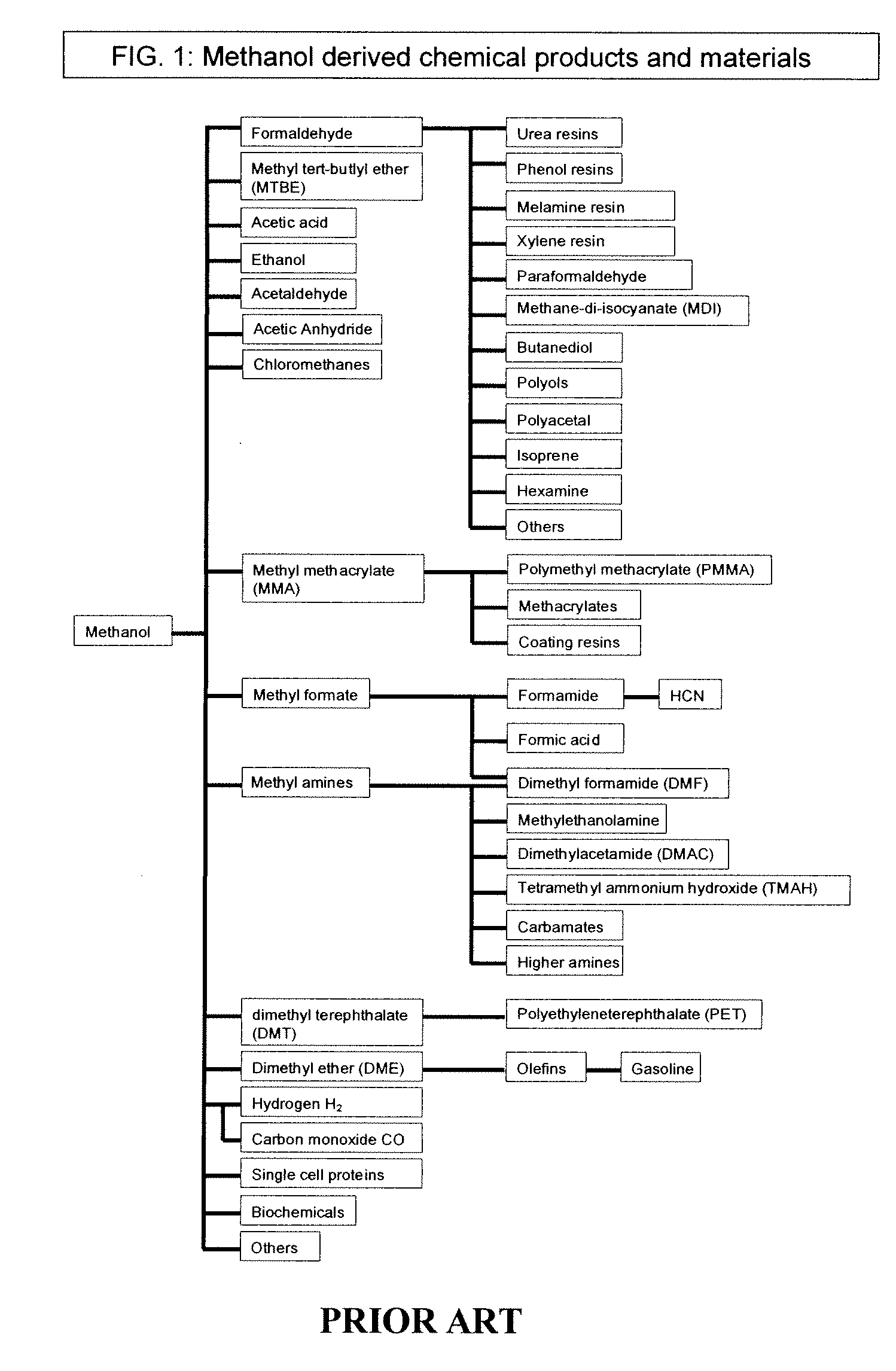
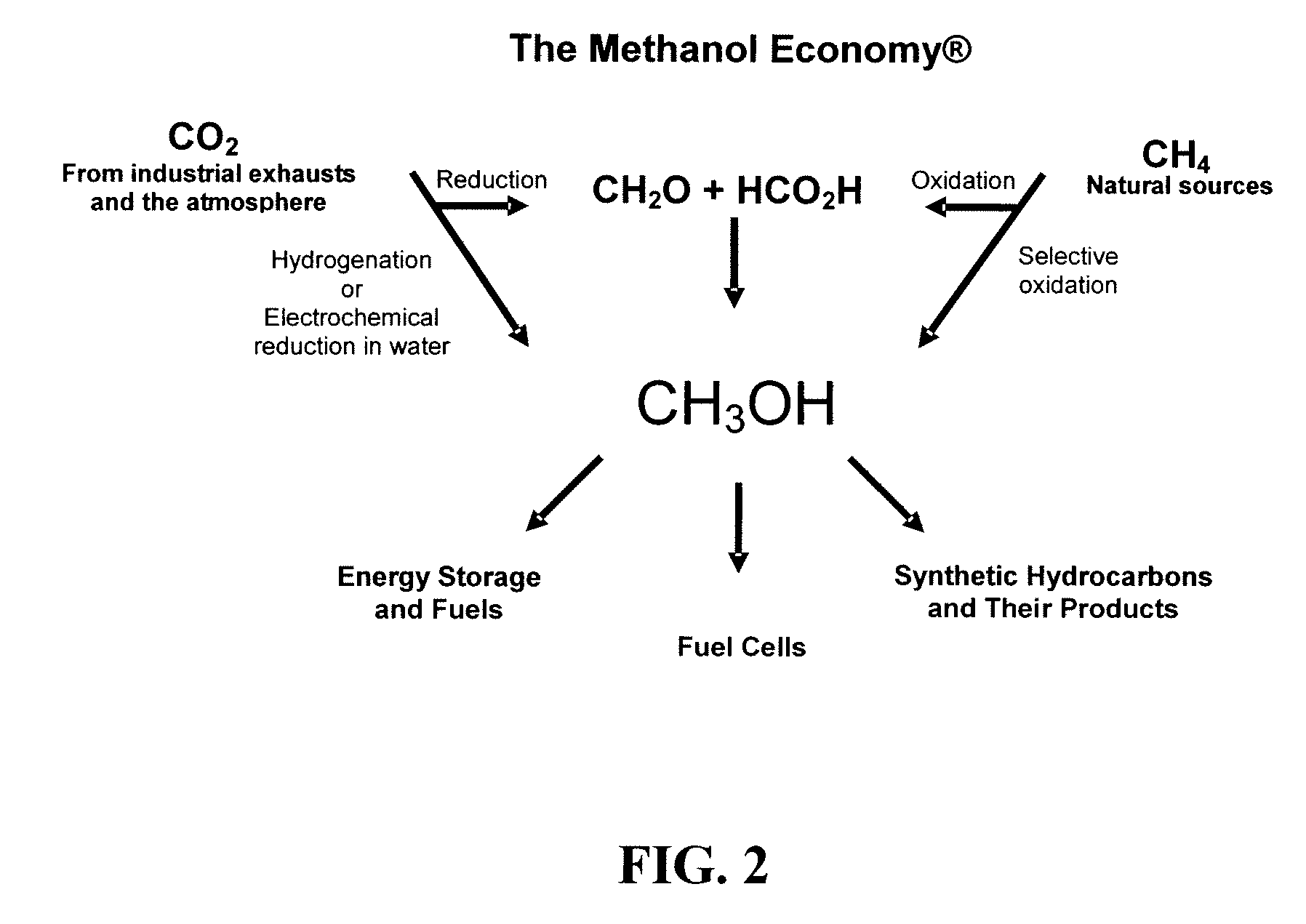
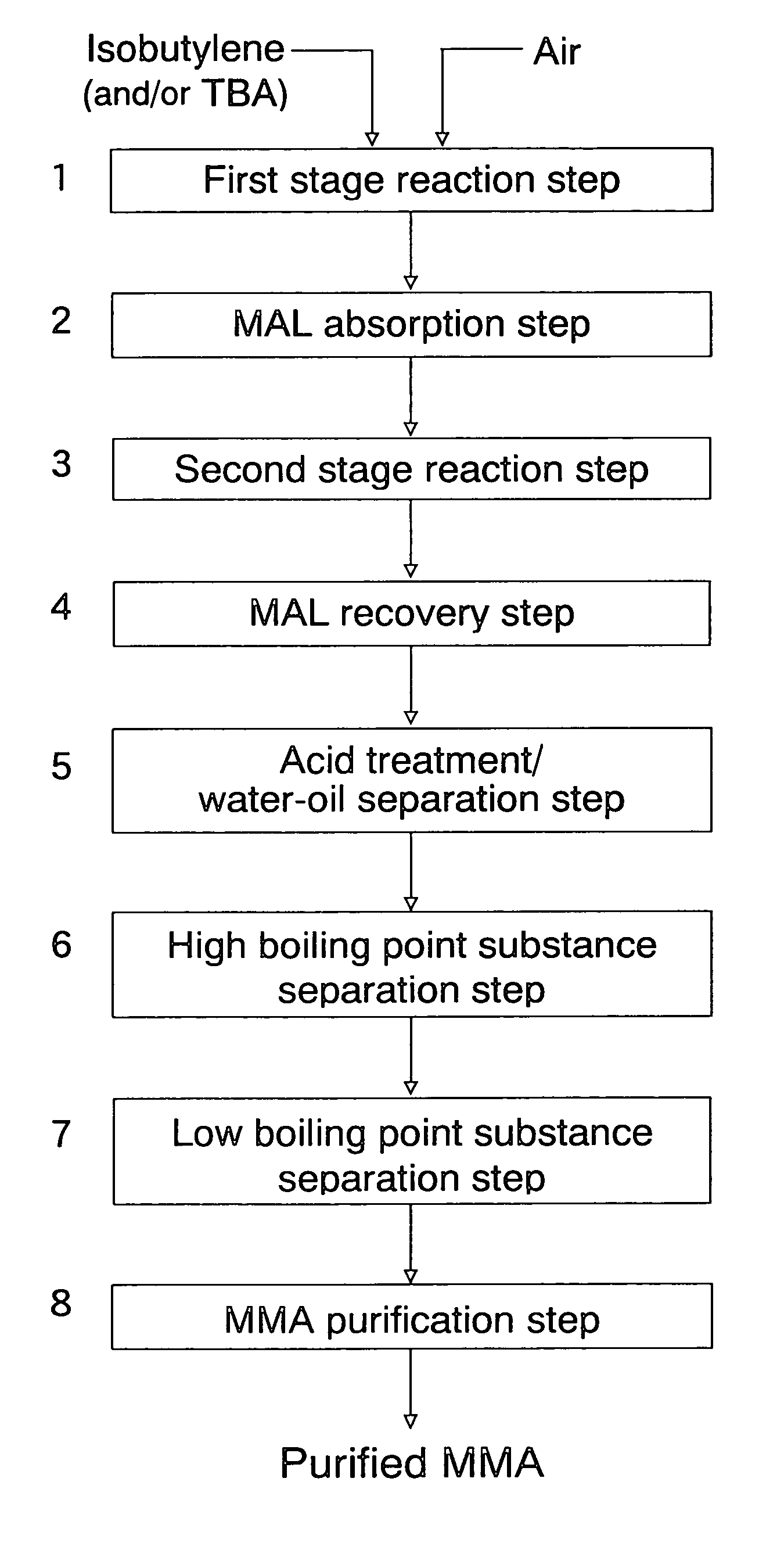
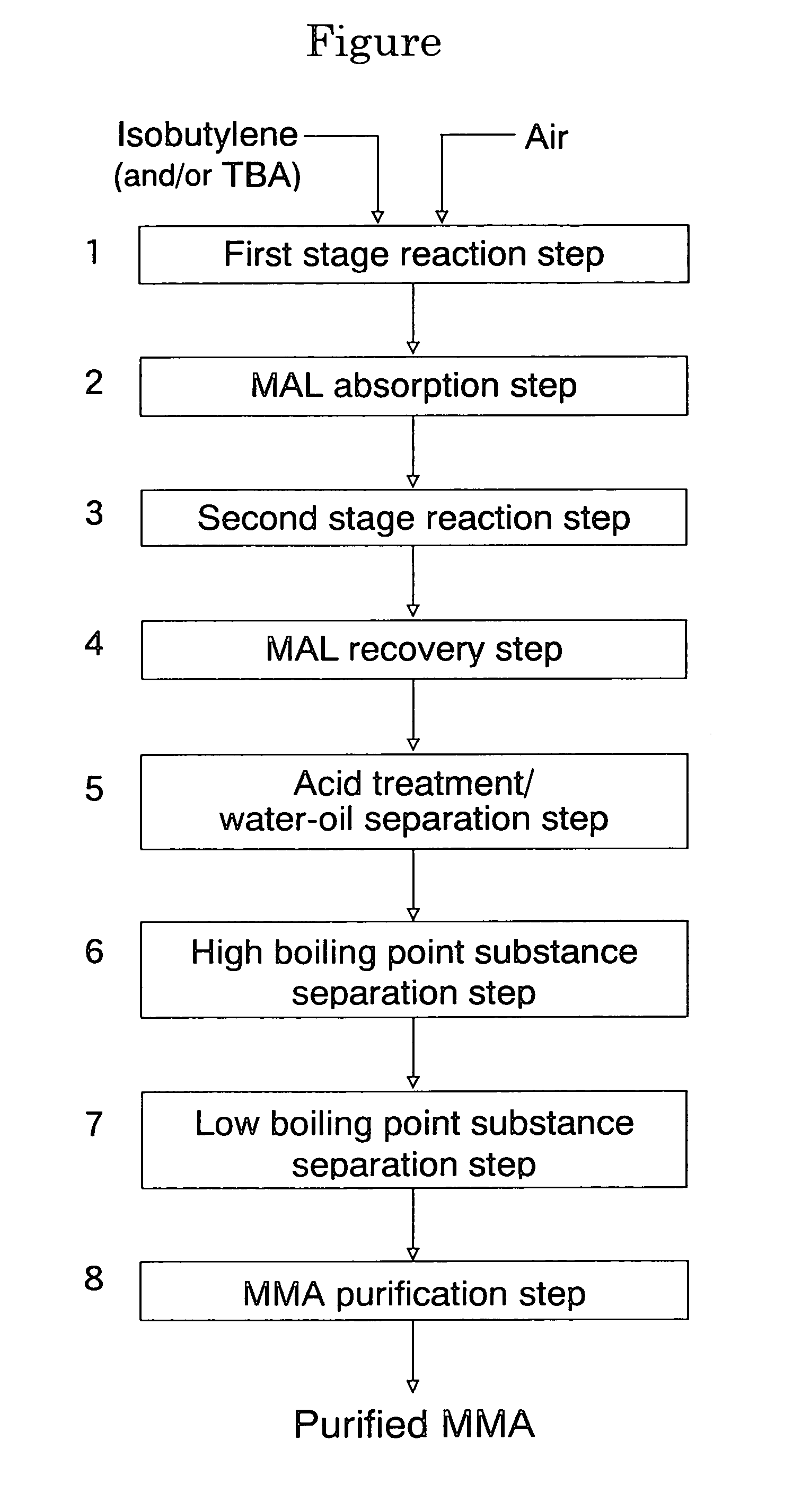
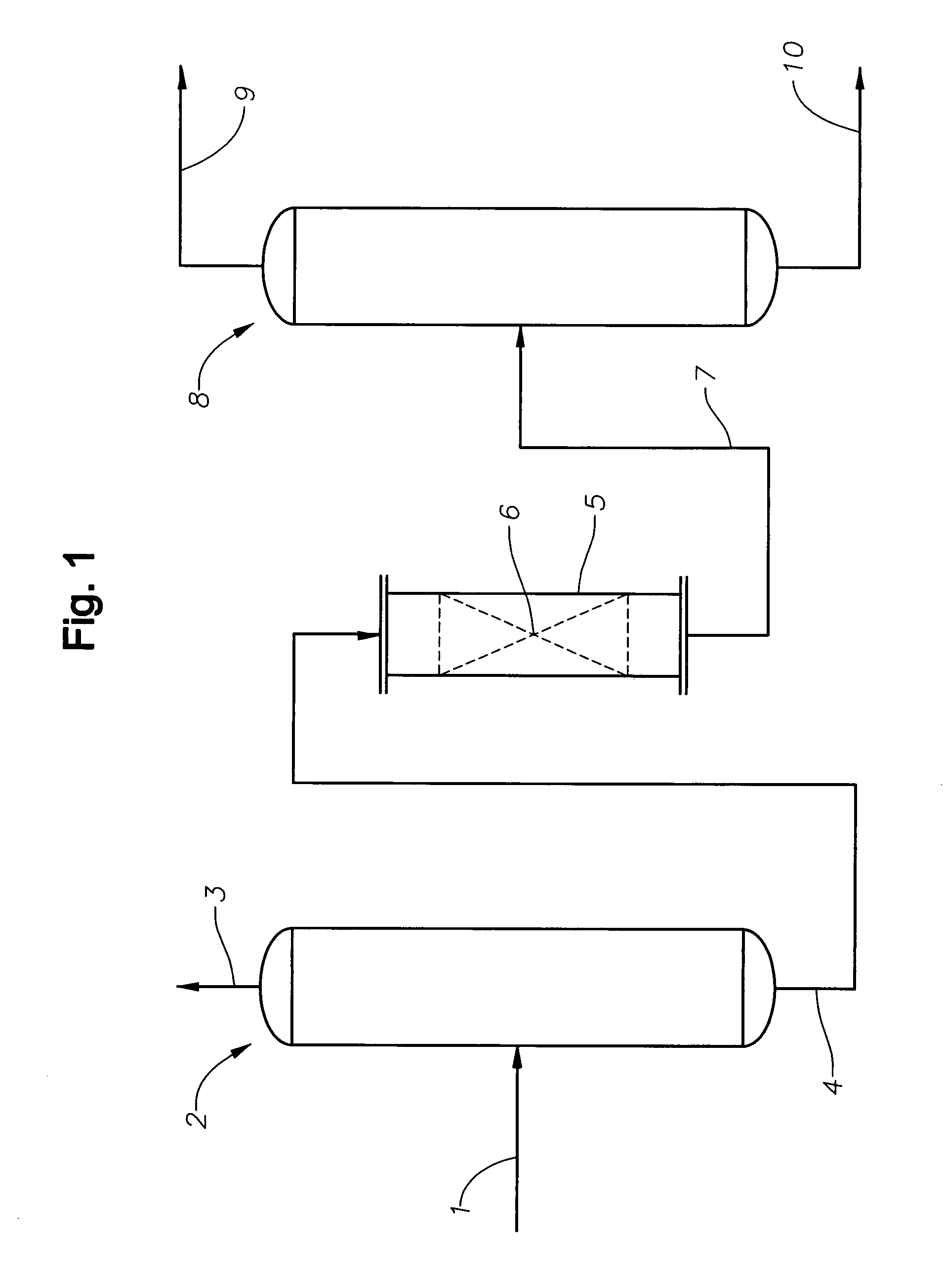
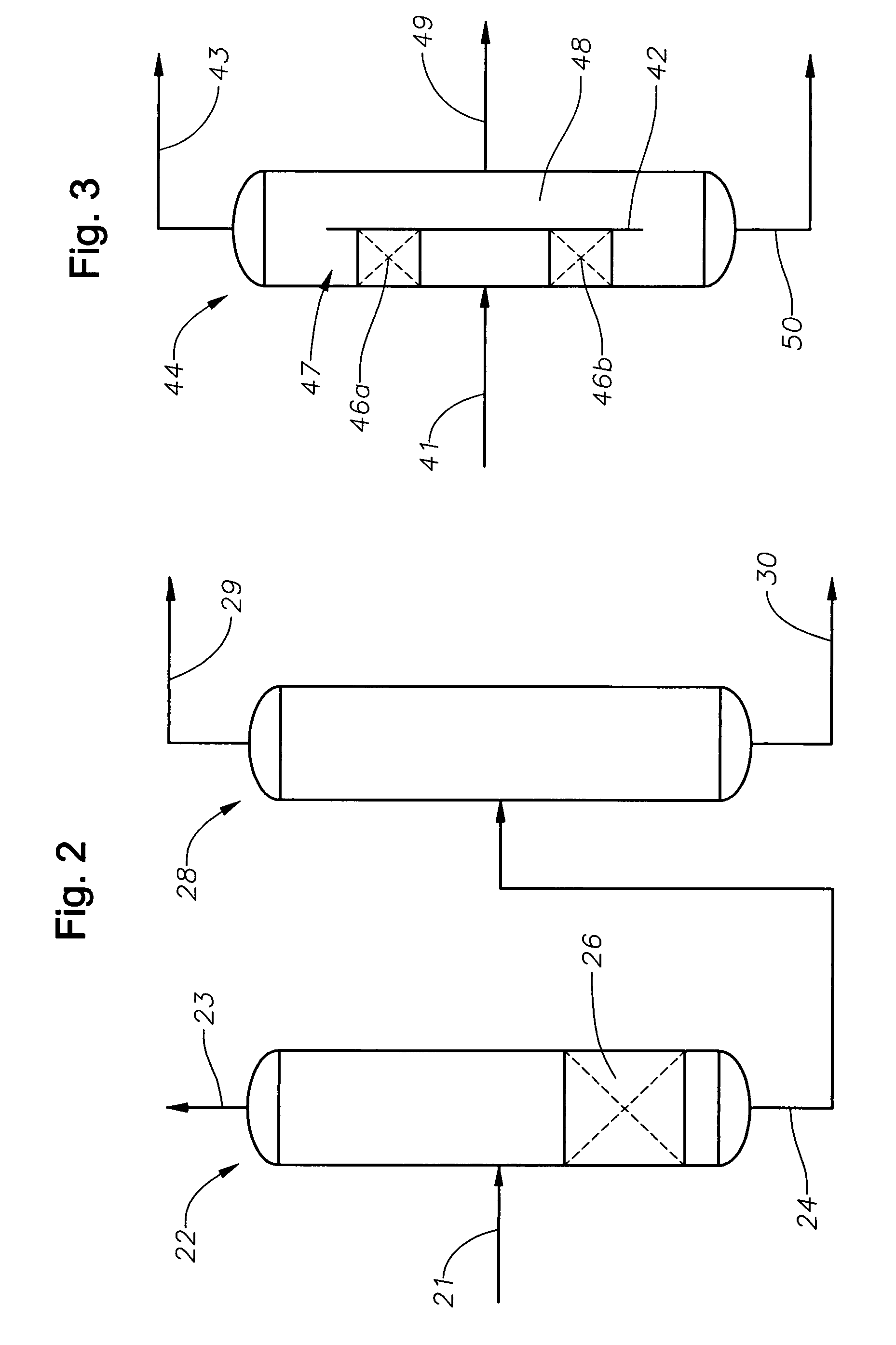
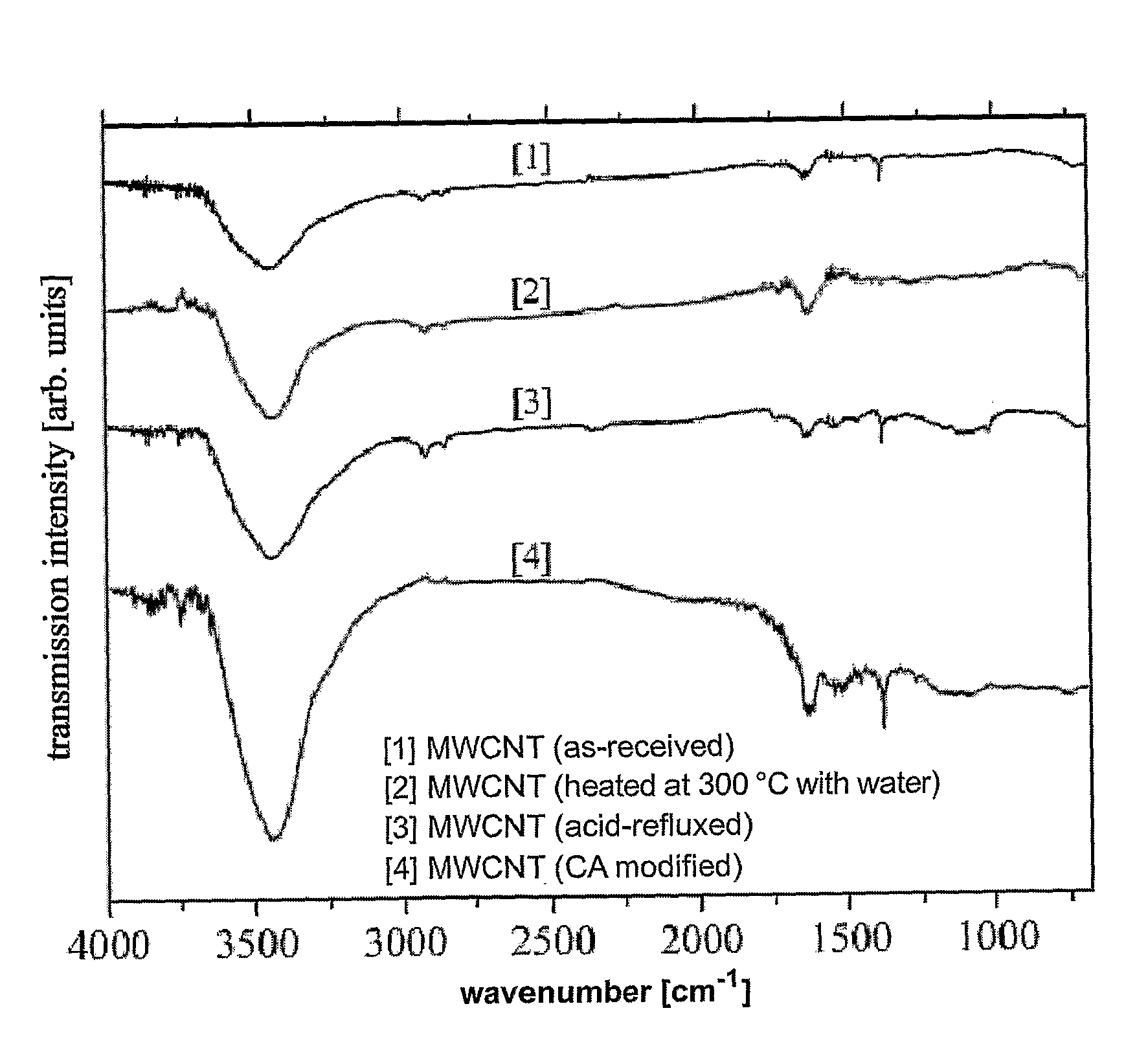
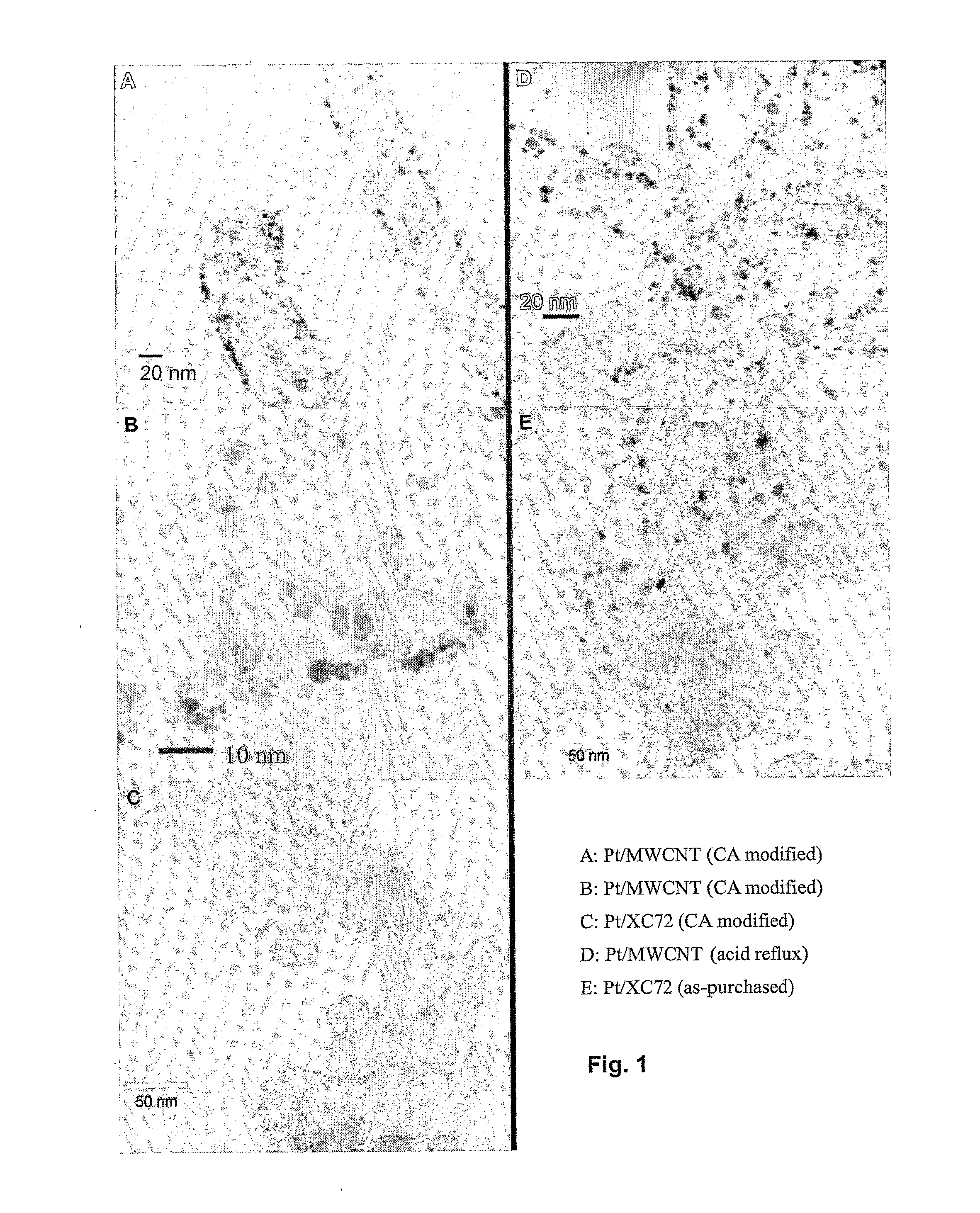
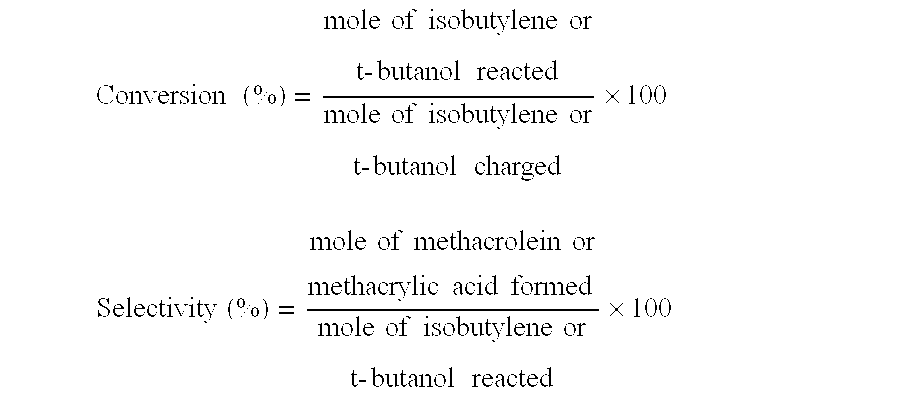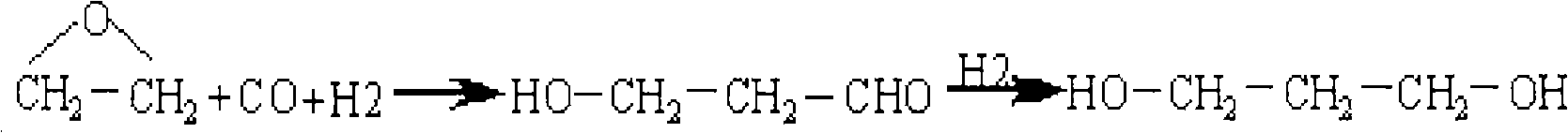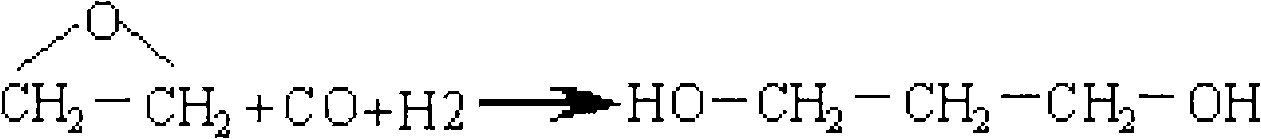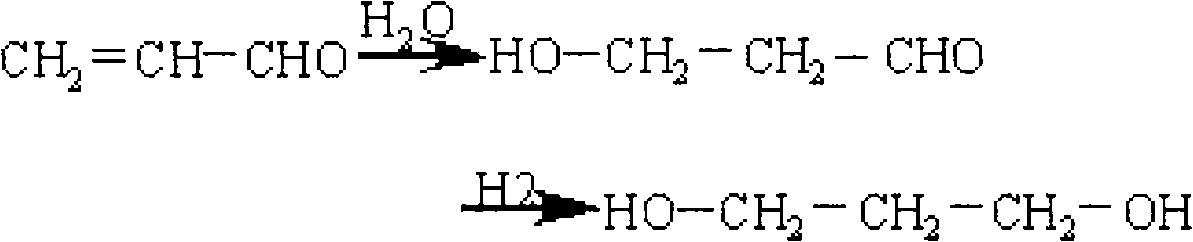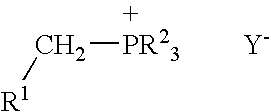Patents
Literature
1441results about "Preparation by hydrolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Algae biomass fractionation
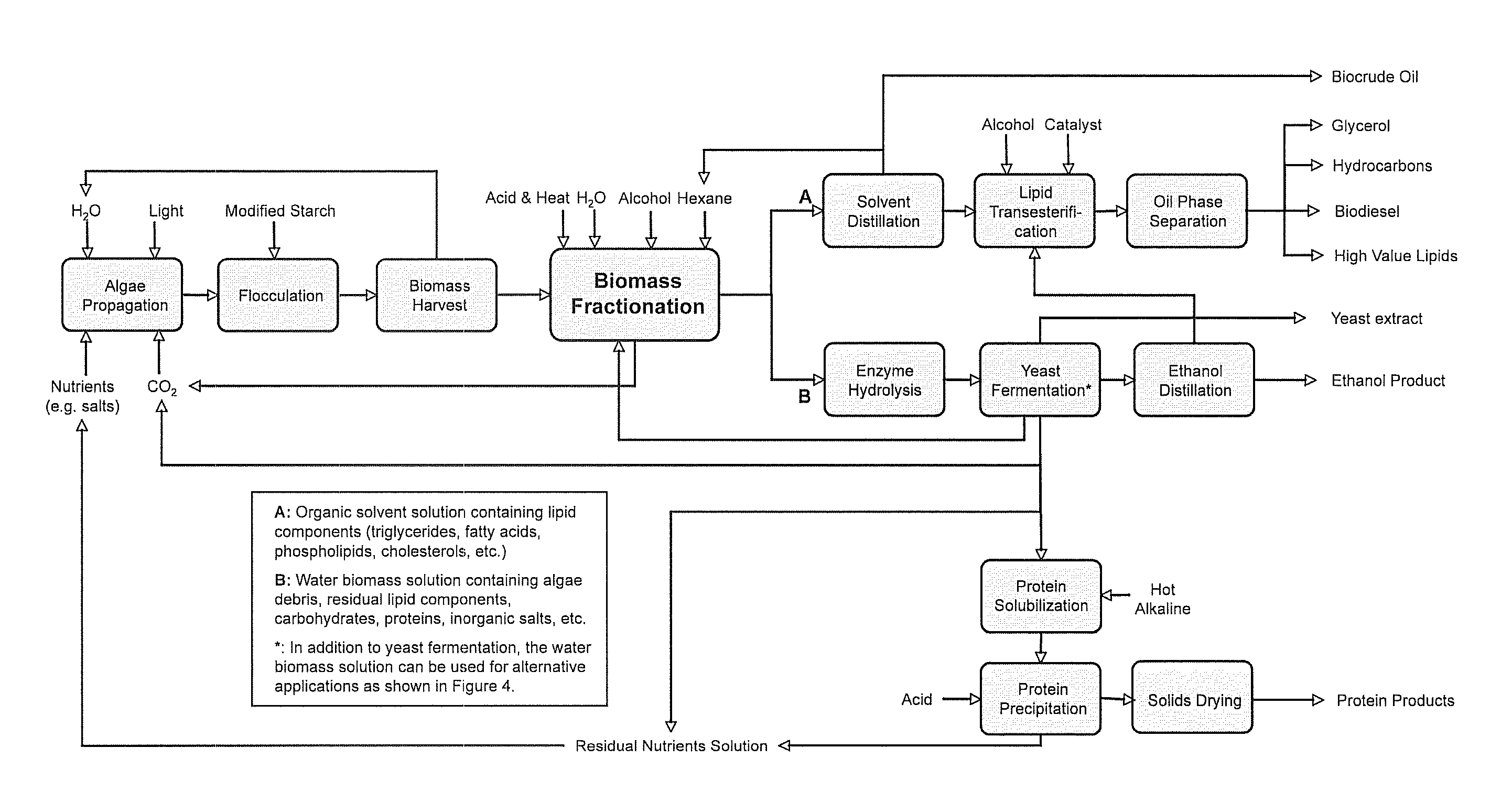
