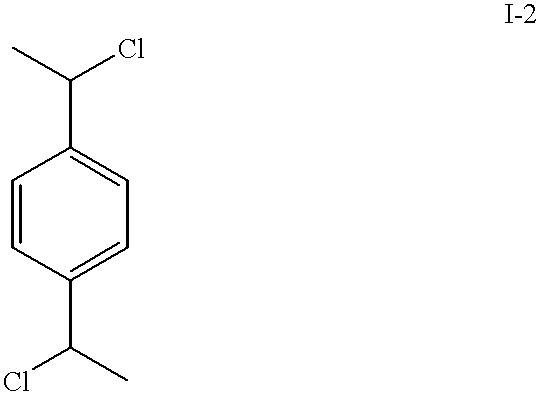
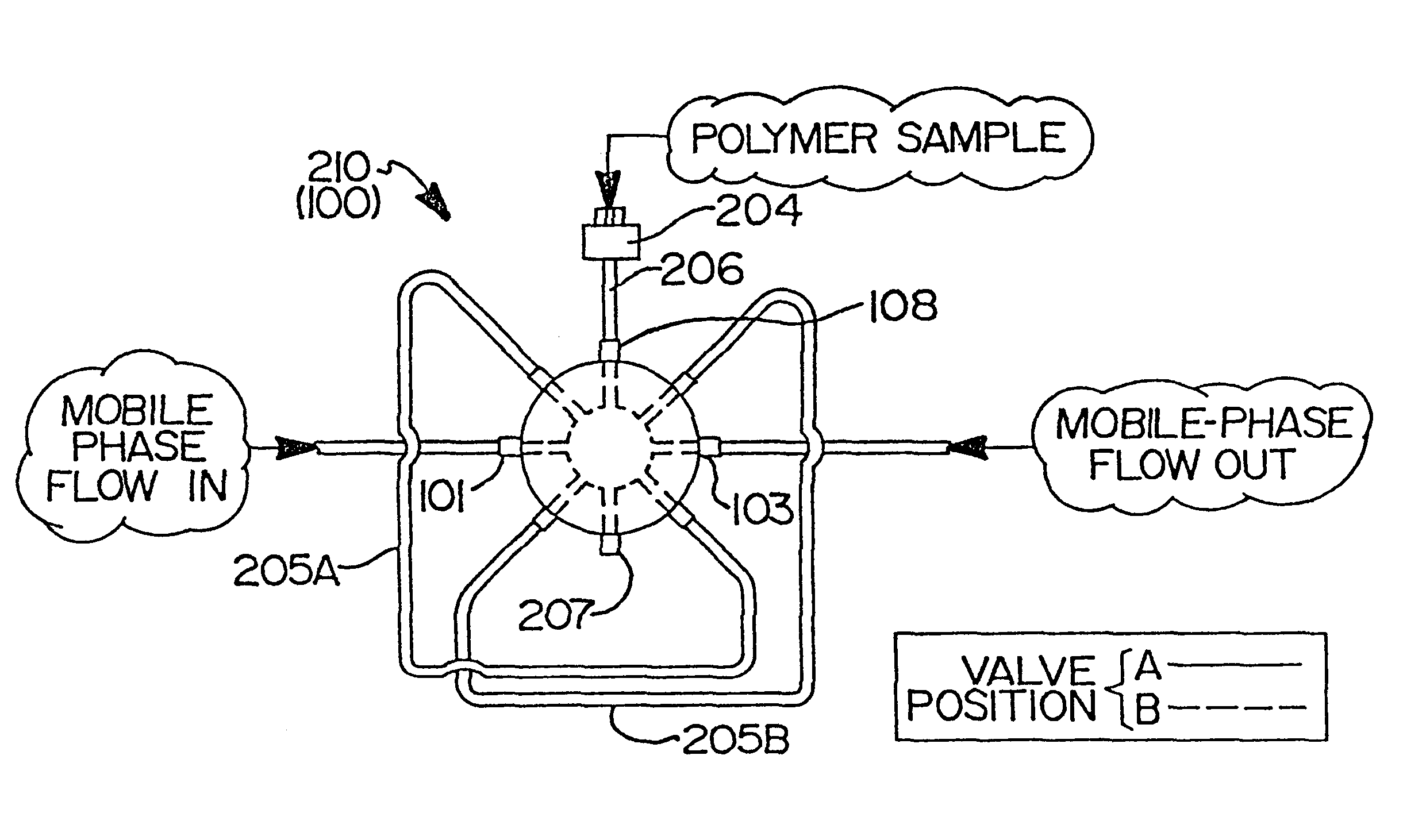
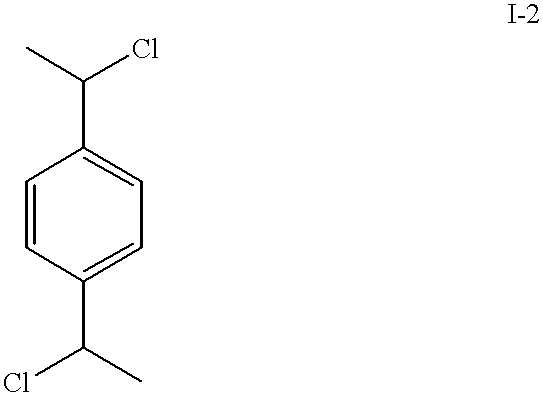
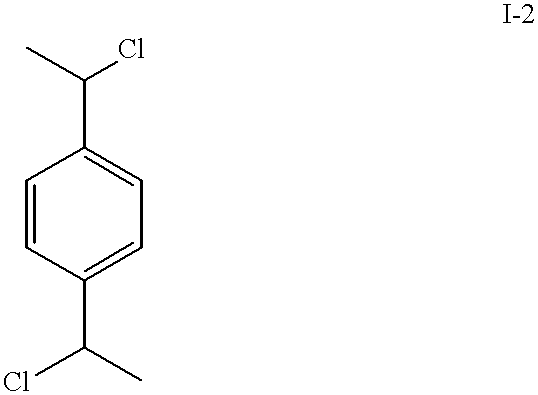
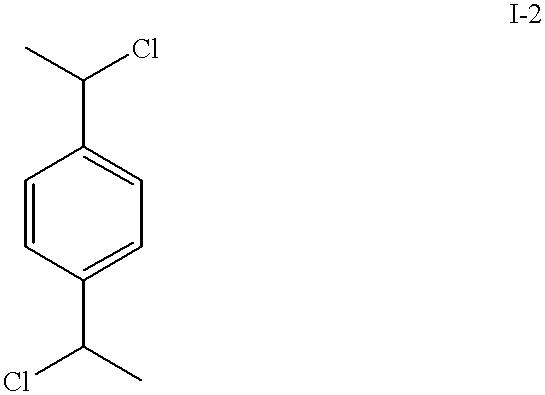
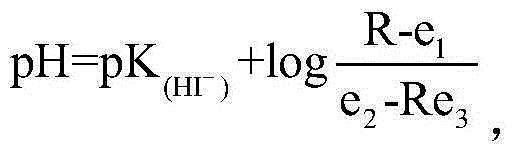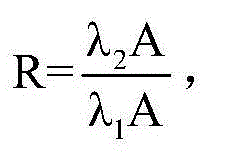Patents
Literature
126 results about "Flow injection analysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Flow injection analysis (FIA) is an approach to chemical analysis. It is accomplished by injecting a plug of sample into a flowing carrier stream. The principle is similar to that of Segmented Flow Analysis (SFA) but no air is injected into the sample or reagent streams.
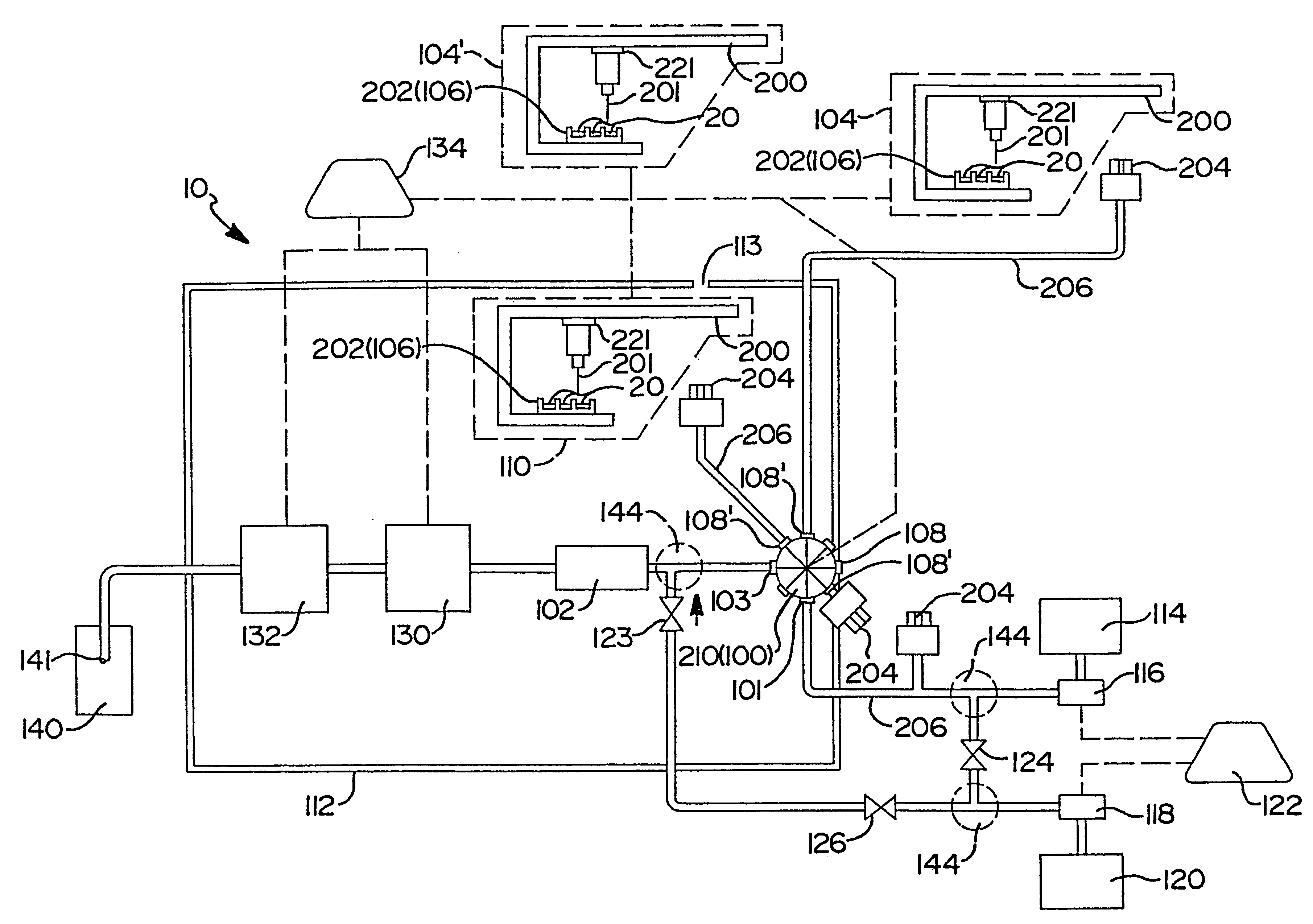
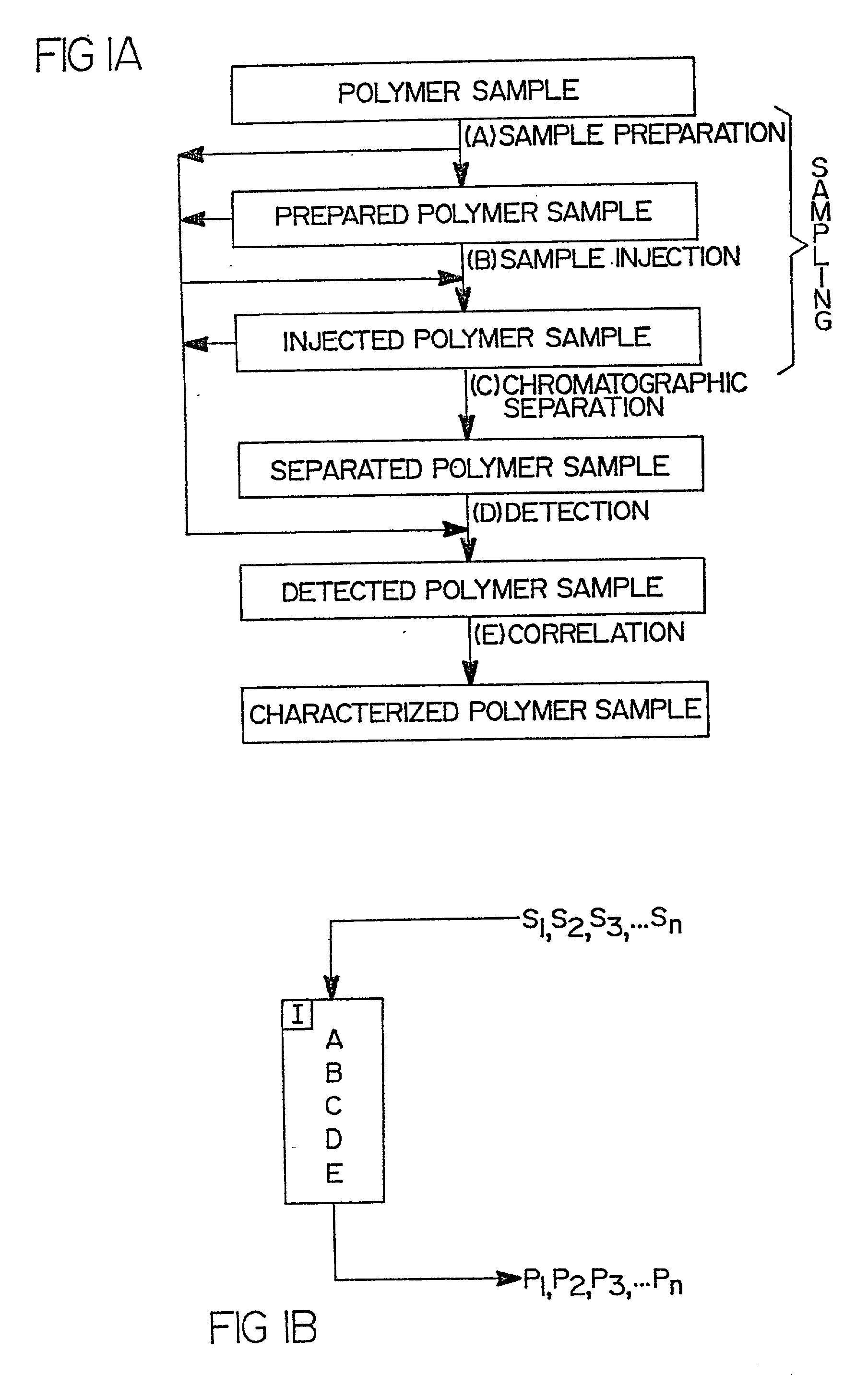
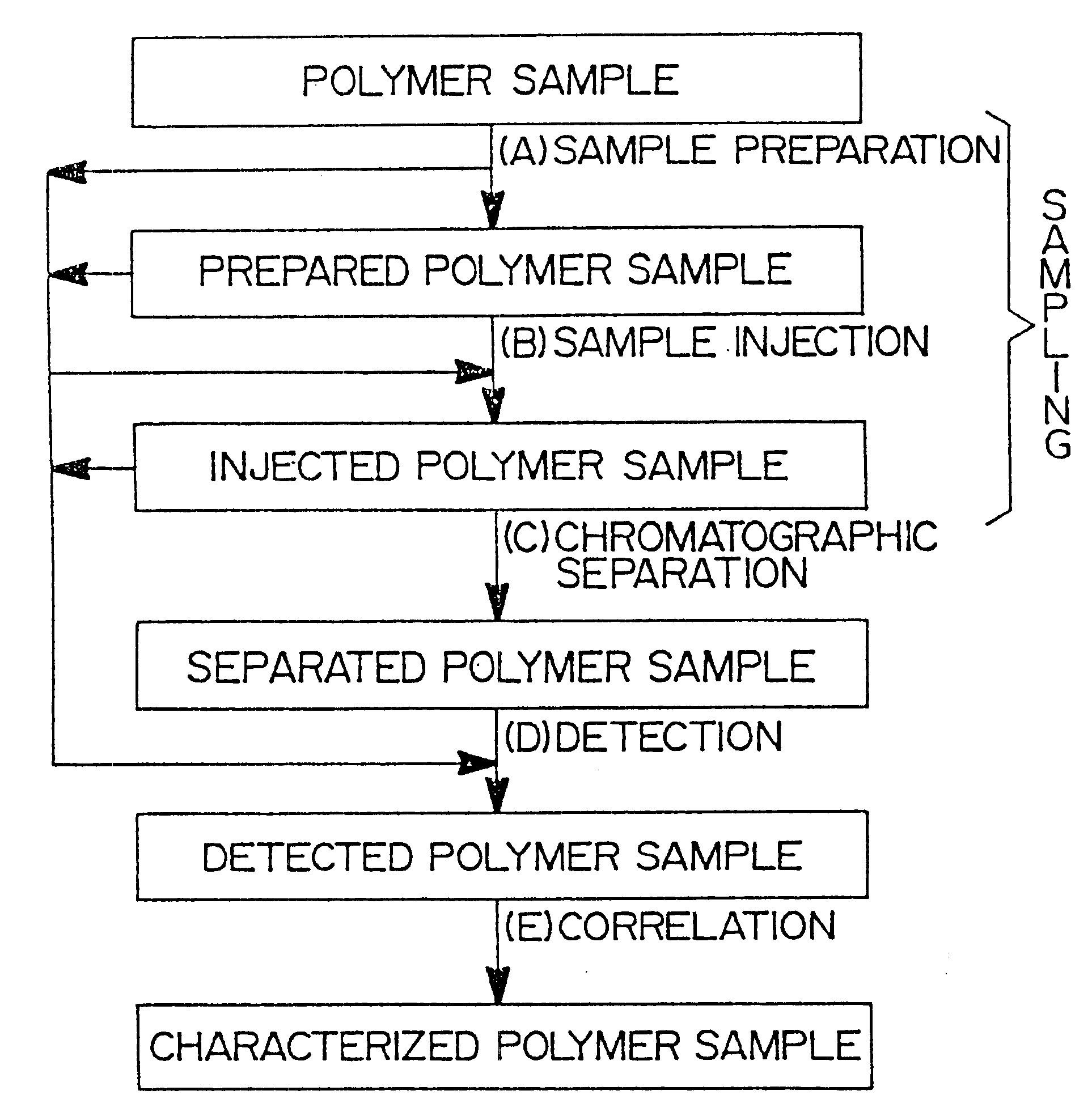
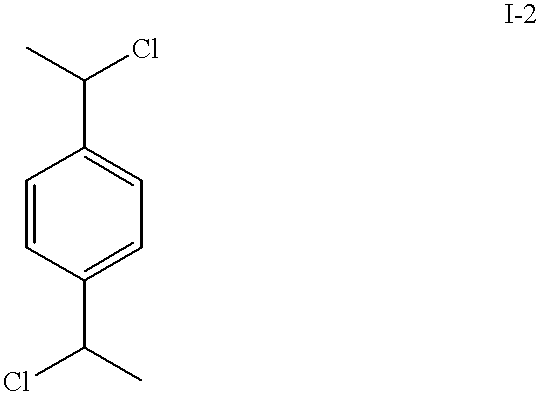
Flow-injection analysis and variable-flow light-scattering methods and apparatus for characterizing polymers
InactiveUS6175409B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFlow injection analysisPolymer
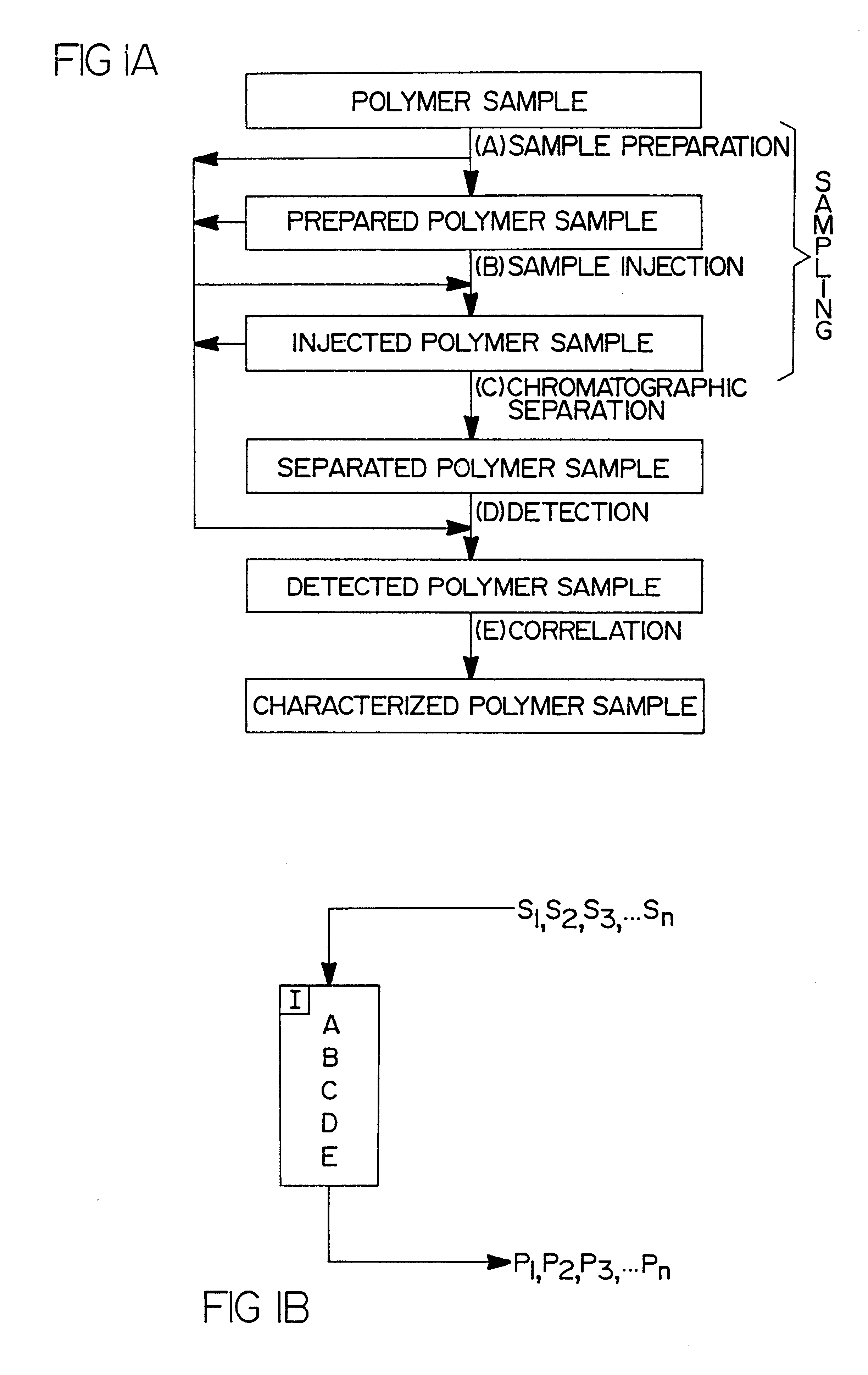
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High-temperature characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6260407B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationElutionChromatography column
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. In preferred high-temperature embodiments, the polymer sample is maintained at a temperature of not less than about 75° C. during sample preparation, loading into a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, injection into a mobile phase of a liquid chromatography or flow-injection analysis system, and / or elution from chromatographic column. The described methods, systems, and device have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Rapid characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6406632B1More separatedHigh sample throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFluid phasePhysical chemistry
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Indirect calibration of polymer characterization systems
InactiveUS6294388B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputIon-exchange process apparatusSamplingPolymer characterizationFlow injection analysis
