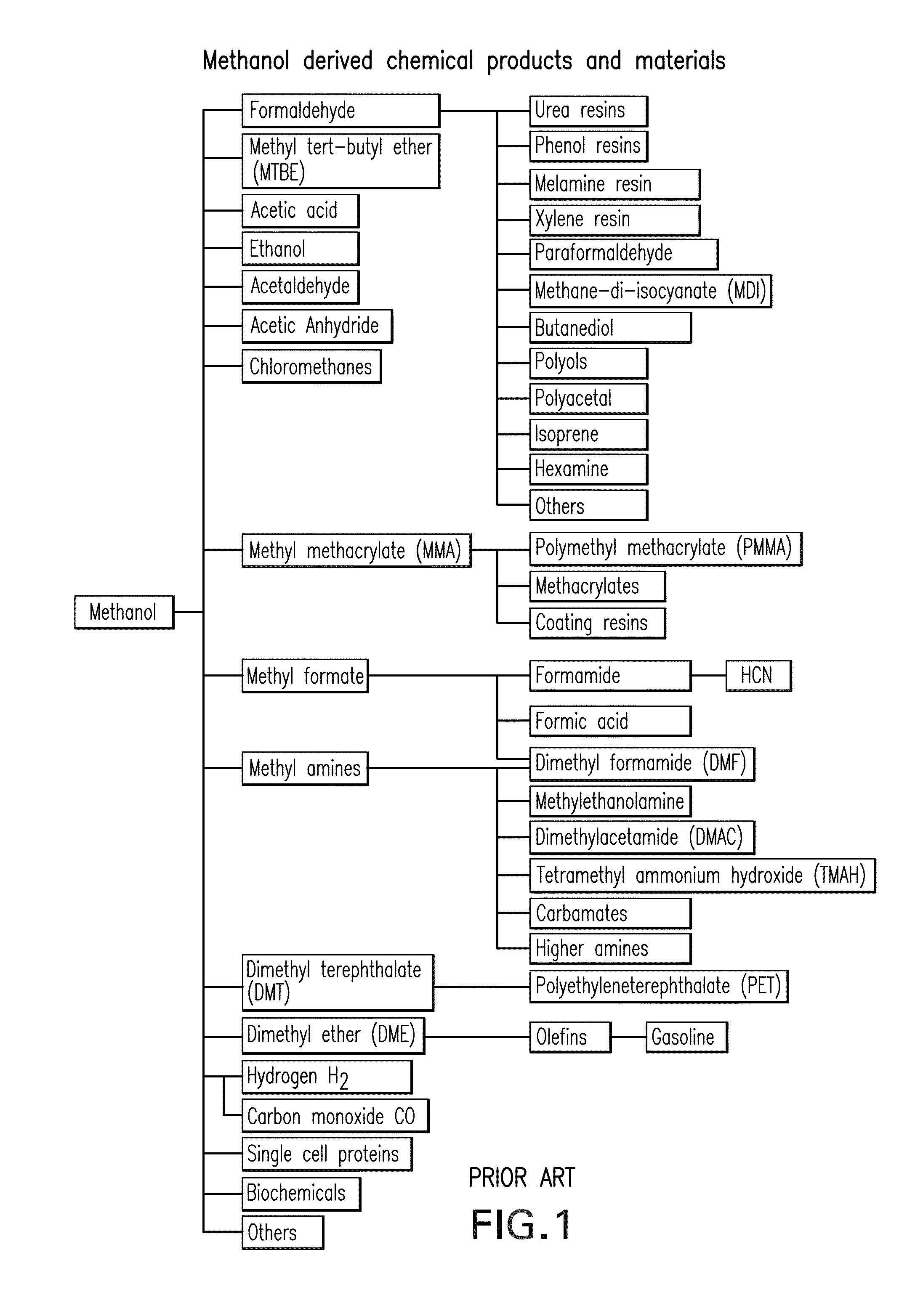
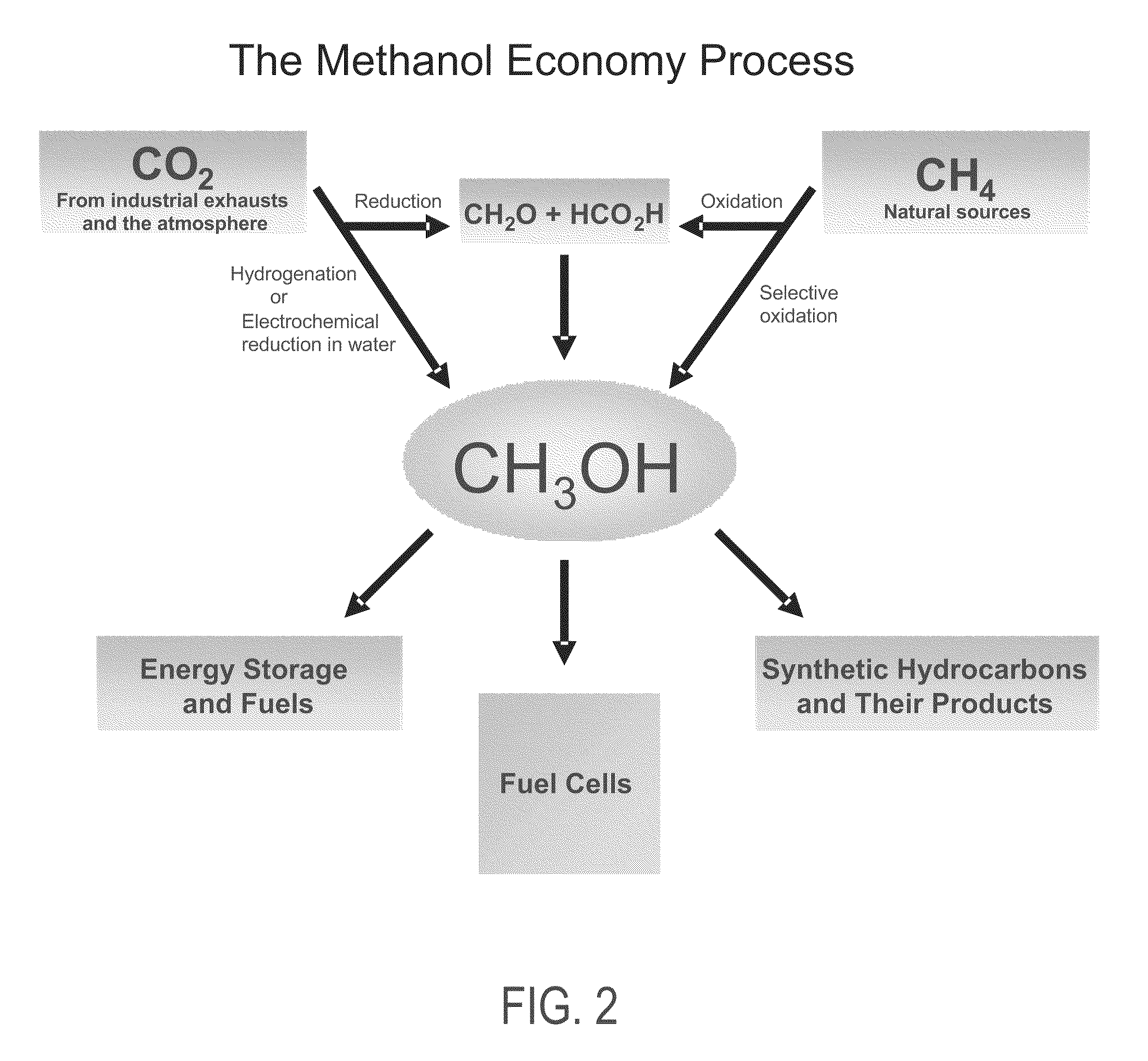
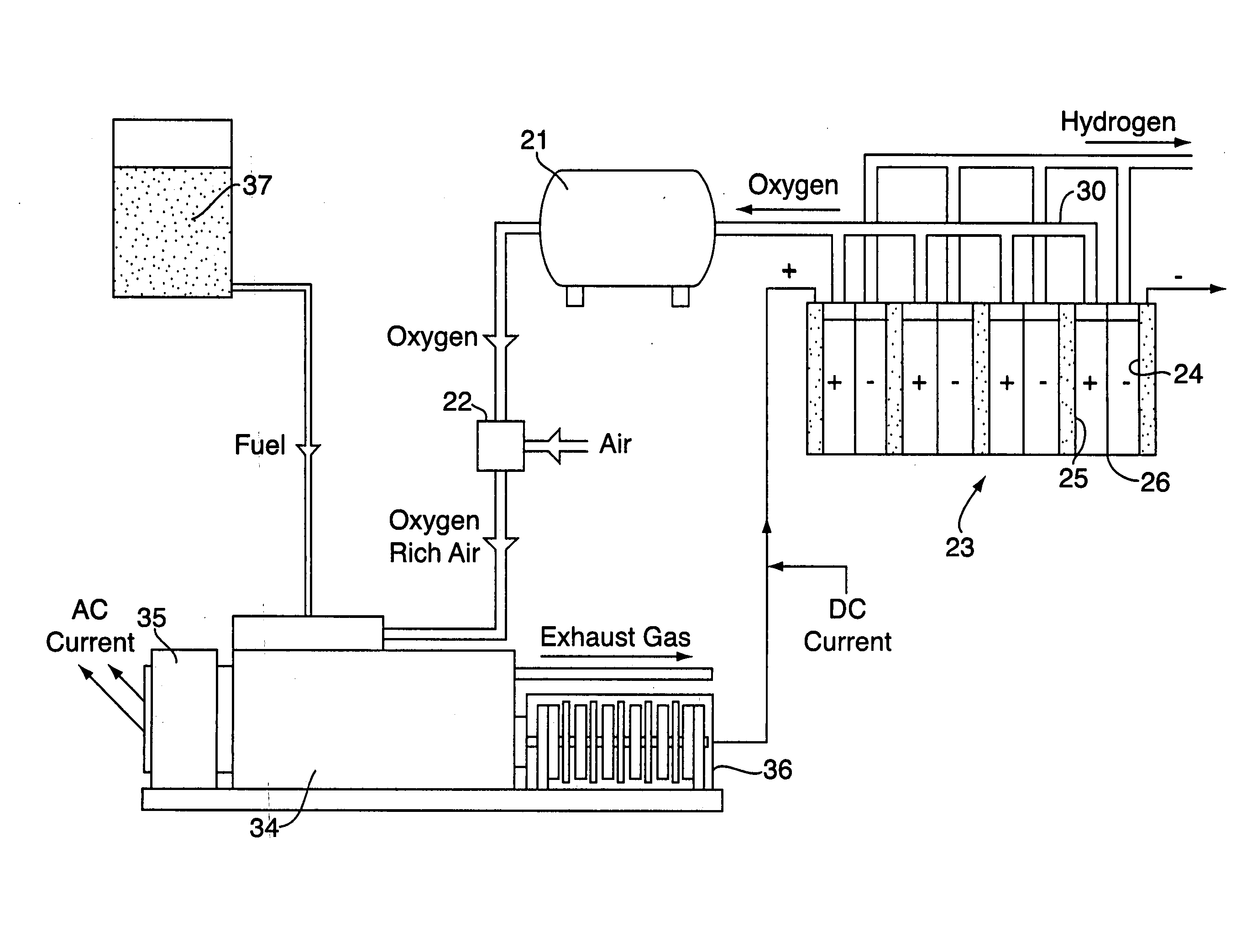
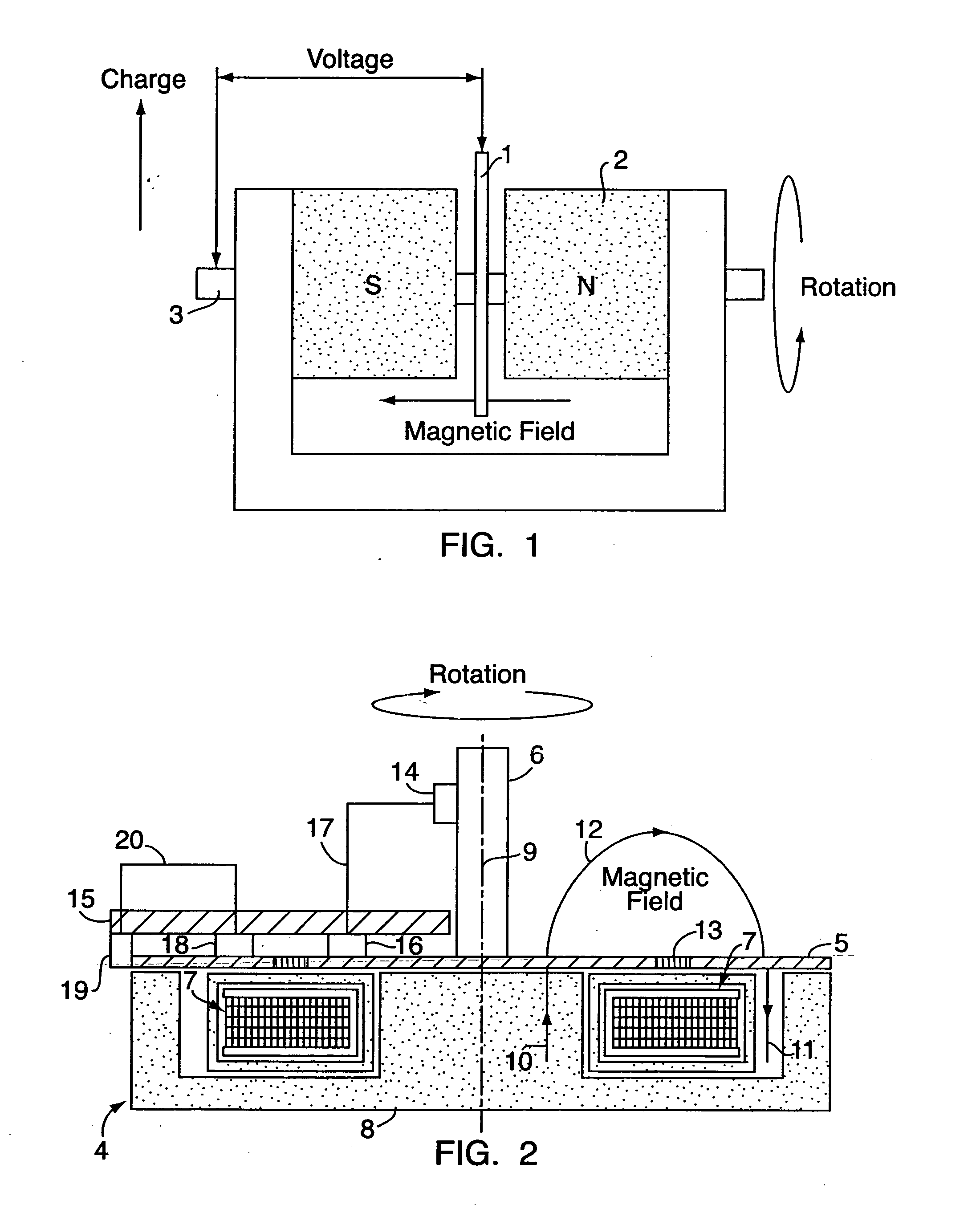
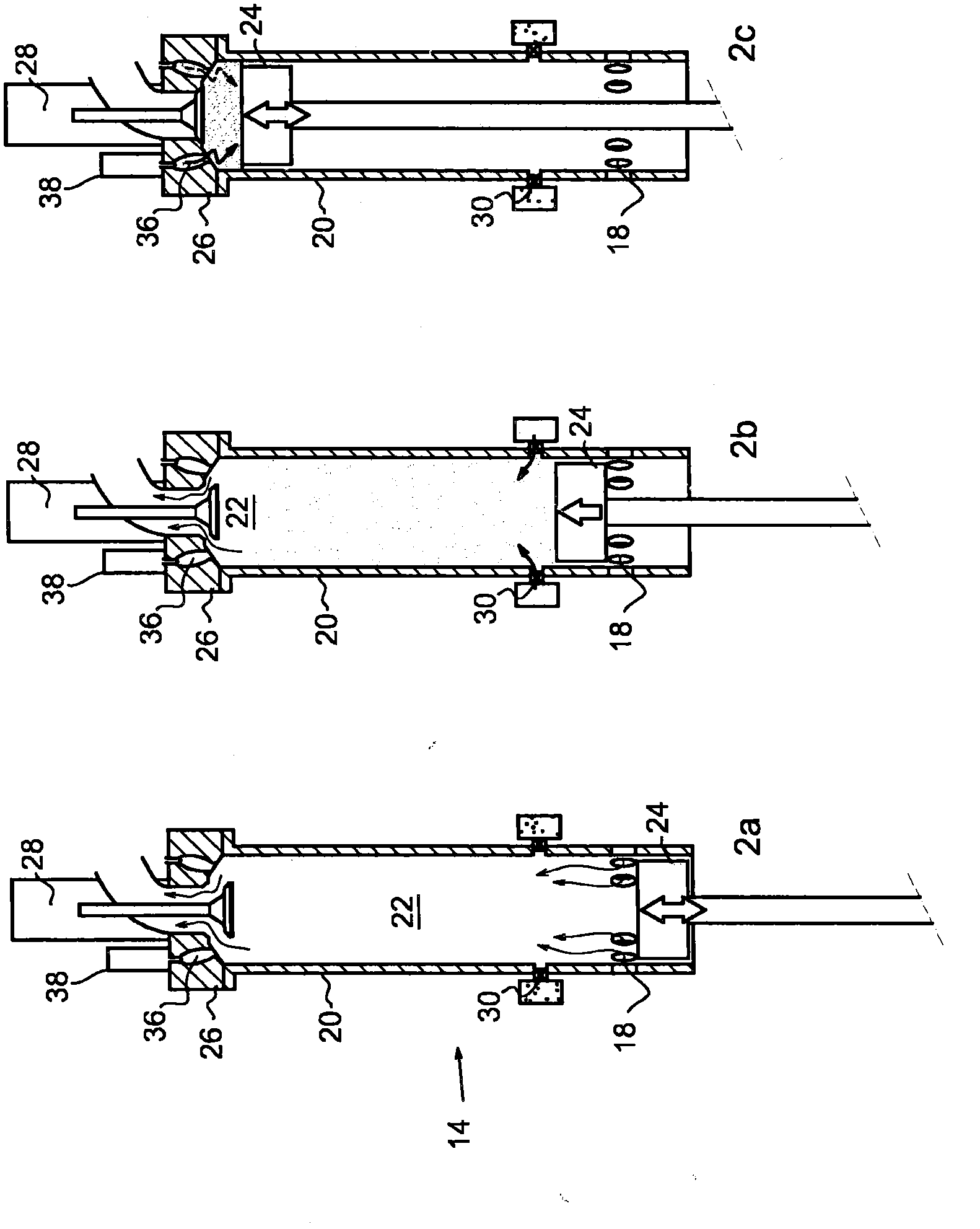
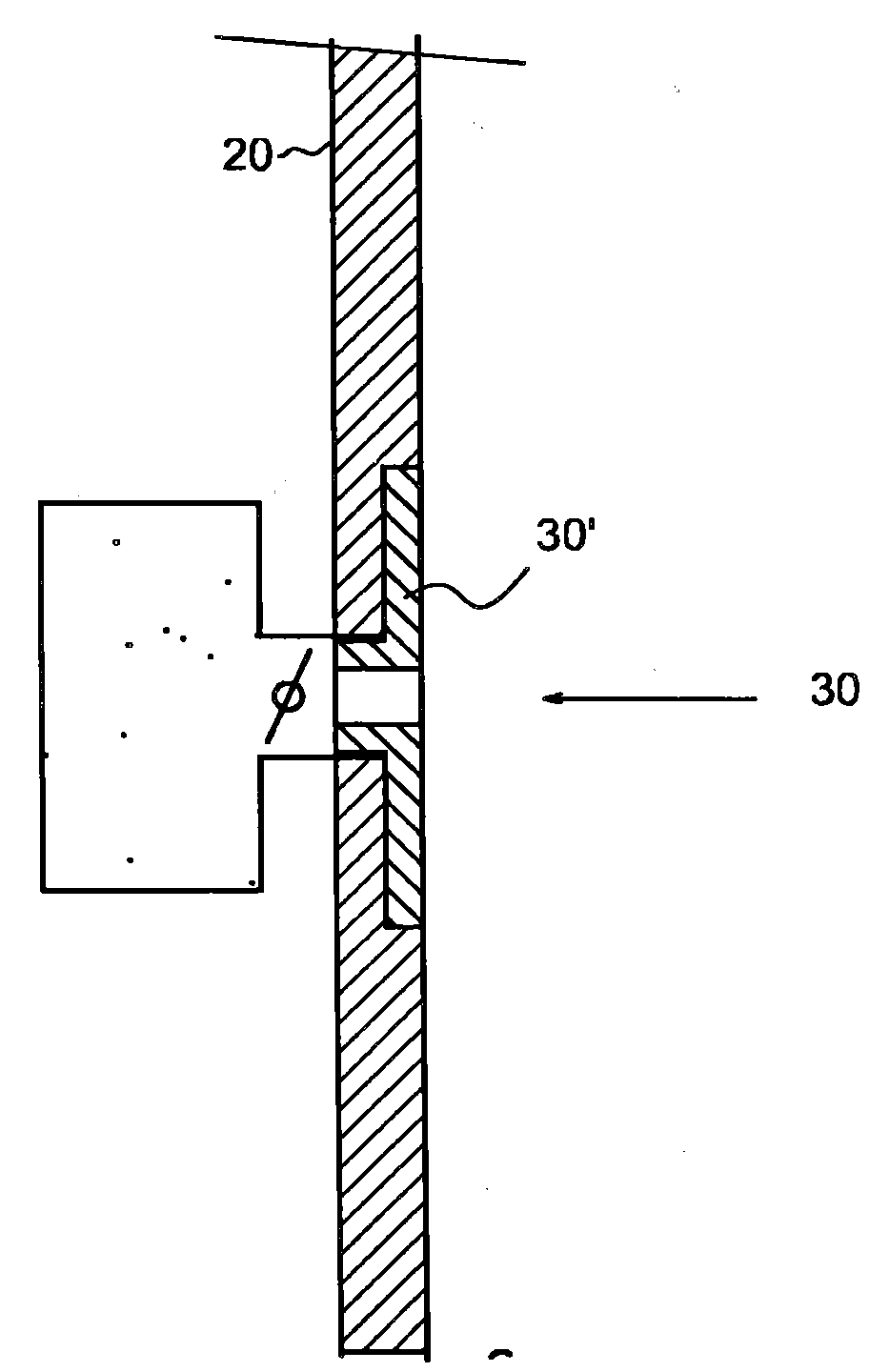
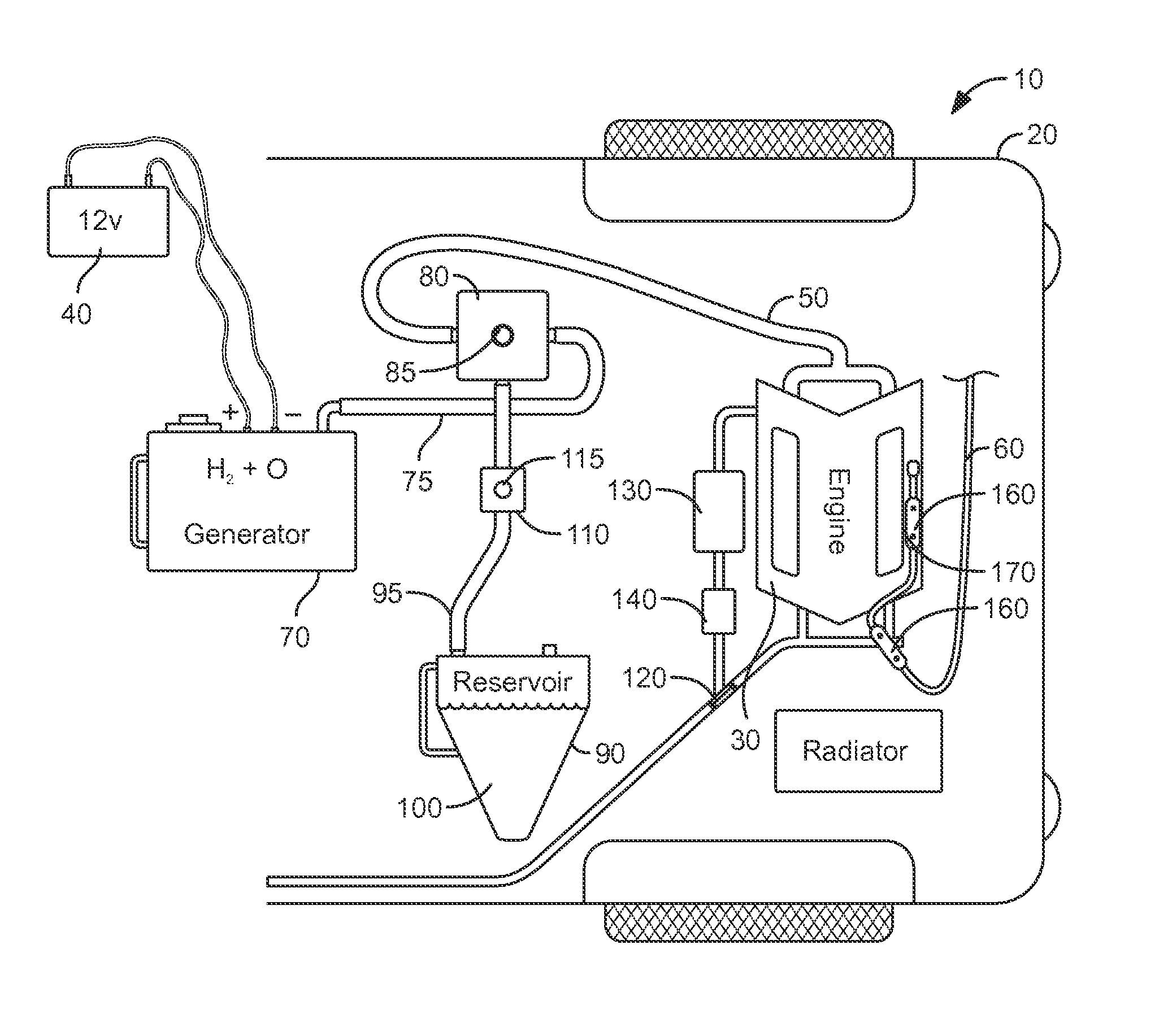
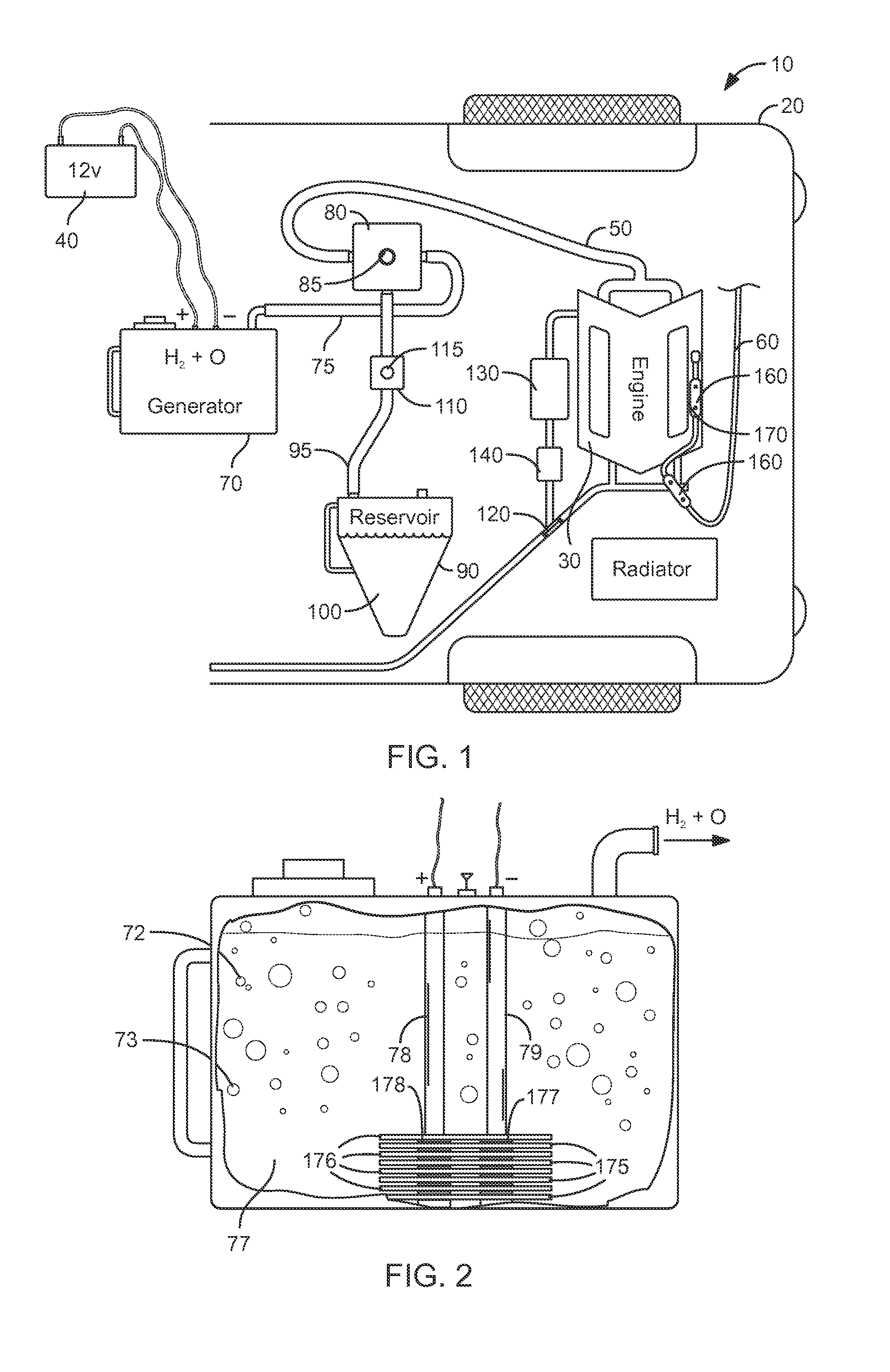
Patents
Literature
831results about How to "Efficient combustion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
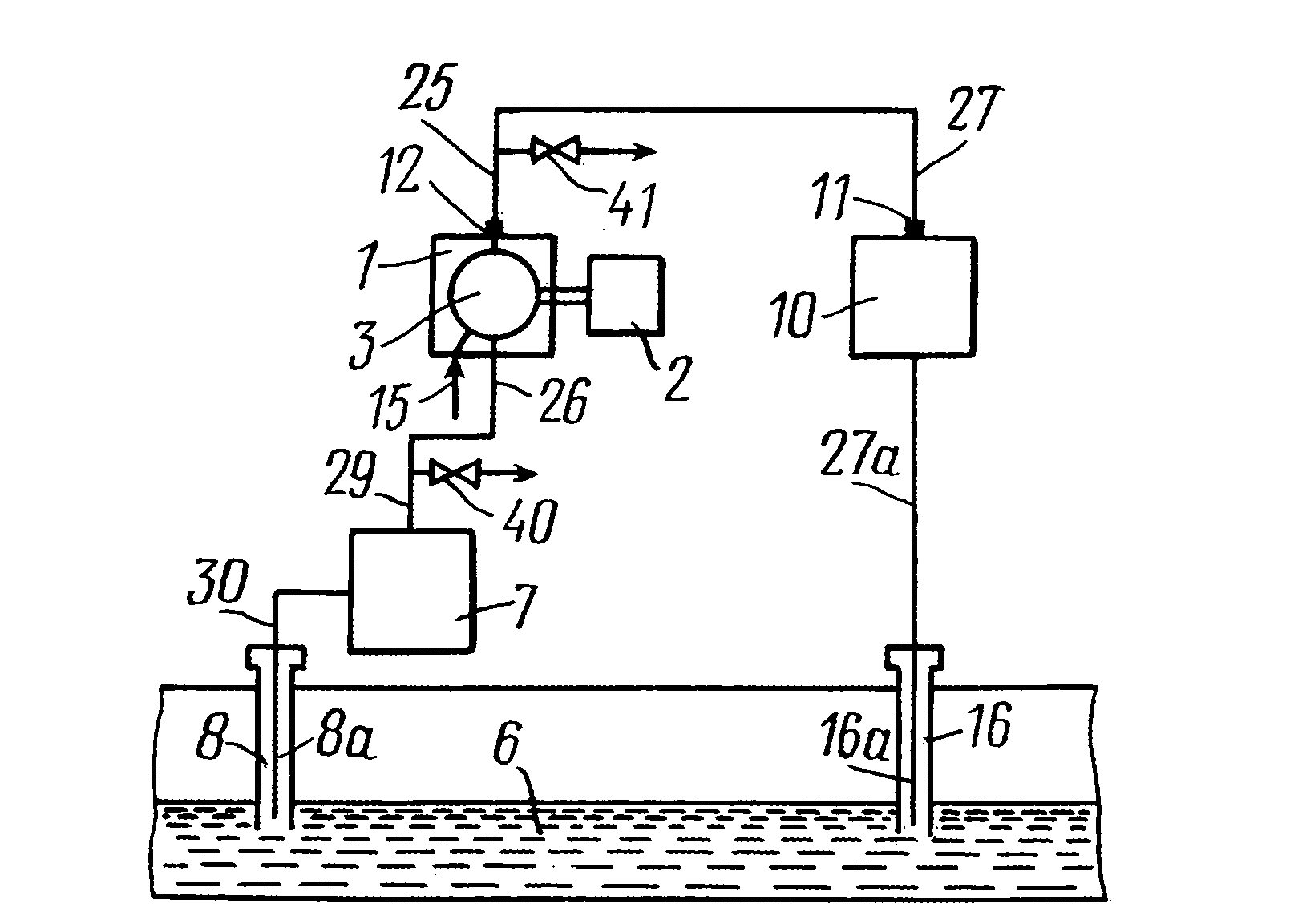
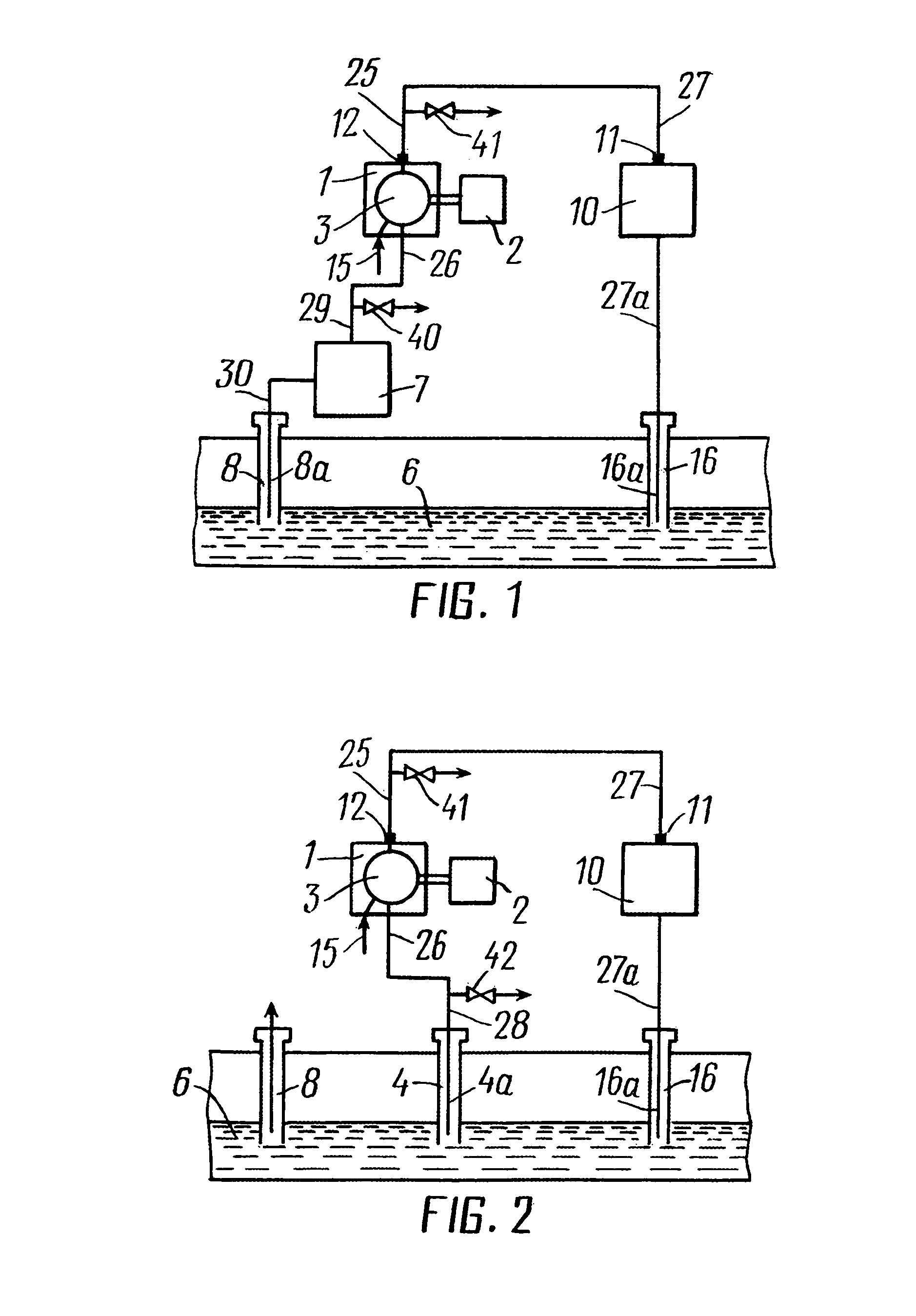
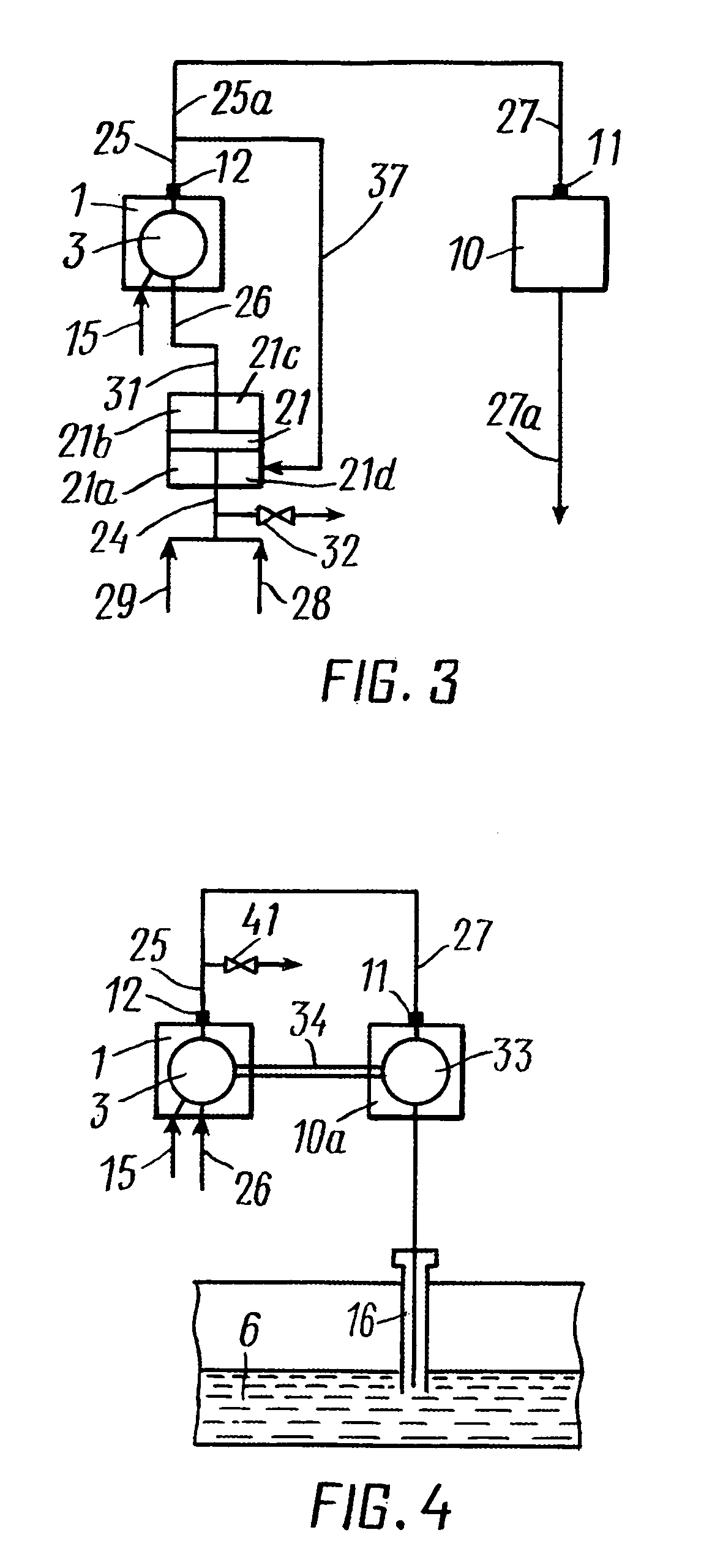
Method and system for recovery of hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon-bearing information
InactiveUS7299868B2Promote recoveryQuality improvementOther gas emission reduction technologiesInsulationCombustionPower station
A method and system for recovery of hydrocarbons from a hydrocarbon-bearing formation. A gaseous component of the produced hydrocarbon-containing fluid is separated from the fluid. The gaseous component is combusted with air in a power plant. Mixing and compressing of the gaseous component and air are realized to produce a flammable and pressurized gas-air mixture prior to combustion. An exhaust gas resulting from combustion is injected into the formation.
