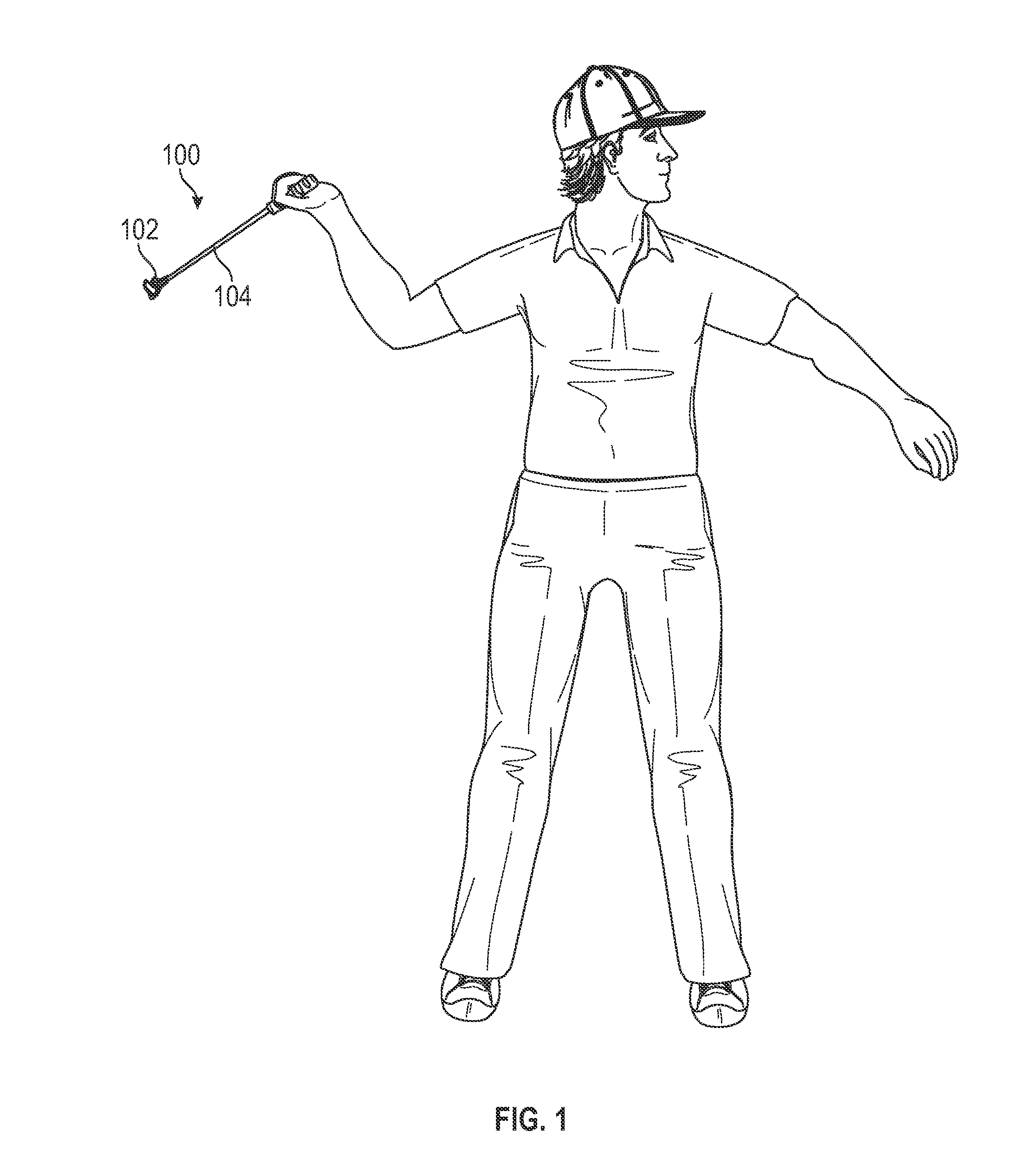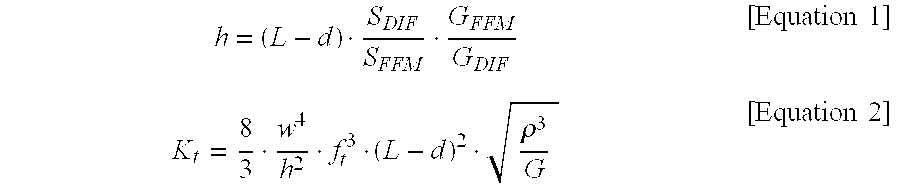Patents
Literature
73results about How to "Avoid less friction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
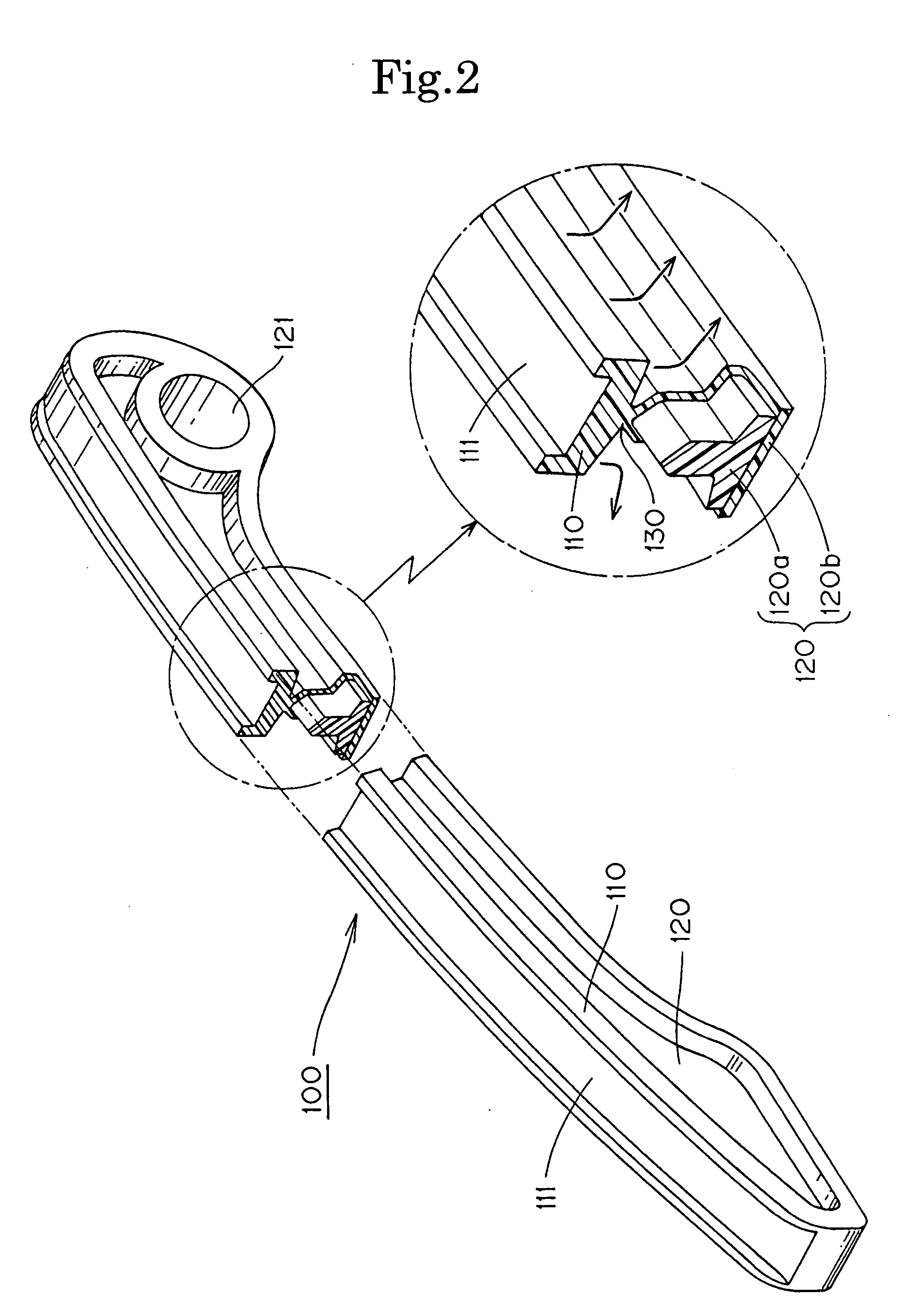
Auto-loading firearm with gas piston facility
ActiveUS7832326B1Prevent accumulationOvercome limitationWeapon cleaningWeapon testingPistonReciprocating motion
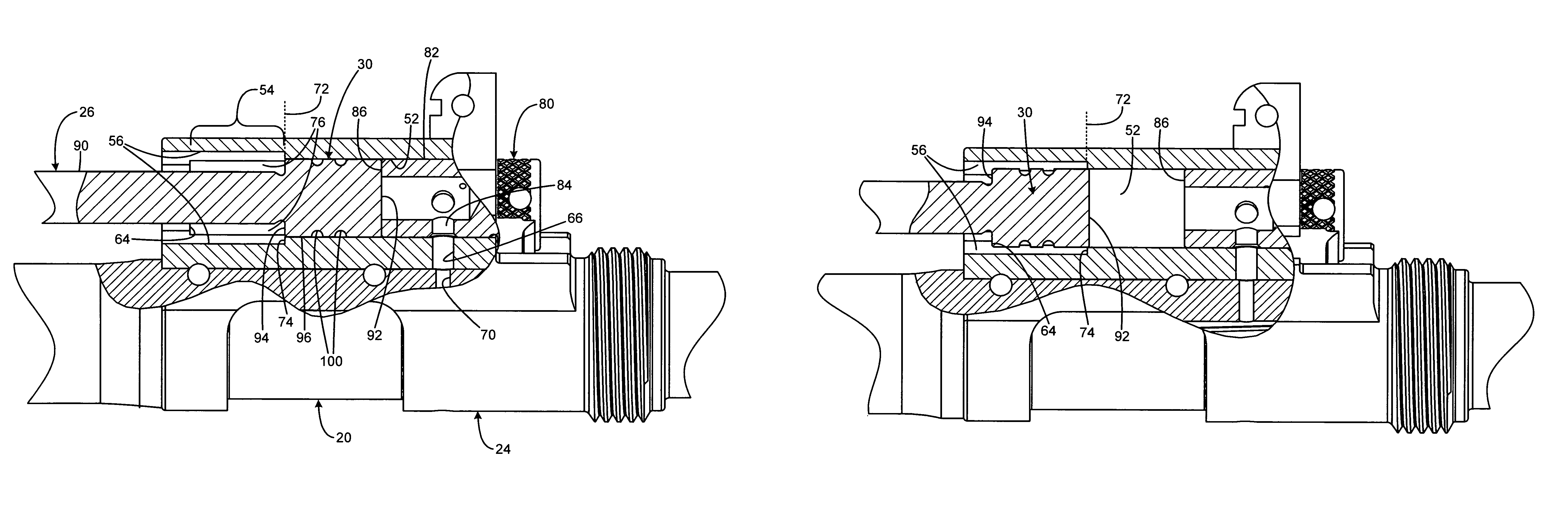
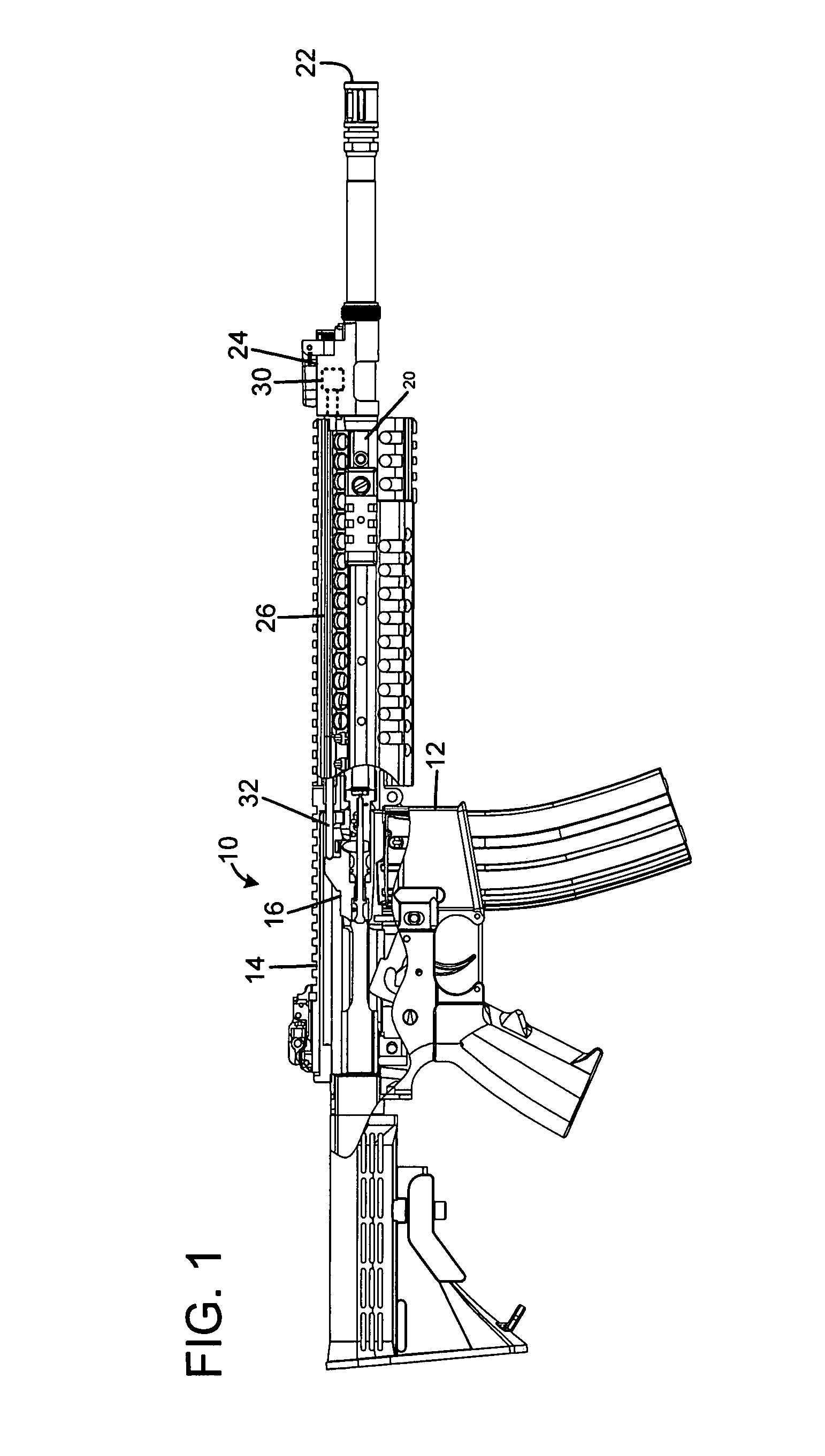
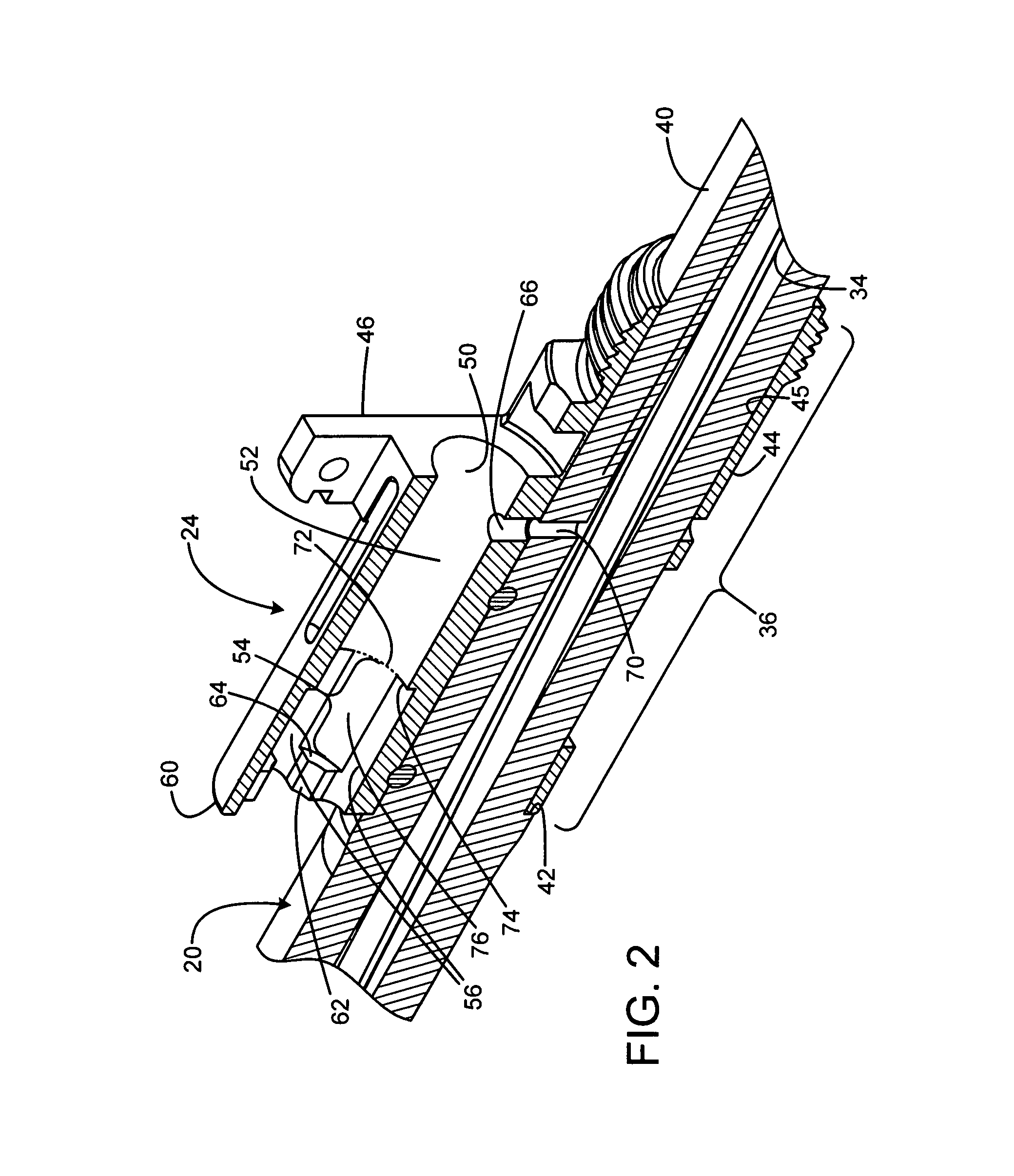
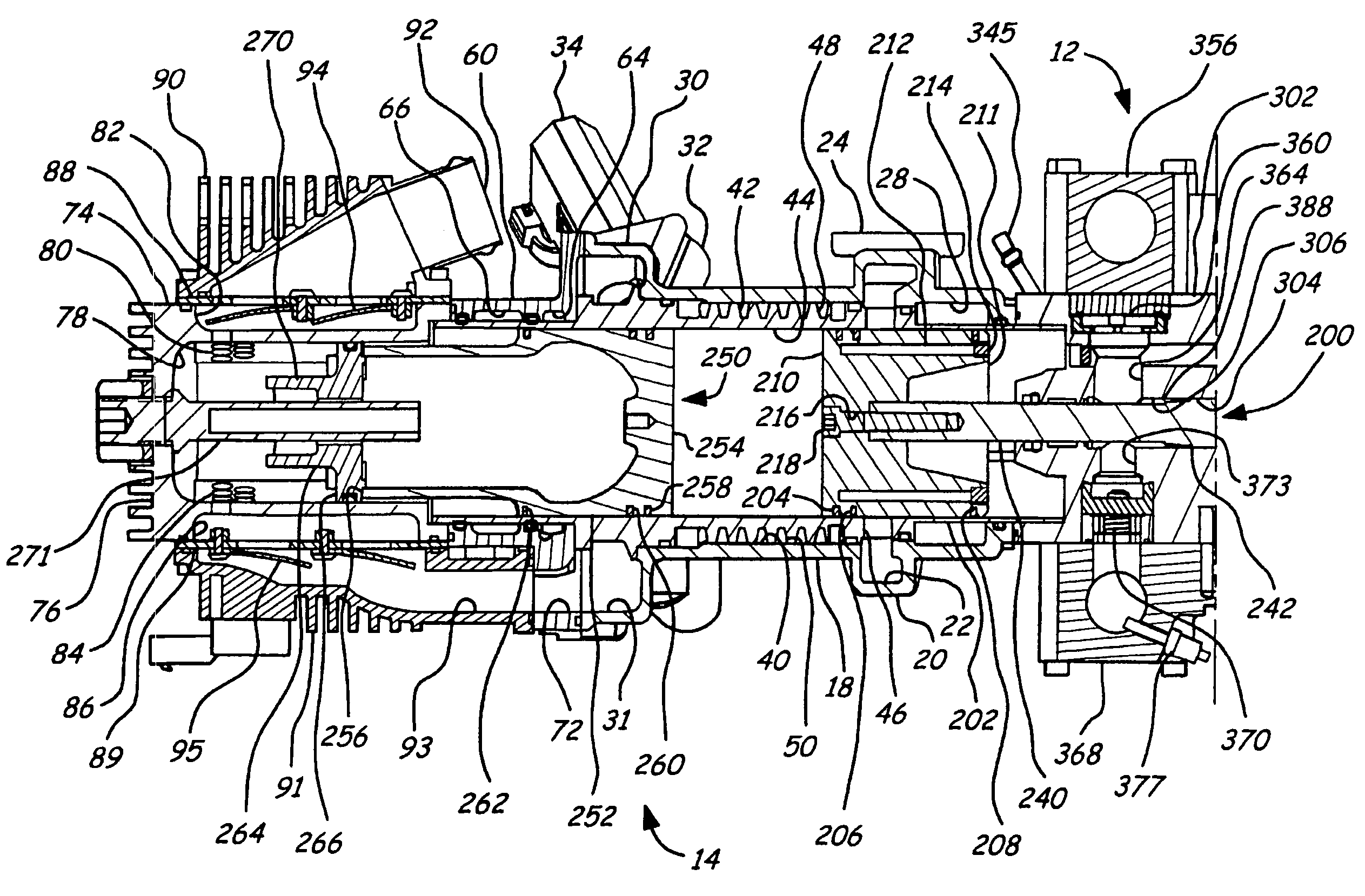
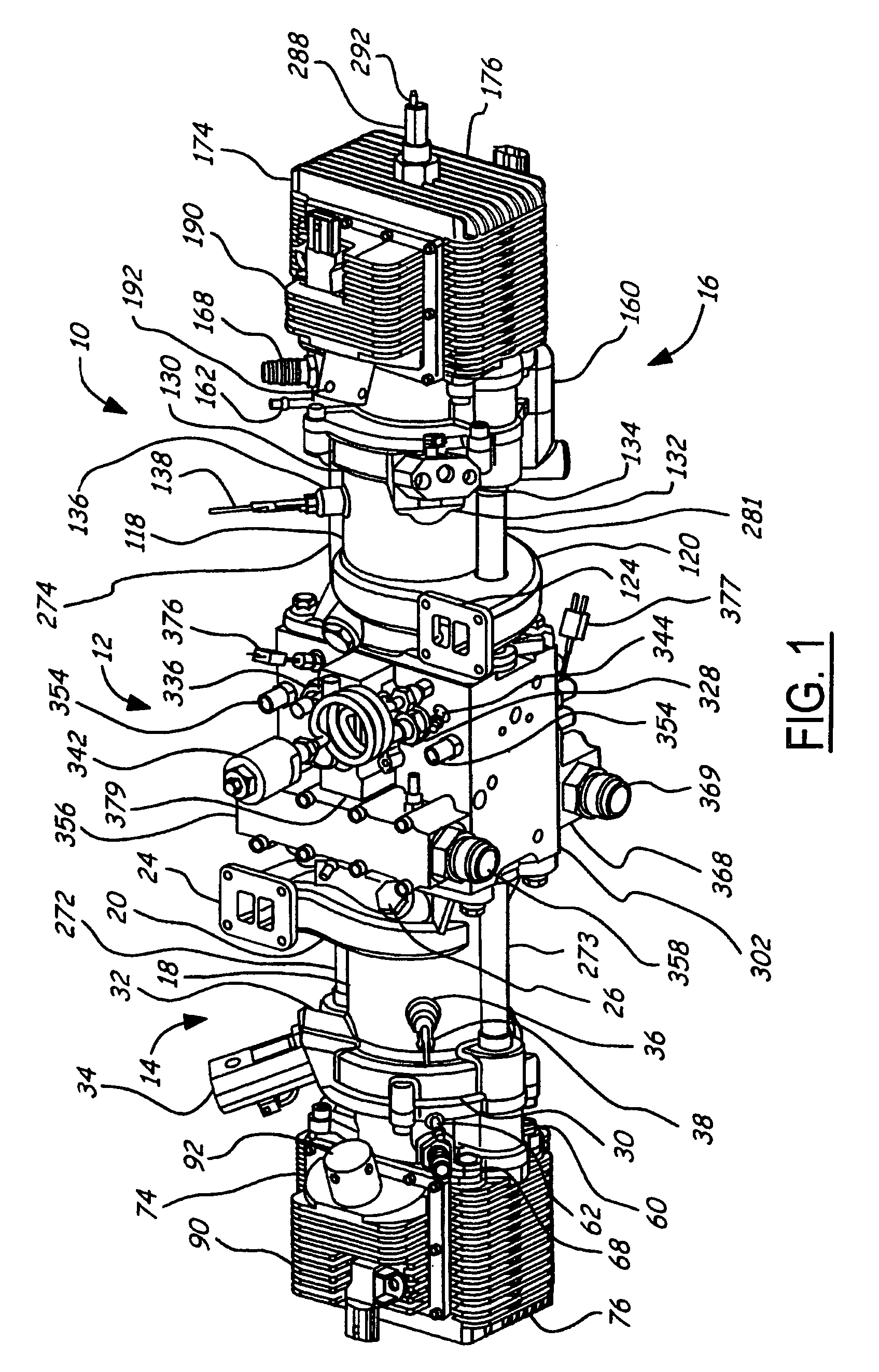
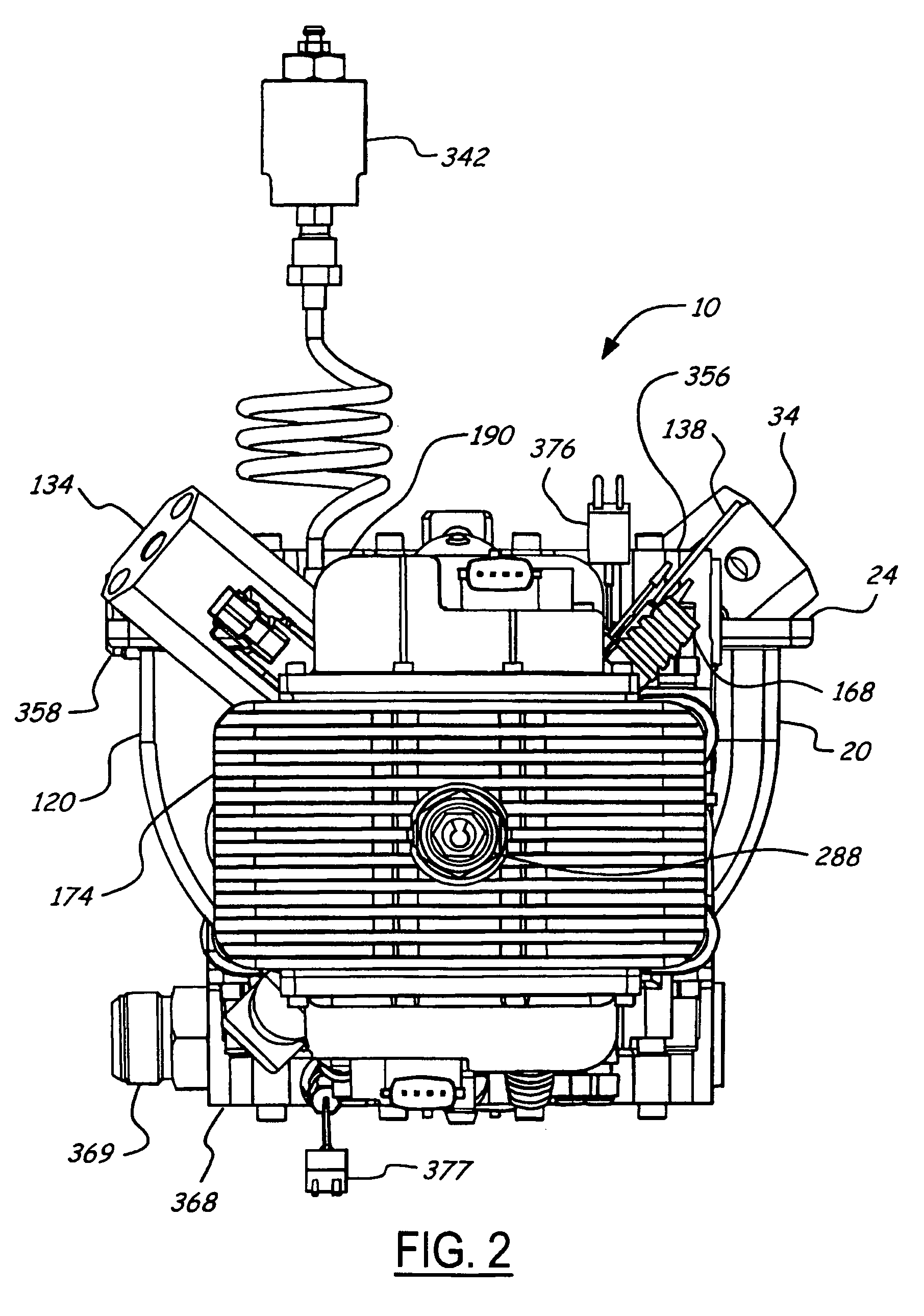
A firearm has a body with a bolt assembly reciprocating within the body. A barrel having a bore extends from the body. A gas block with an elongated chamber is connected to the barrel, and a gas passage connects the barrel bore to the gas block chamber. An operating rod has a forward end portion closely received in the gas block chamber and a rear end positioned to operably engage the bolt assembly. The gas block chamber has a forward portion closely receiving the forward end portion of the rod, and the gas block chamber has a rear portion with a profile larger than the forward portion. The forward portion of the rod may be a cylinder, and the rear portion of the gas block chamber may be fluted to provide clearance for flushing out contaminants. The rod may rotate freely to prevent accumulation of contaminants.
