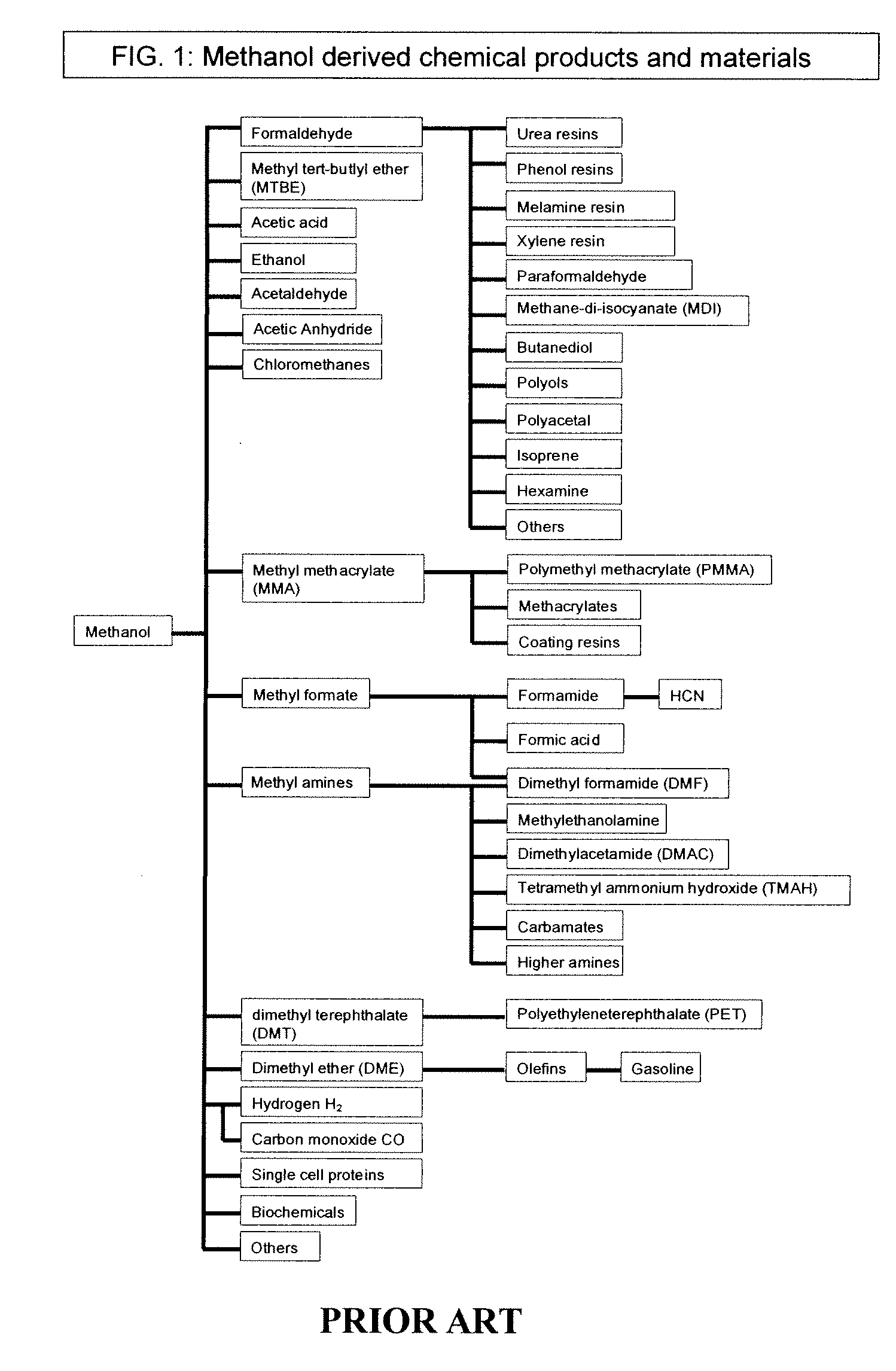
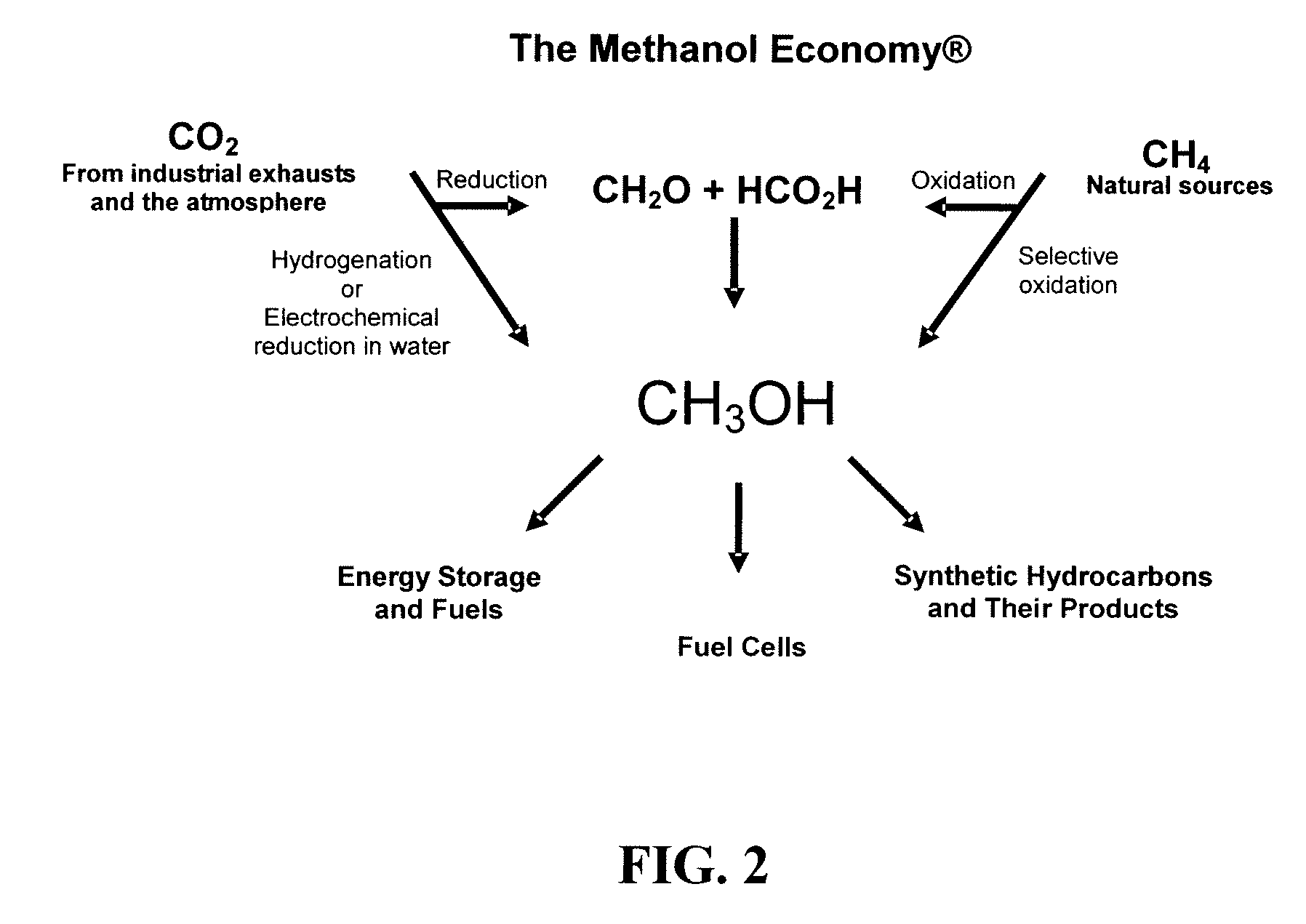
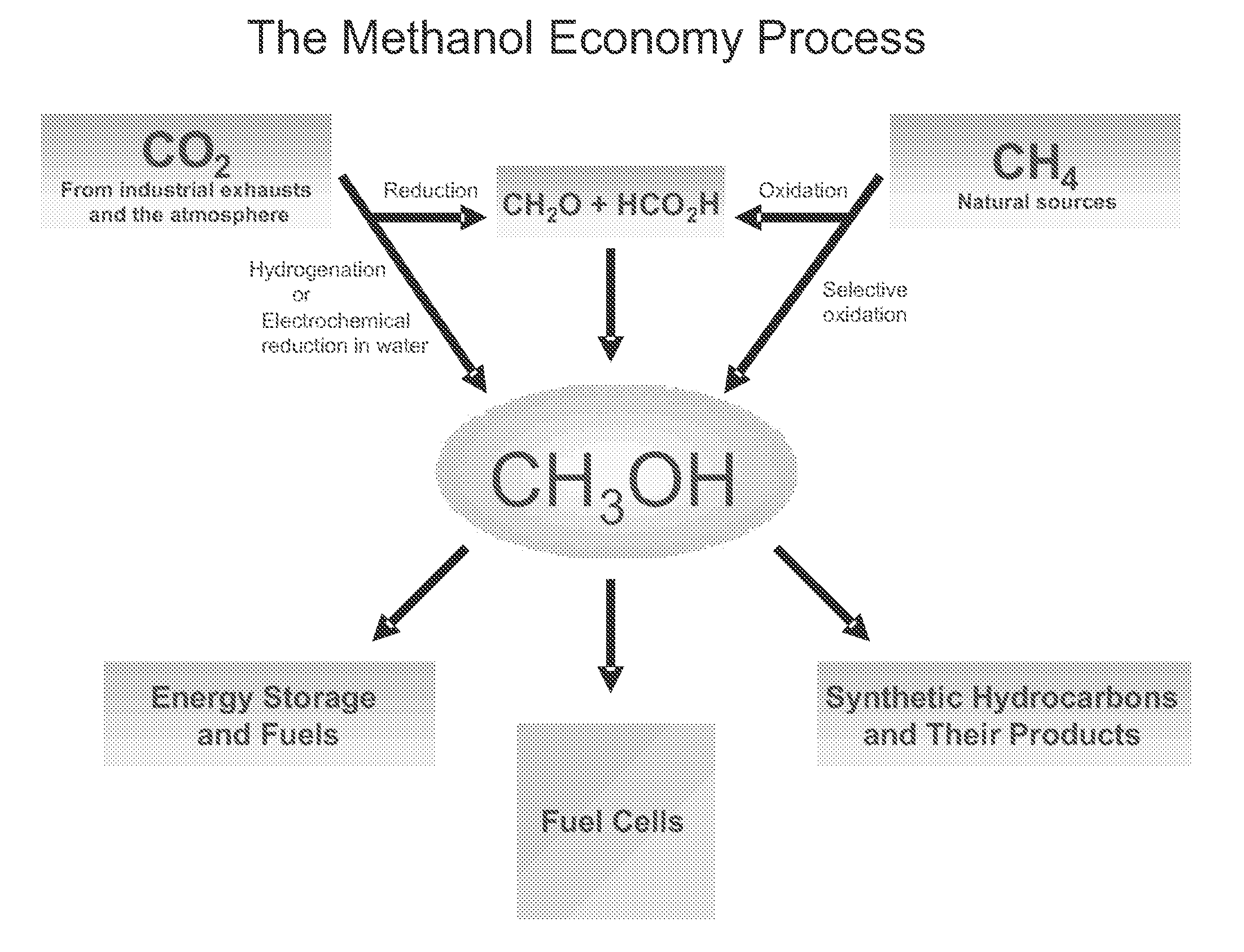
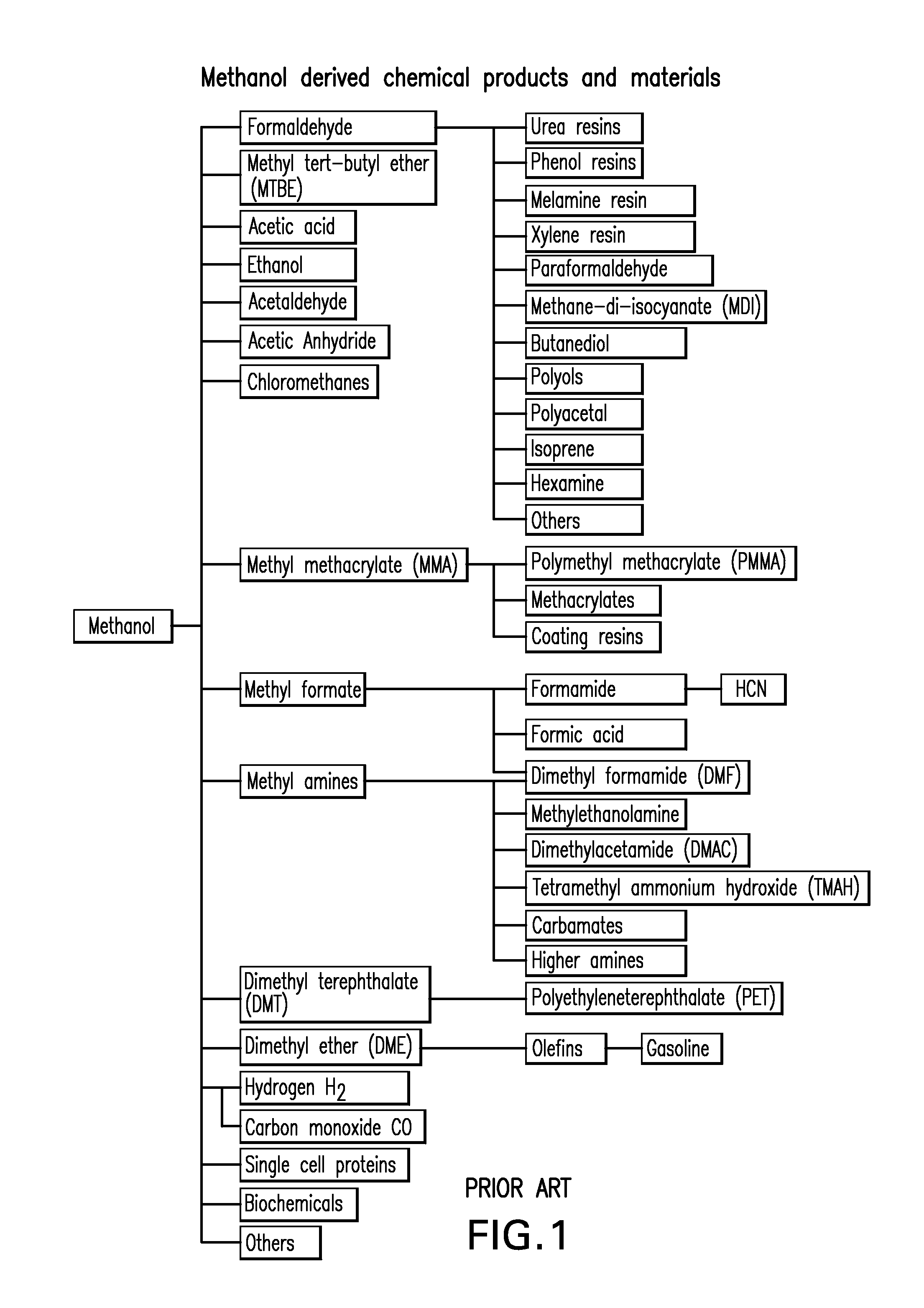
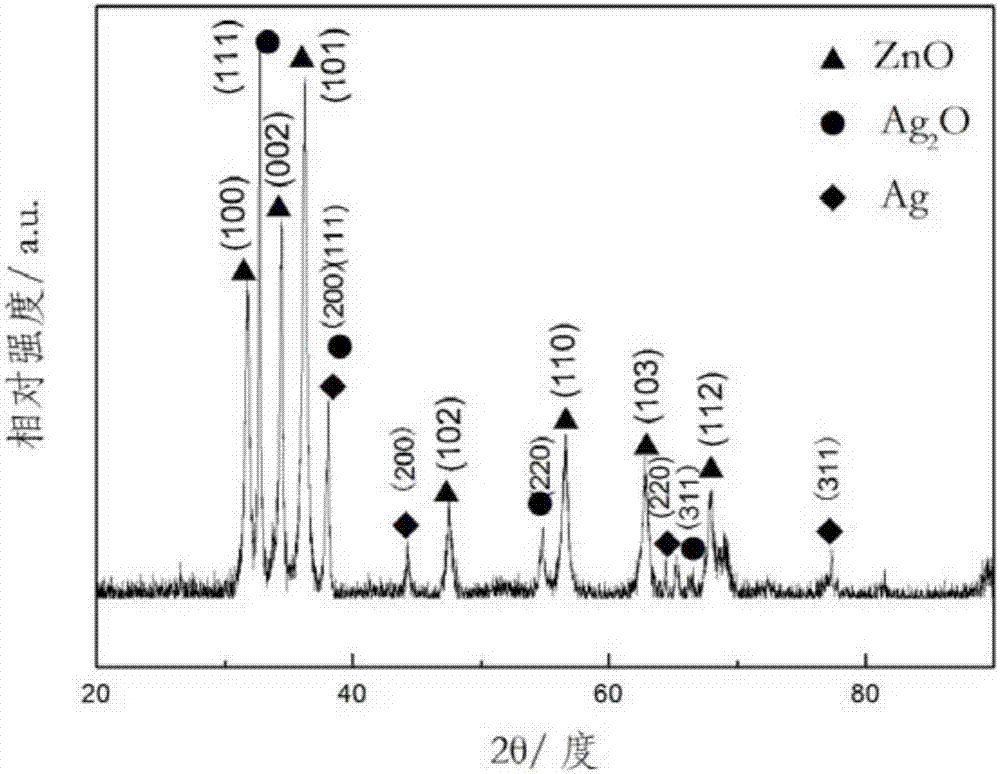
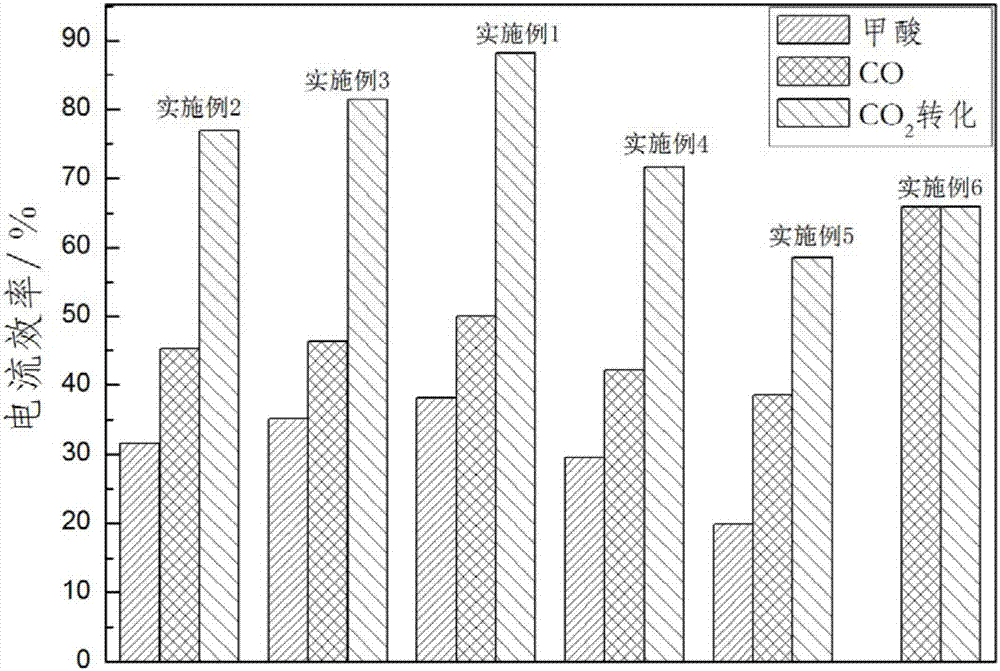
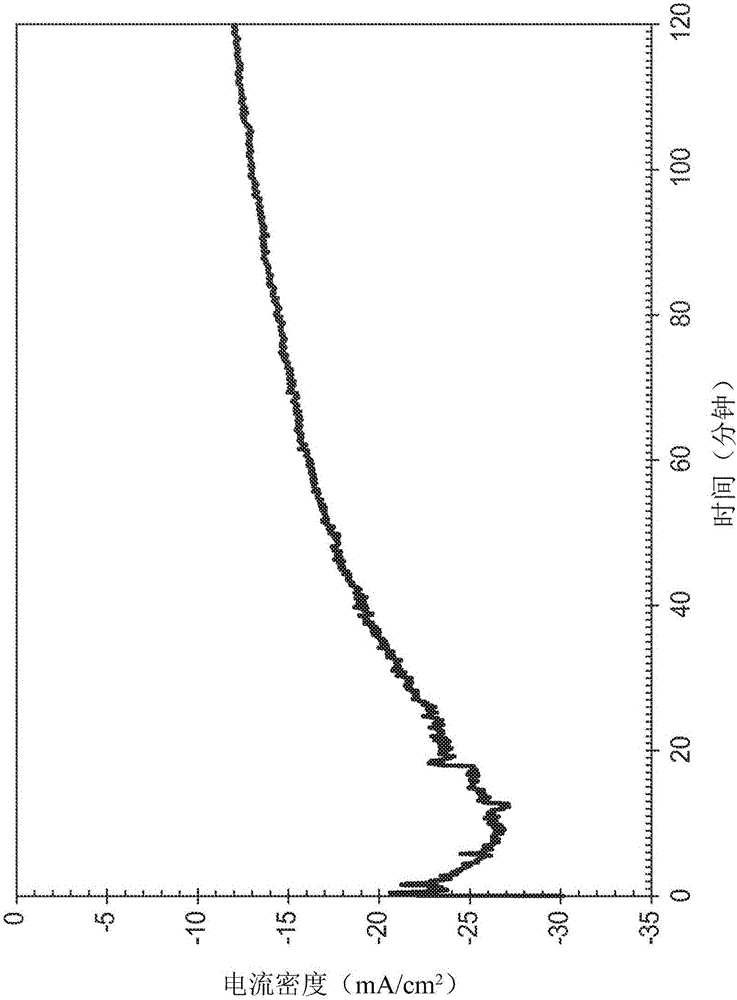
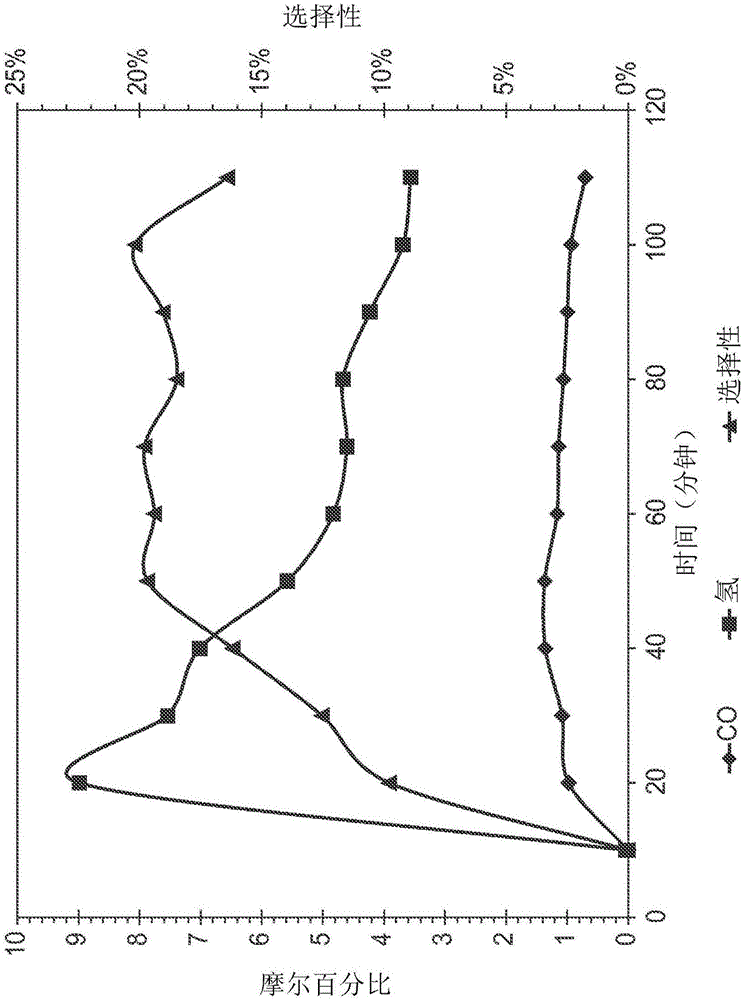
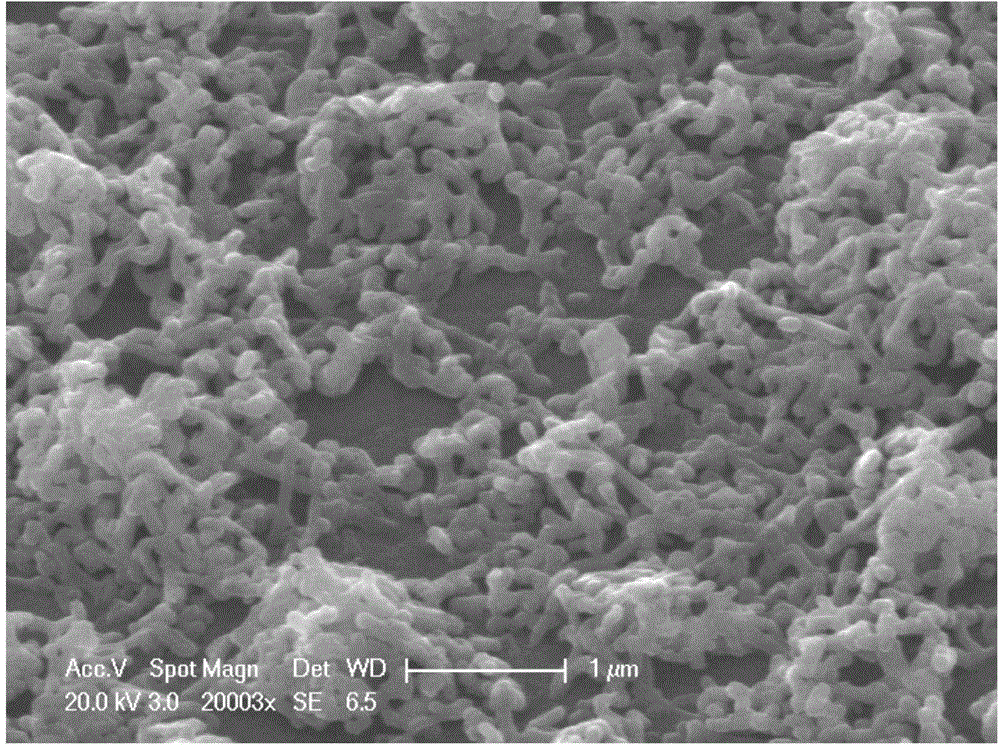
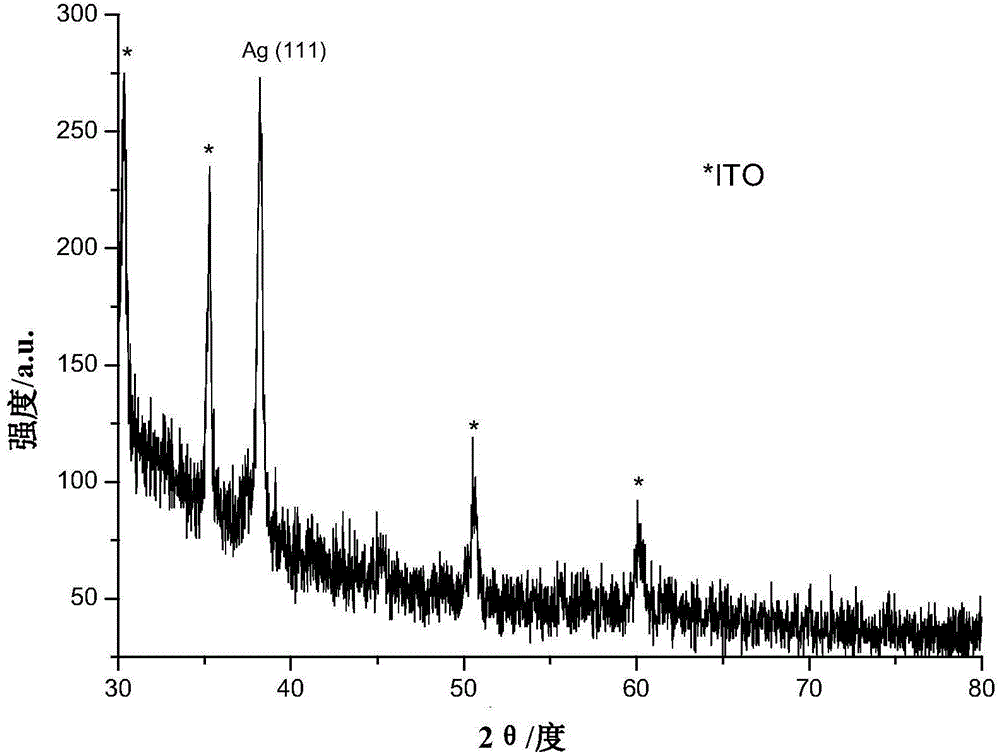
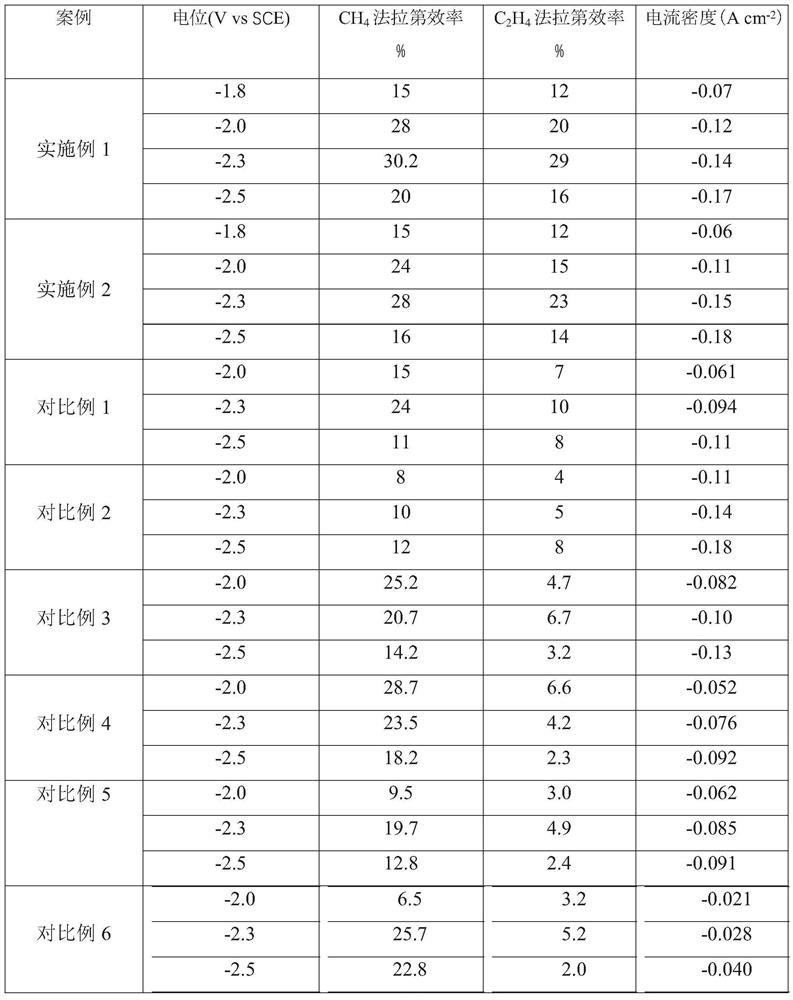
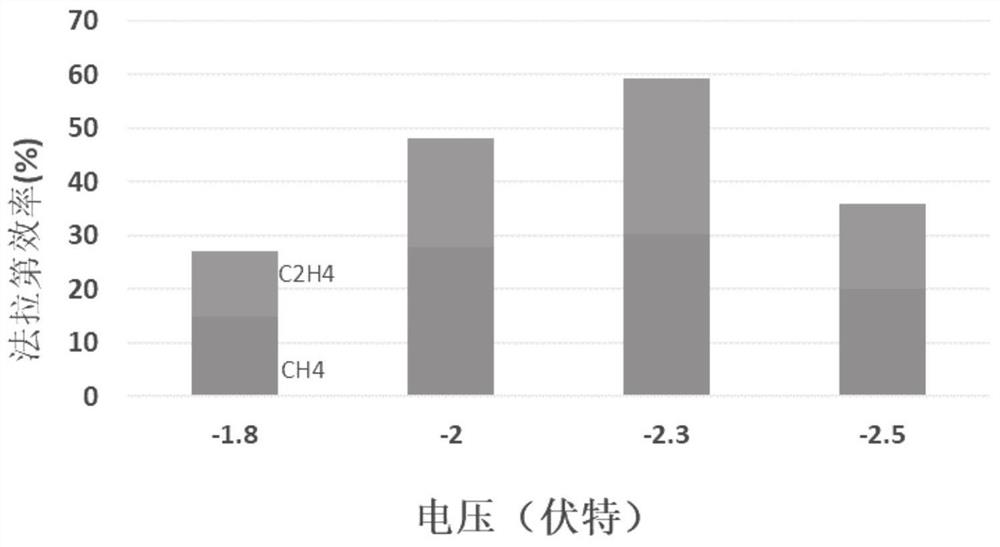
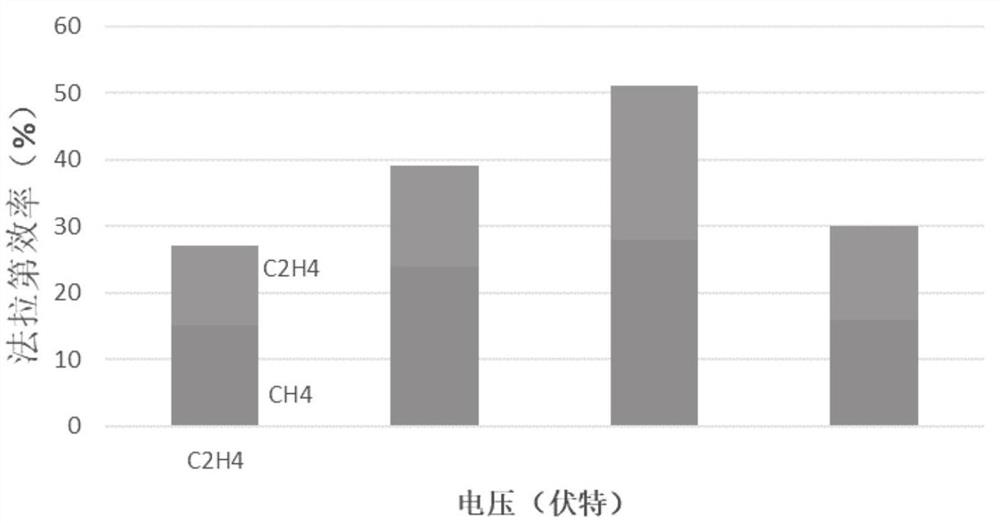