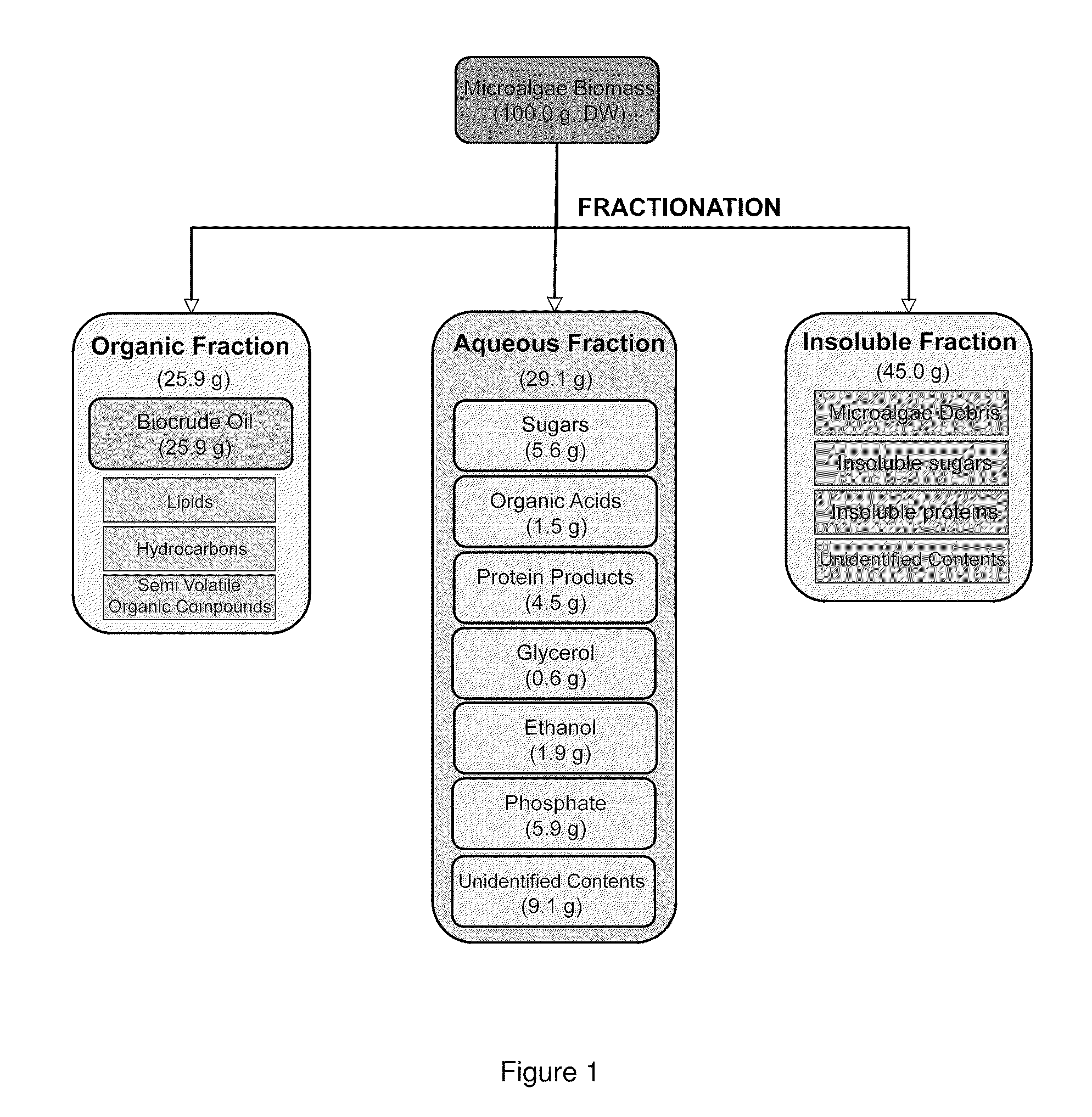
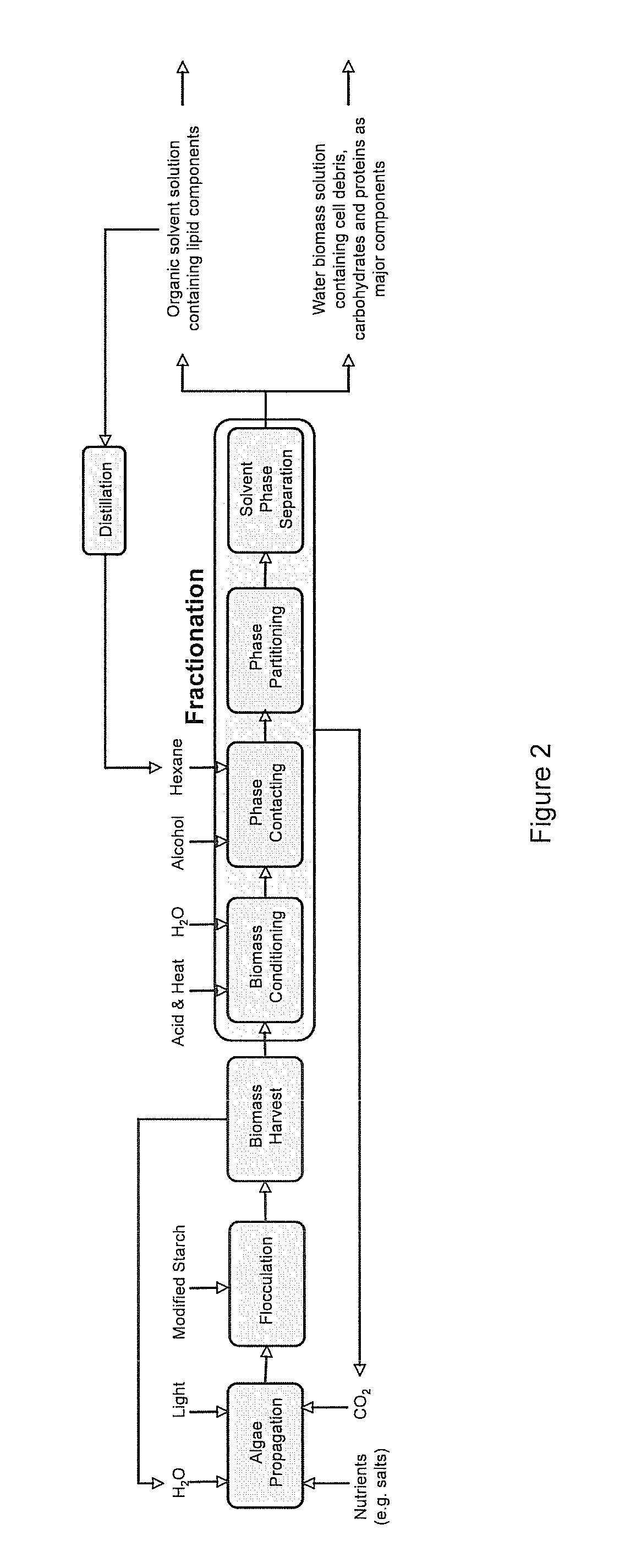
A method of fractionating biomass, by permeability conditioning biomass suspended in a pH adjusted solution of at least one water-based polar solvent to form a conditioned biomass, intimately contacting the pH adjusted solution with at least one non-polar solvent, partitioning to obtain an non-polar solvent solution and a polar biomass solution, and recovering cell and cell derived products from the non-polar solvent solution and polar biomass solution. Products recovered from the above method. A method of operating a renewable and sustainable plant for growing and processing algae.