Owner:ZAPADINSKI ALEXEI
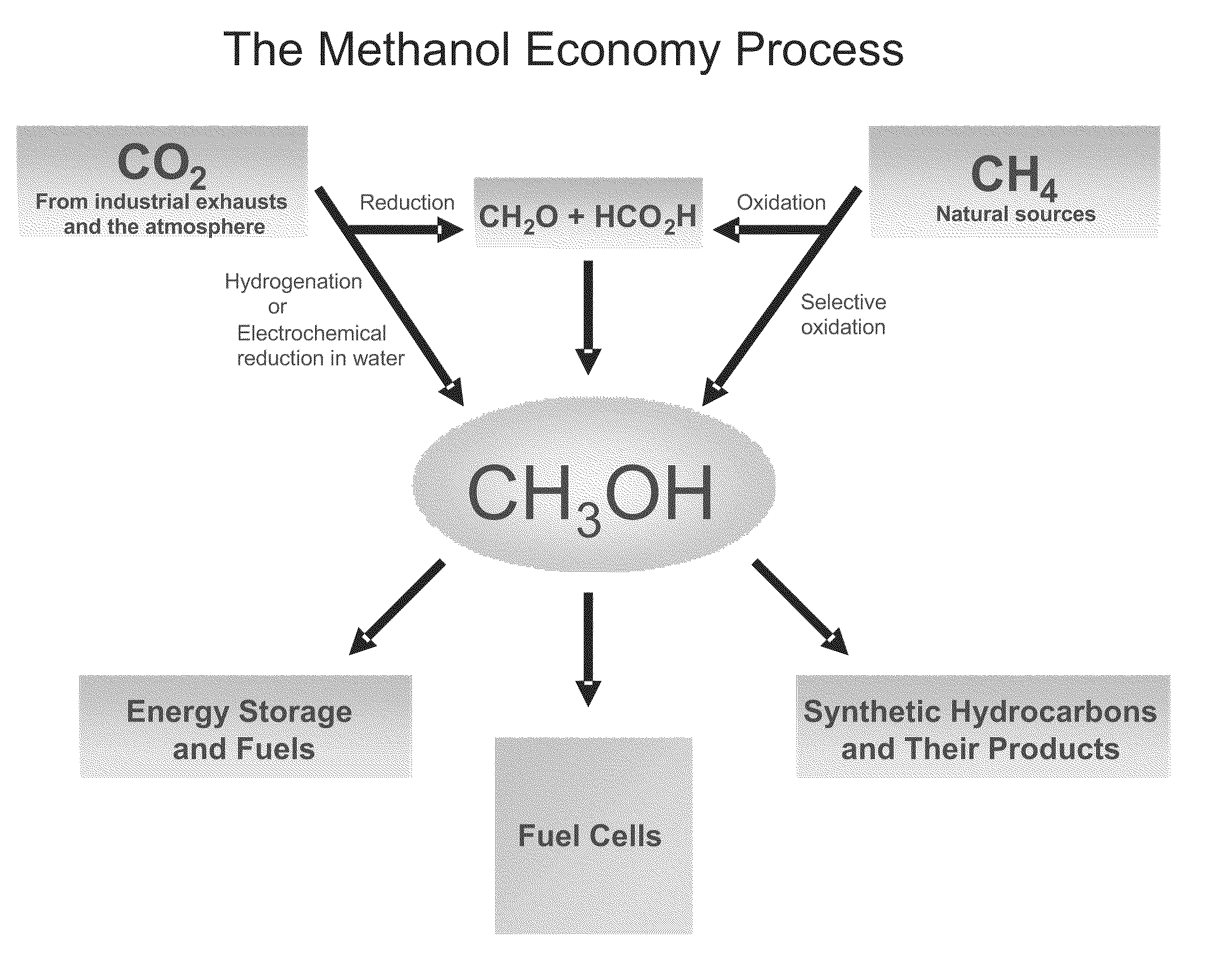
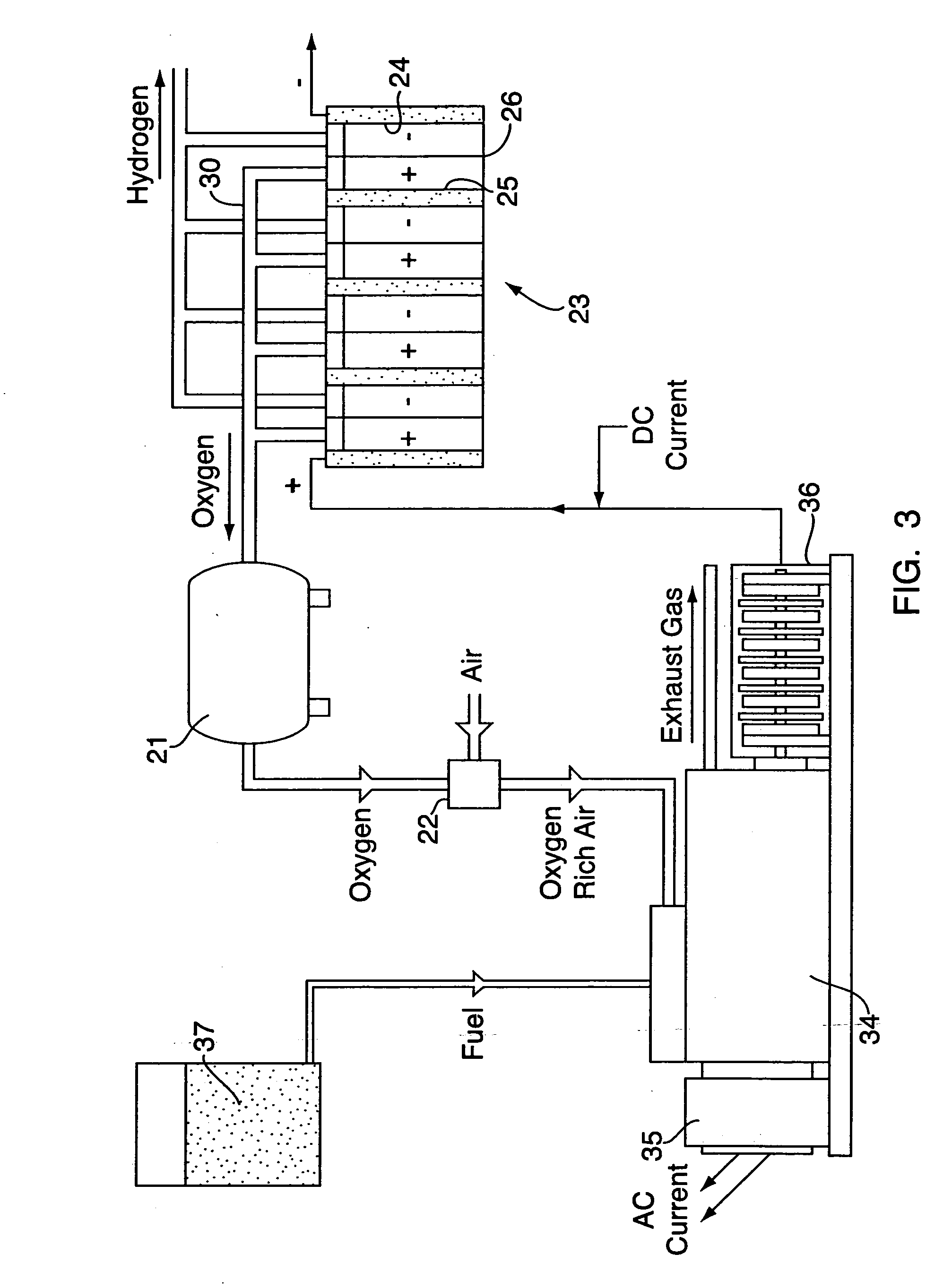
Electrolysis of carbon dioxide in aqueous media to carbon monoxide and hydrogen for production of methanol
ActiveUS8138380B2Efficient combustionPhotography auxillary processesElectrolysis componentsElectrolysisOxygen
An environmentally beneficial method of producing methanol from varied sources of carbon dioxide including flue gases of fossil fuel burning power plants, industrial exhaust gases or the atmosphere itself. Converting carbon dioxide by an electrochemical reduction of carbon dioxide in a divided electrochemical cell that includes an anode in one compartment and a metal cathode electrode in a compartment that also contains an aqueous solution comprising methanol and an electrolyte. An anion-conducting membrane can be provided between the anode and cathode to produce at the cathode therein a reaction mixture containing carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be subsequently used to produce methanol while also producing oxygen in the cell at the anode. The oxygen produced at the anode can be recycled for efficient combustion of fossil fuels in power plants to exclusively produce CO2 exhausts for capture and recycling as the source of CO2 for the cell.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Integrated renewable energy system
InactiveUS20070001462A1Reduce environmental pollutionFuel efficiencyElectrolysis componentsInternal combustion piston enginesElectrolysisOxygen
A system and method are disclosed comprising coupling a compression ignition engine (17) to an AC electrical generator (18) and / or a DC hompolar generator (19), wherein the homopolar generator (19) produces an electric current which is used to electrolyse water into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen from the water electrolysis process may be used as a renewable fuel, either in the form of a gaseous fuel or a reactant in a fuel cell. The oxygen from the water electrolysis unit (23) may be used to produce an oxygen enriched combustion atmosphere in the engine (17). The oxygen may optionally be used as a reactant, along with the hydrogen, in a fuel cell.
Owner:H EMPOWER CORP
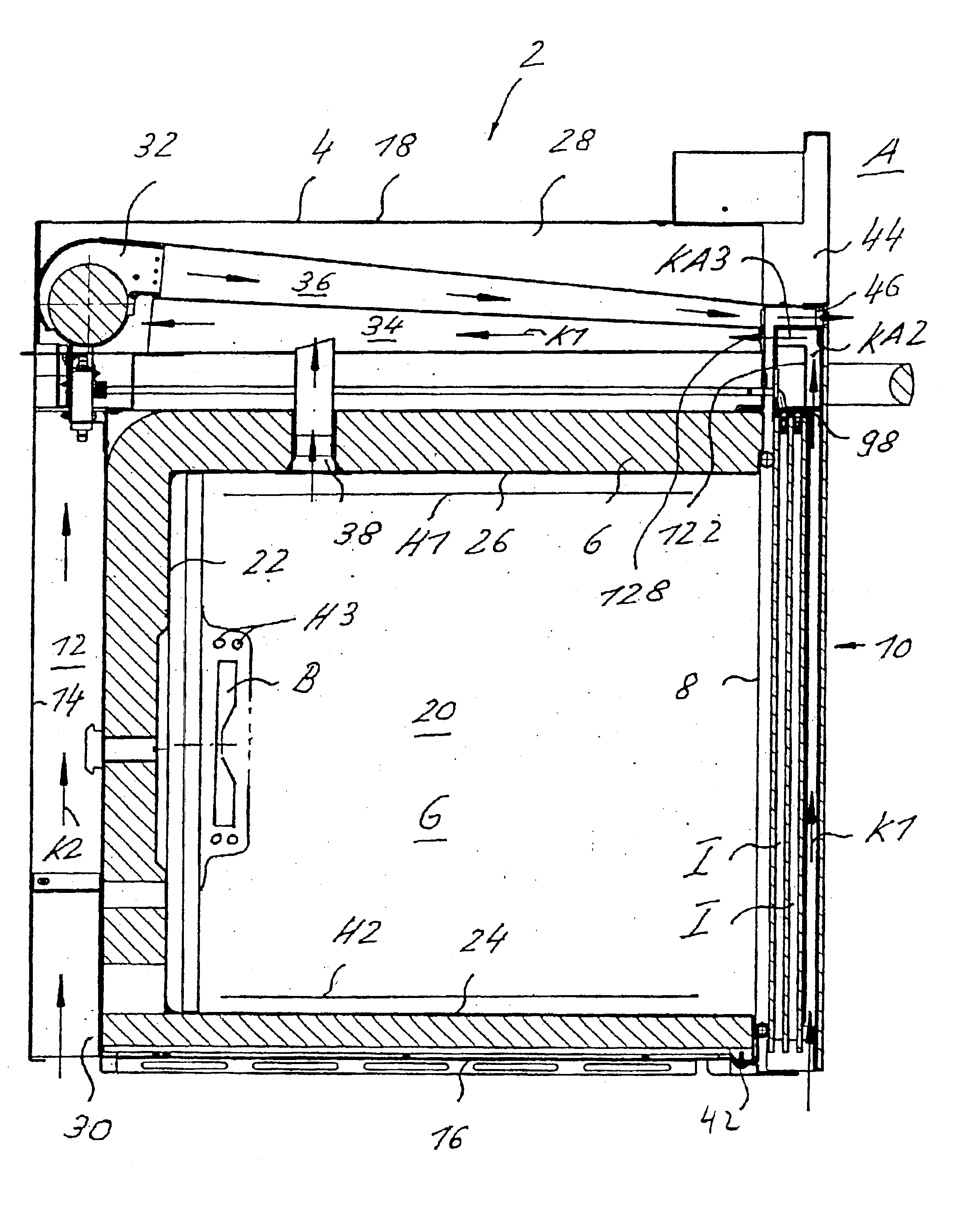
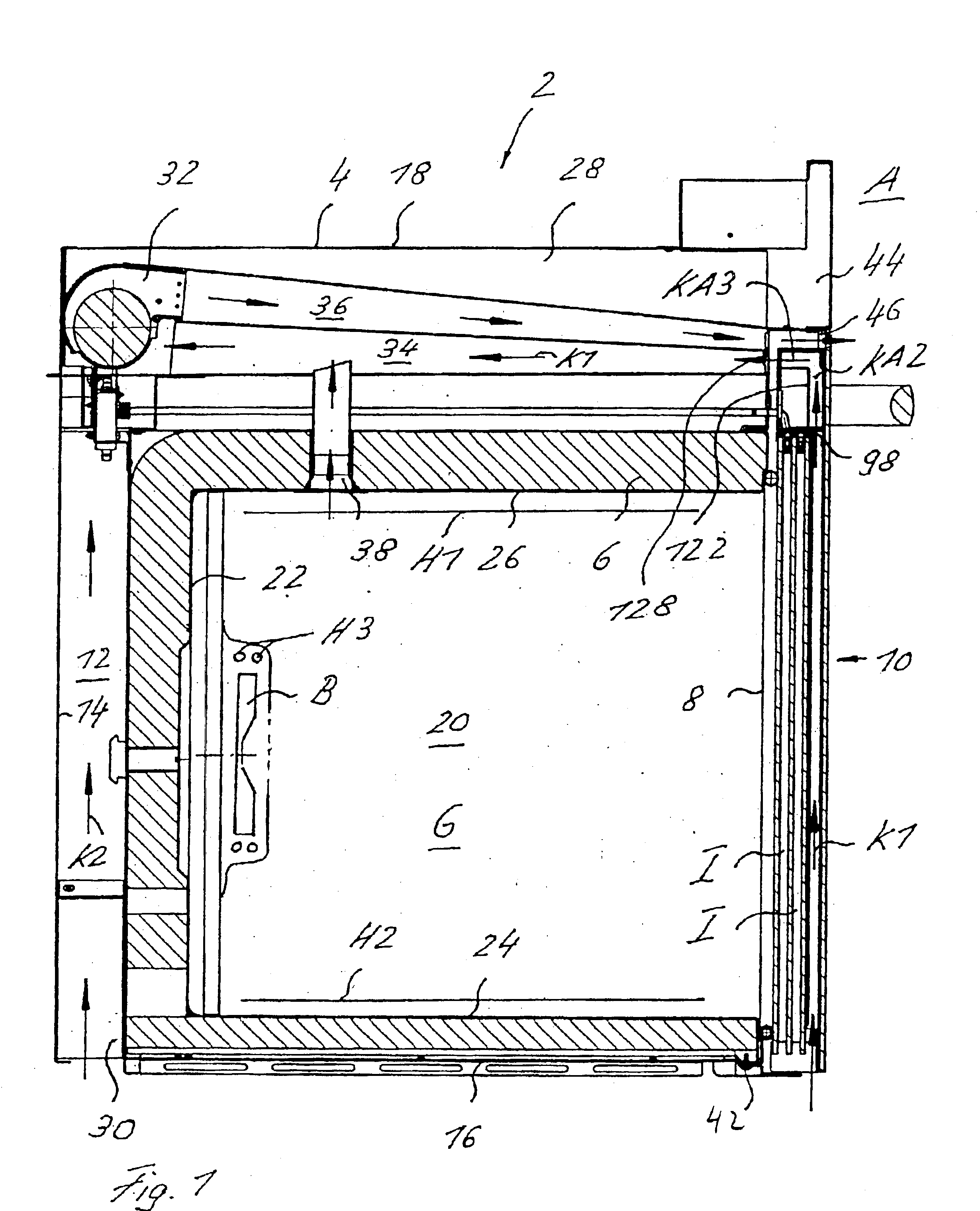
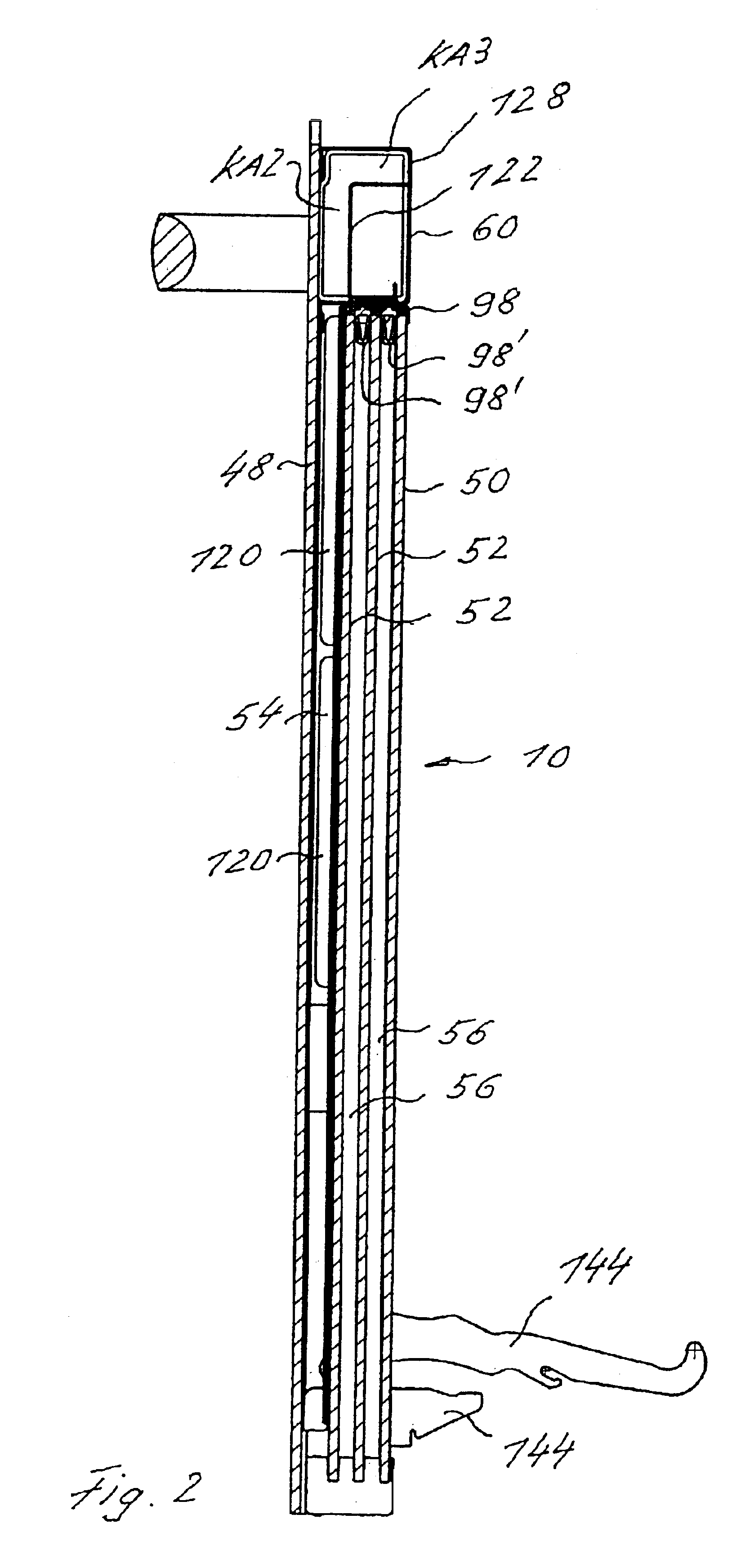
Cooking oven with a cooled door that permits pyrolysis
InactiveUS6904904B2Improves pyrolytic cleaningImprove cooling effectDomestic stoves or rangesDoors for stoves/rangesEngineeringMechanical engineering
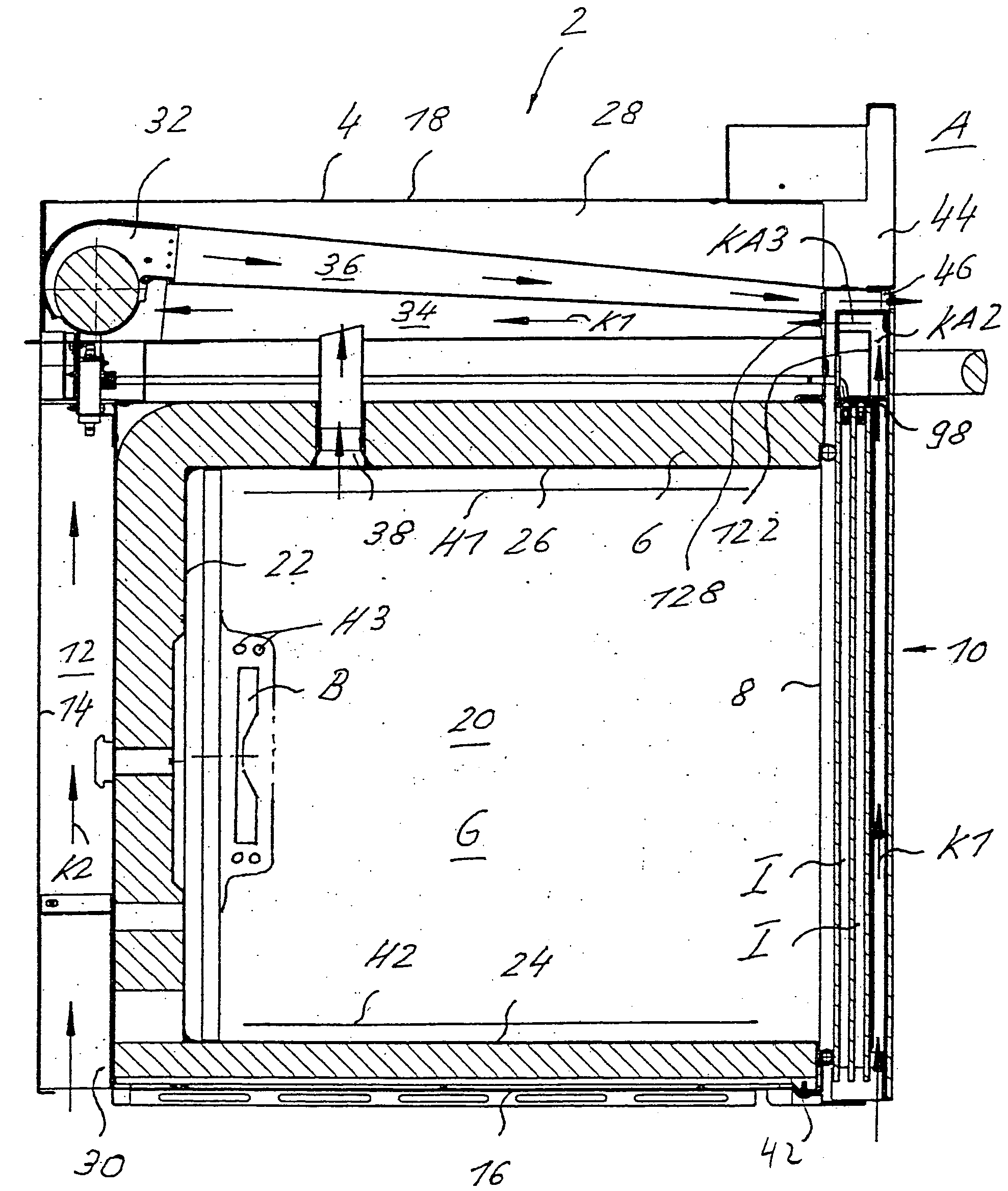
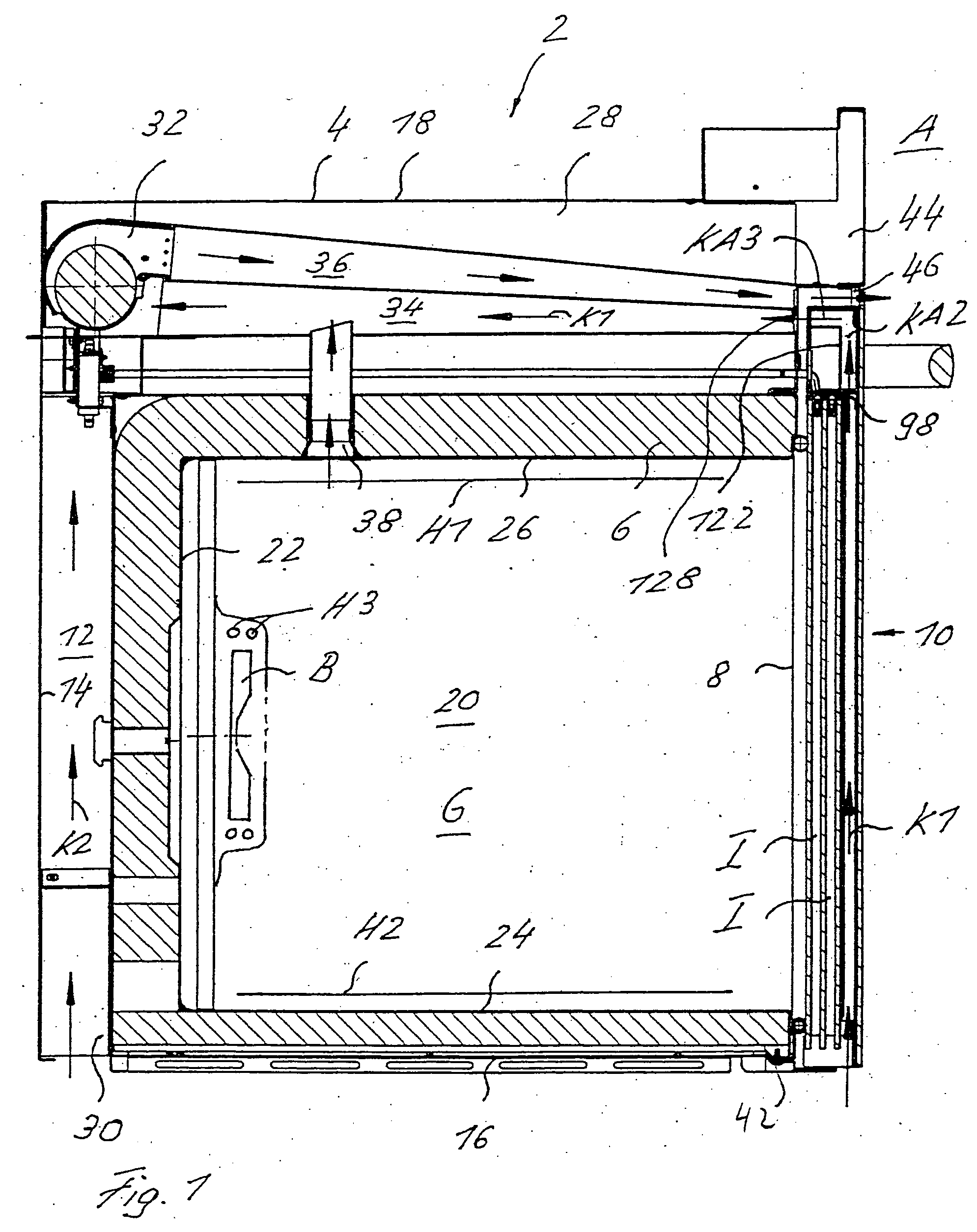
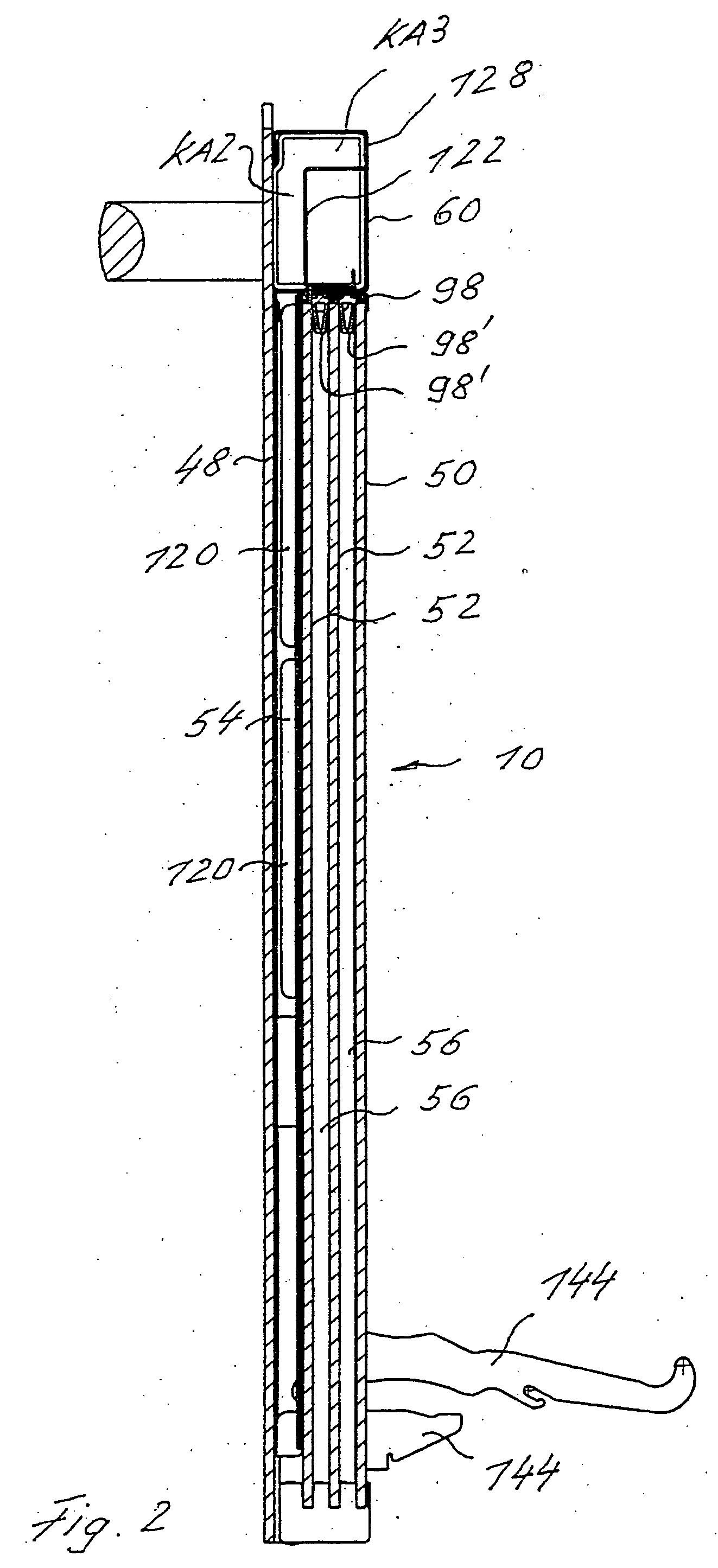
A cooking oven includes a heatable oven chamber (6) that can be loaded with product from the outside area (A) through a loading port (8). An oven door (10) serves to close off the loading port (8) of the oven chamber (6) from the outside area (A). An inner pane (50) faces the oven chamber (6), an outer pane (48) faces the outside area (A), and one or several intermediate panes (52) are positioned between the inner pane (50) and the outer pane (48). An outer cavity (54) is between the outer pane (48) and the neighboring intermediate pane (52) and an inner cavity space (56) is between the inner pane (50) and the neighboring intermediate pane (52). A cooling system moves cooling air (K1) through the outer cavity (54) while thermally insulating air (I) can be held stationary in the inner cavity (56).
Owner:ELECTROLUX HOME PROD CORP NV
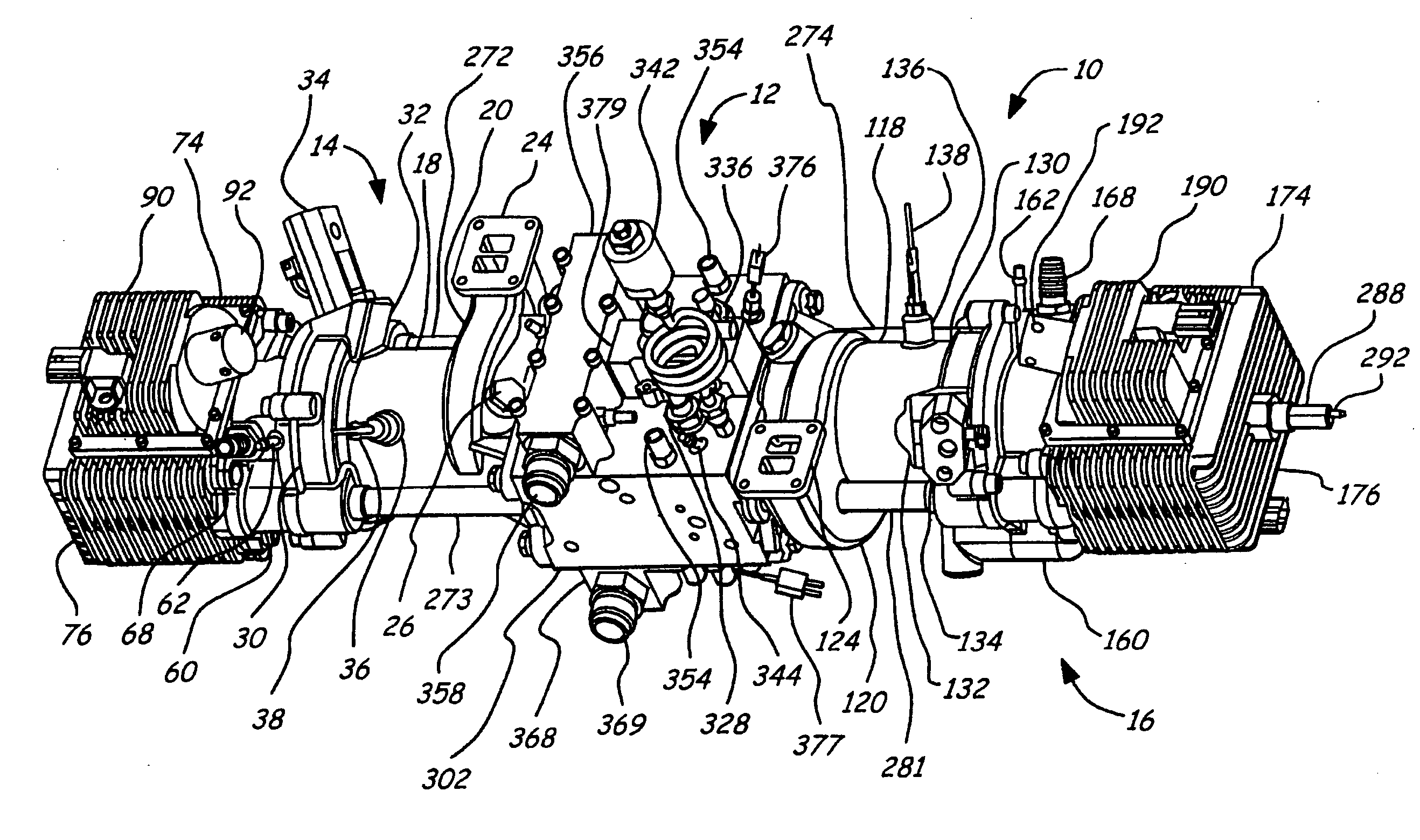
Exhaust gas recirculation for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6925971B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gas recirculationFree-piston engineExhaust valve
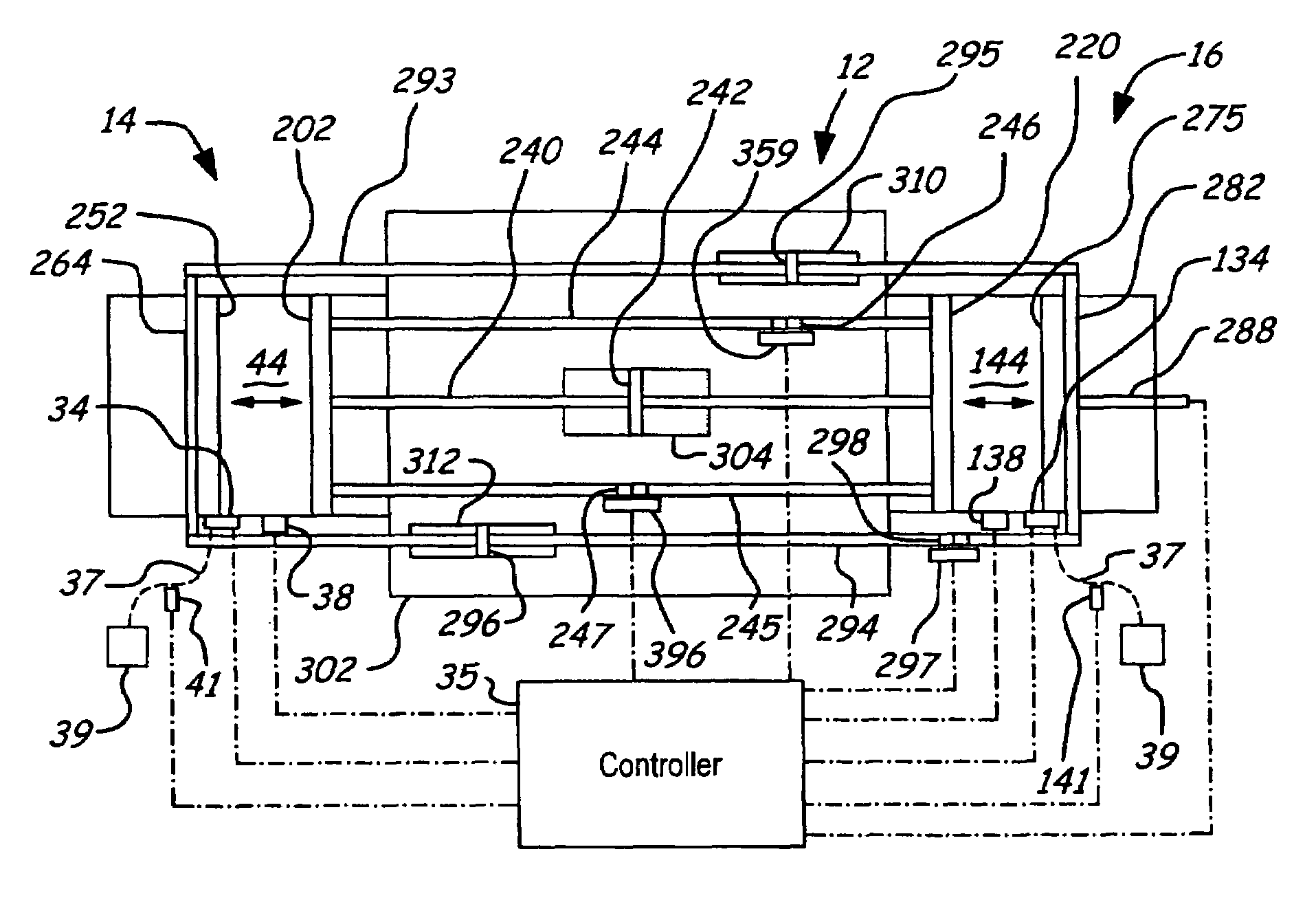
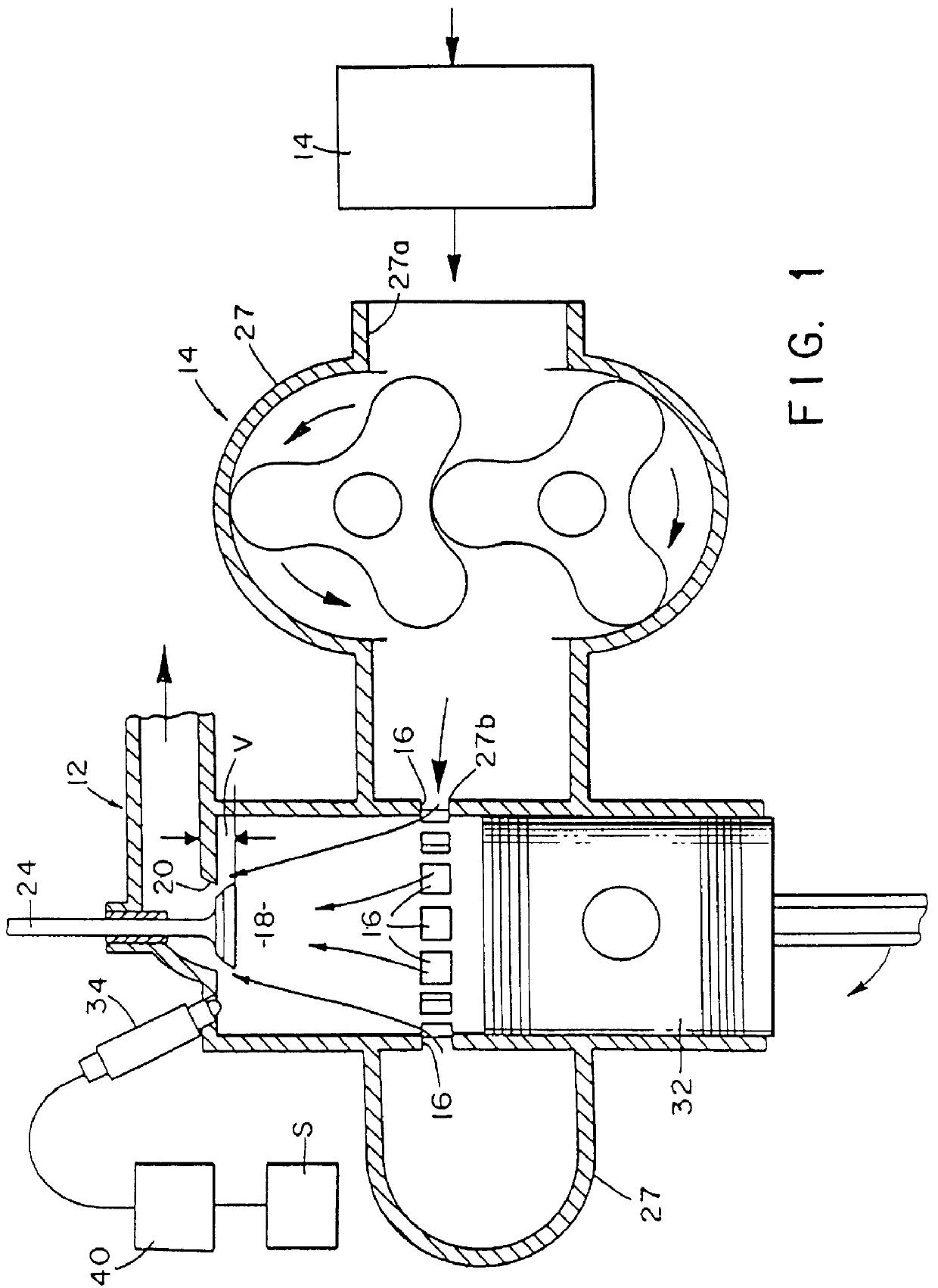
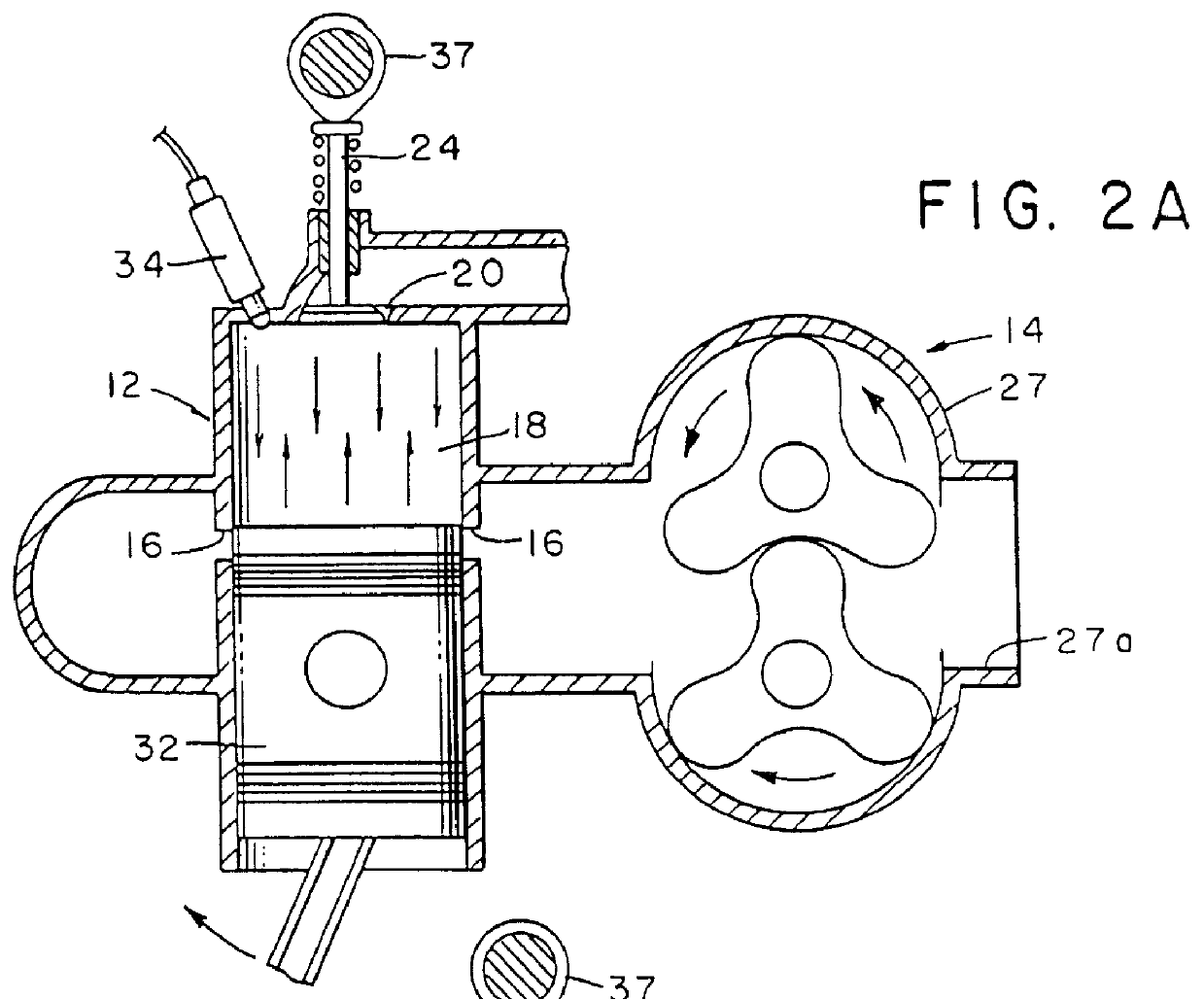
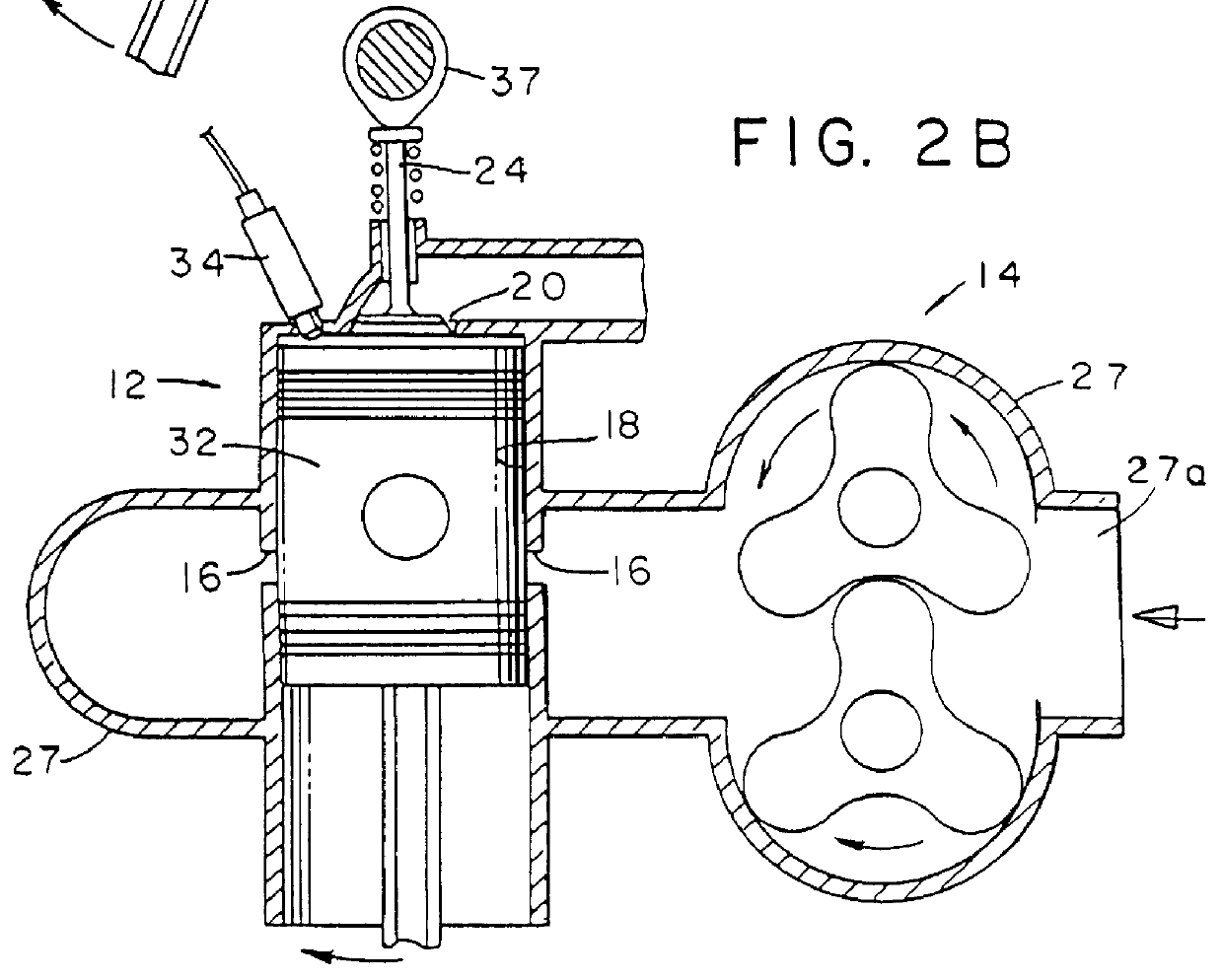