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Automated sampling methods for rapid characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6265226B1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Rapid characterization of polymers for combinatorial, analytical and process control applications
InactiveUS20010027949A1Avoid backlogImprove throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High-temperature characterization of polymers with HPLC system having multiple mobile-phase reservoirs
InactiveUS6345528B2More separatedHigh sample throughputSequential/parallel process reactionsComponent separationFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Characterization of non-biological polymers using flow-injection analysis with light-scattering detection
InactiveUS6577392B1More separatedHigh sample throughputIon-exchange process apparatusSequential/parallel process reactionsBiopolymerFlow injection analysis
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
Microfluidic assay system with dispersion monitoring
InactiveUS20090068760A1High data reliabilityQuality improvementLaboratory glasswaresBiological testingAnalyteReference Region
Disclosed is a microfluidic assay system and methods that apply flow injection analysis to permit dispersion monitoring. A solution containing a reagent that binds an analyte and a tracer is delivered via pressure-driven flow into the receiving end of the injection channel of the system of the invention. A sample fluid suspected of containing the analyte is delivered into the upstream end of the input channel under conditions permitting flow of the sample fluid toward the downstream end of the assay channel and permitting dispersion of the reagent into the sample fluid. The amount of tracer present in the fluid as it passes over the reference region and the capture region and the amount of binding between the analyte and the capture region are detected. The amount of binding detected between the analyte and the capture region is correlated to the amount of tracer detected in the reference region.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Microfluidic assay system with dispersion monitoring
InactiveUS7736891B2Quality improvementImprove reliabilityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAnalyteReference Region
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Chromatographic column for rapid characterizations of polymers
InactiveUS6416663B1More separatedHigh sample throughputIon-exchange process apparatusSequential/parallel process reactionsChromatographic columnFlow injection analysis
