Tumor burden as measured by cell free DNA
A PD-L1, cancer technology, applied in the direction of anti-tumor drugs, measuring devices, microbial measurement/inspection, etc., can solve the problems that cannot be effectively eliminated
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0136] Materials and methods
[0137] Patient samples. Plasma Samples Obtained from Patients Enrolled in a Phase 1 / 2 Clinical Trial to Evaluate the Safety, Tolerability, and Pharmacokinetics of an Anti-PD-L1 Antibody (Durvalumab) in Subjects with Advanced Solid Tumors . Plasma samples from 28 patients with lung cancer (non-small cell lung cancer) and 29 patients with bladder cancer were obtained during patient screening before treatment (Durvalumab at 10.0 mg / kg) and were obtained at It was reacquired at week 8 after 4 treatment doses (given at week 6).
[0138] ctDNA assay / NGS. Next-generation sequencing and ctDNA testing were performed using the Guardant360 Gene Panel (Guardant Health, Inc., Redwood City, CA). The panel includes 73 genes and provides mutant allele frequencies for each detected SNV, indel, and fusion, and copy number for each detected amplification.
example 1
[0139] Example 1: Reduced ctDNA mean variant allele frequencies observed in reactive NSCLC patients
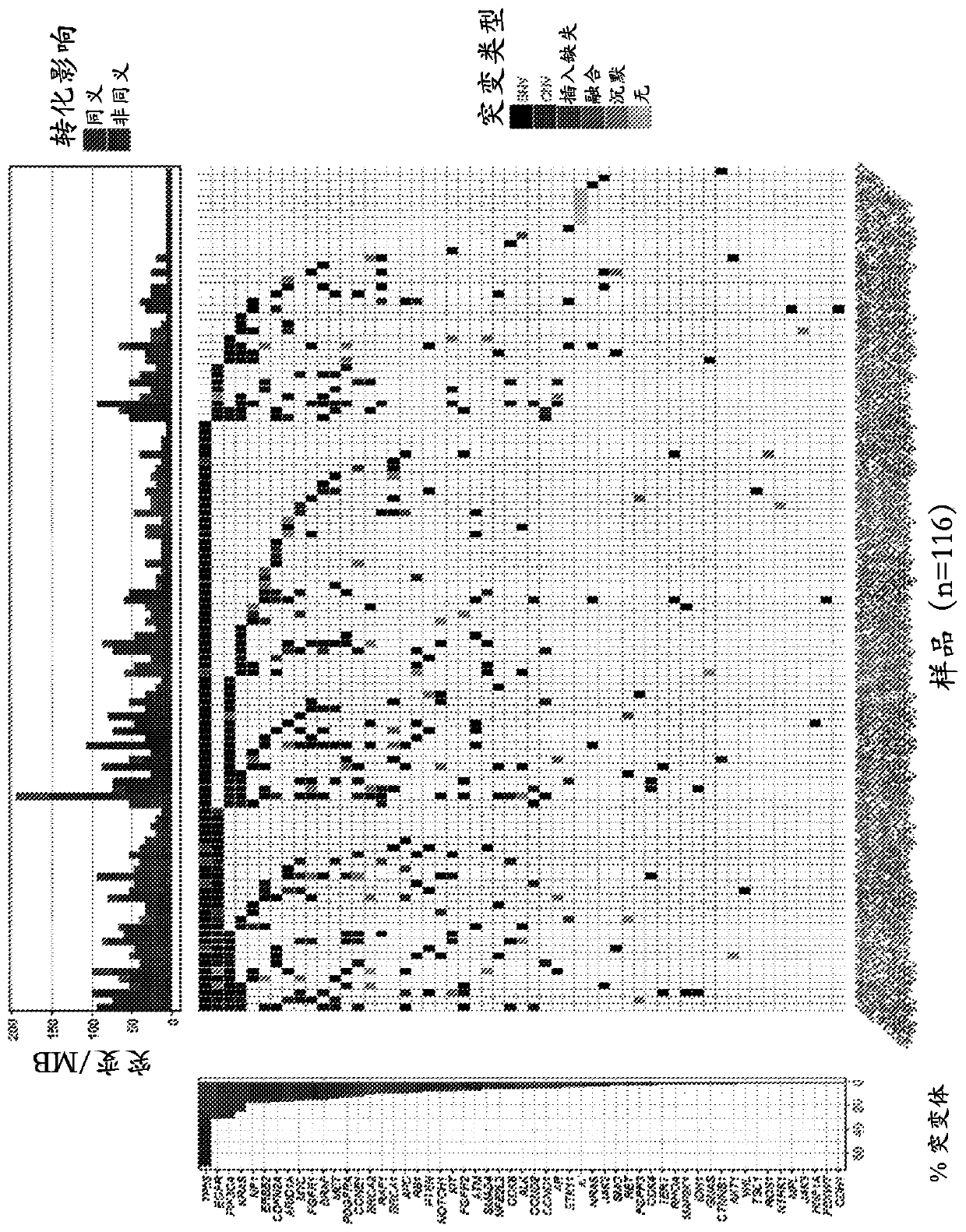
[0140] Analysis of patient samples confirmed that ctDNA was detectable in cell-free DNA isolated from plasma. Analysis of samples obtained from 116 patients during screening identified variants in 96% of samples (111 / 116), with several variants frequently observed, including TP53 (69% of samples), PIK3CA (29% of samples), EGFR (28% of samples), KRAS (24% of samples) and CDKN2A (16% of samples). see figure 1 .
