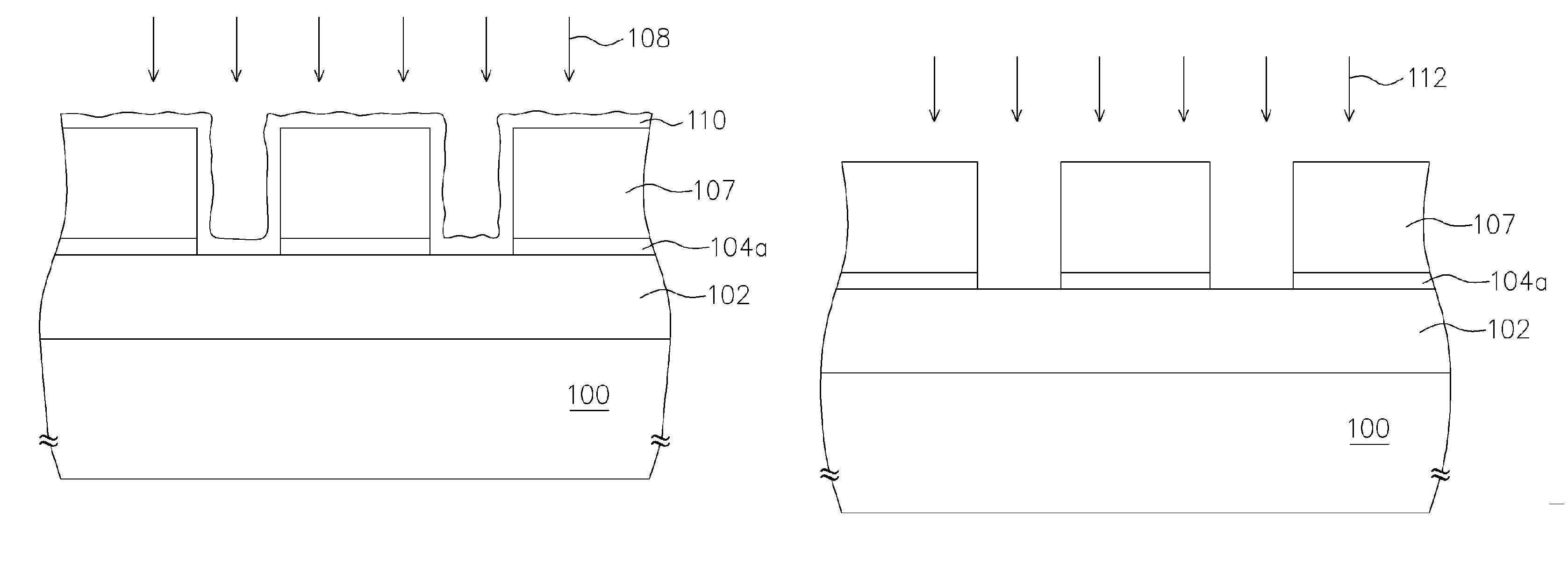Patents
Literature
30results about How to "Linewidth also decrease" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
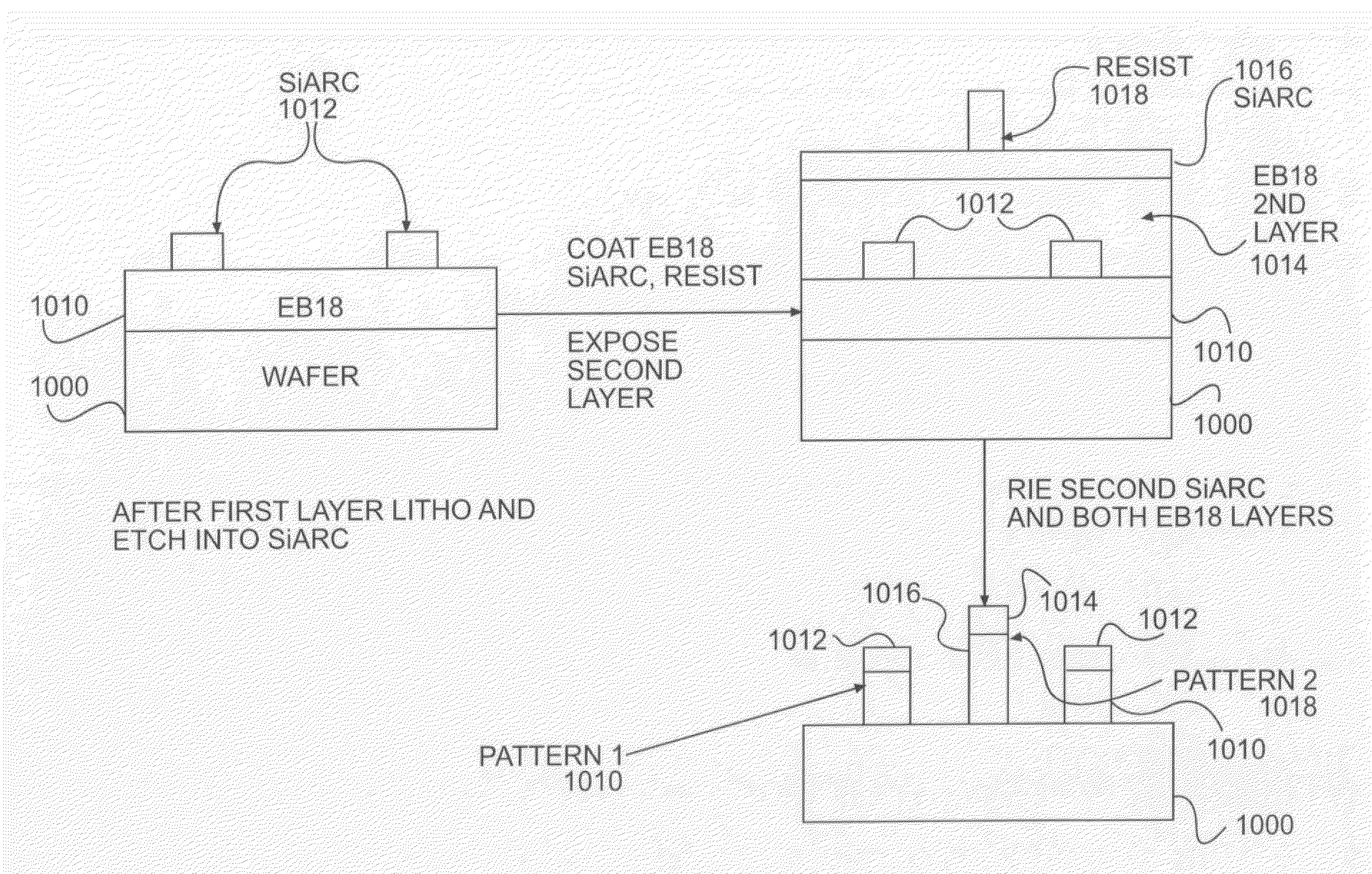
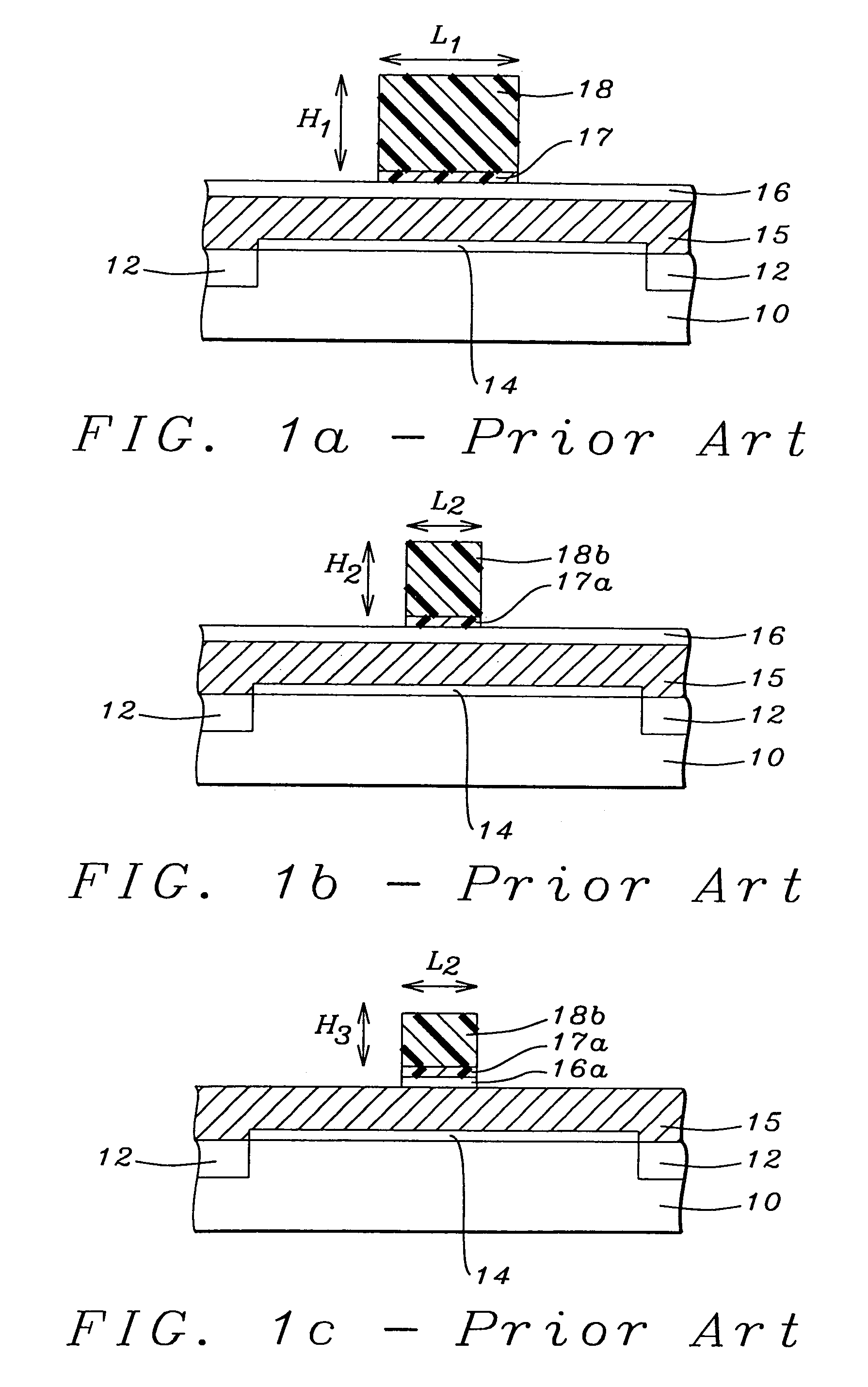
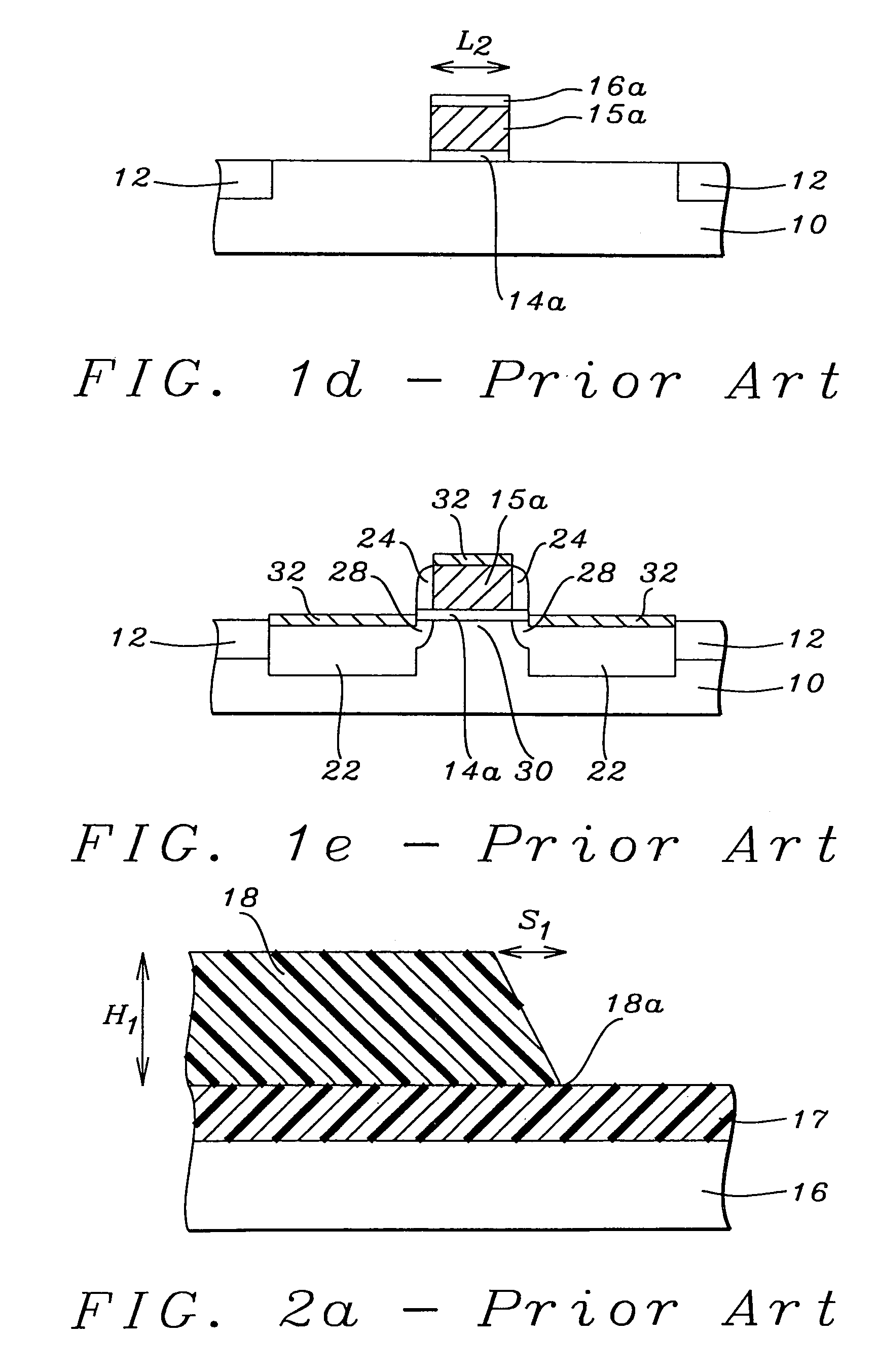
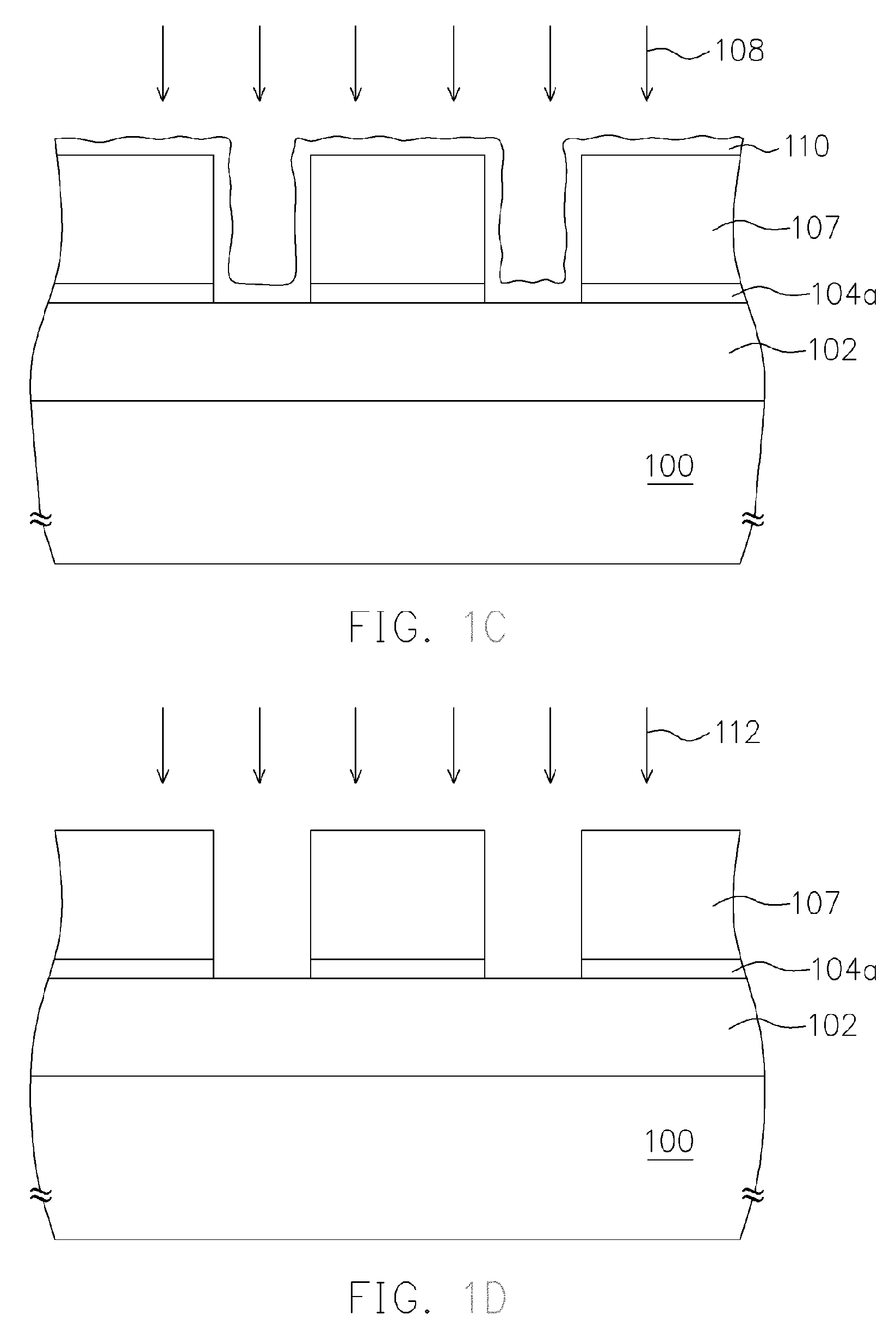
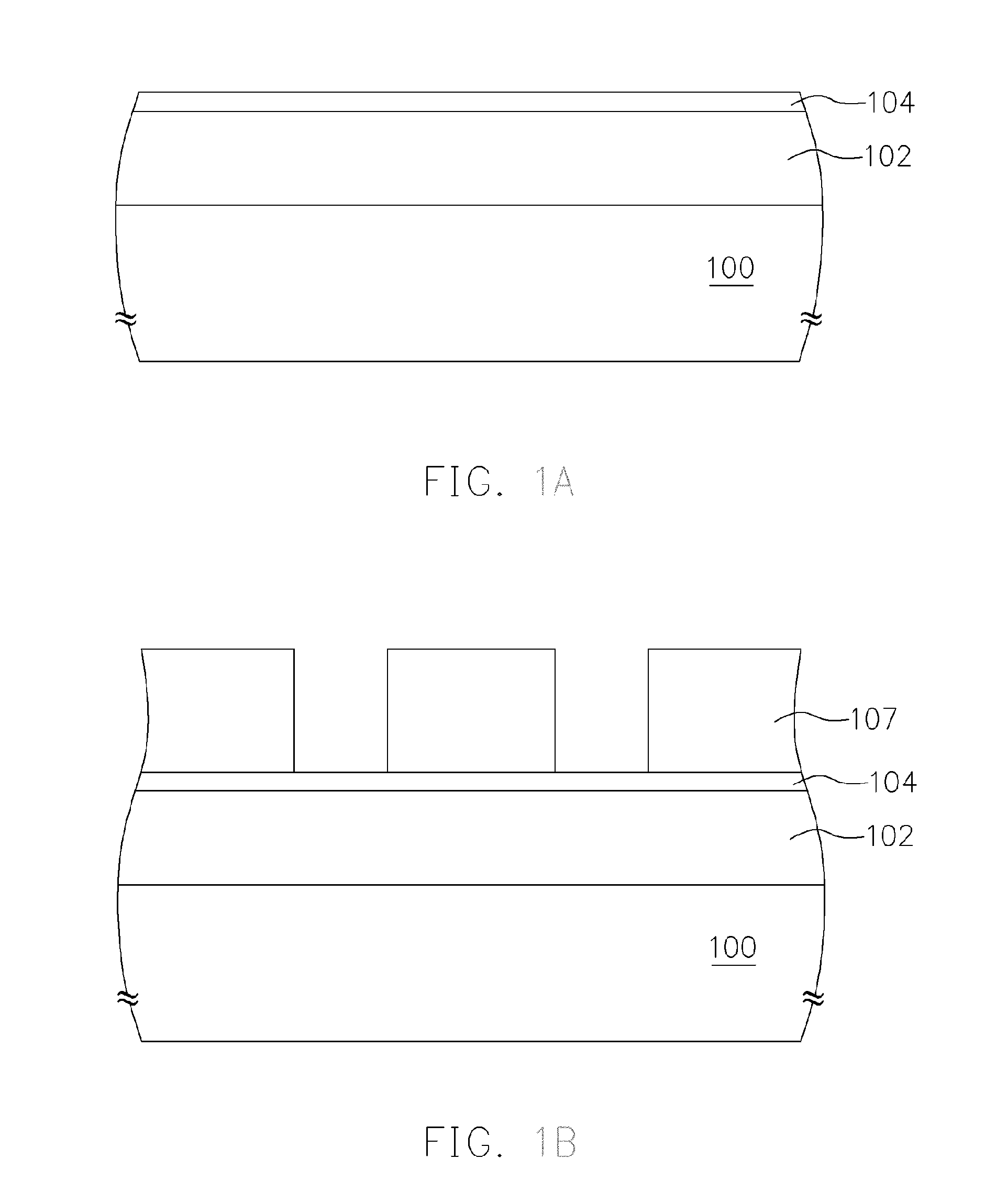
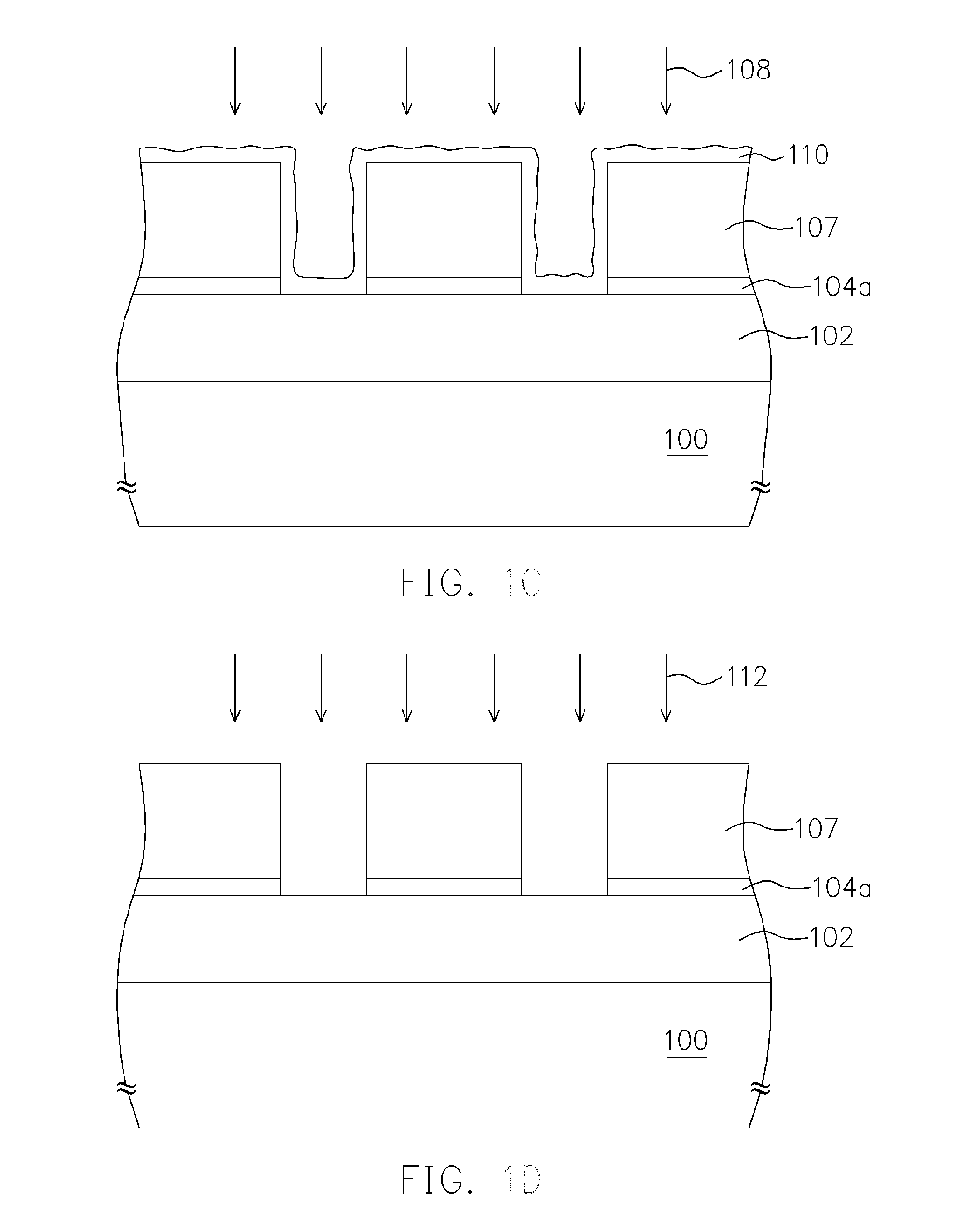
Chemical trim of photoresist lines by means of a tuned overcoat material
InactiveUS20090311490A1Linewidth also decreaseSuperior linewidth controlPhotosensitive materialsLayered productsLithography processLine width
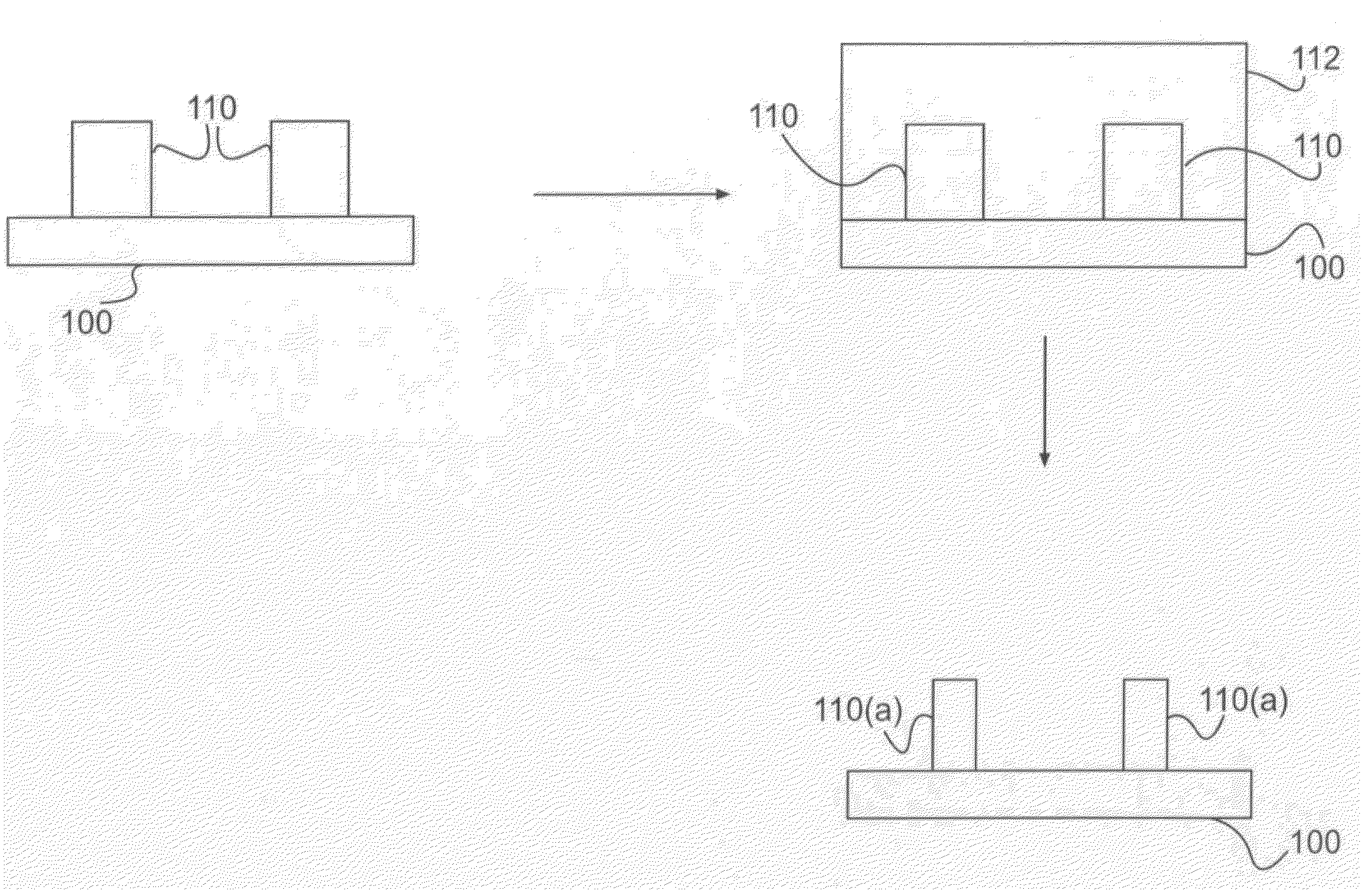
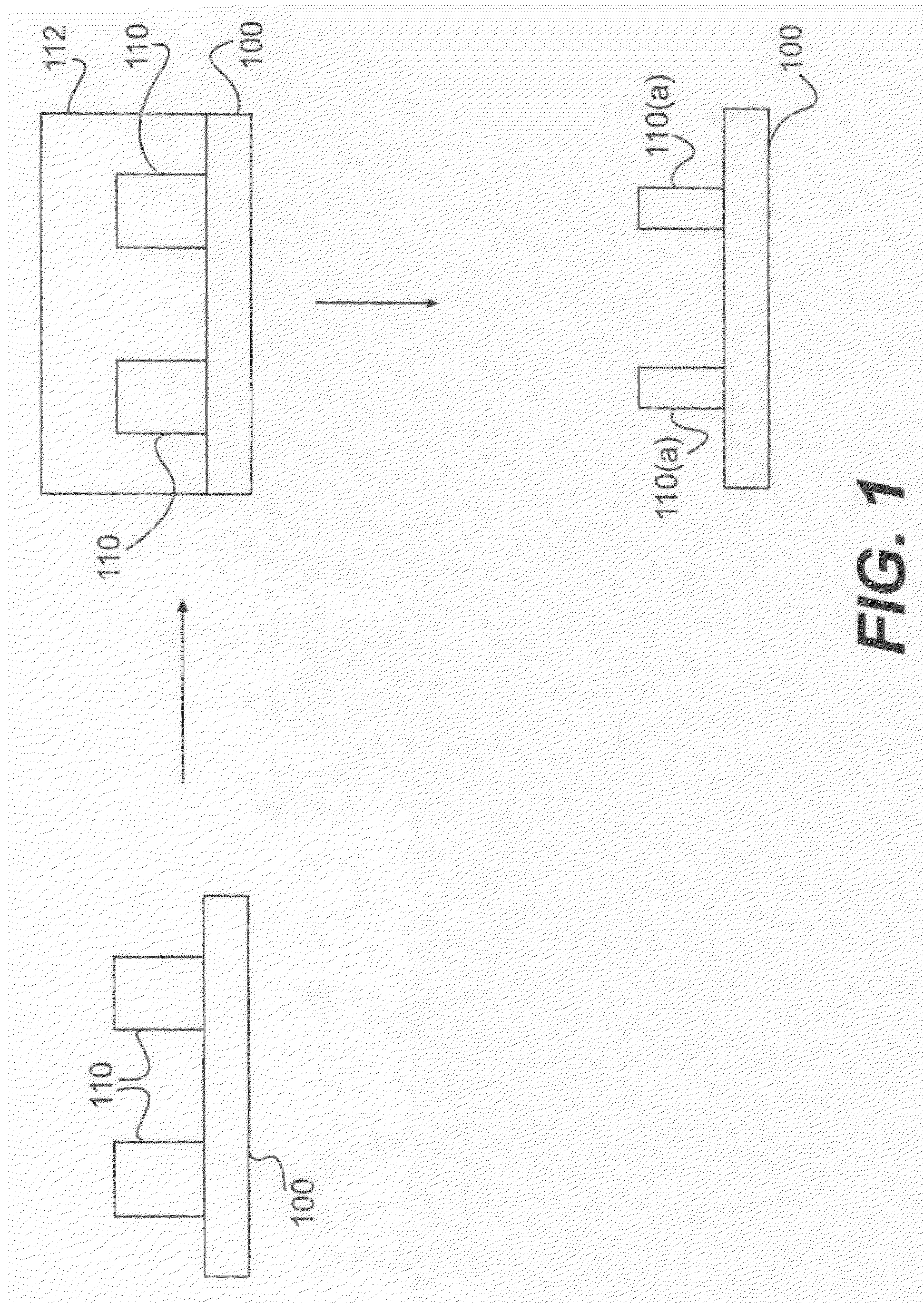
A new lithographic process comprises reducing the linewidth of an image while maintaining the lithographic process window, and using this process to fabricate pitch split structures comprising nm order (e.g., about 22 nm) node semiconductor devices. The process comprises applying a lithographic resist layer on a surface of a substrate and patterning and developing the lithographic resist layer to form a nm order node image having an initial line width. Overcoating the nm order node image with an acidic polymer produces an acidic polymer coated image. Heating the acidic polymer coated image gives a heat treated coating on the image, the heating being conducted at a temperature and for a time sufficient to reduce the initial linewidth to a subsequent narrowed linewidth. Developing the heated treated coating removes it from the image resulting in a free-standing trimmed lithographic feature on the substrate. Optionally repeating the foregoing steps further reduces the linewidth of the narrowed line. The invention also comprises a product produced by this process.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
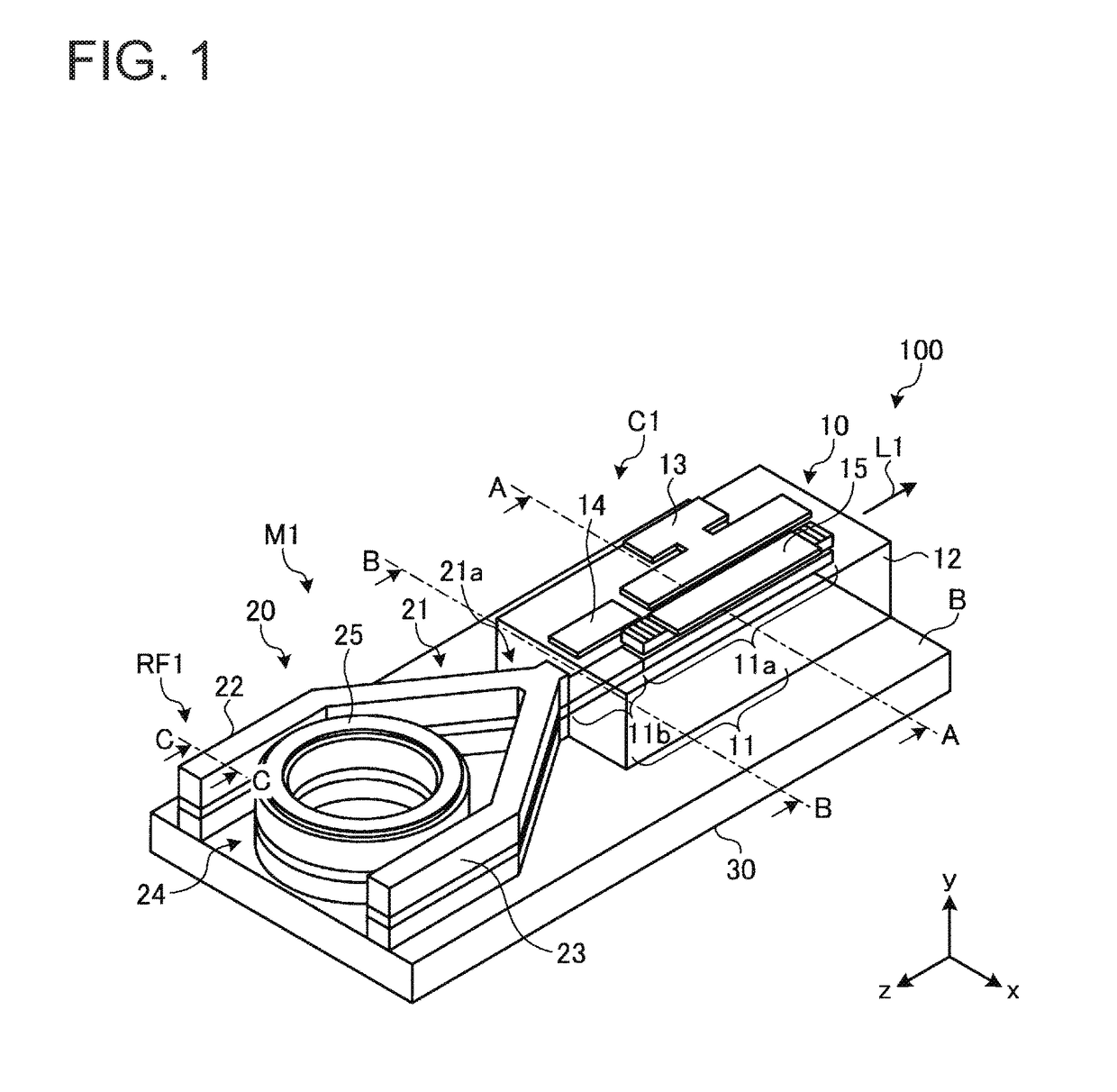
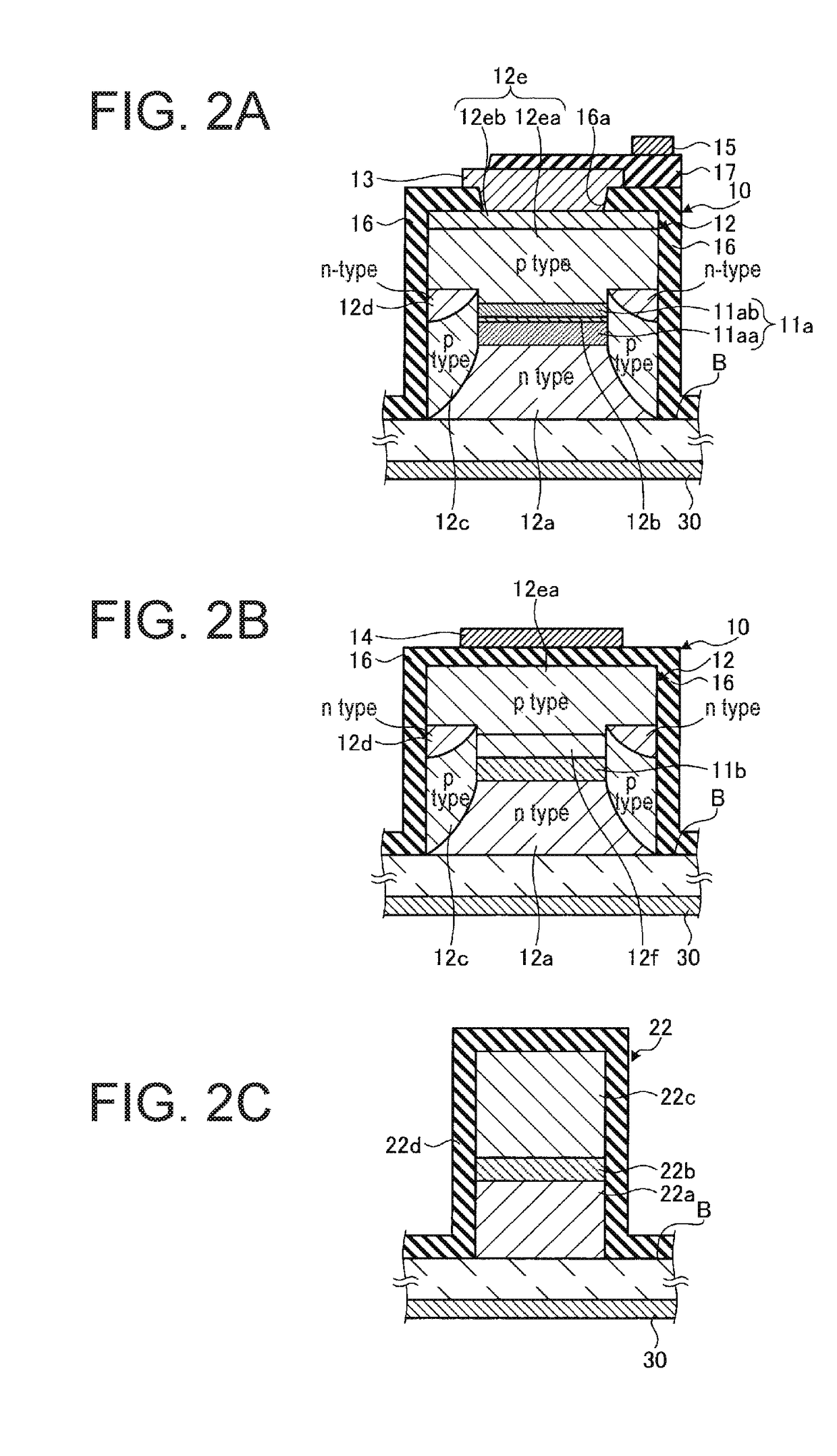
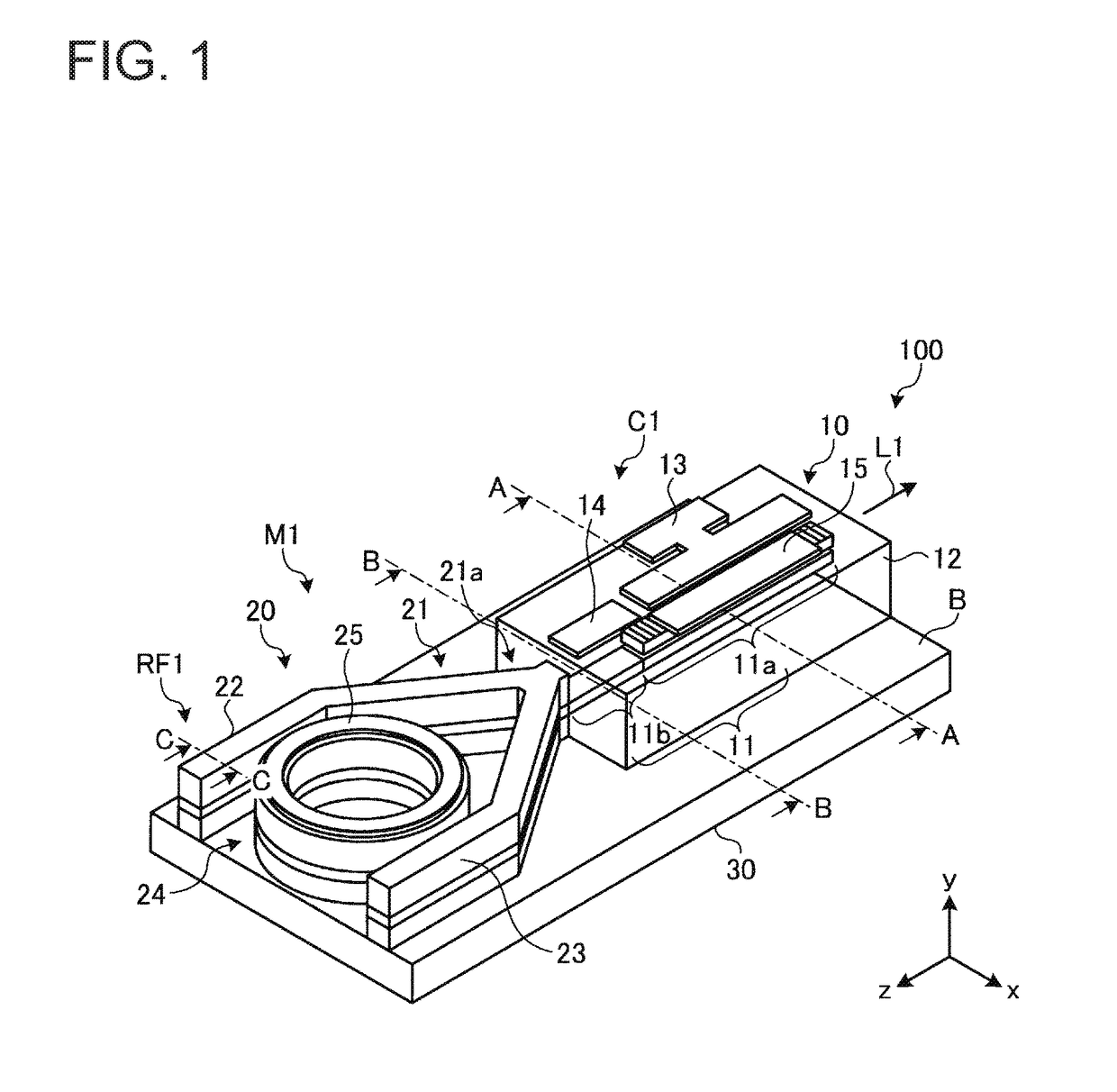
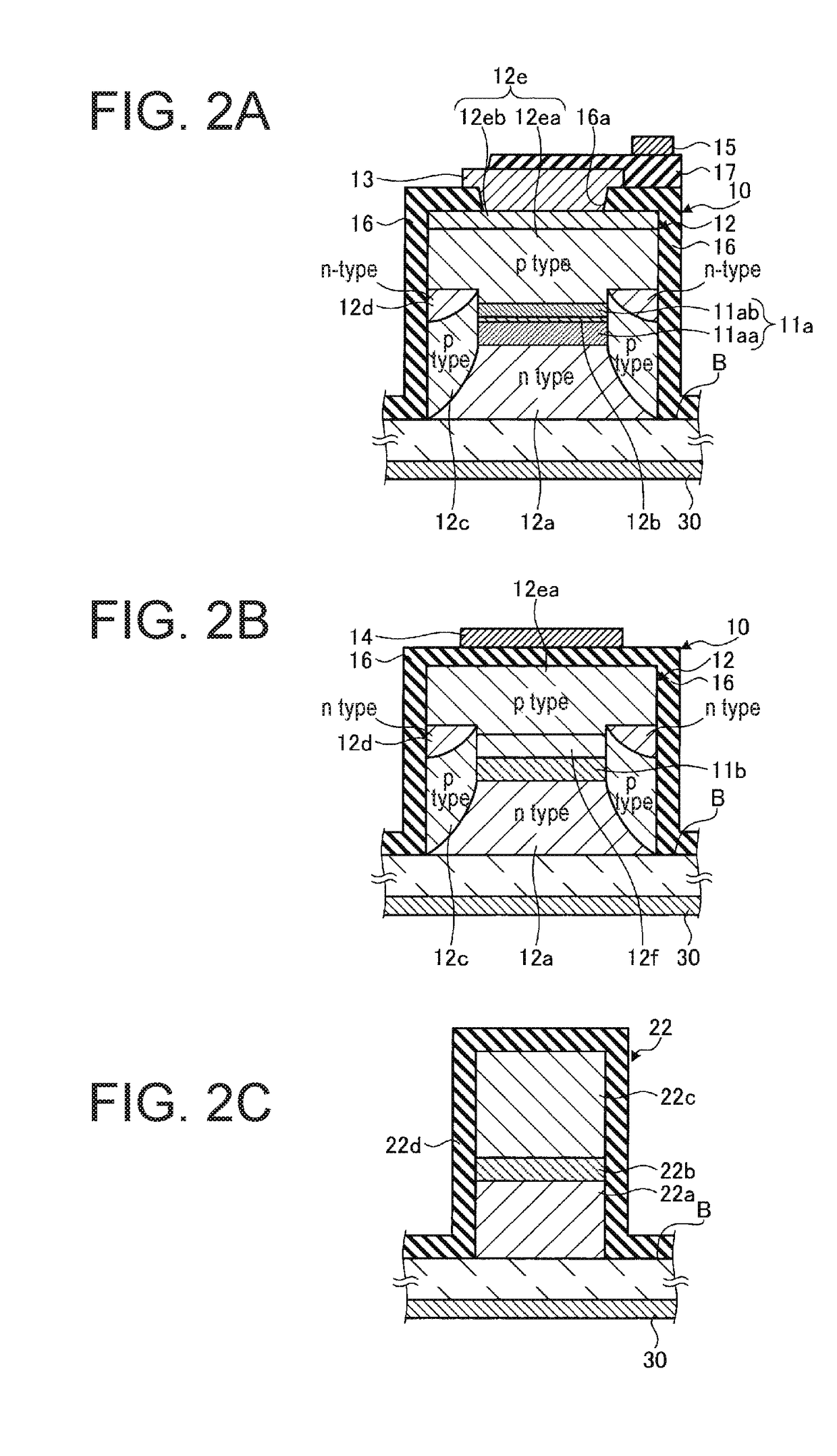
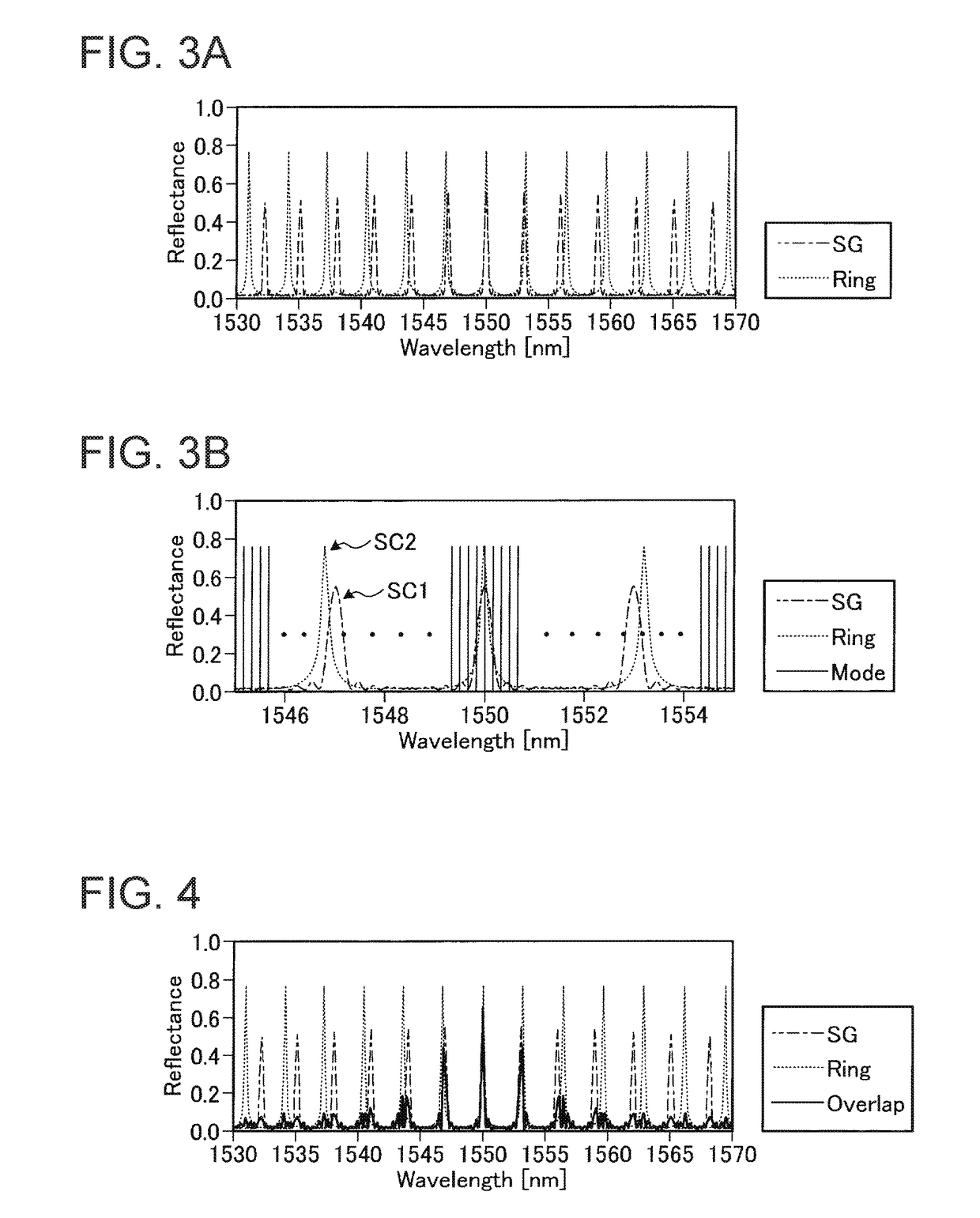
Wavelength tunable laser device and laser module
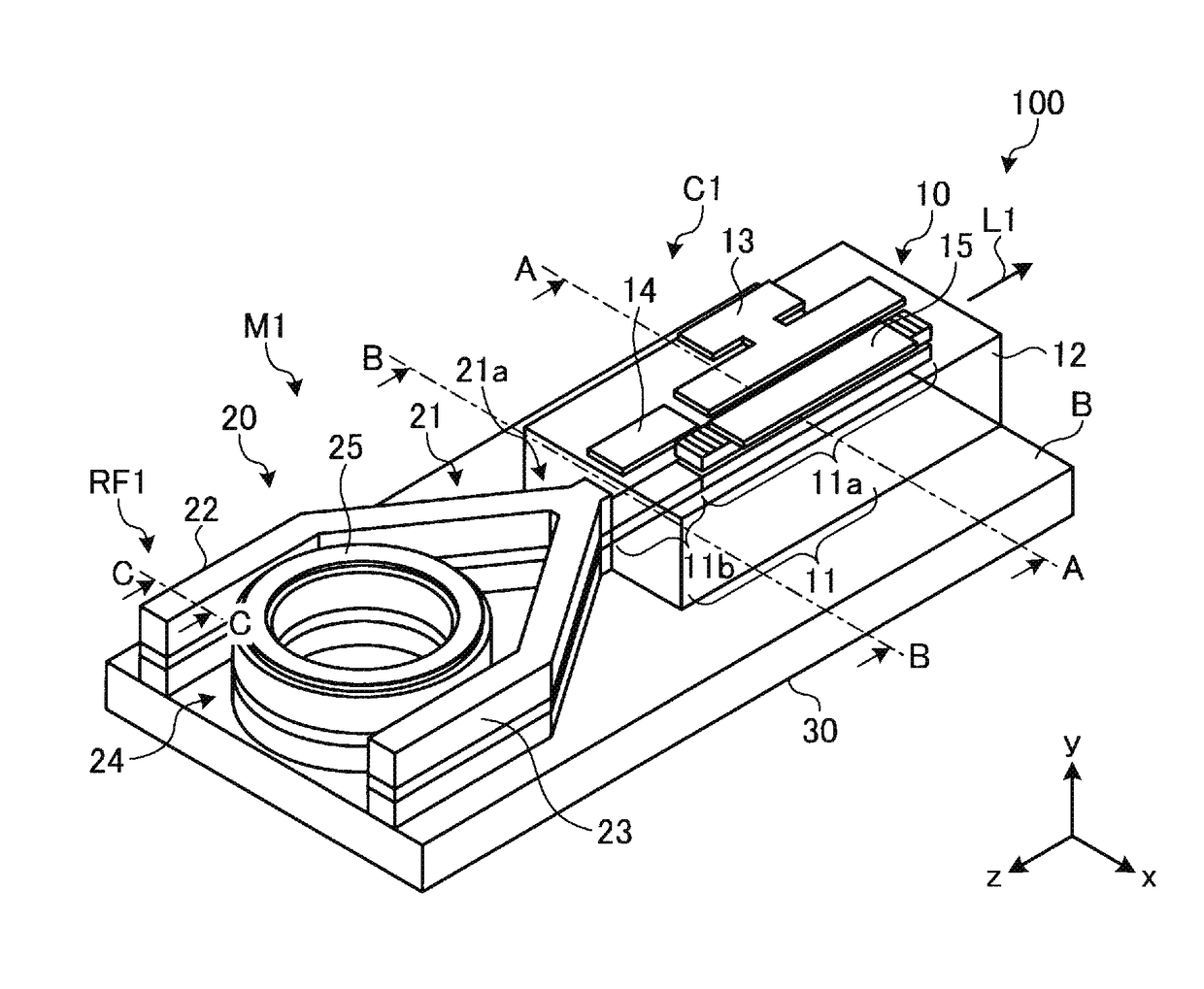
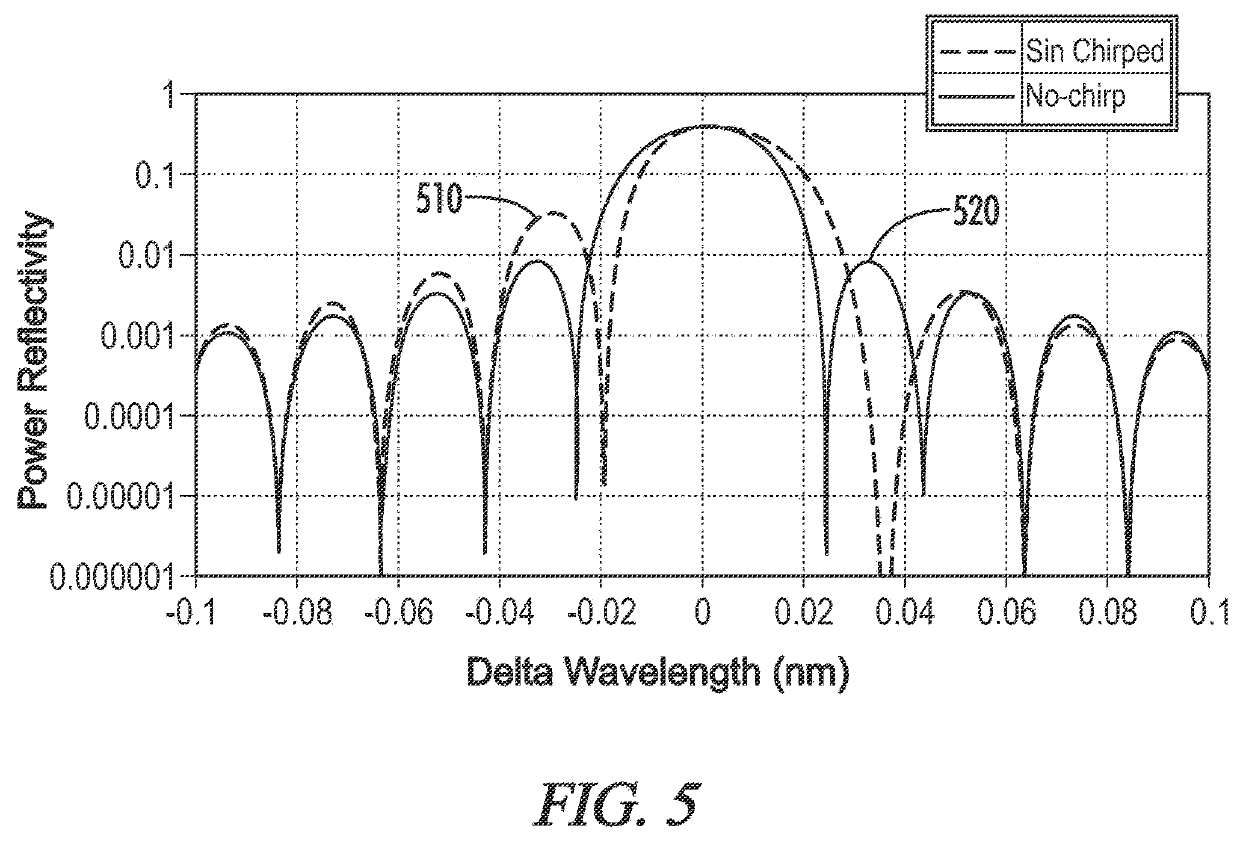
ActiveUS20180026426A1Reduce spacingDifficult to achieveLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingResonator filter
A wavelength tunable laser device includes: a laser cavity formed of a grating and a reflecting mirror including a ring resonator filter; a gain portion; and a phase adjusting portion. The grating creates a first comb-shaped reflection spectrum. The ring resonator filter includes a ring-shaped waveguide and two arms and creates a second comb-shaped reflection spectrum having peaks of a narrower full width than peaks in the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum at a wavelength interval different from that of the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum. One of the peaks in the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum and one of the peaks in the second comb-shaped reflection spectrum are overlapped on a wavelength axis, and a spacing between cavity modes is narrower than the full width at half maximum of the peaks in the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
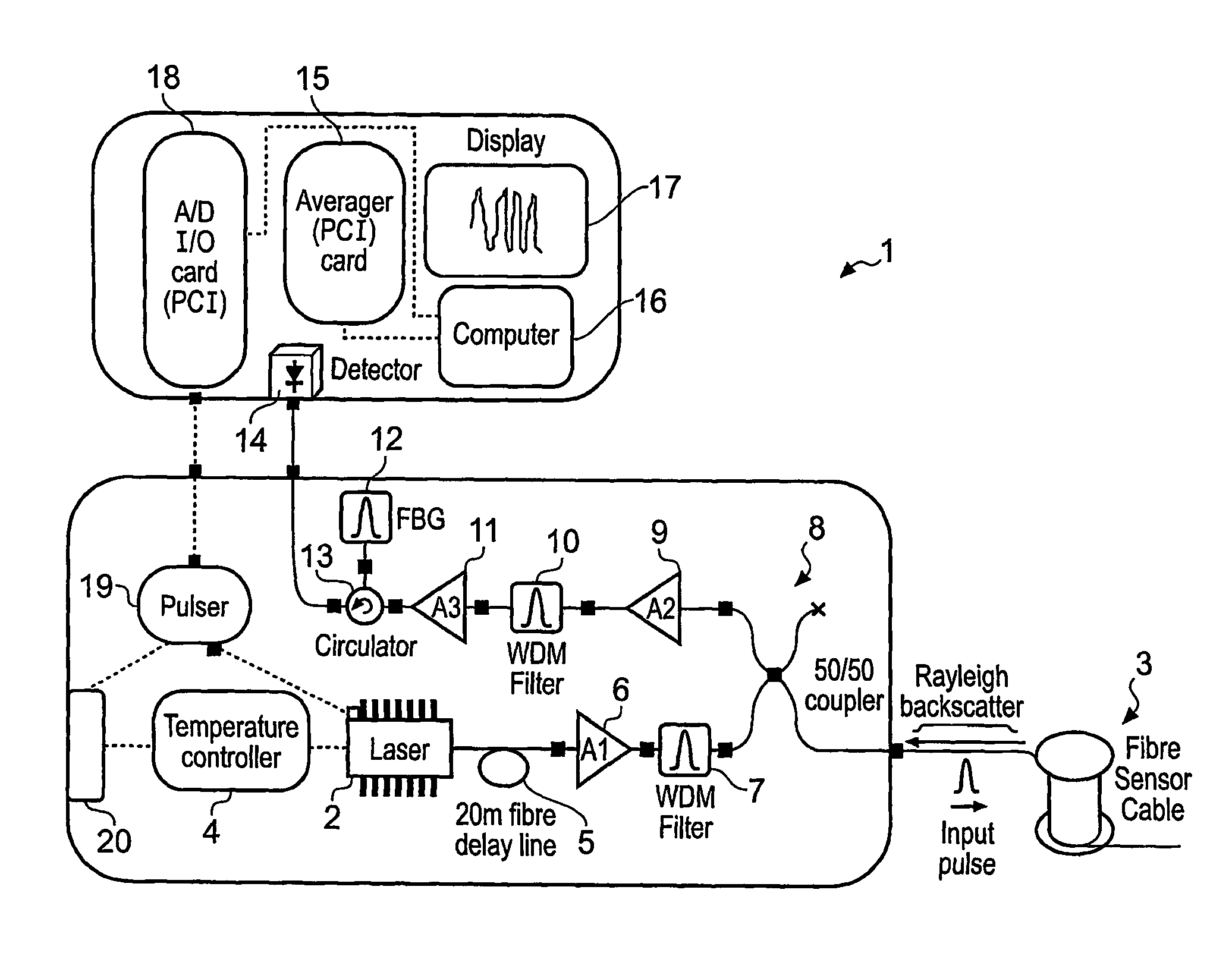
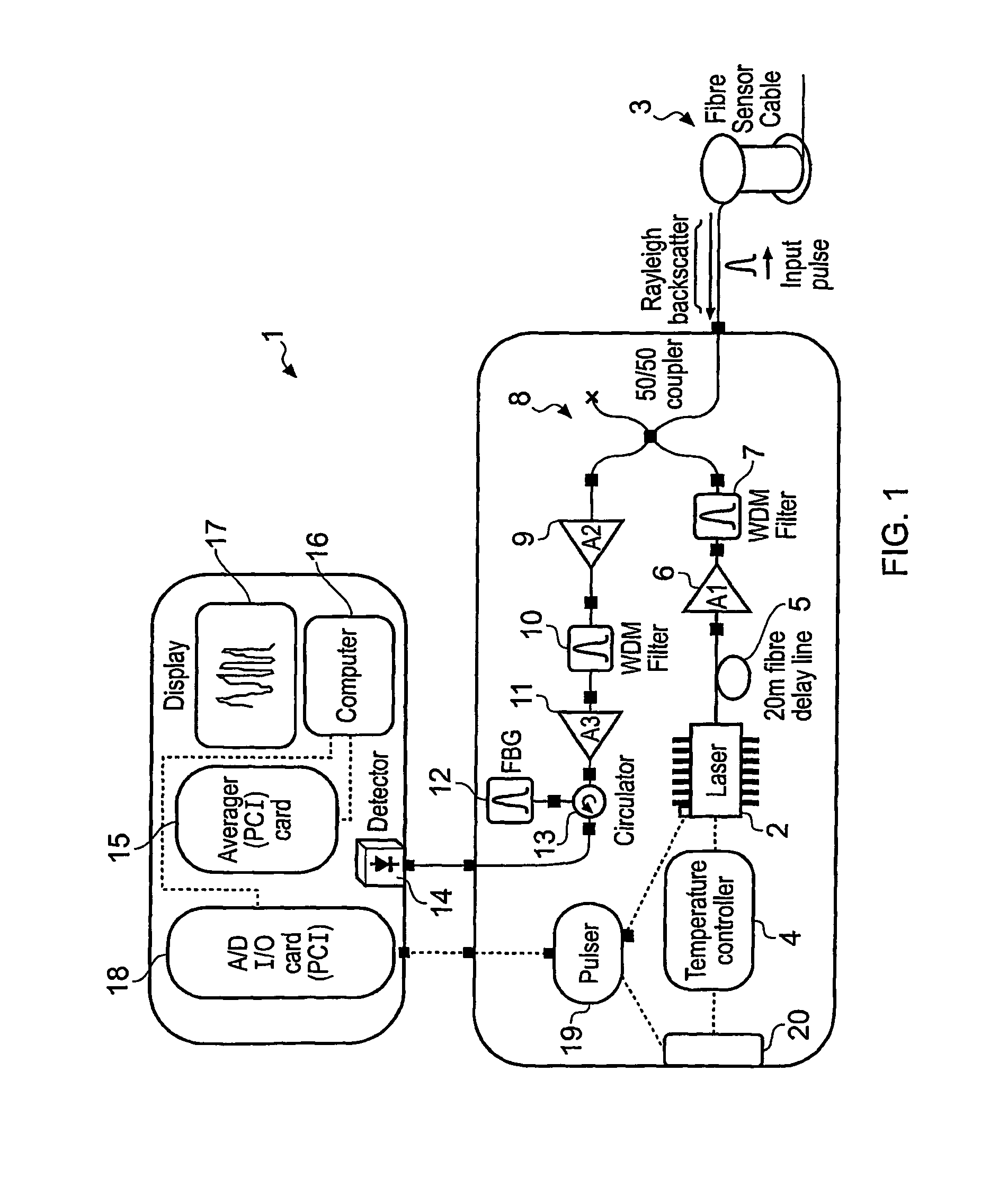
Detecting a disturbance in the phase of light propagating in an optical waveguide
ActiveUS8264676B2Raise the ratioImprove spatial resolutionMaterial analysis by optical meansUsing optical meansGratingPhotodetector