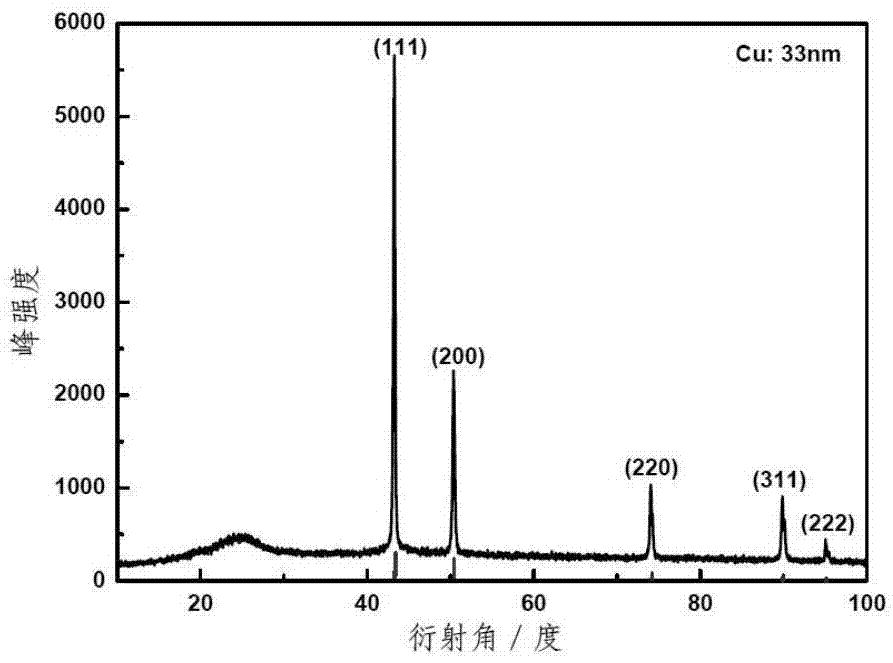
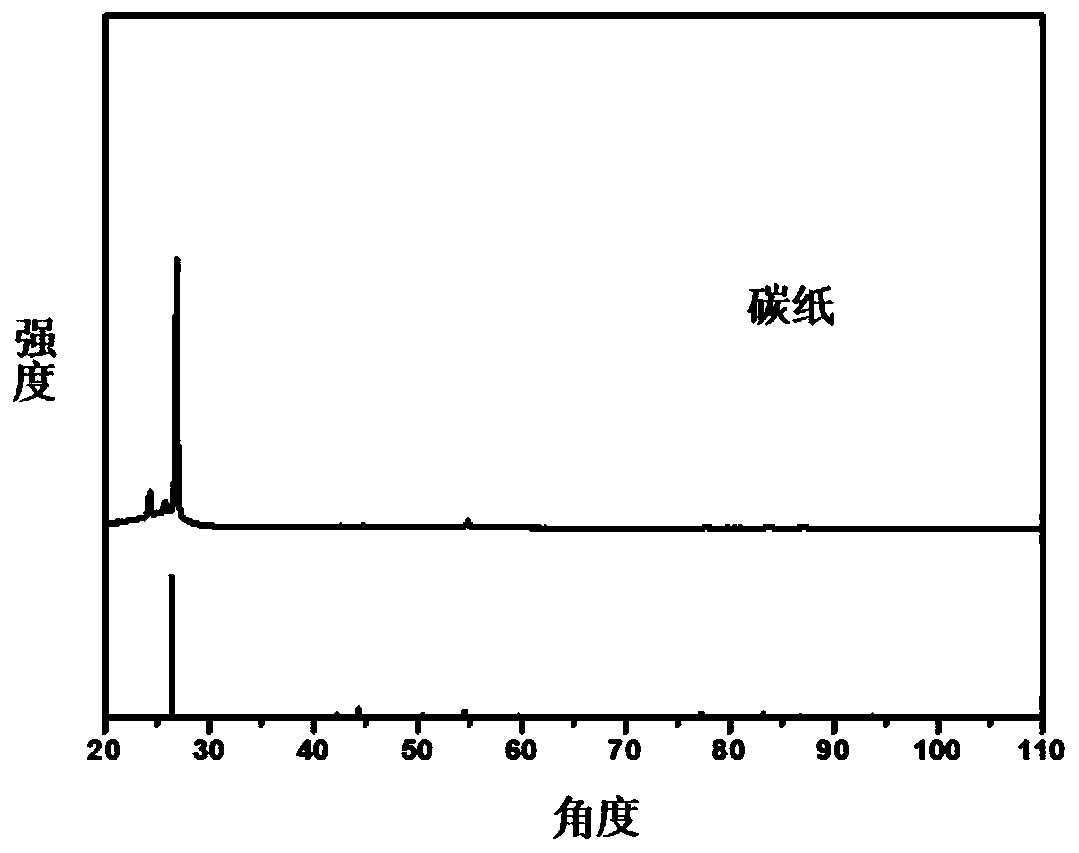
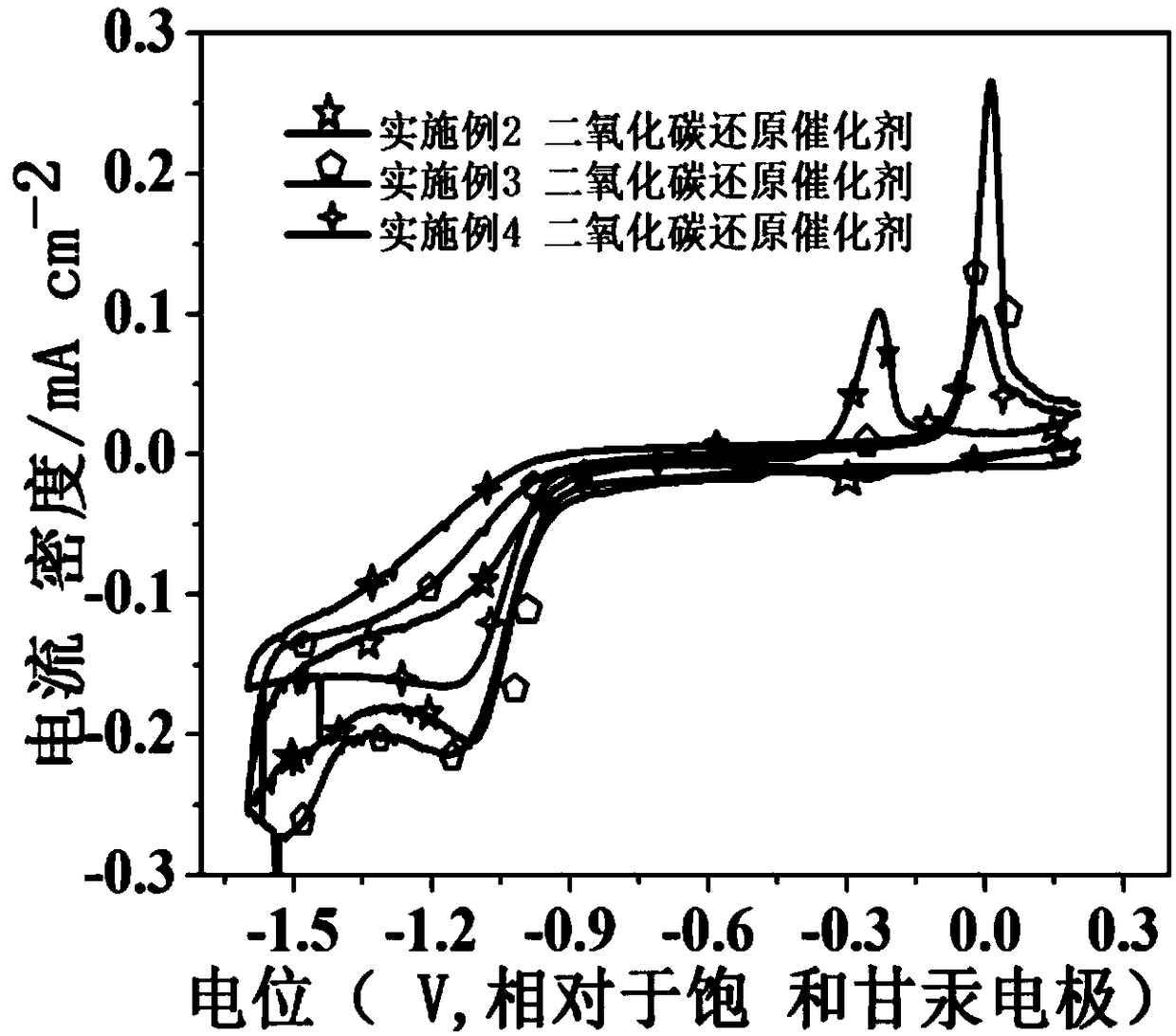
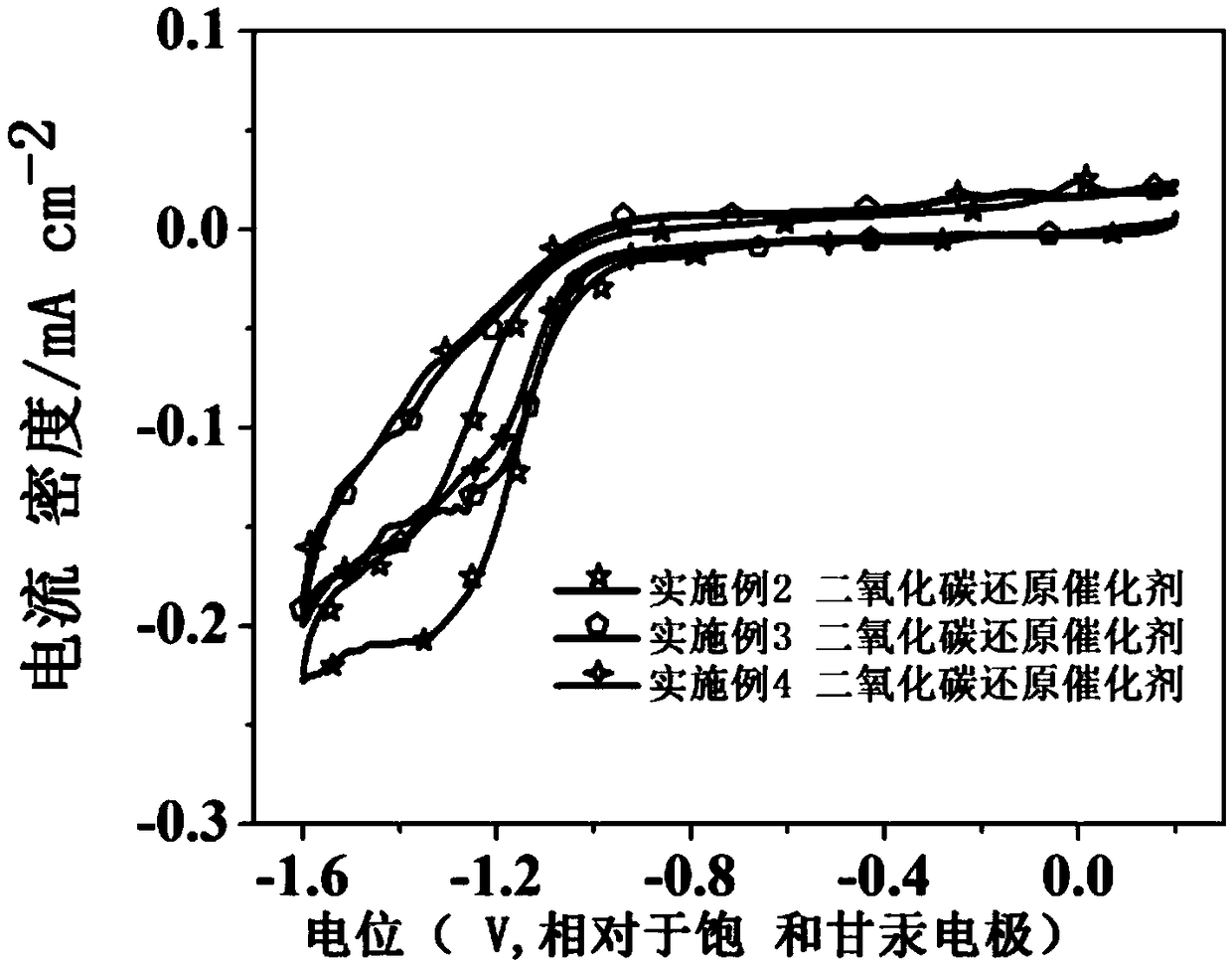
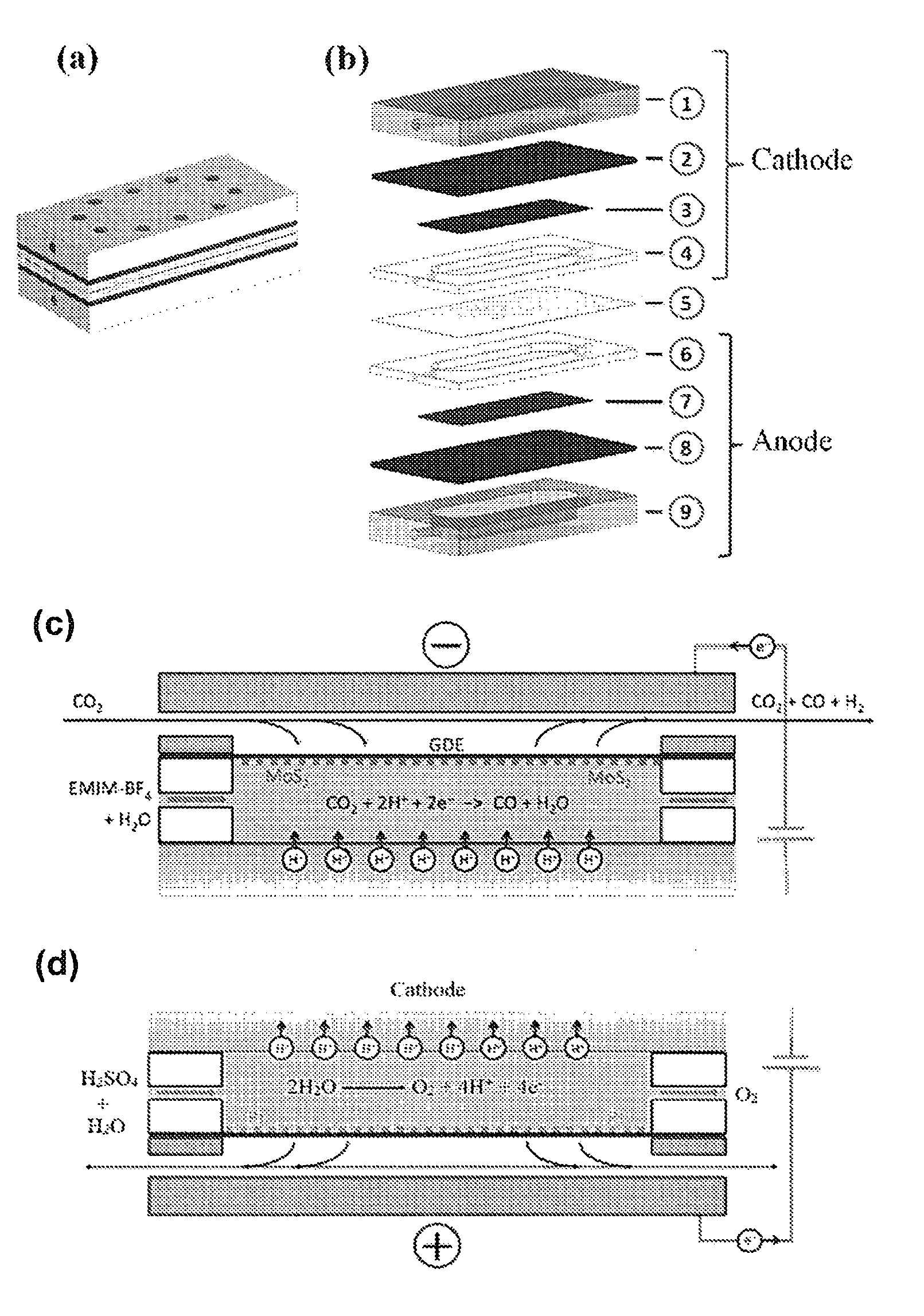
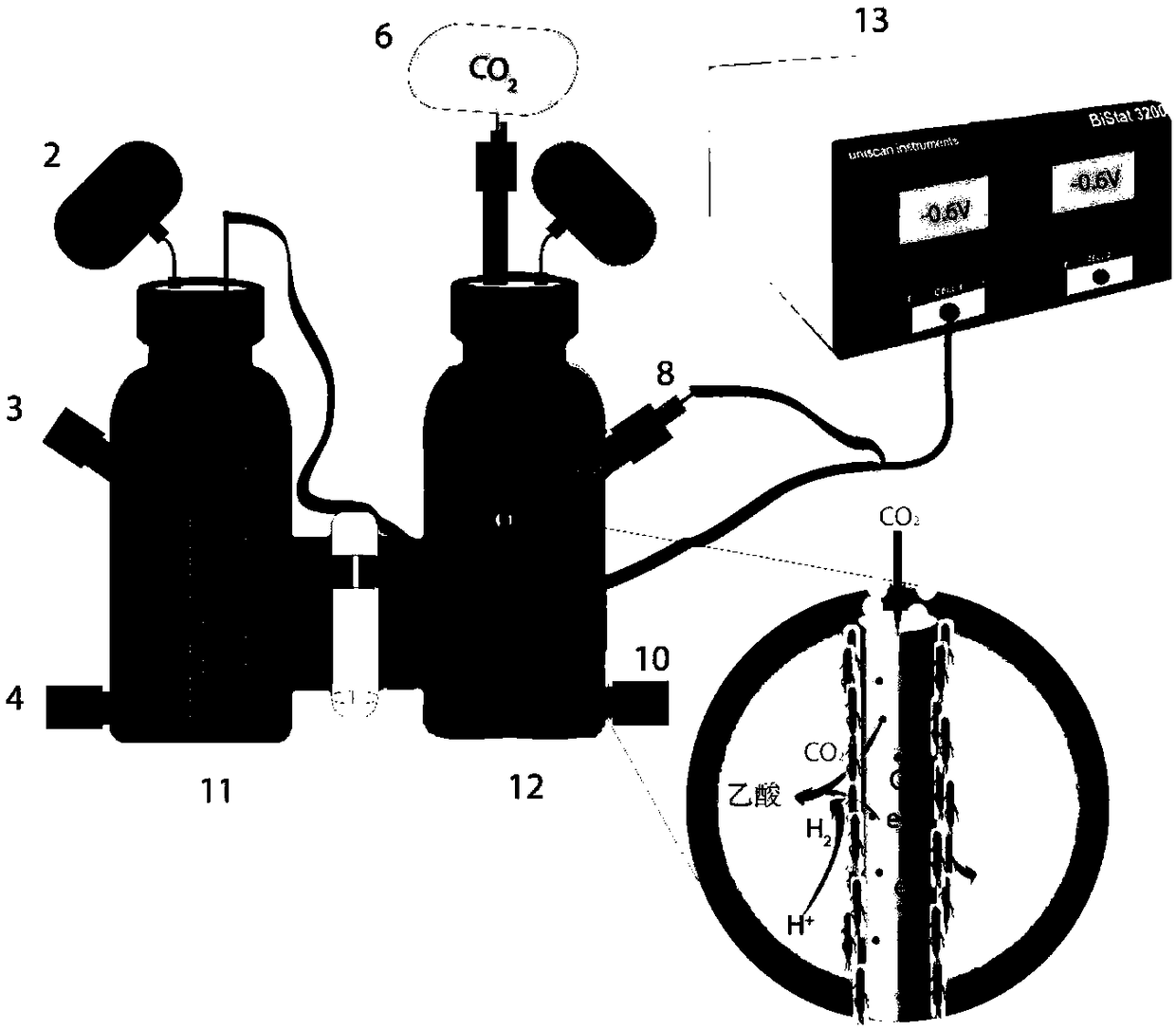
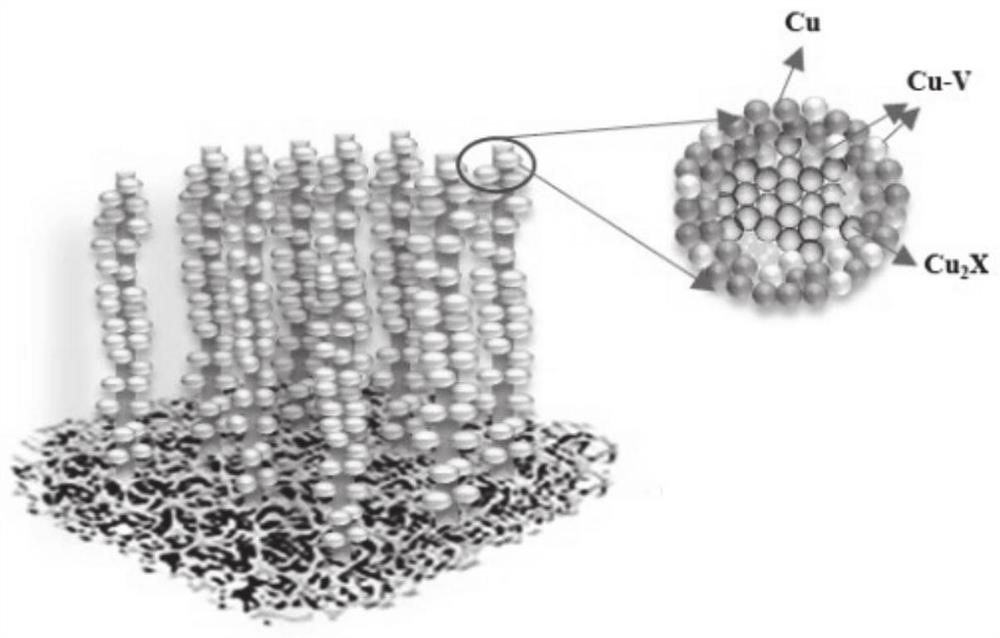
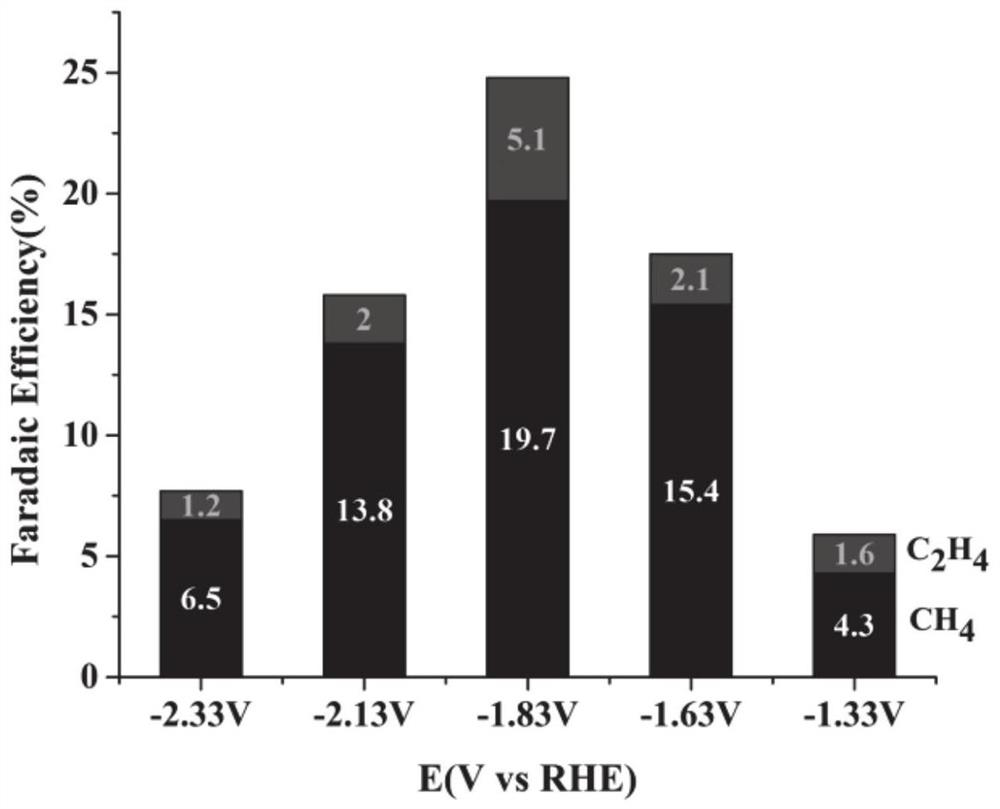
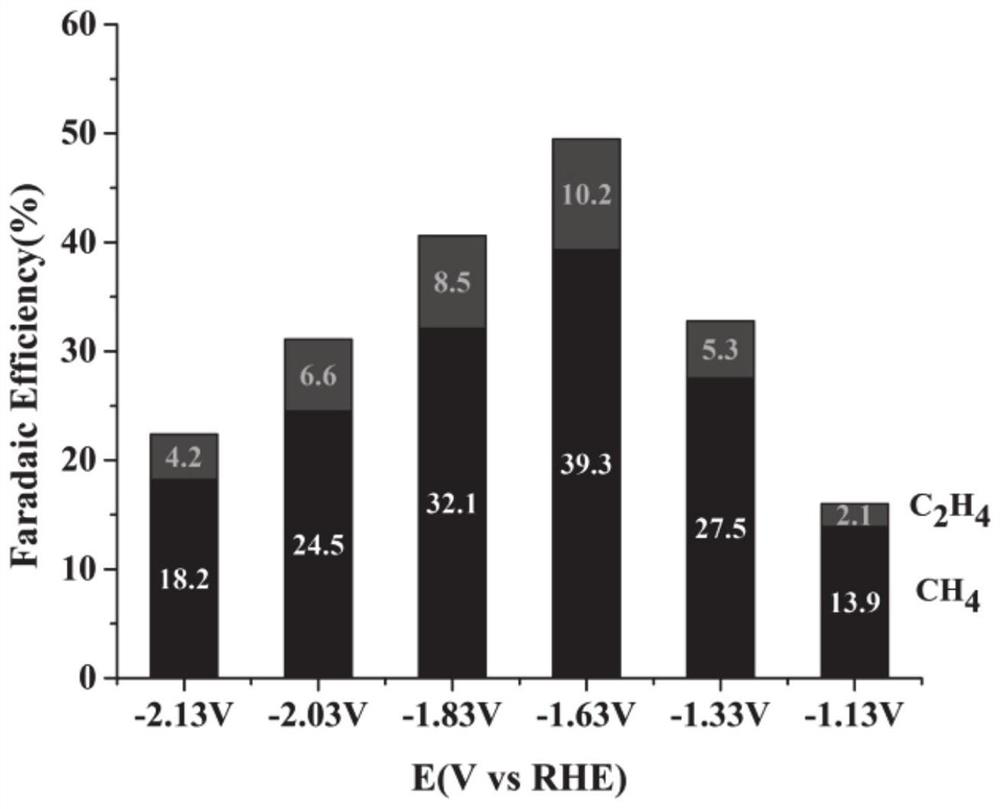
Patents
Literature
129 results about "Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
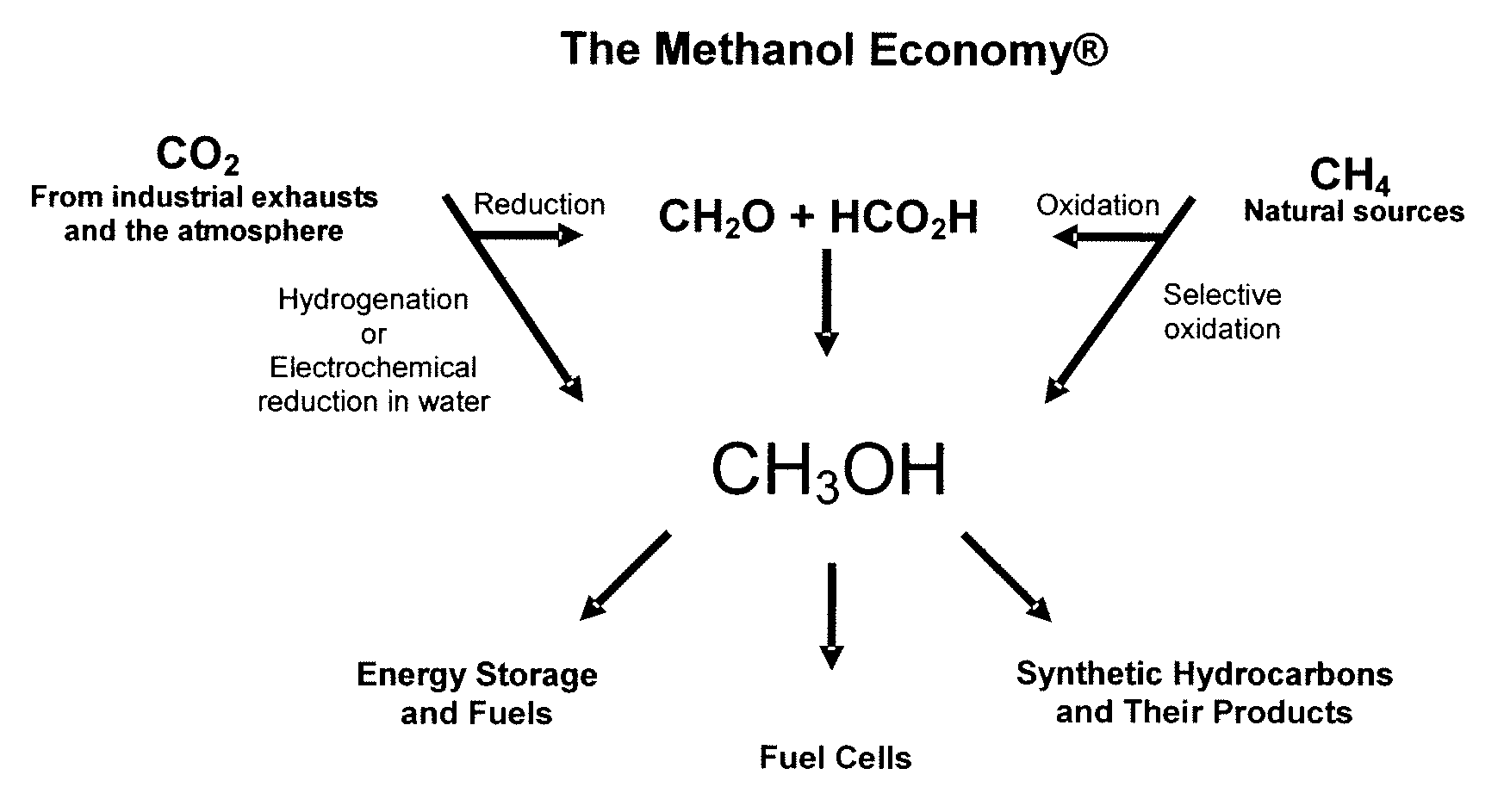
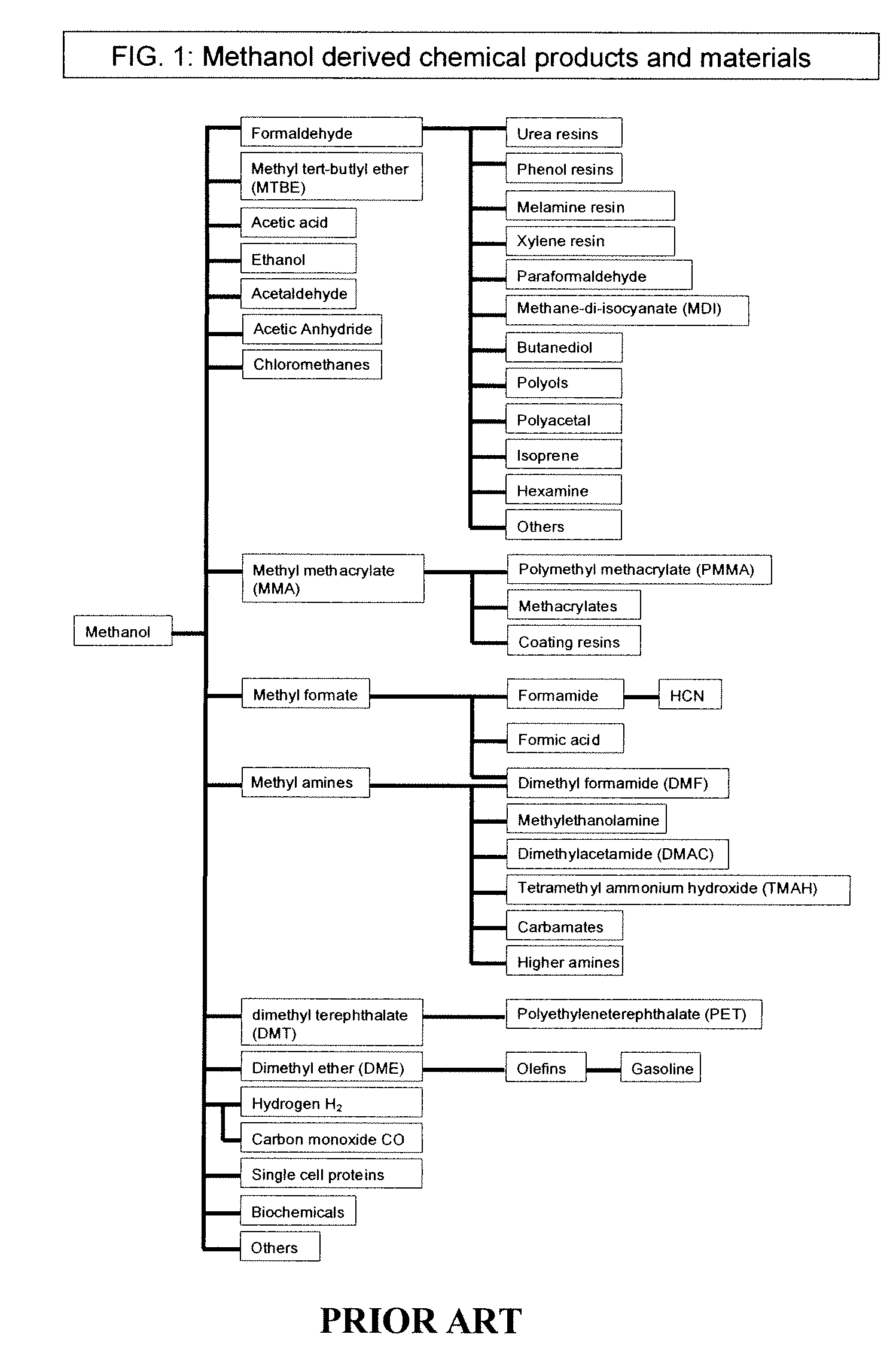