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
System and method for fluid processing with variable delivery for downhole fluid analysis
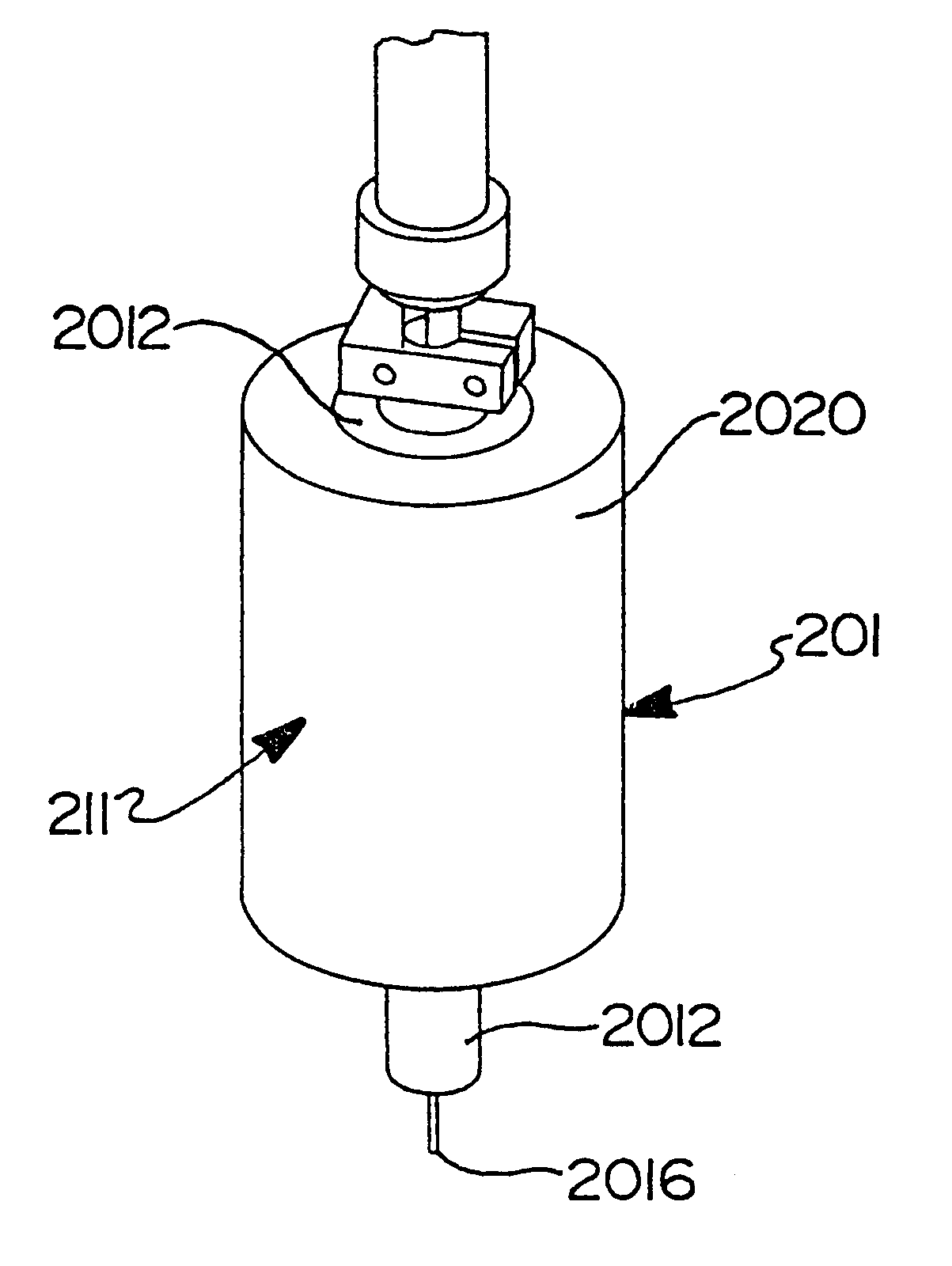
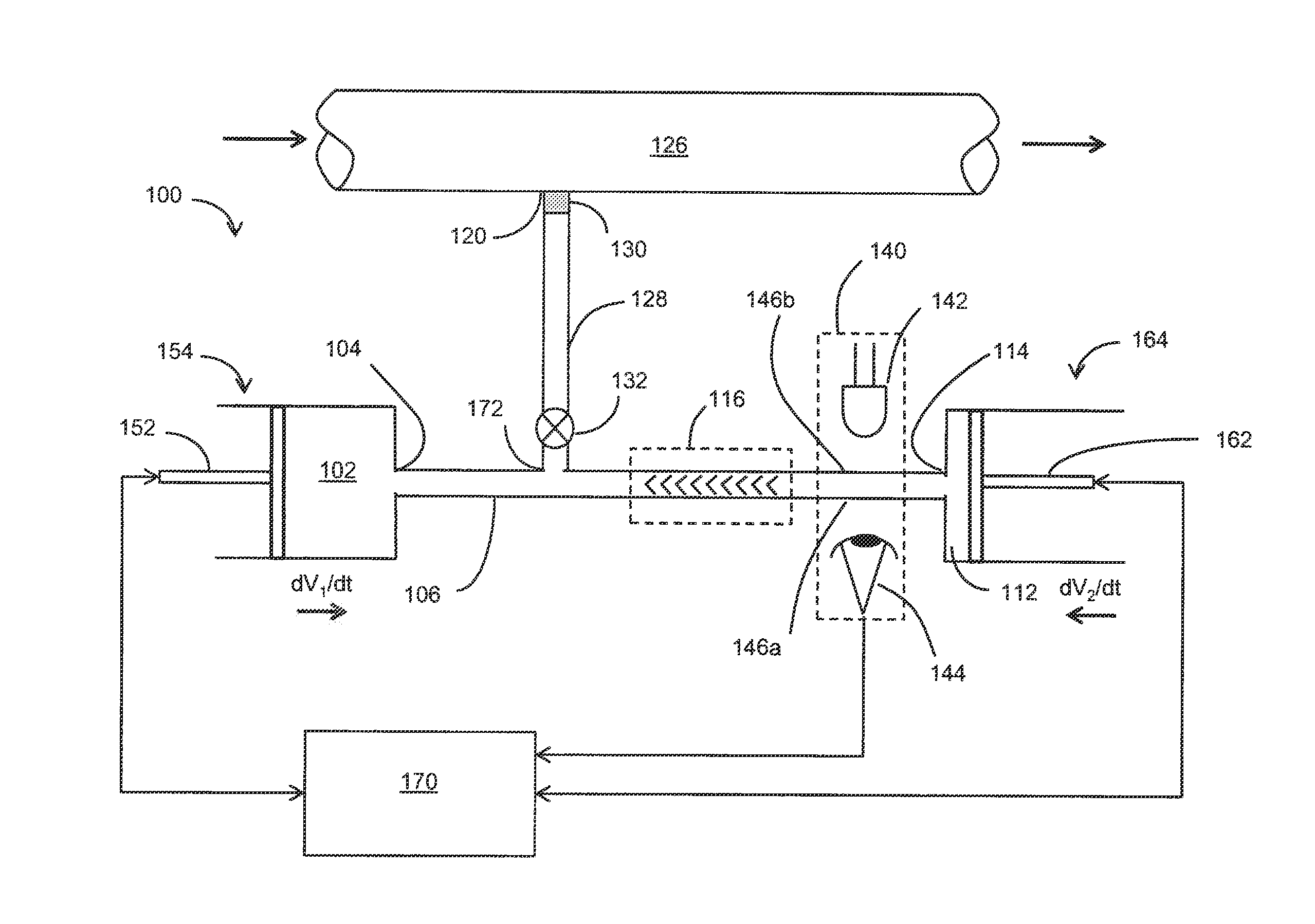
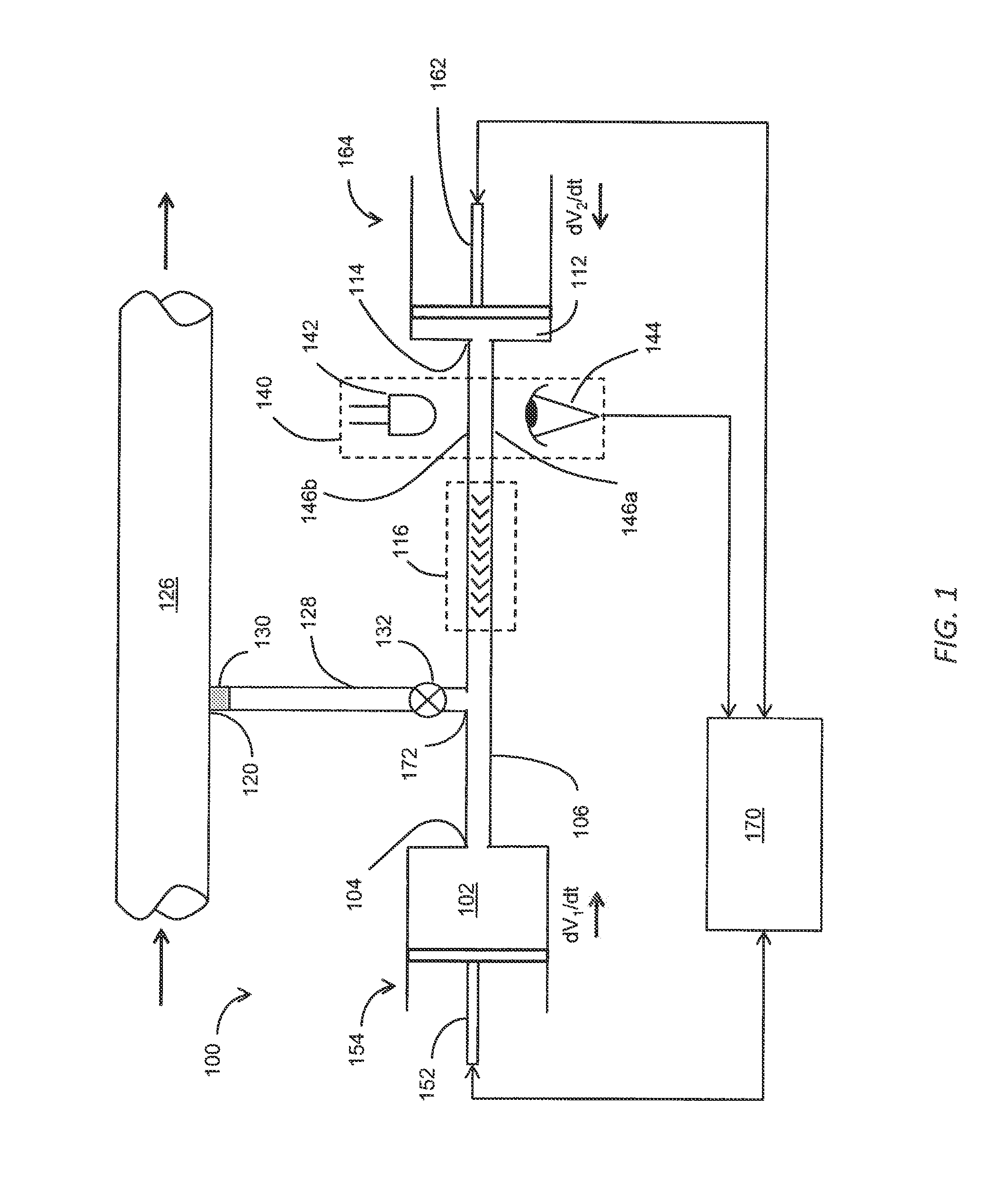
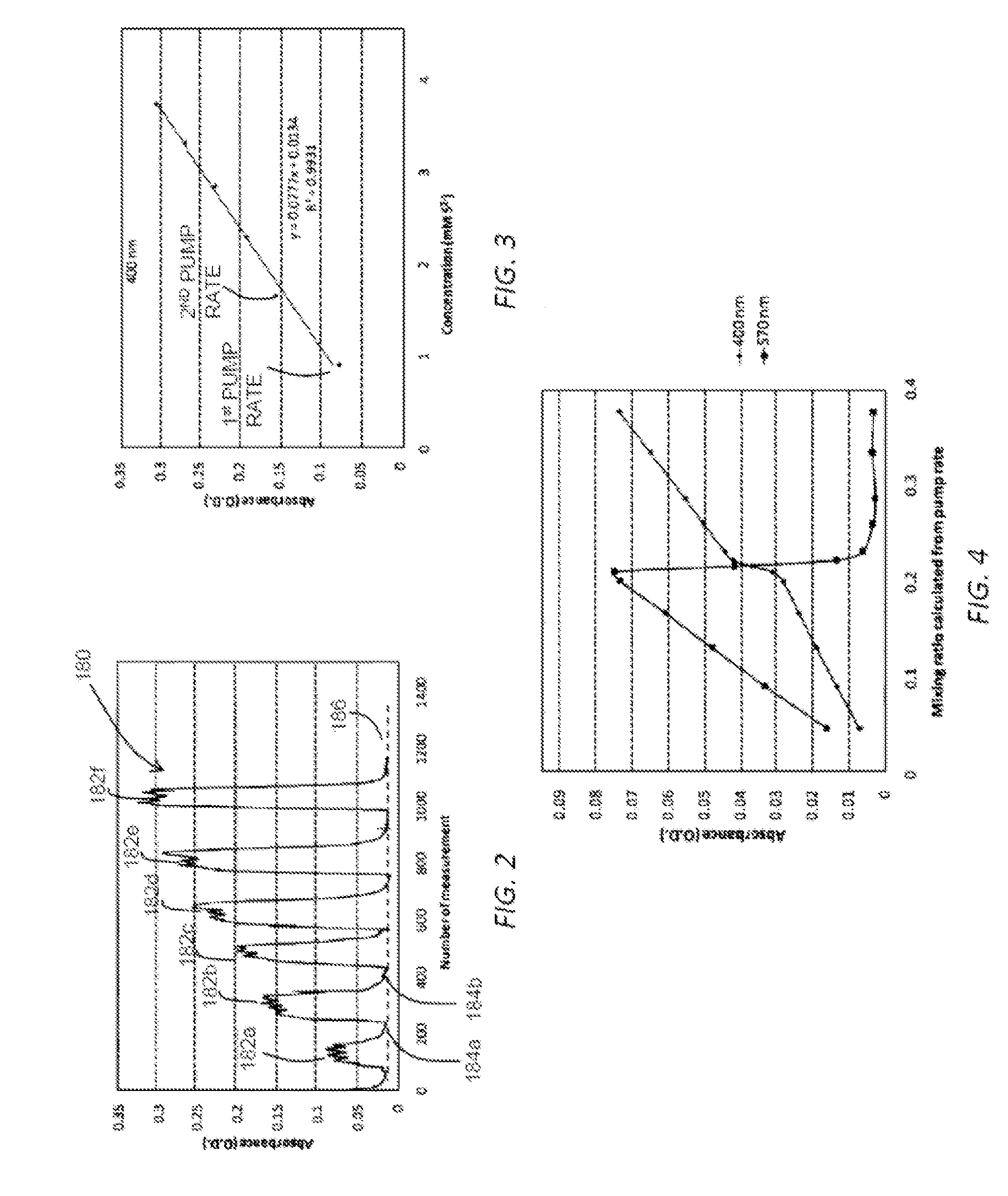
Described herein are variable-volume reservoir (e.g., syringe pump) based processes and systems usable to characterize samples of reservoir fluids, without having to first transport the fluids to the surface. Variable-volume reservoirs are used, for example, for one or more of storing reactants, controlling mixing ratios and storing used chemicals. The processes and systems can be used in various modes, such as continuous mixing mode, flow injection analysis, and titrations. A fluid interrogator, such as a spectrometer, can be used to detect a change in a physical property of the mixture, which is indicative of an analyte within the mixture. In at least some embodiments, a concentration of the analyte solution can be determined from the detected physical property.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
Automated sampling methods with integral serial sample preparation for rapid characterization of polymers
InactiveUS6492184B1More separatedHigh sample throughputIon-exchange process apparatusSequential/parallel process reactionsRapid identificationFlow injection analysis
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
High-temperature characterization of polymers with HPLC system having multiple mobile-phase reservoirs
InactiveUS20010037674A1Material is facilitatedSequential/parallel process reactionsSamplingFlow injection analysisPolymer
Rapid characterization and screening of polymer samples to determine average molecular weight, molecular weight distribution and other properties is disclosed. Rapid flow characterization systems and methods, including liquid chromatography and flow-injection analysis systems and methods are preferably employed. High throughput, automated sampling systems and methods, high-temperature characterization systems and methods, and rapid, indirect calibration compositions and methods are also disclosed. The described methods, systems, and devices have primary applications in combinatorial polymer research and in industrial process control.