Owner:VALICOR
Processes for making ethanol from acetic acid
InactiveUS20100197985A1High selectivityPreparation by oxo-reaction and reductionEthylene productionCeriumCobalt
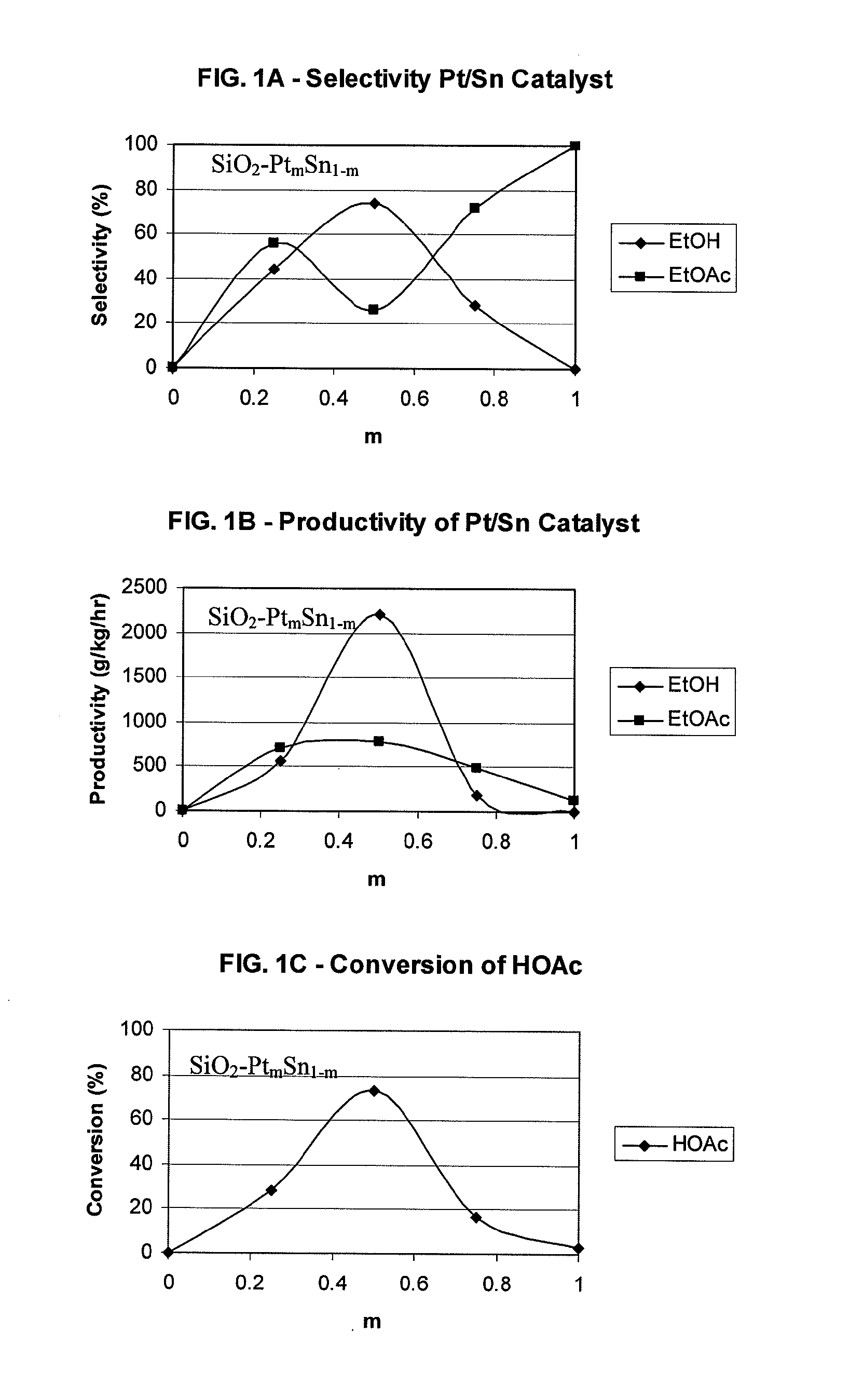
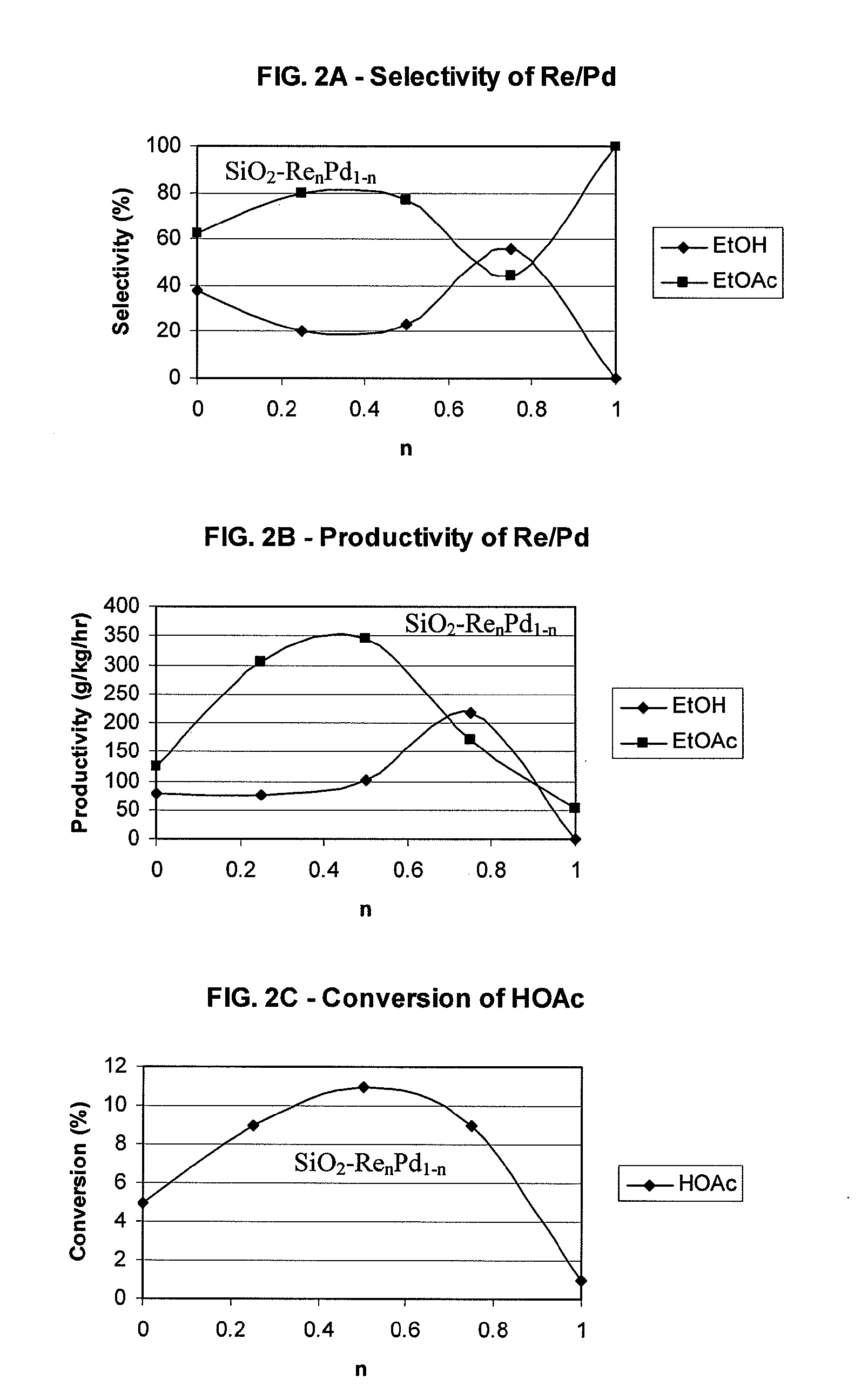
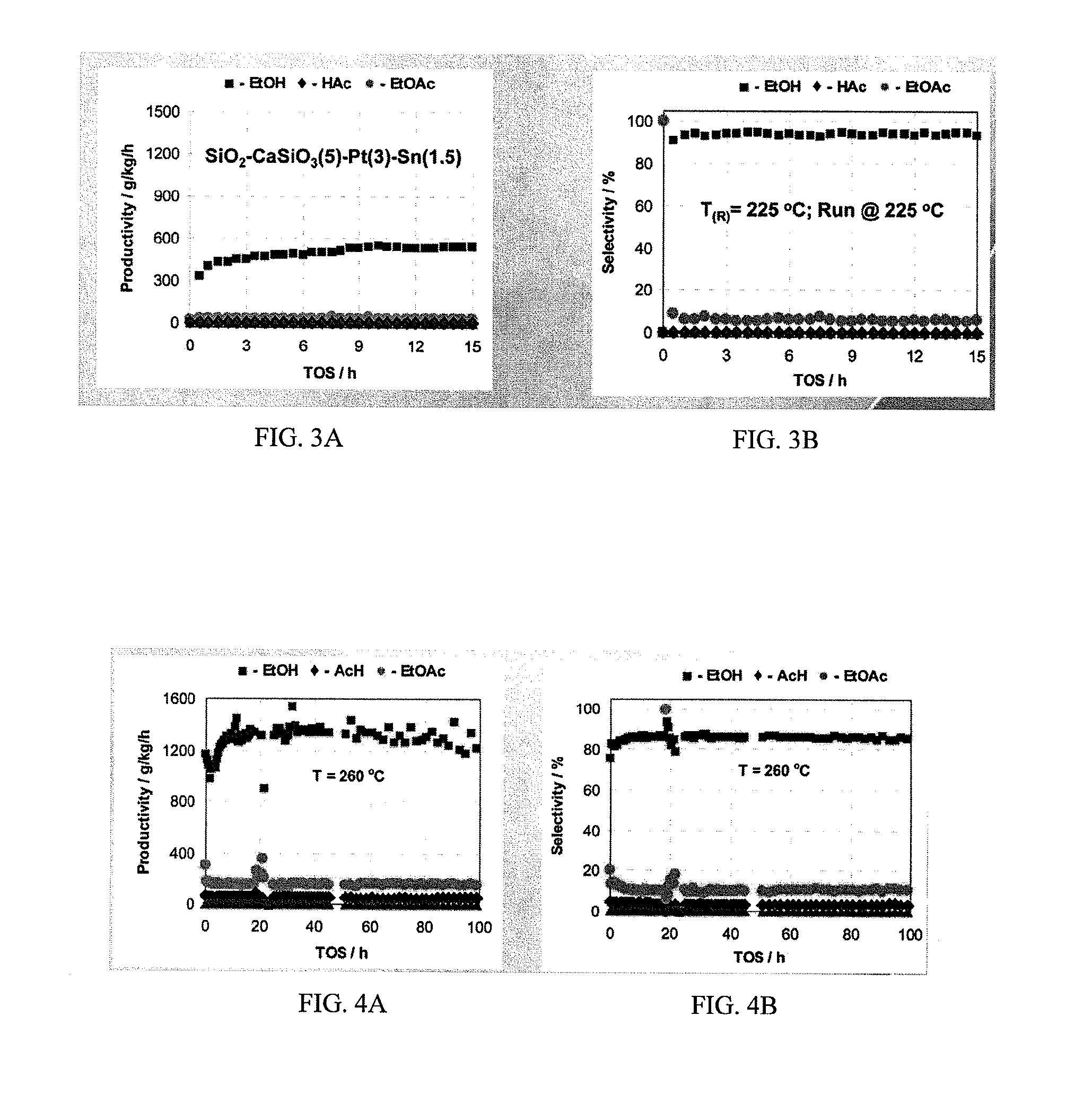
A process for selective formation of ethanol from acetic acid by hydrogenating acetic acid in the presence of first metal, a silicaceous support, and at least one support modifier. Preferably, the first metal is selected from the group consisting of copper, iron, cobalt, nickel, ruthenium, rhodium, palladium, osmium, iridium, platinum, titanium, zinc, chromium, rhenium, molybdenum, and tungsten. In addition the catalyst may comprise a second metal preferably selected from the group consisting of copper, molybdenum, tin, chromium, iron, cobalt, vanadium, tungsten, palladium, platinum, lanthanum, cerium, manganese, ruthenium, rhenium, gold, and nickel.