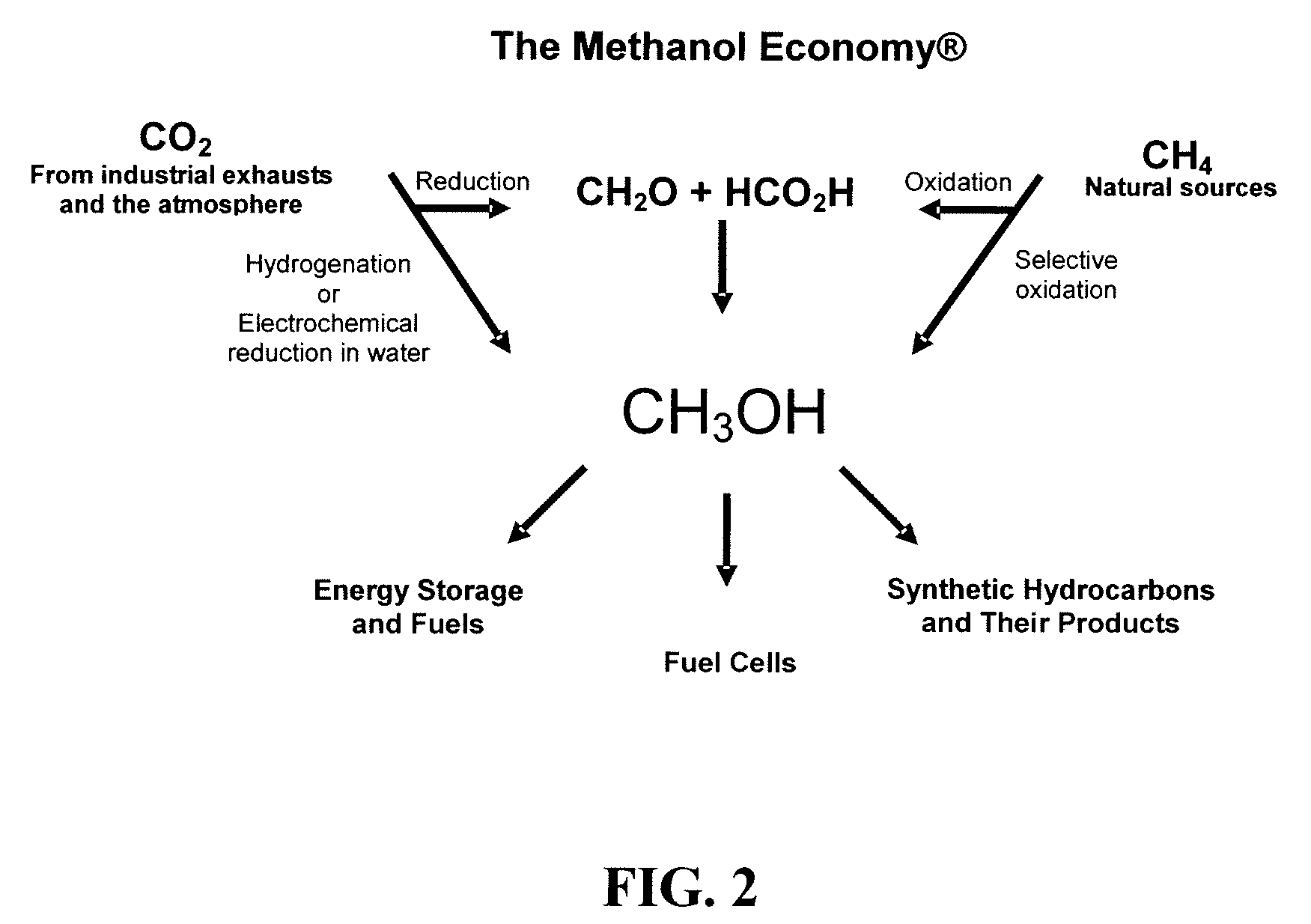
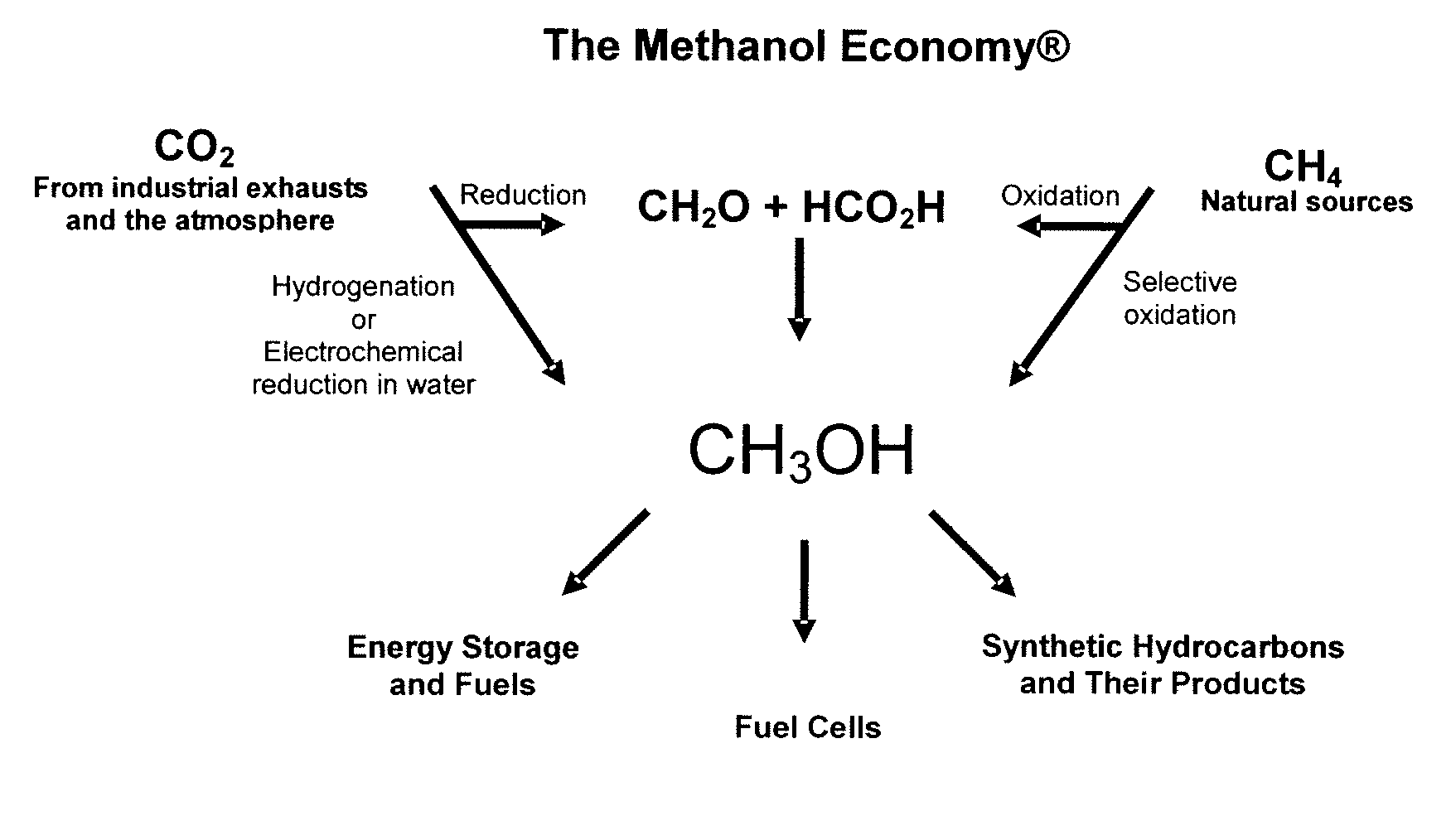
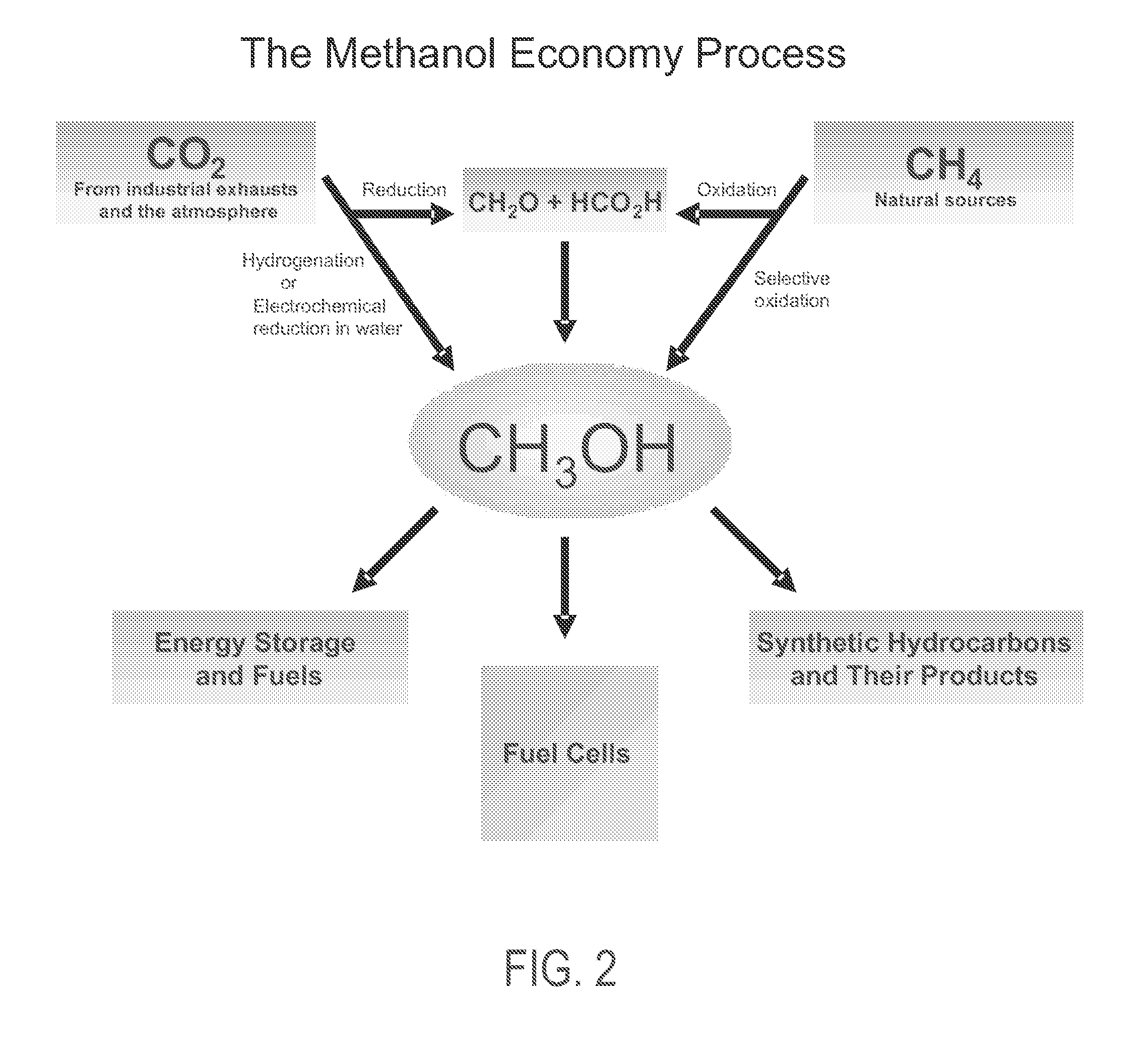
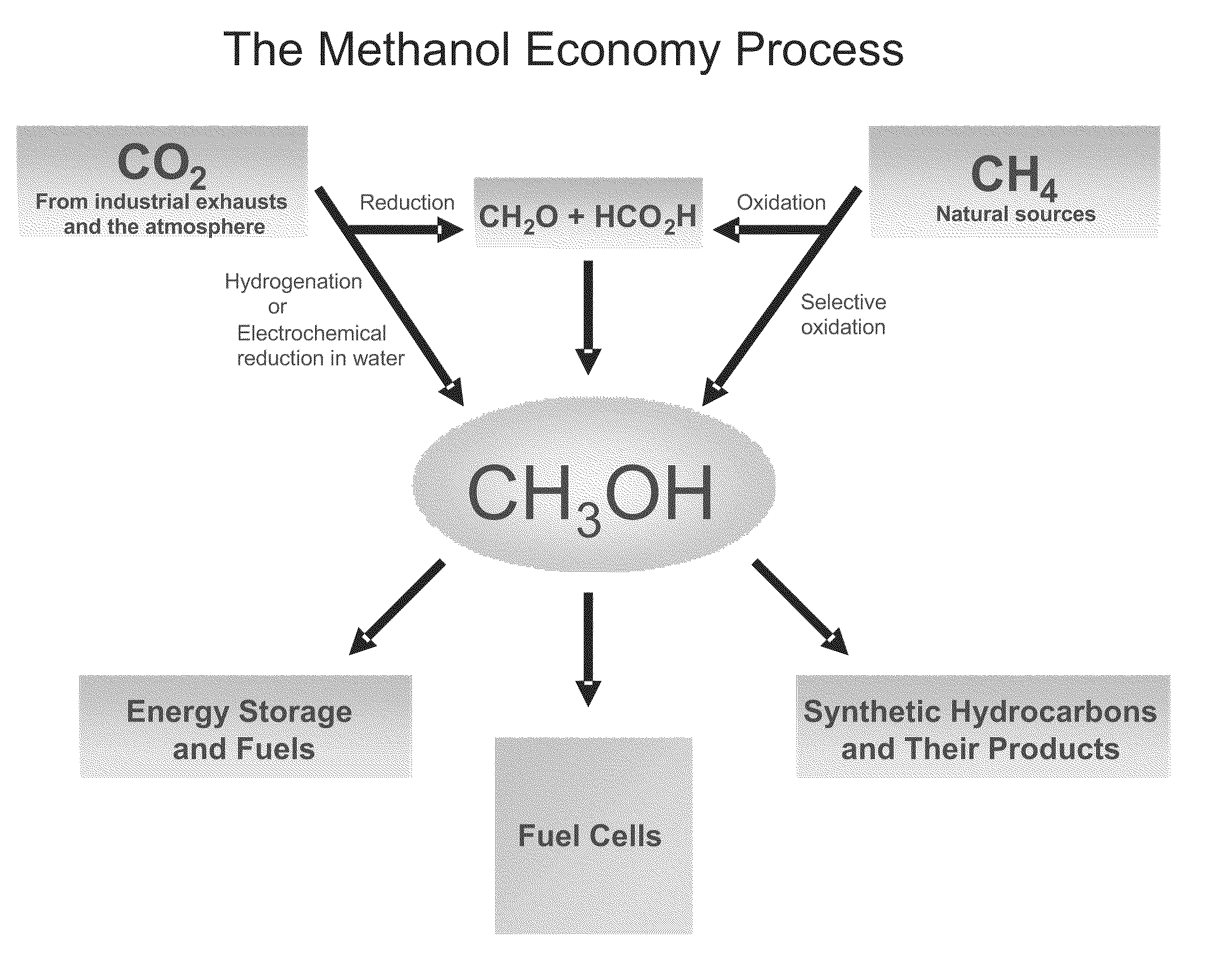
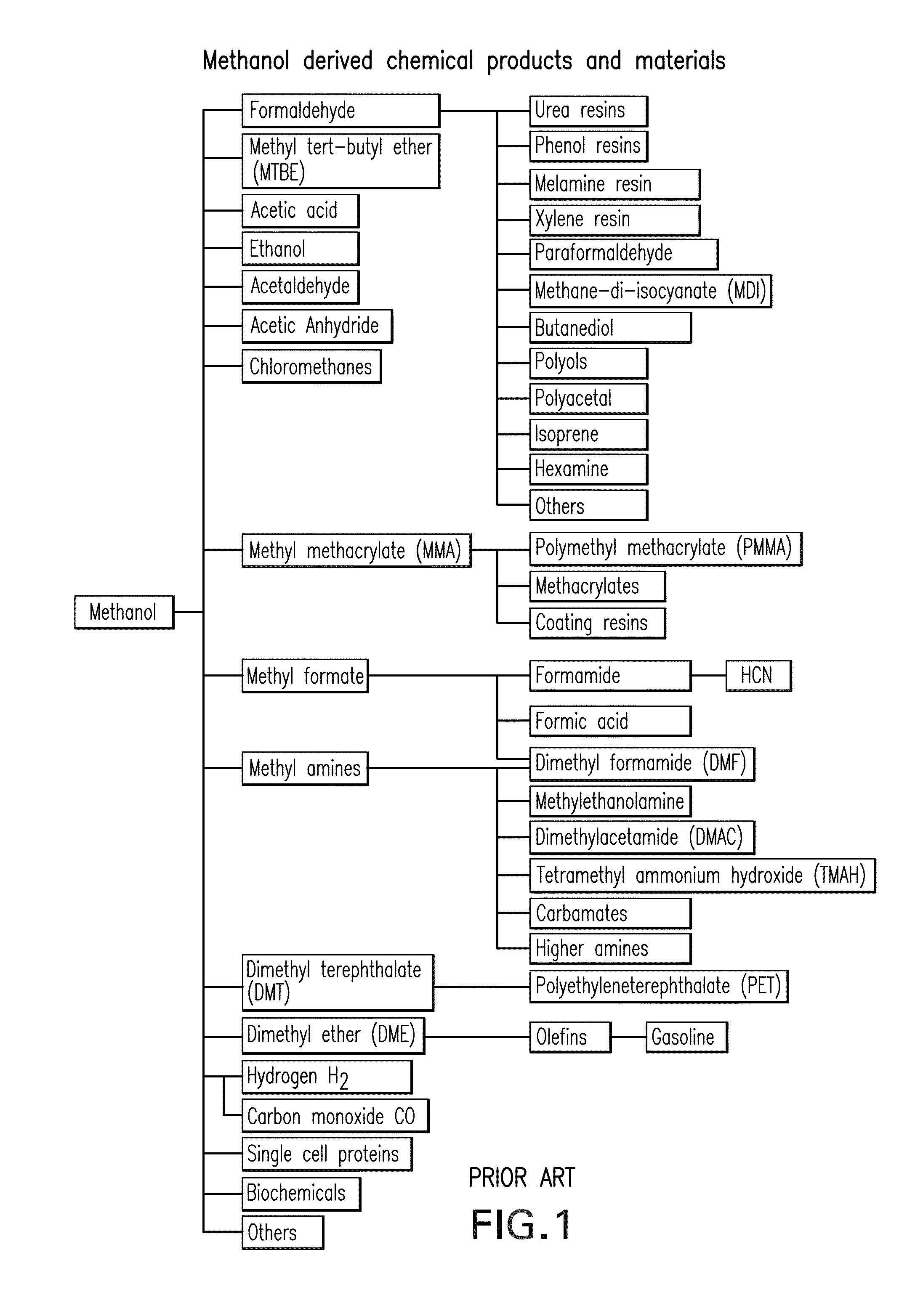
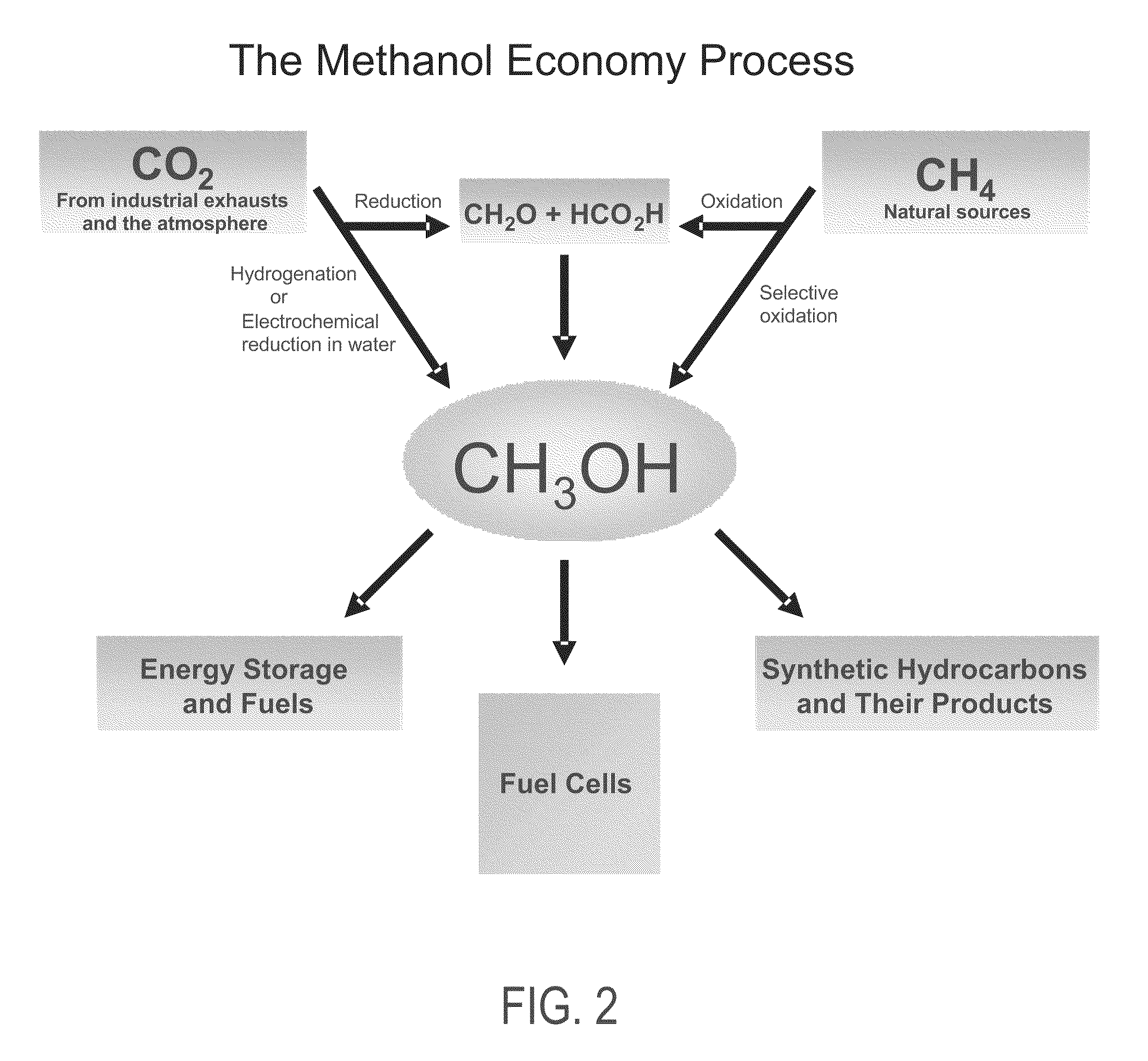
The electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide (ERC) is the conversion of carbon dioxide to more reduced chemical species using electrical energy. The first examples of electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide are from the 19th century, when carbon dioxide was reduced to carbon monoxide using a zinc cathode. Research in this field intensified in the 1980s following the oil embargoes of the 1970s. Electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide represents a possible means of producing chemicals or fuels, converting carbon dioxide (CO₂) to organic feedstocks such as formic acid (HCOOH), methanol (CH₃OH), ethylene (C₂H₄), methane (CH₄), and carbon monoxide (CO). In 2018, researchers from the University of Delaware reported a general techno-economic analysis of CO₂ electrolysis technology.
