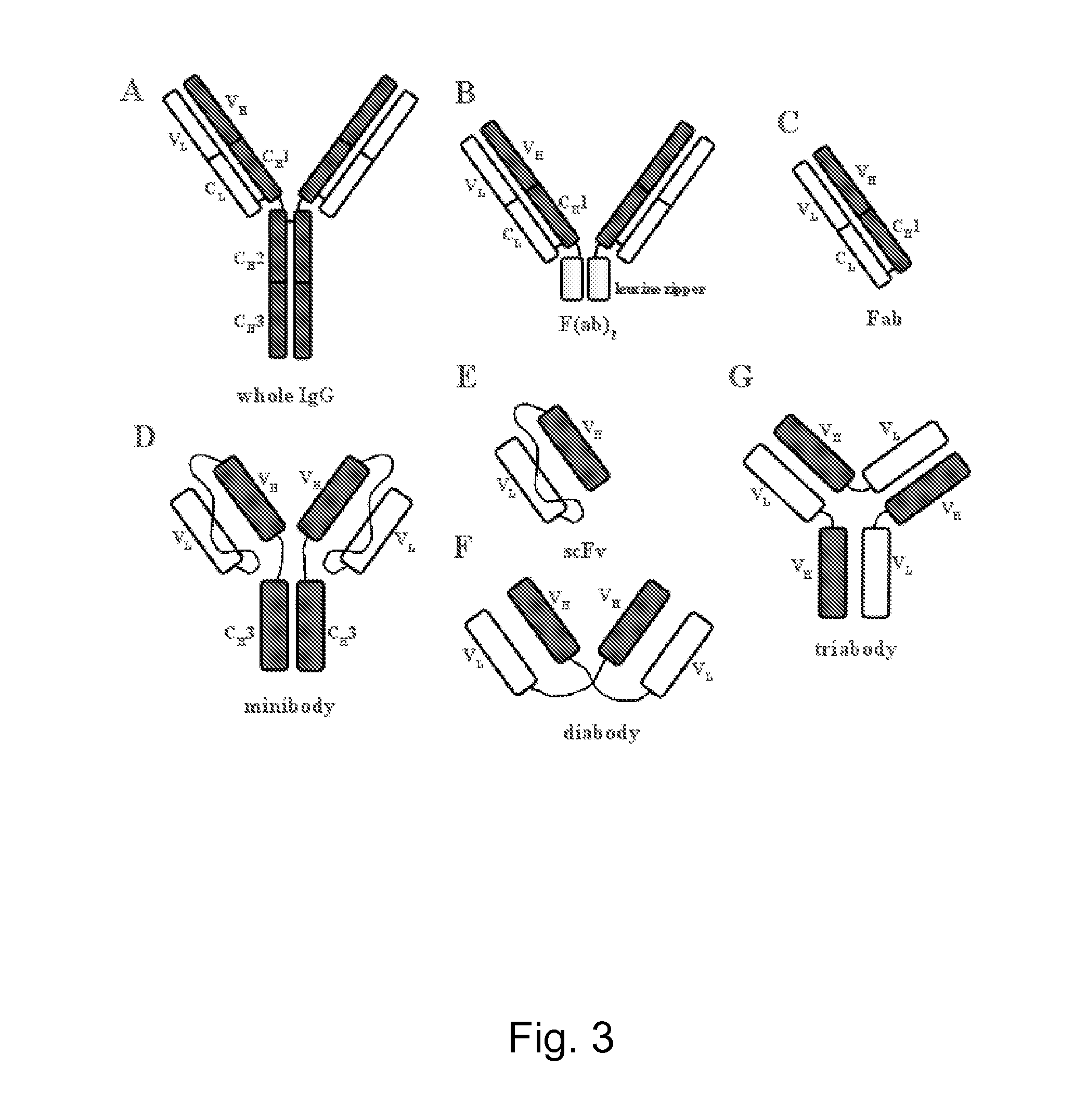
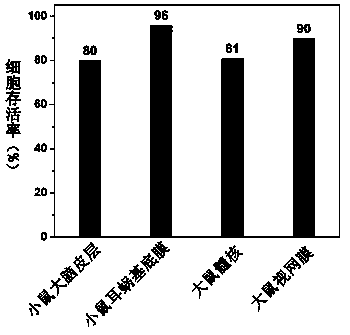
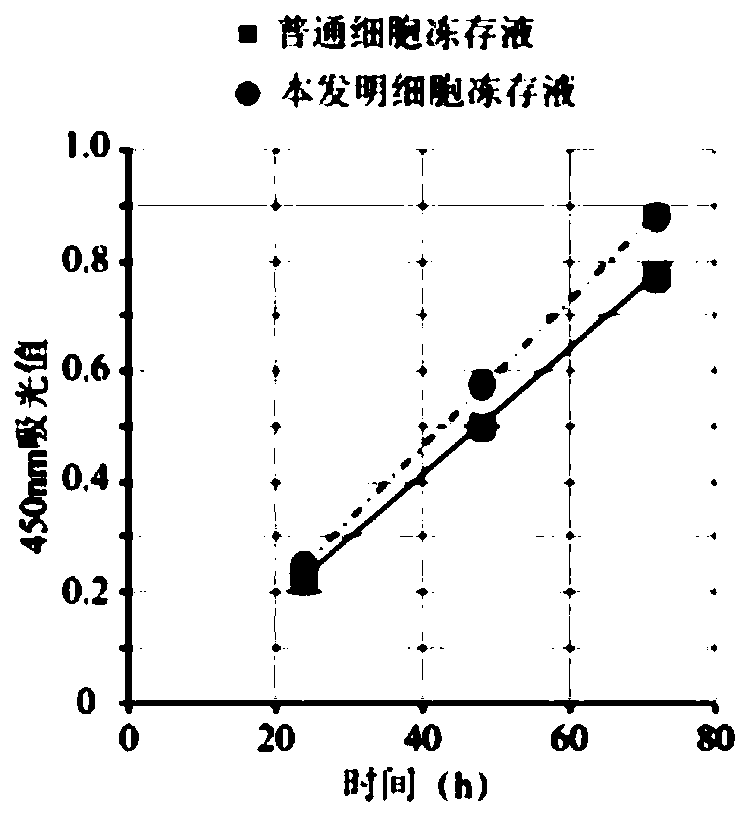
Patents
Literature
416results about How to "Improve cell activity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
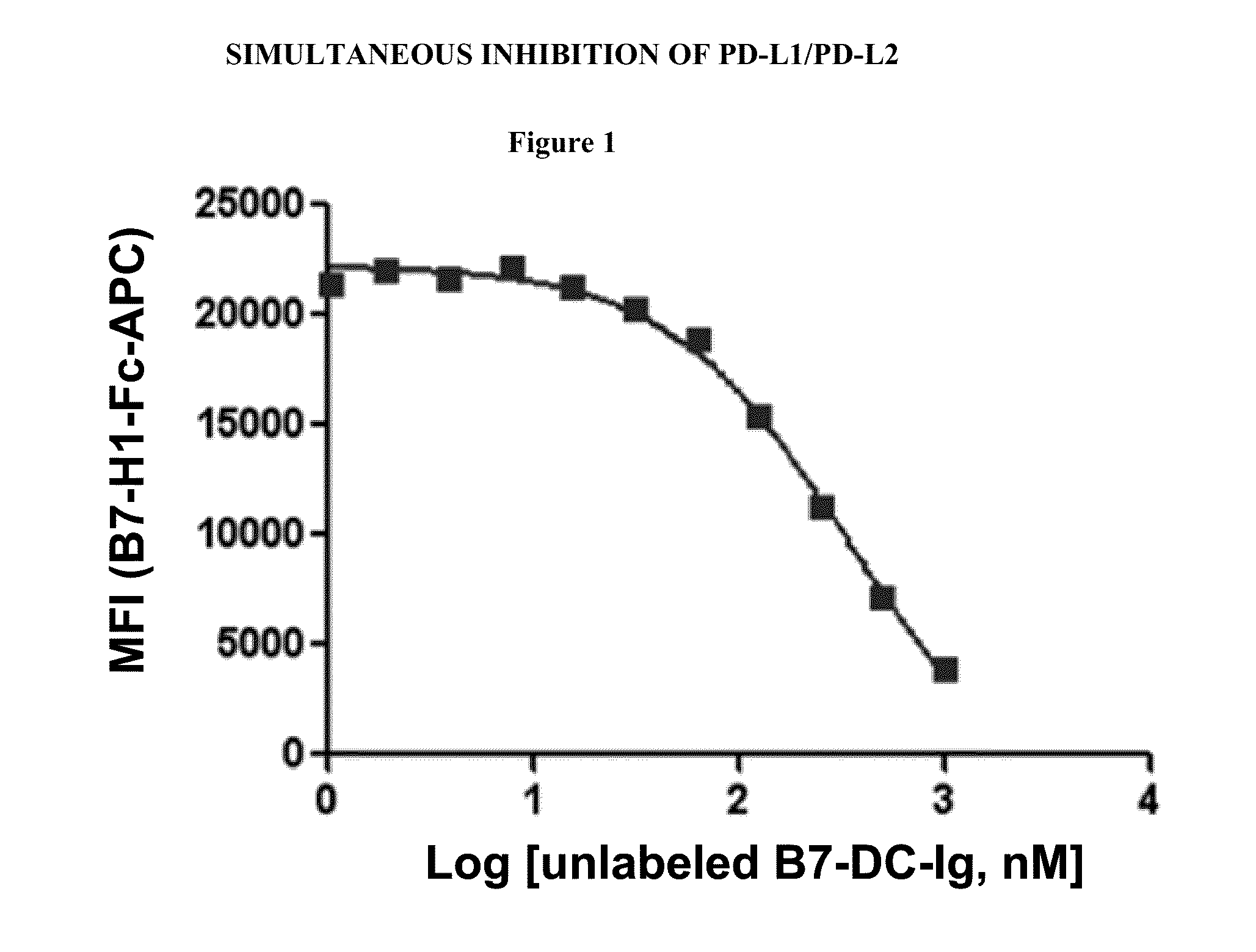
Simultaneous inhibition of pd-l1/pd-l2
InactiveUS20130017199A1Increase frequencyIncrease percentageAntibacterial agentsAntimycoticsDiseaseDendritic cell
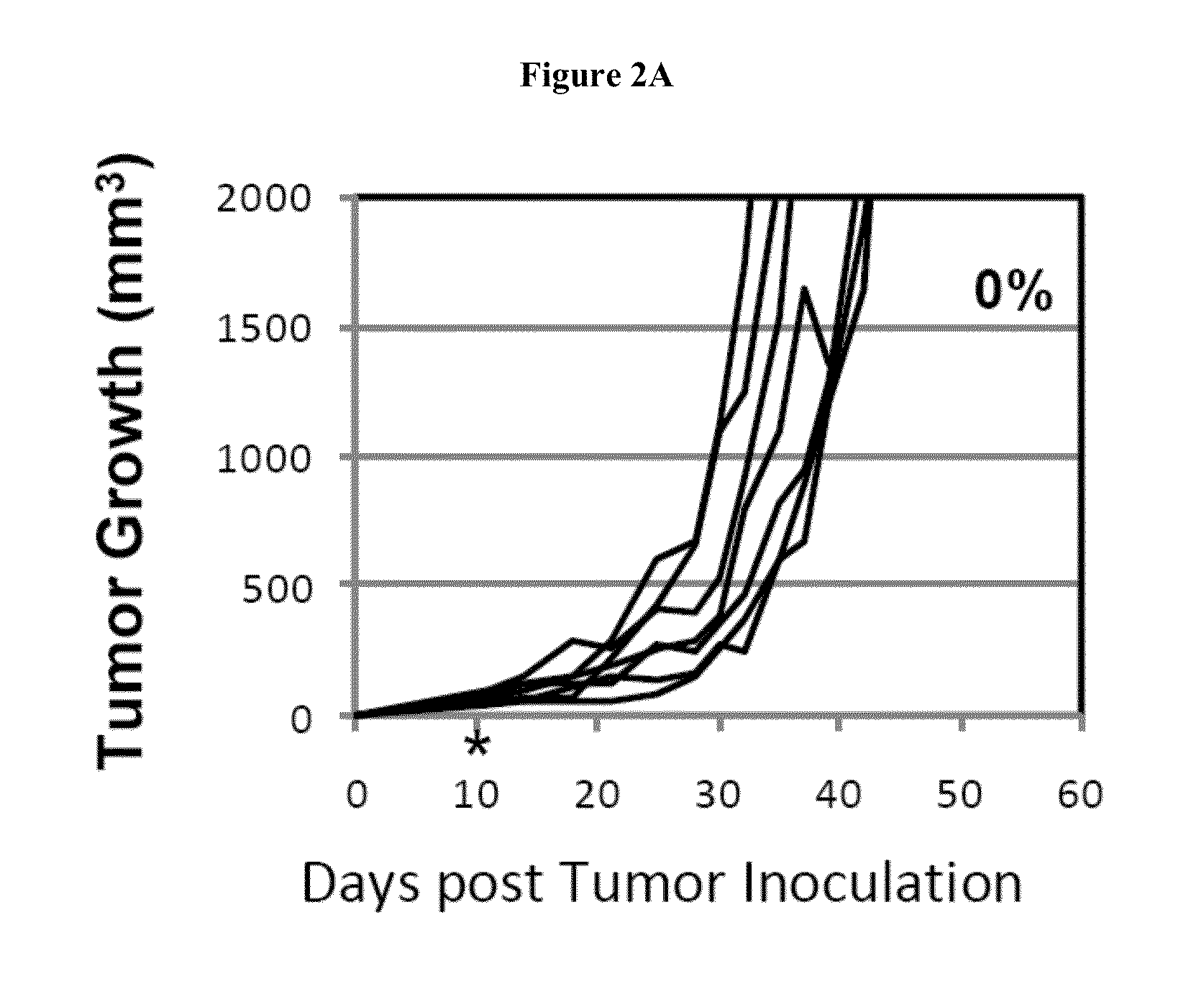
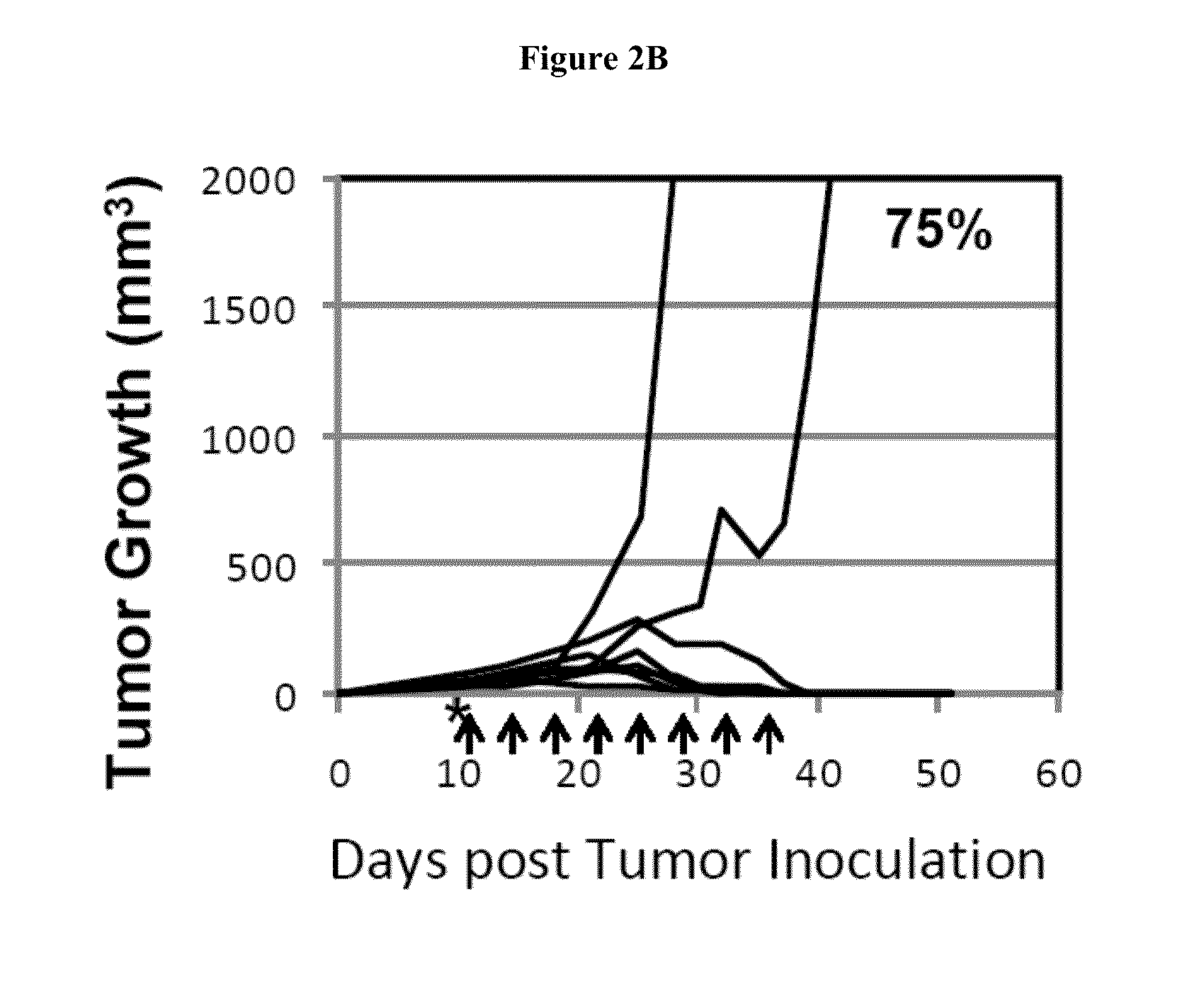
Methods and compositions for treating an infection or disease that results from (1) failure to elicit rapid T cell mediated responses, (2) induction of T cell exhaustion, T cell anergy or both, or (3) failure to activate monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and / or other APCs, for example, as required to kill intracellular pathogens. The method and compositions solve the problem of undesired T cell inhibition by simultaneously inhibiting the PD-1 ligands, PD-L1 and PD-L2. The immune response can be modulated by providing antagonists which bind with different affinity, by varying the dosage of agent which is administered, by intermittent dosing over a regime, and combinations thereof, that provides for dissociation of agent from the molecule to which it is bound prior to being administered again. In some cases it may be particularly desirable to stimulate the immune system, then remove the stimulation.
Owner:AMPLIMMUNE
Method of altering cell properties by administering rna
InactiveUS20060247195A1Less activeMinimise and prevent riskCell differentiationGenetic material ingredientsRNA SequenceIn vivo
The invention relates to the alteration of cell properties using RNA molecules. In particular, it relates to the alteration of the ability of cells to mobilise, migrate, integrate, proliferate and / or differentiate. For example, it relates to the induction of differentiation of stem cells, including the acquisition of the ability to migrate, integrate, and proliferate. It also relates to the induction of in vivo stem cell mobilisation, migration, integration, proliferation and / or differentiation. Accordingly, it relates to the promotion of stem cell-mediated functional repair. The invention also relates to the reversal of differentiation of differentiated cells. All these effects may be effected by providing isolated RNA comprising a RNA sequence extractable from cells comprising the desired cell type(s) to a population of cells under conditions whereby the alteration of the cell property is achieved.
