Patents
Literature
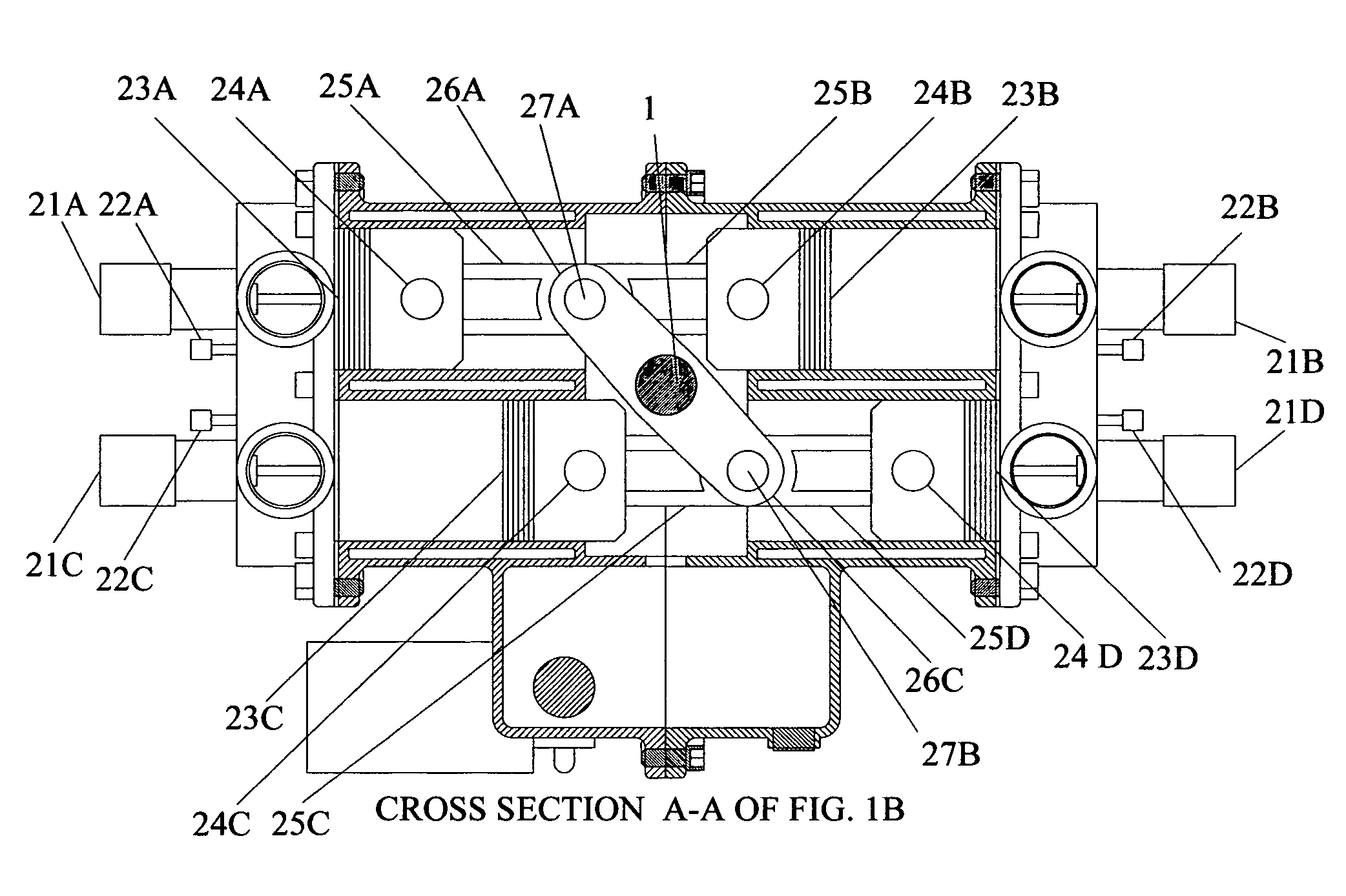
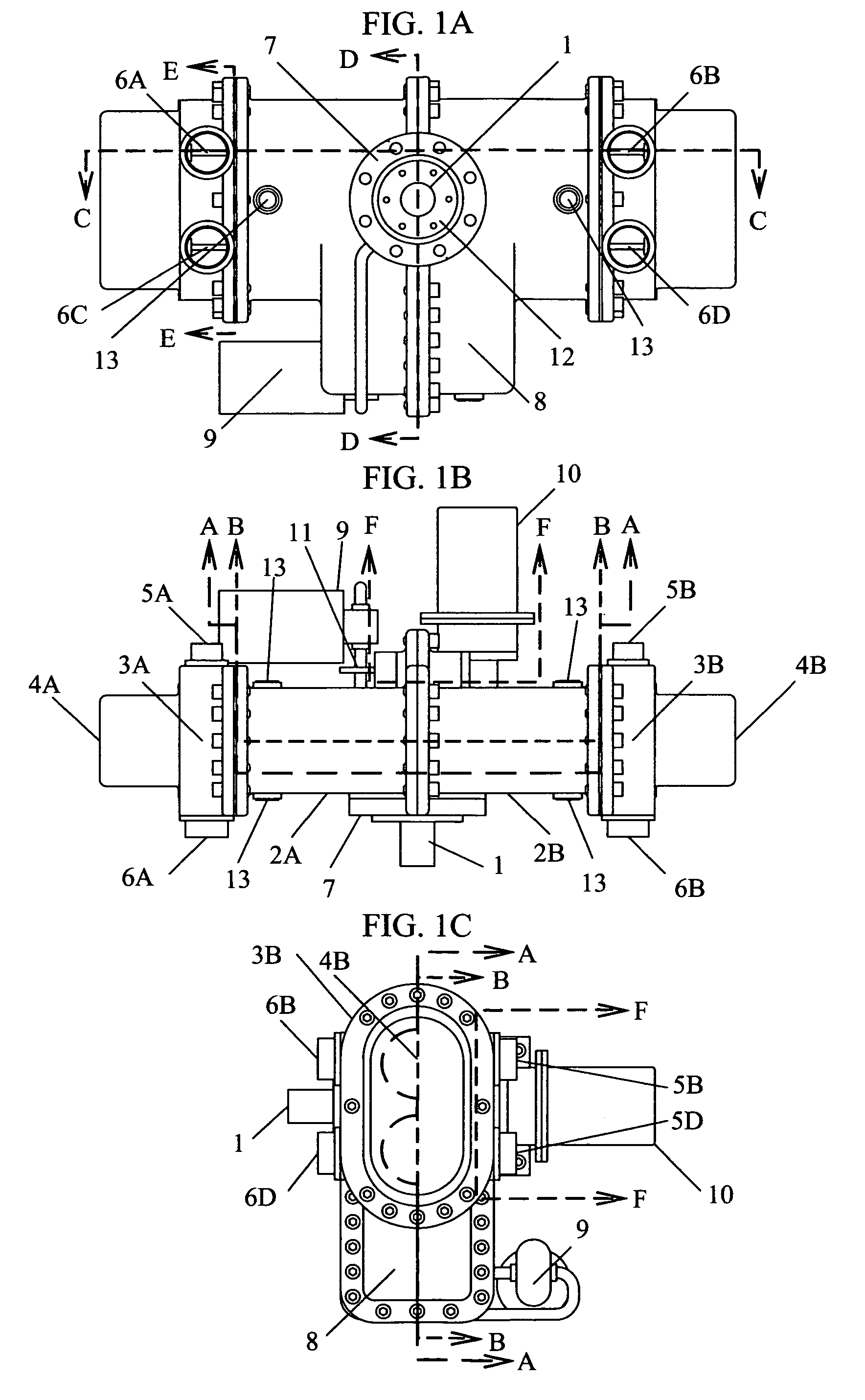
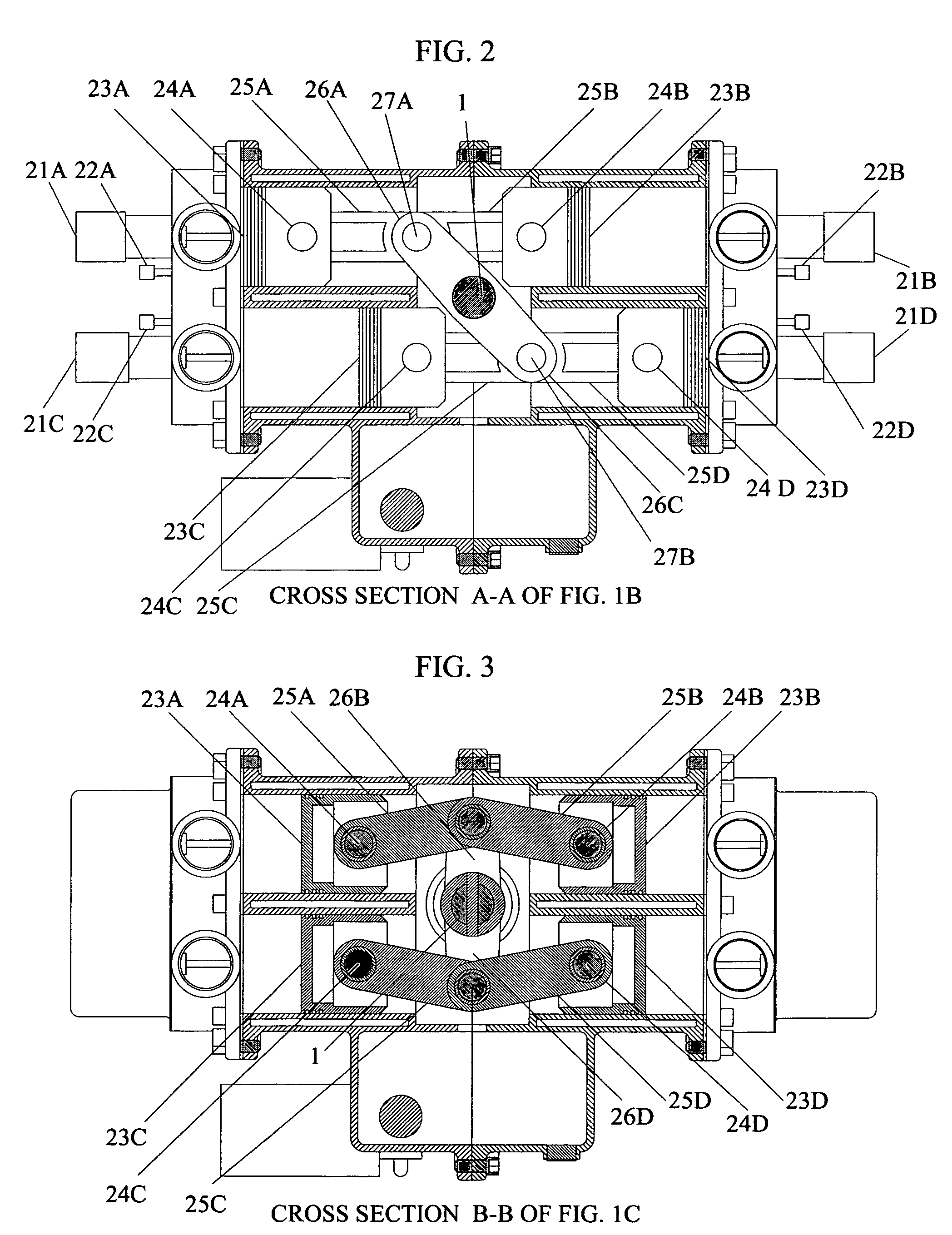
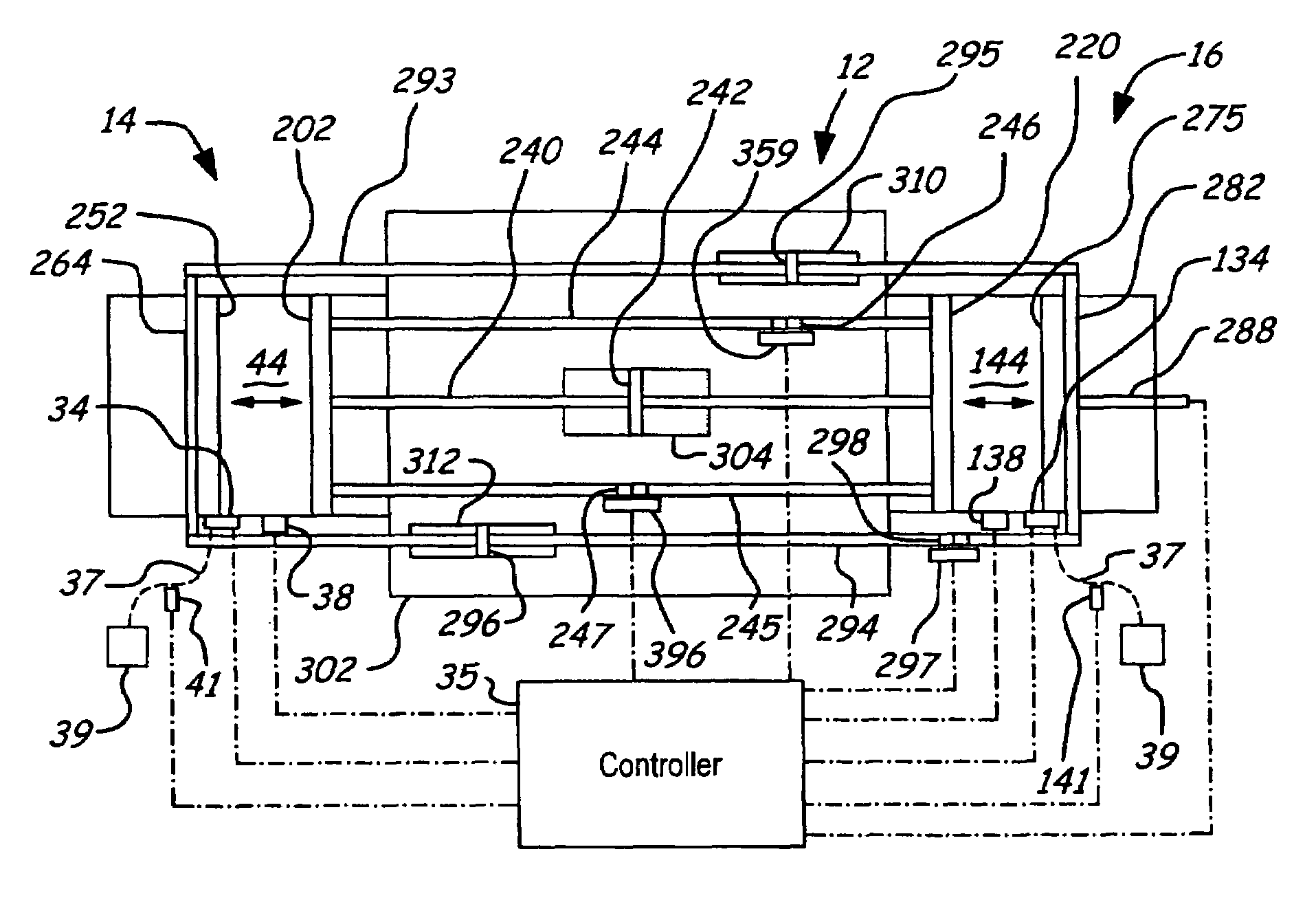
237 results about "Free-piston engine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
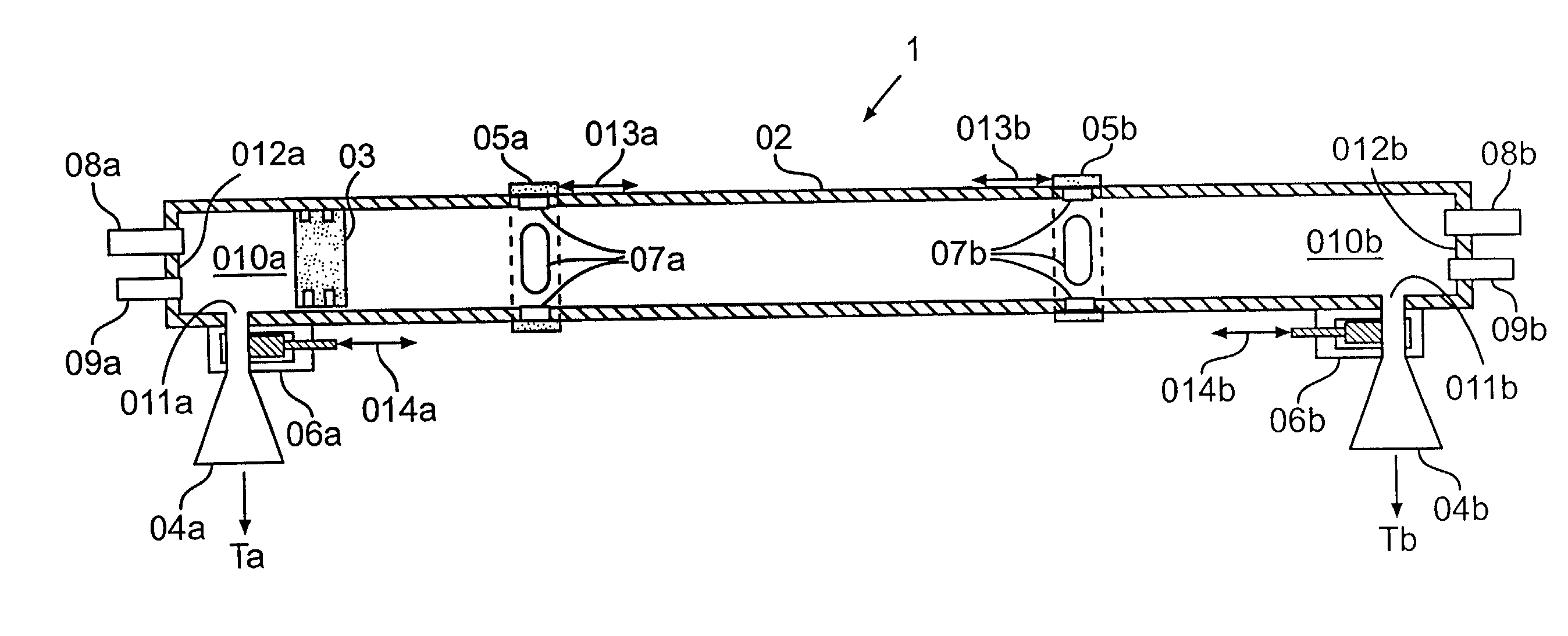
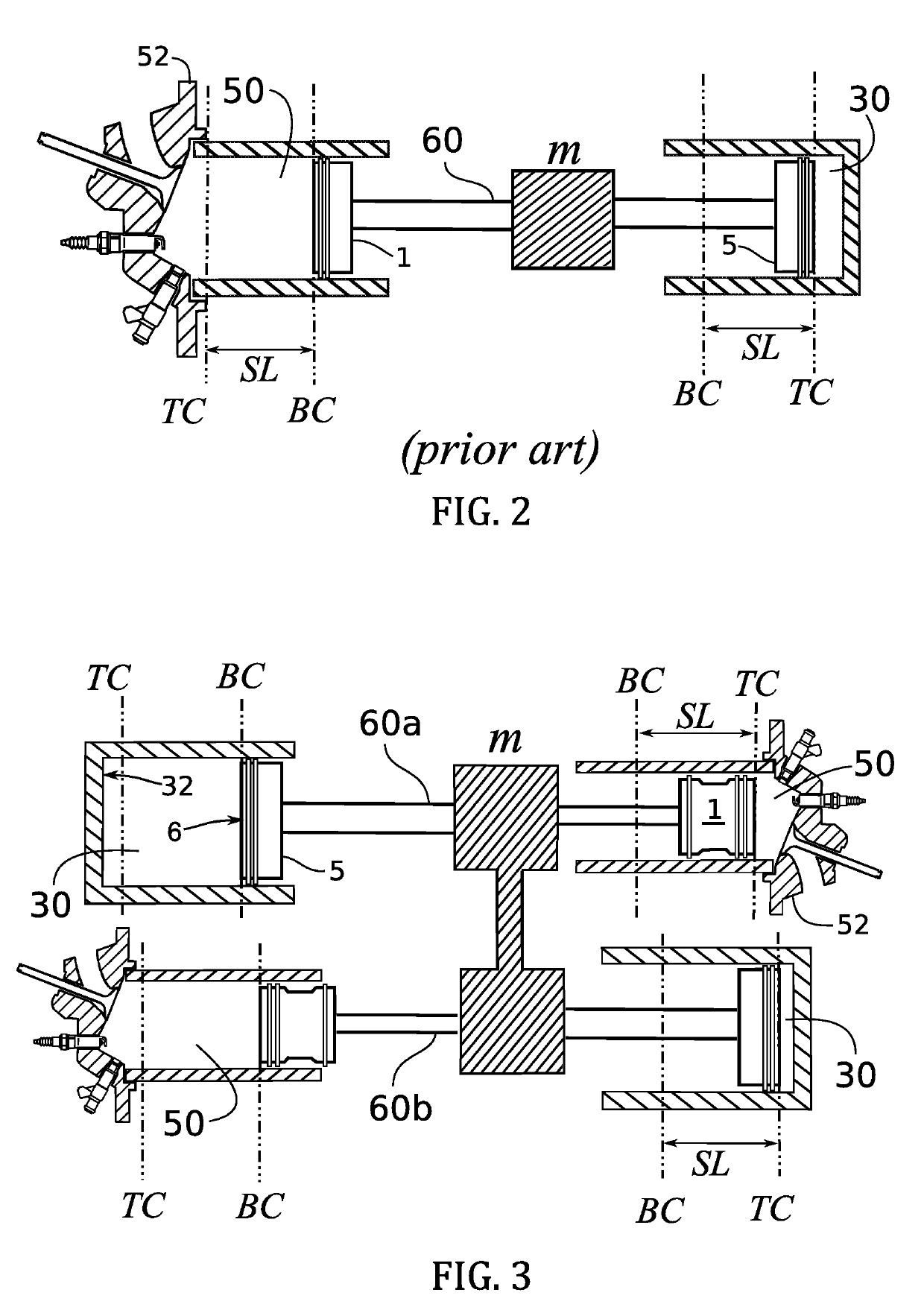
A free-piston engine is a linear, 'crankless' internal combustion engine, in which the piston motion is not controlled by a crankshaft but determined by the interaction of forces from the combustion chamber gases, a rebound device (e.g., a piston in a closed cylinder) and a load device (e.g. a gas compressor or a linear alternator).