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one cell compartment and a metal cathode electrode in another cell compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte of one or more alkyl ammonium halides, alkali carbonates or combinations thereof to produce therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one cell compartment and a metal cathode electrode in another cell compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte of one or more alkyl ammonium halides, alkali carbonates or combinations thereof to produce therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
ActiveUS20100193370A1Efficient combustionElectrolysis componentsPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysisAtmospheric air
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one compartment and a metal cathode electrode in a compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte. An anion-conducting membrane can be provided between the anode and cathode to produce at the cathode therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode. The oxygen produced at the anode can be recycled for efficient combustion of fossil fuels in power plants to exclusively produce CO2 exhausts for capture and recycling as the source of CO2 for the cell.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
ActiveUS8138380B2Efficient combustionPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisOxygen
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one compartment and a metal cathode electrode in a compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte. An anion-conducting membrane can be provided between the anode and cathode to produce at the cathode therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode. The oxygen produced at the anode can be recycled for efficient combustion of fossil fuels in power plants to exclusively produce CO2 exhausts for capture and recycling as the source of CO2 for the cell.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one cell compartment and a metal cathode electrode in another cell compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte of one or more alkyl ammonium halides, alkali carbonates or combinations thereof to produce therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Method for preparing hydrocarbon through electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
InactiveCN105420751AImprove solubilityImprove Faraday efficiencyElectrolysis componentsElectrolytic organic productionElectrochemistryInorganic electrolyte
The invention relates to a method for preparing hydrocarbon through electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. An electrolytic tank is divided into a left cavity and a right cavity through a proton exchange membrane, the left cavity and the right cavity are not communicated with each other, and the two cavities serve as a cathode chamber and an anode chamber respectively; and the cathode chamber is filled with an electrolyte solution, the electrolyte solution is an inorganic electrolyte aqueous solution where the carbon dioxide is dissolved, and an organic solvent is further added into the electrolyte solution. The method of combining inorganic salts and the organic solvent is adopted, and metal Cu electrodes in different shapes and forms serve as cathodes, anodes are formed by Pt pieces or Pt wire electrodes and the like, and therefore the conversion rate of the carbon dioxide and the energy cycle utilization rate are greatly increased.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
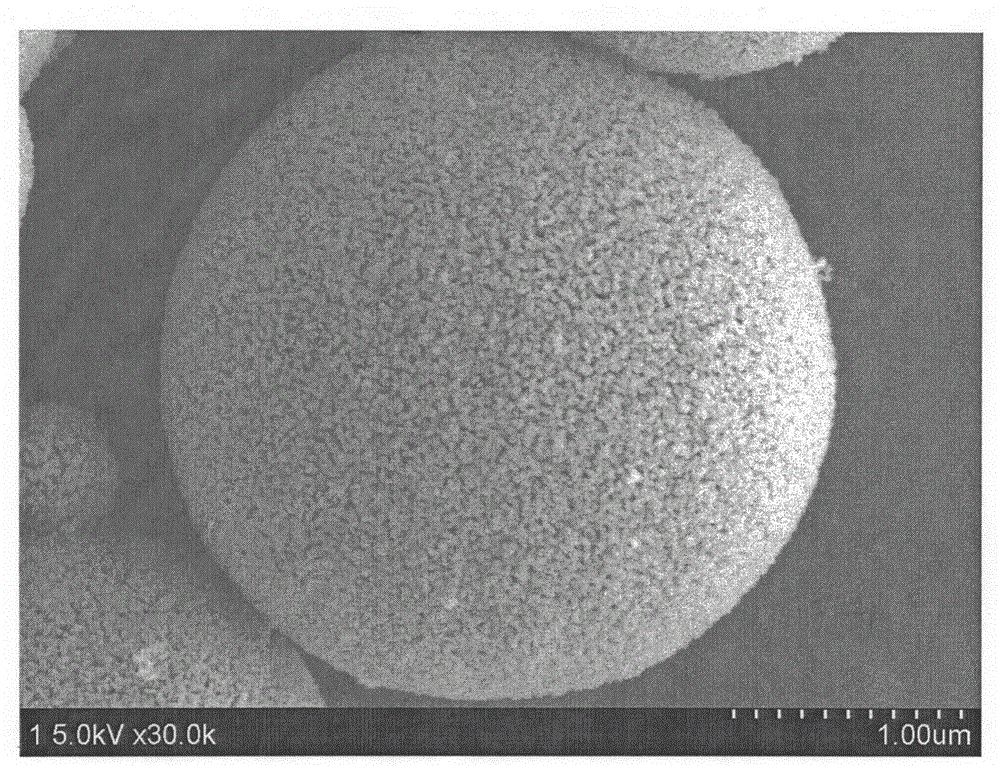
Tin dioxide multi-stage structured nanosphere carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst, preparation method and application of tin dioxide multi-stage structured nanosphere carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst
InactiveCN104549214AIncrease contact areaIncrease profitElectrolytic organic productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsTin dioxideElectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
The invention discloses a tin dioxide multi-stage structured nanosphere carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst, a preparation method and application of the tin dioxide multi-stage structured nanosphere carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst. The tin dioxide multi-stage structured nanosphere carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst comprises a tin dioxide multi-stage structured nanosphere which is synthesized by hydrothermal reaction, wherein synthesis raw materials comprise a mixed solution of stannic chloride, glucose and ethyl alcohol / deionized water. According to the invention, the electrochemical reduction catalytic activity of carbon dioxide by the catalyst is improved obviously, the utilization of carbon dioxide is improved, especially the formic acid generation efficiency is improved; moreover, the hydrogen evolution reaction is inhibited effectively, and the product selectivity is reinforced.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Graphene material inlaid with single metal atoms and preparing method and application thereof
ActiveUS20190186029A1Atom utilization is highImprove catalytic performanceCell electrodesGrapheneDoped grapheneCvd graphene
The present invention relates to a graphene material inlaid with single metal atoms, the preparation method thereof and its application of being used as the catalyst for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide. The graphene material inlaid with single metal atoms comprises single metal atoms and graphene; the single metal atoms are dispersed in the framework of the graphene; and the graphene is at least one selected from N doped graphene and N and S co-doped graphene. The material is used for the electrochemical reduction reaction of carbon dioxide, which significantly improves the utilization efficiency of the metal atoms and enhances the catalytic activity for the electroreduction of carbon dioxide, improves the catalytic stability, inhibits effectively the hydrogen evolution reaction, improves the selectivity for CO product, and broadens the electric potential window of reducing carbon dioxide to generate CO.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
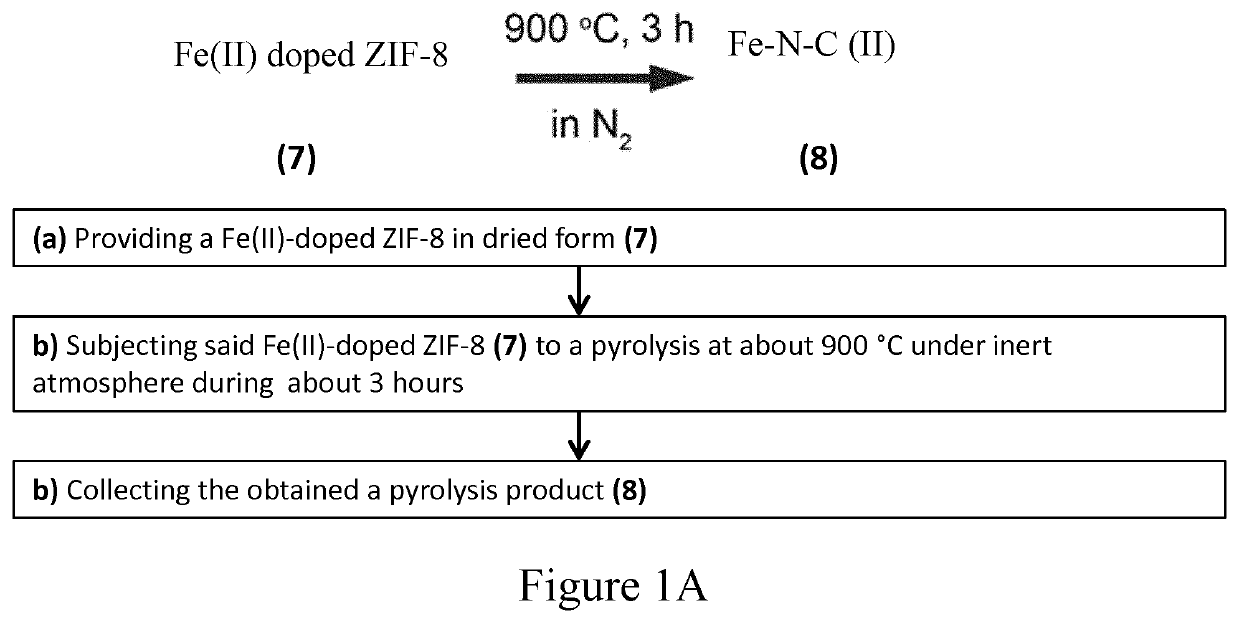
Fe-N-C CATALYST, METHOD OF PREPARATION AND USES THEREOF
PendingUS20210047741A1High catalytic activityHigh selectivityMolecular sieve catalystsMultiple component coatingsPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
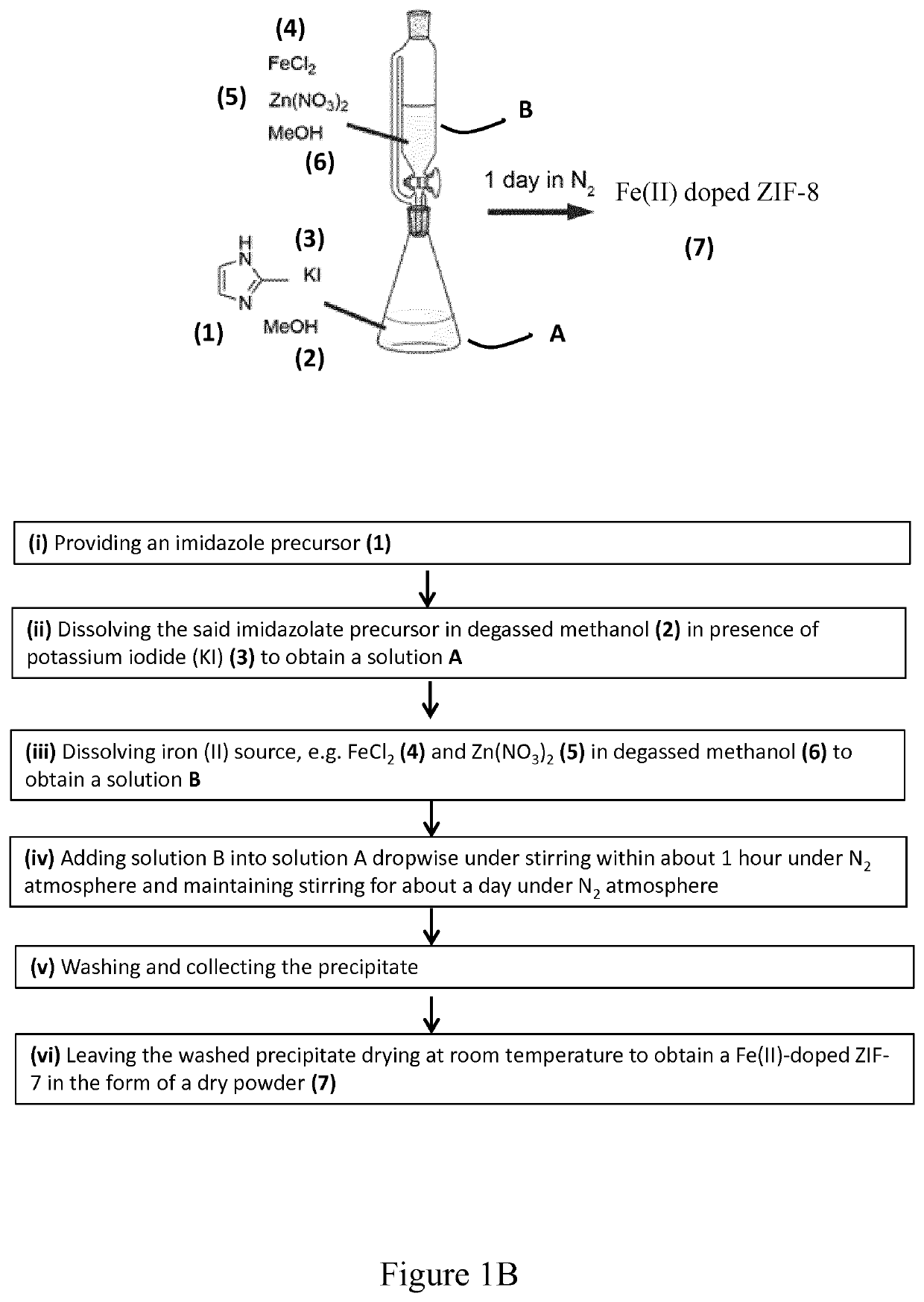
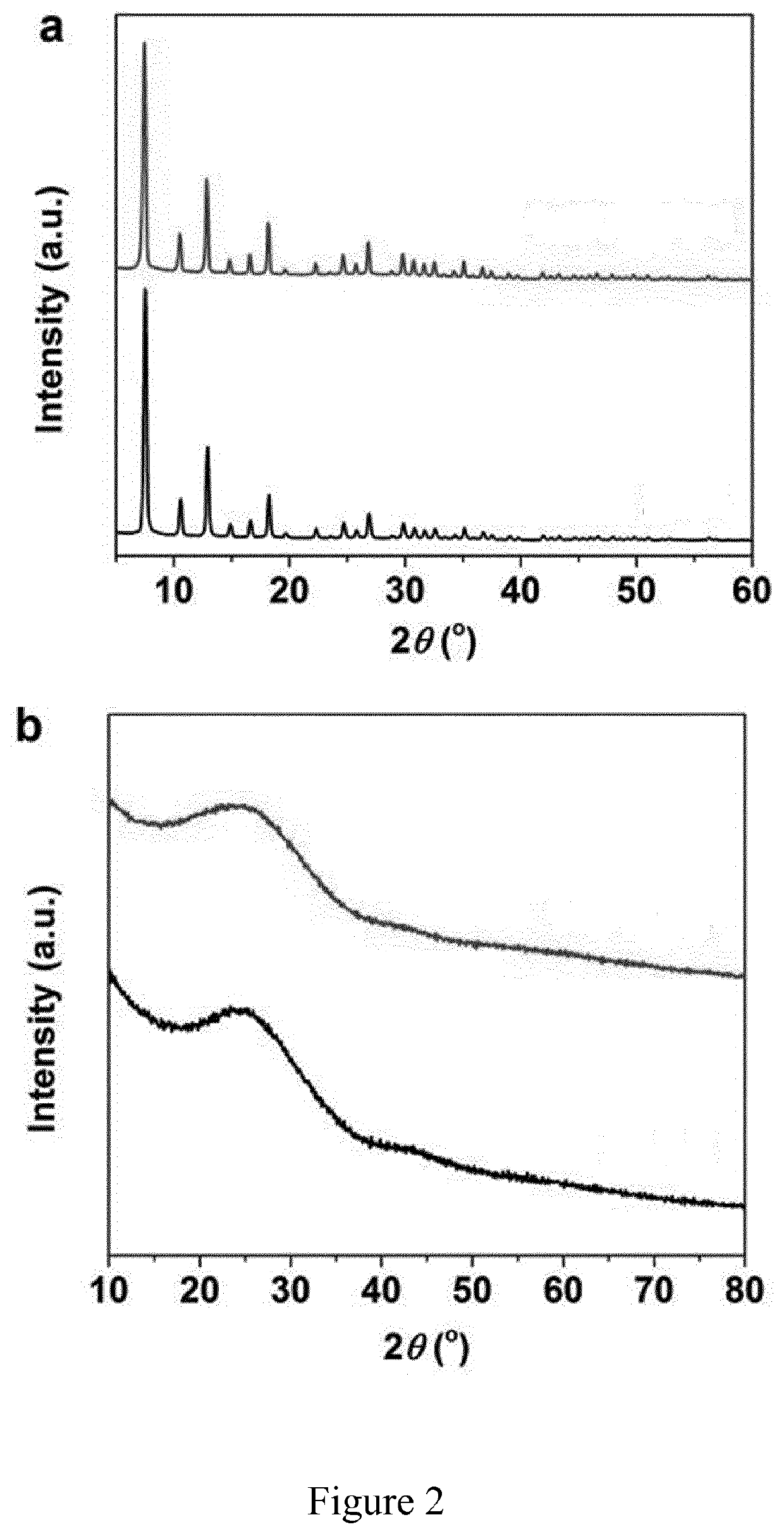
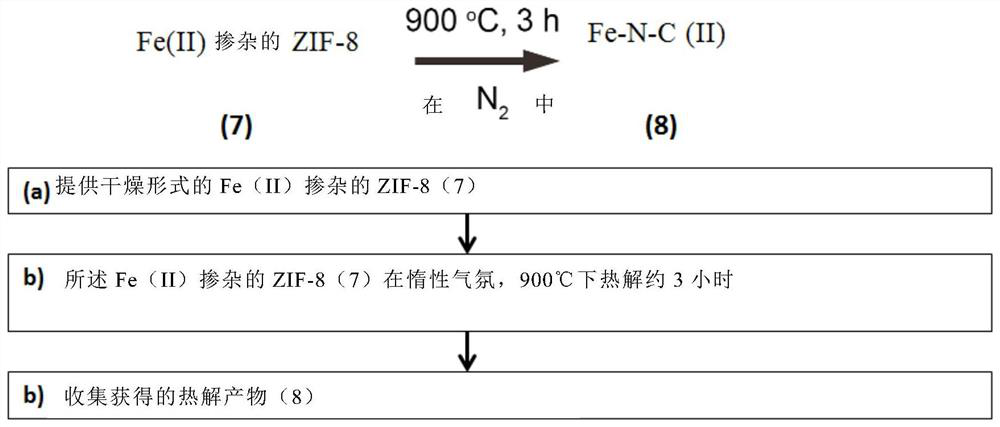
The invention relates to single-atom Fe catalysts useful for the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, method of preparation as uses thereof. In particular, the invention relates to a method of preparation of Fe(II) doped Zn-ZIF precursor material and use thereof in the preparation of a catalyst containing Fe single atoms on N doped carbon matrix derived from the pyrolysis of this Fe(II) doped Zn-ZIF precursor material.
Owner:GAZNAT SA
Fe-N-C catalyst, method of preparation and uses thereof
PendingCN111727170AMolecular sieve catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationPtru catalystPhysical chemistry
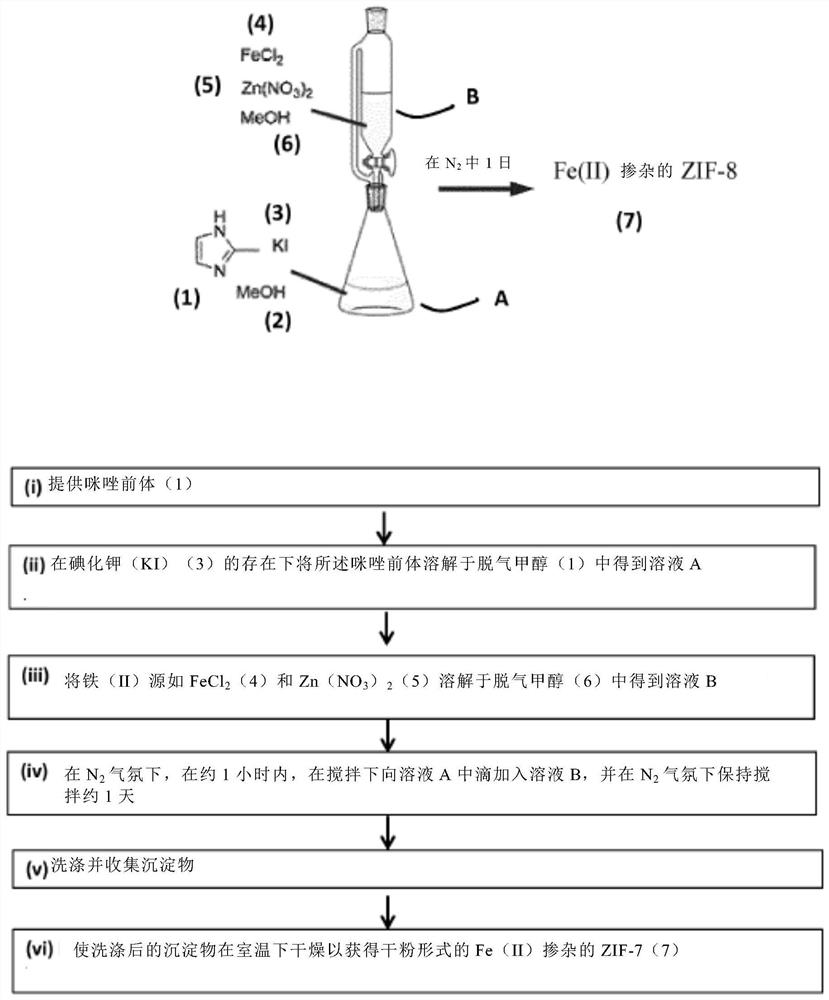
The invention relates to single-atom Fe catalysts useful for the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, method of preparation as uses thereof. In particular, the invention relates to a method ofpreparation of Fe(II) doped Zn-ZIF precursor material and use thereof in the preparation of a catalyst containing Fe single atoms on N doped carbon matrix derived from the pyrolysis of this Fe(II) doped Zn-ZIF precursor material.