Owner:RIBOSTEM
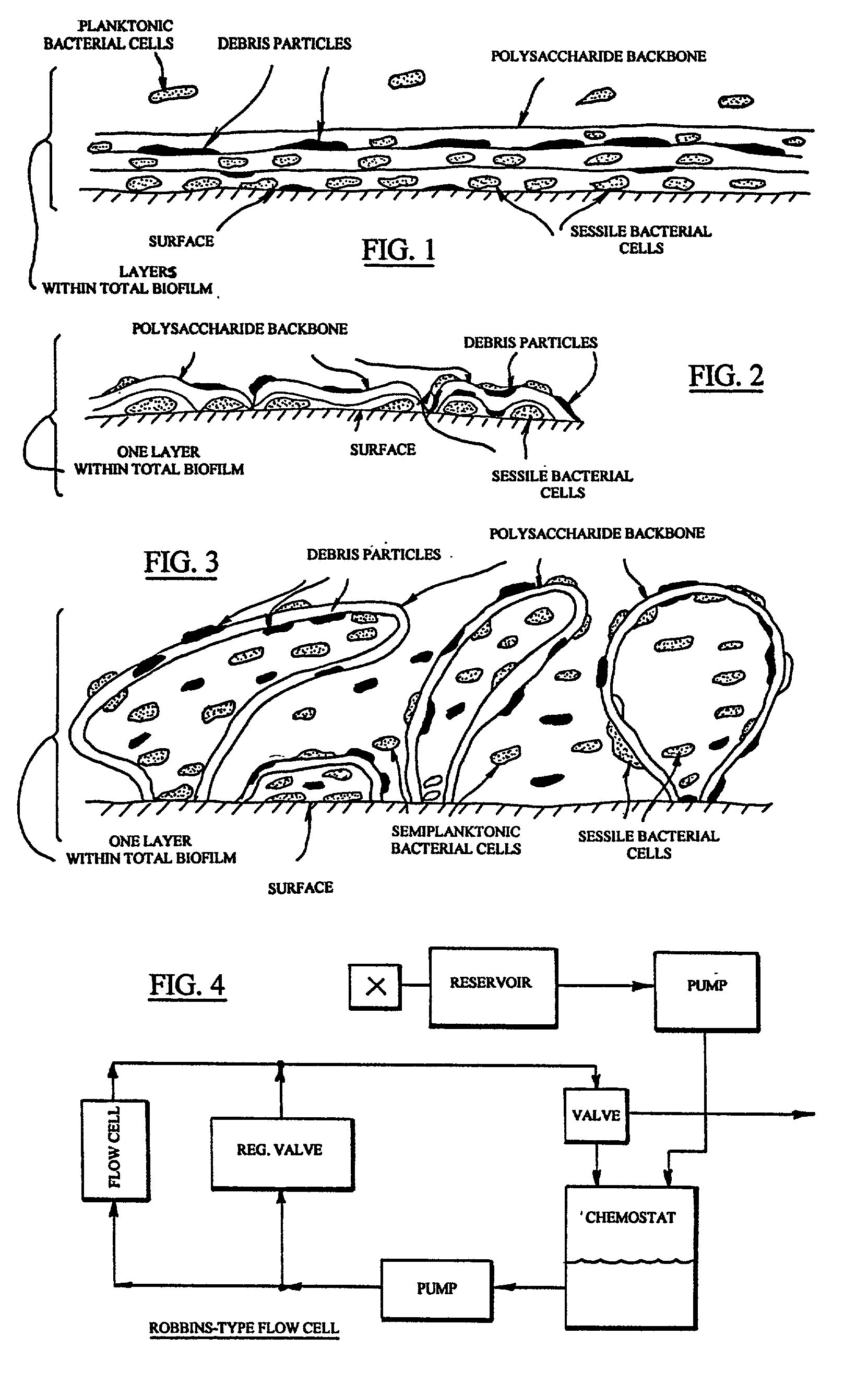
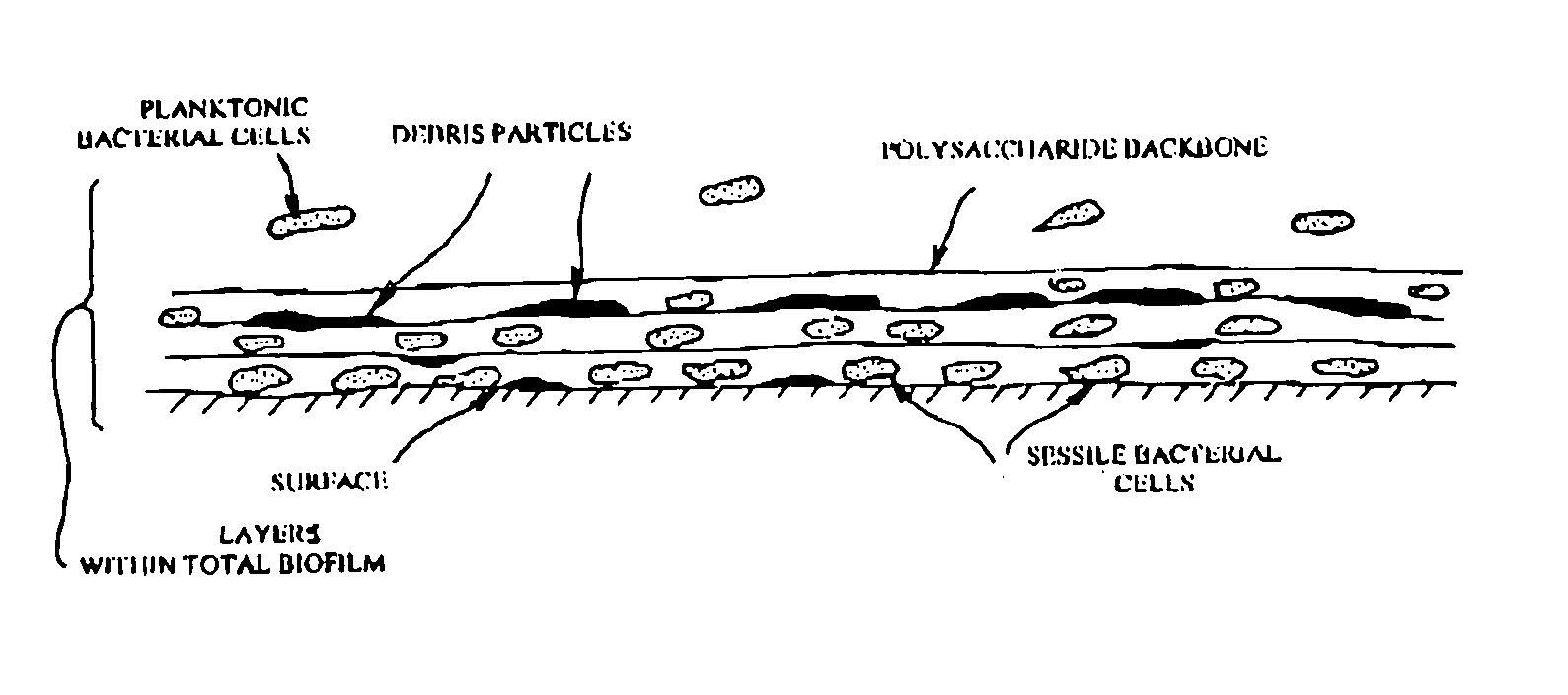
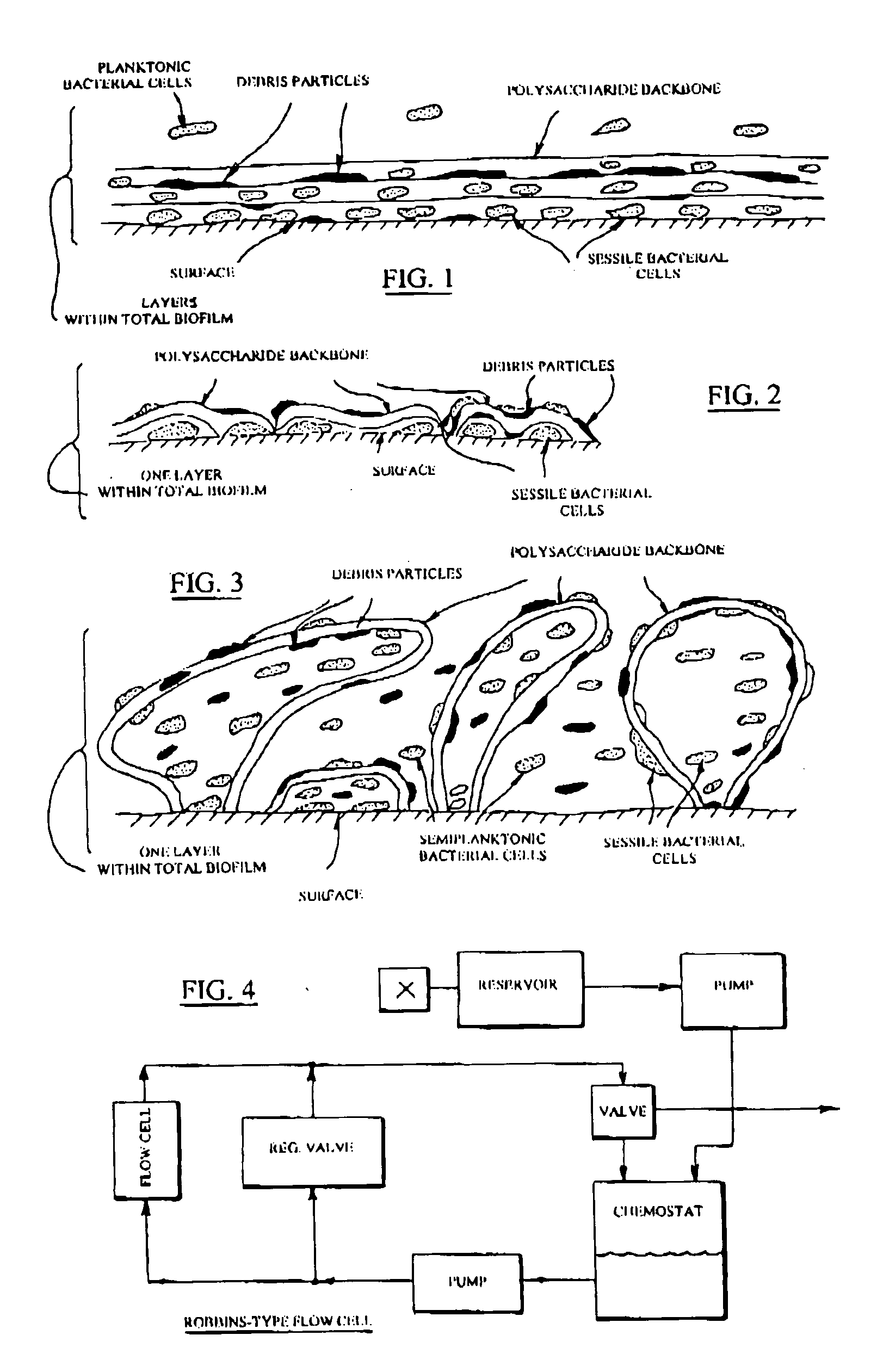
Compositions for treating biofilm
InactiveUS20020037260A1Improve the immunityReduced metabolic activityCosmetic preparationsBiocideBiofilmMicrobiology
Owner:BUDNY JOHN A +1
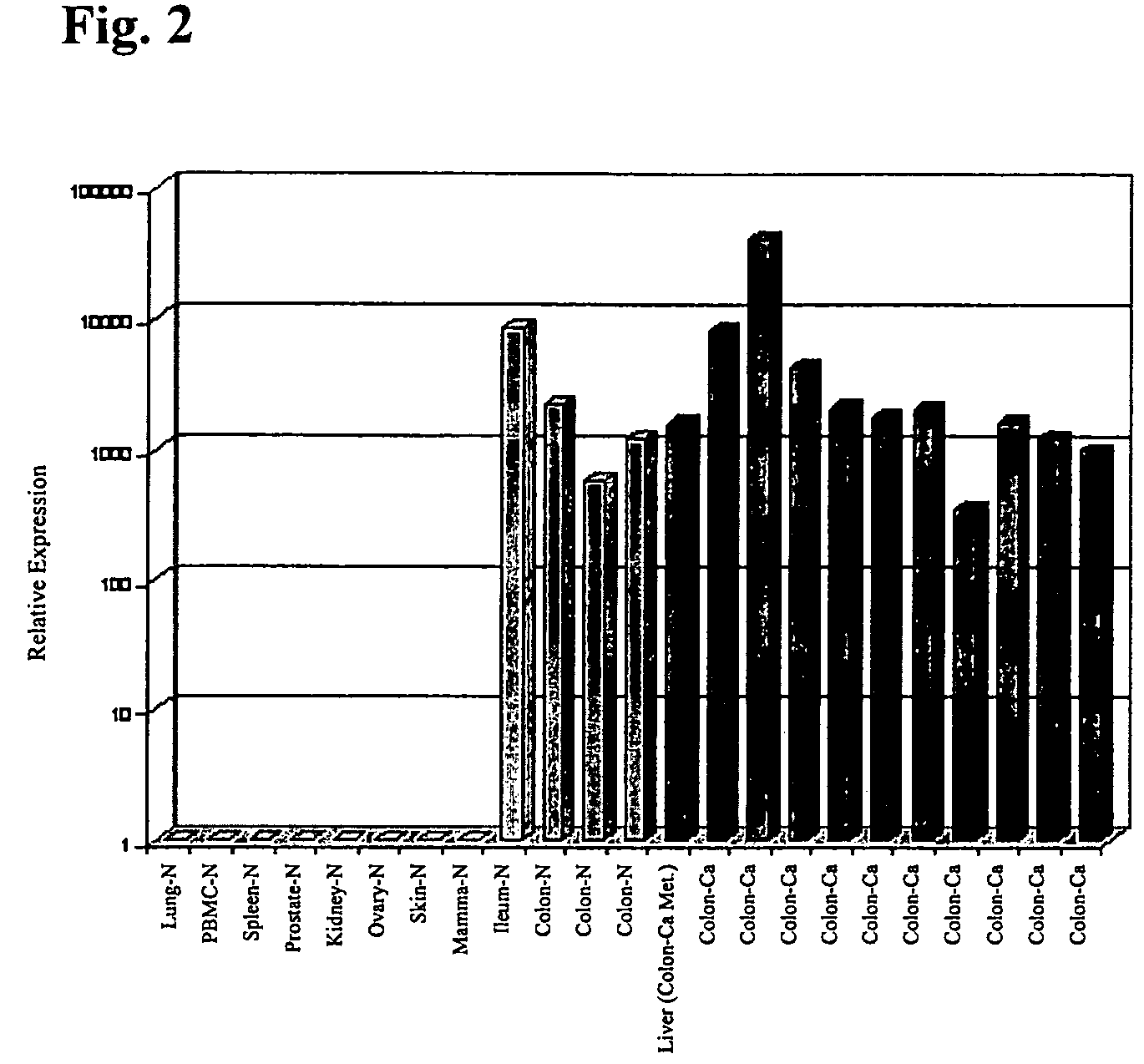
Genetic products differentially expressed in tumors and the use thereof
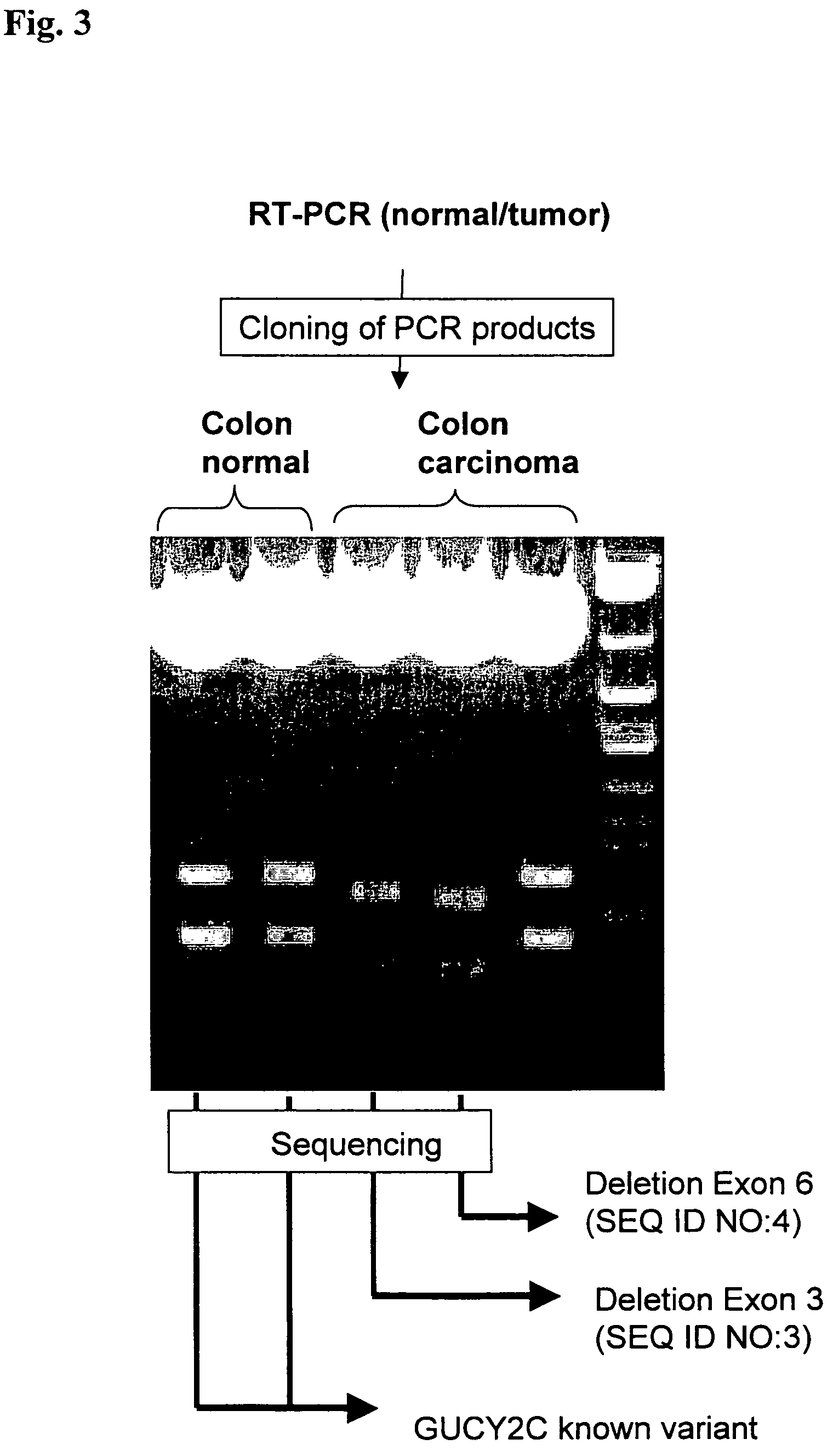
ActiveUS7527933B2Improve cell activityEfficient disseminationCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCancer researchDisease cause
The invention relates to the identification of genetic products expressed in association with tumors and to coding nucleic acids for the expressed products. An embodiment of the invention also relates to the therapy and diagnosis of disease in which the genetic products are aberrantly expressed in association with tumors, proteins, polypeptides and peptides which are expressed in association with tumors, and to the nucleic acids coding for the polypeptides, peptides and proteins.
Owner:GANYMED PHARMA AG
Method to enhance osteoblast functionality and measure electrochemical properties for a medical implant
InactiveUS20110301716A1Good cell compatibilityEnhancing and increasing functionalityAnodisationElectrotherapyOsseous CellElectrochemistry
A method to enhance osteoblast functionality of a medical implant. The method may include obtaining the medical implant and treating a surface of the medical implant to modify the surface characteristics causing increase functionality of adjacent positioned osteoblasts. A method of increasing cellular activity of a medical implant is also disclosed. A medical device having enhanced cytocompatibility capabilities includes a metallic substrate with an outer surface. Attached to the outer surface is a composition of nanosized structures. A biosensor for use with a medical device, includes an electrode that is attached to an outer surface of the medical device. The biosensor measures electrochemical changes adjacent to the medical implant. Further, a method of manufacturing a medical implant with a biosensor for use in vivo and a method of integrating a biosensor with a medical implant for use in monitoring conductivity and electrochemical changes adjacent to the medical implant are disclosed.
Owner:BROWN UNIVERSITY
Il-21 antagonists
InactiveUS20070122413A1Increasing in vivo serum half-lifeModulate antibody responseNervous disorderAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAutoimmune conditionAutoimmune disease