Owner:INTERMOLECULAR
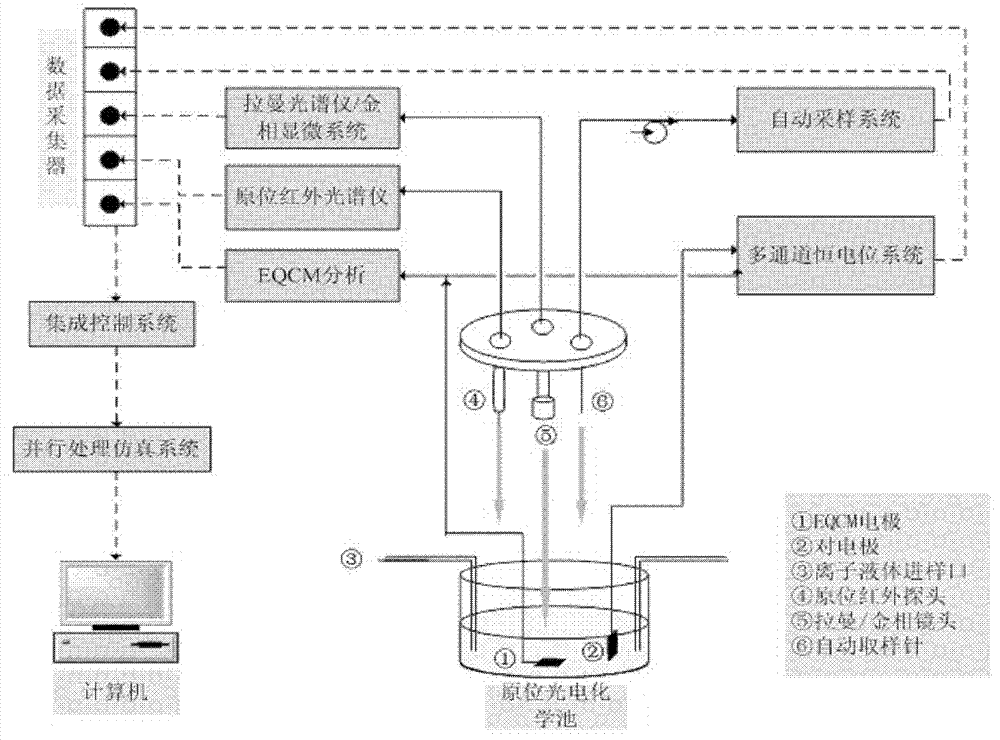
Ionic liquid system electrochemical process in-situ research device
InactiveCN103196963AEasy to set upImprove developmentMaterial electrochemical variablesDecompositionEngineering
The invention relates to an ionic liquid system electrochemical process in-situ research device. According to the device, an in-situ photo-electrochemical tank is adopted as a core. Under the control and adjustment of a multifunctional automatic adjusting rack, devices such as a flow injection analyzer, an in-situ infrared spectrometer, a Raman spectrometer, a metallurgical microscope, a multi-channel electrochemical workstation, a quartz crystal microbalance, and the like can be applied in combination. Detection liquid is placed in the in-situ photo-electrochemical tank, and a reaction process is subjected to real-time monitoring by using a computer control system. With the device provided by the invention, on a basis of conventional electrochemical tests, morphology, structure, composition, concentration change characterizations upon electrode surface / interface sediment, electrolyte, decomposition products, gas product, and the like can be realized, and powerful support can be provided for ionic liquid electrochemical process researches. The device has the characteristics of compact structure, high operation automation degree, precise detection, reasonable design, and the like.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
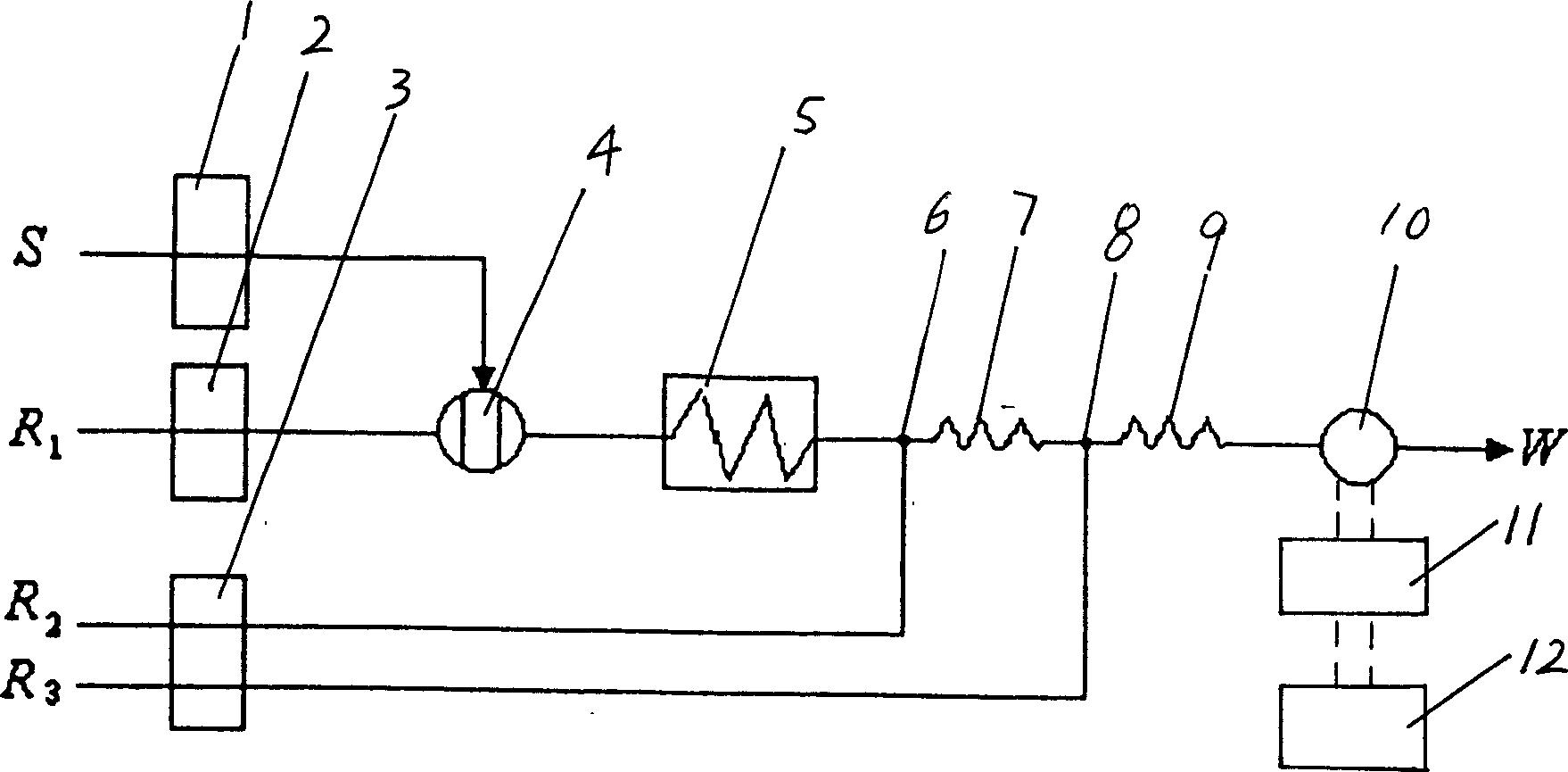
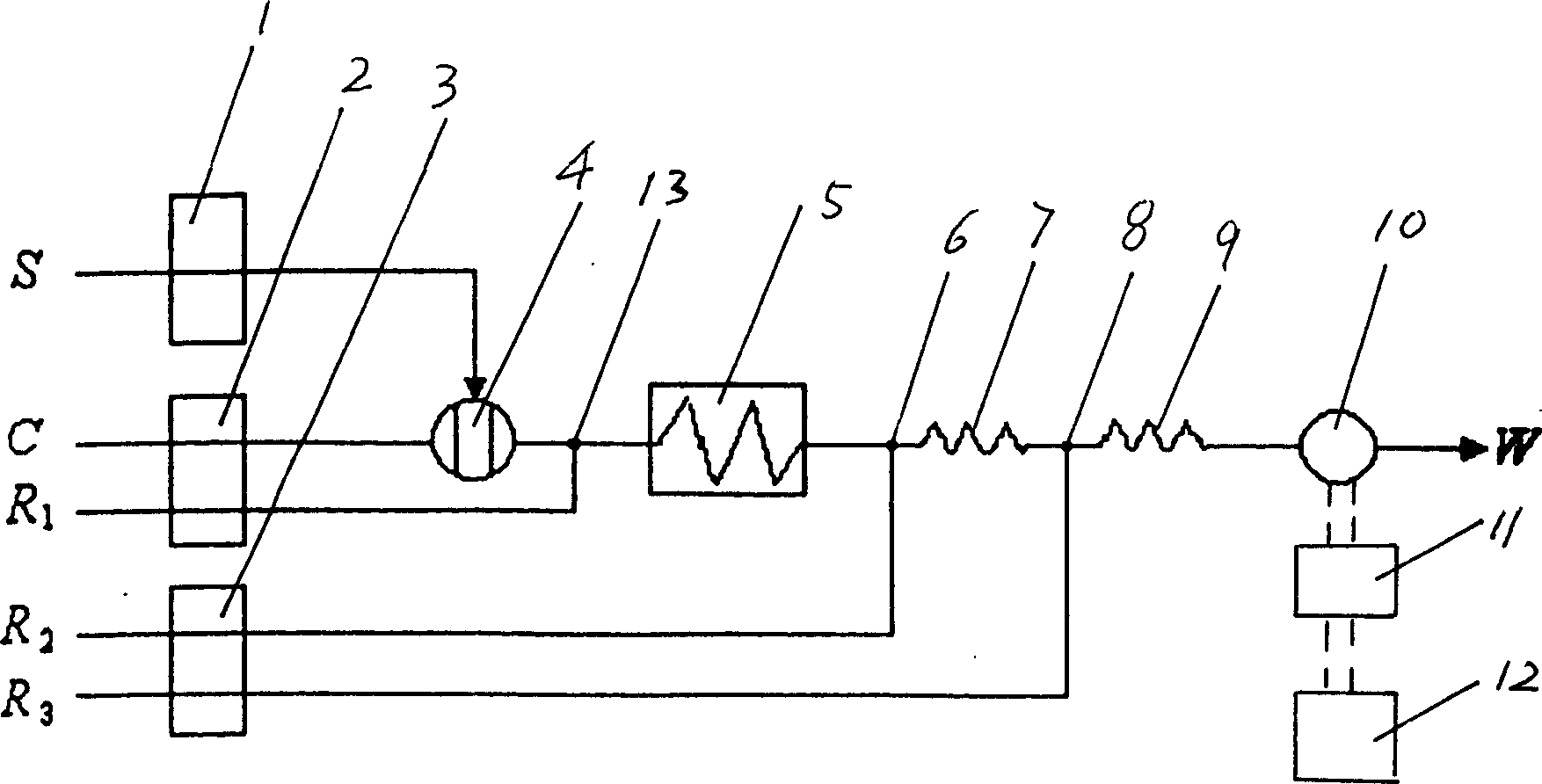
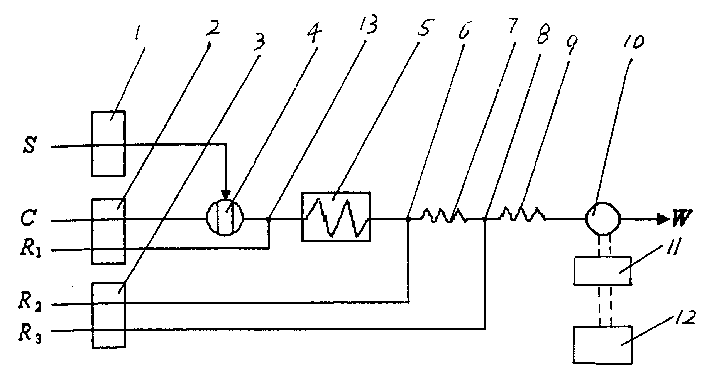
Flow injection analysis device for nitrite or nitrate in water
InactiveCN102226770AHigh selectivityImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorFlow cellFour-way valve
The invention relates to a flow injection analysis device for nitrite or nitrate in water. The device comprises a photoelectric flow cell, a reactor, a developer bottle, a carrier liquid bottle, a copper-cadmium column, an injection pump of carrier liquid, a developer delivery pump, a sample delivery pump, a triple valve, a four-way valve and two six-way sampling valves, with the components and valves connected by capillaries. In the device, a phosphoric acid solution with a pH of 1.8 is taken as the carrier liquid which is continuously injected into the pipelines of the capillaries by the constant-current injection pump. A quantitative water sample and a developer are pitched into the carrier liquid by the sampling valves. Then the water sample diffuses in the oriented flowing carrier liquid and mixes and reacts with the developer, and the reaction liquid is brought into the colorimetric flow cell (i.e. the photoelectric flow cell) by the carrier liquid. After absorption of lights with a wavelength of 540nm and photoelectric conversion, an absorbance value can be tested. And finally, the carrier liquid flows out of the outlet capillaries of the flow cell. With accurate test data and substantially shortened test period, the analysis device of the invention is suitable for rapid detection of nitrite and nitrate.
Owner:DELIN ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION TECH
Liquid chromatographic sampling passage cleaning device
ActiveCN104690047AEasy to cleanExtended service lifeHollow article cleaningDrying gas arrangementsParticulatesIon chromatography
The invention provides a liquid chromatographic sampling passage cleaning device. The liquid chromatographic sampling passage cleaning device mainly comprises a microfluidic pump, a compressed air source, a capillary flow limiter, a liquid-gas switching valve, a sampling-cleaning switching valve, a waste liquid collecting cup, a waste liquid bottle, a sampling valve, a sampling port and a program controller. After sampling, a cleaning solution is used for reversely rinsing a liquid chromatographic sampling passage to reversely rinse particles left on a filter in the sampling process and discharge the particles out of a sampling pipeline first and then microflow gas is used for reversely purging the sampling passage to expel liquid left inside the pipeline so as to avoid sample dilution during sampling once again. The liquid chromatographic sampling passage cleaning device is suitable for various analytical-grade liquid chromatographs, comprising positive chromatography, reverse chromatography, ion chromatography and the like, as well as suitable for cleaning a sampling loop for flow injection analysis, so that cross pollution of samples is avoided, the sampling repeating precision is improved, and the service life of the sampling filter can be greatly prolonged.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Systems and Methods for Rapidly Screening Samples by Mass Spectrometry
ActiveUS20130240723A1Samples introduction/extractionParticle spectrometer methodsVariable windowINTRODUCTION device
Systems and methods are used to rapidly screening samples. A fast sample introduction device that is non-chromatographic is instructed to supply each sample of a plurality samples to a tandem mass spectrometer using a processor. The fast sample introduction device can include a flow injection analysis device, an ion mobility analysis device, or a rapid sample cleanup device. The tandem mass spectrometer is instructed to perform fragmentation scans at two or more mass selection windows across a mass range of each sample of the plurality of samples using the processor. The two or more mass selection windows across the mass range can have fixed or variable window widths. The tandem mass spectrometer can be instructed to obtain a mass spectrum of the mass range before instructing the tandem mass spectrometer to perform the fragmentation scans.
Owner:DH TECH DEVMENT PTE
A concentration gradient diffusion sampling device for an online detection system of a bioreactor
The invention relates to a sampling device suitable for bioreactors such as microbial fermentation and cell culture, in particular to a concentration gradient diffusion sampling device, which is based on the concentration difference caused by the concentration difference of each component in the liquid in the solution on both sides of the separation membrane. The principle is to form a concentration gradient distribution of components (measured samples) in the sampling pipeline, and the flux or rate of diffusion follows Fick's law. Using this device to sample the samples in the bioreactor has the advantages of effectively preventing sampling pollution and good safety; there is no filtration process of the solution, the membrane pores should not be blocked, and the stability of continuous sampling is high; the sample components are in the sampling pipeline A gradient distribution is formed, which can be measured without cumbersome dilution, making the online detection system simpler, with faster measurement speed and wider linear range, and is especially suitable for on-line detection of various flow injection analysis systems.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Flow cell device suitable for synchronous on-line detection of absorption spectrum and fluorescence spectrum
InactiveCN101776574ALight structureReduce volumeComponent separationColor/spectral properties measurementsFiberAction spectrum
The invention discloses a flow cell, which is a five-way body consisting of a light source spectrum fiber interface hole, an ultraviolet-visible light fiber interface hole, a fluorescence spectrum fiber interface hole, a liquid inlet pipe hole and a liquid outlet pipe hole, wherein the diameter of a linear passage pipe between the ultraviolet-visible light fiber interface hole and the light source spectrum fiber interface hole is 0.5 to 0.7 millimeter; the liquid inlet pipe hole and the liquid outlet pipe hole are distributed in parallel, and the central distance of the two holes is 1 centimeter; the fluorescence spectrum fiber interface hole and the light source spectrum fiber interface hole are distributed in a vertical right angle; the inside diameters of the holes are thickened, and matched inner threads are machined in the holes; and a fiber or a pipeline is connected and fixed to the cell via a joint and a buckling sleeve. The flow cell can be widely applied to the field of a flow cell device applicable in the ultraviolet-visible light absorption and fluorescence detection on a flow injection analysis instrument.
