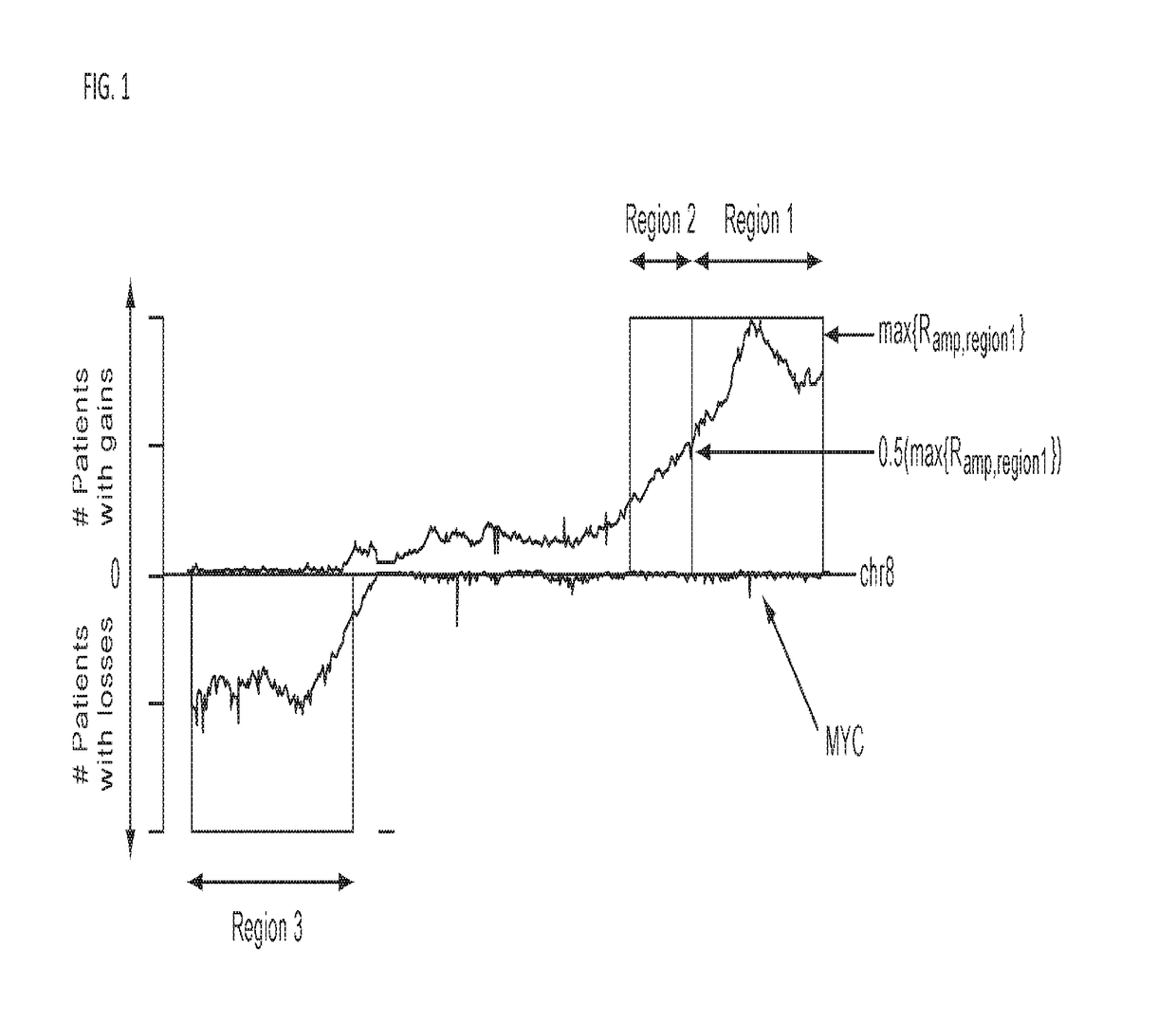
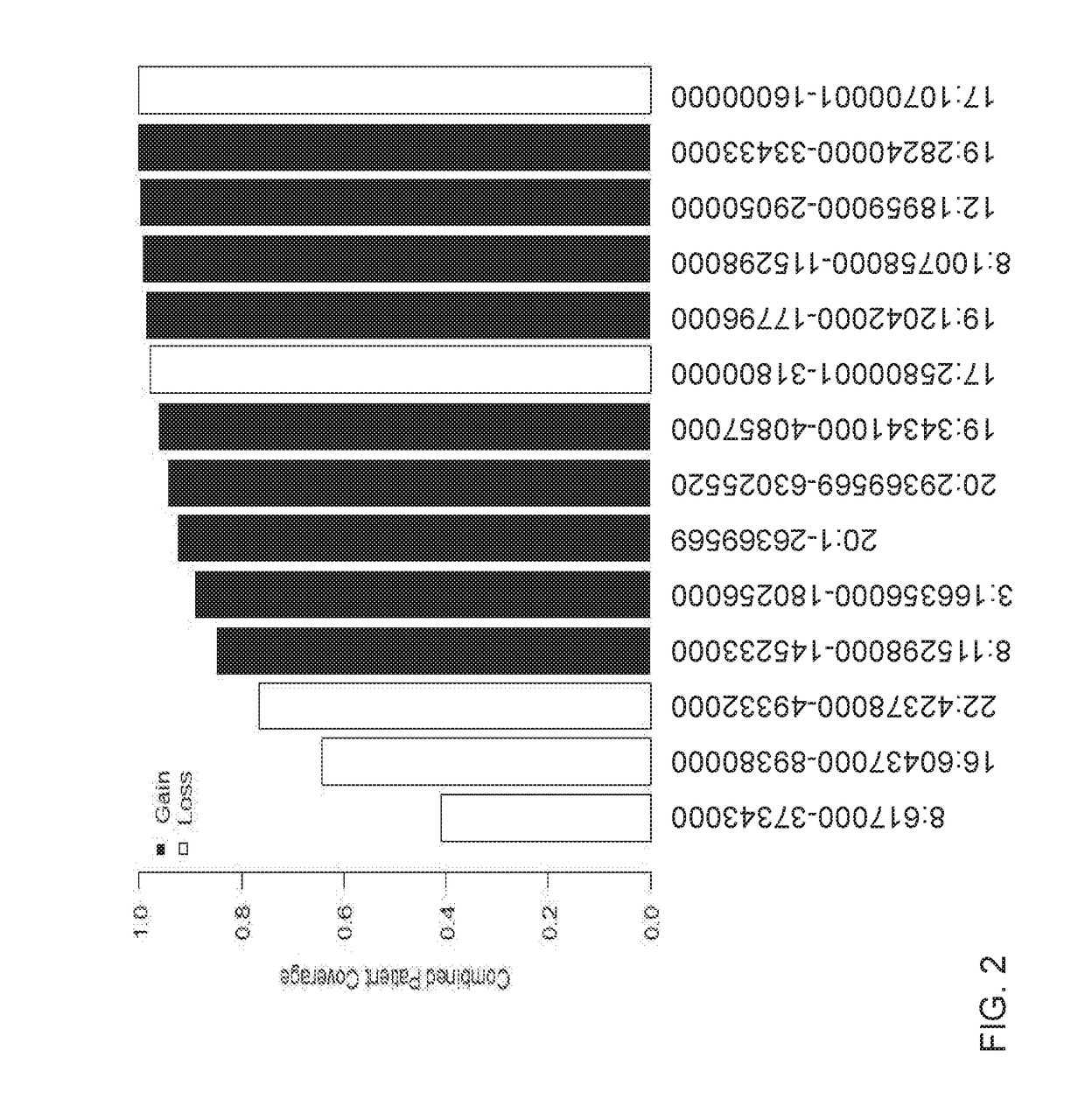
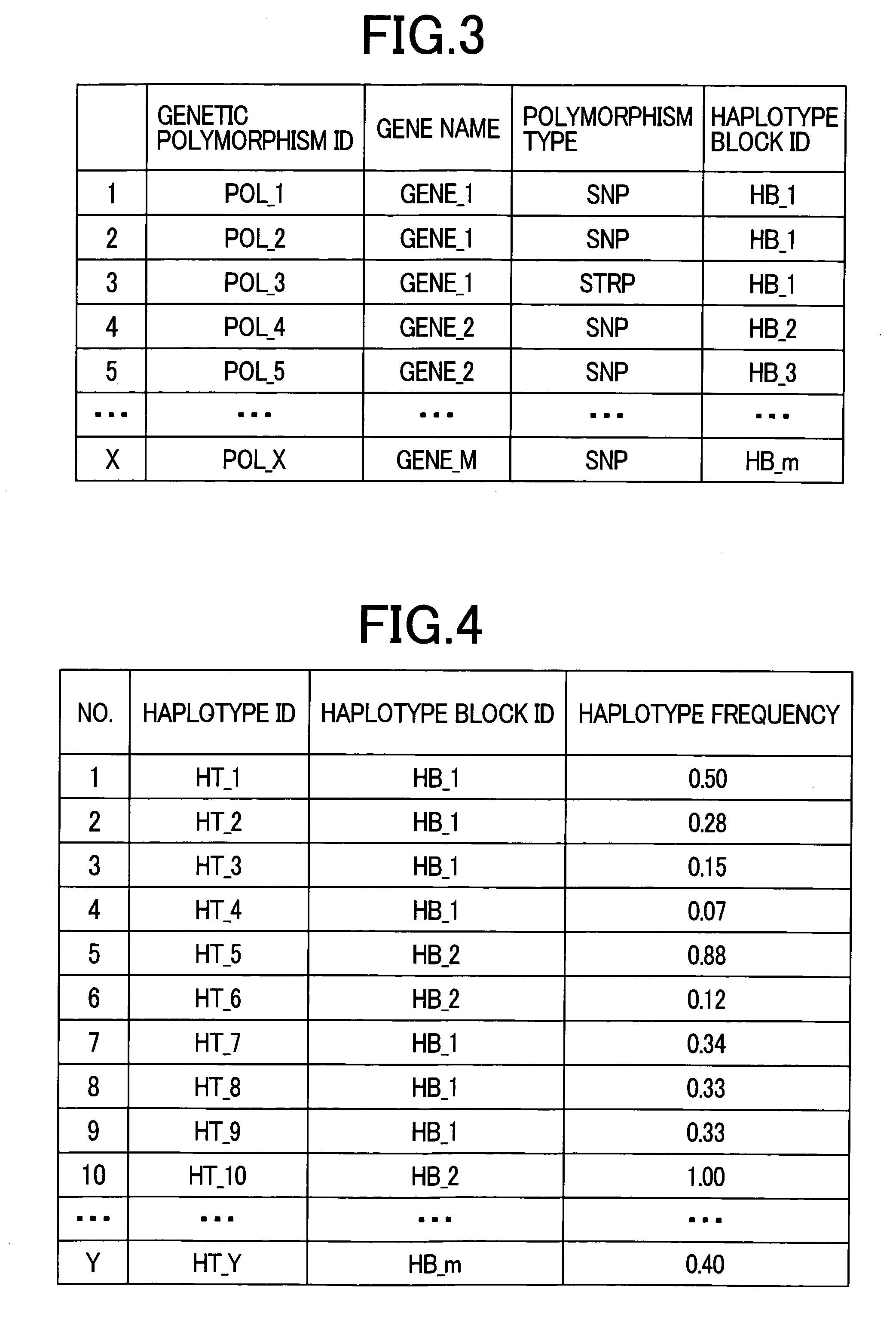
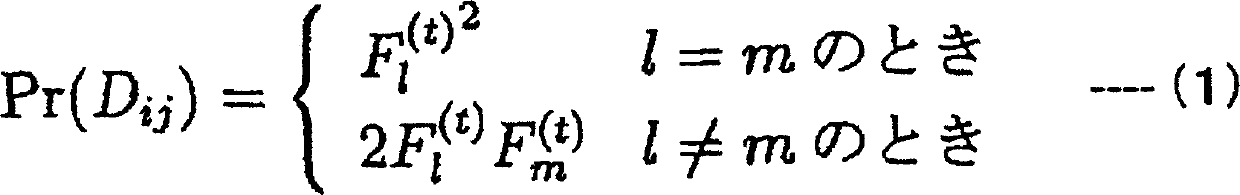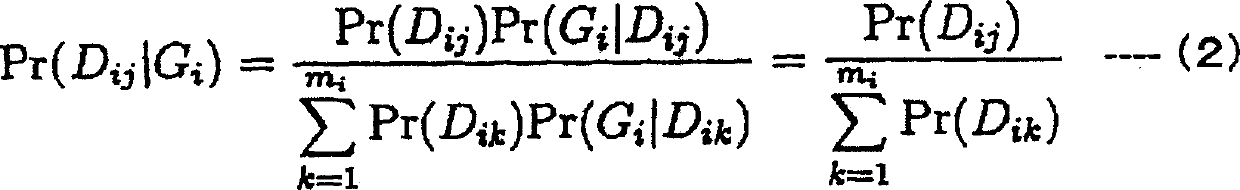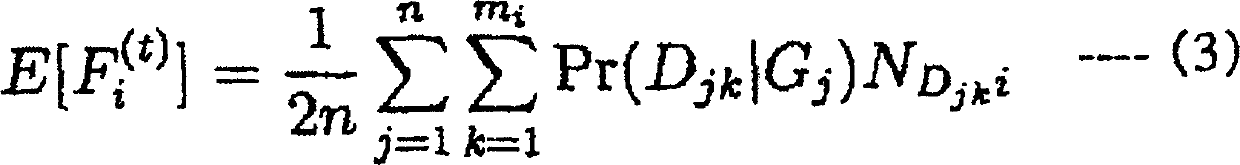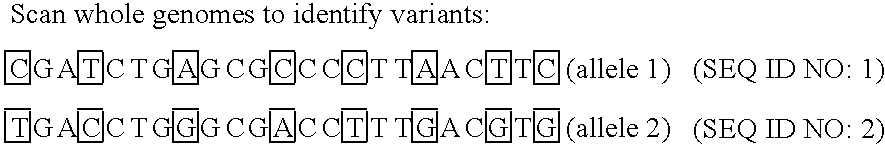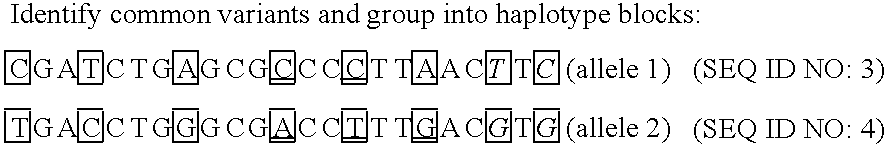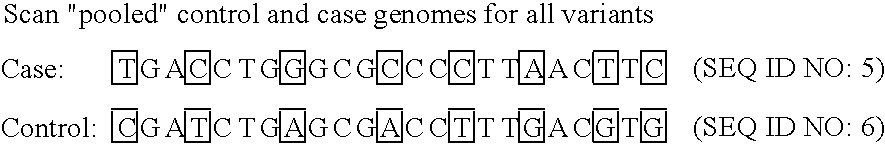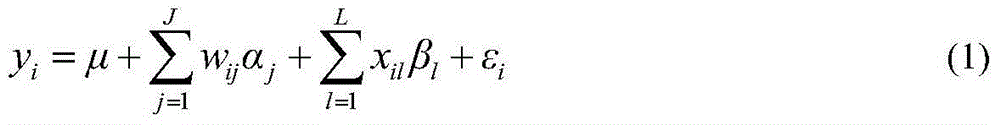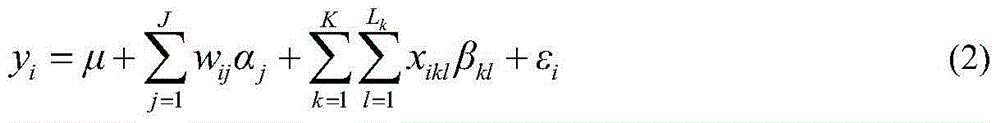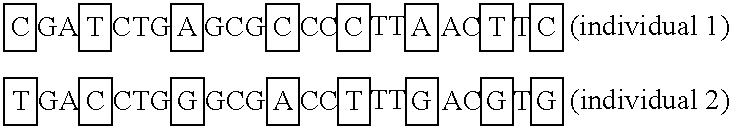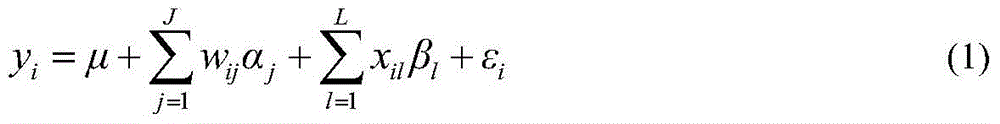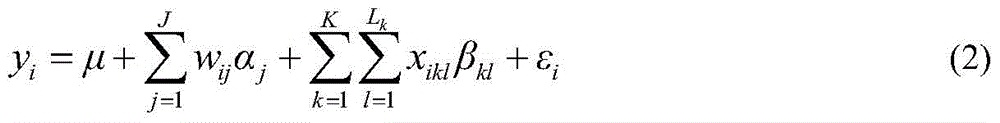Patents
Literature
32 results about "Haplotype block" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
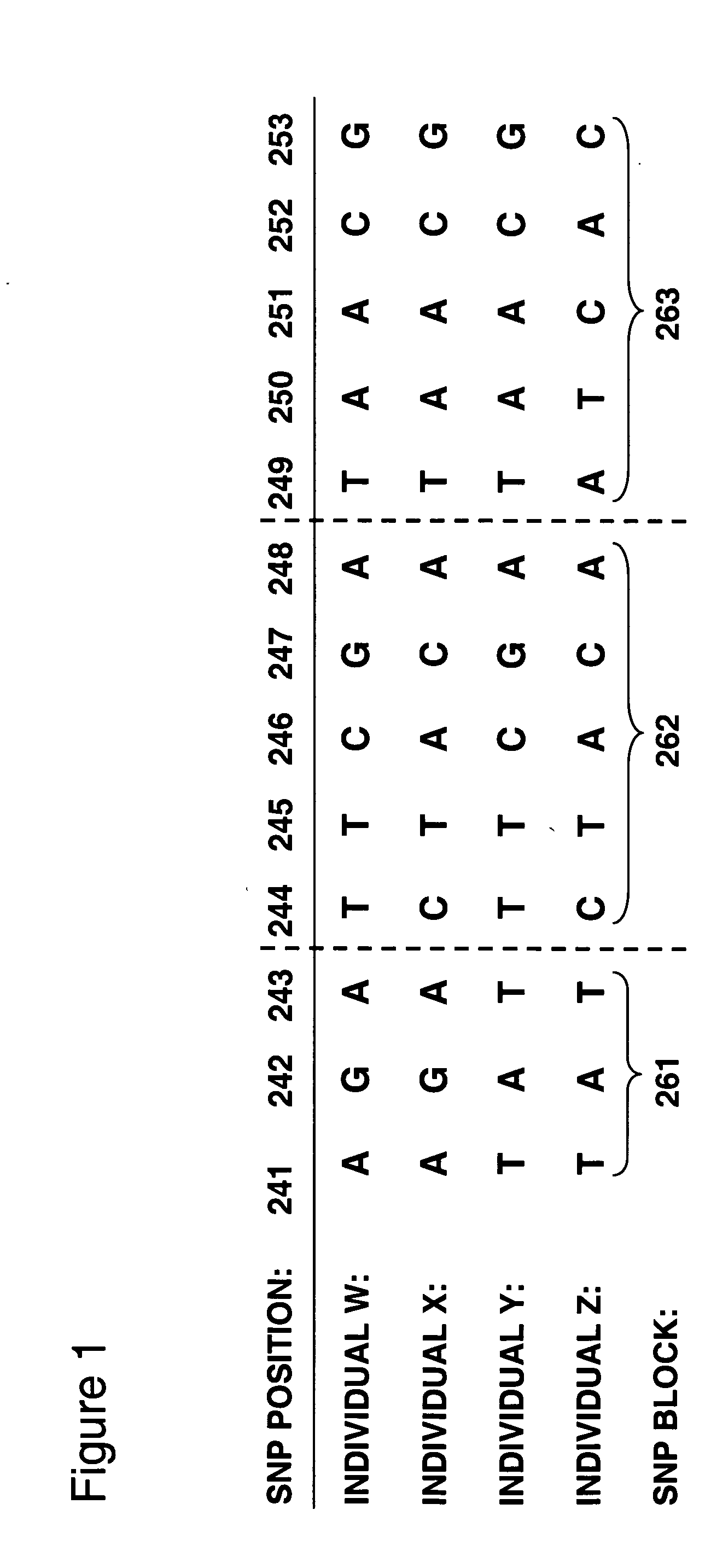
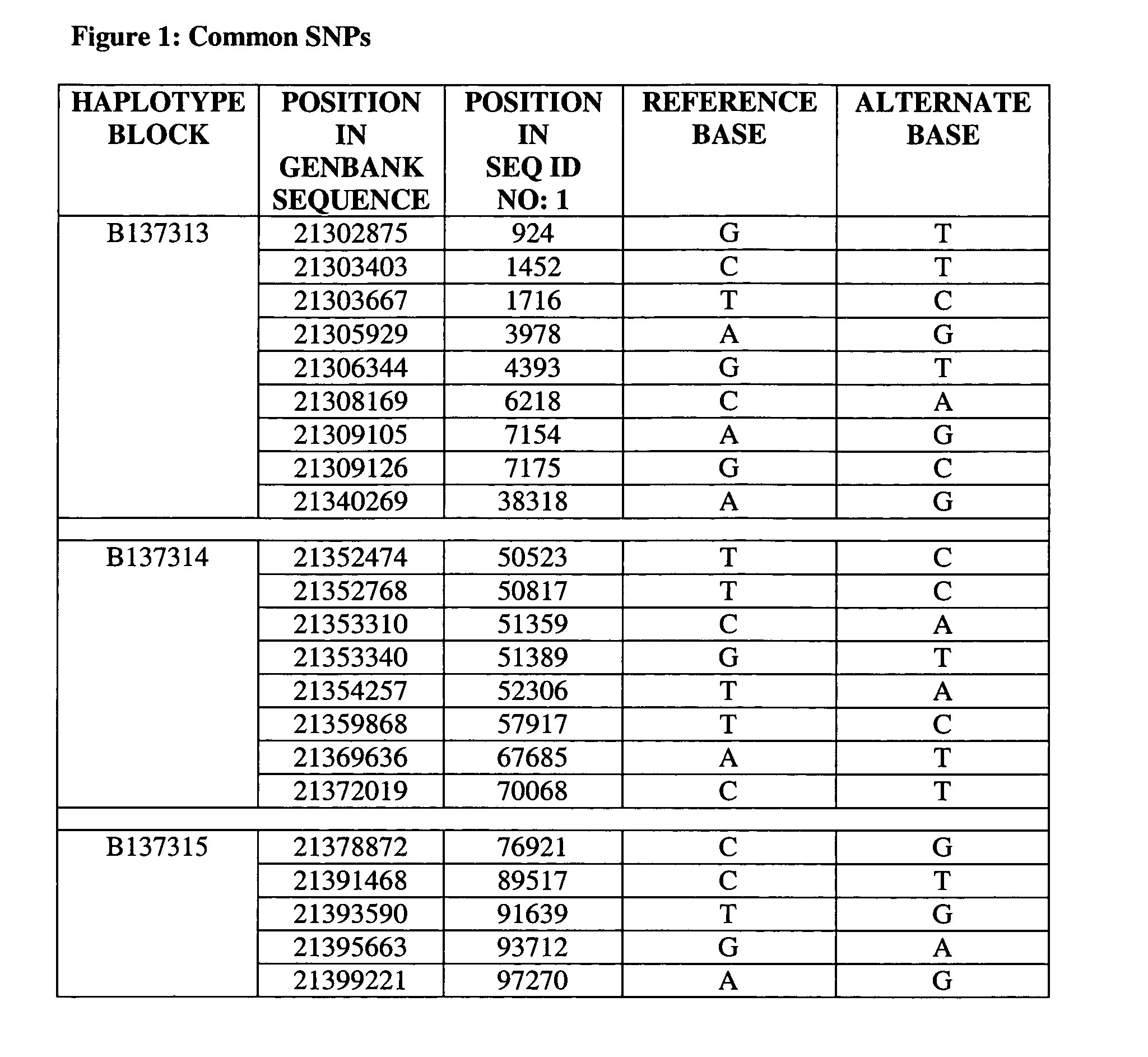
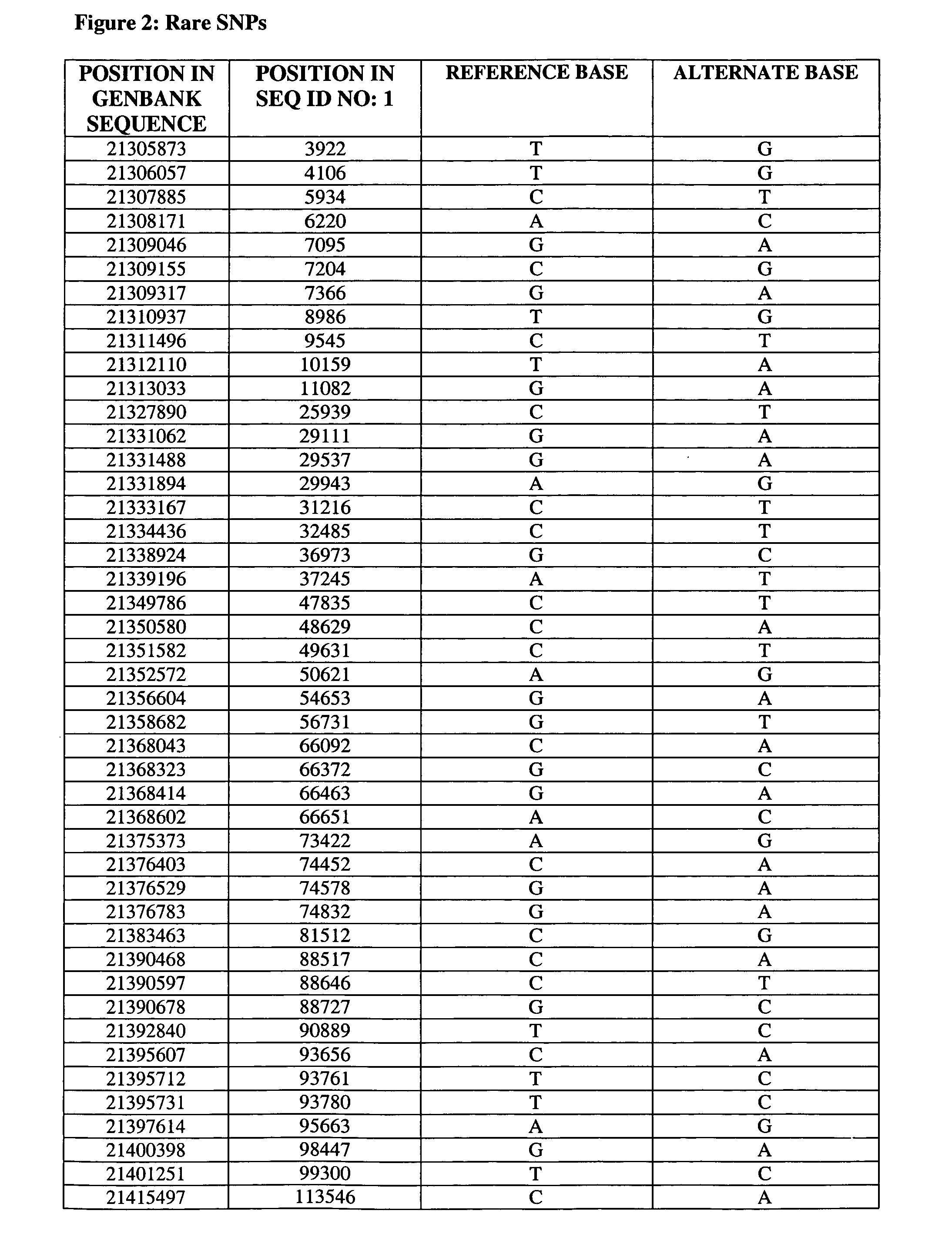
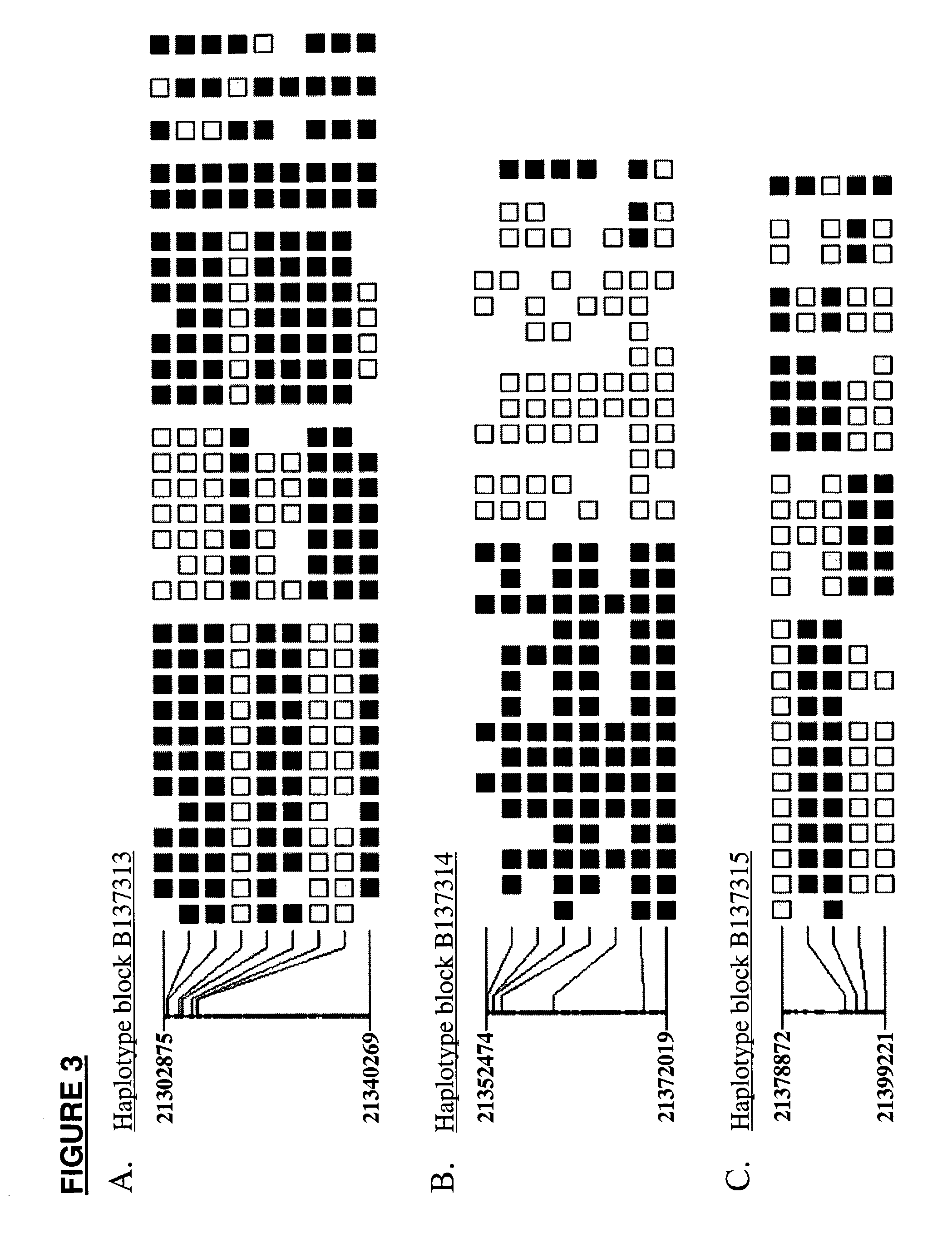
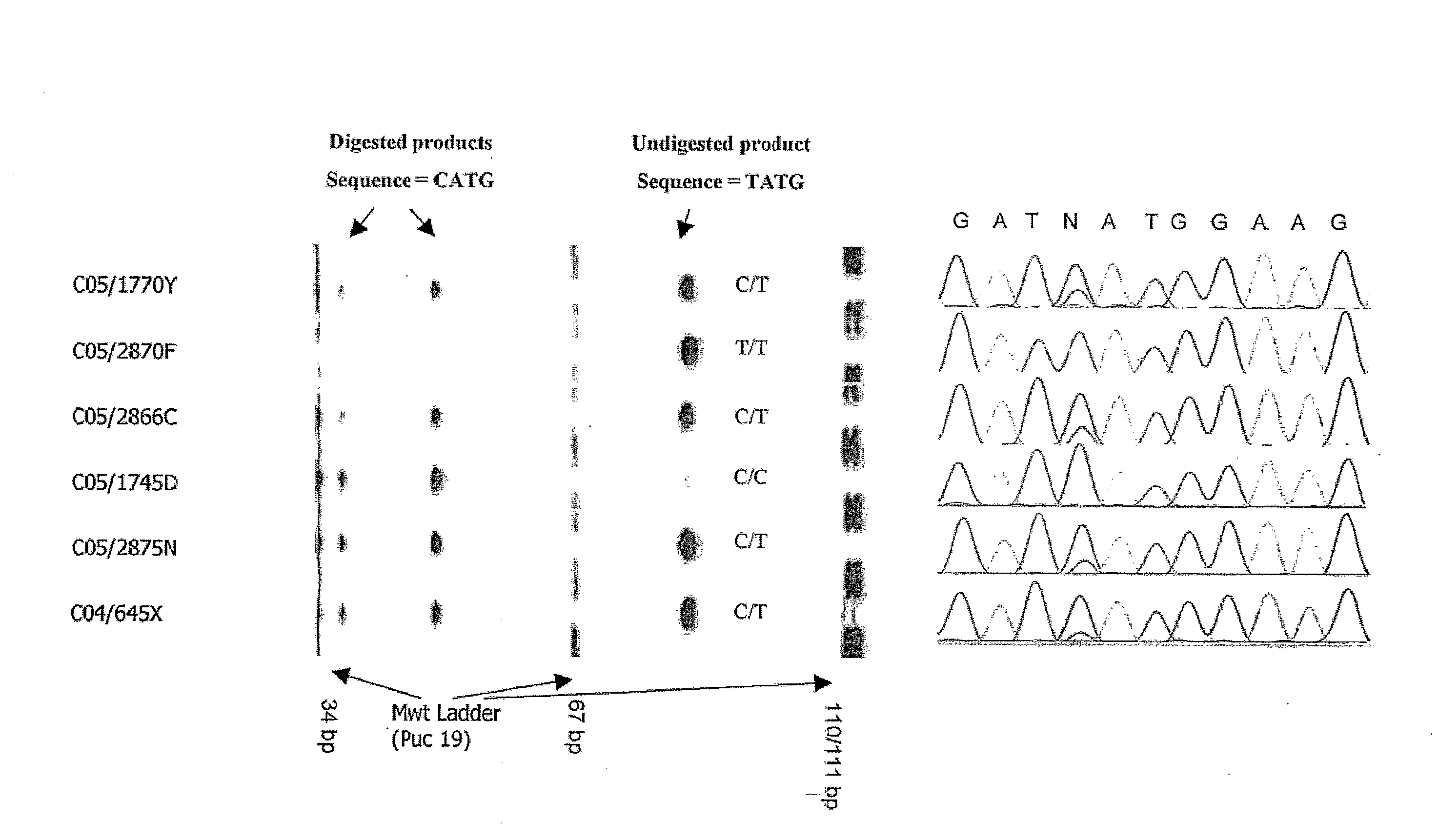
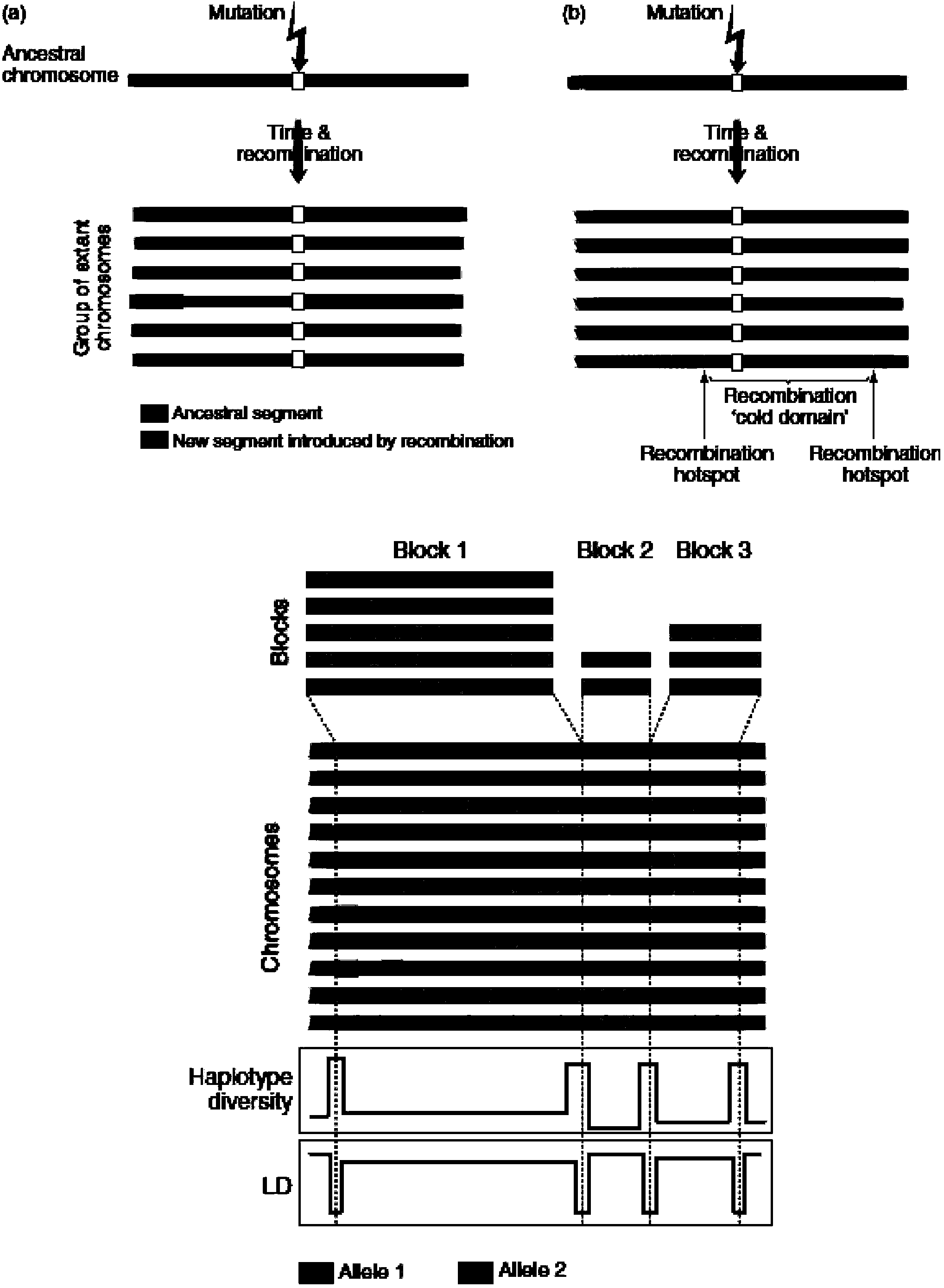
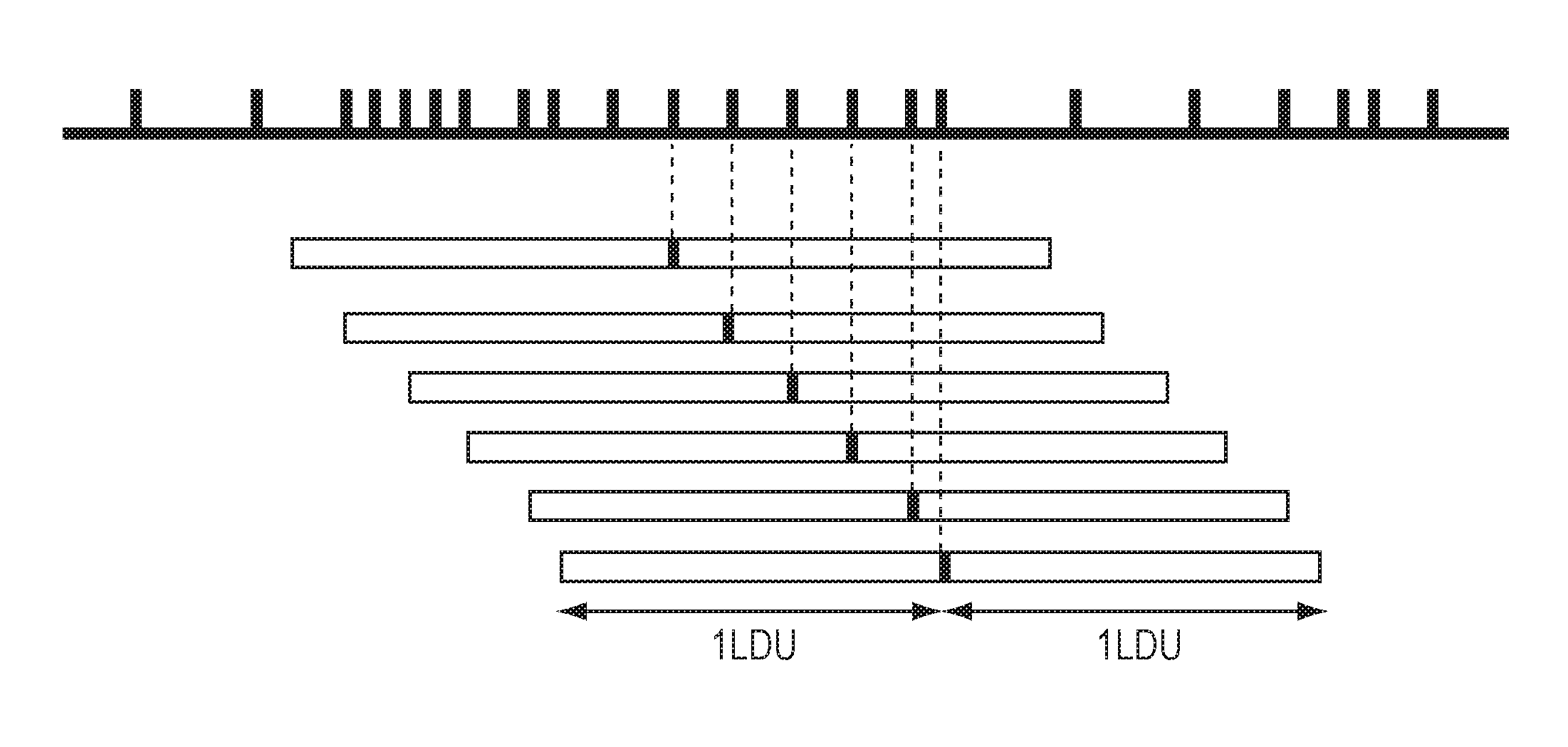