Owner:加兹纳特股份公司
Preparation of porous copper electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide and electrode and application thereof
InactiveCN106868536ALow costImprove efficiencyElectrolytic organic productionElectrode shape/formsPorosityCopper electrode
The invention provides a preparation method of a porous copper electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. The preparation method comprises the following steps: 1) a layer of a sacrificial metal is electrolytic deposited on a copper base material; 2) a heat treatment is conducted under the protection of an inert gas, so that a solid state diffusion between a metal copper and sacrificial metal atoms occurs, and an alloy layer of the sacrificial metal and the copper is obtained on the surface of the copper; 3) the electrochemical dealloying is conducted. The porosity of the porous copper electrode is 50%-95%, the pore size is 50 nm-500 nm, and the sacrificial metal content is no more than 5%. The porous copper electrode has the characteristics of adjustable pore size and quantity, good air permeability and high specific surface area. The porous copper electrode has better specificity for the selection of target products and is suitable for electrochemical reduction reaction of carbon dioxide catalyzing.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalyst for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide and preparation method of catalyst
ActiveCN107252705AMany active sitesIncrease current densityMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectrodesElectrolysisDecomposition
The invention provides a catalyst for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. The catalyst is a carbon-loaded nano AgxZnyOz or AgxZny alloy, wherein x is greater than 0 and less than 1, y is greater than 0 and less than 1, x+y is equal to 1, and z is less than or equal to 2x+y. The invention further provides a preparation method of the catalyst. The particle sizes of two catalyst active components of the catalyst reach a nano level, thus ensuring that the catalyst has multiple active sites and a relatively large current density. The catalyst provided by the invention is high in CO2 electric reduction catalytic activity, low in decomposition voltage and high in CO2 conversion efficiency. Two preparation methods of the catalyst are high in process amplification capability and comprise core steps of double decomposition and precipitation or impregnation and calcinations which are easy to control.
Owner:BEIJING FUMEIJIA ENERGY TECH CO LTD
Gas diffusion electrode, preparation method thereof and application thereof in electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
ActiveCN108823596AIncrease the catalytic activity of electrochemical reductionImprove Faraday efficiencyElectrolytic organic productionMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsFaraday efficiencyElectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
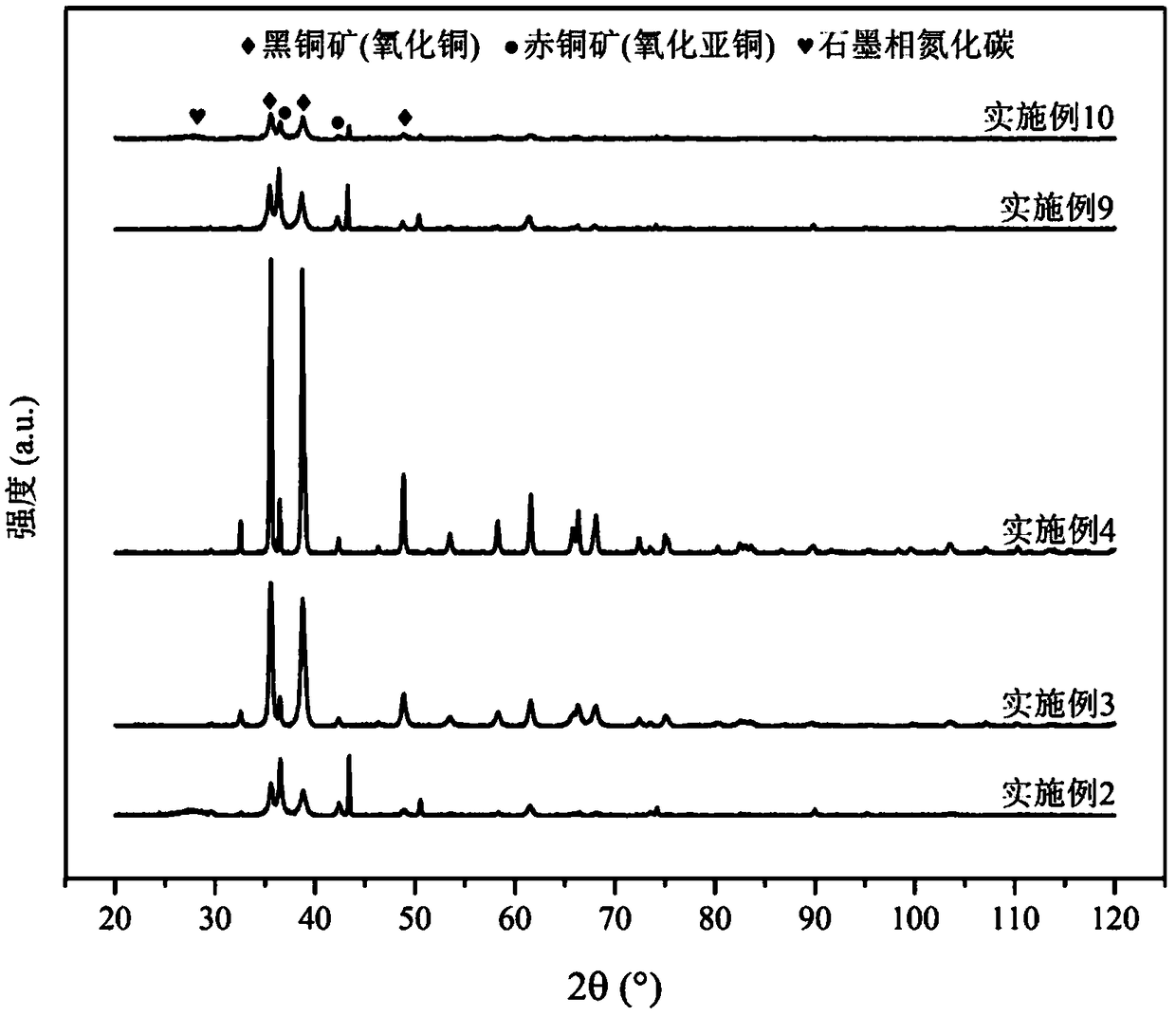
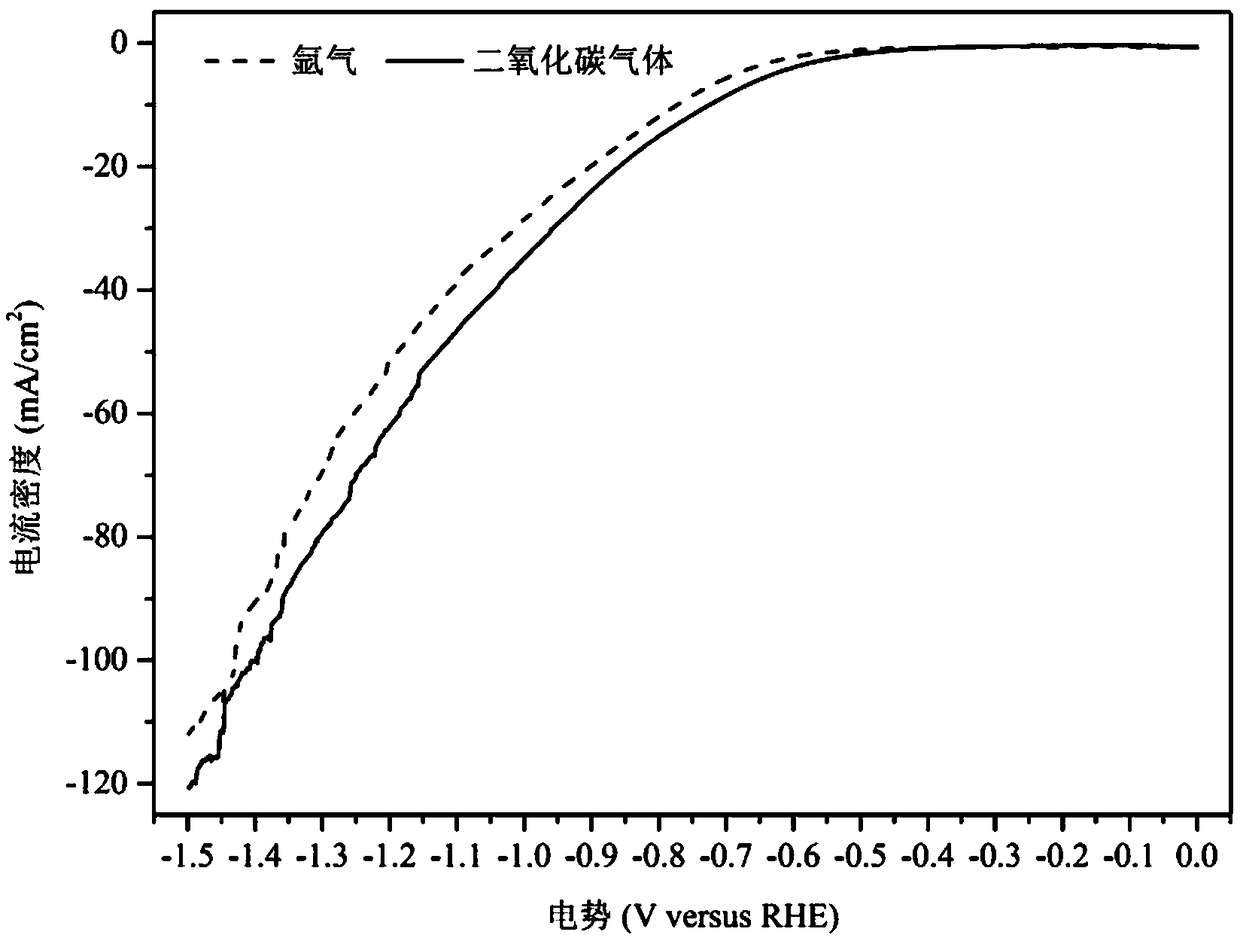
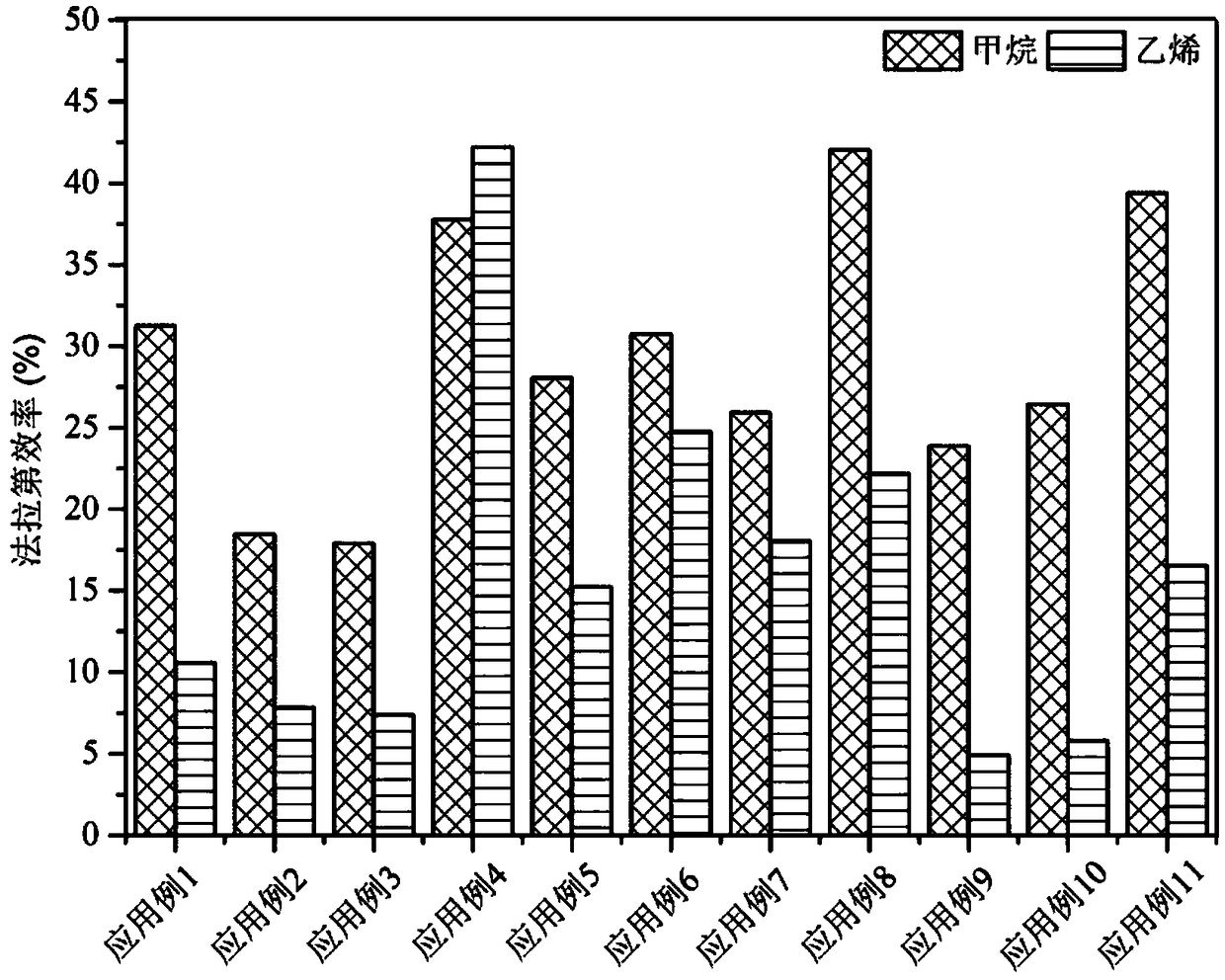
The invention relates to a gas diffusion electrode, a preparation method of the gas diffusion electrode, and the application of the gas diffusion electrode in electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. The gas diffusion electrode comprises a gas diffusion electrode body and carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalysts loaded on the gas diffusion electrode body. Nano copper oxide supportedon graphite phase carbon nitride serves as the carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalysts and has two crystal forms of tenorite and cuprit. The gas diffusion electrode can improve the Faradayefficiency of carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction products such as methane, ethylene and other hydrocarbons, and also can effectively inhibit hydrogen evolution reaction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Ionic polymer membrane for a carbon dioxide electrolyzer
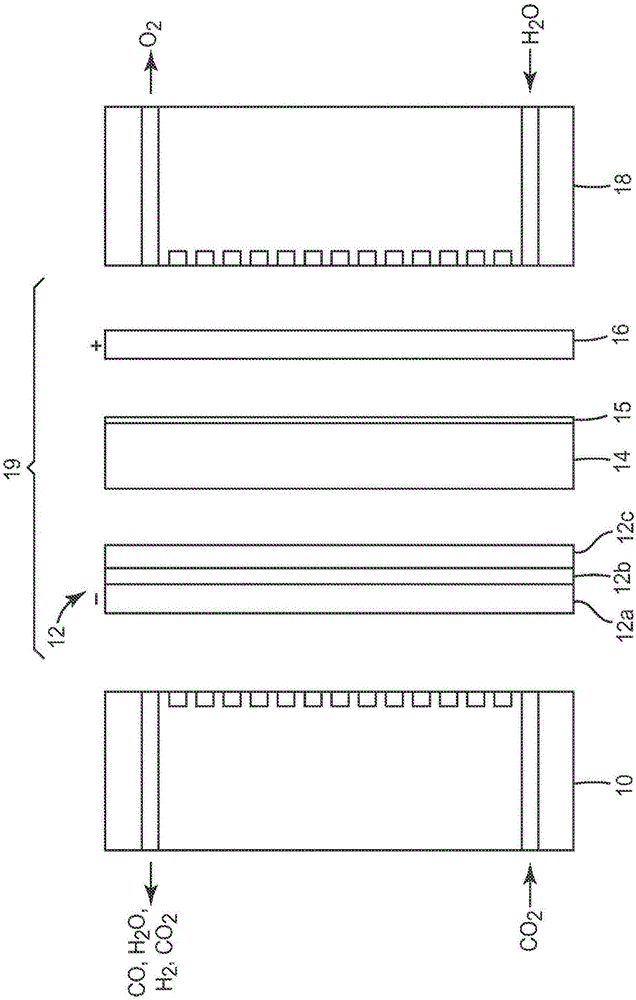
Described herein is a process for the reduction of carbon dioxide comprising: providing an electrochemical device comprising an anode, a cathode, and a polymeric anion exchange membrane therebetween, wherein the polymeric anion exchange membrane comprises an anion exchange polymer, wherein the anion exchange polymer comprises at least one positively charged group selected from a guanidinium, a guanidinium derivative, an N-alkyl conjugated heterocyclic cation, or combinations thereof; introducing a composition comprising carbon dioxide to the cathode; and applying electrical energy to the electrochemical device to effect electrochemical reduction of the carbon dioxide.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Supported silver nanonet, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN104911639ANo pollution in the processEasy to operateLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingElectroforming processesToxic materialNanostructure
The invention discloses a supported silver nanonet, and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: by using a copper sulfate-n-propanol mixed solution as an electrolyte, Ag / AgCl as a reference electrode, a platinum sheet as a counter electrode and ITO (indium tin oxide) as a work electrode, preparing cuprous oxide nano cubes supported on an ITO substrate by a constant voltage process, cleaning the surface, drying in a vacuum drying oven, adding silver nitrate to sufficiently react by using the cuprous oxide nano cubes supported on the ITO substrate as a template and reducer, taking out, cleaning with deionized water, and carrying out vacuum drying to obtain the ITO-supported net silver nano structure which is the supported silver nanonet. The material can be used for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. The net silver nano structure electrode material has application potential in electrochemical catalytic reduction of carbon dioxide. The preparation method is simple to operate and easy to control, and does not generate any toxic substance.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Nano copper electrode material as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108560018AUniform sizeRough surfaceMaterial nanotechnologyTransportation and packagingNano copperNanometre
The invention discloses a nano copper electrode material which comprises a conductive substrate and super-aerophilic copper nanowire aggregate attached to the surface of the conductive substrate, wherein multiple grain boundaries exist on the copper nanowire surface. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the nano copper electrode material and application thereof in electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide and application thereof
ActiveCN111676482AEasy to makeThe preparation process is simple and controllableElectrolytic inorganic material coatingElectrolytic organic productionElectrolytic agentPtru catalyst
The invention relates to an electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide and application thereof. A catalyst is an ordered core-shell catalyst. The preparation method of the electrode comprises the following steps: pretreatment of a substrate: immersing a substrate layer into a certain amount of a mixture of sodium hydroxide and oxide, and preparing a CuOx nanowire / Cu substrate by a chemical oxidation method; adding a reducing agent and an additive into copper salt, mixing according to a certain proportion, performing Cu deposition by utilizing variable current density, carrying out washing, drying and baking, and then putting the obtained electrode into a CO2 saturated electrolyte for reduction at a constant potential, and carrying out washing and drying; and soaking the prepared gas diffusion electrode in a concentrated hydrochloric acid solution with the concentration of 36%-38% to obtain the electrode. The vacancy copper has more active areas and defect sites and the coupling synergistic effect among the components is utilized, so that the selectivity and activity of the hydrocarbon are improved. By utilizing the interaction between Cu<+> and each metal, CO2 electroreduction is limited in a functional structural domain, so that the loss of the catalyst in the CO2 reduction process is avoided, and the stability of the catalyst is improved.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Method for preparing gas diffusion electrode of hydrocarbon through electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
ActiveCN106868535ALow costPreserve the diffuse distribution propertiesElectrolytic organic productionNanotechnologyFiberCarbon fibers