Owner:XINJIANG MEDICAL UNIV
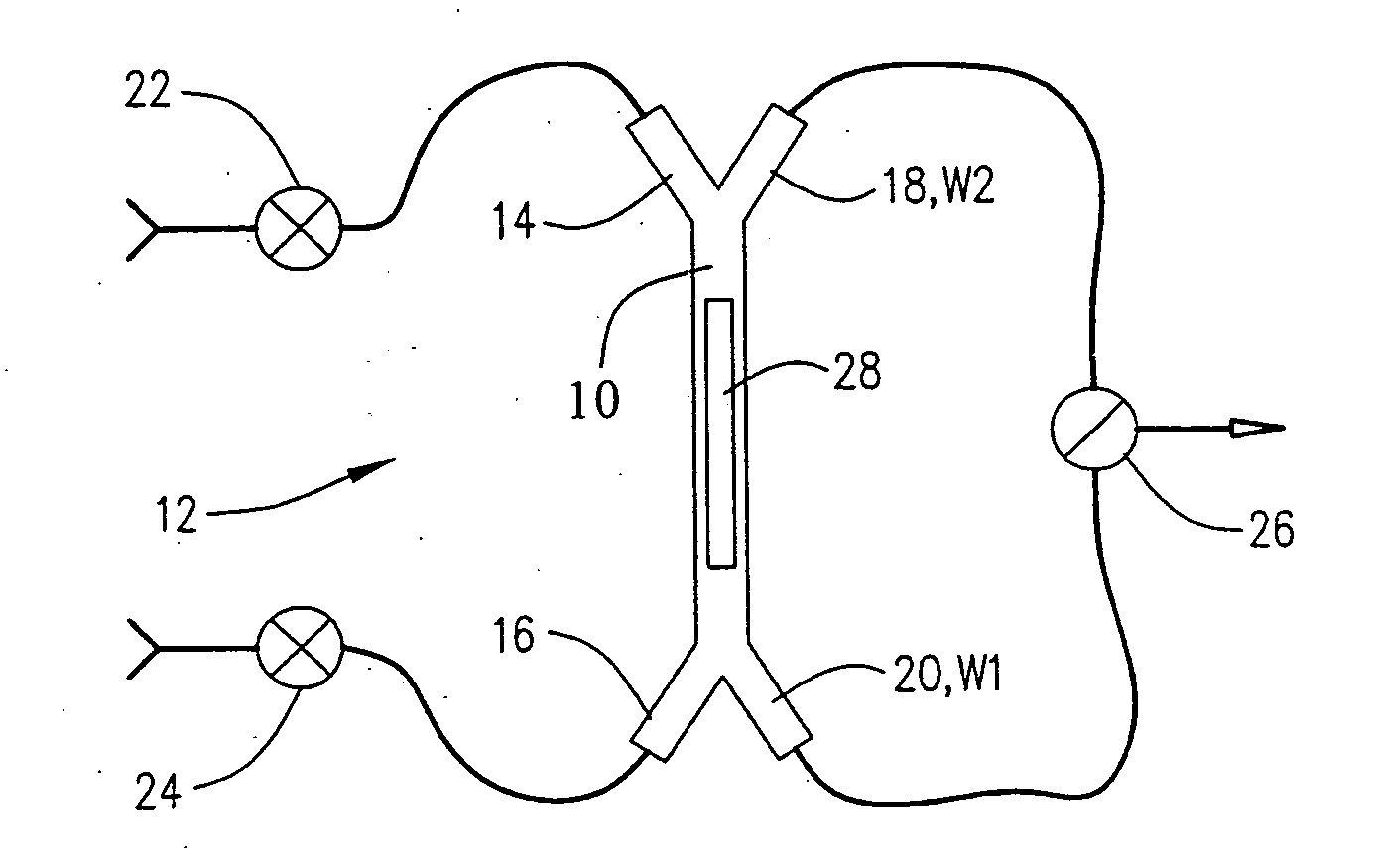
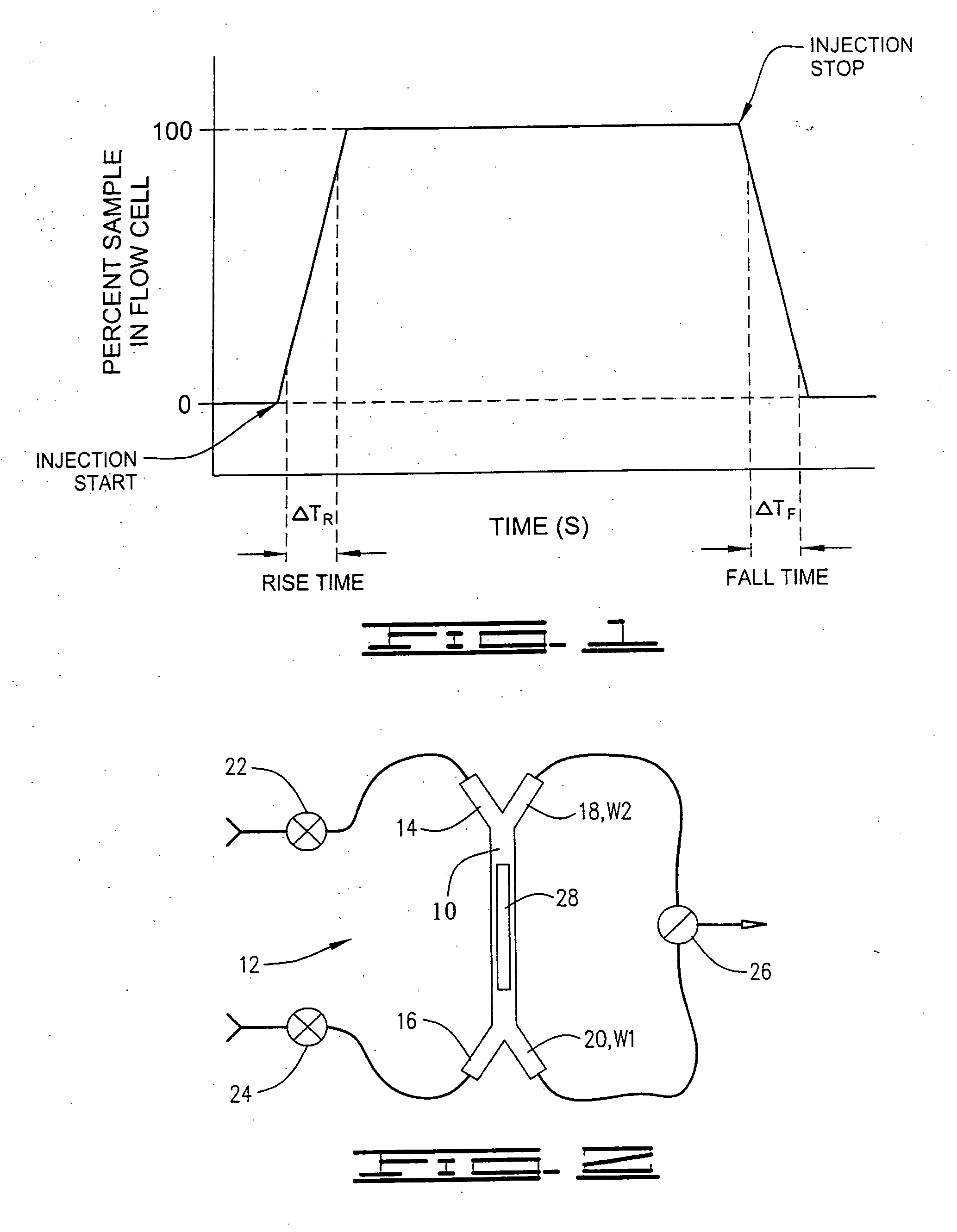
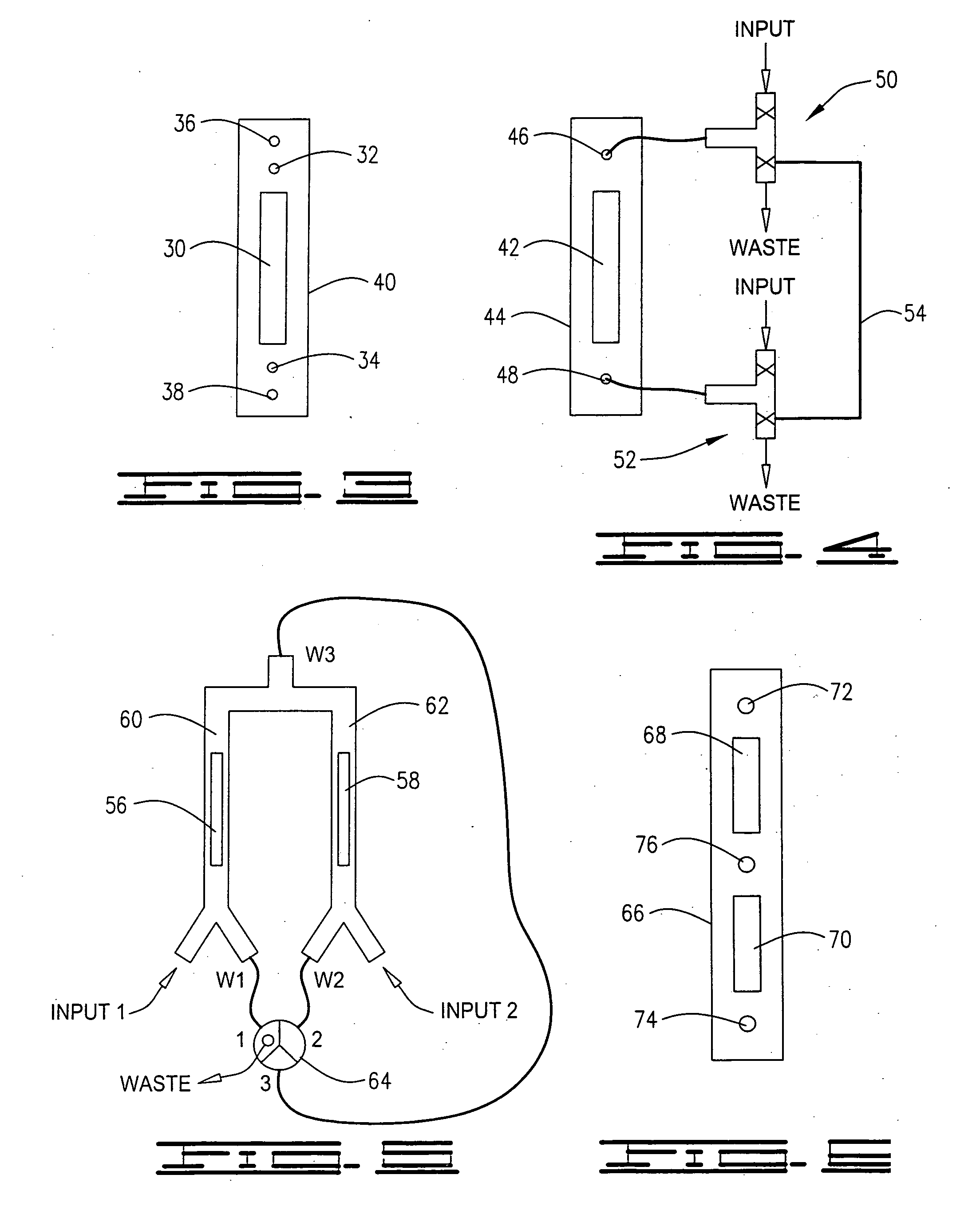
Fluidic configuration for flow injection analysis
ActiveUS20100196205A1Extending kinetic rangeReduce dead volumeSolid-state devicesLaboratory glasswaresFlow cellCounter flow
A fluidic configuration, both structural and methodological, for the injection of sample greatly reduces dead volume allowing rapid transition to 100% sample in a flow cell. For a continuous flow injection analysis system the structure and method provide counter flows to remove in one direction the dispersed region of the sample to waste before injecting non-dispersed sample into the flow cell by reversing the effective flow direction. The injection point itself is directly adjacent to the flow cell where all channels are microfluidic channels. Therefore, only the flow cell volume needs to be displaced during injection of sample in order to achieve 100% transition to sample within the flow cell. This greatly accelerates the rise and fall times thereby extending the kinetic range of the real-time interaction analysis instrument. In addition such rapid transition to sample improves overall data quality thereby improving kinetic model fitting.
Owner:SARTORIUS BIOANALYTICAL INSTR INC
Ultrasensitive SERS flow detector
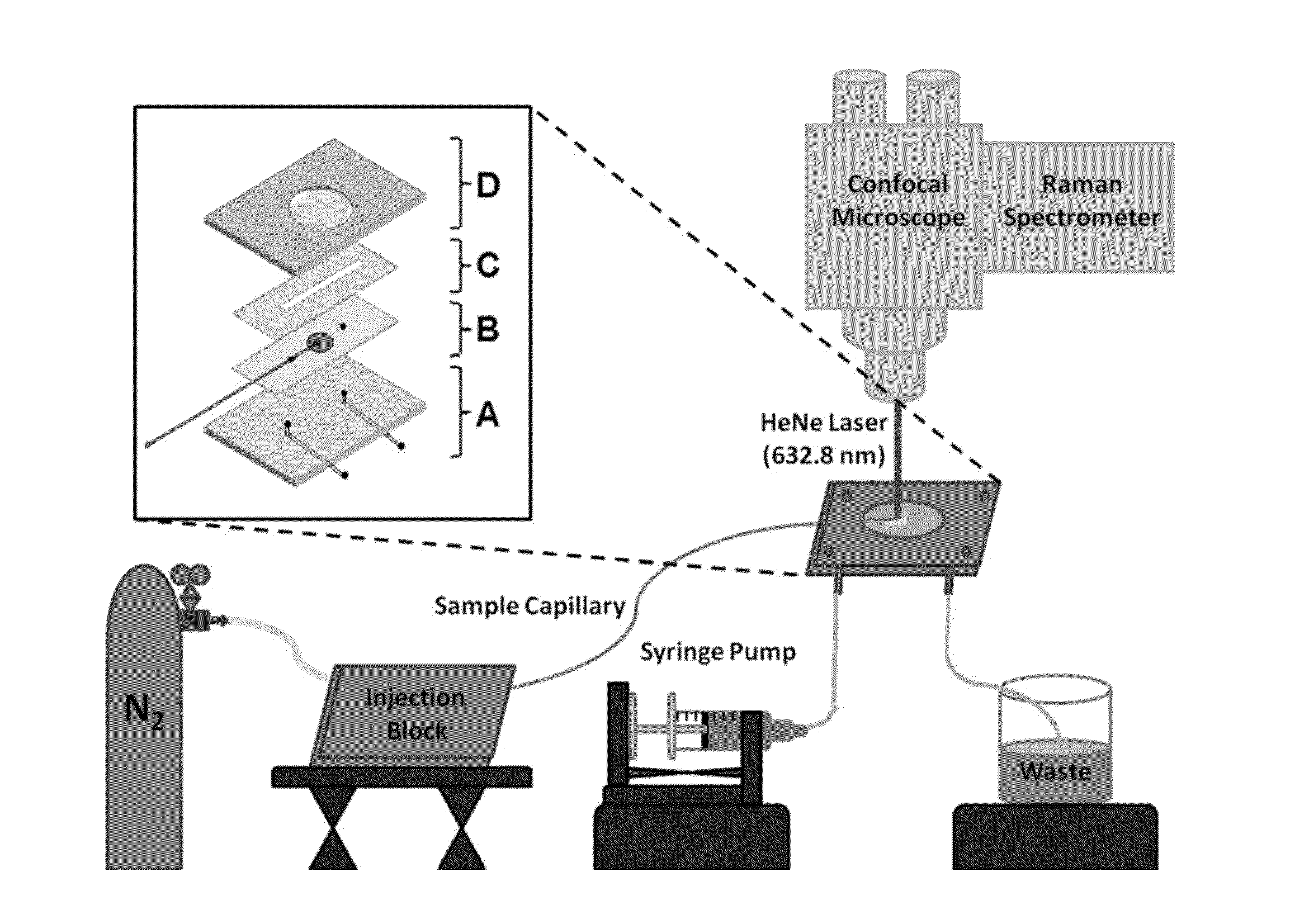
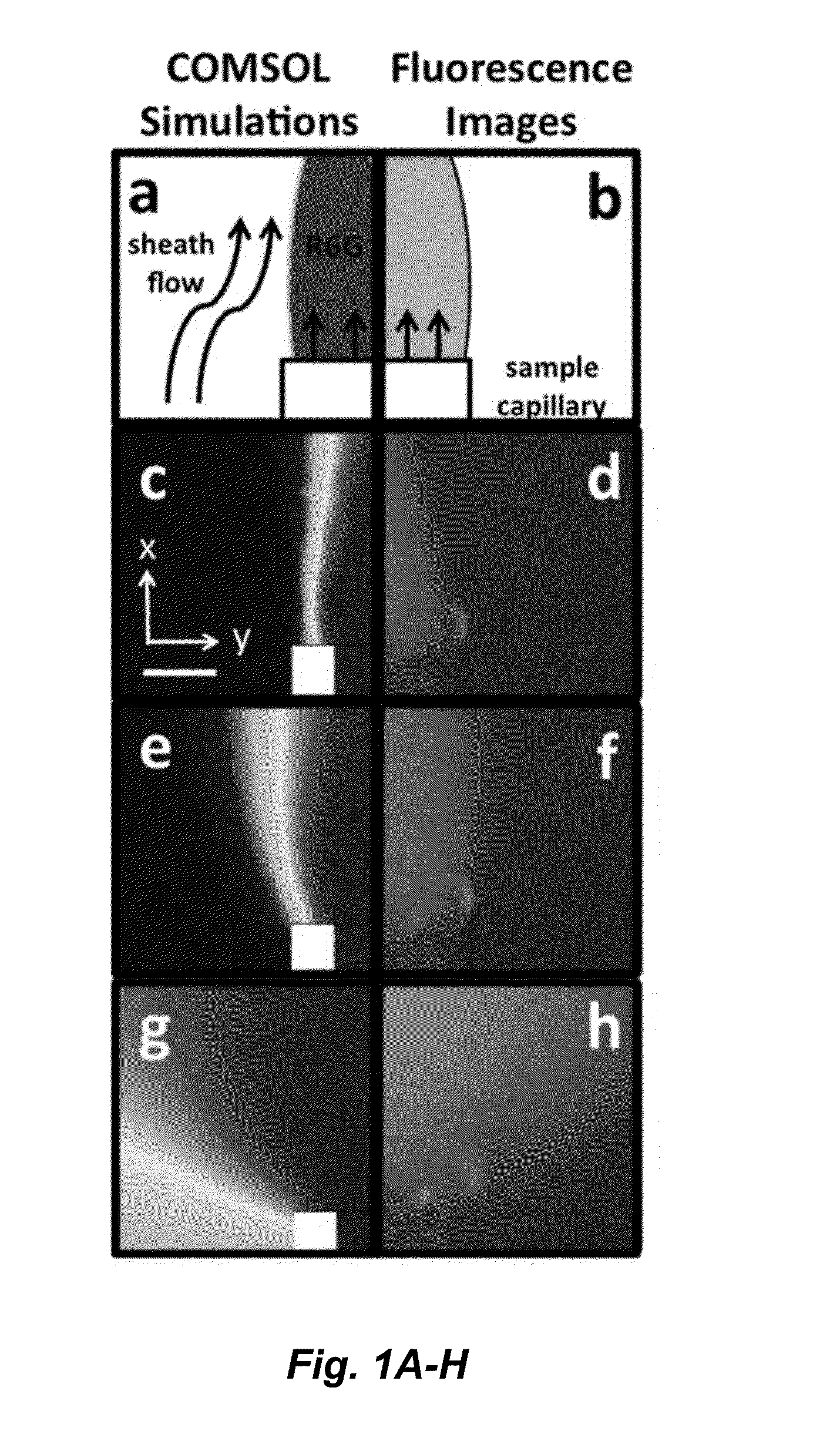
ActiveUS20150338348A1Enhanced signalShort acquisition timeRadiation pyrometryRaman scatteringDesorptionFlow injection analysis
The invention provides an apparatus and methods for label-free, chemical specific detection in flow for high throughput characterization of analytes in applications such as flow injection analysis, electrophoresis, and chromatography. A surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) flow detector capable of ultrasensitive optical detection on the millisecond time scale has been developed. The device employs hydrodynamic focusing to improve SERS detection in a flow channel where a sheath flow confines analyte molecules eluted from a capillary over a planar SERS-active substrate. Increased analyte interactions with the SERS substrate significantly improve detection sensitivity. Raman experiments at different sheath flow rates showed increased sensitivity compared with the modeling predictions, indicating increased adsorption. At low analyte concentrations, rapid analyte desorption is observed, enabling repeated and high-throughput SERS detection. The flow detector offers substantial advantages over conventional SERS-based assays such as minimal sample volumes and high detection efficiency.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
Automatic analysis method for COD in sea water
InactiveCN1492233AConvenient online automatic detectionFast online automatic detectionTesting waterColor/spectral properties measurementsChemical oxygen demandTest sample
The automatic analysis of COD in sea water includes flowing injection analysis and spectrophotometric detection. After the oxidizing liquid enters the analysis and detection flow channel, it is pushed by the pushing liquid into the heating reactor for mixing with acidifying liquid into the flow channel, and the mixture solution is pushed to mix and react with reducing-displaying liquid into the flow channel to produce base line to be measured. The standard sample or test sample entering the analysis and detection flow channel is pushed to mix with the oxidizing liquid and heating oxidized, reacted with the acidifying liquid, and the mixture liquid is pushed to mix and react with the reducing-displaying liquid to produce spectrogram to be drawn. By means of the method and instrument, sea water may be automatic detected in COD accurately and reliably.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Measurement device and measurement method for high-accuracy in-situ detection on pH of seawater