Monoclonal antibodies are identified that bind the IL-21 protein. These antibodies are used to identify regions of the IL-21 protein to where binding neutralizes IL-21 activity. Hybridomas and methods of producing anti-IL-21 monoclonal antibodies are described. The monoclonal antibodies are useful in treating IL-21-mediated diseases, which may include autoimmune and inflammatory diseases such as pancreatitis, type I diabetes (IDDM), Graves Disease, inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), Crohn's Disease, ulcerative colitis, irritable bowel syndrome, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, diverticulosis, systemic lupus erythematosus, psoriasis, ankylosing spondylitis, scleroderma, systemic sclerosis, psoriatic arthritis, osteoarthritis, atopic dermatitis, vitiligo, graft vs. host disease (GVHD), cutaneous T cell lymphoma (CTCL), Sjogren's syndrome, glomerulonephritis, IgA nephropathy, graft versous host disease, transplant rejection, atopic dermatitis, anti-phospholipid syndrome, and asthma, and other autoimmune diseases.
Owner:ZYMOGENETICS INC
Human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102127522AEasy to operateHigh purity and cell viabilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsDigestionBone marrow
The invention discloses a human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell and a preparation method thereof. The human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell is prepared by carrying out aseptic treatment, mechanical shearing, Wharton jelly exposure, collagenase digestion and isolated culture on an umbilical stalk of a healthy fetus by a term abdominal delivery. After freezing and thawing, the cell activity does not decline dramatically, thereby ensuring that the human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell is an ideal seed cell for cellular therapy. The invention also relates to a primitive mesenchymal stem cell prepared by the method, and the primitive mesenchymal stem cell is confirmed as the mesenchymal stem cell by the identification of morphology, immunophenotype and invitro differentiation experiments in accordance with the mesenchymal stem cell standards established by International Society for Cellular Therapy (ISCT). The cell count, cell activity, purity, doubling time and multiplication capacity of the human umbilical mesenchymal stem cell are apparently higher than those of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell.