In genetics, a haplotype block is a region of an organism's genome in which there is little evidence of a history of genetic recombination, and which contain only a small number of distinct haplotypes. According to the haplotype-block model, such blocks should show high levels of linkage disequilibrium and be separated from one another by numerous recombination events.
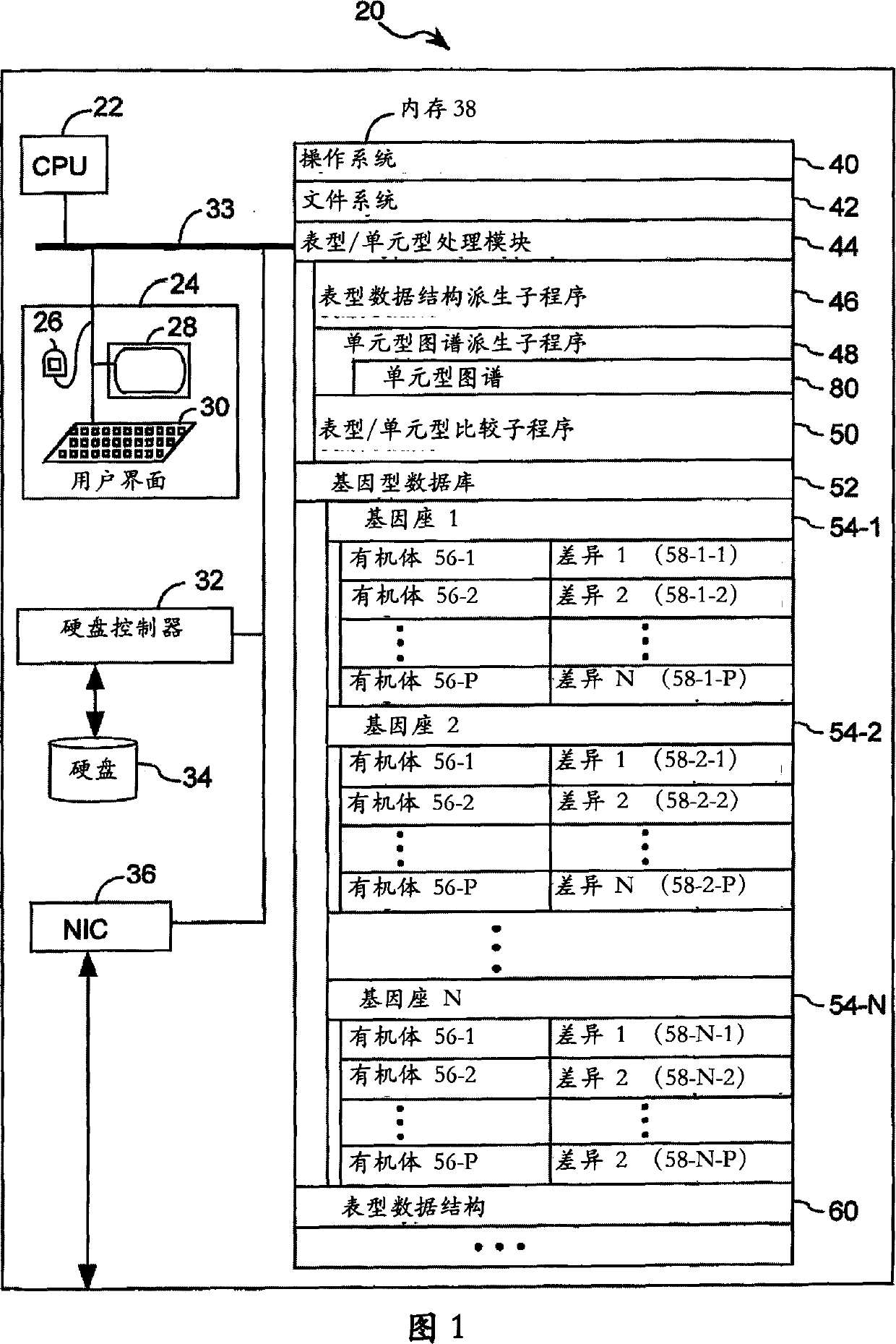
Methods for genomic analysis
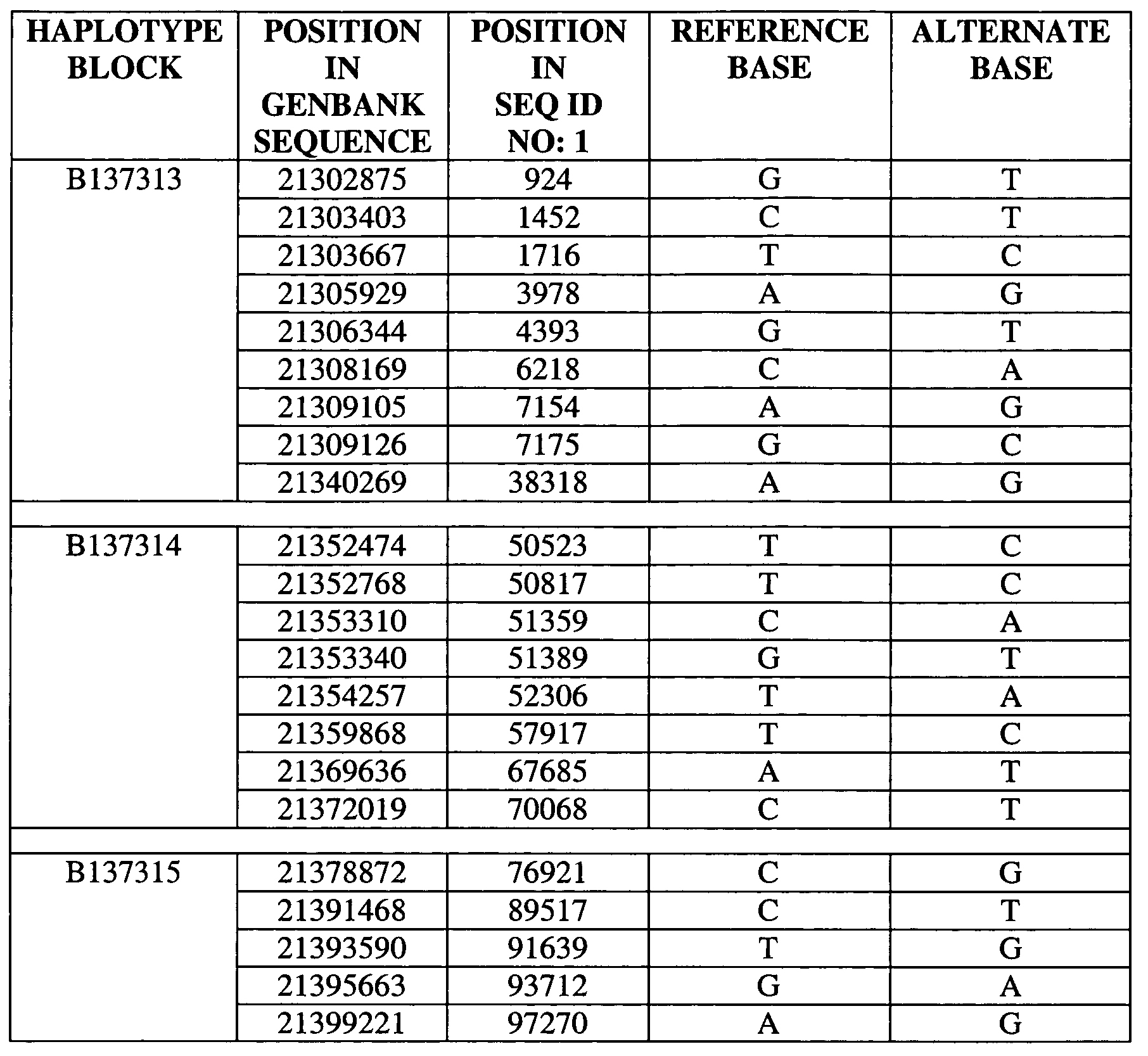
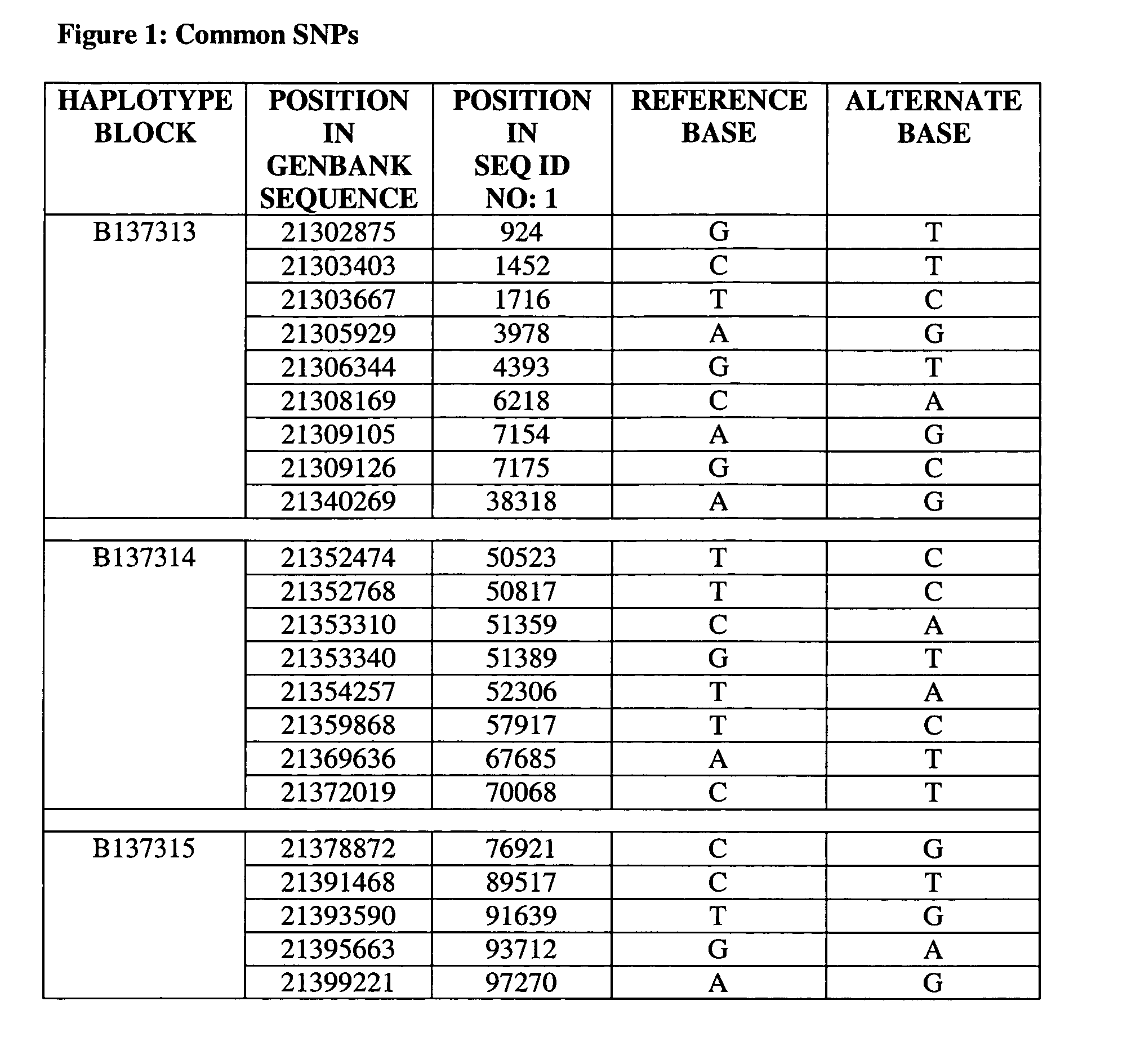
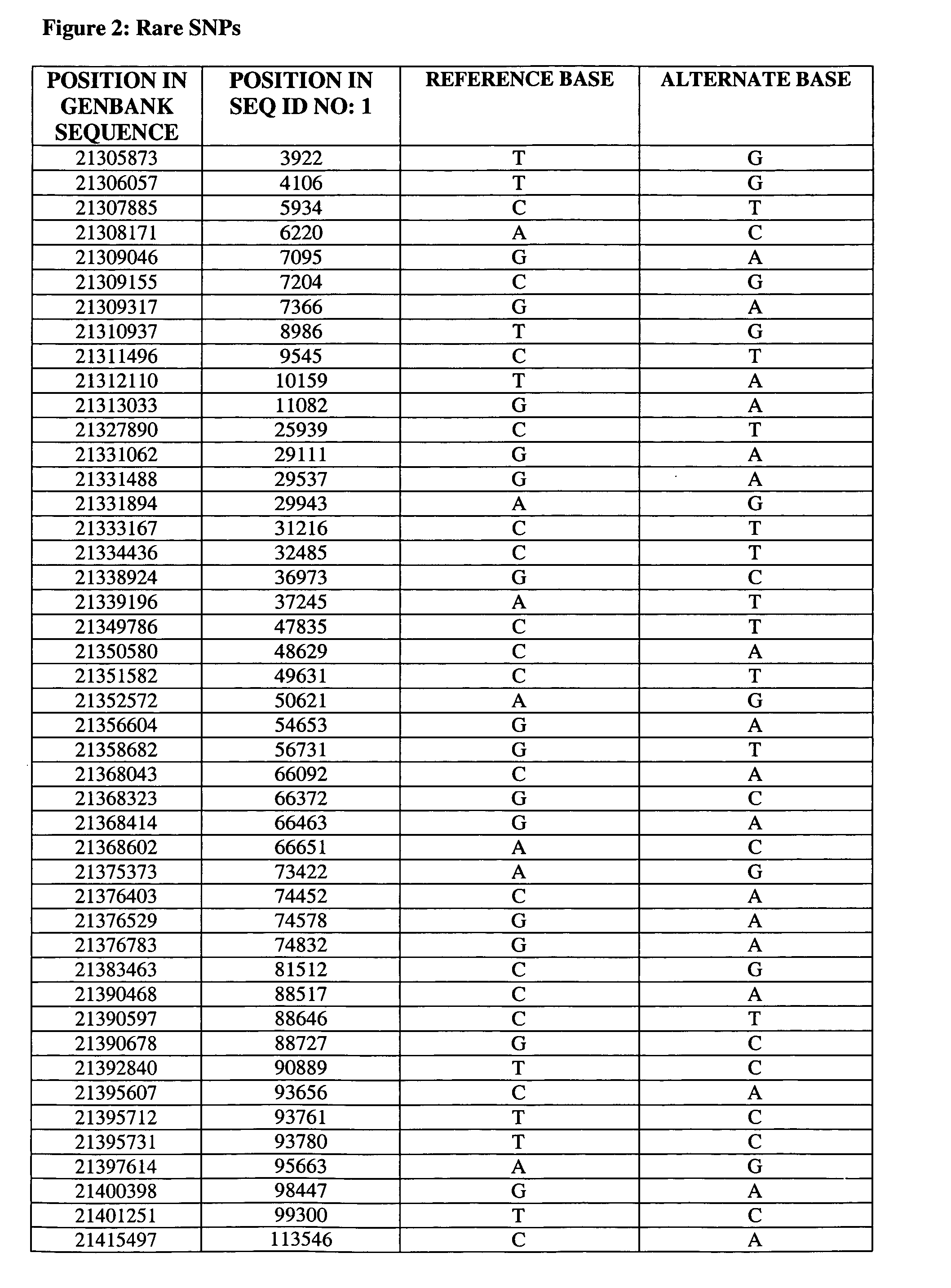
InactiveUS6969589B2Quick scanSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenetics
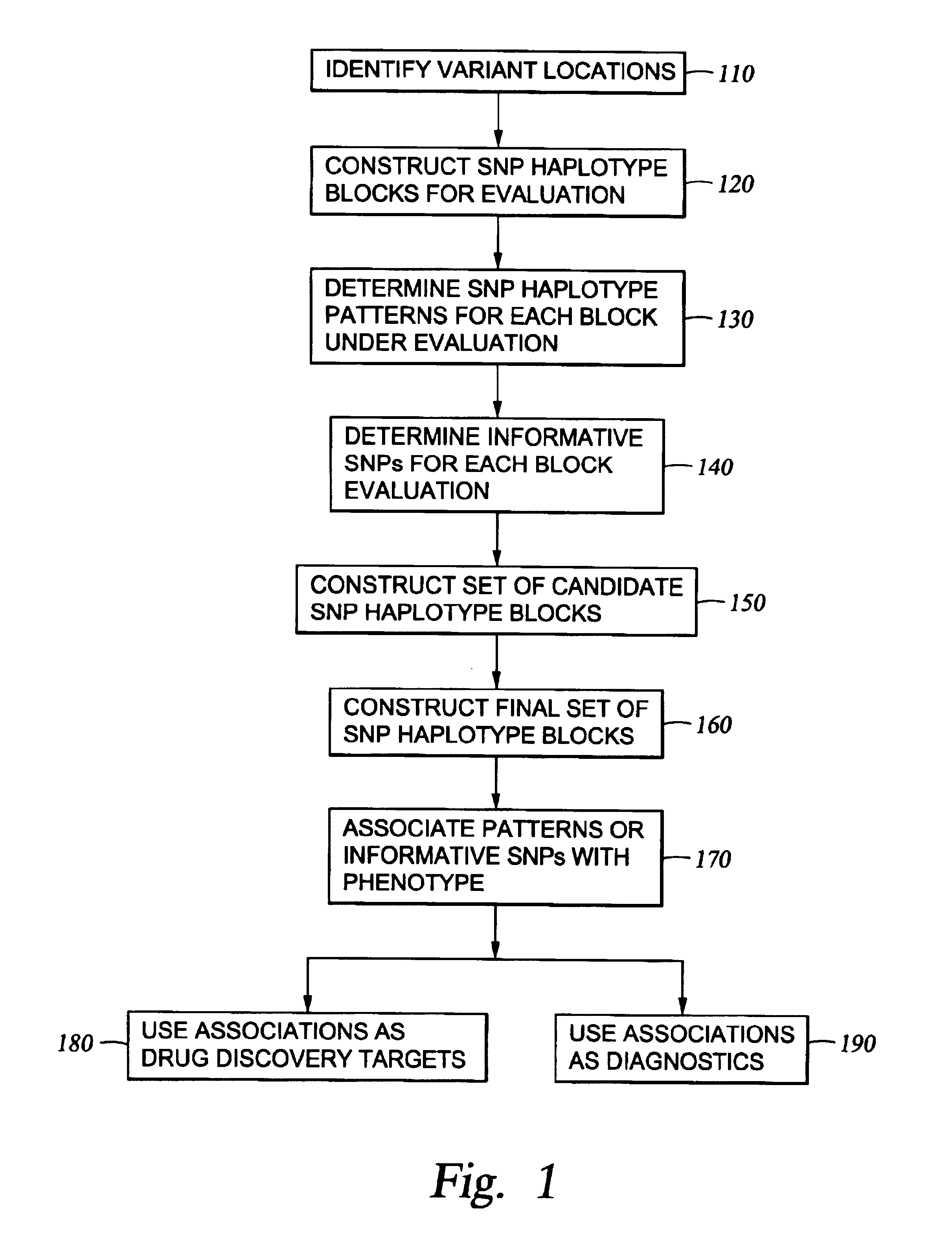
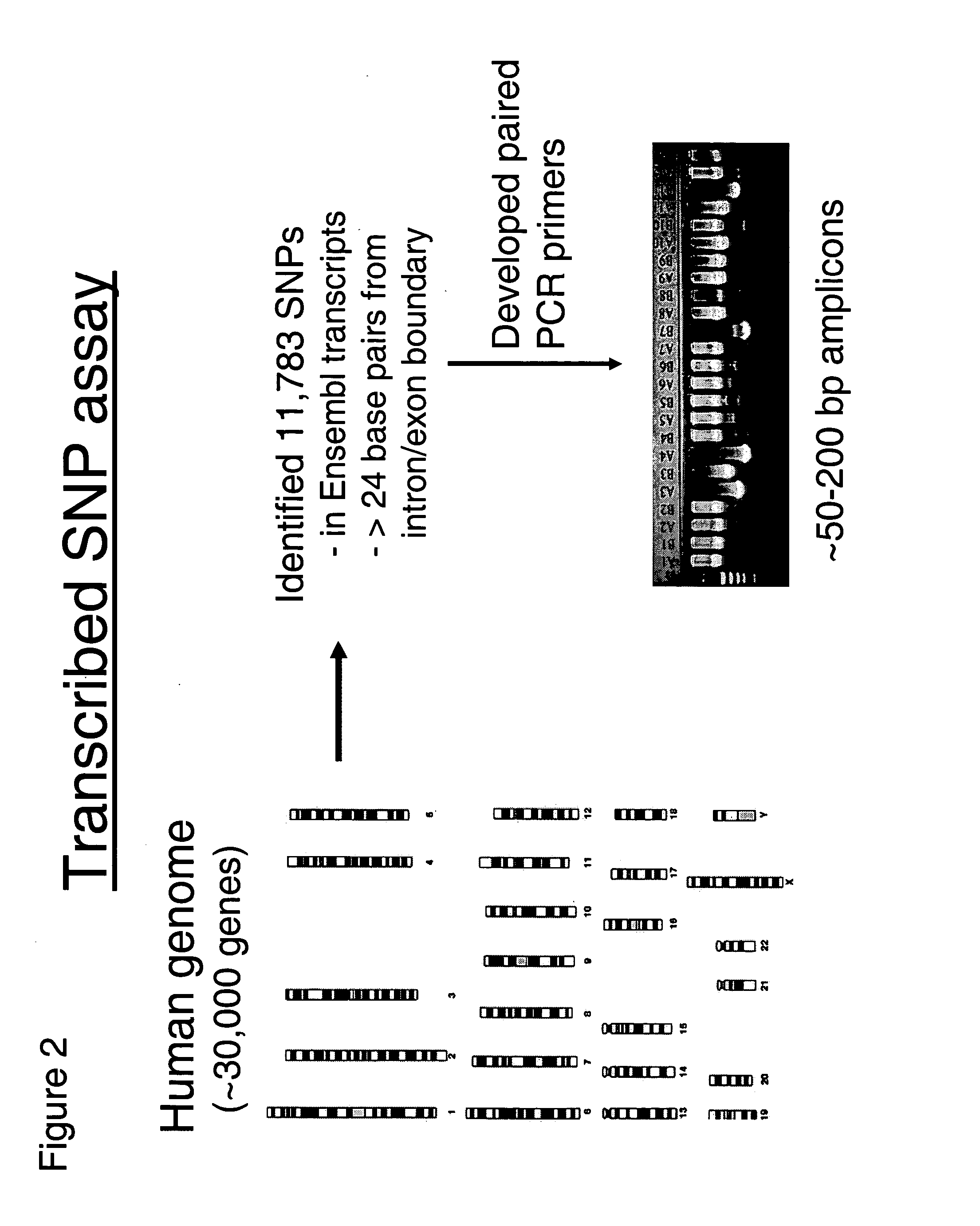
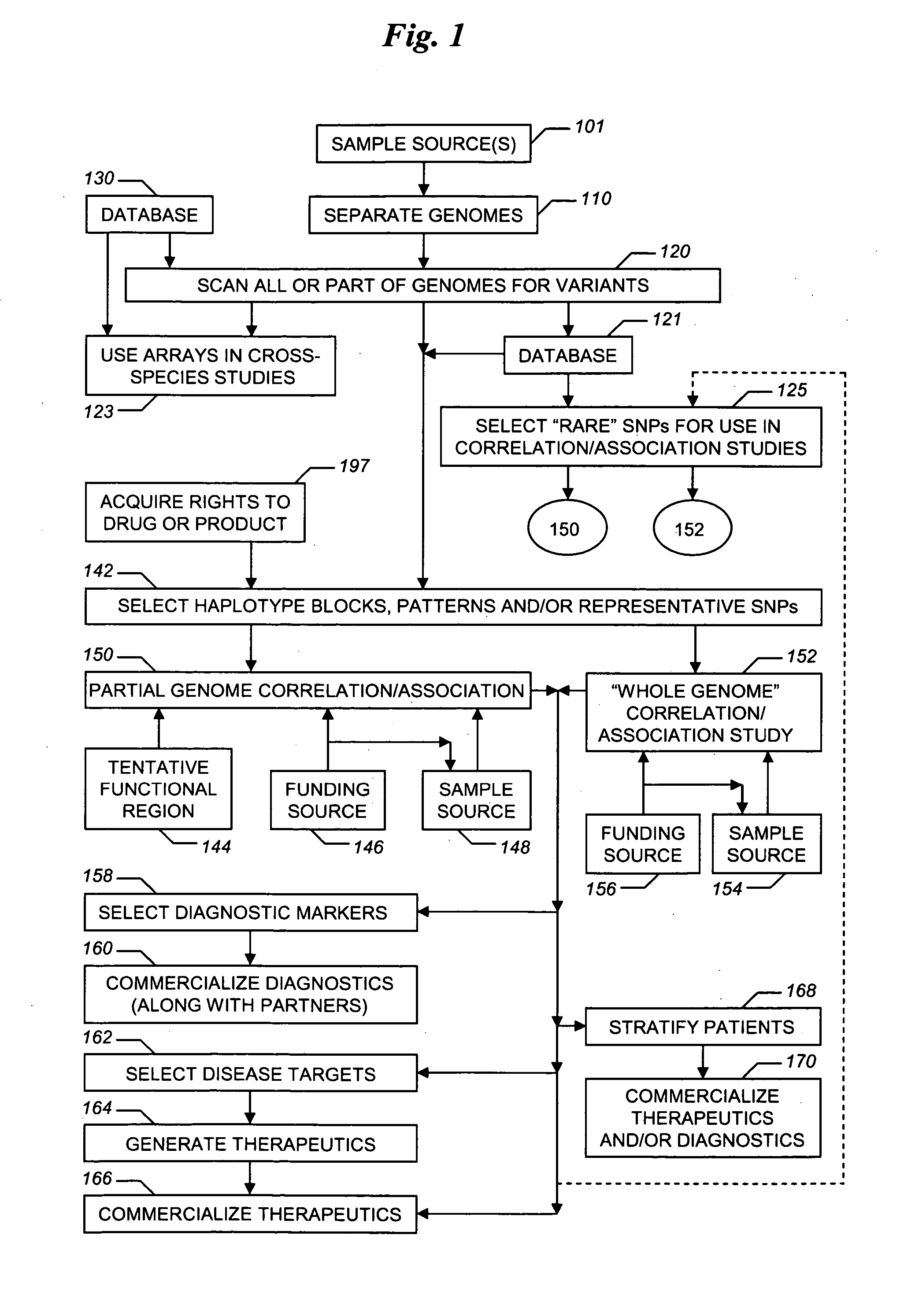
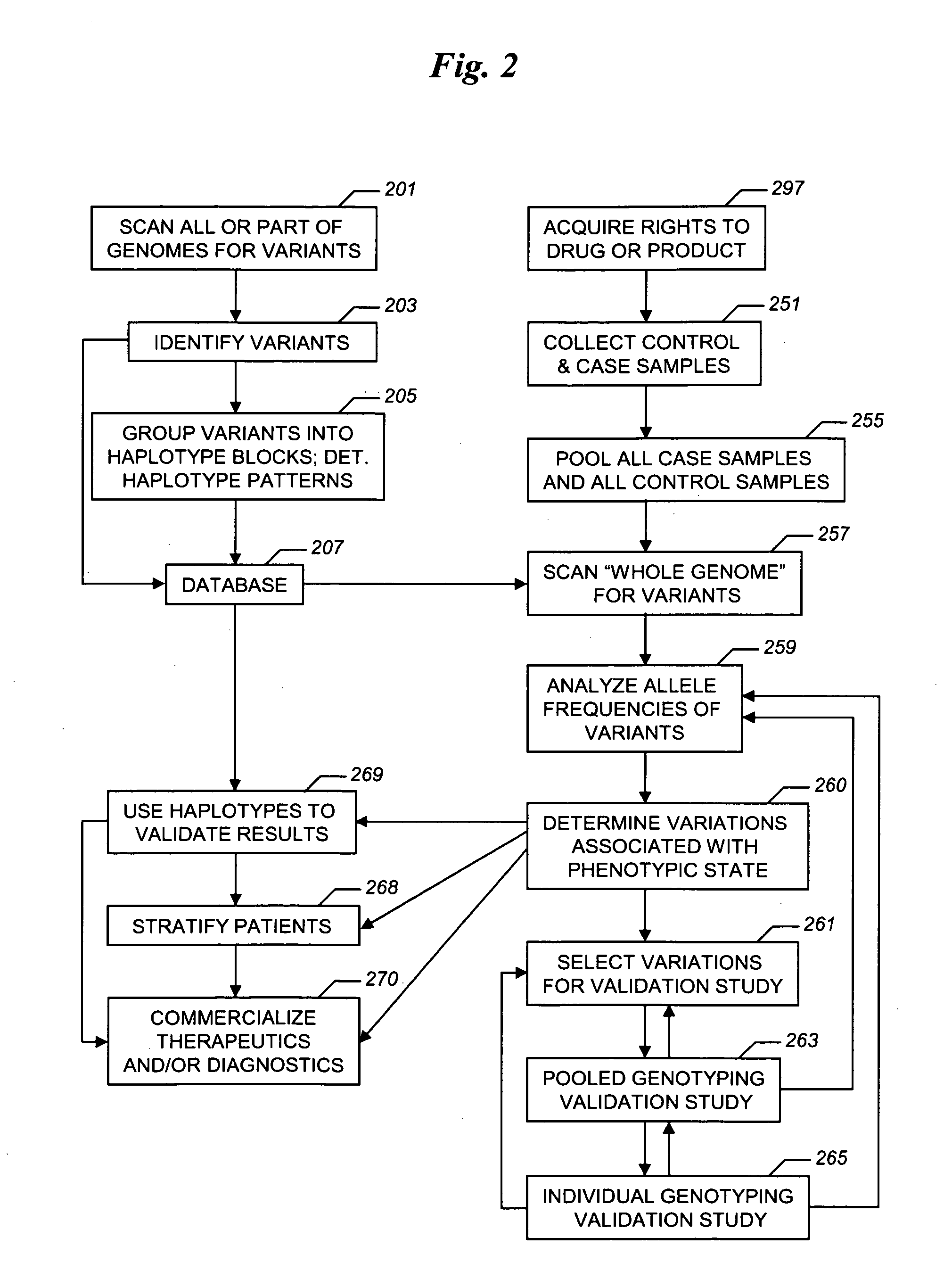
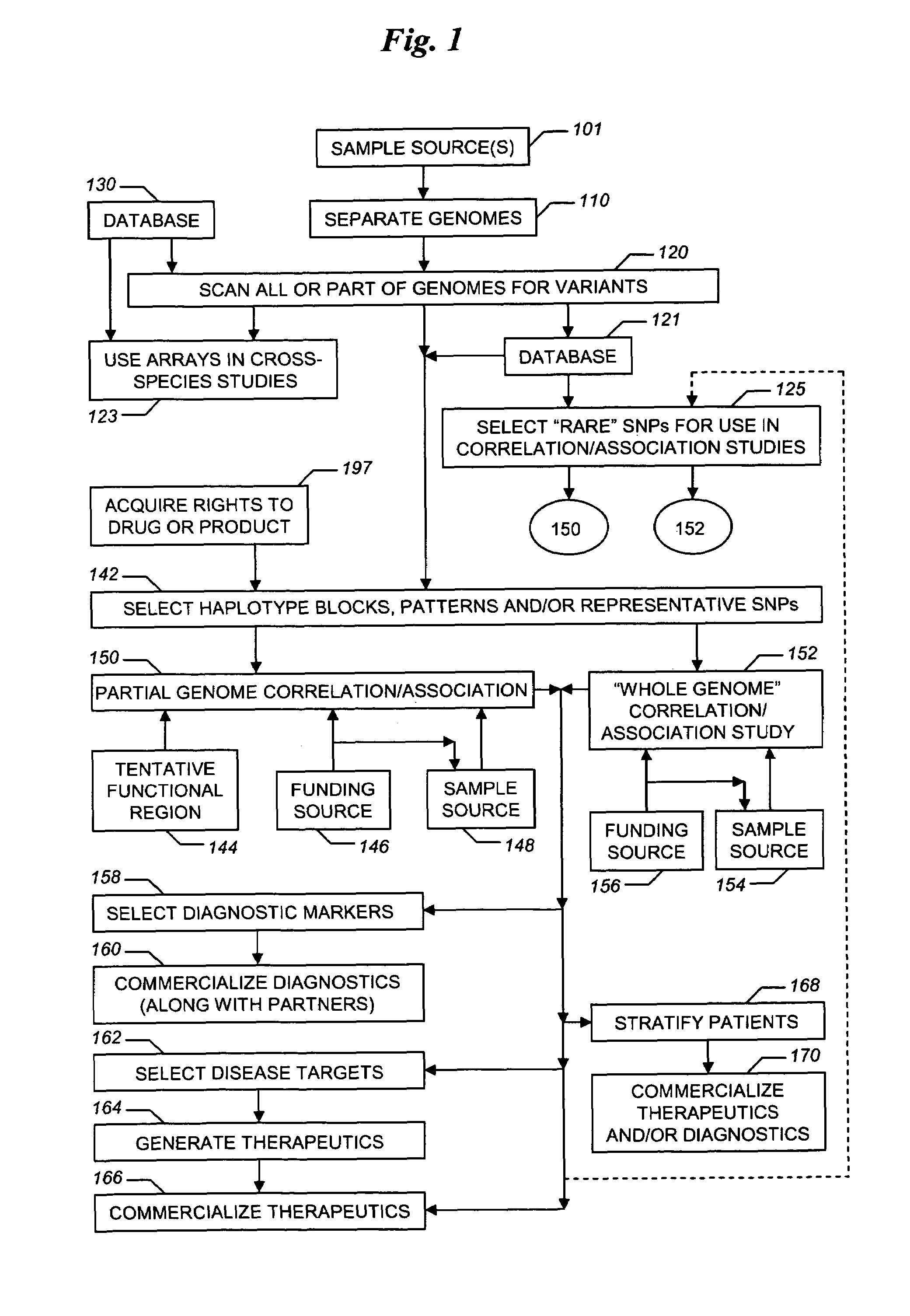
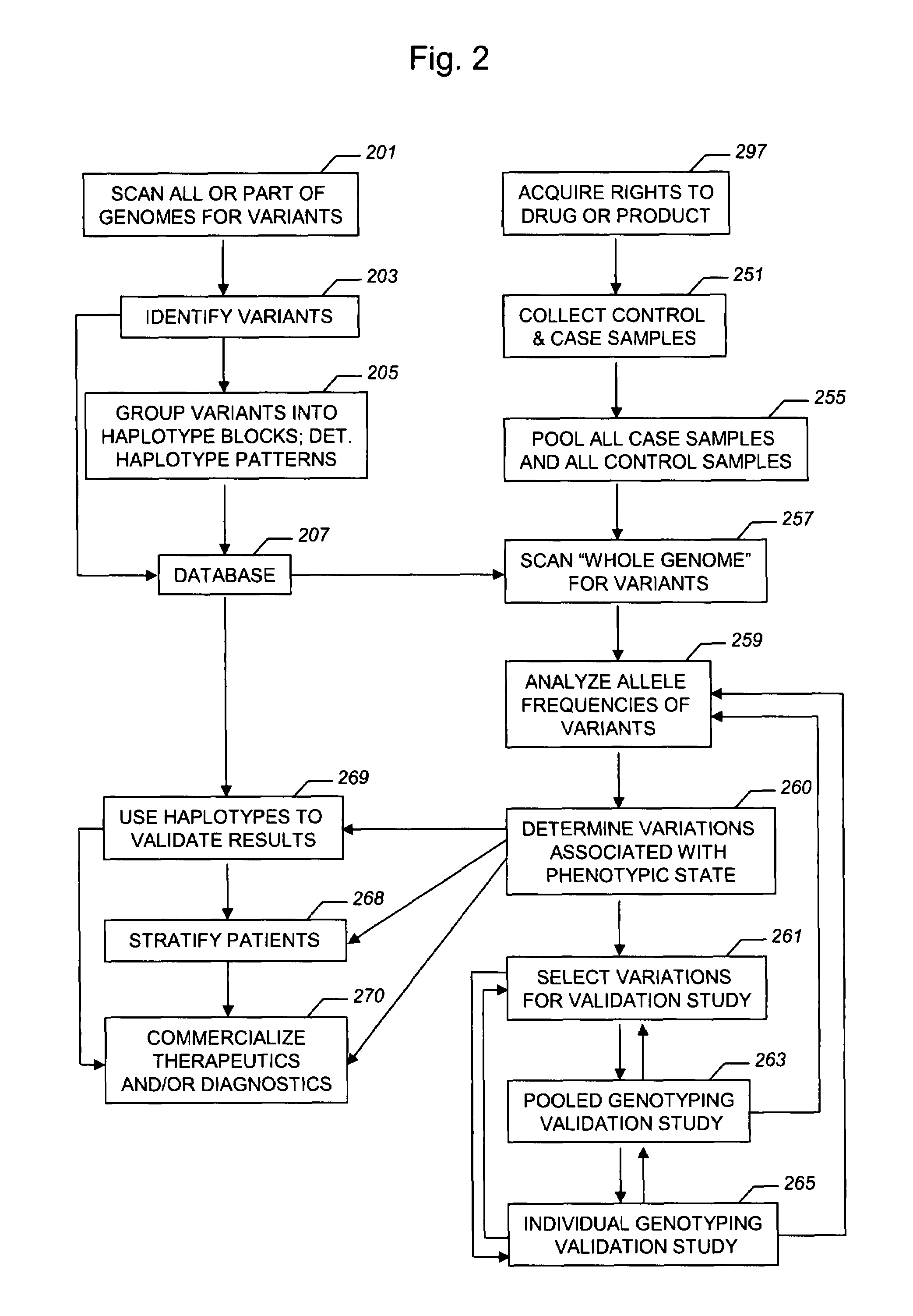
The present invention relates to methods for identifying variations that occur in the human genome and relating these variations to the genetic basis of disease and drug response. In particular, the present invention relates to identifying individual SNPs, determining SNP haplotype blocks and patterns, and, further, using the SNP haplotype blocks and patterns to dissect the genetic bases of disease and drug response. The methods of the present invention are useful in whole genome analysis.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC +1
Methods and compositions for determining ploidy
The invention provides improved methods, compositions, and kits for detecting ploidy of chromosome regions, e.g. for detecting cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus. The methods can utilize a set of more than 200 SNPs that are found within haploblocks and can include analyzing a series of target chromosomal regions related to cancer or a chromosomal abnormality in a gestating fetus. Finally the method may use knowledge about chromosome crossover locations or a best fit algorithm for the analysis. The compositions may comprise more than 200 primers located within haplotype blocks known to show CNV.