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. The exhaust ports for each engine cylinder are sized and located to retain the desired amount of internal EGR in each cylinder without the need for exhaust valves. As an alternative, an external EGR system may supplement the internal EGR in order to obtain the desired EGR at the desired temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Two-stroke internal combustion engine, method of operating two-stroke internal combustion engine and method of converting two-stroke engine
ActiveCN103748334AEmission reductionSimple structureInternal combustion piston enginesGaseous engine fuelsExhaust valveTop dead center
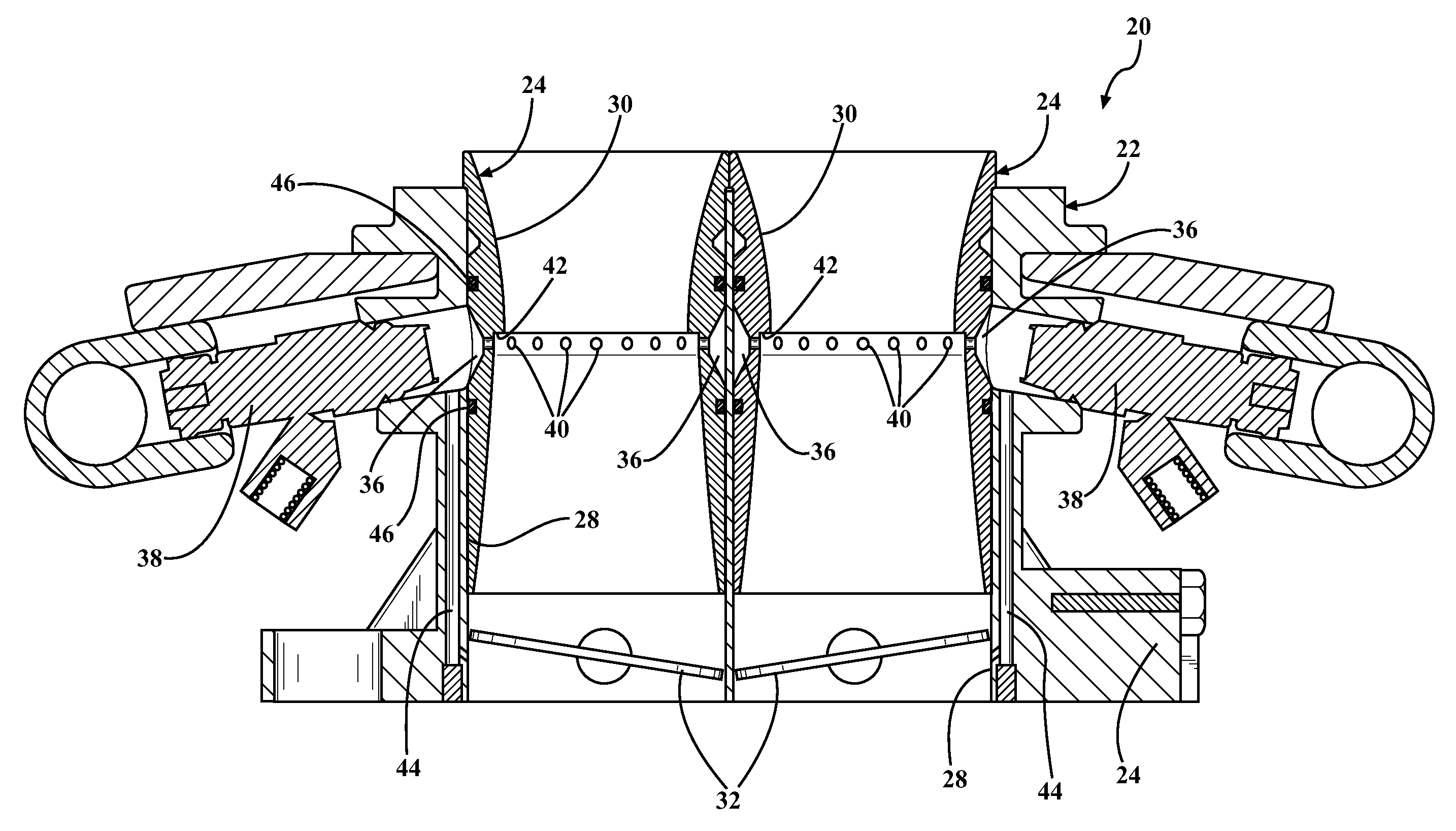
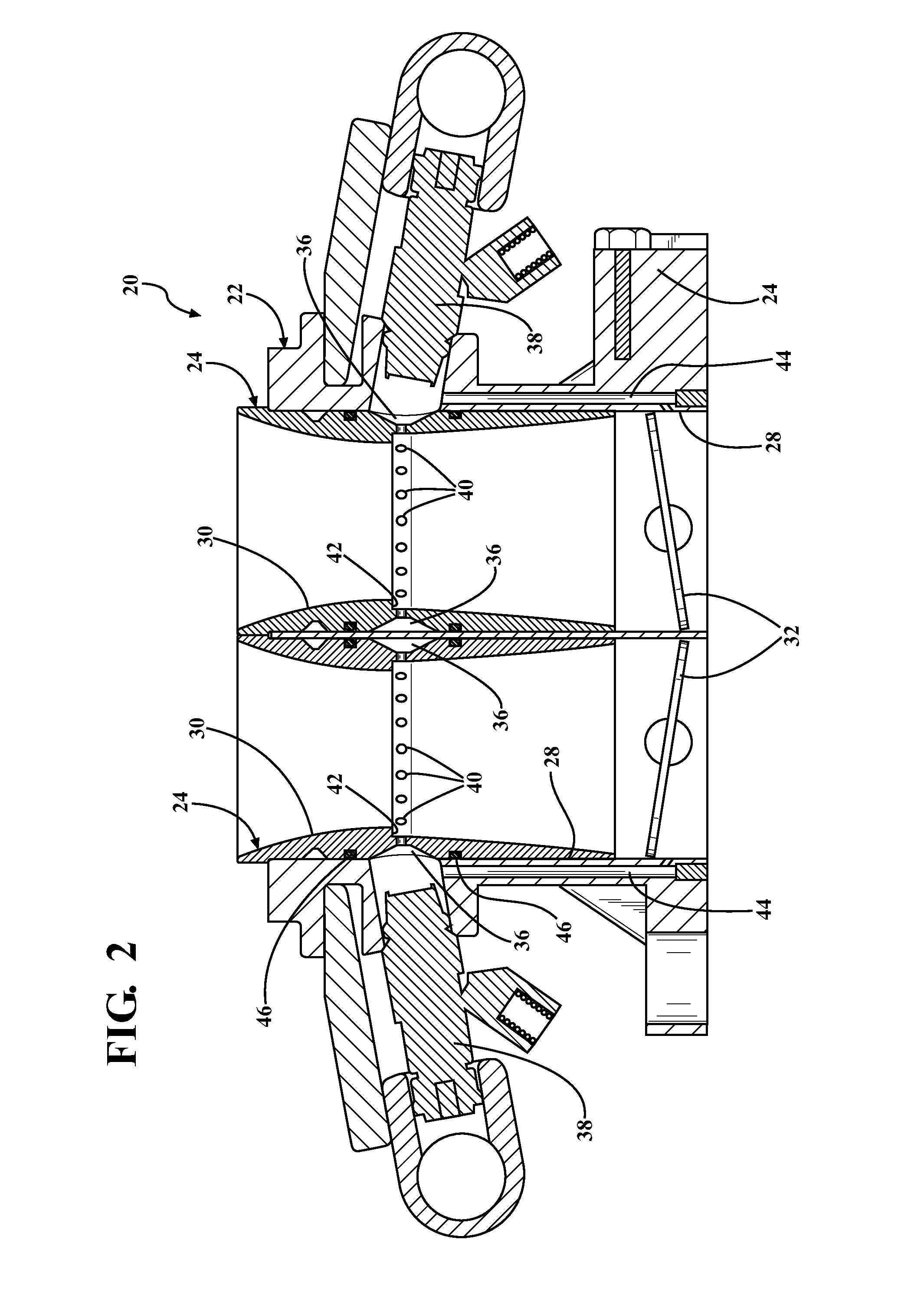
The invention relates a two-stroke internal combustion engine (10) comprising at least one cylinder (20) with a piston (24) arranged reciprocateably between its top dead center and bottom dead center, and a cylinder cover (26) defining a combustion chamber (22), oxygen containing gas inlet (18) in the lower part of the cylinder (20) to be open into the combustion chamber (22) at least while the piston is at its bottom dead center position, a gaseous fuel inlet (30) arranged in the cylinder between the oxygen containing gas inlet (18) and the cylinder cover(26), and an exhaust valve (28) arranged to the cylinder cover at a center axis of the cylinder. The cylinder cover(26) is provided with pilot ignition pre-chambers (36) opening into the combustion chamber (22) through pre-chamber ports (34).The preset invention relates also to method of operating the two-stroke engine (10).
Owner:WAERTSILAE SCHWEIZ AG
Engine fuel efficiency improvements
InactiveUS7458368B1Good fuel atomizationEfficient combustionPhotography auxillary processesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFuel efficiencyInternal combustion engine
The present invention is a system for increasing the fuel efficiency of a vehicle of the type having an internal combustion engine, a battery, a vacuum line, and a fuel line that feeds fuel to the engine. The system comprises a hydrogen gas generator and a vacuum regulator. A vacuum regulator is in fluid communication with the vacuum line of the vehicle and an output line of the gas generator. The vacuum regulator includes a vacuum pressure adjustment means for controlling the amount of hydrogen gas that is introduced into the vacuum line of the vehicle. In use, hydrogen gas is introduced into the vehicle vacuum line and then into the engine where it is mixed with the fuel from the fuel line and ambient air. The hydrogen gas increases the atomization of the fuel for more efficient burning thereof in the engine. A fuel additive including an acetone-based compound, a xylene-based compound, and an upper cylinder lubricant may be mixed with the hydrogen gas to further atomize the fuel. An oxygen sensor signal generator that generates a bypass signal replicates the output of a vehicle oxygen sensor under normal operating conductions to keep the air mixture of the engine unaffected. The system may additional include at least one fuel heating means fixed to a high-temperature portion of the engine, such that the fuel is heated before being introduced into the engine so as to further increase atomization of the fuel for more efficient burning thereof in the engine.
Owner:HUFFMAN DANIEL
Convectively cooled, single stage, fully premixed controllable fuel/air combustor
InactiveUS6220034B1Improve efficiencyImprove simplicityContinuous combustion chamberEngine manufactureCombustorSingle stage
A premixer for a combustor system has a venturi-type mixing tube with a flow axis, an inlet adjacent one axial mixing tube end, and a nozzle assembly at the opposite axial mixing tube end. The mixing tube inlet is flow connected to a source of compressed air and a source of fuel, and the mixing tube is connected to combustion chamber, an annular or can-type liner and an inlet, and the nozzle assembly extends into the combustion chamber and has at least one port for distributing the fuel / air mixture within a single stage combustion zone. In a preferred configuration, a pair of premixers are located at diametrically opposed positions on an annular combustion chamber, and the venturi axes are both radially disposed and axially inclined with respect to the combustion chamber axis. A single, centrally located, cylindrical air valve controls compressed air flow to both premixers through a manifold and distribution conduits.