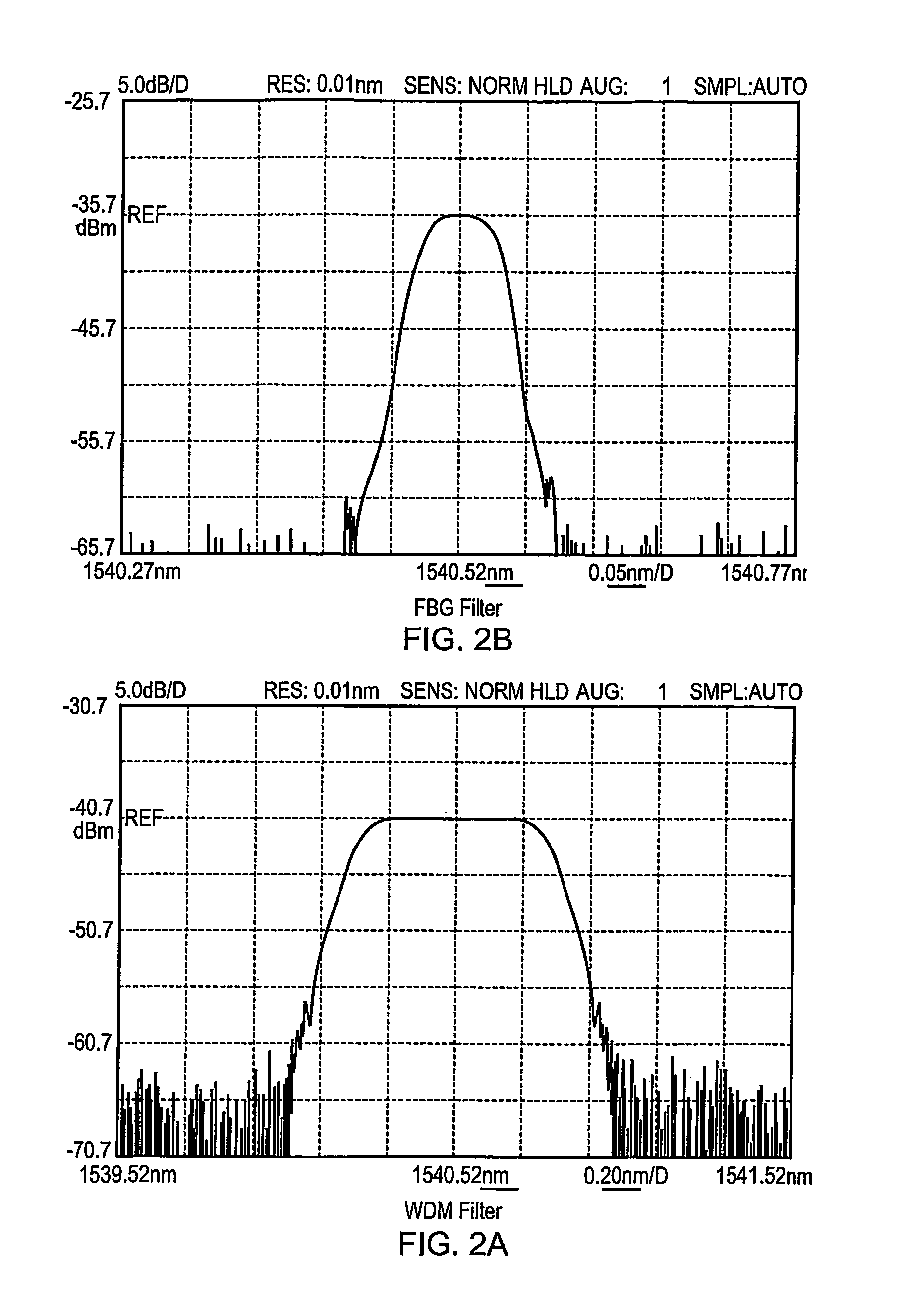
A partially coherent Optical Time Domain Reflectometry (OTDR) apparatus has a light source comprising a directly modulated semiconductor Distributed FeedBack (DFB) laser diode for transmitting partially coherent light pulses along a monomode optical fibre. Light Rayleigh backscattered from the light pulses as they travel along the optical fibre is output from the end of the fibre into which the light pulses are transmitted to a Fibre Bragg Grating (FBG) filter. The FBG filter reduces the supectral width of light received at a photodetector. In one embodiment, the supectral width of the FBG filter is around one fifth of the supectral width of the light pulse after it has travelled around 1 km along the optical fibre. As a consequence of reducing the supectral width of the light received at the photodetector, the FBG filter increases the temporal coherence of the light. So, the FBG filter can ensure that the detected light is sufficiently coherent that a temporal supeckle pattern can be detected at the photodetector. At the same time, the light traveling in the optical fibre can be relatively supectrally broad so that non-linear effects in the optical fibre, such as Brillouin scattering, can be reduced.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
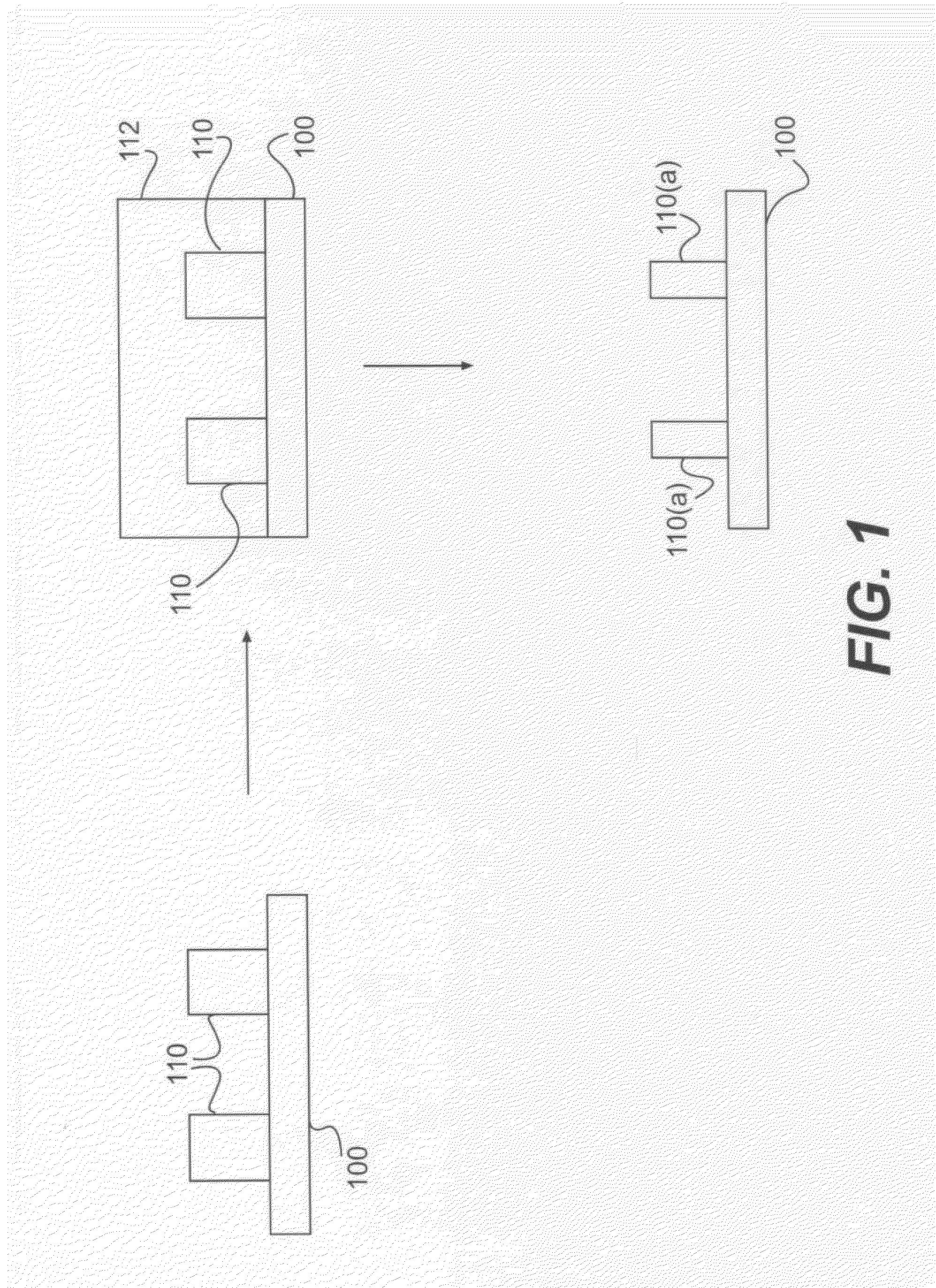
Chemical trim of photoresist lines by means of a tuned overcoat material
InactiveUS7862982B2Linewidth also decreaseEasy to controlPhotosensitive materialsDecorative surface effectsResistLine width
A new lithographic process comprises reducing the linewidth of an image while maintaining the lithographic process window, and using this process to fabricate pitch split structures comprising nm order (e.g., about 22 nm) node semiconductor devices. The process comprises applying a lithographic resist layer on a surface of a substrate and patterning and developing the lithographic resist layer to form a nm order node image having an initial line width. Overcoating the nm order node image with an acidic polymer produces an acidic polymer coated image. Heating the acidic polymer coated image gives a heat treated coating on the image, the heating being conducted at a temperature and for a time sufficient to reduce the initial linewidth to a subsequent narrowed linewidth. Developing the heated treated coating removes it from the image resulting in a free-standing trimmed lithographic feature on the substrate. Optionally repeating the foregoing steps further reduces the linewidth of the narrowed line. The invention also comprises a product produced by this process.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES U S INC
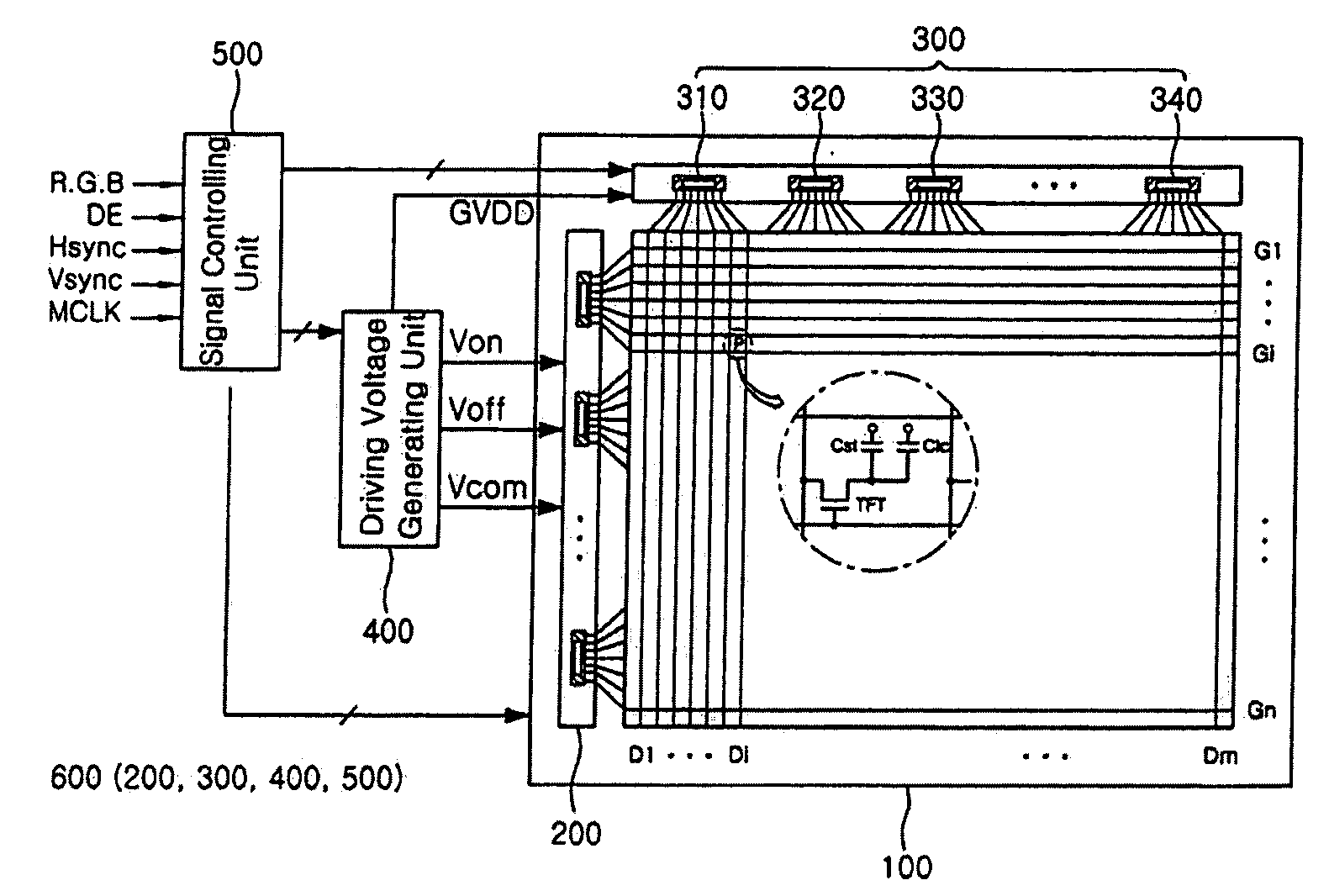
Driving chip and display apparatus having the same
InactiveUS20080273002A1Connection line be increasedLinewidth broadeningStatic indicating devicesNon-linear opticsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
A driving chip and a display apparatus having the same. The driving chip includes a plurality of driving circuits which generate a driving signal, a plurality of output pads which output the driving signals to external signal lines, a plurality of connection lines which connect the plurality of driving circuits and the plurality of output pads, respectively, wherein at least one of the plurality of connection lines includes a resistance-control unit which controls resistance values of the connection lines to be the same, and reduces a resistance deviation between the connection lines.Thus, resistances of connection lines are controlled to be substantially the same, or resistance deviation is reduced by adjusting the resistances of the respective connection lines of an output port. Accordingly, a signal delay or a signal distortion induced by the resistance deviation of the connection lines in the driving chip is prevented, and defective images are removed.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