Methods of combining a series of more efficient aircraft engines into a unit, or modular units
InactiveUS20100251692A1More thermal capacityReduce environmental pollutionContinuous jet plantsRocket engine plantsRamjetFree-piston engine
The present invention generally relates to units of engines and more particularly to units containing a unique combined-cycle (combustion-detonation) “counter-rotation, anti-gyration, gyroscopic,” turbine fan-jet / free-piston engine configuration for induced air supercharging and boosting the performance of novel Ramjet engines or Ramjet engine configurations by improving internal air-stream dynamics. These dynamics are the result of co-operative air stream intermixing through convergent, supercharge-attenuated, inducted, compressed, tuned, pre-heated ambient air. Achieved through the varying of the geometric structural form and the utilization of unique engines and air induction and propulsion conformations, aided with supplemental air, fuel, oxygen and optiomal water and electrolyte charging.
Owner:KINDE SR RONALD AUGUST
Liquid piston internal combustion power system
InactiveUS7191738B2Reduce pollutionRotary slide valveSteam engine plantsFree-piston engineCombustion
Methods, devices, and systems for power generation through liquid piston internal combustion engine. The liquid piston internal combustion engine of the invention utilizes a novel, synergetic combination of internal combustion and steam piston engines within the framework of one and the same system. The engine may comprise a plurality of cylinders, each having a liquid piston.
Owner:LIQUIDPISTON INC
Free piston engine and power generation system therewith
InactiveUS20050109295A1Improve efficiencyReduce vibrationMechanical energy handlingFree piston enginesFree-piston engineEngineering
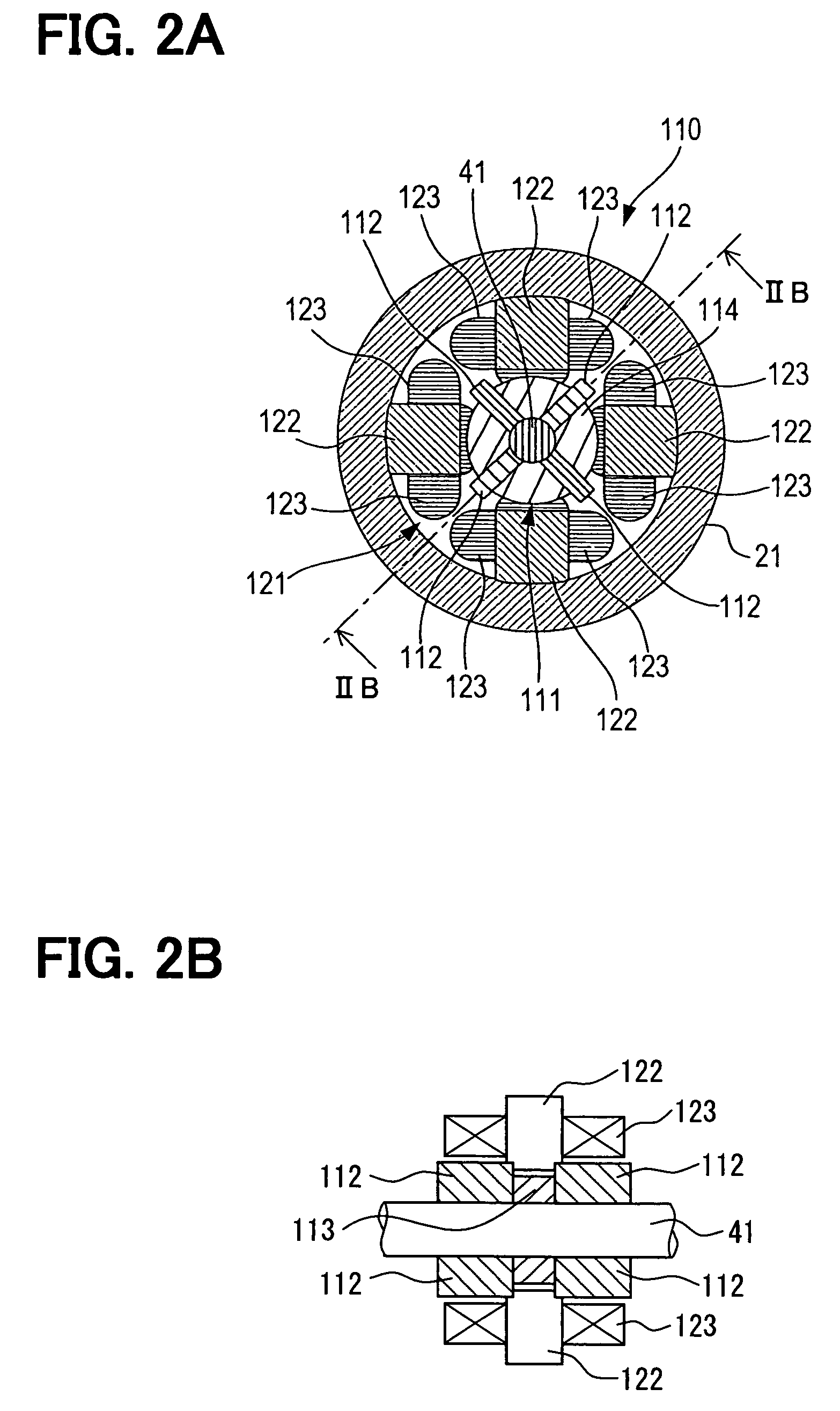
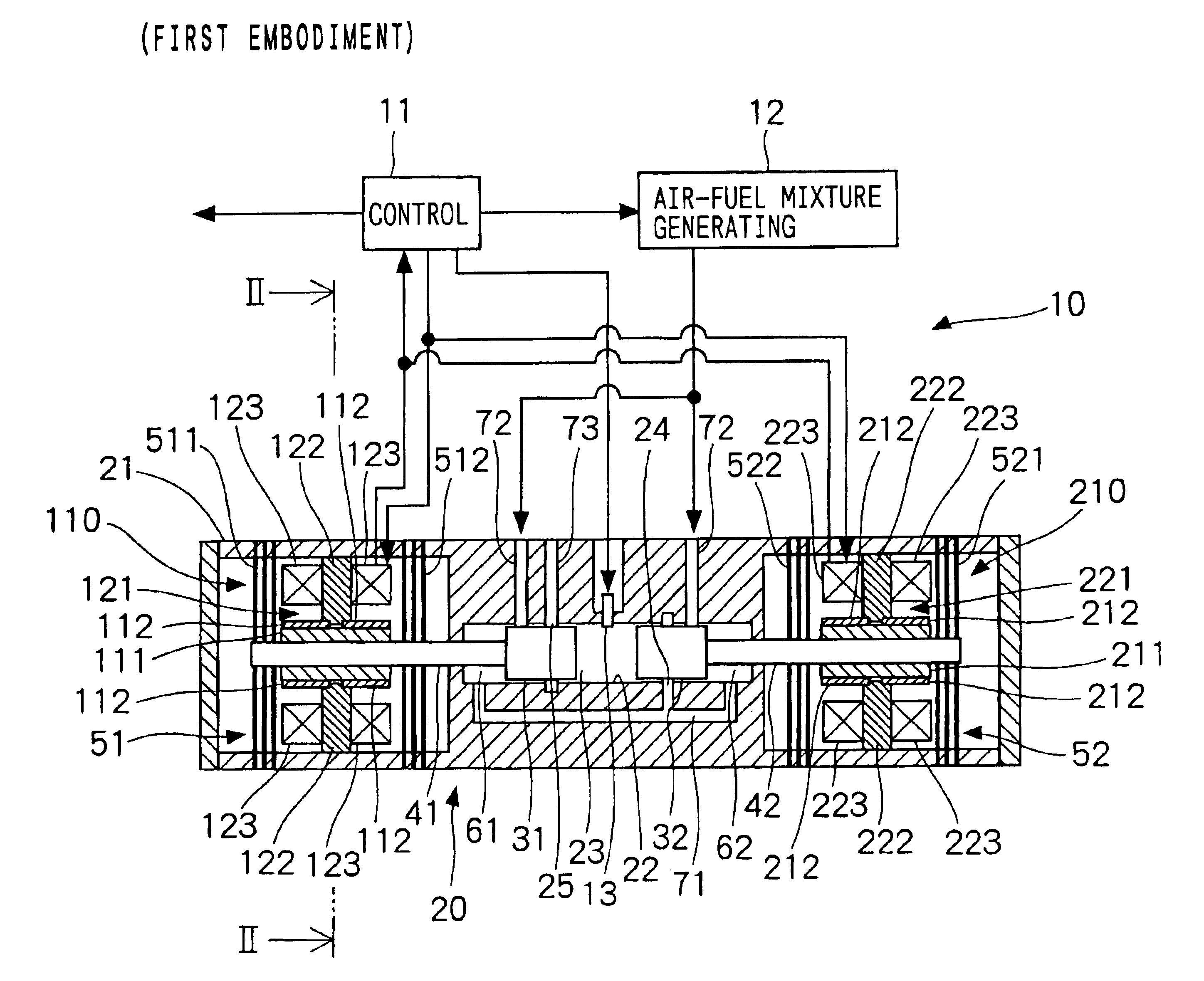
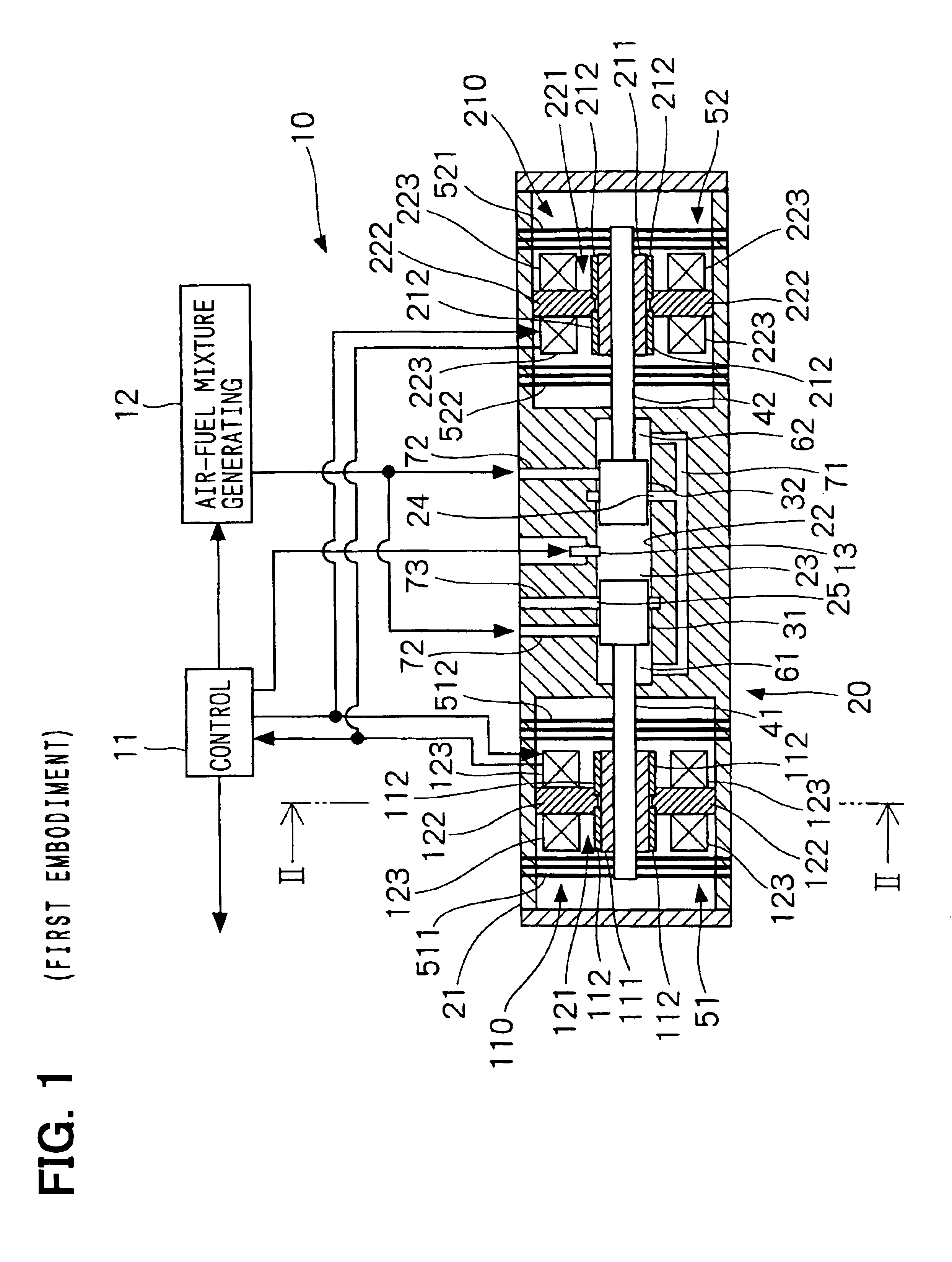
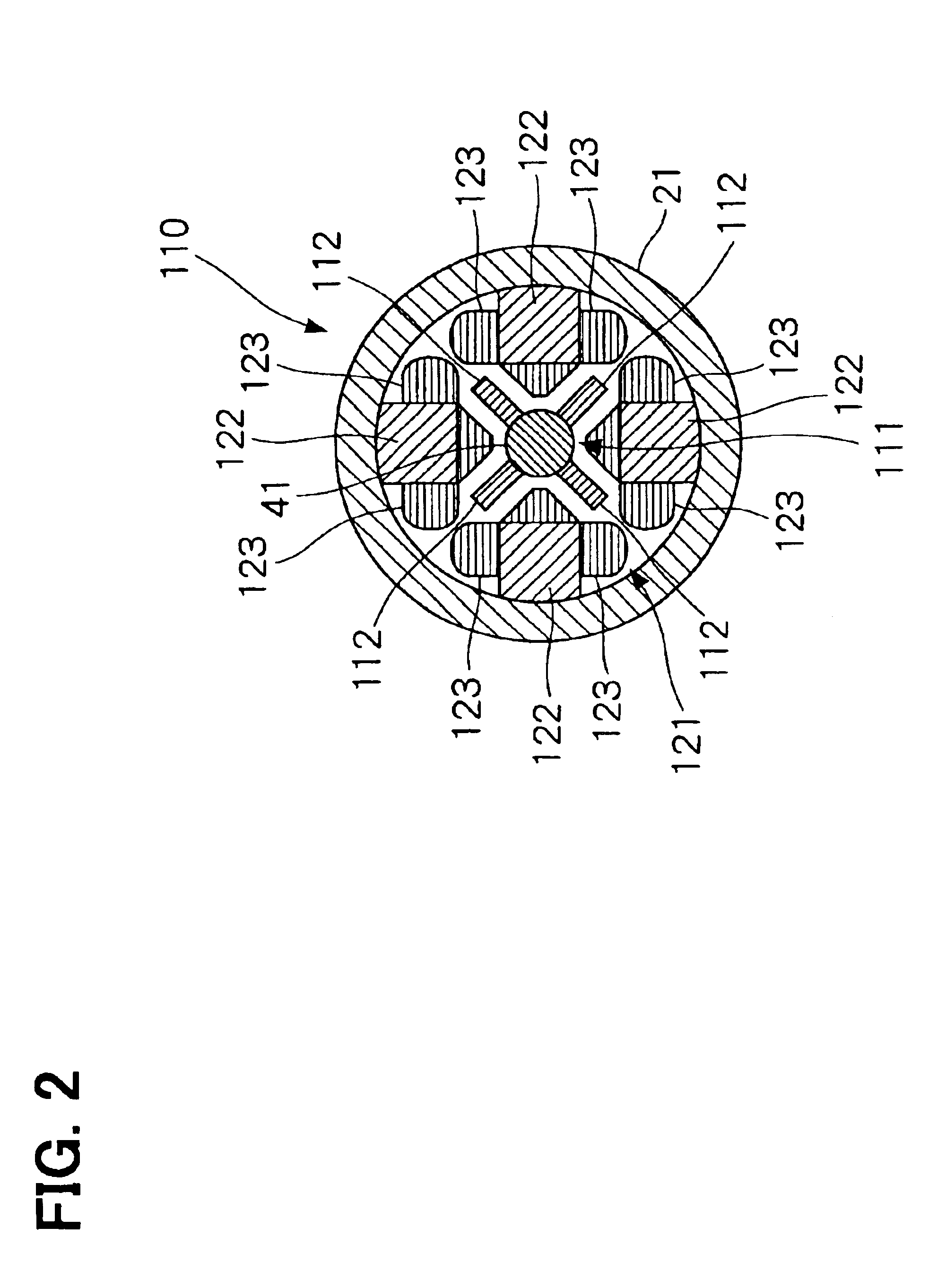
A first piston connected to a first shaft and a second piston connected to a second shaft are supported within a housing by using a first leaf-spring unit and a second leaf-spring unit, respectively. Therefore, axial movement of the first shaft or the second shaft can be allowed, while circumferential rotational movement and radial movement can be restricted. The first leaf-spring unit includes two leaf-spring groups that are disposed in a row around the first shaft in the direction of the axis of the first shaft; similarly, the second leaf-spring unit includes two leaf-spring groups that are disposed in a row around the second shaft in the direction of the axis of the second shaft. Therefore, inclinations of the first shaft and the second shaft can be decreased. This results in reduction in contact between the first and second shafts and a cylinder within the housing and friction due to the contact.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Four-Stroke Free Piston Engine
InactiveUS20080271711A1Expand accessIncrease loadInternal combustion piston enginesFree piston enginesFree-piston engineCombustion chamber
A free piston engine utilizes a shuttle frame external to combustion chambers to rigidly link shuttle parts reciprocating along a centerline. If the shuttle parts are spaced apart along the centerline, the shuttle frame may be struts extending from the shuttle parts and linked by rods. Alternatively the shuttle parts are within a tubular shuttle frame that forms part of the combustion chamber boundary. If one shuttle part is arranged around the other with both centered about the centerline, the shuttle frame may include an annular plate between a cylindrical inner shuttle part and an annular outer shuttle part. Alternatively the shuttle frame may include an inner tube with a cylindrical inner shuttle part within the inner tube, and an outer tube with an annular outer shuttle part arranged between the inner and the outer tubes so that the shuttle frame forms part of the combustion chamber boundary.