Owner:UNION STEMCELL & GENE ENG
Tissue equivalents
InactiveUS6197296B1Easy pretreatmentPrevent thrombosisBiocideTissue cultureLeiomyocytePhases of clinical research
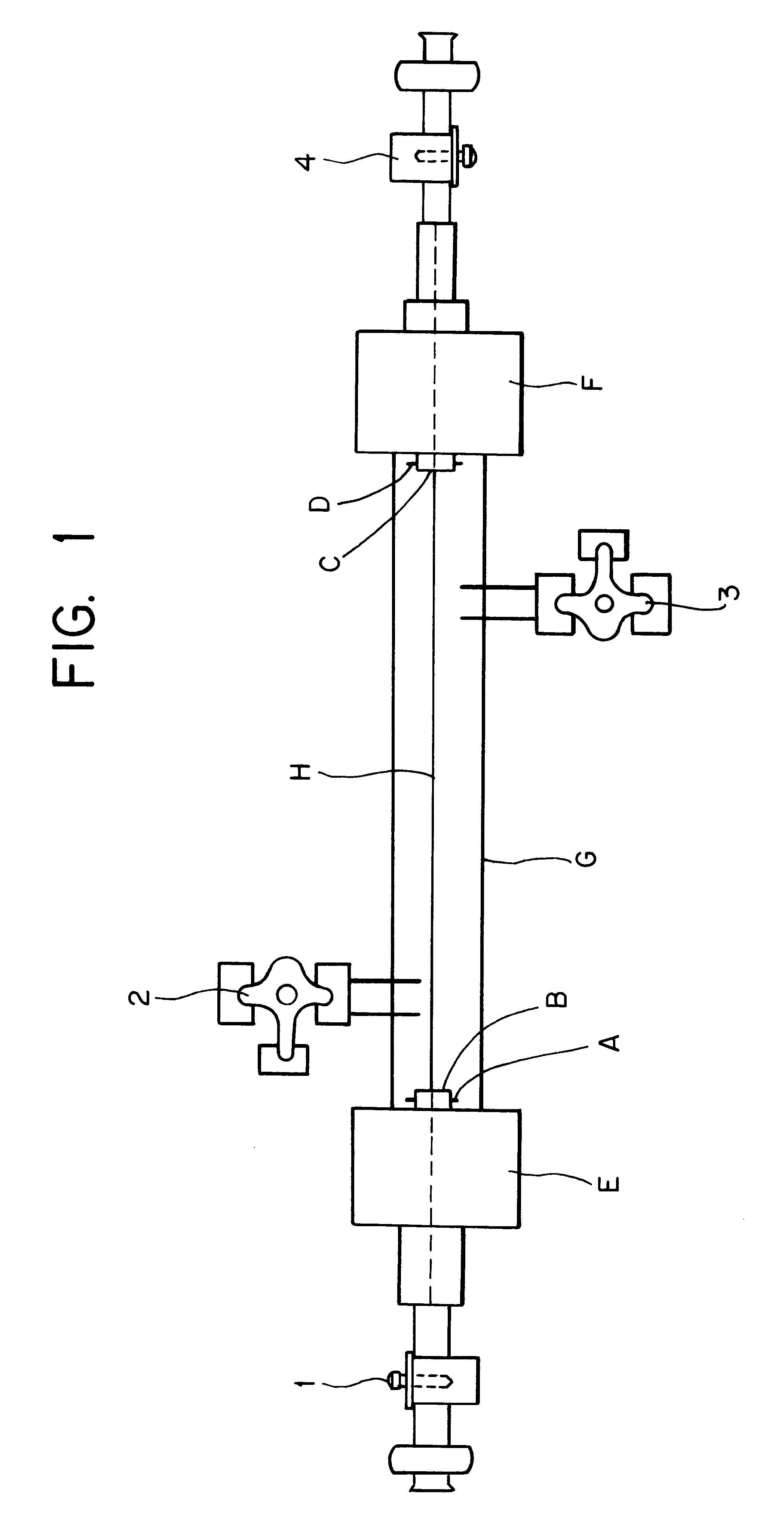
A method of forming a tissue equivalent is described. A length of polyester tube is threaded over a mandrel (H) and attached at either end by clips at A and D. A block (F) is then screwed into place. The polyester is then pre-soaked by injecting through Tap (2) an acidified collagen solution for approximately one hour. After a suitable period of time the excess solution is aspirated off. Following this stage, a second, alkaline solution is injected into the apparatus which contains smooth muscle cells (SMC). Thus, neutralisation of the collagen impregnated within the fabric of the tube occurs leading to spontaneous fibrillogenesis within the interstices of the cloth, eliminating the risk of delamination. The apparatus is then incubated. The collagen contracts down onto the fabric tube and the cell-impregnated gel becomes incorporated into the presoaked collagen. The pre-impregnated collagen and the collagen provided in the aqueous mixture contract down as one into a coherent whole with the SMC. The tissue equivalent is then lined with endothelial cells and the apparatus again incubated and fed at increasing intraluminal pressures applied either statically or dynamically. This is believed to cause the vessel to become preconditioned to the pressure it will work under as an implant. This allows organization of the basement membrane which in turn promotes EC attachment and theoretically prevents smooth muscle cell hyperplasia.
Owner:TISSUEMED LTD
Treatment of Insulin Resistance and Diabetes
InactiveUS20080260703A1Increase perfusionImprove cell activityBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsAngiogenesis growth factorSkeletal muscle
Disclosed are methods, compositions, and cells useful for increasing insulin sensitivity, as well as lack of insulin production in a host in need thereof. One aspect of the invention discloses methods of increasing skeletal muscle perfusion through administration of cells capable of directly and / or indirectly stimulatory of angiogenesis and / or vascular responsiveness. Another aspect provides means of increasing sensitivity to insulin through administration of a cell composition capable of integrating into host insulin responsive tissue and upregulating responsiveness either through mobilization of host cells capable of responding to insulin, mobilization of host cells capable of endowing insulin responsiveness on other host cells, exogenously administered cells taking the role of insulin responsiveness, or exogenously administered cells endowing insulin responsiveness on other host cells. Another aspect comprises modifying said host to allow for concurrent insulin sensitization and upregulated production of insulin.
Owner:CREATIVE MEDICAL HEALTH
Compositions for treating biofilm
InactiveUS20050158253A1Increased susceptibilityOpportunities decreaseCosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsBiofilmEnzyme complex
A two component composition comprises an anchor enzyme complex to degrade biofilm structures and a second anchor enzyme component having the capability to act directly upon the bacteria for a bactericidal effect.
Owner:PHARMACAL BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
BTLA nucleic acids
InactiveUS7304149B2Decrease autoreactive lymphocyte activityEnhanced signalCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSugar derivativesLymphocyteInhibitory receptors
The present invention provides a novel lymphocyte inhibitory receptor termed BTLA which is expressed on both T and B cells, and identifies B7 family member B7x as interacting with BTLA to attenuate lymphocyte activity. Methods and compositions for modulating BTLA-mediated negative signaling and interfering with the interaction of BTLA and B7x for therapeutic, diagnostic and research purposes are also provided.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
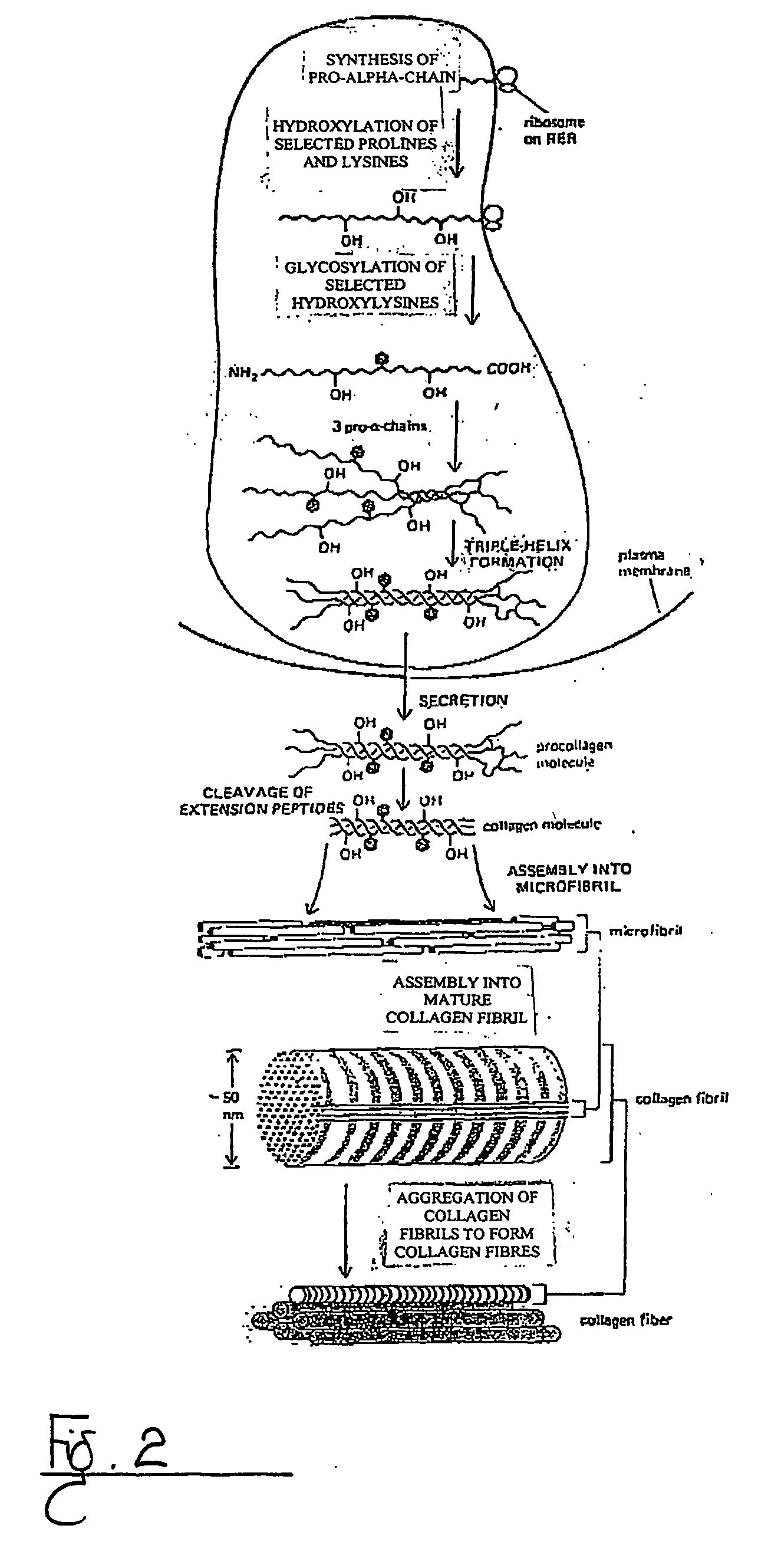
Method of stimulating collagen formation
InactiveUS20040210275A1Improve cell activityIncreased collagen formationSurgical instrument detailsLight therapySkin treatmentsSurgery