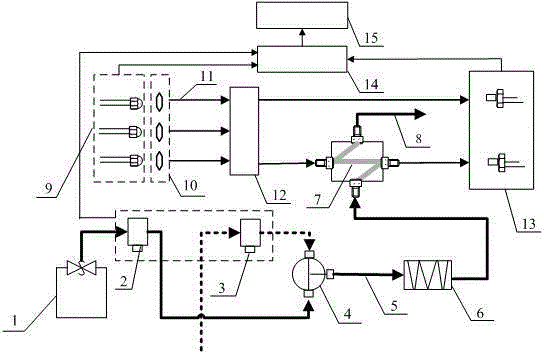
ActiveCN104062247AHighly integratedExquisite structureColor/spectral properties measurementsPeristaltic pumpMeasurement device
The invention provides a measurement device and a measurement method for high-accuracy in-situ detection on pH of seawater. The measurement device comprises a water path component, a light path component, a circuit control system and a computer processing system. Sample introduction and mixing of the seawater and an indicator are completed only by a peristaltic pump, a pulse pump, a tee joint and a flow cell, furthermore, in the light path system, an light emitting diode (LED) lamp and a photodiode replace a thermal radiation light source and a commercialized detector, so that the cost and the power consumption are lowered, and the measurement device can be conveniently used in field monitoring sensors. Based on a spectrophotonetry and flow injection analysis, the measurement device for the detection on the pH of the seawater can be used as a section or fixed point analysis meter for the detection on the pH of the seawater. The measurement device can calculate the pH of the seawater through detecting the absorbance of a mixed solution of the seawater and the indicator, has the high precision degree and good accuracy, and is applicable to field monitoring, and the step of baseline correction by adopting an electrode detection method is omitted.
Owner:OCEANOGRAPHIC INSTR RES INST SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
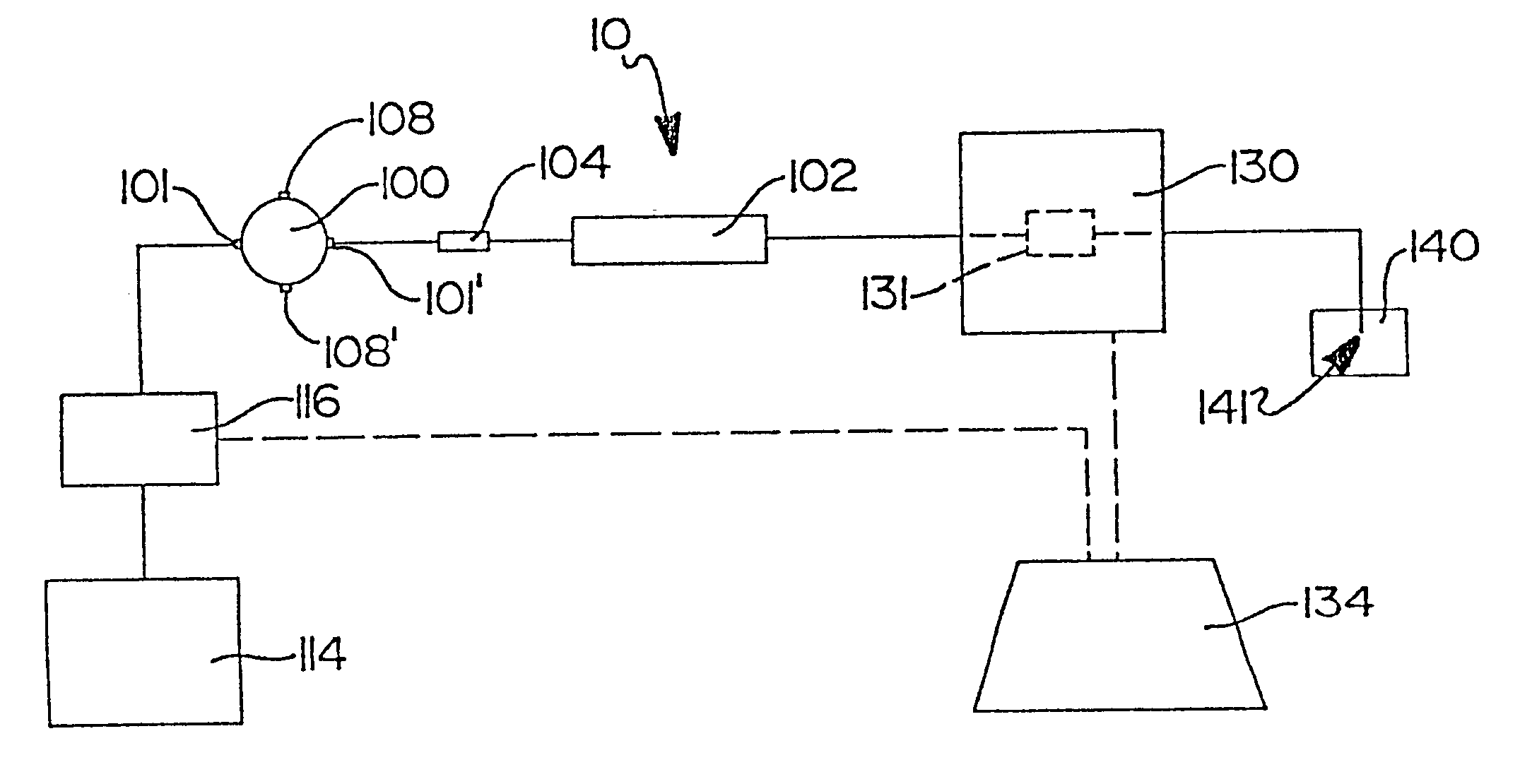
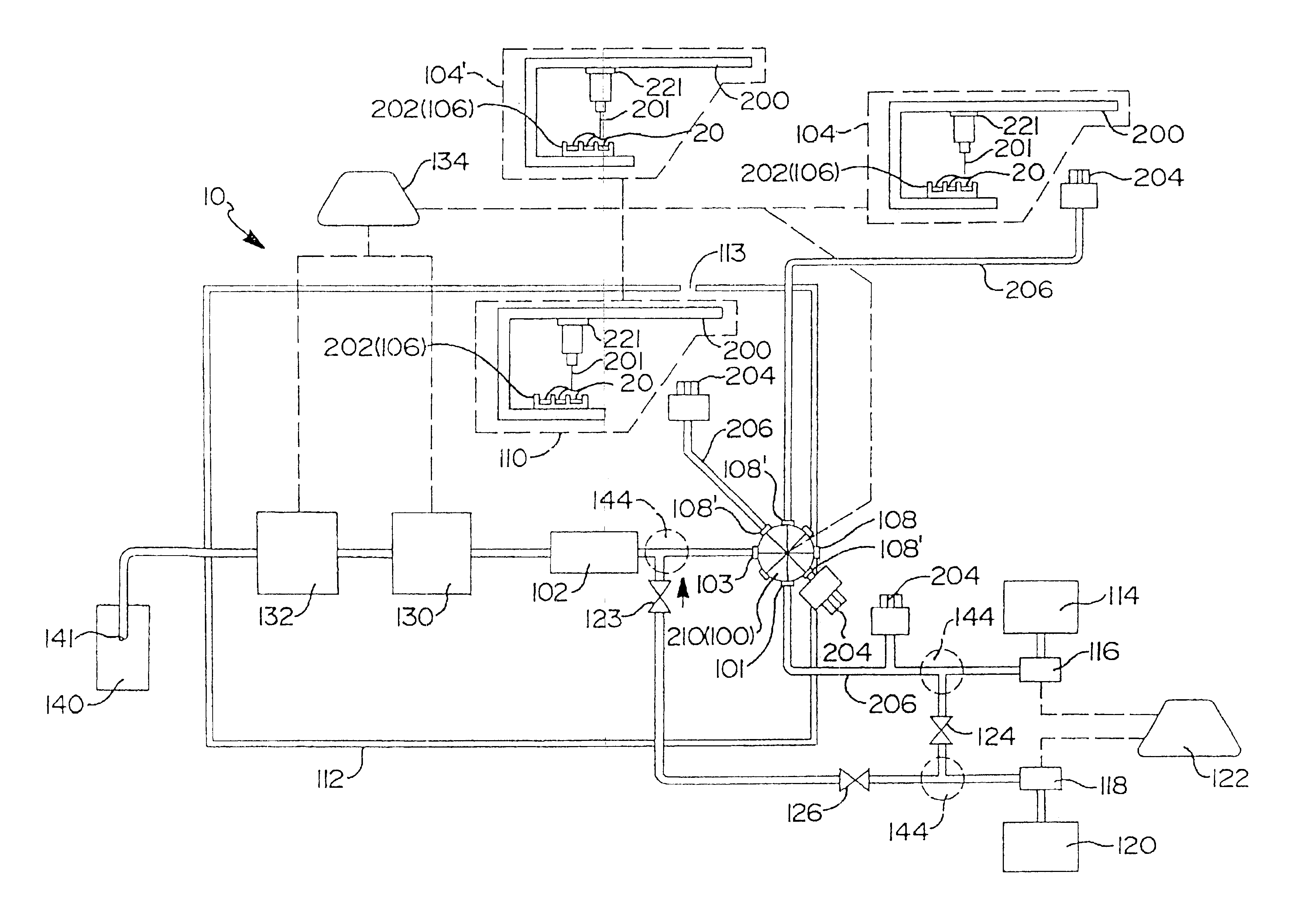
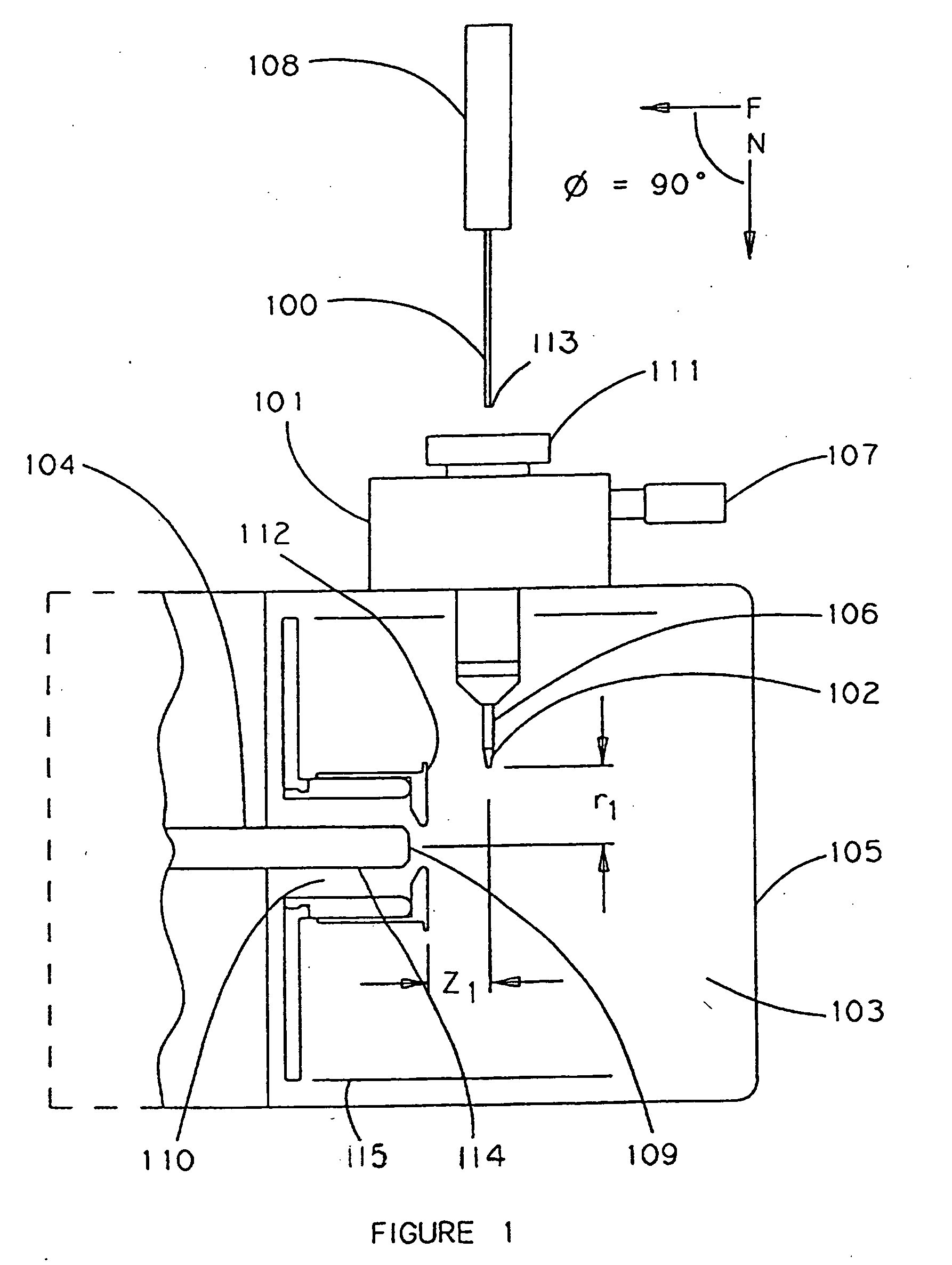
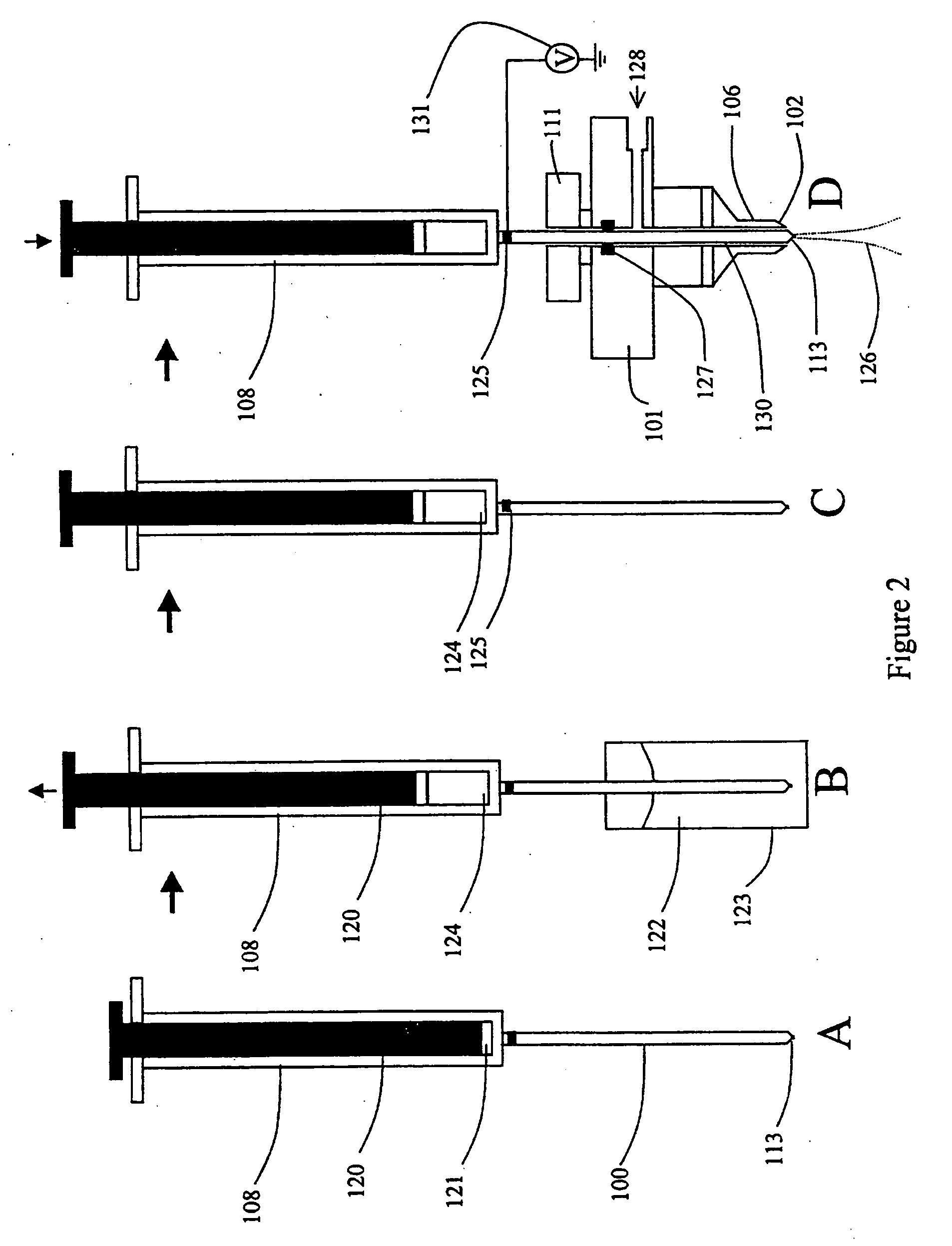
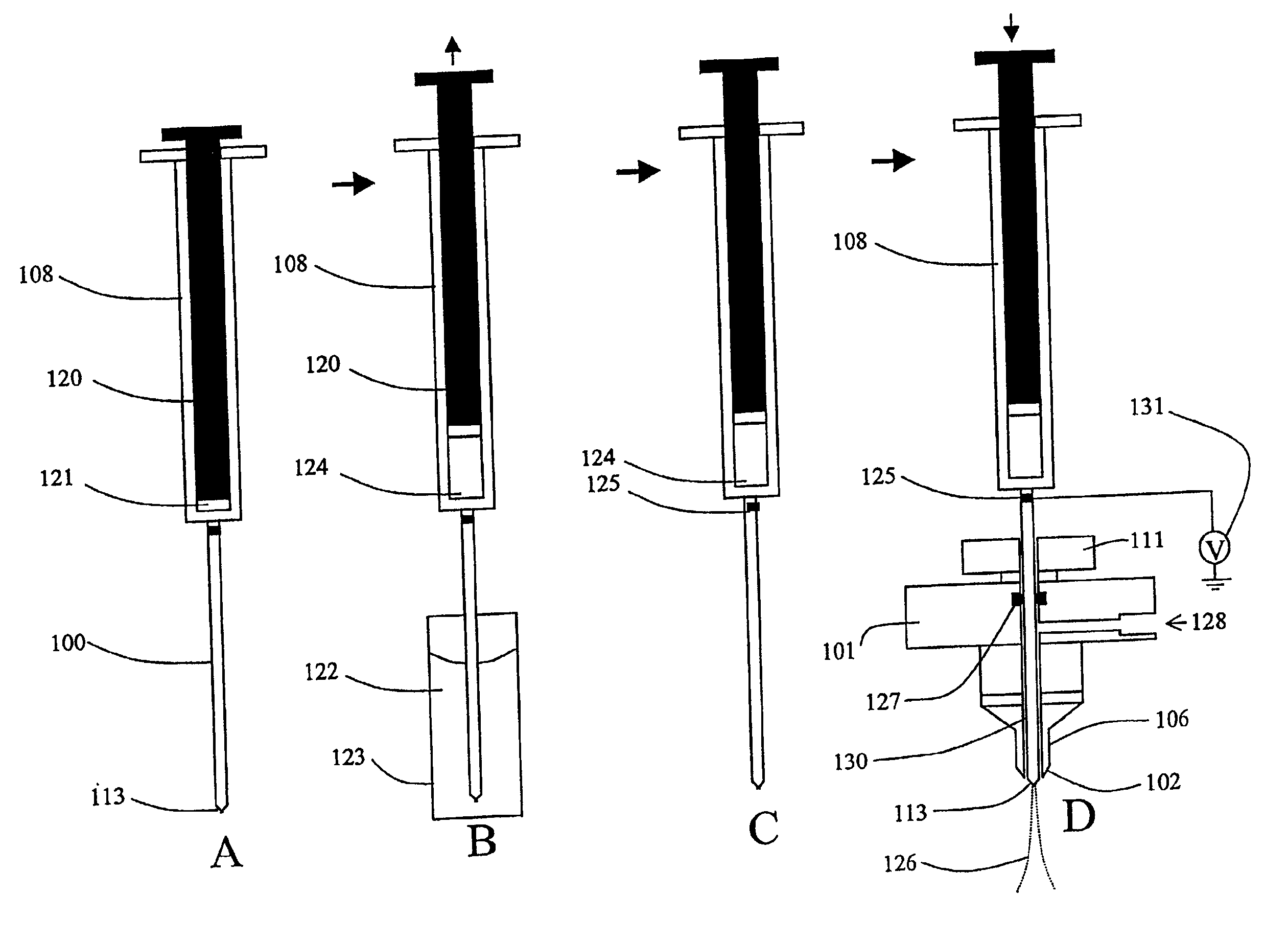
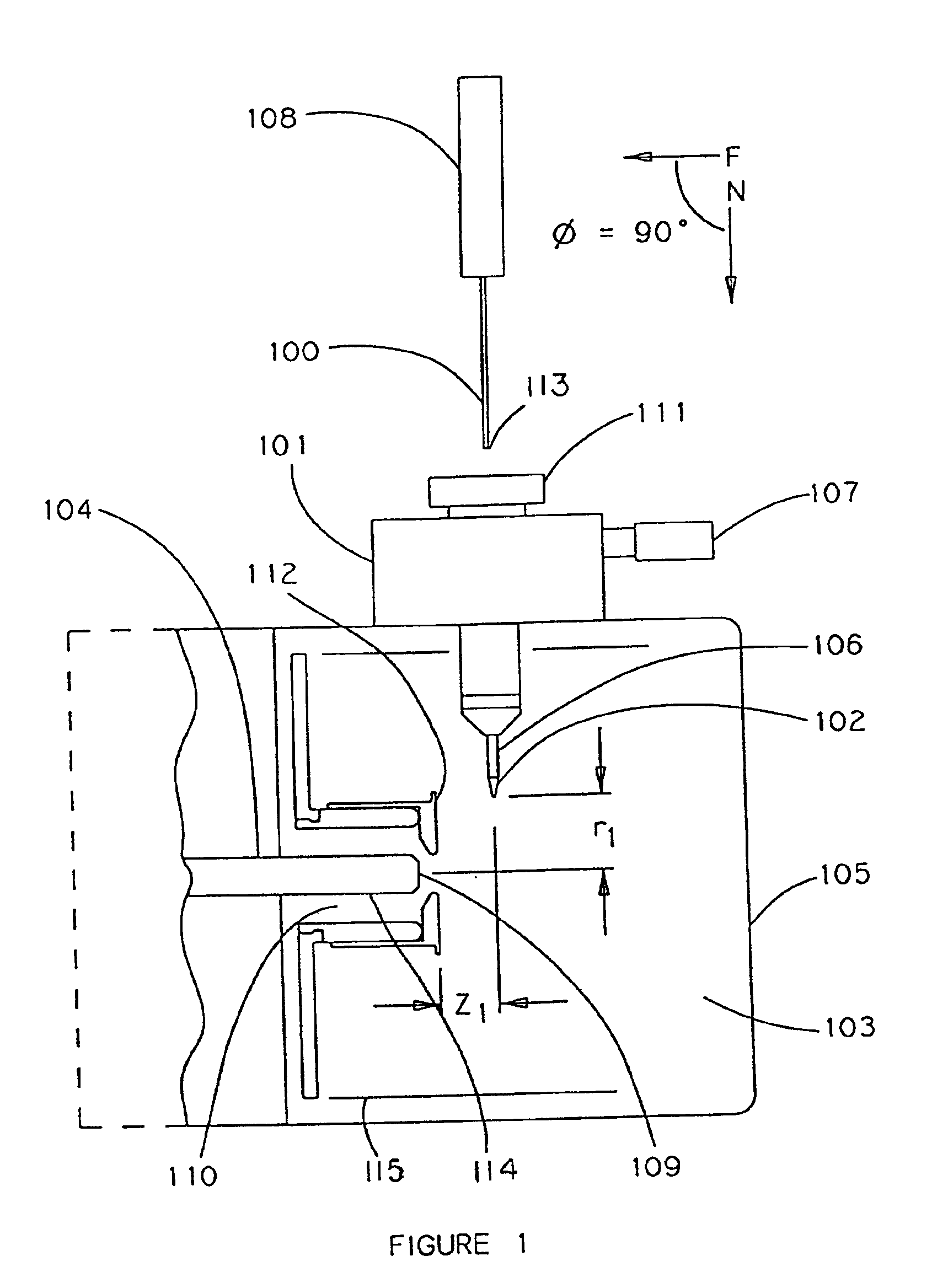
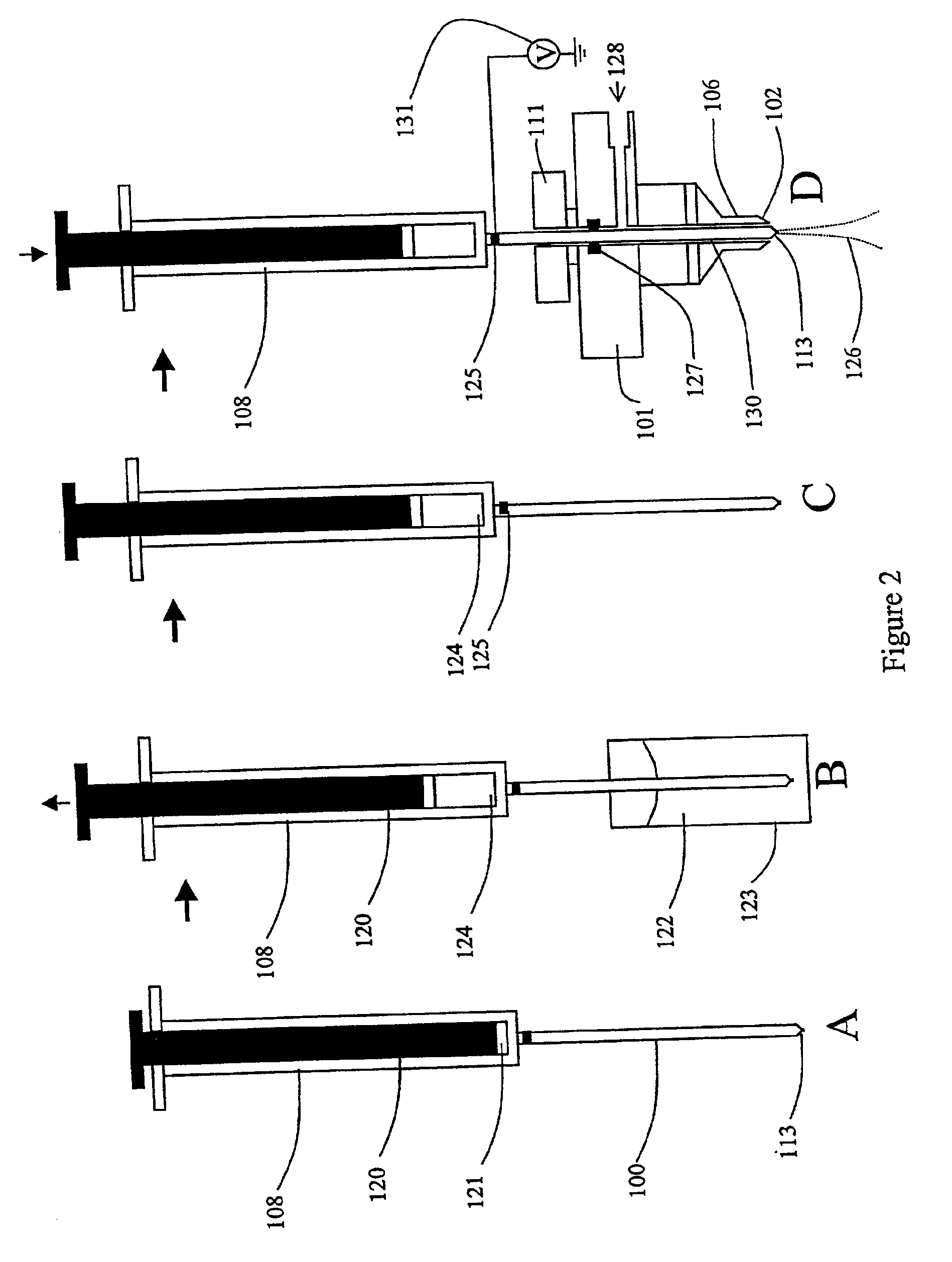
Direct flow injection analysis nebulization electrospray and APCI mass spectrometry
InactiveUS20060145069A1Increase ratingsMaximize throughputComponent separationSamples introduction/extractionDead volumeSolvent
A method and apparatus for Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) into Atmospheric Pressure Ion sources (API) including Electrospray (ES) and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization (APCI) sources whereby the sampling and spray needles are one and the same. The sampling and spray needle configured with an autoinjector apparatus or used in manual injection is introduced directly into a mating ES or APCI probe configured in an API source. Such a sampling and spray needle eliminates the need for injector valves, transfer lines or additional fluid delivery systems in FIA into API sources interfaced to mass spectrometers or other chemical analyzers. The use of a sampling and spray needle configuration reduces component costs, liquid dead volume, sample dilution effects, and minimizes cross contamination effects, solvent consumption and waste while increasing sample throughput.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