Owner:CHEESEMAN PETER CHARLES
Air charging system for an opposed piston opposed cylinder free piston engine
InactiveUS6957632B1Avoid less frictionEfficient chargingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
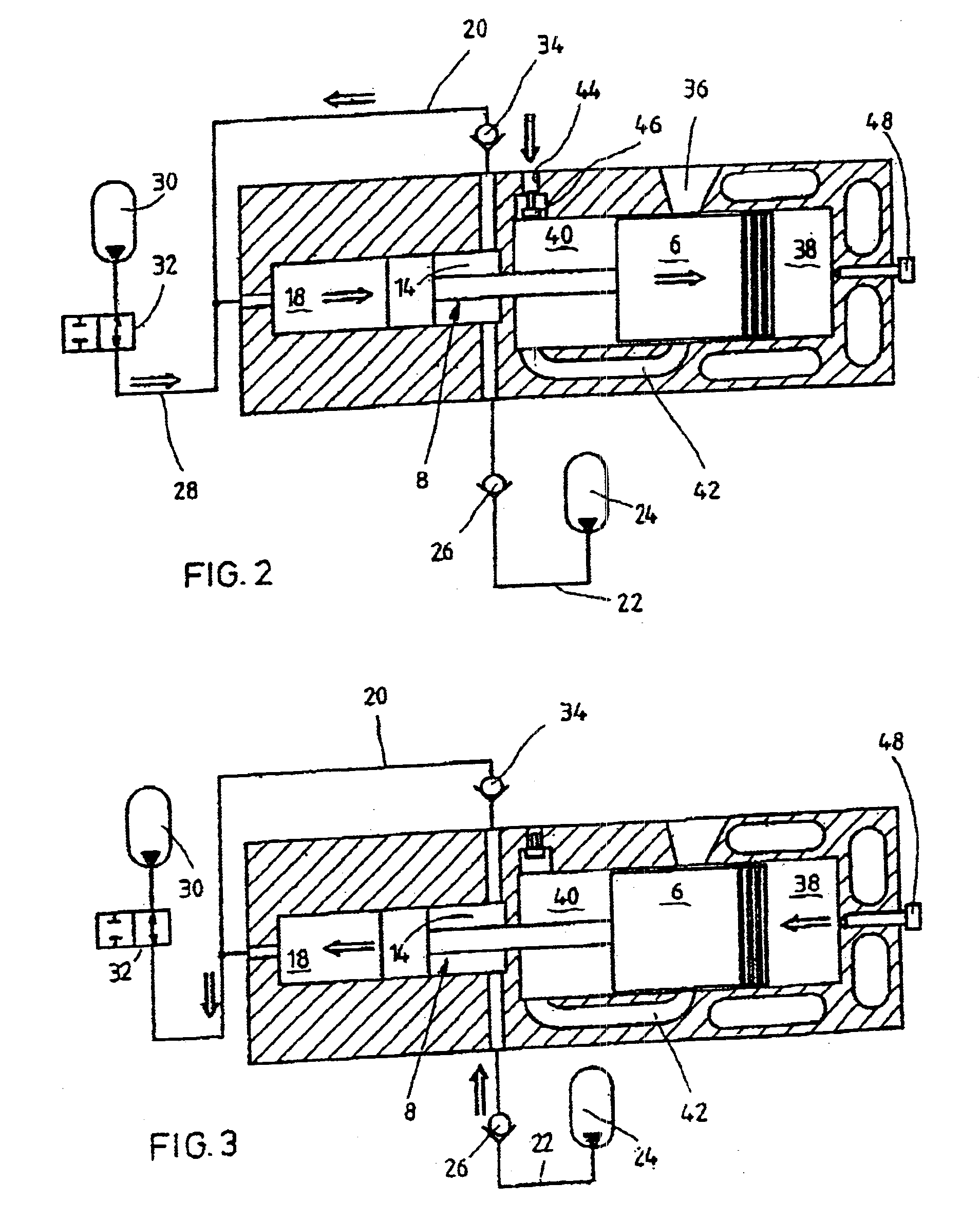
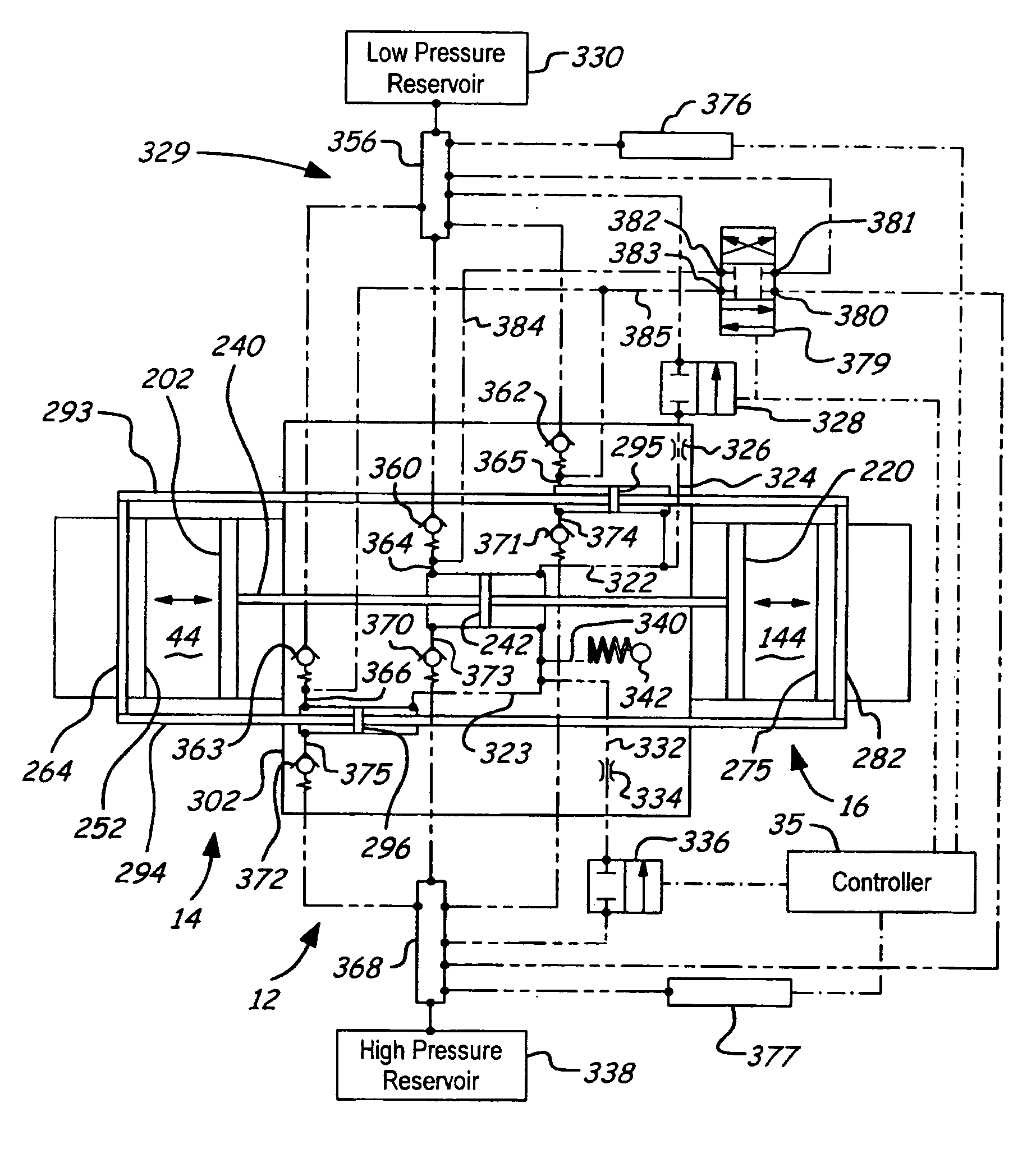
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Each outer piston cooperates with an integrated scavenge pump in order to compress the charge air, thus significantly increasing the air charge density into the engine cylinders for each stroke of the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Exhaust gas recirculation for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6925971B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeNon-fuel substance addition to fuelExhaust gas recirculationFree-piston engineExhaust valve
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. The exhaust ports for each engine cylinder are sized and located to retain the desired amount of internal EGR in each cylinder without the need for exhaust valves. As an alternative, an external EGR system may supplement the internal EGR in order to obtain the desired EGR at the desired temperature.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
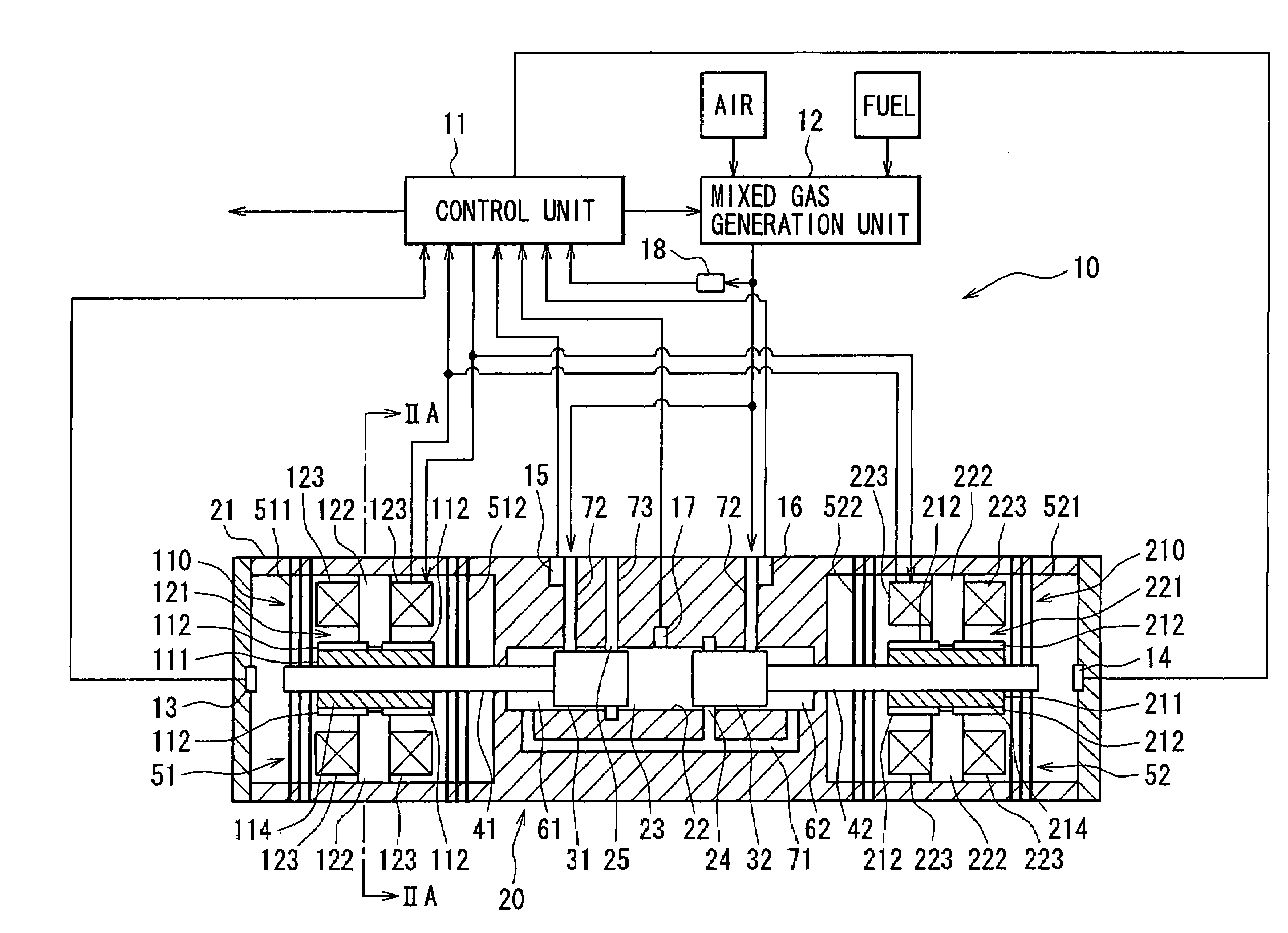
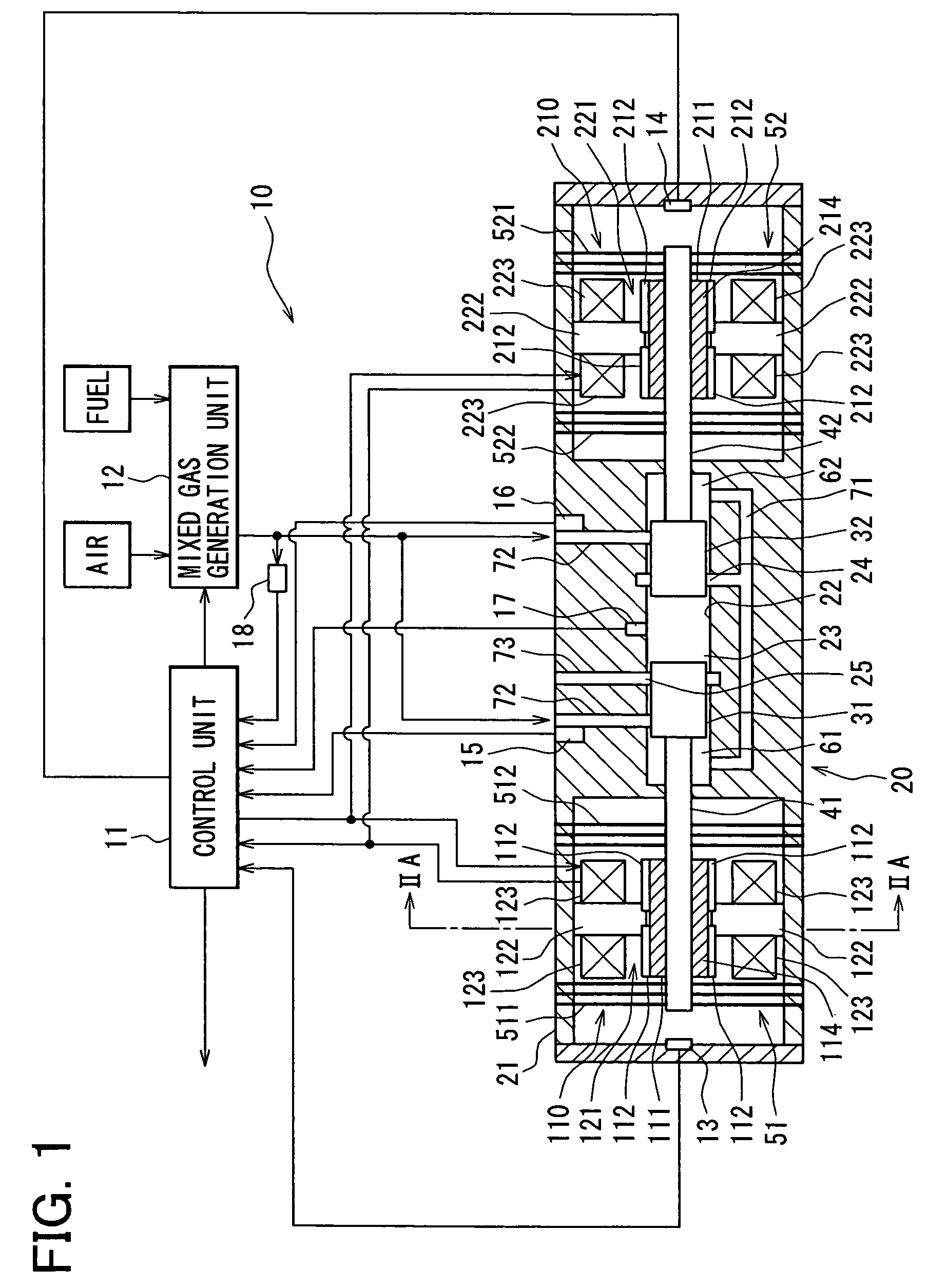
Control device for free piston engine and method for the same
InactiveUS7258085B2Easy to operateEnergy efficiencyFree piston enginesFree-piston engineCombustion chamber
A free piston engine has a pair of pistons opposing to each other and movable in a cylinder, to form a combustion chamber between the pistons. A mixed gas of air and fuel is supplied into the combustion chamber and the mixed gas is auto-ignited when it is compressed by the pistons. A temperature and / or an air-fuel ratio of the mixed gas, and / or a pressure in the combustion chamber is detected to control displacements of the pistons, so that the mixed gas is auto-ignited at an optimum timing to efficiently operate the free piston engine.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Free piston engine and power generation system therewith
InactiveUS6945202B2Reduce outputIncreased durabilityMechanical energy handlingFree piston enginesFree-piston engineLeaf spring
Owner:DENSO CORP
Four-cylinder, four-cycle, free piston, premixed charge compression ignition, internal combustion reciprocating piston engine with a variable piston stroke
ActiveUS7258086B2Increase the compression ratioImprove engine efficiencyElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFree-piston engineHomogeneous charge compression ignition
A four-cycle, four-cylinder, premixed charge compression ignition internal combustion reciprocating free piston engine with a variable piston stroke and a compression ratio that varies as needed to provide charge ignition, to offer the potential of higher efficiency, lower emissions, and multi-fuel operation. The engine does not have a crankshaft, and therefore does not provide direct rotary output. Instead its free pistons oscillate, in a manner similar to a two cycle free piston engine. For many applications, such as piston pumps and compressors, the engine provides an output directly driven by the oscillating pistons. In other applications, such as but not limited to use as a gas generator for a power turbine, the engine provides an indirect means of producing rotary power. When the engine is used with high-speed power turbines, the power turbine may be directly coupled to a high-speed alternator for electrical power output.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE ENERGY TECH DEV TRUST
Position sensing for a free piston engine
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also connected between the pistons are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the inner piston assembly. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also engaging the outer piston assembly are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the outer piston assembly. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