A method of stimulating collagen formation in a selected area of mammalian skin in which the selected area is irradiated with a source of visible or near infra-red radiation. The radiation is absorbable by intracellular chromophores to enhance cellular activity and increase collagen formation. A skin treatment device for carrying out the method of the invention is also described.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MEDITEC AG
Ceria and strontium titanate based electrodes
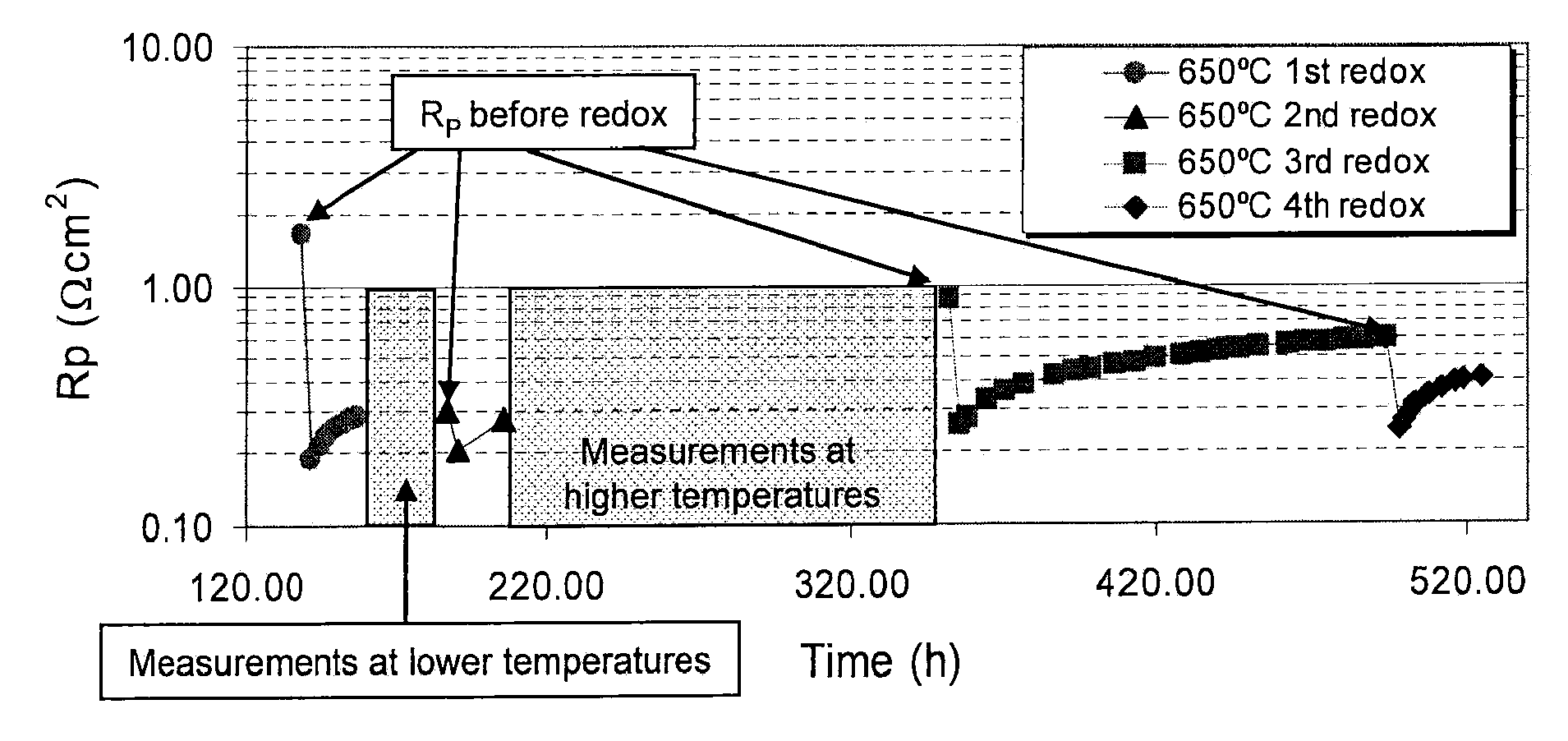
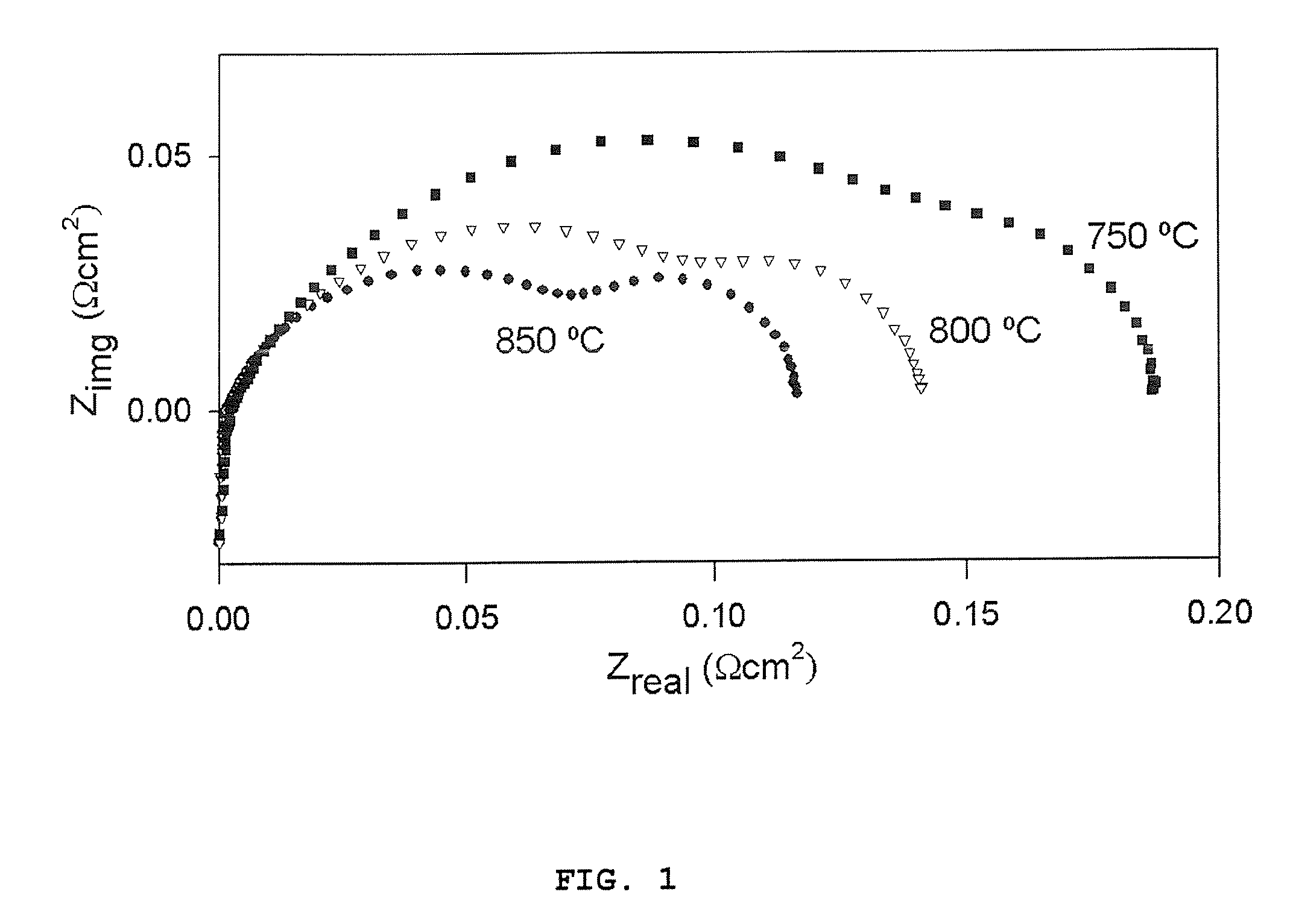
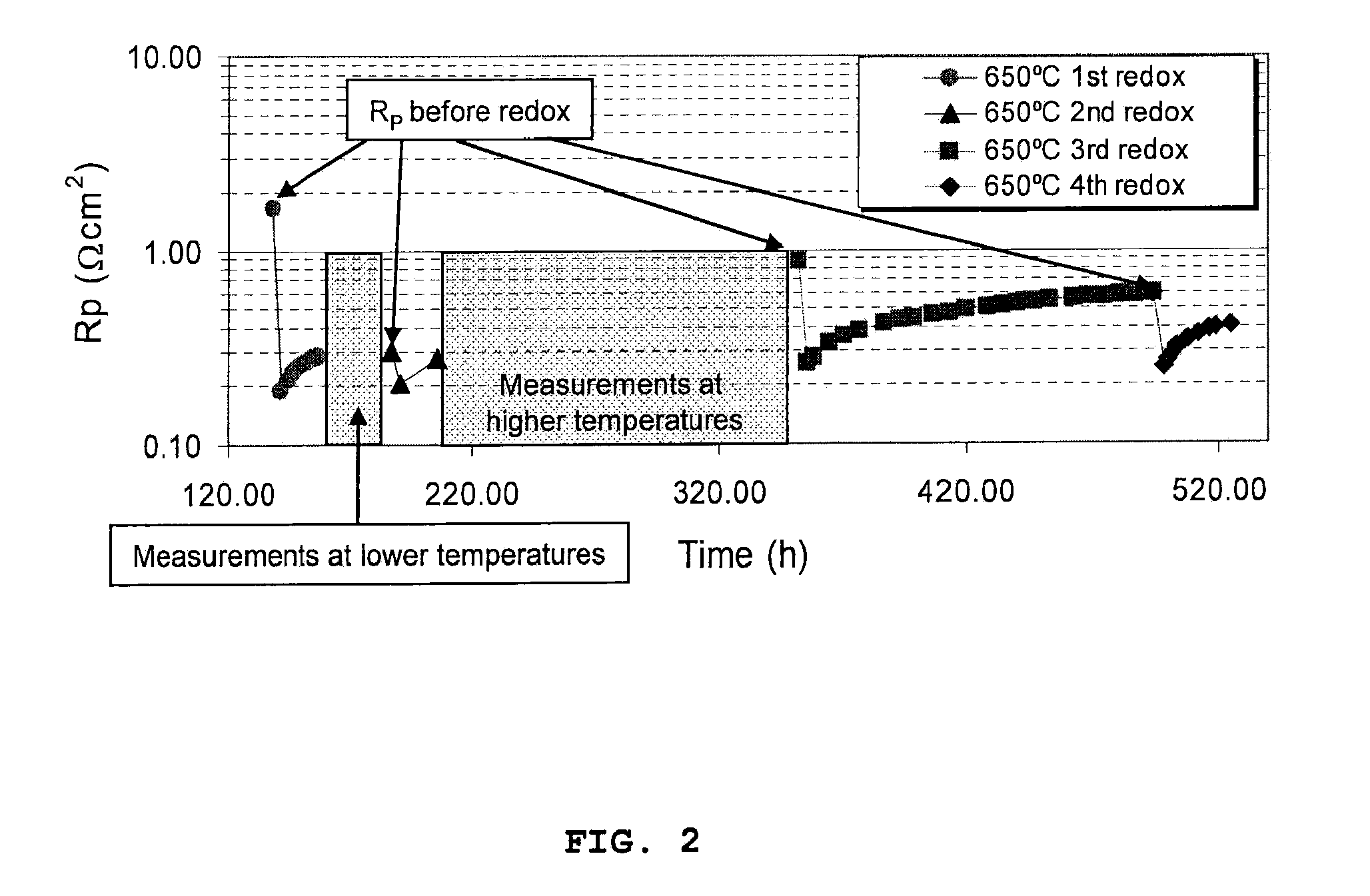
InactiveUS20090061284A1High BET surface areaSpeed up calcination procedureFuel cells groupingCell electrodesStrontium titanateVanadium doping
A ceramic anode structure obtainable by a process comprising the steps of: (a) providing a slurry by dispersing a powder of an electronically conductive phase and by adding a binder to the dispersion, in which said powder is selected from the group consisting of niobium-doped strontium titanate, vanadium-doped strontium titanate, tantalum-doped strontium titanate, and mixtures thereof, (b) sintering the slurry of step (a), (c) providing a precursor solution of ceria, said solution containing a solvent and a surfactant, (d) impregnating the resulting sintered structure of step (b) with the precursor solution of step (c), (e) subjecting the resulting structure of step (d) to calcination, and (f) conducting steps (d)-(e) at least once.
Owner:DANMARKS TEKNISKE UNIV
Medical nano-fiber sponge material and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN102657893AExcellent healing propertiesImproves anti-adhesion and cell viabilityAbsorbent padsBandagesFreeze dryNanofiber
The invention relates to a medical nano-fiber sponge material, of which the porosity is 90-98 percent and the diameter of a nano-fiber is 50-1,000 nanometers. The medical nano-fiber sponge material consists of the following components in percentage by mass: 0.5-8.5 percent of bioactive glass fine particles, 65-88 percent of gelatin, 0.2-5.0 percent of hyaluronic acid, 0.2-5.0 percent of chitosan and the balance of water. A preparation method of the medical nano-fiber sponge material comprises the following steps of: adding bioactive glass fine particles and ethanol into a gelatin aqueous solution, and stirring uniformly; performing low-temperature phase separation and freeze drying to obtain nano-fiber sponge obtained by compounding gelatin and bioactive glass fine particles; and performing soaking, refrigerating and freeze drying with a hyaluronic acid solution and a chitosan solution in sequence under a negative pressure condition to obtain a porous composite sponge material in which nano-fibers are crosslinked and coated statically with hyaluronic acid and chitosan. The nano-fiber sponge has excellent bioactivity, bacteriostasis and mechanical property, and can be widely applied in the fields of regenerative repair of various skin wounds and skin tissue engineering.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Yeast with increased butanol tolerance involving cell wall integrity pathway
Increasing tolerance to butanol in yeast has been accomplished by increasing activity of the cell wall integrity pathway. Yeast with increased expression of SLT2p, a mitogen activated protein kinase of the MAPK module of the cell wall integrity pathway had increased tolerance to isobutanol. These yeast may be used for improved butanol production.
Owner:GEVO INC
Methods and compositions for modulating interleukin-21 receptor activity
InactiveUS7198789B2Enhance immune cell activityReduce Fc receptor bindingBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInfectious DisorderNatural Killer Cell Inhibitory Receptors
Methods and compositions for modulating interleukin-21 (IL-21) / IL-21 receptor (MU-1) activity using agonists or antagonists of IL-21 or IL-21 receptor (“IL-21R” or “MU-1”), are disclosed. IL-21 / IL-21R antagonists can be used to induce immune suppression in vivo, e.g., for treating or preventing immune cell-associated pathologies (e.g., pathologies associated with aberrant activity of one or more of mature T cells (mature CD8+, mature CD4+ T cells), mature NK cells, B cells, macrophages and megakaryocytes, including transplant rejection and autoimmune disorders). IL-21 / IL-21R agonists can be used by themselves or in combination with an antigen, e.g., as an adjuvant (e.g., a vaccine adjuvant), to up-regulate an immune response in vivo, e.g., for example, for use in treating cancer and infectious disorders.