Owner:BARRETT FIREARMS MFG INC
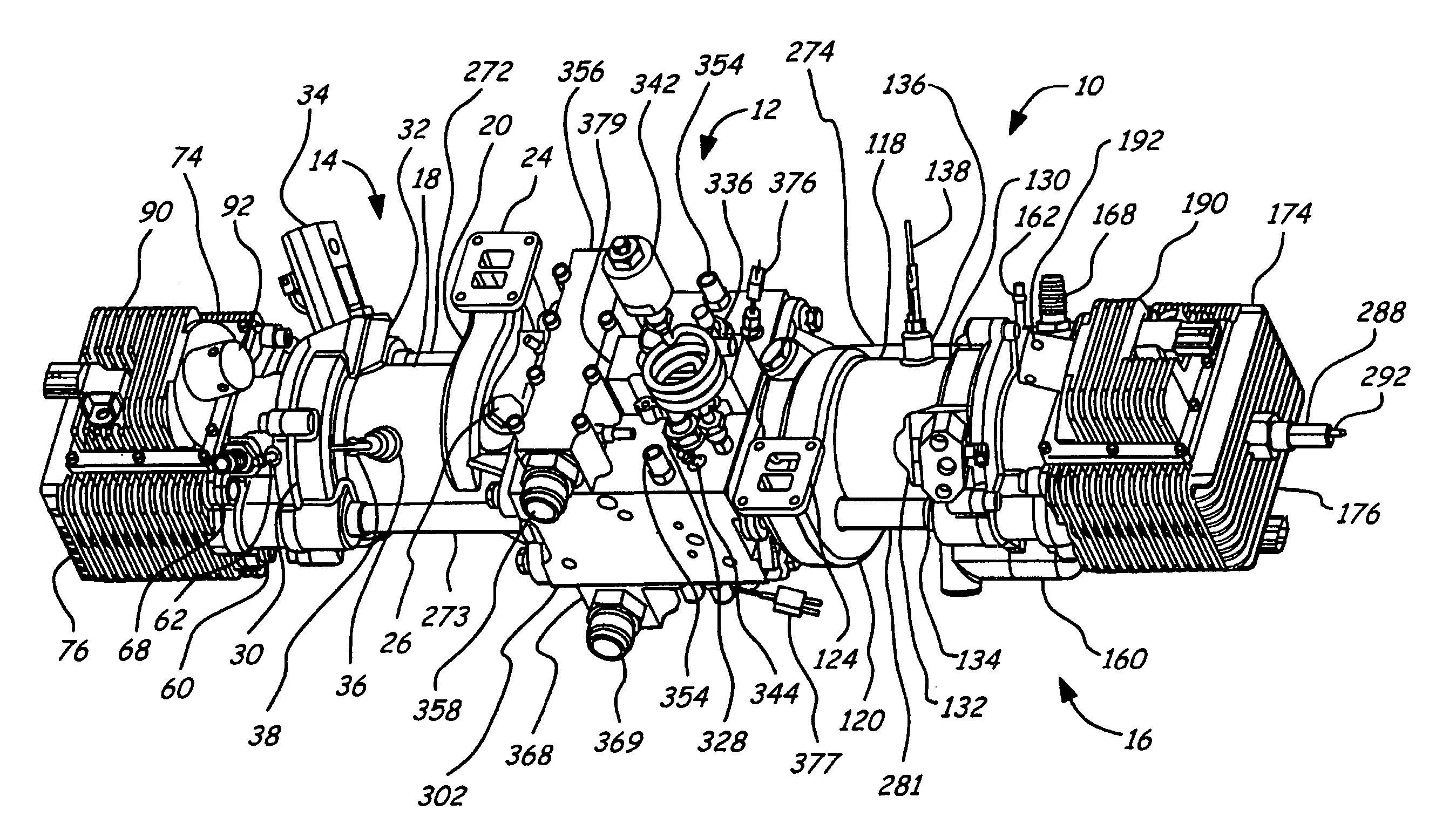
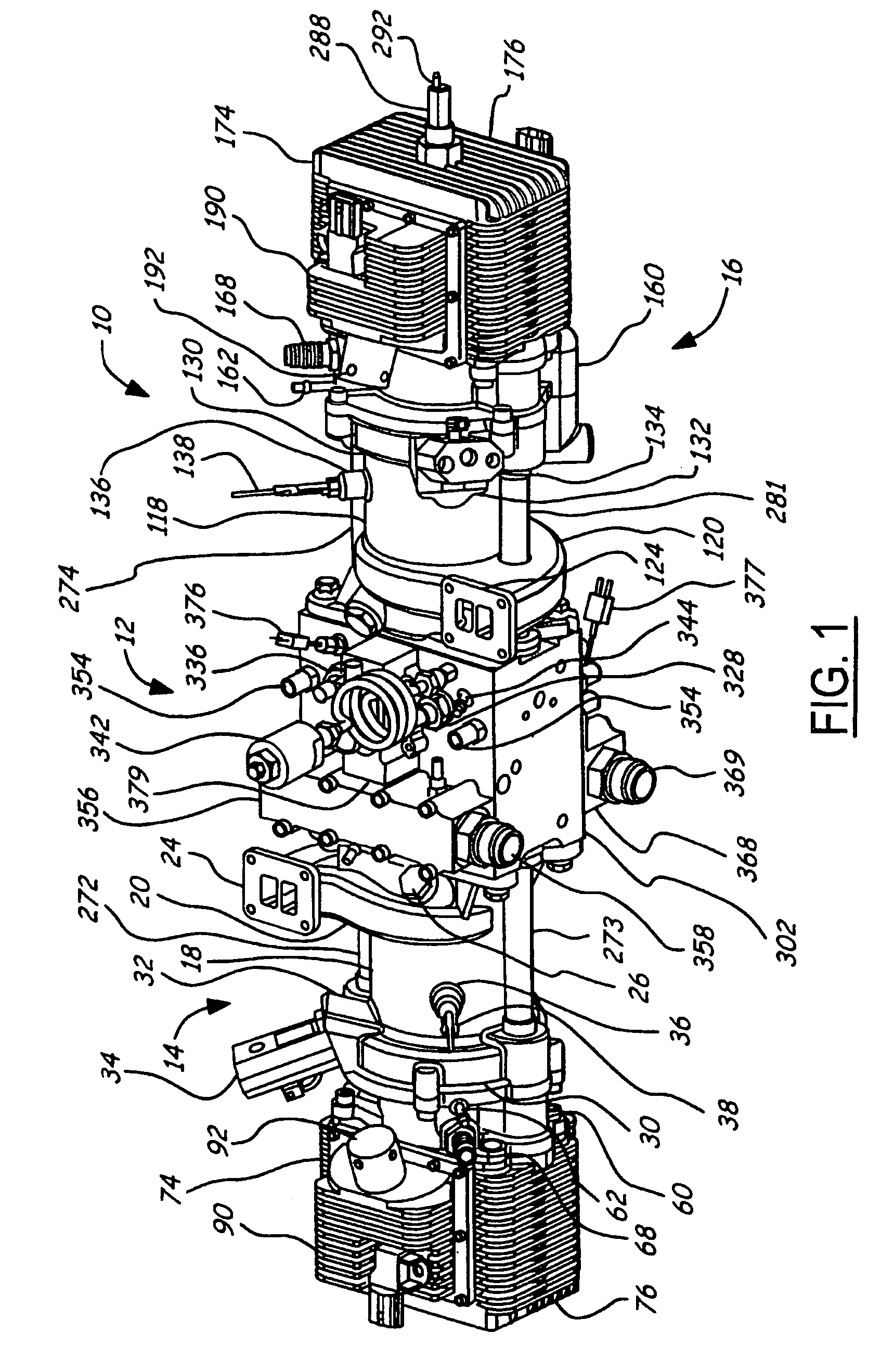
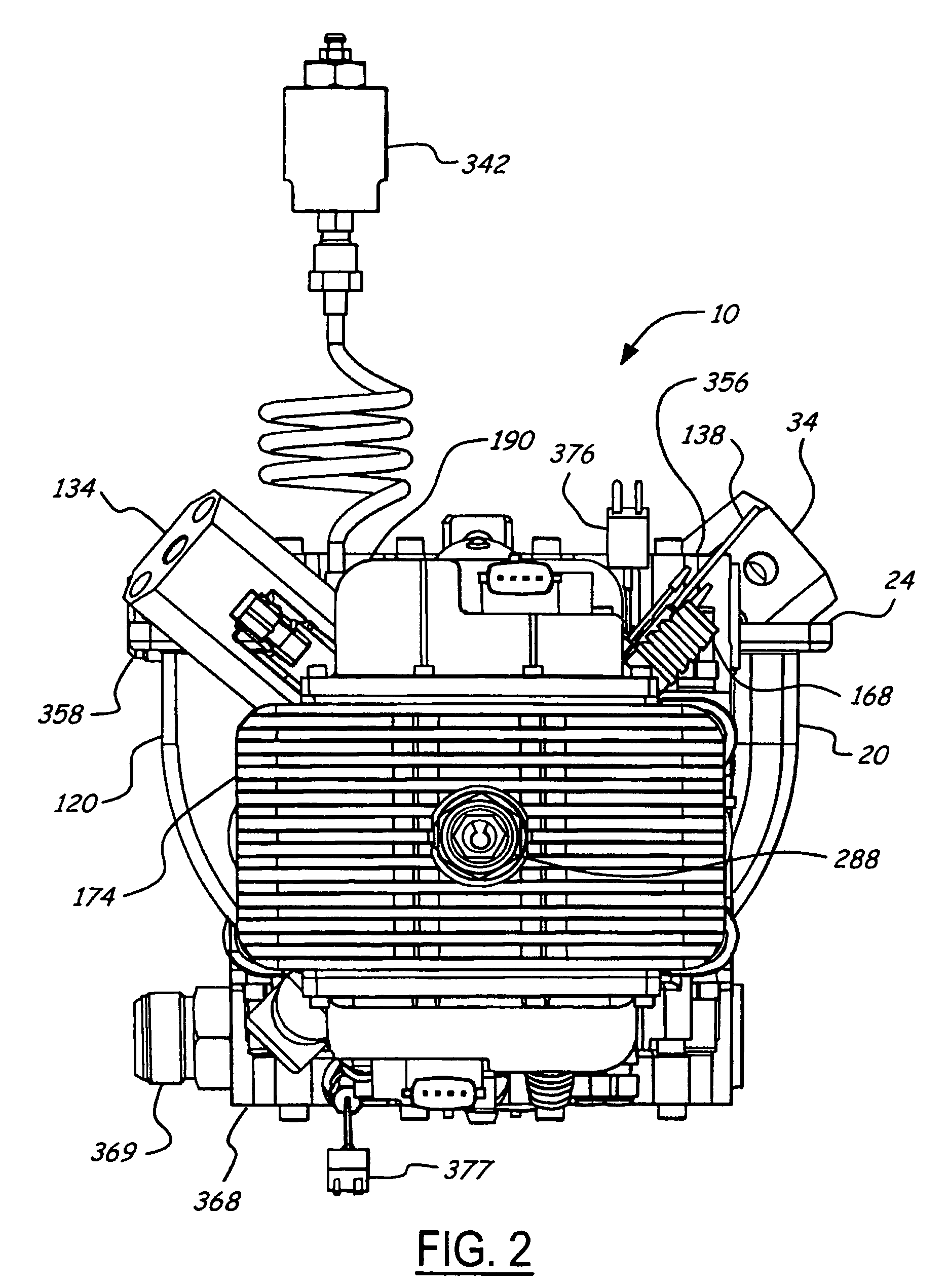
Air charging system for an opposed piston opposed cylinder free piston engine
InactiveUS6957632B1Avoid less frictionEfficient chargingElectrical controlInternal combustion piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Each outer piston cooperates with an integrated scavenge pump in order to compress the charge air, thus significantly increasing the air charge density into the engine cylinders for each stroke of the engine.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Packaging for containing and dispensing large quantities of wire
InactiveUS6889835B2Without tanglingEasy to transportContainers for annular articlesFilament handlingWire rodCarton
A package for containing and dispensing wire from a coil of wire having an outer surface, an inner surface, and a top and bottom defining a coil height comprising an outer carton having a rectangular bottom wall and four side panels extending upwardly from the bottom wall. The package further includes an octagonal inner liner having eight walls and wherein every other wall engages a portion of one of the side panels of the outer carton. The package has a planar retainer ring which engages the top of the wire coil and which has an opening forming an inner edge and an outer periphery comprising a plurality of nodes extending radially outwardly beyond the outer surface of the wire coil. Adjacent nodes are connected by a node edge extending inwardly across the outer surface of the coil, and at least one of the nodes interengages with the liner at a corner between adjacent walls thereof to prevent the retainer ring from rotating relative to the inner liner and to prevent the wire from passing the outer peripheral edge of the retainer ring.
Owner:LINCOLN GLOBAL INC
Hemostasis pad and method
InactiveUS6890344B2Shorten the timeReduce the possibilitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsPuncture WoundBiopolymer
The present invention relates generally to medical devices for applying hemostatic composition to a puncture or wound site with indwelling tubular element, such as catheter, introducer or tube therein, particularly a hemostatic pad with an opening therethrough in order to allow egress of the indwelling tubular element through the hemostatic pad as the hemostatic pad provide hemostasis at the hemorrhaging site. The device may be applied to, or removed from, the wound site while the tubular element is in place. A method for effecting hemostasis at a puncture wound, includes applying pressure proximal to the puncture wound, and directing a cationic biopolymer of glucosamine application surface of a closure pad against the puncture wound with force sufficient to prevent fluid from exiting the puncture wound. Then the pressure proximal to the puncture wound is removed and the force on the closure pad is maintained for at least a first predetermined time period. The force on the closure pad is removed if hemostasis is verified. The puncture wound may then be dressed over the closure pad, and the dressing and the closure pad removed after a second predetermined time period.