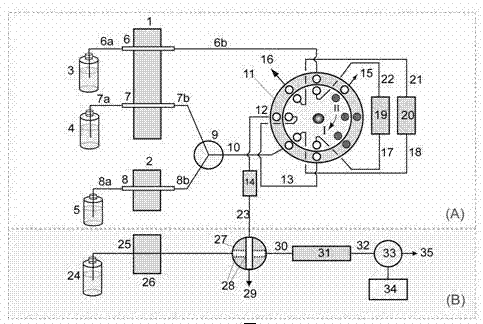
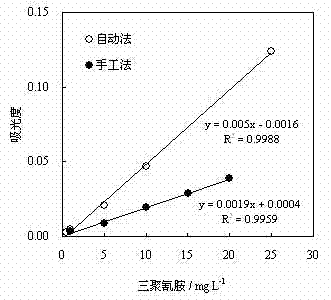
A method and device for rapid and automatic determination of melamine content in dairy products
InactiveCN102262163AAchieve enrichmentEnsure thoroughnessComponent separationColor/spectral properties measurementsEngineeringMelamine
The invention discloses a rapid and automatic determination method and device for tripolycyanamide content in dairy products, belonging to the field of food analysis. The method comprises the following steps that: in a unit (A) under an operating procedure, a first step, a multifunctional valve is in a state I, a pump A rotates, a pump B stops, a first sample flows into a column 2 for enriching tripolycyanamide, and the eluent flows into a column 1 for regenerating tripolycyanamide; a second step, the pump A stops, the pump B rotates, the cleanout fluid flows into the column 2 for cleaning the impurities therein; a third step, the multifunctional valve is switched to a state II, eluent flows into the column 2 for eluting and regenerating tripolycyanamide; the tripolycyanamide in the column 2 is substituted by the eluent and directly enters into a sampling ring of a unit (B) in the form of a sample plug, so as to perform volume quantification, injection, re-separation and detection, and a response signal is processed by a computer; and meanwhile, a second sample enters into the column 1 for enrichment, and the process of the column 2 is repeated. The method and the device are high in automation degree and excellent in reproducibility, and can analyze about 30 samples per hour; and the unit (A) in the invention can be used with various flow injection analysis systems.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
Preparation method for high-sensitivity amperometric glucose sensor
InactiveCN102645463AIncrease surface areaImprove electrocatalytic performanceMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityGlucose sensors
The invention relates to a preparation method for a high-sensitivity amperometric glucose sensor. Alpha-Ni(OH)2 sol and a nanostructured membrane are first prepared, cut FTO (fluorine-doped tin oxide) electrodes are then ultrasonically washed sequentially with isopropanol and methanol for 15 minutes, and are dried in the air, and under the rotational speed of 2500rpm, the spin-coating method is adopted to spin-coat the prepared Alpha-Ni(OH)2 sol on each electrode within 1.0cm2 of limited area for 2 minutes; finally, the electrode is dried under vacuum for 24 hours and then roasted under 240 DEG C for 30 minutes, and thereby the nanostructured membrane-modified electrochemical sensor formed by Alpha-Ni(OH)2 is obtained. Cyclic voltammetry and flow injection analysis indicate that the sensor shows enlarged surface area and enhanced electrocatalytical property.
Owner:WUXI BAILING SENSING TECH
A light scattering detector and capillary tube electrophoresis device for the detector
InactiveCN1448707AScattering properties measurementsMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRayleigh scatteringRayleigh Light Scattering