Owner:GENETICS INST INC
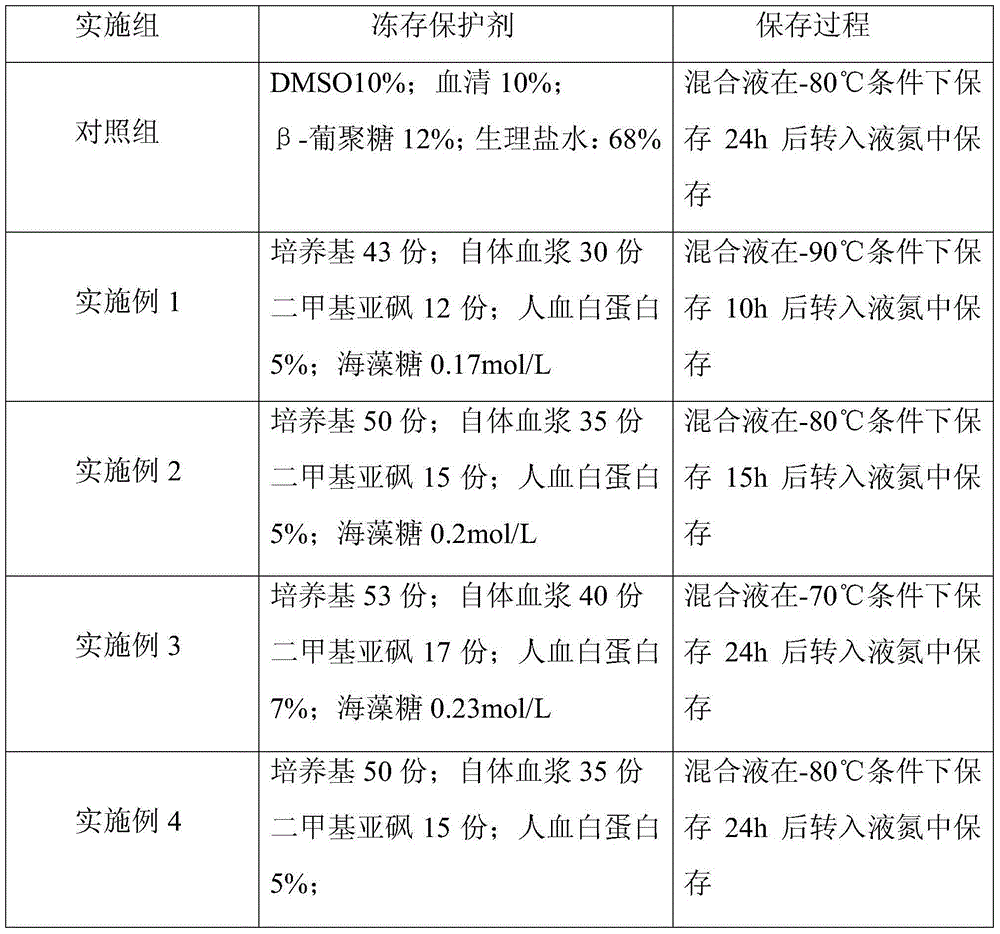
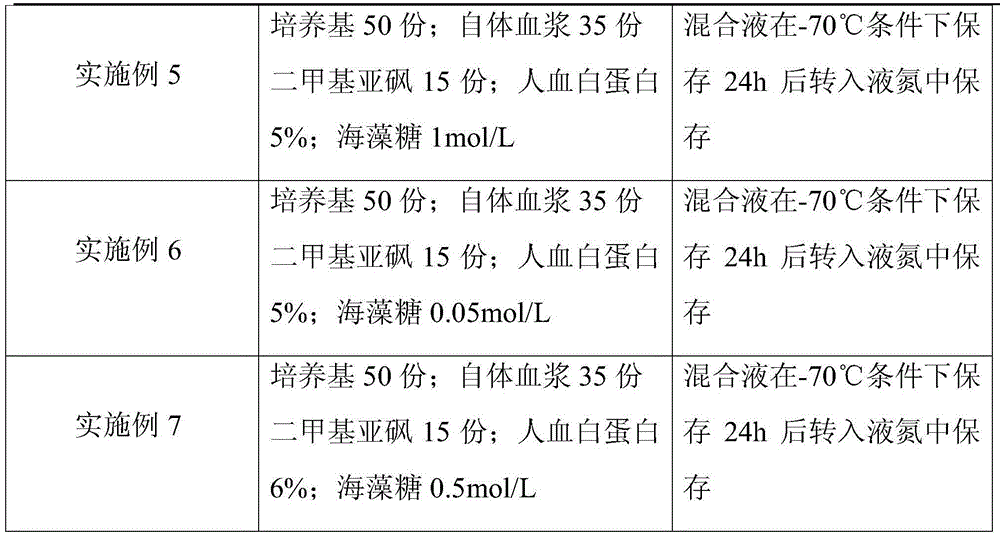
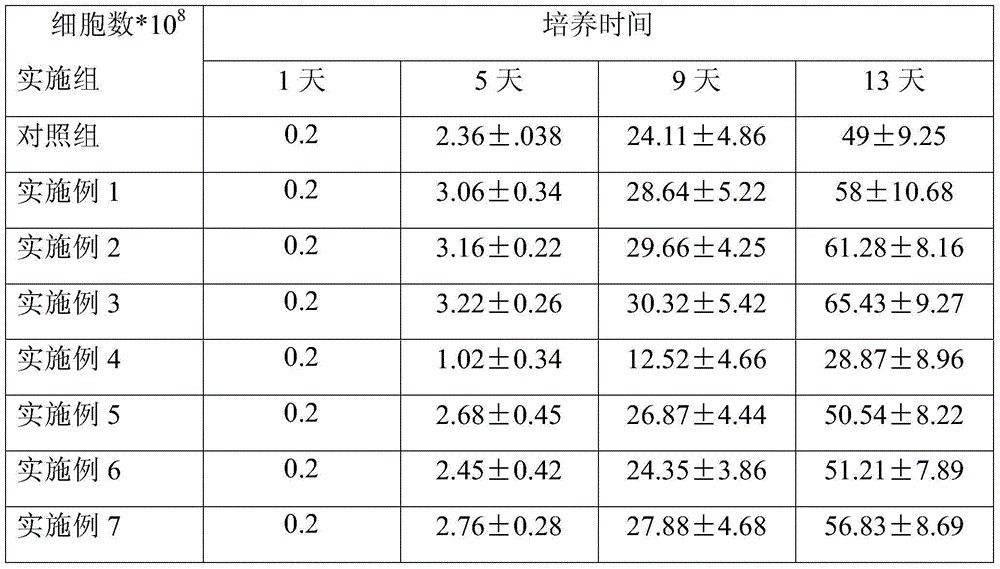
Cryoprotective agent of peripheral blood mononuclear cells and preservation method of cryoprotective agent
ActiveCN104082277AImprove survival rateImprove cell activityDead animal preservationPeripheral blood mononuclear cellMotility
The invention discloses a cryoprotective agent of peripheral blood mononuclear cells. The cryoprotective agent is prepared from the following ingredients in parts by weight: 43-53 parts of a culture medium, 30-40 parts of auto-plasma, 12-17 parts of dimethyl sulfoxide, 5-7% of human serum albumin, and the balance being 0.17-0.23mol / L trehalose. The invention discloses a preservation method of the cryoprotective agent. The preservation method comprises the steps of collecting fresh anticoagulation blood, preparing peripheral mononuclear cells into cell suspension by using human serum albumin, adding the cryoprotective agent with the same volume as that of the cell suspension, mixing uniformly, preserving for 10-20h at below 90-below-70-below DEG C, and preserving in liquid nitrogen. According to the cryoprotective agent and the preservation method thereof, a cryopreserved cell has the high motility rate and the strong cell activity and can shorten the Cytokine Induced Killer (CIT) cell induced amplification period.
Owner:CHENGDU QINGKE BIOTECH
Natural plant whitening soap
InactiveCN102311892ATo promote metabolismImprove cell activitySoap detergent compositionsFungicideChemistry
The invention discloses a natural plant whitening soap, which contains the following components: 9-13% of aloe glue, 25-40% of plant whitening liquid, 40-54% of grease substance, 5-10% of strong base substance, 2-3% of sodium chloride, 0.5-0.8% of fungicide, and 0.2-0.7% of germicide. The soap provided by the invention has functions of diminishing inflammation, sterilizing and protecting the skin, and also has remarkable effects of eliminating speckle and whitening the shin; and the soap has the capabilities of whitening, smoothening and refreshing the skin after used for a long time.
Owner:李正全
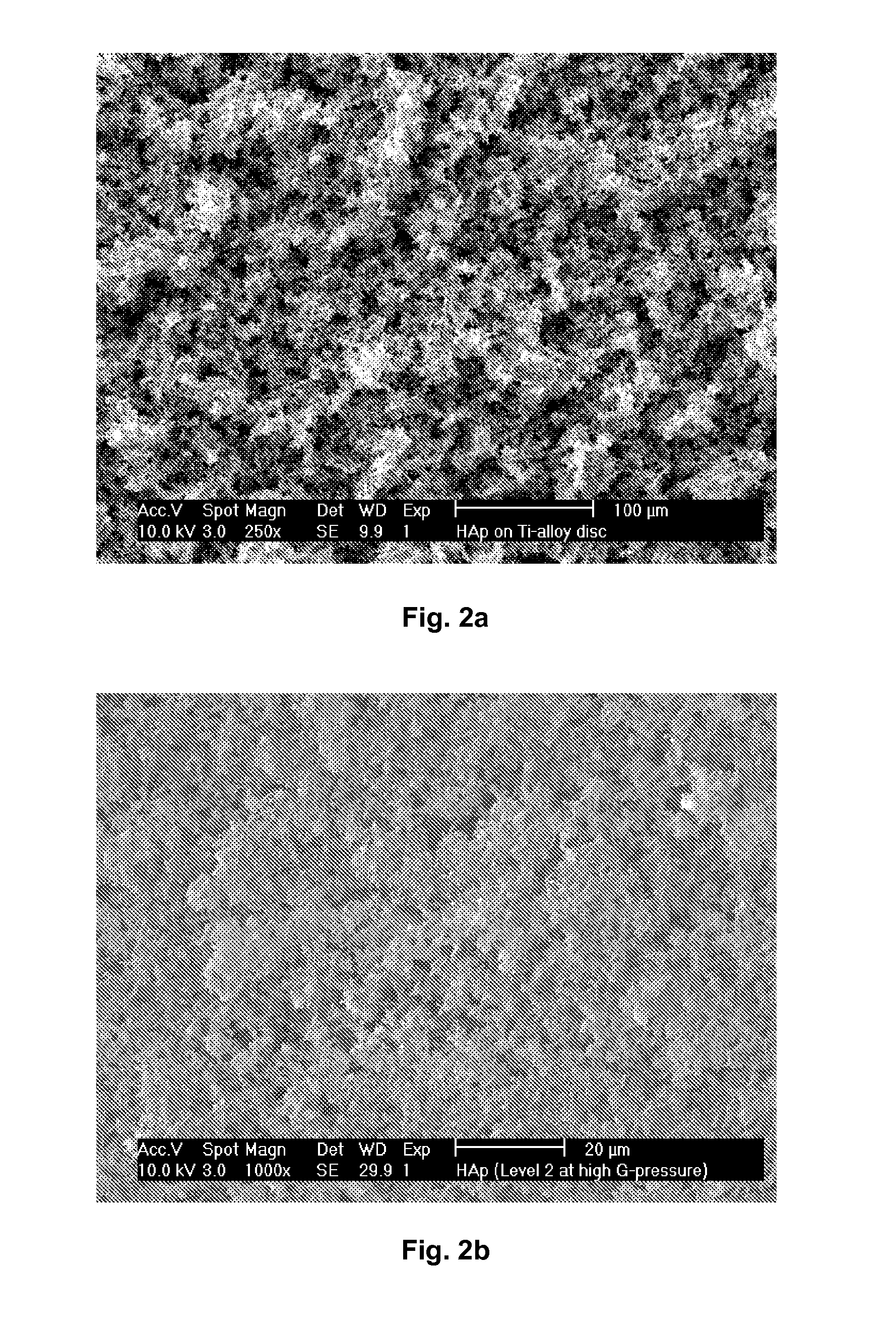
Nanostructured Hydroxyapatite Coating for Dental and Orthopedic Implants
ActiveUS20120276336A1Reduces HAp dissolutionIncrease deposition rateSpecial ornamental structuresPharmaceutical delivery mechanismOsseointegrationApatite
A high-strength coating for dental and orthopedic implants utilizing hydroxyapatite (HAp) nanoparticles provides for a high level of osseointegration through a range of surface pore sizes in the micro- to nanoscale. Zinc oxide (ZnO) nanoparticles may be incorporated with the HAp nanoparticles to form a composite coating material, with ZnO providing infection resistance due to its inherent antimicrobial properties. A textured surface, consisting of “islands” of roughly square coating structures measuring about 250 μm on a side, with spacing of 50-100 μm therebetween, may further promote the osseointegration and antimicrobial properties of the implant coating.
Owner:P&S GLOBAL HLDG LLC +1
Bone cement containing calcium citrate and preparation method of bone cement
ActiveCN105396175AImproved ability to resist collapseStrong plasticityTissue regenerationProsthesisSolid phasesOrthopedic department
The invention belongs to the field of bone damage repair medicinal materials and particularly relates to a preparation method and application of bone cement containing calcium citrate. The bone cement containing calcium citrate is composed of a solid phase part and a liquid phase part, the solid phase part is formed by compounding the calcium citrate and calcium phosphate salt, and the mass ratio of the calcium citrate to the calcium phosphate salt is (2-5):1; the liquid-solid ratio is (0.5-1.5):1. The bone cement containing the calcium citrate has comprehensive biomedical properties such as good plasticity, bone guidance, bone induction activity, cell activity and good degradation rate and is applicable to the orthopedics department, the thoracic surgery department and shaping and restoration of skull and jaw surfaces.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Cosmetic composition for anti-aging of the skin comprising phaseolus radiatus seed extracts by fermentation and enzyme treatment
ActiveCN102112106APrevent agingLess irritatingCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsIrritationAdditive ingredient
Provided is a cosmetic composition for skin protection containing Phaseolus radiatus extract of fermentation-enzyme treatment, prepared by fermenting Phaseolus radiatus with Saccharomyces cerevisiae or Lactobacillus and treating thereof with protease as an active ingredient, and a make-up method using the same. The Phaseolus radiatus extract of fermentation-enzyme treatment of the present invention contains higher isoflavone and has activities of increasing skin cell activity, alleviating skin irritation, and accelerating synthesis of skin cell protein such as collagen, so that it brings the effect of improving skin troubles caused by aging and protecting skin as well.
Owner:COREANA COSMETICS
Expression of monoclonal antibodies in ciliate host cells
The present invention is related to a system for the heterologous expression of a monoclonal Antibody (mAb) or a fragment or derivative thereof, said system comprising at least one ciliate host cell, and incorporated, into said ciliate host cell, at least one heterologous nucleic acid molecule encoding for said monoclonal Antibody, or a fragment or derivative thereof.