Owner:HIJA HLDG
Hybrid carburetor and fuel injection assembly for an internal combustion engine
ActiveUS9115671B2Efficient combustionCheap to createLow pressure fuel injectionMachines/enginesCarburetorHybrid fuel
A hybrid fuel injection and carburetor assembly for delivering a fuel and air mixture into an intake manifold of an engine is provided. The assembly includes a housing and a plurality of inserts with Venturi-shaped bores to establish low pressure regions in the flow of air. The housing and inserts cooperate with one another to present cavities, and the inserts include apertures extending between the cavities and the low-pressure regions. The assembly also includes fuel injectors in fluid communication with the cavities. In operation, fuel is injected at a high pressure into the cavities to the point, and the pressurized fuel is delivered into the low pressure air via the apertures. Because of the large pressure difference between the pressurized fuel in the cavities and the low pressure air, the fuel becomes very atomized.
Owner:HOLLEY PERFORMANCE PRODUCTS
Cooking oven with a cooled door that permits pyrolysis
InactiveUS20050076900A1Avoid turbulenceImprove cooling effectDoors for stoves/rangesDomestic stoves or rangesEngineeringMechanical engineering
A cooking oven includes a heatable oven chamber that can be loaded with product from the outside area through a loading port. An oven door serves to close off the loading port of the oven chamber from the outside area. An inner pane faces the oven chamber, an outer pane faces the outside area, and one or several intermediate panes are positioned between the inner pane and the outer pane. An outer cavity is between the outer pane and the neighboring intermediate pane and an inner cavity space is between the inner pane and the neighboring intermediate pane. A cooling system moves cooling air through the outer cavity while thermally insulating air can be held stationary in the inner cavity.
Owner:ELECTROLUX HOME PROD CORP NV
Position sensing for a free piston engine
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also connected between the pistons are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the inner piston assembly. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also engaging the outer piston assembly are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the outer piston assembly. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
System and method for purging fuel vapors using exhaust gas
ActiveUS7331334B2Emission reductionHigh activityInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust fumesFuel vapor
A system for a vehicle, comprising of an engine, and a fuel vapor storage system coupled to the engine configured to store and release fuel vapors, the system further configured to route exhaust gas from the engine to the vapor storage system and where adsorbed vapors are released into the exhaust gas before the exhaust gas is re-inducted into the engine to be burned.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Dual solenoid fuel injector with catalytic activator section
InactiveUS20100126471A1Efficient combustionStart fastLiquid surface applicatorsSpray nozzlesCombustionInternal combustion engine
The present invention is provides a fuel injector having a hydraulically actuated injection pin, also referred to as an injector stem. In accordance with invention, the fuel injector provides for more efficient fuel combustion within internal combustion engines, such as vehicle engines. According to various embodiments of the invention, the fuel injector achieves efficient fuel combustion by (i) fast and responsive actuation, (ii) heating the fuel to a supercritical temperature, (iii) maintaining fuel at a supercritical pressure, and (iv) using a catalyst in the oxidization of the fuel. Some embodiments of the invention utilize a dual solenoid to actuate the fuel injector pin and a heating element to heat the fuel to a supercritical temperature.