Owner:NATERA
Diagnostic decision support system and method of diagnostic decision support
InactiveUS20050216208A1Improve accuracyHigh precision analysisData processing applicationsHealth-index calculationClinical informationBiology
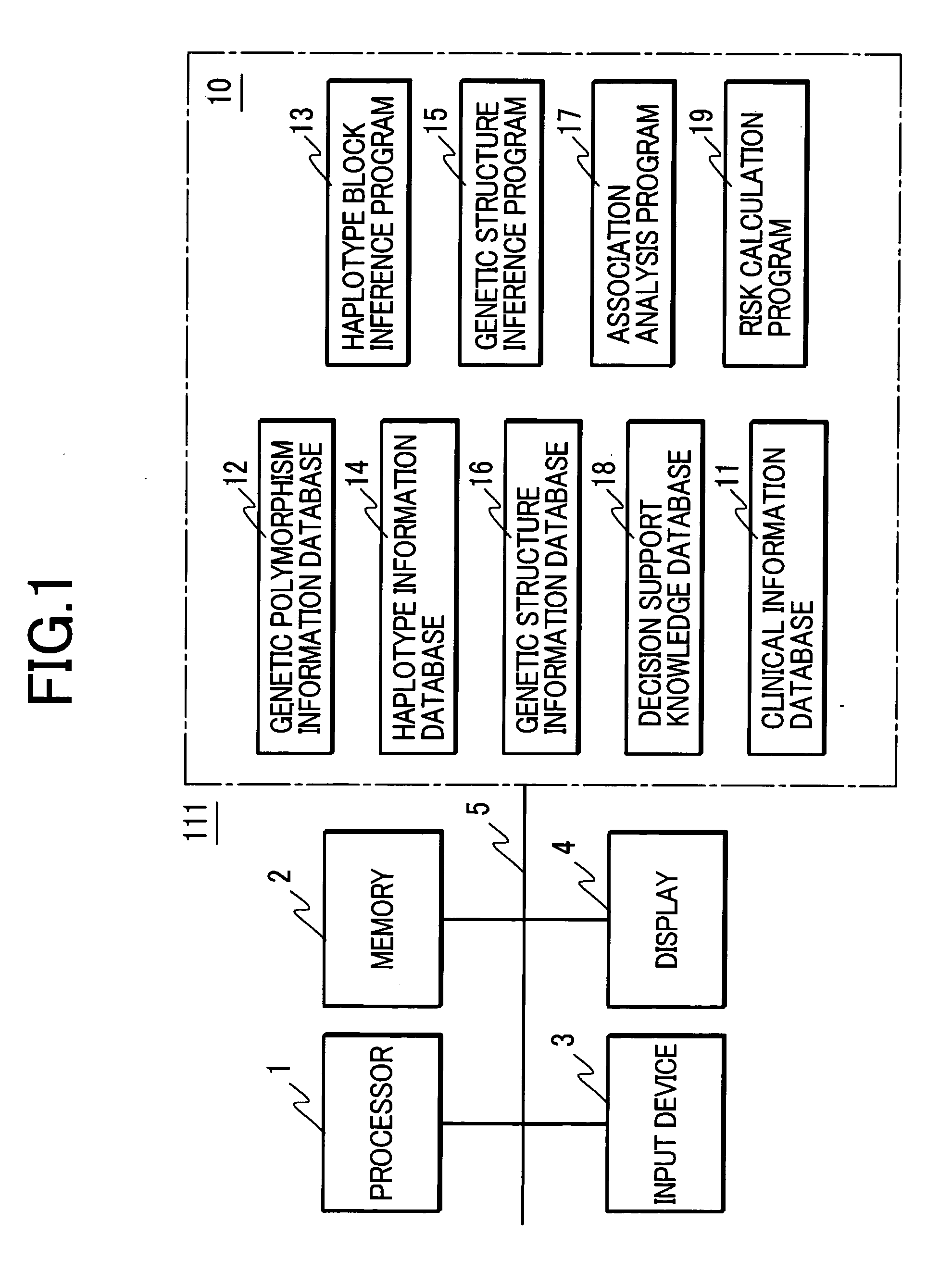
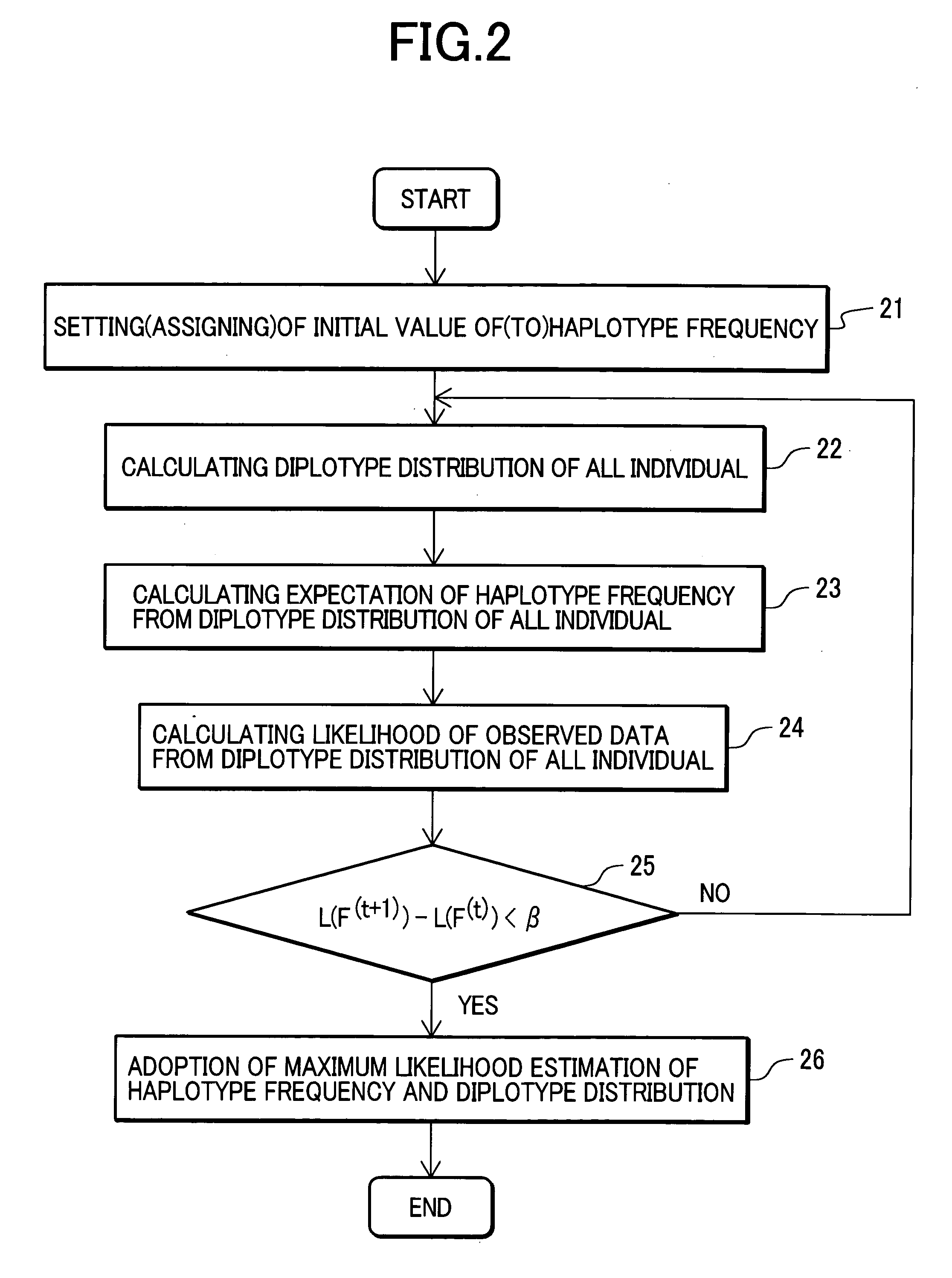
There is provided a system performing high-accuracy diagnostic decision support in consideration of the influence of a haplotype block and a genetic structure. Haplotype block inference means 13 infers the positions of haplotype blocks, and analyzes each of the haplotype blocks to infer a haplotype pattern of individuals with high accuracy. Genetic structure inference means 15 performs clustering the individuals on the basis of the haplotype pattern to divide a population into some subpopulations, and removes the influence of a genetic structure existing in the population. A genetic structure information database 16 and a clinical information database 11 are used to analyze association of clinical information with genetic information for providing high-accuracy diagnostic decision support knowledge. On the basis of the diagnostic decision support knowledge obtained by analyzing the association of clinical information with genetic information, risk calculation means 19 calculates a risk that a predetermined individual is affected by disease.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Diagnostic decision support system and method of diagnostic decision support
InactiveCN1674028AHigh precisionEliminate the effects ofData processing applicationsHealth-index calculationDiseaseClinical information
There is provided a system performing high-accuracy diagnostic decision support in consideration of the influence of a haplotype block and a genetic structure. Haplotype block inference means 13 infers the positions of haplotype blocks, and analyzes each of the haplotype blocks to infer a haplotype pattern of individuals with high accuracy. Genetic structure inference means 15 performs clustering the individuals on the basis of the haplotype pattern to divide a population into some subpopulations, and removes the influence of a genetic structure existing in the population. A genetic structure information database 16 and a clinical information database 11 are used to analyze association of clinical information with genetic information for providing high-accuracy diagnostic decision support knowledge. On the basis of the diagnostic decision support knowledge obtained by analyzing the association of clinical information with genetic information, risk calculation means 19 calculates a risk that a predetermined individual is affected by disease.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Human genomic polymorphisms
InactiveUS20060188875A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingInformative snps
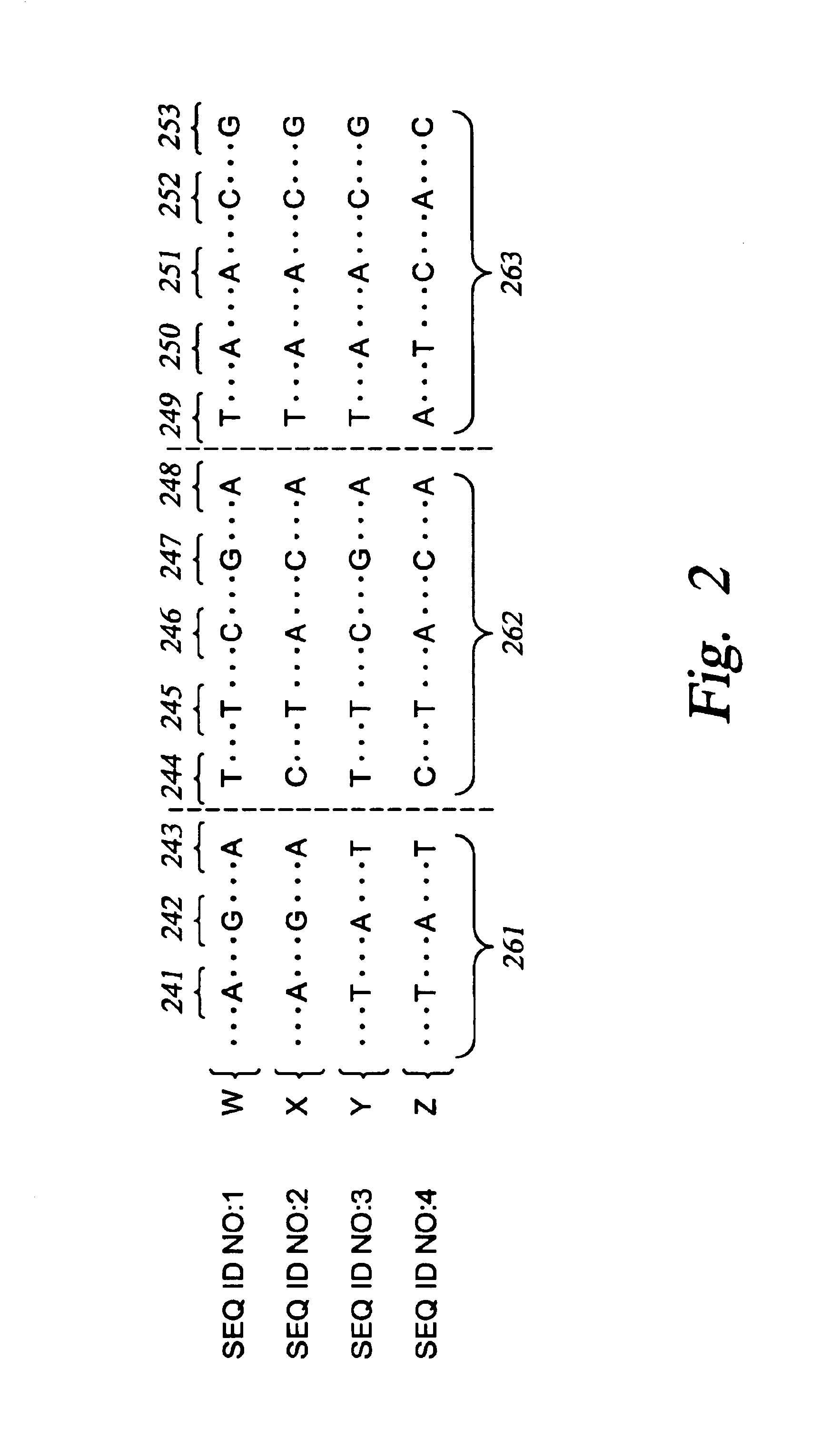
The invention provides nucleic acid segments of the human genome including polymorphic sites, SNP haplotype blocks, SNP haplotype patterns for each block and informative SNPs for each pattern. Allele-specific primers and probes hybridizing to regions flanking these sites are also provided. The nucleic acids, primers and probes are used in applications such as association studies and other genetic analyses.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
Allele-specific expression patterns
The invention provides methods of analyzing genes for differential relative allelic expression patterns. Haplotype blocks throughout the genomes of individuals are analyzed to identify haplotype patterns that are associated with specific differential relative allelic expression patterns. Haplotype blocks that contain associated haplotype patterns may be further investigated to identify genes or variants of genes involved in differential relative allelic expression patterns.
Owner:PERLEGEN SCIENCES INC
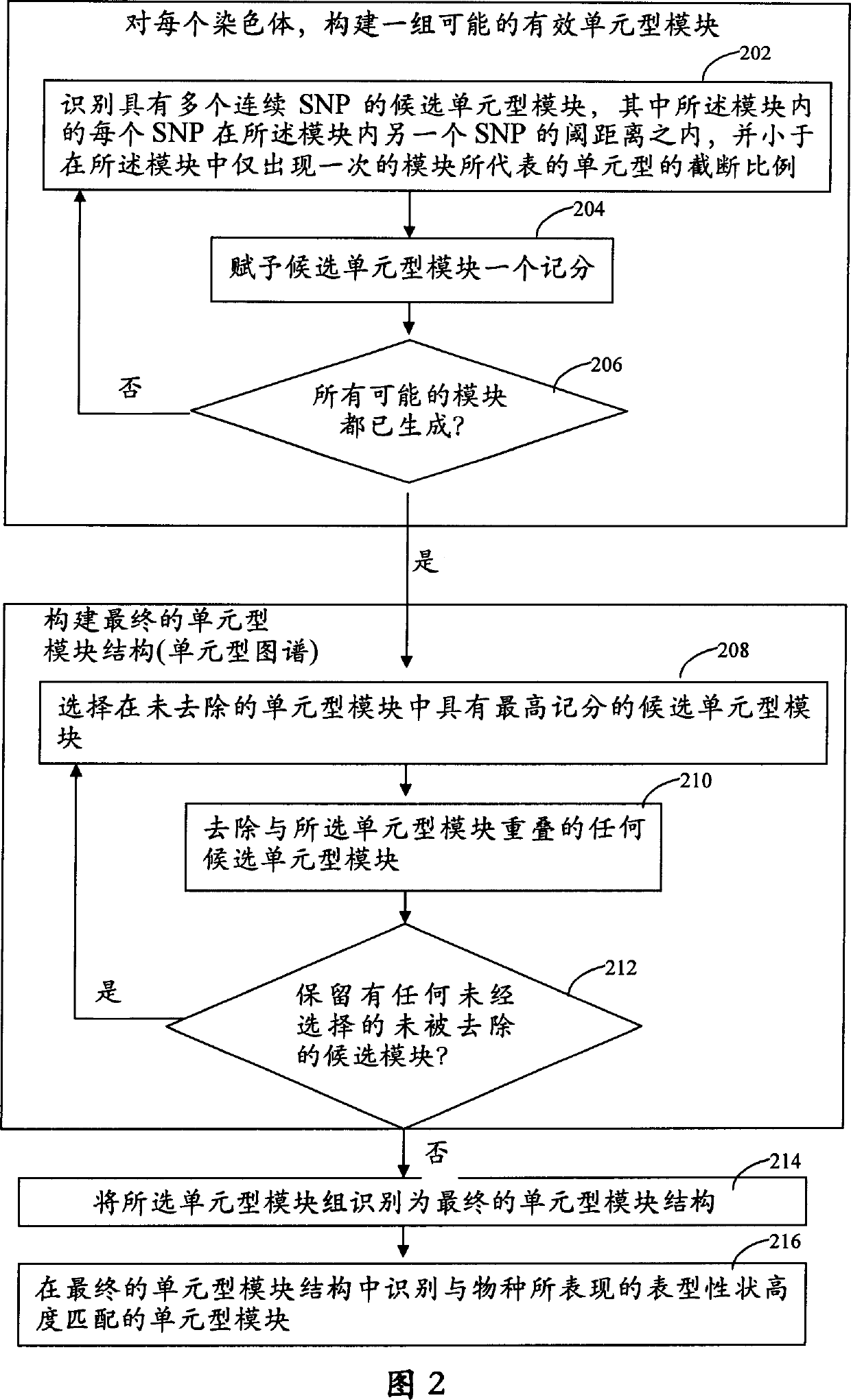
Systems and methods for predicting specific genetic loci that affect phenotypic traits
A database of genetic variations is analyzed to produce a haplotype map of the genome for strains of a single species. A computational method is used to rapidly map complex phenotypes onto the haplotype blocks within the haplotype map. The specific genetic locus regulating three different biologically important phenotypic traits in mice is identified using these systems and methods.
Owner:SANDHILL BIO CORP +1
Life sciences business systems and methods
Improved life sciences business systems and methods are disclosed. One or more genomes are scanned for single nucleotide polymorphisms. The polymorphisms are assigned to haplotype blocks, and representative SNPs from the haplotype blocks are used in association studies for pharmaceutical and diagnostic developments.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Pharmaceutical and diagnostic business systems and methods
Improved pharmaceutical and diagnostic business systems and methods are disclosed. One or more genomes are scanned for single nucleotide polymorphisms. The polymorphisms are assigned to haplotype blocks, and representative SNPs from the haplotype blocks are used in association studies for pharmaceutical and diagnostic development.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
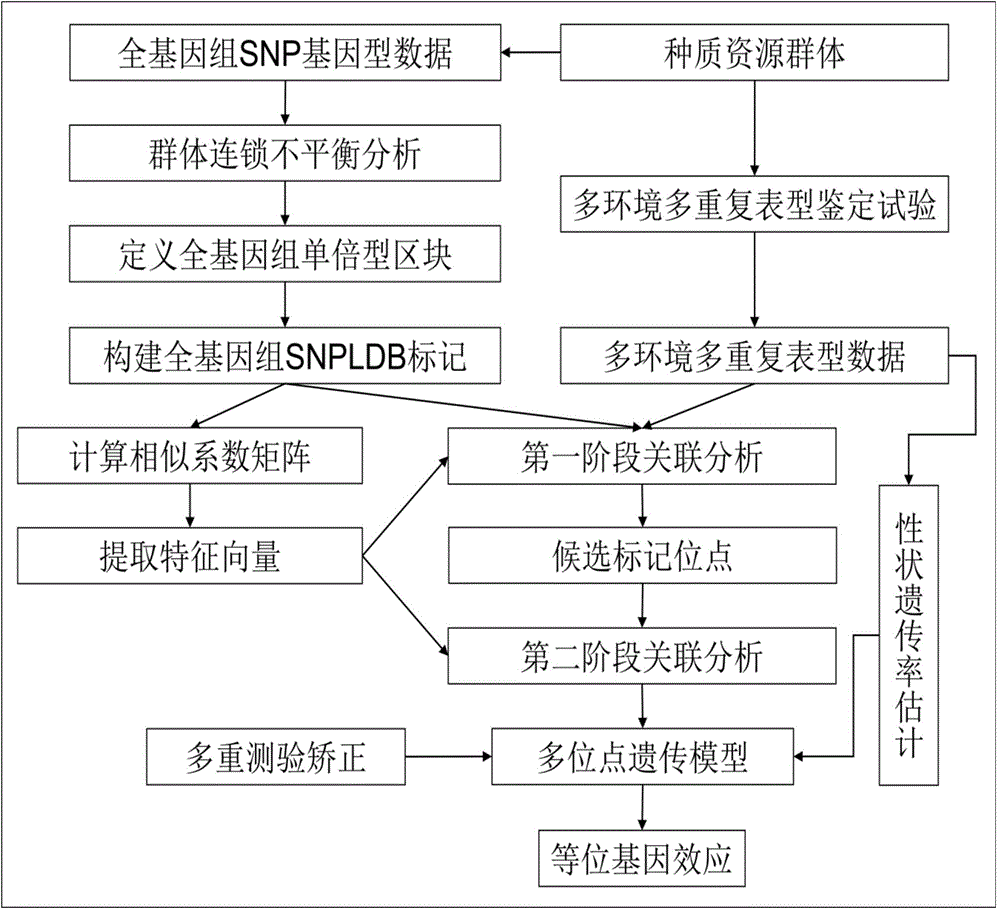
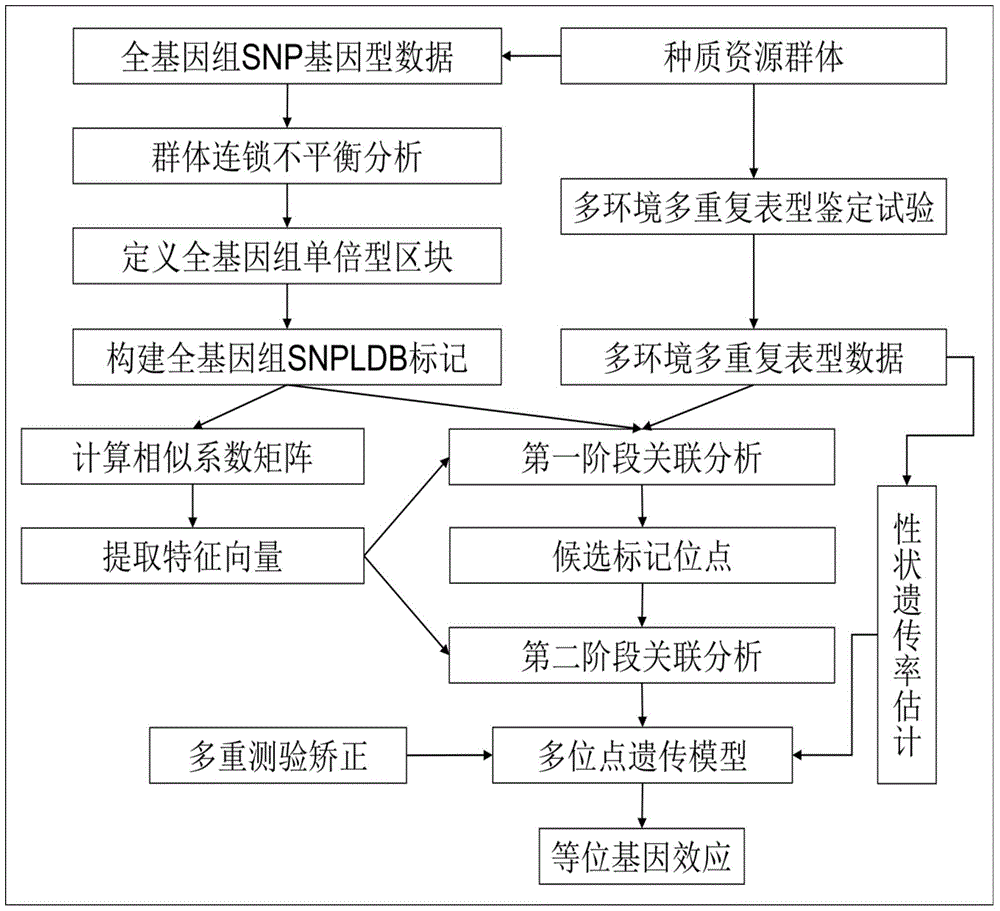
Restrictive two-stage genome-wide association study (GWAS) method based on SNPLDB mark
InactiveCN104651517AShorten the attenuation distanceMultiple allelic variationMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMulti siteRegression analysis
The invention discloses a restrictive two-stage genome-wide association study (GWAS) method based on an SNPLDB mark, and aims at solving the problems that a traditional method cannot be used for estimating multiple allele information, and is high in false positive rate and low in efficiency of detection on inbreeding crops. By combination of the SNPLDB mark constructed on the basis of a haplotype block, correction of deviation of an inbreeding population relation analysis model and a two-stage relation analysis strategy under a multi-site model, the GWAS method suitable for conventional breeding of inbreeding crops is built; the SNPLDB mark is applied to GWAS, so that a method is provided for multiple allele estimation; candidate sites are screened on the basis of a single-site model in the first stage, and are further screened on the basis of a progressive regression analysis method in the multi-site model in the second stage, so as to balance the problems of missing of heritability and over-high heritability estimation. Therefore, the interpretation ratio of a final genetic model is controlled at trait heritability. The positioning accuracy and efficiency are improved by a feature vector and an appropriate significant level of a similarity coefficient matrix estimated by the SNPLDB mark by GWAS.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Life sciences business systems and methods
InactiveUS20060008834A1Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsHaplotype block
Improved life sciences business systems and methods are disclosed. One or more genomes are scanned for single nucleotide polymorphisms. The polymorphisms are assigned to haplotype blocks, and representative SNPs from the haplotype blocks are used in association studies for pharmaceutical and diagnostic developments.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Genetic variations (SNPs) adjacent to the AKT1 gene locus, and diagnostic and prognostic uses thereof
InactiveUS20060204969A1Increased muscle cross sectional areaIncrease volumeSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementAkt1 geneCortical volume
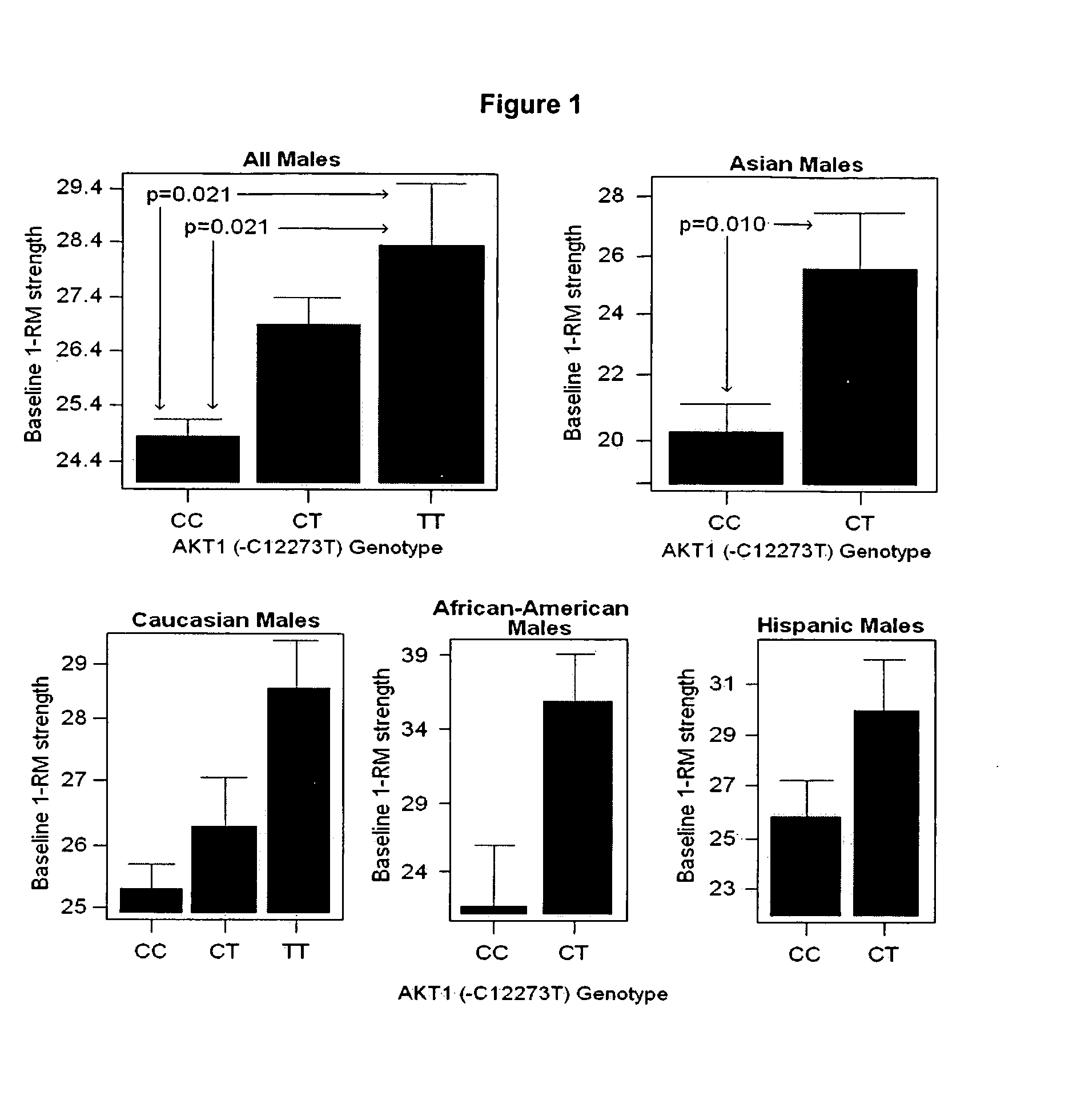
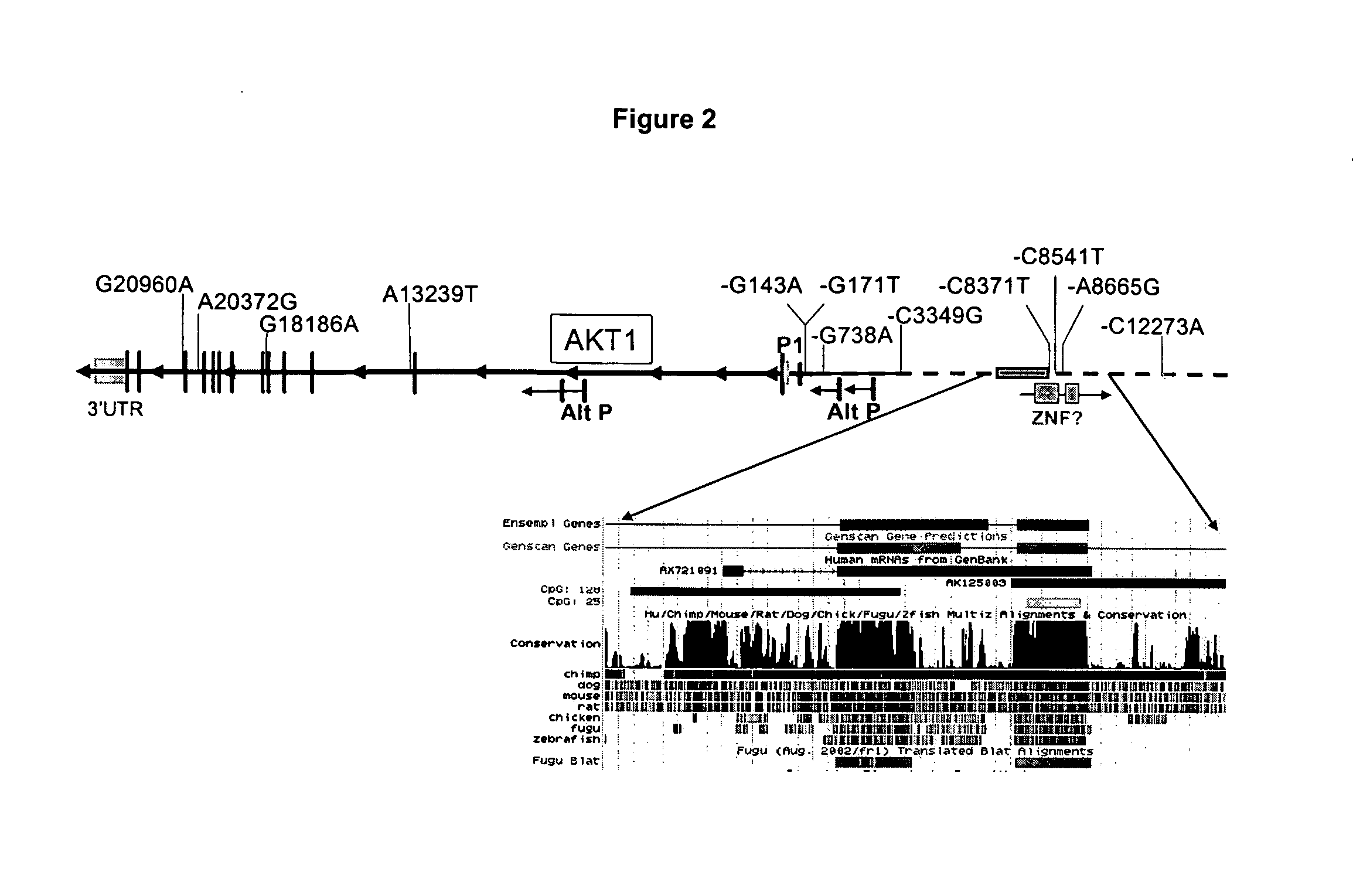
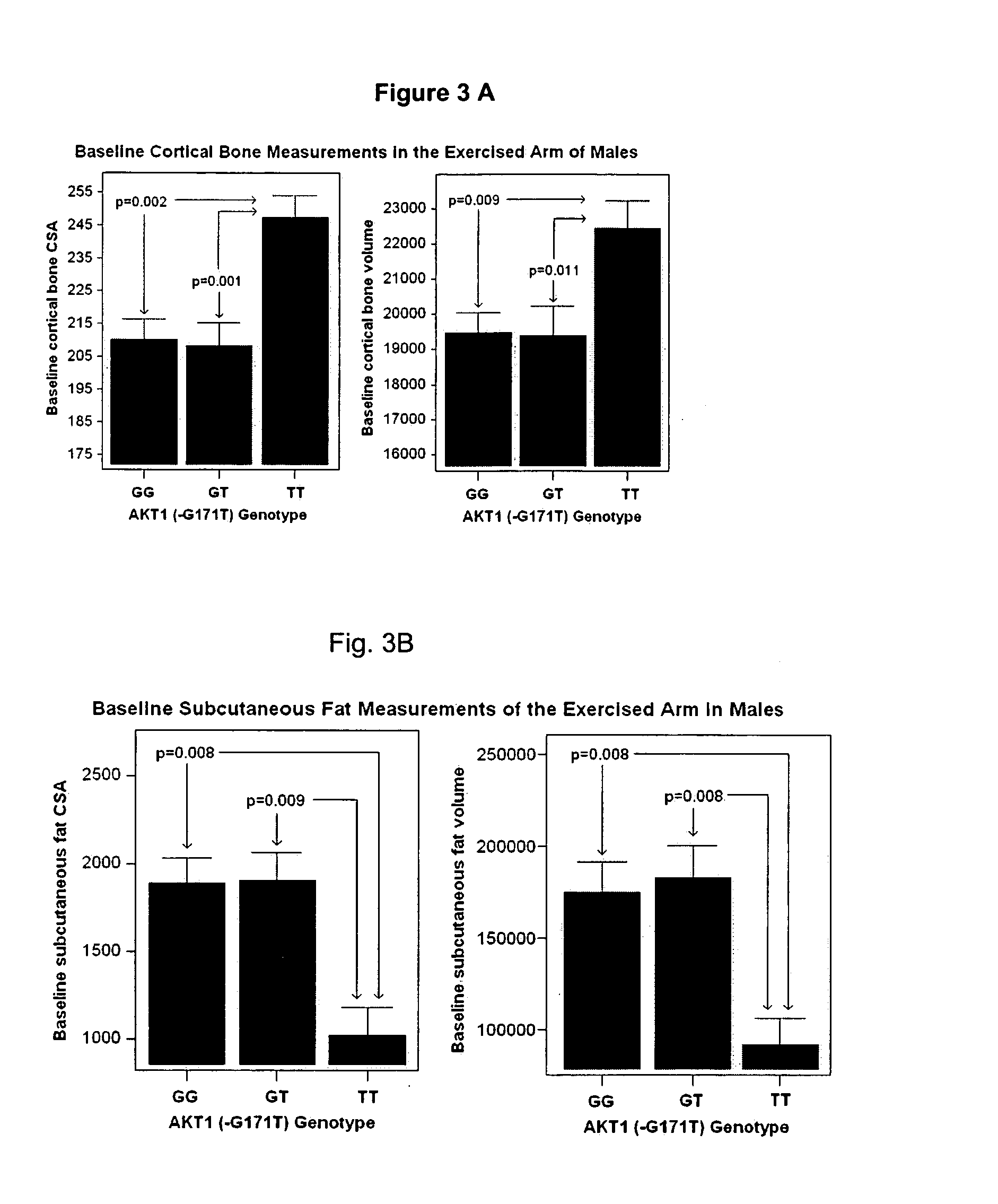
We have identified and isolated a 12 kb region immediately upstream of the AKT1 gene containing eight single nucleotide polymorphic polynucleotides (SNPs) in 4 haplotype regions that show strong association with body composition, Basal Mass Index, and AKT1 expression enhancement in human males. A four-locus haplotype (Haplotype 2) was defined where residues within highly conserved regulatory regions were altered. This haplotype explained up to 26% of population variation in bone cortical volume, 12% of subcutaneous fat volume, and 9% of strength variation, resulting in a body build with large bones, strong muscles, and low subcutaneous fat. Other SNPs detect, presymptomatically, the potential for increased amounts of subcutaneous fat and Type II diabetes. The detection of these SNPs by the techniques described herein forms the foundation for genotype-specific clinical interventions designed to slow the rapid population increases in obesity and Type II diabetes.