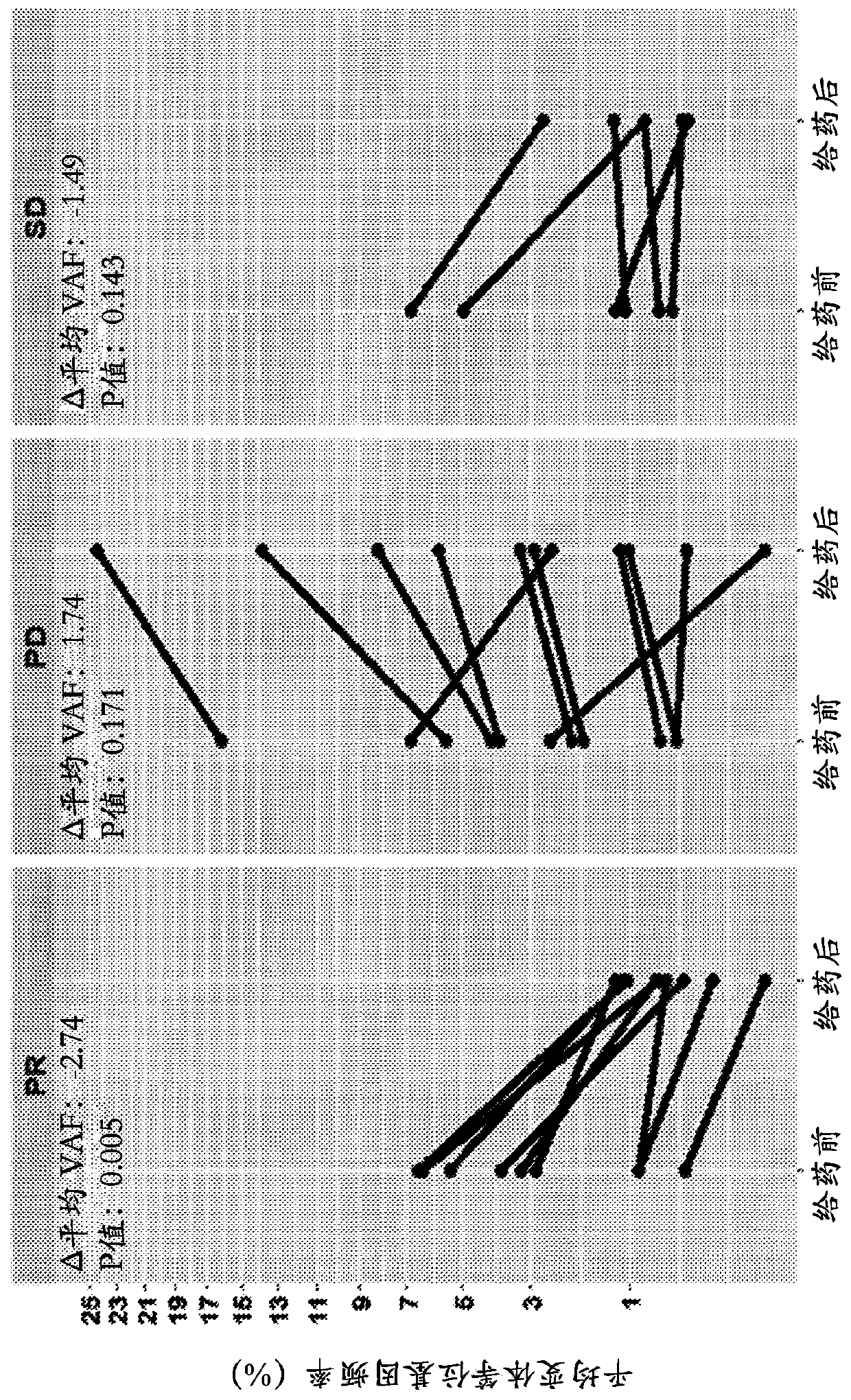
[0141] Changes in mean variant allele frequency (VAF) over the course of treatment correlated with disease progression. After 4 doses / treatment, responding patients (PR) had significantly reduced (-1.6%, p=0.008) ctDNA VAF, while non-responders had an observable increase in mean VAF (+1.4%, p=0.05). see figure 2 , which included SNVs and indels with an allele frequency ≥0.3% at screening, and depicts the probability of PFS and probability of OS for patients who e...