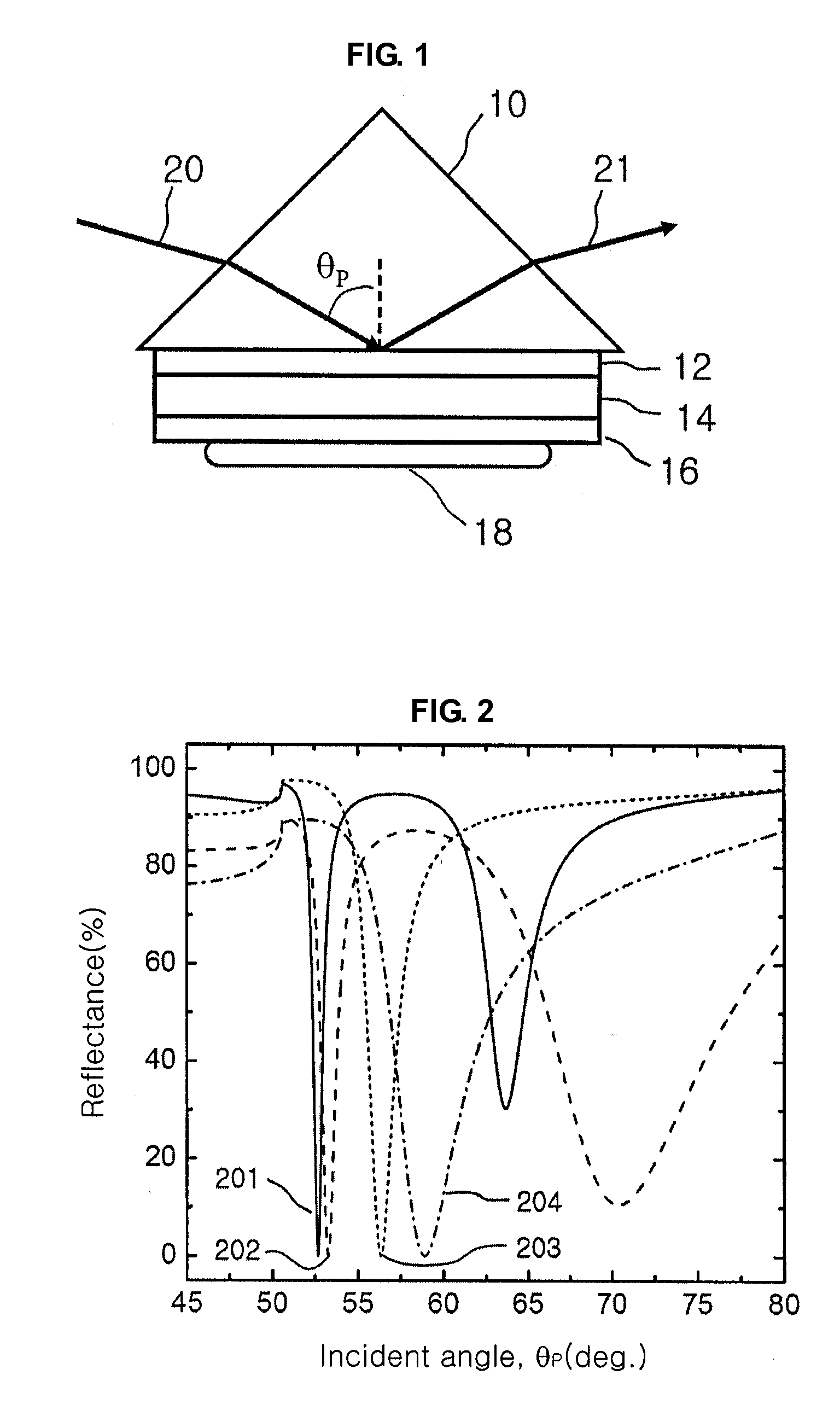
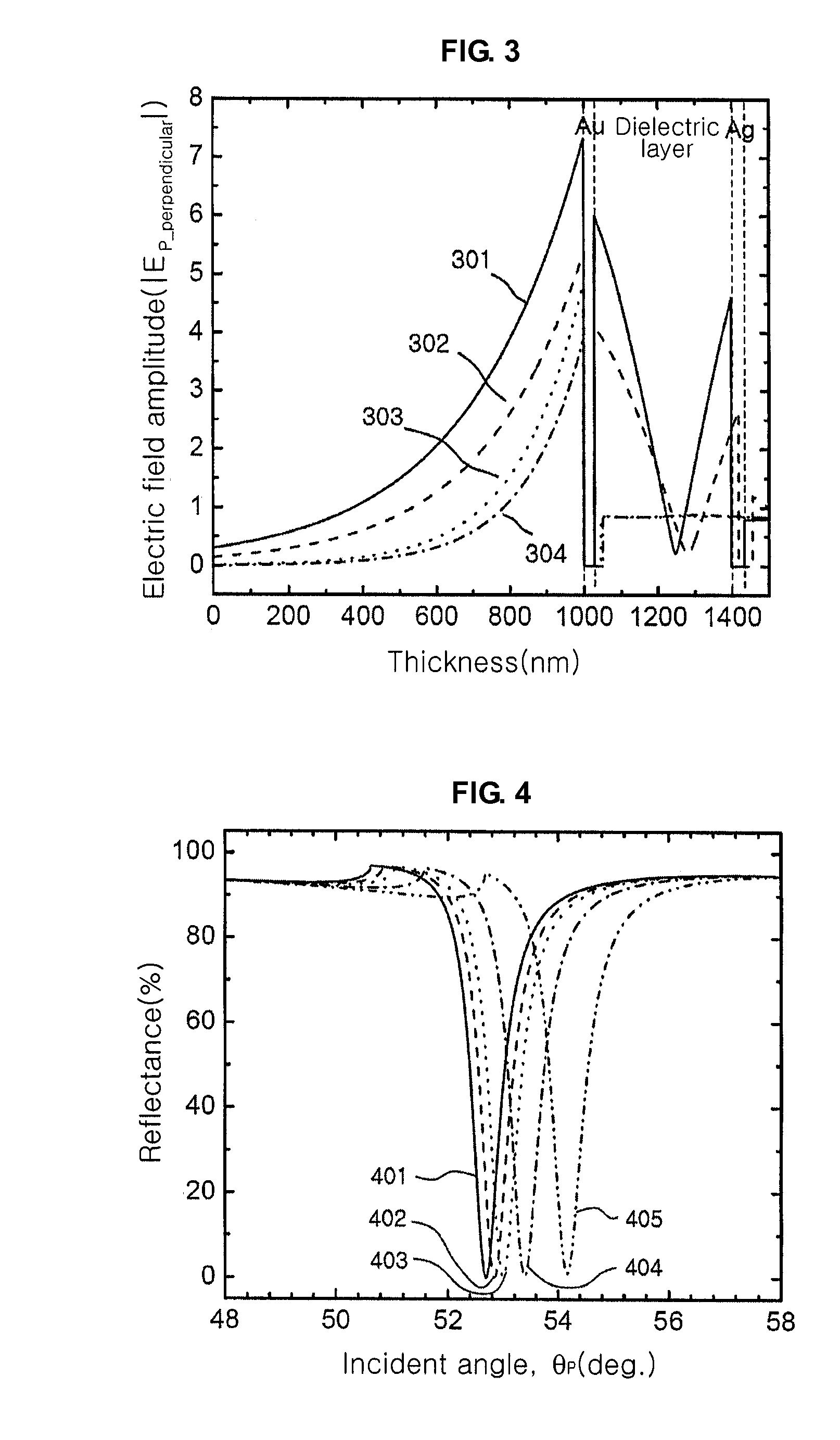
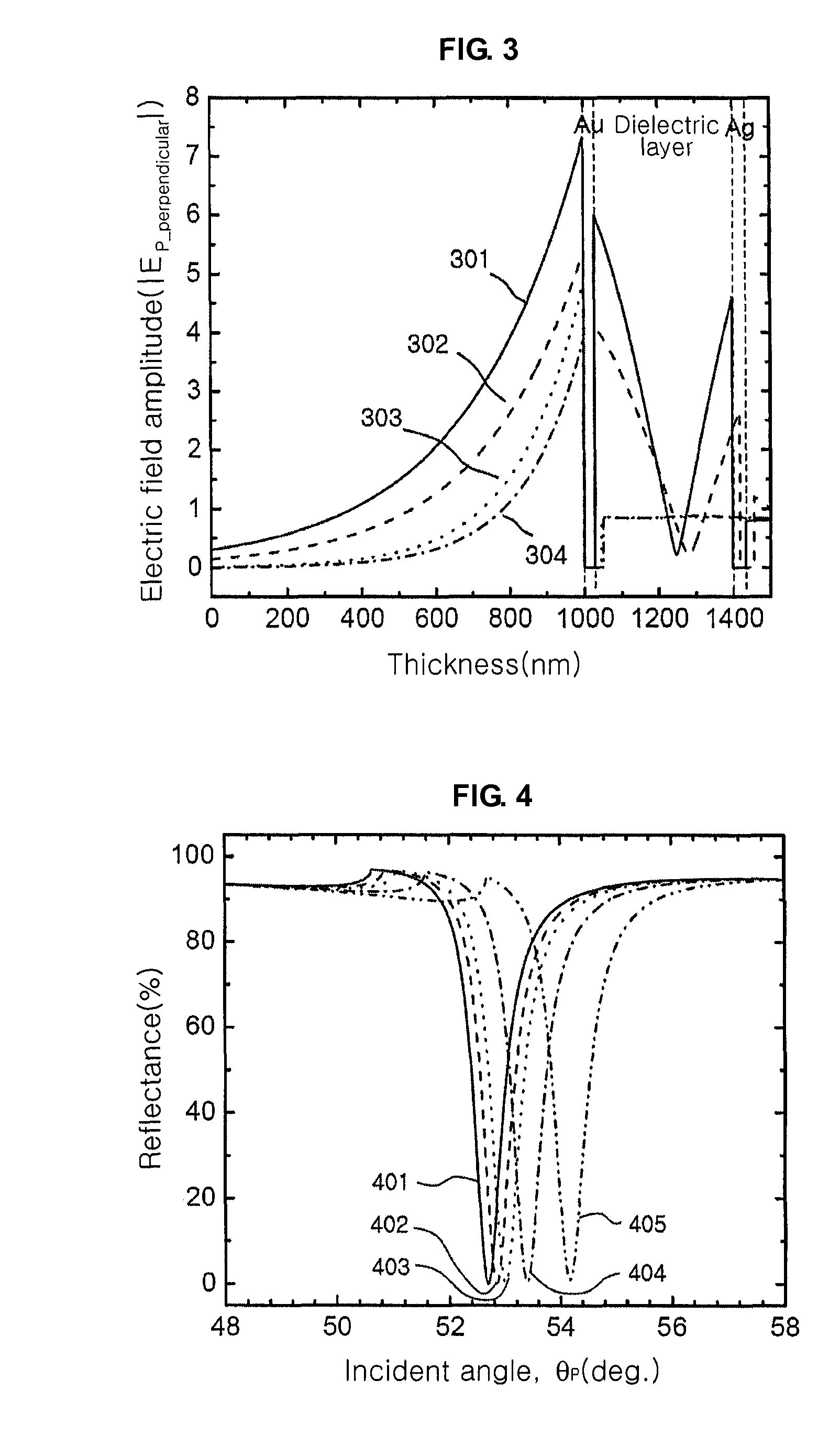
High resolution surface plasmon resonance sensor and sensor system thereof
InactiveUS20100128273A1Linewidth also decreaseImprove responseScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLight beamSurface plasmon resonance imaging
Provided is a surface plasmon resonance sensor including: a part of delivering light by which a signal beam is incident to generate an evanescent field; and a part of exciting surface plasmon for exciting surface plasmons by the generated evanescent field and giving rise to a surface plasmon resonance, wherein a dielectric waveguide layer is inserted between metal layers of the part of exciting surface plasmon, and surface plasmon resonance properties are changed by an object to be analyzed.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Electron beam lithography method using new material
InactiveUS7144680B2Linewidth also decreaseLinewidth of patterns can be further reducedElectric discharge tubesRadiation applicationsLithographic artistThin layer
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Novel approach to improve line end shortening
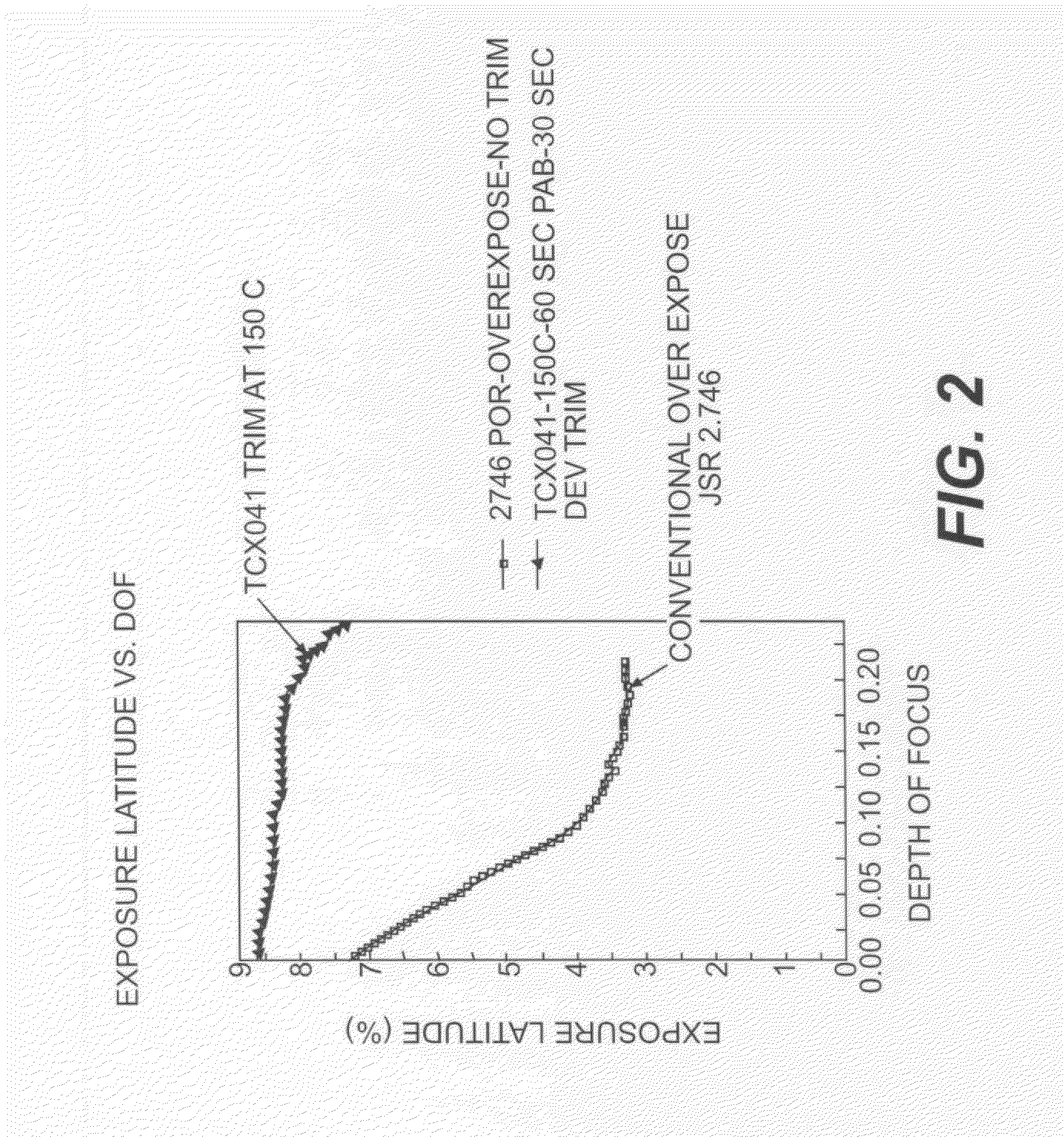
InactiveUS20050191832A1Improve toleranceEasy to controlRadiation applicationsPhotomechanical apparatusEngineeringProcess window
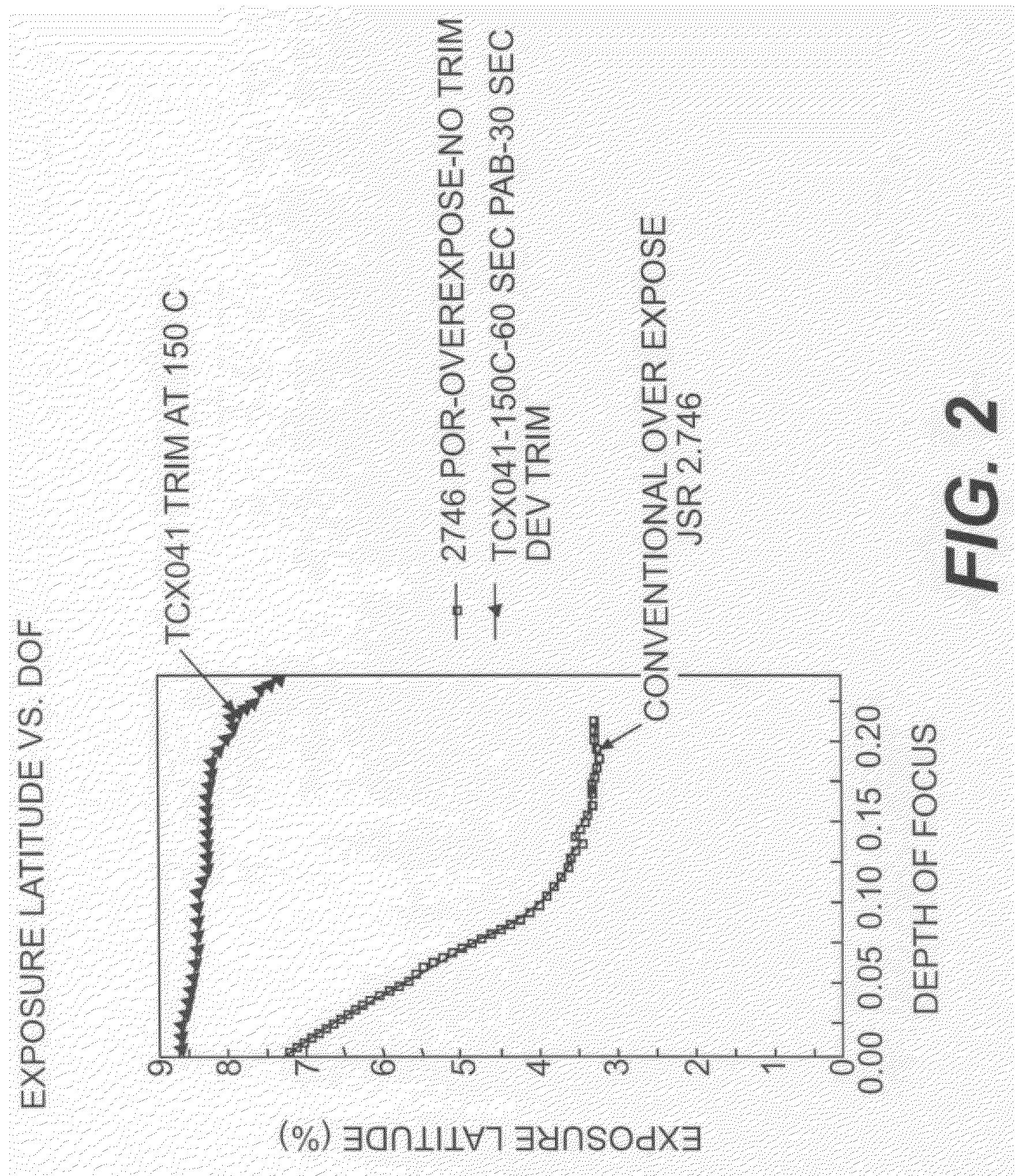
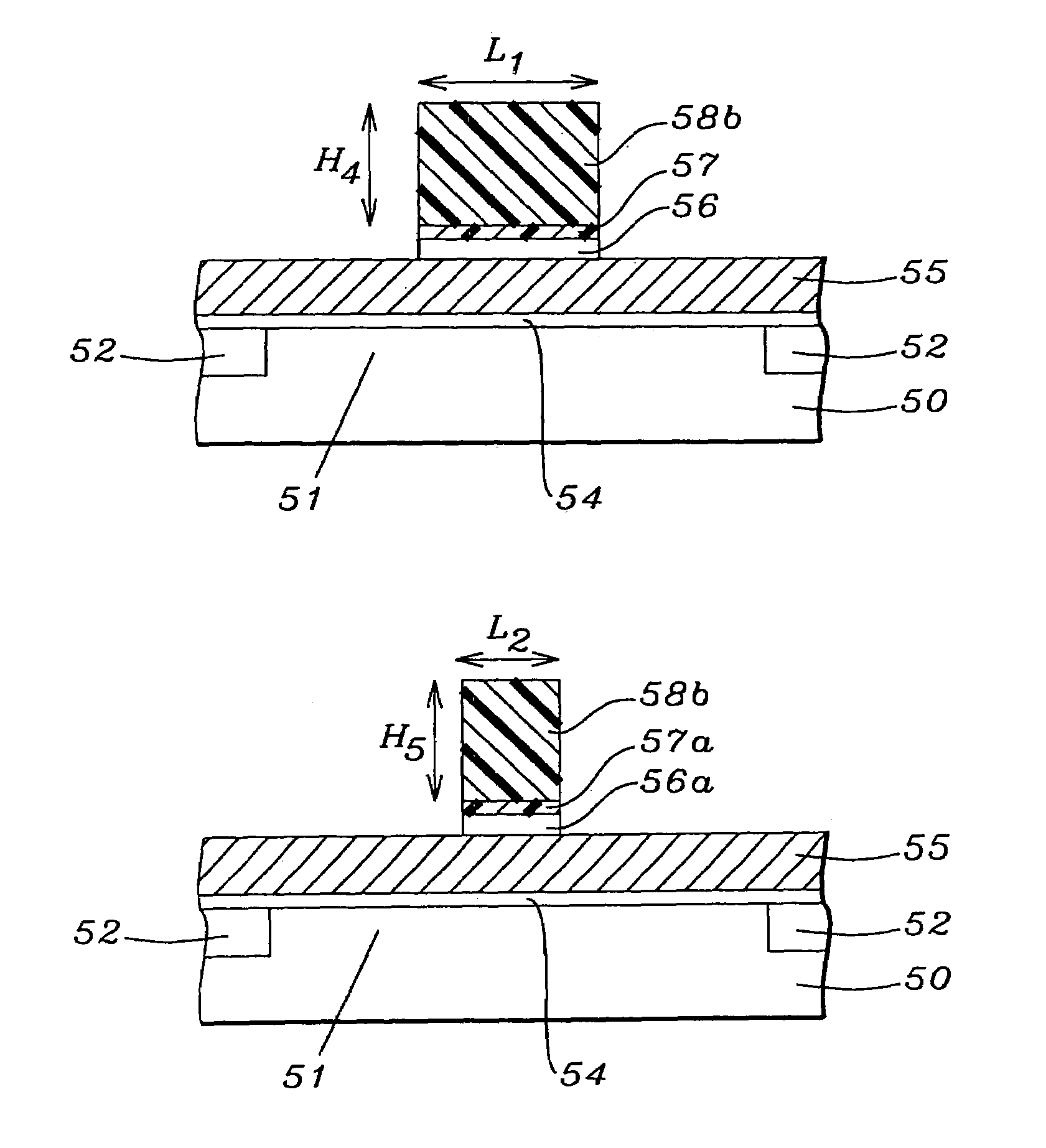
A process is described for transferring a photoresist pattern into a substrate. In one embodiment a stack comprised of a top photoresist layer, a middle ARC layer, and a bottom hardmask is formed over a gate electrode layer. A line in the photoresist pattern is anisotropically transferred through the ARC and hardmask. Then an isotropic etch to trim the linewidth by 0 to 50 nm per edge is performed simultaneously on the photoresist, ARC and hardmask. This method minimizes the amount of line end shortening to less than three times the dimension trimmed from one line edge. Since a majority of the photoresist layer is retained, the starting photoresist thickness can be reduced by 1000 Angstroms or more to increase process window. The pattern is then etched through the underlying layer to form a gate electrode. The method can also be used to form STI features in a substrate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
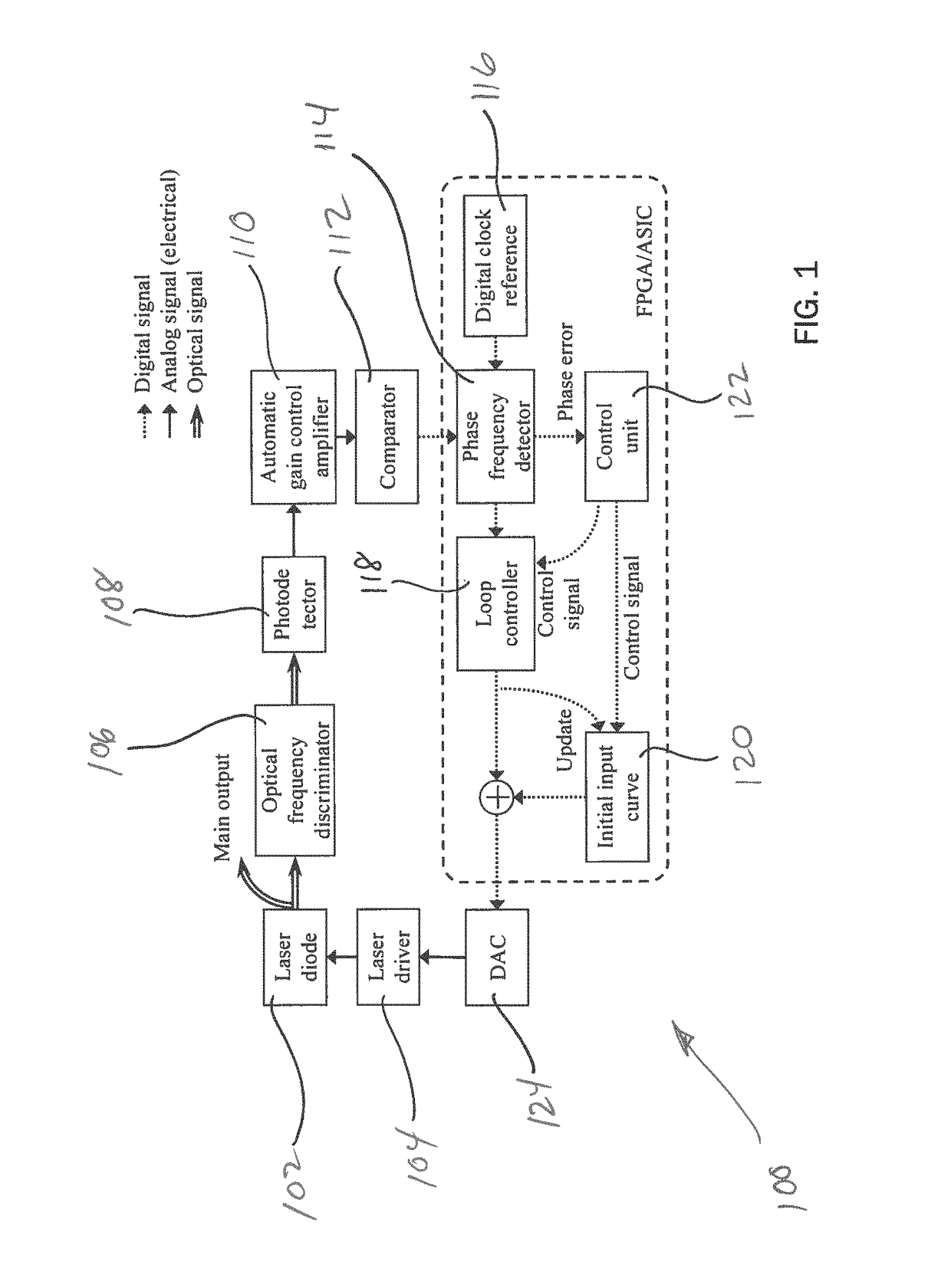
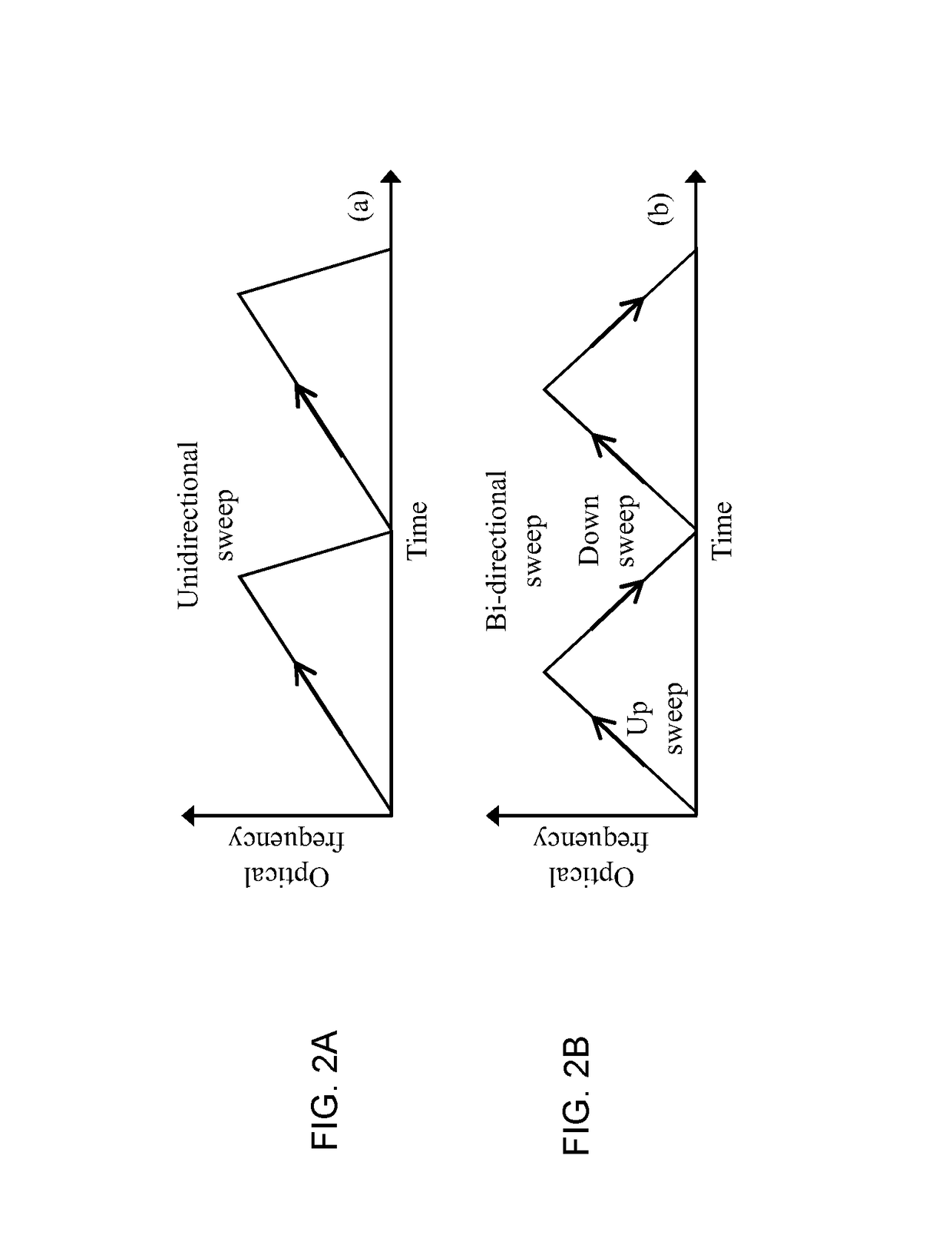
Method and apparatus for coherence enhancement of sweep velocity locked lasers via all-electronic upconversion
InactiveUS20190027897A1Linewidth also decreaseSmall footprintLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLine widthEngineering
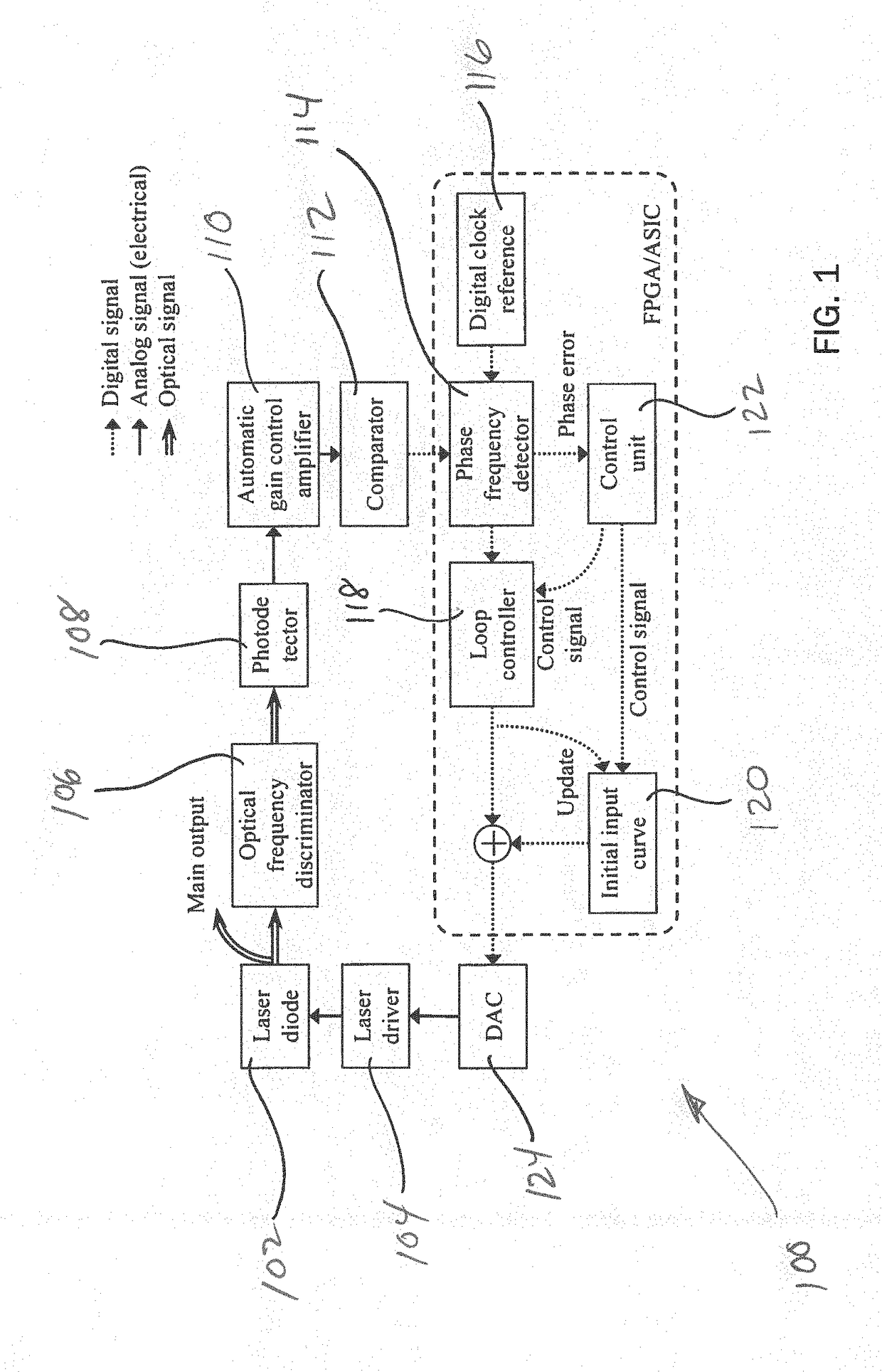
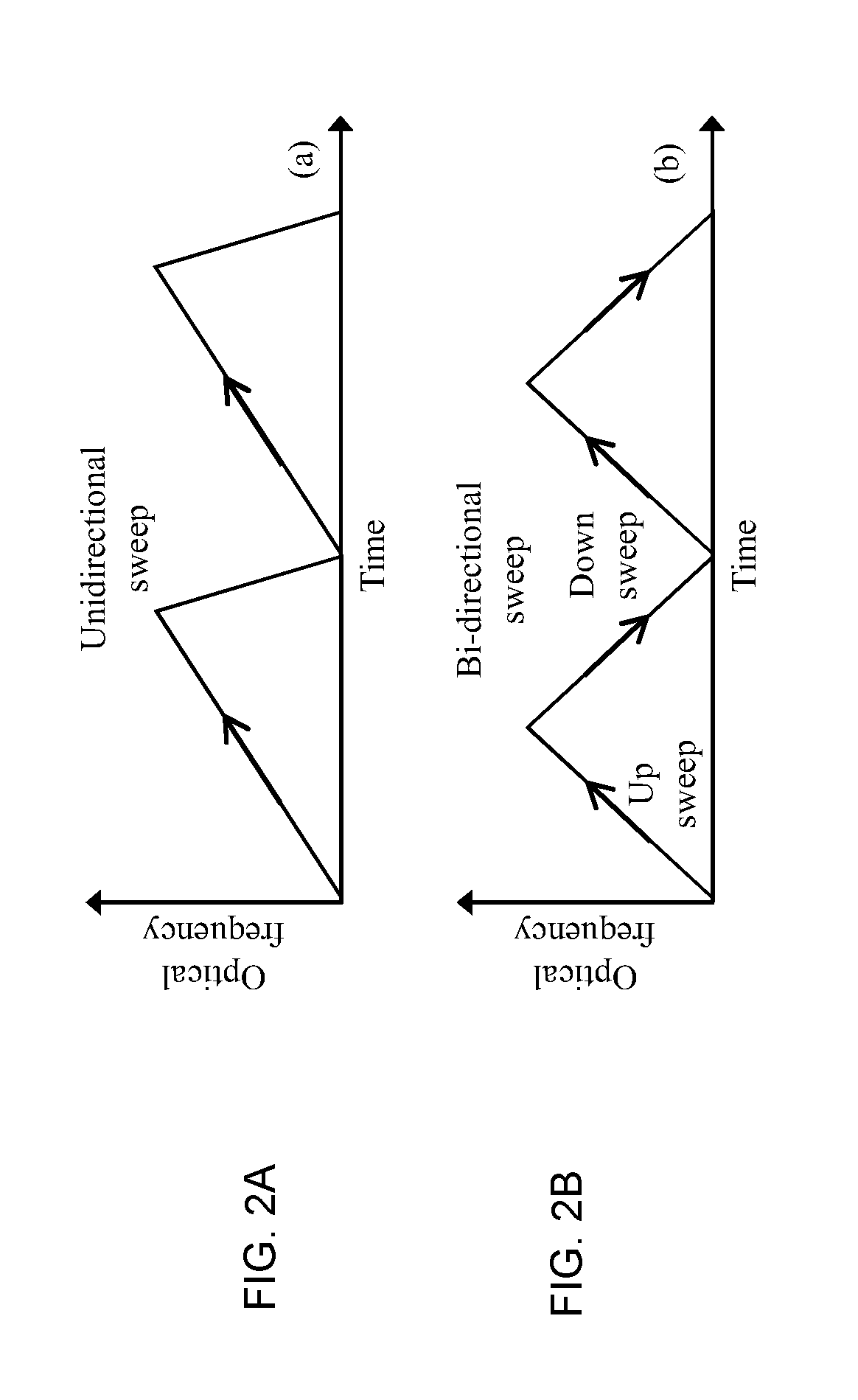
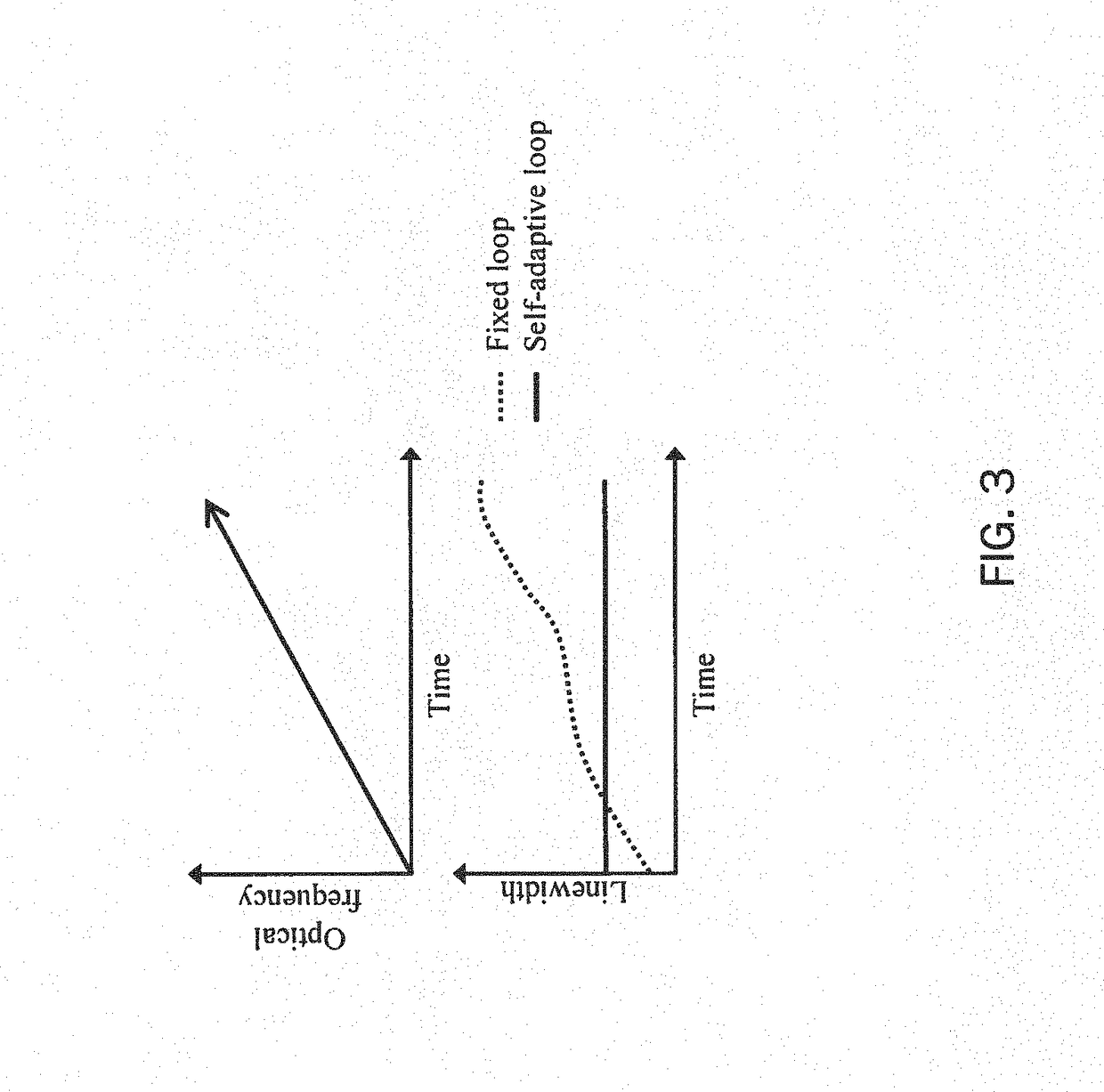
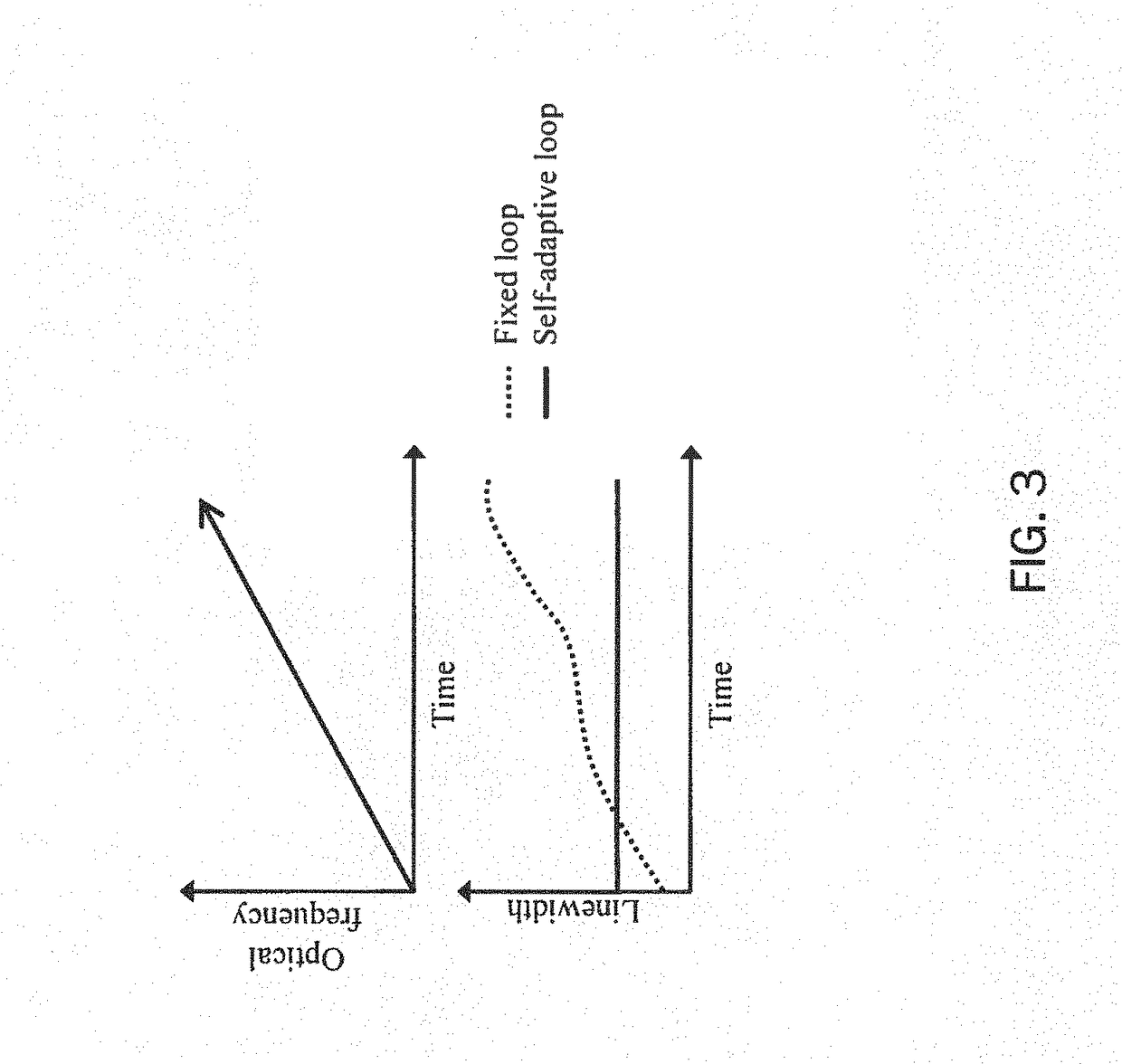