Owner:HOFFMAN ERIC +1
Methods for genomic analysis
InactiveUS20050272086A1Quick scanSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman DNA sequencingGenetics
The present invention relates to methods for identifying variations that occur in the human genome and relating these variations to the genetic basis of disease and drug response. In particular, the present invention relates to identifying individual SNPs, determining SNP haplotype blocks and patterns, and, further, using the SNP haplotype blocks and patterns to dissect the genetic bases of disease and drug response. The methods of the present invention are useful in whole genome analysis.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
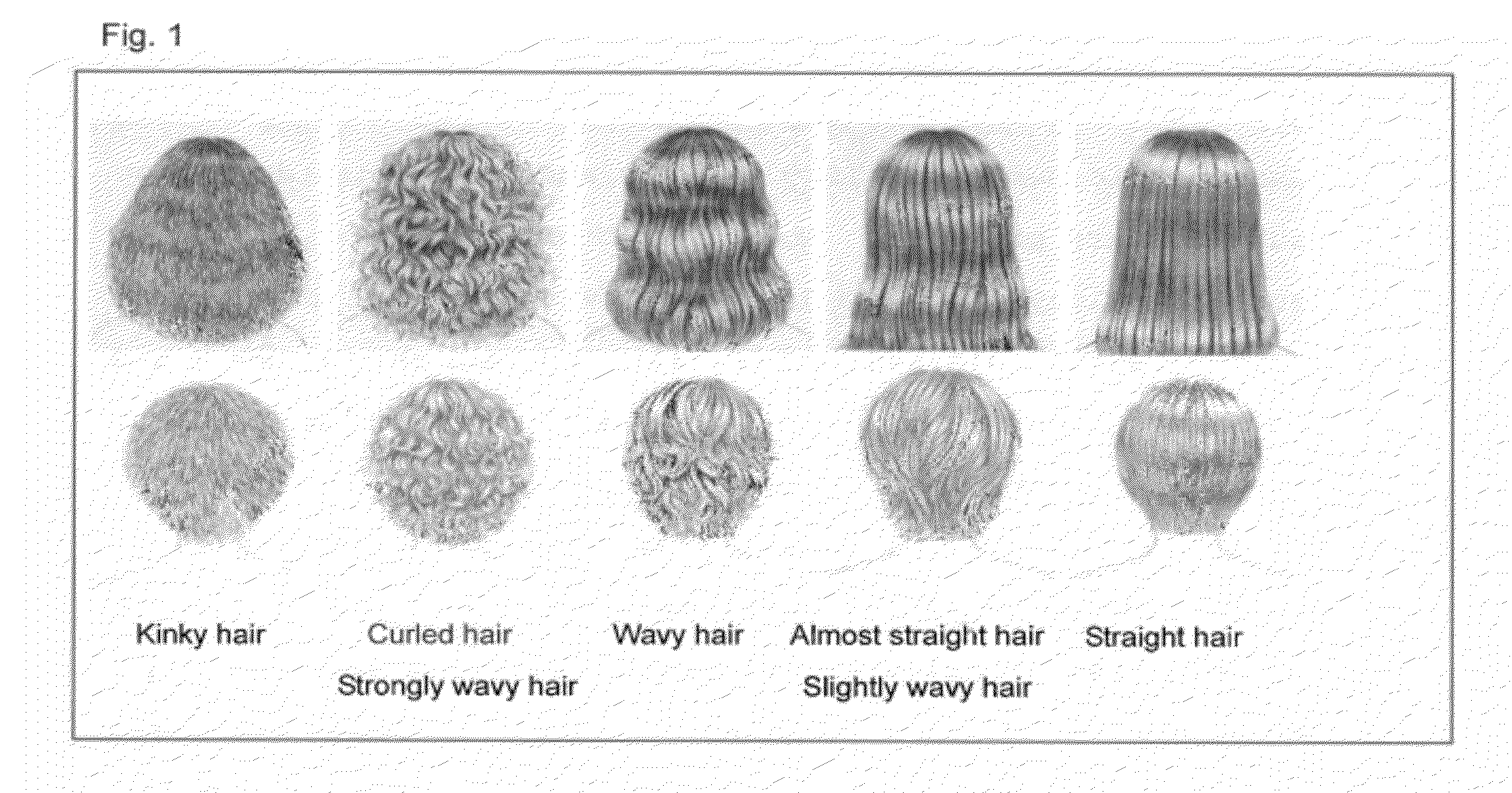
Hair Shape Susceptibility Gene
InactiveUS20120329726A1Cosmetic preparationsPeptide/protein ingredientsAllele frequencyGenetic linkage disequilibrium
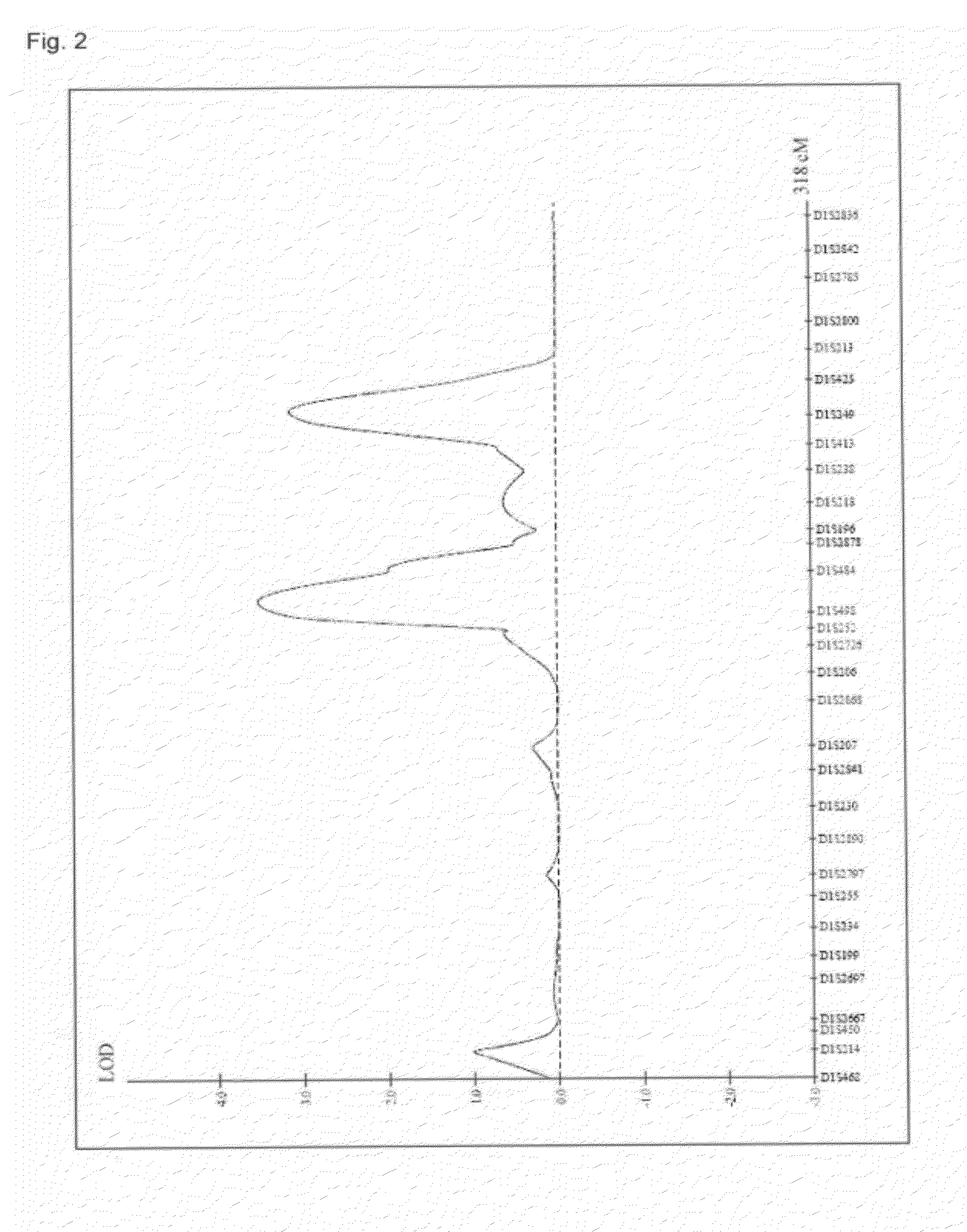
A genetic polymorphism and a hair shape susceptibility gene that are related to hair shape, and a method for determining the genetic susceptibility to hair shape in individual test subjects are provided. Disclosed is a hair shape susceptibility gene, which overlaps with a haplotype block in 1q21.3 region (D1S2696 to D1S2346) of human chromosome 1 and comprises a portion or the entirety of the base sequence of the haplotype block, wherein the haplotype block is determined by a linkage disequilibrium analysis conducted on a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker whose allele frequency differs statistically significantly between a group having a curly hair trait and a group having a non-curly hair trait, and consists of a base sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NO: 1 to NO: 5.
Owner:KAO CORP
Life sciences business systems and methods
InactiveUS7427480B2Data processing applicationsMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideGenetics
Improved life sciences business systems and methods are disclosed. One or more genomes are scanned for single nucleotide polymorphisms. The polymorphisms are assigned to haplotype blocks, and representative SNPs from the haplotype blocks are used in association studies for pharmaceutical and diagnostic developments.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Systems and methods for predicting specific genetic loci that affect phenotypic traits
A database of genetic variation was analyzed to generate genomic haplotype maps of single species lines. In silico methods are used to rapidly map complex phenotypes into haplotype blocks within haplotype maps. Specific genetic loci regulating three different biologically important phenotypic traits in mice were identified using these systems and methods.
Owner:SANDHILL BIO CORP
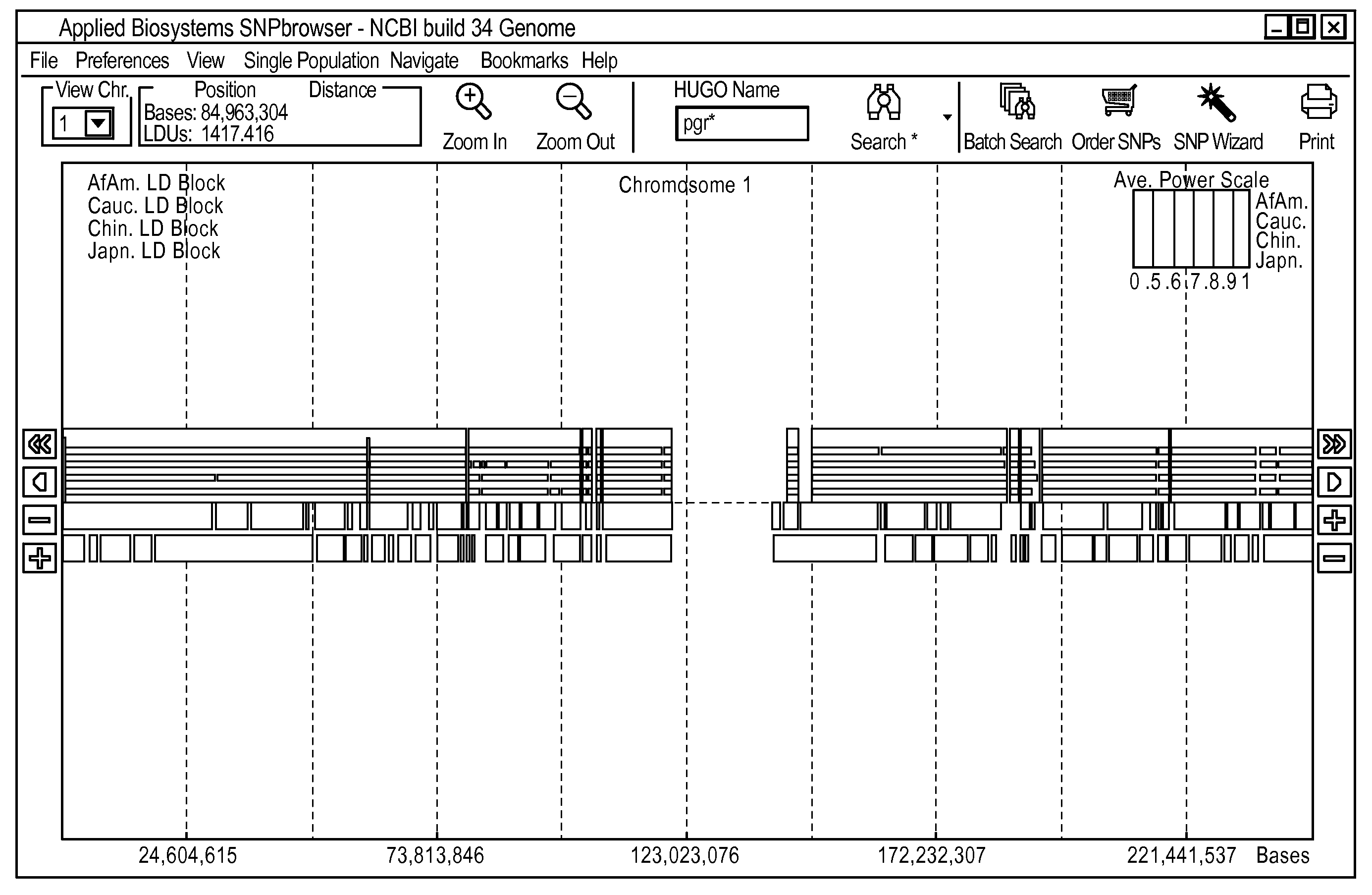
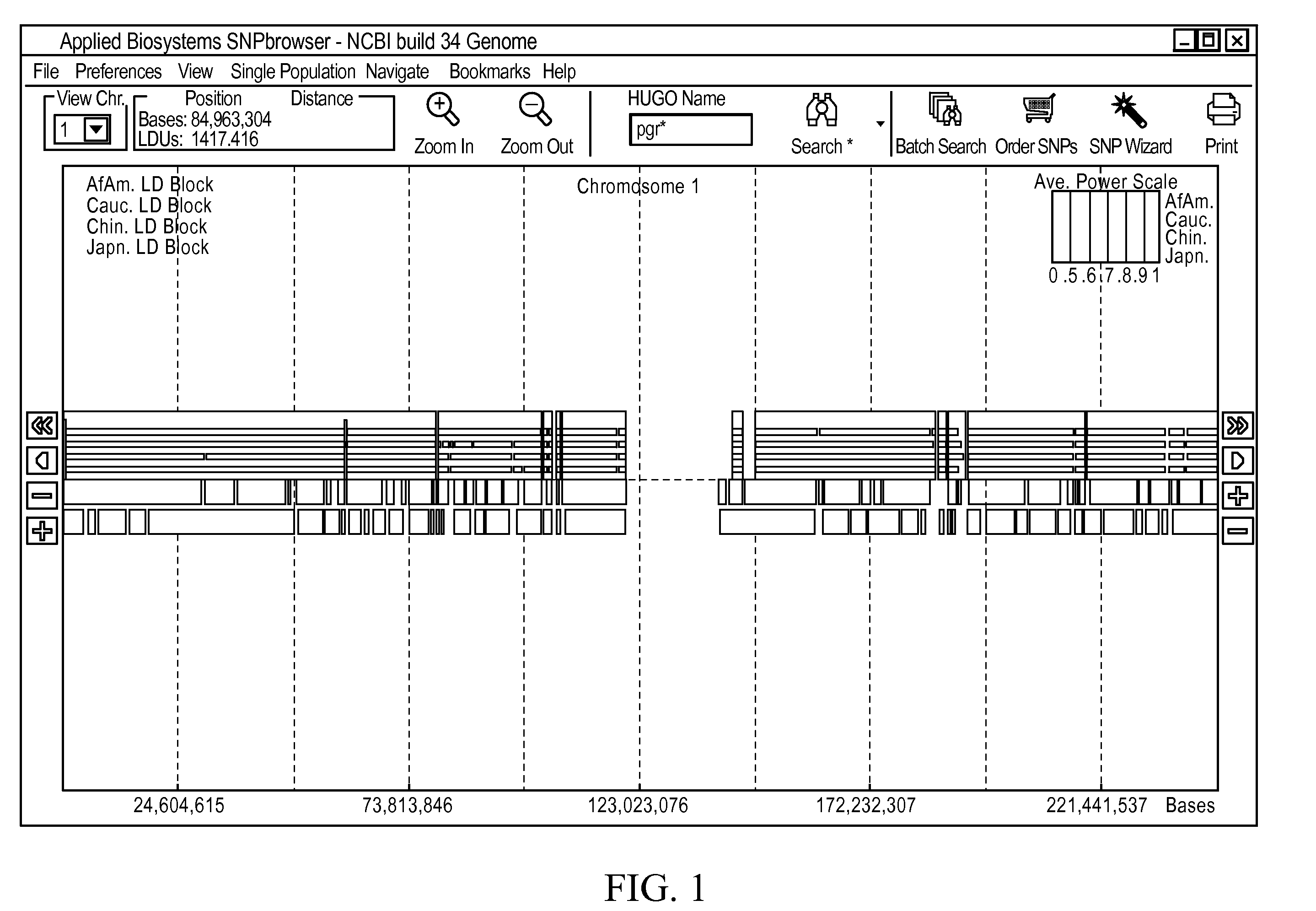
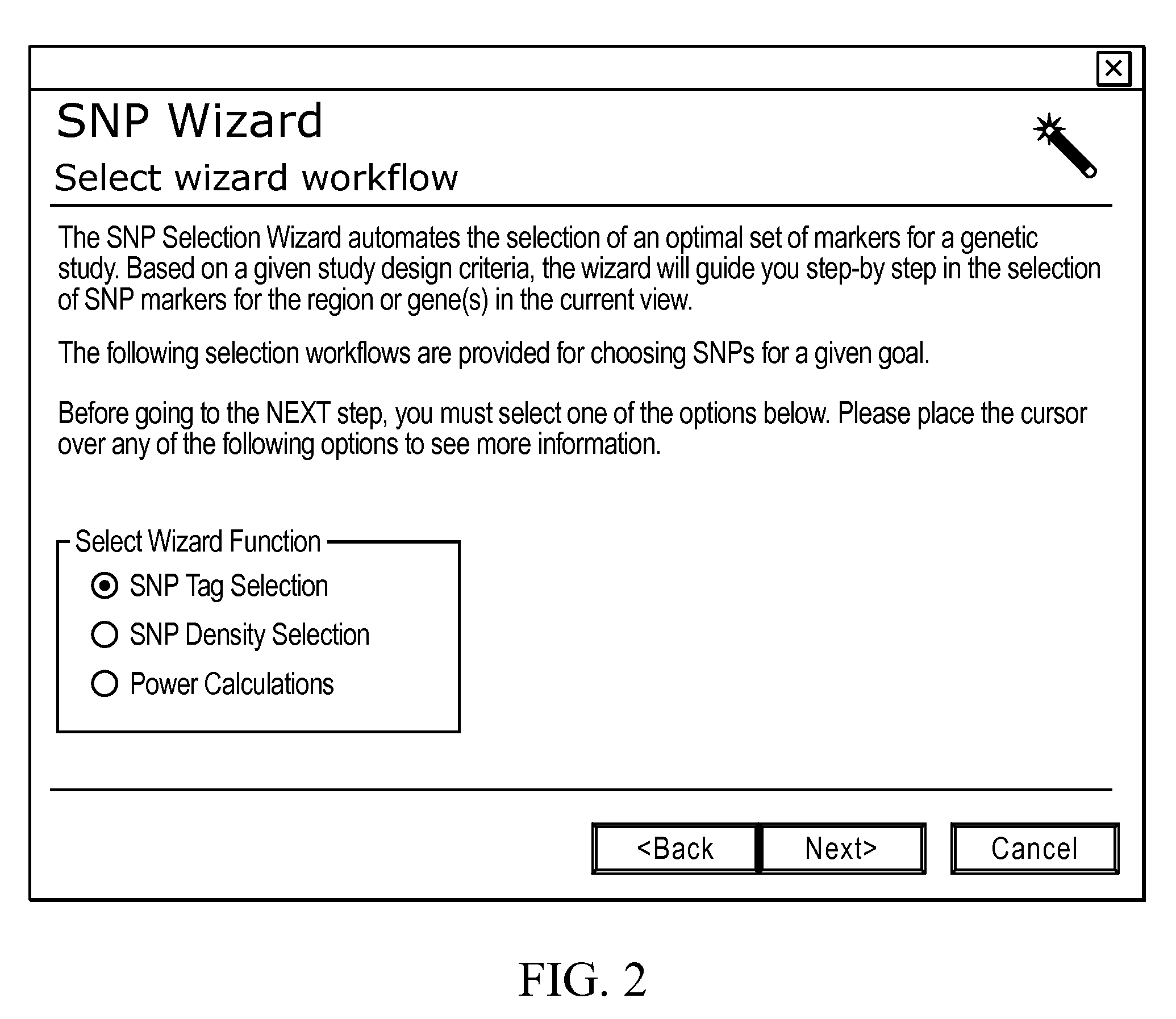
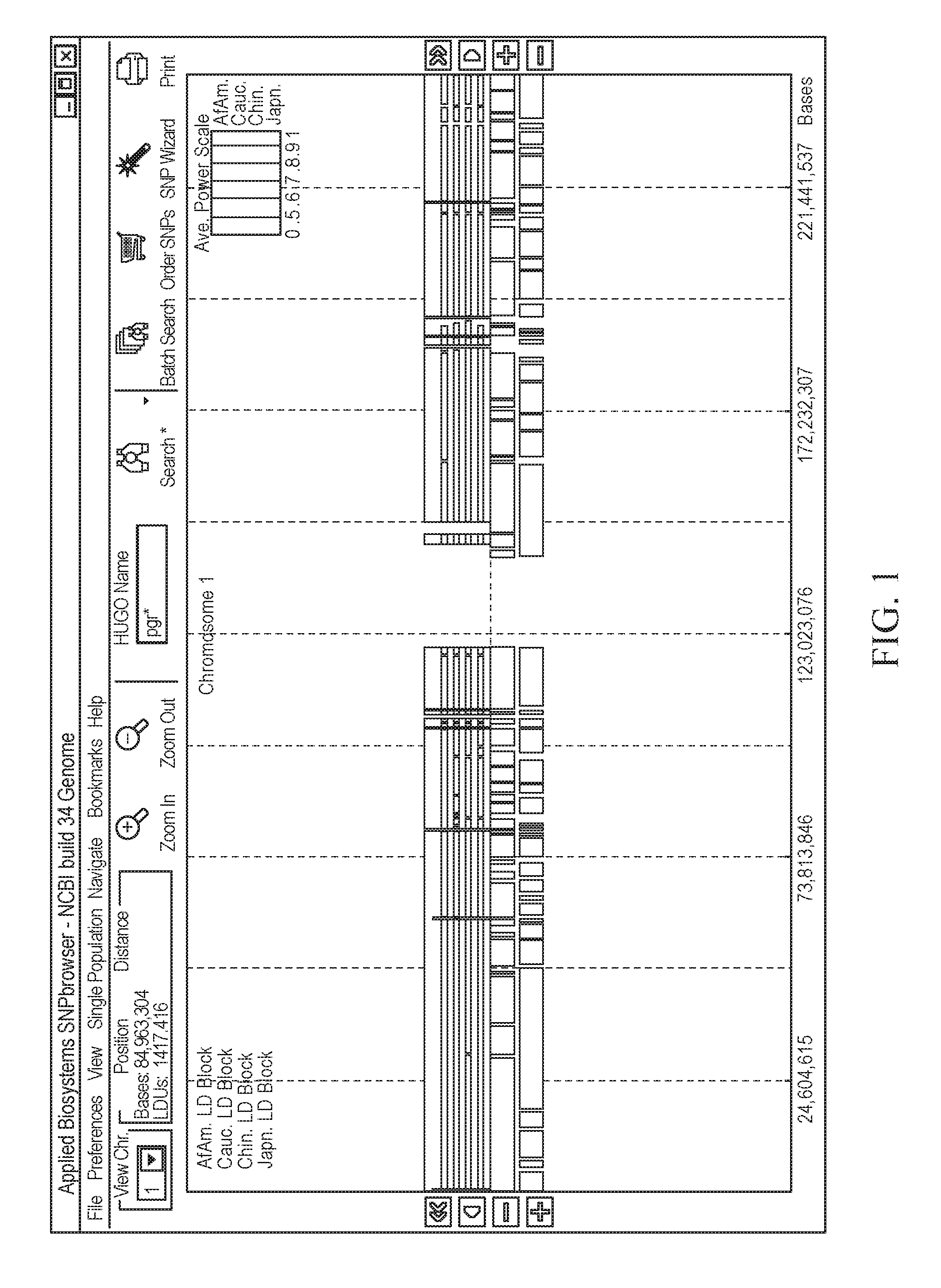
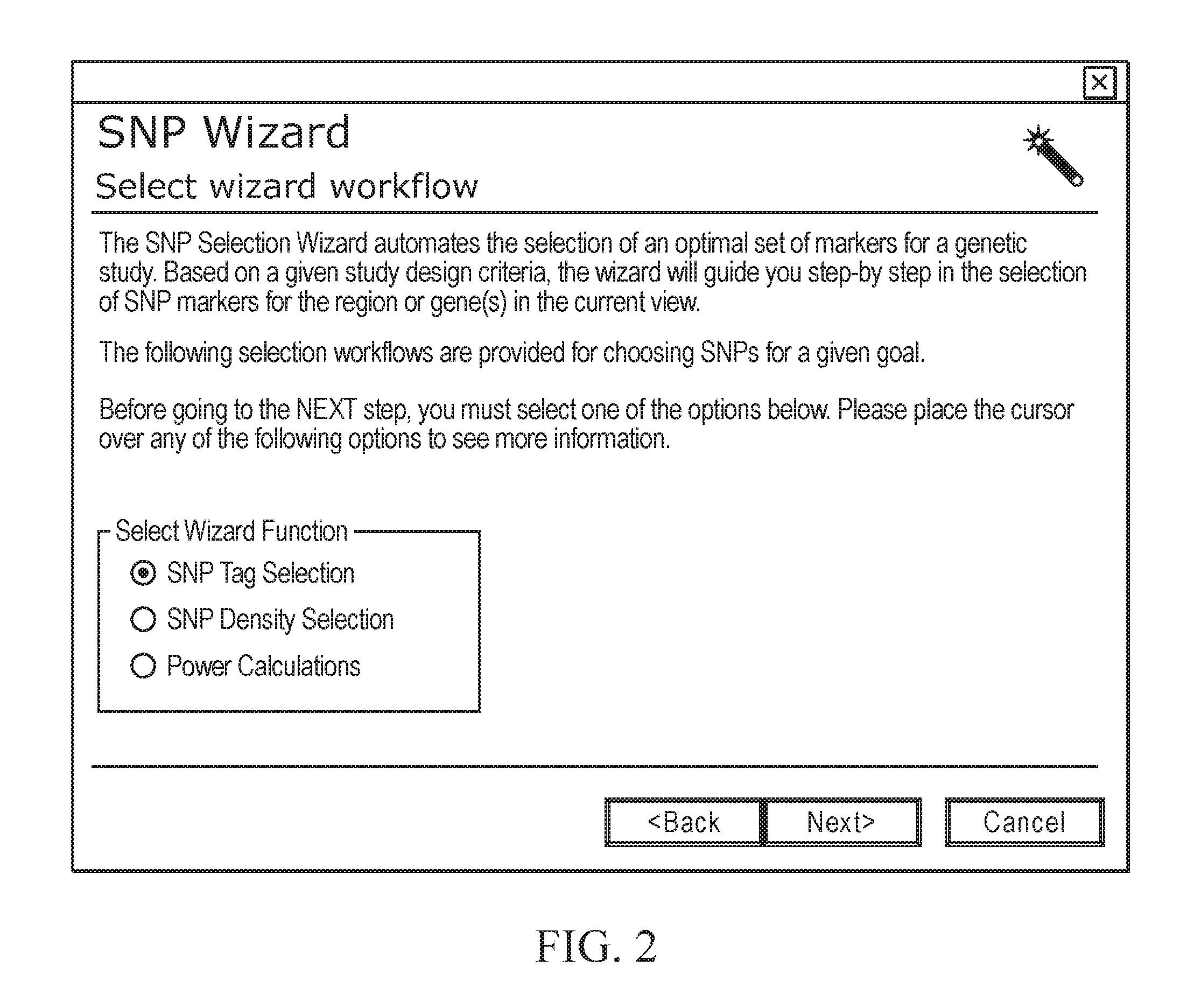
Methods and Workflows for Selecting Genetic Markers Utilizing Software Tool
InactiveUS20100153017A1Improve usabilityIncrease probabilityData visualisationProteomicsGenome mapGenetic linkage disequilibrium
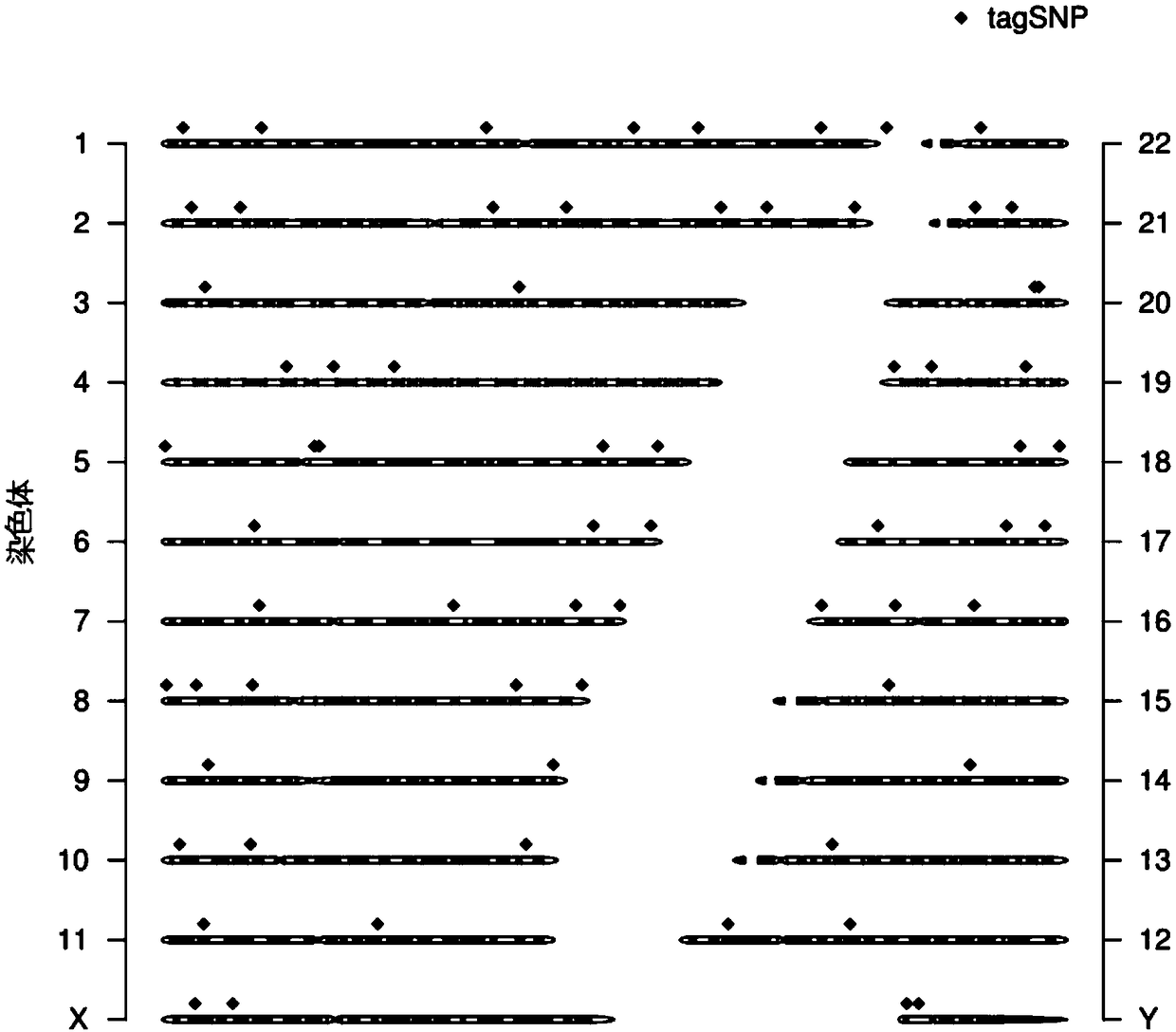
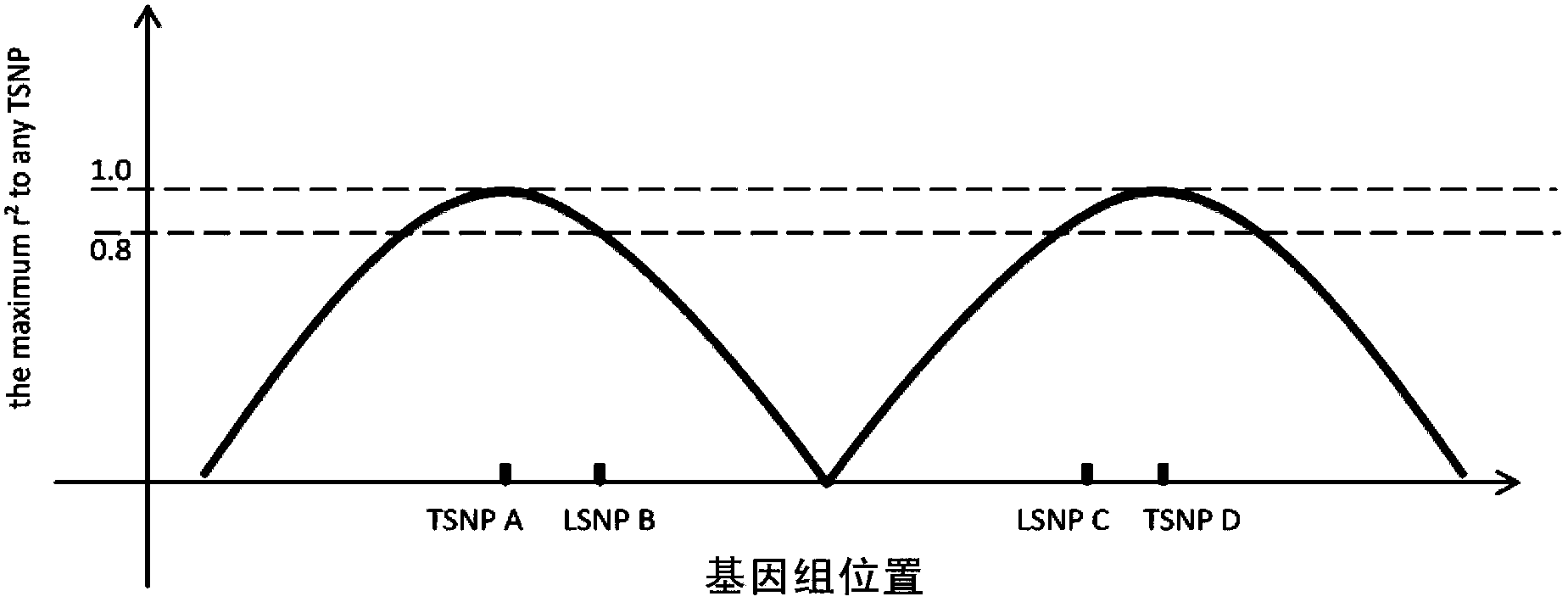
A visual tool facilitates selecting SNPs for genotyping experiments comprises a first memory containing a datastore of pre-calculated linkage disequilibrium map information; a second memory containing a datastore of haplotype block information; and a third memory containing at least one set of tagging SNPs. A graphical user interface provides visualization of SNPs, integrated with a physical genome map. A stepwise selection tool associated with the graphical user interface facilitates selection of tagging SNPs by selectively using the information in at least one of the first, second and third memories.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
