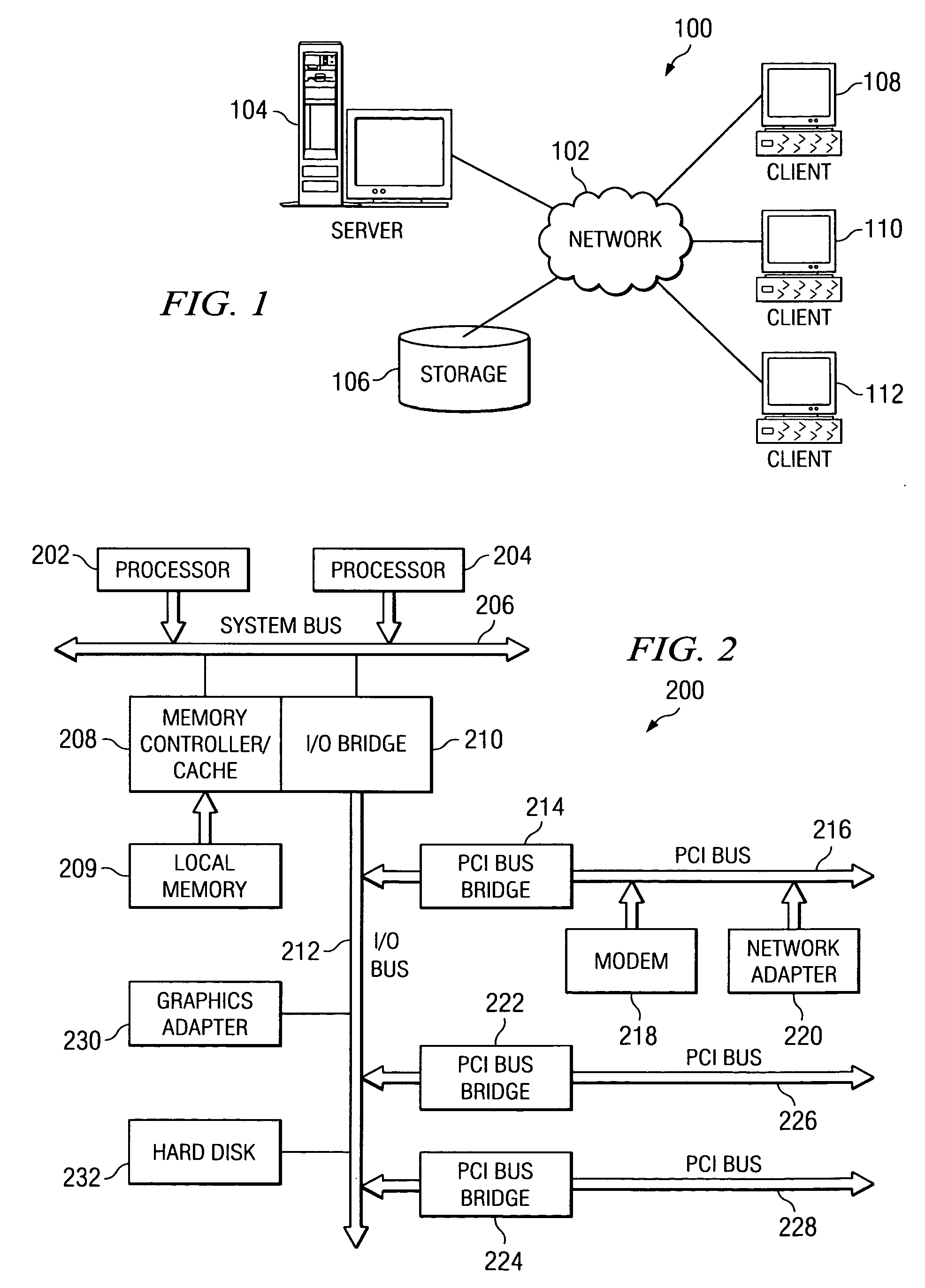
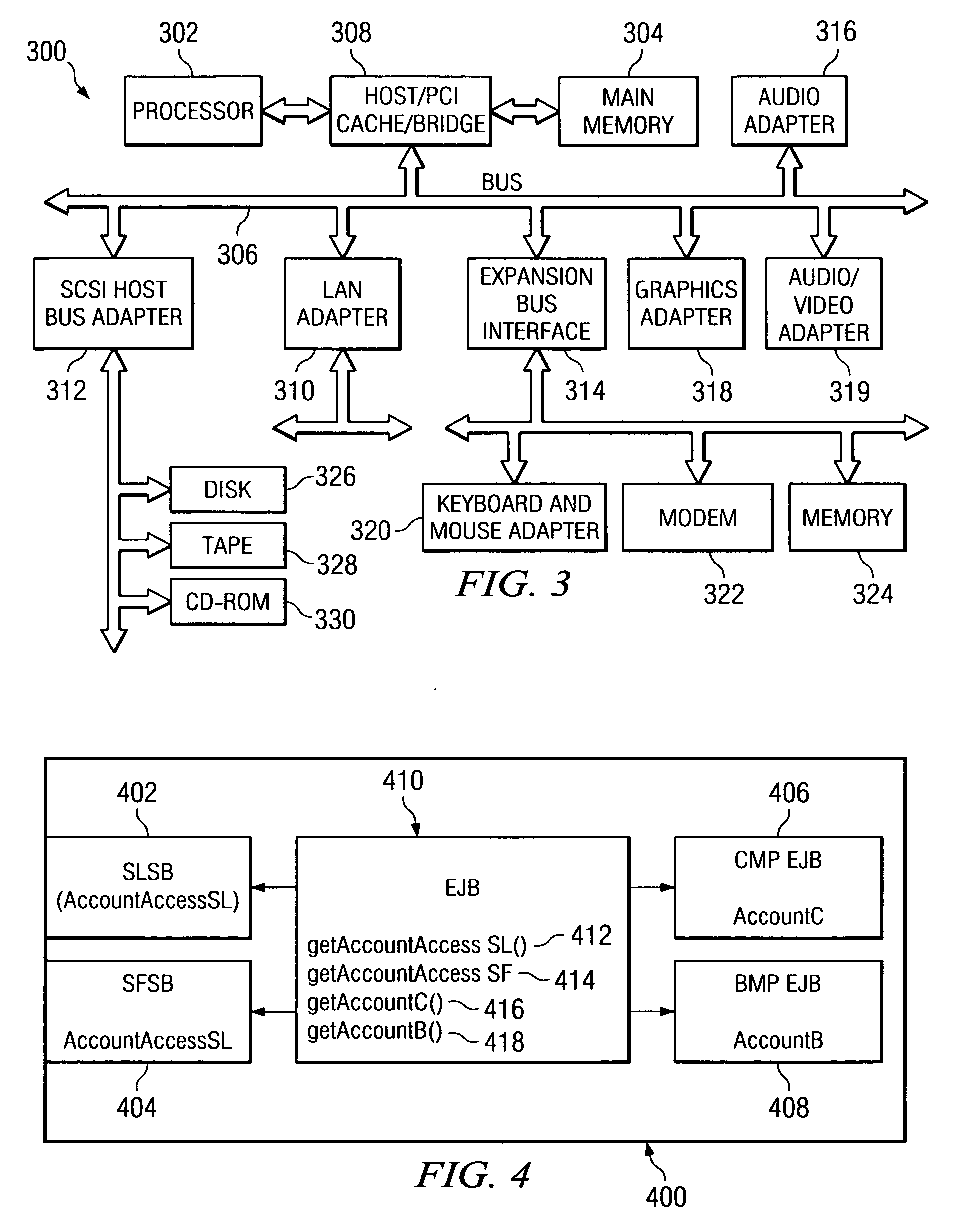
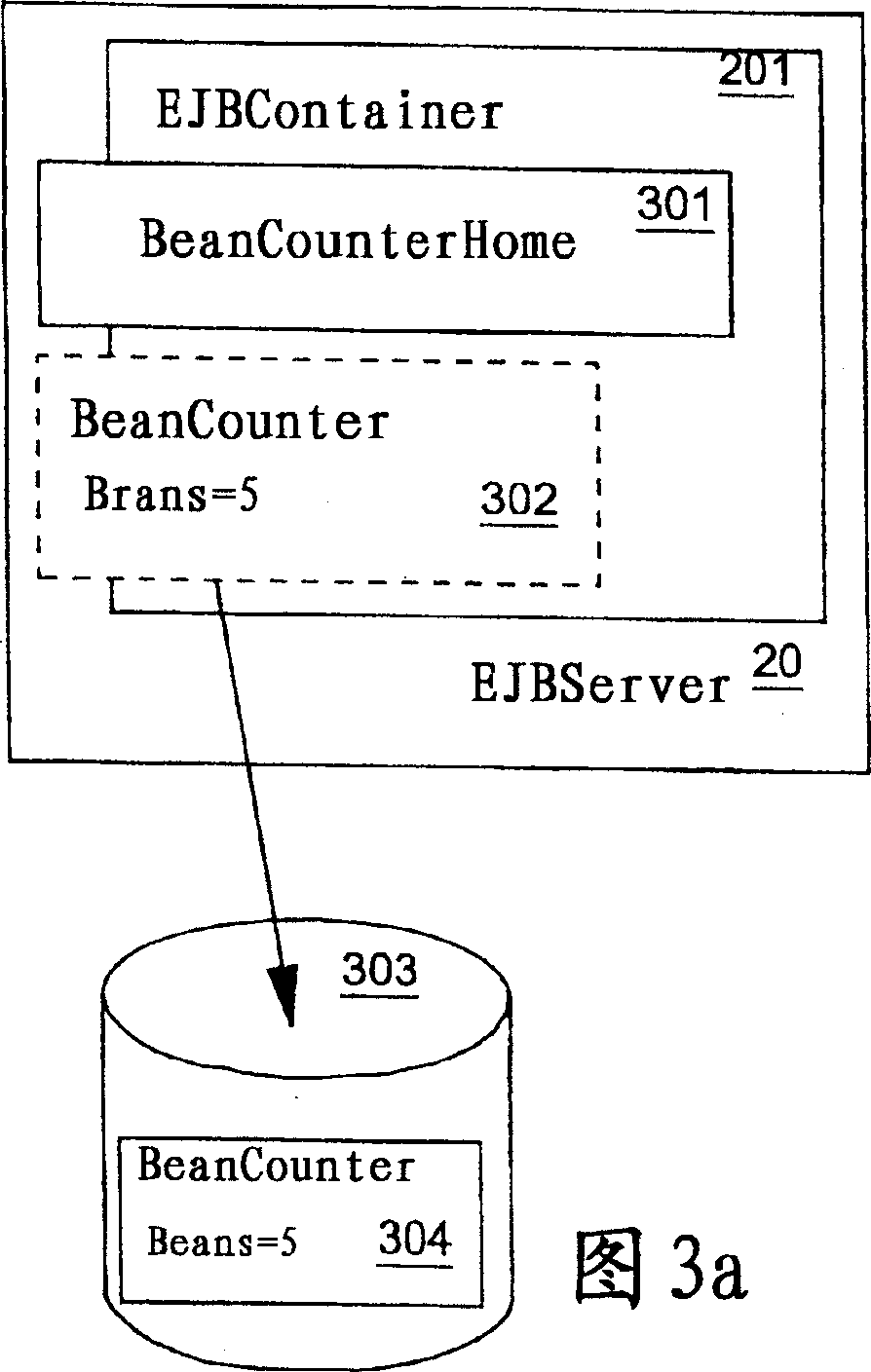
Patents
Literature
39 results about "Enterprise JavaBeans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
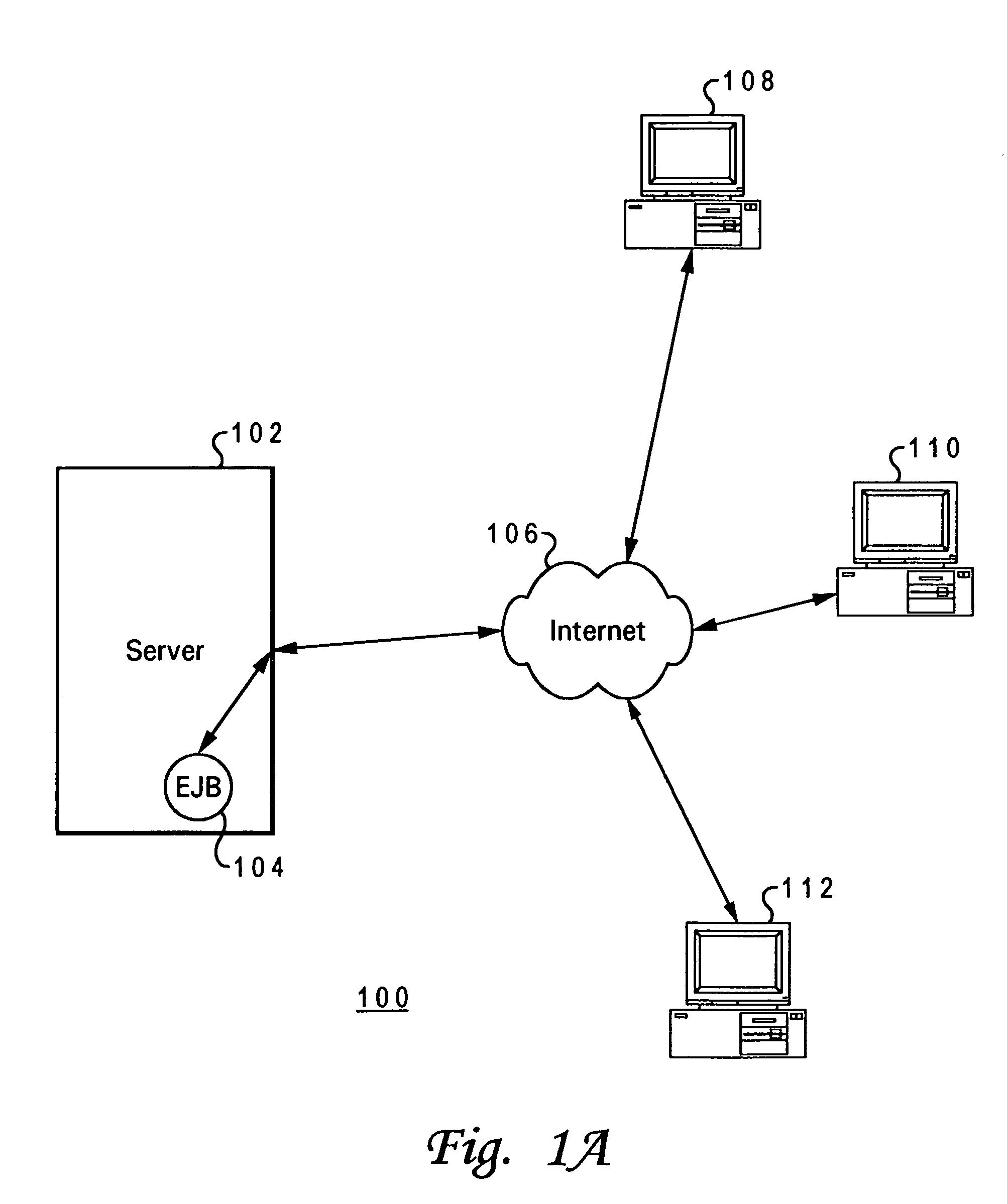
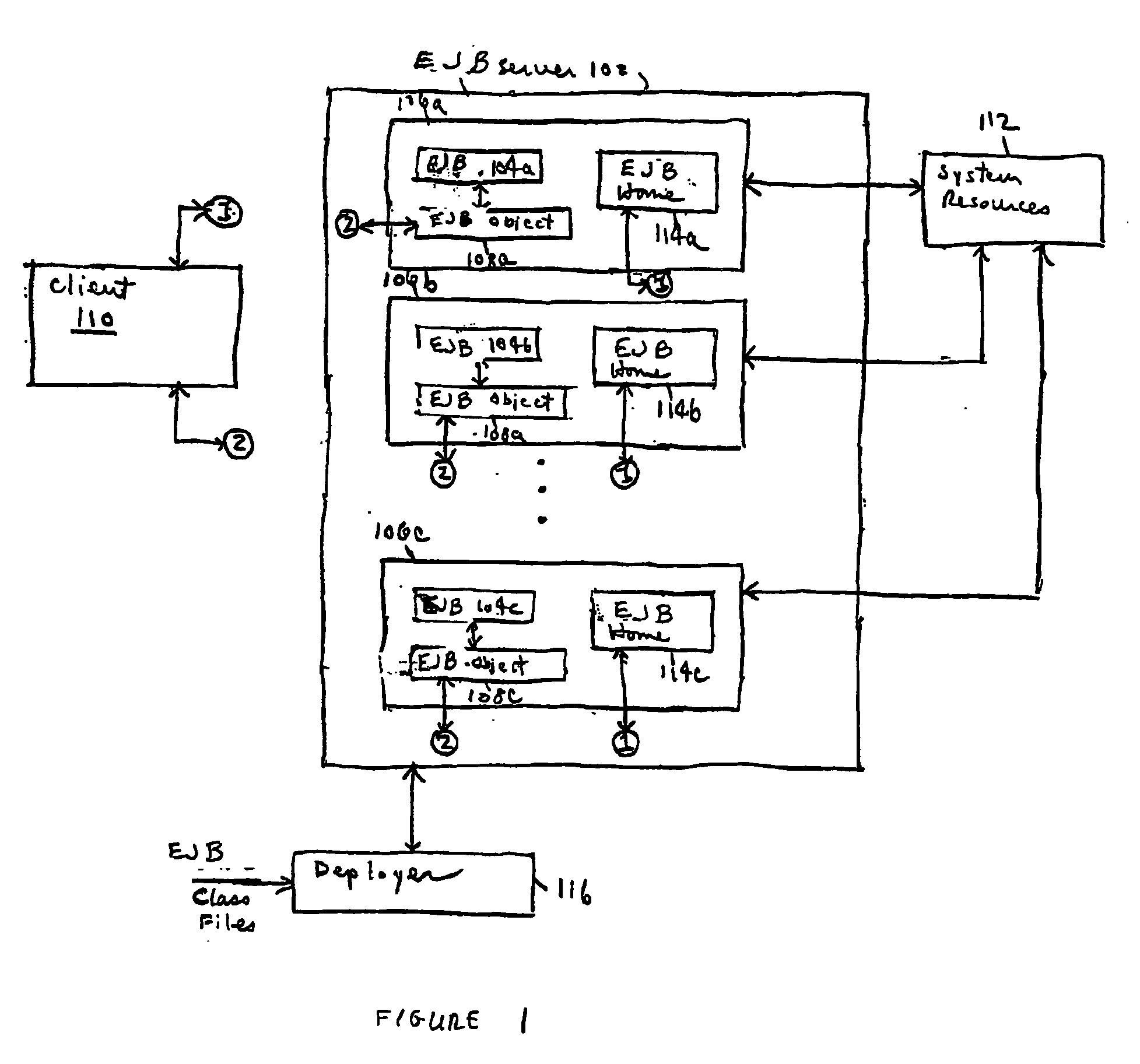
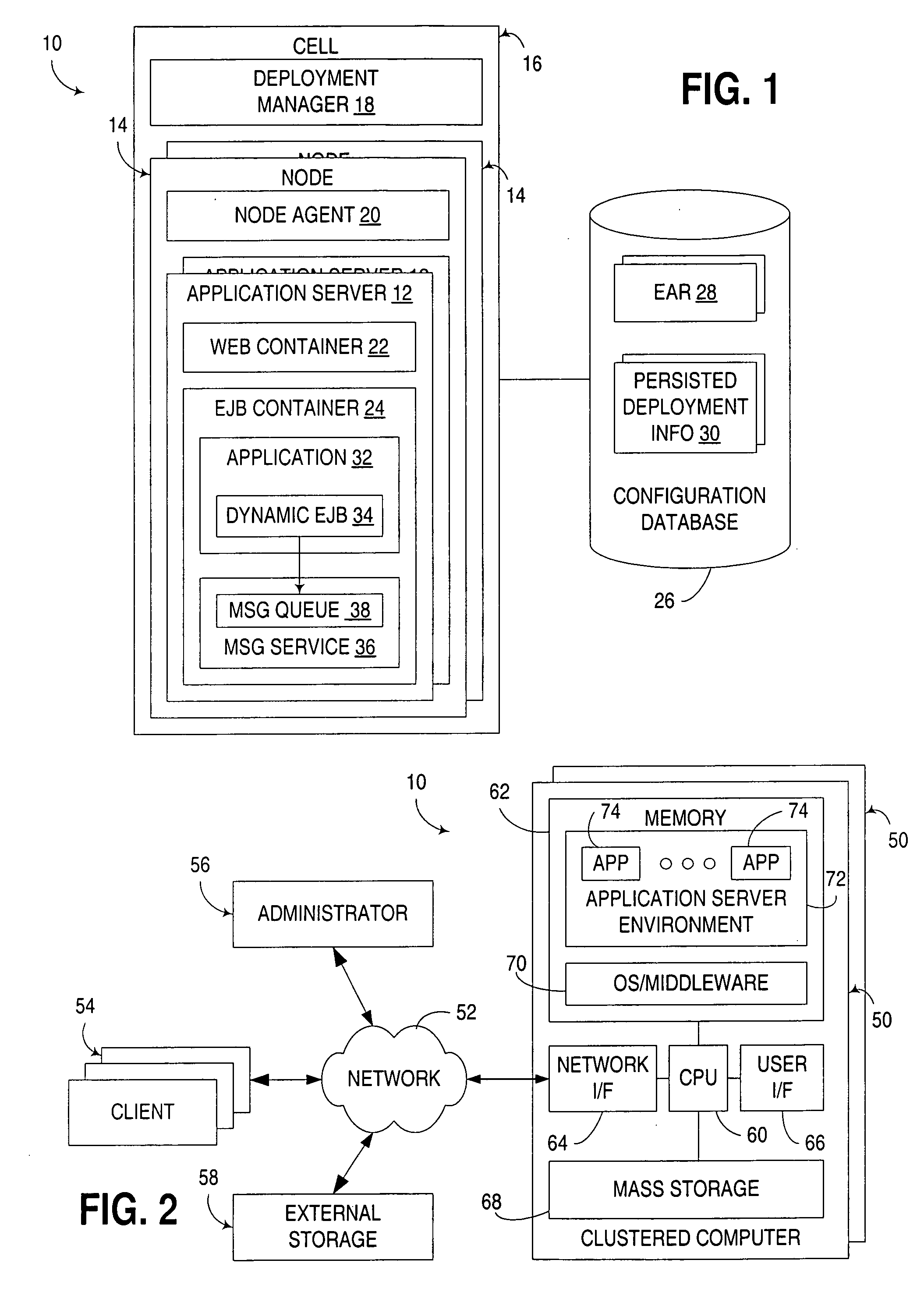
Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) is one of several Java APIs for modular construction of enterprise software. EJB is a server-side software component that encapsulates business logic of an application. An EJB web container provides a runtime environment for web related software components, including computer security, Java servlet lifecycle management, transaction processing, and other web services. The EJB specification is a subset of the Java EE specification.