Owner:CELANESE INT CORP
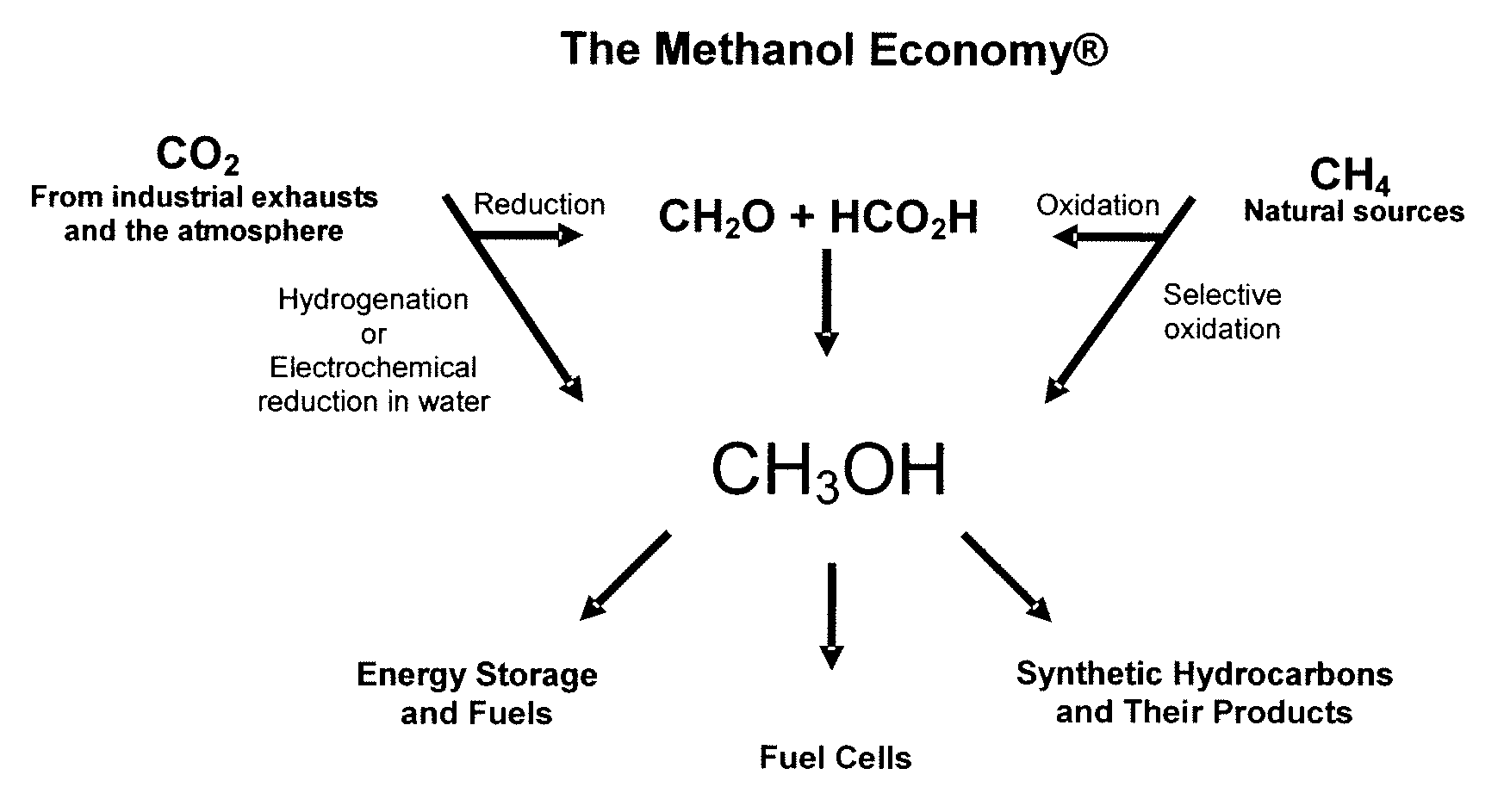
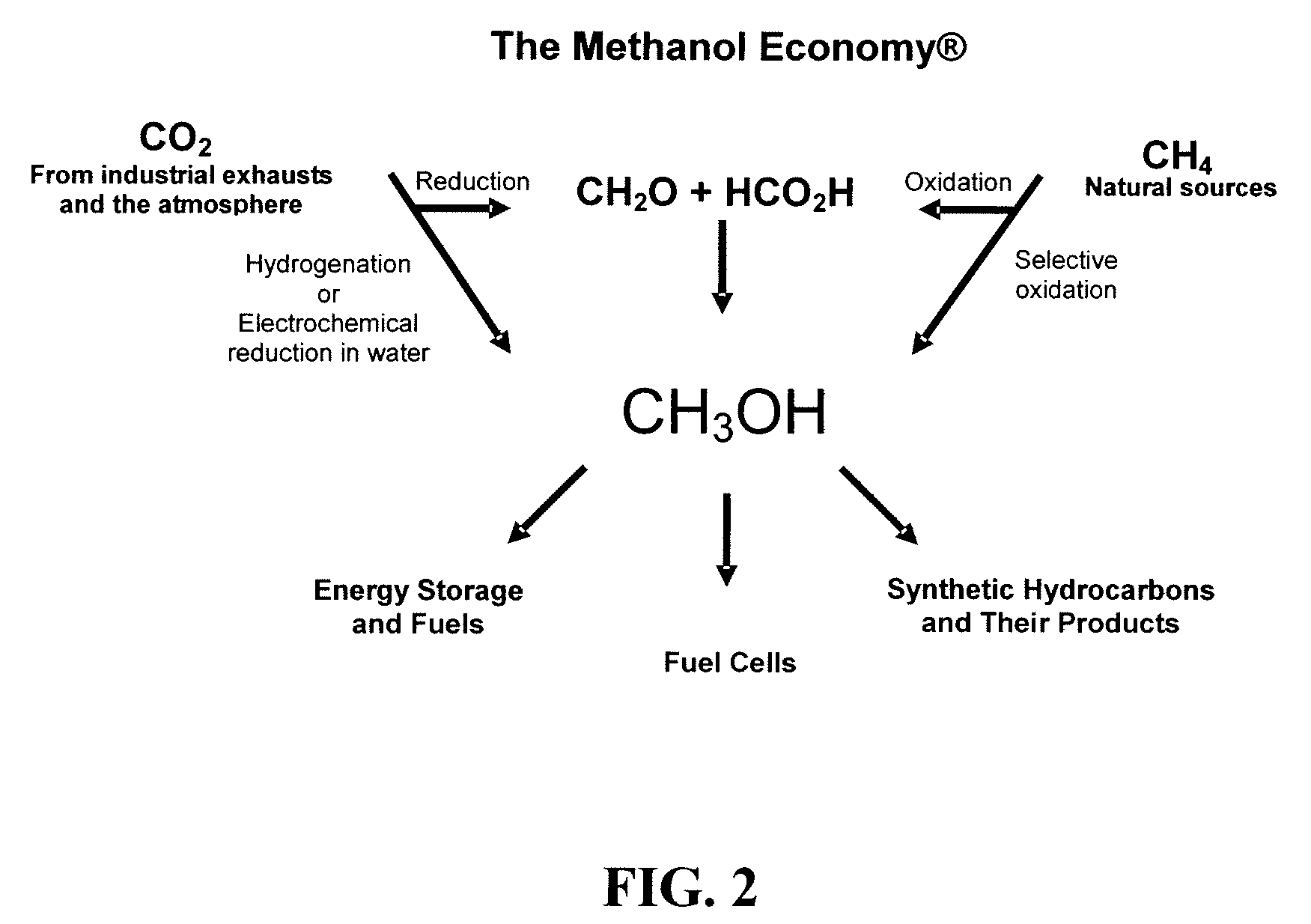
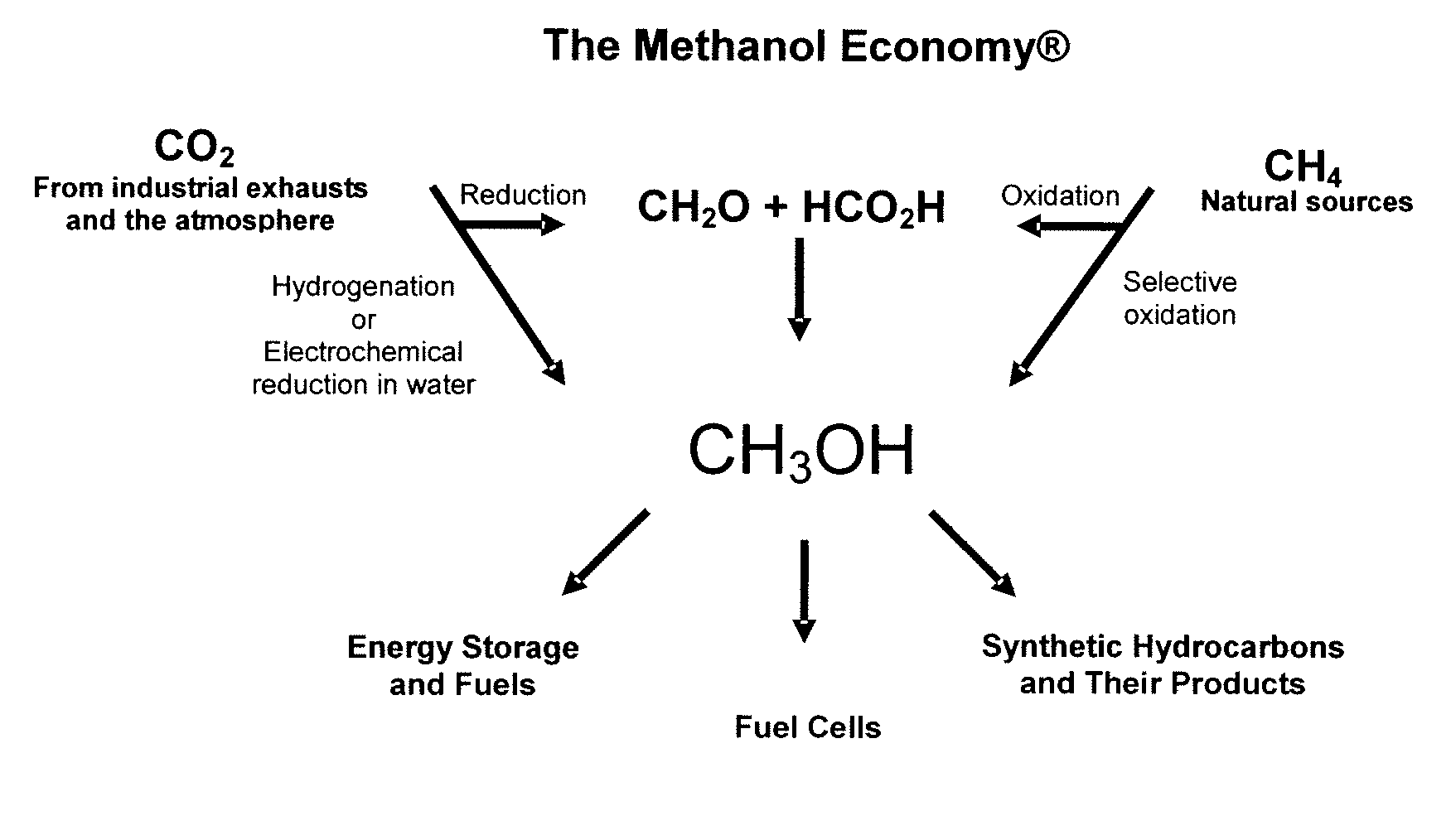
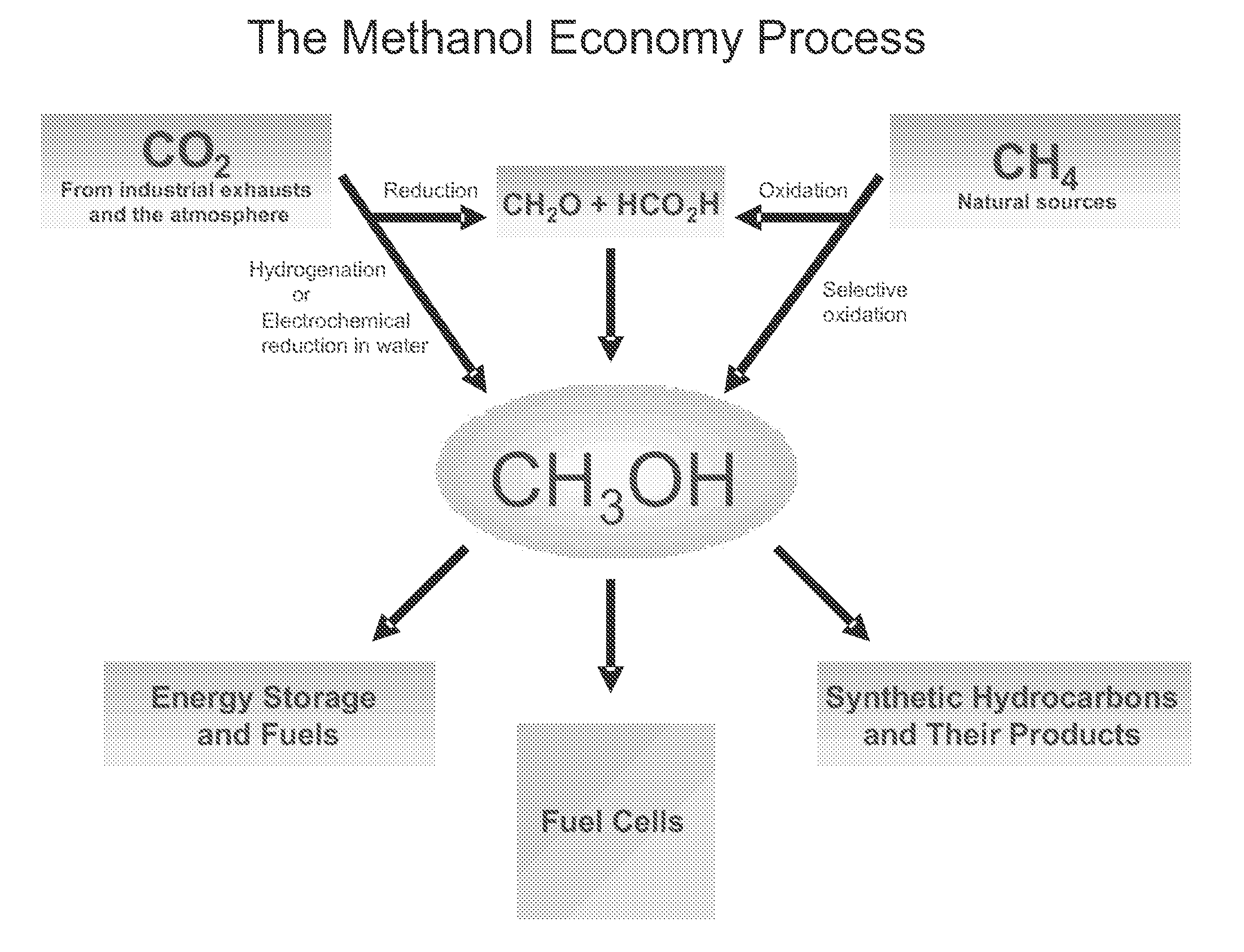
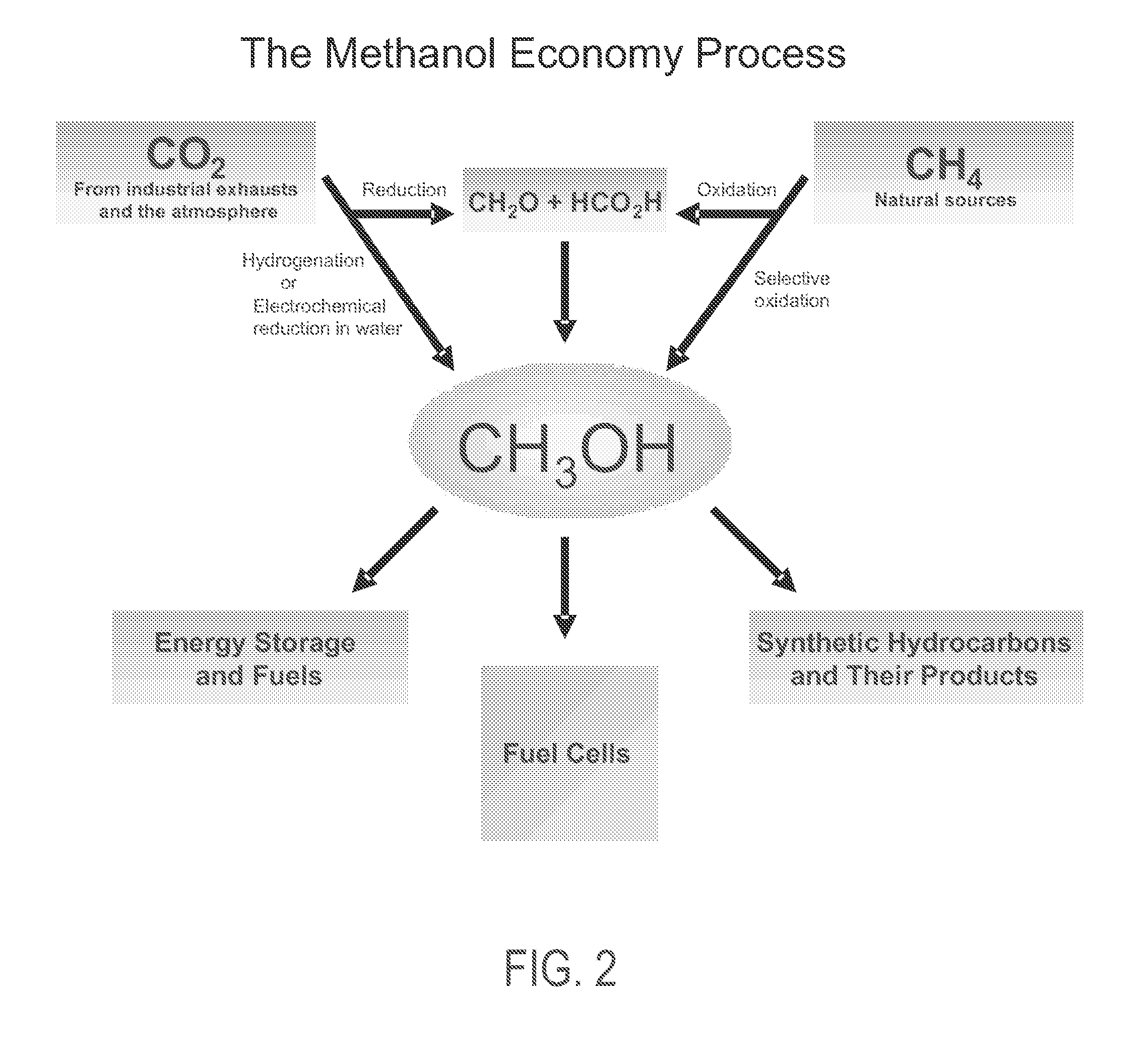
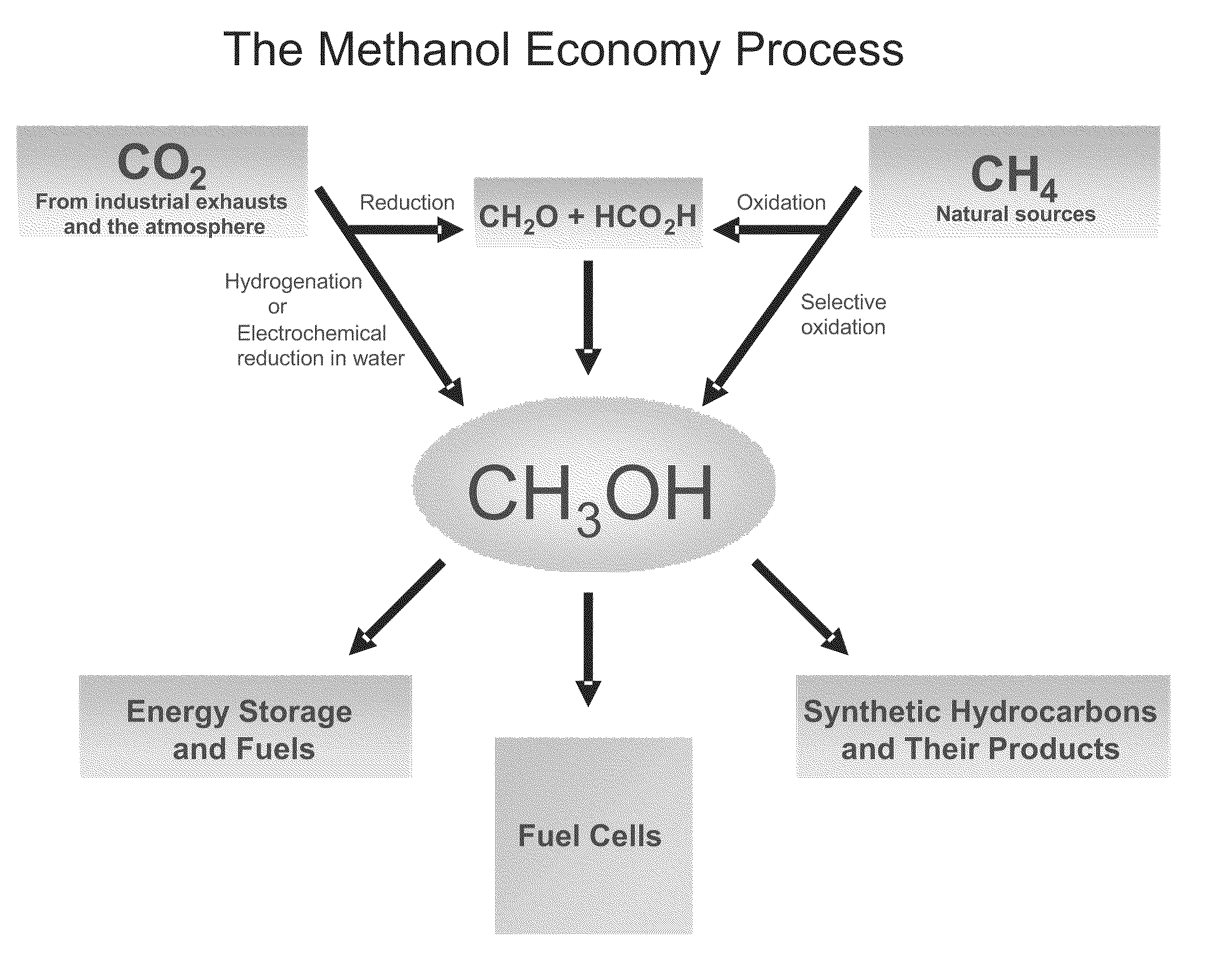
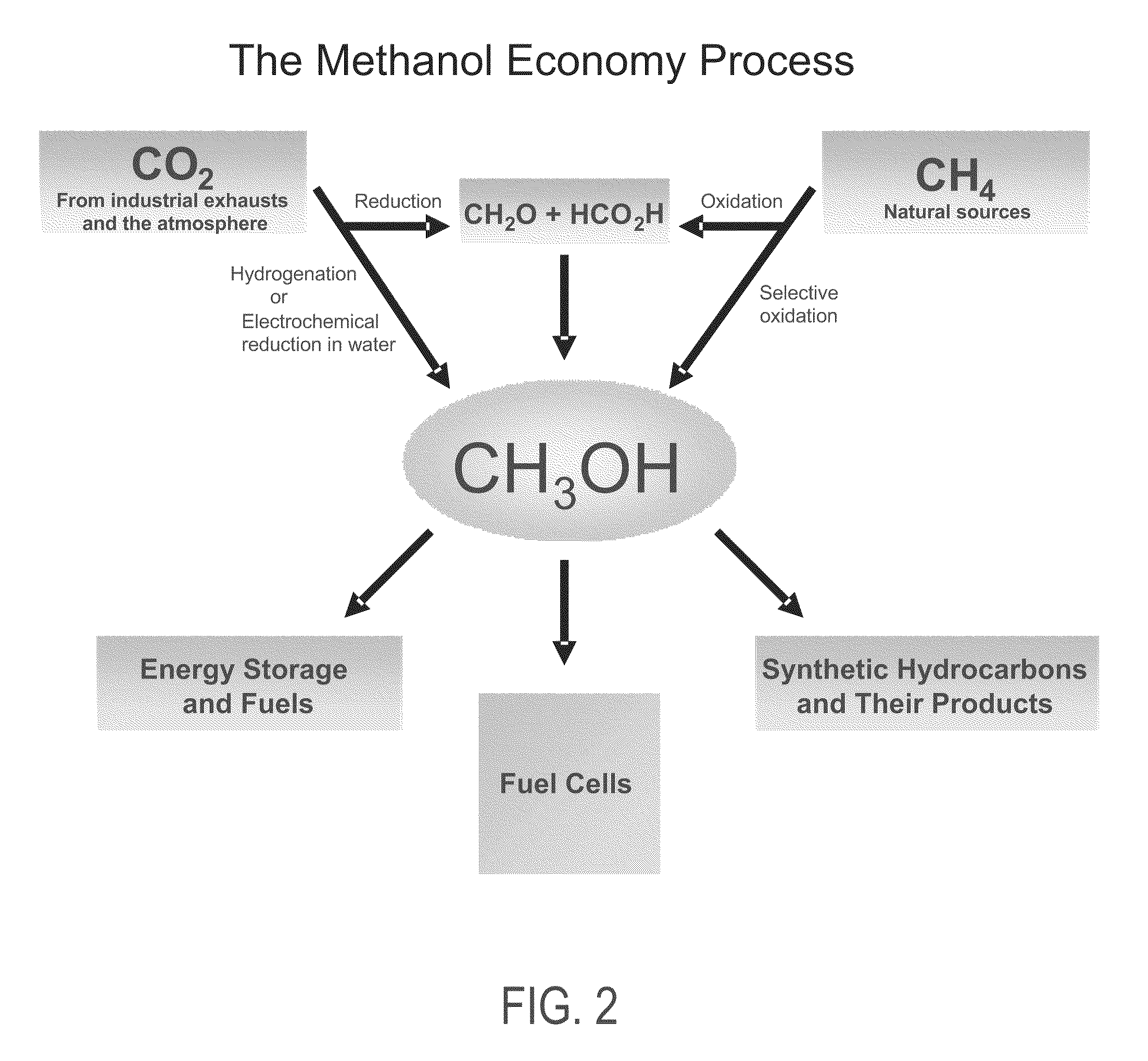
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one cell compartment and a metal cathode electrode in another cell compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte of one or more alkyl ammonium halides, alkali carbonates or combinations thereof to produce therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Process for extraction and purification of lutein, zeaxanthin and rare carotenoids from marigold flowers and plants
InactiveUS6262284B1Oxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationBeta-CaroteneBeta-cryptoxanthin
A process for simultaneously extracting, saponifying, and isolating lutein and zeaxanthin, and a mixture of several rare carotenoids in high purity from plants without the use of harmful organic solvents. Lutein crystals containing 5% zeaxanthin were obtained from the dried petals of Marigold flowers Tagete erecla while zeaxanthin was isolated and purified from the berries of Lycium Chinese Mill (LCM berries). Similarly, this process has been employed to isolate and purify a mixture of lutein, beta-carotene, neoxanthin, violaxanthin, and lutein epoxide from green plants, preferably, kale, collard green, and spinach. These plants, to a lesser extent, also serve as a source of several rare carotenoids such as alpha-cryptoxanthin (Marigolds) and beta-cryptoxanthin (LCM berries). The purified carotenoids isolated by this process are free from impurities and serve as a safe source of nutritional supplement for human consumption as well as providing a suitable and effective color additive for human foods.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Fullerene nanotube compositions
InactiveUS20080063585A1High yieldModerate temperatureMaterial nanotechnologyFullerenesFullereneNanotube
This invention relates generally to a fullerene nanotube composition. The fullerene nanotubes may be in the form of a felt, such as a bucky paper. Optionally, the fullerene nanotubes may be derivatized with one or more functional groups. Devices employing the fullerene nanotubes of this invention are also disclosed.