The invention provides a method for preparing a gas diffusion electrode of hydrocarbon through electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. The method comprises the following steps: (1), taking porous carbon material as a substrate, and carrying out thermal treatment in the air to remove the coating on the surface of carbon fiber and increase the hydrophilia of the carbon fiber to aqueous solution so as to obtain a gas diffusion substrate; (2) preparing supported nano Cu / C; (3) taking the porous carbon material subjected to thermal treatment as the substrate, and depositing particles containing Cu / C on the surface and the cross section of the carbon material under negative pressure; (4) soaking the gas diffusion electrode sample in HCl acid solution for at least 24 h, and cleaning the gas diffusion electrode sample up; and (5) spraying alcoholic solution of perfluorosulfonic acid resin on the gas diffusion electrode, and drying at the room temperature to obtain the gas diffusion electrode of hydrocarbon through electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. The method has the following advantages: the raw material cost is low, the preparation process is simple, the dispersion distribution characteristic of Cu particle can be kept to the maximum to prevent agglomeration of nano Cu particles, and high catalytic activity to hydrocarbon during the electrochemical reduction process of CO2 is ensured.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Gas diffusion electrode used for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide and preparation method and application of gas diffusion electrode
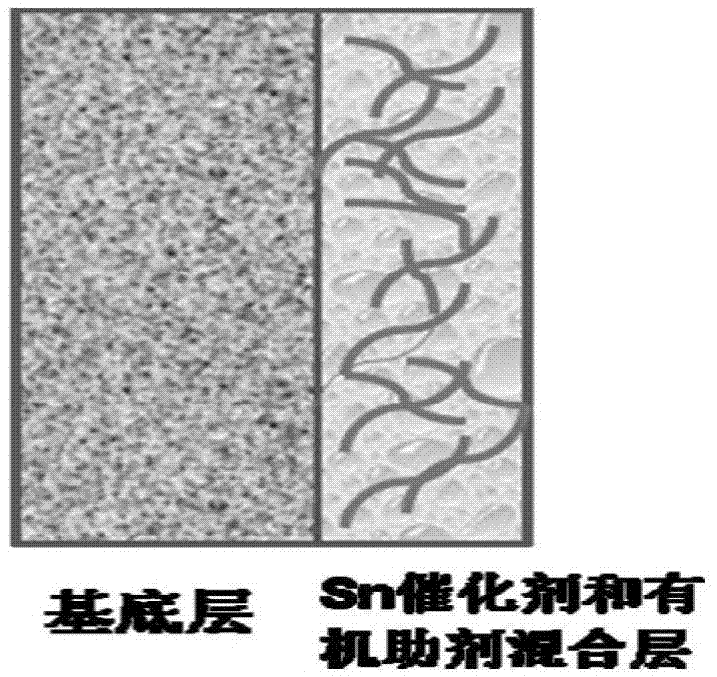
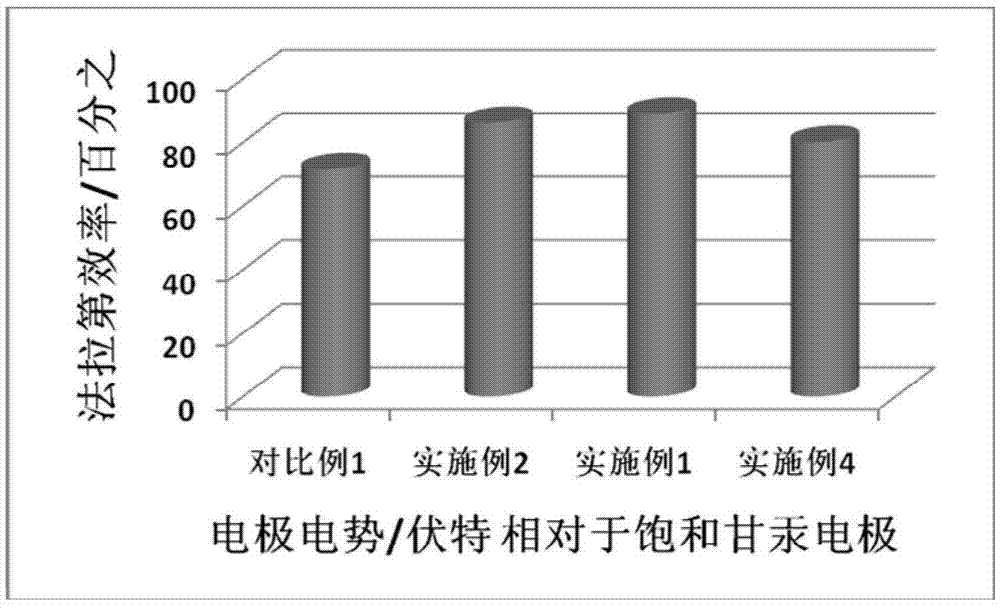
ActiveCN106876722AAvoid affecting performanceIncreased reaction current densityCell electrodesChemical reactionElectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
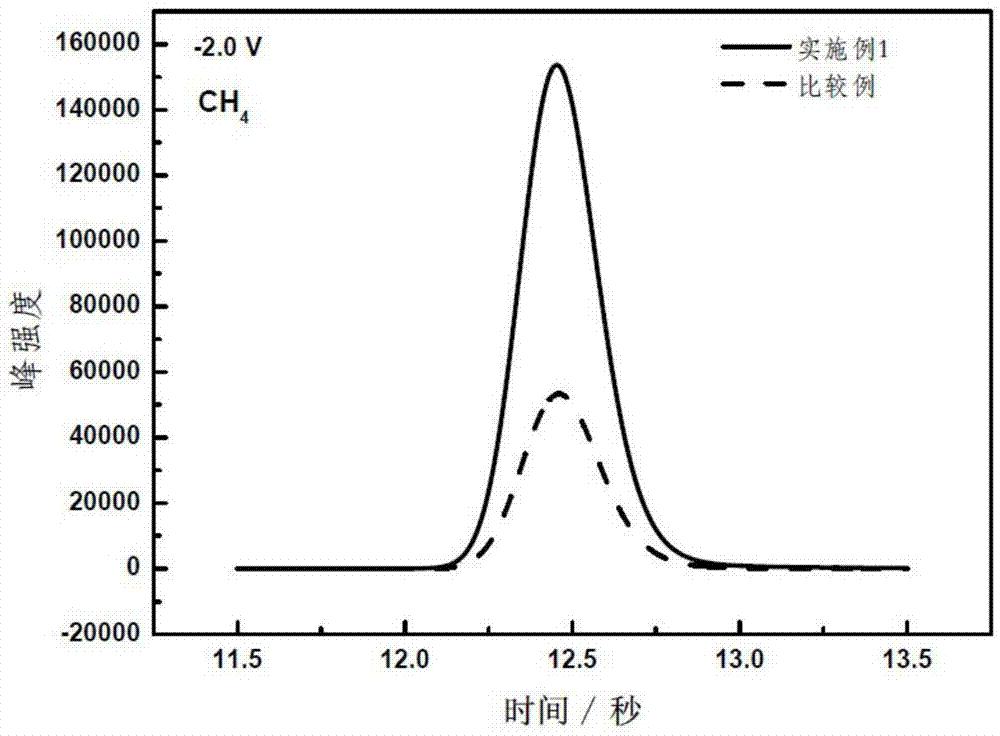
The invention relates to a gas diffusion electrode used for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide and a preparation method and an application of the gas diffusion electrode. The electrode comprises a base layer, and a Sn catalyst and an organic accessory ingredient mixing layer attached on the base layer; the molar ratio of the Sn catalyst to the organic accessory ingredient is 100:1 to 30:1; and the loading amount of the Sn catalyst in the electrode is 0.1-5mg / cm<-2>. In the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, the base layer plays the effects of a supporting body, electric conduction, and forming liquid and gas transmission channels; the Sn catalyst catalyzes reduction of carbon dioxide while the organic accessory ingredient can stabilize an intermediate reactant CO<2>.-, so that the concentration of CO<2> is improved, overpotential in electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide is lowered, and current density and efficiency are improved; and in addition, the accessory ingredient in the electrode also anchors the Sn catalyst on the surface of the carbon base, so that the electrode has quite high stability.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Copper oxide nanowire loaded silver particle composite electrode, preparation method and application
ActiveCN112076761AImprove conductivityIncrease current densityCatalyst activation/preparationElectrolytic organic productionComposite electrodeLight irradiation
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Copper nano-electrode with high-index crystal face and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN111534833AUniform sizeGood choiceMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic organic productionSide reactionElectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrode materials, and particularly relates to a copper nano-electrode with a high-index crystal face and a preparation method and application of thecopper nano-electrode. The electrode comprises a conductive substrate and a copper nanowire aggregate loaded on the surface of the conductive substrate; the length of the copper nanowire is 10-200 microns, the length-diameter ratio of the copper nanowire is larger than 1000, the surface of the copper nanowire is in a step shape and has high-index crystal faces, and the high-index crystal faces include but are not limited to high-index crystal faces (200), (220), (222), (311), (310), (320), (331), (400), (510), (511), (533), (610) and (755). The invention further discloses a preparation methodand application of the above electrode. The electrode material with the high-index crystal face is prepared for the first time, side reaction can be well inhibited when the electrode material is usedfor electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, and the electrode material has good selectivity on high-carbon products such as ethylene, ethanol and isopropanol.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst and preparation method thereof and catalyst loaded gas diffusion electrode
InactiveCN108654623AMany active sitesReduce overpotentialCatalyst activation/preparationElectrolytic organic productionNano catalystFaraday efficiency
The invention relates to the technical field of electrochemical reduction catalysts, in particular to a carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst and a preparation method thereof and a catalyst loaded gas diffusion electrode. The carbon dioxide electrochemical reduction catalyst is of a nano-catalyst and is specifically a nickel-copper lamellar bimetallic oxide with a composite lamellar structure of nickel-copper oxide and copper oxide, or nickel-tin lamellar bimetallic oxide with a composite lamellar structure of nickel oxide and tin oxide. The nano-catalyst with the structure is highin catalytic activity, overpotential in electrochemical reduction process is greatly reduced, and meanwhile, hydrogen evolution reaction in the process of carbon dioxide reduction is effectively restrained. The invention further provides the preparation method of the catalyst and the catalyst loaded gas diffusion electrode, the problem about excessive low reduction current can be solved, and theFaradic efficiency in the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide is effectively improved.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalysts for Carbon Dioxide Conversion
ActiveUS20160145752A1Improve conversion performanceLow costCellsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalytic methodOverpotential
The disclosure relates generally to improved methods for the reduction of carbon dioxide. The disclosure relates more specifically to catalytic methods for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide that can be operated at commercially viable voltages and at low overpotentials. The disclosure uses a transition metal dichalcogenide and helper catalyst in contact within the cell.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, as well as preparation method and application of electrode
The invention discloses an electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, as well as preparation and application of the electrode. The electrode comprises a basal layer and a Sn catalyst nanolayer attached to the basal layer, wherein the carrying capacity of a Sn catalyst is 1mg / cm<-2> to 6mg / cm<-2>; and Sn in the electrode is composed of one, two or more of 1-500nm nanowire, nanorod and nanofiber. According to the invention, the Sn nanorod with rich edge active sites grows on a base in situ, so that the specific area and active area of the electrode are remarkably increased, and the Faraday efficiency of electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide into formic acid by the electrode is improved.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Catalytic composition for the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
InactiveUS20150072853A1Catalyst activation/preparationMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsTin dioxideArgon atmosphere
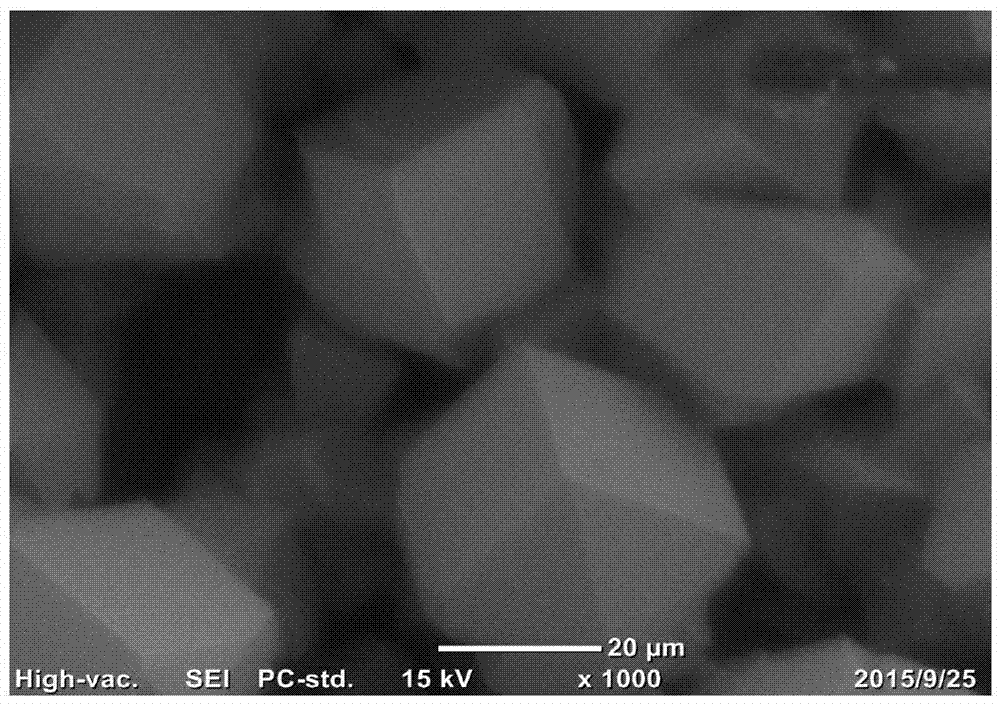
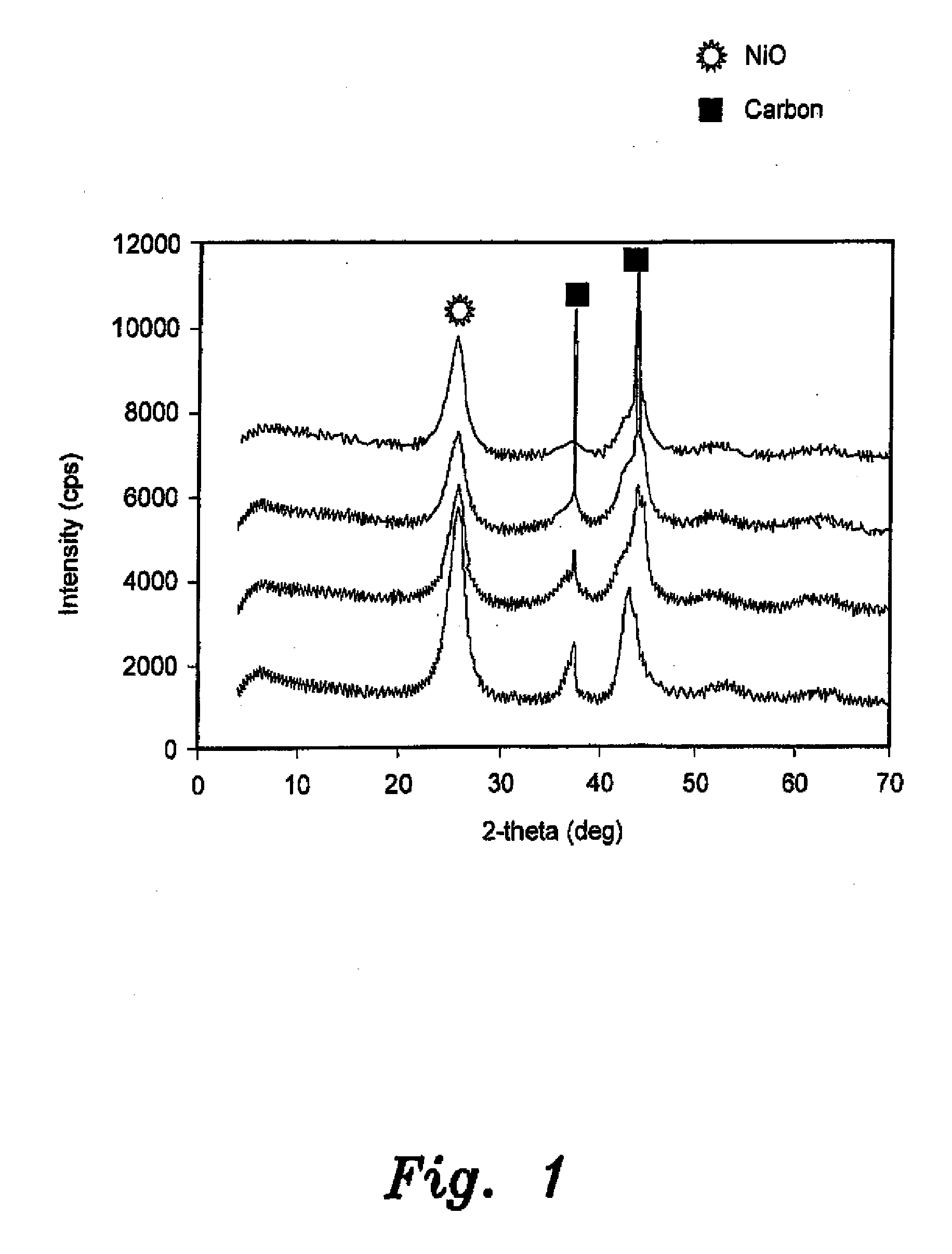
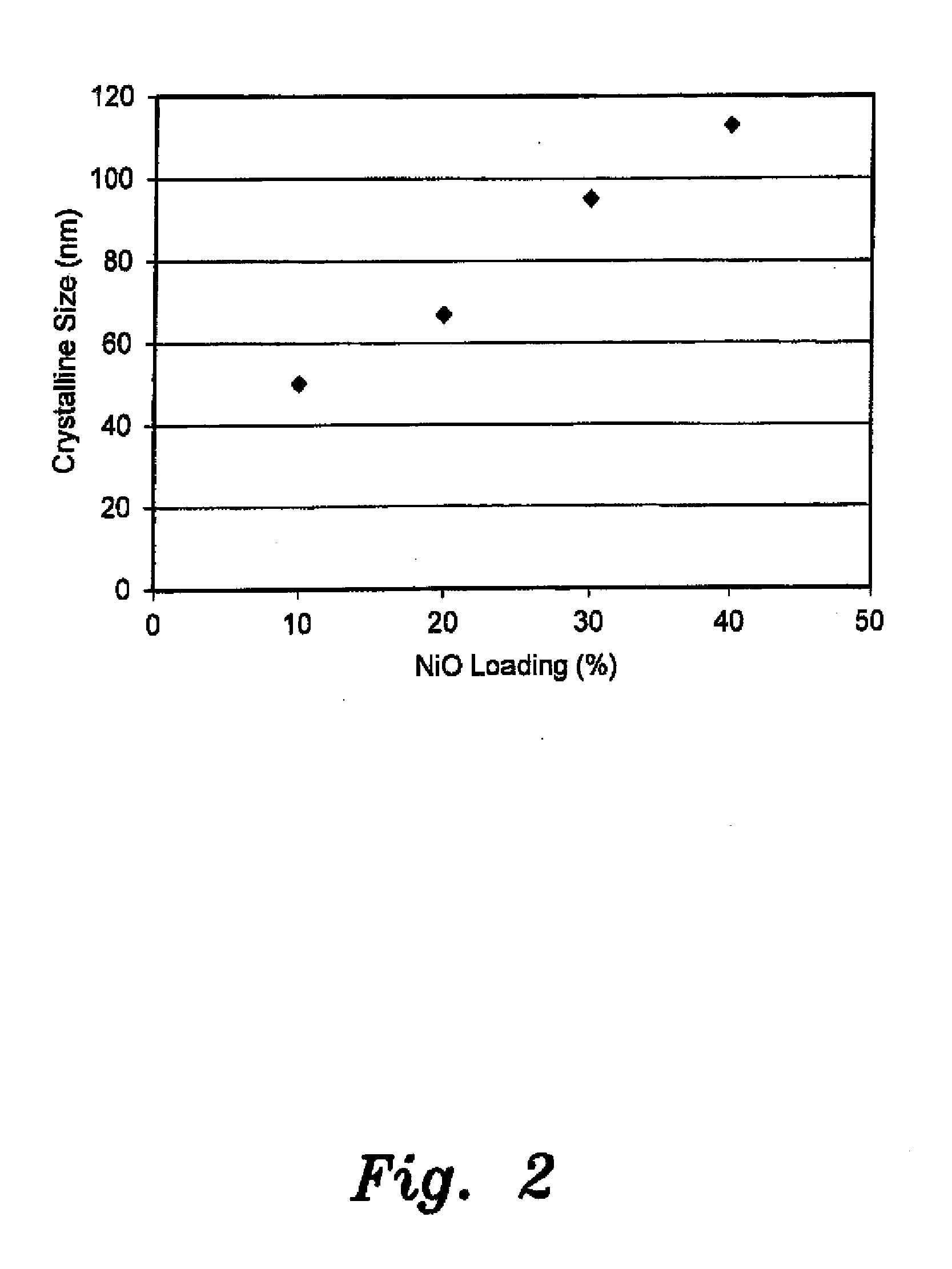
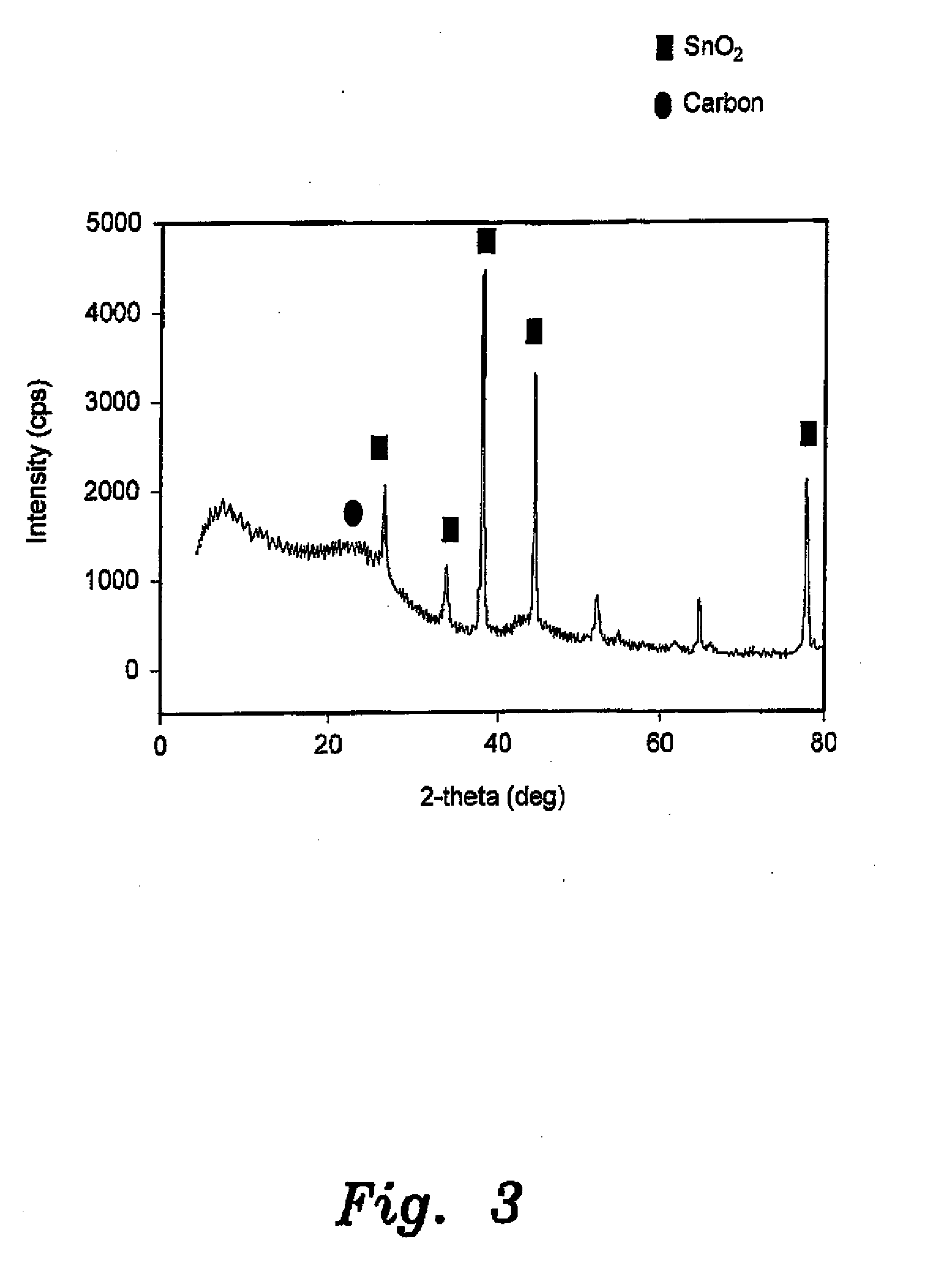
The catalytic composition for the electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide is a metal oxide supported by multi-walled carbon nanotubes. The metal oxide may be nickel oxide (NiO) or tin dioxide (SnO2). The metal oxides form 20 wt % of the catalyst. In order to make the catalysts, a metal oxide precursor is first dissolved in deionized water to form a metal oxide precursor solution. The metal oxide precursor solution is then sonicated and the solution is impregnated in a support material composed of multi-walled carbon nanotubes to form a slurry. The slurry is then sonicated to form a homogeneous solid solution. Solids are removed from the homogeneous solid solution and dried in an oven for about 24 hours at a temperature of about 110° C. Drying is then followed by calcination in a tubular furnace under an argon atmosphere for about three hours at a temperature of 450° C.