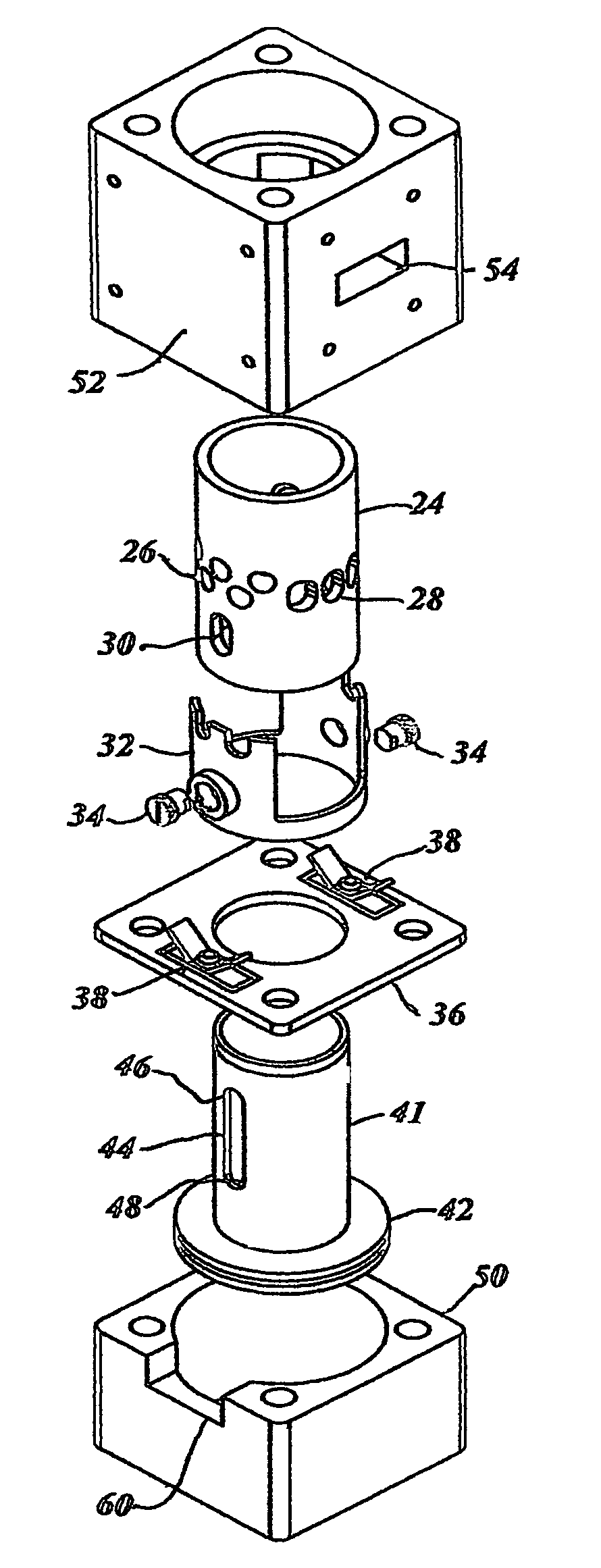
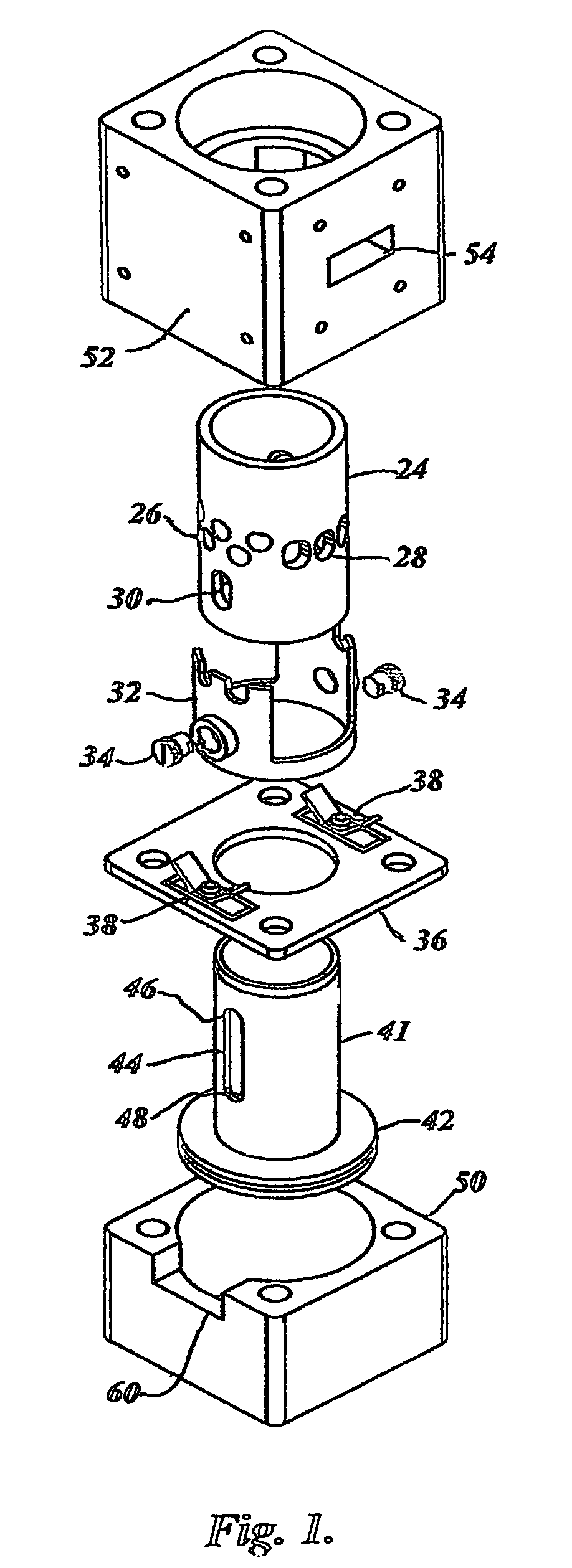
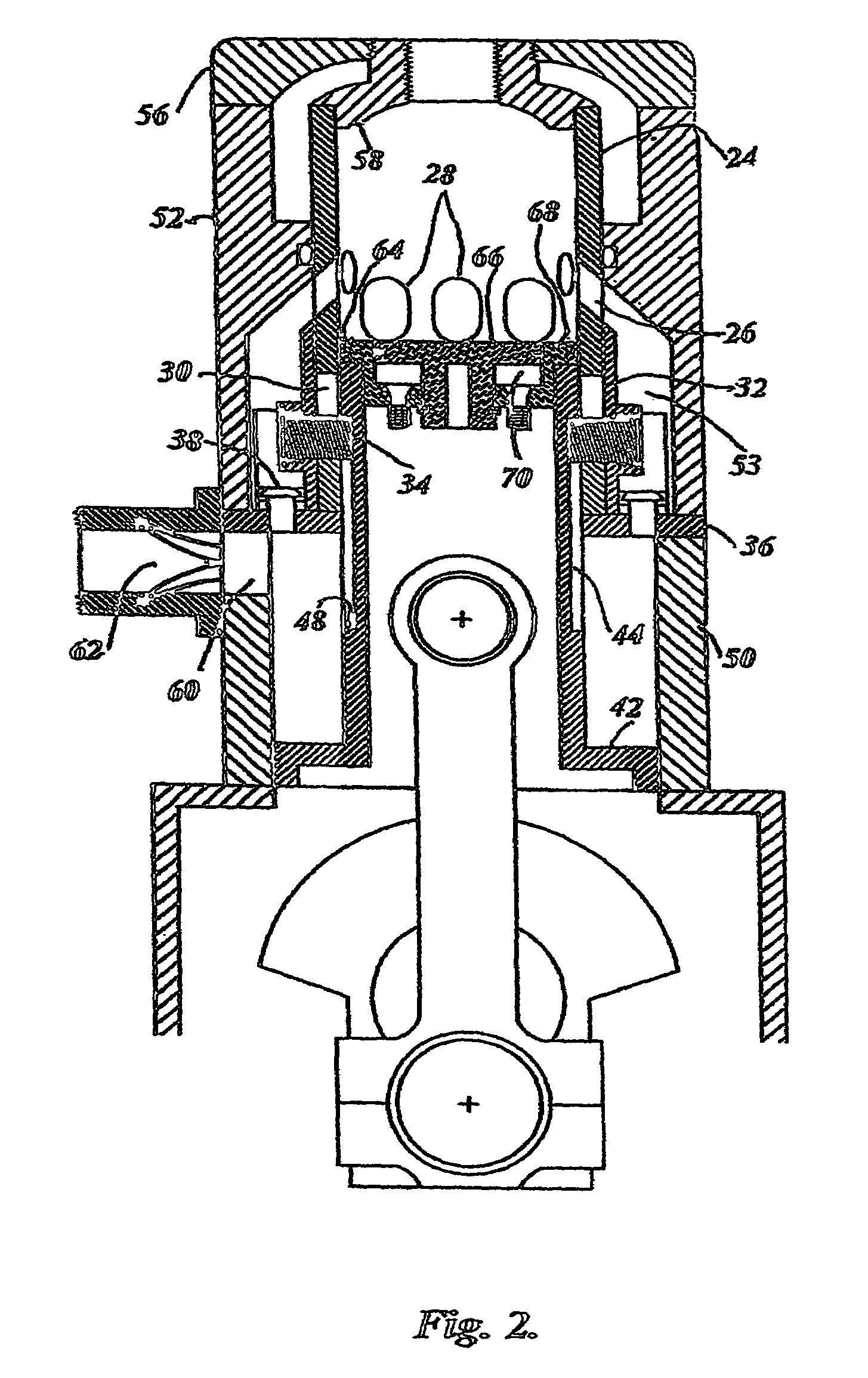
Single-piston type hydraulic free piston engine
InactiveCN101363397AReduce axial sizeSolve unfavorable situations such as economic deterioration and emission deteriorationReciprocating piston enginesFree-piston engineEnergy transfer
The invention discloses a single-piston type hydraulic free piston engine; in the invention, a traditional reciprocating piston internal combustion engine and a plunger-typed hydraulic pump are integrated into a whole, a pump piston and two compression pistons are simultaneously and directly connected with a power piston in a rigid manner to form a piston component, therefore, a crank link mechanism which can transform the reciprocating movement of the pistons into rotary motion in the internal combustion engine, and a swash plate mechanism which can transform the rotary motion of the pistons into reciprocating movement in a plunger pump can be omitted, and the piston of the internal combustion engine is directly connected with the plunger of the hydraulic pump in a rigid manner. By adopting the technical proposal of the invention, a driving chain can be shortened, the repeated transformation between different movement forms can be omitted, the energy transfer form between an engine and a drive system can be optimized, and the soft readjustment of a power drive unit can be realized.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
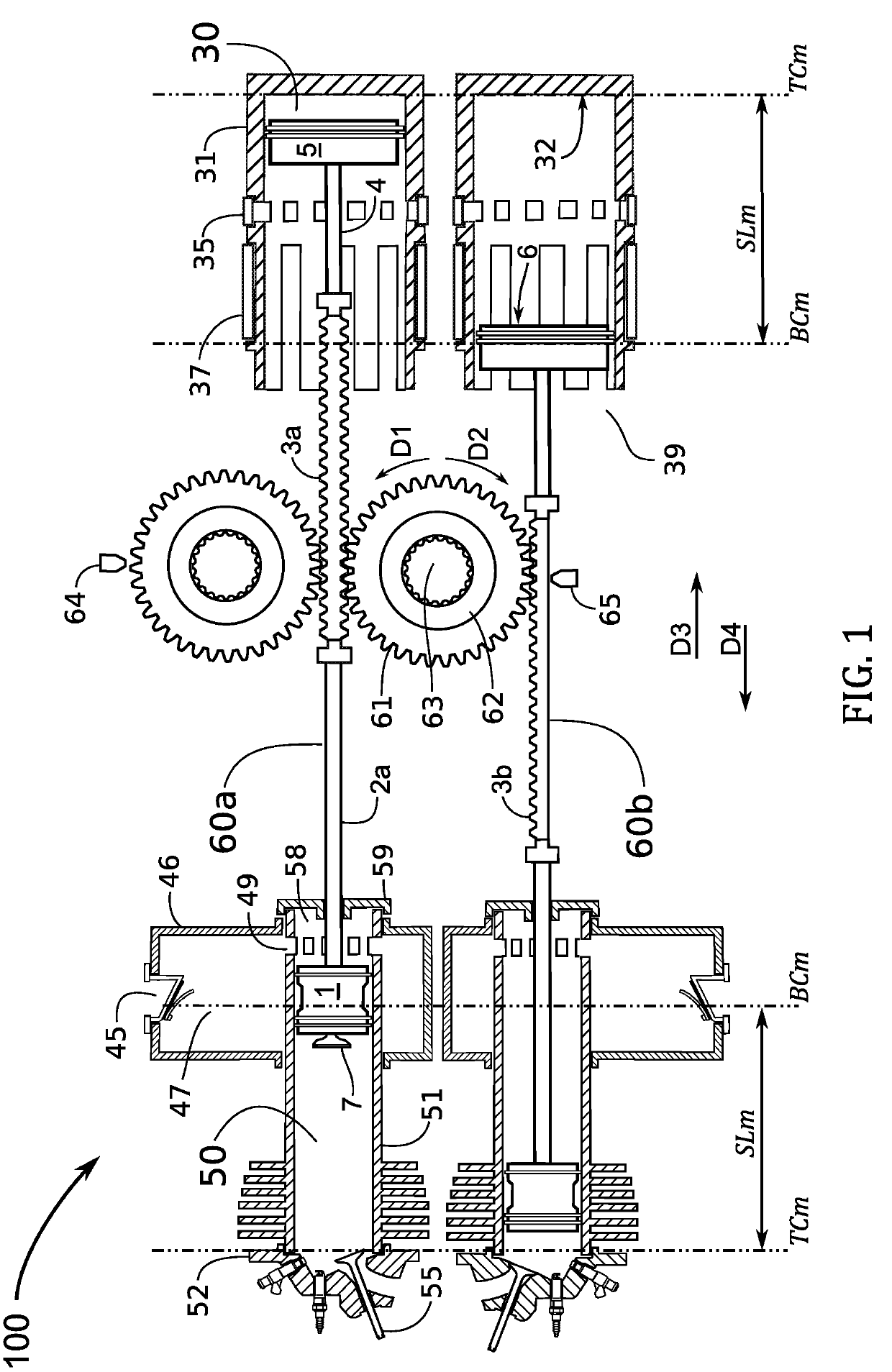
Quasi Free Piston Engine
A quasi free piston engine uses, a small, lightweight crankshaft to connect the piston assemblies of the free piston engine with a flywheel. While most of the power output from the combustion pistons is extracted by pumping pistons as hydraulic power, the small crankshaft and flywheel ensure exact TDC position of the combustion pistons in operation, and provide a rotating means to drive combustion cylinder intake and exhaust valves. Flywheel speed may be monitored to provide feedback on power extraction for further control of the system. In addition, a hydraulic push-rod system for efficient valve actuation is provided.
Owner:UNITED STATE OF AMERICA AS REPRESENTED BY THE ADMINISTATOR OF THE U S ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION AGENCY THE
Method and device for monitoring the direction of rotation of a piston engine
InactiveUS6975935B2Simple wayAnalogue computers for vehiclesElectrical controlFree-piston engineInlet channel
A method and device for detecting the rotation direction of a piston engine, internal combustion engine or piston compressor. The piston engine includes at least one cylinder, a piston movable back and forth in the cylinder, a cylinder chamber formed inside the cylinder which is delimited by an inner cylinder wall and the piston, an inlet channel opening into the cylinder chamber via at least one inlet valve, an outlet channel opening into the cylinder chamber via at least one outlet valve, and at least one triggerable throttling device situated in the inlet channel. To detect the rotation direction in a reliable, timely, and simple manner, the pressure prevailing in the inlet channel is measured when a rotary motion is detected, compared with a predefinable threshold value, and the rotation direction is determined based on the comparison result, the throttling device being closed at least for the pressure measurement time.
Owner:ROBERT BOSCH GMBH
Two stroke, opposed-piston engines with engine braking
ActiveUS20120210985A1Simple and inexpensiveHigh trafficInternal combustion piston enginesNon-fuel substance addition to fuelFree-piston engineSwing-piston engine
In a two-stroke opposed-piston engine, a ported cylinder with a pair of opposed pistons is equipped with an engine brake including an engine braking valve that can be opened to release air from the cylinder as the pistons cycle between BDC and TDC positions.