The present disclosure provides methods and apparatus to improve the dynamic coherent length of a sweep velocity-locked laser pulse generator (SV-LLPG) in an all-electronic fashion. A digital SV-LLPG is disclosed with two operation modes, i.e., unidirectional and bidirectional sweep modes; self-adaptive and time-dependent loop parameters (gain and location of poles / zeros); and, self-adaptive initial input curve. High frequency locking architectures, both single-side band (SSB) modulation method and direct phase measurement method, are provided to suppress the linewidth, or improve the coherent length, of the swept laser. A combination of high and low frequency locking, or a combination of multiple architectures disclosed in this invention, is utilized to achieve a higher level of linewidth reduction. The enhanced laser coherence extends the measurement range by at least one order of magnitude for applications including frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) light detection and ranging (LiDAR) and optical fiber distributed sensing applications.
Owner:UNIV OF RHODE ISLAND BOARD OF TRUSTEES
Highly efficient second harmonic generation (SHG) vertical external cavity surface emitting laser (VECSEL) system
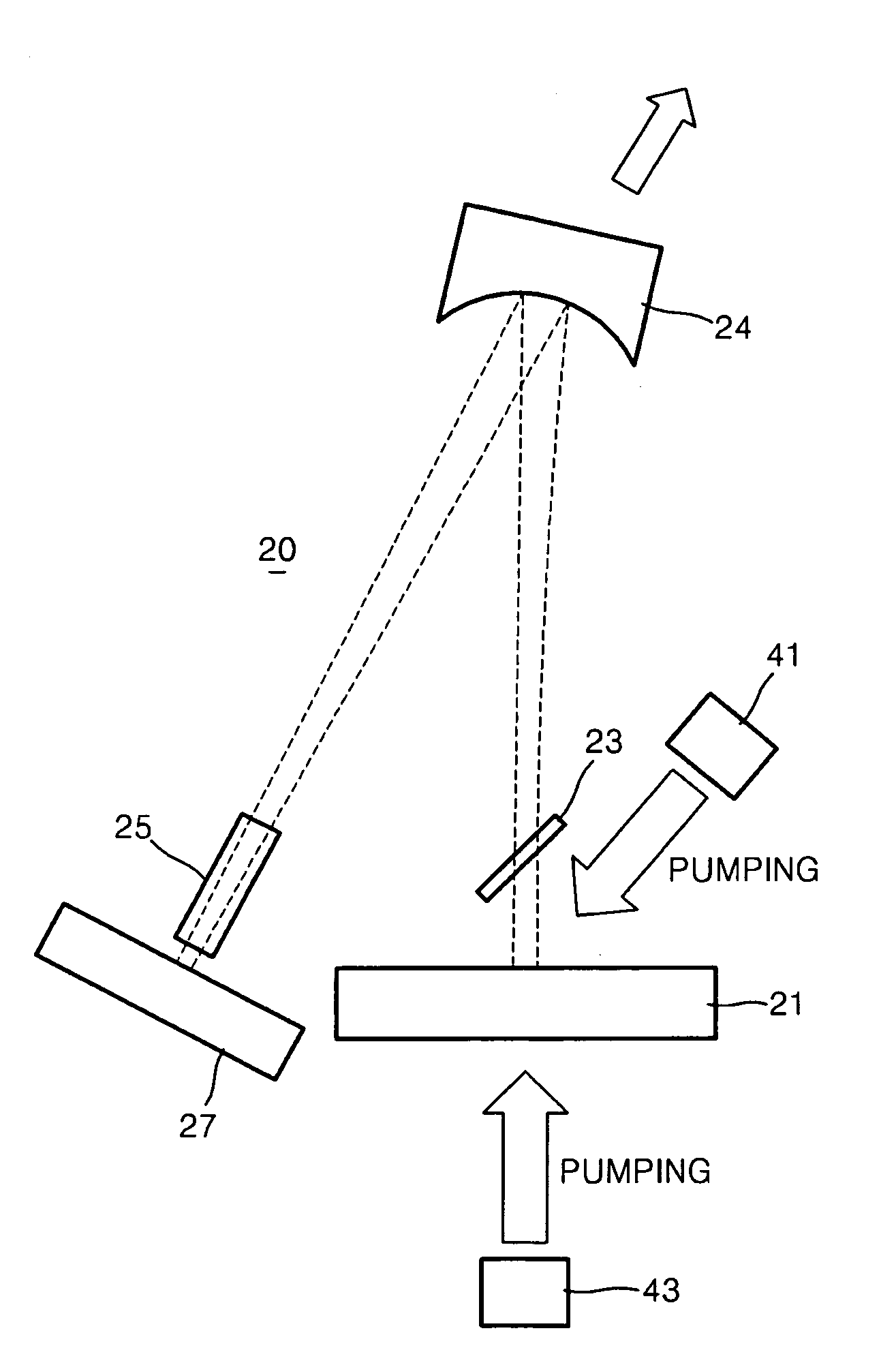
ActiveUS20070147444A1Improve efficiencyEasy alignmentProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionLine widthHarmonic
A Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VECSEL) system is provided. The VECSEL system includes a laser device including an active layer in which laser light is generated by pumping and a reflector reflecting the laser light generated in the active layer; an optical element that forms a cavity together with the reflector of the laser device and reduces a linewidth of laser light; and a SHG (Second Harmonic Generation) device that is disposed between the laser device and the optical element and doubles the frequency of laser light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Overcoating composition for photoresist and method for forming photoresist pattern using the same
InactiveUS20040142279A1Linewidth of the pattern may be reducedLinewidth also decreasePhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLithography processPhotoresist
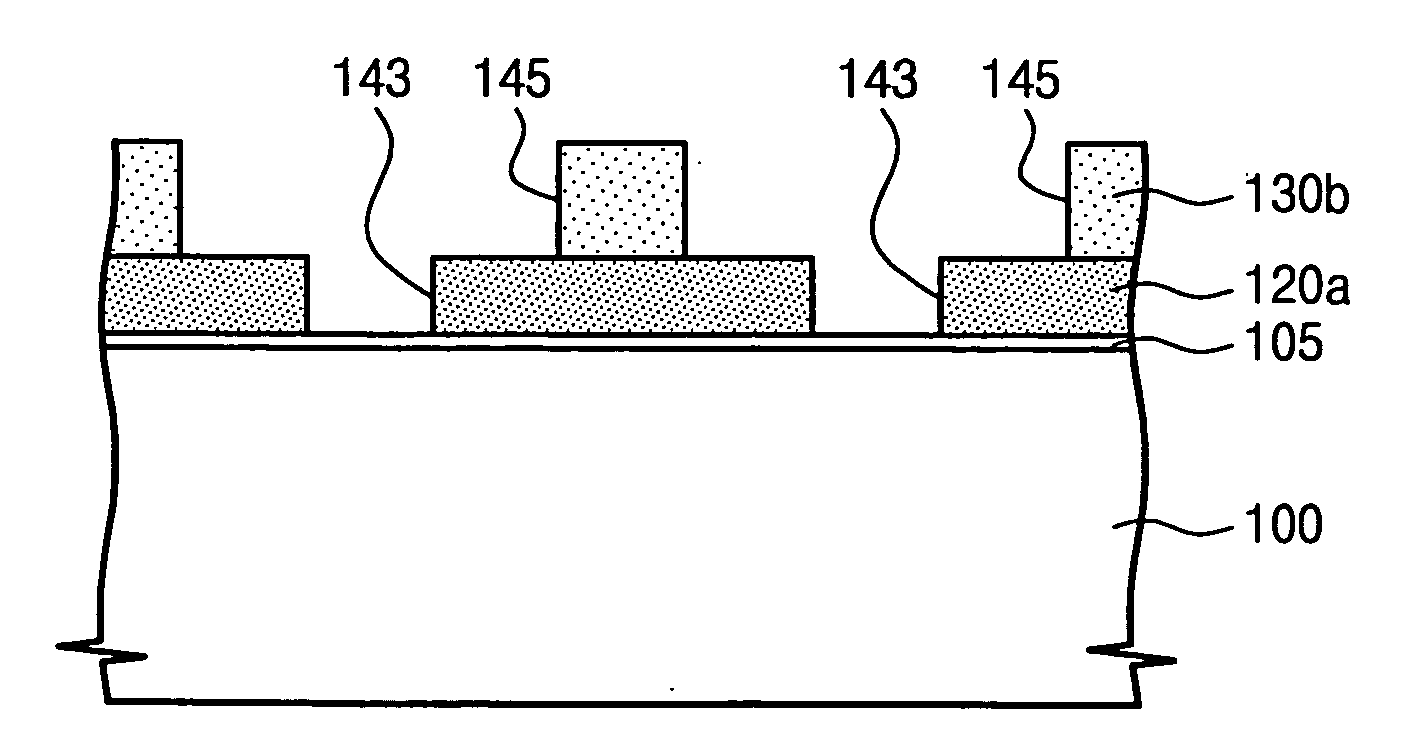
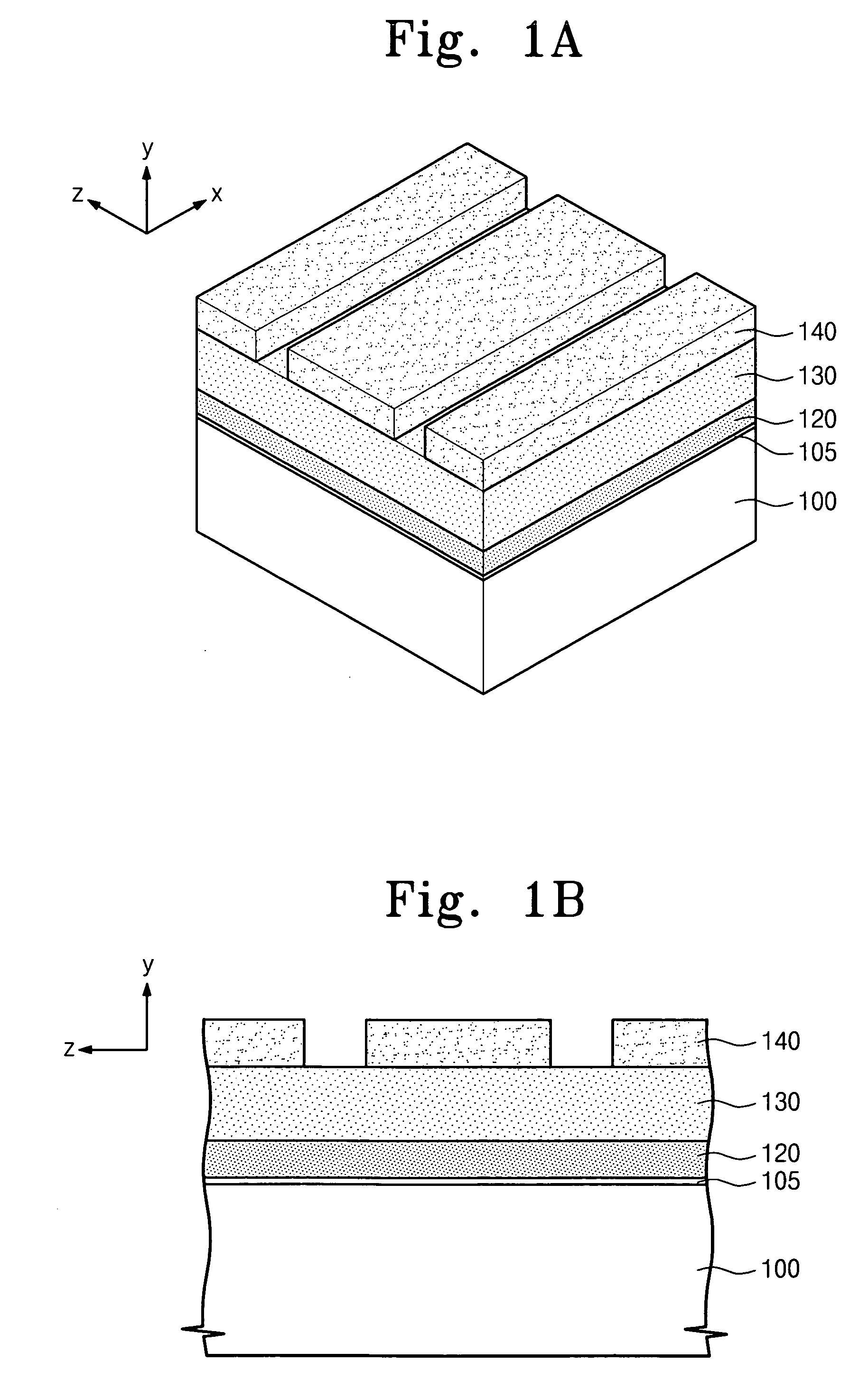
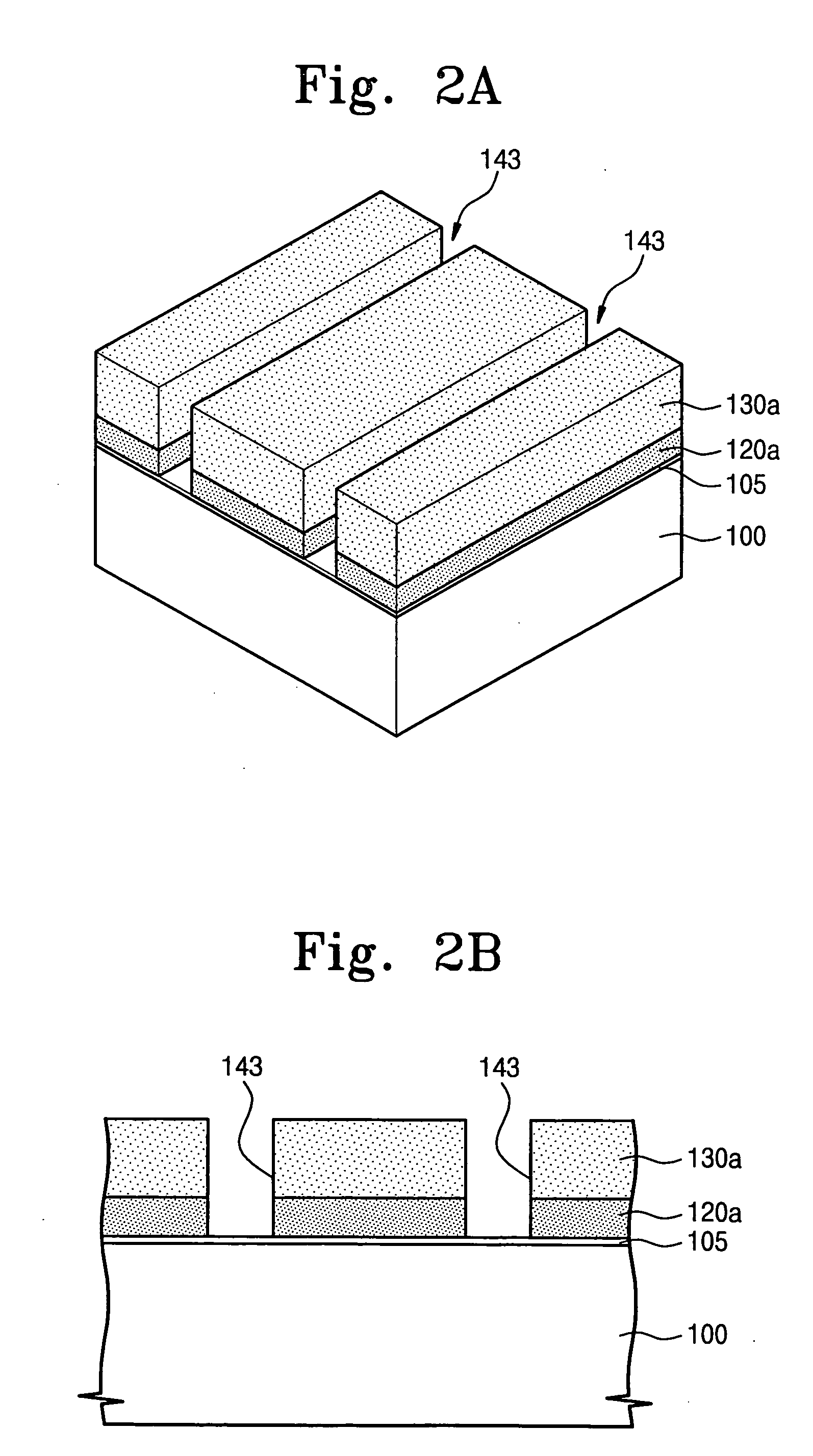
Overcoating compositions for photoresist and methods for reducing linewidth of the photoresist patterns are disclosed. More specifically, an overcoating composition containing acids is coated on a whole surface of a photoresist pattern formed by a common lithography process to diffuse the acids into the photoresist pattern. The photoresist in the portion where the acids are diffused is developed with an alkali solution to be removed. As a result, the linewidth of positive photoresist patterns can be reduced, and the linewidth of negative photoresist patterns can be prevented from slimming in a subsequent linewidth measurement process using SEM.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Compact LIDAR system
ActiveUS10168429B2Linewidth also decreaseImprove linearityLaser detailsOptical rangefindersWhispering galleryRadar systems
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Method of fabricating semiconductor device
InactiveUS20080085472A1Linewidth also decreaseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPhotosensitive material processingDevice materialEngineering
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Approach to improve line end shortening including simultaneous trimming of photosensitive layer and hardmask