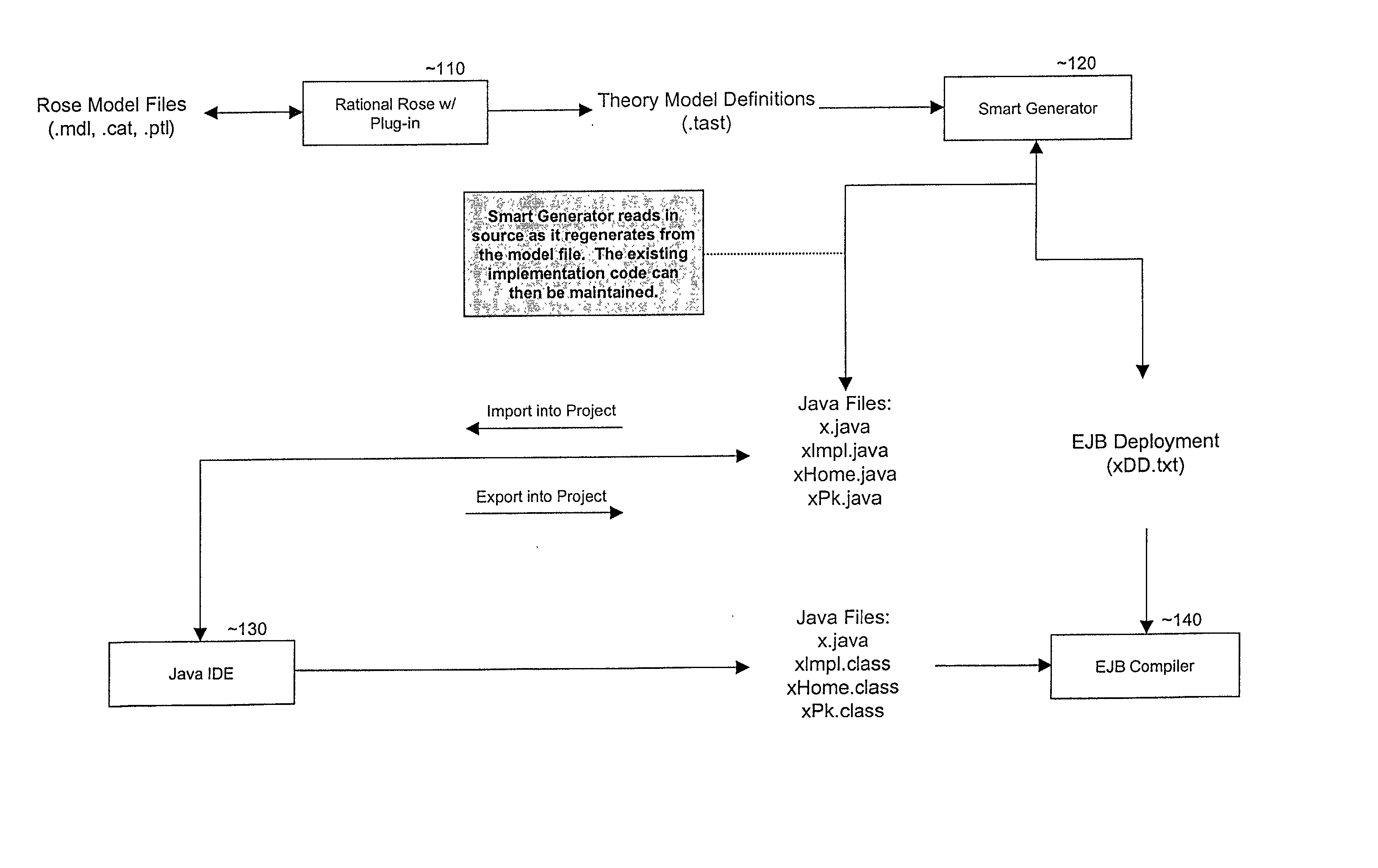
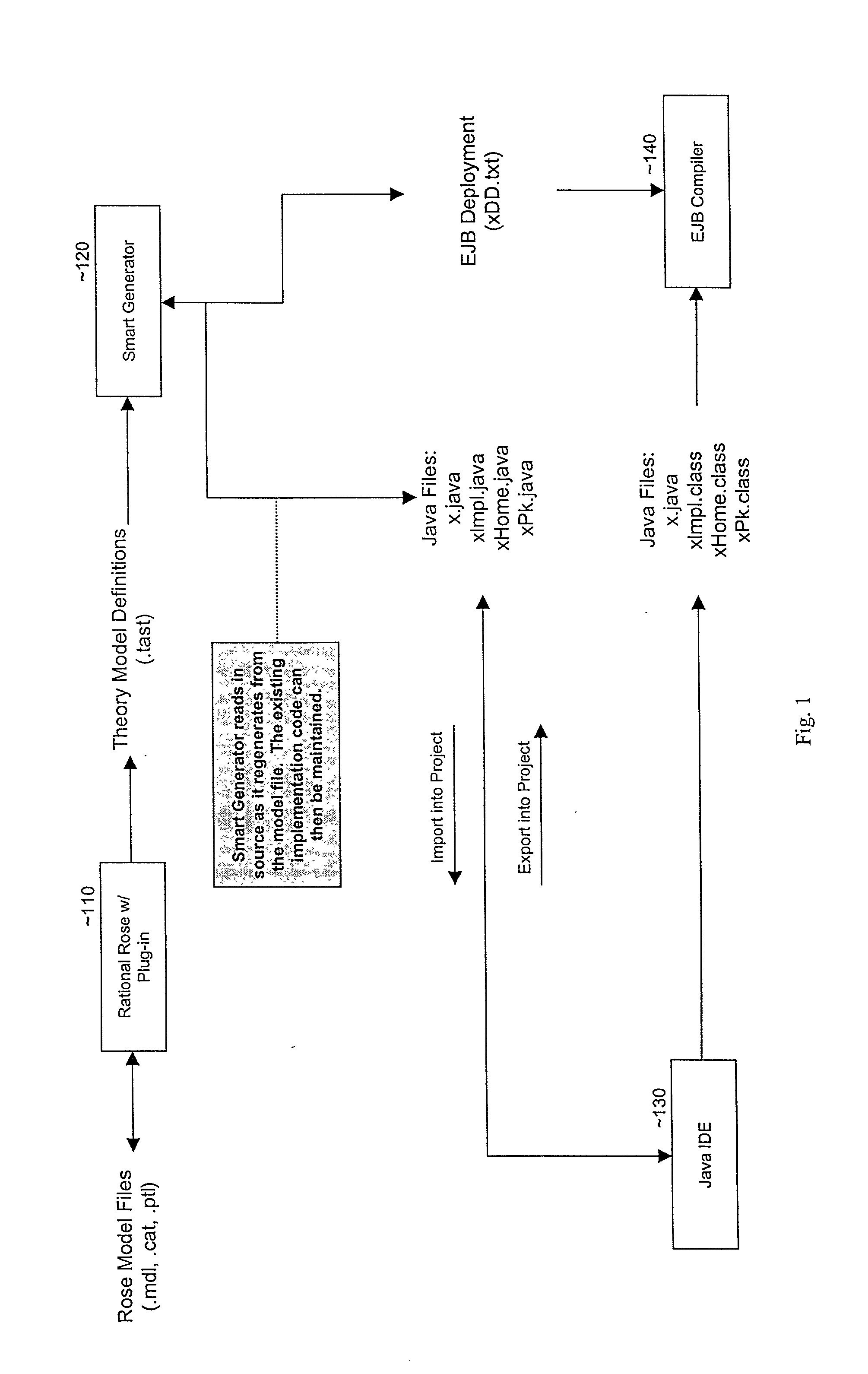
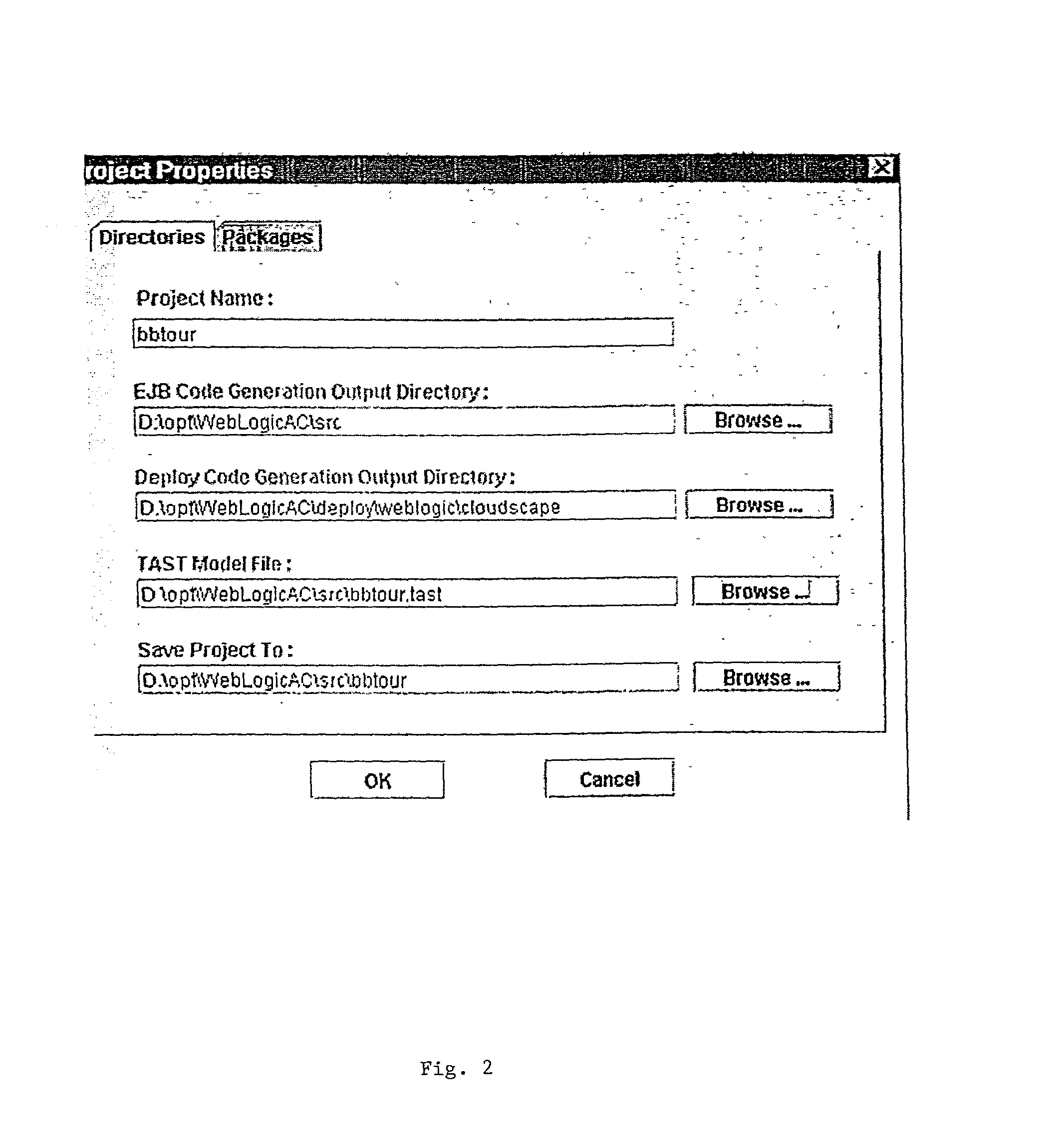
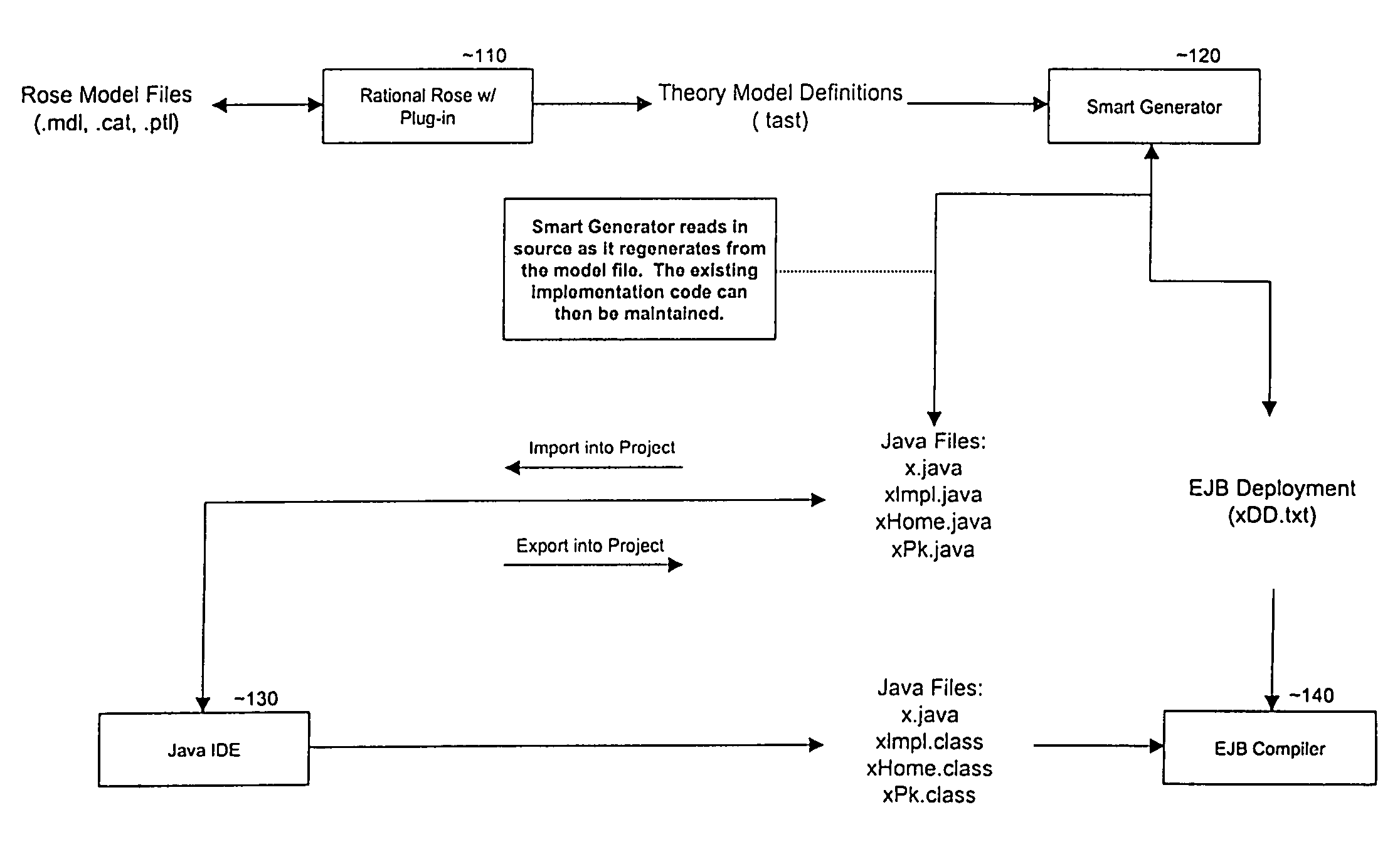
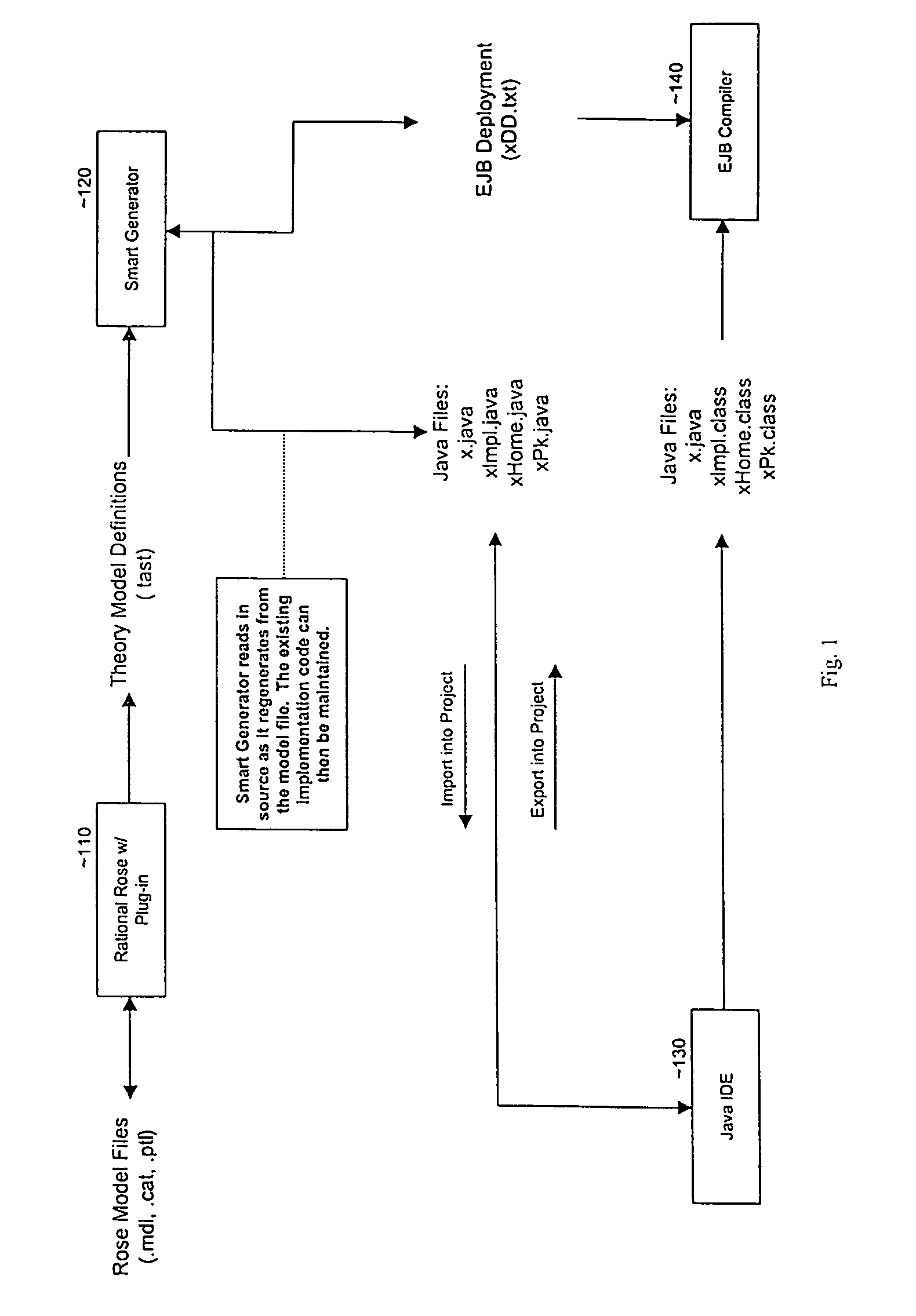
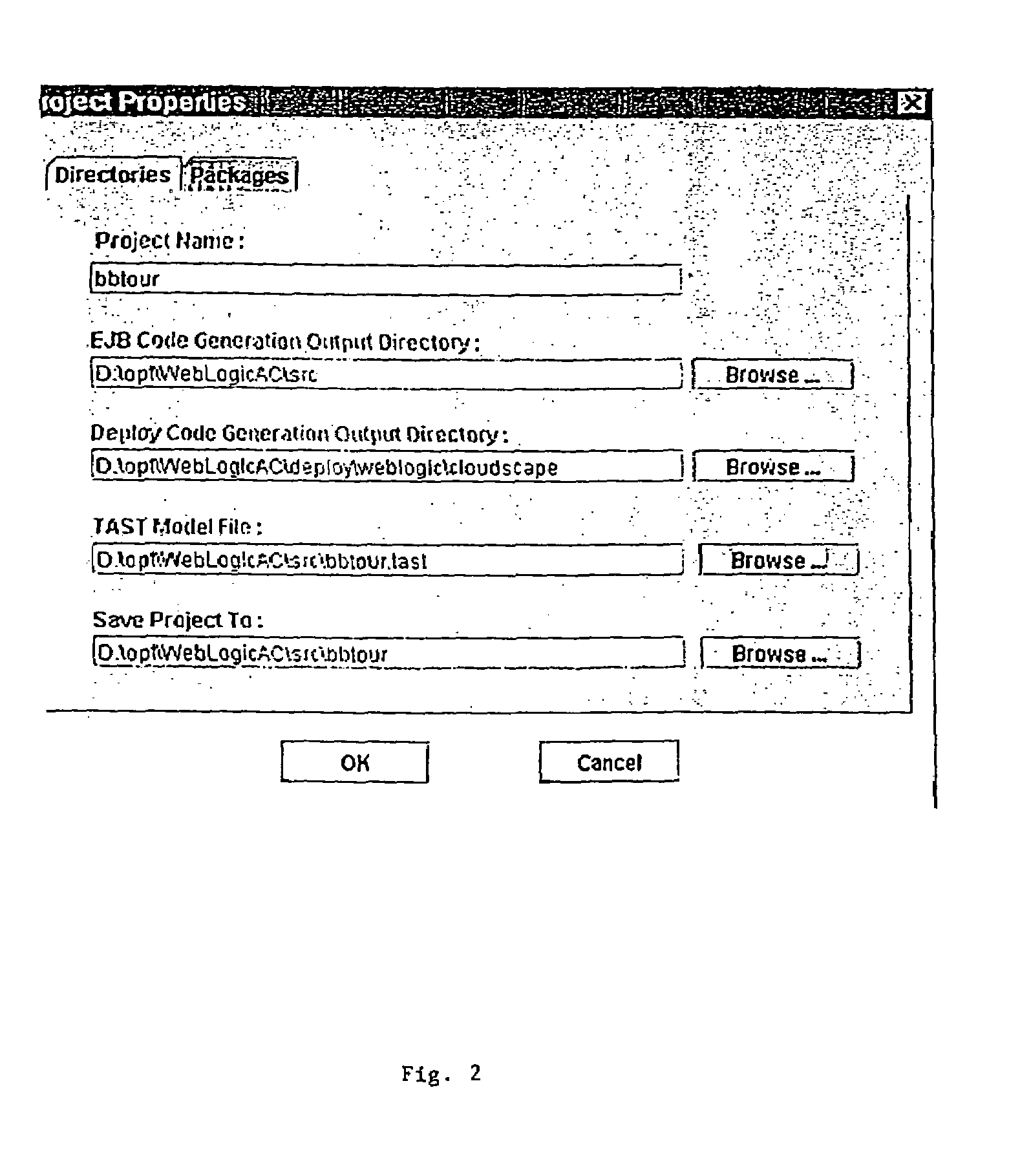
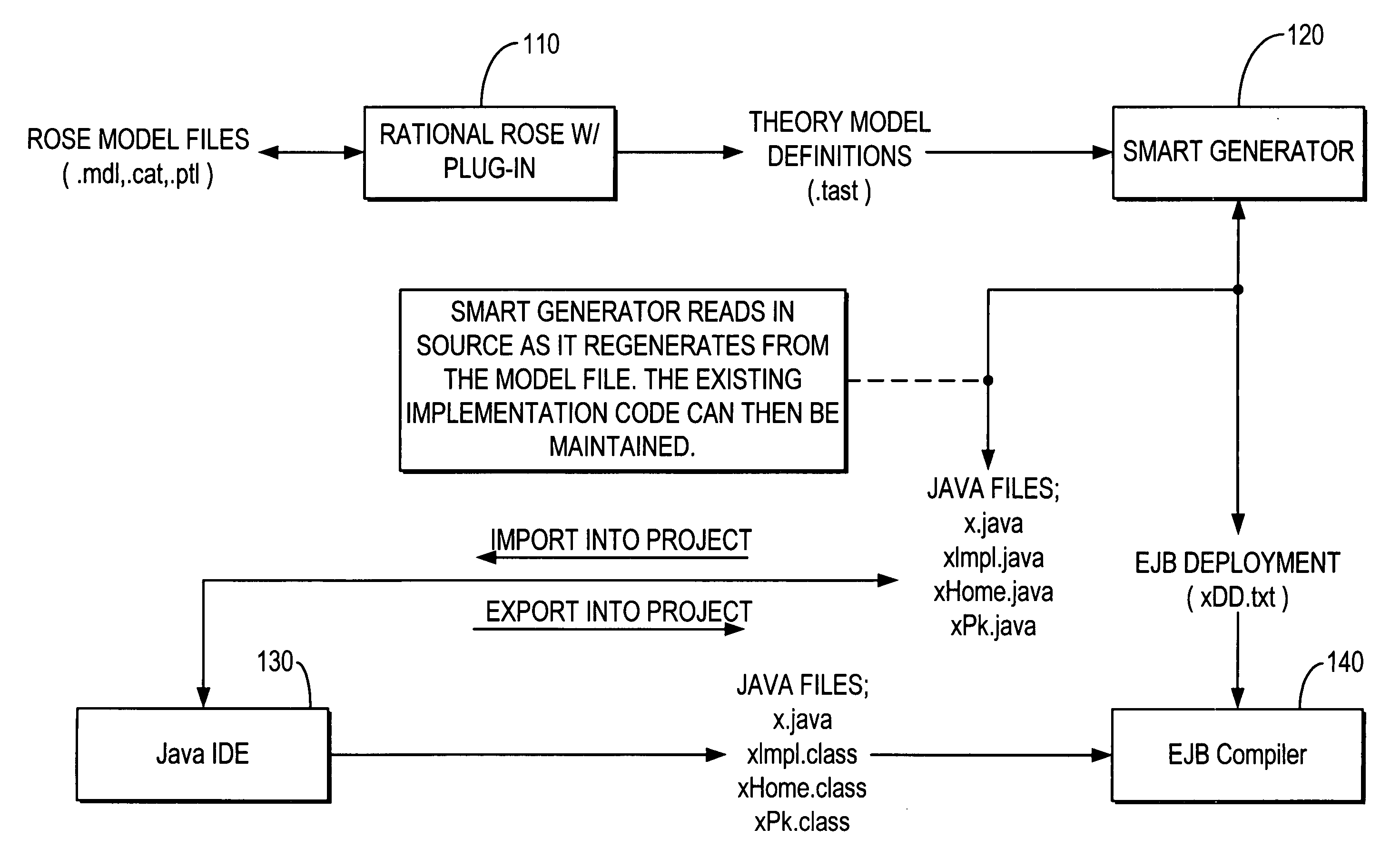
Smart generator
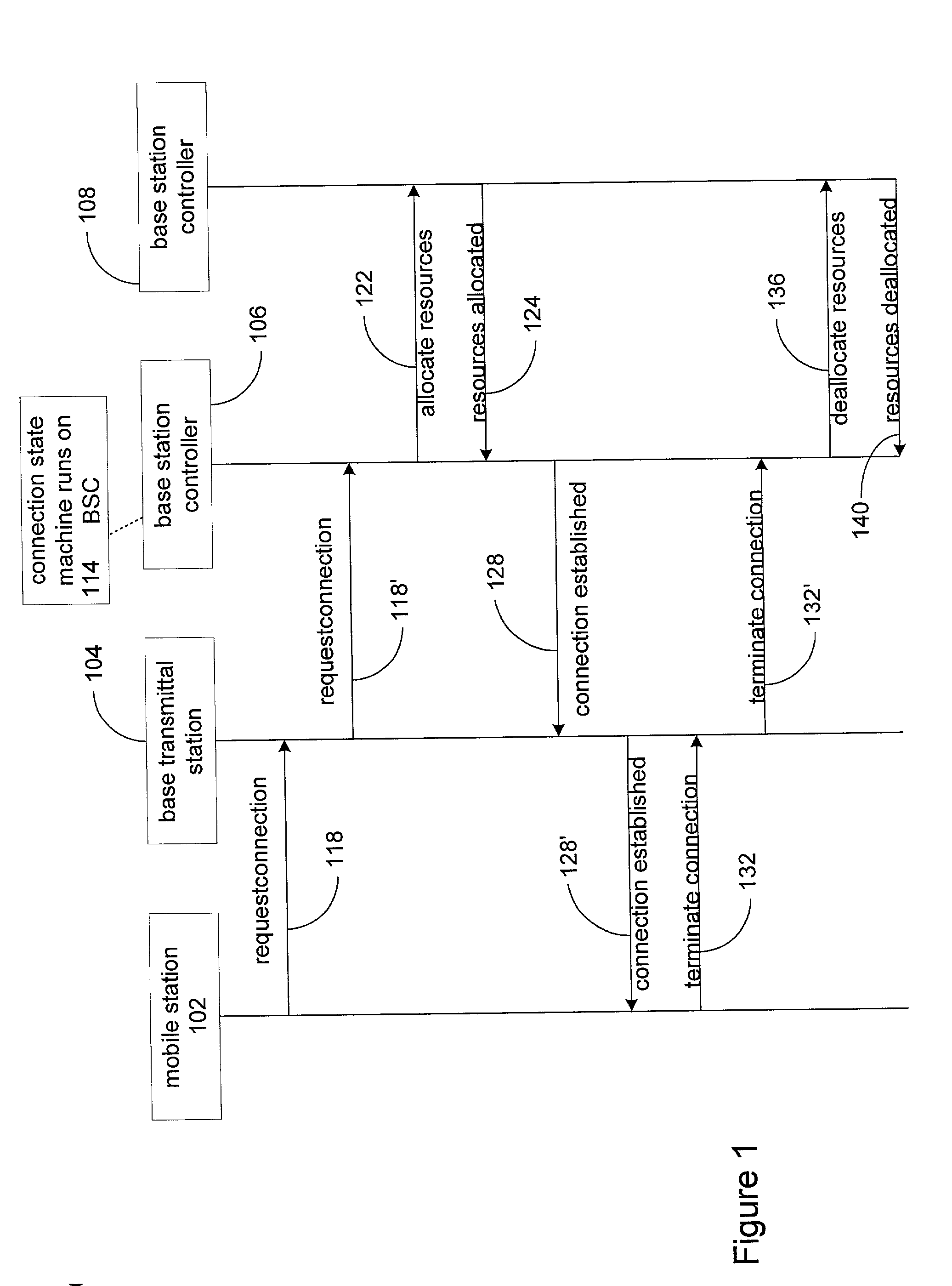
ActiveUS20020147763A1Laborious taskDigital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess methodDEVS
The Smart Generator of the present invention allows the designer / developer / user to model the EJB components in a natural way without being concerned with implementation-specific details. The developer models the business objects using a UML drawing tool and the Smart Generator creates a set of classes that implements these objects with reference to the Enterprise JavaBeans specification. That is, the Smart Generator automatically create access methods and handling containment of references from the UML diagram.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
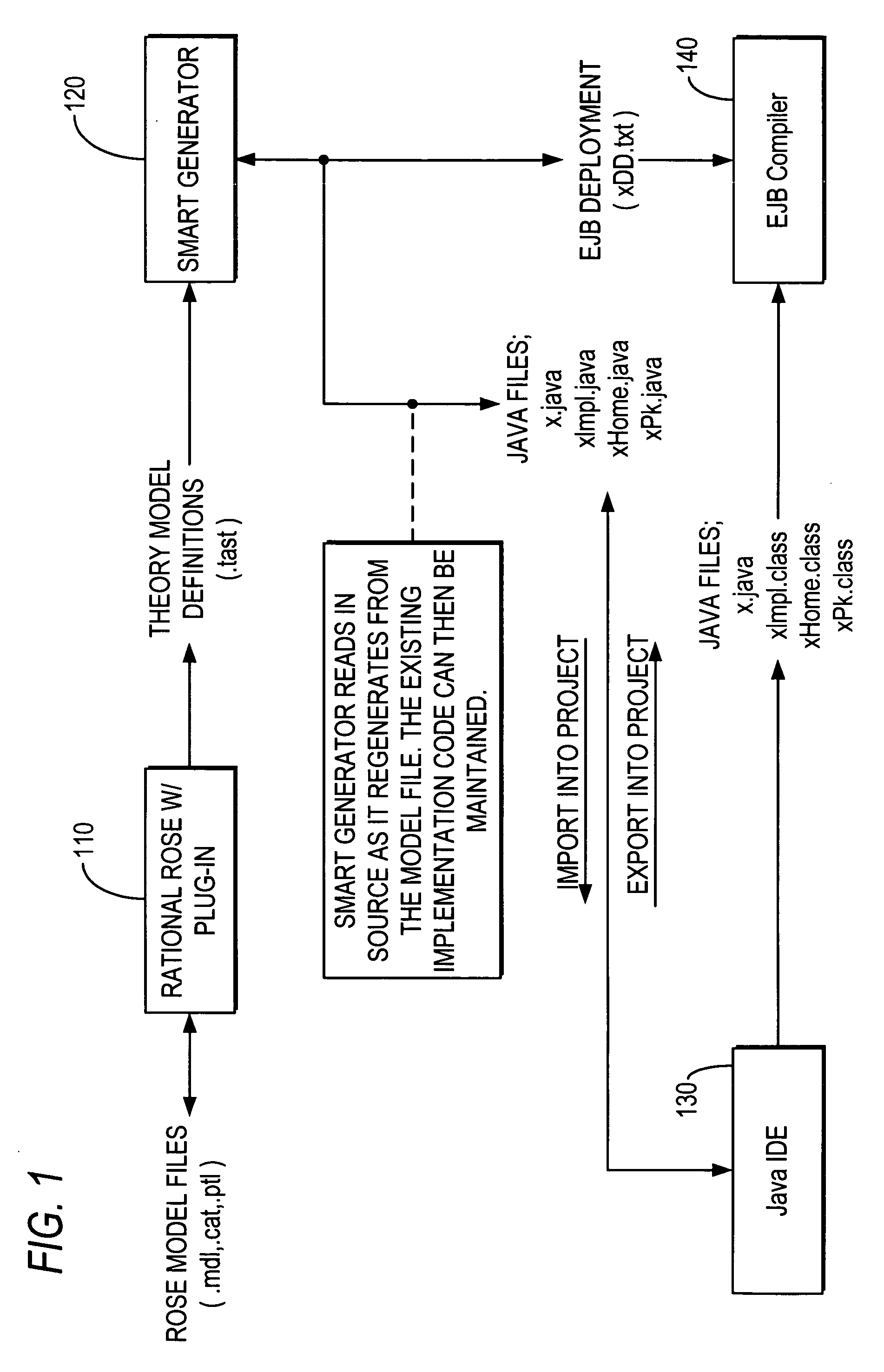
Smart generator
ActiveUS7404175B2Digital data information retrievalMultiple digital computer combinationsAccess methodDEVS
The Smart Generator of the present invention allows the designer / developer / user to model the EJB components in a natural way without being concerned with implementation-specific details. The developer models the business objects using a UML drawing tool and the Smart Generator creates a set of classes that implements these objects with reference to the Enterprise JavaBeans specification. That is, the Smart Generator automatically create access methods and handling containment of references from the UML diagram.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
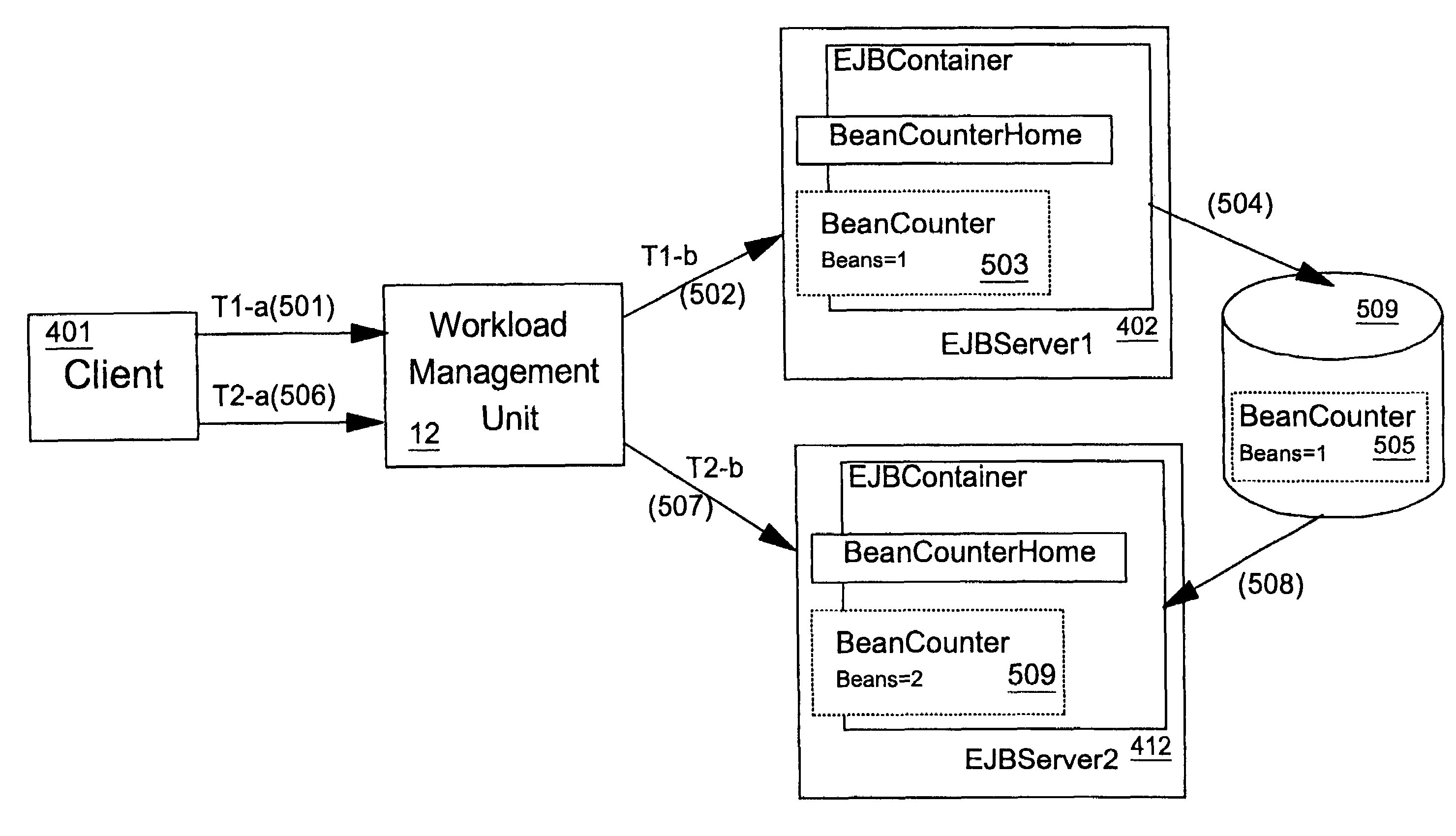
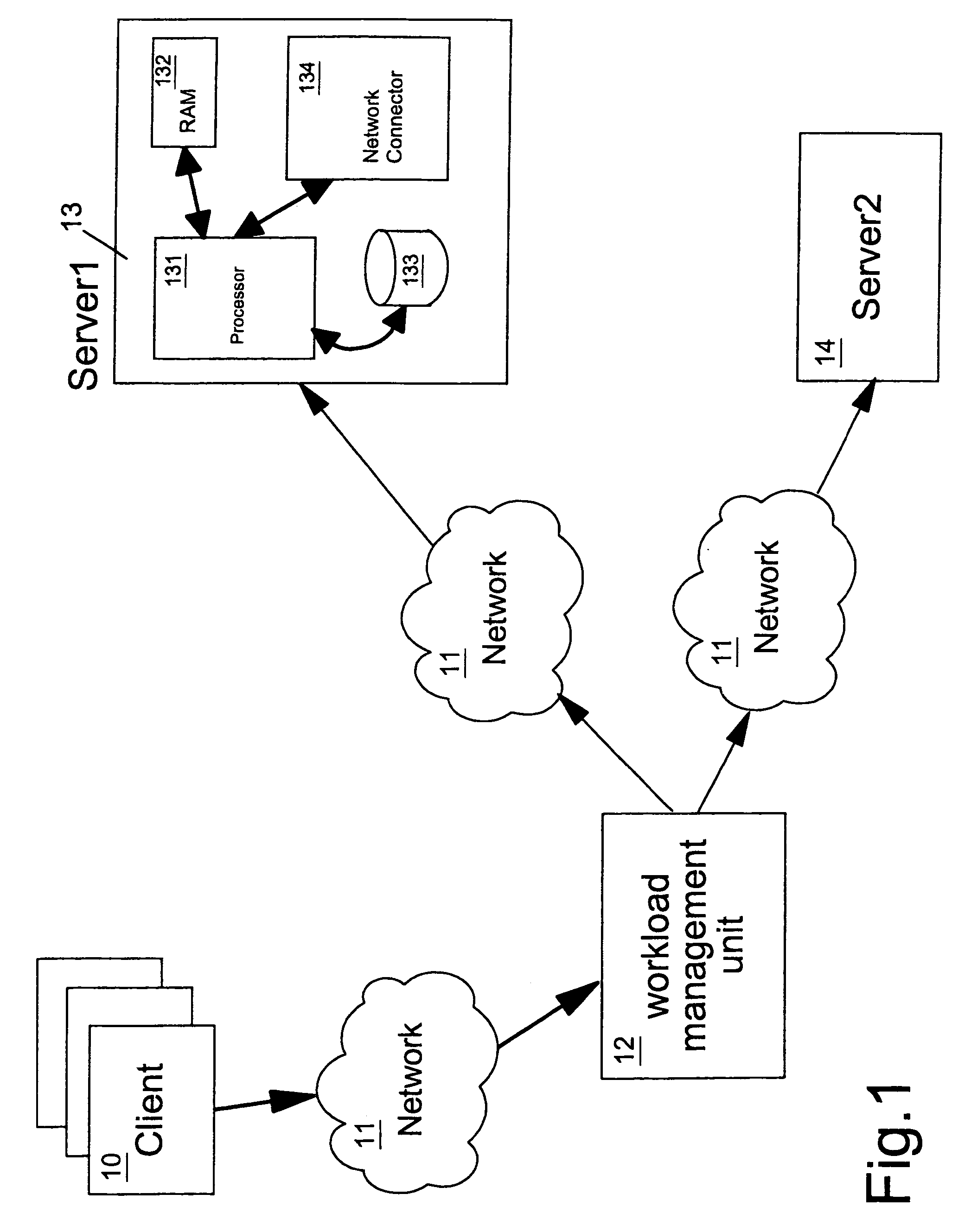
Workload management of stateful program entities
InactiveUS7349970B2Need be provideReduce accessResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsMass storageRouting table
In a workload managed system comprising a plurality of server processes each capable of supporting a given program entity, such as an Enterprise JavaBeans™ specified stateful session bean, a stateful session bean instance is passivated, by writing it to a bean store, on completion of a unit of work. On next use the session bean is reactivated, by reading it from the bean store, in any one of the