Owner:ACHATES POWERS INC
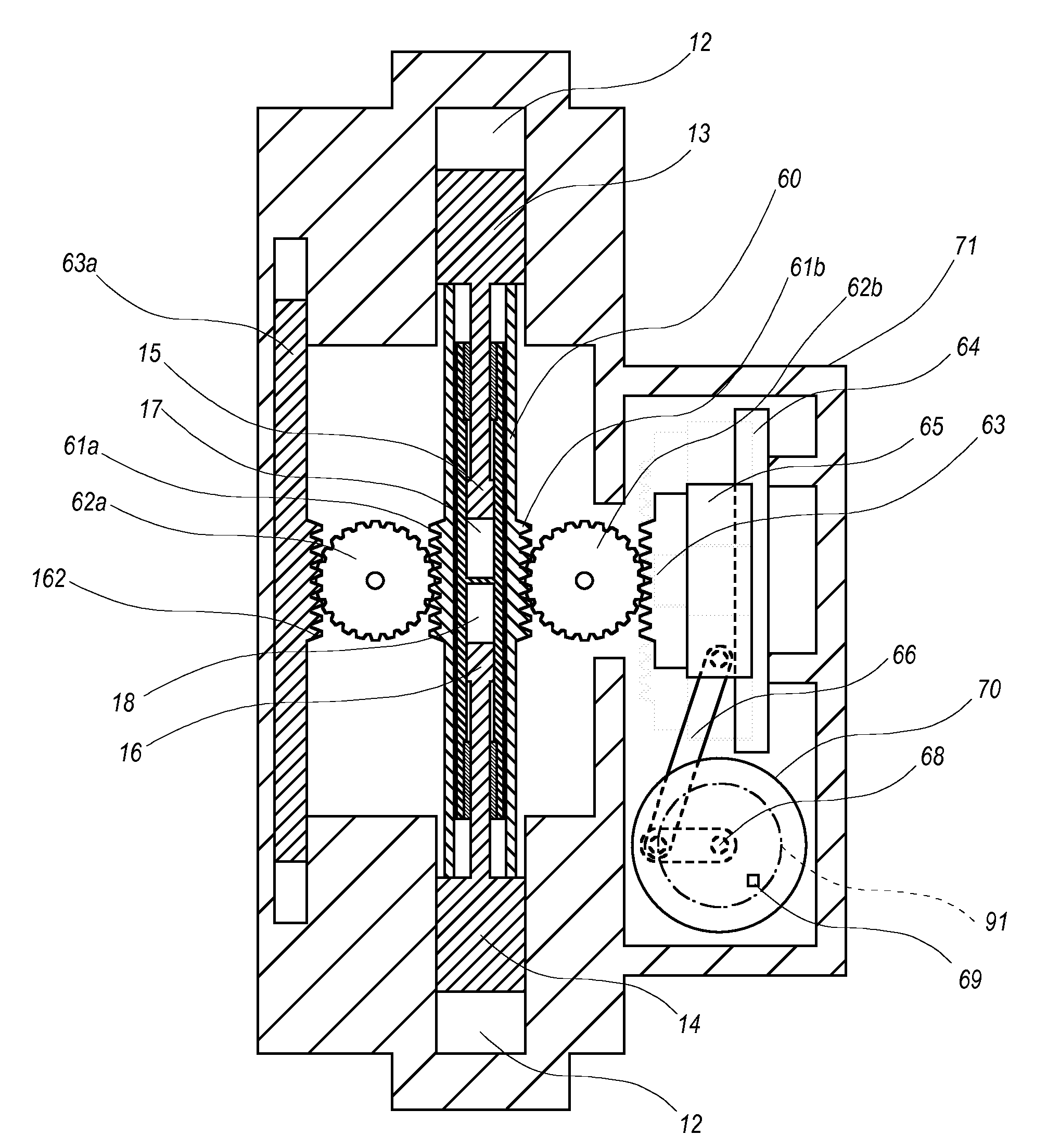
Piston guides for a free piston engine
InactiveUS20050284426A1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeFree piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Piston guide posts are fixed and guide the outer pistons as they reciprocate within the engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Piston guides for a free piston engine
InactiveUS7032548B2More balancedEfficient chargingFree piston enginesFree-piston engineReciprocating motion
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Piston guide posts are fixed and guide the outer pistons as they reciprocate within the engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Internal combustion engine
ActiveUS20080087255A1Improve thermal efficiencyAvoid knockingInternal combustion piston enginesOutput powerFree-piston engineTop dead center
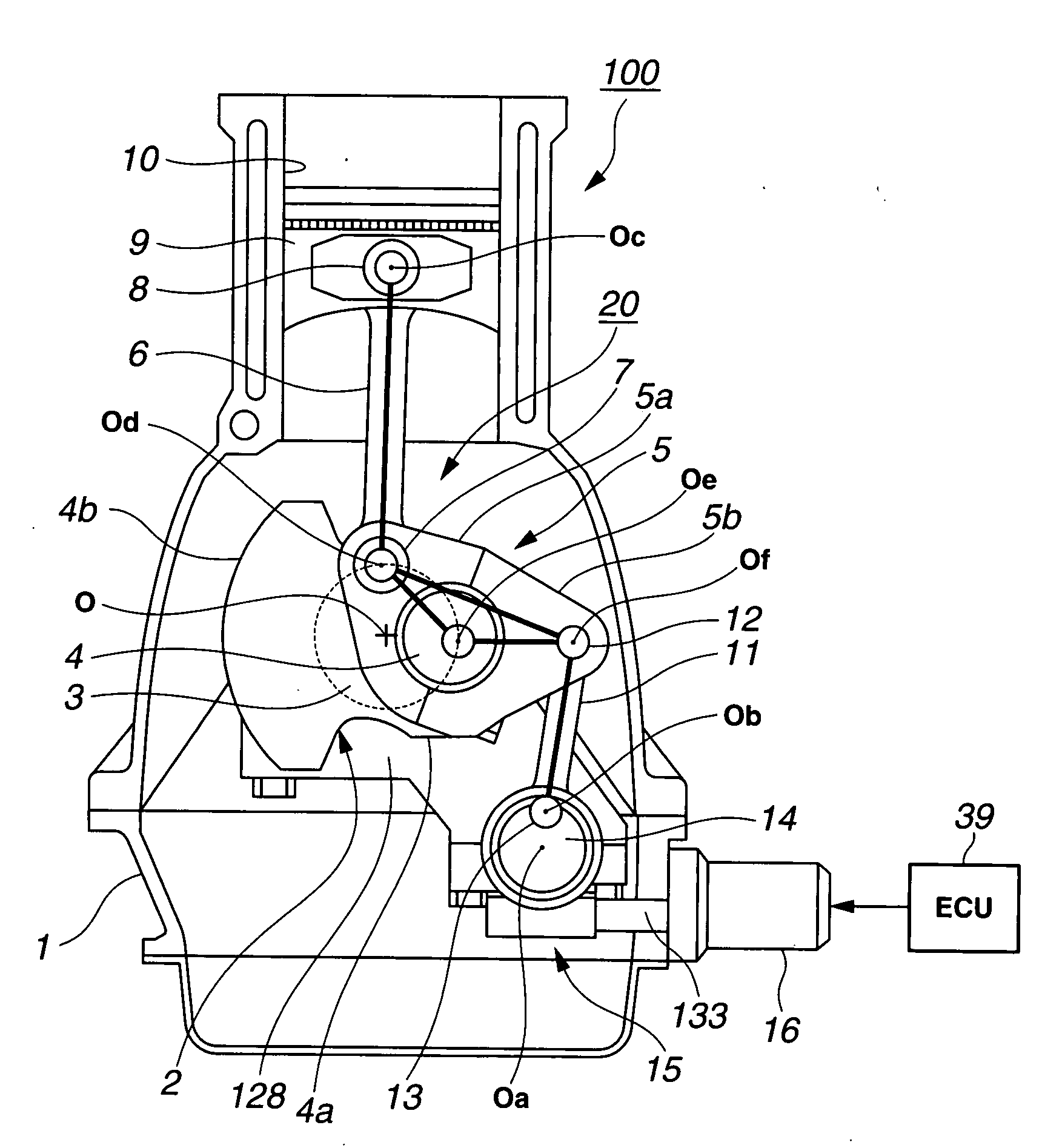
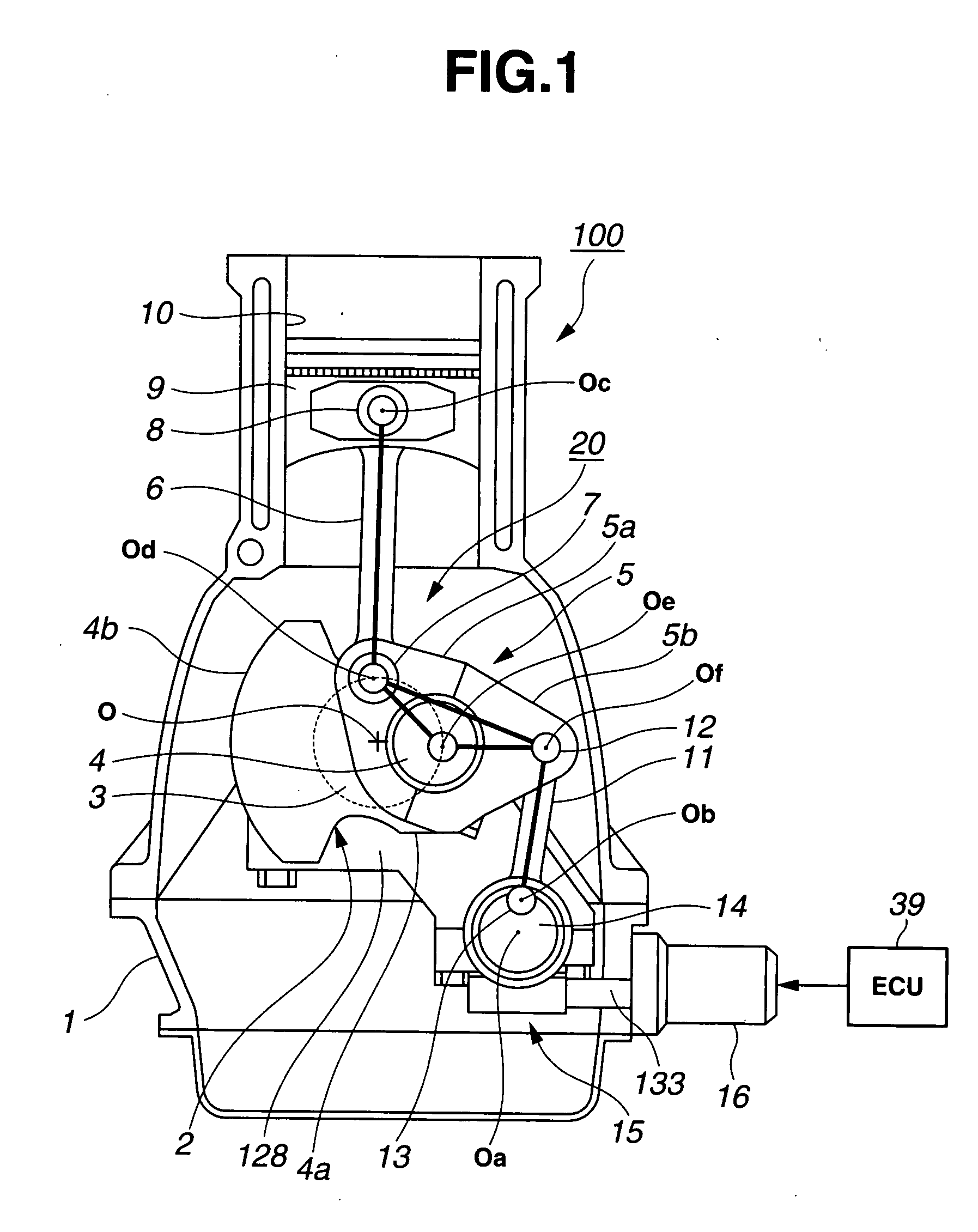
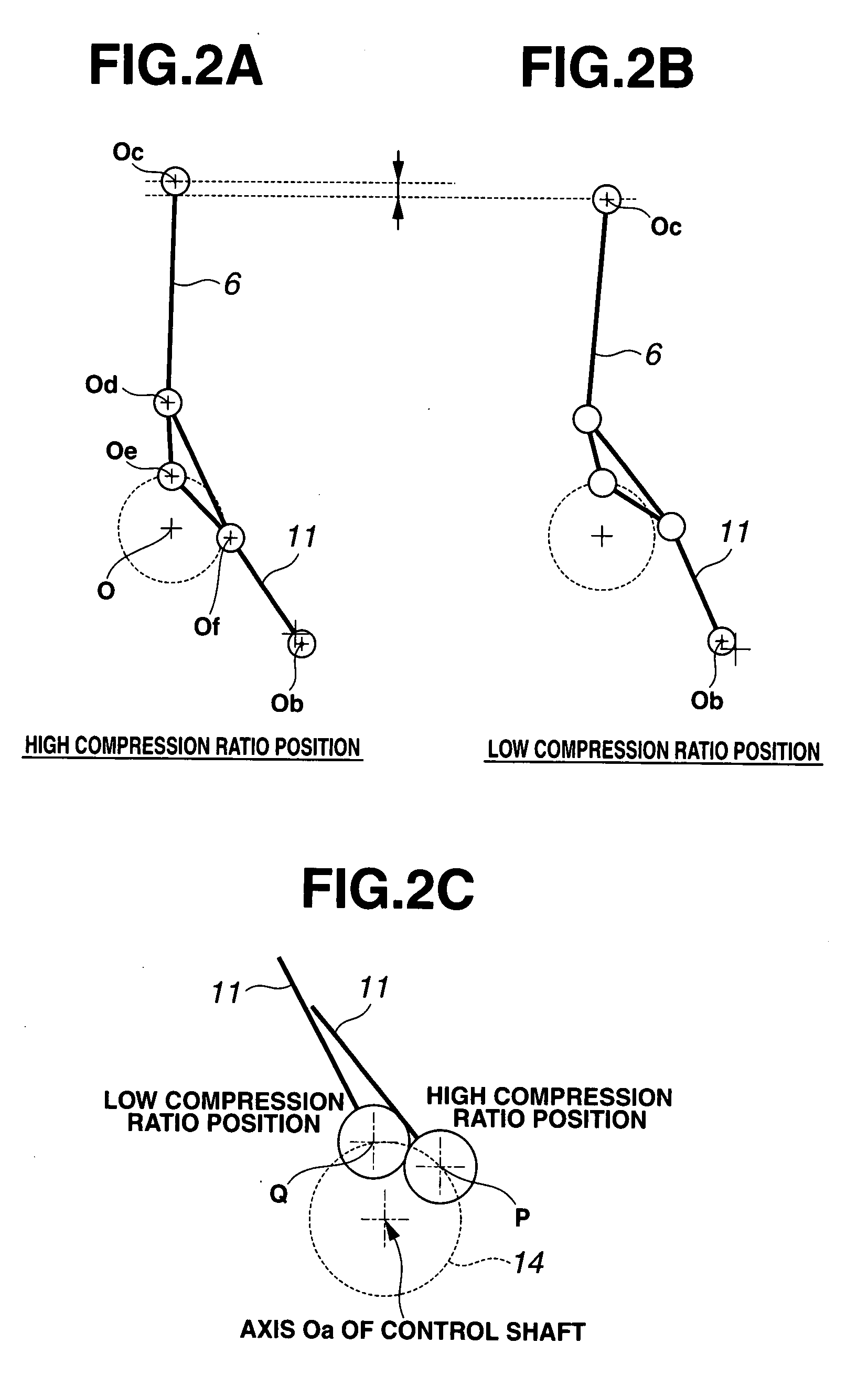
In a reciprocating piston engine employing a variable compression ratio mechanism configured to be linked to a reciprocating piston for variably adjusting a geometrical compression ratio by varying at least a top dead center position of the piston responsively to a controlled variable, a controller is configured to control the variable compression ratio mechanism depending on an engine operating condition. A part of a wall surface of a combustion chamber is formed of a non-metallic material having a higher heat-insulating and heat-reserving property as compared to a base structural material of each of the combustion chamber and the piston.
Owner:NISSAN MOTOR CO LTD
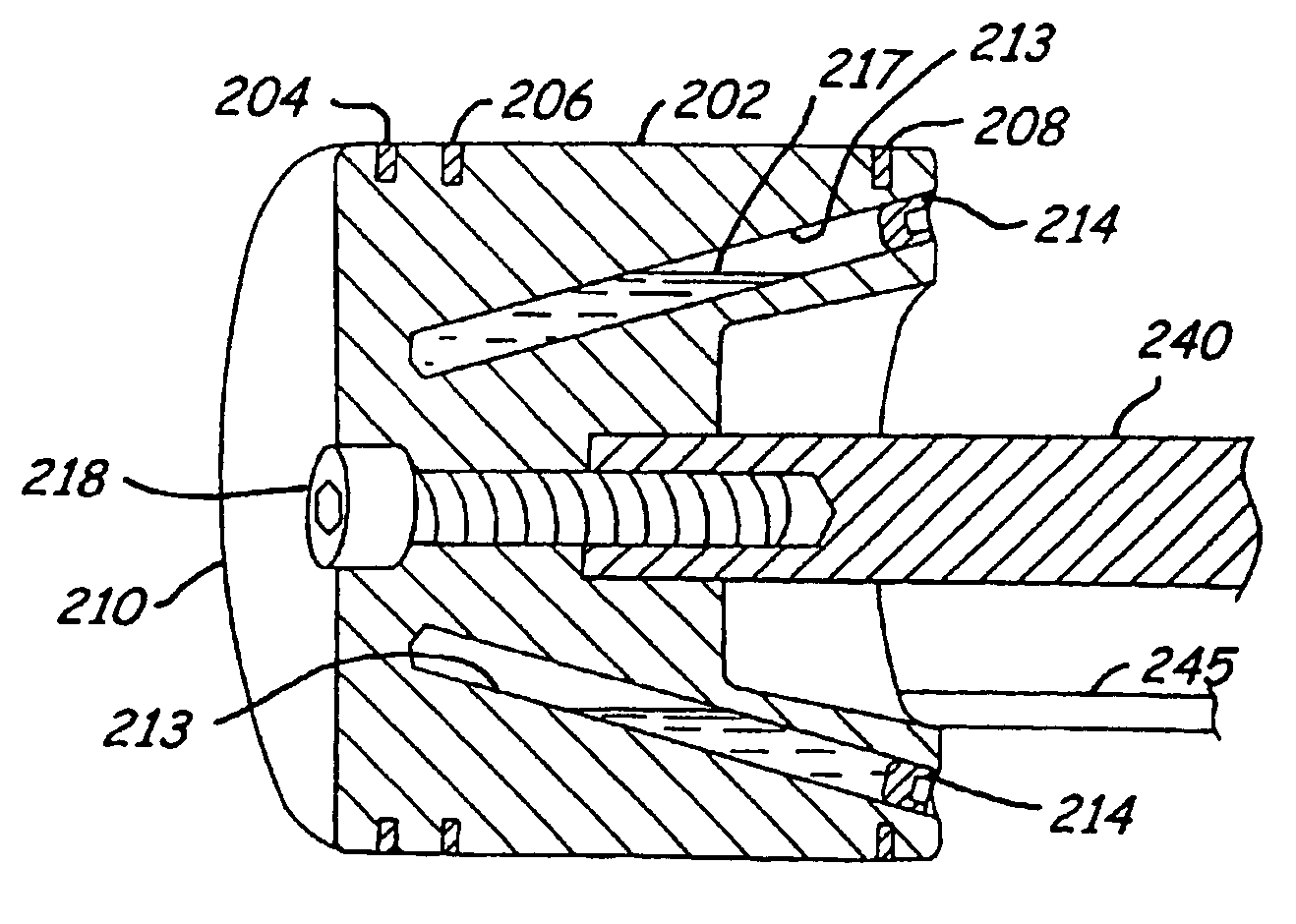
Free piston engine and self-actuated fuel injector therefor
InactiveUS20020092485A1Fuel injection apparatusFree piston enginesFree-piston engineCombustion chamber
Owner:ALEXIUS RICHARD C +1
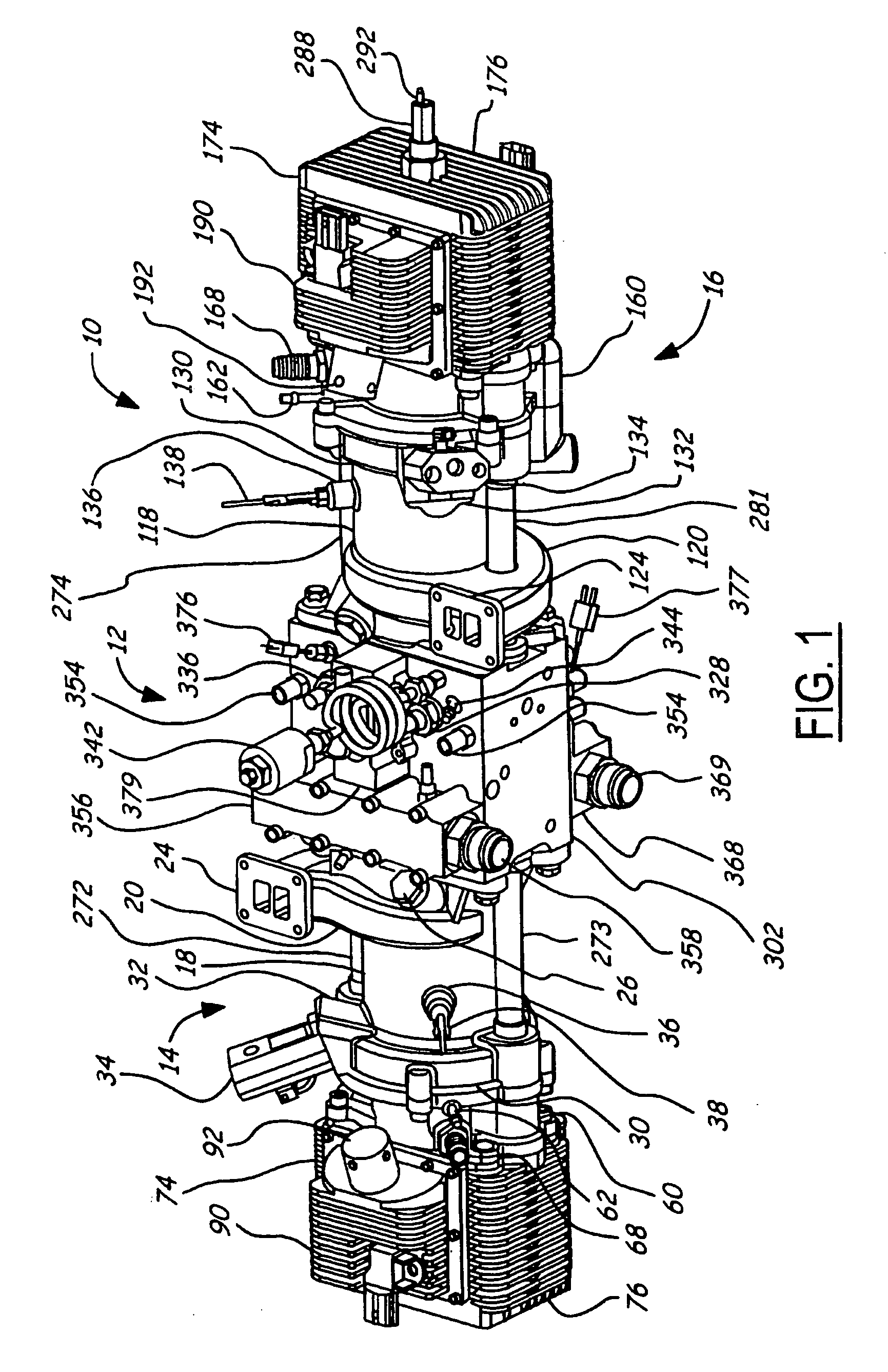
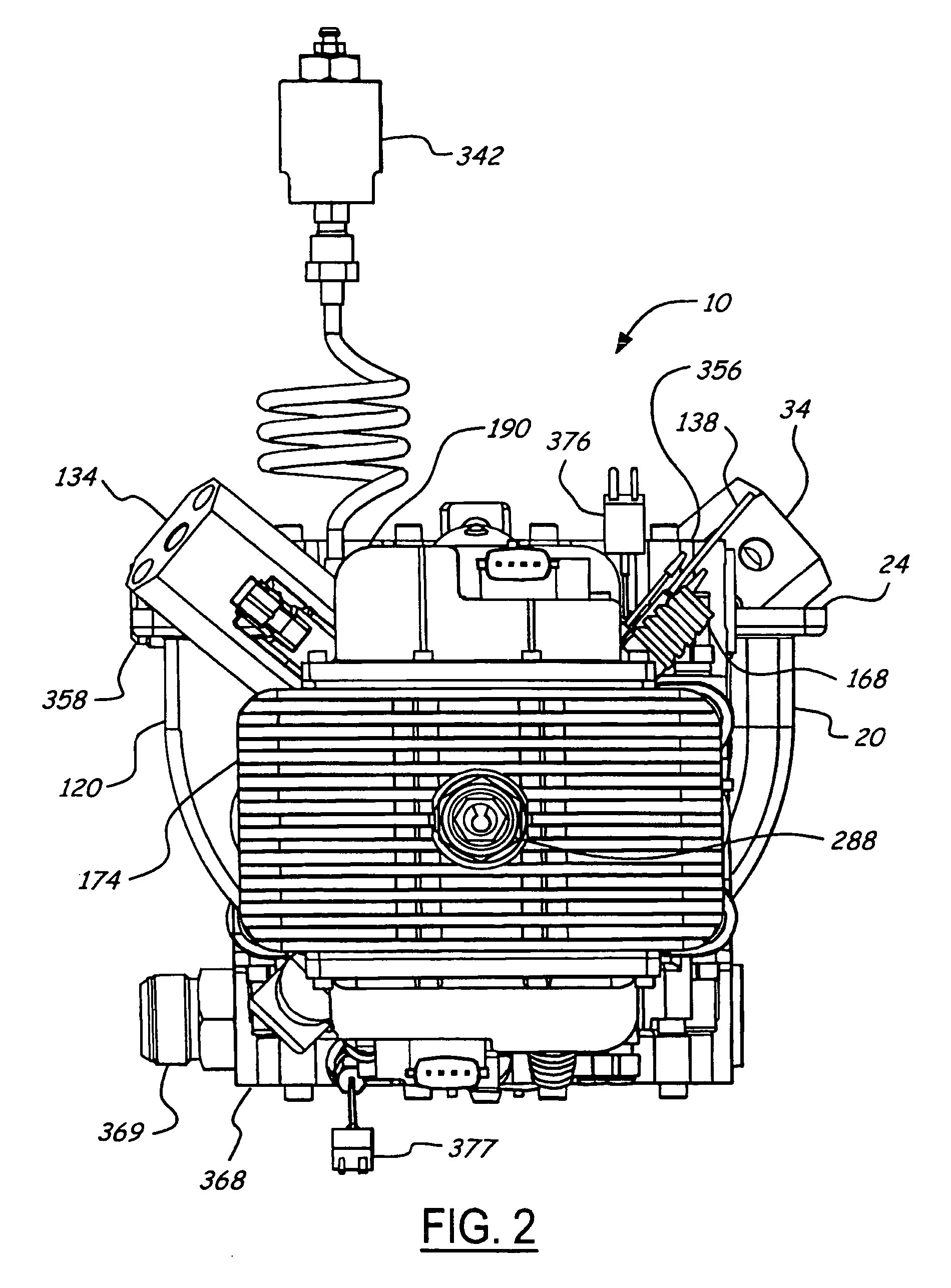
Free piston engine
InactiveUS6931845B2Reduce spendingLow production costFluid couplingsFree piston enginesFree-piston engineEngineering