Owner:RICE UNIV
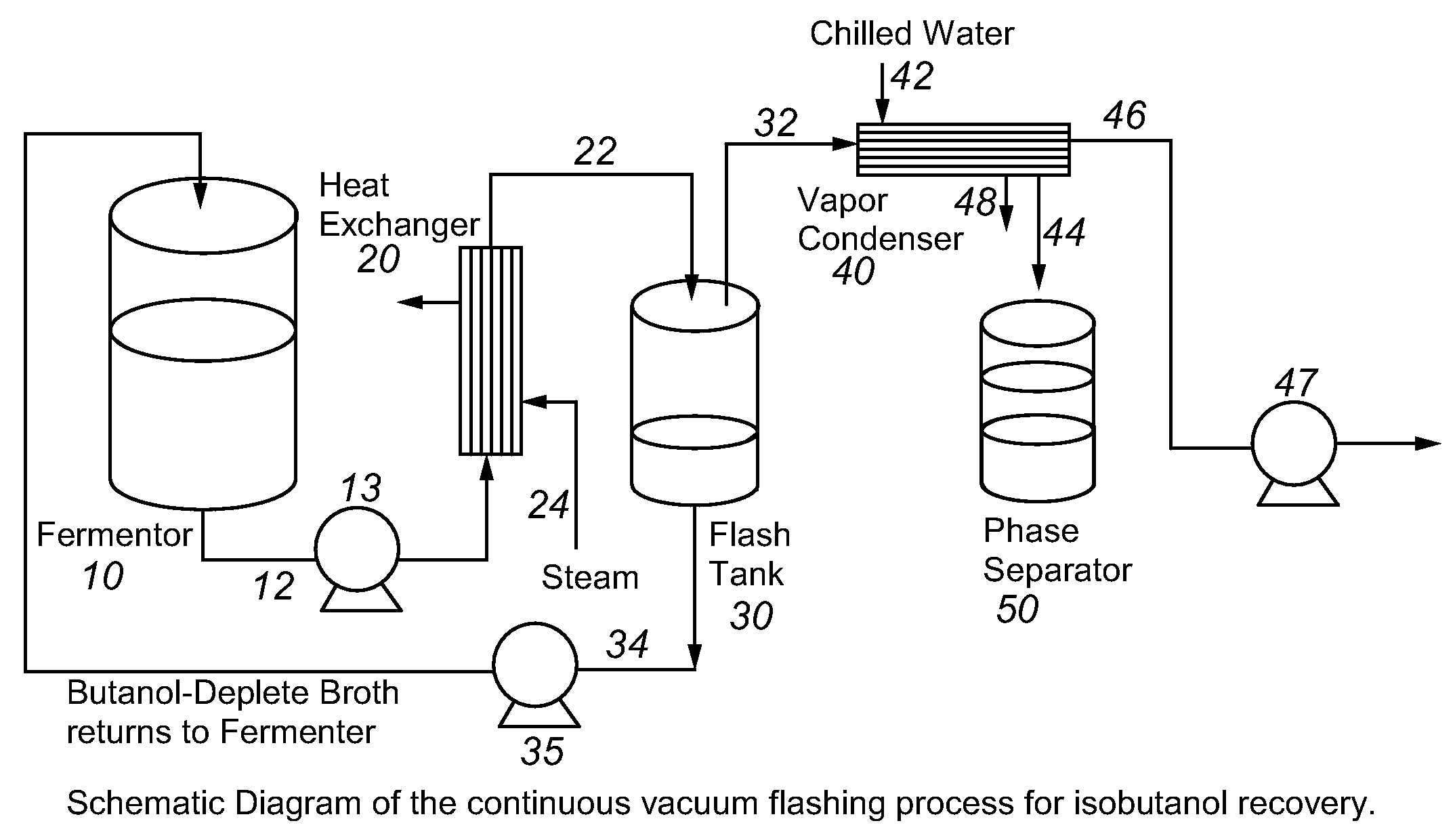
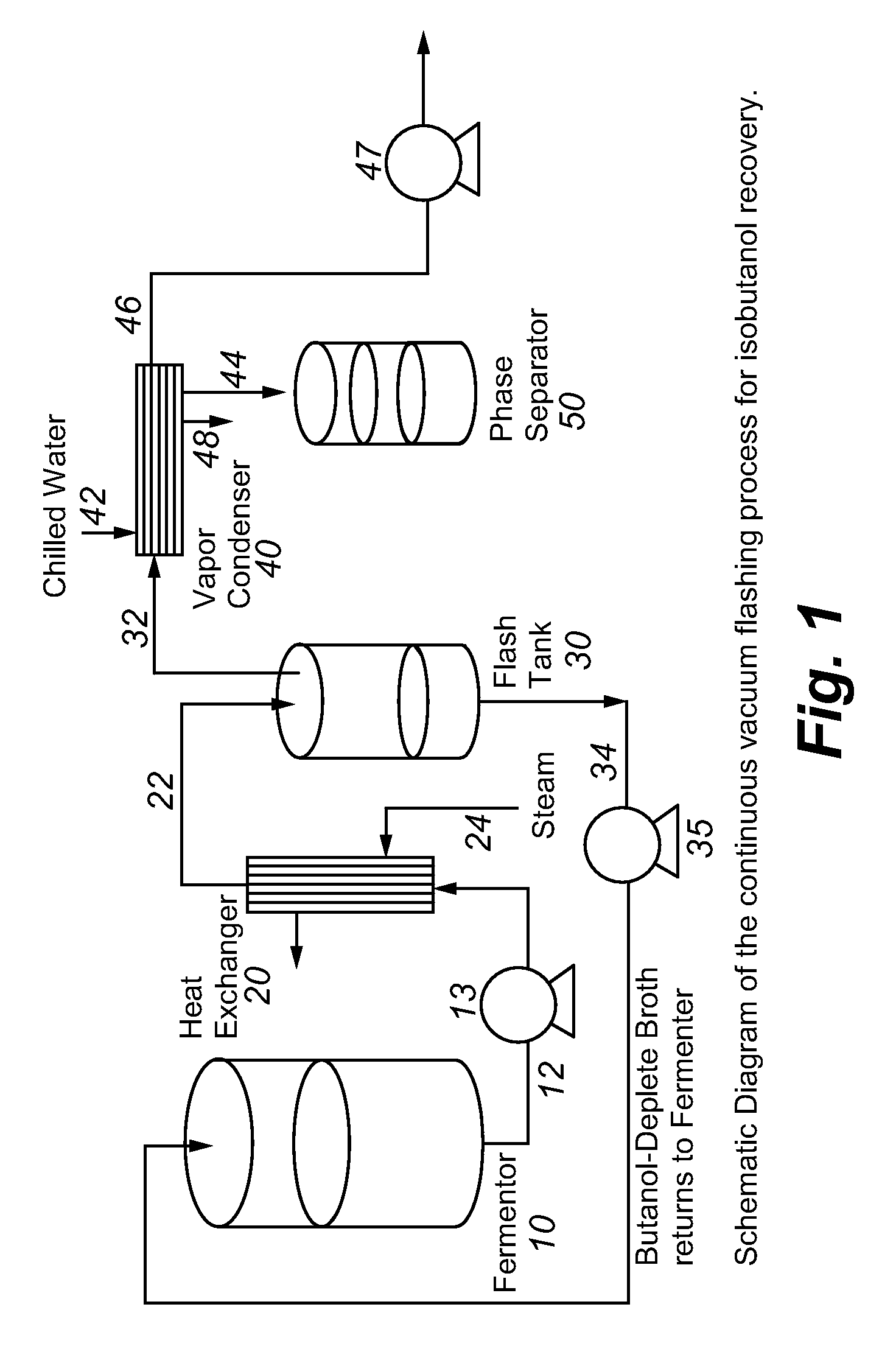
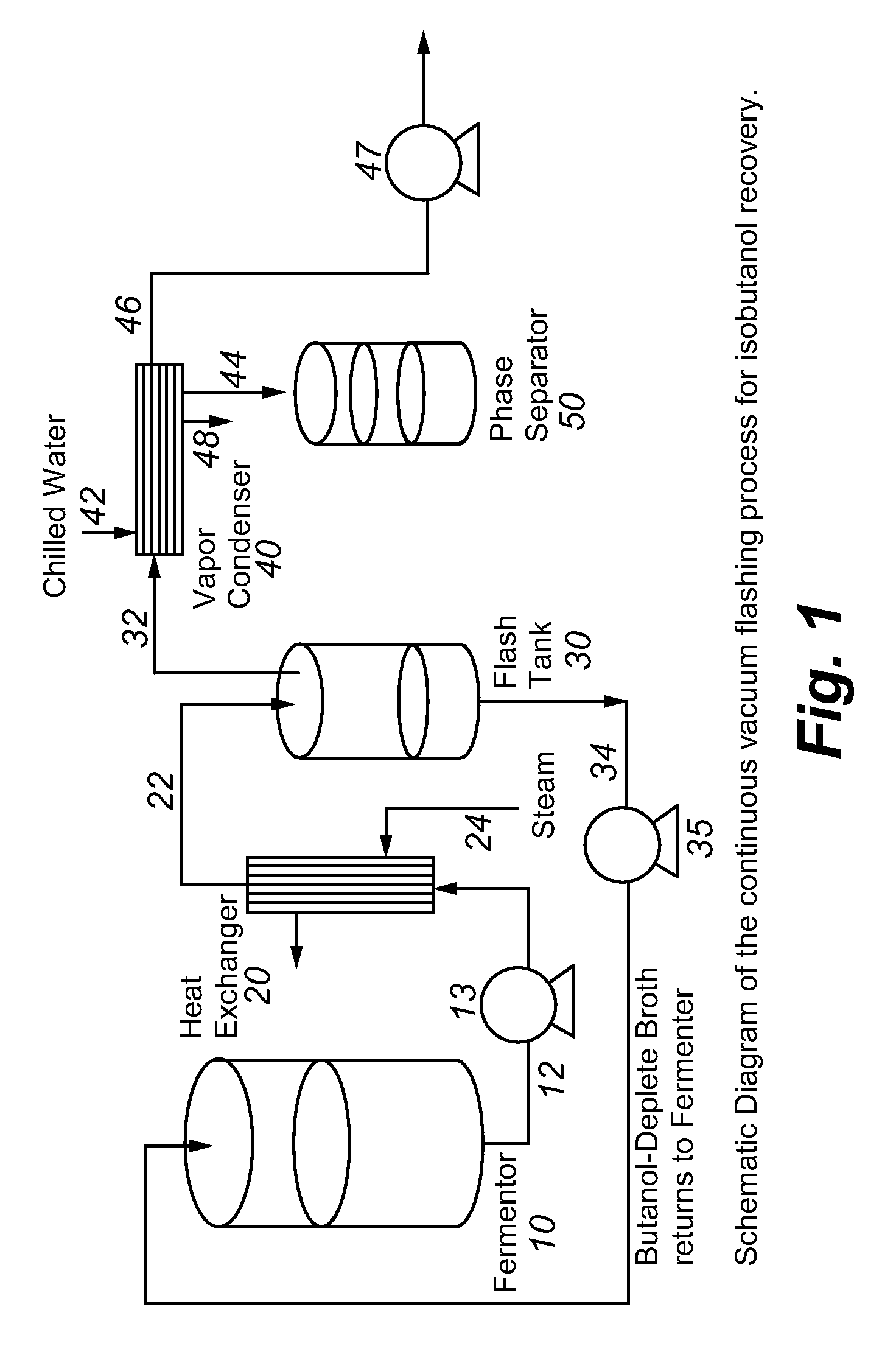
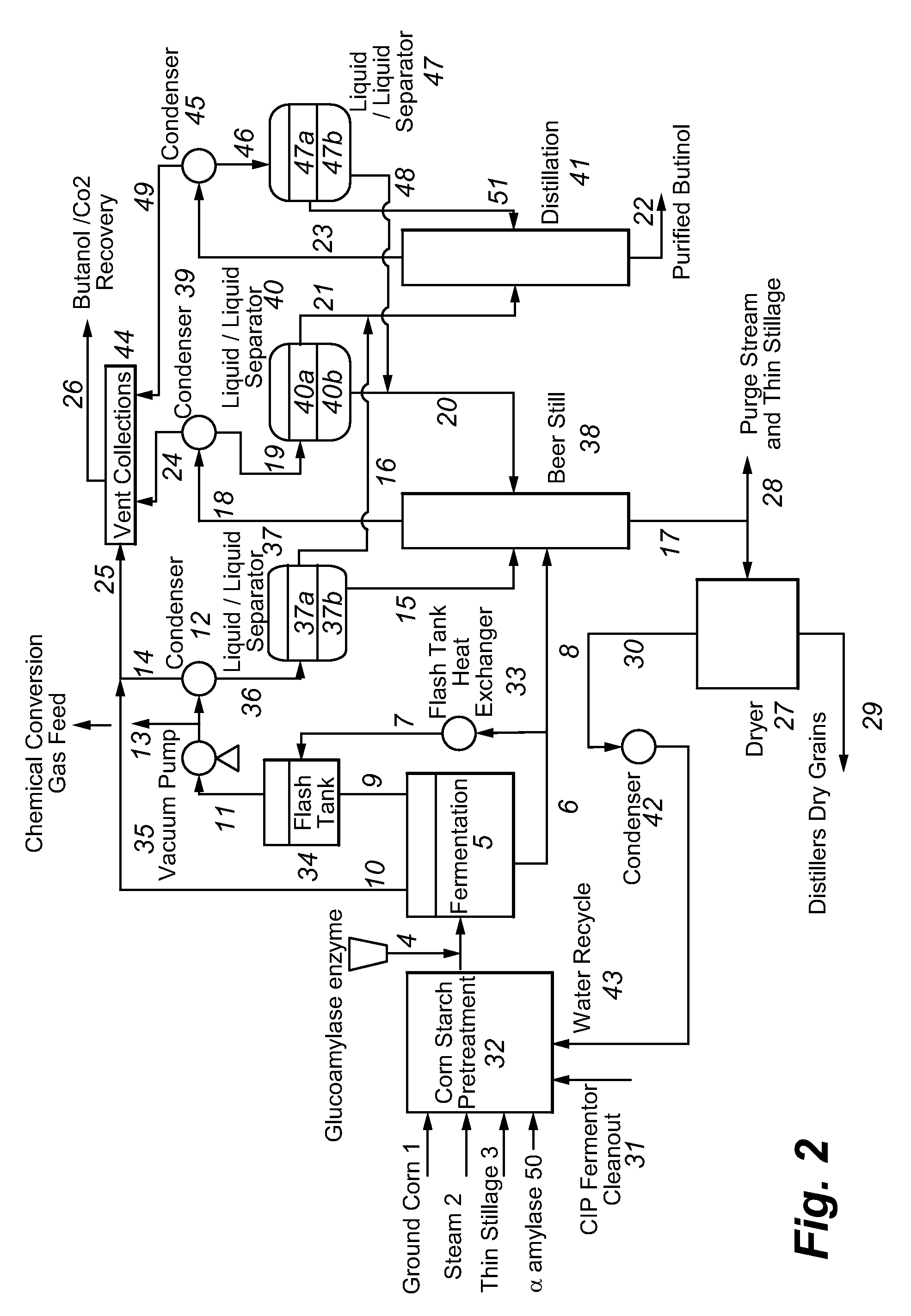
Recovery of higher alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions
ActiveUS20090171129A1High activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProduction rateAqueous solution
This invention is directed to methods for recovery of C3-C6 alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions, such as fermentation broths. Such methods provide improved volumetric productivity for the fermentation and allows recovery of the alcohol. Such methods also allow for reduced energy use in the production and drying of spent fermentation broth due to increased effective concentration of the alcohol product by the simultaneous fermentation and recovery process which increases the quantity of alcohol produced and recovered per quantity of fermentation broth dried. Thus, the invention allows for production and recovery of C3-C6 alcohols at low capital and reduced operating costs.