plurality of servers thereby allowing workload management for stateful session beans. A routing table is maintained, in non-volatile mass storage, that contains location information for units of work and stateful session bean instances, used to maintain unit of work-server affinity for the lifetime of the unit of work Stateful session beans instances are associated with ID keys that include a flag that is used to indicate whether or not the routing table contains location information for the bean instance.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
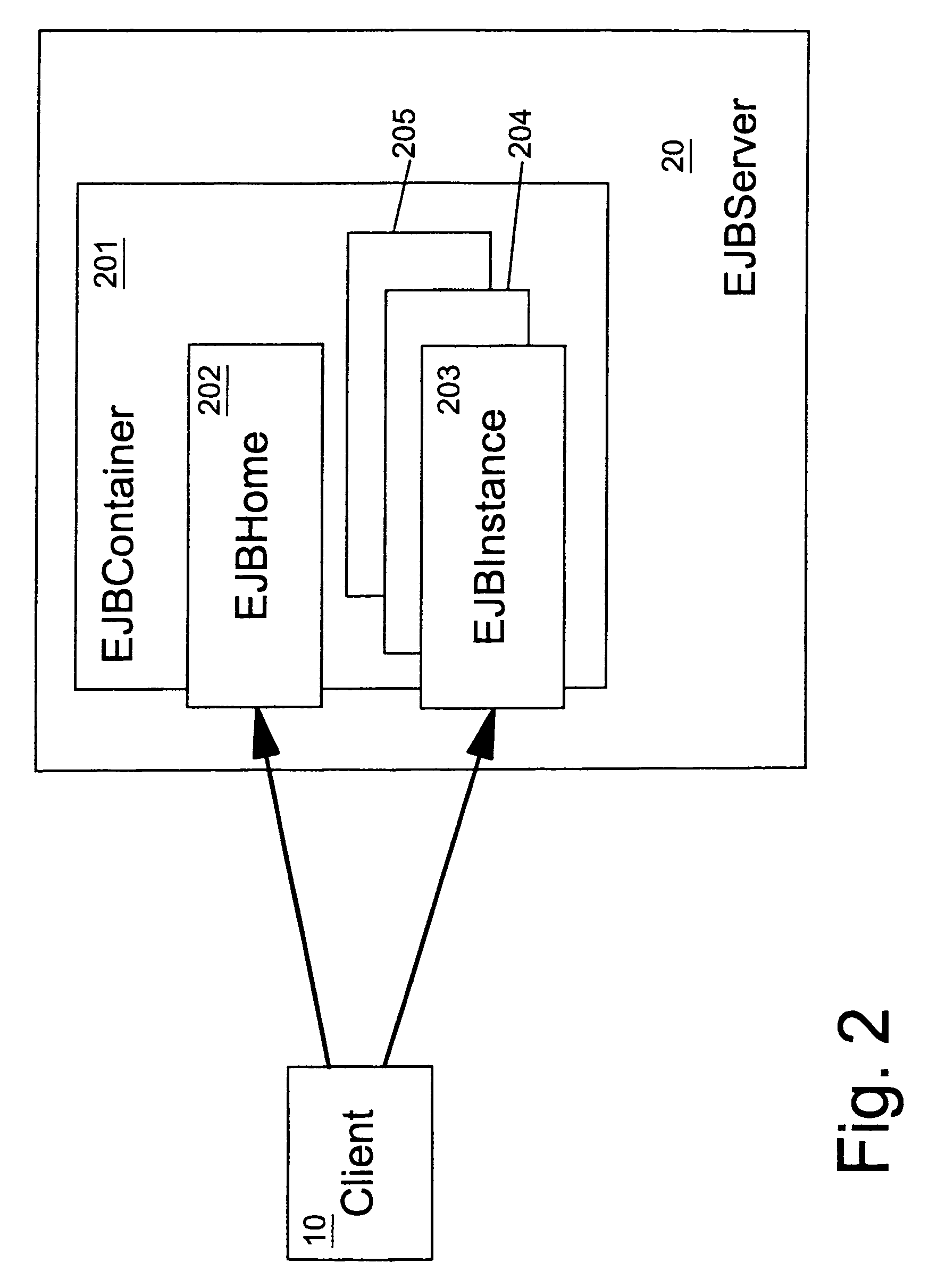
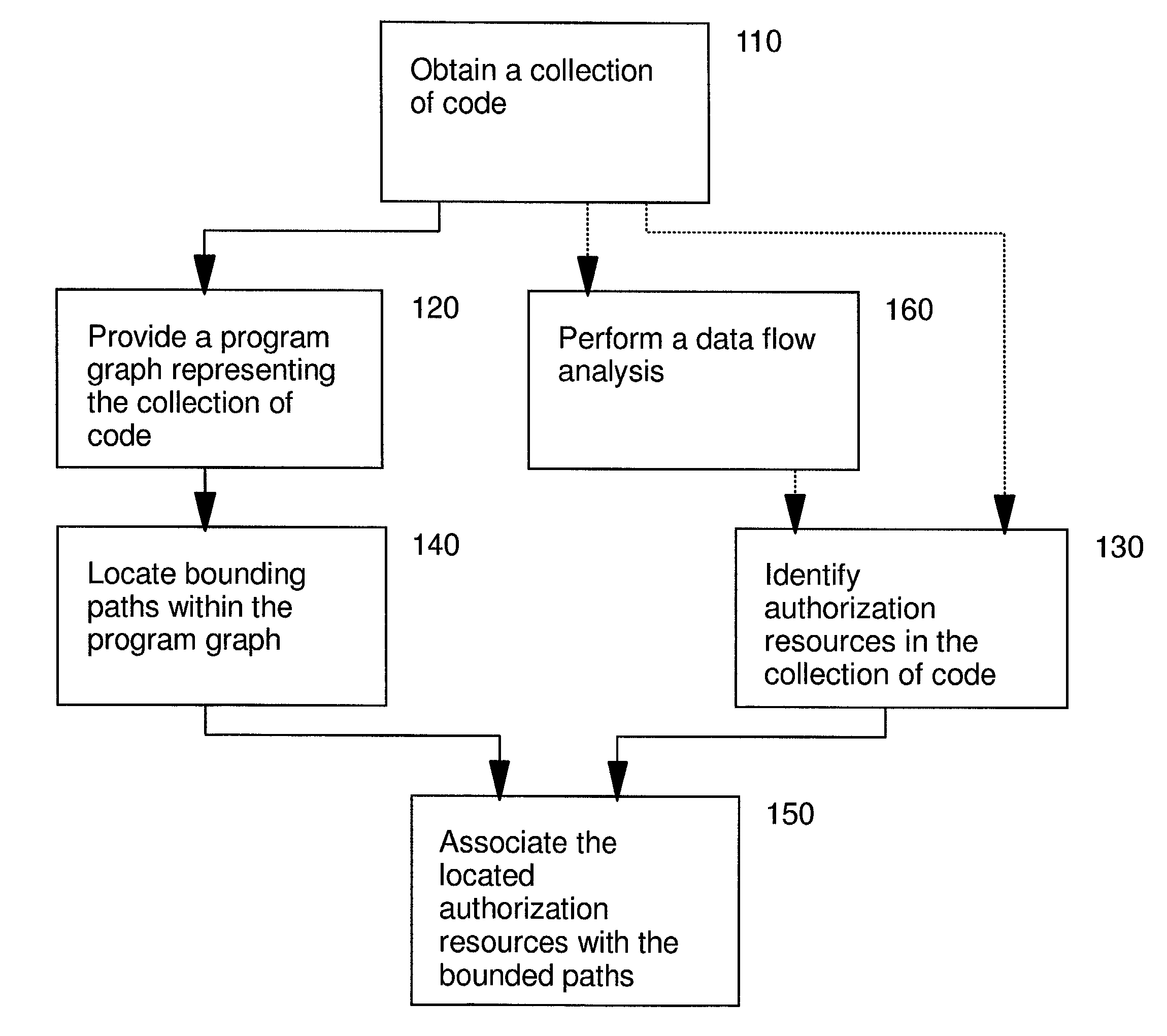
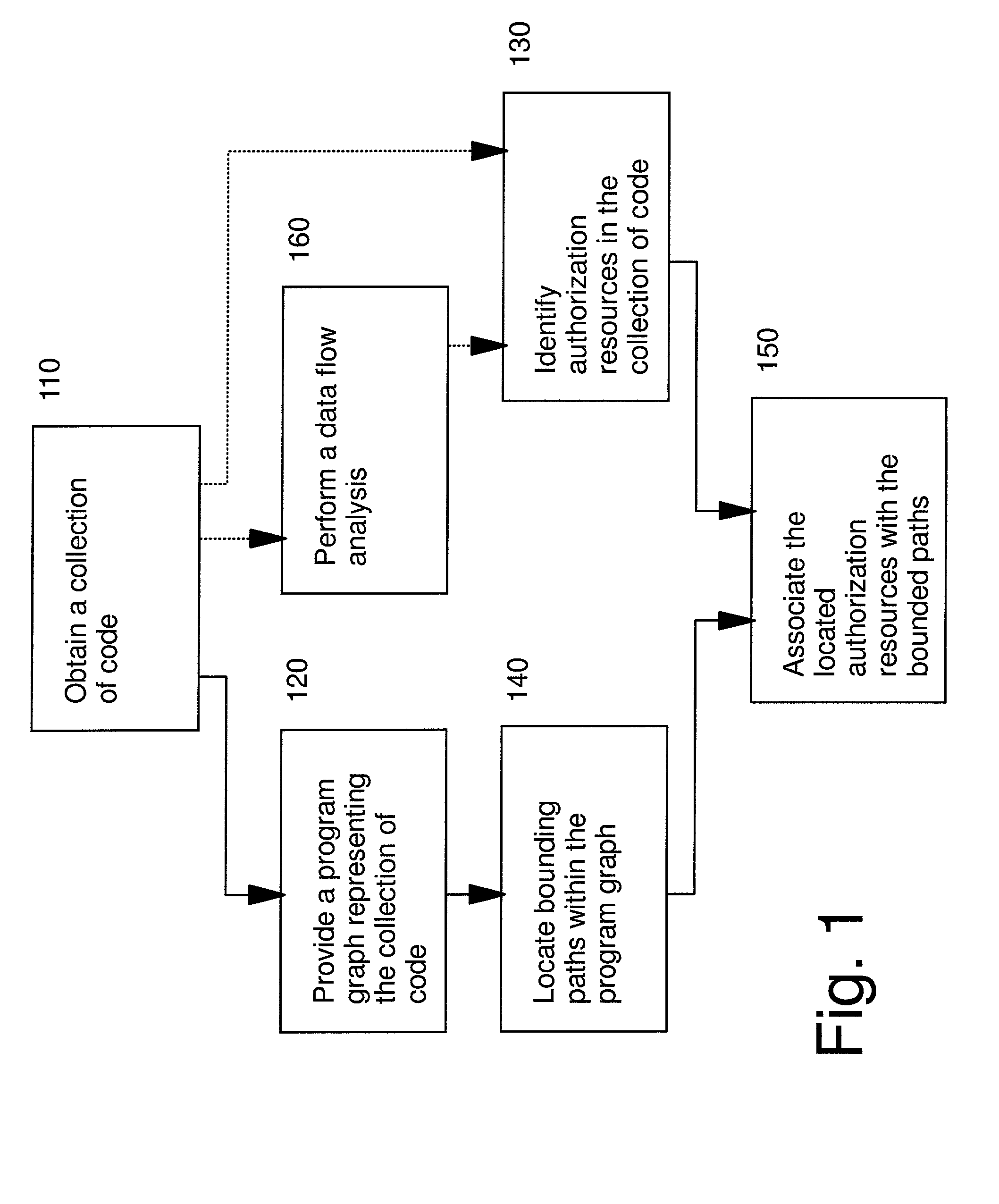
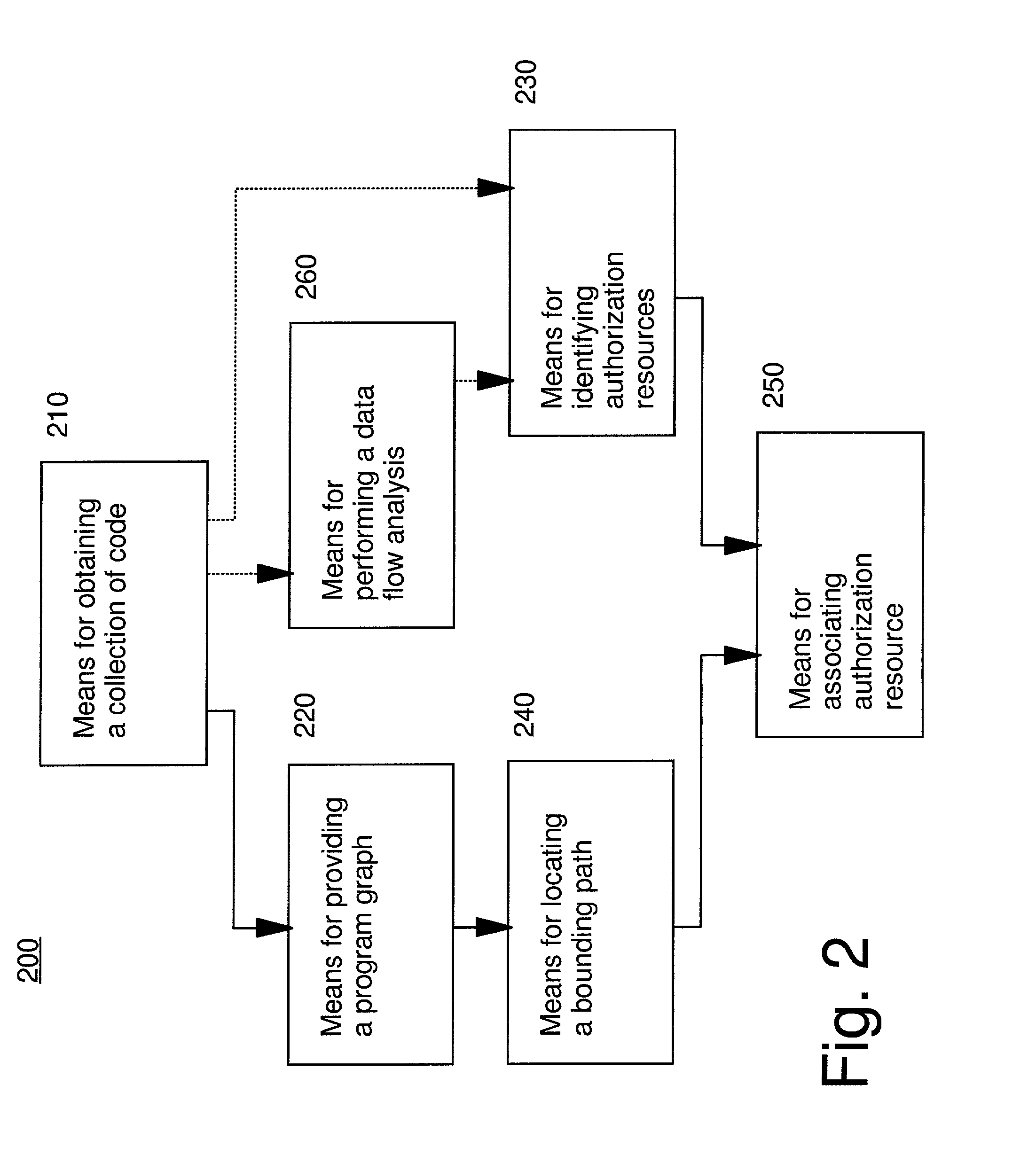
Automated program resource identification and association
This invention provides methods and apparatus for determining a set of authorization usage for collection of code. By using a program graph, the present invention identifies the code within in bounded paths in the program graph that use authorization. The level of precision is able to identify authorization usage to the level of basic blocks, methods, classes or other collections of code. By using the analysis technique described in this invention, we can determine the authorizations needed by collections code, including Java applets, servlets, and Enterprise JavaBeans. By using the present invention, it is possible, prior to loading the mobile code, to prompt the administrator or end-user to authorize or deny the code access to restricted the resources, or determine whether authorization testing will be required.
Owner:IBM CORP
Web browser-based object oriented application component test client
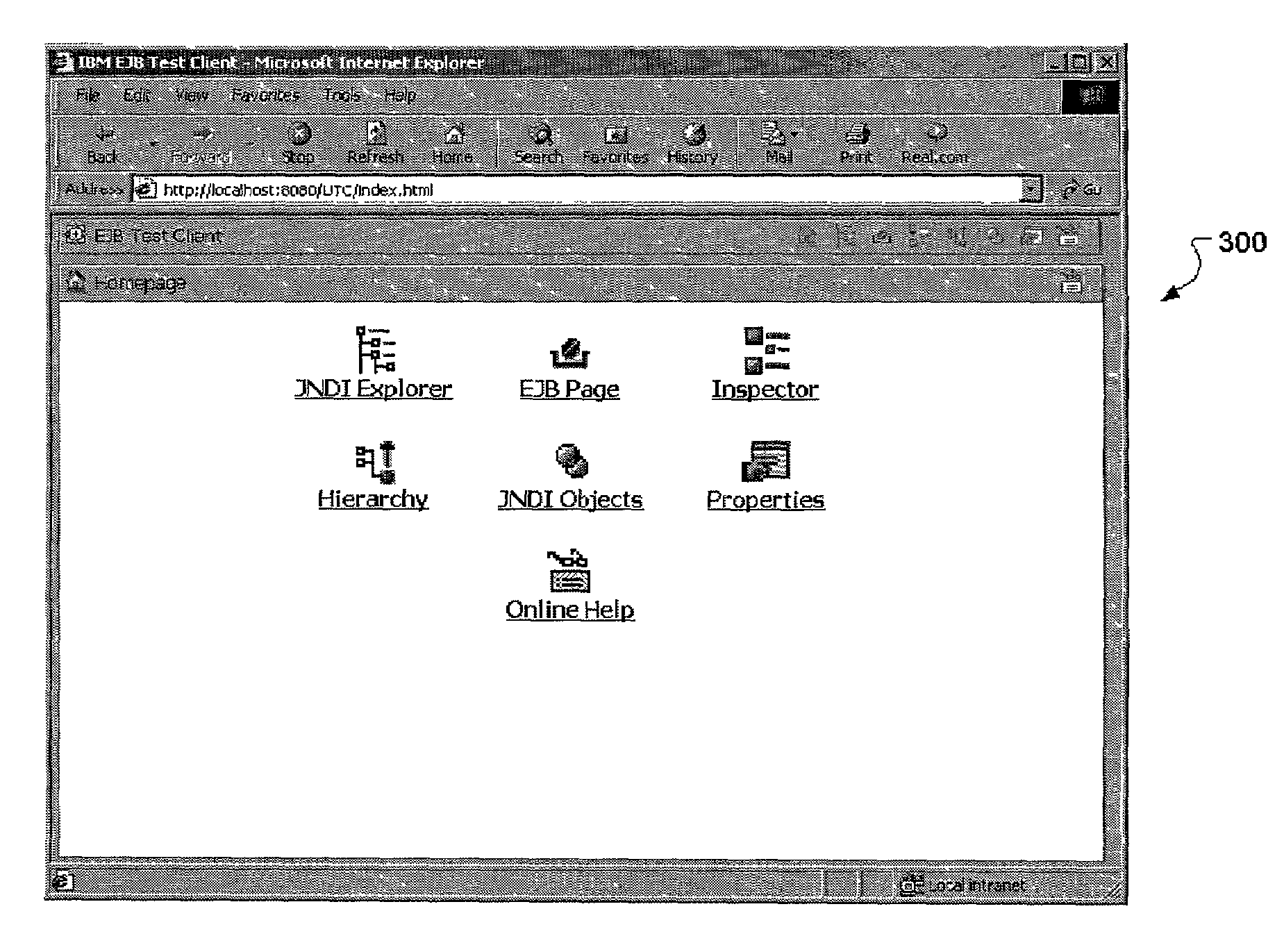
ActiveUS7043460B2Easy to testDigital computer detailsSoftware testing/debuggingWeb browserApplication server
The universal, Web browser-based Enterprise JavaBean (EJB) test client is itself a Java 2 Enterprise Edition (J2EE) application packaged in a Web archive file. This archive, when extracted, consists of a set of files that are installed on a target application server. The installation makes it possible for a user of a Web browser on a workstation remote from the application server to perform a number of tests on, and invoke, methods in EJB beans that are installed on the staging, or even production, servers. It is also possible to perform tests in real time under real conditions.
