Method of manufacture of a multi-layer phosphorescent organic light emitting device, and articles thereof
A device, phosphorescence technology, applied in the field of manufacturing multilayer phosphorescent organic light-emitting devices
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
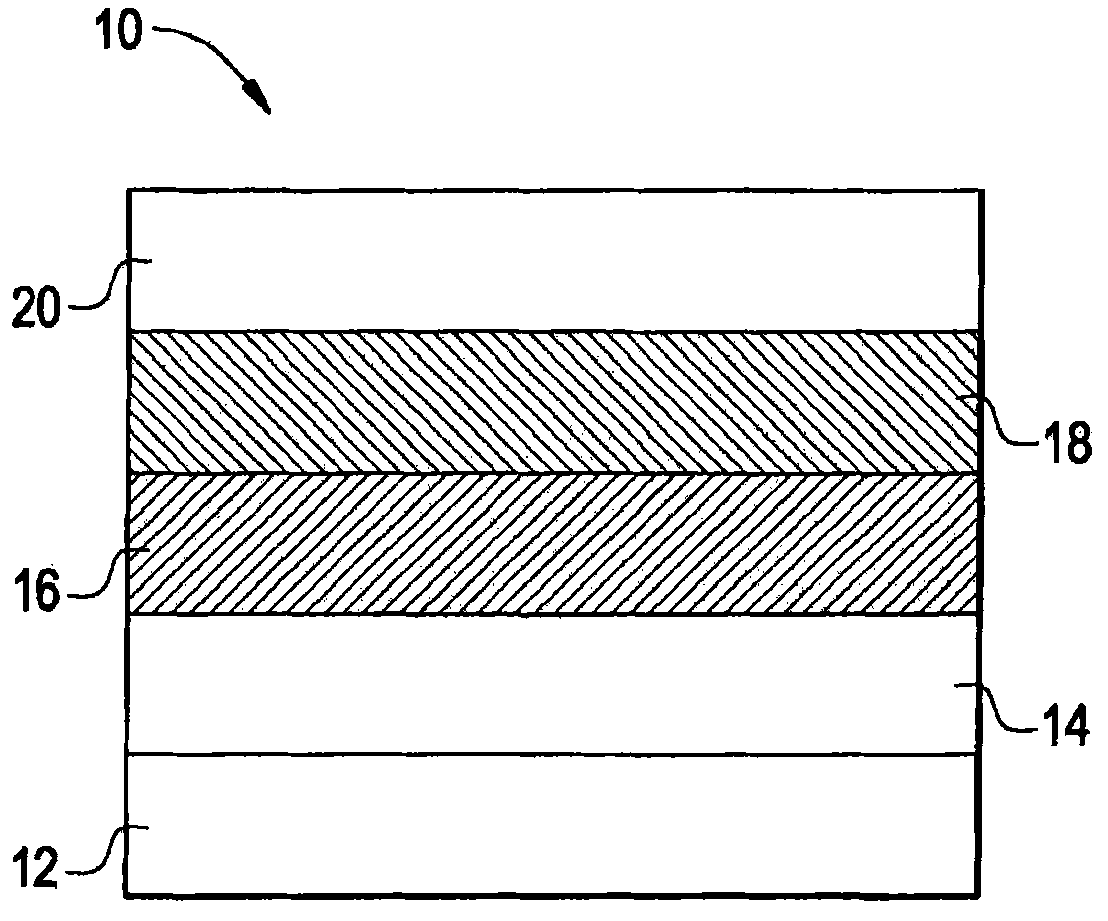
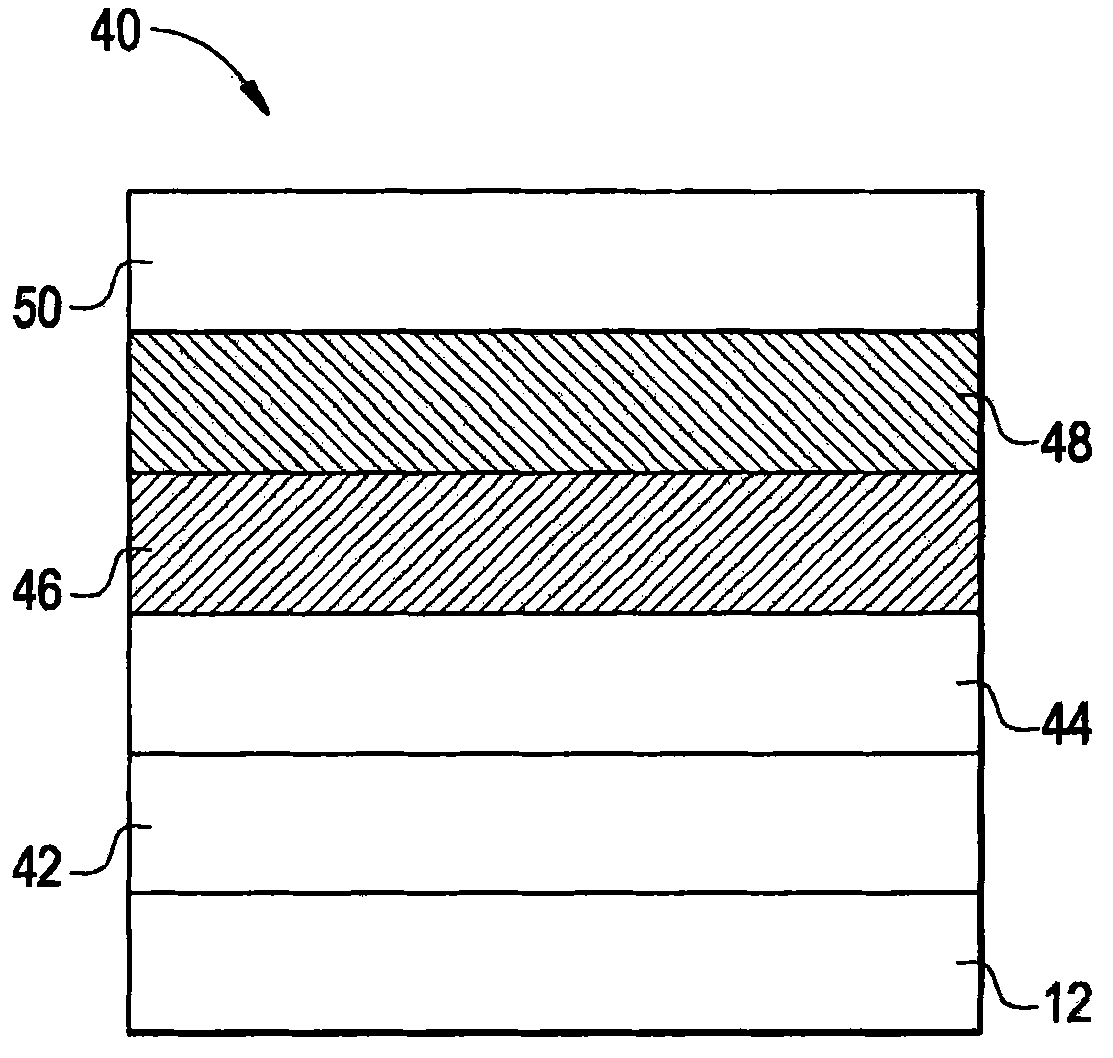
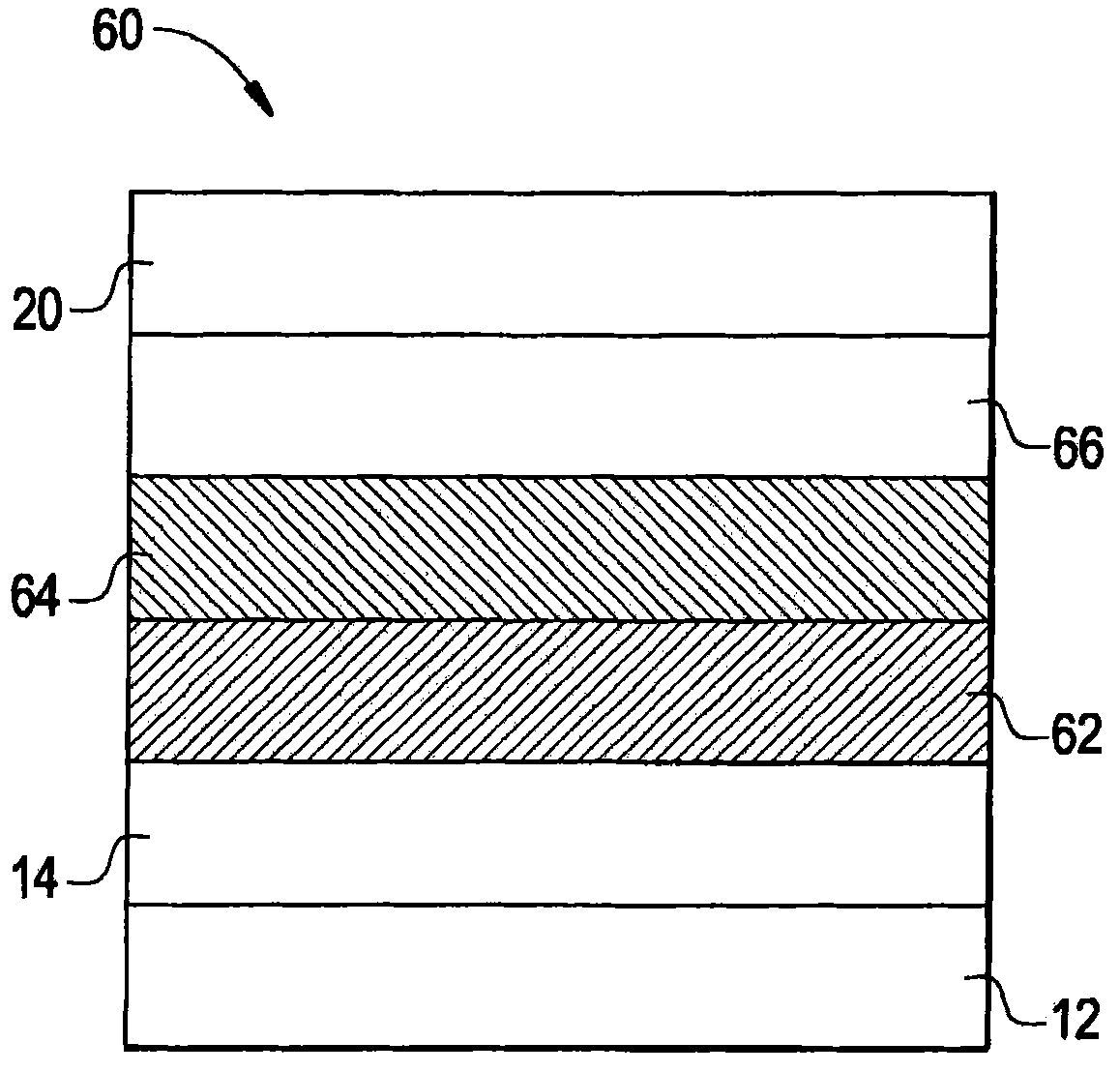
[0105] The multilayer phosphorescent OLED was constructed as follows. A phosphorescent OLED includes a blue phosphorescent polymer light-emitting layer and a red phosphorescent layer. Pre-patterned ITO-coated glass was used as the anode substrate and cleaned with UV-ozone for 10 minutes. A layer (60 nm) of polystyrenesulfonic acid-doped poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOT:PSS) obtained from H.C. Starck was deposited on top of ITO by spin coating, followed by air Bake at 180°C for 1 hour. The coated substrate was then transferred into an argon-filled glove box (humidity and oxygen less than 1 ppm). A blue phosphorescent polymer emitting layer of 275-44-5 (about 30 nm thick) was subsequently spin-coated on top of the PEDOT:PSS layer from a chlorobenzene solution and baked on a hotplate (preheated to 120 °C) 10 minutes. Next, OXD-7 (1,3-bis[(p-tert-butyl)phenyl-1,3,4- A mixture of oxadiazolyl]benzene) and ADS069RE in a weight ratio of 90:10 (OXD-7:ADS069RE) was spin-cas...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com