Owner:SCION CARDIO VASCULAR
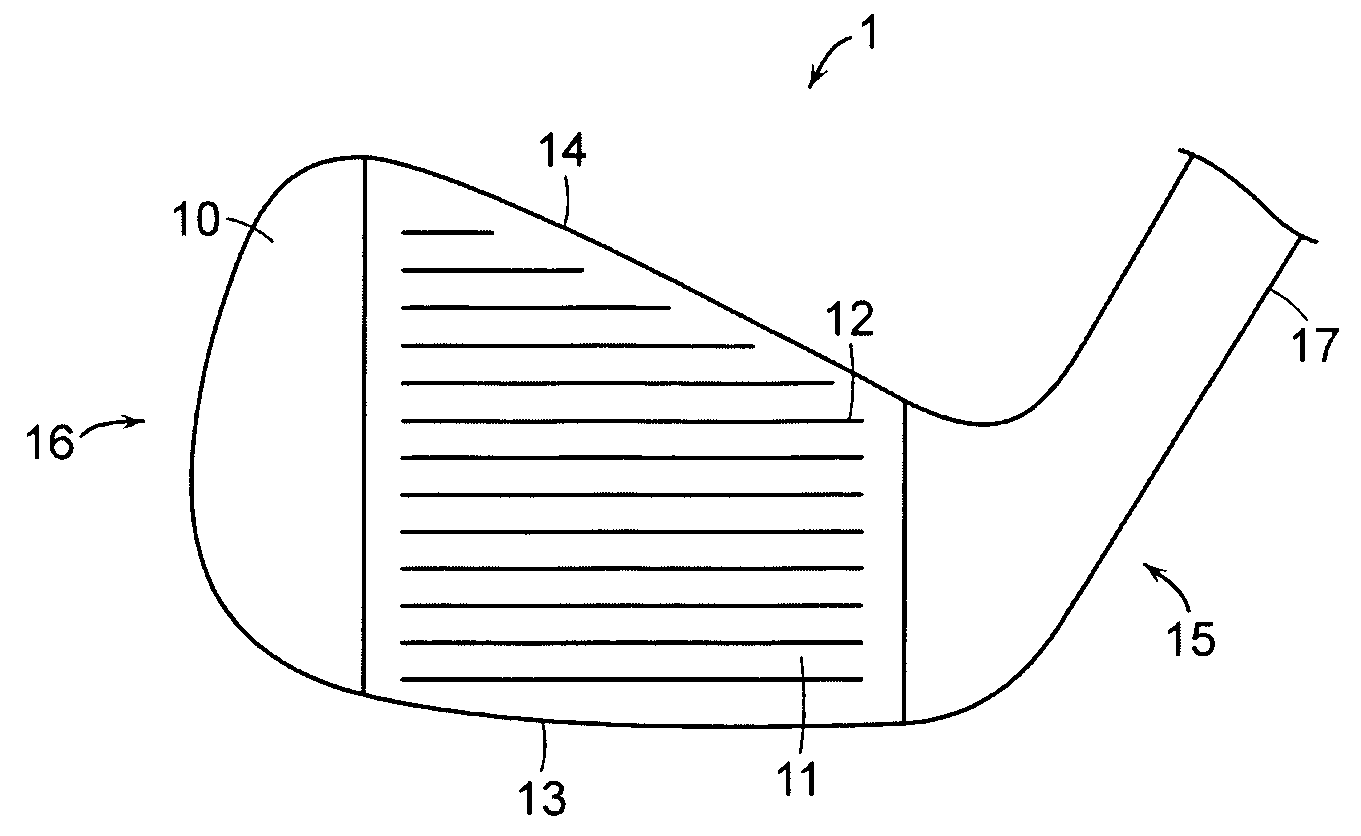
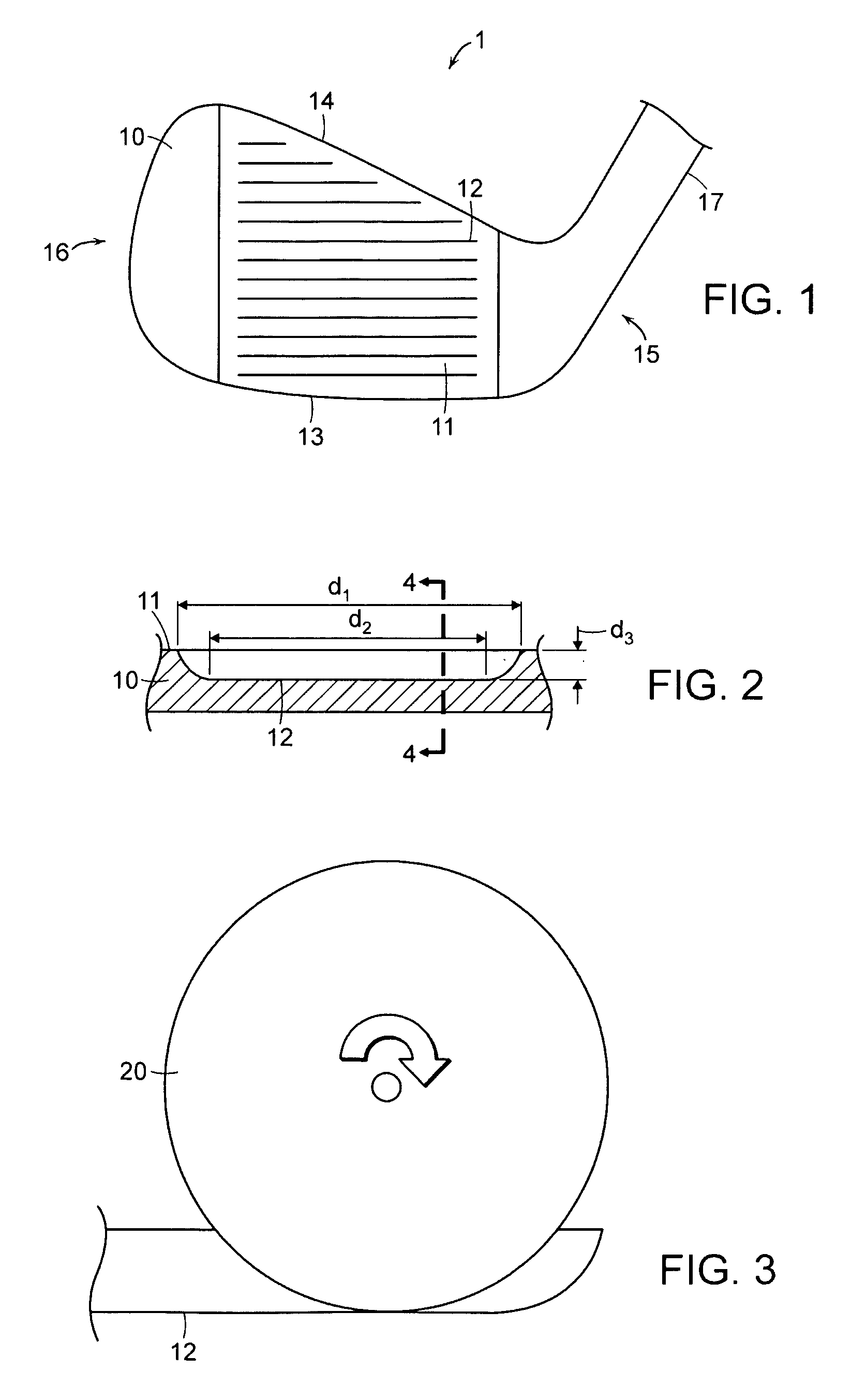
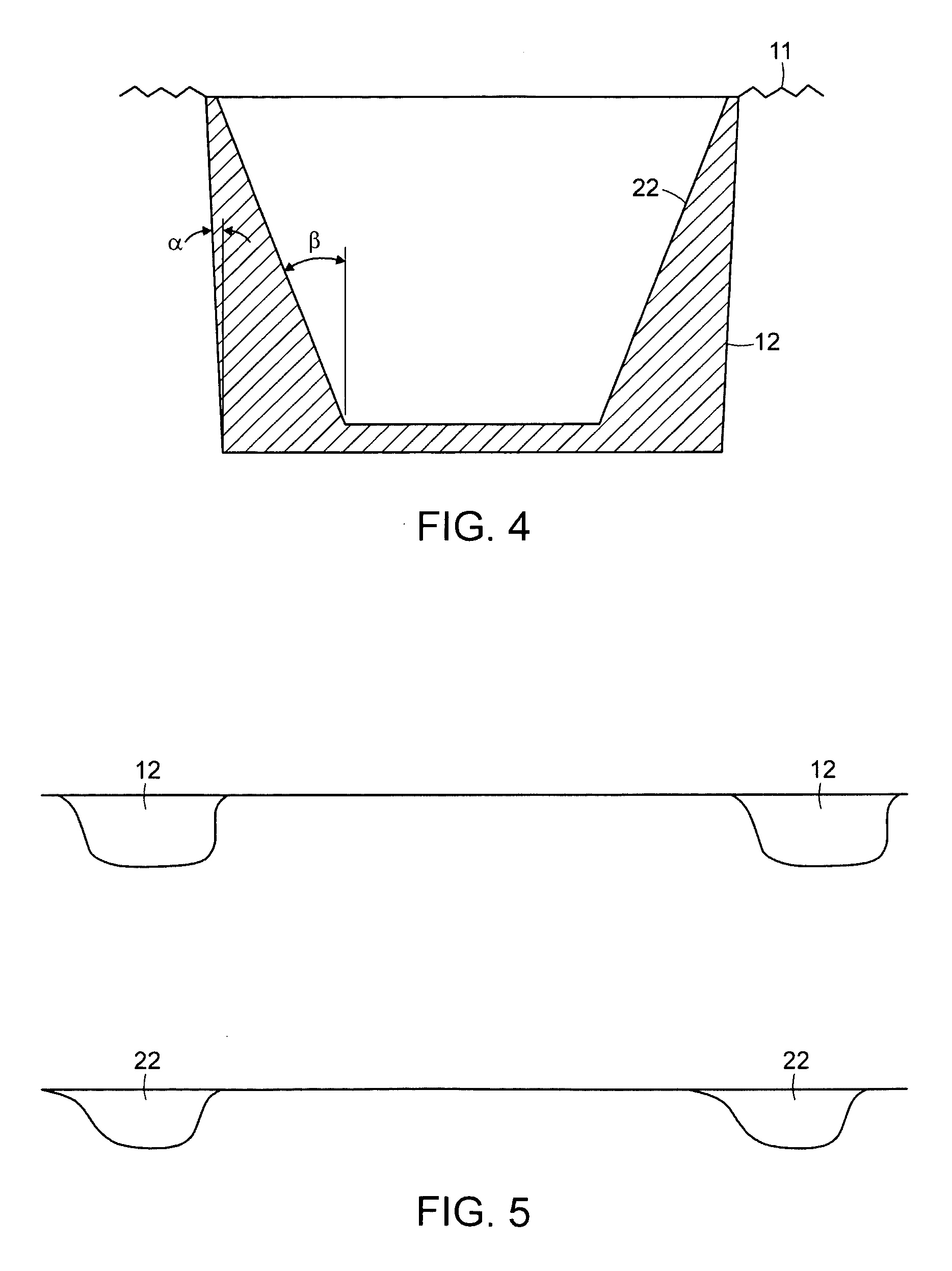
Golf club head with varying face grooves
The present invention is directed to a golf club head with an improved striking surface. Grooves are machined into the strike surface with tight tolerances. The grooves have sharp edges, radiused ends, and a draft angle between about 2° and 12°. The striking face is machined such that it has a uniform texture with a roughness of more than 40 Ra. The grooves may contain a plurality of portions, including a radiused or angled portion, a portion having substantially parallel walls, a portion having a v-shape, and a curved portion. The grooves may also be characterized by various dimensions, including draft angle, inclusive side wall angle, width, depth, cross-sectional area, spacing, and pitch ratio. Preferred values for these dimensions are provided. A golf club head having a variety of groove types and a set of golf clubs with grooves varying among the individual clubs of the set are also disclosed.
Owner:ACUSHNET CO
Continuously variable belt drive transmission
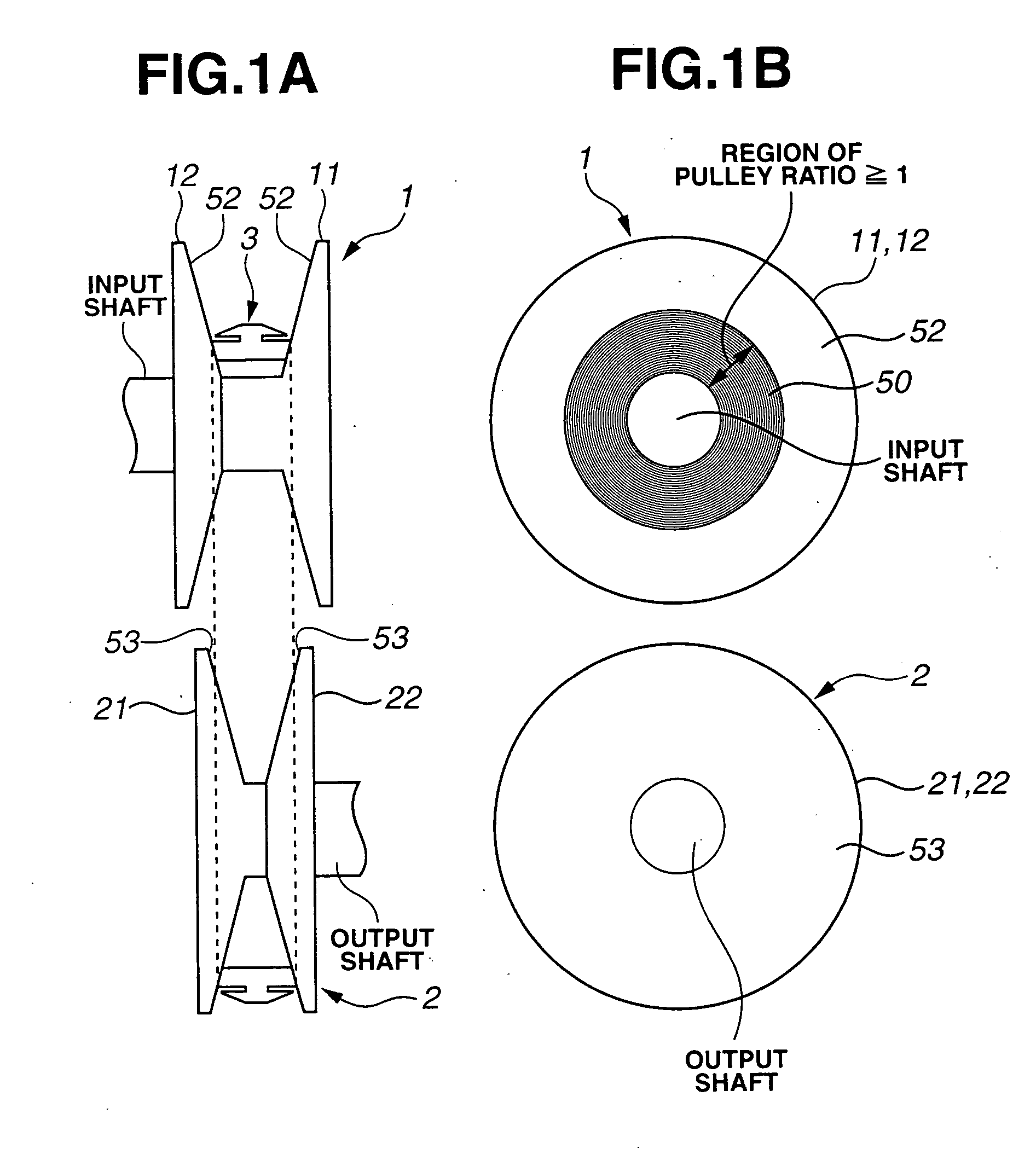
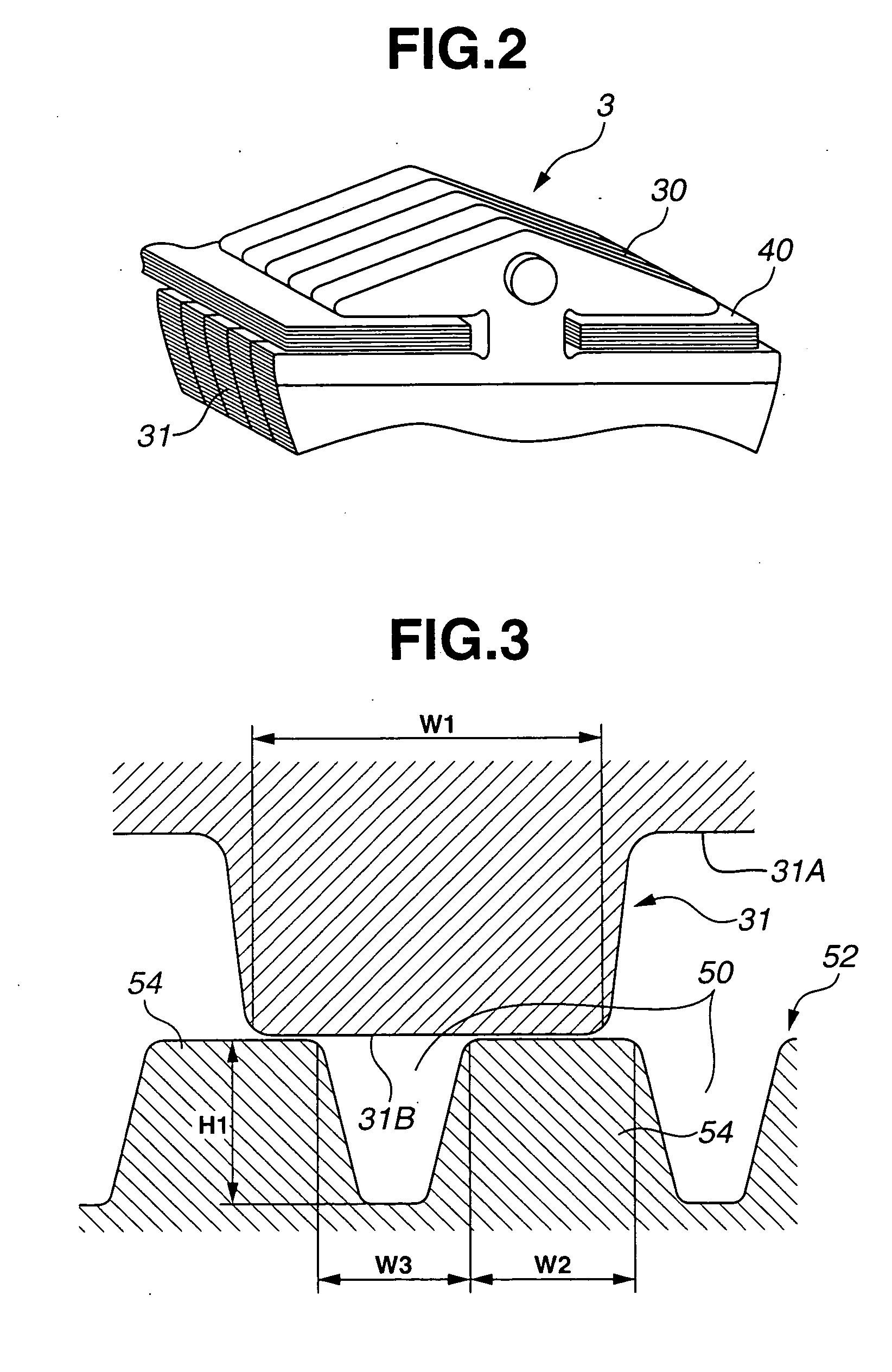
InactiveUS20050221938A1Improve friction coefficientEnhance fuel economyV-beltsGearingElectrical and Electronics engineeringPulley
A continuously variable belt drive transmission, including input and output pulleys each having axially opposed tapered surfaces, and an endless belt including a plurality of metal elements each having opposed side faces contacted with the respective tapered surfaces of the input and output pulleys. Each of the opposed side faces is formed with a plurality of microscopic projections and recesses arranged along a radial direction of the input and output pulleys upon being in contact with the respective tapered surfaces of the input and output pulleys. The tapered surfaces of at least the input pulley are formed with microgrooves that are radially spaced from one another and have a pitch not more than a width of each of the microscopic projections on the side faces of the metal element.
Owner:JATCO LTD
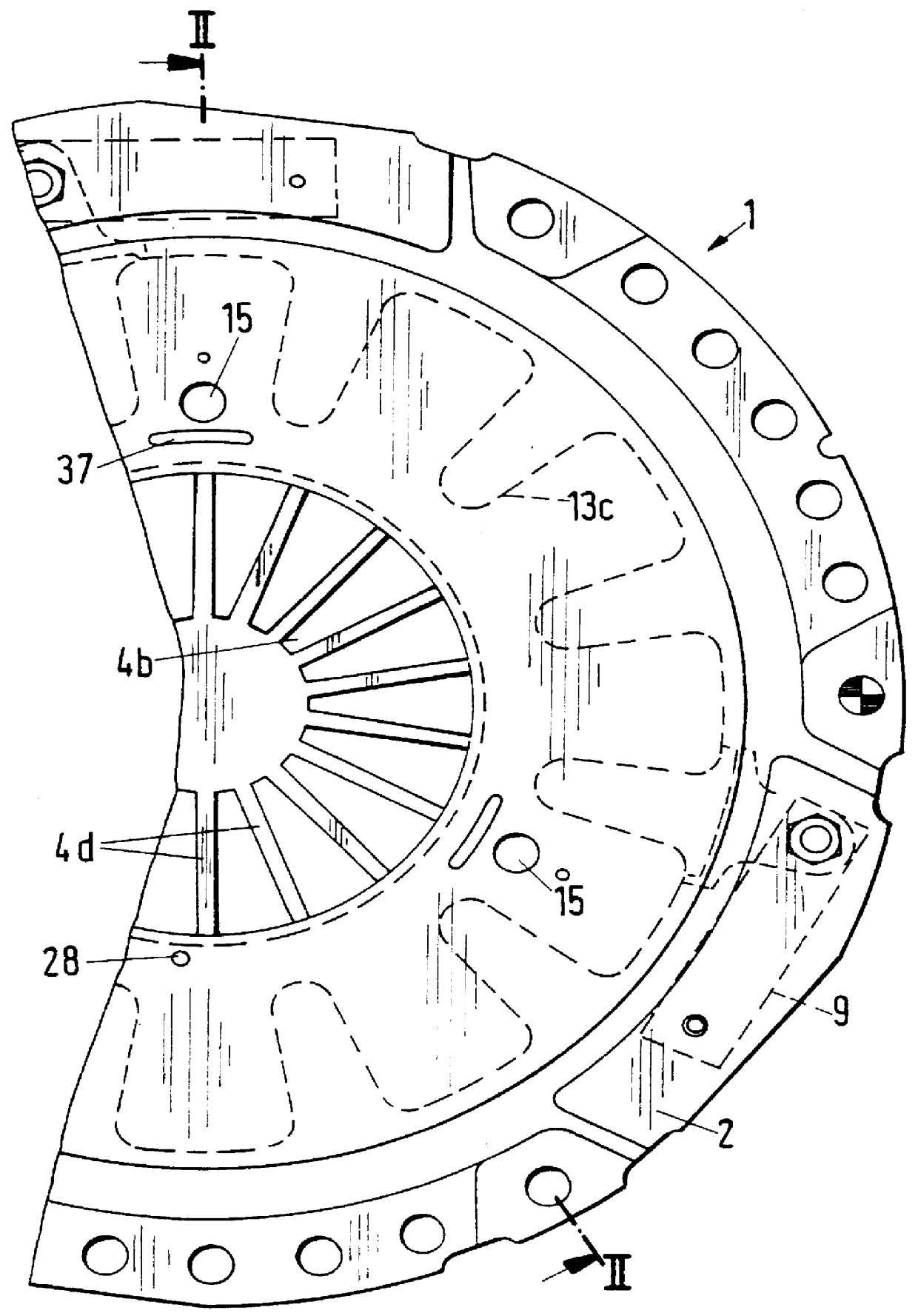
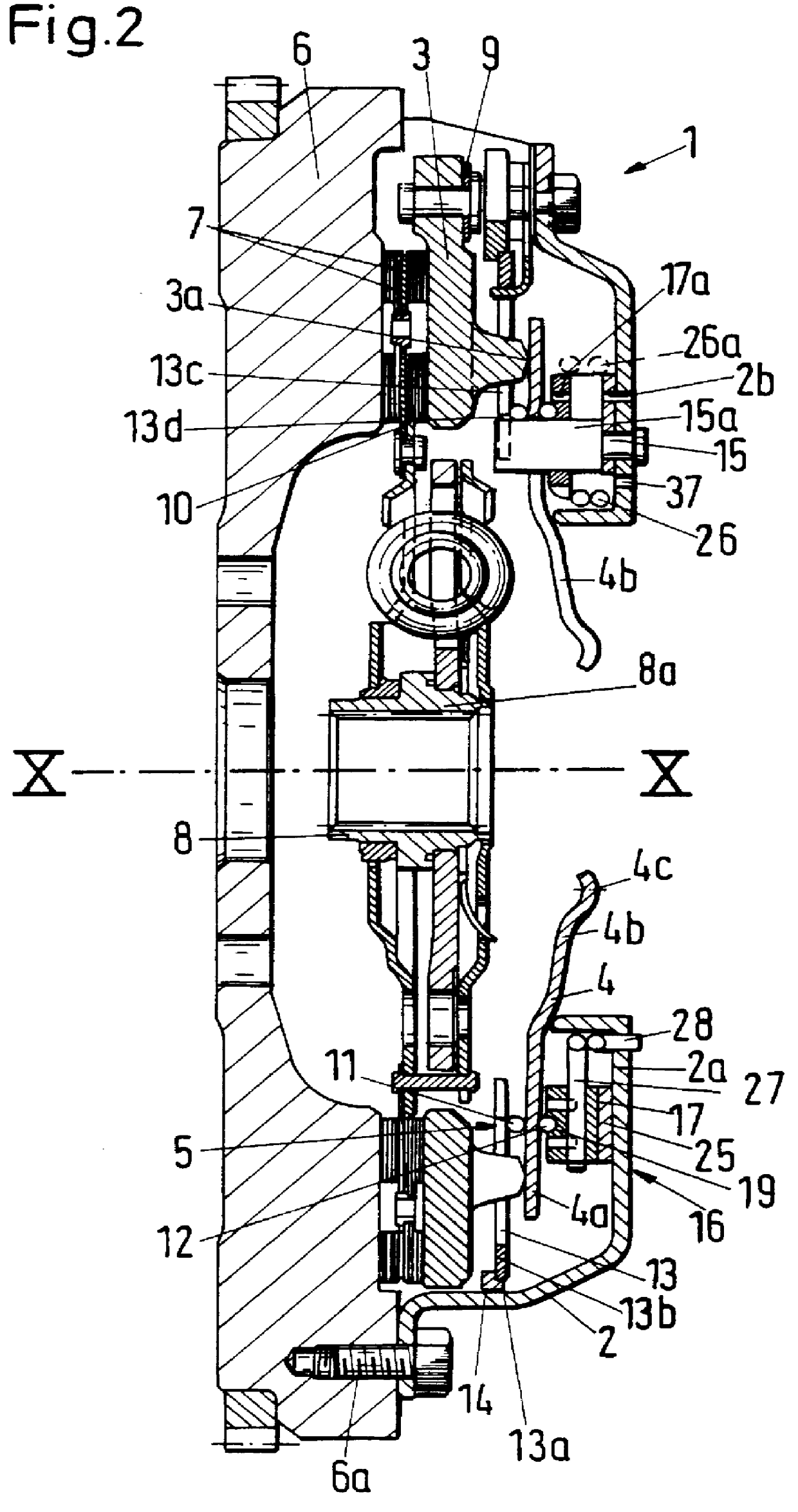
Self-adjusting friction clutch
A friction clutch wherein a pressure plate is axially movably but non-rotatably coupled to a cover and is biased by a diaphragm spring to urge the friction linings of a clutch disc against a flywheel which is driven by the engine of a motor vehicle. The diaphragm spring is tiltable relative to a seat which is carried by the cover, and a second spring is provided to bias a portion of the seat against the diaphragm spring. The latter can be moved axially of the flywheel to compensate for wear upon the friction linings, particularly when the flywheel is idle or is driven at a relatively low speed. The unit which compensates for wear upon the friction linings is installed between the diaphragm spring and the cover, and its purpose is to ensure that the bias of the diaphragm spring upon the pressure plate in the engaged condition of the friction clutch remains at least nearly constant regardless of the extent of wear upon the friction linings and upon certain other parts, including (1) the diaphragm spring, (2) the pressure plate, (3) springs which form part of the clutch disc to urge two sets of friction linings axially and away from each other against the flywheel and the pressure plate, respectively, (4) leaf springs which connect the pressure plate to the cover, and (5) one or more springs which are active during certain stages of disengagement of the clutch.