Owner:KING FAHD UNIVERSITY OF PETROLEUM AND MINERALS +1
Device for microorganism electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide using microorganisms
InactiveCN108893754ALow costImprove energy utilizationCellsElectrolytic organic productionFiberElectrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
The invention discloses a device for microorganism electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide, in order to solve the problems of the prior art that carbon dioxide is difficult to transfer between solution and microorganisms, the surface area of a microorganism electrochemical cathode material is low and the like. The invention comprises: 1) adopting the microorganism as a cathode catalyst for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide and converting carbon dioxide into an organic product; 2) adopting a porous metallic hollow fiber cathode and connecting an external carbon dioxide bag throughan air guide pipe so as to supply an inorganic carbon source for the growth of the microorganisms on the porous metallic hollow fiber cathode. According to the method provided by the invention, a three-dimensional cathode material with large surface area and being beneficial to direct transmission of carbon dioxide can be prepared; the method is beneficial to the growth of the microorganisms on the cathode; the device for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide provided by the invention is low in cost, can be used for a long time, is high in use ratio of energy, and is suitable for large-scale application in carbon dioxide reduction, electrode material preparation and microorganism electrolytic tanks.
Owner:XIAN MODERN CHEM RES INST
Preparation and application of copper electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide
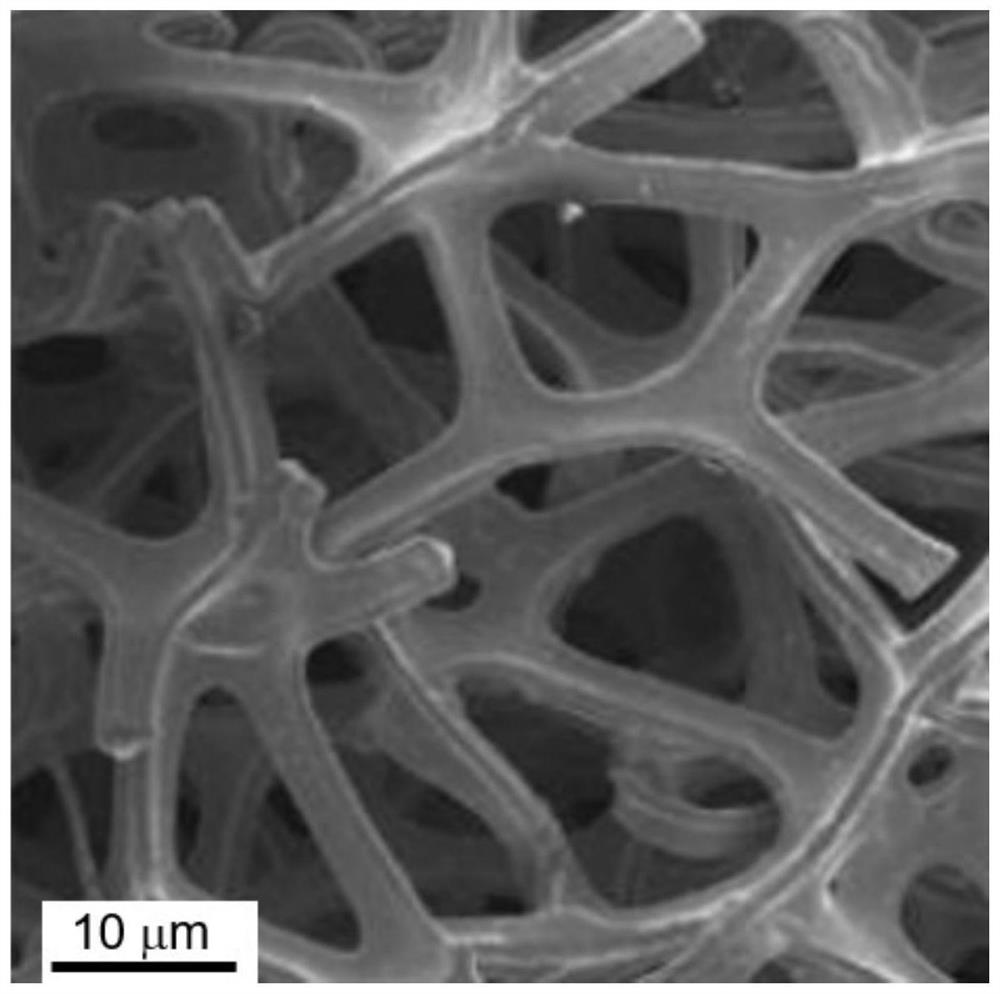
ActiveCN111636074AAvoid unevennessPolygonal active sitesElectrolytic organic productionLiquid/solution decomposition chemical coatingNanowireActive agent
The invention relates to preparation and application of a copper electrode for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide. The preparation method of the electrode comprises the following steps: treating a substrate, oxidizing the substrate at a high temperature, mixing a precursor copper salt solution with an alkaline precipitator, a reducing agent and an additive according to a certain ratio, depositing copper by a hydrothermal method, performing electrochemical potentiostatic reduction, and washing with concentrated hydrochloric acid to prepare the copper electrode. According to the invention, the Cu oxide with the nanowire structure grows on the substrate through a chemical oxidation reaction; then, thin-layer nano-particles grow on the surface through hydrothermal reaction; a surfactant and a reducing agent are introduced in the hydrothermal reaction process; the surface active agent is used for directionally adsorbing the surface of the substrate metal; the growth orientation ofthe metal oxide can be regulated and controlled, a reducing agent is introduced through hydrothermal reaction deposition, the nanowire part of the substrate layer is reduced to form hole copper, nanocopper particles with high specific surface area are deposited on the surface of the hole copper, the active specific surface area of the copper electrode is increased, and the proportion of edge andcorner active sites is increased.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV
Nanometer tin based catalyst for electrochemical reduction carbon dioxide reaction and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN108441878ALarge specific surface areaRich grain boundary structureMaterial nanotechnologyElectrolytic organic productionTin dioxideNanowire
The invention discloses a nanometer tin based catalyst for an electrochemical reduction carbon dioxide reaction and a preparation method and application thereof. The nanometer tin based catalyst is ofa one-dimensional structure composed of a stannic oxide nanotube and a stannic oxide nanowire. The stannic oxide nanotube is arranged on the outer portion of the stannic oxide nanowire in a sleevingmanner. The nanometer tin based catalyst is prepared and obtained through combination of the one-step electrostatic spinning process and calcining treatment. The nanometer tin based catalyst in the special shape can be used for catalyzing the electrochemical reduction carbon dioxide reaction, and the Faradic efficiency and the current density of the reaction can be obviously improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Efficient coupling method of anode oxidization hypochlorite production and cathode carbon dioxide reduction
ActiveCN109881213AImprove Faraday efficiencyEfficient reductionPhysical/chemical process catalystsElectrodesHypochloriteFaraday efficiency
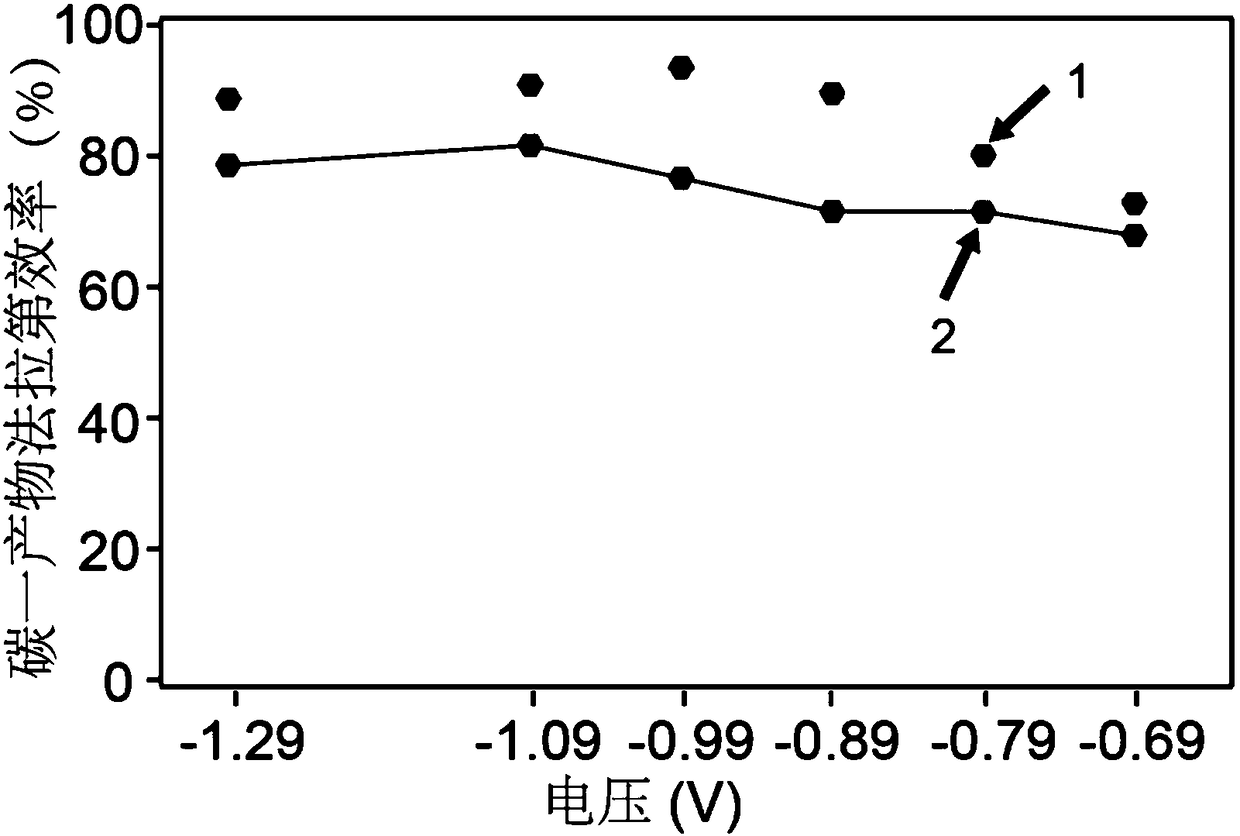
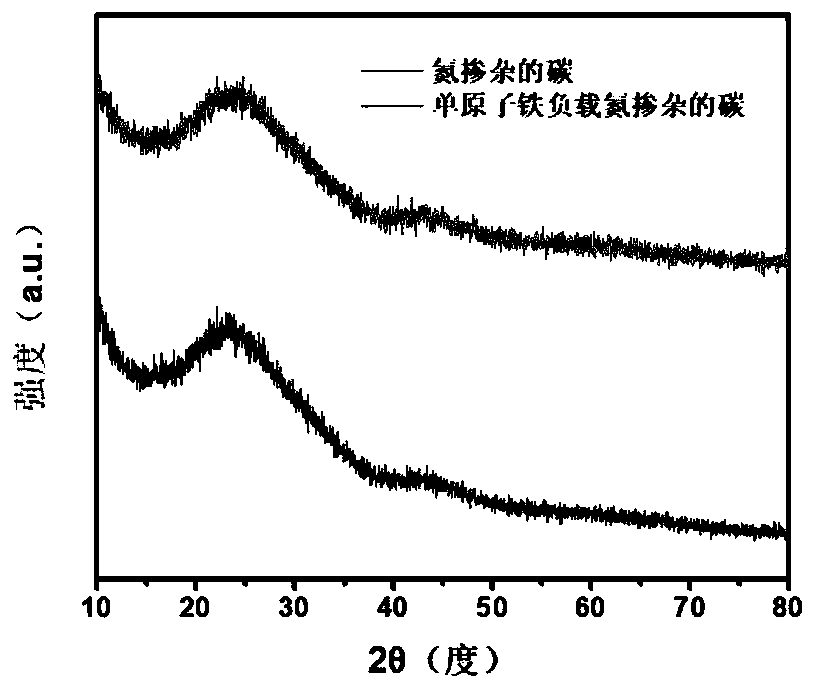
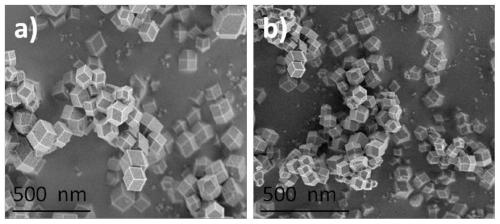
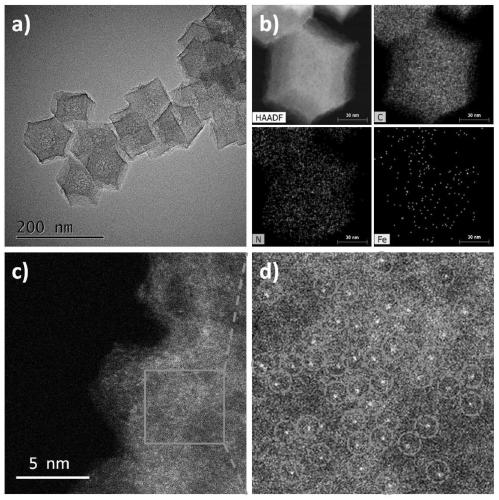
The invention provides a coupling method of anode oxidization hypochlorite production and cathode carbon dioxide reduction. A single-atom iron loaded nitrogen doping carbon material is used as a catalyst to perform electrocatalytic reduction on CO2; meanwhile, the anode oxidization can produce hypochlorite, so that the goal of efficiently producing hypochlorite and reducing carbon dioxide into carbon monoxide at the same time can be achieved; the single-atom iron loaded nitrogen doping carbon material has a polyhedron microstructure with the length and width in the nanometer scale dimensions;the loaded metal in the single-atom iron loaded nitrogen doping carbon material is dispersed in a single atom form. The material is used for electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide; the current efficiency for selectively reducing the carbon dioxide into the carbon monoxide is as high as 99.63 percent or higher; the stability is high; meanwhile, the current efficiency for producing the hypochlorite by the anode is as high as 99.47 percent; high faradic efficiency can be maintained for a long time.
Owner:HUAZHONG NORMAL UNIV
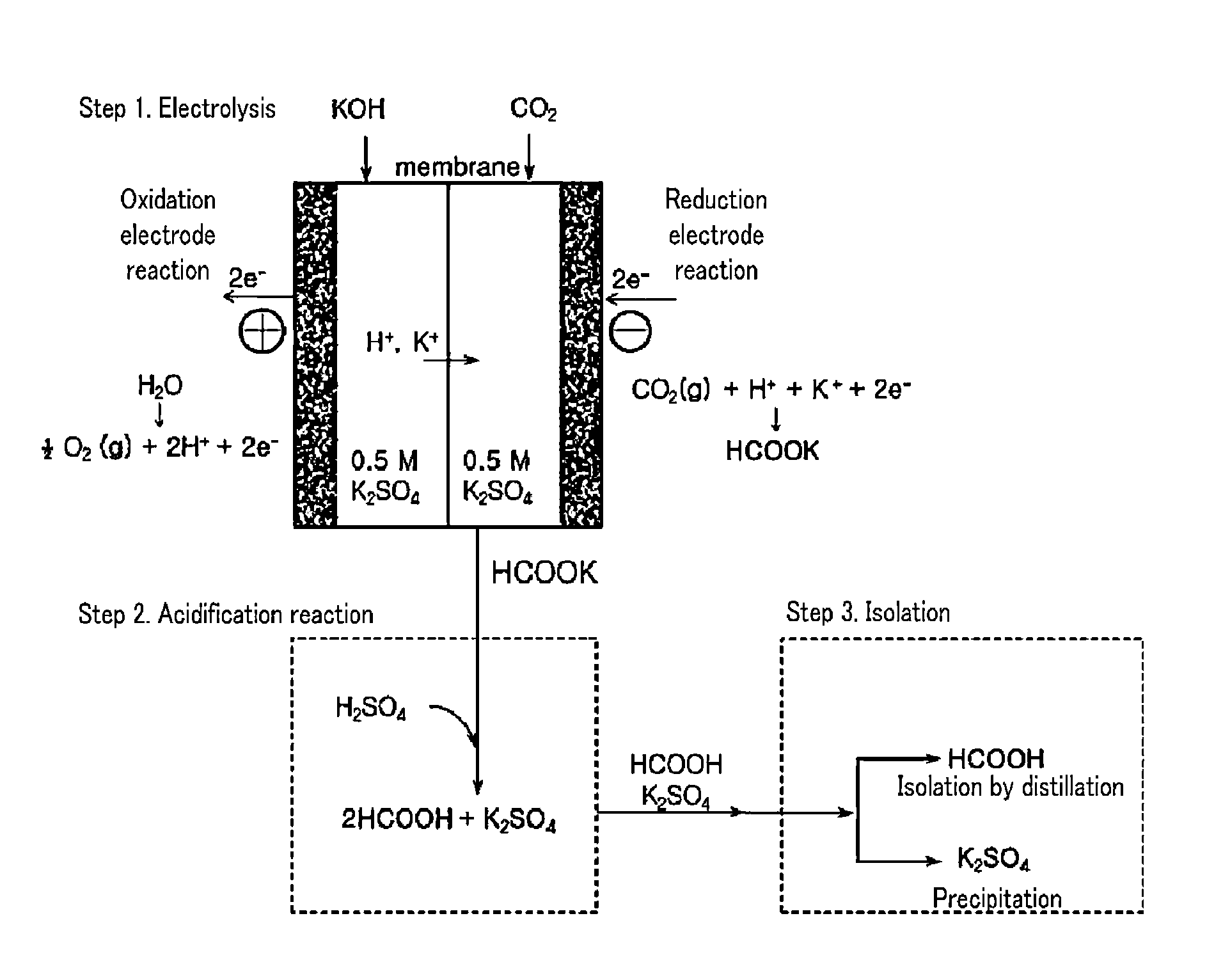
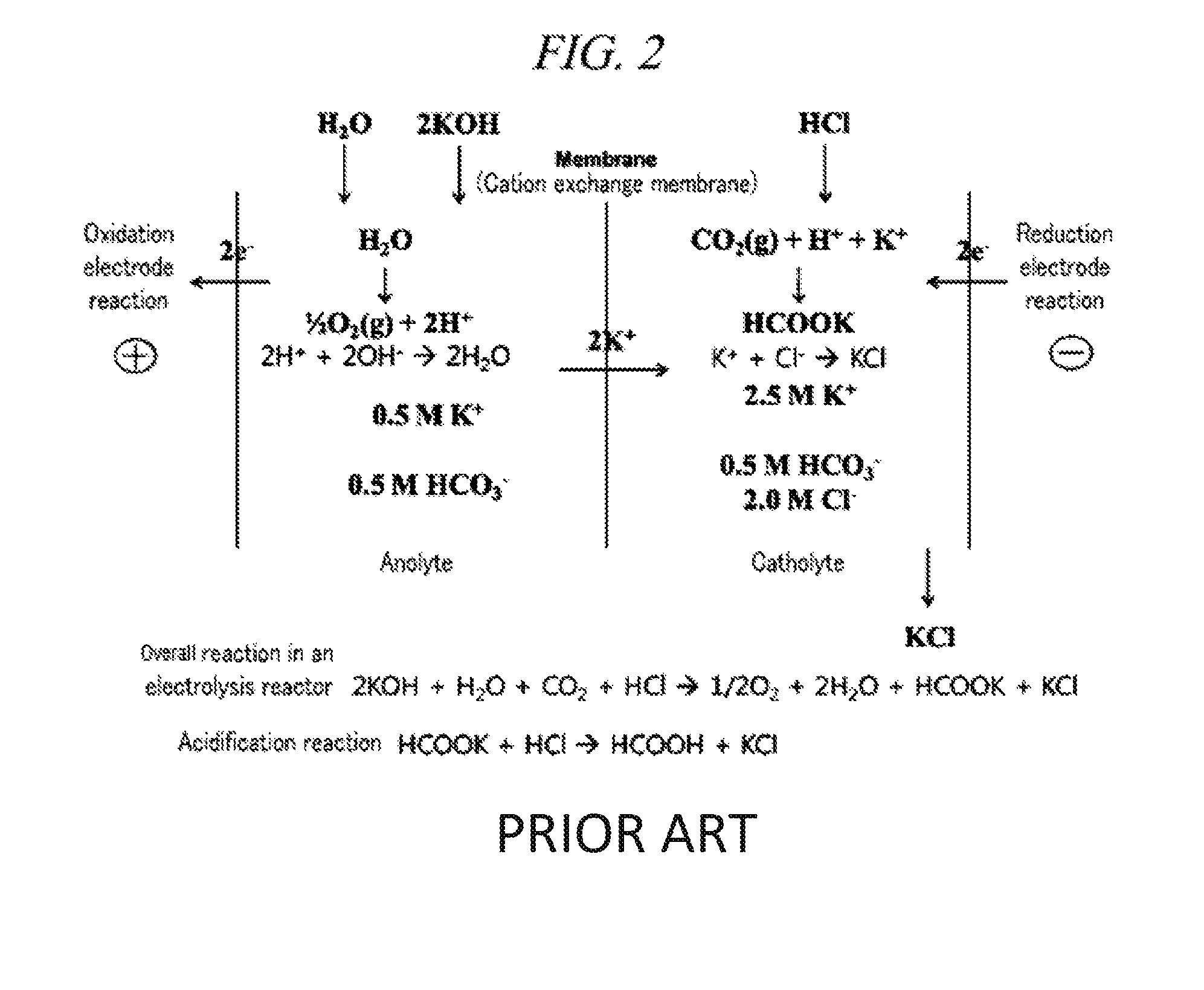
Electrochemical reduction method of carbon dioxide using solution containing potassium sulfate
ActiveUS9481938B2Improve conversion efficiencyLow costElectrolytic organic reductionElectrodesElectrochemistryPotassium sulfate
The embodiments described herein pertain generally to an electrochemical reduction method of carbon dioxide under a solution condition containing potassium sulfate.
Owner:SOGANG UNIV RES FOUND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com