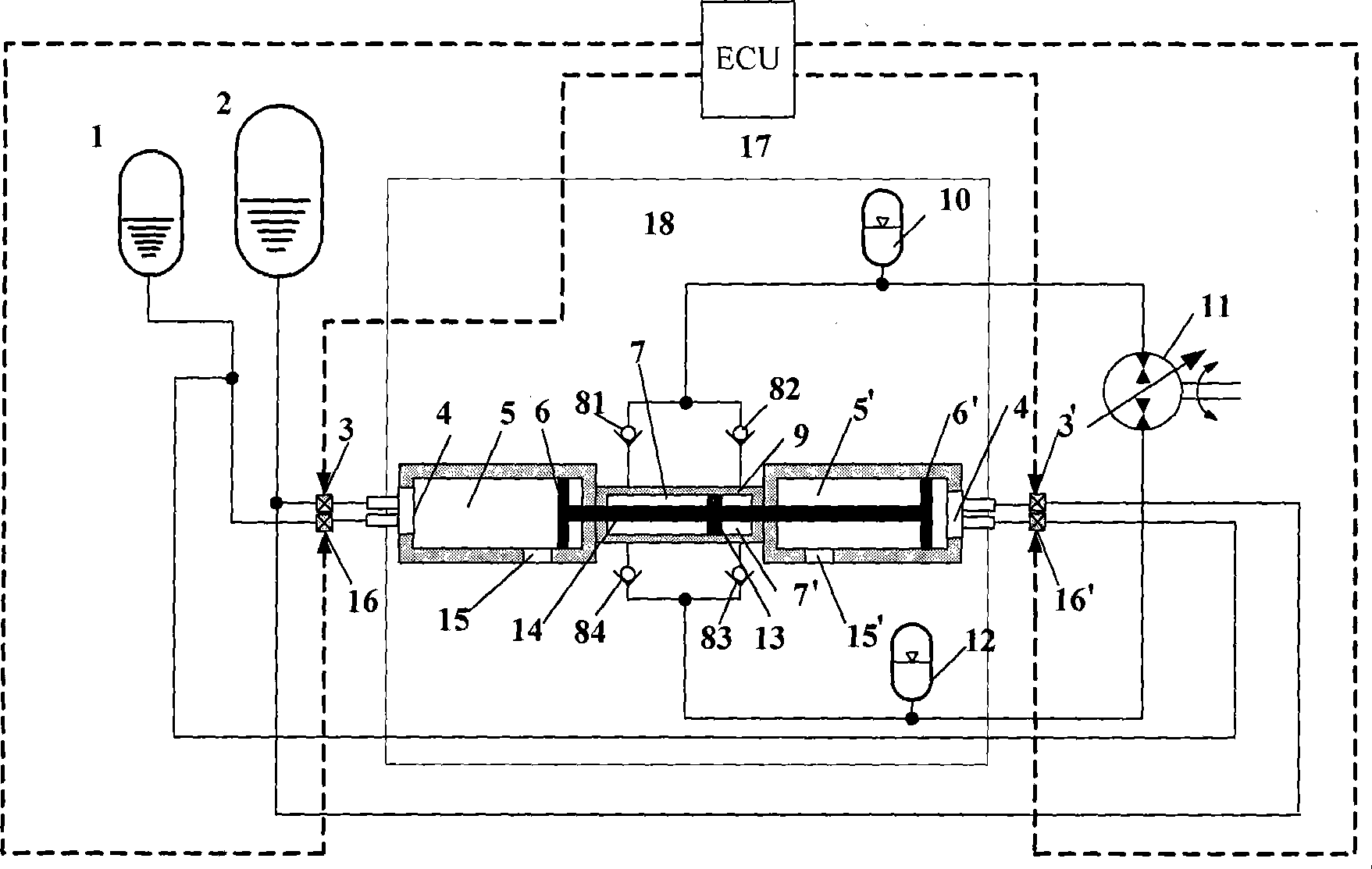
A free-piston engine has a stepped piston having a larger end face thereof guided in the compression cylinder, and a smaller end face in the work cylinder. Both the work cylinder and the compression cylinder are connected with a common high-pressure accumulator for initiating the compression stroke or for charging during the expansion stroke.
Owner:BOSCH REXROTH AG
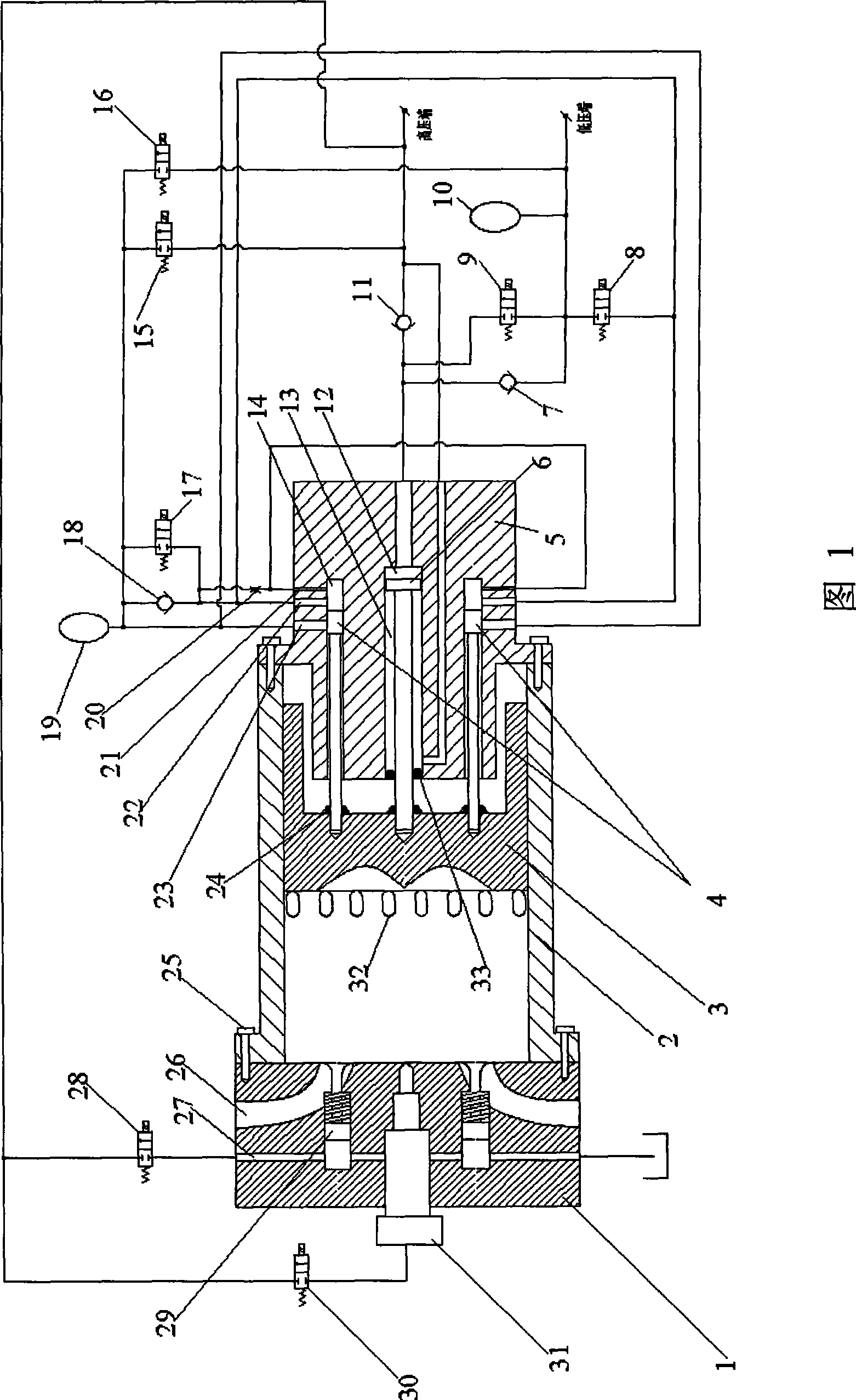
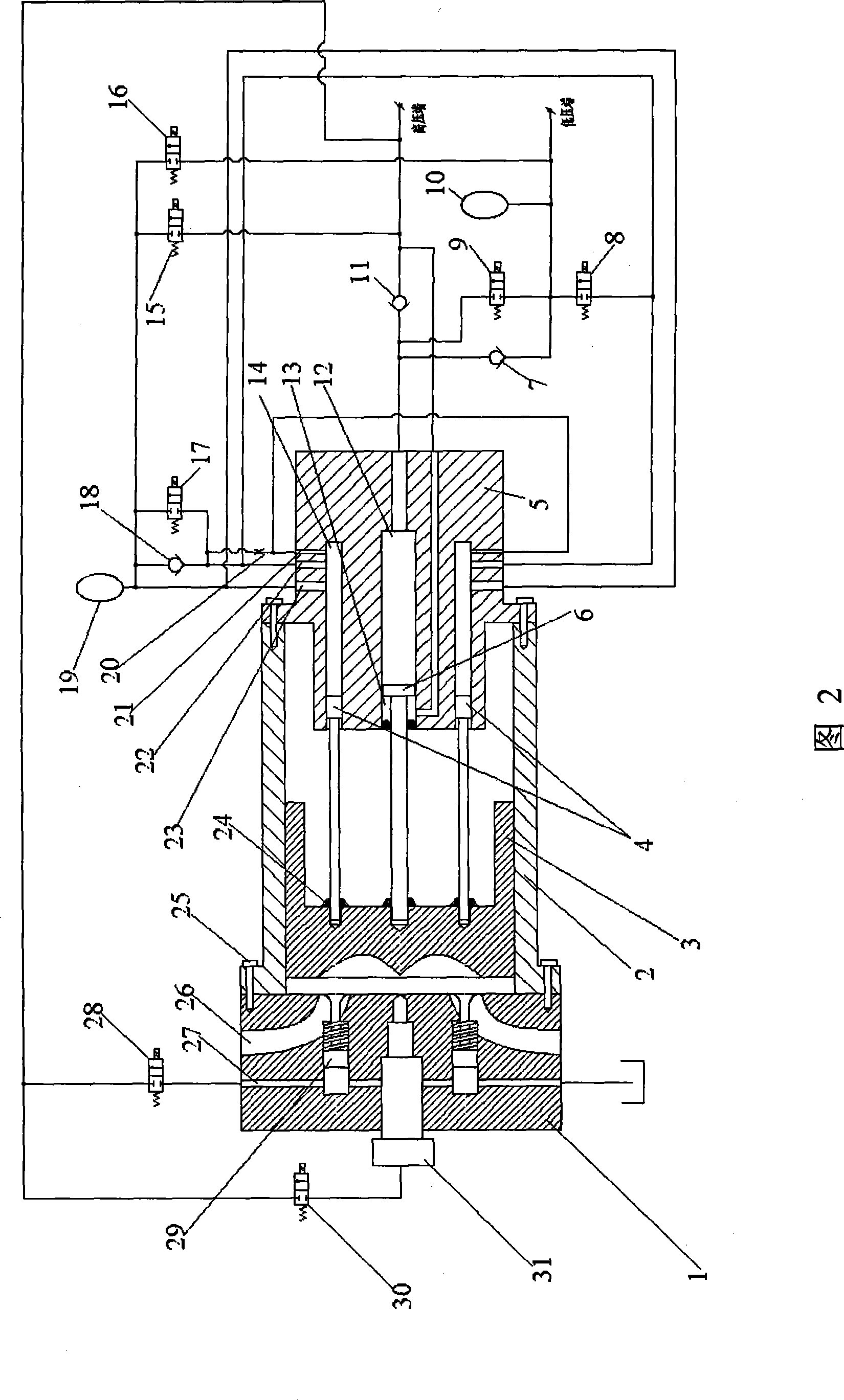
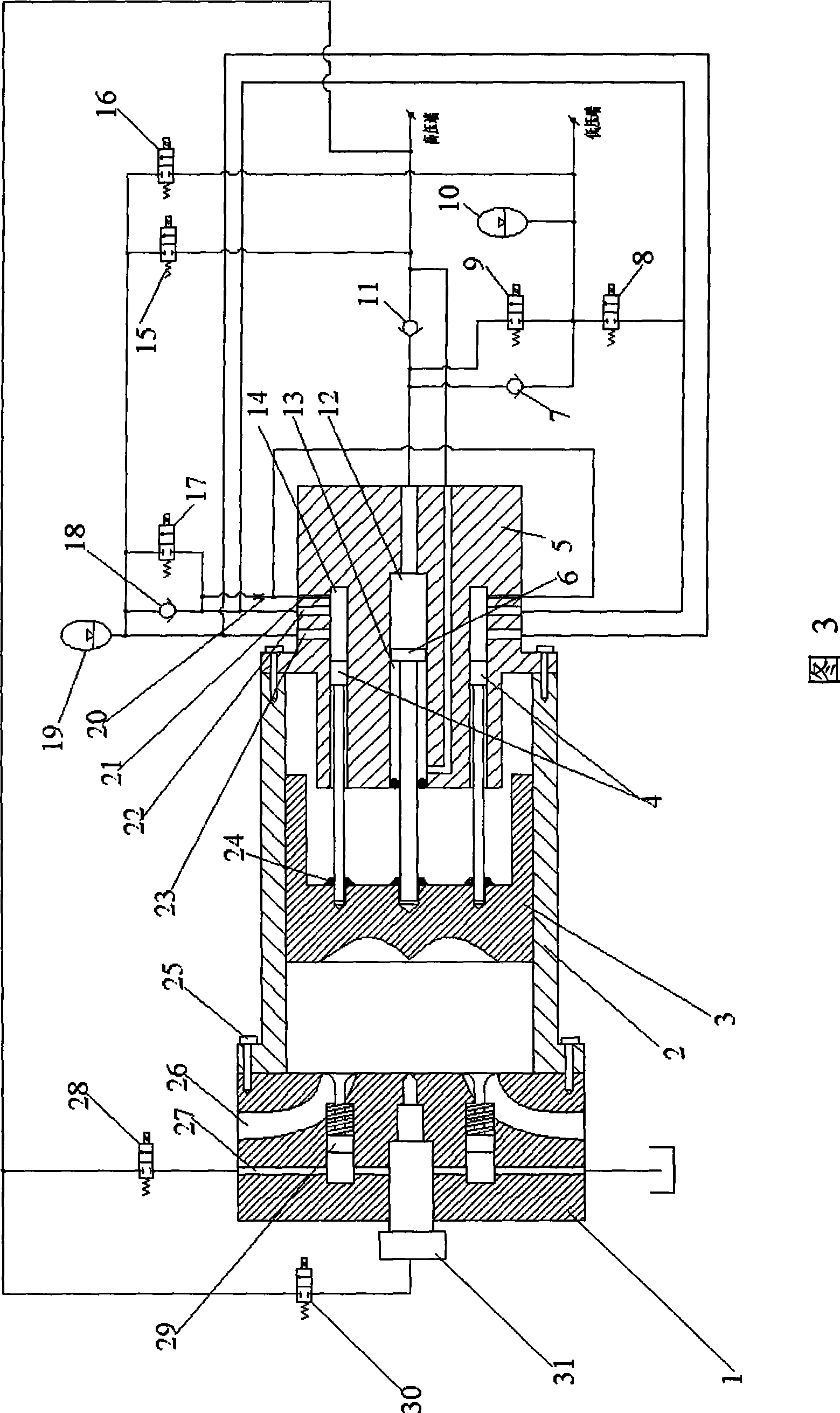
Free piston engine
ActiveCN104329164AStable pressureStable pressure supplyFree piston enginesFree-piston engineCombustion chamber
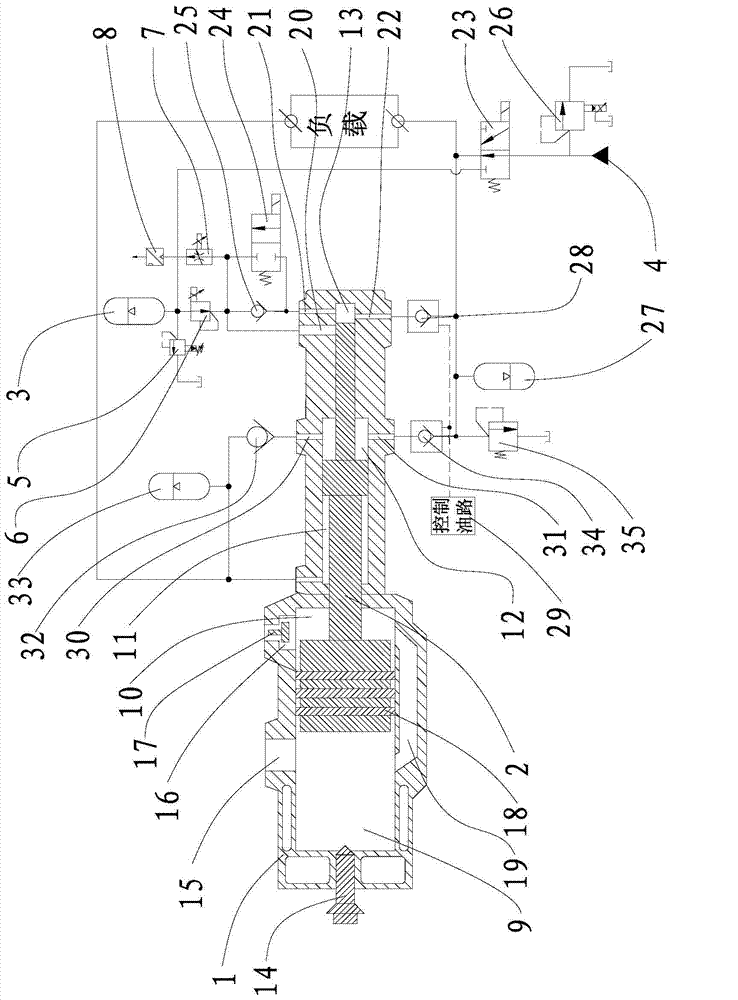
The invention provides a free piston engine, which comprises a cylinder block, a compression accumulator, a pump station and a piston assembly, and also comprises a first proportional overflow valve, a proportional pressure reducing valve, a proportional velocity regulating valve and a pressure sensor; a piston chamber in the cylinder block is divided into a combustion chamber, an air intake chamber, a balance chamber, a pump chamber and a compression chamber by the piston assembly. As a pipeline connected with two inlets of a compression main port and a compression starting port of the compression chamber and the compression accumulator is provided with the proportional pressure reducing valve, the proportional velocity regulating valve, a reversing valve, the proportional overflow valve and the pressure sensor, according to the detection signal of the pressure sensor connected with the compression accumulator, the reversing valve is switched between the compression accumulator and an oil supply accumulator, and therefore oil supply work on high and low-pressure two oil lines is completed by utilizing one hydraulic pump station; moreover, after hydraulic oil in the compression accumulator flows through the proportional pressure reducing valve, stable pressure can be obtained and supplied for the compression chamber, so that the pressure of the inlet of the compression chamber is stable.