Owner:SCHAEFFLER TECH AG & CO KG +1
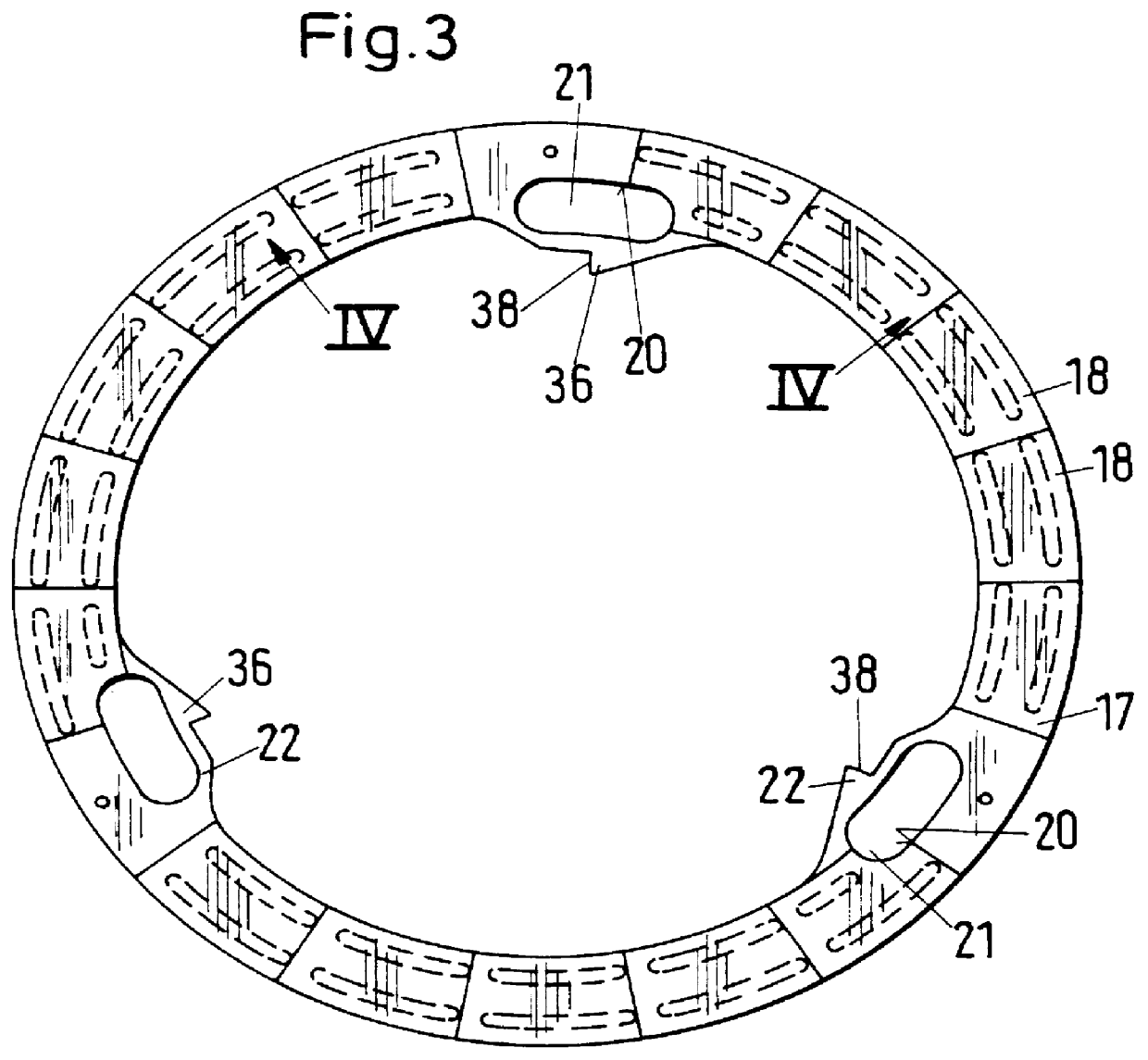
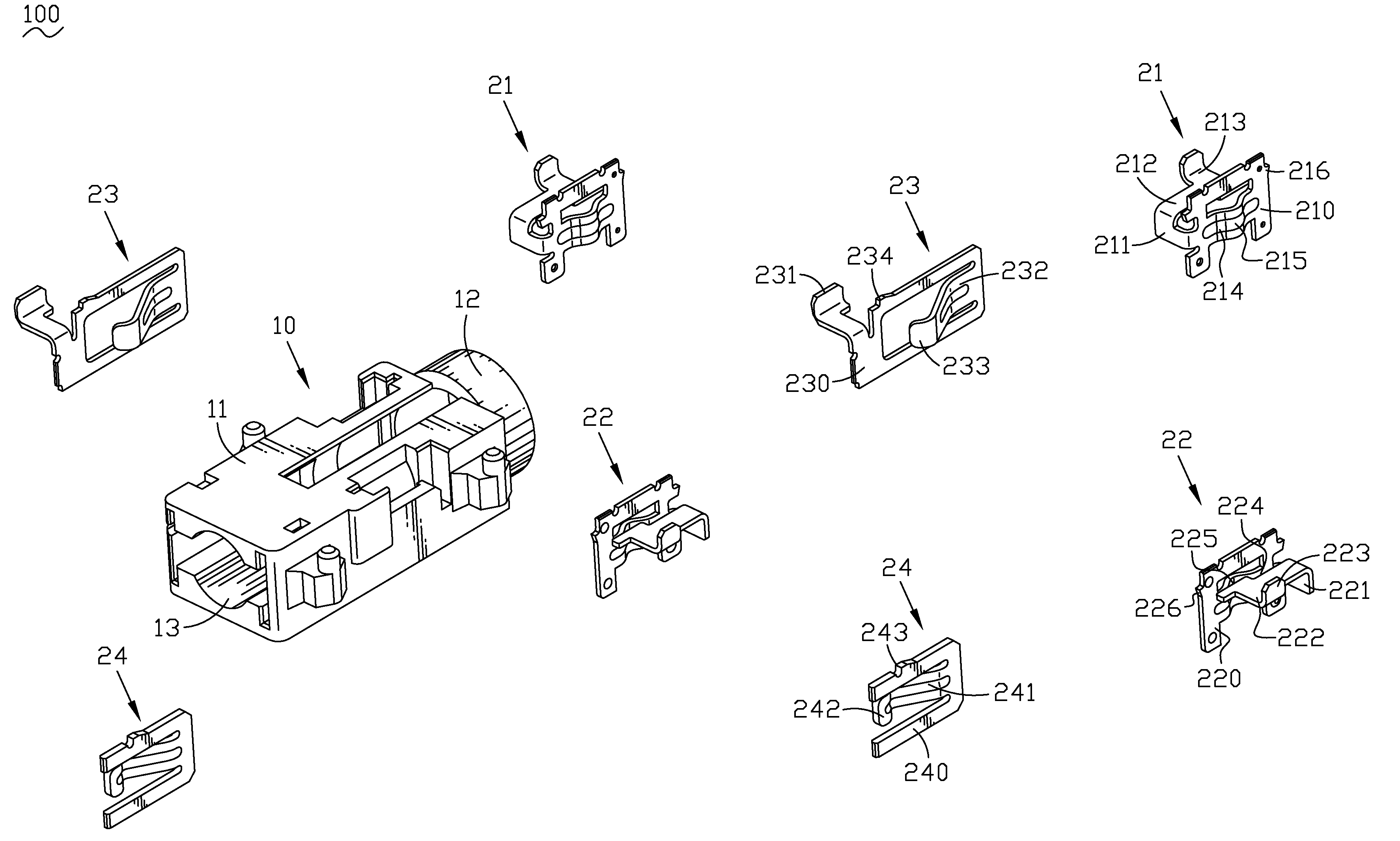
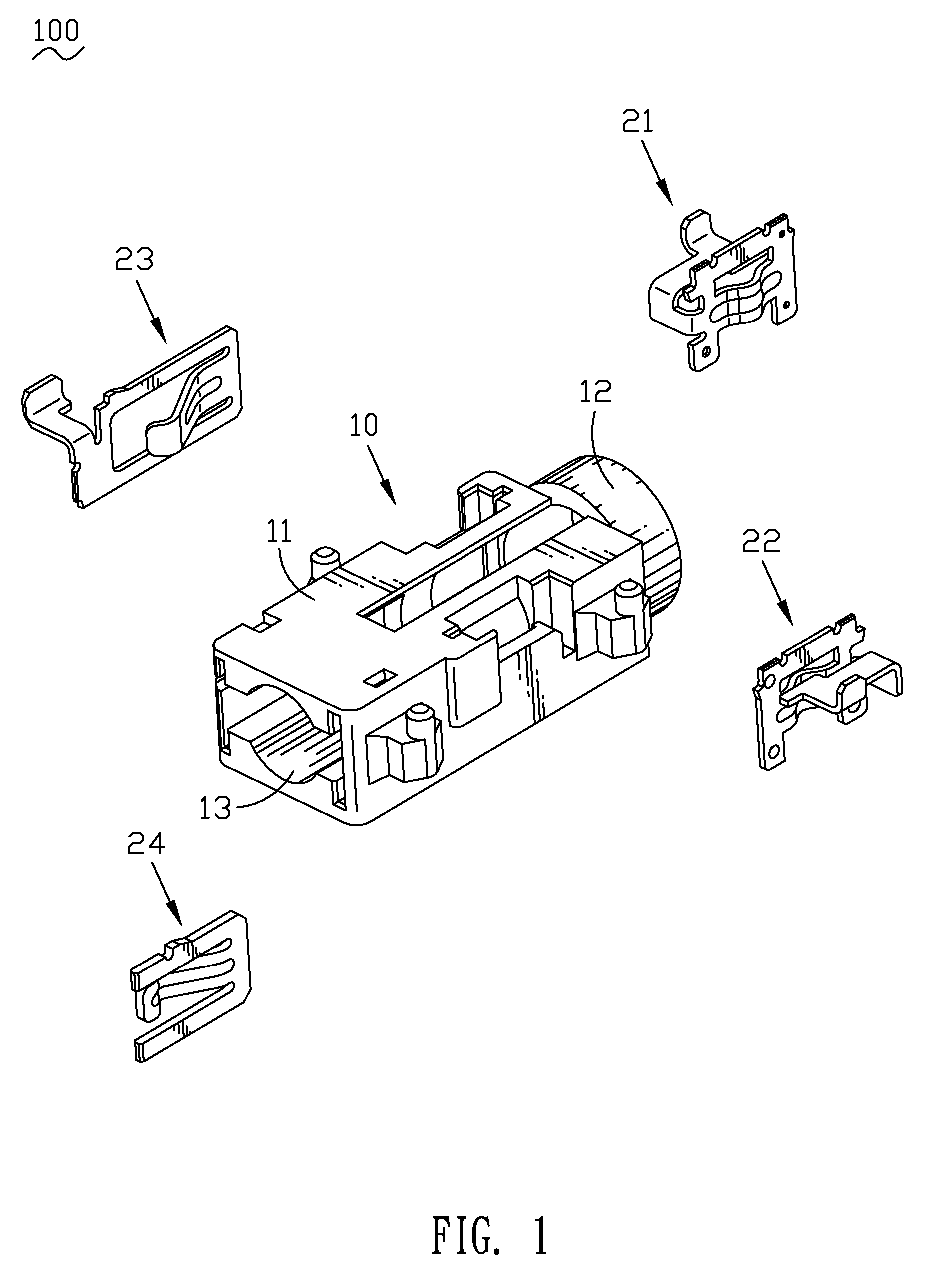
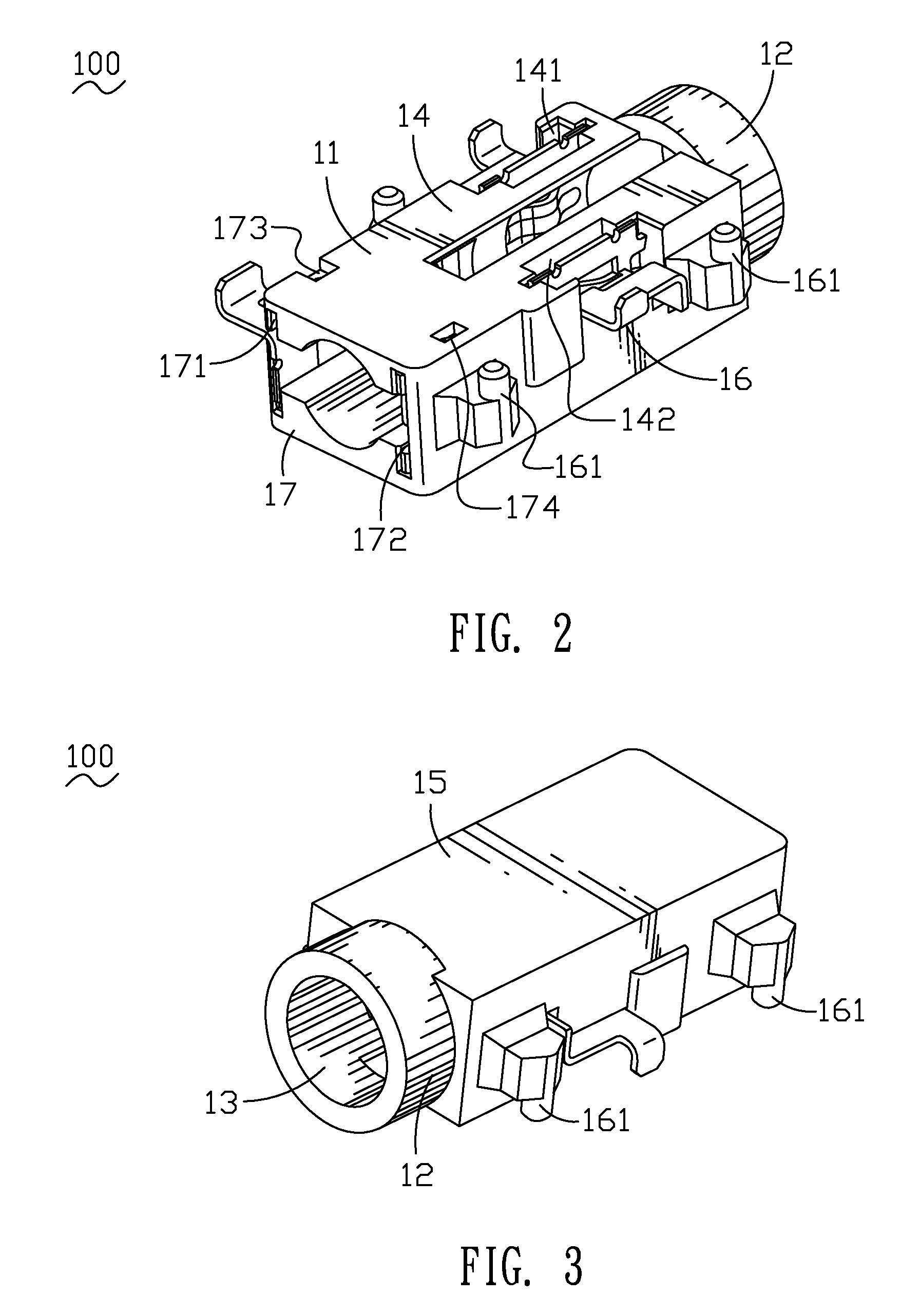
Audio jack connector
InactiveUS7387543B1More forceAvoid less frictionSecuring/insulating coupling contact membersTwo-part coupling devicesCantilevered beamEngineering
An audio jack connector includes an insulative housing and a terminal group received in the insulative housing. The housing has a body, a mating portion extending from one end of the body along an axis direction of the body and an insertion hole defined in the mating portion and passing through the body and mating portion along the axis direction of the body. At least slots connected to the insertion hole are defined in the body. The terminal group includes a first set of terminals with simple supported beam structure and a second set of terminals with cantilever beam structure. The first set of terminals with simple supported beam structure have an U-shaped fixed portion with two side arms defined at the opposite sides of the fixed portion. A resilient arm connects the side arms together. The resilient arm has a contact portion at the middle, the contact portion projects inward into the insertion hole, so the outer surface of the first resilient arm is formed as a concave.
Owner:CHENG UEI PRECISION IND CO LTD
Hydraulic synchronizing coupler for a free piston engine
InactiveUS20060042575A1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeFree piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. A hydraulic coupler in communication with the pumping chambers will synchronize the motion of the inner and outer piston assemblies to assure that the pistons in the opposed cylinders are operating in opposition to one another.