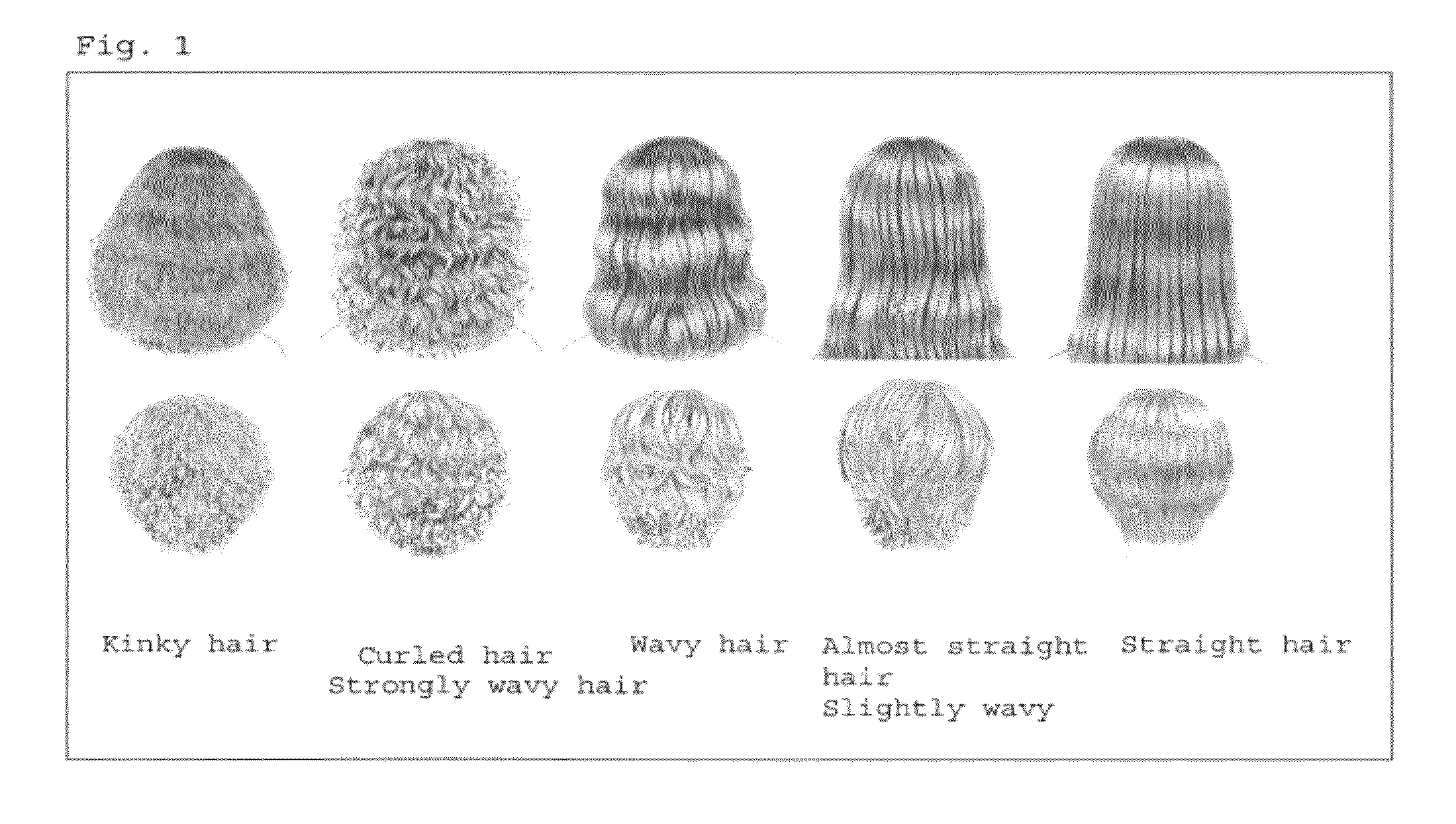
Hair Shape Susceptibility Gene
A genetic polymorphism and a hair shape susceptibility gene that are related to hair shape, and a method for determining the genetic susceptibility to hair shape in individual test subjects are provided. Disclosed is a hair shape susceptibility gene, which overlaps with a haplotype block in the 1q32.1 to 1q32.2 region (D1S249 to D1S2891) of human chromosome 1 and comprises a portion or the entirety of the base sequence of the haplotype block, wherein the haplotype block is determined by a linkage disequilibrium analysis conducted on a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker whose allele frequency differs statistically significantly between a group having a curly hair trait and a group having a non-curly hair trait, and consists of a base sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NO:1 to NO:3.
Owner:KAO CORP
Genetic marker group and individual gene identification card and application thereof
InactiveCN109321660AImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationIndividual geneHaplotype block
The invention discloses a genetic marker group and an individual gene identification card and application thereof. The genetic marker group comprises multiple SNP sites, wherein the multiple SNP sitesare tagSNPs located in different haplotype areas, the MAF is between 0.48 to 0.505, the adjacent SNP sites are not in linkage relationships, the distance among the adjacent SNP sites is larger than 1M, and variation information non A / T or C / G and the SNPs are evenly distributed in all chromosomes. By applying the technical scheme, through effective combination of the SNP sites, the set of genetic marker group which is simple in technology, economical and practical is formed, and can be used as the individual DNA identification card, and when the SNP sites are selected, linkage relationships,the MAF, distance, variation situations and the evenness of distribution on the chromosomes of the sites are taken into account, so that the accuracy of judging a certain gene sample is improved.
Owner:BEIJING USCI MEDICAL LAB CO LTD
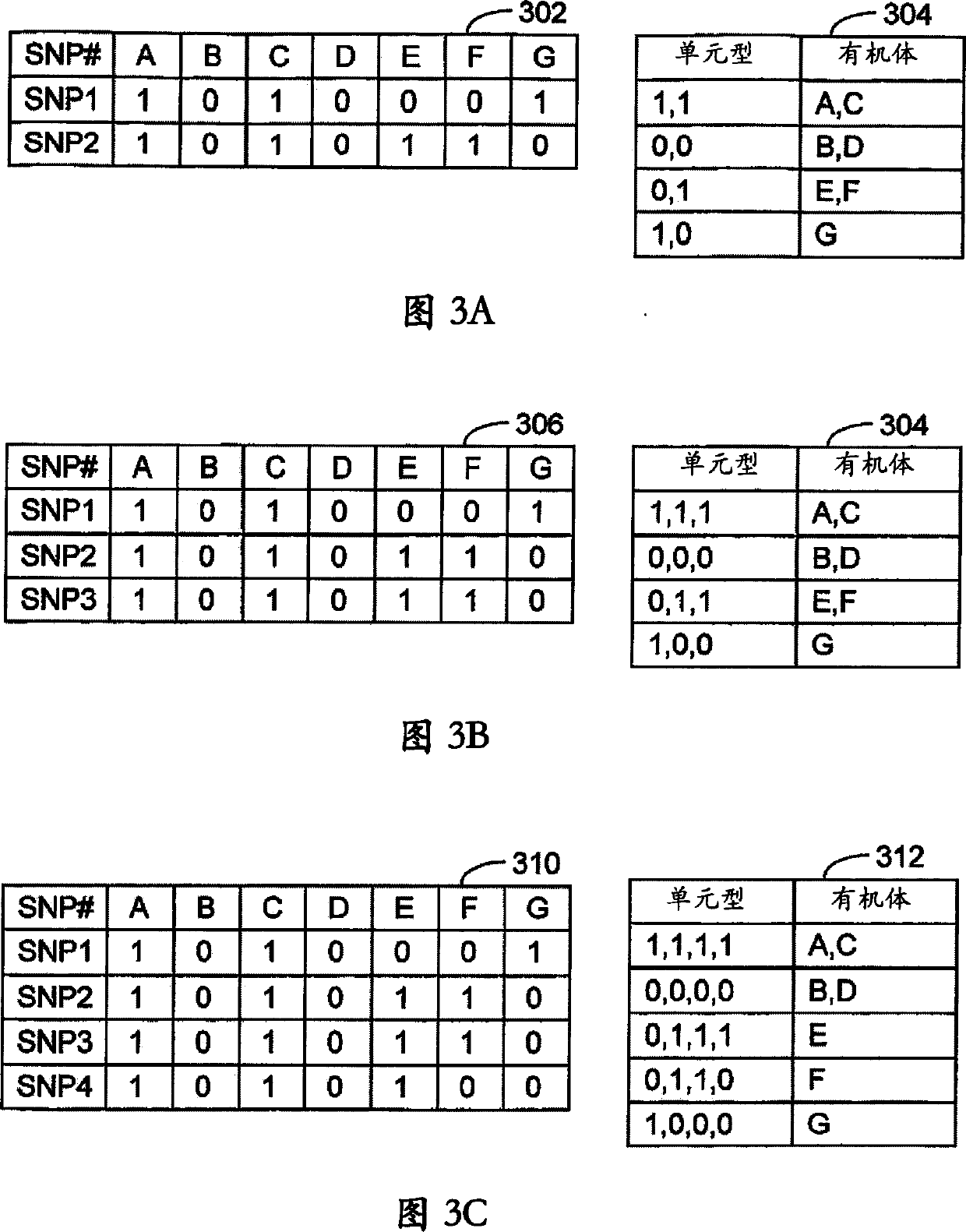
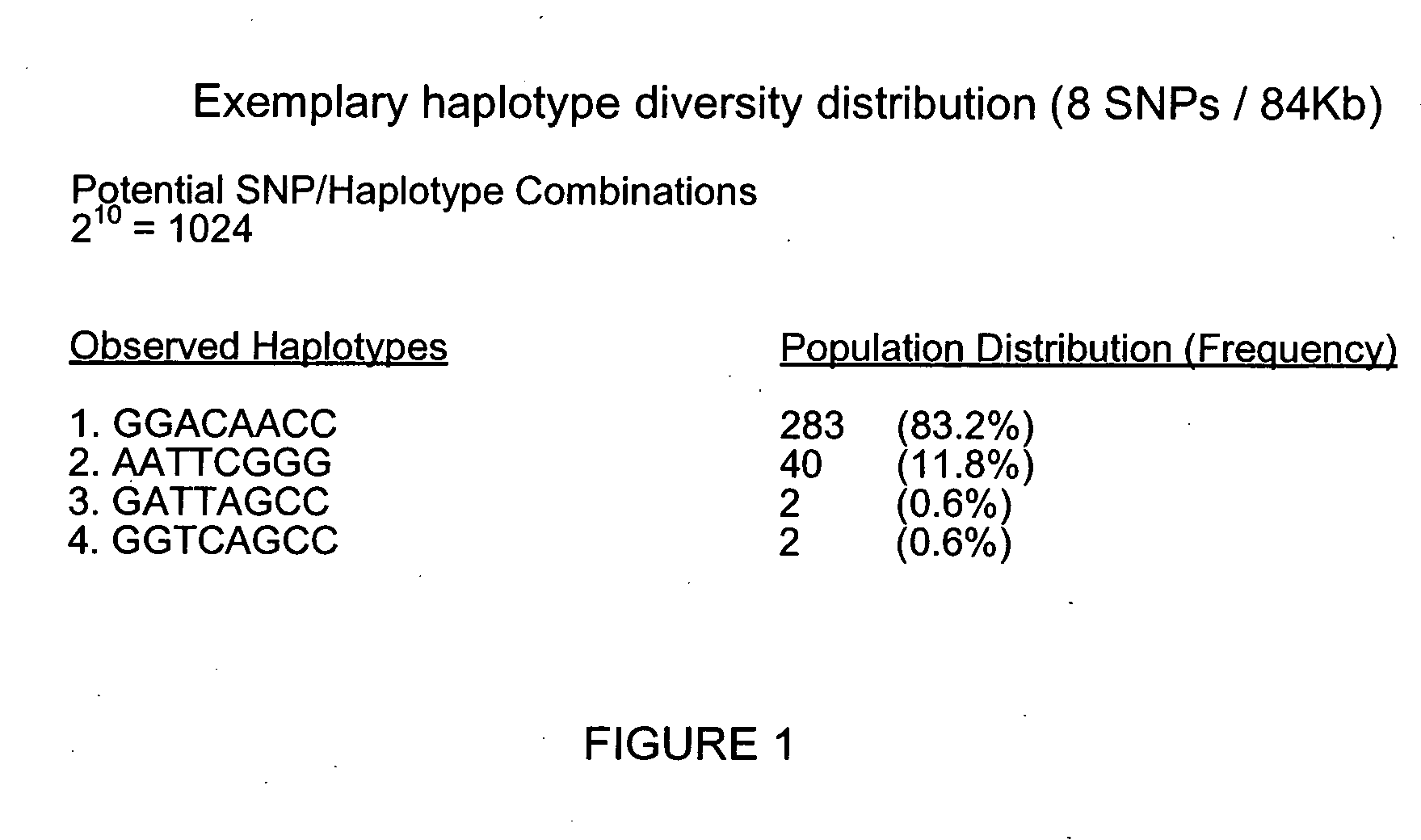
Identification of haplotype diversity
InactiveUS20050009046A1Increase percentageReduce in quantityMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsData setGenetics
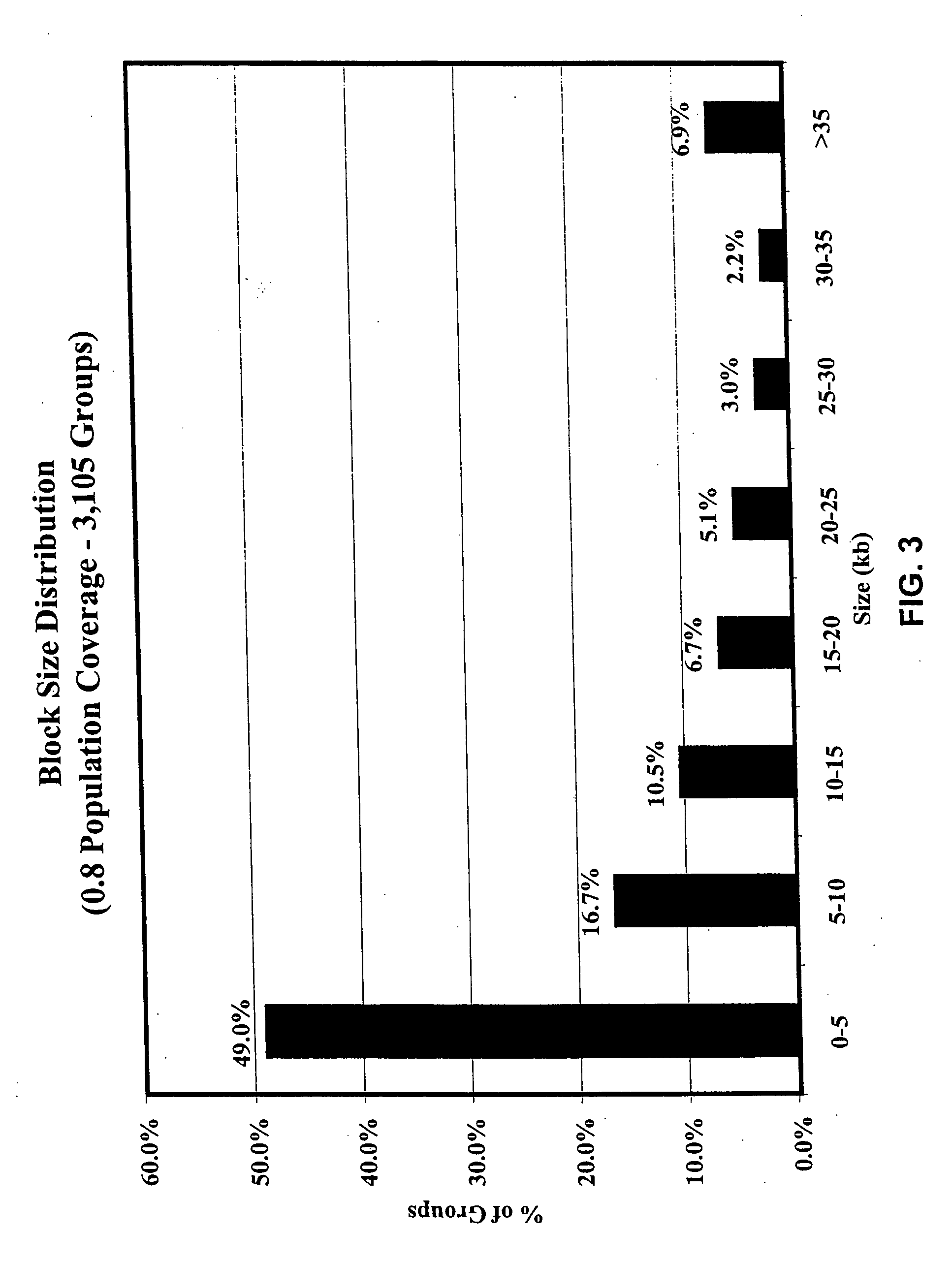
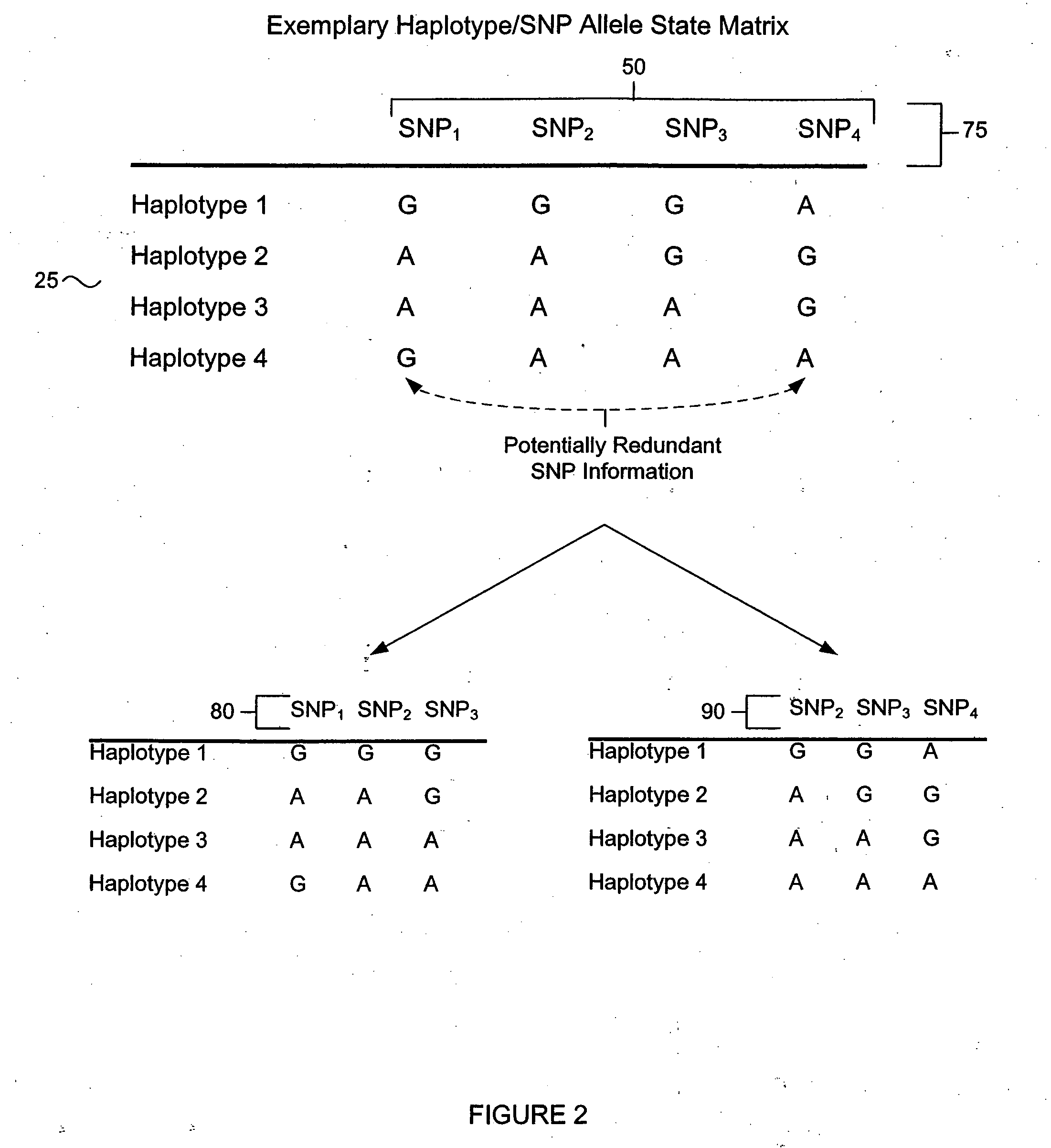
A numerical approach used to select a reduced subset of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) from a larger superset and useful for efficiently identifying haplotype blocks or other genetic loci. In general, the methods may be configured to select for the reduced SNP subset with little or no loss of haplotype diversity information. The methods may also be adapted to operate in a more aggressive mode to further reduce the SNP set while maintaining diversity of haplotype blocks with minimal loss of information. Computation of the reduced SNP subset is generally rapid and the methods perform well even when applied to large data sets spanning significant genomic distances.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
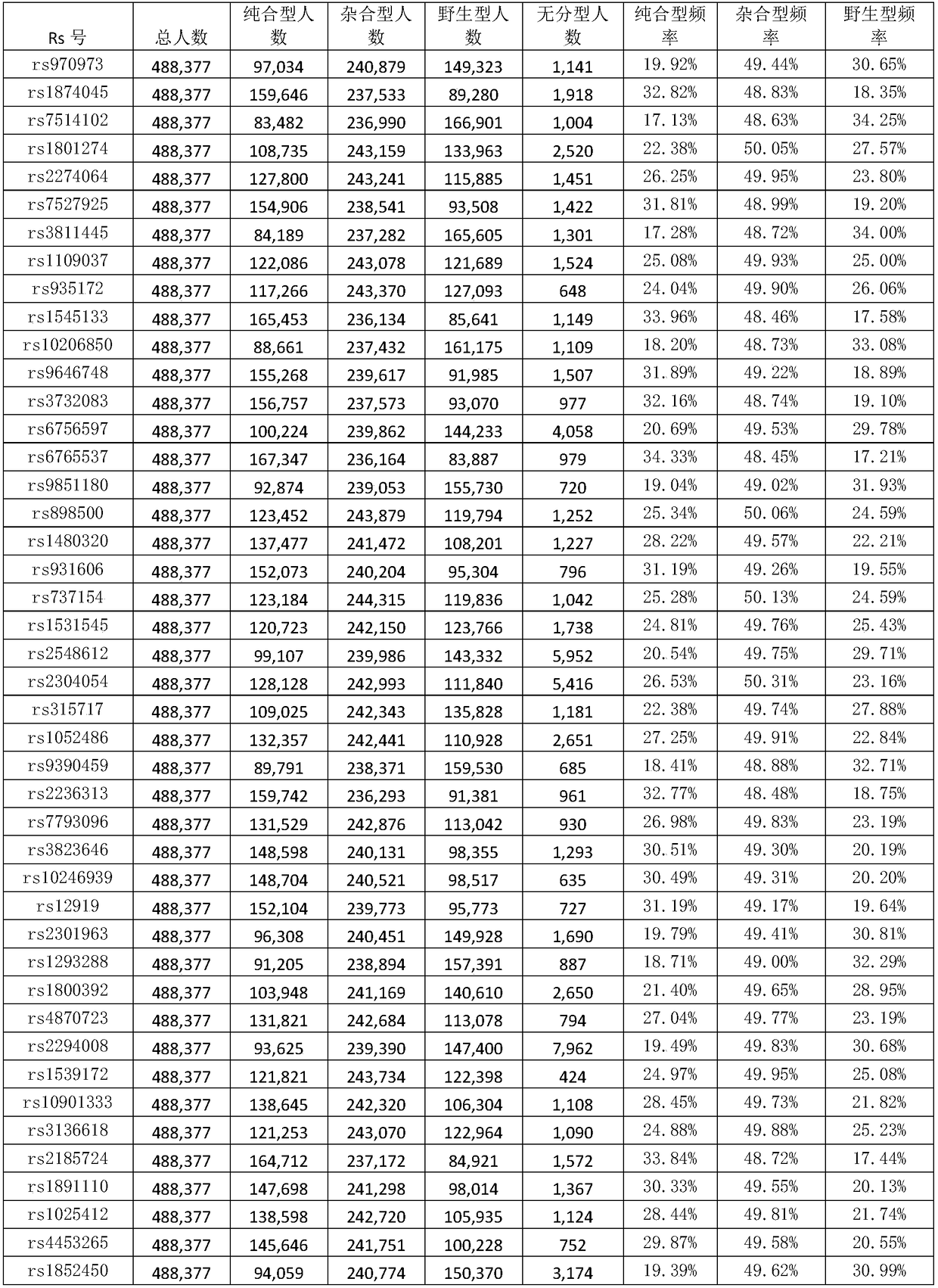
Set of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), biological marker and haplotype block tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (tagSNPs) for diagnosing hyperbilirubinemia
InactiveCN102533968APredict in advanceEarly diagnosisMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBILIRUBINAEMIADisease
The invention relates to a set of single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP), a biological marker and haplotype block tag single nucleotide polymorphisms (tagSNPs) for diagnosing hyperbilirubinemia in the technical field of biology. An SNP locus is one of the fifteen SNP loca shown in a table, and the biological marker is 1A4 intron SNPc.867+101G>T. The set of the SNP, the biological marker and the haplotype block tagSNPs can detect whether an individual has the risk of diseases or not, diagnose specific types of the hyperbilirubinemia suffered by the individual according to difference of the SNP loca of a specific marker, and achieve the purposes of early prediction, early diagnosis, early intervention and early treatment. The biological marker can further be used for developing a diagnostic reagent kit and can be applied to clinical research, analysis and diagnosis.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Deconvolution and Detection of Rare DNA in Plasma
PendingUS20200087731A1Accurate estimateMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsGerm layerMethylation analysis
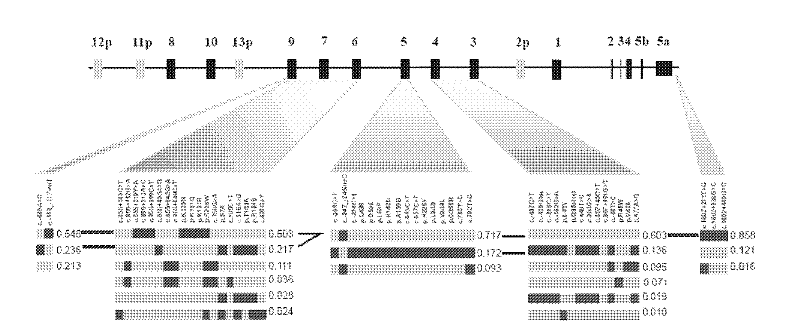
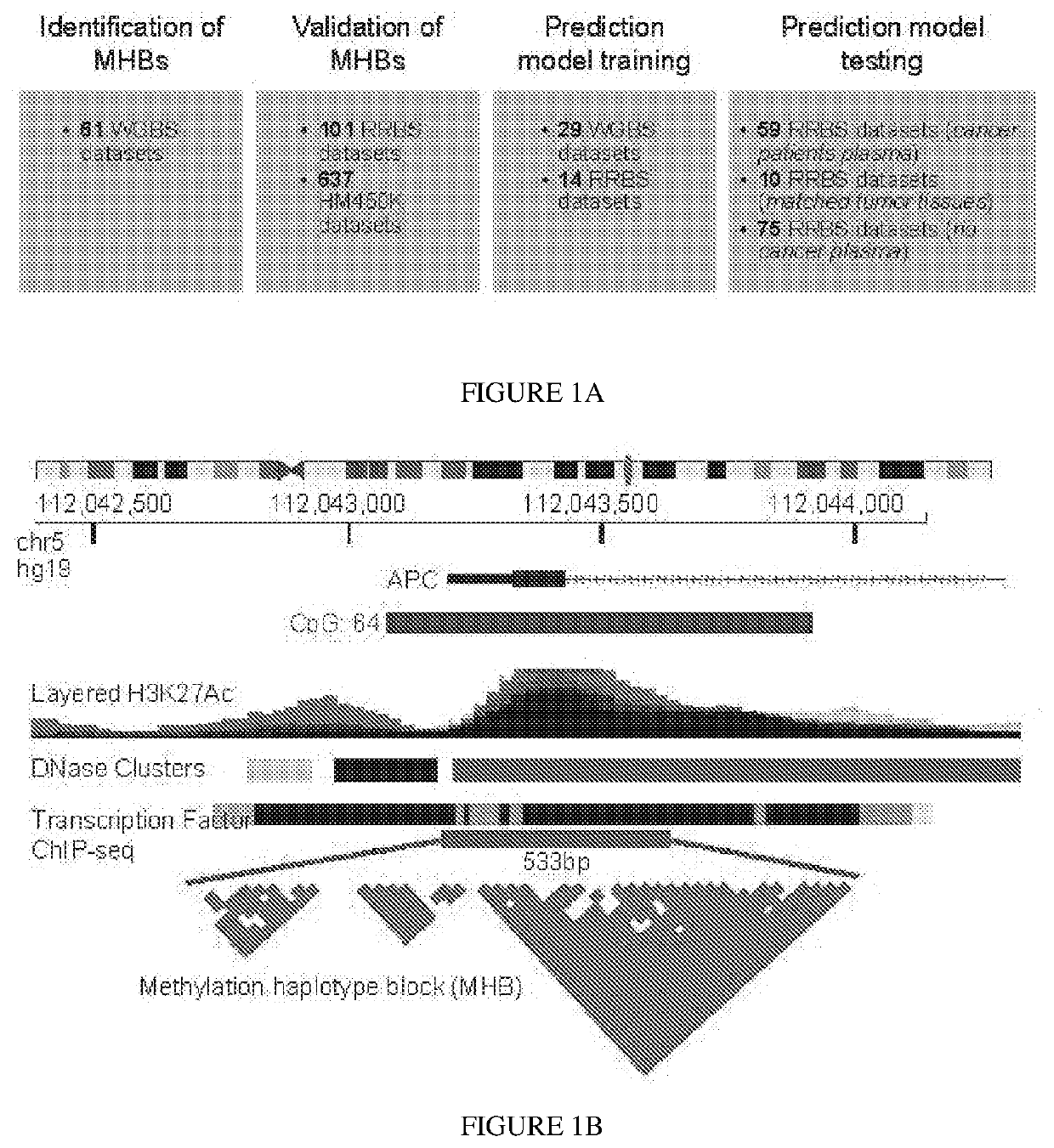
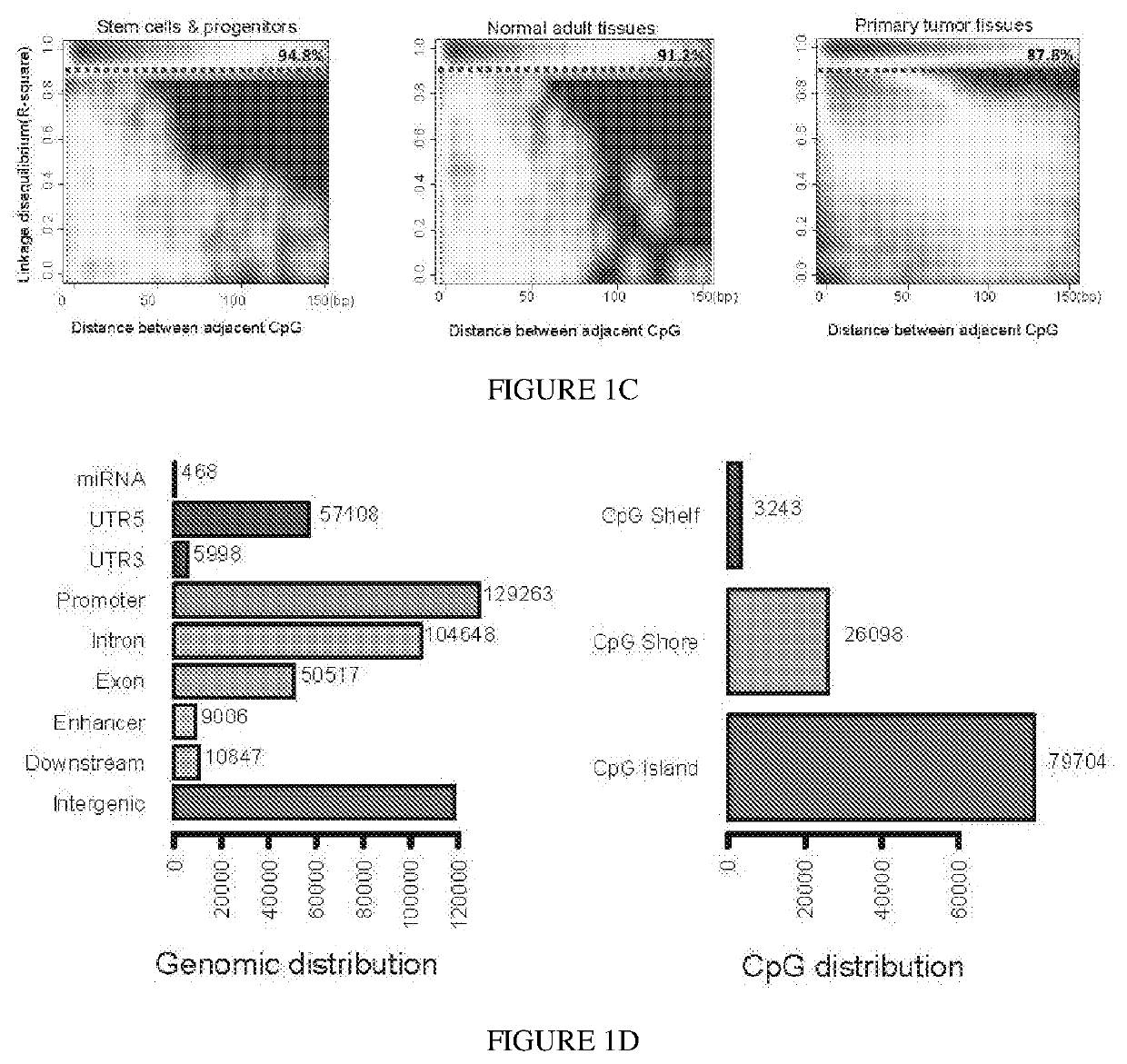
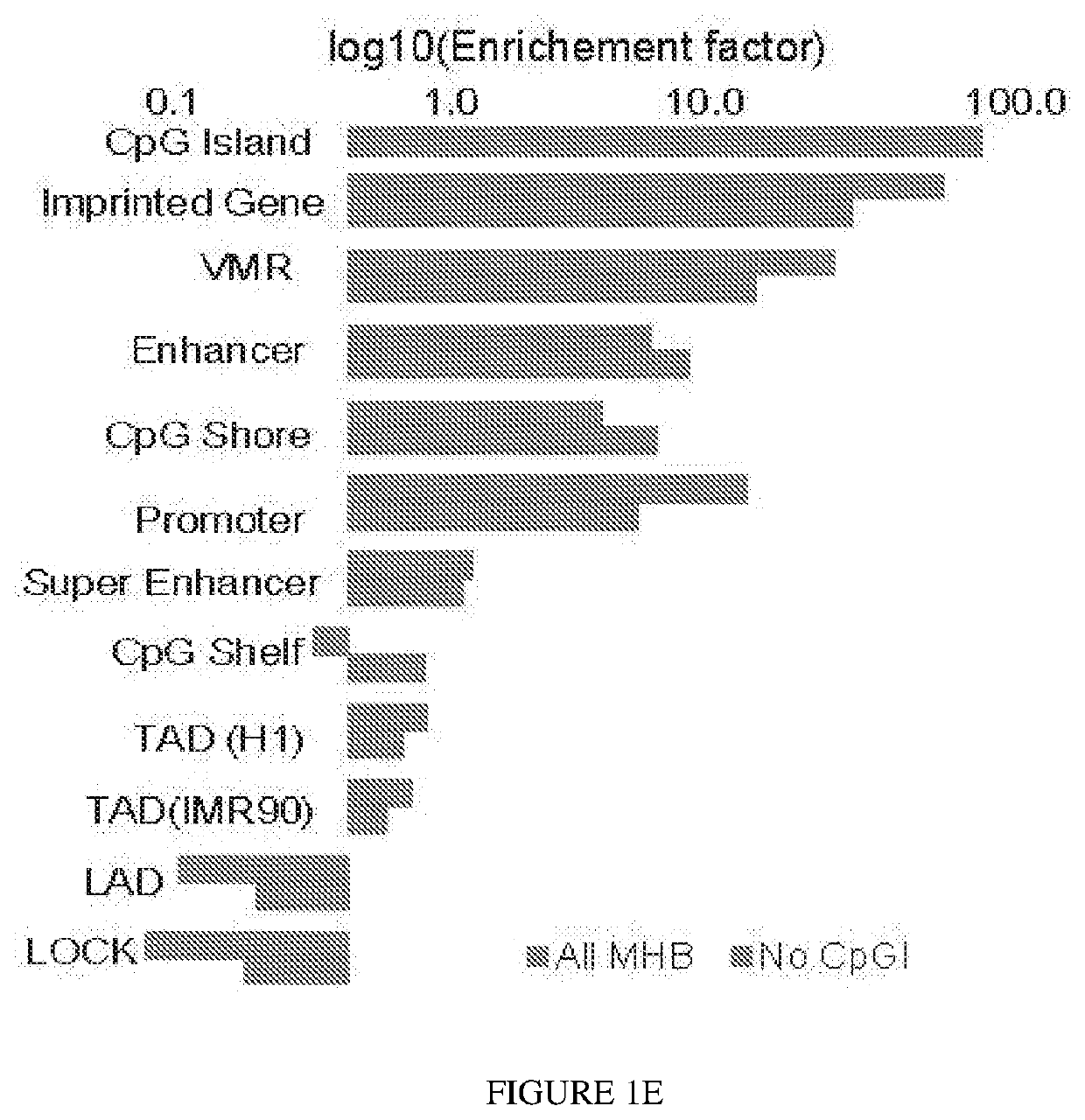
Some embodiments relate to a method for detecting the presence of one or more nucleic acids indicative of a health condition, tissue of origin, germ layer of origin or organ of origin in a mixture of nucleic acids comprising performing methylation analysis on a sample comprising a plurality of nucleic acids and determining whether the sample includes a plurality of methylation haplotype blocks indicative of the presence one or more nucleic acids indicative of a health condition, tissue of origin, germ layer of origin or organ of origin wherein the methylation haplotype blocks comprise a plurality of methylation sites for which the methylation status is coordinated.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
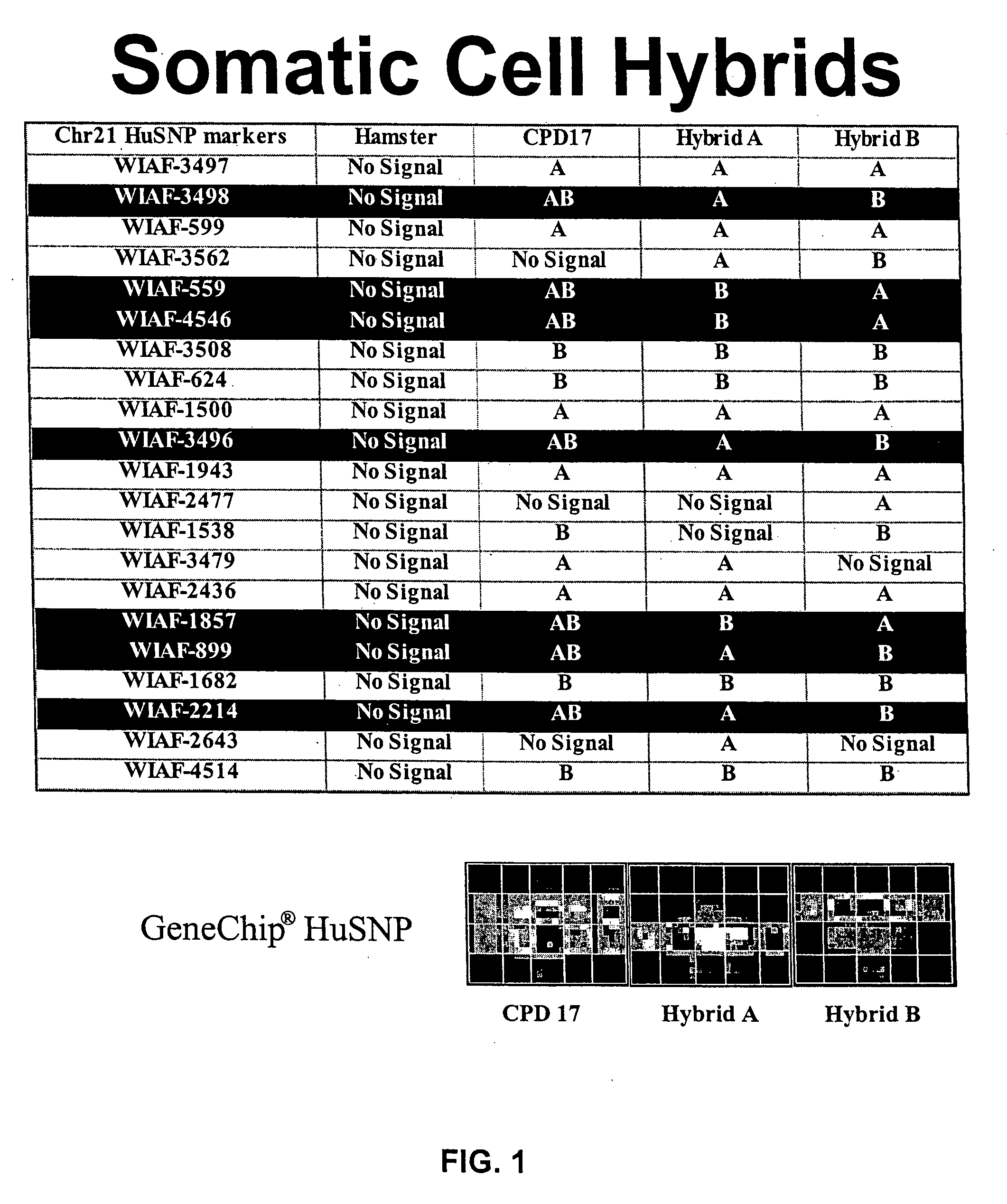
Haplotype structures of chromosome 21
InactiveUS7115726B2Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsLinkage disequilibrium
The present invention includes the use of any of the polymorphisms, SNP haplotype blocks or SNP haplotype patterns. In one embodiment, susceptibility to a phenotype resulting from an allele or marker in linkage disequilibrium with such polymorphic forms is evaluated. Novel therapeutic and diagnostic compounds and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Identification of ancestral haplotypes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20090220953A1Reduce riskSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseComplement control protein
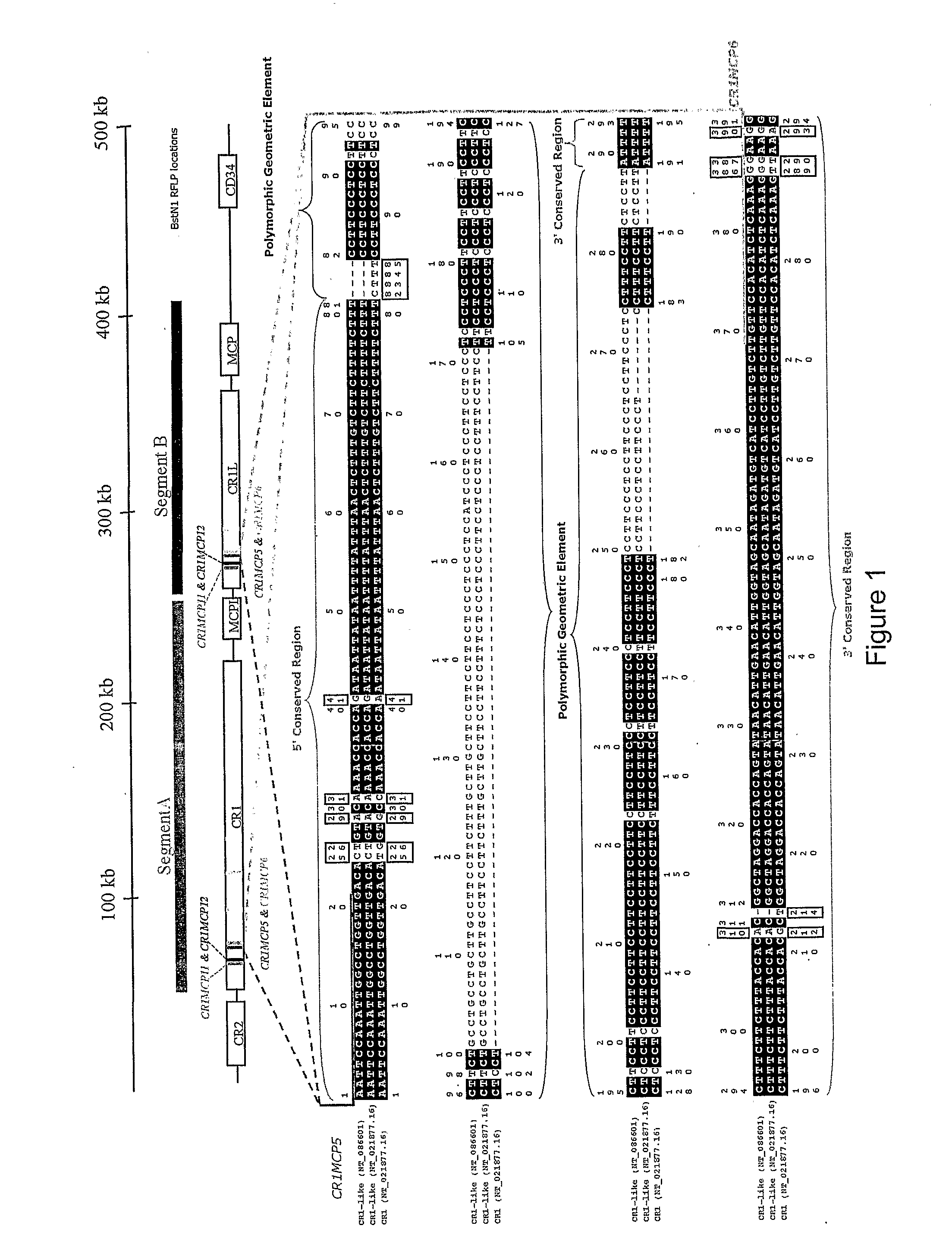
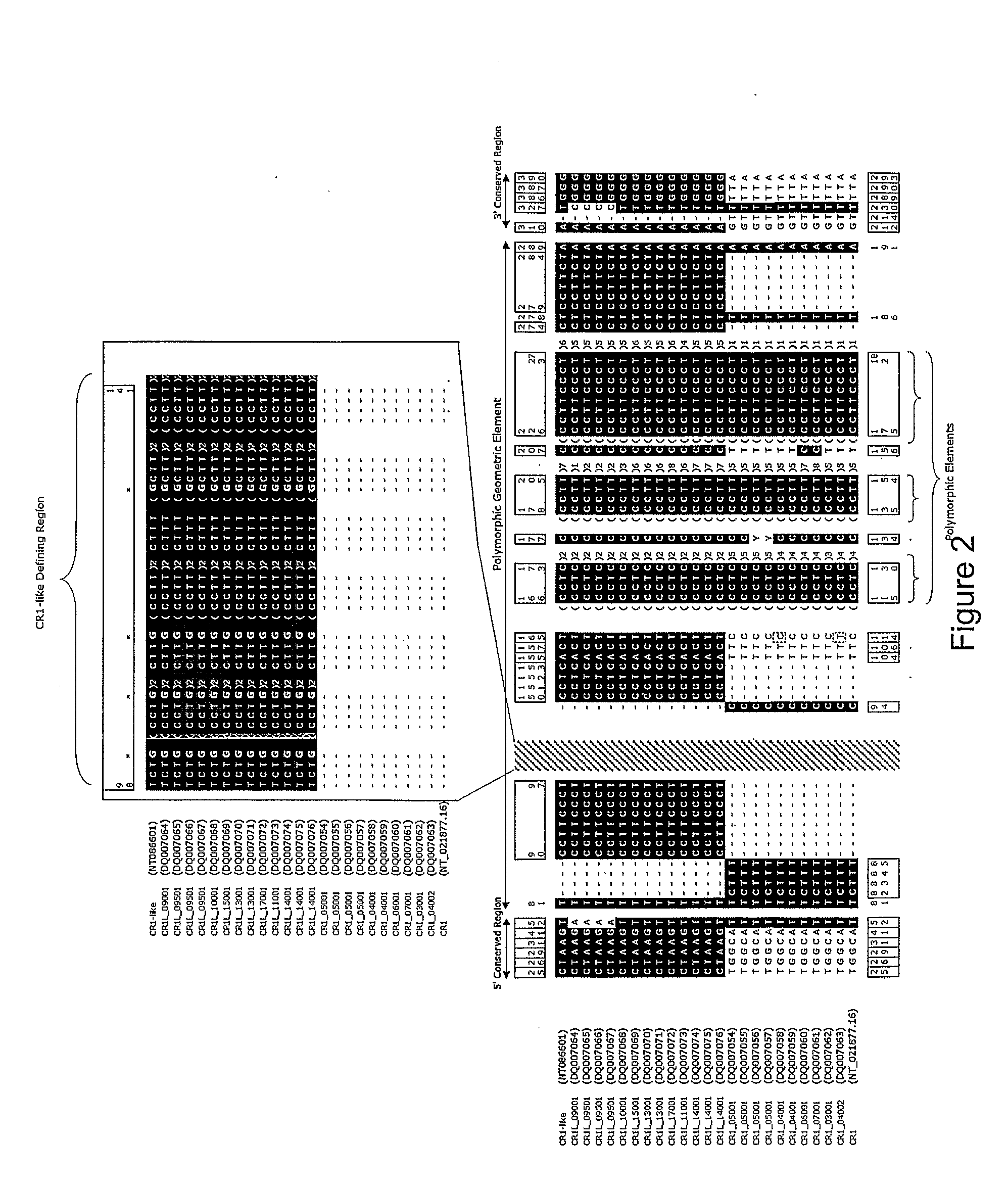
The present invention relates to the identification of haplospecific geometric elements (HGEs) in a multigene cluster comprising genes encoding complement control proteins. The present invention also relates to methods of performing genomic matching techniques (GMT) which enables the identification of HGEs of a duplicated region within a haplotype block. HGEs identified using the methods of the invention can also be analysed to determine if they are markers for a trait of interest such as a disease trait. Furthermore, the present invention relates to methods of determining an individual's susceptibility or predisposition to age-related macular degeneration, recurrent spontaneous abortion, Sjögren's Syndrome and / or psoriasis vulgaris by analysing the genotype of the individual within a multigene cluster comprising genes encoding complement control proteins.
