Efficient coupling method of anode oxidization hypochlorite production and cathode carbon dioxide reduction
A carbon dioxide and hypochlorite technology, applied in the field of catalysis, can solve problems such as catalyst deactivation, and achieve the effects of less metal loading, easy synthesis conditions, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
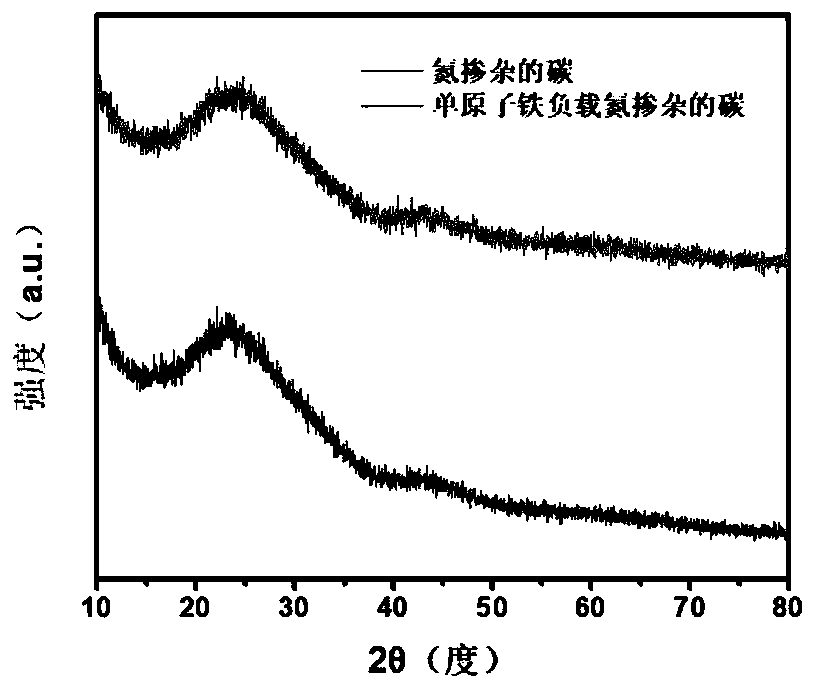
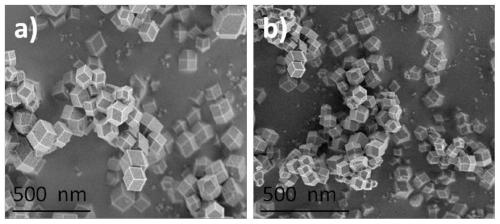
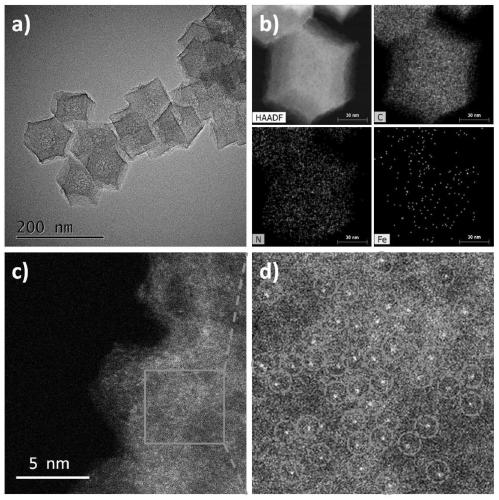
[0039] Preparation of monoatomic iron-supported nitrogen-doped carbon materials:
[0040] Dissolve 0.5g of zinc nitrate hexahydrate in 10mL of methanol to obtain liquid A, and dissolve 0.55g of dimethylimidazole in 10mL of methanol to obtain liquid B. Add liquid A to liquid B, ultrasonicate, and react at 30°C for 10 hours. The solid product after the reaction was collected by centrifugation, washed three times with DMF and methanol respectively, and the washed solid product was collected by centrifugation, and dried in a vacuum oven at 80°C to obtain ZIF-8; take 0.1g of the above ZIF-8 powder and add 10ml 0.01 % iron acetylacetonate in tetrahydrofuran solution, sonicated for 1h to make it fully and uniformly mixed; vacuumed for 1h to obtain a solid powder; the above powder was calcined at 950°C for 2h in an Ar atmosphere, and after naturally cooling to room temperature, the reaction product was collected to obtain Nitrogen-doped carbon supported on monoatomic iron. Tested by ...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Construction of the electrolysis system:
[0051] Weigh 10 mg of monoatomic iron-supported nitrogen-doped carbon as a precursor, ultrasonically disperse it into a mixture of 1 mL of Nafion (2 wt%) and isopropanol, and then add 150 μL of monoatomic iron-supported nitrogen-doped carbon suspension to lcm on the surface 2 The surface of the glassy carbon electrode was dried under an infrared lamp to prepare a nitrogen-doped carbon / glassy carbon electrode supported by single-atom iron. The catalyst loading in the electrode was 1.5mg / cm 2 .
[0052] In an electrolytic cell separated by a proton exchange membrane into an anode tank and a cathode tank, the nitrogen-doped carbon catalyst electrode supported by monoatomic iron is used as the working electrode (cathode), the ruthenium titanium is the auxiliary electrode (anode), and the anode and catholyte solutions are 0.1M sodium chloride solution, carbon dioxide is passed into the cathode tank to saturation, and then electric...
Embodiment 3
[0058] Electrocatalytic cathodic reduction of CO 2 And the realization of anode hypochlorite production:
[0059] When carbon dioxide is reduced at a cell pressure of 1.0V, the current efficiency of carbon monoxide is 33.99%, and the current efficiency of hypochlorite produced by the anode is 23.75%. The current efficiency of chlorate is 51.47%; the current efficiency of reducing carbon dioxide at a cell pressure of 2.0V is 81.22%, and the current efficiency of the anode producing hypochlorite is 78.195%; reducing carbon dioxide at a cell pressure of 2.5V, carbon monoxide The current efficiency is 99.63%, the current efficiency of hypochlorite produced by the anode is 99.47%, the carbon monoxide is reduced at a cell voltage of 3.0V, the current efficiency of carbon monoxide is 99.21%, and the current efficiency of hypochlorite produced by the anode is 99.08%. Experimental results such as Figure 8 Shown: when the cell voltage is 2.5V, its Faraday efficiency is the best. Fi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length width height | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com