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Sodium cooled pistons for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6904876B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeAir coolingPistonsFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. At least one of the pistons includes one or more generally axially extending bores partially filled with a sodium compound. As the piston reciprocates, the sodium moves back and forth in each cooling bore, thereby better distributing heat in the piston.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Guide for transmission device
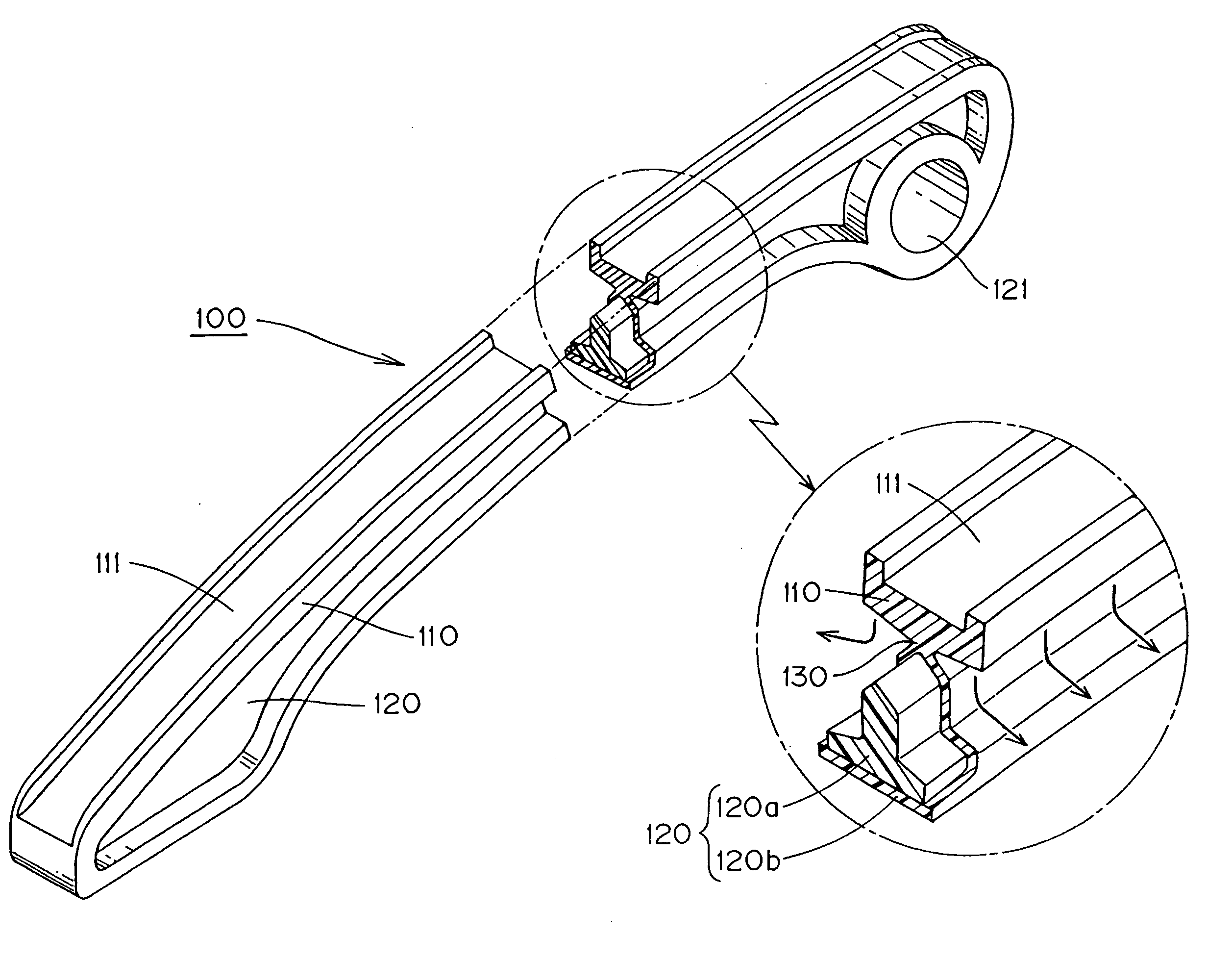
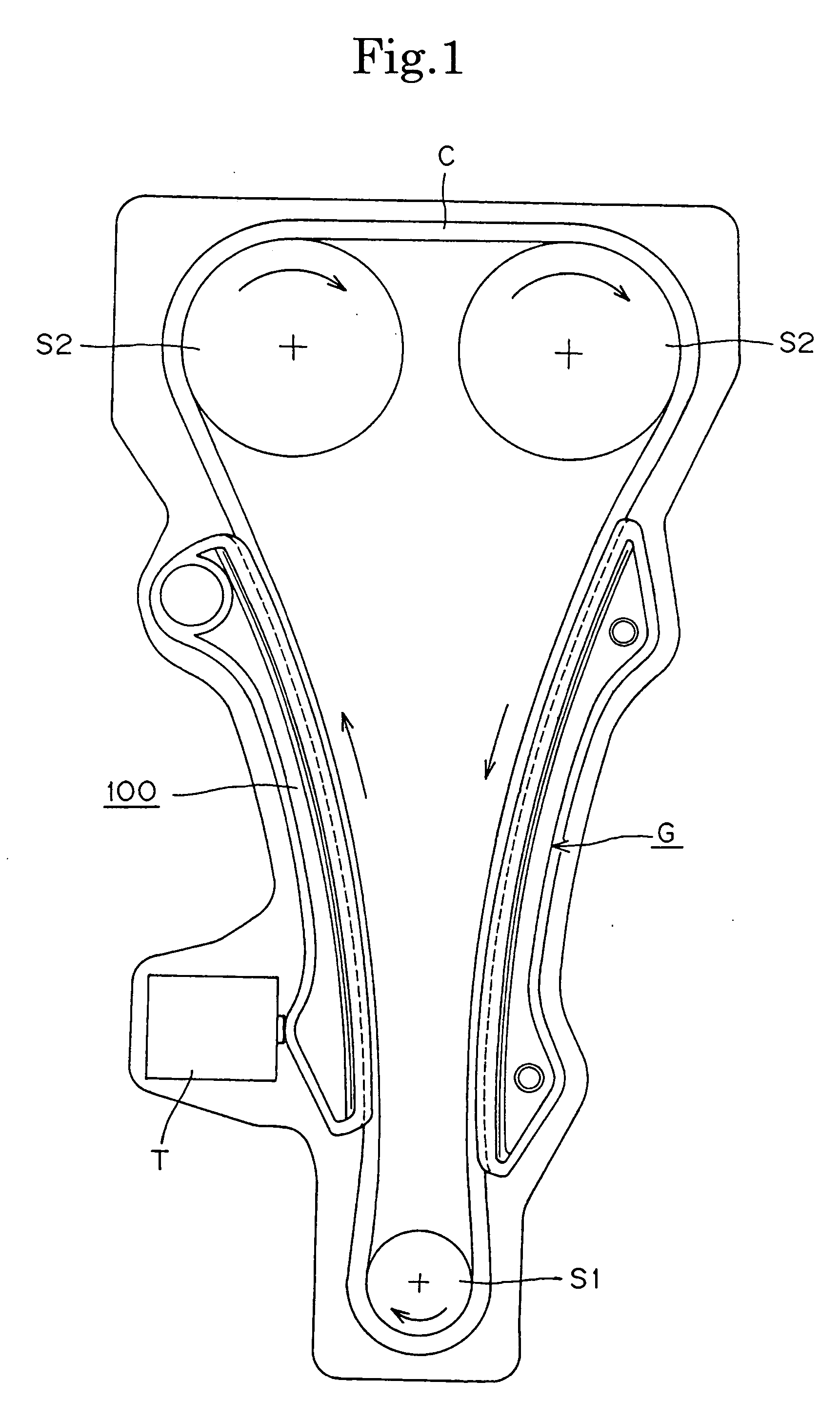
In a guide for a timing chain, a slide rail and a rail support are formed by sandwich molding. The rail support includes a core formed of a glass fiber reinforced polyamide 66 resin and a skin layer formed of a polyamide 66 resin. The slide rail is composed entirely of a polyamide 66 resin and is continuous with the skin layer of the rail support. A narrow connecting region formed of polyamide 66 resin is disposed between the rail support and the slide rail. The narrow connecting region prevents the glass fiber-reinforce resin from entering the slide rail in the sandwich molding process.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
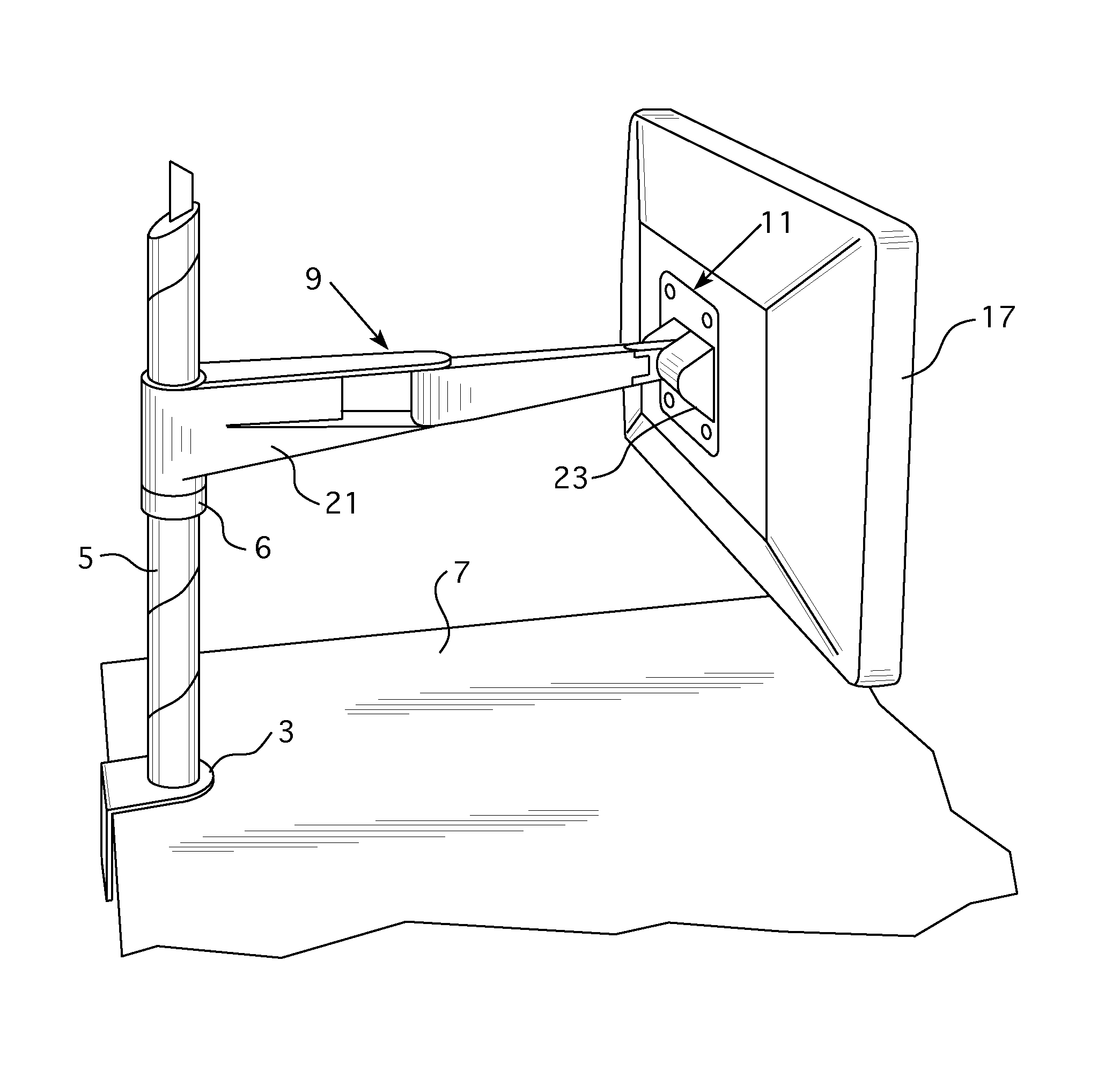
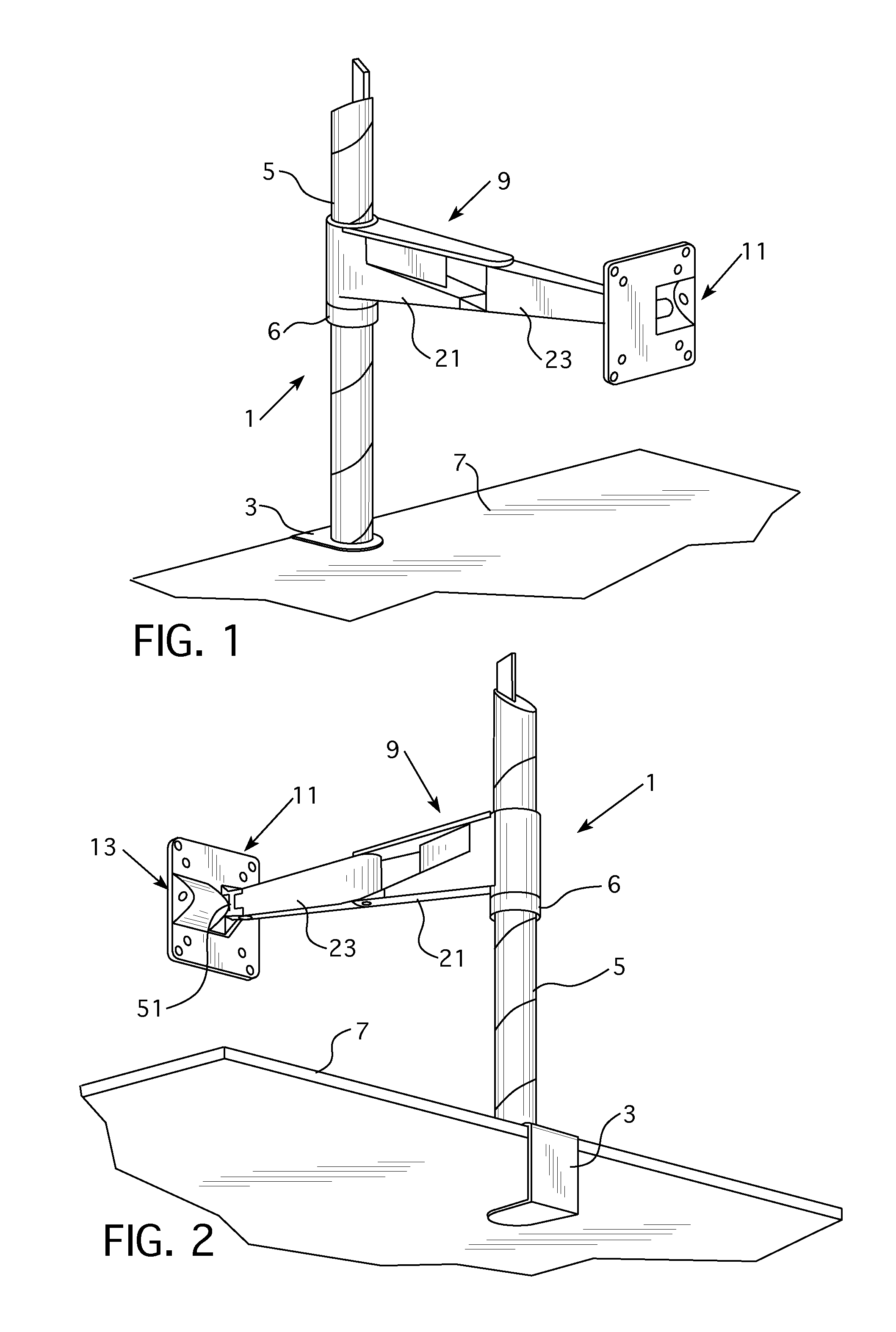
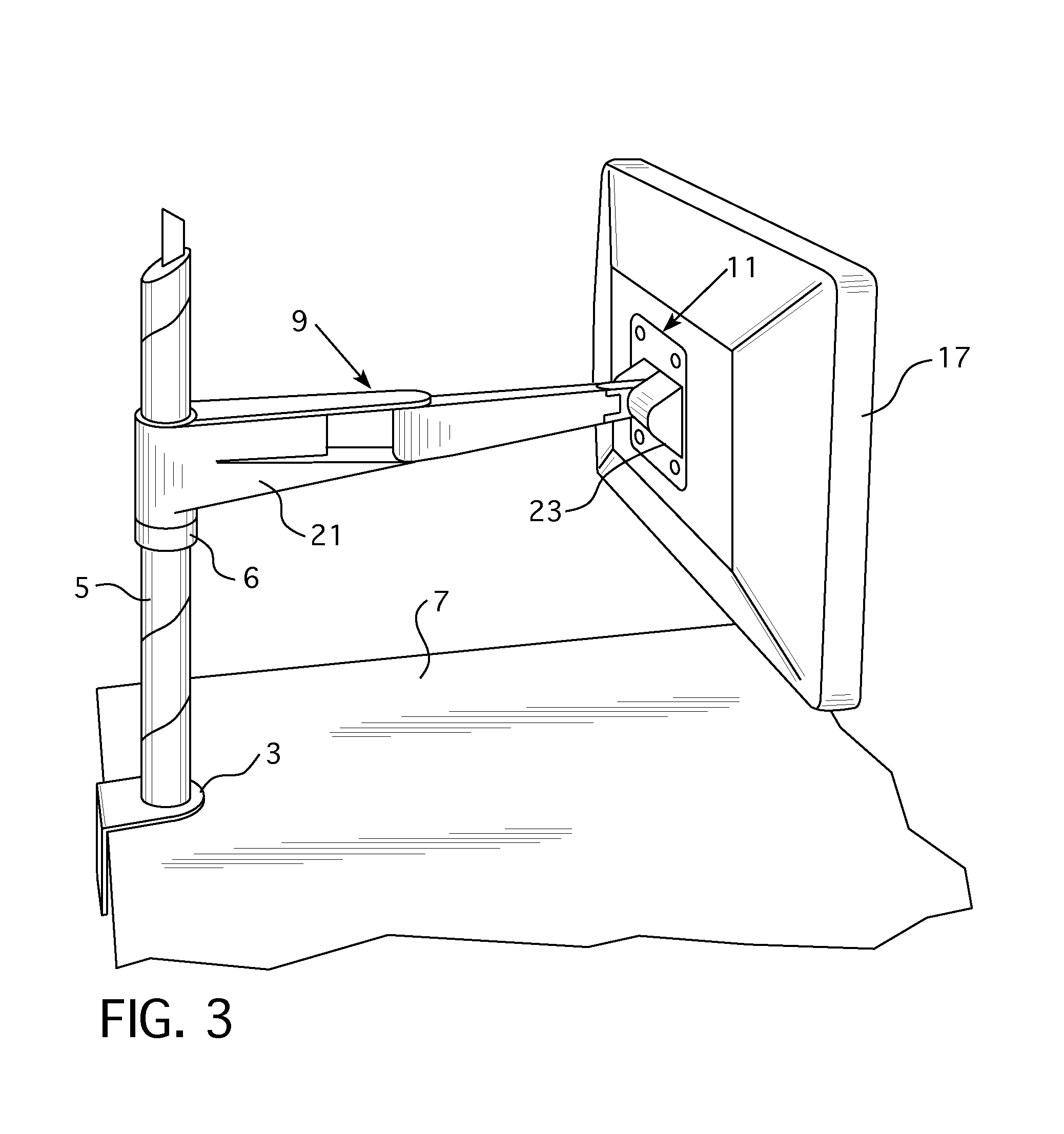
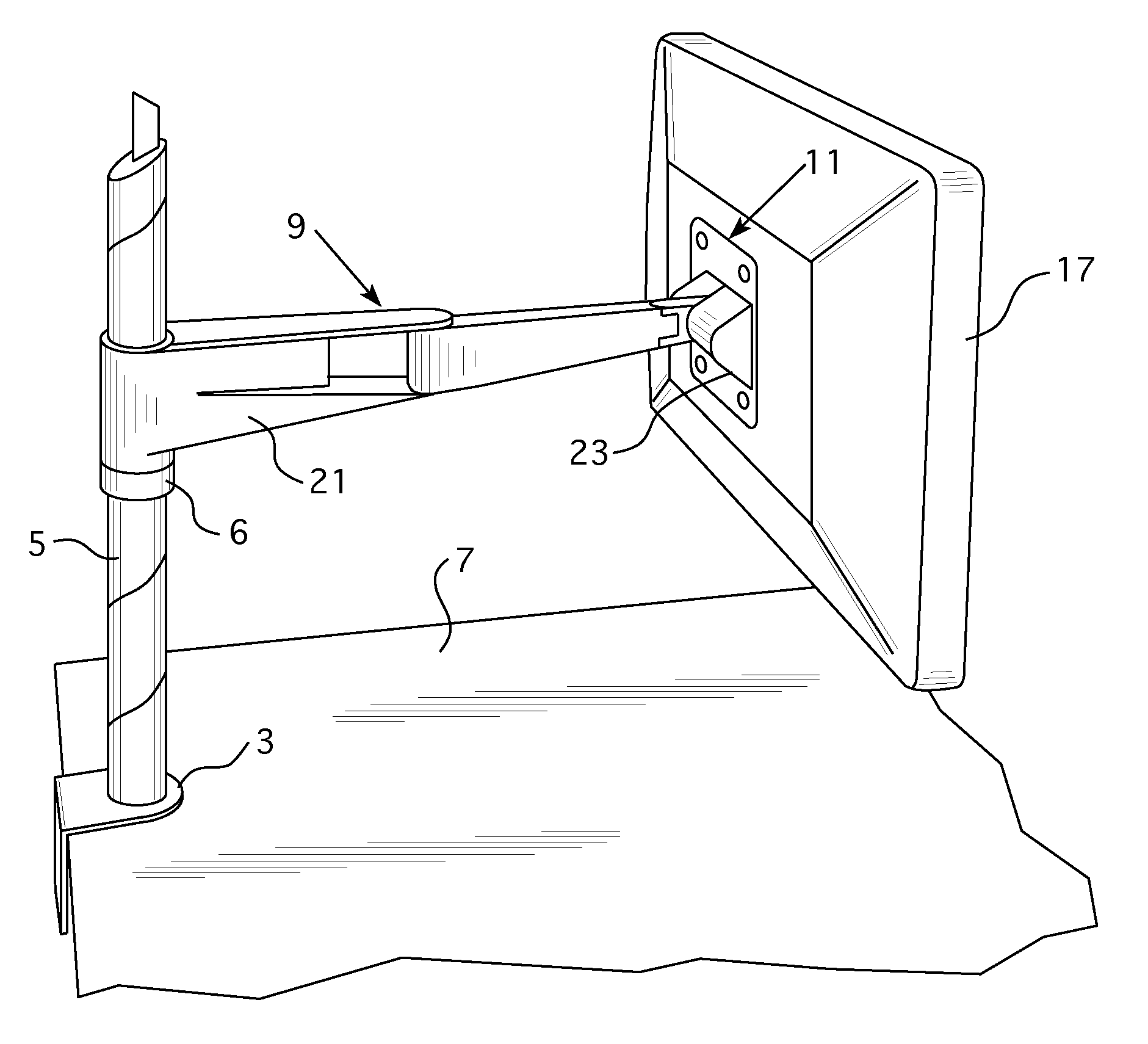
Friction adjustment mechanism for a support apparatus
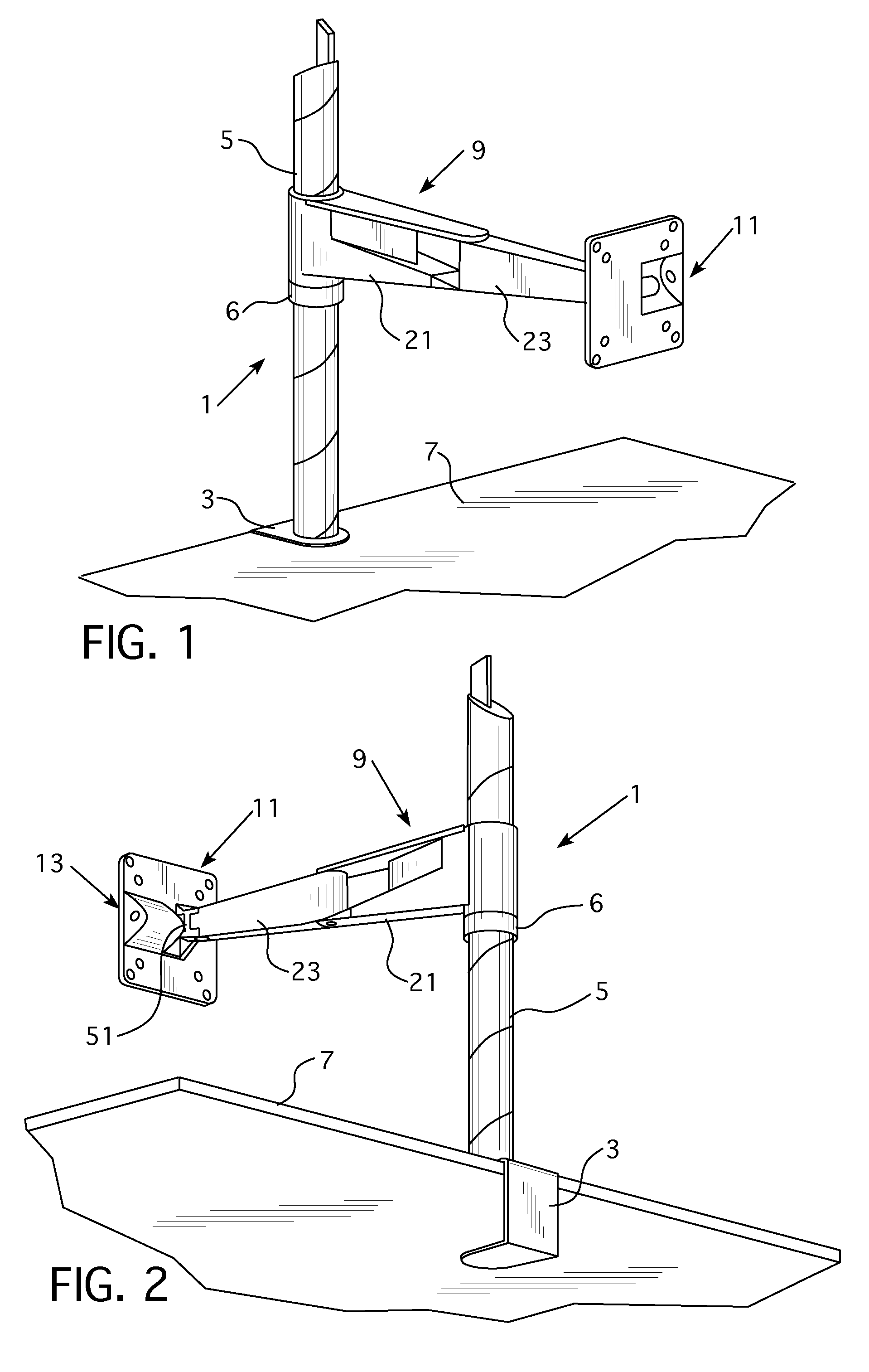
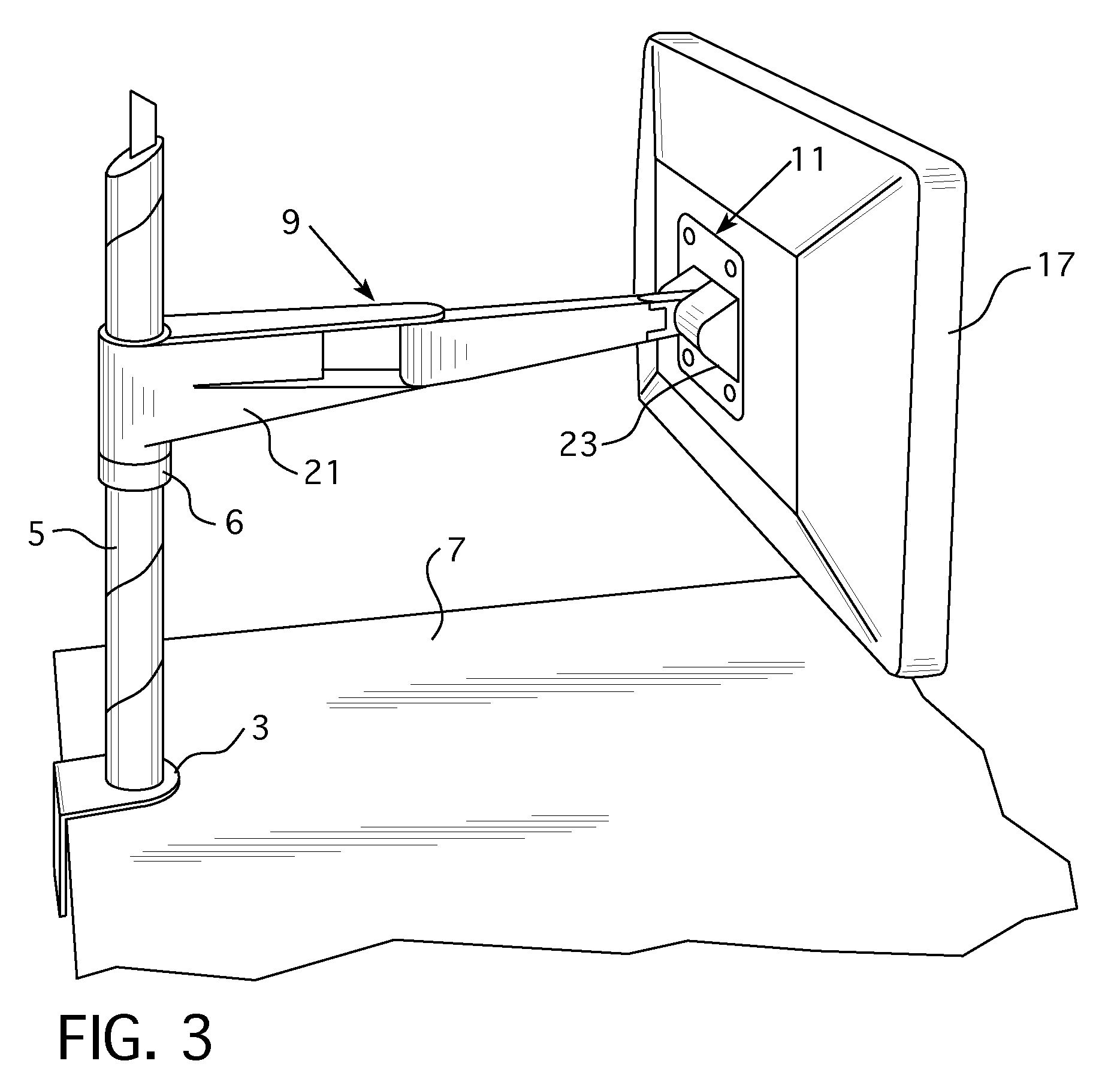
ActiveUS20130221174A1Increase or decreaseAvoid less frictionCandle holdersLighting support devicesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A support apparatus includes an arm assembly attached to a mounting body. A frictional adjustment mechanism is provided between the mounting body and the arm assembly that permits an amount of friction induced by tilting of the mounting body to be adjusted so that a greater or lesser amount of force is needed by a user to tilt the mounting body and any object held by the mounting body. Preferably, the mounting body is configured to hold a monitor, liquid crystal display, or other display device.