Owner:GEVO INC
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one cell compartment and a metal cathode electrode in another cell compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte of one or more alkyl ammonium halides, alkali carbonates or combinations thereof to produce therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Oxide catalyst composition
InactiveUS7012039B2High selectivityLow selectivityOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationLanthanideMethacrolein
An oxide catalyst composition for use in producing methacrolein or a mixture of methacrolein and methacrylic acid, wherein the oxide catalyst composition is represented by the formula (Mo+W)l2BiaAbBcFedXeSbfOg, wherein: A is at least one member selected from the group consisting of Y and the elements of the lanthanoid series exclusive of Pm; B is at least one member selected from the group consisting of K, Rb and Cs; X is Co solely, or a mixture of Co and at least one member selected from the group consisting of Mg and Ni; and a, b, c, d, e, f and g are, respectively, the atomic ratios of Bi, A, B, Fe, X, Sb and O, relative to twelve atoms of the total of Mo and W, wherein the atomic ratios (a to f) of the elements and the relationship between the amounts of the elements are chosen so as to satisfy specific requirements.
Owner:ASAHI KASEI CHEM CORP
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
ActiveUS20100193370A1Efficient combustionElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisAtmospheric air
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one compartment and a metal cathode electrode in a compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte. An anion-conducting membrane can be provided between the anode and cathode to produce at the cathode therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode. The oxygen produced at the anode can be recycled for efficient combustion of fossil fuels in power plants to exclusively produce CO2 exhausts for capture and recycling as the source of CO2 for the cell.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Process for the synthesis of unsaturated alcohols
ActiveUS7176336B2Increase the number ofIncrease productionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationPolymer scienceDecene
A process of preparing an unsaturated alcohol (olefin alcohol), such as, a homo-allylic mono-alcohol or homo-allylic polyol, involving protecting a hydroxy-substituted unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester, such as methyl ricinoleate, derived from a seed oil, to form a hydroxy-protected unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester; homo-metathesizing or cross-metathesizing the hydroxy-protected unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester to produce a product mixture containing a hydroxy-protected unsaturated metathesis product; and deprotecting the hydroxy-protected unsaturated metathesis product under conditions sufficient to prepare the unsaturated alcohol. Preferably, methyl ricinoleate is converted by cross-metathesis or homo-metathesis into the homo-allylic mono-alcohol 1-decene-4-ol or the homo-allylic polyol 9-octadecene-7,12-diol, respectively.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
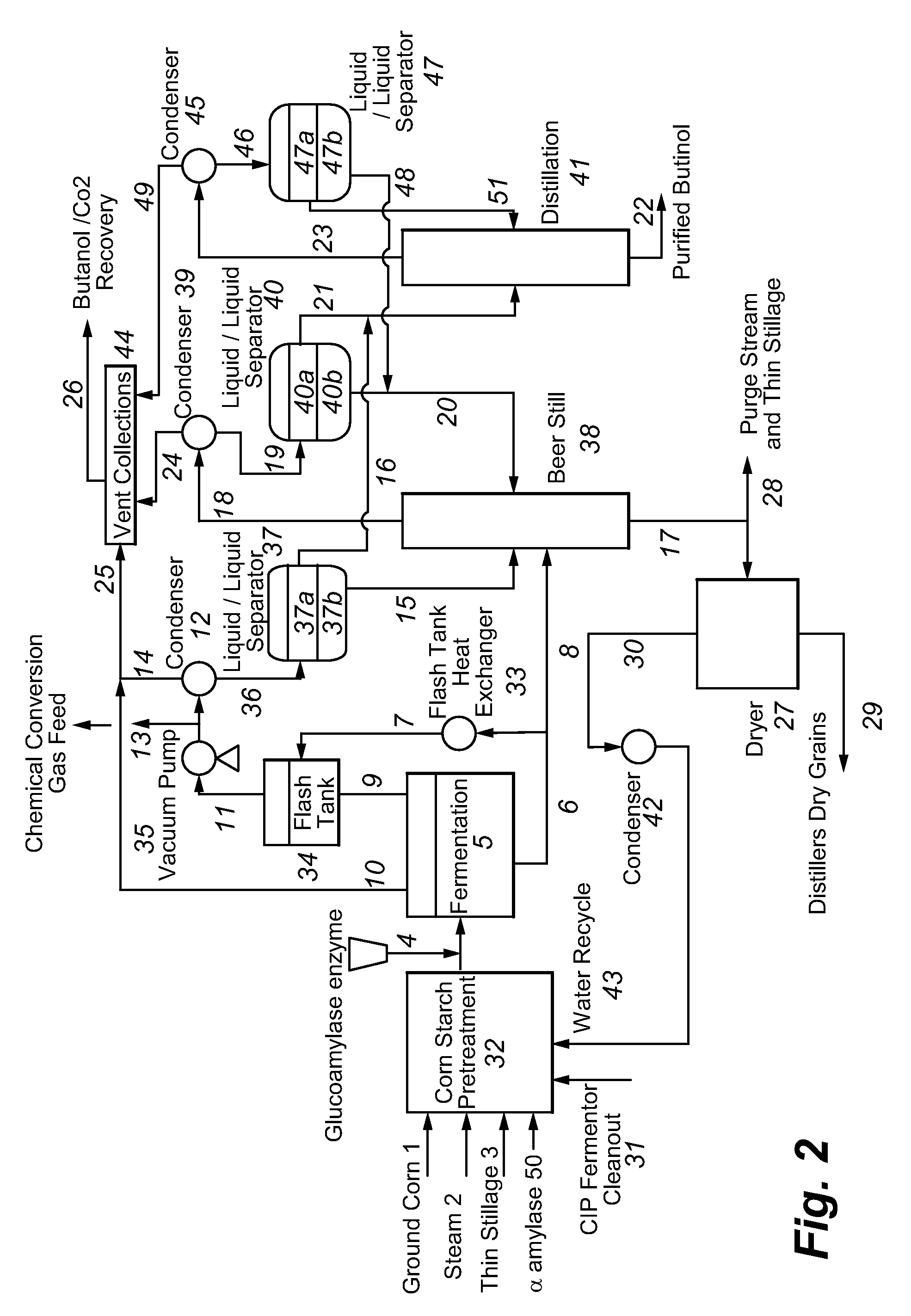
Recovery of higher alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions
ActiveUS8101808B2High activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAqueous solutionAlcohol products
This invention is directed to methods for recovery of C3-C6 alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions, such as fermentation broths. Such methods provide improved volumetric productivity for the fermentation and allows recovery of the alcohol. Such methods also allow for reduced energy use in the production and drying of spent fermentation broth due to increased effective concentration of the alcohol product by the simultaneous fermentation and recovery process which increases the quantity of alcohol produced and recovered per quantity of fermentation broth dried. Thus, the invention allows for production and recovery of C3-C6 alcohols at low capital and reduced operating costs.
Owner:GEVO INC
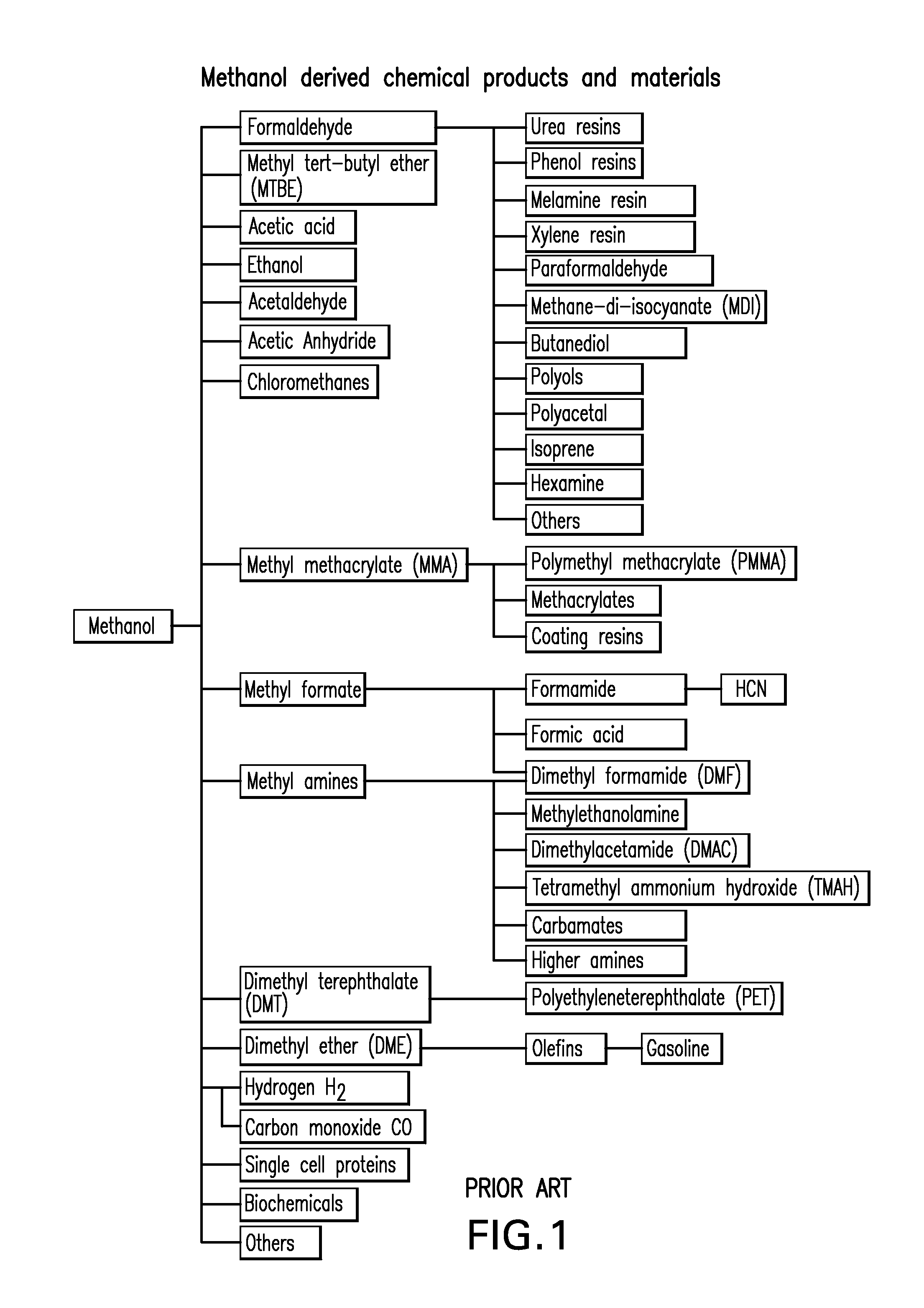
Method for simultaneously producing 1,3-propylene glycol and 1,2-propylene glycol
The invention relates to a chemical material production method, in particular to a method for simultaneously producing 1,3-propylene glycol and 1,2-propylene glycol. Alkyl carboxylic acid vinyl ester carries out hydroformylation with carbon monoxide and hydrogen under the action of olefin hydroformylation catalyst, so that 3-alkylacyloxy propaldehyde and 2- alkylacyloxy propaldehyde are produced, the 3-alkylacyloxy propaldehyde and the 2- alkylacyloxy propaldehyde react with hydrogen under the action of aldehyde hydrogenation catalyst, so that 3-alkylacyloxy propyl alcohol and 2-alkylacyloxy propyl alcohol are produced, and the 3-alkylacyloxy propyl alcohol and the 2-alkylacyloxy propyl alcohol are hydrolyzed under the action of esterolytic catalyst, so that the 1,3-propylene glycol and the 1,2-propylene glycol are produced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Manufacture of alcohols
Owner:EXXONMOBIL CHEM PAT INC
Process for preparing ethandiol by catalyzing epoxyethane hydration
InactiveCN1463960AHigh activityGood choiceBulk chemical productionPreparation by hydrolysisEpoxideEnergy consumption
The present invention relates to process of catalytic hydration of ethylene epoxide to prepare glycol and aims at solving the problems of available corresponding process. The said process is especially suitable for low water ratio operation, and has the features of very low heat energy consumption and power consumption, high activity, selectivity and stability of catalyst, and low production cost. The said process may be used in industrial production of glycol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method of functionalizing a carbon material
InactiveUS20110053050A1Material nanotechnologyGroup 8/9/10/18 element organic compoundsCarboxylic acidMaterials science
The present invention relates to a method of functionalizing a carbon material. A carbon material is contacted with a carboxylic acid, whereby a mixture is formed. The mixture is heated for a suitable period of time at a temperature below the thermal decomposition temperature of the carbon material.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Microorganisms and methods for conversion of syngas and other carbon sources to useful products
A non-naturally occurring microbial organism having an isopropanol, 4-hydroxybutryate, or 1,4-butanediol pathway includes at least one exogenous nucleic acid encoding an isopropanol, 4-hydroxybutryate, or 1,4-butanediol pathway enzyme expressed in a sufficient amount to produce isopropanol, 4-hydroxybutryate, or 1,4-butanediol. The aforementioned organisms are cultured to produce isopropanol, 4-hydroxybutryate, or 1,4-butanediol.
Owner:GENOMATICA INC
Mesoporous material with active metals
A process for treating organic compounds includes providing a composition which includes a substantially mesoporous structure of silica containing at least 97% by volume of pores having a pore size ranging from about 15 Å to about 30 Å and having a micropore volume of at least about 0.01 cc / g, wherein the mesoporous structure has incorporated therewith at least about 0.02% by weight of at least one catalytically and / or chemically active heteroatom selected from the group consisting of Al, Ti, V, Cr, Zn, Fe, Sn, Mo, Ga, Ni, Co, In, Zr, Mn, Cu, Mg, Pd, Pt and W, and the catalyst has an X-ray diffraction pattern with one peak at 0.3° to about 3.5° at 2θ. The catalyst is contacted with an organic feed under reaction conditions wherein the treating process is selected from alkylation, acylation, oligomerization, selective oxidation, hydrotreating, isomerization, demetalation, catalytic dewaxing, hydroxylation, hydrogenation, ammoximation, isomerization, dehydrogenation, cracking and adsorption.
Owner:ABB LUMMUS GLOBAL INC
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
ActiveUS8138380B2Efficient combustionPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisOxygen
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one compartment and a metal cathode electrode in a compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte. An anion-conducting membrane can be provided between the anode and cathode to produce at the cathode therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode. The oxygen produced at the anode can be recycled for efficient combustion of fossil fuels in power plants to exclusively produce CO2 exhausts for capture and recycling as the source of CO2 for the cell.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Catalyst for producing ethylene glycol from hydrogenation of oxalic ester
ActiveCN101474561AImprove stabilityImprove technical effectMolecular sieve catalystsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsLow activityMolecular sieve
The invention relates to a catalyst for ethanediol production by oxalic ester hydrogenation, which solves the problems of small specific surface, low activity and poor stability of the catalyst in the previous technique. The catalyst used in the invention is composed of the following active components, assistants and carriers in terms of parts by weight: (a) 5-80 parts of active components; (b) 0-40 parts of assistants and (c) 1-30 parts of carriers, wherein the active component is copper, copper oxide or mixture thereof, the assistant is selected from at least one of Zn, Mn, Ba, Cr, Ni or Fe or oxides thereof and the carrier is selected from at least one of the alumina, silica, zirconia or molecular sieve. When the active component is copper, the technical scheme that the value of (b) is more than zero solves the problem in a good way. The catalyst can be used for ethanediol production in the industry.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
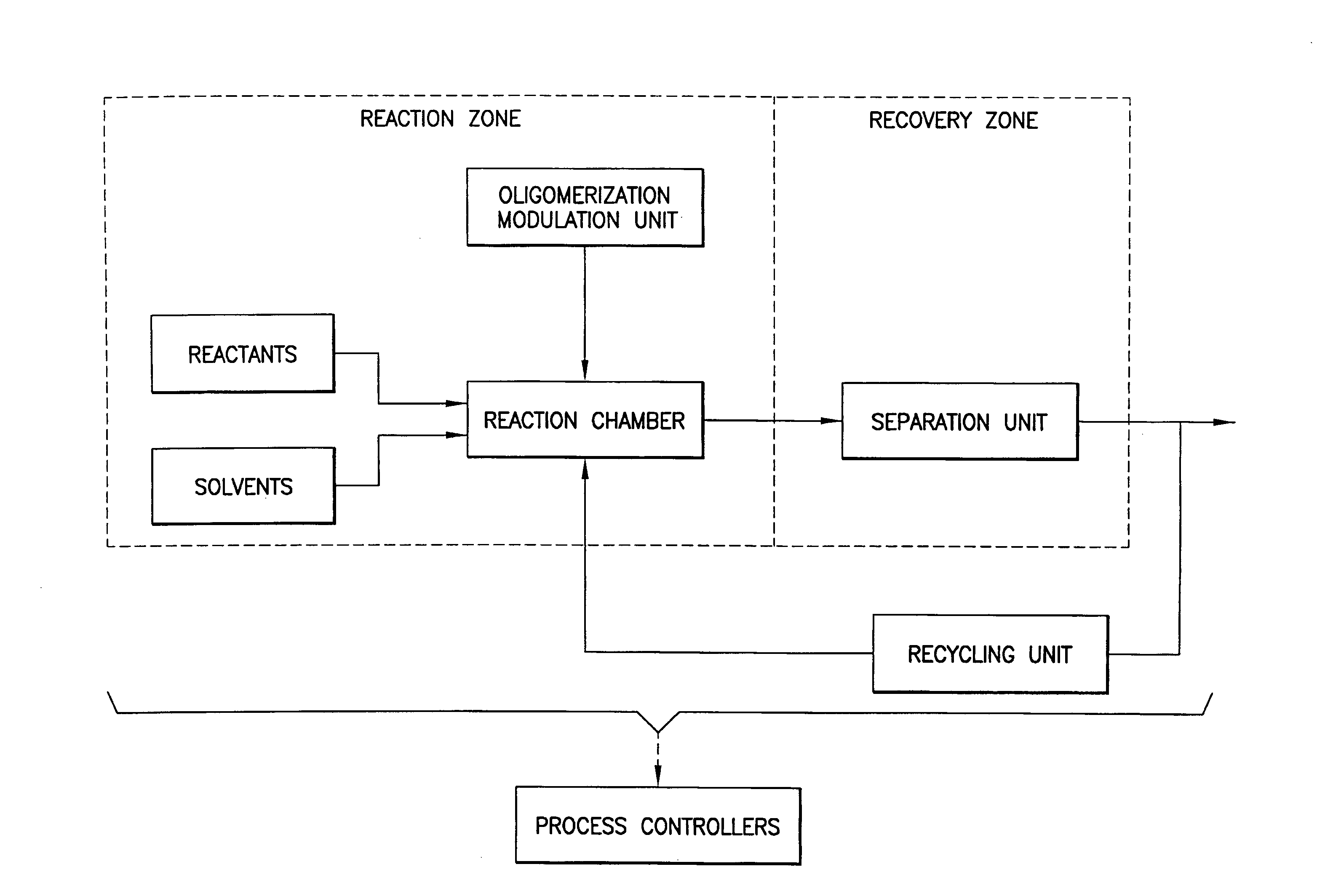
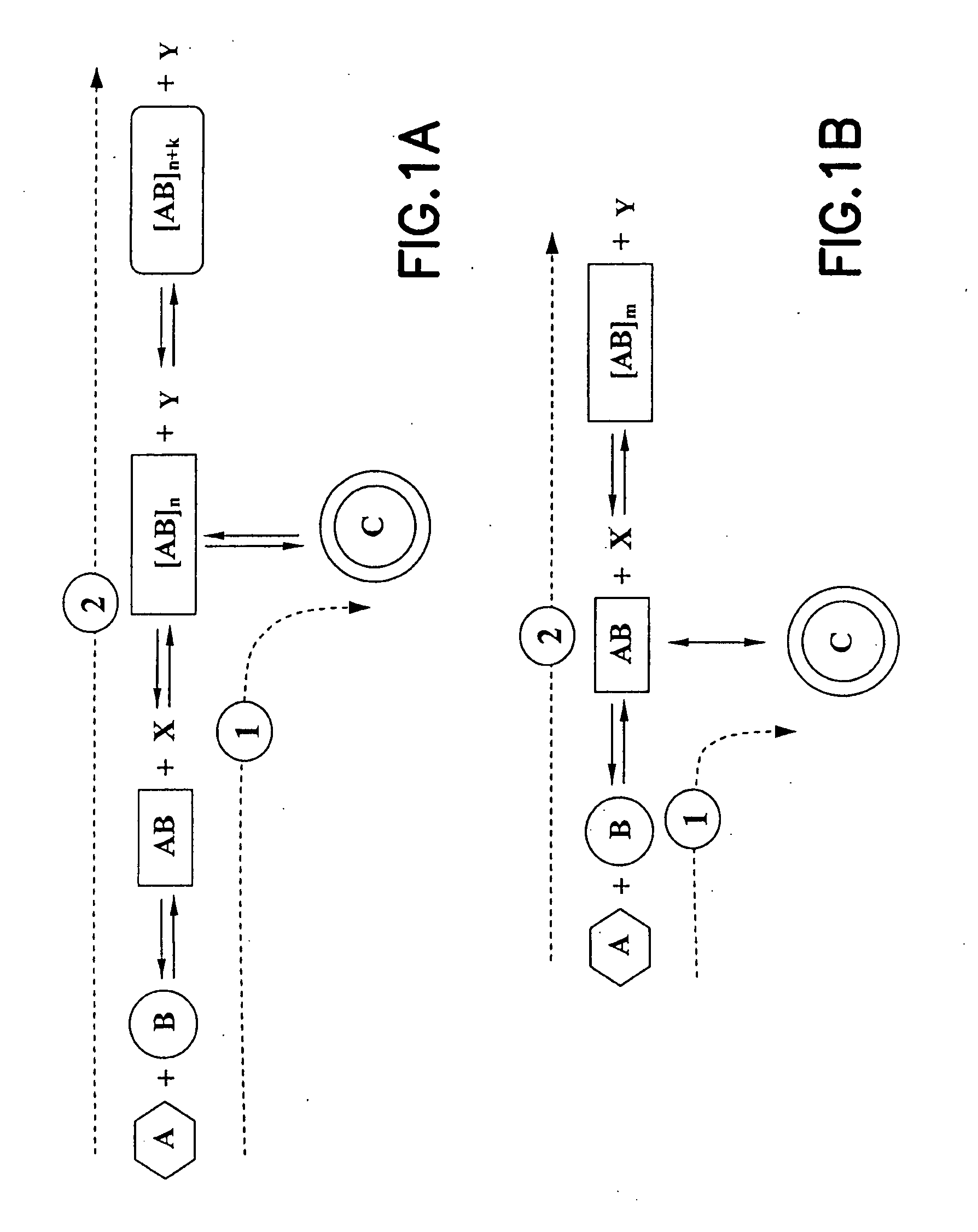
Methods, compositions, and apparatuses for forming macrocyclic compounds
ActiveUS20070217965A1Improve production efficiencyHigh yieldHydrocarbon by dehydrogenationCyclic peptide ingredientsOligomerFiltration
This invention relates to methods, compositions, and apparatuses for producing macrocyclic compounds. First, one or more reactants are provided in a reaction medium, which are capable of forming the macrocyclic compound through a desired reaction pathway that includes at least cyclization, and which are further capable of forming undesired oligomers through a undesired reaction pathway that includes undesirable oligomerization. Oligomerization of such reactions in the reaction medium is modulated to reduce formation of undesired oligomers and / or to reduce separation of the undesired oligomers from the reaction medium, relative to a corresponding unmodulated oligomerization reaction, thereby maximizing yields of the macrocyclic compound. The macrocyclic compound so formed is then recovered from the reaction medium. Preferably, the macrocyclic compound spontaneously separates from the reaction medium via phase separation. More preferably, the macrocyclic compound spontaneous precipitates from the reaction medium and therefore can be easily recovered by simple filtration.