InactiveUS7115450B2Linewidth also decreaseMinimizing the line end shorteningRadiation applicationsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingResistEngineering
A process is described for transferring a photoresist pattern into a substrate. In one embodiment a stack comprised of a top photoresist layer, a middle ARC layer, and a bottom hardmask is formed over a gate electrode layer. A line in the photoresist pattern is anisotropically transferred through the ARC and hardmask. Then an isotropic etch to trim the linewidth by 0 to 50 nm per edge is performed simultaneously on the photoresist, ARC and hardmask. This method minimizes the amount of line end shortening to less than three times the dimension trimmed from one line edge. Since a majority of the photoresist layer is retained, the starting photoresist thickness can be reduced by 1000 Angstroms or more to increase process window. The pattern is then etched through the underlying layer to form a gate electrode. The method can also be used to form STI features in a substrate.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Etching process and patterning process
ActiveUS7195716B2Accurate transferLinewidth also decreaseDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusPhotoresistPolymer
An etching process is described. A material layer having a bottom anti-reflection coating (BARC) and a patterned photoresist layer thereon is provided. An etching step is performed to the BARC using the patterned photoresist layer as a mask. A cleaning step is performed to remove the polymer formed on the surface of the patterned photoresist layer. Thereafter, another etching step is performed to the material layer using the patterned photoresist layer as a mask.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Etching process and patterning process
ActiveUS20060076313A1Accurate pattern transferAccurate transferDecorative surface effectsPhotomechanical apparatusPhotoresistPolymer
An etching process is described. A material layer having a bottom anti-reflection coating (BARC) and a patterned photoresist layer thereon is provided. An etching step is performed to the BARC using the patterned photoresist layer as a mask. A cleaning step is performed to remove the polymer formed on the surface of the patterned photoresist layer. Thereafter, another etching step is performed to the material layer using the patterned photoresist layer as a mask.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Wavelength tunable laser device and laser module
ActiveUS10193305B2Linewidth also decreaseOscillation stabilityLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionGratingResonator filter
A wavelength tunable laser device includes: a laser cavity formed of a grating and a reflecting mirror including a ring resonator filter; a gain portion; and a phase adjusting portion. The grating creates a first comb-shaped reflection spectrum. The ring resonator filter includes a ring-shaped waveguide and two arms and creates a second comb-shaped reflection spectrum having peaks of a narrower full width than peaks in the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum at a wavelength interval different from that of the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum. One of the peaks in the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum and one of the peaks in the second comb-shaped reflection spectrum are overlapped on a wavelength axis, and a spacing between cavity modes is narrower than the full width at half maximum of the peaks in the first comb-shaped reflection spectrum.