Owner:CY OCONNOR ERADE VILLAGE FOUND
Method for detecting exome mononucleotide coverage rate
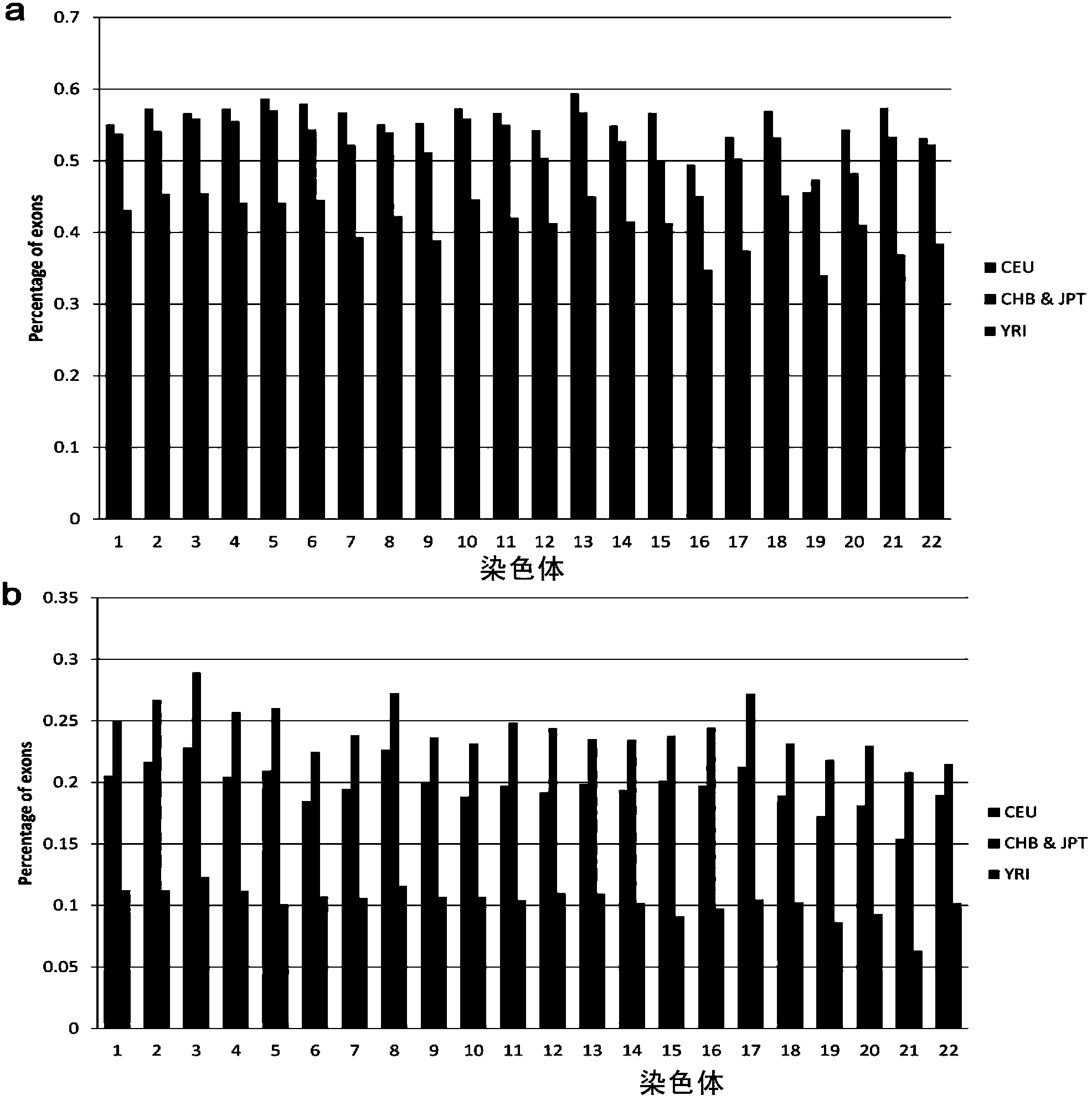
InactiveCN103455732AReduce false positive rateImprove accuracySpecial data processing applicationsData setGenetic linkage disequilibrium
The invention discloses a method and a system for unbiasedly evaluating whole genome SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) chip exome and analyzing gene coverage rate, and evaluating SNP coverage rate condition of DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid) fragments. False positive rate of the existing methods can be reduced and accuracy thereof can be improved while advantages of the existing evaluating methods are preserved. The technical scheme includes establishing models according to population genetics classical theory haplotype block and linkage disequilibrium theory, loading the established data models to a data processing unit, processing dataset to be detected or sequence position information, outputting image results and calculating the results, inputting the results to a calculating module to analyze, and acquiring annotation of coverage rate condition and r2 according to image information and data information.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods and Workflows for Selecting Genetic Markers Utilizing Software Tool
InactiveUS20160224216A1Improve usabilityIncrease probabilityData visualisationProteomicsGenome mapGenetic linkage disequilibrium
A visual tool facilitates selecting SNPs for genotyping experiments comprises a first memory containing a datastore of pre-calculated linkage disequilibrium map information; a second memory containing a datastore of haplotype block information; and a third memory containing at least one set of tagging SNPs. A graphical user interface provides visualization of SNPs, integrated with a physical genome map. A stepwise selection tool associated with the graphical user interface facilitates selection of tagging SNPs by selectively using the information in at least one of the first, second and third memories.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Haplotype structures of chromosome 21
The present invention includes the use of any of the polymorphisms, SNP haplotype blocks or SNP haplotype patterns. In one embodiment, susceptibility to a phenotype resulting from an allele or marker in linkage disequilibrium with such polymorphic forms is evaluated. Novel therapeutic and diagnostic compounds and methods are also disclosed.
Owner:GENETIC TECHNOLOGIES LIMTIED
Hair shape susceptibility gene
A genetic polymorphism and a hair shape susceptibility gene that are related to hair shape, and a method for determining the genetic susceptibility to hair shape in individual test subjects are provided. Disclosed is a hair shape susceptibility gene, which overlaps with a haplotype block in the 1q32.1 to 1q32.2 region (D1S249 to D1S2891) of human chromosome 1 and comprises a portion or the entirety of the base sequence of the haplotype block, wherein the haplotype block is determined by a linkage disequilibrium analysis conducted on a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) marker whose allele frequency differs statistically significantly between a group having a curly hair trait and a group having a non-curly hair trait, and consists of a base sequence set forth in any one of SEQ ID NO:1 to NO:3.
Owner:KAO CORP
A restricted two-stage genome-wide association analysis method based on snpldb markers
InactiveCN104651517BShorten the attenuation distanceMultiple allelic variationMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsMulti siteRegression analysis
The invention discloses a restrictive two-stage genome-wide association study (GWAS) method based on an SNPLDB mark, and aims at solving the problems that a traditional method cannot be used for estimating multiple allele information, and is high in false positive rate and low in efficiency of detection on inbreeding crops. By combination of the SNPLDB mark constructed on the basis of a haplotype block, correction of deviation of an inbreeding population relation analysis model and a two-stage relation analysis strategy under a multi-site model, the GWAS method suitable for conventional breeding of inbreeding crops is built; the SNPLDB mark is applied to GWAS, so that a method is provided for multiple allele estimation; candidate sites are screened on the basis of a single-site model in the first stage, and are further screened on the basis of a progressive regression analysis method in the multi-site model in the second stage, so as to balance the problems of missing of heritability and over-high heritability estimation. Therefore, the interpretation ratio of a final genetic model is controlled at trait heritability. The positioning accuracy and efficiency are improved by a feature vector and an appropriate significant level of a similarity coefficient matrix estimated by the SNPLDB mark by GWAS.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
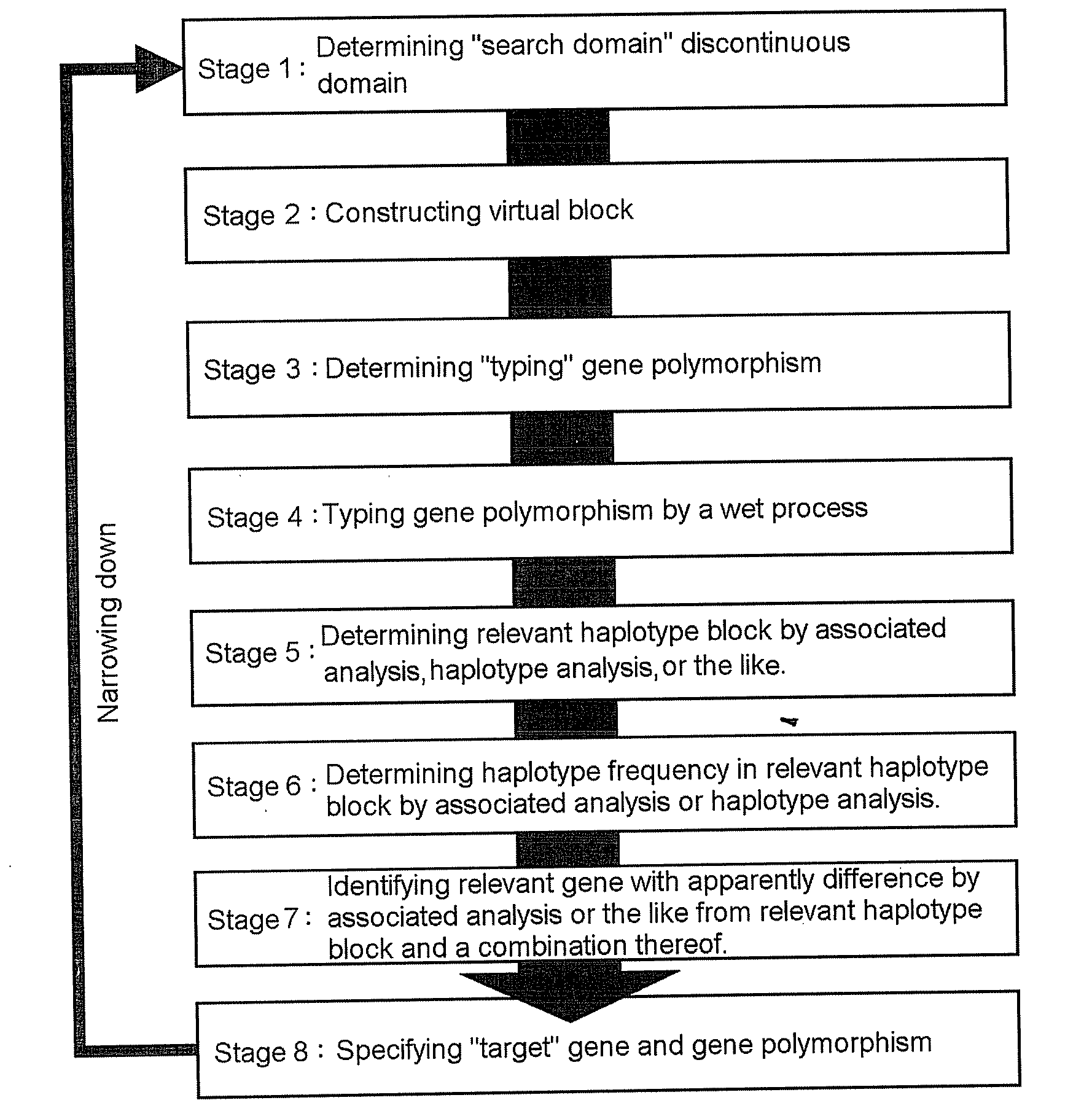
Method of Systematic Analysis of Relevant Gene in Relevant Genome Region (Including Relevant Gene/Relevant Haplotype)
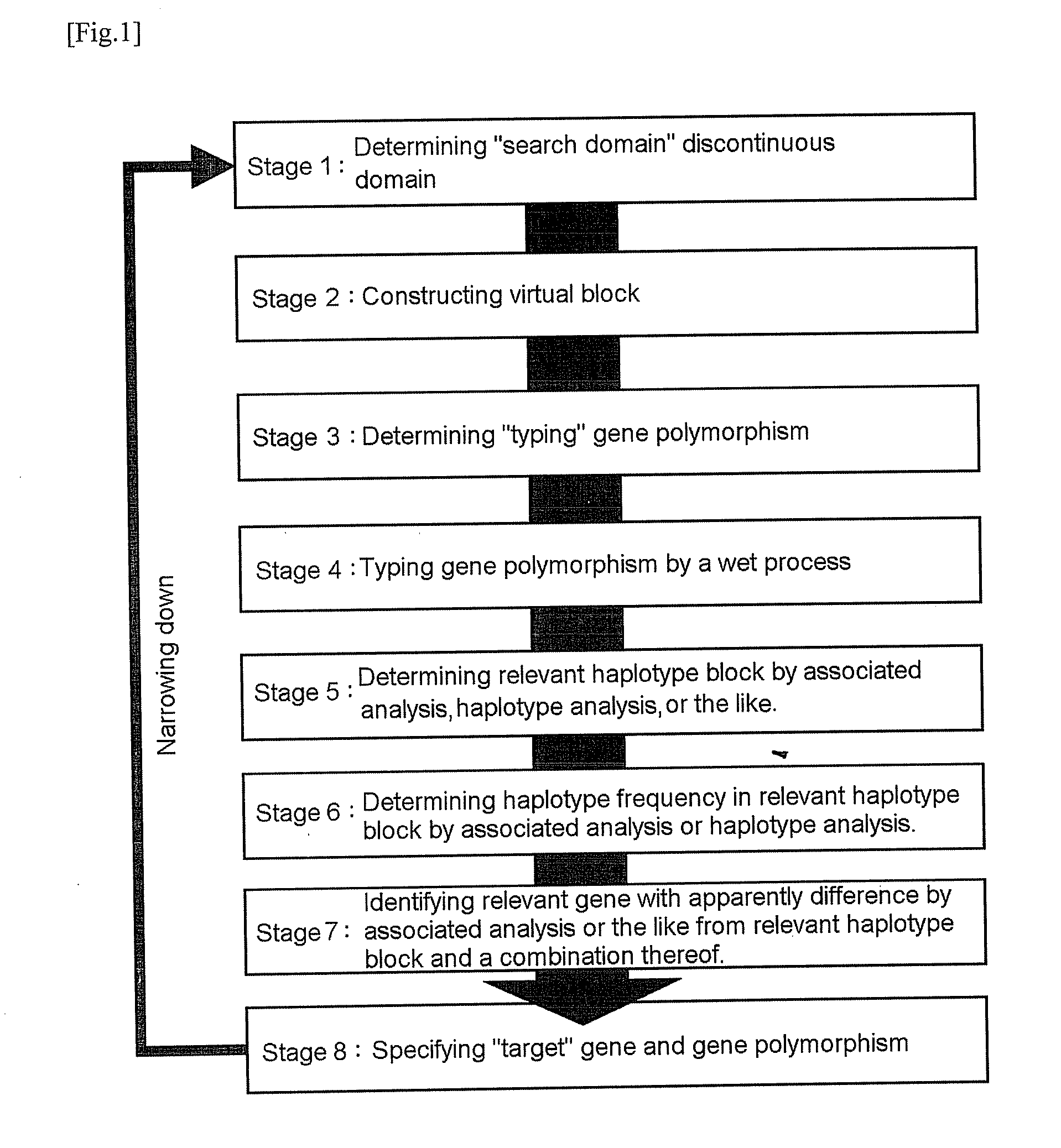
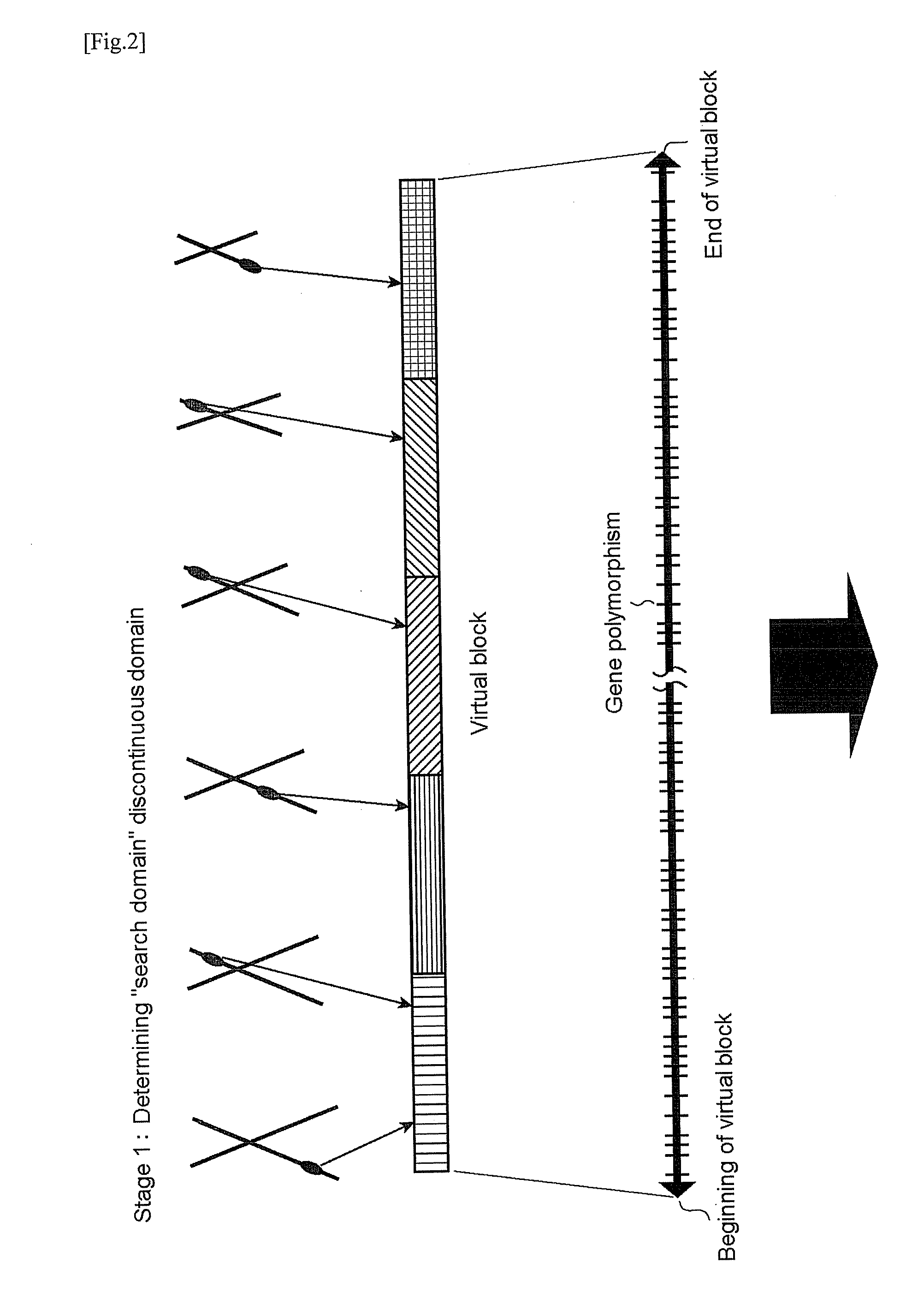
InactiveUS20080133144A1Analogue computers for chemical processesBiostatisticsSystems analysisAnalysis method
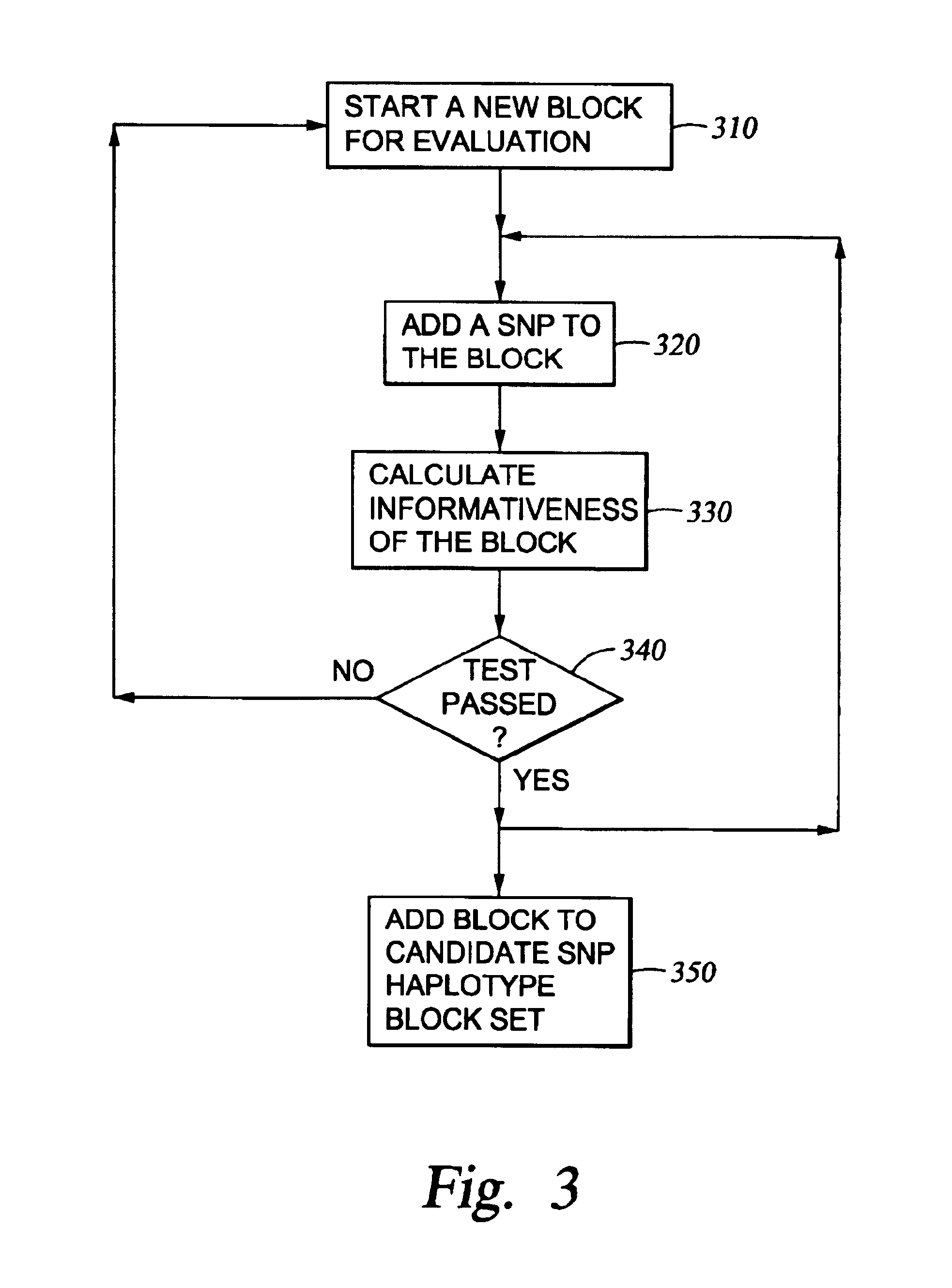
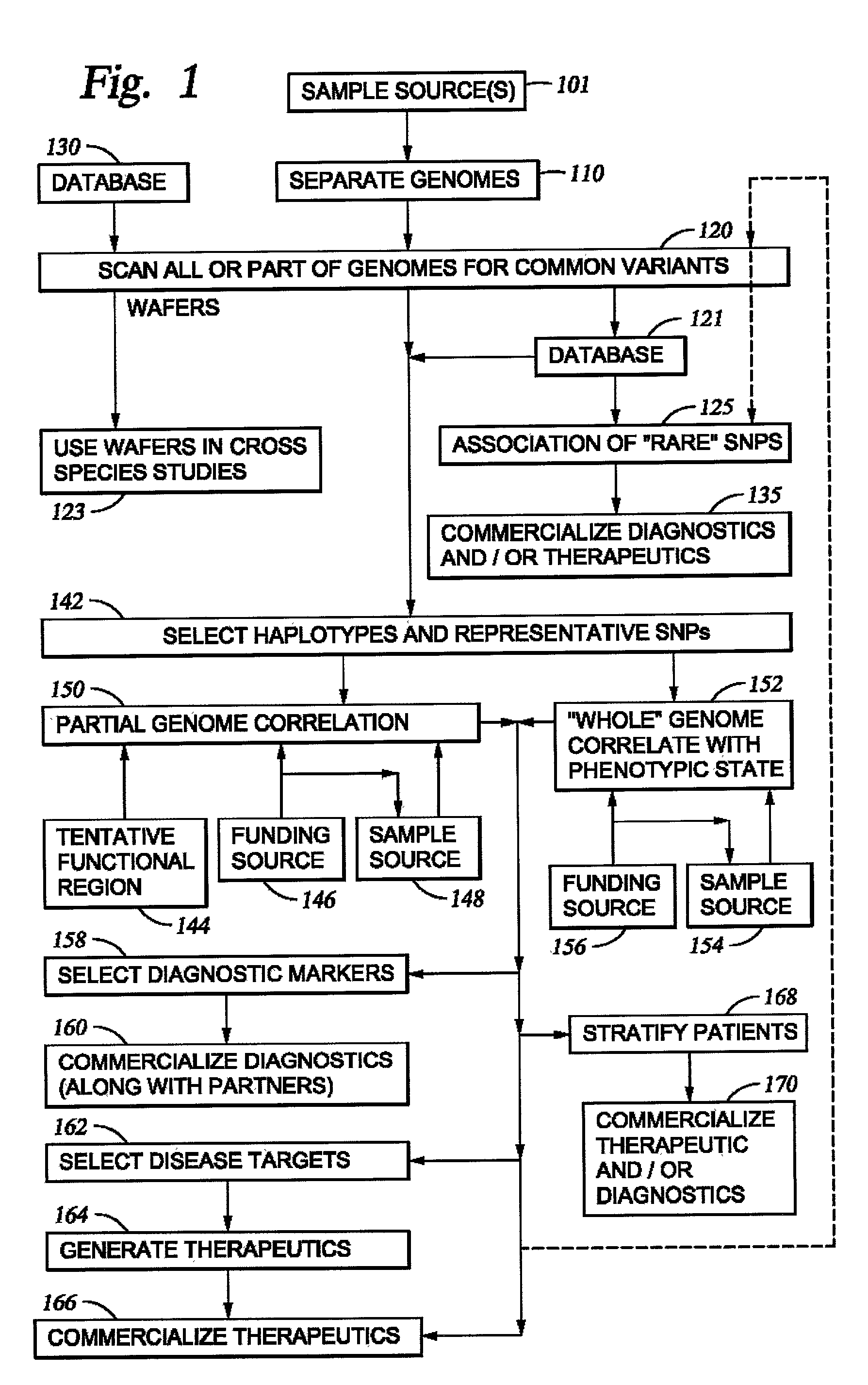
It is intended to provide a systematic analysis method wherein the virtual haplotype of a gene polymorphism serving as a marker is assumed and then a relevant haplotype block and a gene or a genome domain relating to a phenotype are successively determined from the whole genome domain or a genome domain of interest. As FIG. 1 shows, a discontinuous analysis method of the embodiment 1 comprises repeating the steps of constructing a virtual block from a discontinuous genome domain, determining a haplotype block based on a virtual haplotype, and then analyzing the relevancy to thereby determine a genome domain relating to a phenotype. Thus, it is possible to determine a relevant haplotype block, a relevant haplotype and a relevant gene.
Owner:DIGITAL INFORMATION TECH CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com