Owner:TWITTER INC
Method for enumerating data pages in a stateless, distributed computing environment
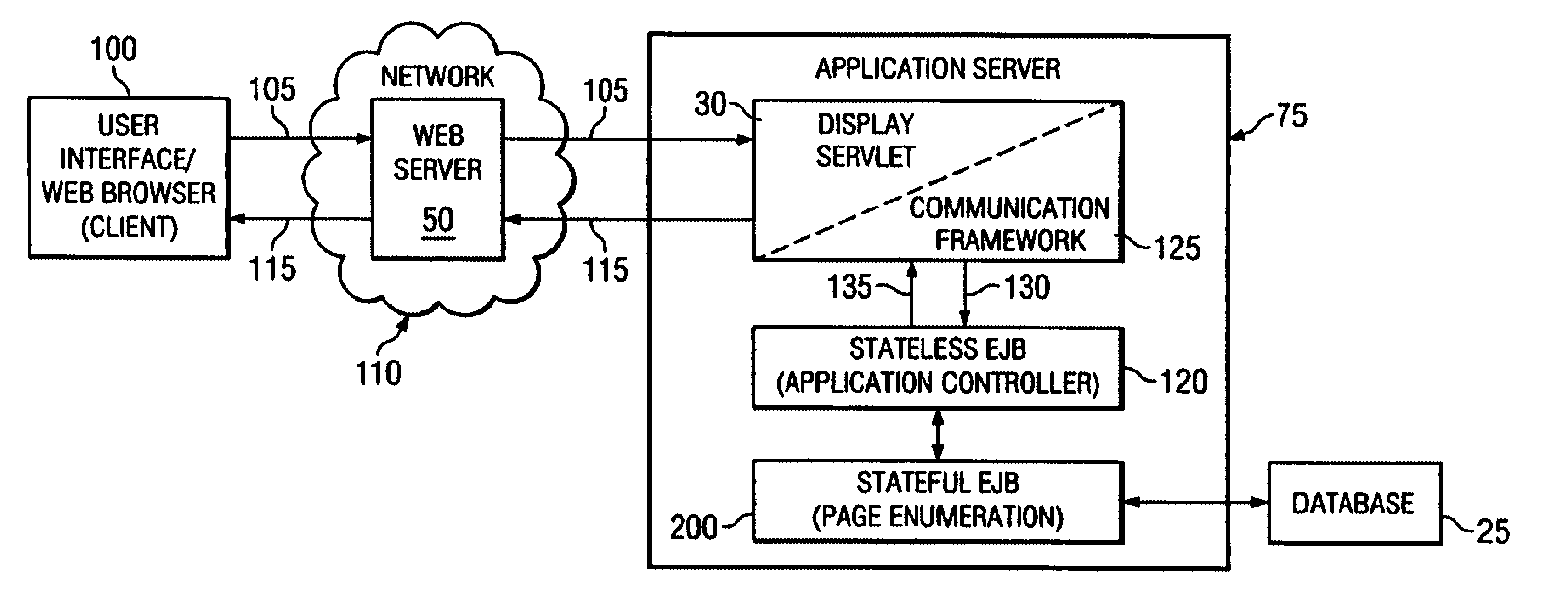
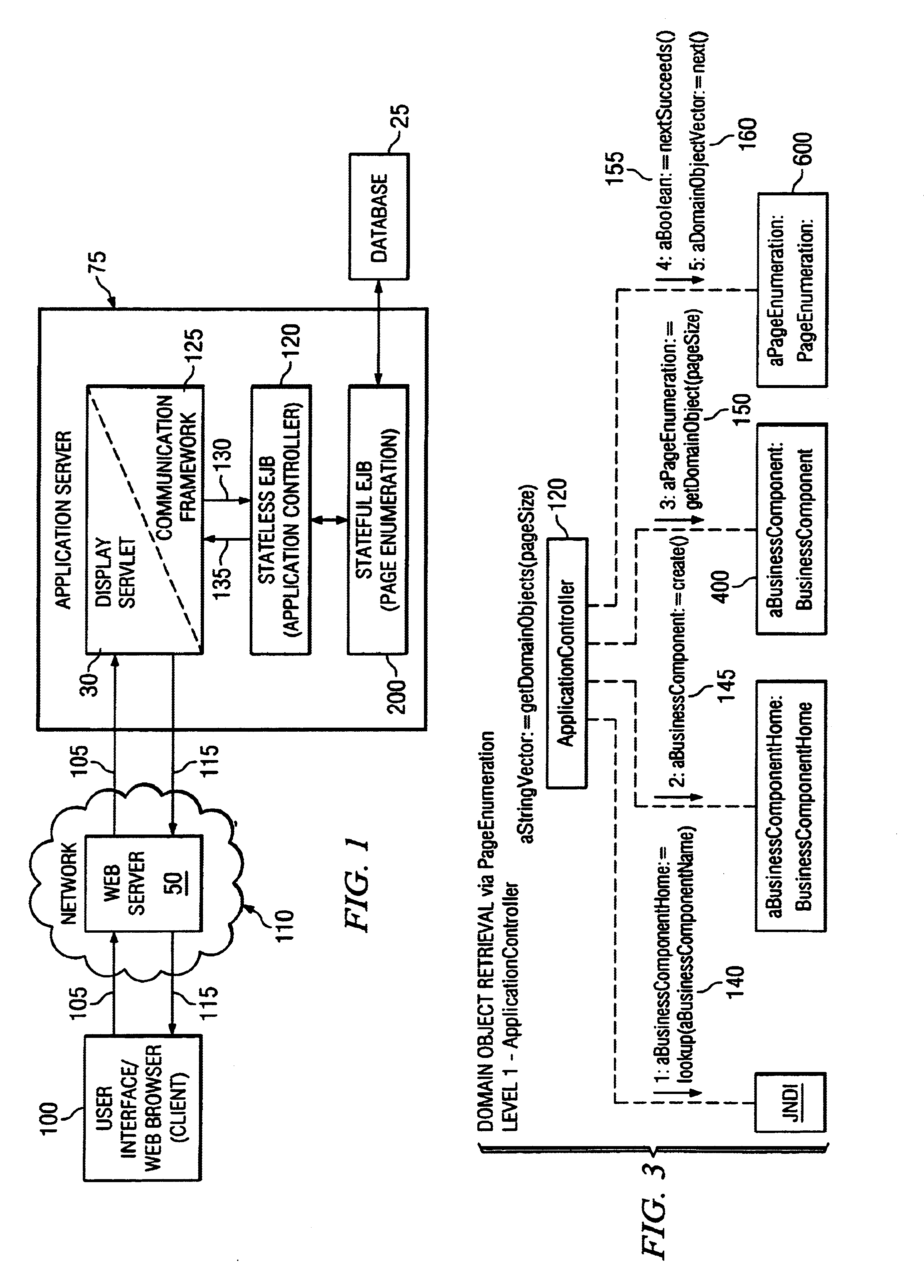
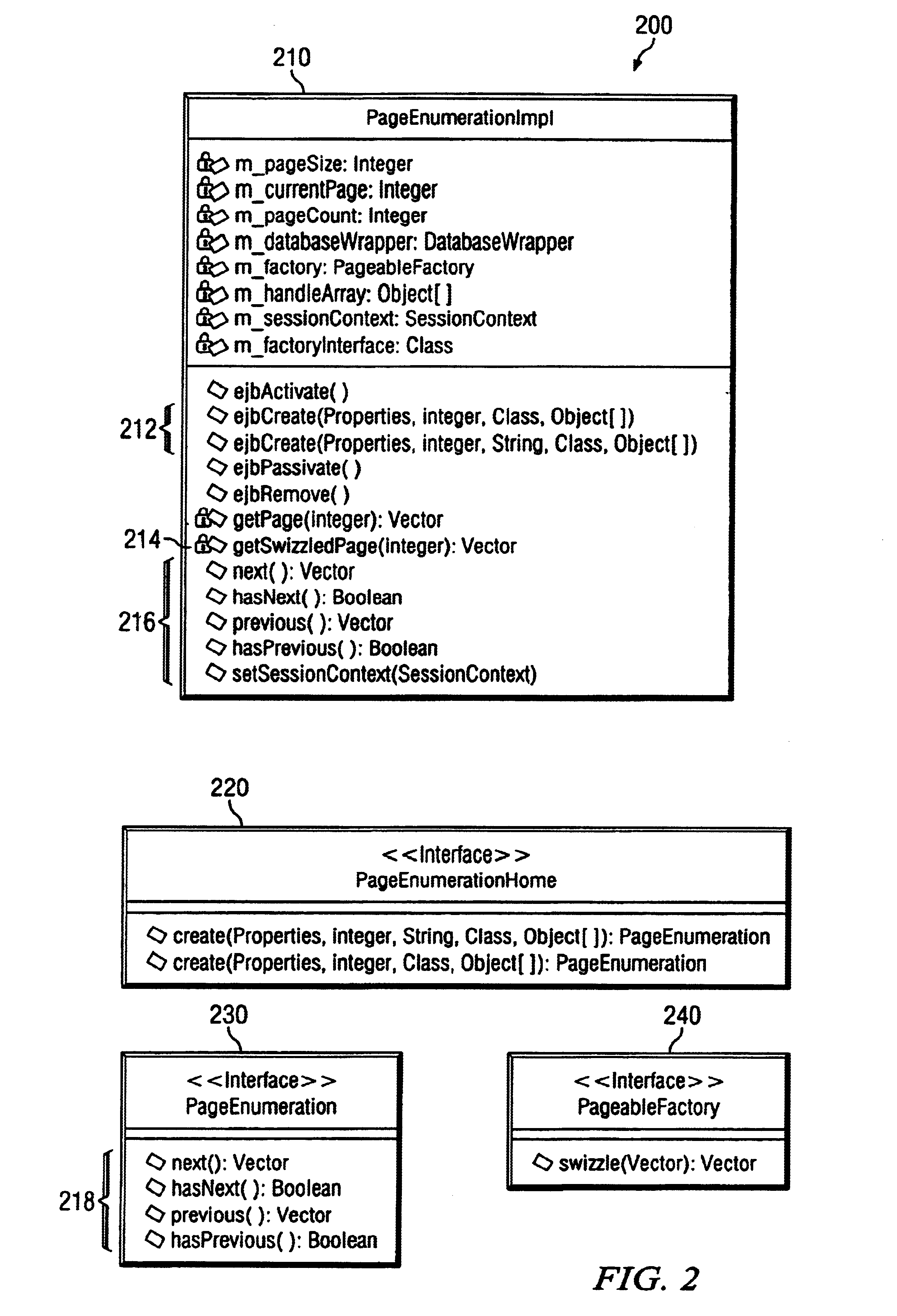
InactiveUS6856995B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDistributed Computing EnvironmentApplication software
The present invention discloses a method for enumerating data pages in a stateless, distributed computing environment. A user operating a uses interface calls a stateless application, which in turn invokes a stateful data structure to retrieve data from a datastore. Stateful data residing within the stateful data structure is converted to stateless data, and a display page comprising stateless data is returned to the user. Preferably, the stateless application and the stateful data structures are Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) compliant session beans. In a preferred embodiment, a servlet generates the display page by retrieving the stateless data from the stateful session bean, the display page is returned to the user interface via a communication framework, and data is retrieved from the datastore via a persistence framework.
Owner:CENTURYLINK INTPROP
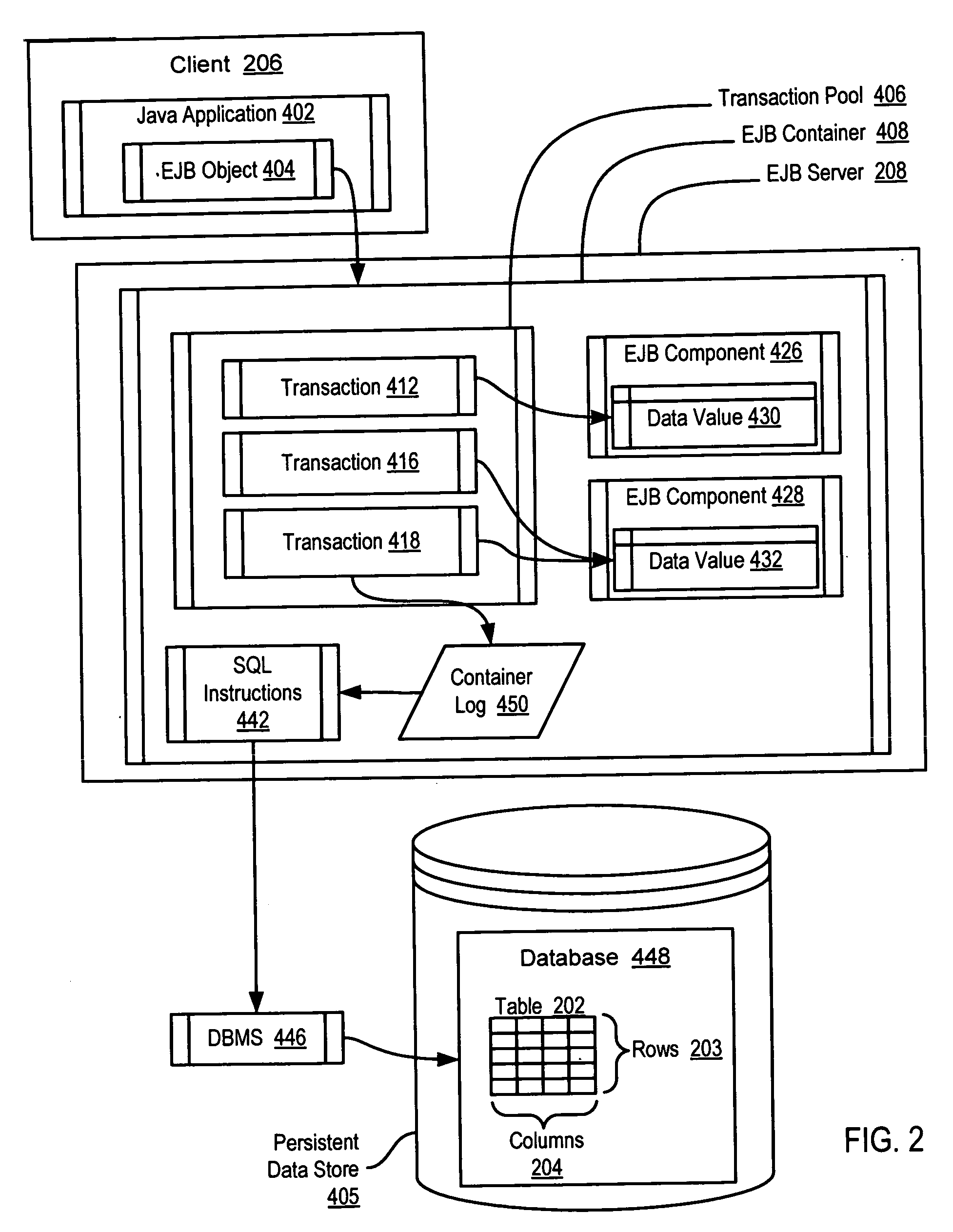
Managing transactions for Enterprise JavaBeans
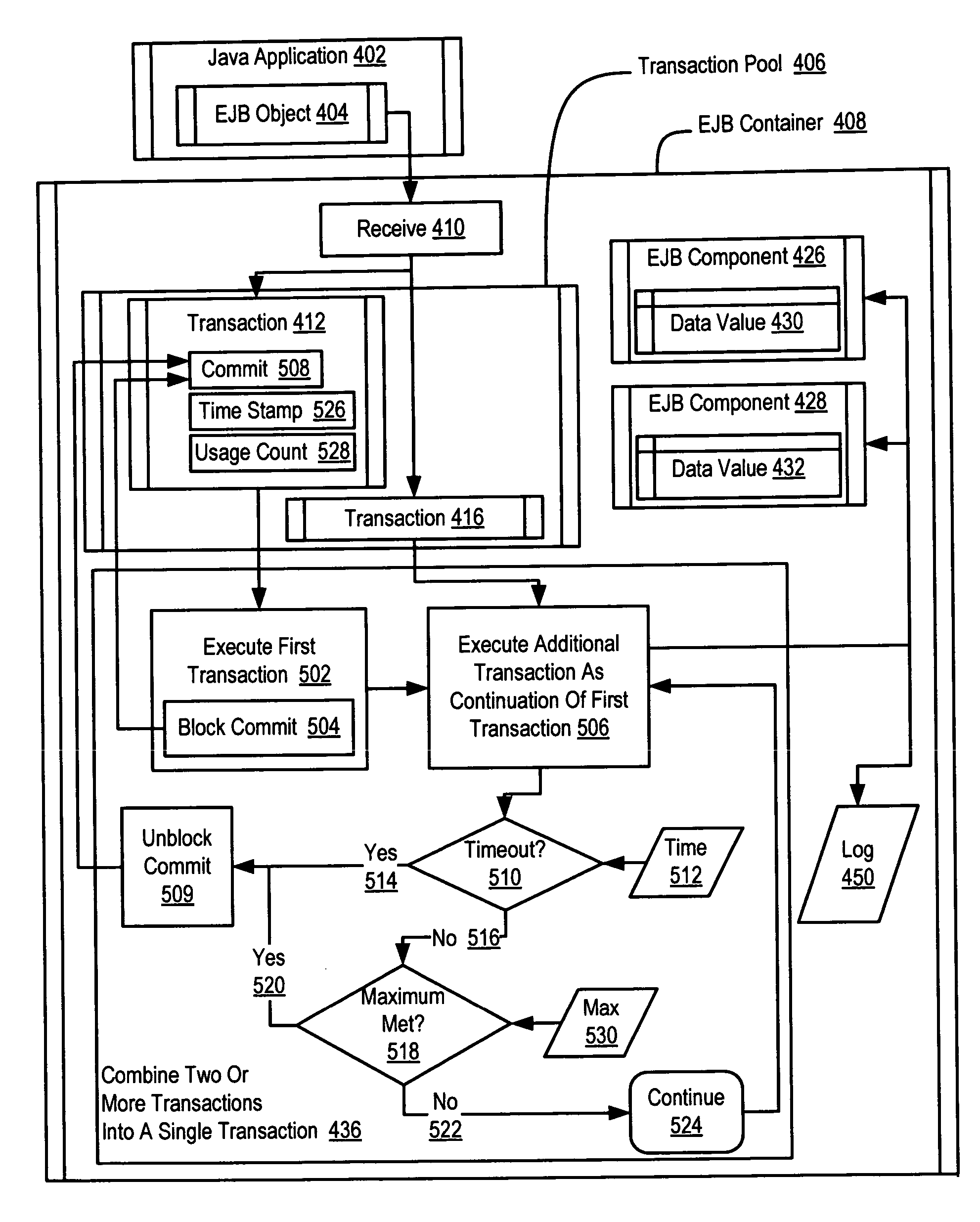
InactiveUS20060230402A1Improve efficiencySoftware simulation/interpretation/emulationMemory systemsEnterprise Java BeanData value
Exemplary methods, systems, and products are disclosed for managing transactions for Enterprise Java Beans (“EJBs”) that typically include receiving in an EJB container a plurality of container managed transactions for EJB components having container managed persistence. Each transaction typically comprises at least one computer program instruction affecting a data value of an EJB component, and typical embodiments include combining two or more of the transactions into a single transaction. Typical embodiments also include combining two or more of the instructions into a single instruction. Embodiments may include maintaining, by an EJB container, a pool of open transactions.
Owner:IBM CORP
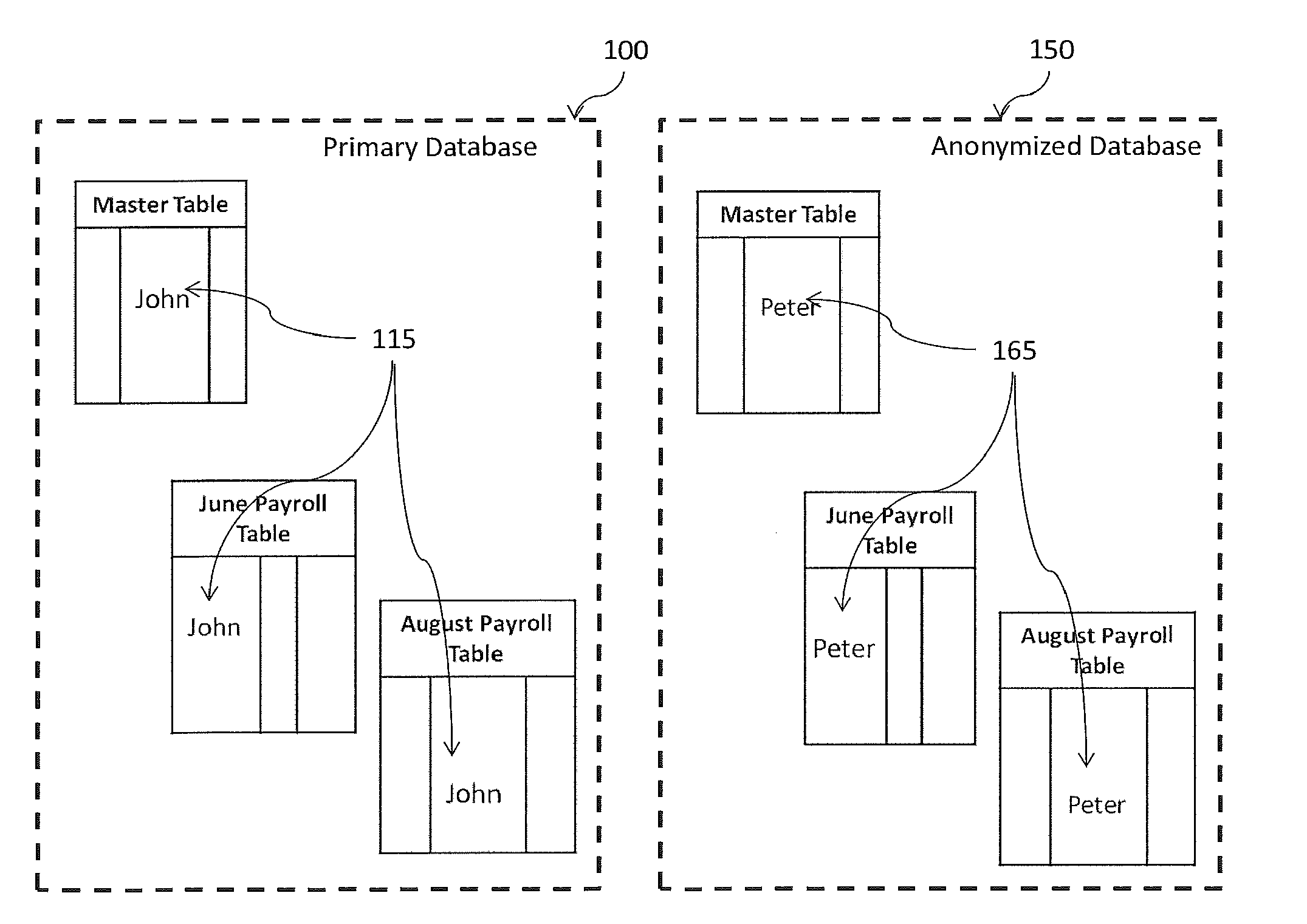
Secure data copying
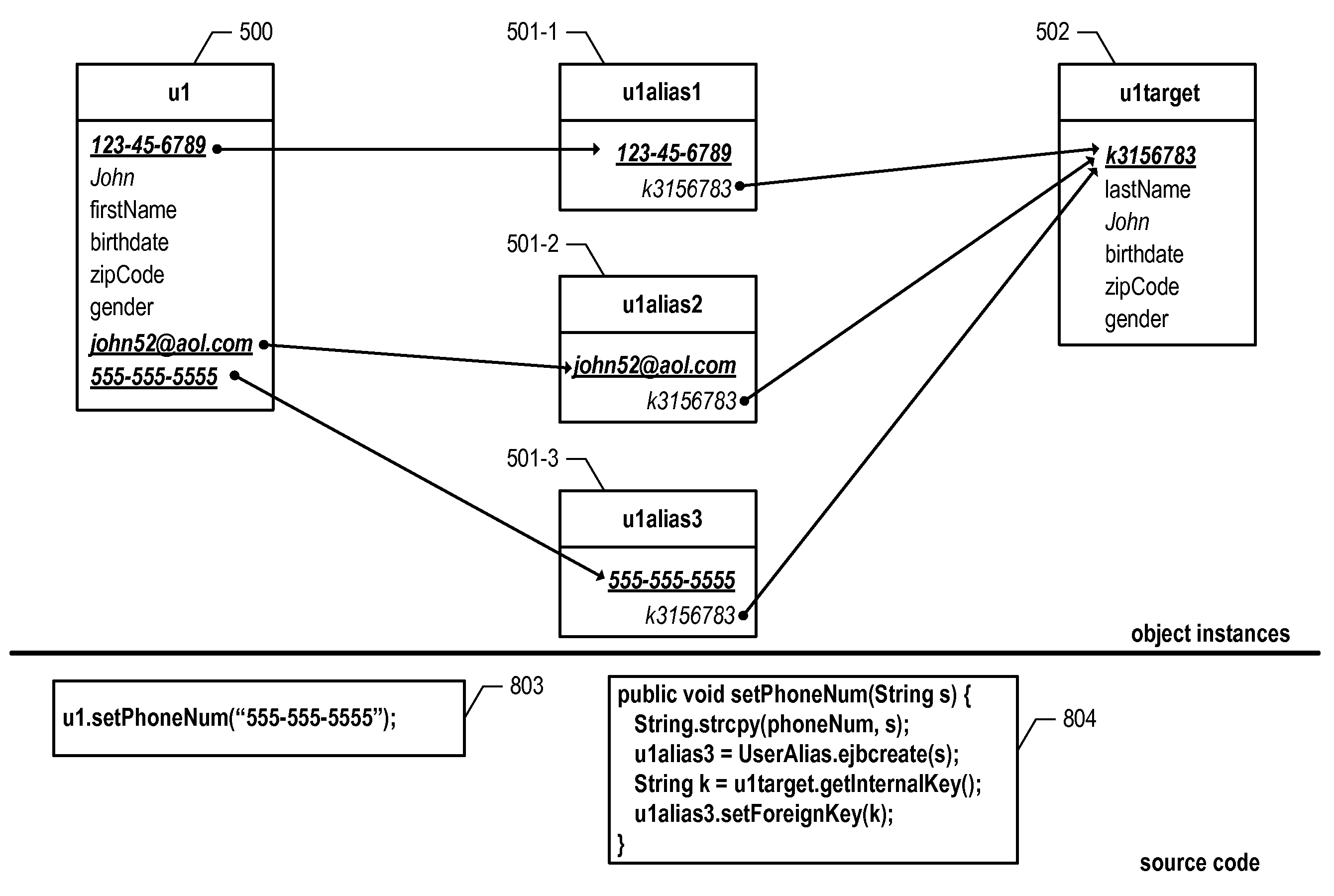
ActiveUS20140137262A1Digital data processing detailsError detection/correctionData fieldBusiness object
A method, computer program product, and system for the anonymization of sensitive data from a plurality of selected business objects or tables stored in a plurality of data fields in at least one primary database included in an enterprise database system when copying portions of the at least one primary database to a secondary database or updating an existing database with anonymized values for the sensitive fields therein. A plurality of data fields is specified for copying from the at least one primary database. At least one integrity map is generated and populated for each data field in the primary database requiring anonymization before copying to the secondary database. The at least one integrity map is stored in a table associated with the primary database. An anonymized value is generated for each data field in the primary database requiring anonymization. Each data field in the primary database requiring anonymization is substituted with the anonymized value. The portions of the at least one primary database including anonymized values are copied to a secondary database.