Owner:FURUKAWA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Apparatus for atomic clock, its operating method and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS20170003658A1Improve uniformityLinewidth also decreaseApparatus using atomic clocksPulse automatic controlSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
An apparatus for an atomic clock includes first and second distinctive substrates, each having at least a planar surface substantially parallel therebetween. The apparatus also includes a medium having particles capable of undergoing energetic transition between at least two energy levels, said medium being located in the space defined between the planar surfaces. It further includes a magnetic device arranged to the first substrate and generating at least in the volume of the medium a predetermined static magnetic field B the direction of which is substantially parallel or perpendicular to the planar surfaces and an excitation device arranged to the second substrate and generating an excitation magnetic field H at, at least an excitation frequency, the direction of said excitation magnetic field H in the volume of the medium being substantially orthogonal to said direction of the static magnetic field B.
Owner:MEMSCAP
High resolution surface plasmon resonance sensor and sensor system thereof
InactiveUS8786859B2Linewidth also decreaseImprove responseScattering properties measurementsColor/spectral properties measurementsLight beamSurface plasmon resonance imaging
Provided is a surface plasmon resonance sensor including: a part of delivering light by which a signal beam is incident to generate an evanescent field; and a part of exciting surface plasmon for exciting surface plasmons by the generated evanescent field and giving rise to a surface plasmon resonance, wherein a dielectric waveguide layer is inserted between metal layers of the part of exciting surface plasmon, and surface plasmon resonance properties are changed by an object to be analyzed.
Owner:KOREA INST OF SCI & TECH
Ultra-low noise, highly stable single-mode operation, high power, bragg grating based semiconductor laser
ActiveUS20190372307A1Lower performance requirementsLarge slopeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLow noiseGrating
A low noise, single mode laser includes a semiconductor gain element generating light and having a highly reflective first end forming a first end of a laser cavity. The gain element may be monolithically or discretely integrated with, or distinct from, and coupled to a waveguide comprised of a low loss material with a refractive index ‘n’ greater than 3. The waveguide includes a Bragg grating forming the second end of the laser cavity. A cavity phase control section may be provided between the gain element and the Bragg grating. Two photodetector monitors provide a feedback signal for locking the light from the gain element to a specific wavelength on the Bragg grating reflection spectrum by varying at least one of the cavity phase control section and the gain element bias current. The Bragg grating may have a physical length larger than 10 mm and that occupies at least 50% of the optical length of the external cavity.
Owner:MORTON HYBRID LASERS LLC
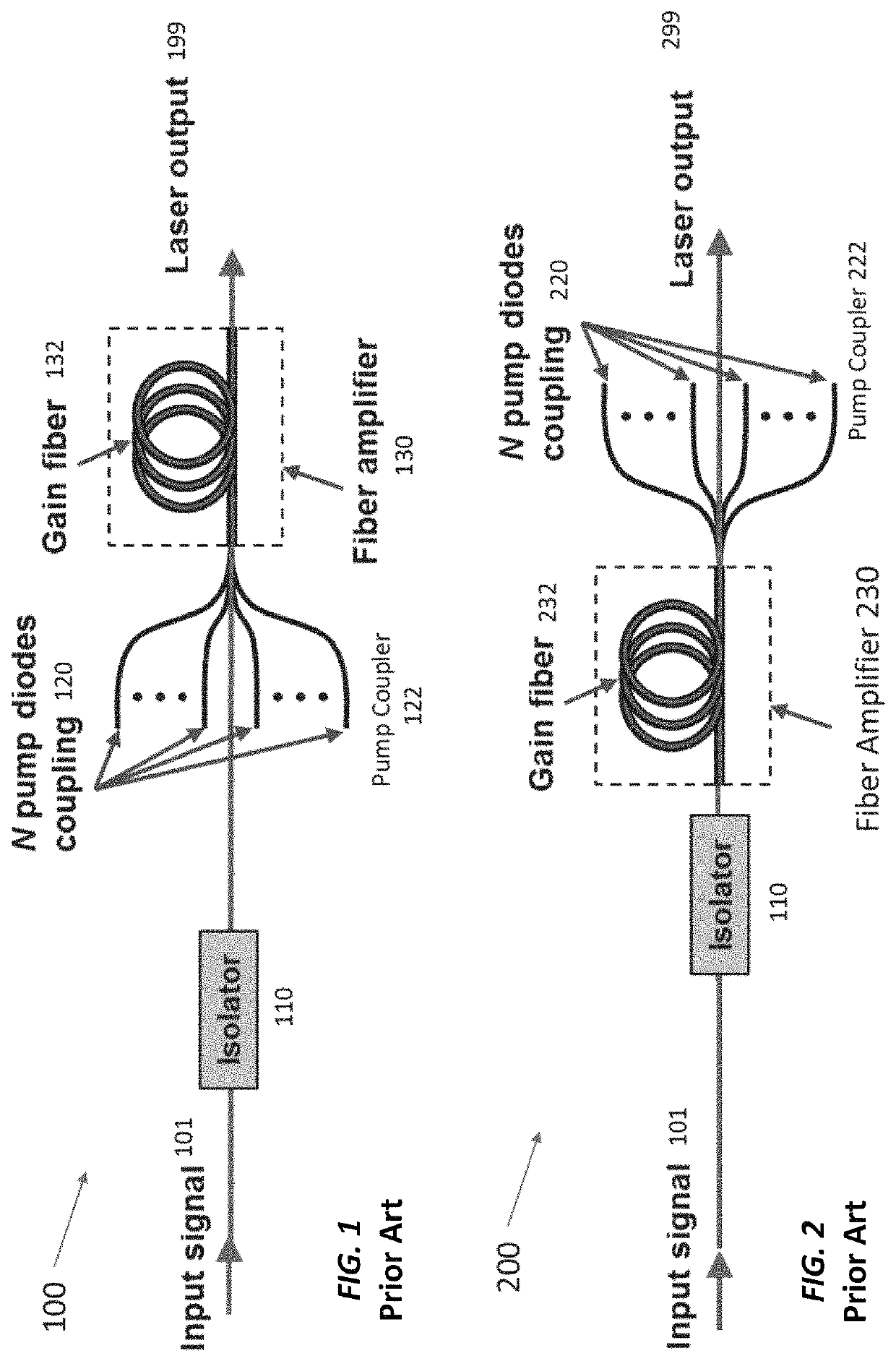
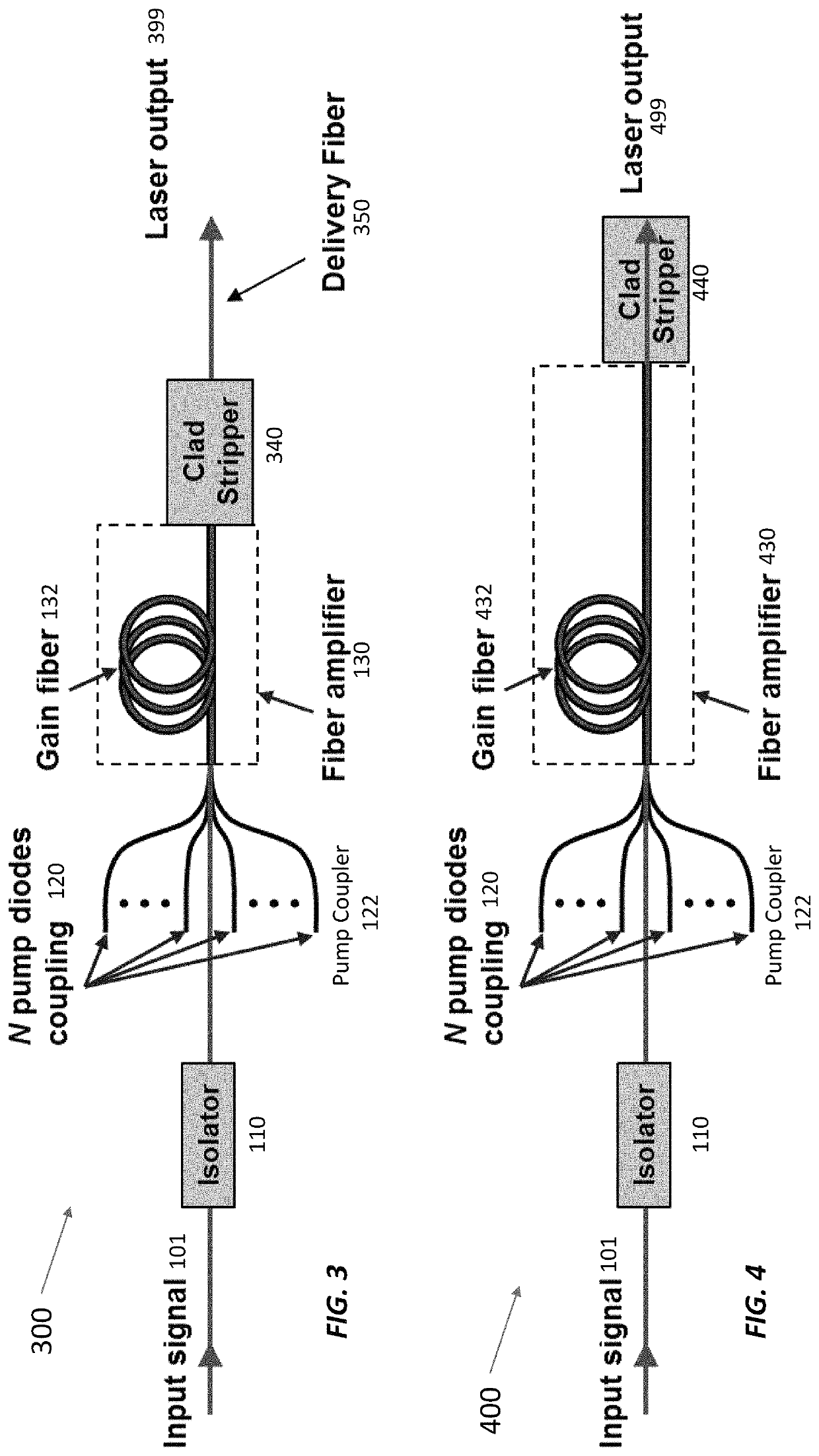
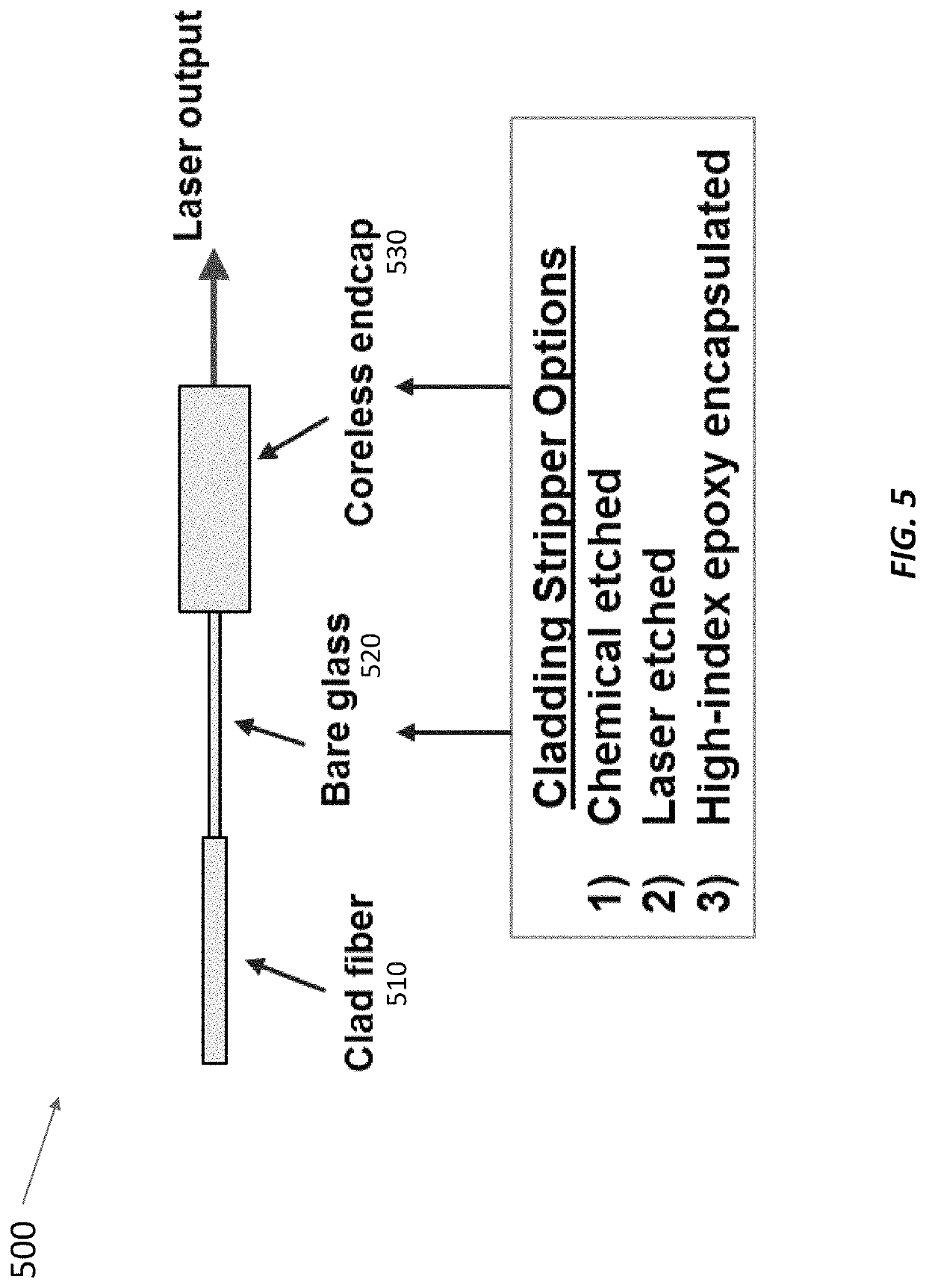
Single-frequency fiber amplifier with distal cladding stripper
ActiveUS11108209B2Linewidth also decreaseReduce total powerLaser using scattering effectsActive medium shape and constructionLine widthLight beam
Stimulated Brillouin scattering (SBS) limits the maximum power in fiber lasers with narrow linewidths. SBS occurs when the power exceeds a threshold proportional to the beam area divided by the effective fiber length. The fiber lasers disclosed here operate with higher SBS power thresholds (and hence higher maximum powers at kilohertz-class linewidths) than other fiber lasers thanks to several techniques. These techniques include using high-absorption gain fibers, operating the laser with low pump absorption (e.g., ≤80%), reducing the length of un-pumped gain fiber at the fiber output, foregoing a delivery fiber at the output, foregoing a cladding light stripper at the output, using free-space dichroic mirrors to separate signal light from unabsorbed pump light, and using cascaded gain fibers with non-overlapping Stokes shifts. The upstream gain fiber has high absorption and a larger diameter for high gain, and subsequent gain fiber has a smaller diameter to improve beam quality.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Laser source with reduced linewidth