example 2
[0145] Example 2: Reduced ctDNA mutational burden observed in reactive NSCLC patients
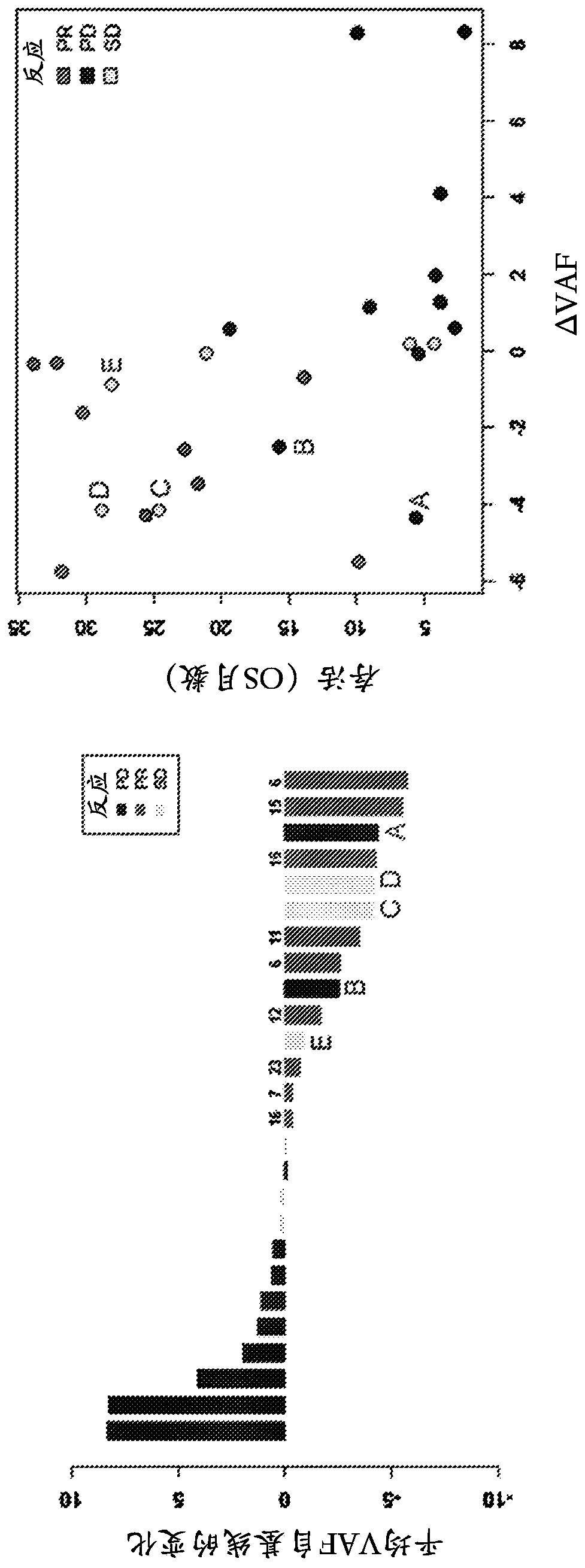
[0146] In addition to the reduction in mean VAF discussed in Example 1, after 8 weeks of treatment, when compared to non-responding (PD / SD) patients (mean difference +1.6, p=0.036, ci(95%)=0.1,3.1) , Responsive patients (PR) exhibited a significant reduction in mutation burden as determined by total mutation counts (mean difference -5.3, p=0.037, and ci (95%)=-10.2, -0.4). see Figure 4 , which plots the total mutation counts at screening (pre-dose) and after dose 4 at week 6 (post-dose).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com