Owner:CILIAN
Porous bacterial cellulose skin repair material with density structure and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102973985AStrong structural continuityGood biocompatibilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicrosphereSkin repair
The invention relates to a porous bacterial cellulose skin repair material with a density structure and a preparation method thereof. The porous bacterial cellulose skin repair material with the 'upper dense and lower loose' structure similar to human skin is prepared by controlling the culture condition of bacterial cellulose and adding sustained-release microspheres in the culture process. A loose layer is tightly combined with a dense layer, so that obvious physical layering is avoided, and the structural continuity is good; and gradient changes of the structures are produced in the loose layer and the dense layer, and multiple pores distributed uniformly are formed in the loose layer, so that the upper dense and lower loose gradient structure of the human skin is simulated to the utmost degree. Cells easily enter the material, the healing period of a wound is obviously shortened, and proliferation of healed scars is effectively reduced; and good air permeability and water holding property of the bacterial cellulose are kept, the wound surface can be kept in a wet environment, and healing of the wound surface is facilitated. The forming process is simple, the culture period is short, the preparation process is environment-friendly, simple, convenient and quick, and the preparation cost is low.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Efficient culture method of CIK (cytokine induced killer) cells
InactiveCN103525763AProliferate fastIncrease the number of cellsBlood/immune system cellsHigh cellPeripheral blood mononuclear cell
The invention aims to provide an efficient culture method of CIK cells. The prepared CIK cell has the characteristics of high multiplication speed, large cell quantity, high cell viability, high killing capacity on cancer cells and the like. The efficient culture method mainly characterized in that a culture flask coated with laminin and fibronectin is used for culturing PBMCs (peripheral blood mononuclear cells), and the cells can be in a half-adherence state by means of the absorption effect of the two kinds of protein, accordingly, the cells can be stimulated by various factors, and the two kinds of protein can promote CIK cell multiplication; and with the adoption of an anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody, the co-stimulation signal of a T cell subset in the CIK cells can be stimulated, and the activation of the CIK cells is promoted. So far, a research report on jointly using laminin, fibronectin and the anti-CD28 monoclonal antibody to prepare the CIK cells is absent. The method for increasing the cell number and improving the killing activity by adding the three factors during preparation of the CIK cells is firstly provided.
Owner:青岛麦迪赛斯生物科技有限公司
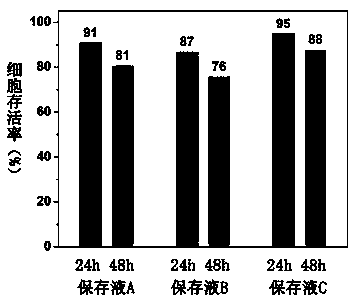
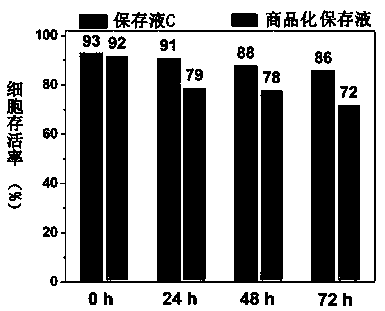
Preserving fluid and preserving method for maintaining high cell activity of tissue sample
InactiveCN111418581AImprove cell activityHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementDead animal preservationHigh cellFresh Tissue
The invention provides a preserving fluid and a preserving method for maintaining high cell activity of a tissue sample, wherein the preserving fluid comprises the components: ion buffer solution components, carbohydrate components,, components avoiding the generation of ice crystals in and out solutions of tissue cells at a low temperature of 0-6 DEG C, components providing supplement, antioxidant and anti-apoptosis components for anabolism of the tissue cells; the preserving fluid has good biocompatibility, does not contain toxic or harmful components, and also does not contain components such as animal-derived protein, antibiotics and hormones influencing tissue gene expression. Different from traditional ultralow-temperature cryopreservation (-80 DEG C), the cryopreservation method disclosed by the invention can effectively realize low-temperature storage (0-6 DEG C) of fresh tissue samples of human beings and animals, maintains high cell activity of tissues, maintains tissue morphology, and is used for preservation and transportation of the tissue samples. Meanwhile, the nucleic acid integrity of the tissue and the stability of gene expression can be effectively maintained, the original state of the tissue is maintained, and the method can be used for gene detection, scientific research and other related experiments.
Owner:上海伯豪生物技术有限公司
Serum-free and DMSO-free cell cryopreservation solution and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN110934132AHigh biosecurityHigh clinical application prospectsDead animal preservationHydroxyethyl starchCytokine
The invention discloses a serum-free and DMSO-free cell cryopreservation solution, which comprises a 16.762-16.825 g / L DMEM / F-12 basal culture medium, 32-34 mg / L cytokines, 0.2-0.8 mg / L hydroxyethyl starch, 1-3 mg / L vitamins, 0.15-0.16 g / L antibiotics, 5-6 mg / L protein polypeptide, 1-4 mg / L lipids and a 0.1-0.41 g / L intracellular and extracellular cryoprotectant. According to the technical scheme,the obtained cell cryopreservation solution does not contain serum or DMSO components, the components of the formula are determined, the cell cryopreservation solution has high biological safety andclinical application prospects, and the cell cryopreservation liquid has a cell recovery survival rate of more than 85%, can maintain good cell activity and good physiological characteristics, and issuitable for the related research fields of primary cells and stem cells.