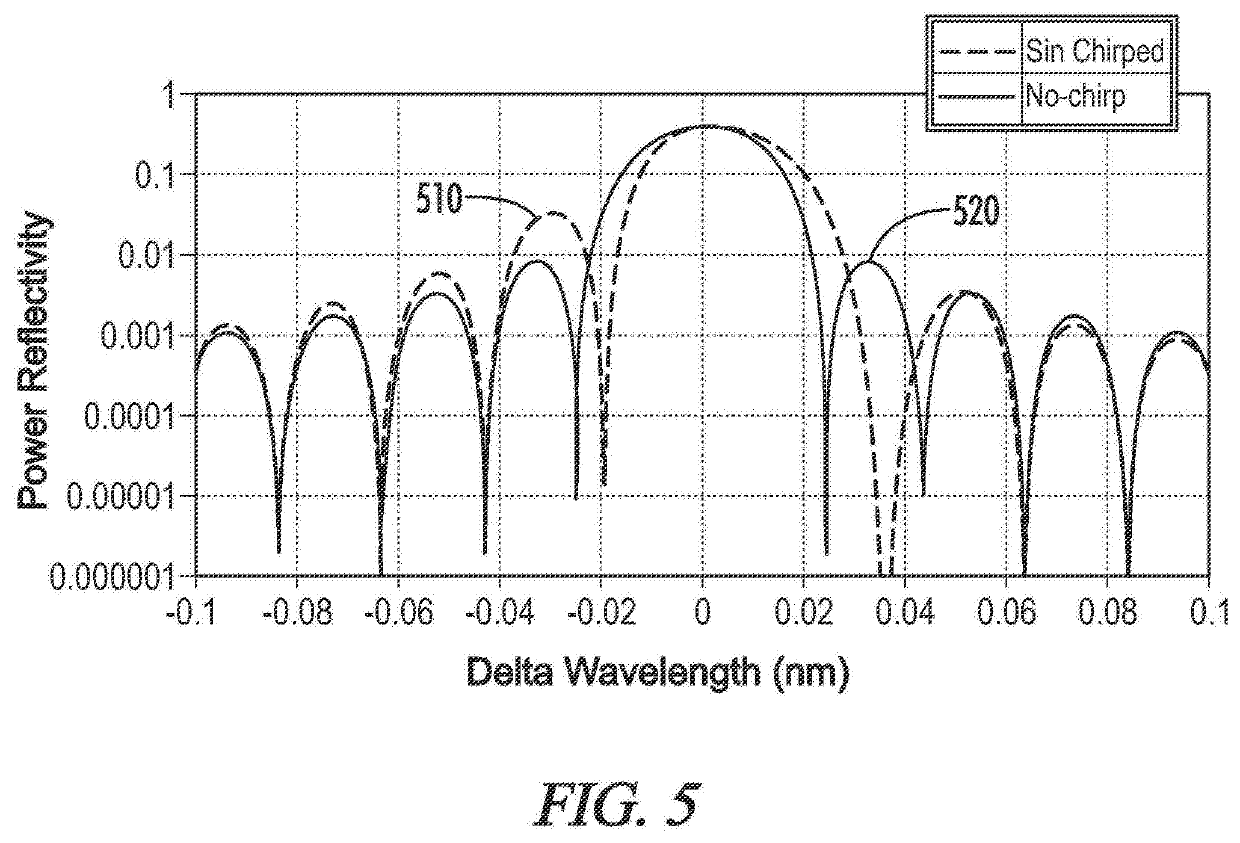
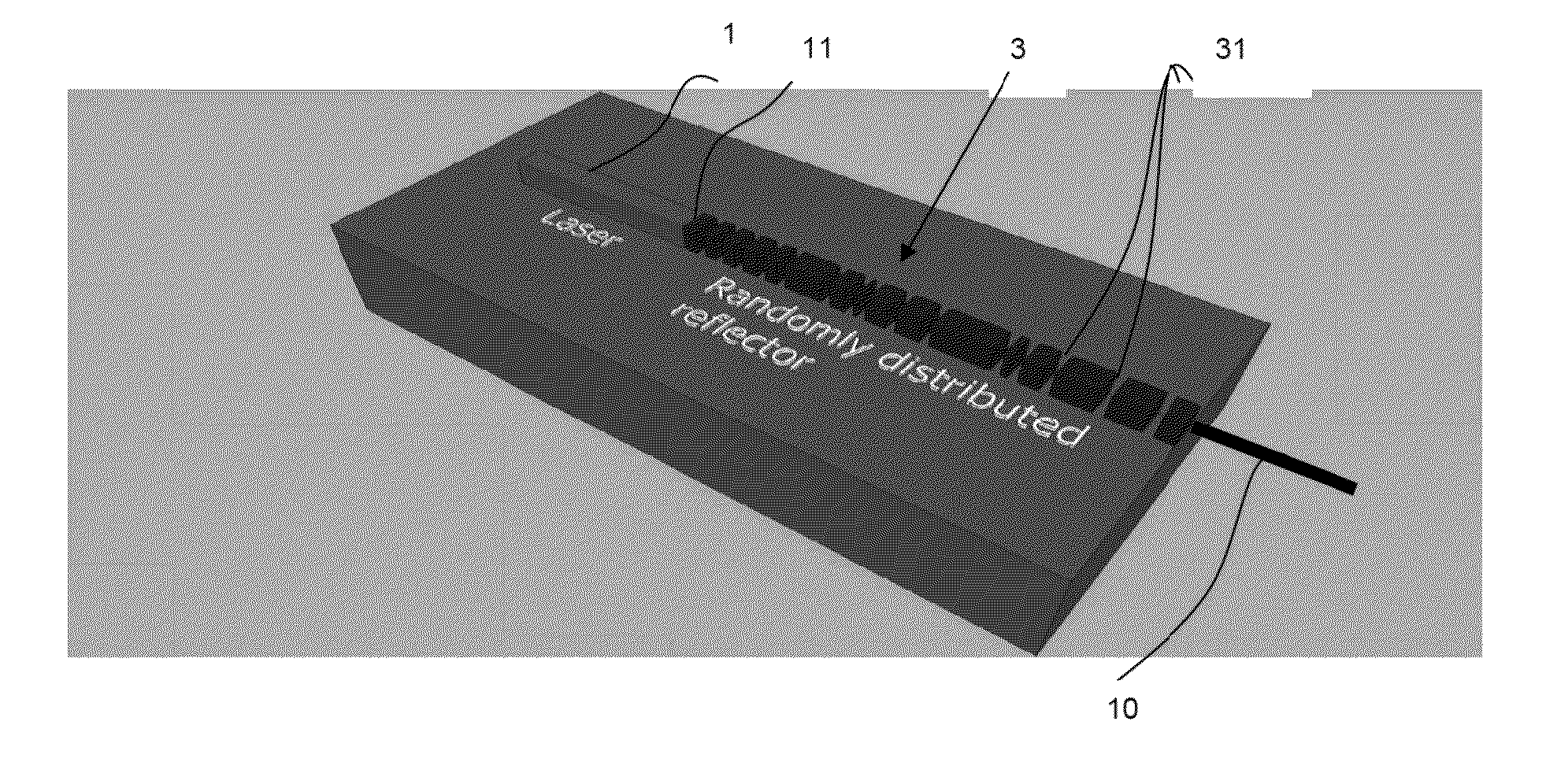
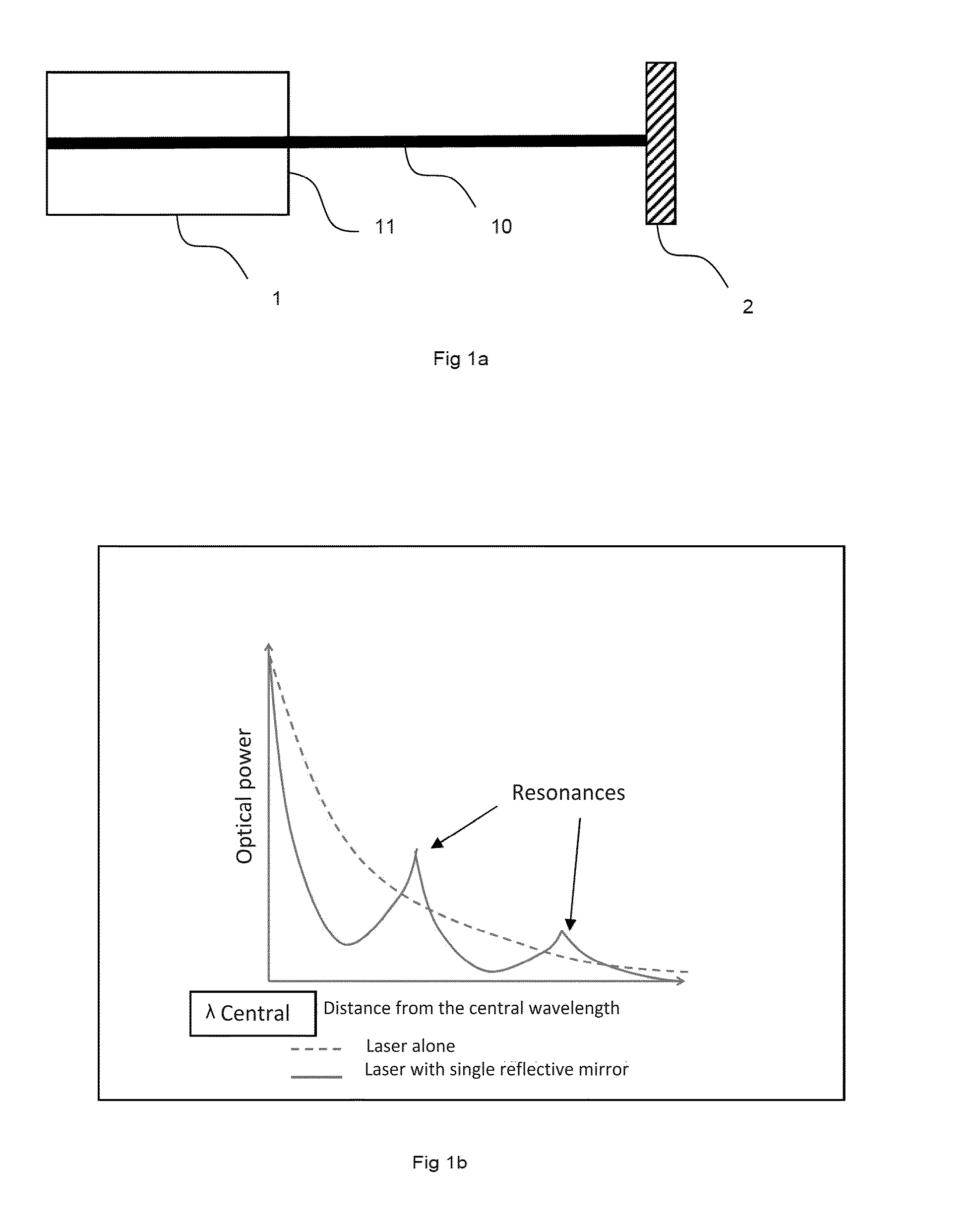
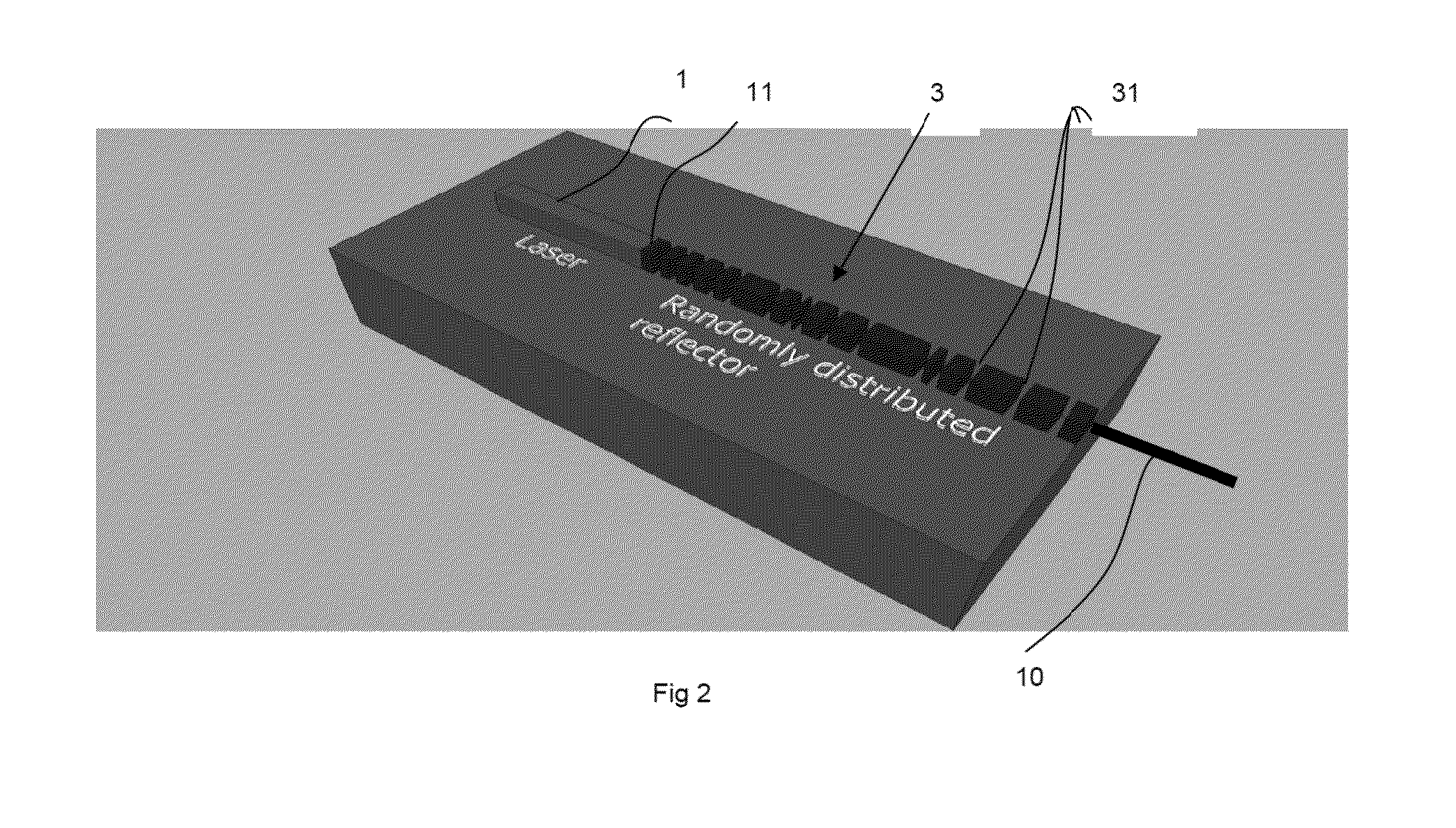
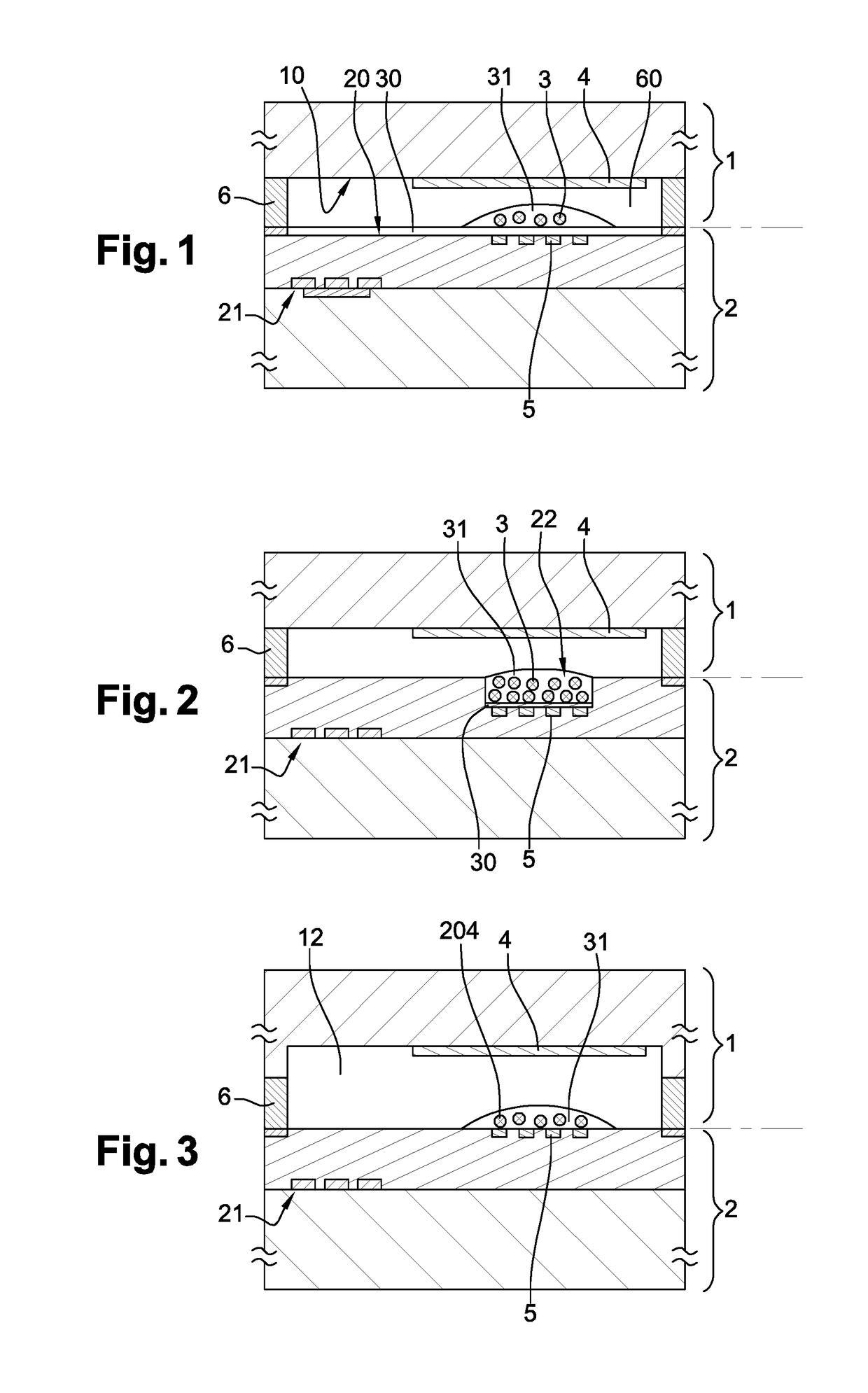
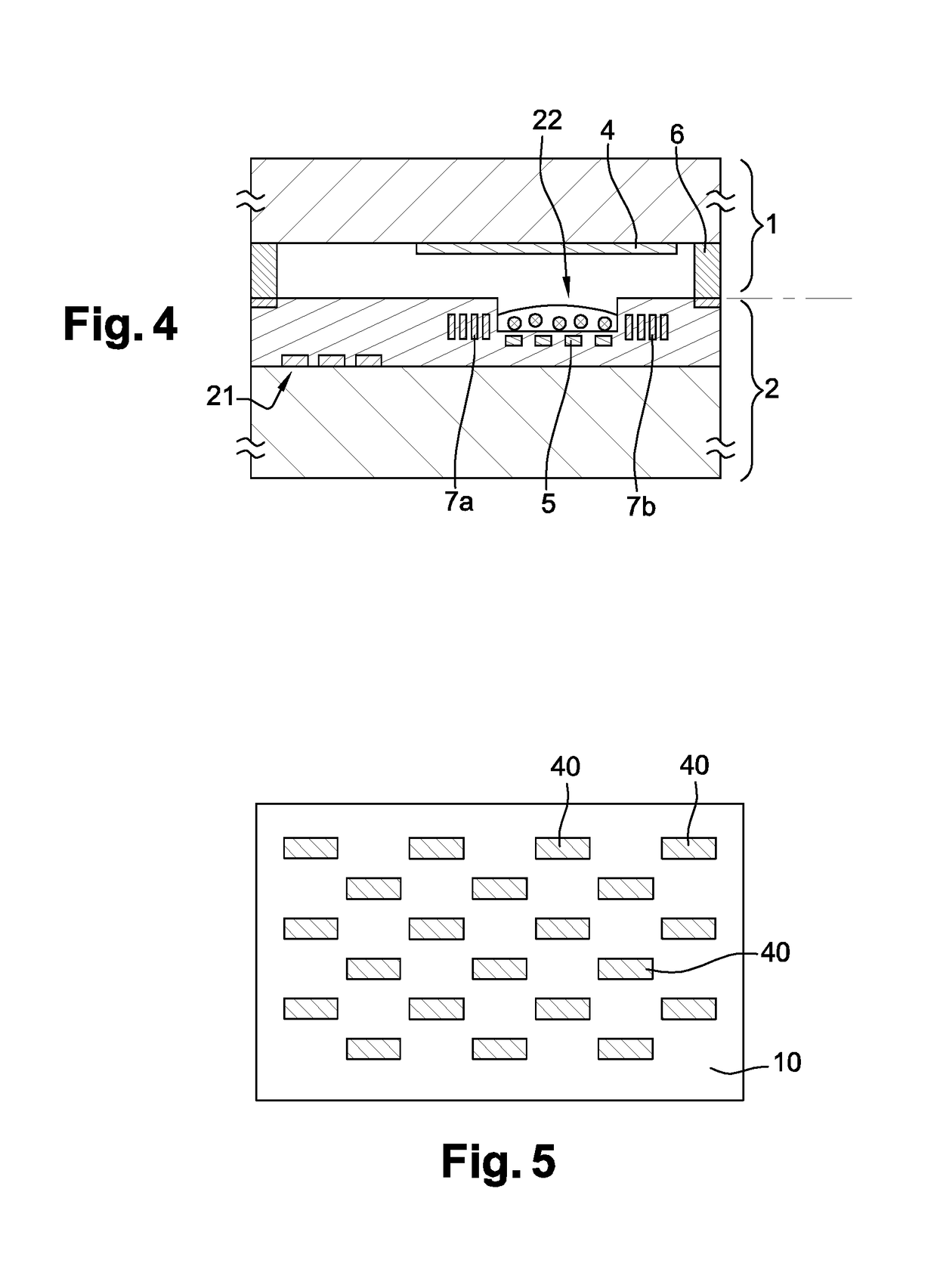
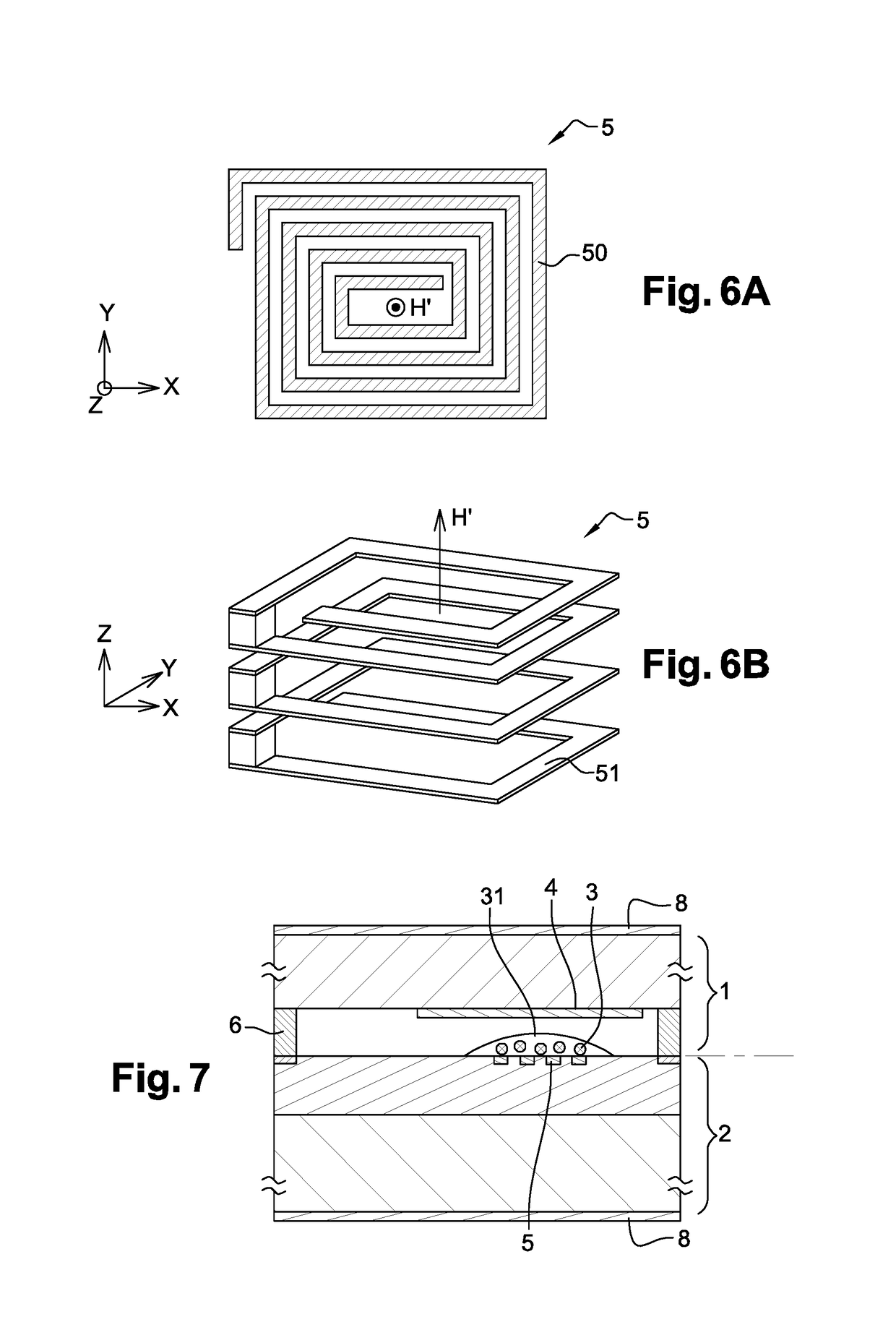
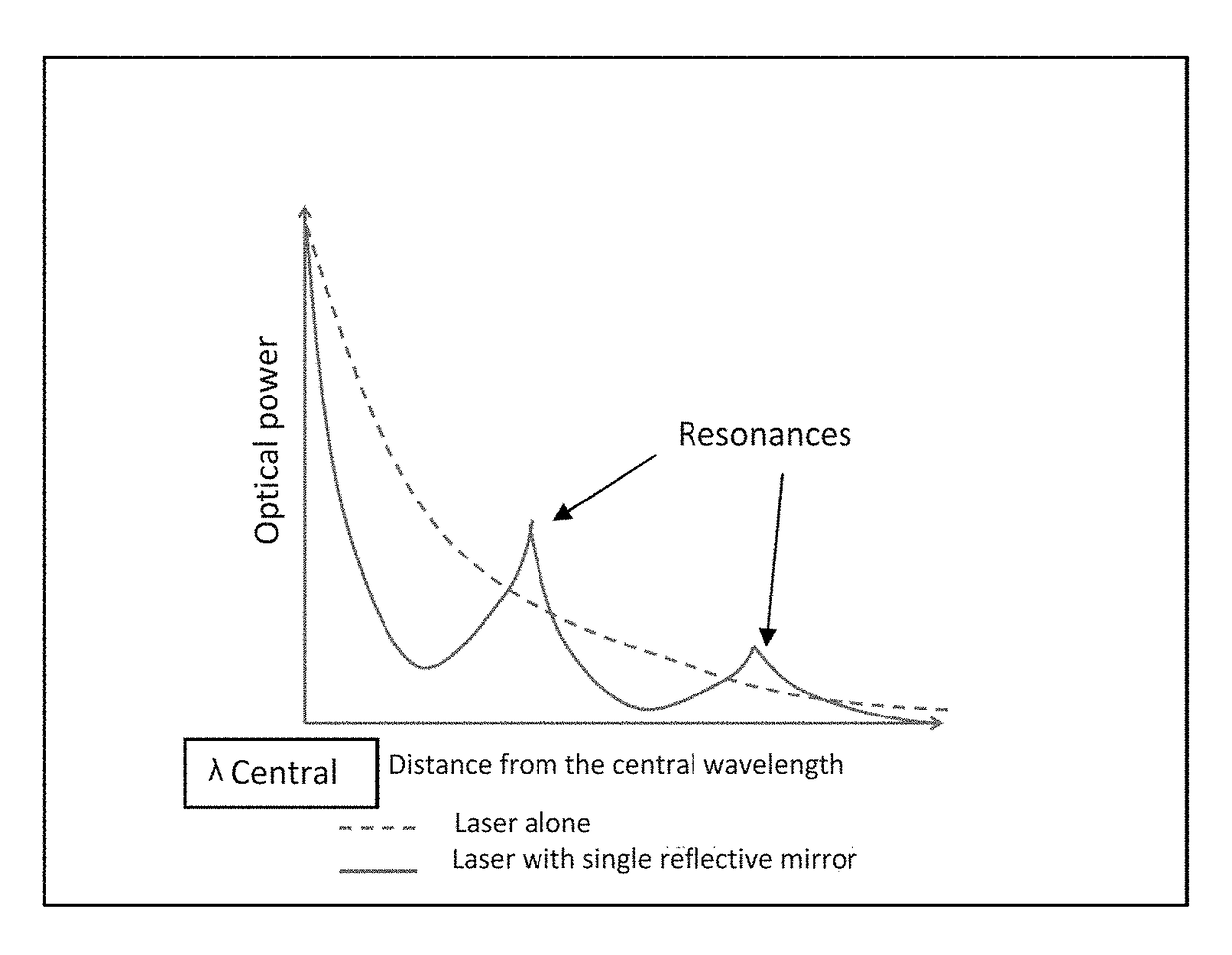
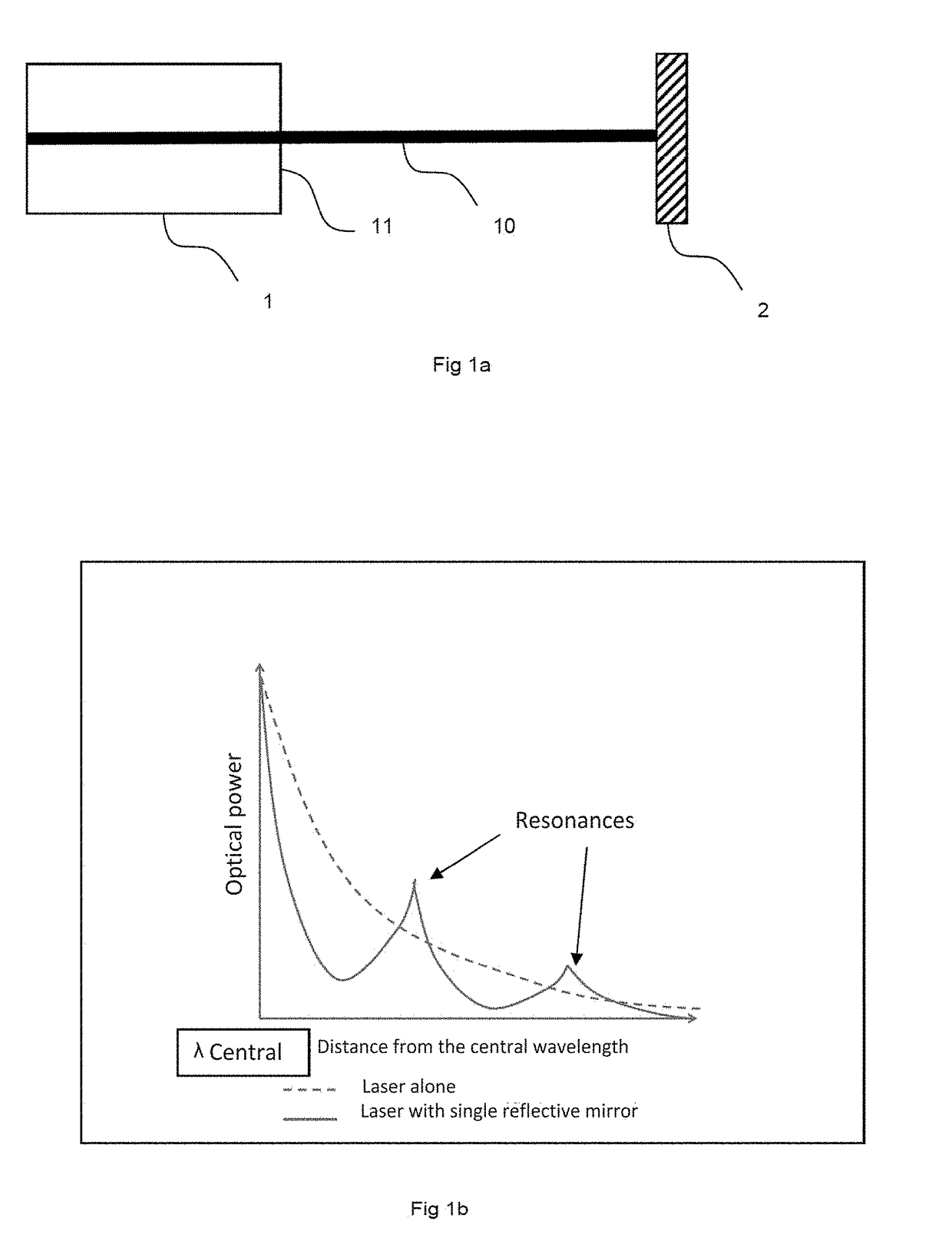
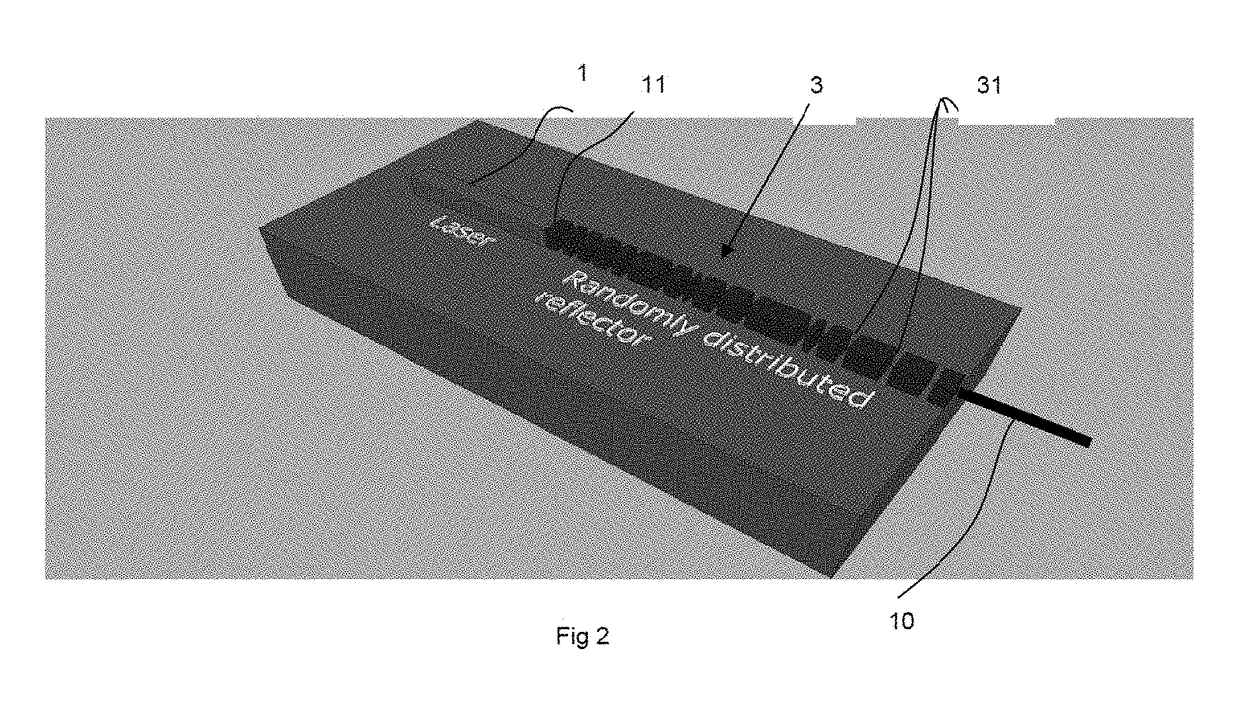
ActiveUS20150171593A1Increase reflectionLinewidth also decreaseLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLine widthRefractive index
In the field of narrow linewidth laser sources and a laser device that comprises a laser source and a waveguide of determined refractive index with which it is coupled, a waveguide is single-mode and includes at least four reflectors in the form of trenches etched into the waveguide and irregularly distributed along the waveguide, the distance separating two neighbouring reflectors being above 1 pm, and the waveguide and the laser source have respective lengths such that the length of waveguide over which the reflectors are located is greater than the length of the laser source itself.
Owner:THALES SA
Ultra-low noise, highly stable single-mode operation, high power, Bragg grating based semiconductor laser
ActiveUS11005233B2Long photon lifetimeEasy to storeLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionLow noiseGrating
A low noise, single mode laser includes a semiconductor gain element generating light and having a highly reflective first end forming a first end of a laser cavity. The gain element may be monolithically or discretely integrated with, or distinct from, and coupled to a waveguide comprised of a low loss material with a refractive index ‘n’ greater than 3. The waveguide includes a Bragg grating forming the second end of the laser cavity. A cavity phase control section may be provided between the gain element and the Bragg grating. Two photodetector monitors provide a feedback signal for locking the light from the gain element to a specific wavelength on the Bragg grating reflection spectrum by varying at least one of the cavity phase control section and the gain element bias current. The Bragg grating may have a physical length larger than 10 mm and that occupies at least 50% of the optical length of the external cavity.
Owner:MORTON HYBRID LASERS LLC
Highly efficient second harmonic generation (SHG) vertical external cavity surface emitting laser (VECSEL) system
ActiveUS7526005B2Improve efficiencyEasy alignmentProjectorsOptical resonator shape and constructionLine widthHarmonic
A Vertical External Cavity Surface Emitting Laser (VECSEL) system is provided. The VECSEL system includes a laser device including an active layer in which laser light is generated by pumping and a reflector reflecting the laser light generated in the active layer; an optical element that forms a cavity together with the reflector of the laser device and reduces a line width of laser light; and a SHG (Second Harmonic Generation) device that is disposed between the laser device and the optical element and doubles the frequency of laser light.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Apparatus for atomic clock, its operating method and its manufacturing method
InactiveUS10216150B2Improve uniformityLinewidth also decreasePulse automatic controlApparatus using atomic clocksSoftware engineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:MEMSCAP
Laser source with reduced linewidth
ActiveUS9711940B2Linewidth also decreaseReduce widthLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsLine widthRefractive index
In the field of narrow linewidth laser sources and a laser device that comprises a laser source and a waveguide of determined refractive index with which it is coupled, a waveguide is single-mode and includes at least four reflectors in the form of trenches etched into the waveguide and irregularly distributed along the waveguide, the distance separating two neighbouring reflectors being above 1 μm, and the waveguide and the laser source have respective lengths such that the length of waveguide over which the reflectors are located is greater than the length of the laser source itself.