Owner:EPI USE SYST
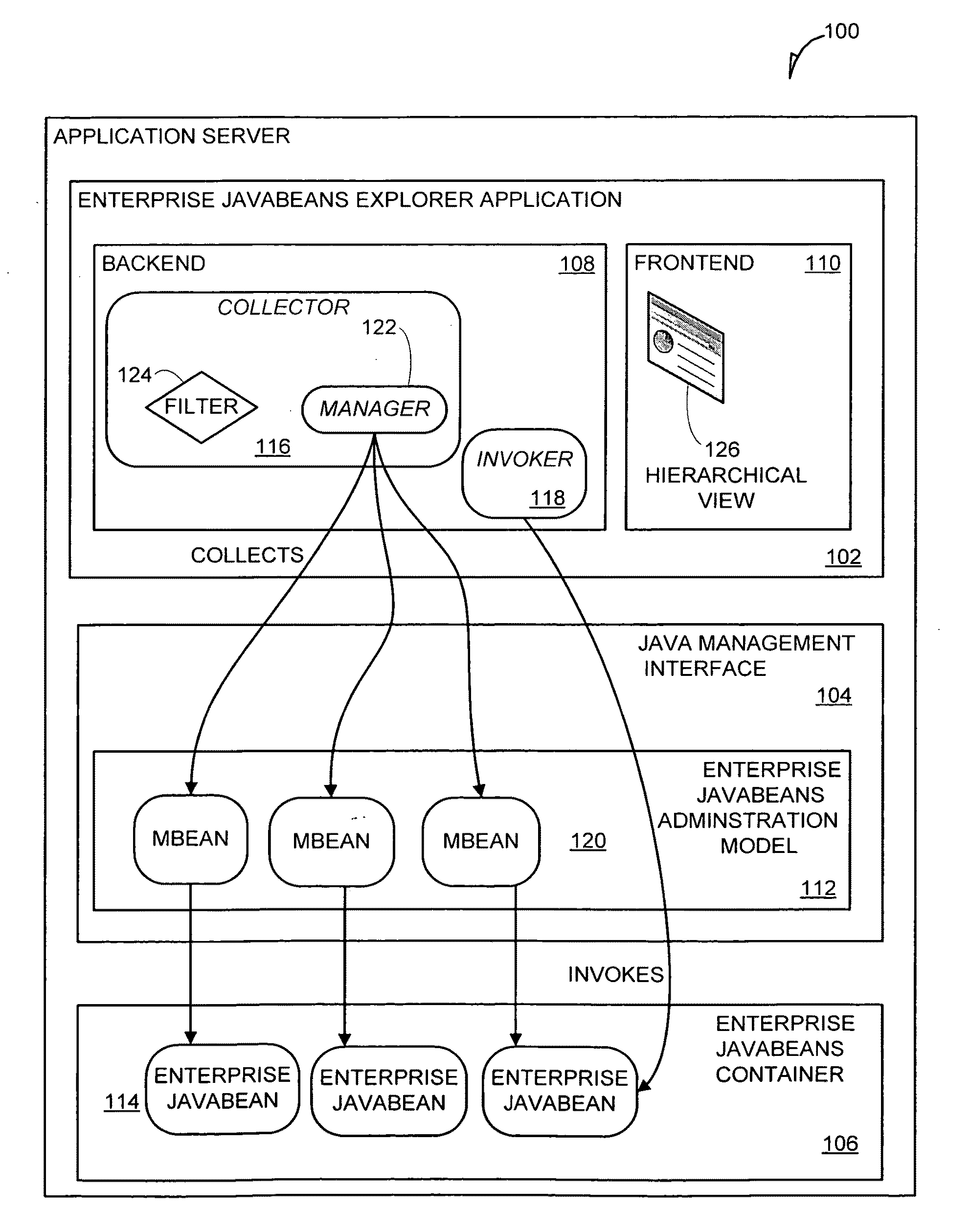
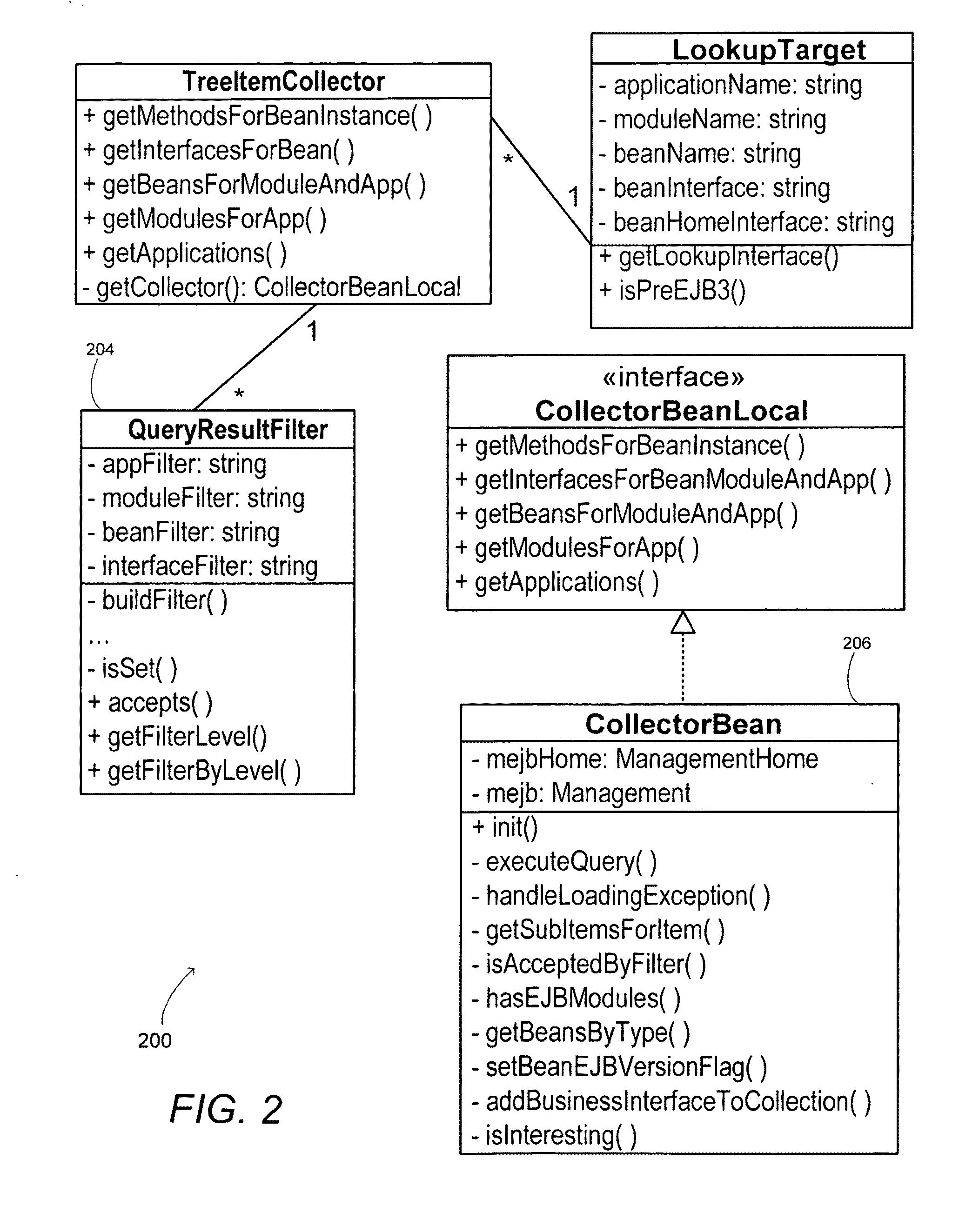
Enterprise javabeans explorer
A system and method to display an application server resource landscape in a hierarchical view and invoke an Enterprise JavaBeans business method with a complex object as an argument. In one embodiment, the hierarchical view permits user input to initialize attribute values for simple and complex arguments. A graphical user interface presents invoked business method execution results.
Owner:SAP AG
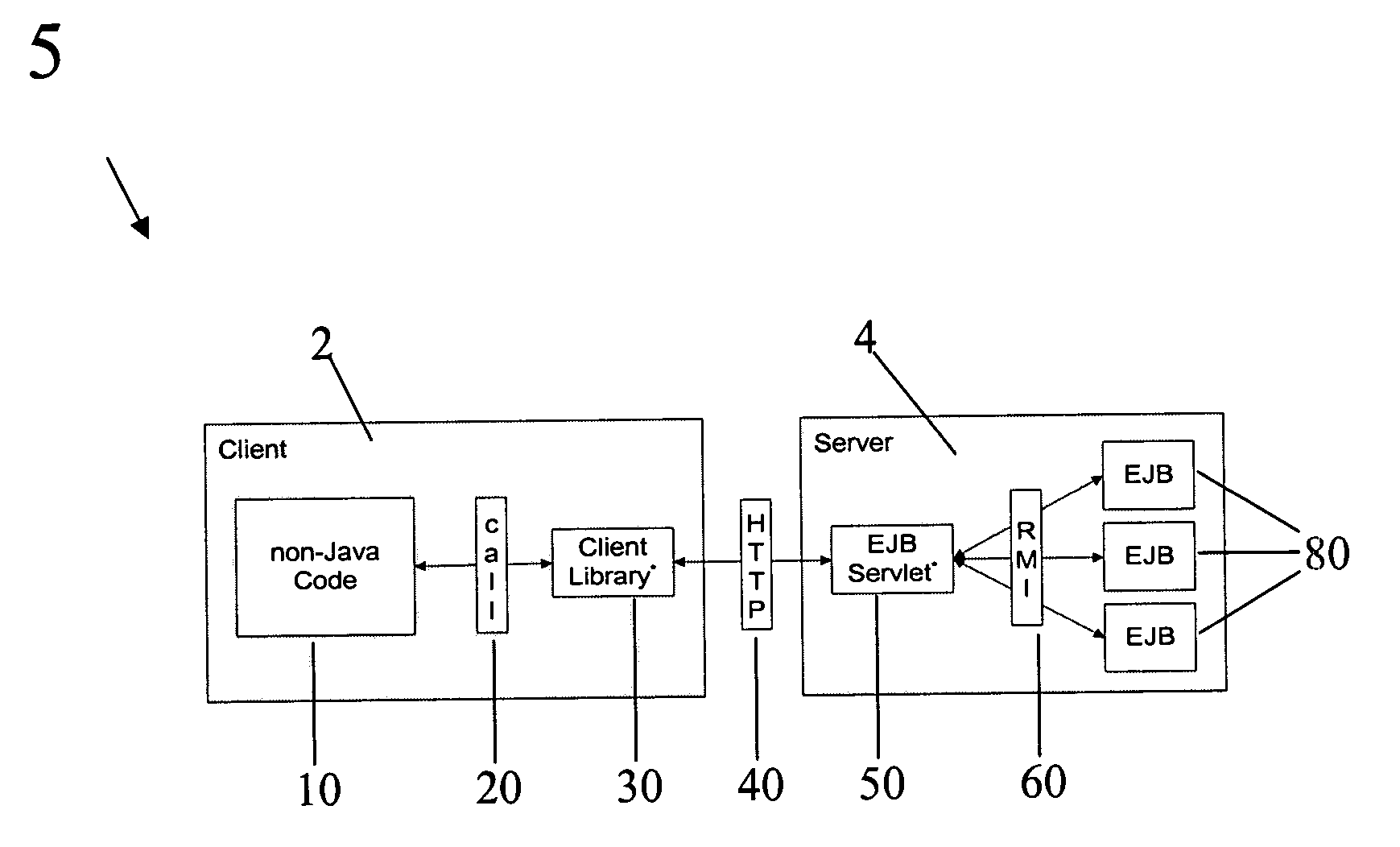
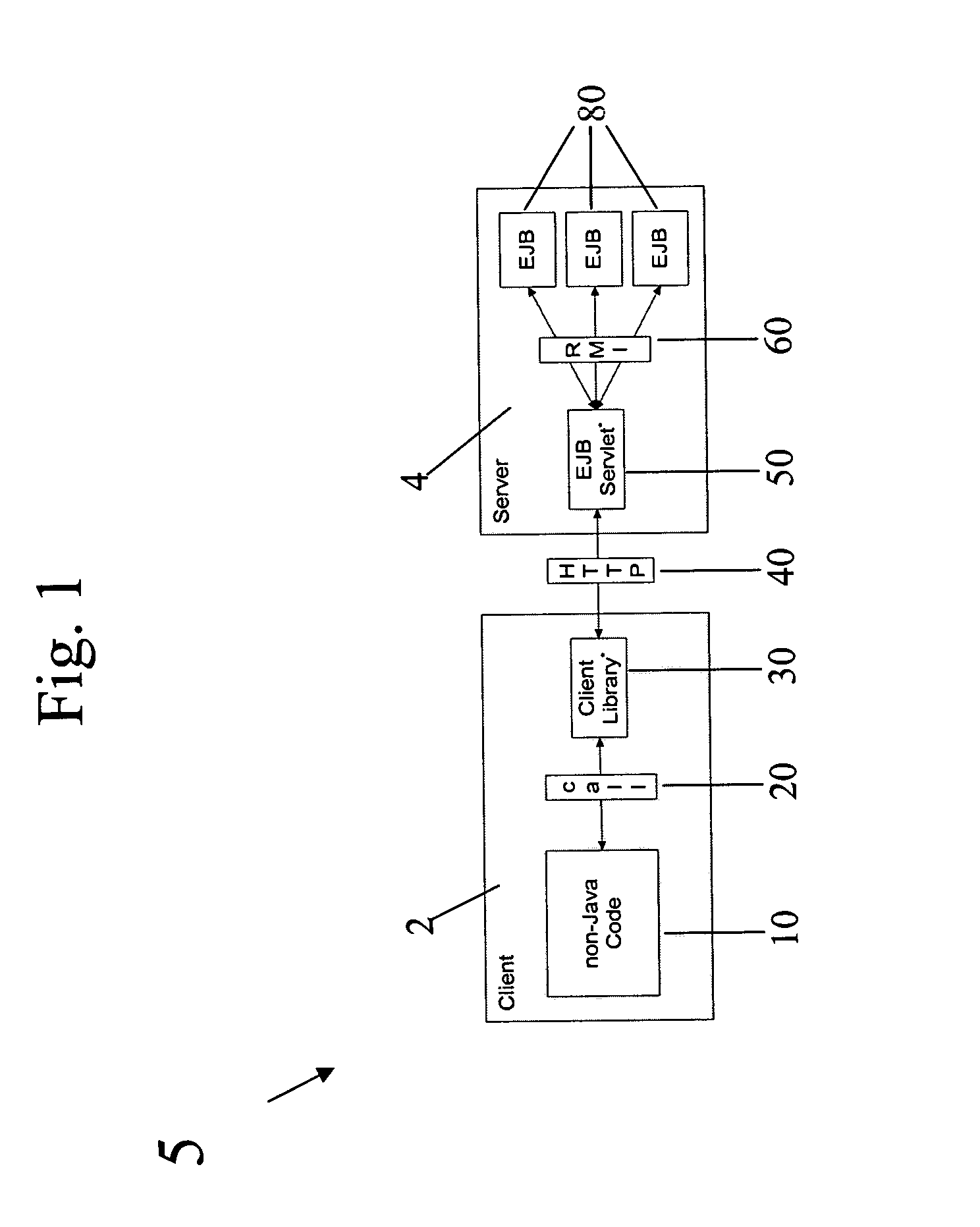
Computer method and system for integrating enterprise JavaBeans into non-Java environments
InactiveUS7617504B1Digital computer detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsEnterprise Java BeanApplication software
Disclosed herein is a method of accessing an Enterprise Java Bean (EJB) by a non-Java application within a computing environment, comprising: calling a client library by the non-Java application; invoking a function within the client library to construct an HTTP request corresponding to the calling input parameters from the non-Java application; passing the HTTP request from the client library to an EjbServlet; invoking a method on an EJB by the EjbServlet based upon the HTTP request; returning information from the invoked method from the EJB to the EjbServlet; decoding the returned information into an HTTP response string by the EjbServlet; transmitting the HTTP response from the EjbServlet to the client library; and parsing the HTTP response by the client library into return information compatible with the non-Java application and then passing the return information from the client library to the non-Java application.
Owner:T MOBILE INNOVATIONS LLC
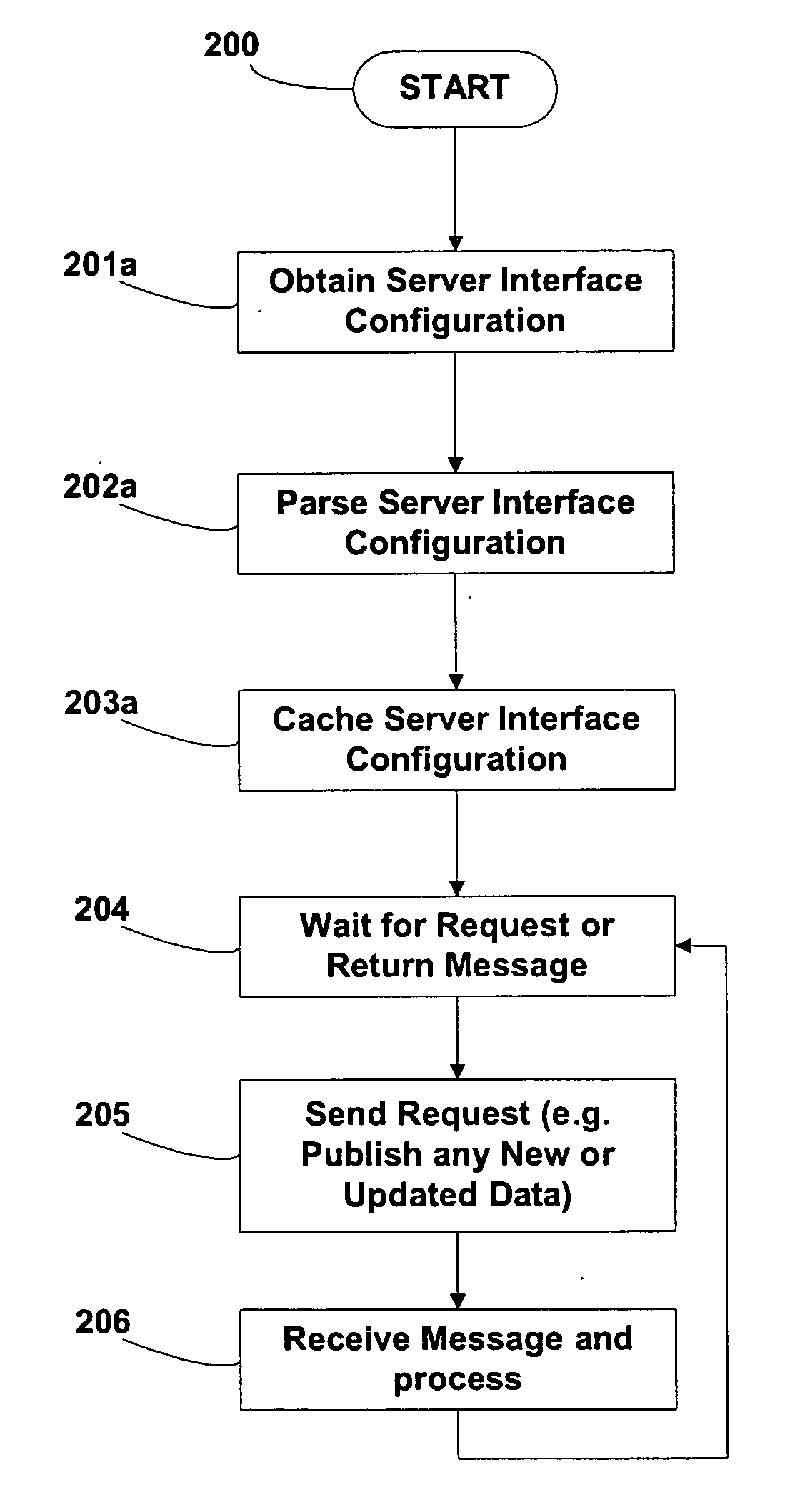
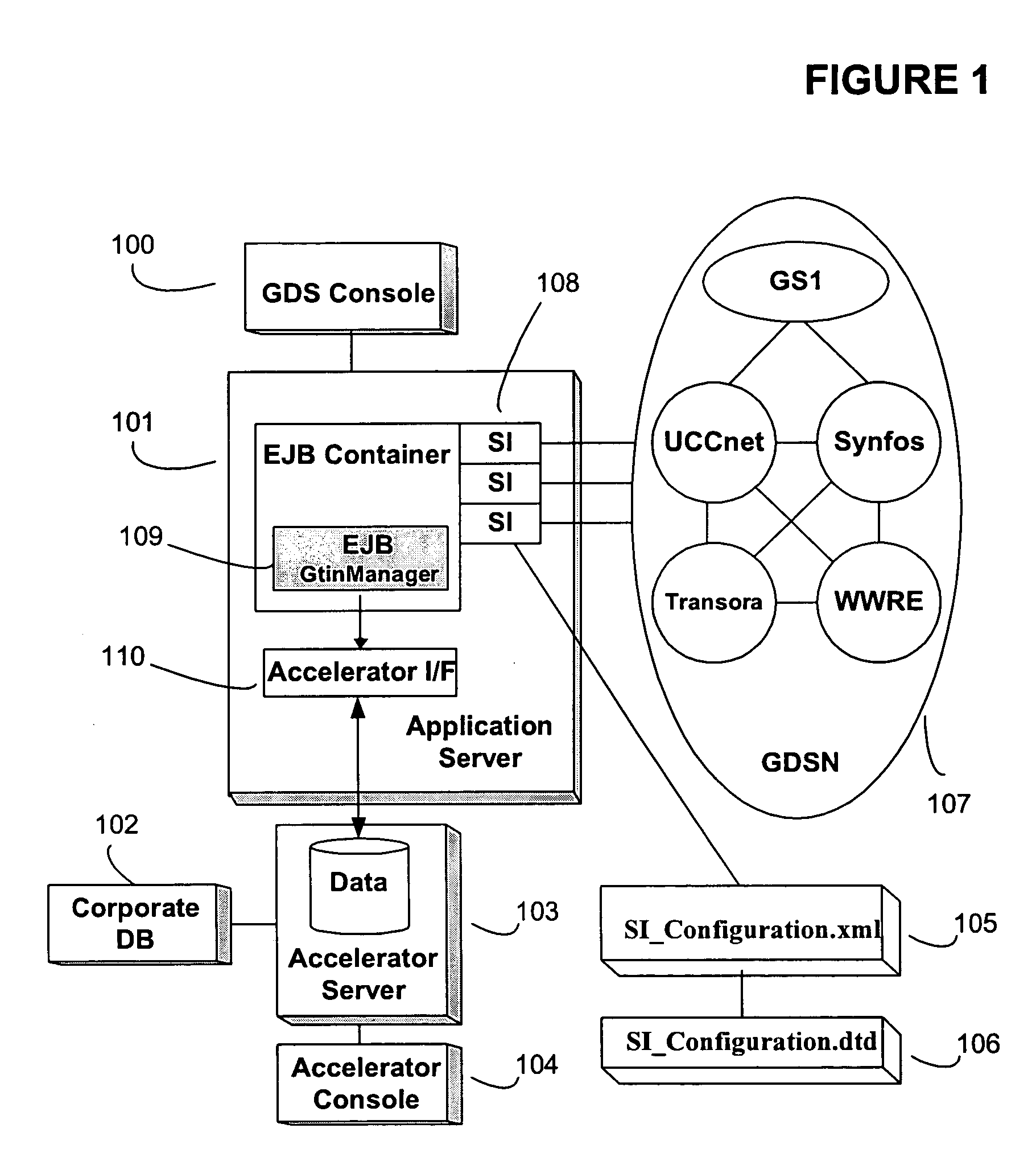
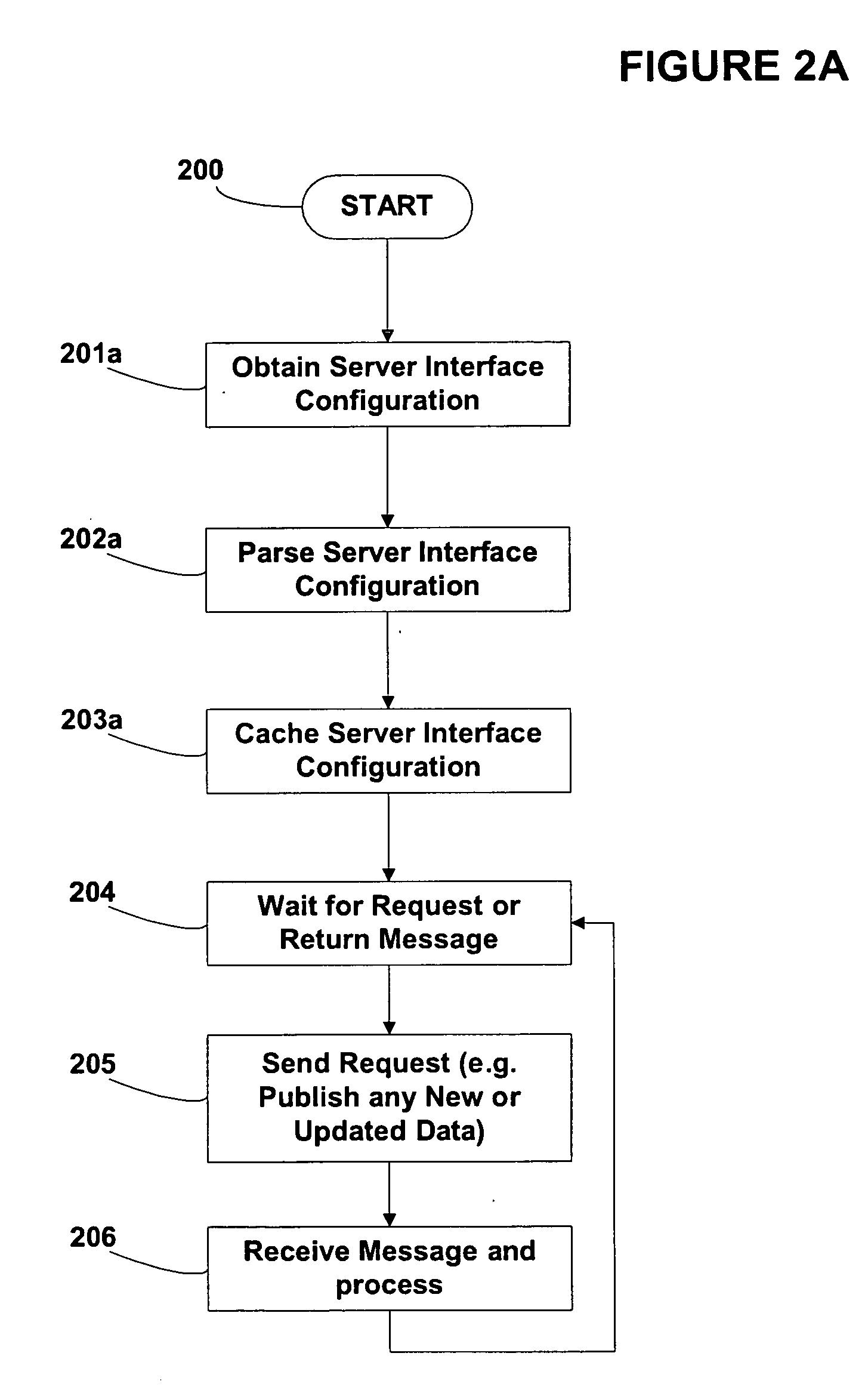
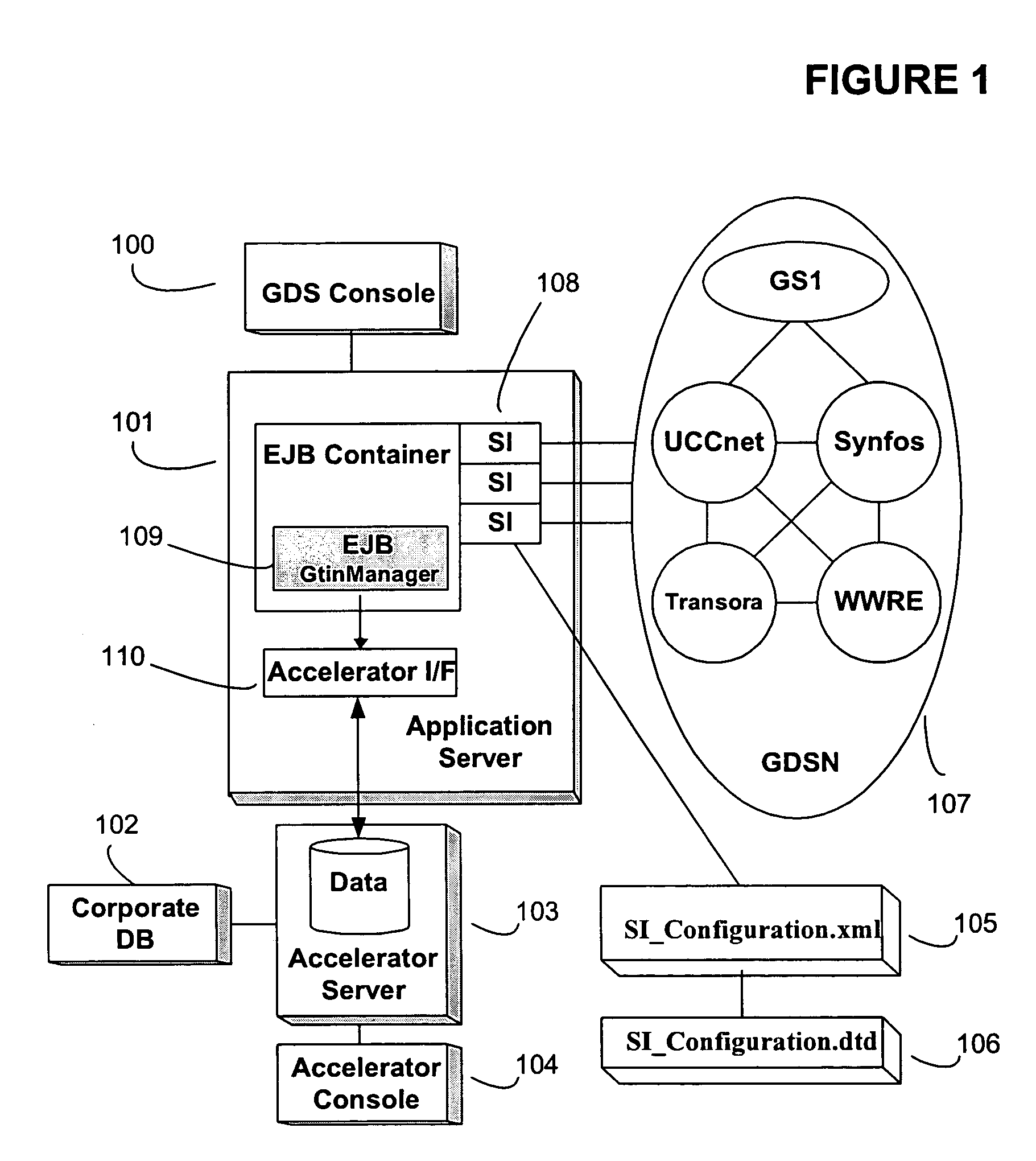
System and method for dynamically modifying synchronized business information server interfaces
ActiveUS20070061427A1Quick couplingReduce skillsDigital computer detailsDatabase distribution/replicationApplication serverConfigfs
One or more embodiments of the invention enable data that is synchronized between businesses to be transferred to any desired data pool or data pool version in a format that may be declaratively specified and dynamically altered to meet the needs of the specific data pool or data pool version. The data pool vendor utilized by a company or the attributes and formats used in communicating with a particular data pool may change over time and embodiments of the invention are capable of automatically detecting and altering the data and format of the data to be transferred to and from the data pool. The server interface configuration may comprise an XML file in one embodiment of the invention. The XML file may be parsed with any compliant schema based or DTD based XML parser and sent to the server interface for dynamic update using JMS for example. The server interface itself may be implemented or make use of a Resource Adapter configured to operate within the Java Connector Architecture of the Enterprise JavaBeans specification. In at least one embodiment of the invention an N-tier architecture may be employed comprising an Application Server. The server interface accepts an incoming server interface configuration request and utilizes information derived from the XML configuration file in order to add or remove data attributes or alter the format of the data attributes that are transferred to and from each data pool. In this embodiment of the invention, data pools may be switched by at run-time without recompiling and redistributing the application.