Owner:KNOLL INC
Method for determining the path and pressure wear condition of a valve mechanism and valve arrangement using such a valve
InactiveUS20100147395A1Avoid less frictionAvoid disturbing influenceProgramme controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesEngineeringPosition sensor
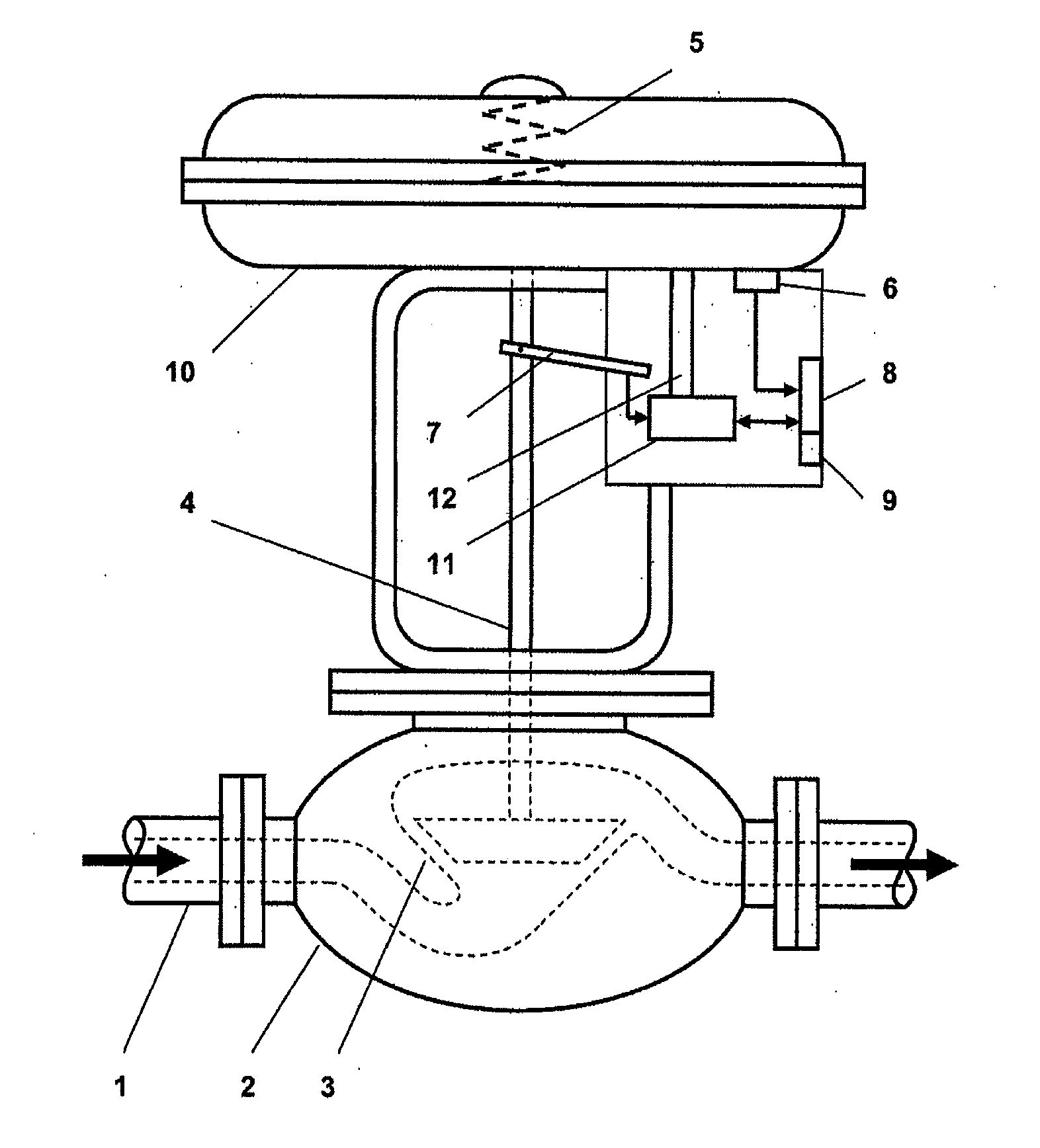
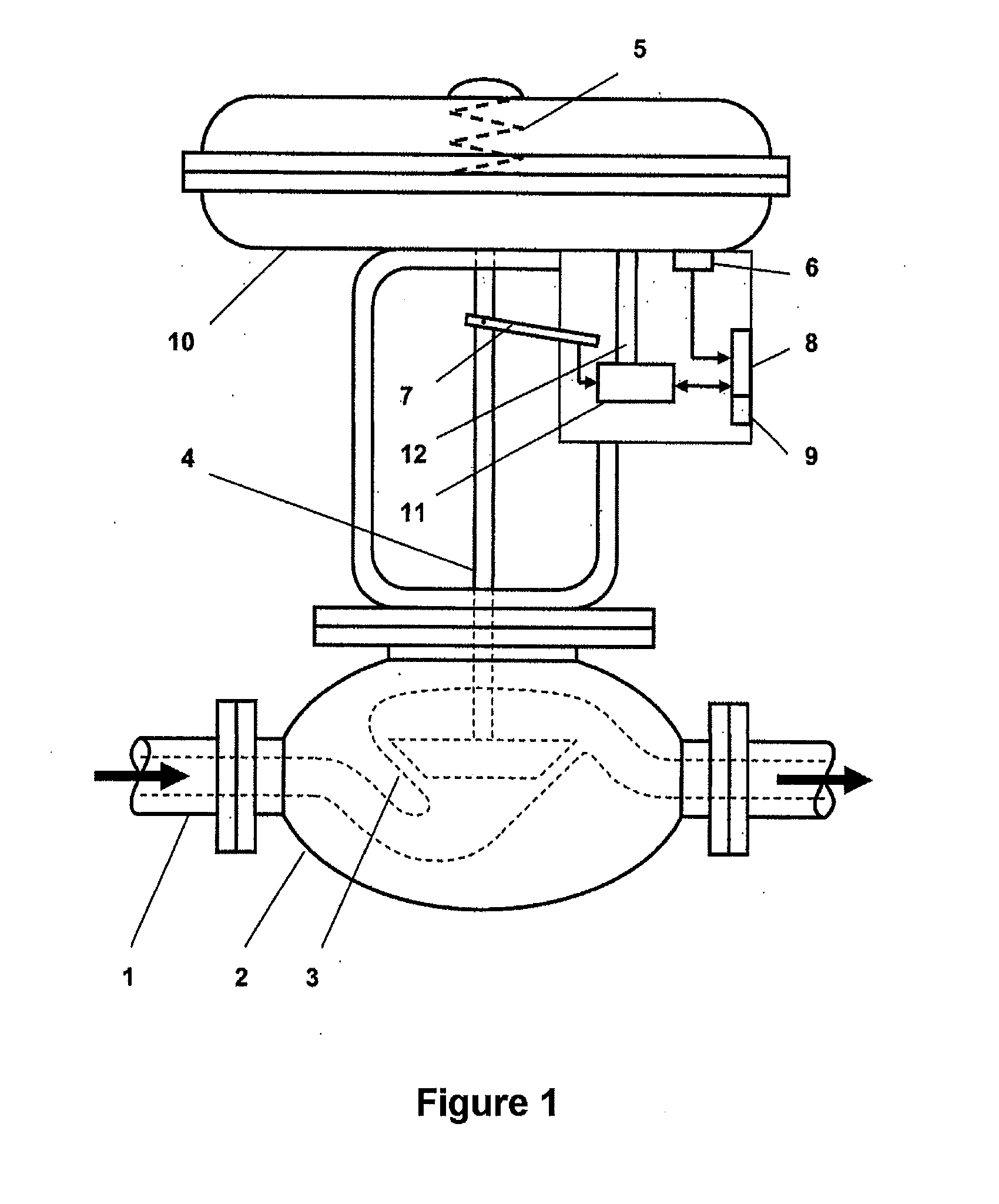
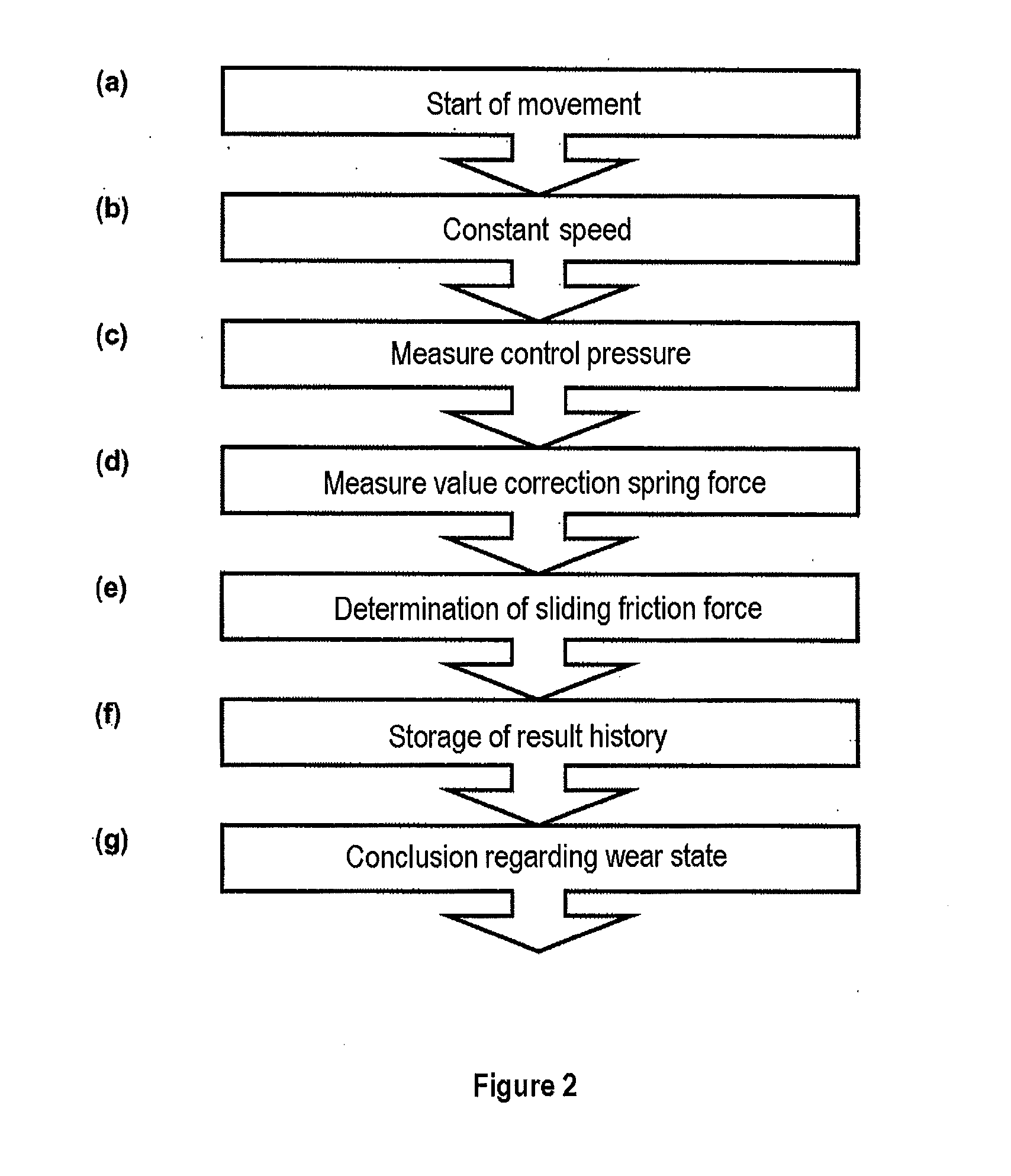
A method for sensor operating-state determination of a valve arrangement to control a process medium flow through a pipeline having a valve element, arranged such that it can move axially within a valve housing via a pneumatic actuating drive by application of control pressure, with the control pressure being measured and evaluated in order to determine the sliding friction during the movement. The valve element can be moved at a constant speed over at least a subarea of the travel movement, the value of which speed is measured via a position sensor system for signal processing, with the currently applied control pressure being measured at approximately the same time for signal processing via a pressure sensor system. The current sliding friction of the valve element can be determined as a measure of wear state from both measured values, by an electronic evaluation unit, based on a proportional drive force expressed by the control pressure which occurs when the valve element is traveling at a constant speed.
Owner:ABB TECH AG
Joint arrangement
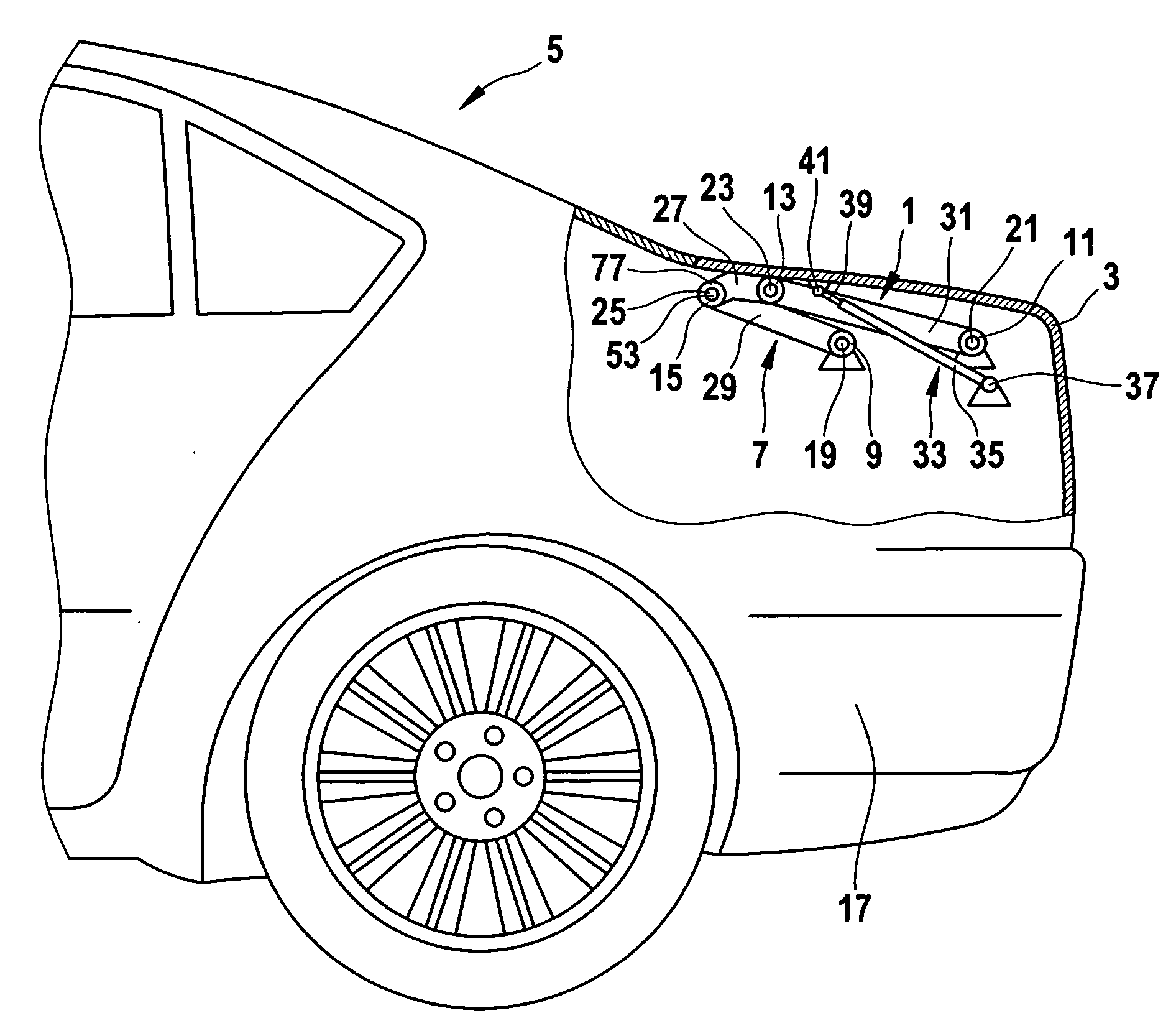
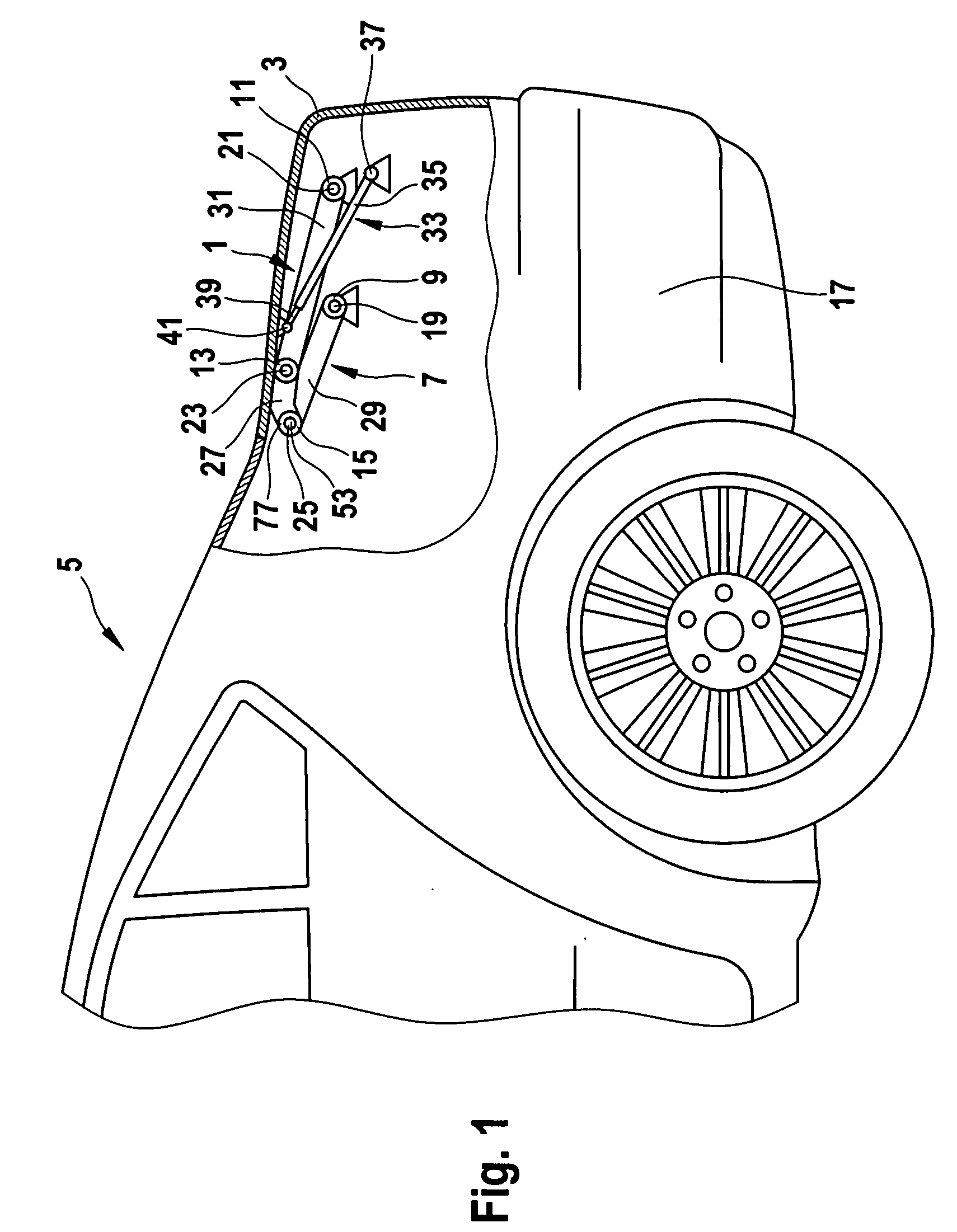
InactiveUS20070209160A1Reduce frictionMinimizing actuation forcePin hingesWing openersEngineeringMechanical engineering
A multi-joint hinge for a motor vehicle having a body and a panel, the hinge allowing the panel to be moved between an open position and a closed position relative to the vehicle body. The hinge includes at joint having at least one roller bearing, and is preferably a four bar joint having two bearings mounted on the body and two bearings mounted on the panel.
Owner:STABILUS
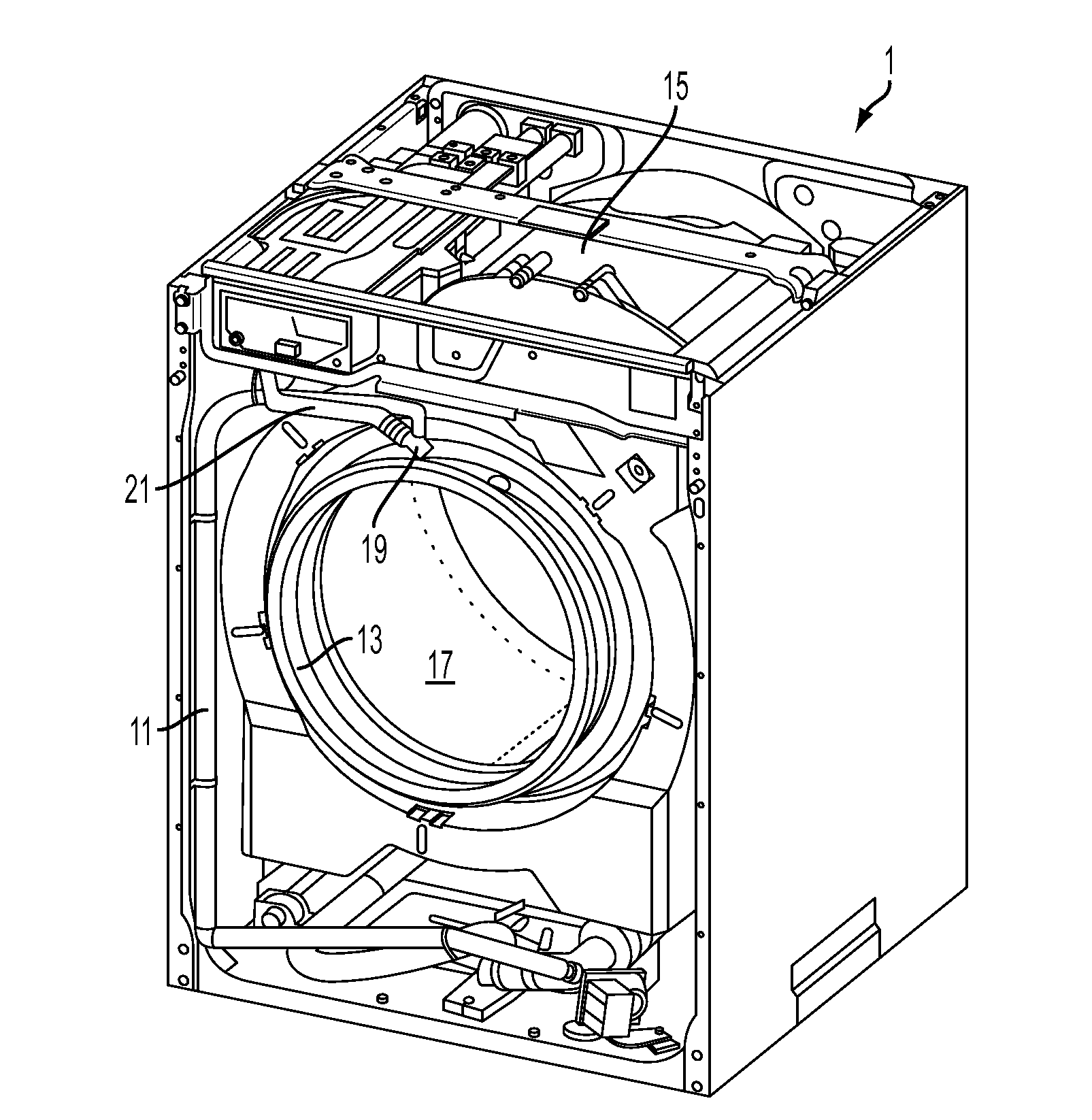
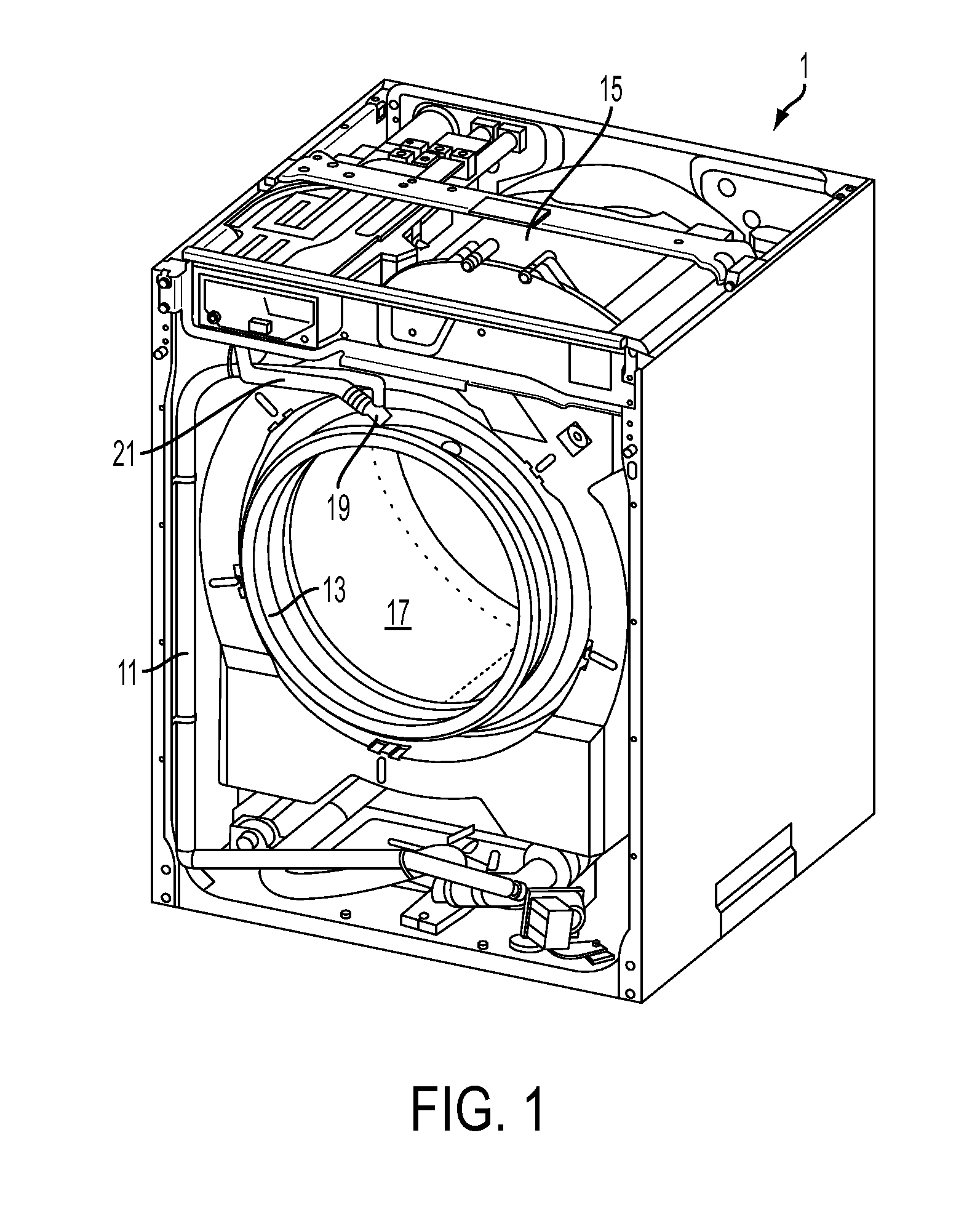
Water Recirculation and Drum Rotation Control in a Laundry Washer
ActiveUS20130081431A1Maximizes exposureImprove wash/rinse effectivenessOther washing machinesControl devices for washing apparatusCost effectivenessEngineering
In a laundry washer, relatively short bursts of operation of a recirculation pump are coordinated with corresponding brief intervals of tub rotation during the initial fill periods. The aim is to thoroughly wet the clothes early in each wash / rinse phase to thus improve the wash / rinse effectiveness, while also avoiding excessive suds formation. Following the initial fill periods and during regular wash / rinse agitations, the recirculation system may also be employed to “recharge” the laundry load with detergent that has settled in the bottom of the tub. In a further aspect of the invention, some or all of the conventional intermediate spin extractions are omitted. In this manner, more water is carried over in the clothes from one wash / rinse cycle to the next. An intermediate spin of reduced speed (RPM) and duration as compared to typical normal intermediate spins may be employed between the wash phase and first rinse.