Owner:TRANSONIC COMBUSTION
Supercritical water oxidation reactor by using auxiliary fuel for supplying heat
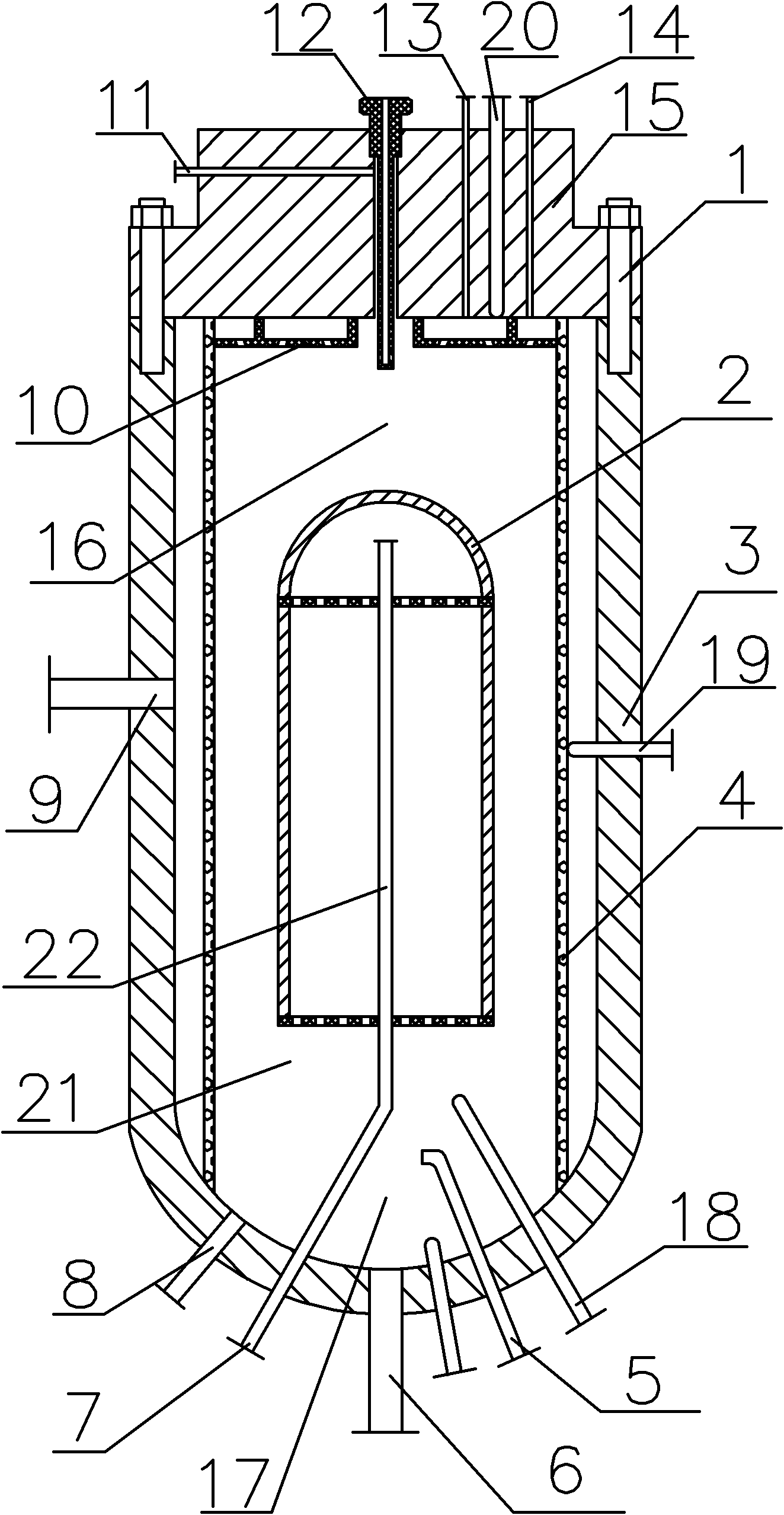
ActiveCN102190363AEfficient mixingEfficient combustionSludge treatmentWater/sewage treatment by oxidationNuclear engineeringOrganic fluid
The invention discloses a supercritical water oxidation reactor by using an auxiliary fuel for supplying heat, the heat required for a reaction can be supplied by using the auxiliary fuel, Material, fuel and an oxidizing agent (air or oxygen) are mixed with a high efficiency through the different directional jets for raising oxidation efficiency. According to the invention, the reactor employs a combination structure of evaporation wall and pot type backflow, the reaction vessel volume is effectively used and the reaction time is increased, the blockage problem generated by salt deposition can be also prevented, the corrosion problem of the reactor is effectively reduced. The temperature of the reactor bottom can be preciously controlled through a cooling water pipeline at the reactor bottom, thereby the safe operation of equipment is guaranteed. The reactor effectively solves the economic problem of a supercritical water reaction system by using the auxiliary fuel for supplying, the invention has the advantage of easy industrial amplification, and is widely applied to organic liquid such as high density and difficult biodegradation organic waste water / garbage leachate and the like for a harmlessness processing.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Low emission power plant and method of making same
InactiveUS6101989AReduce the amount of solutionLower than normal exhaust valve liftNon-fuel substance addition to fuelInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesCombustion chamber
A low emission power generating apparatus which comprises a modified two-stroke diesel engine component and a modified turbocharger component which has a relatively low aspect ratio. The diesel engine component is a modification of a conventional two-stroke diesel engine design and includes an exhaust valve cam of unique design that has a cam profile which results in a later than-normal exhaust valve opening and an earlier-than-normal valve closing so that the time during which the exhaust valve remains open is shorter than normal, thereby causing a substantially greater volume of residual gases to remain in the combustion chamber following the scavenge stroke. This increase in the volume of the residual exhaust gases within the chamber leads to an increase in compression temperature and effectively increases the compression ratio and consequently the compression pressure. Because of the heat absorption capacity of these residual exhaust gases, the exhaust gases remaining in the chamber following the scavenge stroke tend to absorb combustion heat and thereby effectively reduce the peak combustion temperature. This reduction in peak combustion temperature advantageously results in the lower than normal formation of nitrogen oxide (NOx) and, therefore, allows advancement of the injection timing, while still maintaining the NOx emissions coming from the engine lower than those legislatively mandated. Advantageously, the advance in injection timing, which increases NOx emissions, by definition has the effect of also reducing particulate matter emissions. Thus, by increasing the volume of residual exhaust gases within the cylinder, substantial particulate matter emission reductions can be achieved, while at the same time maintaining NOx emissions well below mandated limits. The modified turbocharger component provides an additional charge of oxygen-rich air into the combustion chamber which effectively increases the compression pressure, which, in turn, leads to an earlier start of combustion because of the combustible mixture reaching its auto-ignition temperature at an earlier point in the cycle. This phenomenon leads to more thorough combustion of the fuel and also generally leads to higher exhaust temperatures. Higher exhaust temperatures, in turn, lead to a greater oxidation rate of the soluble organic fraction thus lowering the level of emission from the engine of undesirable particulate matter.
Owner:CLEAN CAM TECH SYST
U-tube diffusion flame burner assembly having unique flame stabilization
InactiveUS6872070B2Efficiently transfer heatEfficient combustionDomestic stoves or rangesBurner noise abatementFuel supplyAcoustic effect
A U-tube diffusion flame burner assembly having improved flame stabilization with no undesirable acoustic effects. The burners are axial units comprised of flame holders and combustors. The flame holders includes secondary air tubes to support the flow of secondary air that have helical walls forming helical passageways along at least a portion of its inner diameter to impart a swirl to the secondary air. The helical passageways impart a swirl to the secondary air exiting the passageways while simultaneously acting as a heat exchanger to heat primary air. The flame holders includes fuel tubes having first ends connected to a fuel supply and second flame ends. A plurality of radially oriented apertures are located at the second flame ends to distribute fuel in a radial direction. Primary air tube surrounds at least the flame ends of the fuel tubes and extend axially from first air supply ends to second flame ends. Air is diverted from air supply ends of the flame burners into primary air tubes through radial apertures located at the first air supply ends of the primary air tubes. Secondary air tubes surround the primary air tubes extending from first air supply ends to second ends opposite the air supply, the secondary air tubes having inner diameters larger than the outer diameters of the primary air tubes. The secondary air tubes extend for a preselected distance beyond the second flame ends of the primary air tubes and are coupled to axially-oriented conical-shaped reducers. Flame at high velocity exits the restricted end of the reducers.
Owner:HAUKE MFG
Method and apparatus for burning oils of varying viscosity
InactiveUS6132203AEfficient combustionPrevents possibility of fire and explosionLiquid fuel feeder/distributionSpraying apparatusHeating oilCombustor
Disclosed is an oil burning system that is capable of burning oils of varying viscosities, including high viscosity waste oils and low viscosity heating oils. Suitable as a new installation or a retrofit modification, the present invention incorporates the use of a variable rate, high-pressure oil delivery system, along with an oil pre-heater, in conjunction with a modified high-pressure atomizing nozzle. Installed in a sliding drawer burner arrangement that allows for quick and easy access, the oil burning system also includes a means by which particulate matter and carbonization build-ups are removed from the burner nozzle automatically, thereby eliminating the need for frequent cleaning.
Owner:MASIN RADEK
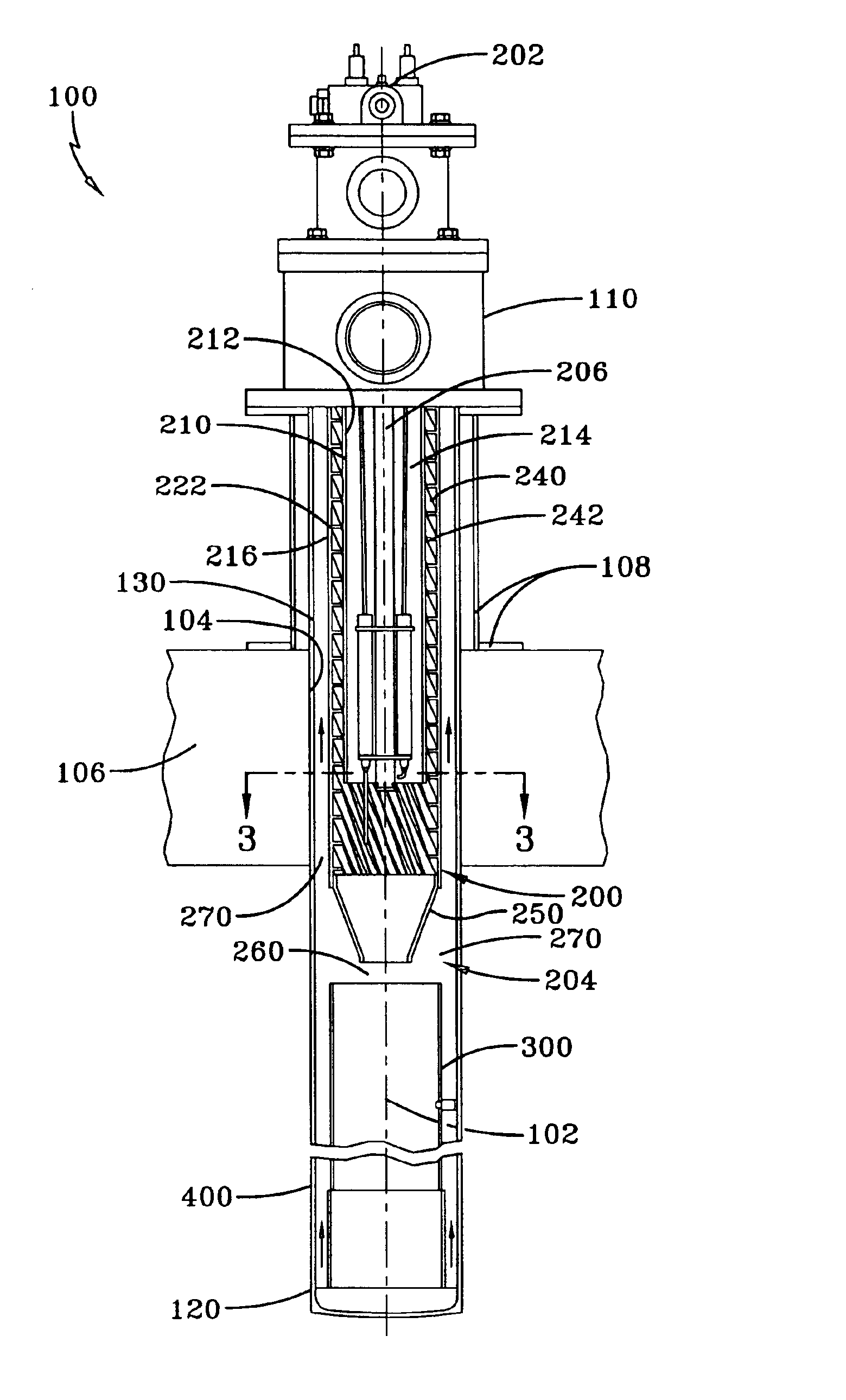
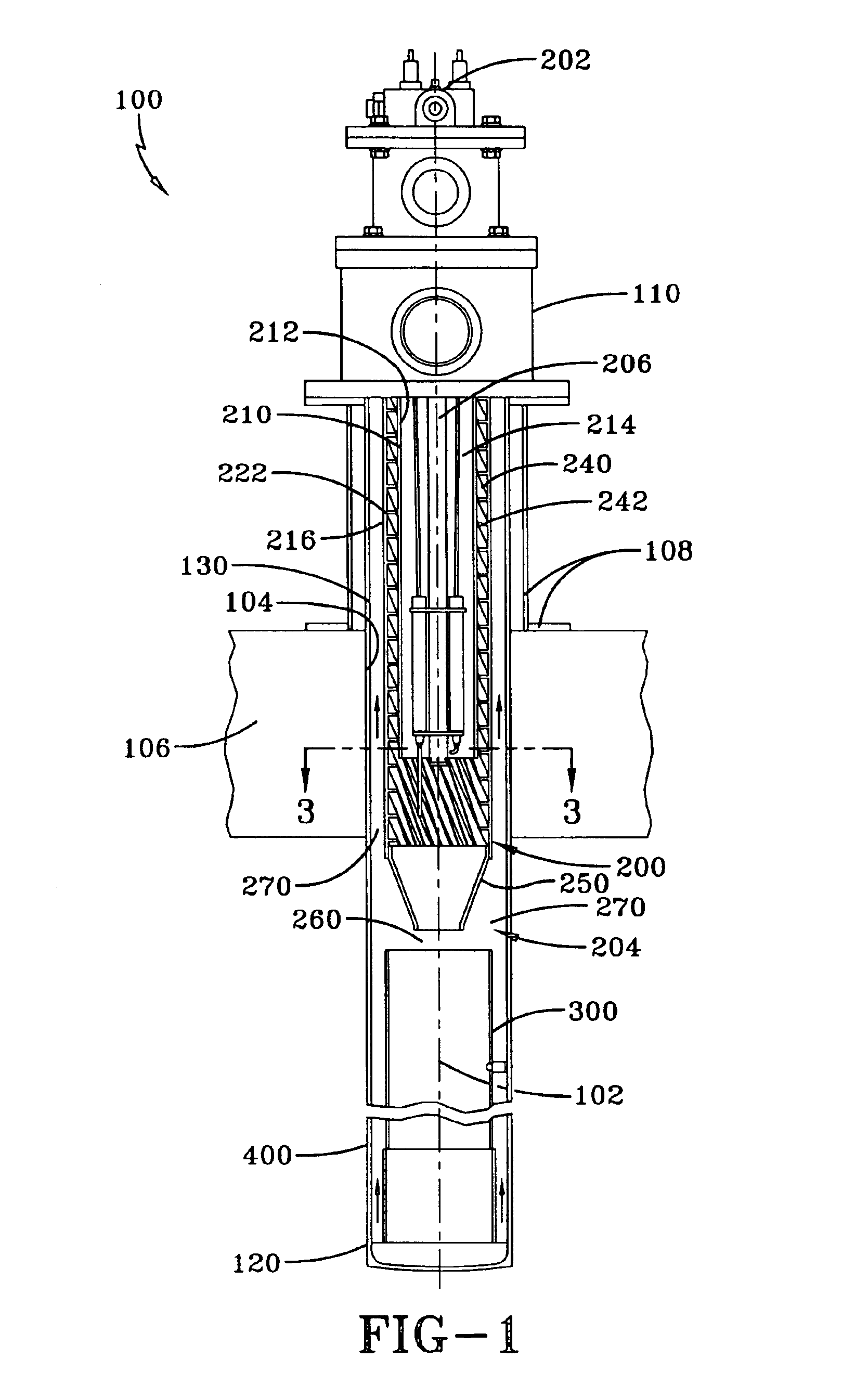
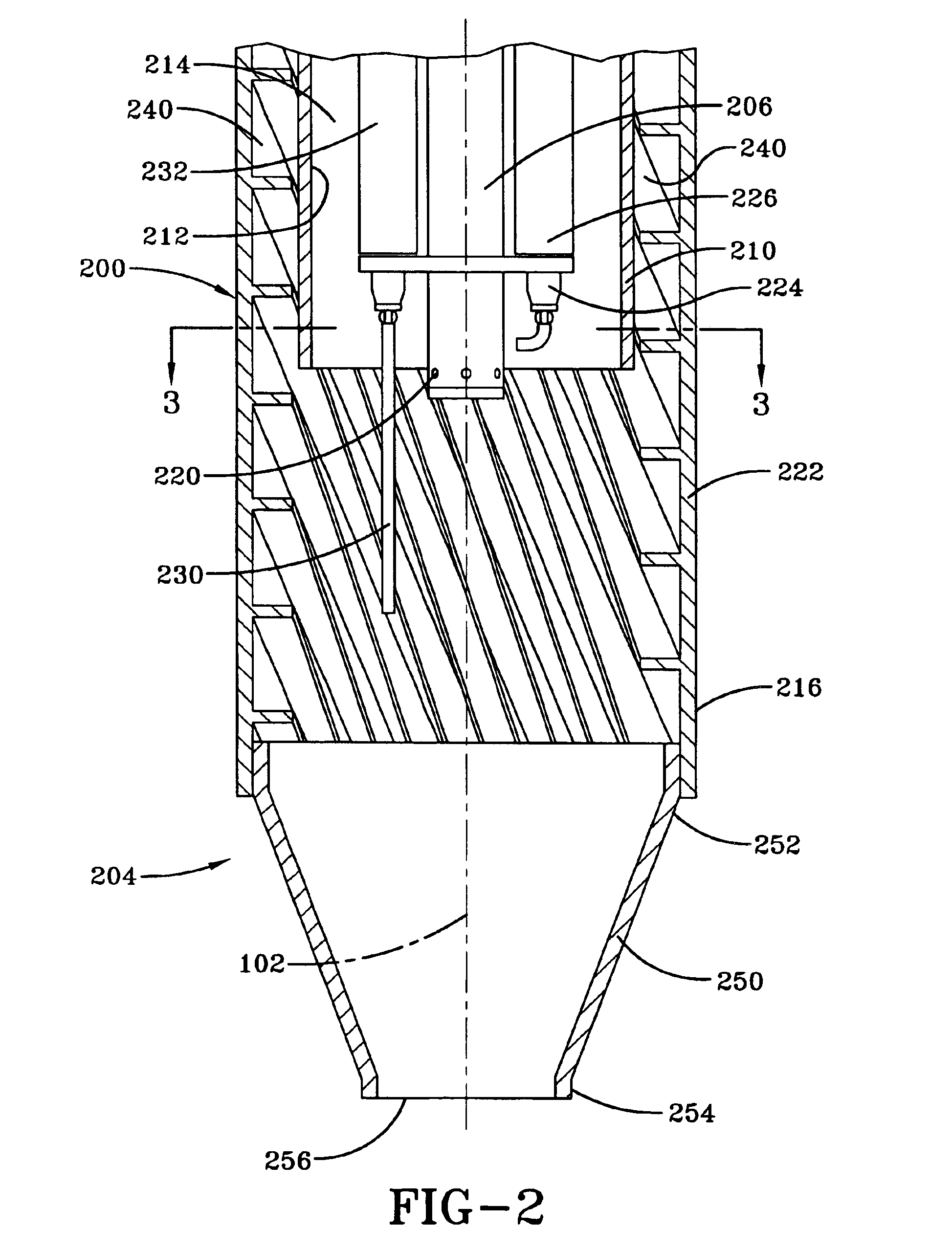
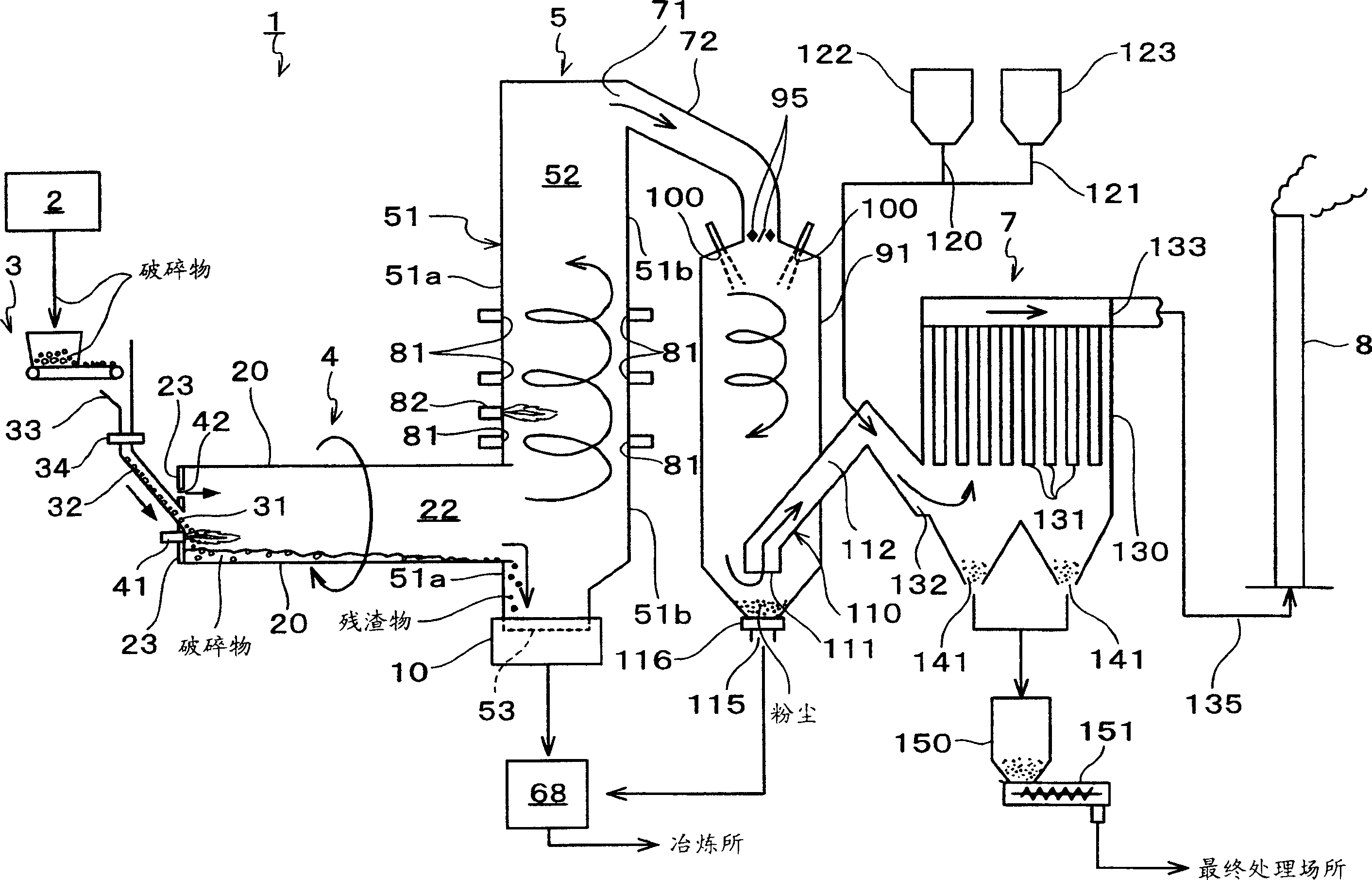
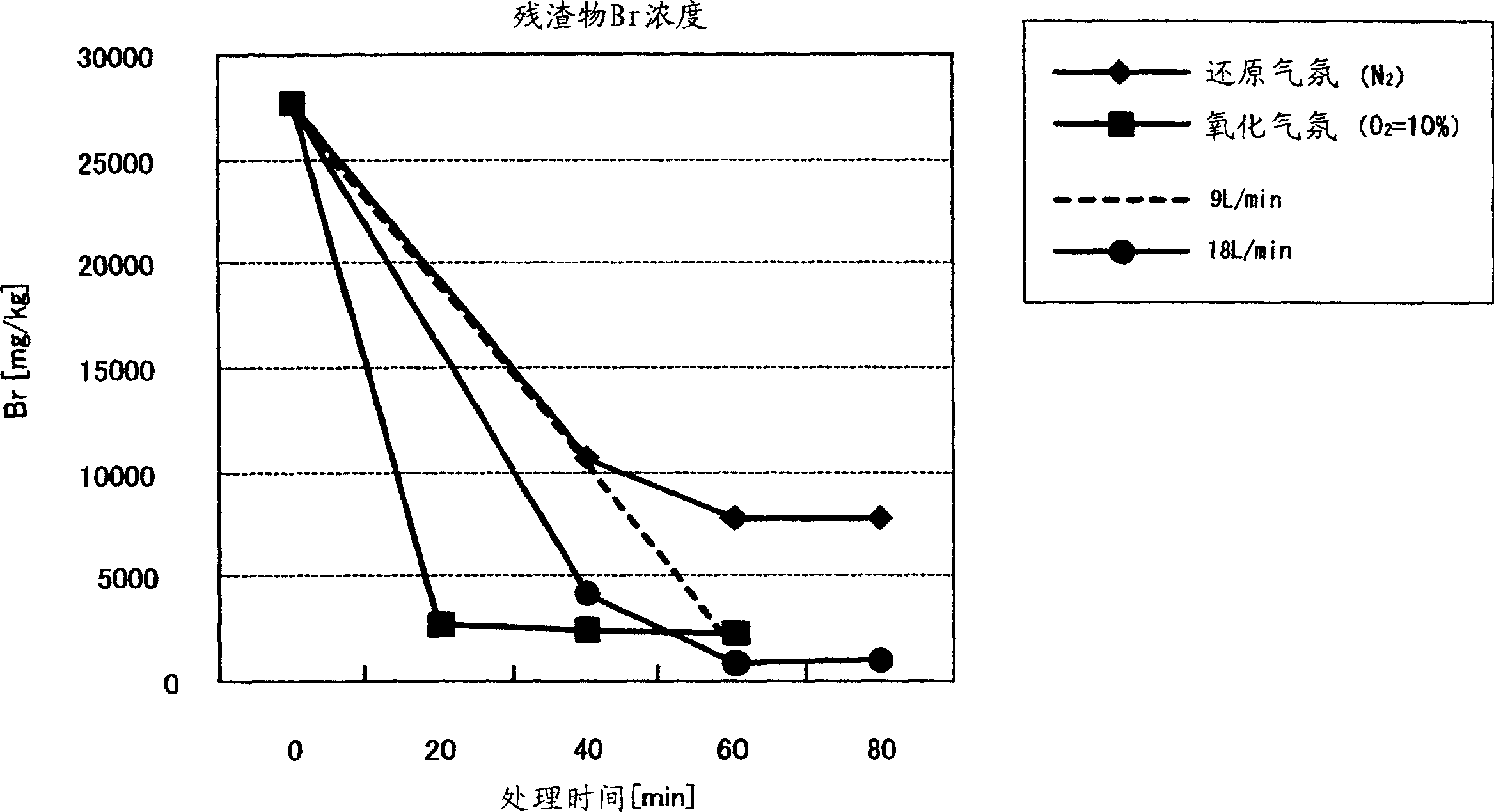
Castoff processing method and system
ActiveCN1834537AEfficient combustionEfficient gasificationProcess efficiency improvementIncinerator apparatusWaste processingHazardous substance
The invention relates to a waste processing method and a waste processing system which can avoid discharging harmful material as dioxins and effectively attain the slag of value metal. Wherein, the method for recycling value metal comprises: burning the waste, recycling the slag that containing value metal, and fully burning generated gas , and cooling said burning gas with the cooling speed that avoiding generating dioxins. With said method, the invention can gasify the resin component in the waste via burning waste, to obtain the slag of value metal in short time.