Owner:HUAQIAO UNIVERSITY
Opposed piston opposed cylinder free piston engine
InactiveCN1957179AInherently balancedFew moving partsAuxillary drivesElectric propulsion mountingFree-piston enginePump chamber
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Hydraulic synchronizing coupler for a free piston engine
InactiveUS20060042575A1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeFree piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. A hydraulic coupler in communication with the pumping chambers will synchronize the motion of the inner and outer piston assemblies to assure that the pistons in the opposed cylinders are operating in opposition to one another.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Sodium cooled pistons for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6904876B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeAir coolingPistonsFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. At least one of the pistons includes one or more generally axially extending bores partially filled with a sodium compound. As the piston reciprocates, the sodium moves back and forth in each cooling bore, thereby better distributing heat in the piston.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
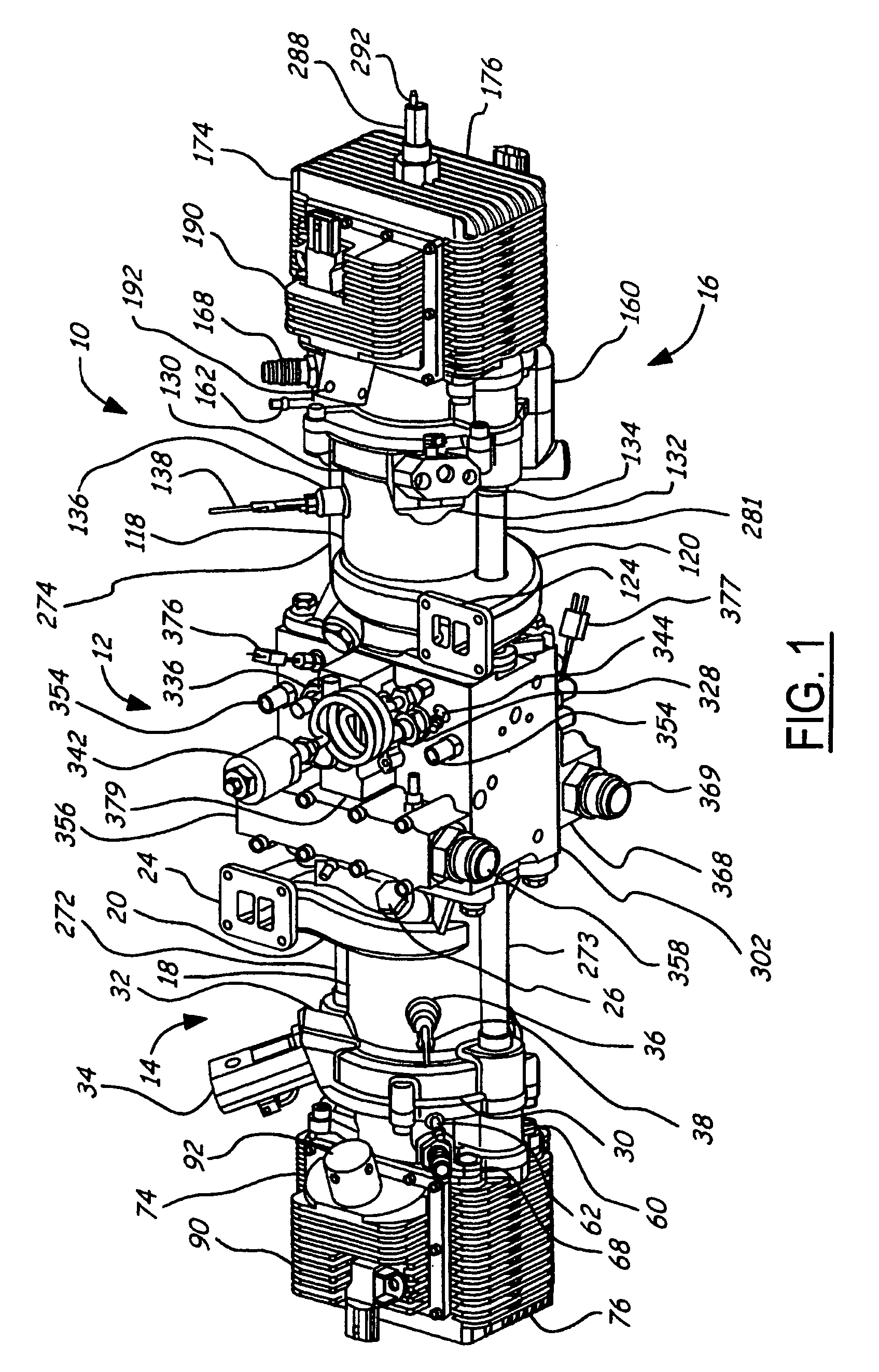
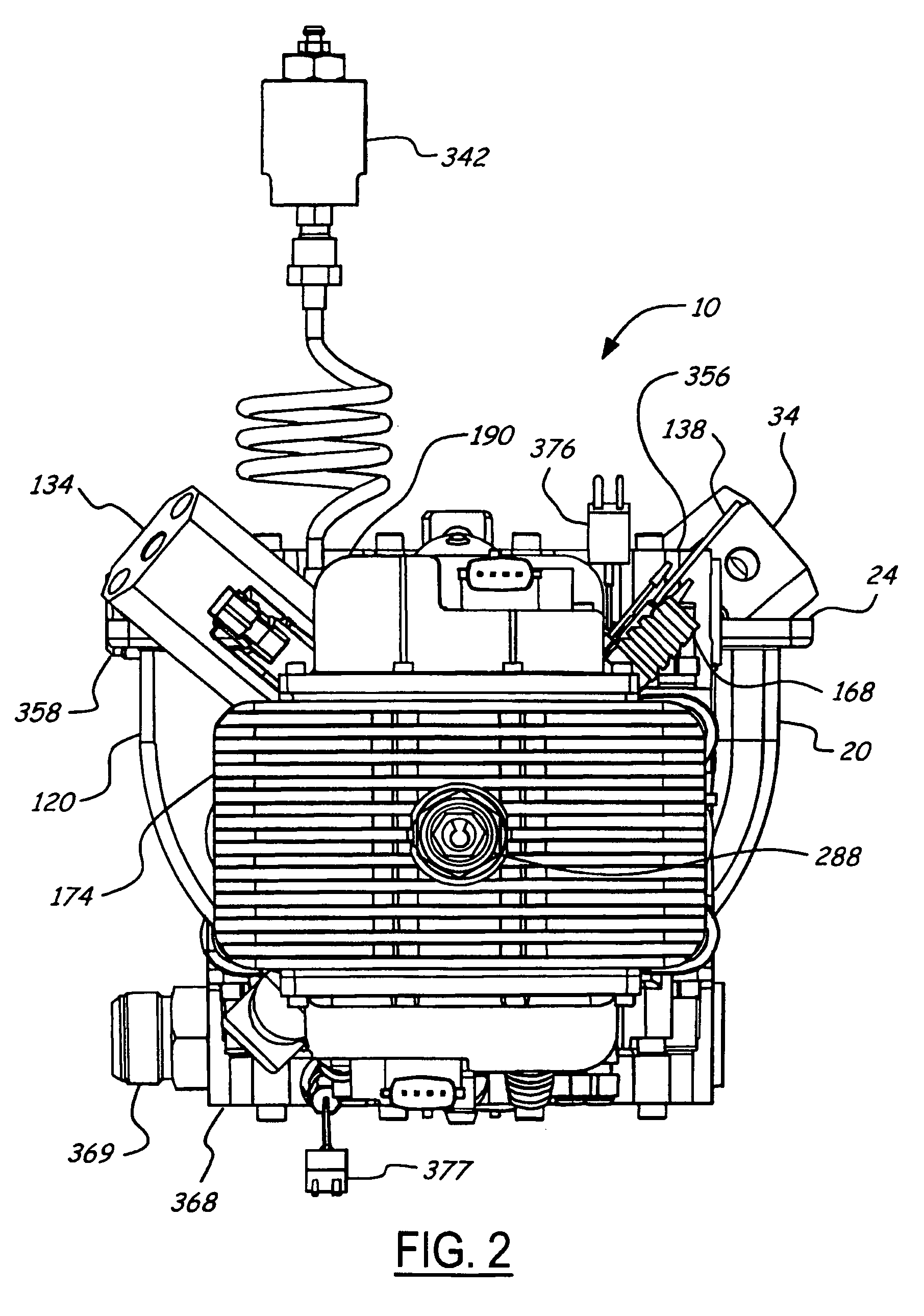
Free-Piston Engine
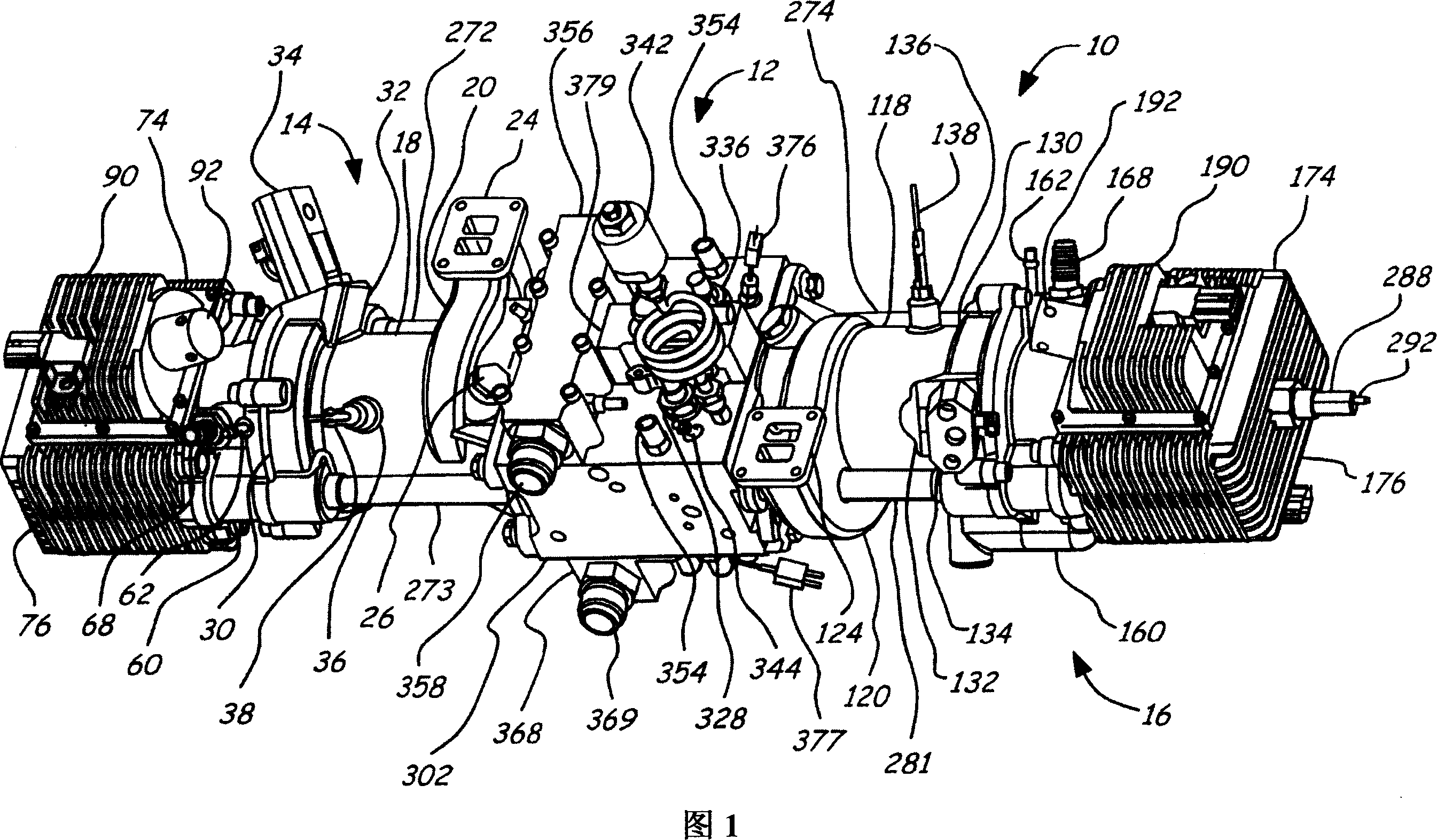
ActiveUS20190153936A1Provide powerPrevent leakageValve drivesCombustion enginesFree-piston engineCombustion chamber
A multicylinder internal combustion free-piston engine (FPE) with synchronized reciprocating plungers. The invention provides a solution for the problem of the slow engine speed typical of FPE's with heavy plunger mass. Bounce chambers fitted with sleeve valves control the engine's speed and stroke length. The invention's configuration prevents piston head-strikes and operates at standard compression ratios. Piston “pop-top” intake valves allow uniflow scavenging and connecting rod oil channels provide lubrication with no combustion chamber contamination. Poppet combustion head valves are operated by linear cams attached to the plungers. Hydraulic valve actuators implement variable valve timing under computer control.