Owner:ELECTROLUX HOME PROD CORP NV
Tripod type constant velocity universal joint
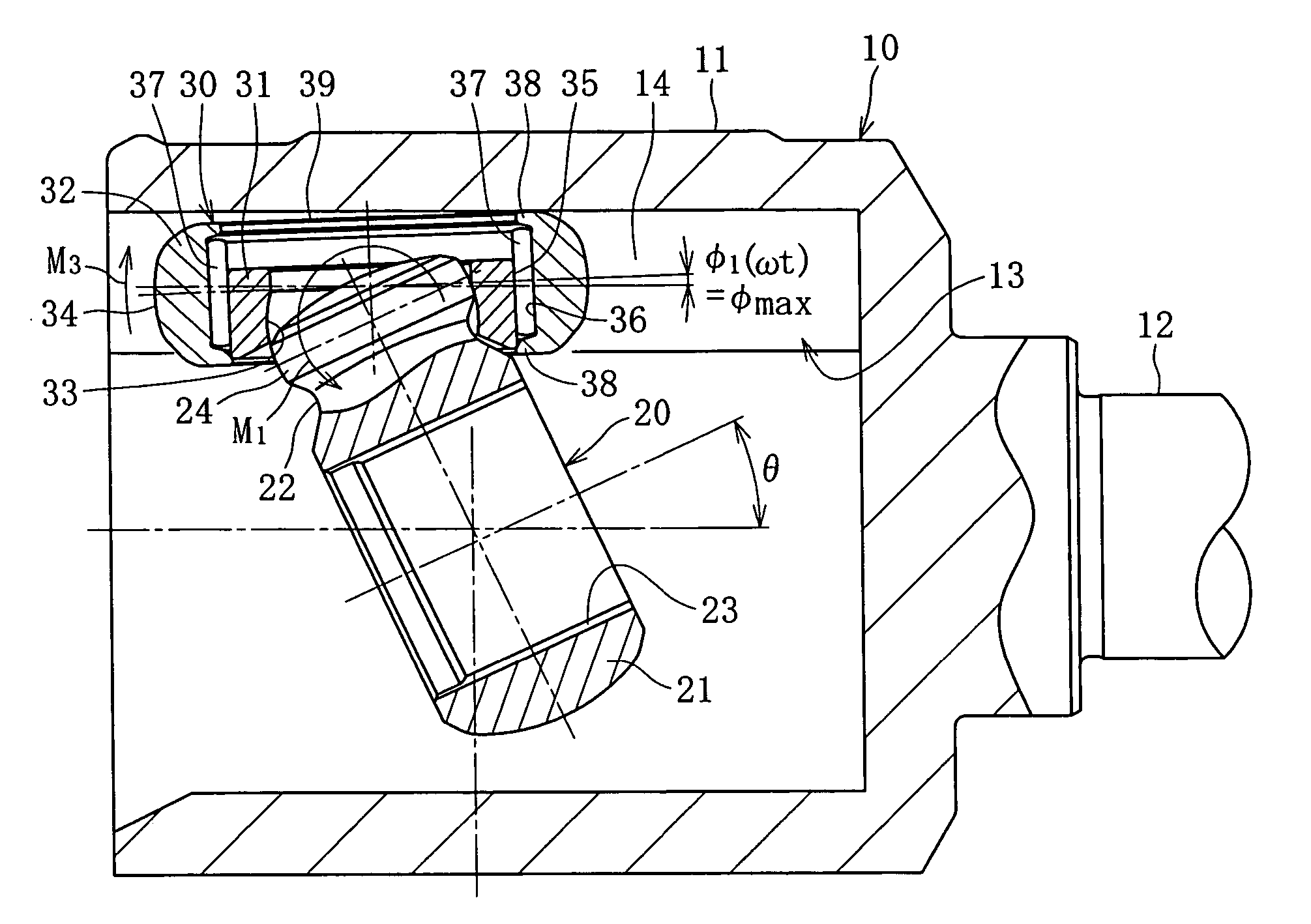
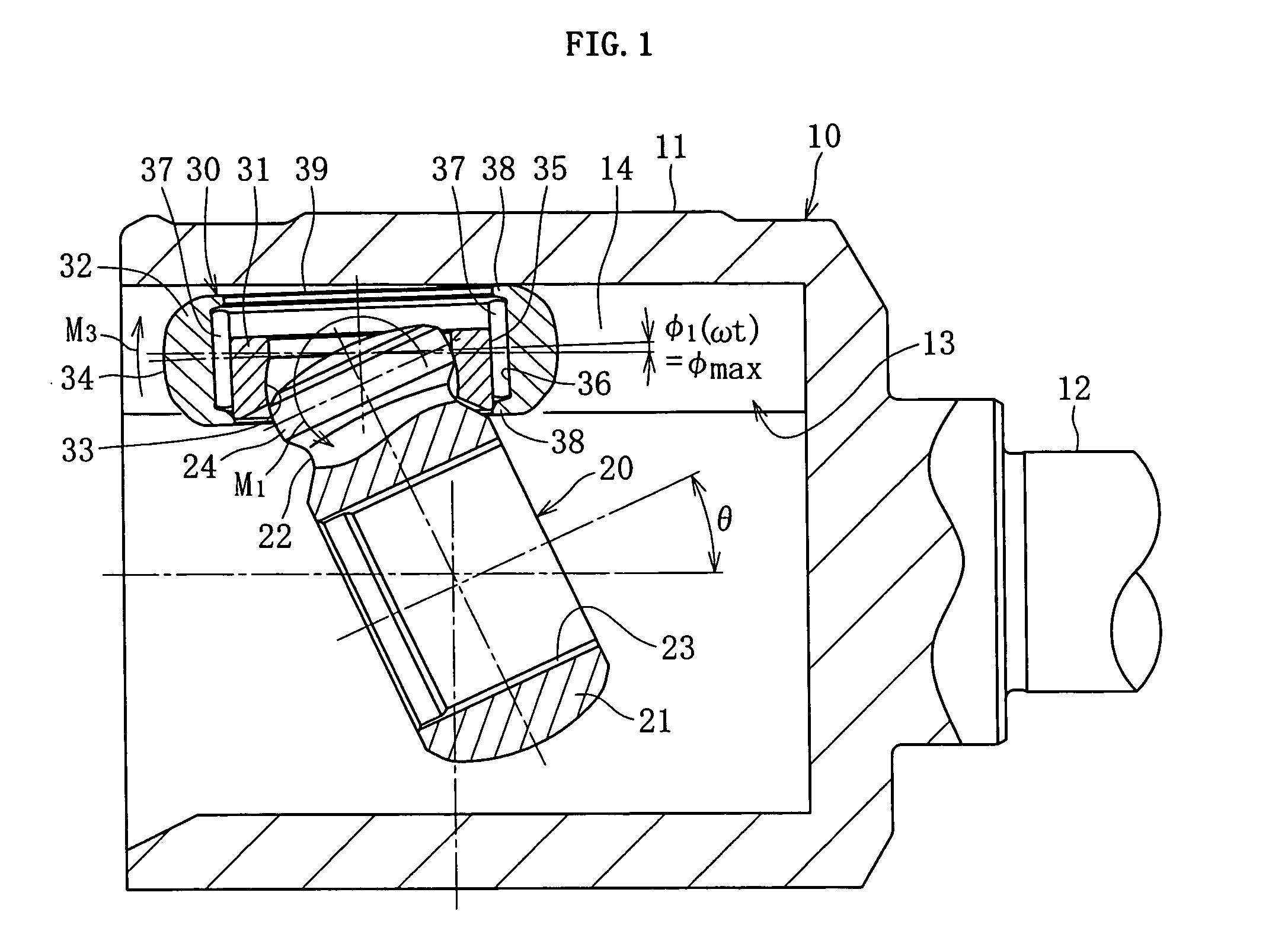
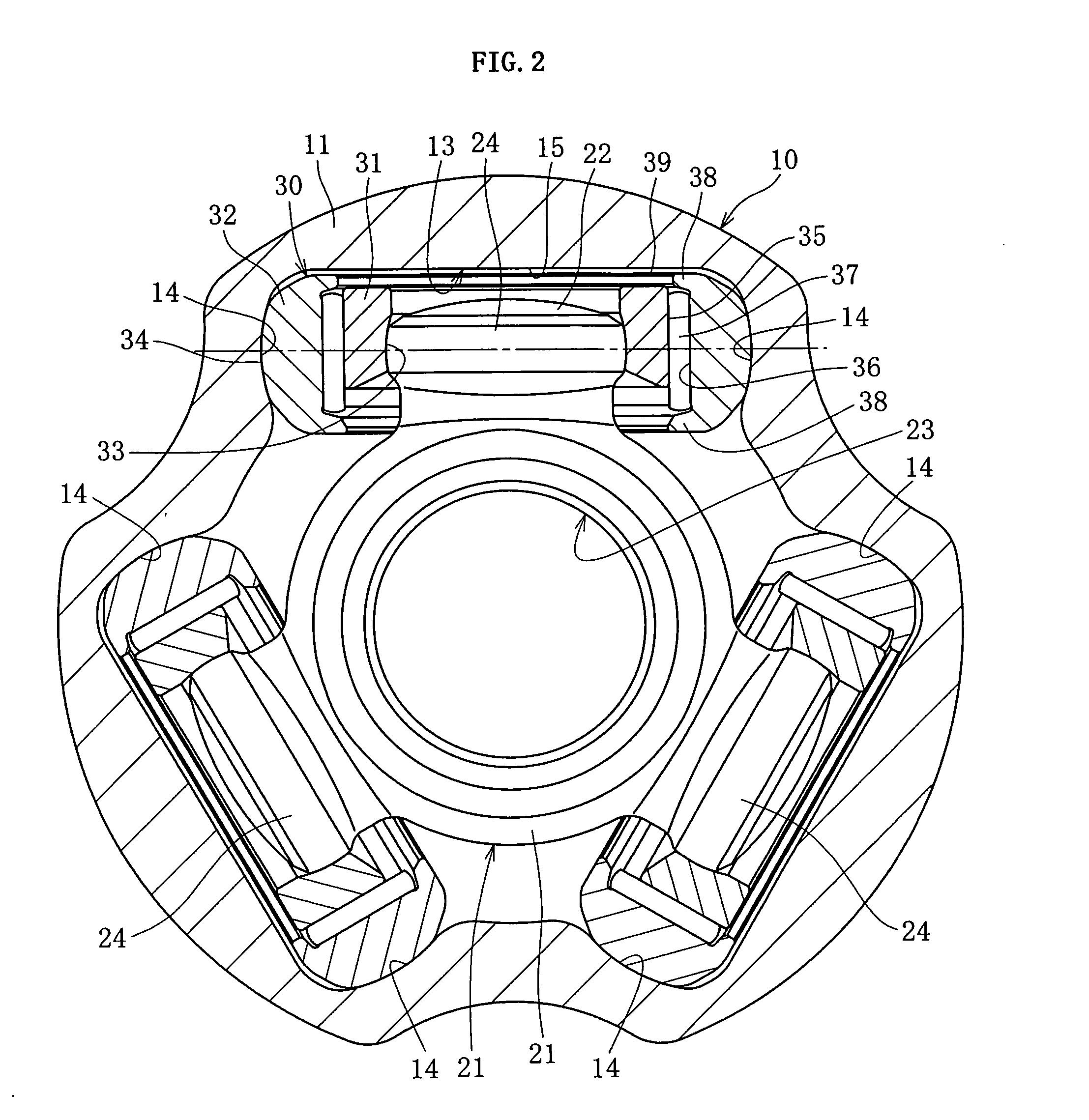
InactiveUS20060030413A1Reduce thicknessImprove retention capabilityYielding couplingRotary machine partsConstant-velocity jointTrunnion
The invention provides a tripod type constant velocity universal joint that can restrain generation of an excessive frictional force inside the joint because of the rotation phase angle of the inner joint member, thereby suppressing vibration and achieving higher rotation durability. The tripod type constant velocity universal joint includes an outer roller rotatably located inside the roller guide section of the outer joint member, and an inner roller spherically fitted to the trunnion of the inner joint member so as to be pivotally rotatable, and to support the outer roller permitting relative rotation and relative axial movement, so that when a torque is applied with the outer joint member and the inner joint member oriented with an operating angle θ, a facet of the outer roller inclined along with the rotation of the inner joint member is sustained by the track groove bottom portion formed in a flat plane.
Owner:NTN CORP
Device and method for launching a projectile across a range
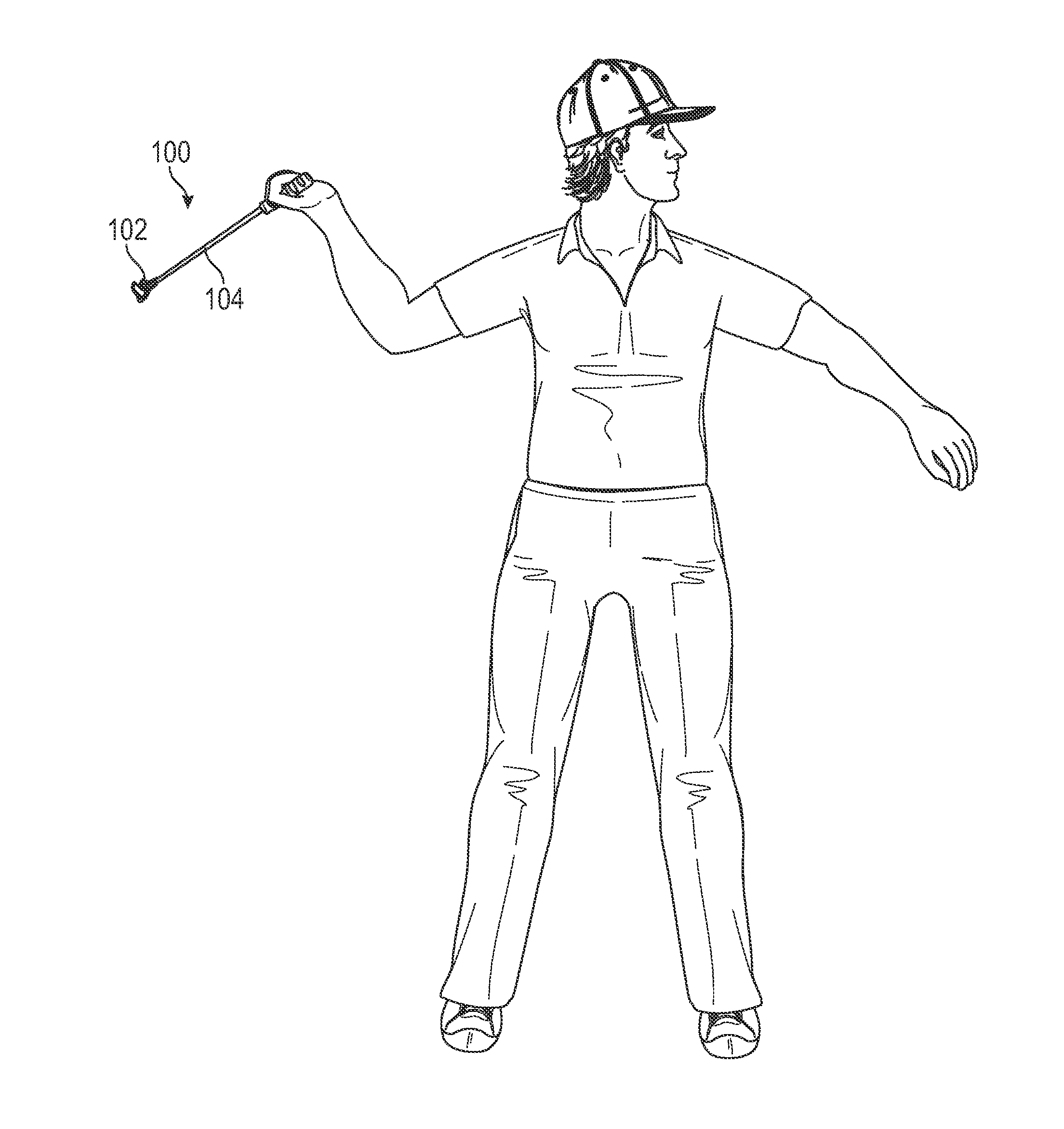
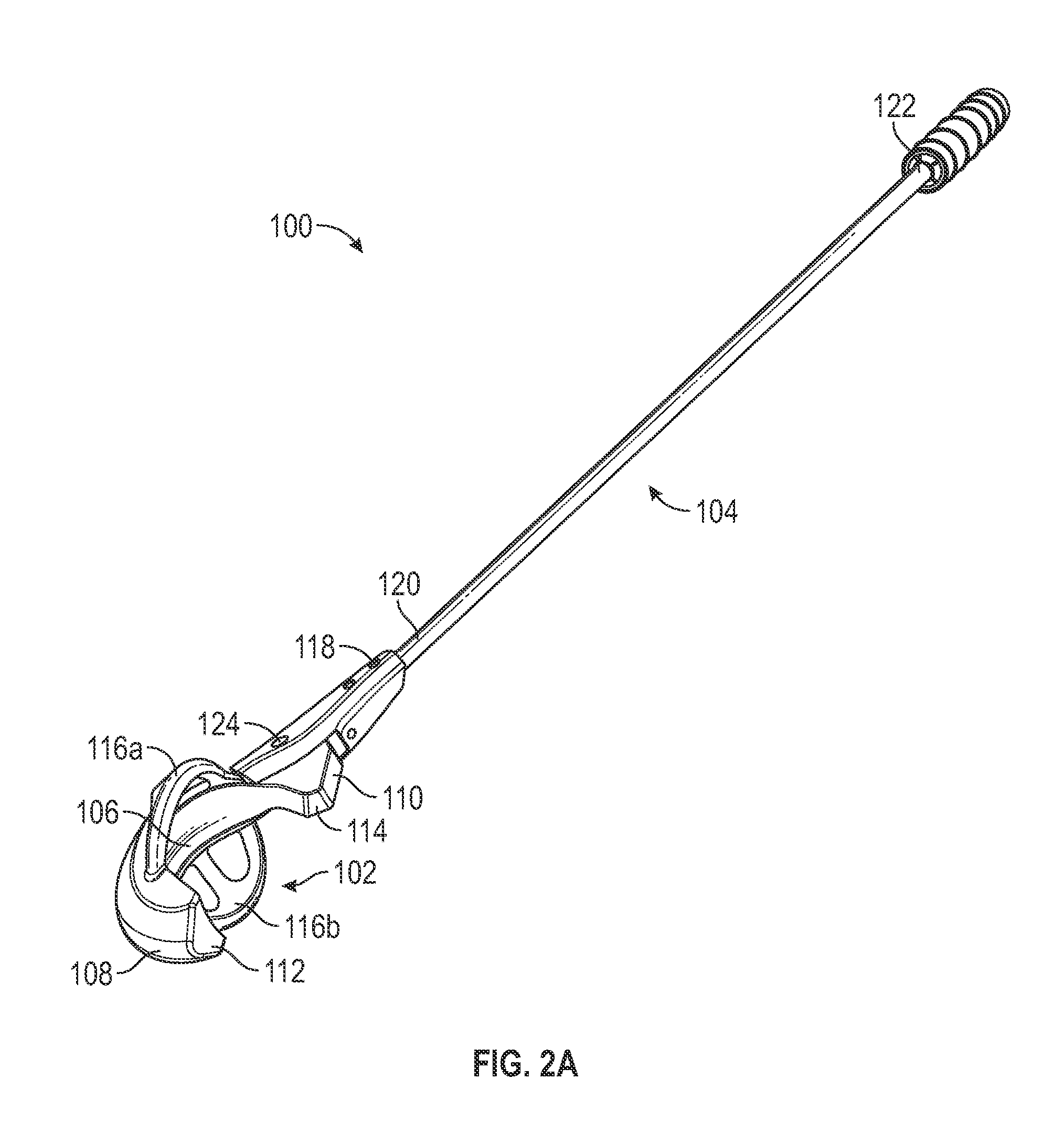
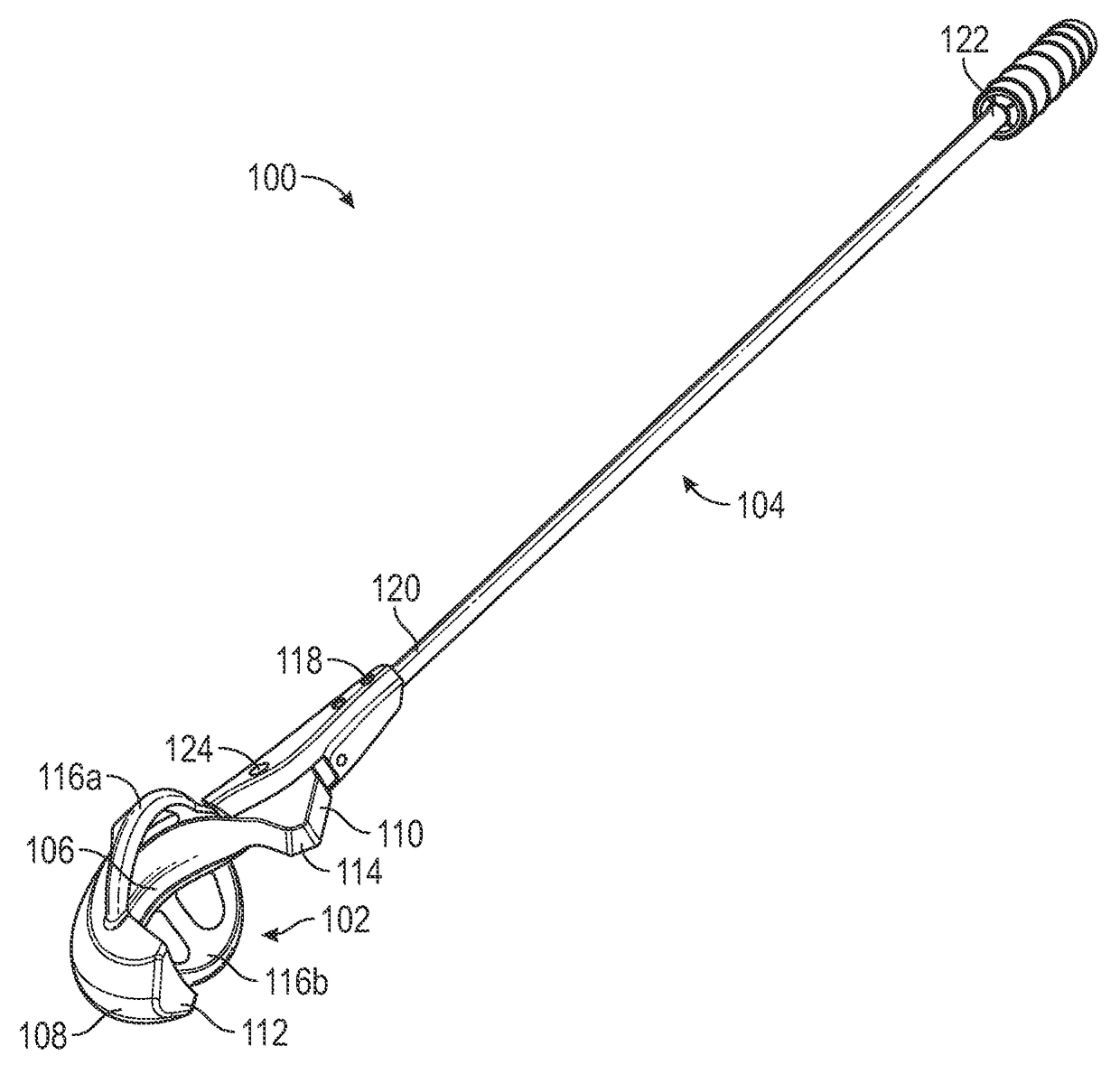
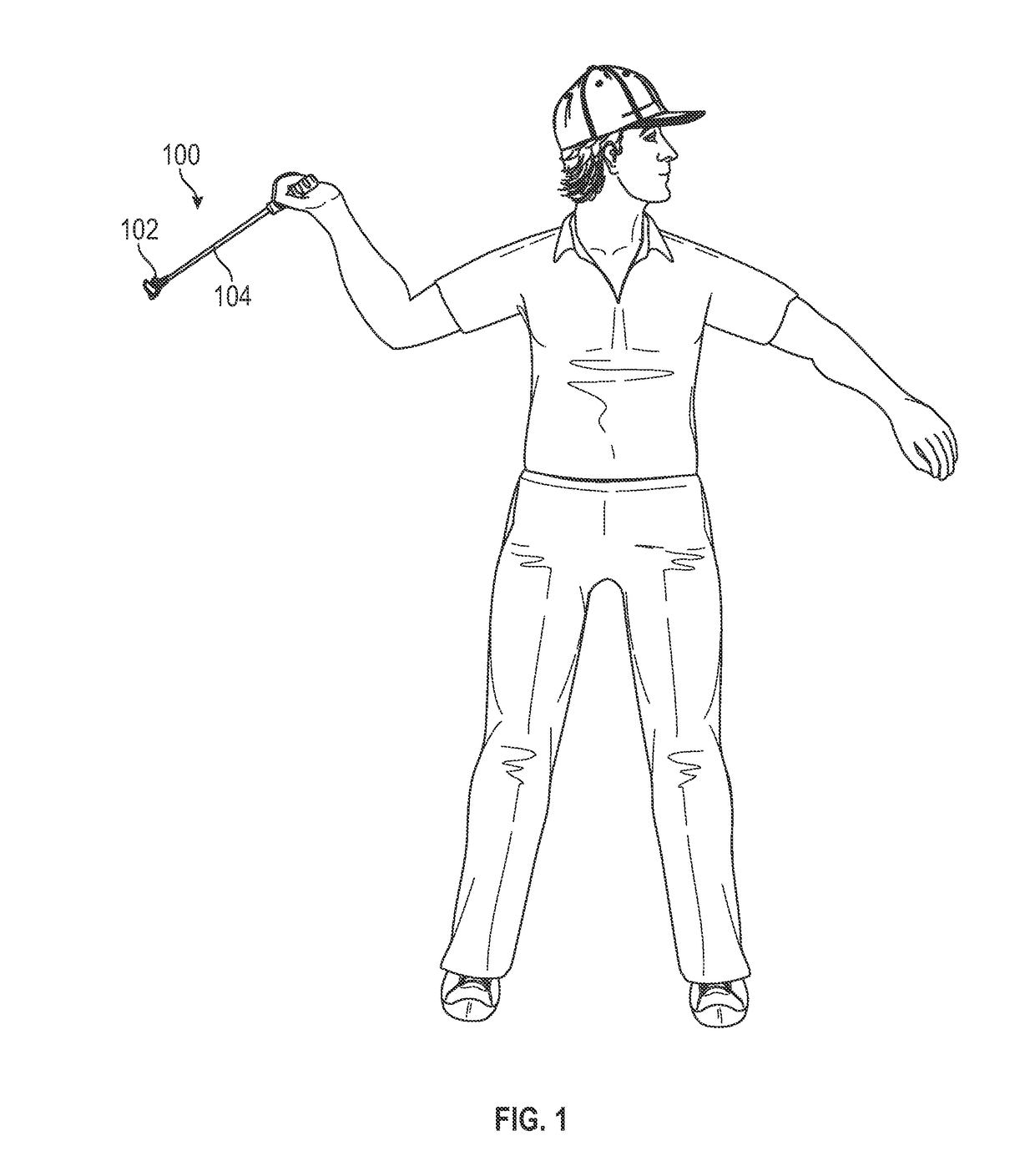
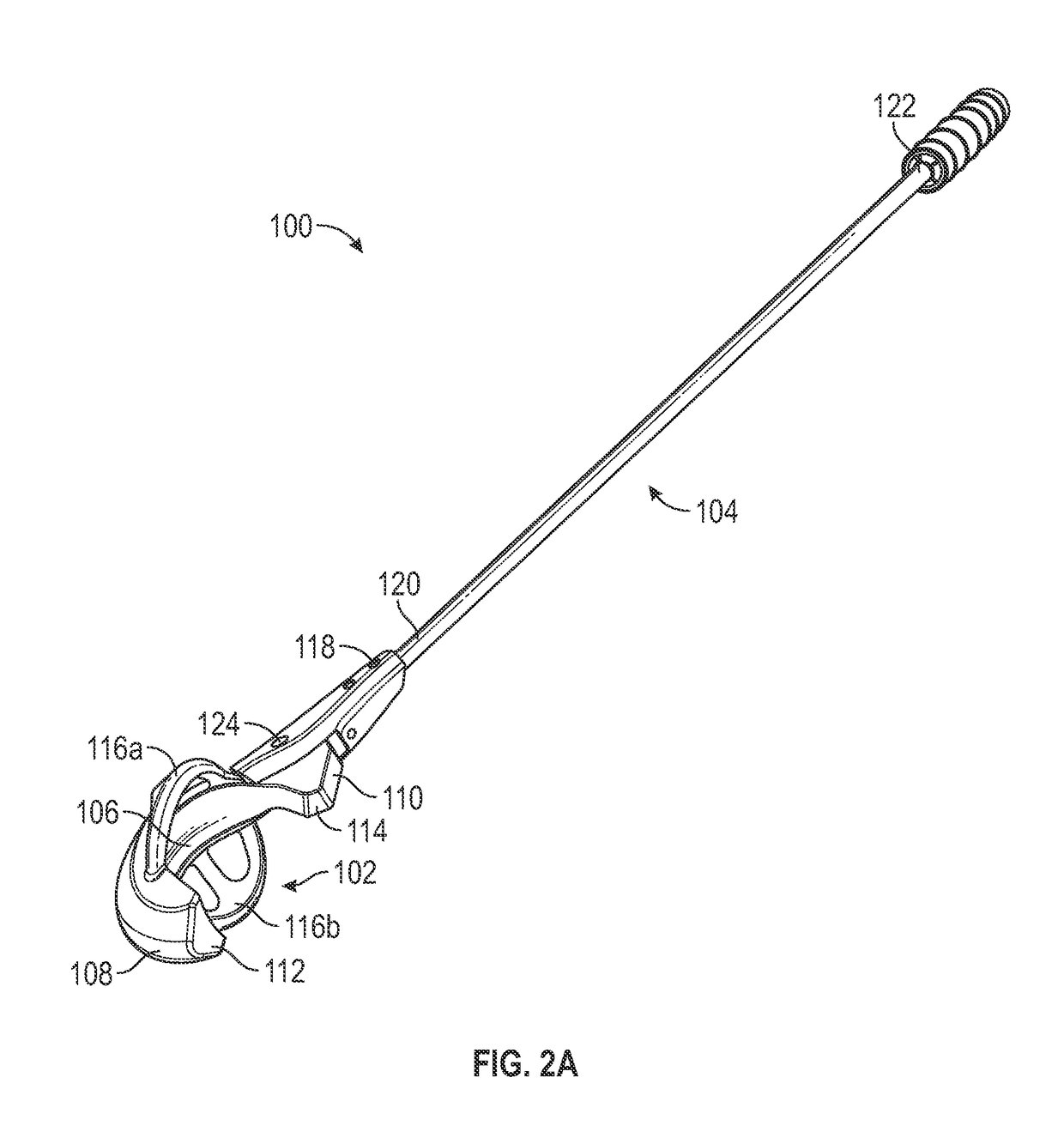
ActiveUS20160375333A1Facilitates launching projectileEasy to controlThrow gamesSpace saving gamesGolf course turfDistal portion