Owner:苏州君欣生物科技有限公司
Methods and Compositions for Treating Obesity
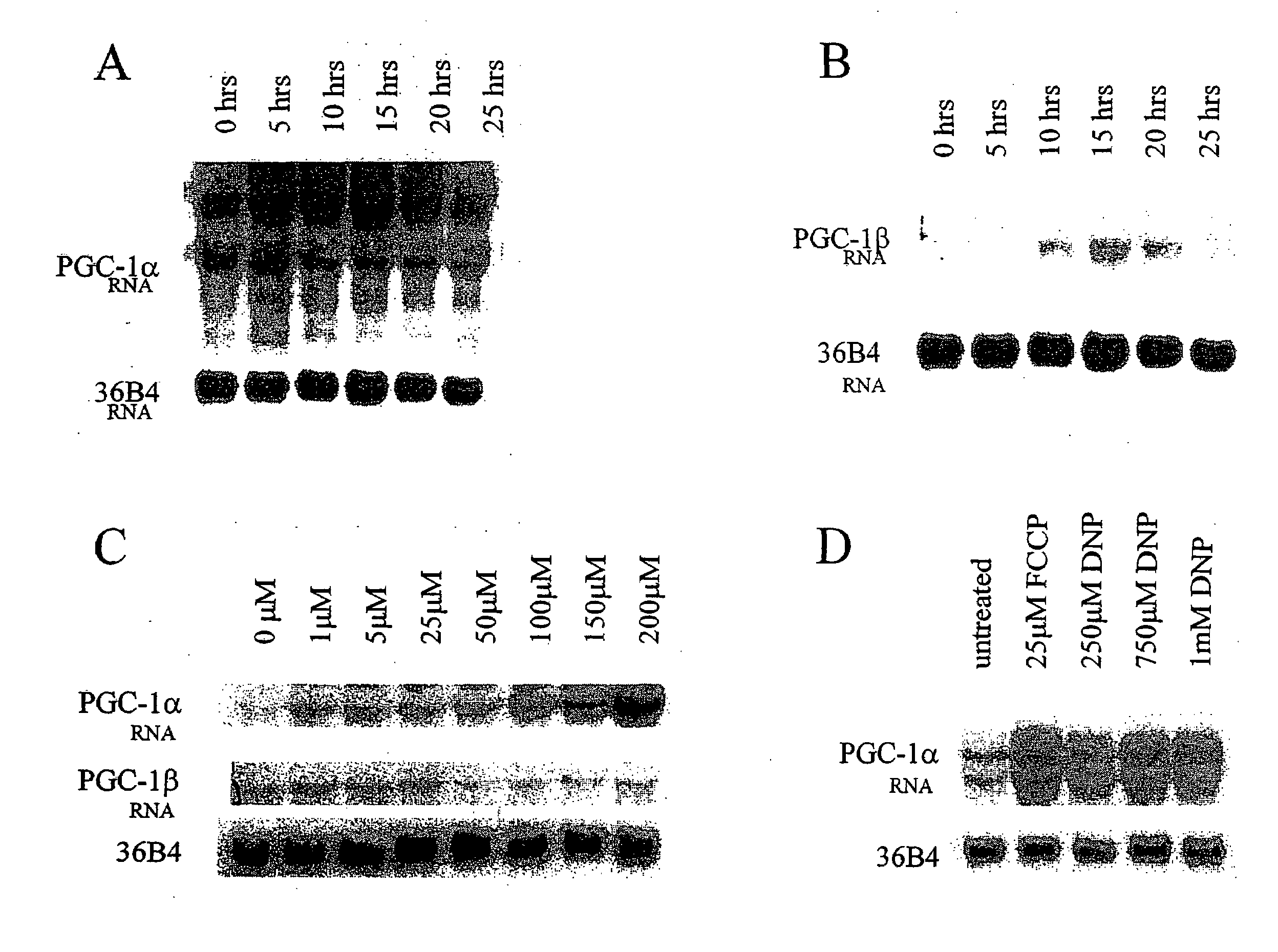
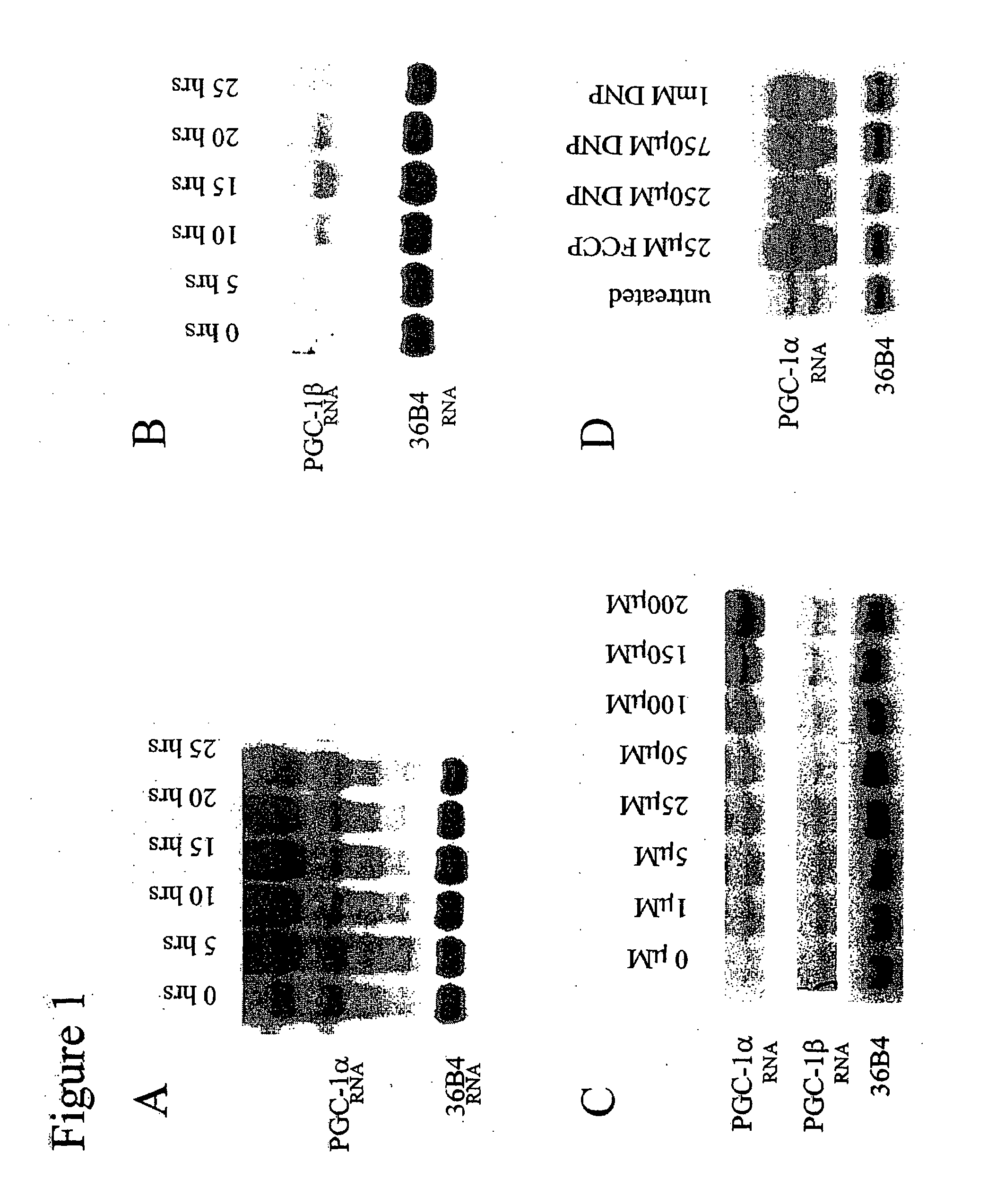
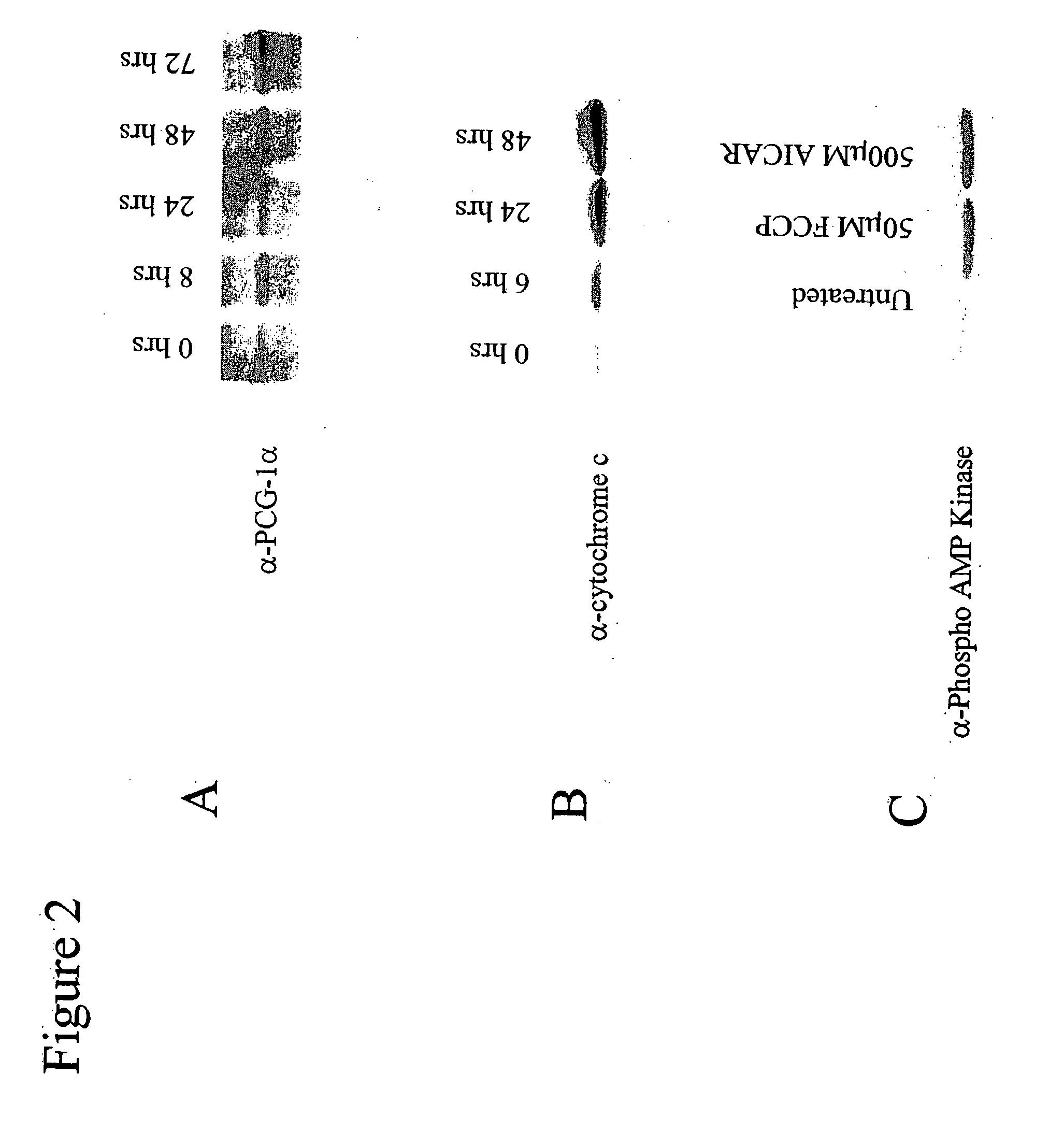
InactiveUS20080262093A1Improve cell activityCompounds screening/testingBiocideUncoupling AgentsAnti obesity
The present invention relates to therapeutic compositions for treating or preventing obesity and obesity-related disorders in a subject. The present invention also relates to the use of PGC-1 expression levels to determine the safe dosage range for known or putative respiration uncoupling agents for use as anti-obesity therapeutics. The present invention further relates to methods for identifying new compounds that have respiration uncoupling activity.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Method for restoring totipotency of mesenchymal stem cell
ActiveCN103667186ARecovery propertiesAchieve maintenanceSkeletal/connective tissue cellsMesenchymal stem cellCultured cell
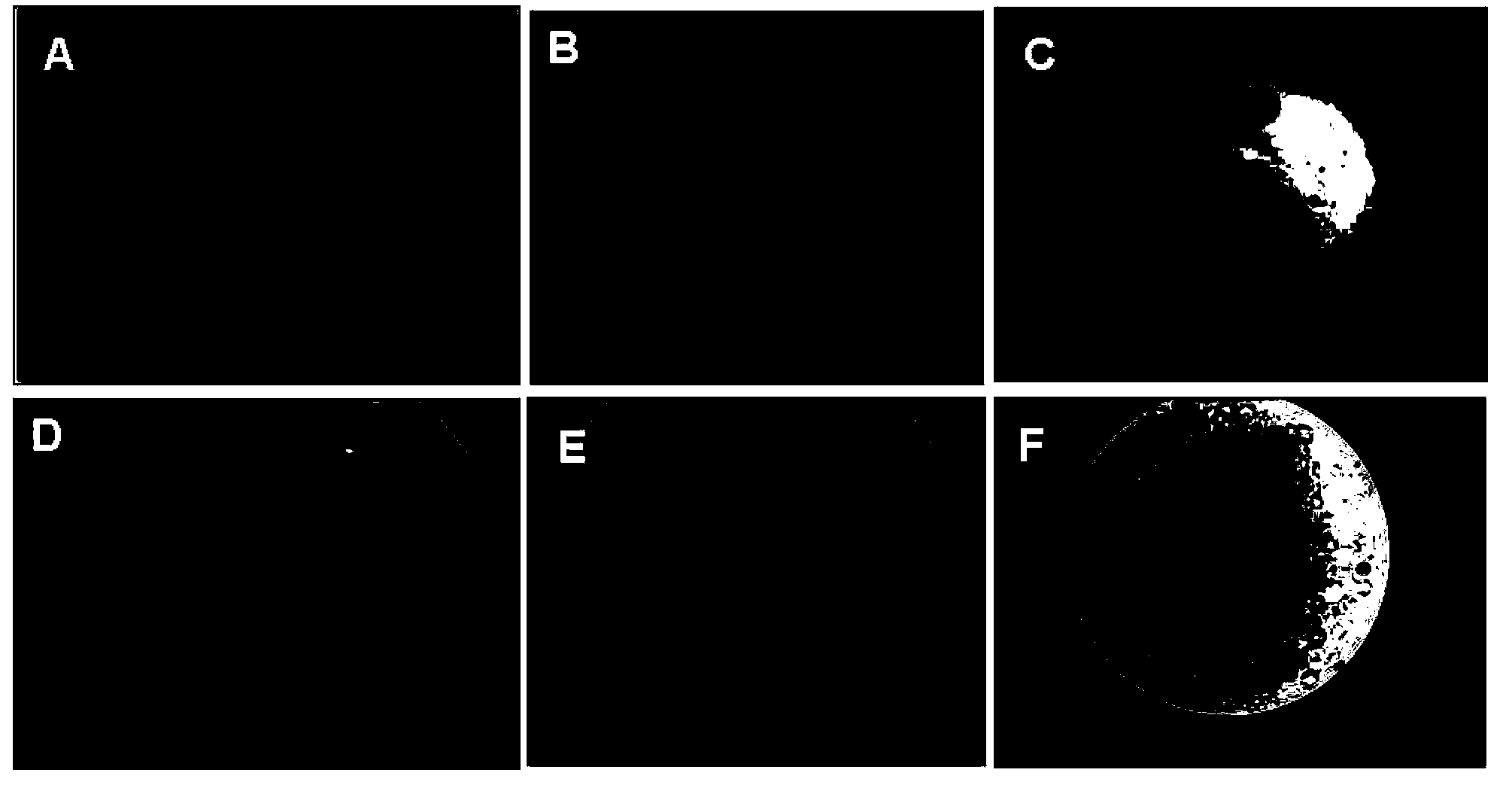
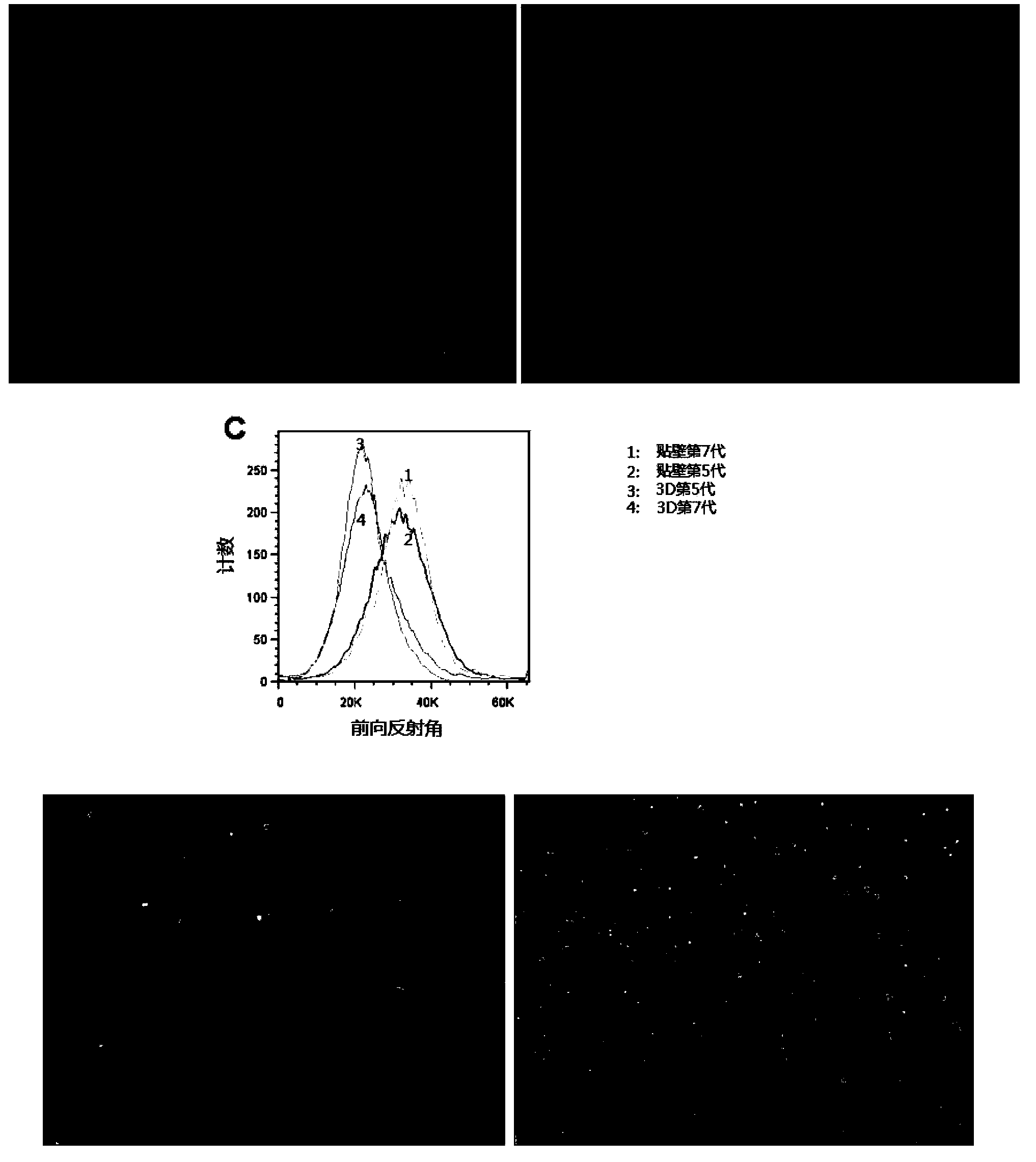
The invention discloses a culture method for restoring totipotency of a mesenchymal stem cell. The method for restoring totipotency of a mesenchymal stem cell, provided by the invention, comprises the following steps: 1) performing hanging-drop culture on an in-vitro mesenchymal stem cell with reduced totipotency, thus obtaining a hanging-drop cultured cell; and 2) further performing suspension culture on the hanging-drop cultured cell, thus realizing totipotency restoration of the mesenchymal stem cell. The experiment of the invention proves that, according to the method for restoring totipotency of a mesenchymal stem cell (specifically 3D culture), after the mesenchymal stem cell (in-vitro mesenchymal stem cell with reduced totipotency) subcultured multiple times is subjected to 3D culture treatment, the increased volume is gradually restored, the cell viability is enhanced, the cloning capability and differentiation capability are enhanced, and the paracrine action is also improved, thereby activating the aged mesenchymal stem cell and restoring the characteristics of the stem cell.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Method for efficientlyobtaining mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord tissues
InactiveCN106282104AImprove cell activityReduce acquisition timeCulture processSkeletal/connective tissue cellsWater bathsSerum free
The invention relates to amethod for efficientlyobtaining mesenchymal stem cells from umbilical cord tissues and aims at solving the problems of the long obtaining time and low efficiency of an existing method. The method comprises the steps that primary isolation of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells is performed: cleaned and cut umbilical cord tissue blocks are predigested by using trypsin and then digestive juice is removed, repeated flushing is performed with DPBS, then digestion is performed on a water bath shaker of 37 DEG C by using collagenase I digestive juice, a complete culture solution is added to the filtrate filtered by a cell strainer to terminate digestive centrifugal separation so as to obtain primary mesenchymal stem cell; residual tissue blocks are collected after filtration, and re-digestion is performed to obtain primary mesenchymal stem cells; the mesenchymal stem cells are inoculated in the complete culture solution, and standing and culture is performed in 5% CO2 culture box at the temperature of 37 DEG C; a culture solution is replaced for one time at intervals of several days; culture multiplication is performed: when the primary cells grow to be 80% and converge, TrypLE heavy suspension cells are subjected to culture multiplication in a serum-free culture solution. The method has the advantages of efficiently obtaining mesenchymal stem cells, and the obtained mesenchymal stem cells have highcell activity and differentiation potential.
Owner:中卫华医(北京)生物科技有限公司 +1
Adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transport protection solution and application thereof
InactiveCN108056095AHigh cell viabilityImprove stability and cell viabilityDead animal preservationSkeletal/connective tissue cellsBiologyHydroxyethyl starch
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, provides a stem cell transport protection solution and particularly relates to an adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transport protection solution suitable for long-distance transport. The stem cell transport protection solution is prepared from 10 to 30 percent DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide), 50 to 150 mu g / mL streptomycin, a 50 to 80 percentDMEM (Dulbecco modified eagle medium) and 8 to 20 percent HES (hydroxyethyl starch). The adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cell transport protection solution has the advantages that the stability of cells and the activity of the cells may be maintained, and convenience is brought to storage and long-distance transport.
Owner:重庆斯德姆生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com