The light scattering detector for in-situ microanalysis collects the Rayleigh scattering signal, which is mach greater than Raman scattering signal, for detection. In the design of optical path, theinterference caused by Raman scattering signal is non-significant. The liquid specimen to be detected needs no atomizing or evaporation in advance. The light scattering detector of the present invention may be used alone for microanalysis, together with capillary electrophoresis apparatus, or together with flow injection analyzer and liquid phase chromatograph for in-situ post-column detection and analysis.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for combined test of total nitrogen and total phosphor phosphorus in soil
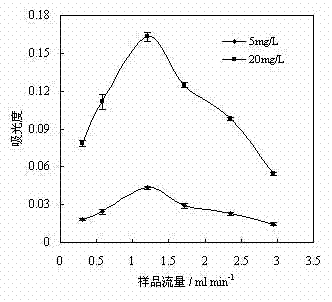
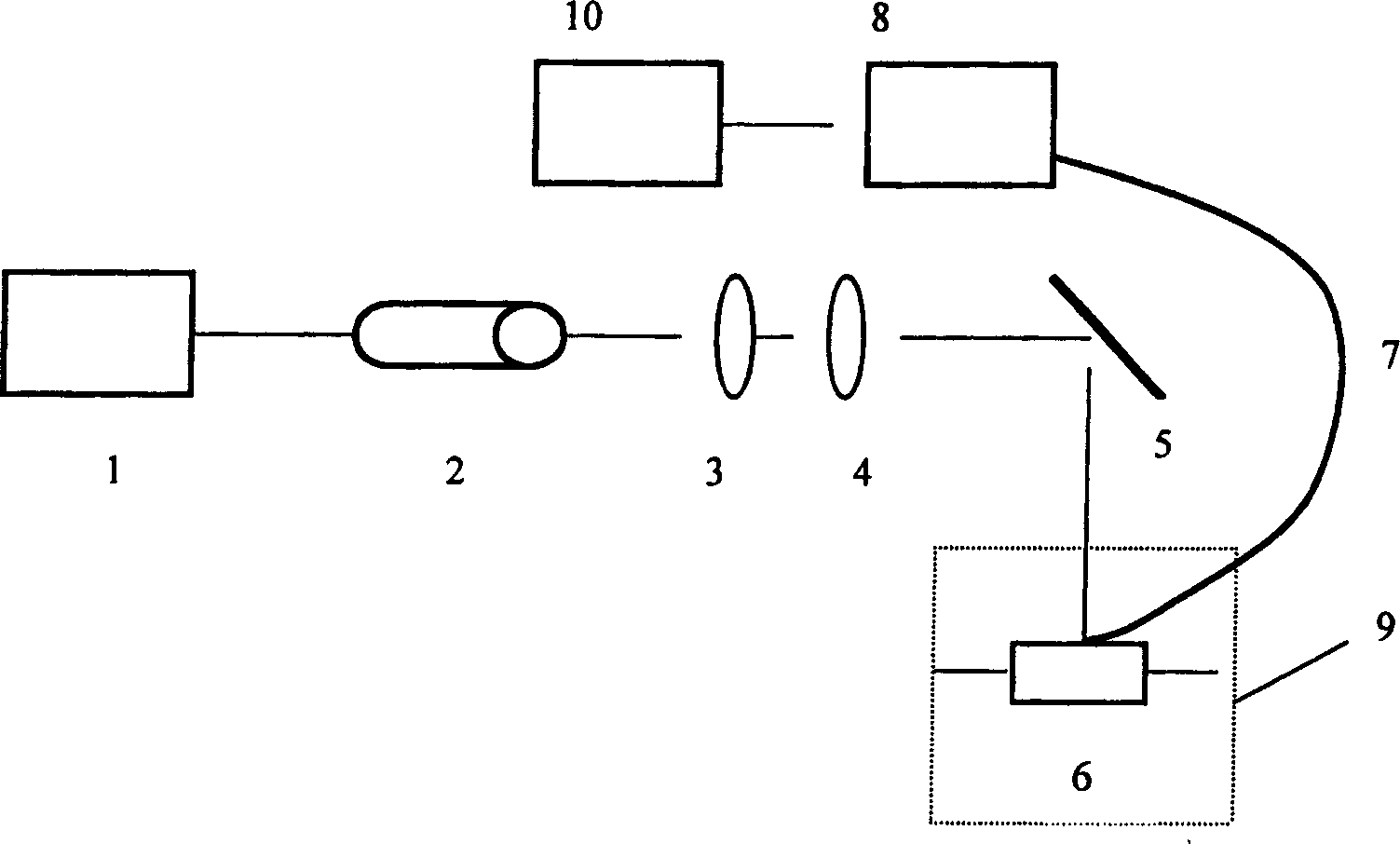
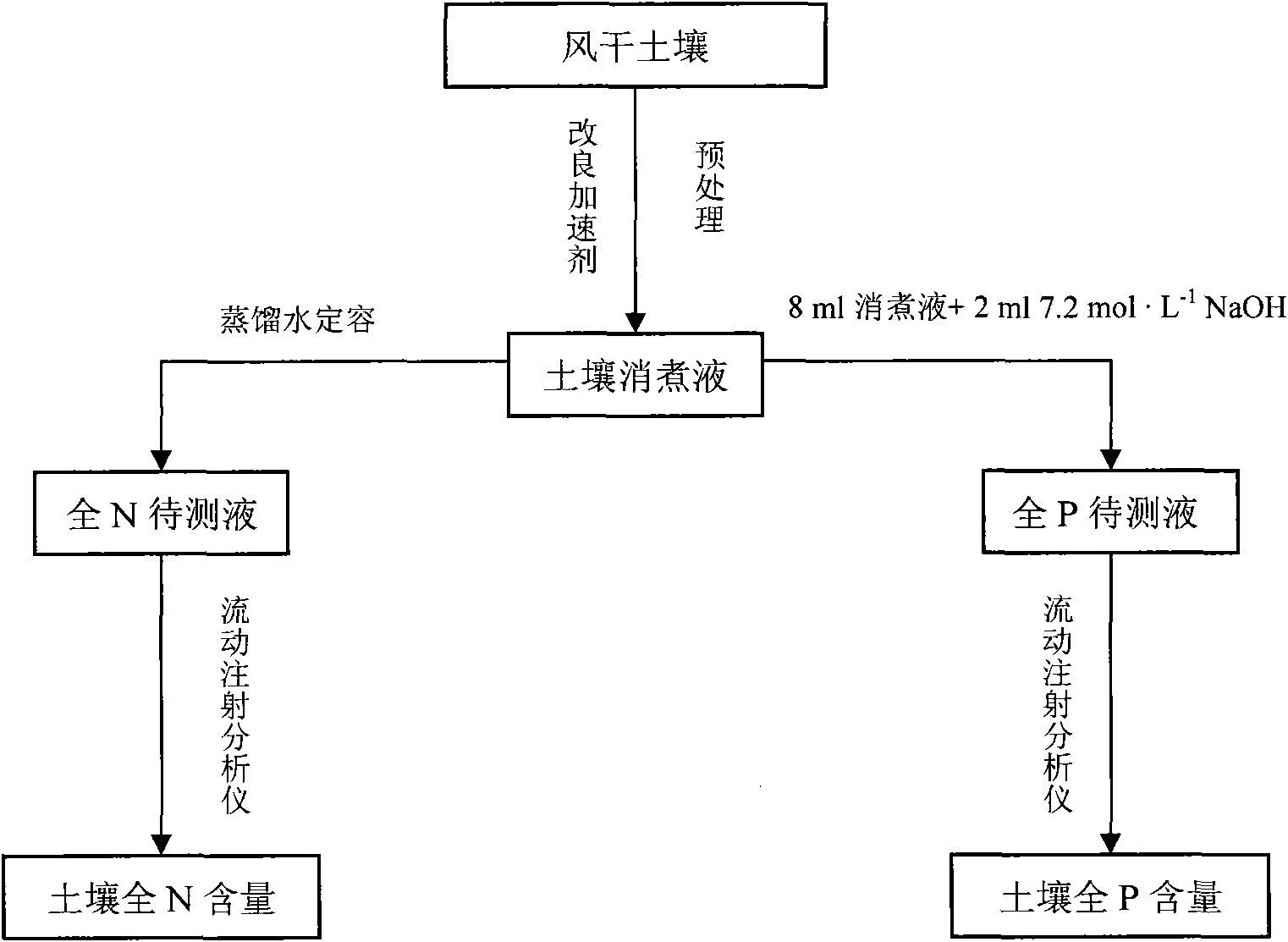
InactiveCN101655484ASimplify the experimental operation processSave time at workChemical methods analysisDigestion TreatmentTotal nitrogen
The invention relates to a method for the combined test of total nitrogen and total phosphor phosphorus in soil, which comprises the following steps: (1) synchronous digestion treatment of soil: weighing a dried and screen soil sample, placing the sample into a digestion tube, adding an accelerator, adding solution of concentrated sulfuric acid and placing the digestion tube in at high-temperatureenvironment for digestion; (2) preparation of soil liquid to be tested: after the digestion liquid obtained after digestion is cool, fixing the volume of the digestion liquid by adding distilled water, using the digestion liquid to test the total nitrogen content of the soil, adjusting the pH value of soil total nitrogen liquid to be tested by using alkaline liquid and using the resulting liquidto test the total phosphor content of the soil; and (3) test of the total nitrogen content and total phosphor content of soil: automatically testing the total nitrogen content and total phosphor content of soil by using a constant flow injection analyzer. The method has the advantages of: 1, avoiding repeated soil sample weighing and soil digestion and simplifying experimental operation process; 2, avoiding damages of selenium powder to human bodies by using potassium sulfate and copper sulfate in place of the accelerator for soil digestion treatment; and 3, improving accuracy and precision bytesting total nitrogen content and total phosphor content of soil by using constant flow injection analyzer.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPLIED ECOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Direct flow injection analysis nebulization electrospray and APCI mass spectrometry
InactiveUS6858437B2Increase ratingsMaximize sample throughputComponent separationIon-exchanger regenerationDead volumeSolvent
A method and apparatus for Flow Injection Analysis (FIA) into Atmospheric Pressure Ion sources (API) including Electrospray (ES) and Atmospheric Pressure Chemical Ionization (APCI) sources whereby the sampling and spray needles are one and the same. The sampling and spray needle configured with an autoinjector apparatus or used in manual injection is introduced directly into a mating ES or APCI probe configured in an API source. Such a sampling and spray needle eliminates the need for injector valves, transfer lines or additional fluid delivery systems in FIA into API sources interfaced to mass spectrometers or other chemical analyzers. The use of a sampling and spray needle configuration reduces component costs, liquid dead volume, sample dilution effects, and minimizes cross contamination effects, solvent consumption and waste while increasing sample throughput.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com