Owner:JOHNSON THOMAS E +1
Biological radical polyatomic alcohol prepared by Jatropha curcas oil
The present invention relates to a preparation method for a biological polybasic alcohol by using of an aleurites fordii. The preparation method is as follows: an alcohol-decomposing agent is added into the aleurites fordii to make the alcohol-decomposing reaction in the catalyzing environment to create a mixing ester of fatty acid; and then an epoxidizing agent is added into the mixing ester of fatty acid to make the epoxidizing reaction in the catalyzing environment to create a mixing epoxidizing ester of fatty acid; the mixing epoxidizing ester of fatty acid takes the opening reaction of epoxidizing key with an opening agent to create a mixing hydroxylic ester of fatty acid, i.e. a biological polybasic alcohol. The biological polybasic alcohol takes the addition reaction with an oxidation alkene in the catalyzing environment to create a biological polybasic alcohol with much higher molar weight. The preparation technics and operation of the present invention are more convenient; the adjustability for the product function is much better with much better performance. The aleurites fordii materials used in the present invention is a reproducible materials; so the cost is much lower and the material is abundant, which can replace the petrifaction polyether glycol to prepare the polyurethane foam plastic so that the dependence to the polyurethane product decreases.
Owner:HONGBAOLI GRP CO LTD
Quaternary phosphonium salt catalysts in catalytic hydrolysis of alkylene oxides
A process for the preparation of alkylene glycols by reacting an alkylene oxide with water in the presence of at least one ionic composition of a quaternary phosphonium cation of the general formula R1R2R3R4P+Whereby each of R1, R2, R3 and R4, independently, may be an alkyl, cycloalkyl, aryl, alkylaryl or arylalkyl group having from 1 to 10 carbon atoms, each of which may carry one or more substituents, or be attached to a polymer and an anion other than metalate or halogen.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
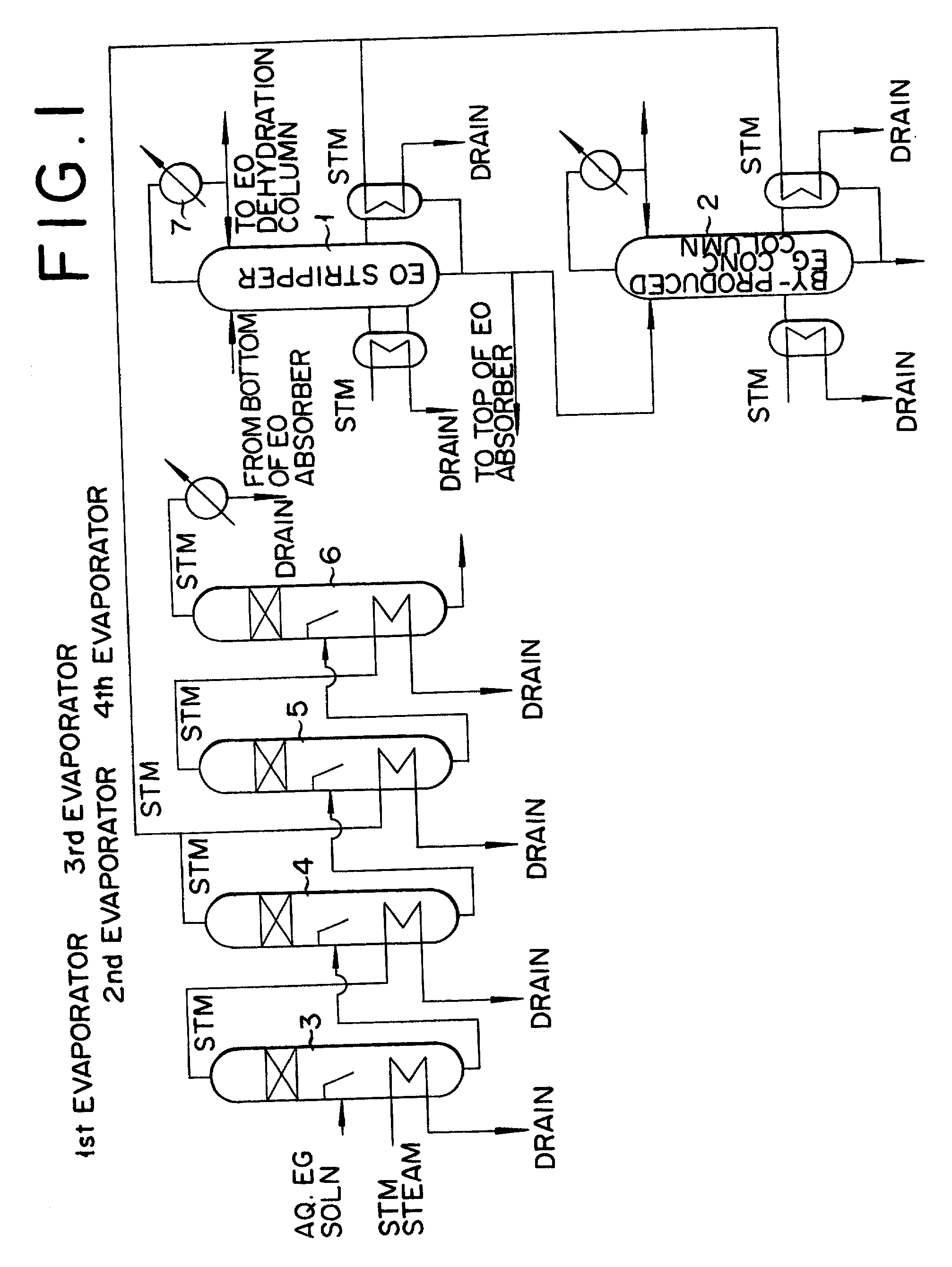
Method for production of ethylene oxide
InactiveUS20020010378A1Efficient comprehensive utilizationEffective utilization can be attainedOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationEthylene oxideMultiple-effect evaporator
In a composite process for subjecting ethylene to catalytic gas phase oxidation thereby obtaining ethylene oxide and causing this ethylene oxide to react with water thereby obtaining ethylene glycol, a method for producing the ethylene glycol is provided which permits effective utilization of the energy at the step for dehydrating and concentrating the resultant aqueous ethylene glycol solution. In the production of ethylene glycol by the supply of the aqueous ethylene glycol solution to a concentrating treatment at the multi-effect evaporator, the method contemplated by this invention for the production of ethylene glycol comprises utilizing as the source of heating at least one specific step the steam generated in the multi-effect evaporator.
Owner:RECOVERYCARE COM +1
Process for the start-up of an epoxidation process, a process for the production of ethylene oxide, a 1,2-diol, a 1,2-diol ether, a 1,2-carbonate, or an alkanolamine
InactiveUS20090281339A1Improve catalytic selectivityHigh selectivityProductsOrganic compound preparationOrganic chloride compoundOxygen
A process is provided for the start-up of an ethylene epoxidation process comprising: (a) contacting a catalyst bed comprising a high selectivity epoxidation catalyst with a feed comprising ethylene, oxygen and an organic chloride for a period of time until an increase of at least 1×10−5 mole-% of vinyl chloride (calculated as the moles of vinyl chloride relative to the total gas mixture), preferably 2×10−5 mole-% of vinyl chloride is detected in a reactor outlet gas or a recycle gas loop; and (b) subsequently adjusting the quantity of organic chloride in the feed to a value sufficient to produce ethylene oxide at a substantially optimum selectivity.
Owner:SHELL OIL CO
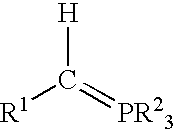
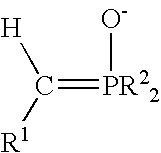
Process for preparing functional group-containing olefinic compounds
ActiveUS6838576B1High yieldStereoselectivity can be controlledPreparation by ester-hydroxy reactionOrganic compound preparationCompound aLeaving group
A process for preparing functional group-containing olefinic compounds comprises the steps of (a) reacting at least one alkylidene phosphorane with at least one carbonyl-containing compound that comprises at least one group that is a leaving group, or that is capable of subsequent conversion to a leaving group, to form an olefinic compound that comprises at least one leaving group, the carbonyl-containing compound being selected from the group consisting of ketones and aldehydes; and (b) reacting the olefinic compound with at least one functional group-containing nucleophile to form a functional group-containing olefinic compound.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Process for the synthesis of unsaturated alcohols
ActiveUS20050080301A1Increase the number of turnoversIncrease productionOxygen-containing compound preparationOrganic compound preparationMethyl ricinoleatePolyol
A process of preparing an unsaturated alcohol (olefin alcohol), such as, a homo-allylic mono-alcohol or homo-allylic polyol, involving protecting a hydroxy-substituted unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester, such as methyl ricinoleate, derived from a seed oil, to form a hydroxy-protected unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester; homo-metathesizing or cross-metathesizing the hydroxy-protected unsaturated fatty acid or fatty acid ester to produce a product mixture containing a hydroxy-protected unsaturated metathesis product; and deprotecting the hydroxy-protected unsaturated metathesis product under conditions sufficient to prepare the unsaturated alcohol. Preferably, methyl ricinoleate is converted by cross-metathesis or homo-metathesis into the homo-allylic mono-alcohol 1-decene-4-ol or the homo-allylic polyol 9-octadecene-7,12-diol, respectively.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Process for preparing ethandiol by catalytic hydration of epoxyethane
InactiveCN1204103CHigh activityGood choiceBulk chemical productionPreparation by hydrolysisEthylene oxideHigh activity
The present invention relates to process of catalytic hydration of ethylene epoxide to prepare glycol and aims at solving the problems of available corresponding process. The said process is especially suitable for low water ratio operation, and has the features of very low heat energy consumption and power consumption, high activity, selectivity and stability of catalyst, and low production cost. The said process may be used in industrial production of glycol.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
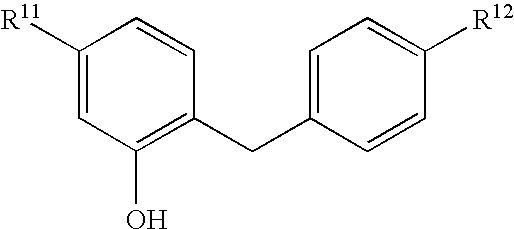
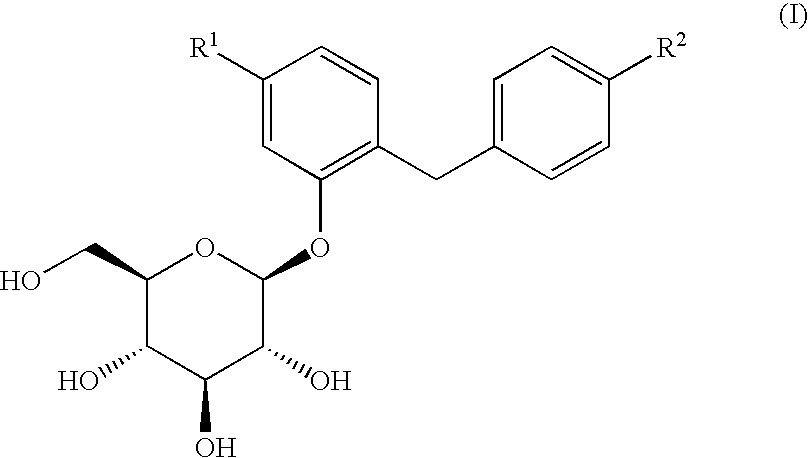
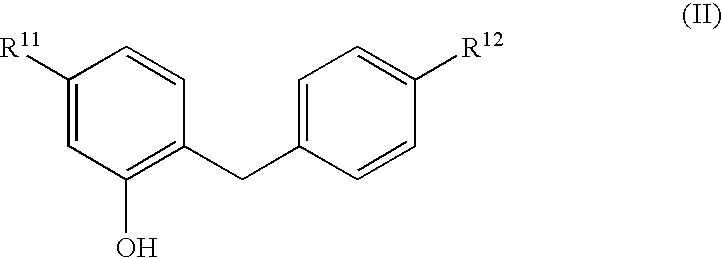
Glucopyranosyloxybenzylbenzene derivatives, medicinal compositions containing the same and intermediates for the preparation of the derivatives
InactiveUS7045665B2Strong inhibitory activityInhibitory activityBiocideSugar derivativesAcute hyperglycaemiaAlkoxy group
The present invention relates to benzylphenol derivatives represented by the general formula:wherein R11 represents a hydrogen atom or a protected hydroxy(lower alkyl) group; and R12 represents a lower alkyl group, a lower alkoxy group, a lower alkylthio group, a protected hydroxy(lower alkyl) group, a protected hydroxy(lower alkoxy) group, a protected hydroxy(lower alkylthio) group, a lower alkoxy-substituted (lower alkyl) group, a lower alkoxy-substituted (lower alkoxy) group or a lower alkoxy-substituted (lower alkylthio) group; with the proviso that R12 is not a methyl group, an ethyl group, an isopropyl group, a tert-butyl group or a methoxy group when R11 is a hydrogen atom, or a salt thereof, which are used as intermediates for making glucopyranosyloxybenzylbenzene compounds having inhibitory activity in human SGLT2 and are useful in treating diseases associated with hyperglycemia, such as diabetes.