Owner:SAP AG
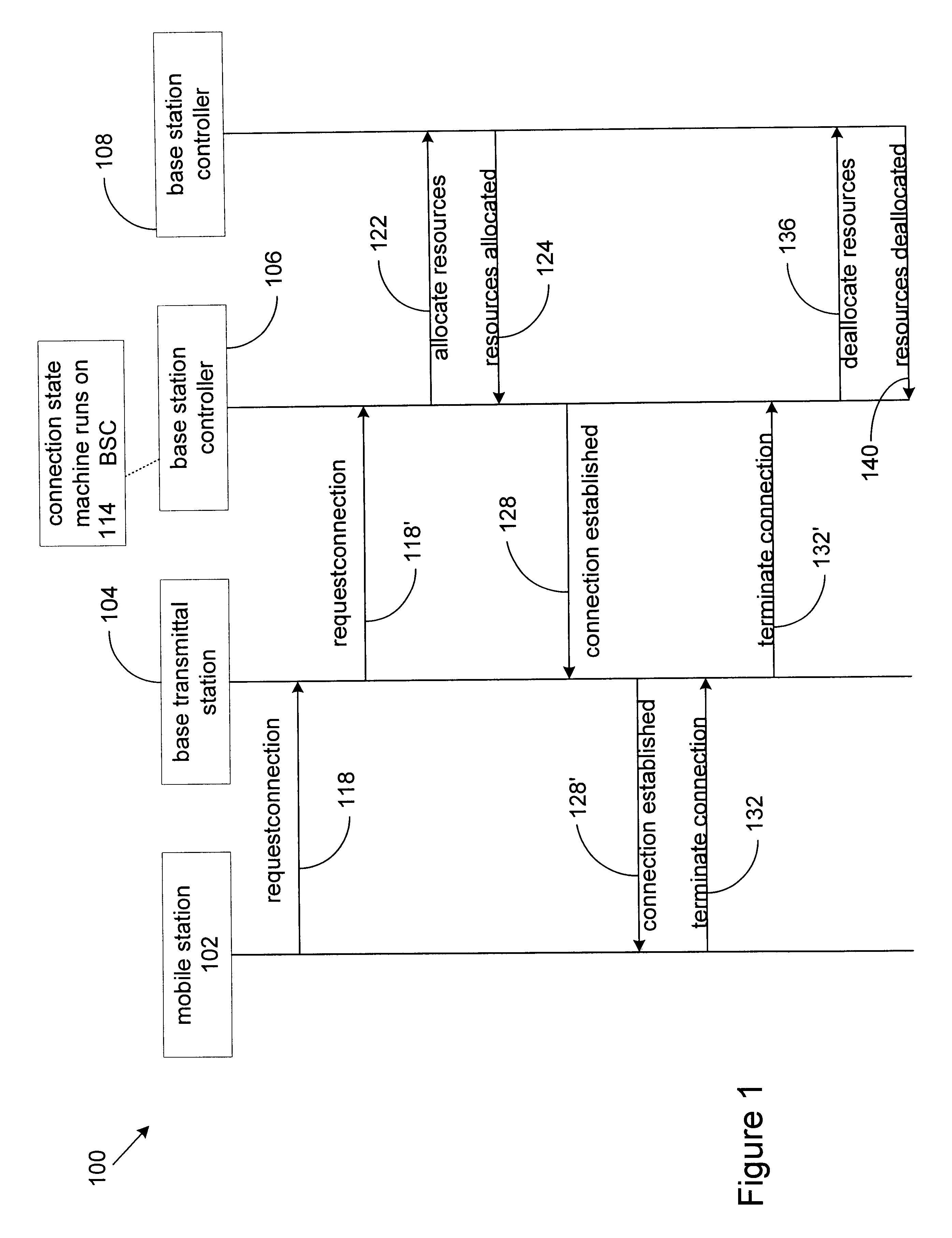
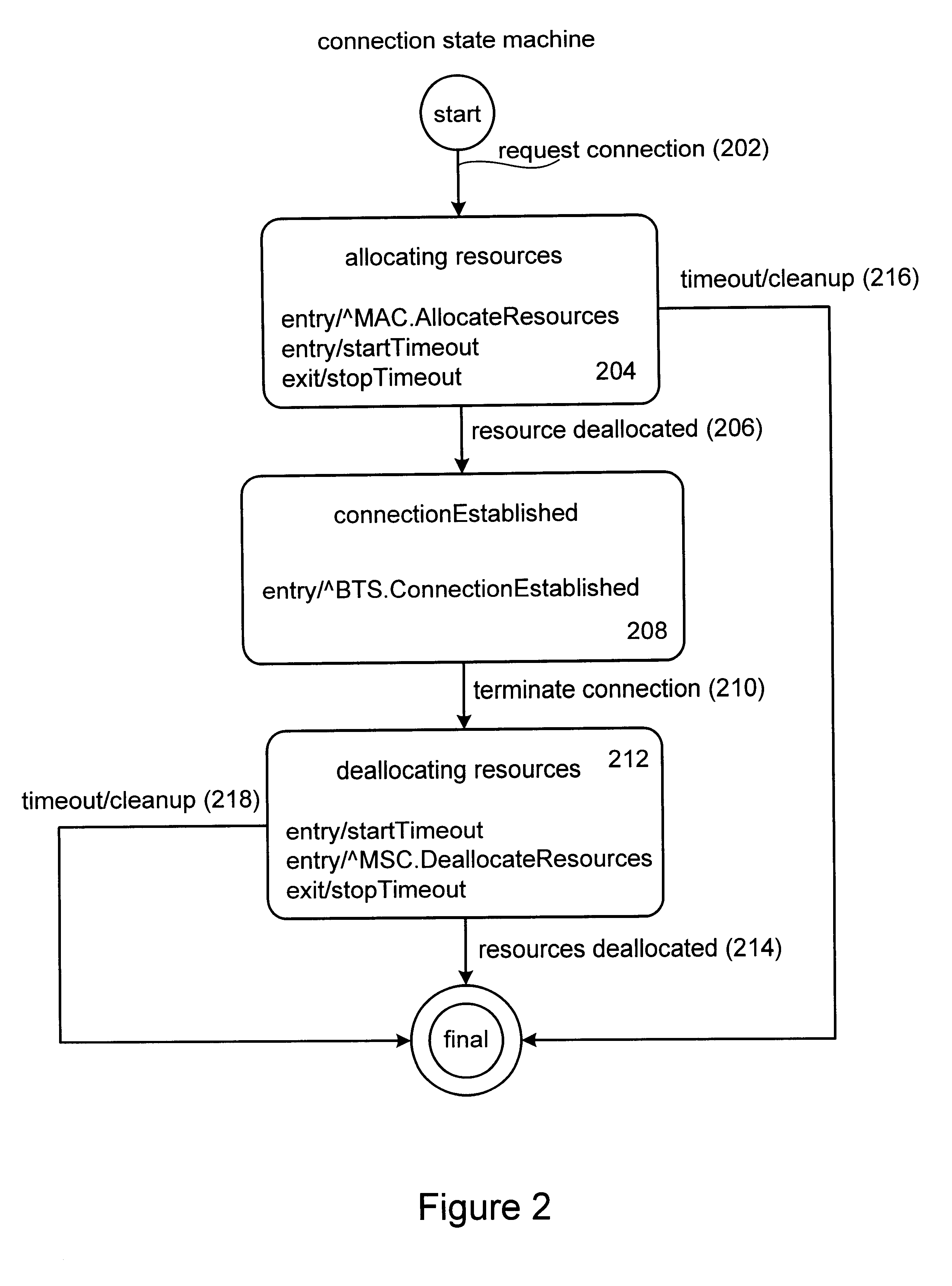
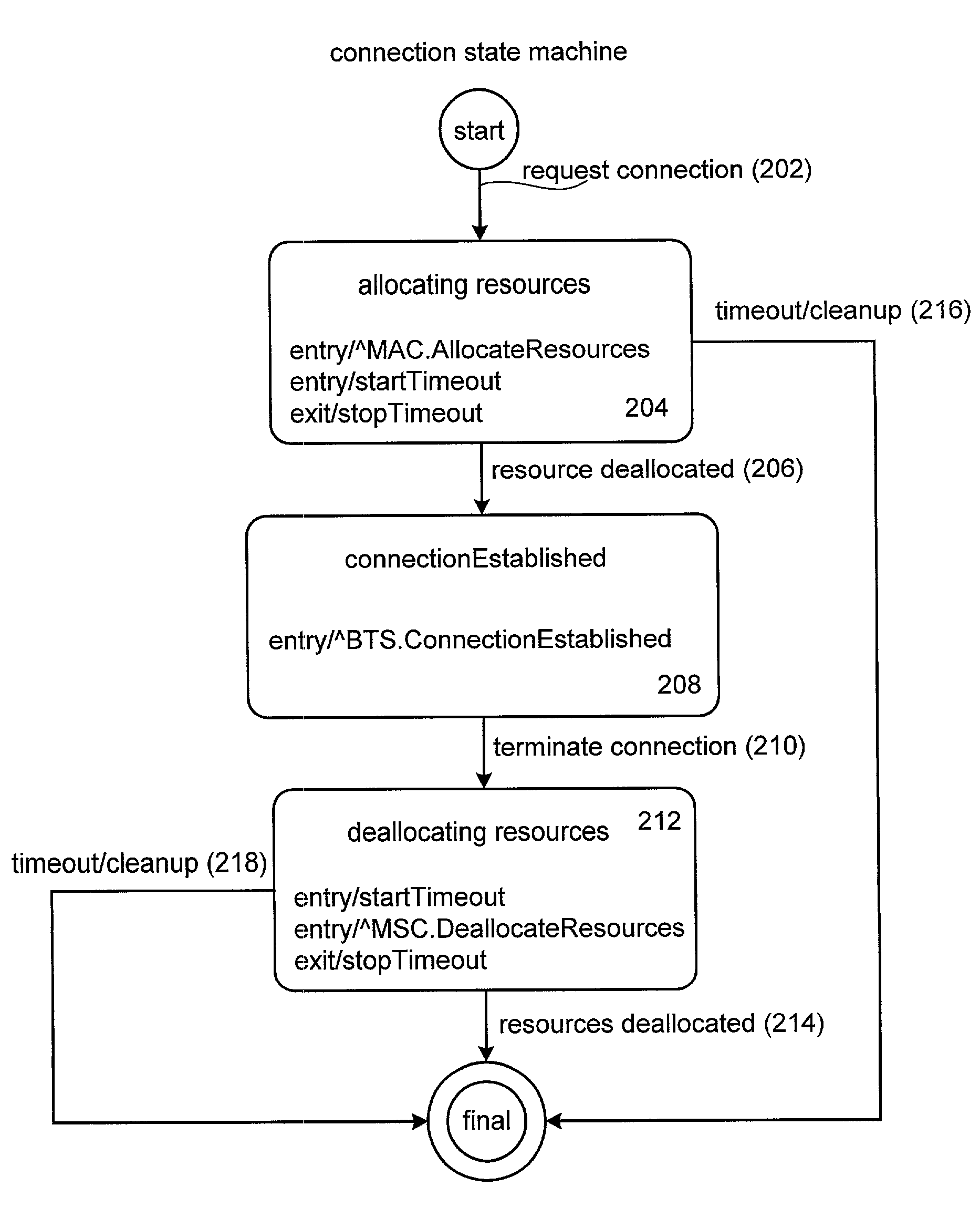
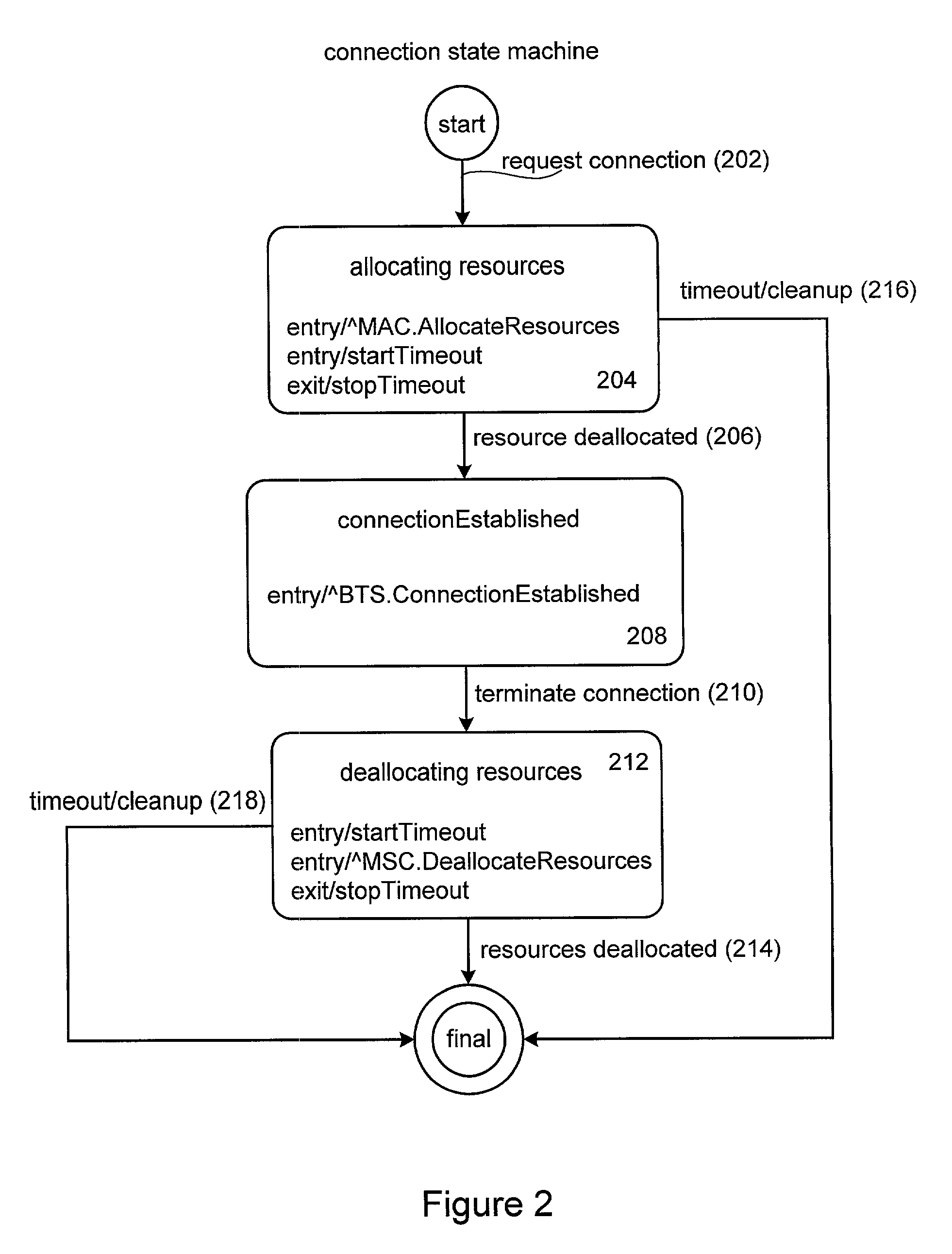
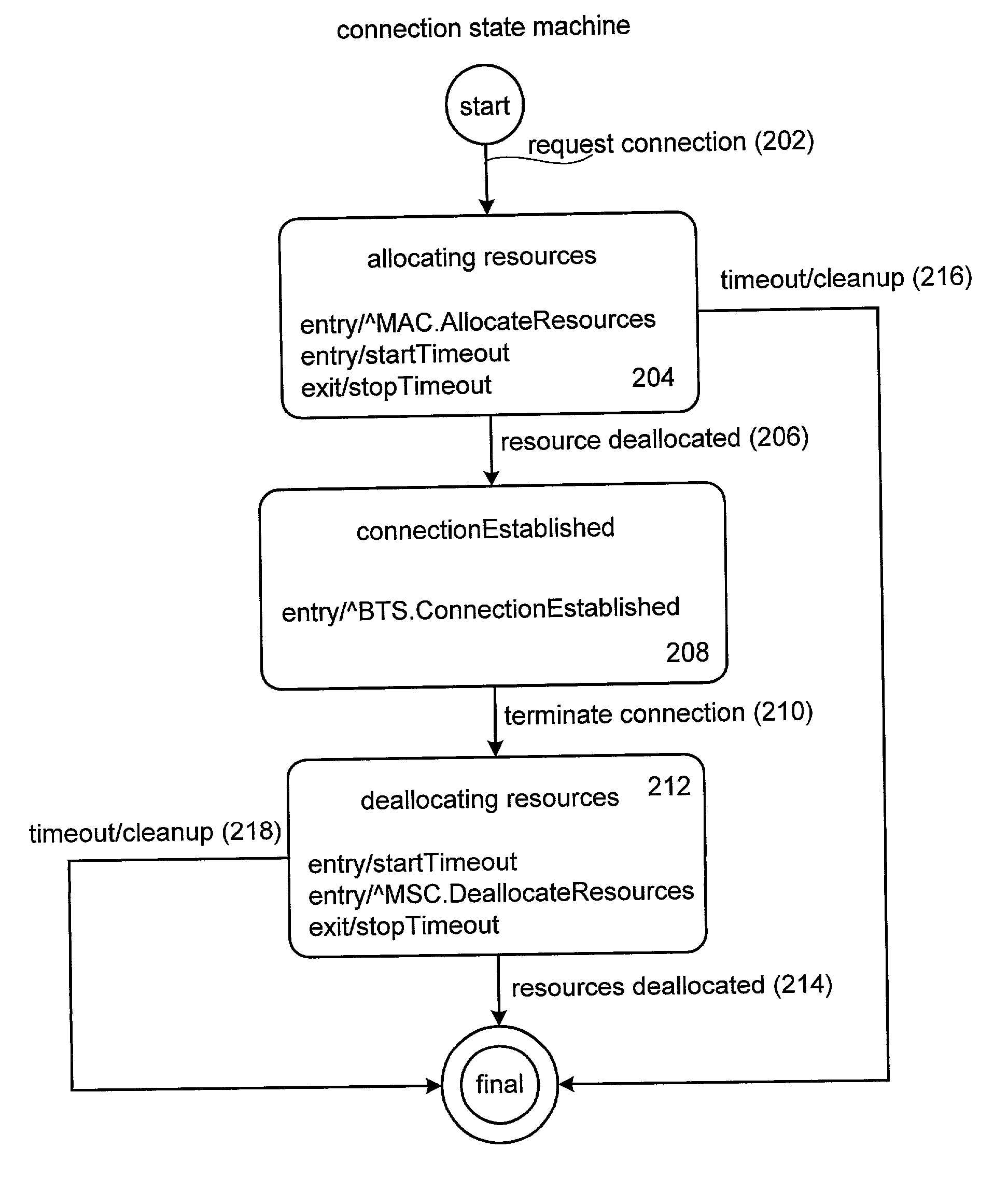
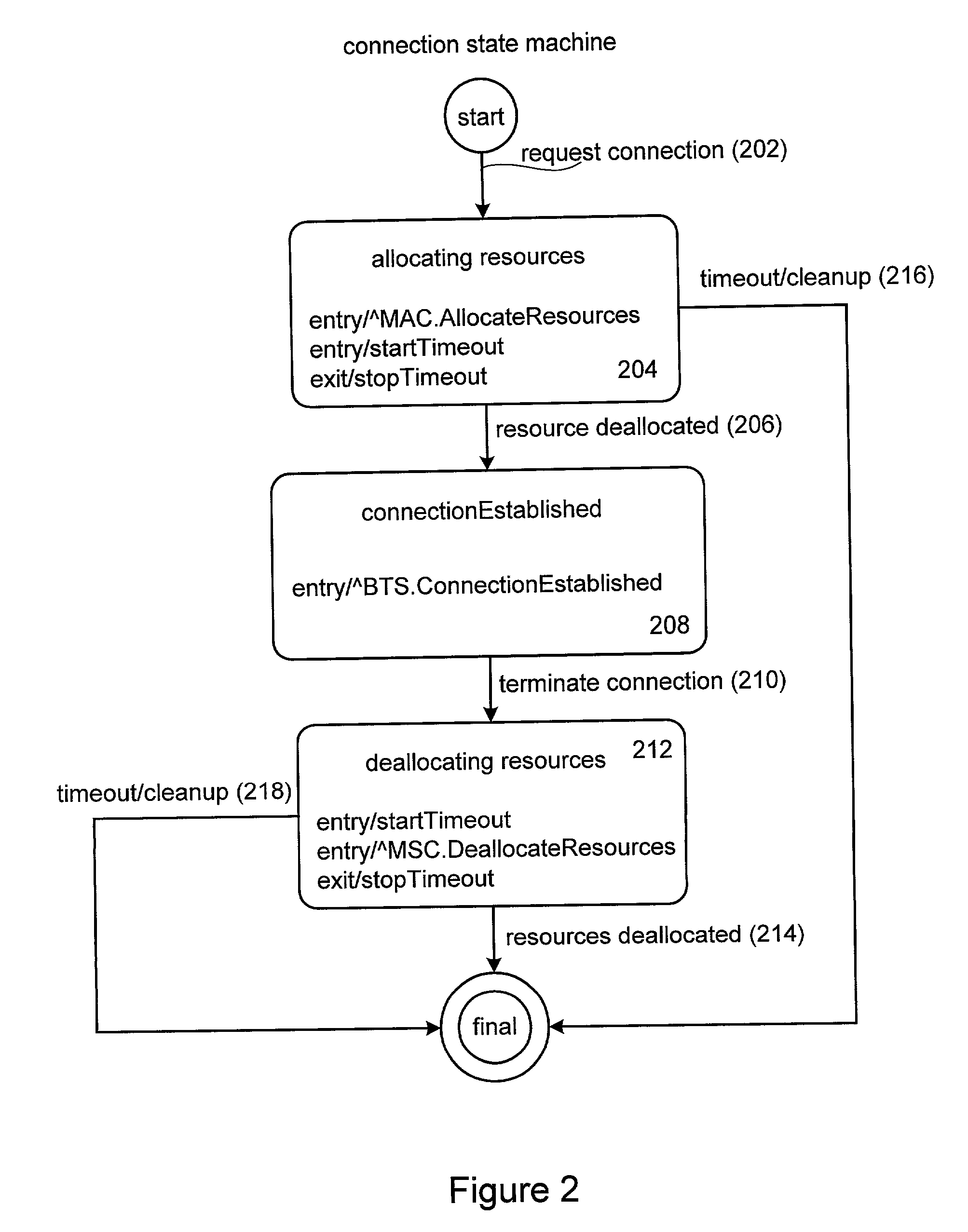
Method and apparatus for implementing timers for enterprise javabean components
InactiveUS6807547B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsProgramming languageTimer
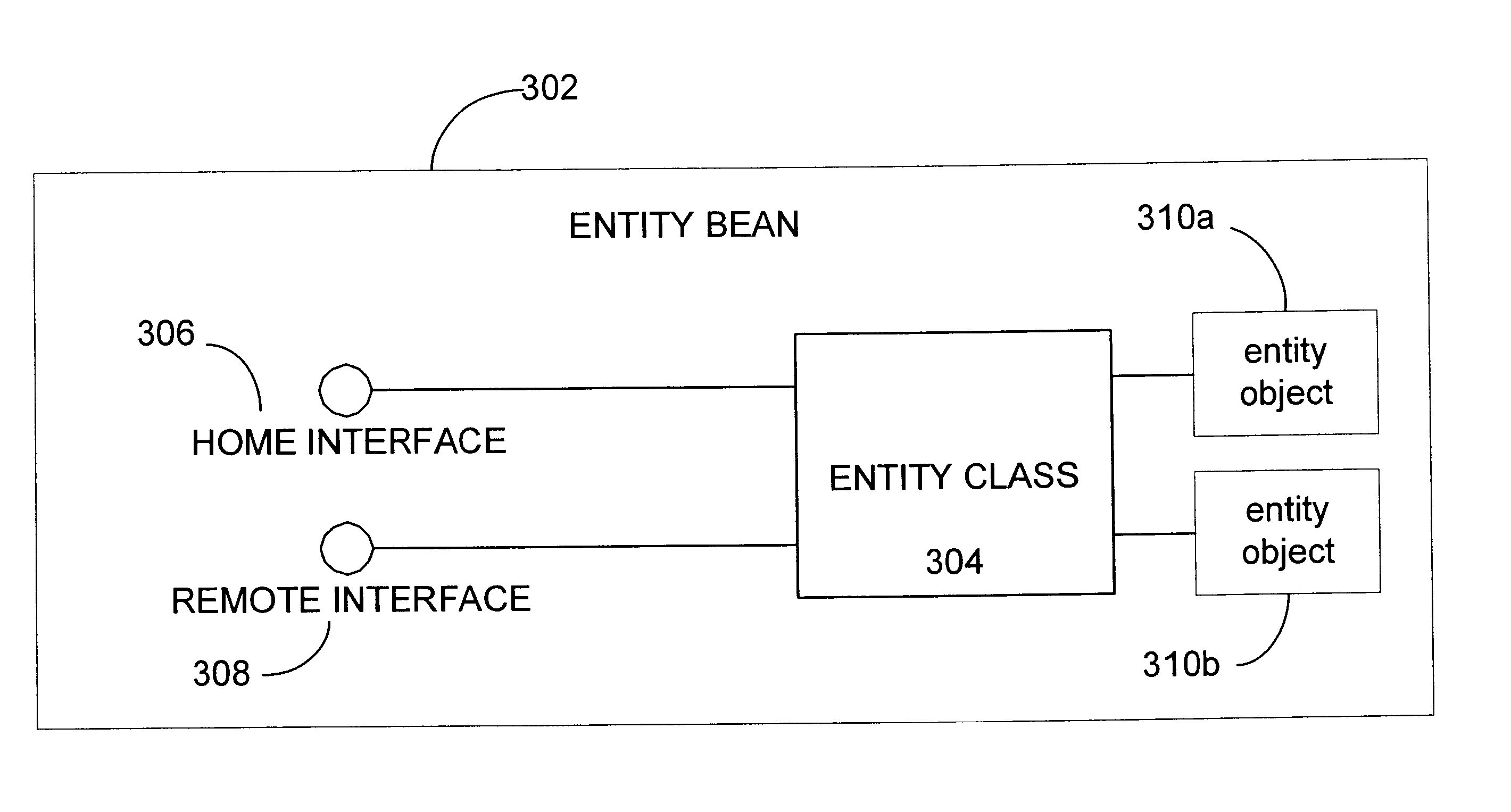
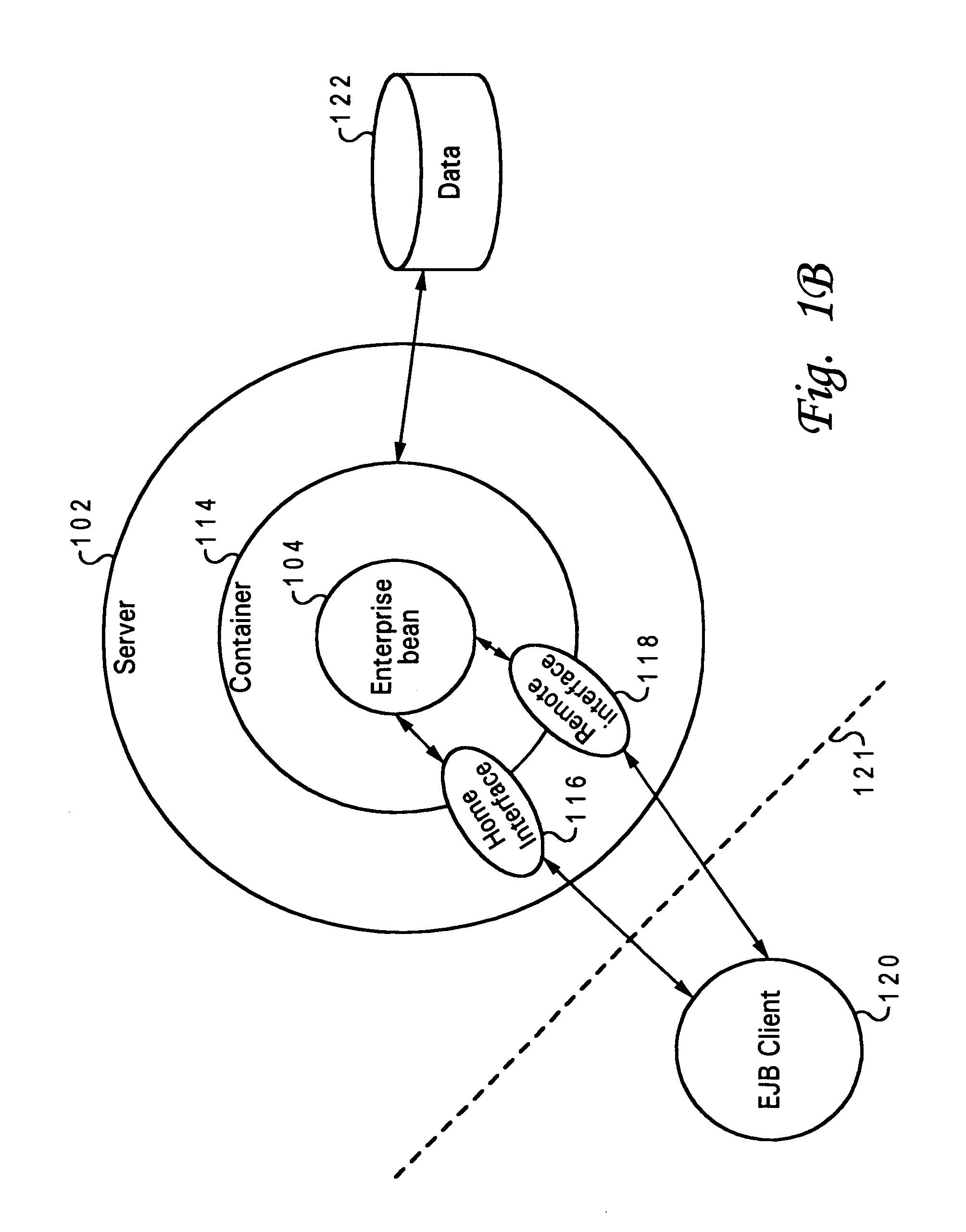
Methods and apparatus for implementing state machines as enterprise beans with reliable or transactional timers on an enterprise platform are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a state machine is arranged to be used within a computing system that supports an enterprise platform. The state machine includes an entity object, a home interface associated with the entity object, and a remote interface associated with the entity object. The home interface is arranged to create, find, and remove entity objects, while the remote interface is arranged to drive the state machine. The entity object is arranged to be deployed in a bean container, which includes a timer. In addition to including a timer, the bean container is arranged to invoke the entity object using the remote. In one embodiment, the timer is transactional.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for implementing state machines as enterprise javabean components
InactiveUS20020040409A1Interprogram communicationSpecific program execution arrangementsDatabaseEntity Bean
Methods and apparatus for implementing state machines as enterprise beans on an enterprise platform are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a state machine which is arranged to be used within a computing system that supports an enterprise platform includes an entity bean class, a home interface associated with the entity bean class, and a remote interface that is also associated with the entity bean class. The home interface is arranged to create, find, and remove entity objects, while the remote interface being arranged to drive the state machine. In one embodiment, the entity bean class is associated with an entity object. In such an embodiment, the entity object, the home interface, and the remote interface are included in an entity bean which may be an Enterprise JavaBean.
Owner:SUN MICROSYSTEMS INC
Smart generator
The Smart Generator of the present invention allows the designer / developer / user to model the EJB components in a natural way without being concerned with implementation-specific details. The developer models the business objects using a UML drawing tool and the Smart Generator creates a set of classes that implements these objects with reference to the Enterprise JavaBeans specification. That is, the Smart Generator automatically create access methods and handling containment of references from the UML diagram.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for assembling Enterprise JavaBeans components
InactiveUS7093264B2Flexible assemblyTransformation of program codeVersion controlSoftware engineeringGlue code
Owner:ELECTRONICS & TELECOMM RES INST
System and method for dynamically modifying synchronized business information server interfaces
ActiveUS7738497B2Quick couplingReduce skillsDigital computer detailsDatabase distribution/replicationApplication serverRunning time
One or more embodiments of the invention enable data that is synchronized between businesses to be transferred to any desired data pool or data pool version in a format that may be declaratively specified and dynamically altered to meet the needs of the specific data pool or data pool version. The data pool vendor utilized by a company or the attributes and formats used in communicating with a particular data pool may change over time and embodiments of the invention are capable of automatically detecting and altering the data and format of the data to be transferred to and from the data pool. The server interface configuration may comprise an XML file in one embodiment of the invention. The XML file may be parsed with any compliant schema based or DTD based XML parser and sent to the server interface for dynamic update using JMS for example. The server interface itself may be implemented or make use of a Resource Adapter configured to operate within the Java Connector Architecture of the Enterprise JavaBeans specification. In at least one embodiment of the invention an N-tier architecture may be employed comprising an Application Server. The server interface accepts an incoming server interface configuration request and utilizes information derived from the XML configuration file in order to add or remove data attributes or alter the format of the data attributes that are transferred to and from each data pool. In this embodiment of the invention, data pools may be switched by at run-time without recompiling and redistributing the application.
Owner:SAP AG
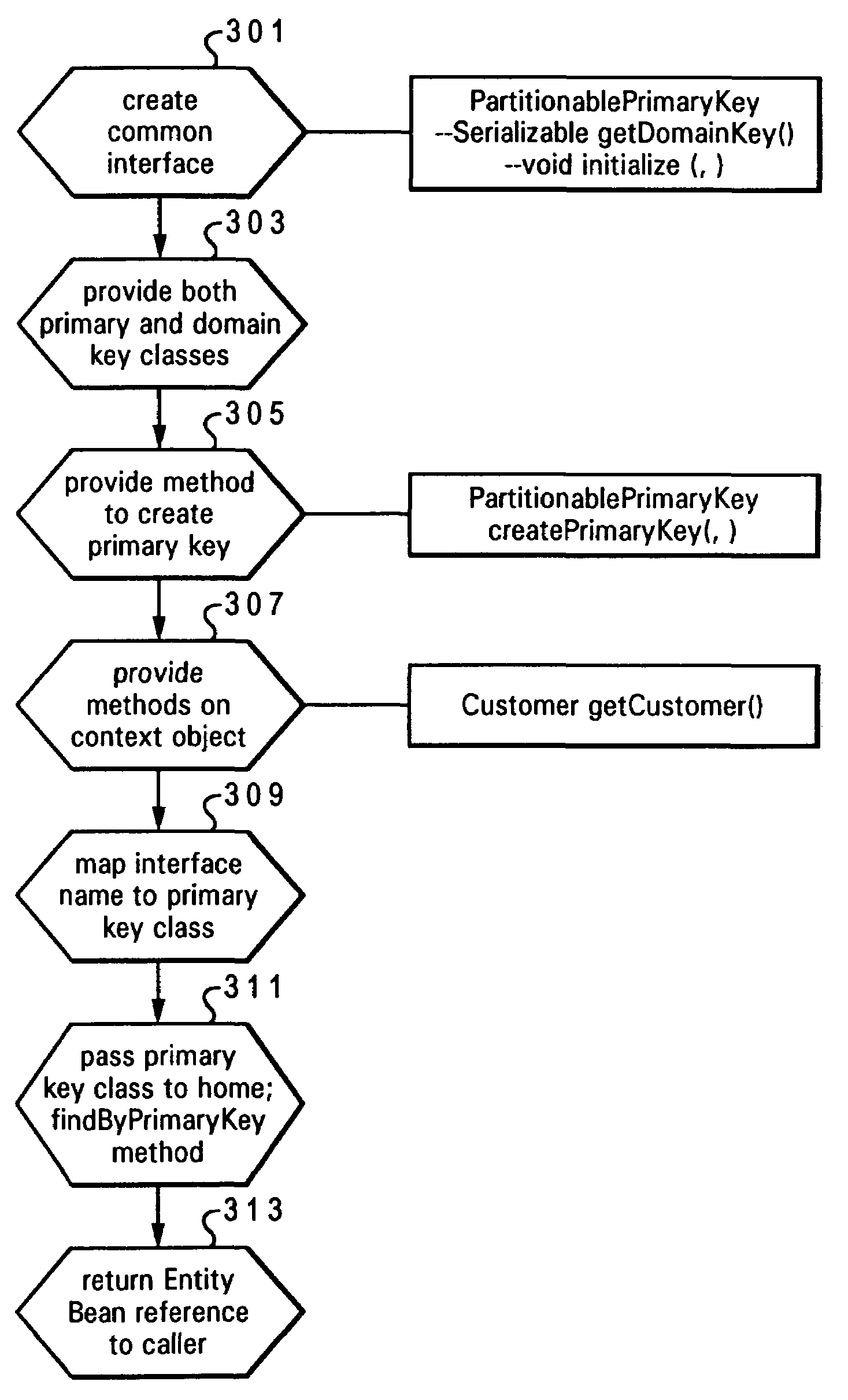
Support for domain level business object keys in EJB
InactiveUS6999964B2Enable reusable business componentsDigital data processing detailsSpecific program execution arrangementsPublic interfaceDomain level