Owner:THALES SA
Method and apparatus for coherence enhancement of sweep velocity locked lasers via all-electronic upconversion
InactiveUS10224694B2Linewidth also decreaseSmall footprintLaser detailsSemiconductor lasersLine widthEngineering
The present disclosure provides methods and apparatus to improve the dynamic coherent length of a sweep velocity-locked laser pulse generator (SV-LLPG) in an all-electronic fashion. A digital SV-LLPG is disclosed with two operation modes, i.e., unidirectional and bidirectional sweep modes; self-adaptive and time-dependent loop parameters (gain and location of poles / zeros); and, self-adaptive initial input curve. High frequency locking architectures, both single-side band (SSB) modulation method and direct phase measurement method, are provided to suppress the linewidth, or improve the coherent length, of the swept laser. A combination of high and low frequency locking, or a combination of multiple architectures disclosed in this invention, is utilized to achieve a higher level of linewidth reduction. The enhanced laser coherence extends the measurement range by at least one order of magnitude for applications including frequency-modulated continuous wave (FMCW) light detection and ranging (LiDAR) and optical fiber distributed sensing applications.
Owner:UNIV OF RHODE ISLAND BOARD OF TRUSTEES
Diode-pumped multipass cavity raman gas sensor and method of use
ActiveUS20220228911A1Compact and economicalLinewidth also decreaseRadiation pyrometryRaman/scattering spectroscopyGratingRaman scattering spectra
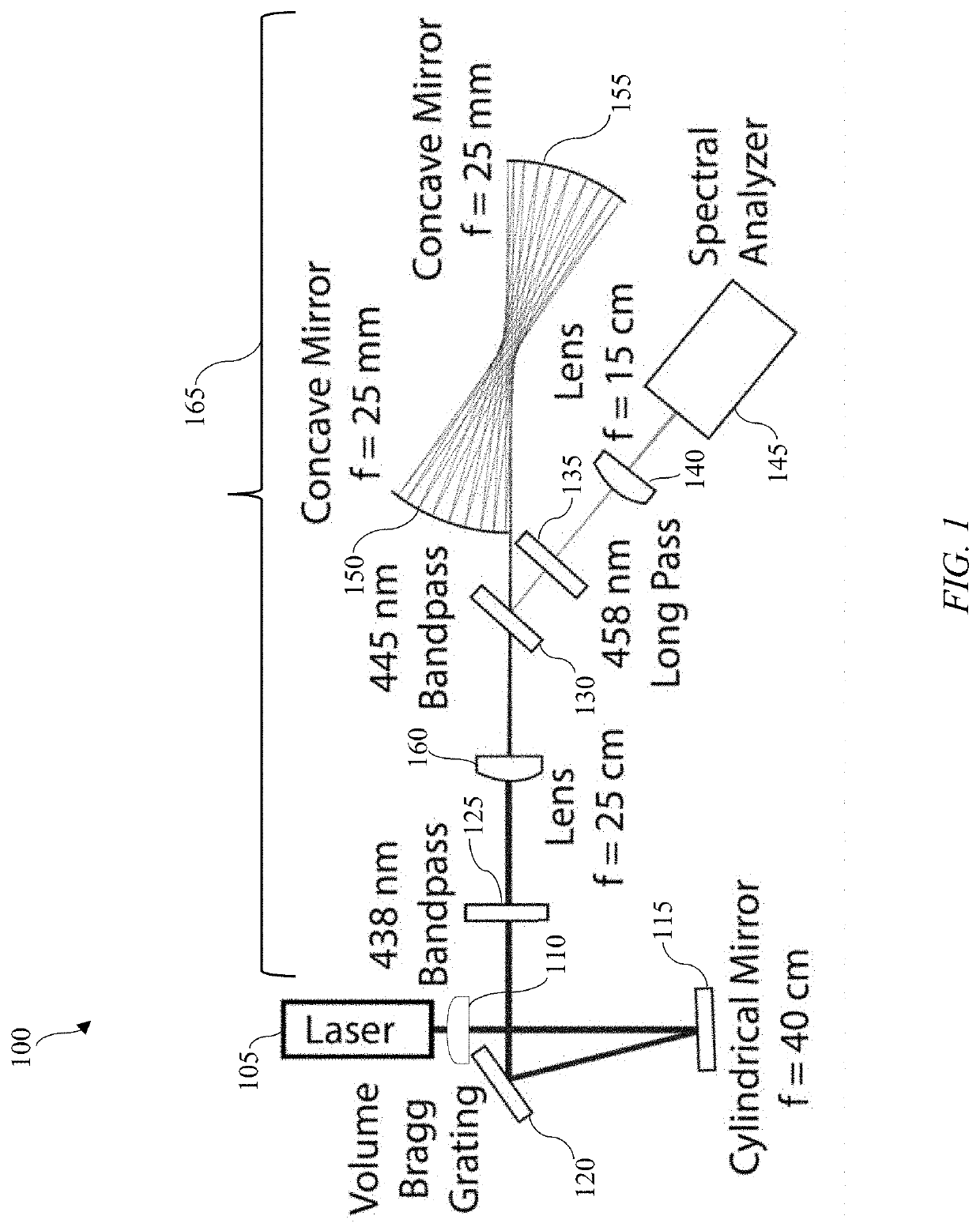
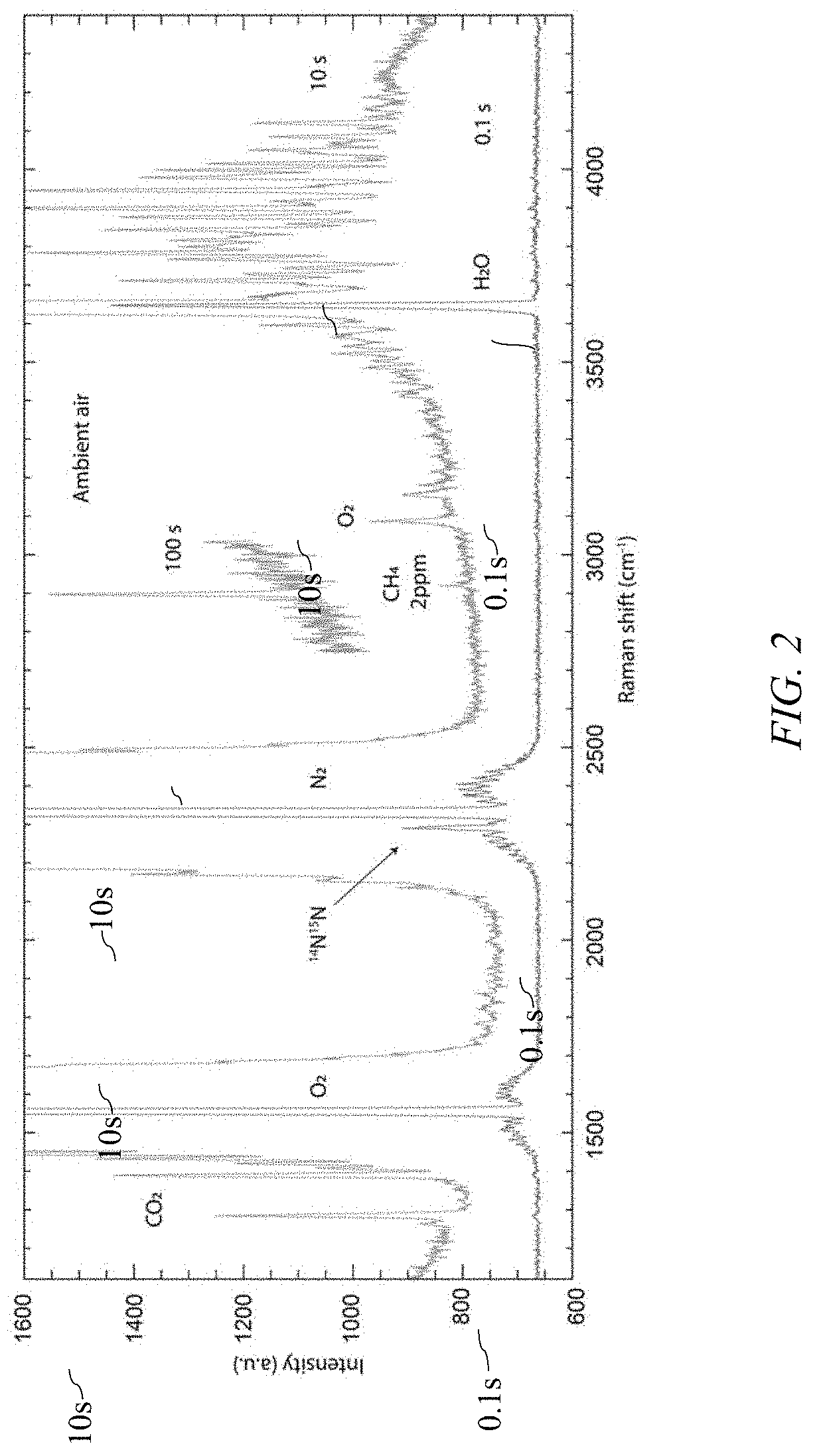
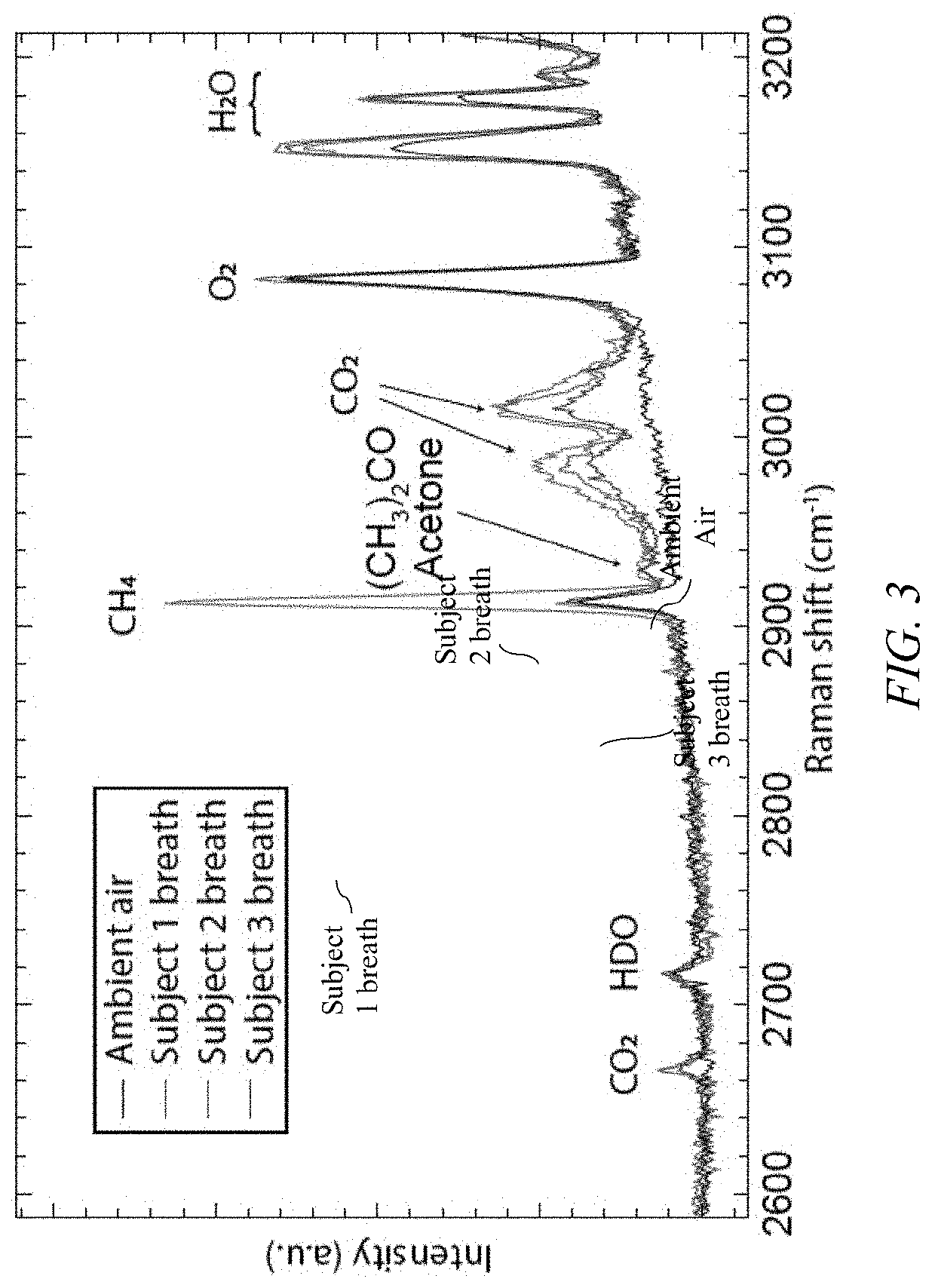
A method for enhancement of spontaneous Raman scattering (SRS) from gases comprising a multimode blue laser diode which receives feedback from a near concentric bidirectional multipass cavity in such a way as to generate a circulating power of order 100 W for a sample volume of 10 mm3. The feedback, provided via a volume Bragg grating, reduces the laser bandwidth to 4 cm−1. Spectra of spontaneous Raman scattering from ambient atmospheric air, detected collinearly with the pump, were recorded with a limit of detection below 1 part-per-million.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTH FLORIDA
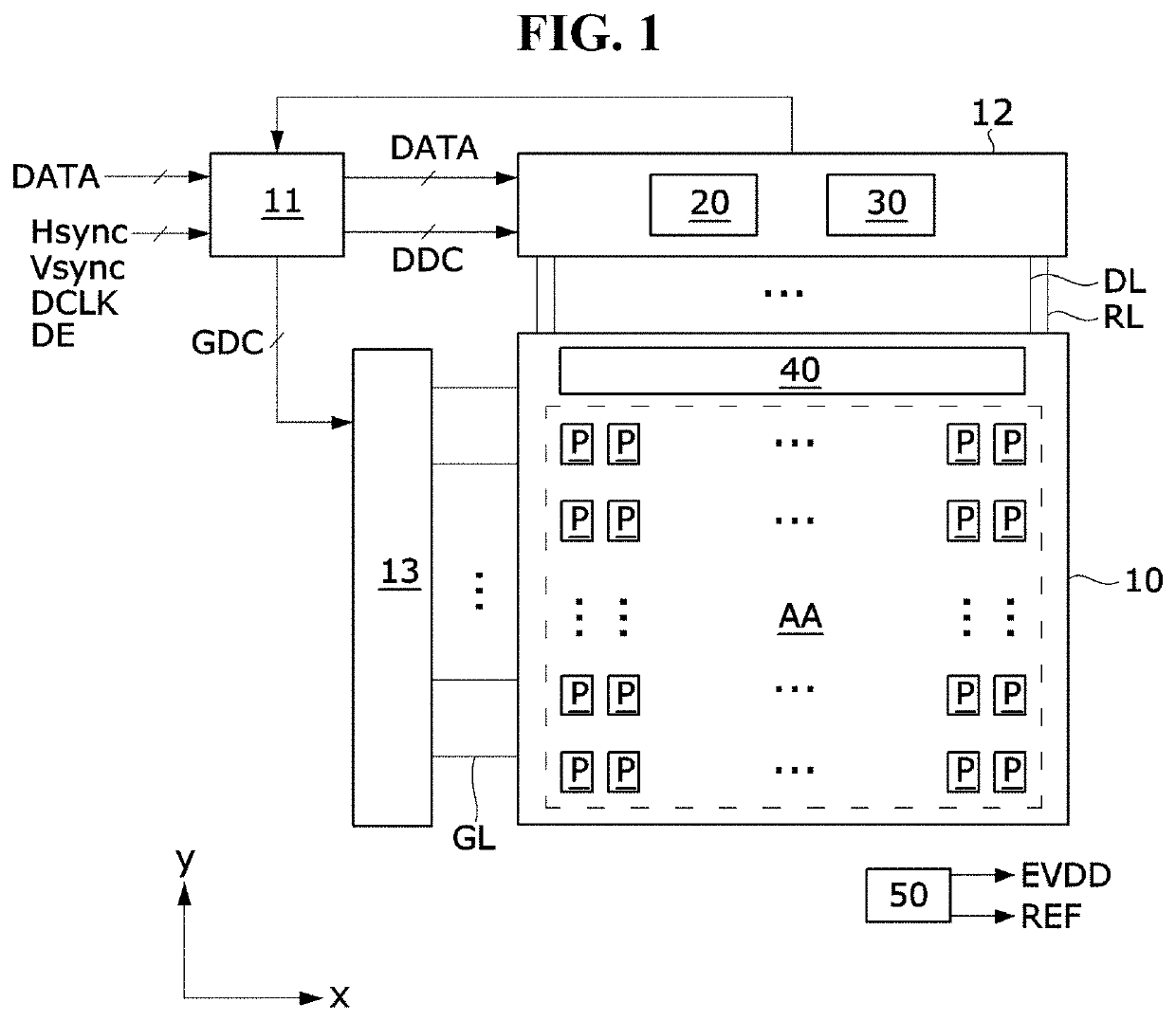
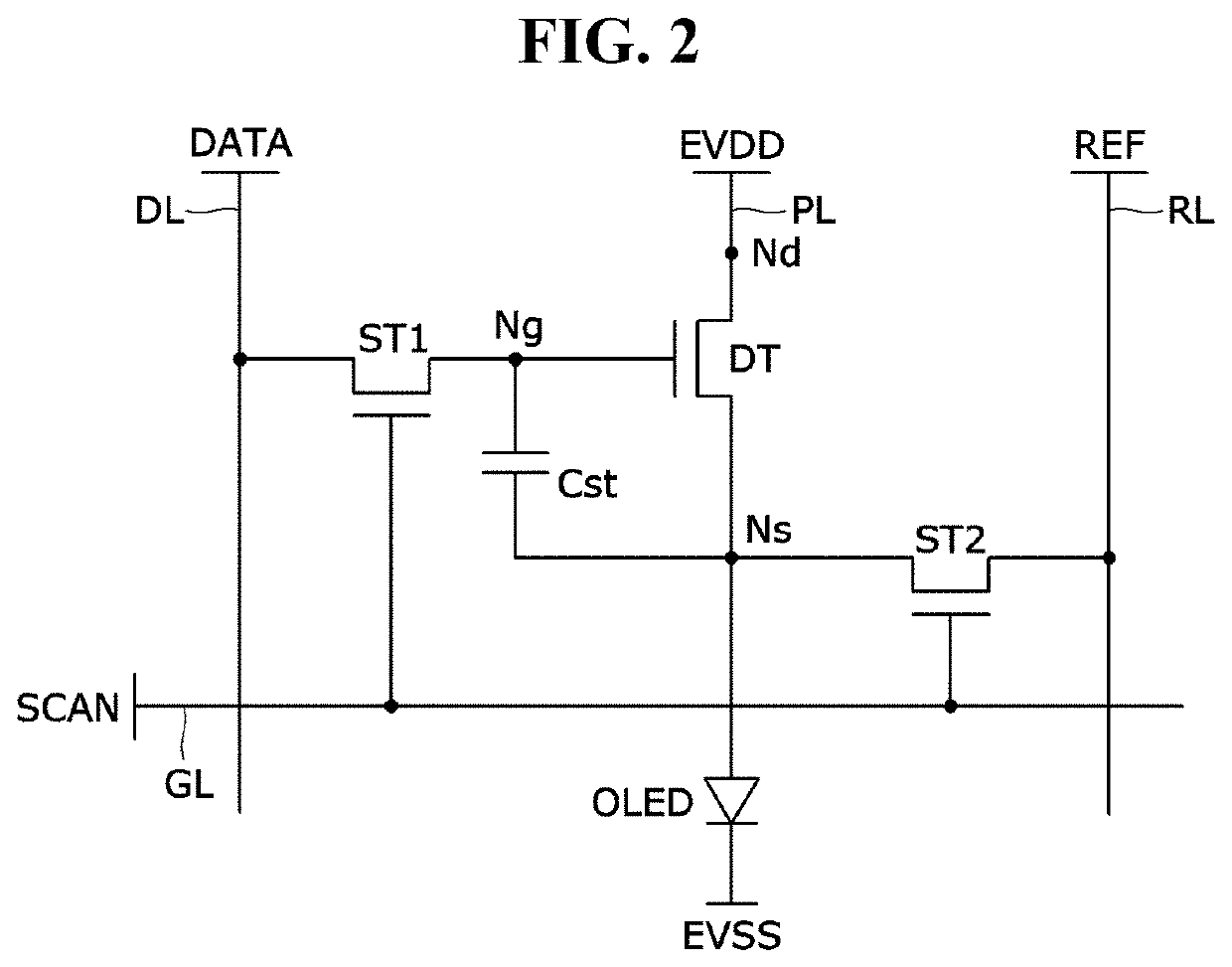
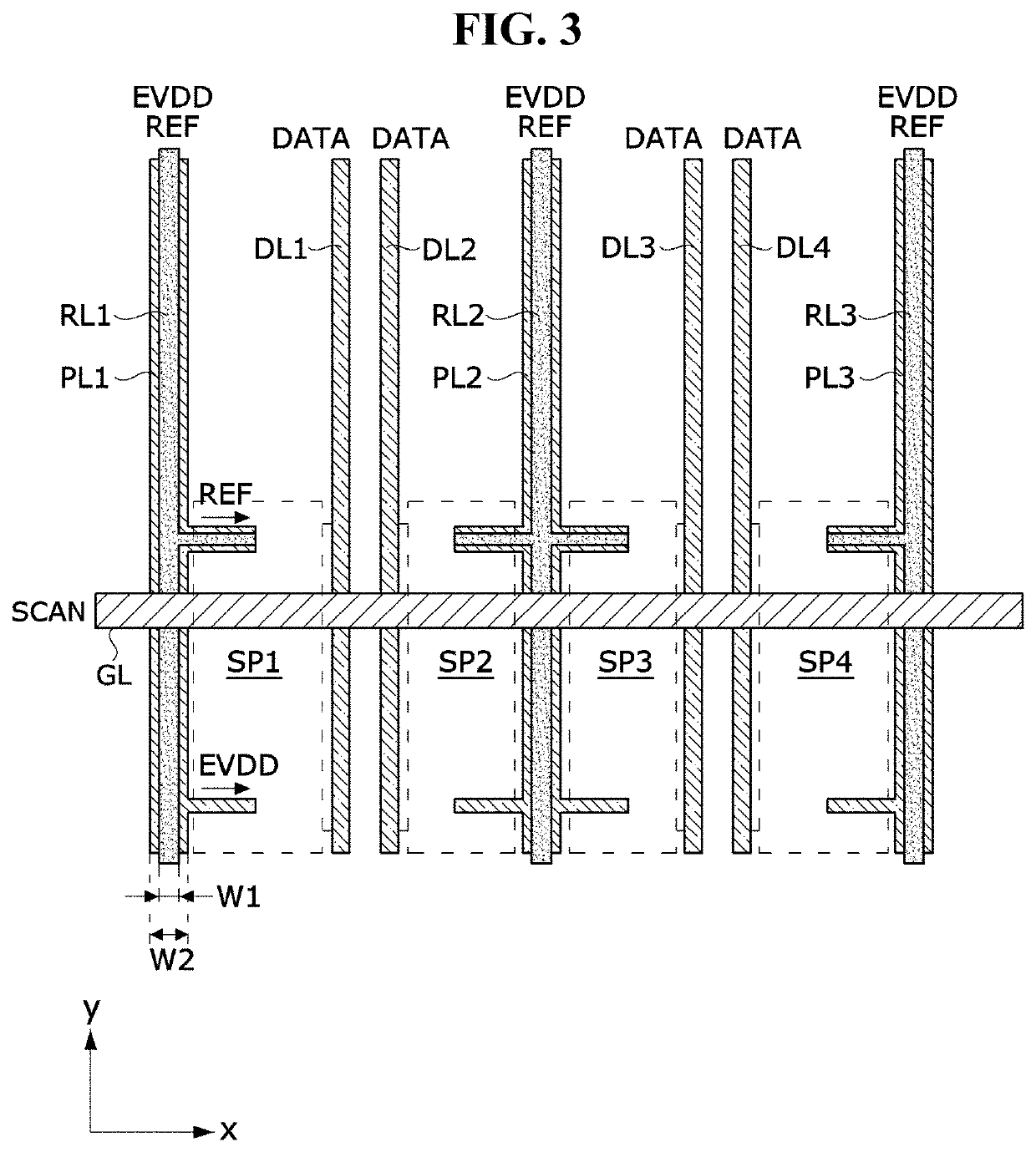
Display panel and display device using the same
ActiveUS20220148519A1Reduce amountLinewidth also decreaseStatic indicating devicesSolid-state devicesVoltage referenceData lines
The present disclosure relates to a display panel and a display device using the same. The display panel includes: a plurality of data lines to which a data voltage is applied; a plurality of pixel driving voltage lines arranged parallel to the data lines, and to which a pixel driving voltage is applied; and a plurality of reference voltage lines overlapping the pixel driving voltage lines with an insulating layer disposed therebetween, arranged in parallel with the data lines, and to which a reference voltage lower than the pixel driving voltage is applied.
Owner:LG DISPLAY CO LTD
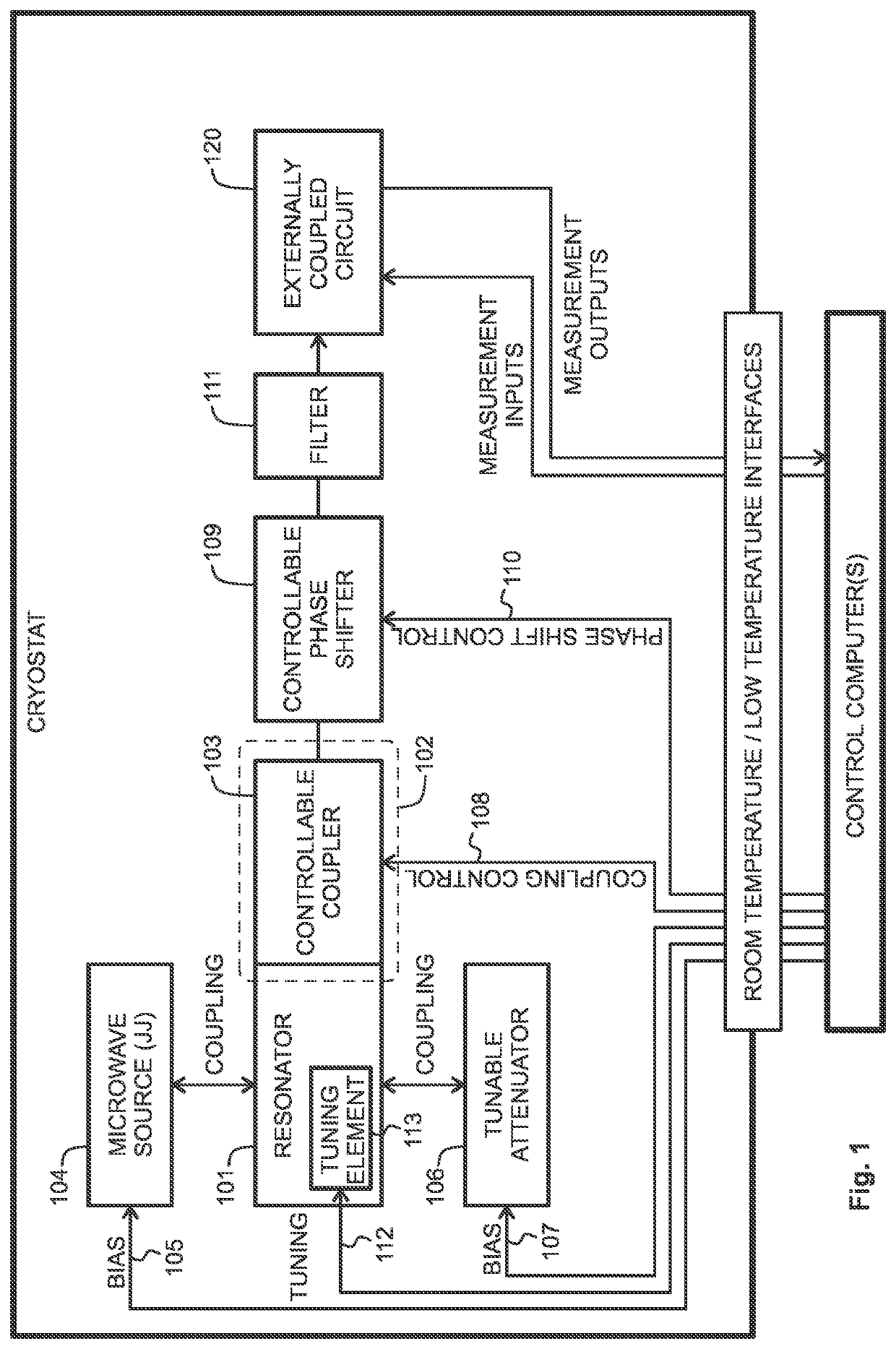
Vector signal generator operating on microwave frequencies, and method for generating time-controlled vector signals on microwave frequencies
PendingUS20220188683A1Precise and lossless controllabilitySmall lossQuantum computersSuperconductors/hyperconductorsSignal onSoftware engineering
A vector signal generator is capable of operating on microwave frequencies. It comprises a microwave resonator, an output for coupling microwave photons out of said microwave resonator, and a Josephson junction or junction array coupled to the microwave resonator for emitting microwave signals into the microwave resonator. A biasing circuit is provided for applying a bias to the Josephson junction or junction array. A tunable attenuator is coupled to said microwave resonator.
Owner:IQM FINLAND OY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com