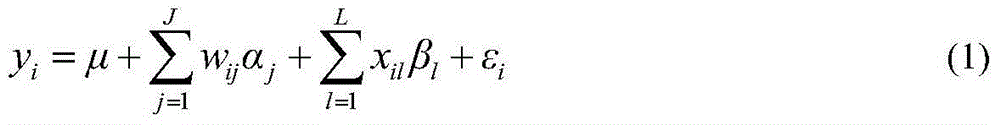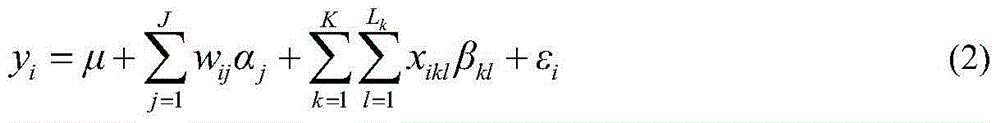Restrictive two-stage genome-wide association study (GWAS) method based on SNPLDB mark
A whole-genome, association analysis technology, applied in the field of molecular quantitative genetics and molecular breeding, can solve the problems of missing heritability, kinship sensitivity, and reduced GWAS efficacy, so as to reduce multiple test problems, reduce false positives, and improve The effect of detection power
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0030] The invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings of the description.
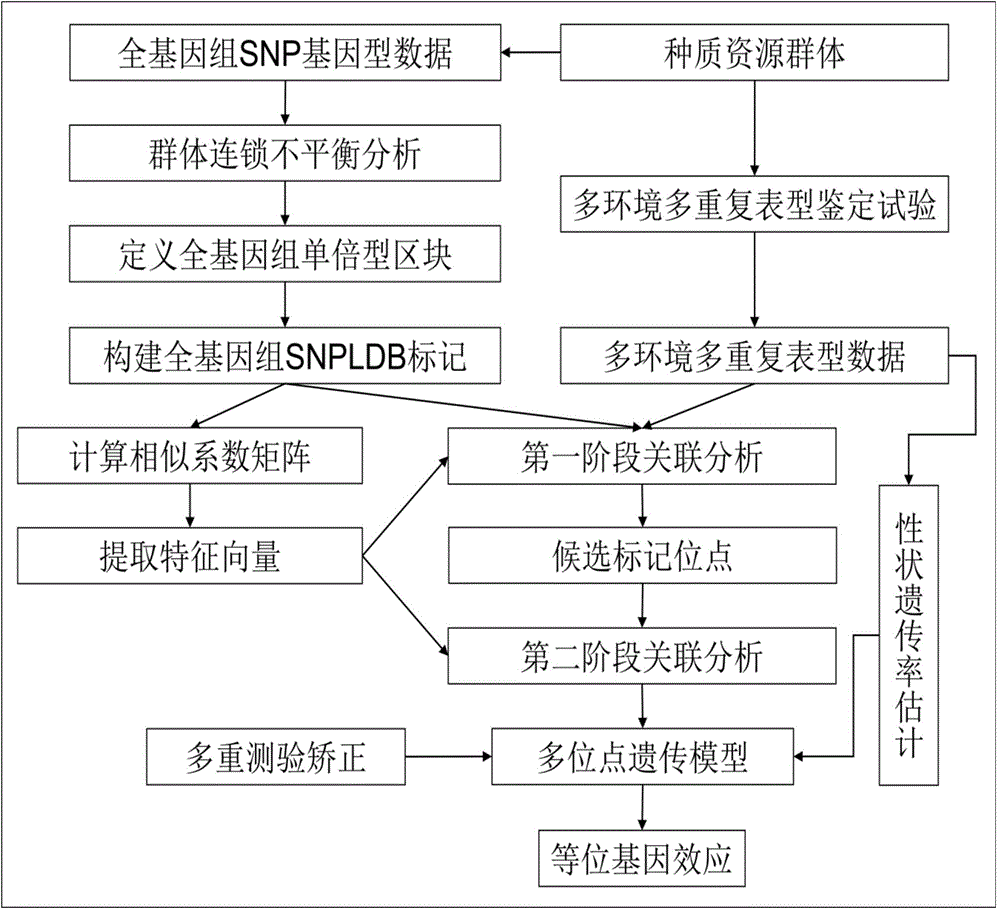
[0031] like figure 1 As shown, a flow chart of a restrictive two-stage genome-wide association analysis method based on SNPLDB markers, and the implementation process of the method is designed. These three steps of the two-stage association analysis under the locus model.
[0032] a) Construction of genome-wide SNPLDB markers
[0033] The genotype data of 145558 SNP molecular markers distributed in the whole genome are obtained after simplified genome sequencing (RAD-seq) and a series of quality control procedures. The minimum allele frequency of each SNP is greater than 1%. Haploview software was used to define the haplotype blocks of SNP molecular markers, the threshold was set to D'>0.7, and the window was set to 200kb. Based on the distribution of 145558 SNP molecular markers in the whole genome of Chinese soybean germplasm resources containing 1024 ma...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com