Owner:JOHNSON ALAN KENT
Cycle piston engine power system
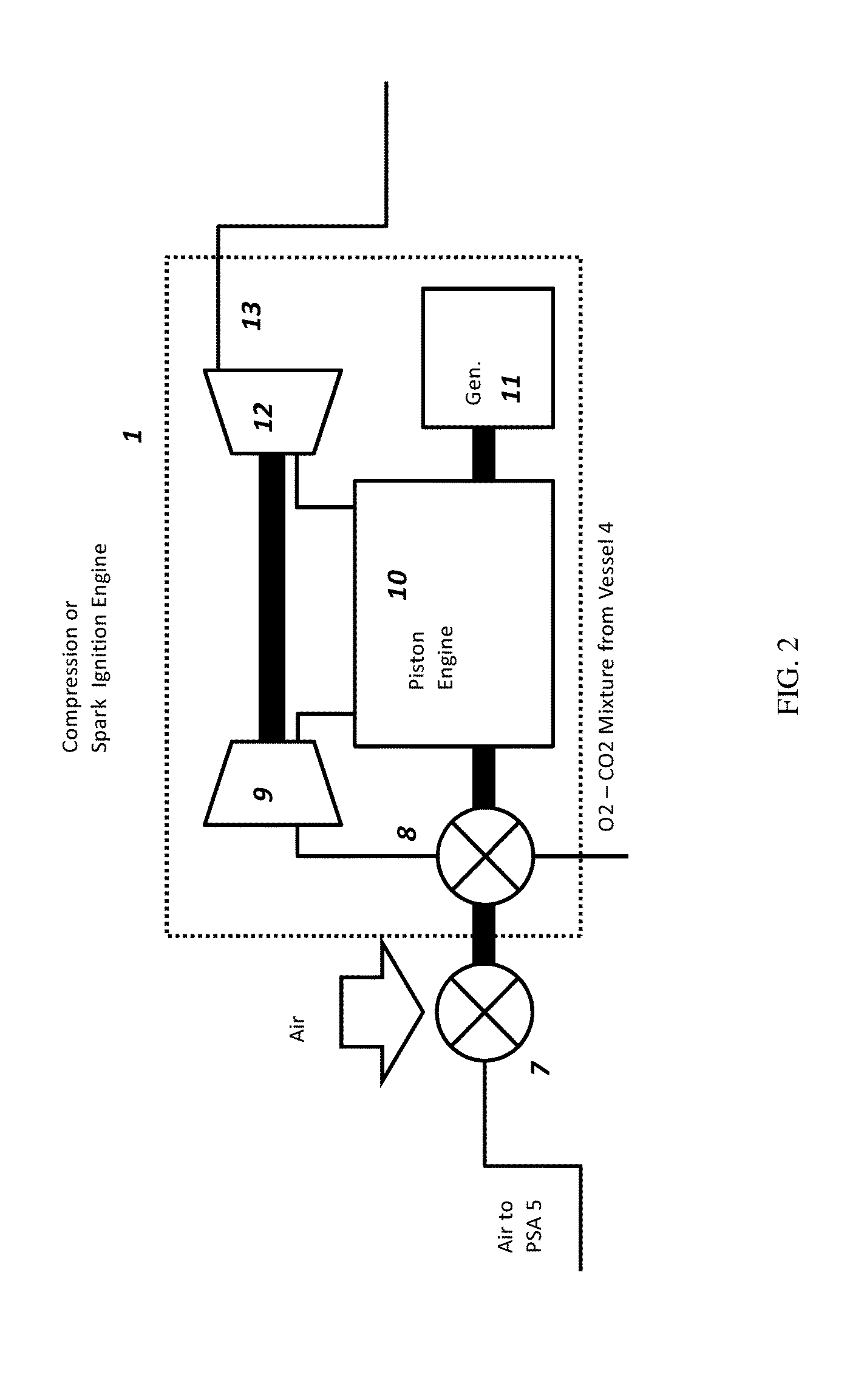
ActiveUS20140060013A1Improve efficiencyLower cost of capitalInternal combustion piston enginesExhaust apparatusFree-piston engineWorking fluid
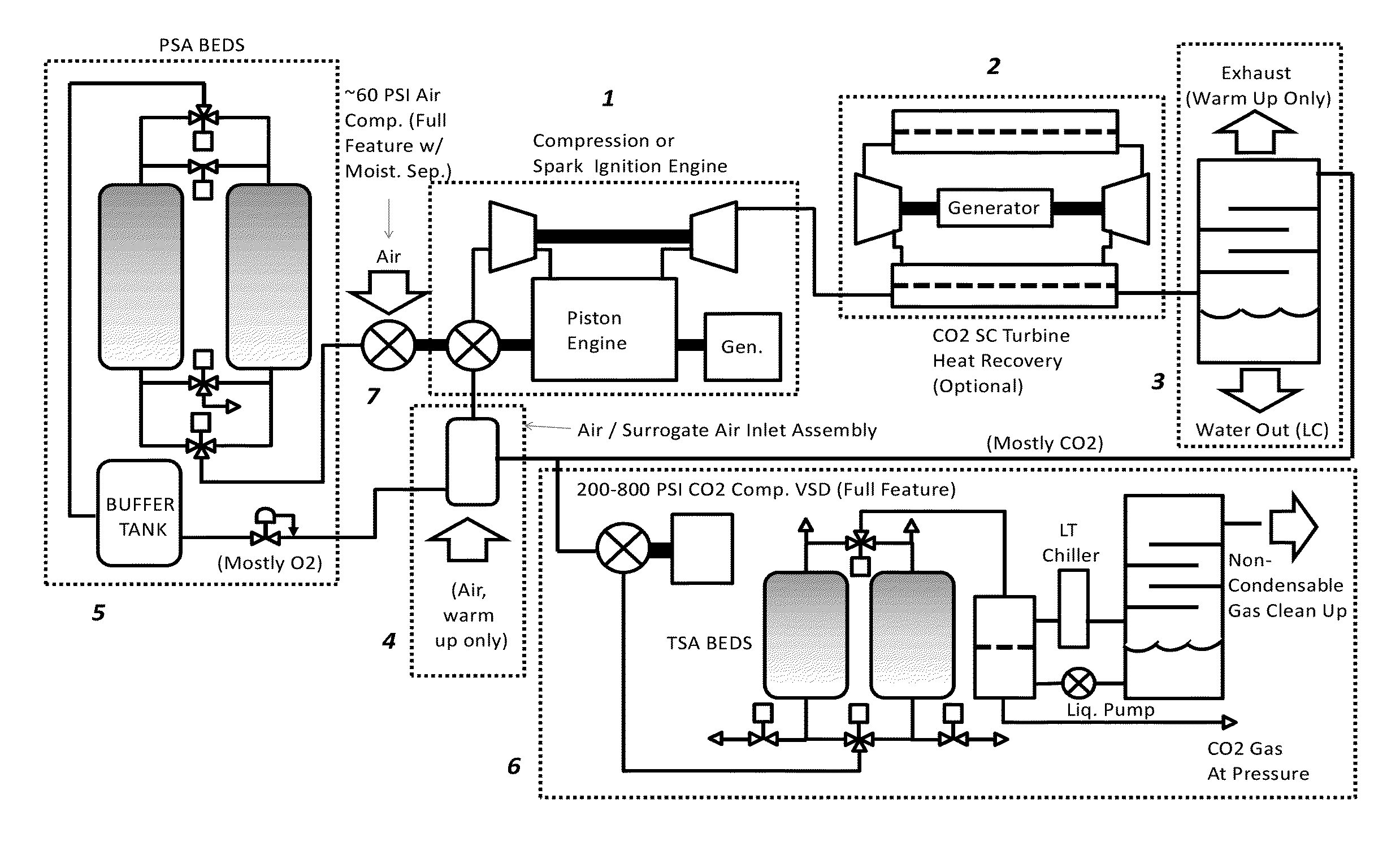
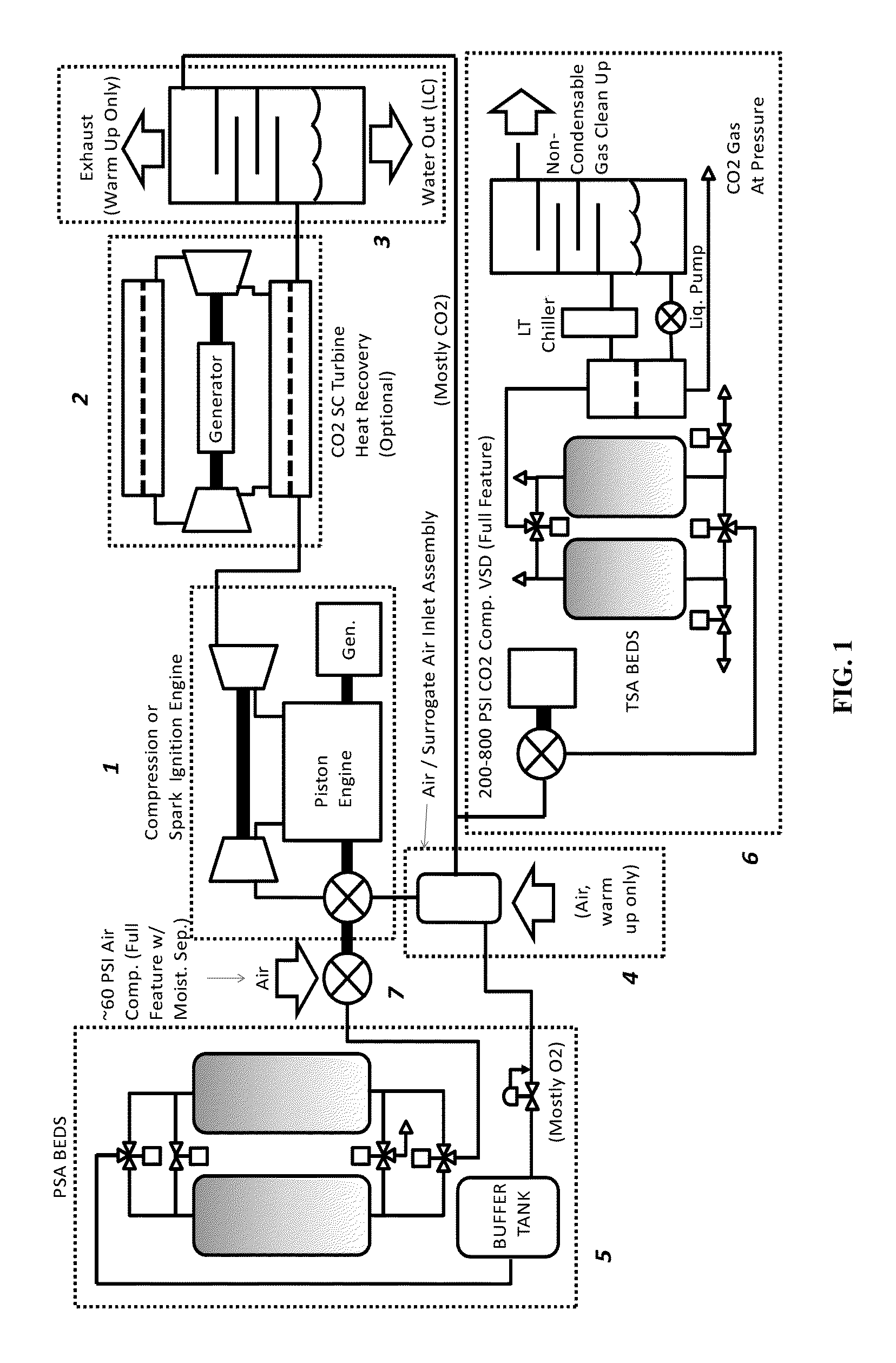
Disclosed is a cycle piston engine power system in which a compression ignition or spark ignition reciprocating piston engine is made non-emissive via a semi-closed cycle, in a manner which produces saleable CO2 product at pressure. The cycle piston engine power system can includes, among other elements, a piston engine for generating power and exhaust gas; a water cooling and separation unit which receives the exhaust gas and cools and removes water from the exhaust gas to create CO2 gas supply; a mixing pressure vessel which receives at least a portion of the CO2 gas supply from the water cooling and separation unit and mixes the CO2 gas supply with oxygen to create a working fluid to be provided to the piston engine; and an oxygen generator for providing oxygen to the mixing pressure vessel.
Owner:ENHANCED ENERGY GRP
Supercharged two-cycle engines employing novel single element reciprocating shuttle inlet valve mechanisms and with a variable compression ratio
This invention relates to novel reciprocating shuttle inlet valves, effective with every type of two-cycle engine, from small high-speed single cylinder model engines, to large low-speed multiple cylinder engines, employing spark or compression ignition. Also permitting the elimination of out-of-phase piston arrangements to control scavenging and supercharging of opposed-piston engines. The reciprocating shuttle inlet valve (32) and its operating mechanism (34) is constructed as a single and simple uncomplicated member, in combination with the lost-motion abutments, (46) and (48), formed in a piston skirt, obviating the need for any complex mechanisms or auxiliary drives, unaffected by heat, friction, wear or inertial forces. The reciprocating shuttle inlet valve retains the simplicity and advantages of two-cycle engines, while permitting an increase in volumetric efficiency and performance, thereby increasing the range of usefulness of two-cycle engines into many areas that are now dominated by the four-cycle engine.
Owner:WIESEN BERNARD
Opposed piston opposed cylinder free piston engine
InactiveUS6953010B1Efficient productionChange direction quicklyAuxillary drivesElectric propulsion mountingFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
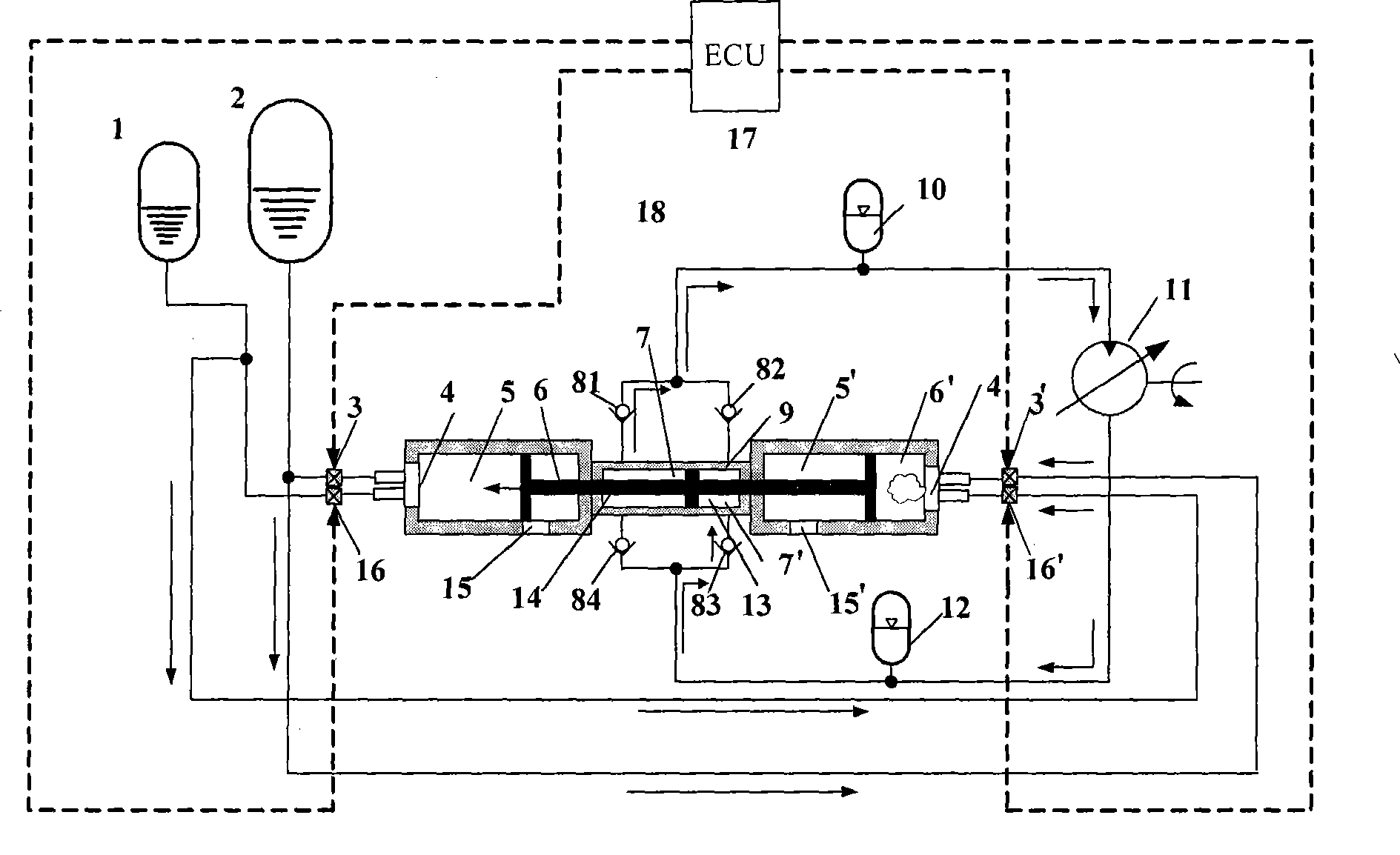
Double group component hydraulic free-piston engine
InactiveCN101372913ASimple structureWork reliablyFree piston enginesFree-piston engineSolenoid valve
A bipropellant hydraulic free piston engine comprises a liquid oxidizer storage tank, a liquid mineral oil fuel storage tank, two oxidizer control electromagnetism valves, two mineral oil fuel control solenoid valves, a double-piston hydraulic free piston engine and an electronic control unit. No outside oxidizer is needed to participate in the working process of the engine and the condensation process of the working quality, no ignition or oil-spraying device is needed, and no jump-start device is needed either; therefore, the engine has the advantages of simple structure, small size, light weight, reliable operation, high energy density, high power density, and long service life, and represents a driving device that can be applied to energy-autonomy walking machinery and hydraulic energy supply in various circumstances with no oxygen or inadequate oxygen. Therefore, the engine can work under circumstances of no oxygen or inadequate oxygen such as a plateau, underwater, the outer space, etc., with a wide range and broad aspects of application in the field of energy-autonomy walking machinery.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Active damping vibration controller for use with cryocoolers
ActiveUS20140325999A1Reduce vibration outputCompression machinesRefrigeration devicesFree-piston engineVibration control
A cryocooler assembly including a cryocooler housing and a free-piston engine arranged within the housing, an absorber housing and a damper motor arranged within the absorber housing, and a controller housing rigidly coupled between the cryocooler and the active damper such that vibrations may pass through the controller. A controller mounted within the controller housing provides power to the cryocooler and monitors the phase and frequency of the power supplied to the cryocooler. The controller monitors the vibration of the cryocooler assembly and provides a damping signal to the active damper. The damping signal generated by the controller is based at least in part on the phase and frequency of the power supplied to the cryocooler and the monitored vibration of the cryocooler assembly.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
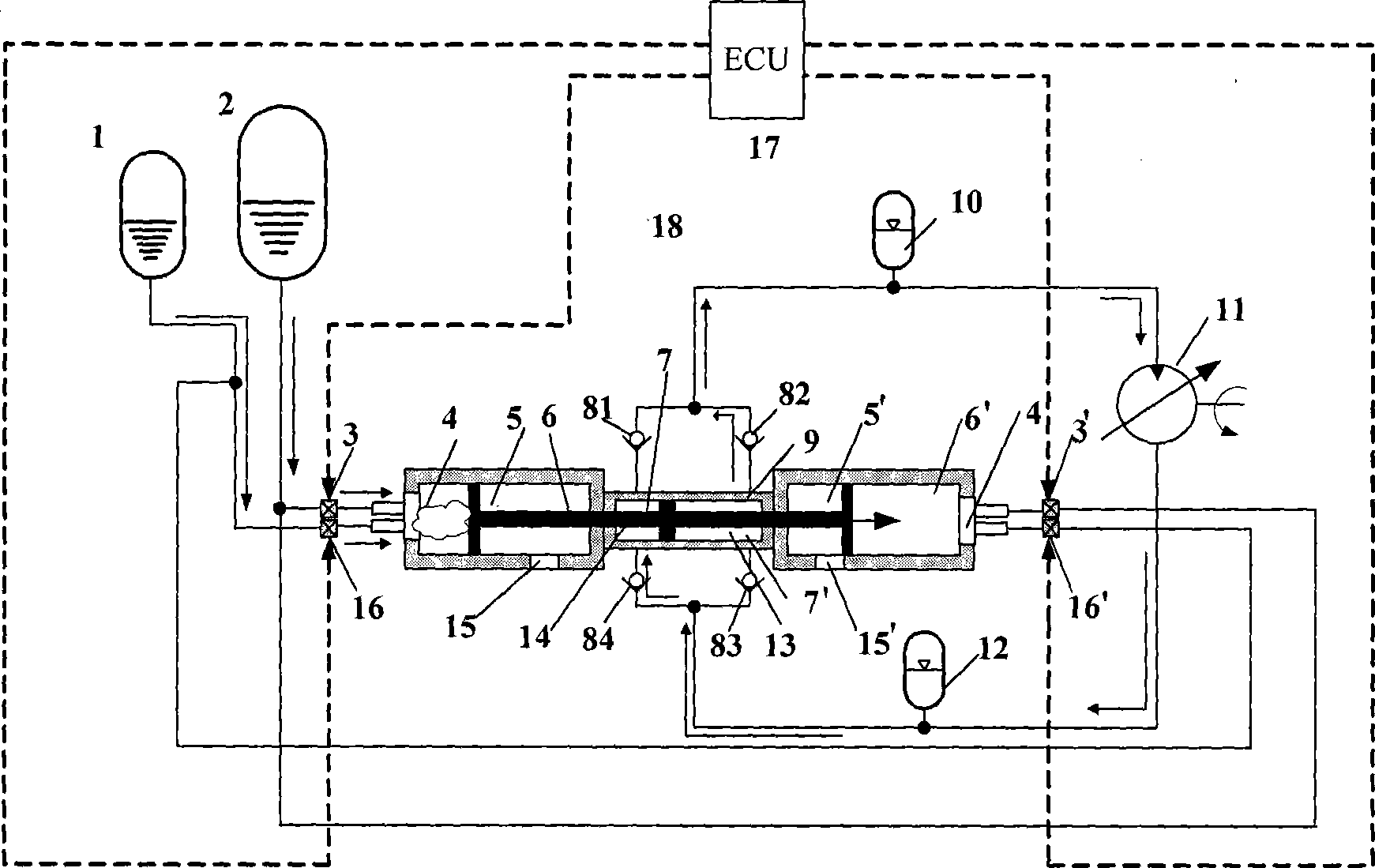
Single piston monopropellant hydraulic free piston engine
InactiveCN101008318ASimple structureWork reliablyEngines without rotary main shaftFree-piston engineHigh energy
A single-piston single-unit hydraulic free-piston engine comprises a single-unit fuel pot, a fuel controlling electromagnetic valve, a catalyze bed, a single-piston hydraulic free-piston engine and an electric-control unit. The invention uses high-density hydrogen dioxide or the mixture of hydrogen dioxide and diesel as fuel, and decomposes the fuel via catalysis and decomposition into high-temperature high-pressure mixture gas to drive the single-piston single-unit hydraulic free-piston engine, to exchange the chemical energy of fuel with the hydraulic energy. The invention has high reliability, small volume, low weight and high energy density, or the like, while it can output power in large range by changing the size of engine or the work-frequency of engine. The invention can be used to supply hydraulic energy in non-oxygen condition or oxygen-lack condition.
Owner:SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com