A method, system and program product for providing domain level business object keys in Enterprise JavaBeans (EJB) applications. An instance of an EntityBean object is provided with both a primary key and a domain key class. The primary key class is associated with a home selected for the EntityBean object, and the domain key class is associated with a particular business application within which the EntityBean object is being utilized. The EntityBean and associated home is utilized across different business applications, while ensuring uniqueness across the different applications. Also, a common interface for the primary key is introduced that has methods, which (1) provide an initialized instance of associated domain key classes from a concrete primary key subclass, wherein a concrete primary key subclass knows its associated domain key and is able to initialize the domain key from a subset of attributes of the primary key, and (2) creates an initialized instance of a primary key subclass from a given domain key and a context object.
Owner:INTERMATIONAL MACHINERY CORPORATIO
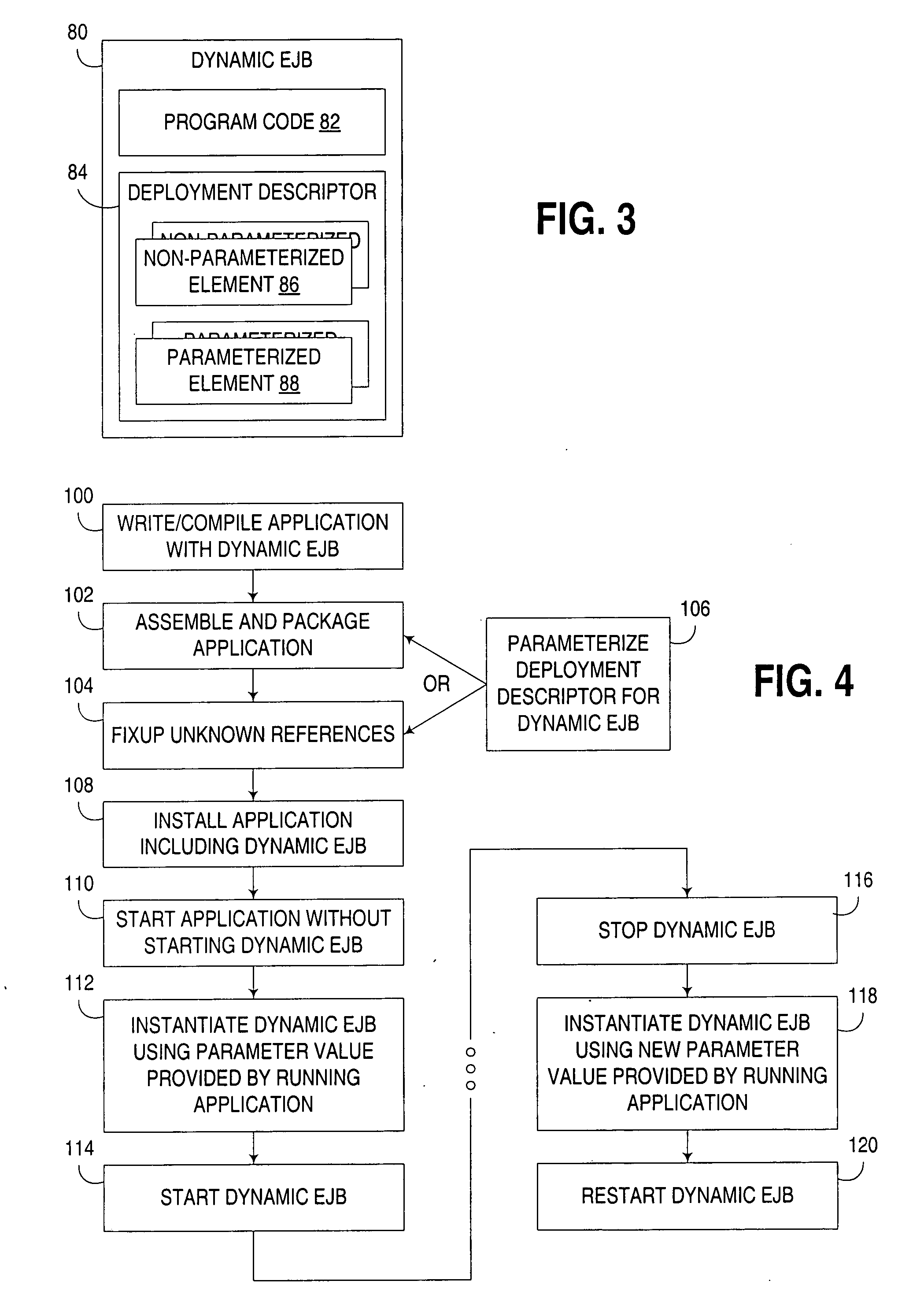
Systems and method for the incremental deployment of Enterprise Java Beans
InactiveUS20050210462A1Program loading/initiatingMemory systemsComputer hardwareEnterprise Java Bean
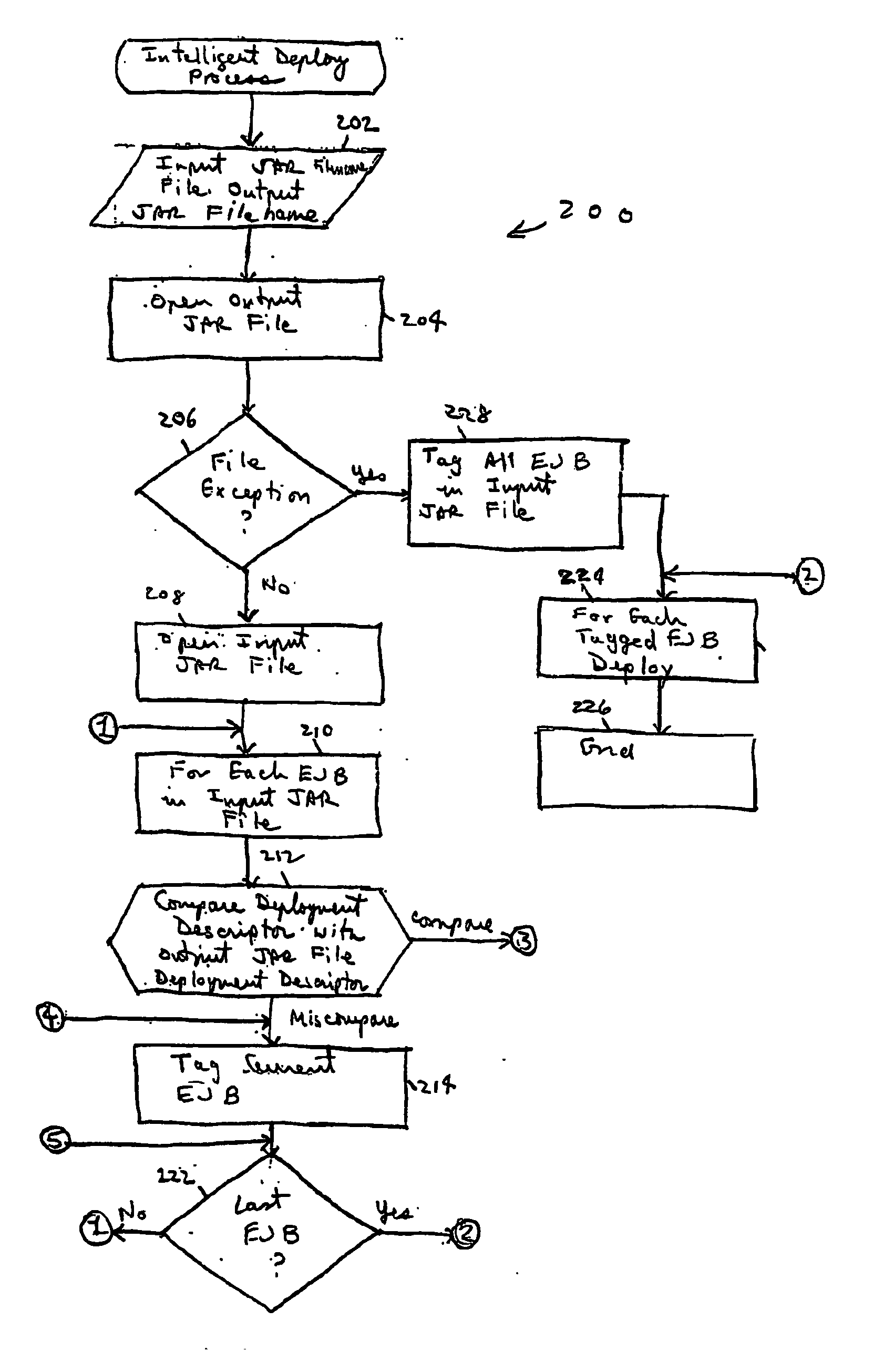
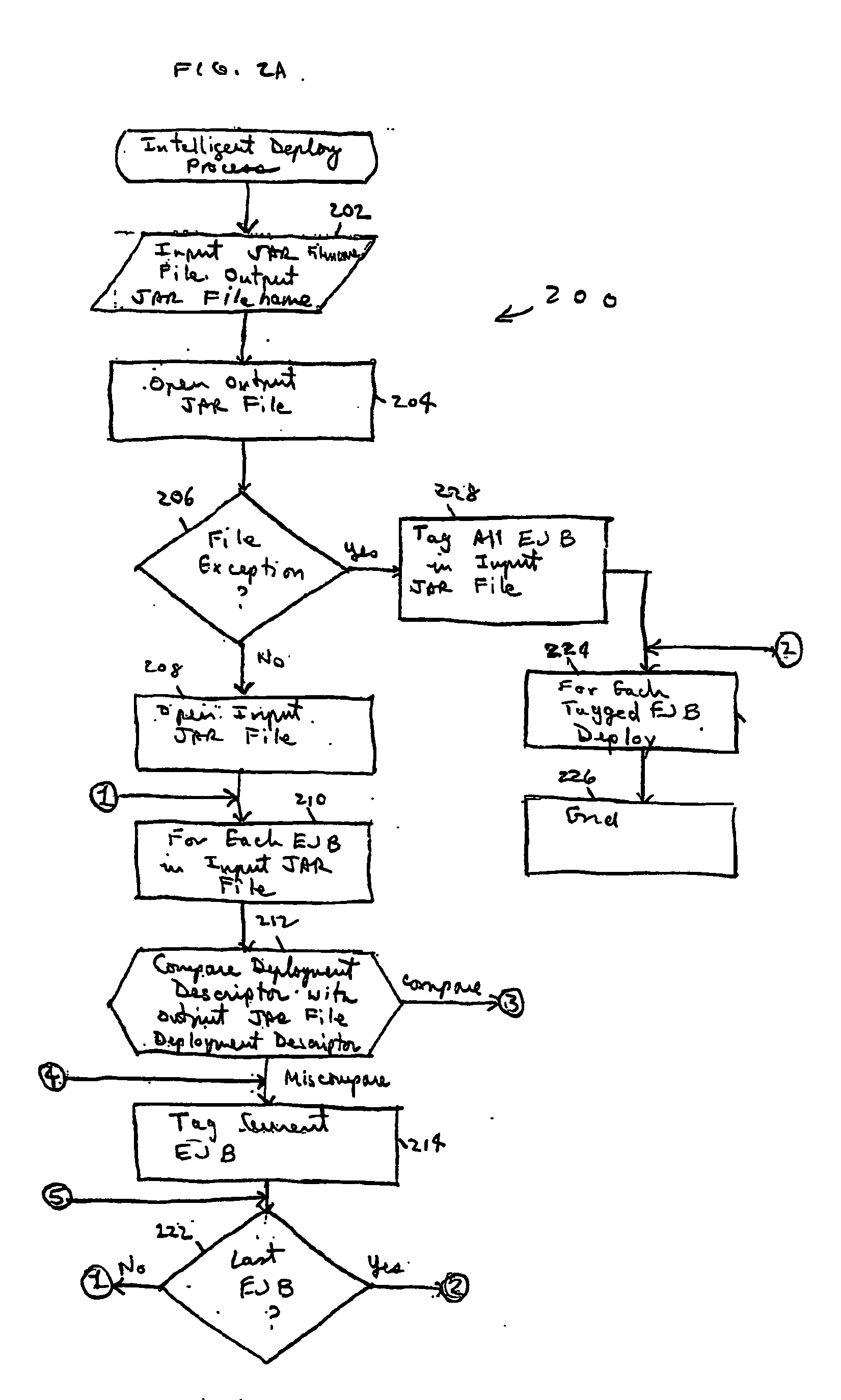
Systems and methods for selectively deploying enterprise software are provided. For each deployable software component (exemplified by, but not limited to Enterprise JavaBeans, or “EJB”s) in an preselected input archive file, interfaces of deployable software components identified in a first and second descriptor file in, respectively, the preselected input archive file and a preselected output archive file are compared. If tan interface miscompares for a first deployable software component, the first deployable software component is tagged. Additionally, if an interface miscompares for a second deployable software the second deployable software component is also tagged. Each tagged deployable software component is deployed.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for deploying a web service
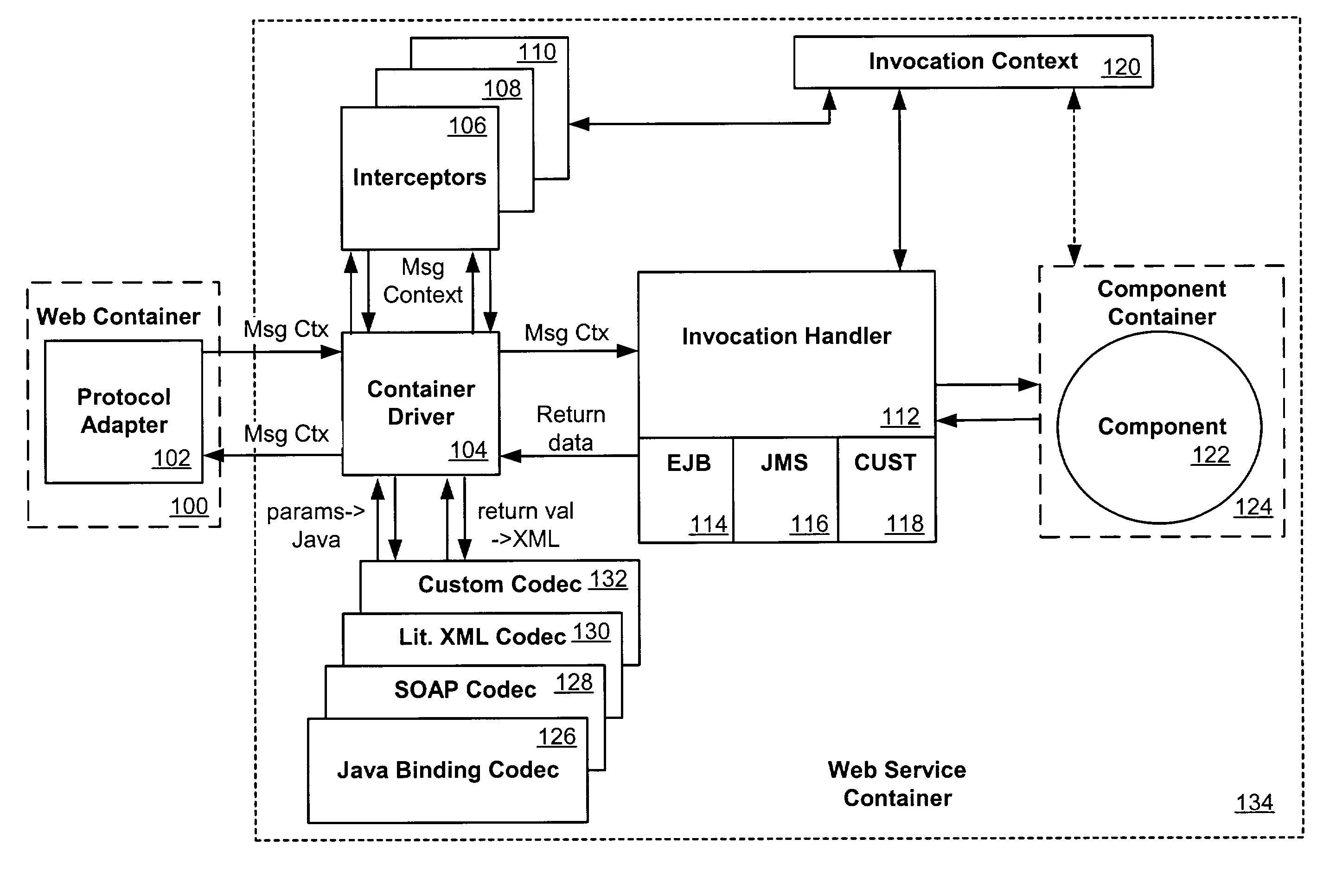
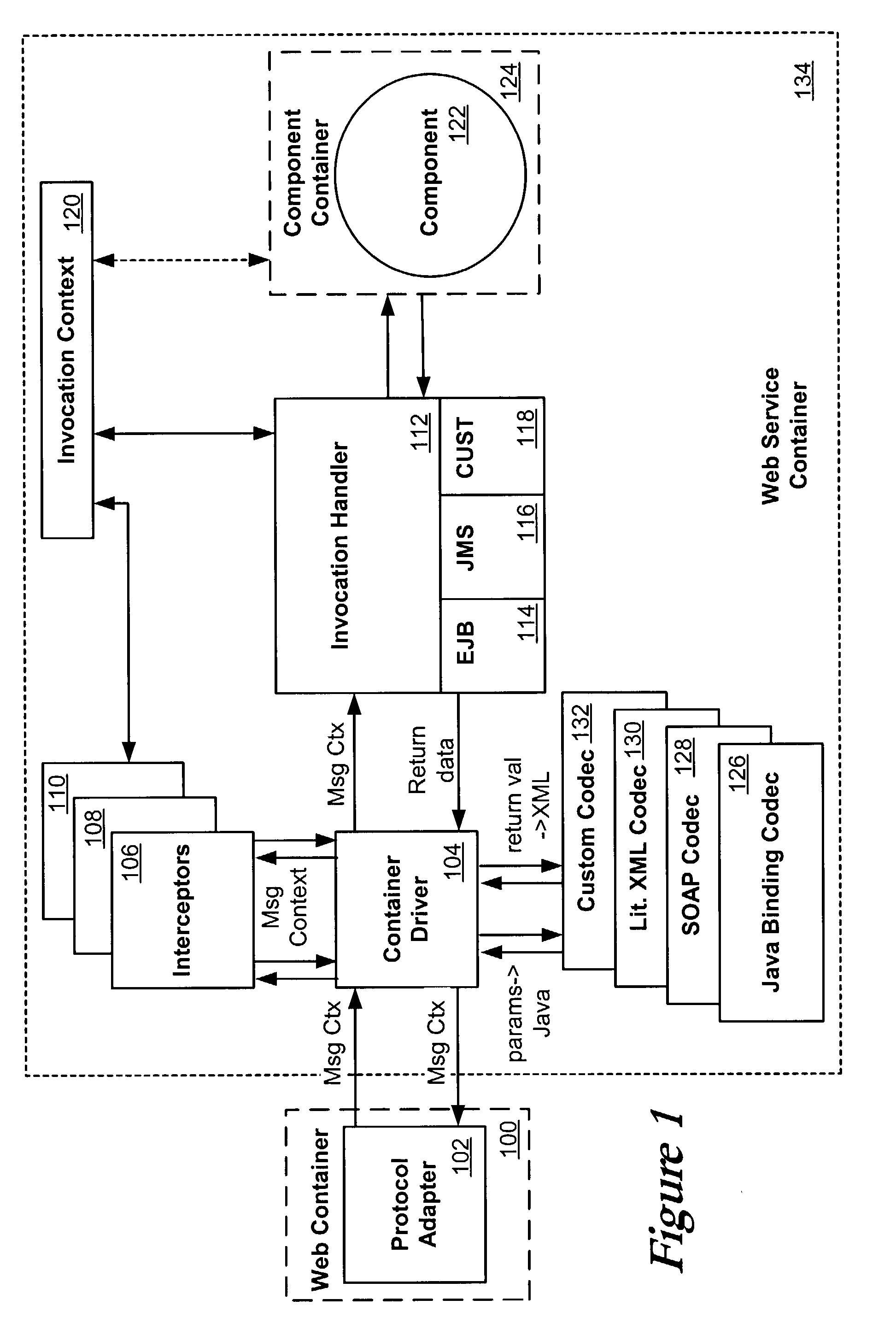
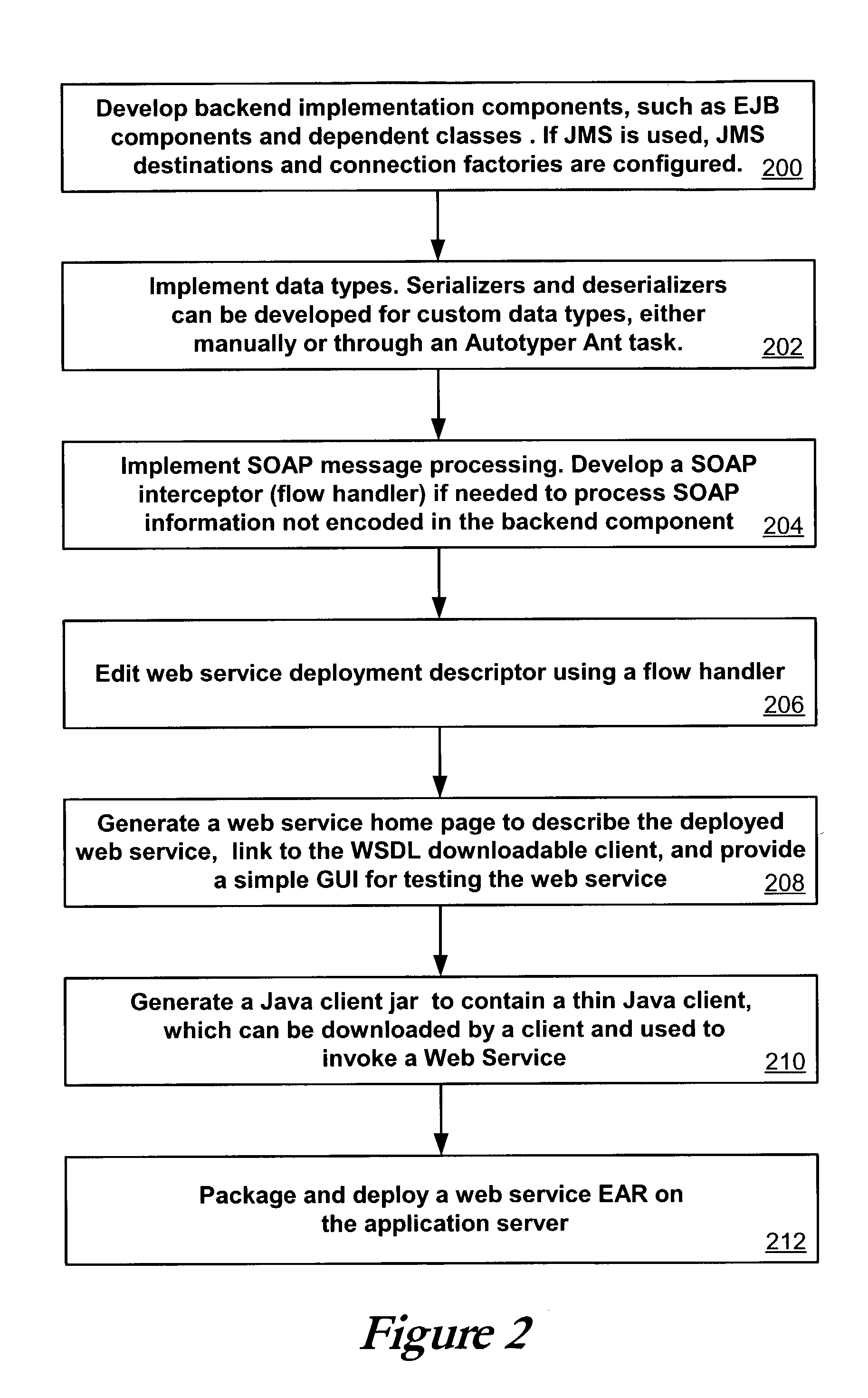
A Web service can be deployed using a backend component such as an Enterprise JavaBean or Java class. The operation of the Web service can be mapped to methods of the backend component. An interceptor can provide access to SOAP contents of a Web service invocation message, passing contents to and from the backend component. The interceptor writes response data received from the backend component to a Web service response message, which can be sent to the client invoking the Web service. A codec, such as a serializer or deserializer, can be used to convert data in the Web service invocation message and invocation response message between XML representations and Java objects for use with the backend component.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Method and apparatus for implementing timers for enterprise javabean components
InactiveUS20020004851A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsProgramming languageTimer
Methods and apparatus for implementing state machines as enterprise beans with reliable or transactional timers on an enterprise platform are disclosed. According to one aspect of the present invention, a state machine is arranged to be used within a computing system that supports an enterprise platform. The state machine includes an entity object, a home interface associated with the entity object, and a remote interface associated with the entity object. The home interface is arranged to create, find, and remove entity objects, while the remote interface is arranged to drive the state machine. The entity object is arranged to be deployed in a bean container, which includes a timer. In addition to including a timer, the bean container is arranged to invoke the entity object using the remote. In one embodiment, the timer is transactional.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
System and method to implement container managed streams in J2EE environments
InactiveUS20060155745A1Automatic generatedSimple methodRelational databasesSpecial data processing applicationsData streamBatch processing
A method, apparatus, and computer instructions for implementing container managed streams in an enterprise JavaBean™ environment. Uses, ownership, reference relationships between entity beans and sessions are specified in a deployment descriptor file. When an input data stream is received for a batch job, the file is processed and a method is generated on the entity beans, wherein the method allows for creating a container managed ownership entity representing a stream object for the input data stream, associates an entity bean with the stream, and returns the last unprocessed object in the stream to the user. A method may also be generated on the entity beans for creating a stream object for an output data stream, associating an entity bean with the stream, rerouting an object to the stream object, and appending the stream object to the end of the batch job queue.
Owner:IBM CORP
Secure Hotspot Roaming
InactiveUS20110258236A1Digital data processing detailsNetwork topologiesService provisionClient-side
Secure hotspot roaming in wireless networks. An enterprise works with one or more hotspot providers to provide secure access to its clients through hotspot locations. The enterprise provides the hotspot provider, or service provider (SP), with the addresses of enterprise controllers used for client authentication. The SP maintains a database for its controllers which maps the enterprise realm to the address of the enterprise controller. When a client connects to a hotspot access point (AP), the hotspot AP sends client information such as MAC address to a SP controller. The SP controller determines if this is a new or a known client by looking up the client information in a local client to realm database. If the client is known and the realm associated with the client has an entry in the realm to enterprise controller database, the hotspot AP is instructed to begin client authentication with the specified enterprise controller. If the client is not known, authentication begins with the SP controller, and the client is queried for realm information. An entry is made in the SP controller's client to realm database for the client. If a corresponding record is present in the realm to enterprise database, the SP controller instructs the hotspot AP to dynamically switch authentication from the SP controller to the enterprise controller. The realm to enterprise database may also be placed on the hotspot AP, so that the hotspot AP may determine if the client should be passed to an enterprise controller and begin authentication with the enterprise controller directly.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