Owner:KISSEI PHARMA
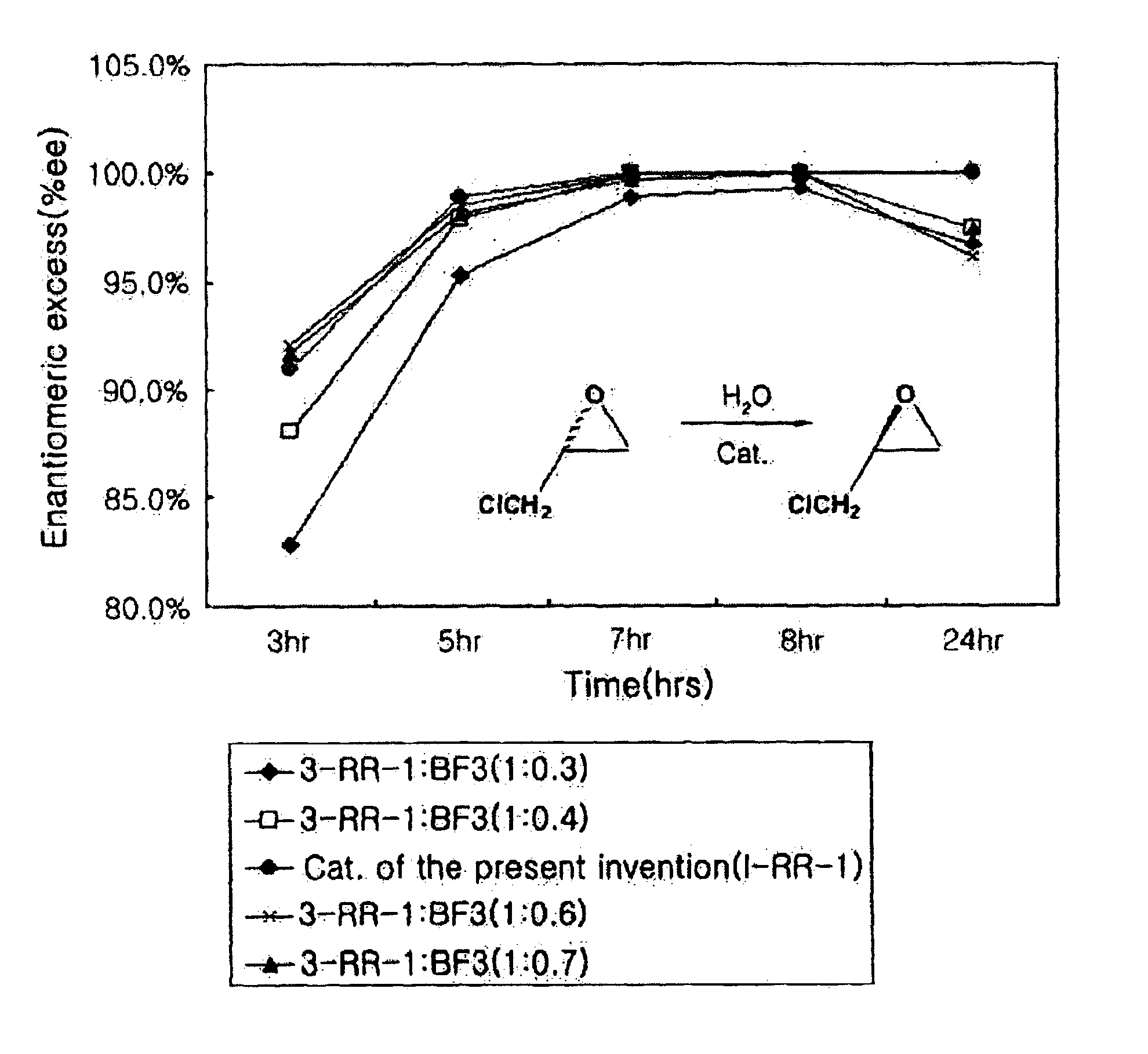
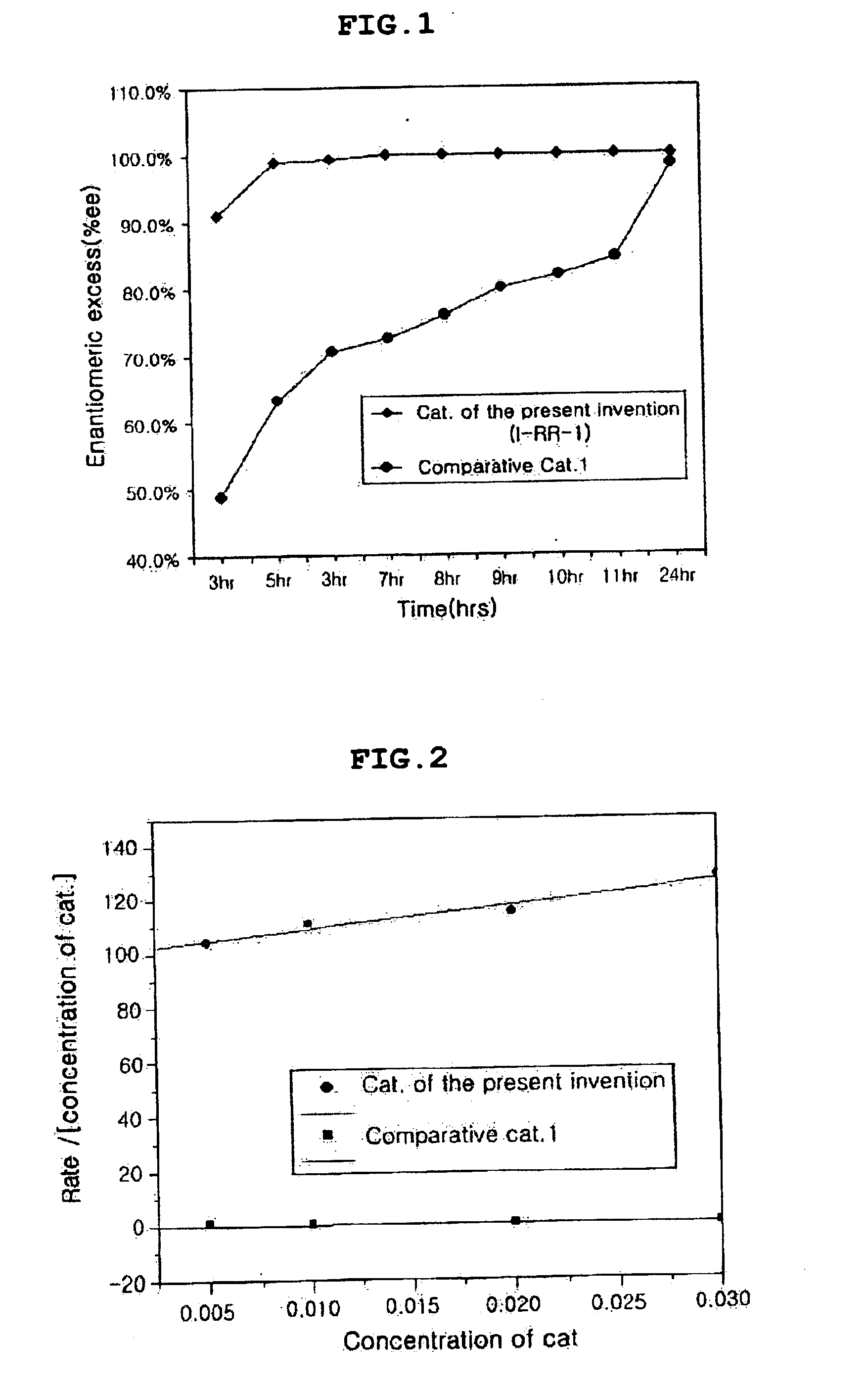
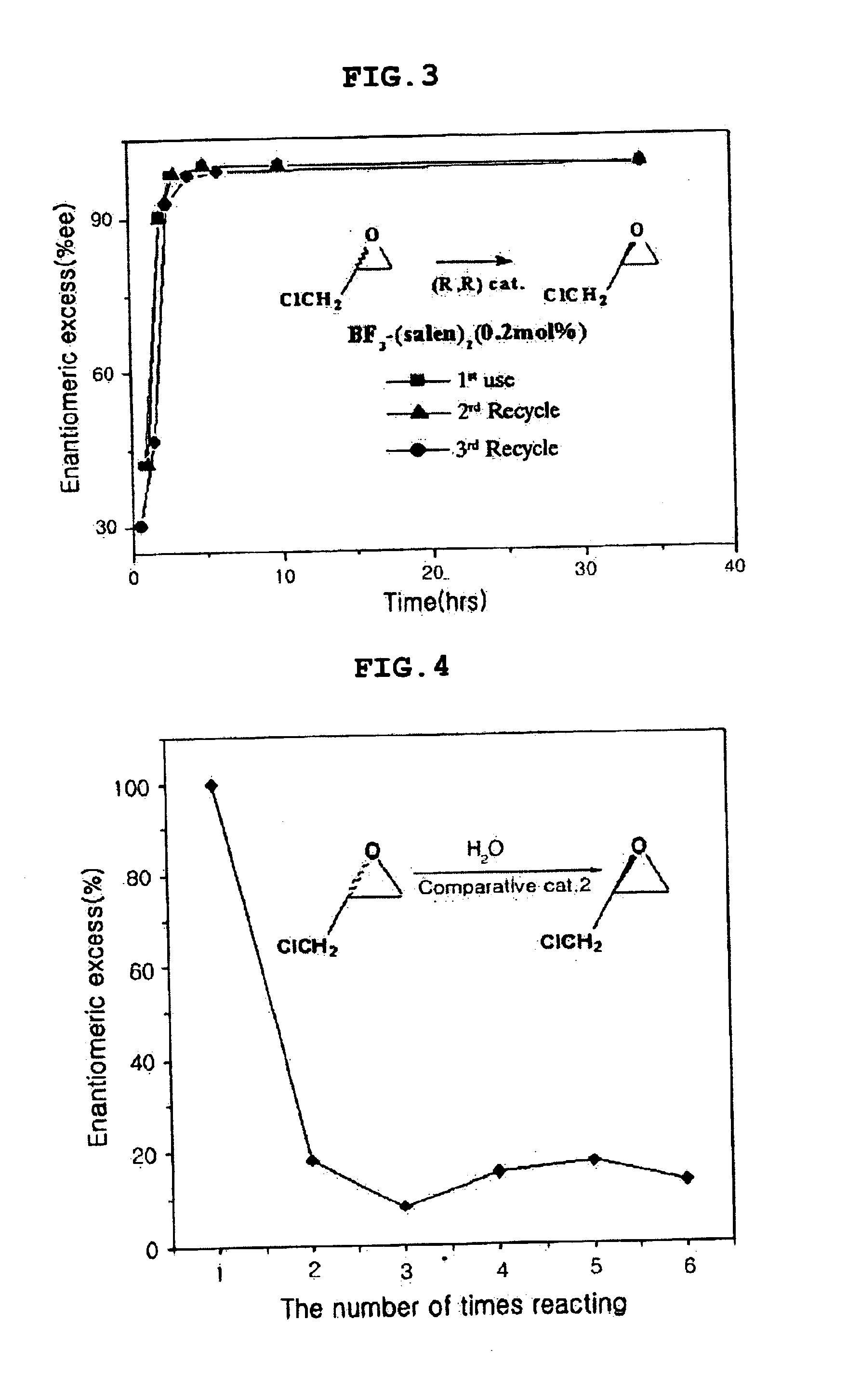
Chiral salen catalyst and methods for the preparation of chiral compounds from racemic epoxides by using new catalyst
InactiveUS6884750B2High optical purityHigh activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCobalt organic compoundsFood additiveEpoxide
The present invention relates to new chiral salen catalysts and methods for the preparation of chiral compounds from racemic epoxides by using new catalyst. More particularly, the present invention is to provide novel chiral salen catalysts and their uses for producing chiral compounds having high optical purity to be used as raw materials for preparing chiral medicines or food additives in a large scale economically, wherein the chirl salen catalyst having a particular molecules structure can be reused continuously without any activating process of used catalysts and cause no or little racemization after the reaction is completed because it maintains its catalytic activity after the reaction process.
Owner:RS TECH CORP
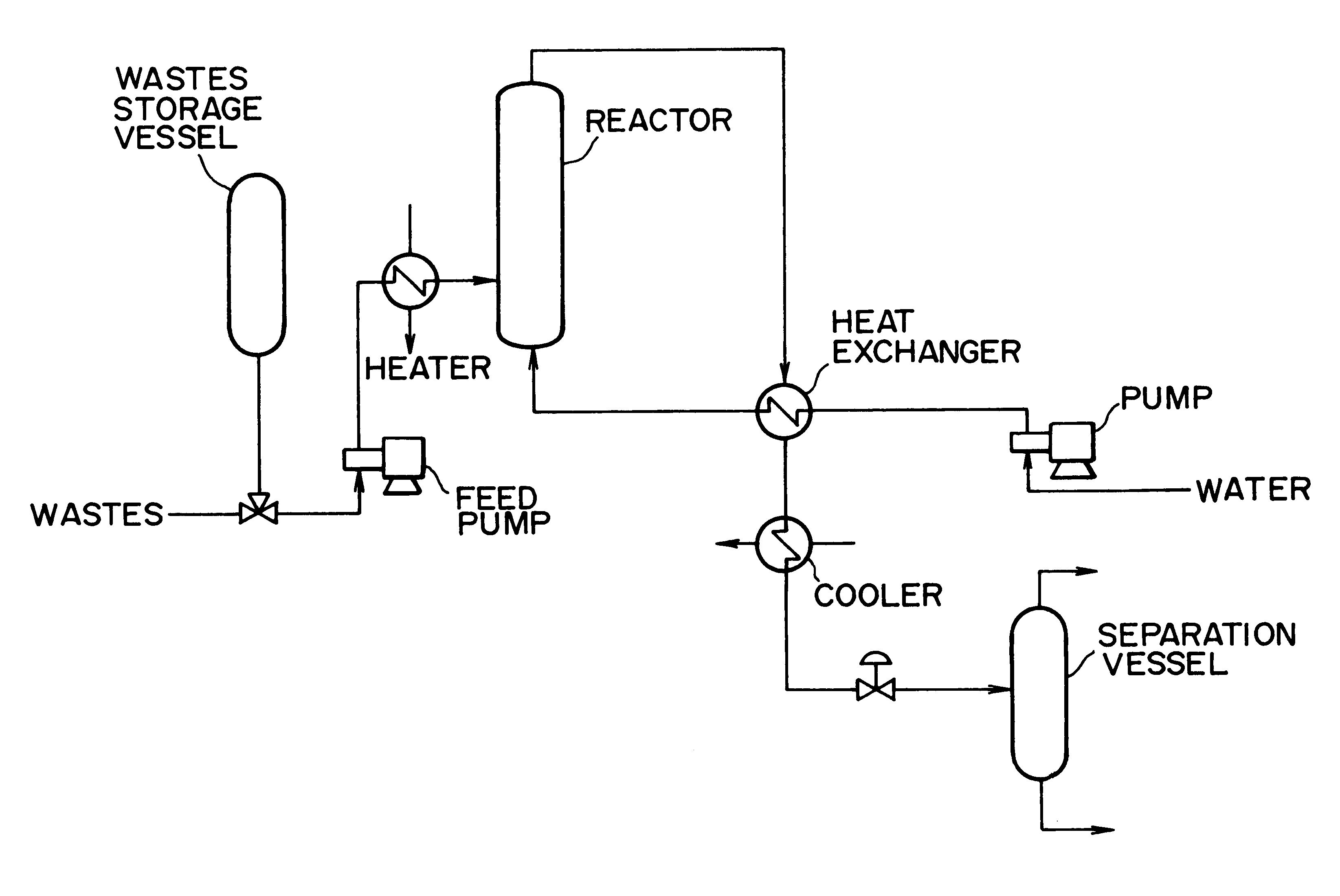
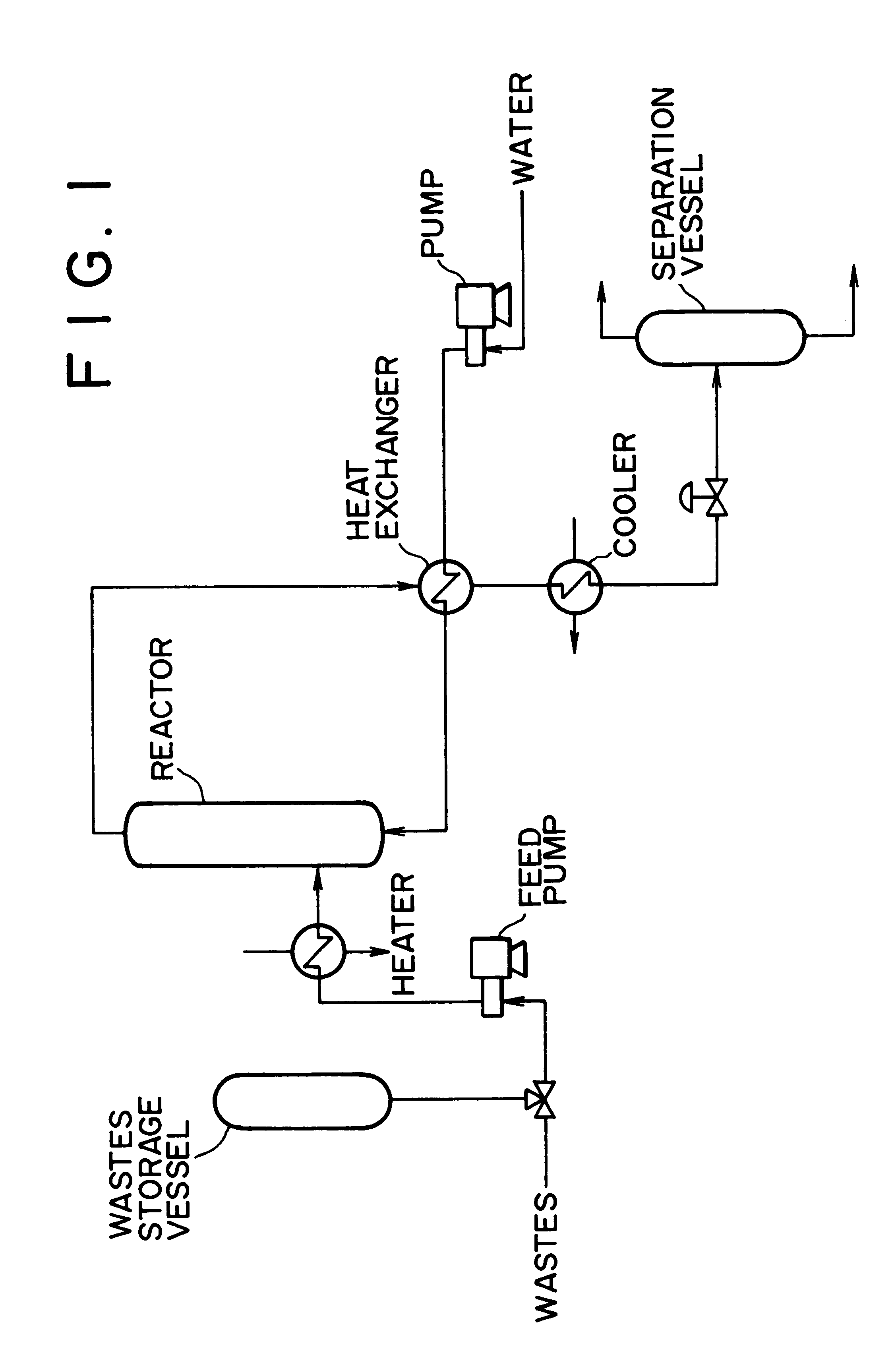
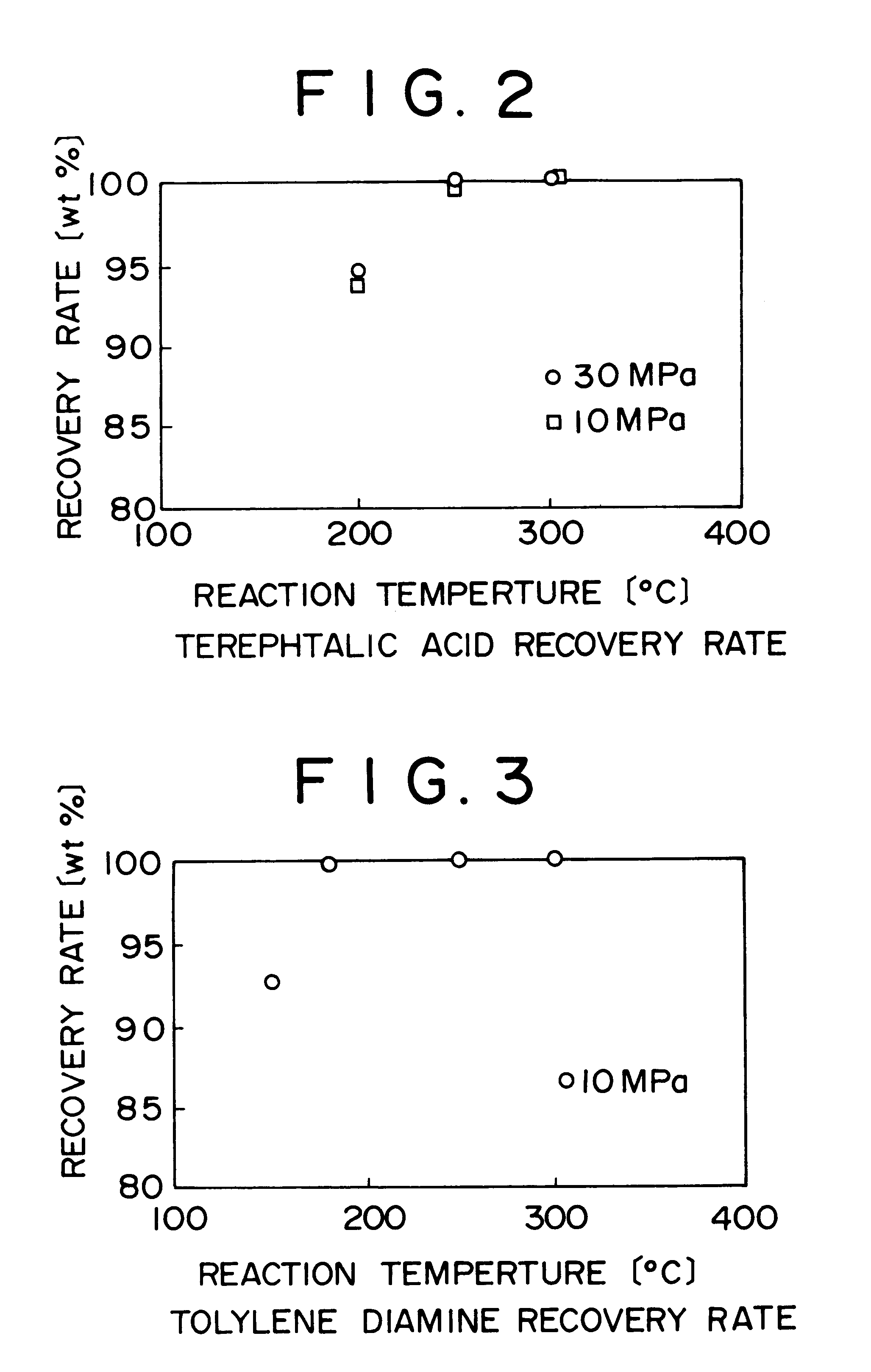
Method of and apparatus for decomposing wastes
InactiveUS6255529B1Useful operationResultant decomposition products can be utilized effectivelySolid waste disposalIndirect heat exchangersMolten stateLiquid state
A method of decomposing wastes containing target compounds having one or more of hydrolyzable bonds of ether bond, ester bond, amide bond and isocyanate bond wherein the method comprises continuously supplying the wastes in a molten state or liquid state to a reactor, continuously supplying super-critical water or high pressure / high temperature water to the reactor, bringing the water into contact with the wastes, thereby decomposing the target compounds and then recovering them as raw material compounds or derivatives thereof for the target compounds. Target compounds contained in wastes in chemical plants which could not be utilized but merely incinerated or discarded so far are continuously decomposed into raw material compounds or derivatives thereof for the aimed compound and can be reutilized effectively.
Owner:TAKEDA CHEM IND LTD 50
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com