Owner:DOWA METALS & MINING CO LTD
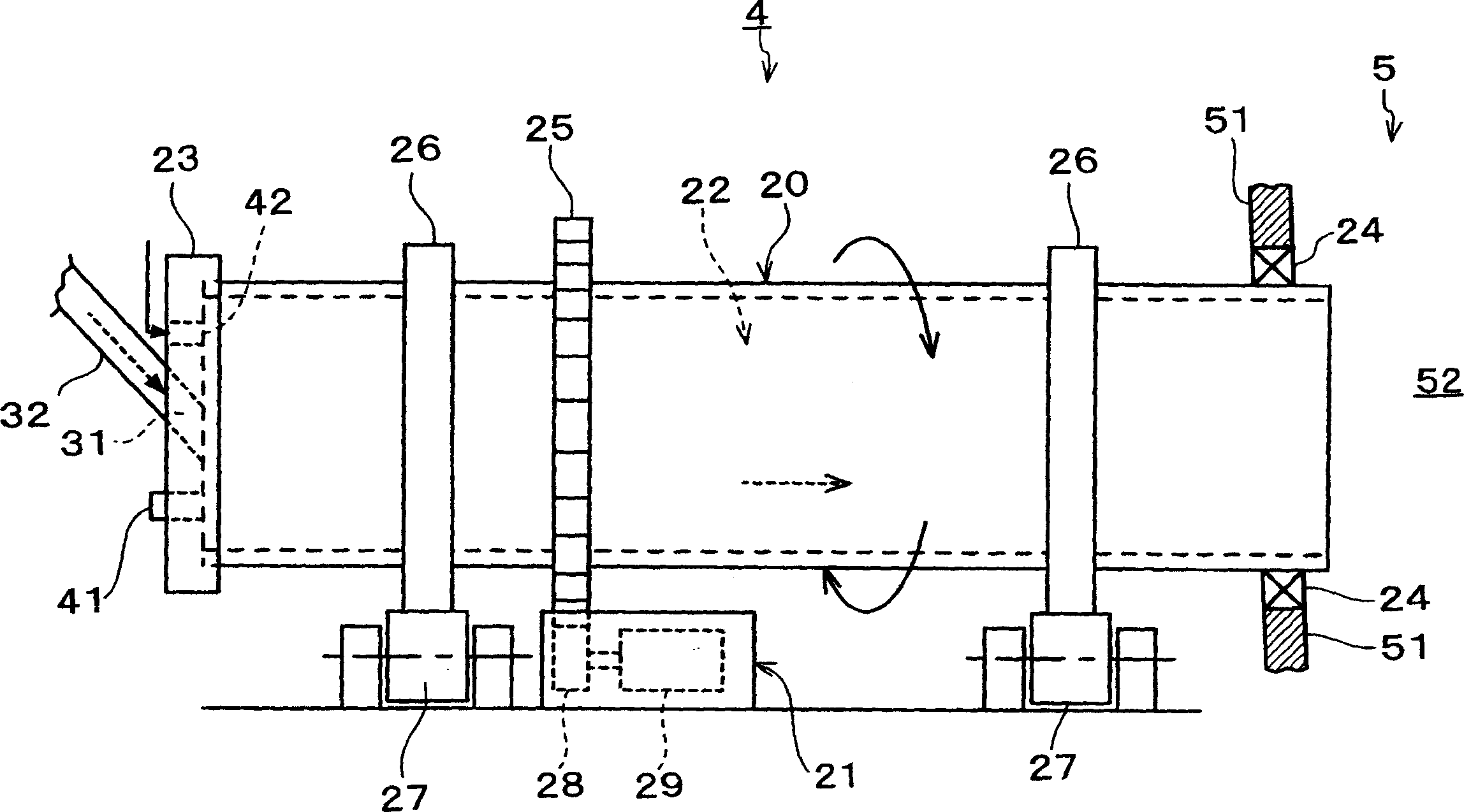
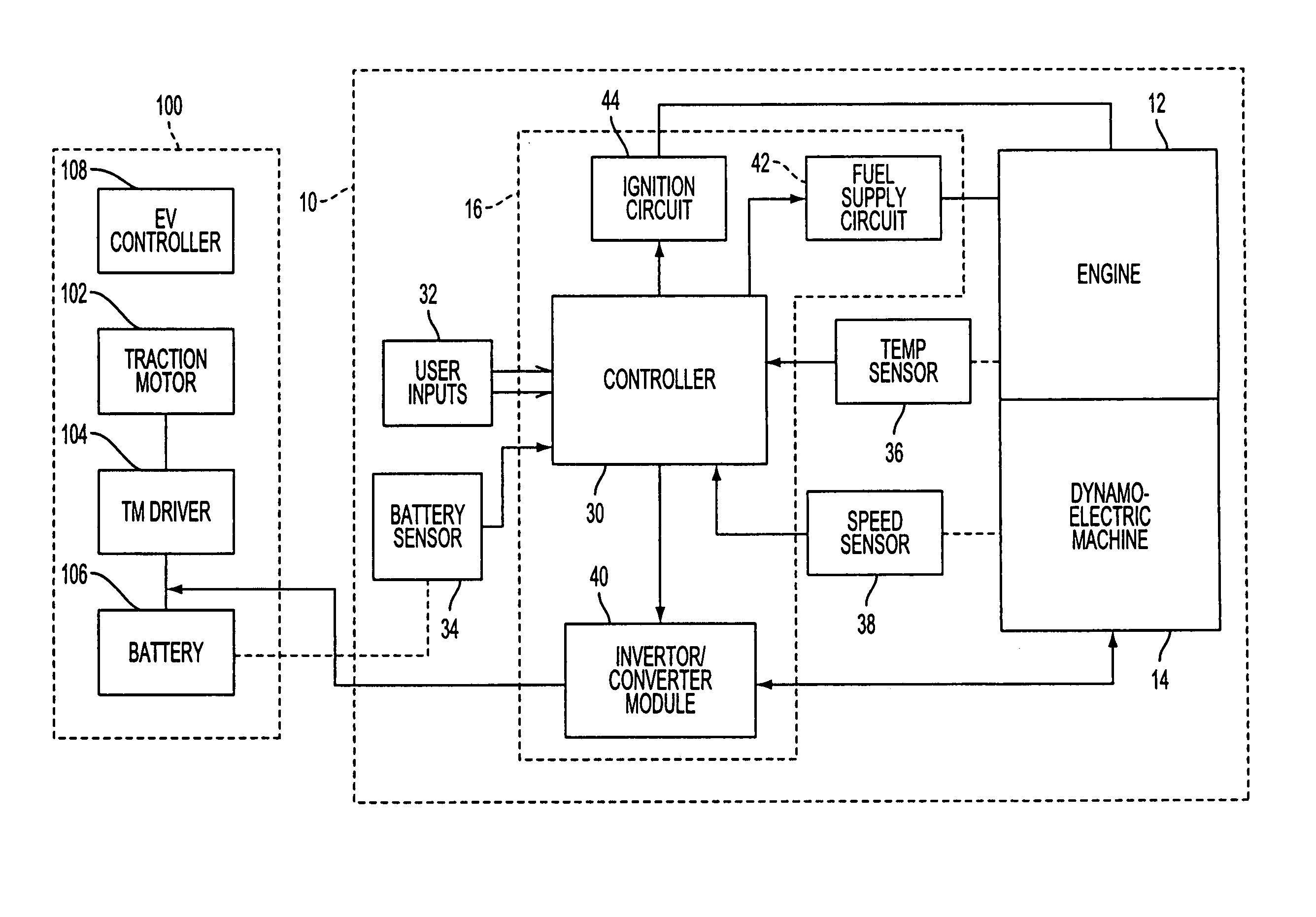
Portable range extender with autonomous control of starting and stopping operations
InactiveUS7449793B2Efficient combustionSmooth rotationElectric motor startersEngine controllersElectricityAutomatic control
A portable range extender can be used to supply electrical power to an electric vehicle operable by an electric traction motor. The portable range extender includes an engine, a dynamoelectric machine coupled to the engine by a shaft, an autonomous range extender controller for controlling operations of the range extender independently of a controller for the vehicle, and circuitry associated with the engine and machine. To start operation, electrical energization is applied from the vehicle battery to the dynamoelectric machine for operation as a motor to drive the shaft. As the shaft accelerates, the rotational speed of the shaft and the temperature of the engine are sensed. When the speed and temperature obtain predetermined thresholds, fuel is supplied to the engine and ignition is activated. The engine then operates as a prime mover to drive the shaft in lieu of the machine. After a period of engine prime mover operation, the machine is activated for operation as a generator to provide an electrical current output for charging the battery or supplying energy to the traction motor. When range extender operation is to be stopped, fuel supply is cut off before ignition termination to avoid engine backfire.
Owner:BLUWAV SYST LLC
Dual mode combustion operation of a pulse detonation combustor in a hybrid engine
InactiveUS7950219B2Easy to operateEfficient combustionContinuous combustion chamberGas turbine plantsCombustion chamberSolenoid valve
A dual mode combustor of a gas turbine engine contains at least one dual mode combustor device having a combustion chamber, a fuel air mixing element, a high frequency solenoid valve and a fuel injector. During a first mode of operation the dual mode combustor device operates in a steady, constant pressure deflagration mode, receiving its fuel from the fuel injector. In a second mode of operation the dual mode combustor device operates in a pulse detonation mode, receiving its fuel from the high frequency solenoid valve.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
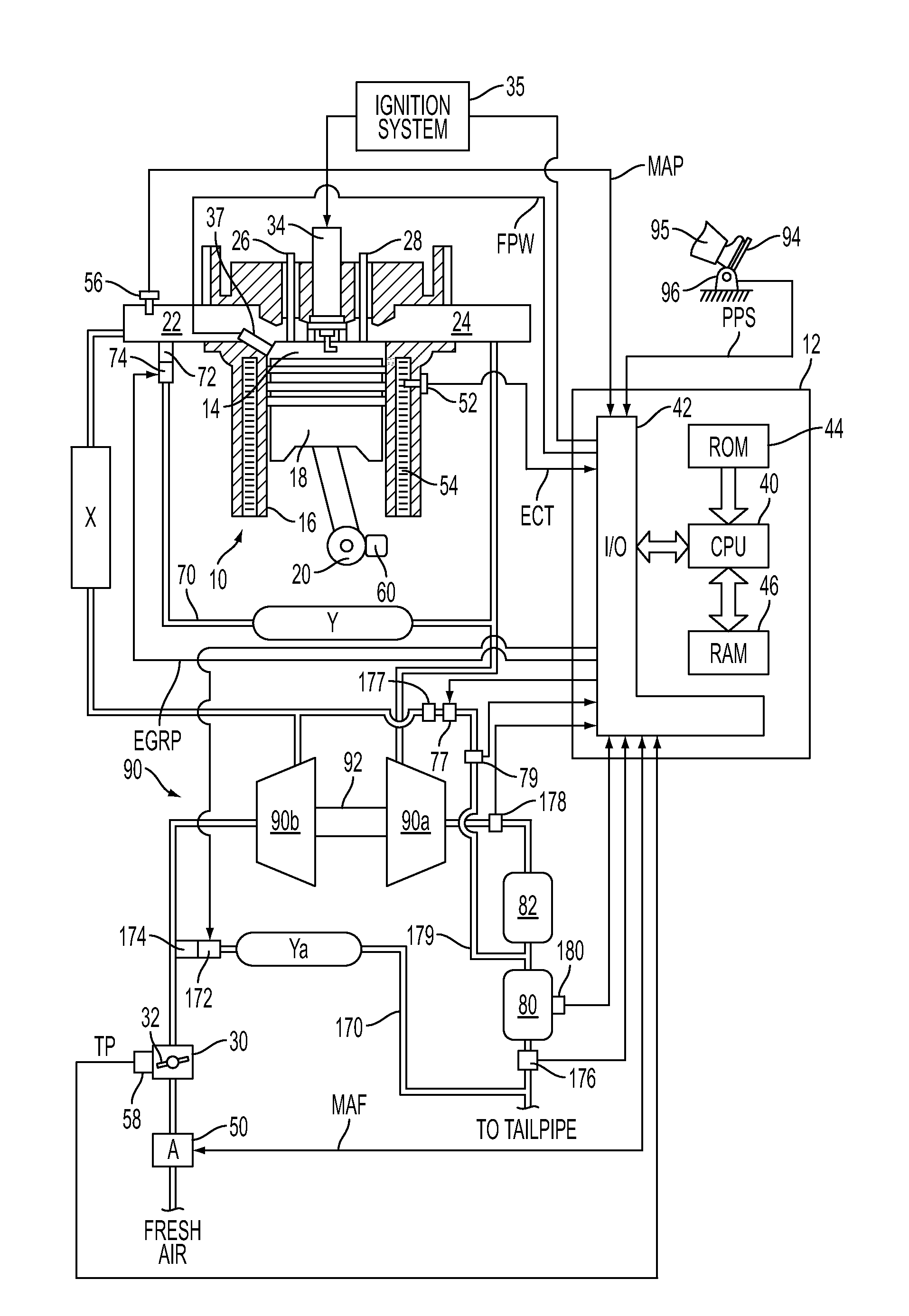
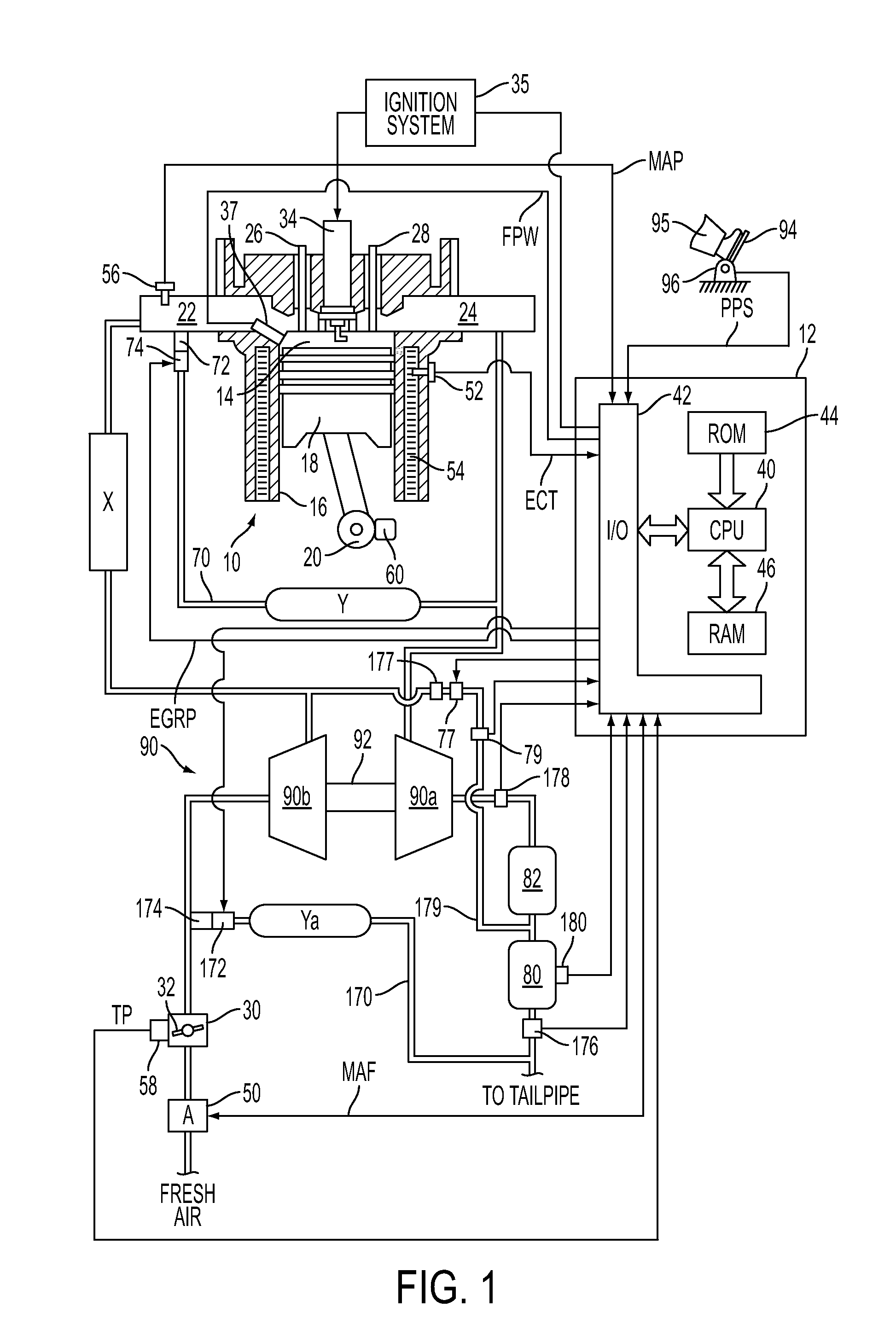
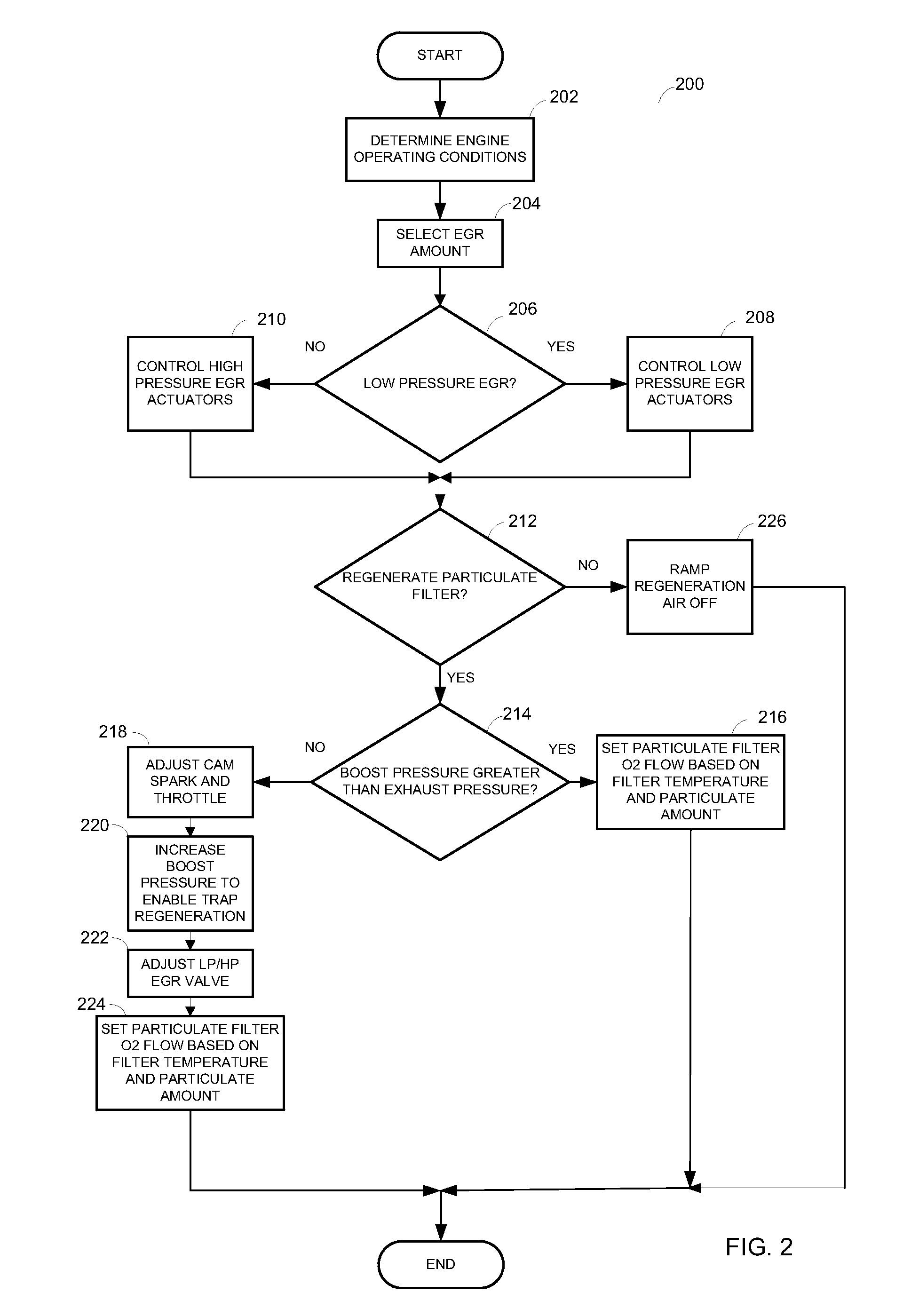
Method for regenerating a particulate filter for a boosted direct injection engine
ActiveUS20110072795A1Improve engine performanceReduce transient air-fuel disturbanceValve arrangementsElectrical controlGasolineEngineering
A method for regenerating a particulate filter is disclosed. In one example, oxygen is pumped from the intake system of a direct injection turobocharged gasoline engine through a cylinder and into the exhaust system by a compressor. In this way, regeneration of a particulate filter may be accomplished without an auxiliary air supply.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Piston guides for a free piston engine
InactiveUS20050284426A1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeFree piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Piston guide posts are fixed and guide the outer pistons as they reciprocate within the engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Method of combusting sulfur-containing fuel
InactiveUS20100077947A1Easy to controlMaintain temperatureFluidized bed combustionAir supply regulationEngineeringComponents of crude oil
A method of combusting sulfur-containing fuel in a circulating fluidized bed boiler includes the steps of (a) feeding sulfur-containing fuel into a furnace of the circulating fluidized bed boiler, (b) combusting the fuel with oxidant gas consisting essentially of pure oxygen and circulated exhaust gas, so as to form exhaust gas having carbon dioxide and water as its main components, and (c) feeding calcium carbonate containing material into the furnace so as to capture sulfur dioxide into calcium sulfate in the furnace. The temperature in the furnace is maintained above 870° C.