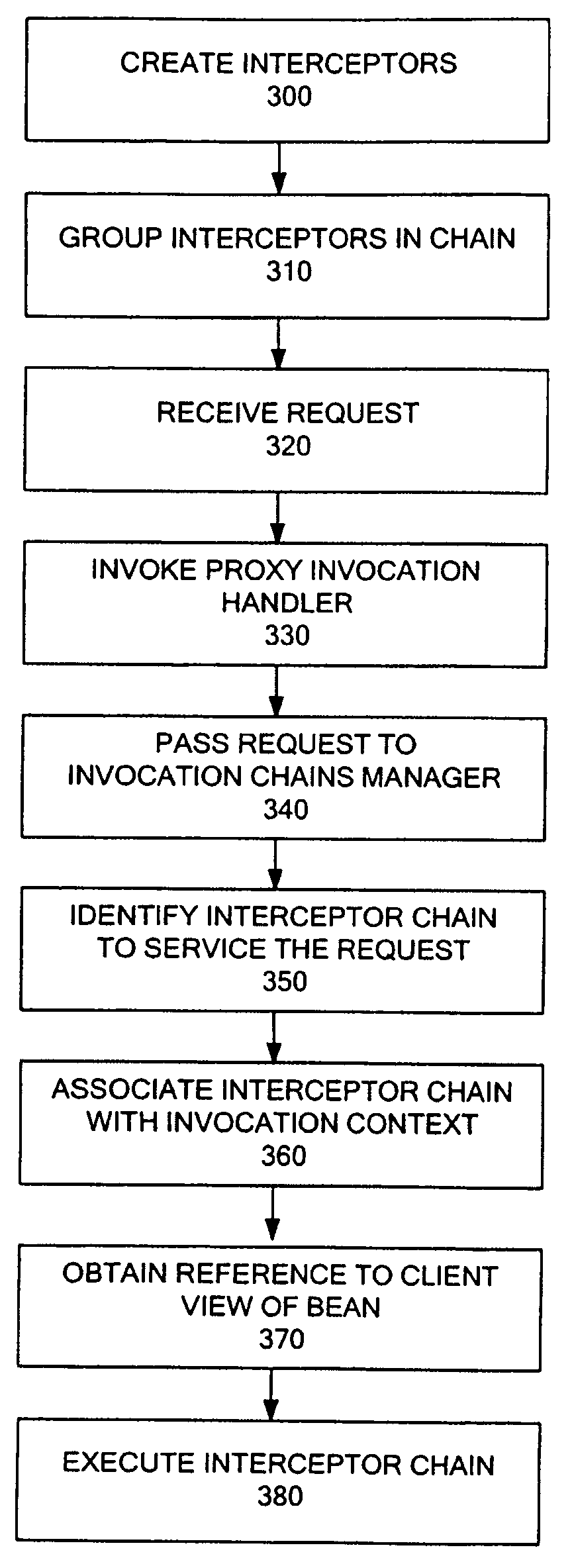
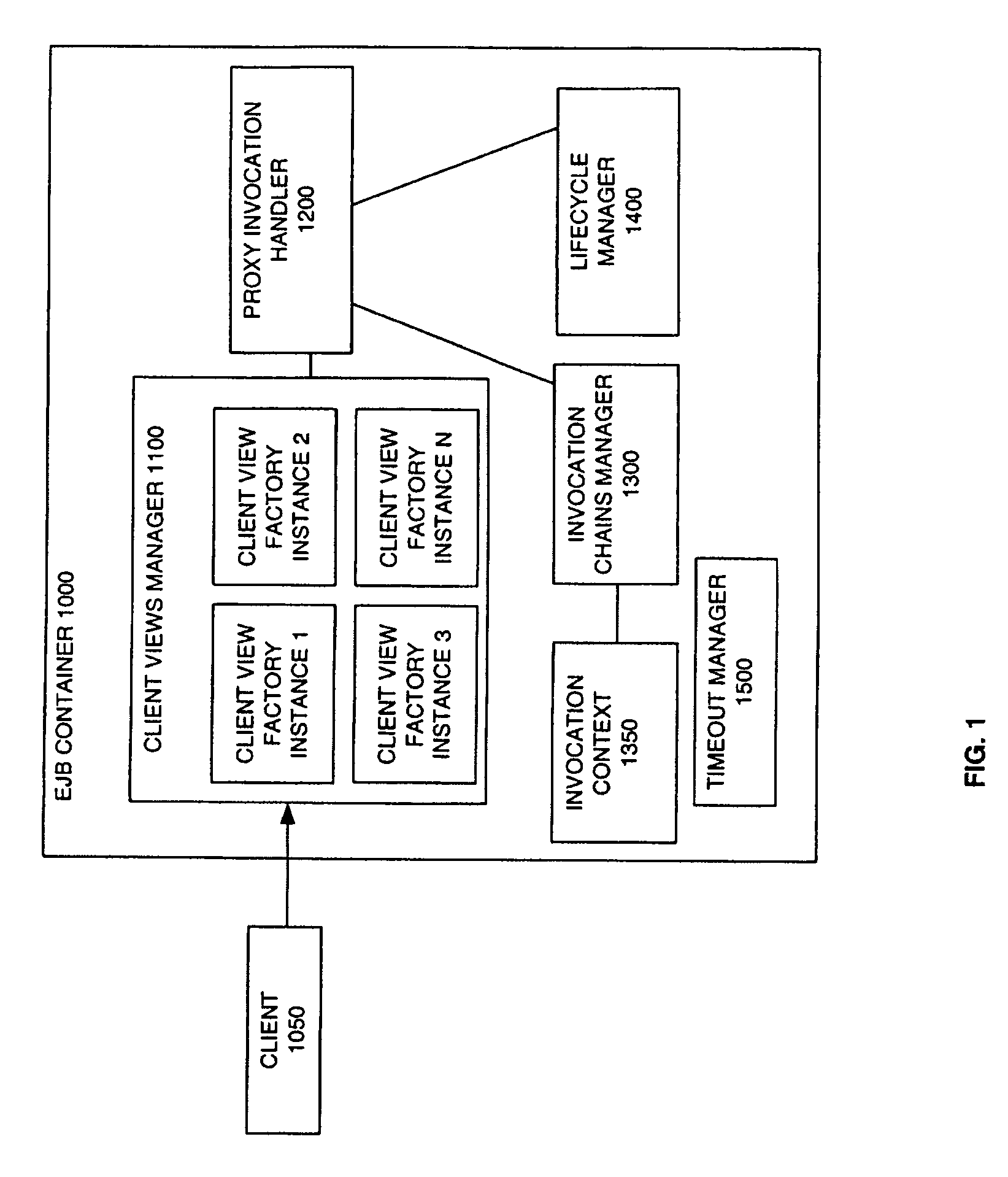
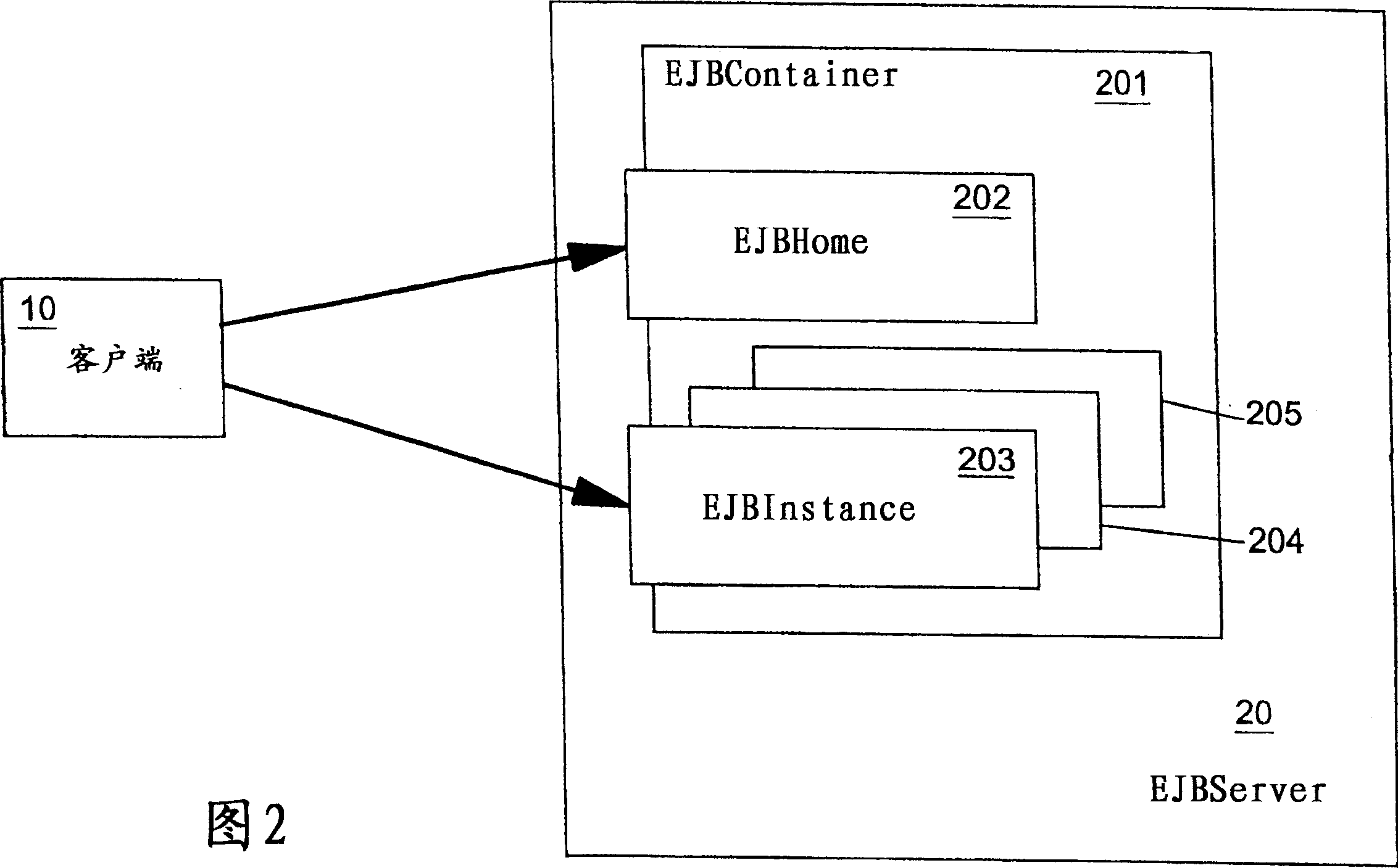
System and method for enterprise javabeans container
InactiveUS20080270986A1Computer security arrangementsTransmissionProgramming languageEnterprise JavaBeans
A system to implement functionality for running Enterprise JavaBeans. The functionality is provided by a set of components. The components include a life cycle manager, a client views manager, a proxy invocation handler, an invocation chain manager, and an invocation context.
Owner:SAP AG
Dynamic enterprise javabeans
ActiveUS20060195471A1Digital data processing detailsProgram controlProgramming languageApplication software
Owner:IBM CORP
Wordload management of stateful program entities
InactiveCN1516831AReduce accessResource allocationMultiple digital computer combinationsMass storageRouting table
In a workload managed system comprising a plurality of server processes each capable of supporting a given program entity, such as an Enterprise JavaBeans(TM) specified stateful session bean, a stateful session bean instance is passivated, by writing it to a bean store, on completion of a unit of work. On next use the session bean is reactivated, by reading it from the bean store, in any one of the plurality of servers thereby allowing workload management for stateful session beans. A routing table is maintained, in non-volatile mass storage, that contains location information for units of work and stateful session bean instances, used to maintain unit of work-server affinity for the lifetime of the unit of work Stateful session beans instances are associated with ID keys that include a flag that is used to indicate whether or not the routing table contains location information for the bean instance.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Method and apparatus for implementing container managed uses, ownerships, and references in an enterprise JavaBean environment
InactiveUS20060155744A1Automatic generatedSimple methodData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDatabaseEntity Bean
Owner:IBM CORP
Method Invocation for Persistent Objects with Dynamic Multikeys
A mechanism is disclosed that enables the invocation of methods of object instances that have persistent data and a mutable key. A mutable key capability is advantageous in a variety of applications, such as monitoring a set of users and their login status on a plurality of media servers (e.g., an email server, an instant messaging server, a voice mail server, a video server, an audio-conferencing server, etc.). The methods that can be invoked include get methods, set methods, unset methods, finder methods, destructors, and business methods. Implementations based on the Enterprise JavaBean specification are disclosed for three illustrative embodiments of the present invention. The illustrative embodiments of the present invention can also be implemented in accordance with object persistence mechanisms other than Enterprise JavaBeans.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Garbage Collection Of Persistent Objects With Dynamic Multikeys
ActiveUS20070276888A1Object oriented databasesSpecial data processing applicationsPersistent objectMedia server
A mechanism is disclosed that enables garbage collection of object instances that have persistent data and a mutable key. A mutable key capability is advantageous in a variety of applications, such as monitoring a set of users and their login status on a plurality of media servers (e.g., an email server, an instant messaging server, a voice mail server, a video server, an audio-conferencing server, etc.). Implementations based on the Enterprise JavaBean specification are disclosed for three illustrative embodiments of the present invention. The illustrative embodiments of the present invention can also be implemented in accordance with object persistence mechanisms other than Enterprise JavaBeans.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Method and apparatus for implementing container managed uses, ownerships, and references in an enterprise JavaBean environment
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and system for incorporating legacy applications into a distributed data processing environment
InactiveCN1526094AEasy to implementEfficient communicationMultiple digital computer combinationsProgram code adaptionPrivate networkBusiness enterprise
A system and method incorporating existing or legacy software applications into a distributed data processing environment by encapsulating each legacy application into a new application which adheres to the Enterprise JavaBean (EJB) interface specifications. The new application with the EJB interfaces allows use of the application in a distributed processing environment such as the Internet or a virtual private network such as an intranet.
Owner:IBM CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com