Owner:FOSTER WHEELER ENERGY CORP
Direct venting vent pipe
InactiveUS6634352B2Facilitate run of unrestricted lengthEfficient combustionPipe supportsDomestic stoves or rangesDirect combustionDouble wall
A venting system for a direct vent fireplace or other direct vent appliance to direct combustion gases to an exterior area. The direct venting vent pipe facilitates unrestricted lengths of pipe installations. The vent pipe has a double wall construction forming an interior axial passageway and a coaxial outer passageway. The double walls are spaced apart by an insert to maintain coaxial spacing. Sections of the vent pipe are lockingly connected to prevent separation and ensure sealing connection between the pipe sections. Elastic seal members are utilized between the matingly connected sections and a mechanical lock assembly prevents separation.
Owner:CARDINAL IP HLDG LLC
Piston guides for a free piston engine
InactiveUS7032548B2More balancedEfficient chargingFree piston enginesFree-piston engineReciprocating motion
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Piston guide posts are fixed and guide the outer pistons as they reciprocate within the engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Portable fire pit system
InactiveUS20120196232A1Efficient combustionDomestic stoves or rangesLiquid carbonaceous fuelsEngineeringSquare Shape
The present invention provides a portable fire pit to be used in conjunction with particularly sized fuel blocks, whereby these fuel blocks are manually positioned in a square-shaped configuration around ventilation holds provided through the base of the fire pit. Alignment flanges on the base provide a positioning and alignment brace structure for the fuel blocks, which are fitted into an abutting relationship with the alignment flanges and one another on the base. The ventilation holes are formed to align with an inner chimney formed by the positioning of the fuel blocks. This chimney is formed over the ventilation holes to allow the fire to burn from the chimney outwardly through the blocks and thereby provide an efficient burning of the fuel.
Owner:SUMMIT WOOD INDS
Quick engine startup system and method
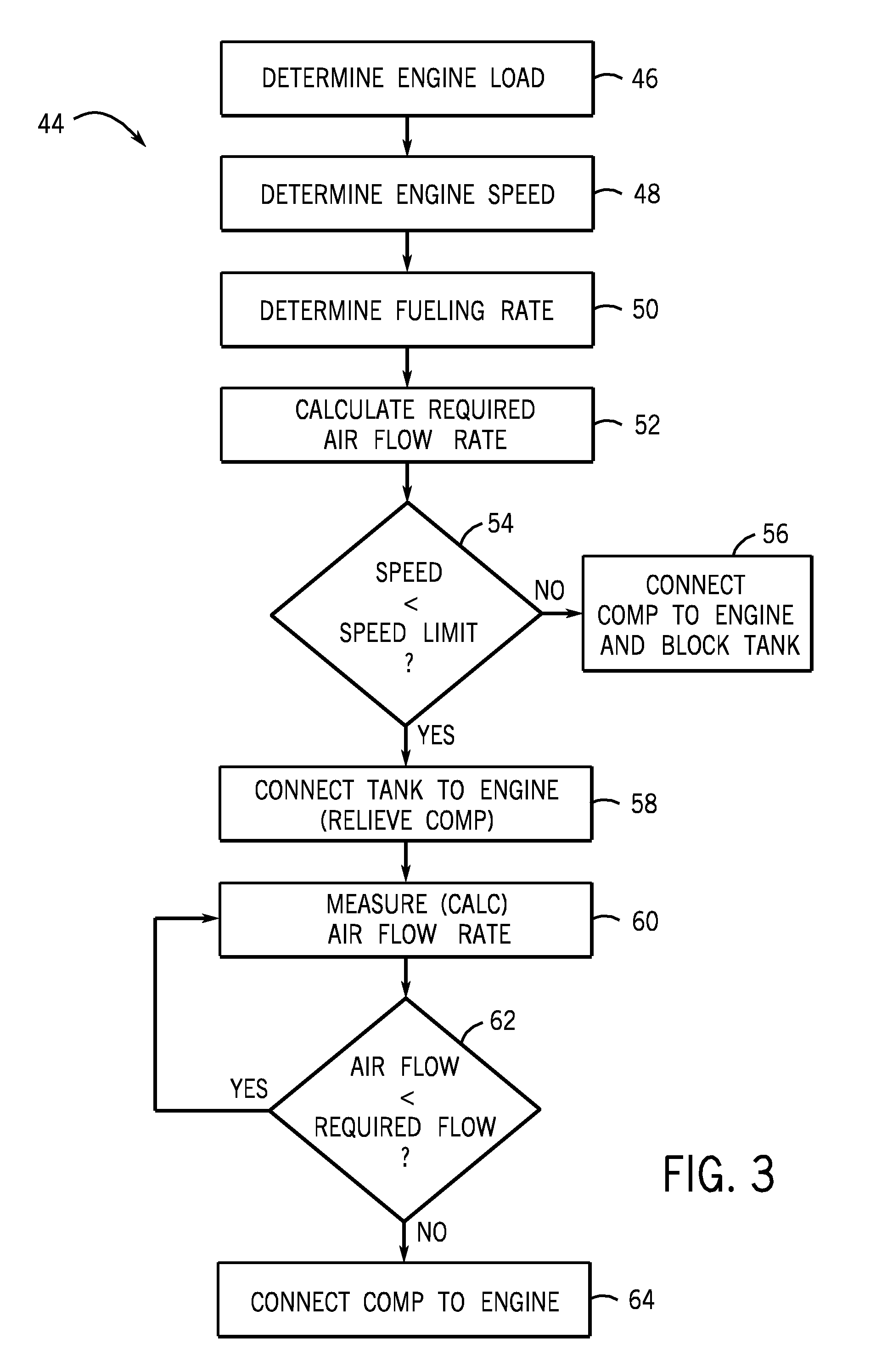
ActiveUS20090217898A1Improve responseReducing depth of speed reductionElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesParticulatesSmoke Emission
A technique is provided for improved response of internal combustion engines to increased load demands. The engine is equipped with an air storage tank that stores compressed air. The air may be stored at an elevated pressure (e.g., manifold air pressure) during normal full load operation of the engine. Valving maintains the compressed air isolated during normal operation. During transitory periods of higher power output demand, the compressed air is directed to the engine, and output of a turbo-driven compressor can be vented to avoid surge. The technique allows for quicker reaction to load demands, and improved combustion during transitory periods, and reduced particulate and smoke emissions.
Owner:GE GLOBAL SOURCING LLC
Method for designing fixed-geometry two-dimensional mixed-compression type supersonic velocity air inlet channel
InactiveCN102748135ASatisfy the starting ability requirementReduce the starting Mach numberTurbine/propulsion air intakesWedge angleInlet channel
The invention discloses a method for designing a fixed-geometry two-dimensional mixed-compression type supersonic velocity air inlet channel. A basic structure of the adopted two-dimensional mixed-compression type air inlet channel comprises an outer pressing section, an inner pressing section, a throat section, an expanding section and a lip. The lip is of a sharp plate structure with a certain wedge angle. When the air inlet channel is designed, designed starting Mach number is improved appropriately, the lip shape is changed, and the starting mach number is effectively reduced to be lower than a requested value through a certain flow on the premise that the flow requirement of the air inlet channel is met. By means of the method, the requirement for starting performance can be met, contraction ratio of the air inlet channel can be increased in design, and accordingly high back pressure resisting capability and low outlet Mach number are obtained in a wide working range to facilitate efficiently combusted organizations in a combustion chamber. Furthermore, small total pressure loss in the working process of the air inlet channel can be achieved through the change of the lip shape. The method for designing the fixed-geometry two-dimensional mixed-compression type supersonic velocity air inlet channel has good actual application value.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Candle having a planar wick and method of and equipment for making same
ActiveUS8348662B2Stable and uniform diameterSpeed up the flowNon-electric lightingCandle holdersEngineeringCandle
A candle having a body of a meltable fuel and a planar wick. When lit, the candle provides a unique flame formation, usable in a variety of decorative applications. The wick can be configured to evenly deplete the meltable fuel, while allowing for candles having relatively large and unique body configurations. The body of candle and / or the wick may include scented oil to promote the release of fragrance upon heating. The wick preferably is formed of wood, thereby providing an acoustic contribution to ambiance and improved combustion that generates less soot than conventional cotton wick candles.
Owner:LUMETIQUE
Ambient-air jet blast flames containment and suppression system
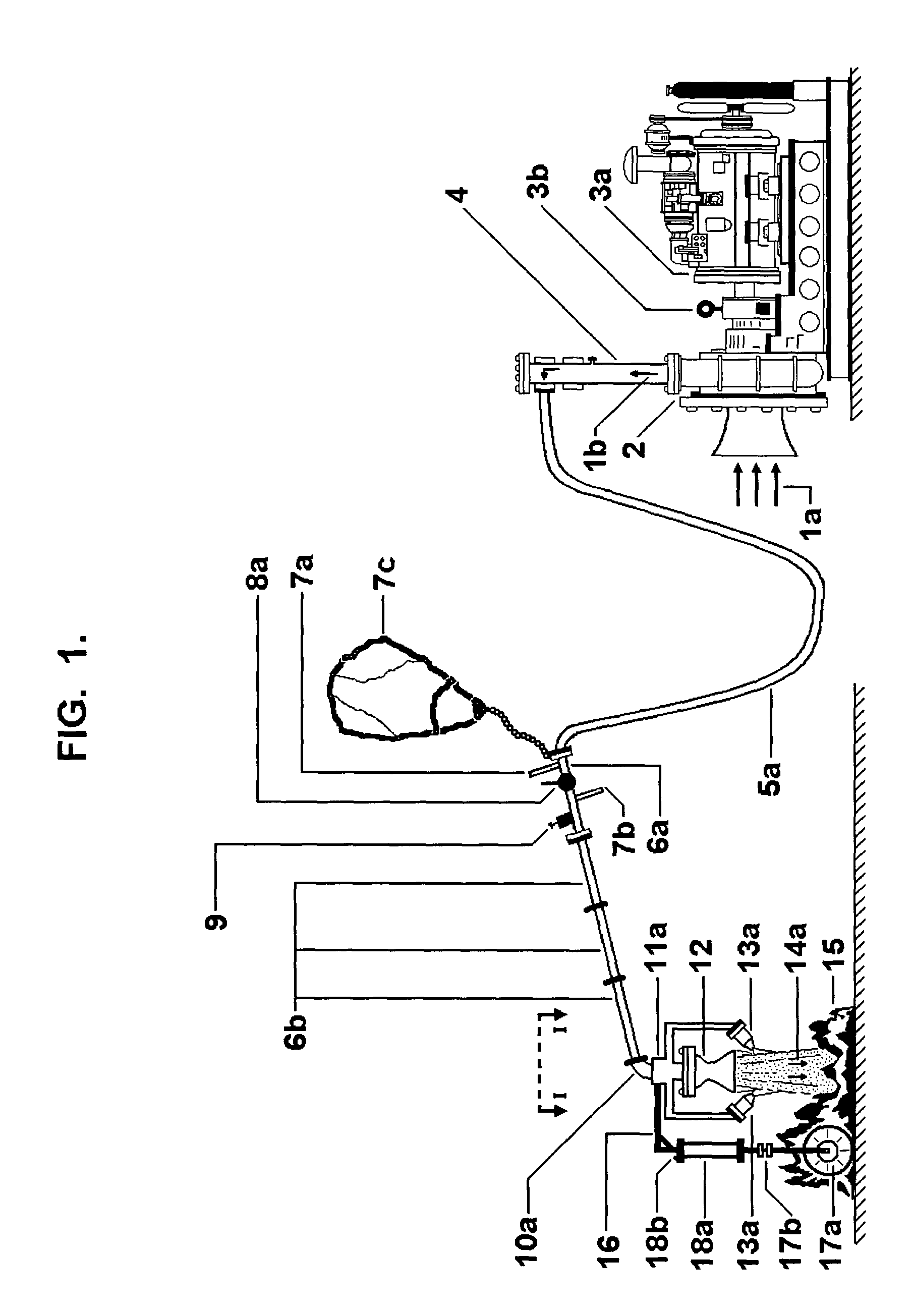
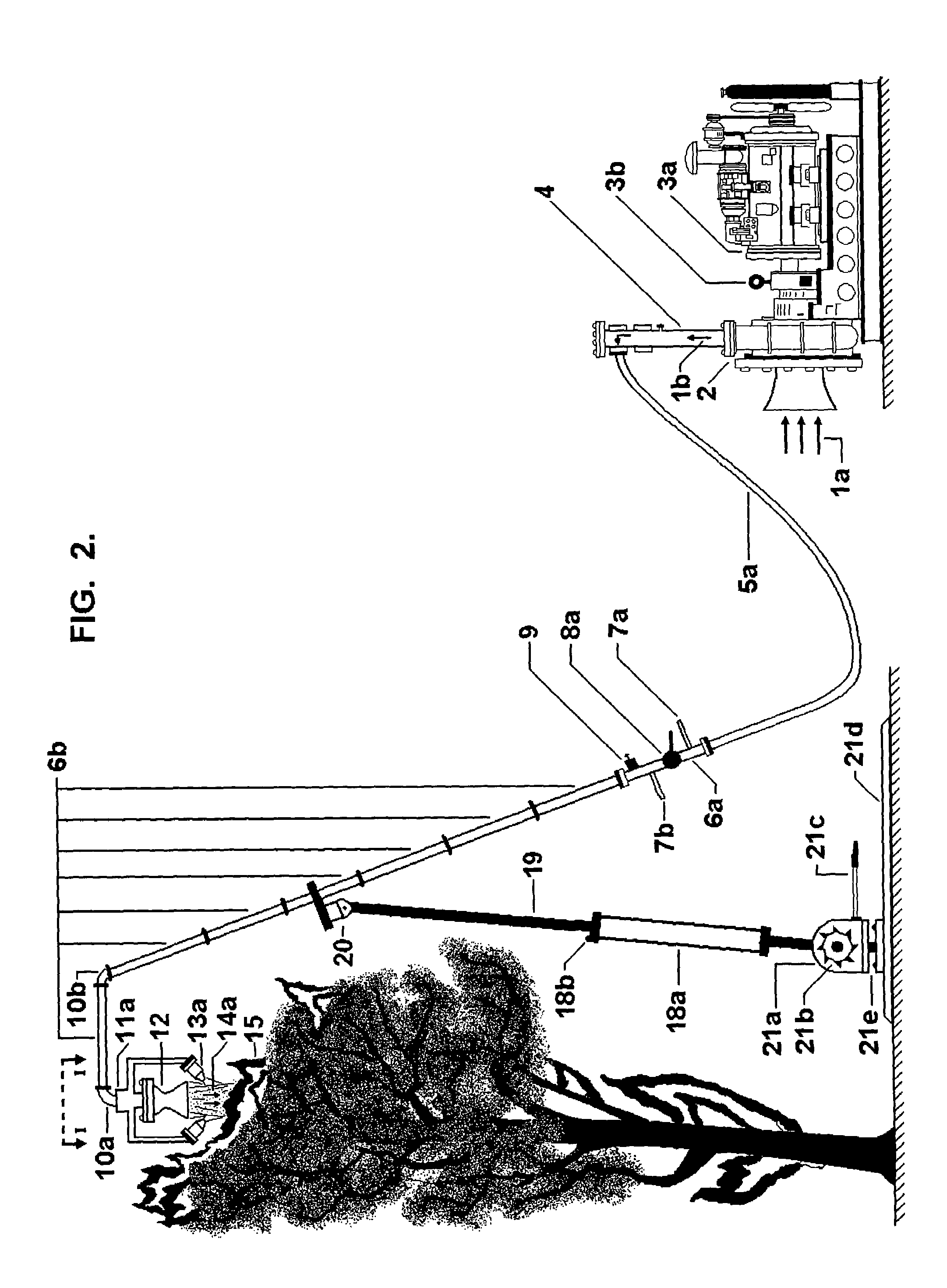
InactiveUS7028783B2Enhance improve suppressionImprove practicalitySpray nozzlesFire rescueShock waveWater vapor
In the fire location, an ambient or atmospheric air mass flow (been a gas mixture of dry air and superheated water vapor) is compressed by a compression package. A hose transports this compressed air mass flow a given distance away up to a flames site, where an arrangement of pipes, elbow accessories, throttle valves, nozzles, and a distribution manifold, conforming together a fire fight boom with a “blast-gun”, allow the operator to direct upon the flames, a high speed ambient air jet containing water droplets with a high flame front aerodynamic penetration capability, which brings about the flames blown off and remaining not burned materials combustion inhibition. Such a high speed air jet containing water droplets is generated by the compressed air mass flow expansion in a jacketed convergent-divergent nozzle, whereinto a condensation sock wave is established producing such water droplets from the local ambient air water vapor contents. The air jet proximity to the flames' origin is important, and the operator's movements can be controlled by a wheel, a pneumatic cylinder, supports, and pivoted anchors. To preclude, in this process, the inflammation of surrounding non burning materials and the existence of run-away flame fronts, different aerodynamic flame containment mechanisms are formed by other air jets produced in convergent nozzles air expansions. To allow the low temperatures required and the successful establishment of the condensation shock wave, a cooling air flow insulates, from the hot flame environment, the air flow expansion in the jacketed convergent-divergent nozzle. The aspersion mechanism formed by the air mass flow expansion, is utilized also to deliver different chemical fire fight agents to the flames sites with a high flame front penetration capability.
Owner:CELORIO VILLASENOR ARMANDO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com