A device and method for launching a projectile, such as a golf ball, across a range. The device enables a golf ball to be launched across a golf course with greater control than is possible with a traditional golf club. The ease of loading the projectile into the launching device and swinging the launching device forward adds greater distance to the projectile due to an increase in angular momentum and back spin on the projectile. The device includes a C-shaped head defined by a nest, a pair of lateral retention arms, and a base. A distal portion is longer than a proximal portion to create backspin on the projectile. The concavity and lateral arms hold the projectile in place. The distal and proximal portions terminate at concave points that grip dimples on the projectile. The base is fixedly attached to a shaft, which is used for swinging the head.
Owner:SYMTAR VENTURES
Friction adjustment mechanism for a support apparatus
ActiveUS8651444B2Increase or decreaseAvoid less frictionCandle holdersLighting support devicesLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
Owner:KNOLL INC
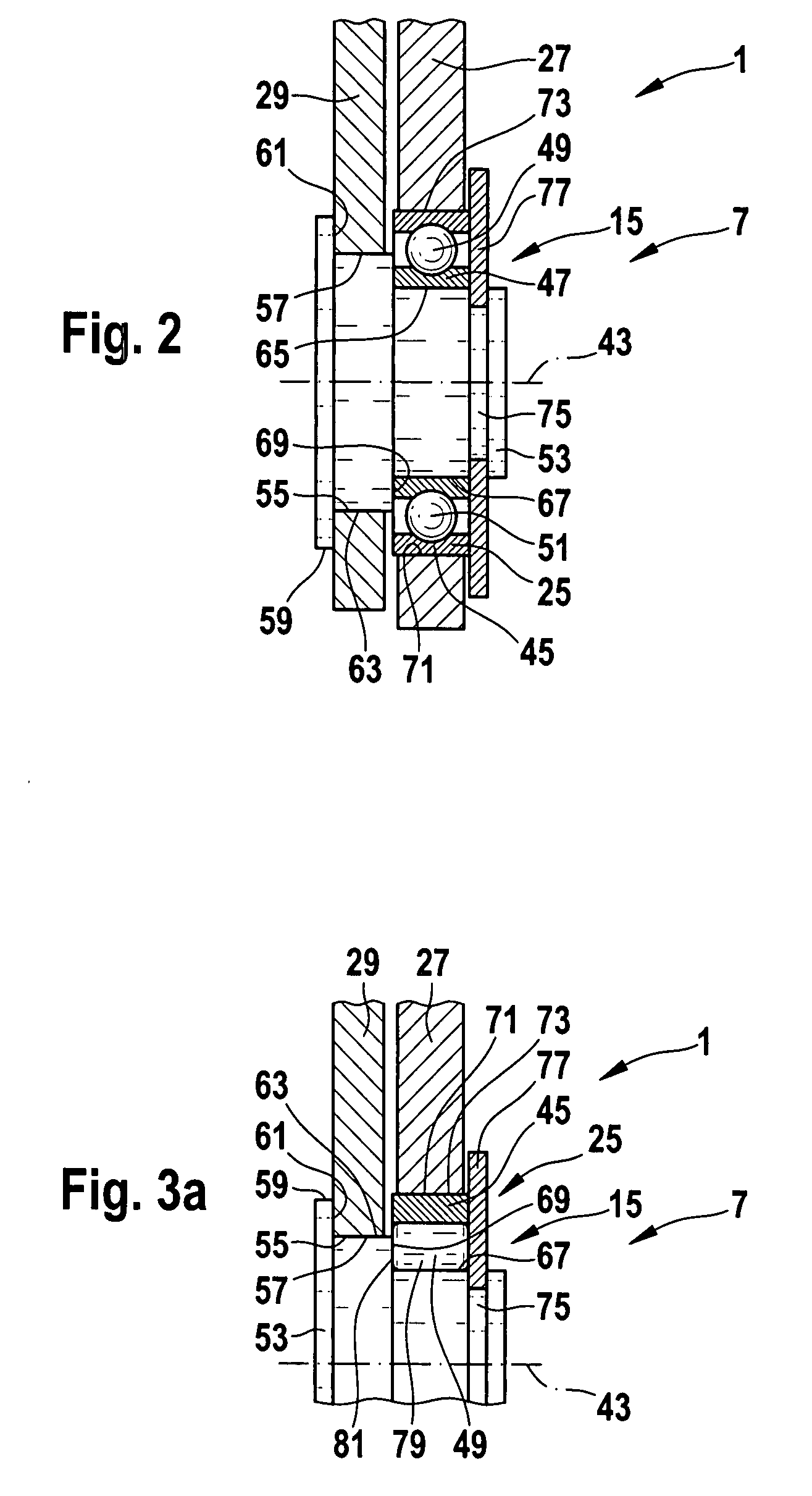
Wet type friction plate
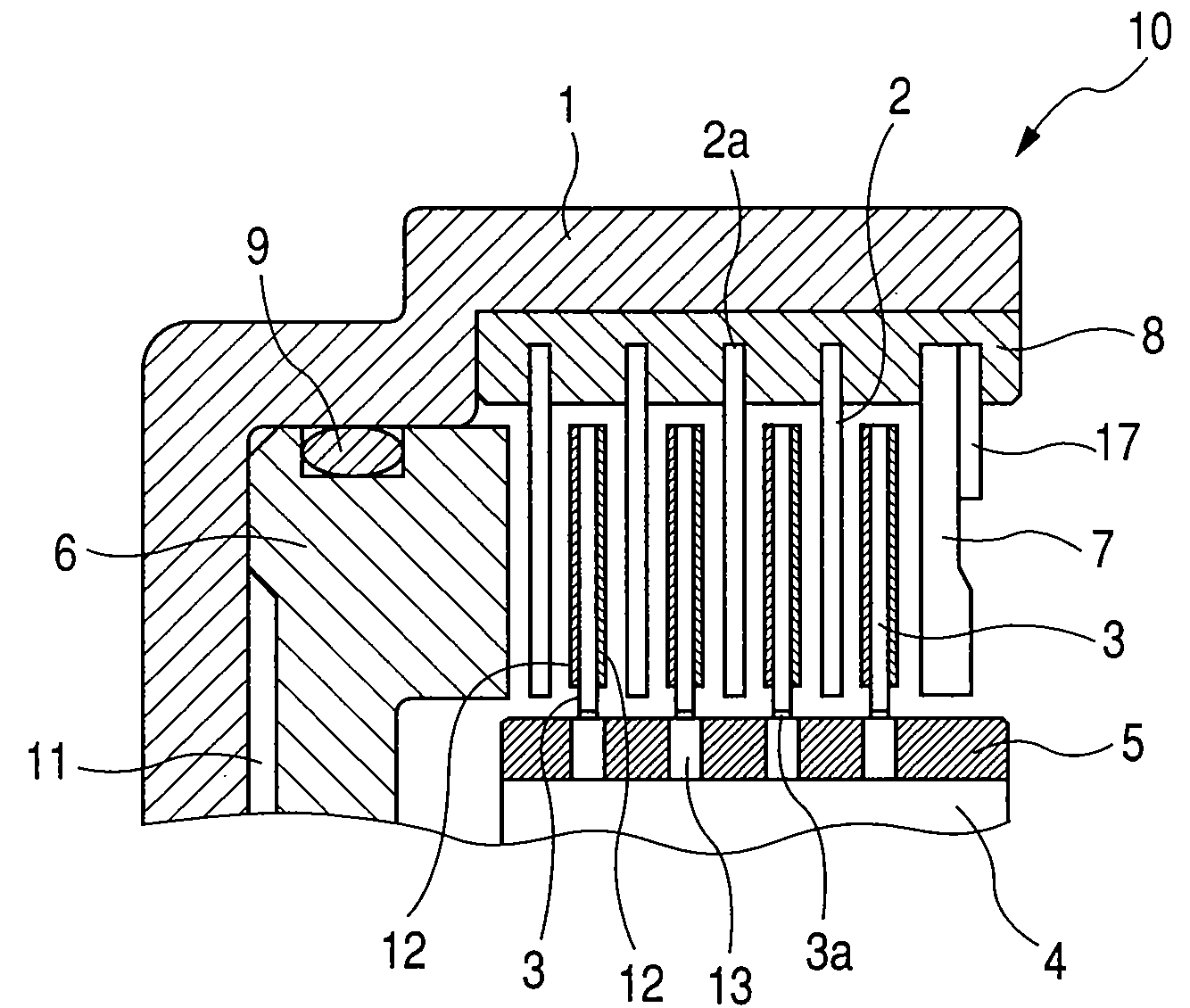
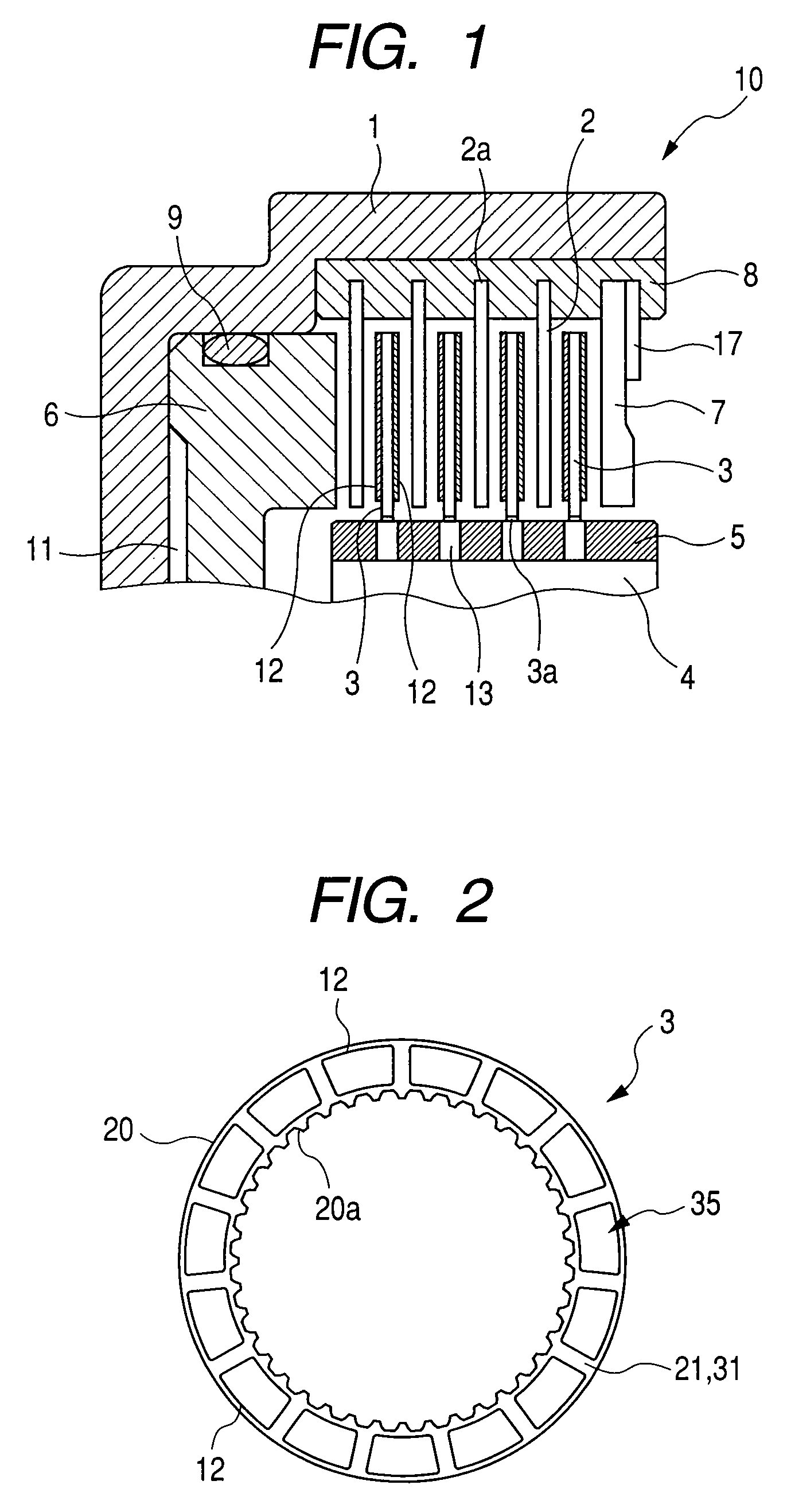
InactiveUS20080236985A1Inhibit migrationWithout decreasing lubricating performanceFluid actuated clutchesFriction clutchesEngineeringMechanical engineering
The present invention provides a wet type friction plate having a friction surface formed by securing a plurality of friction material segments to a substantially annular core plate, in which a groove extending through from an inner diameter side to an outer diameter side is formed between the friction material segments, and a recessed portion facing toward the core plate is formed in a side surface of the friction material segment defining the groove.
Owner:NSK WARNER
Image forming device and method of manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20080013115A1Easy to assembleEasy to operateDigitally marking record carriersDigital computer detailsImage formationEngineering
Owner:MURATA MASCH LTD
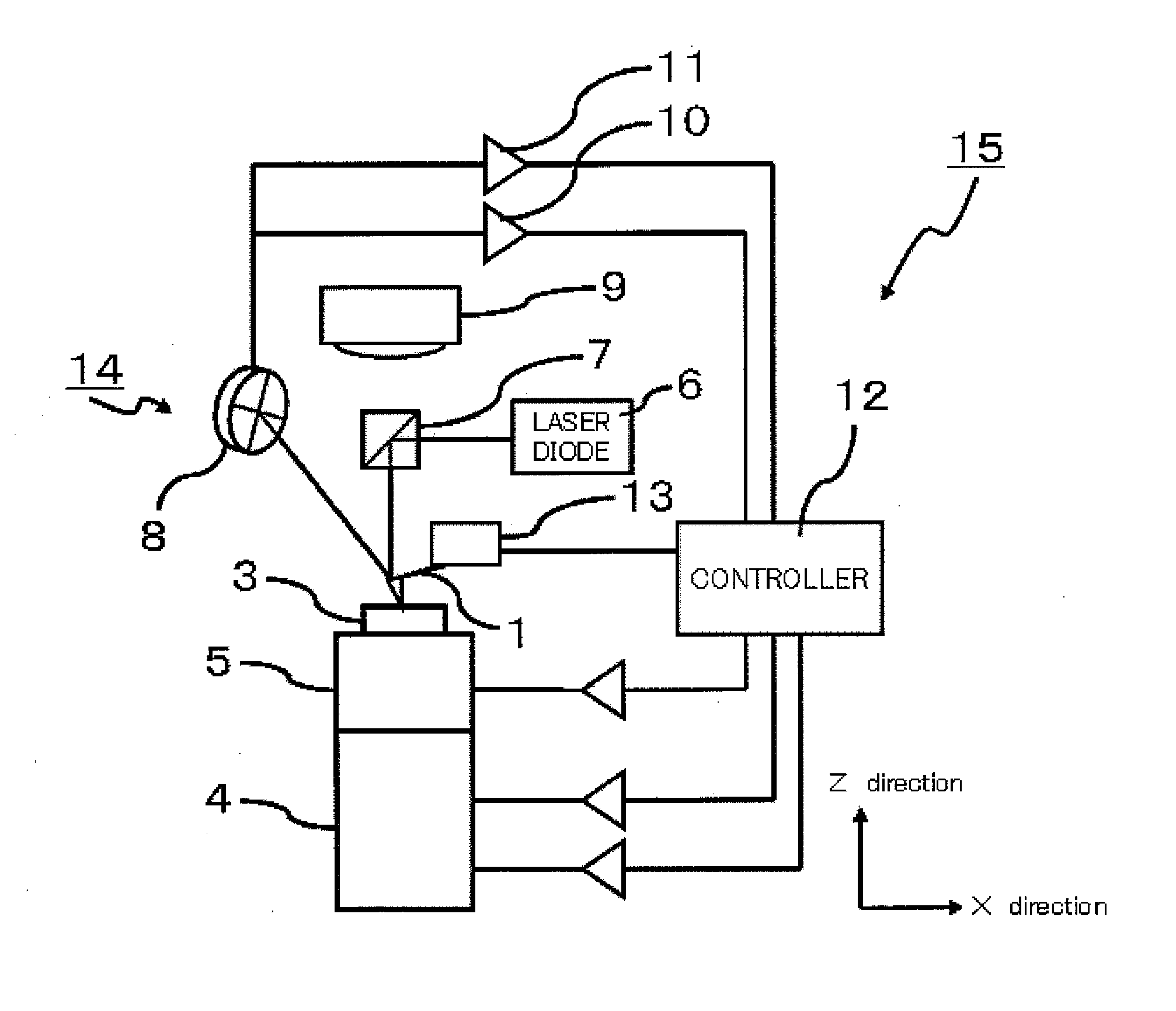
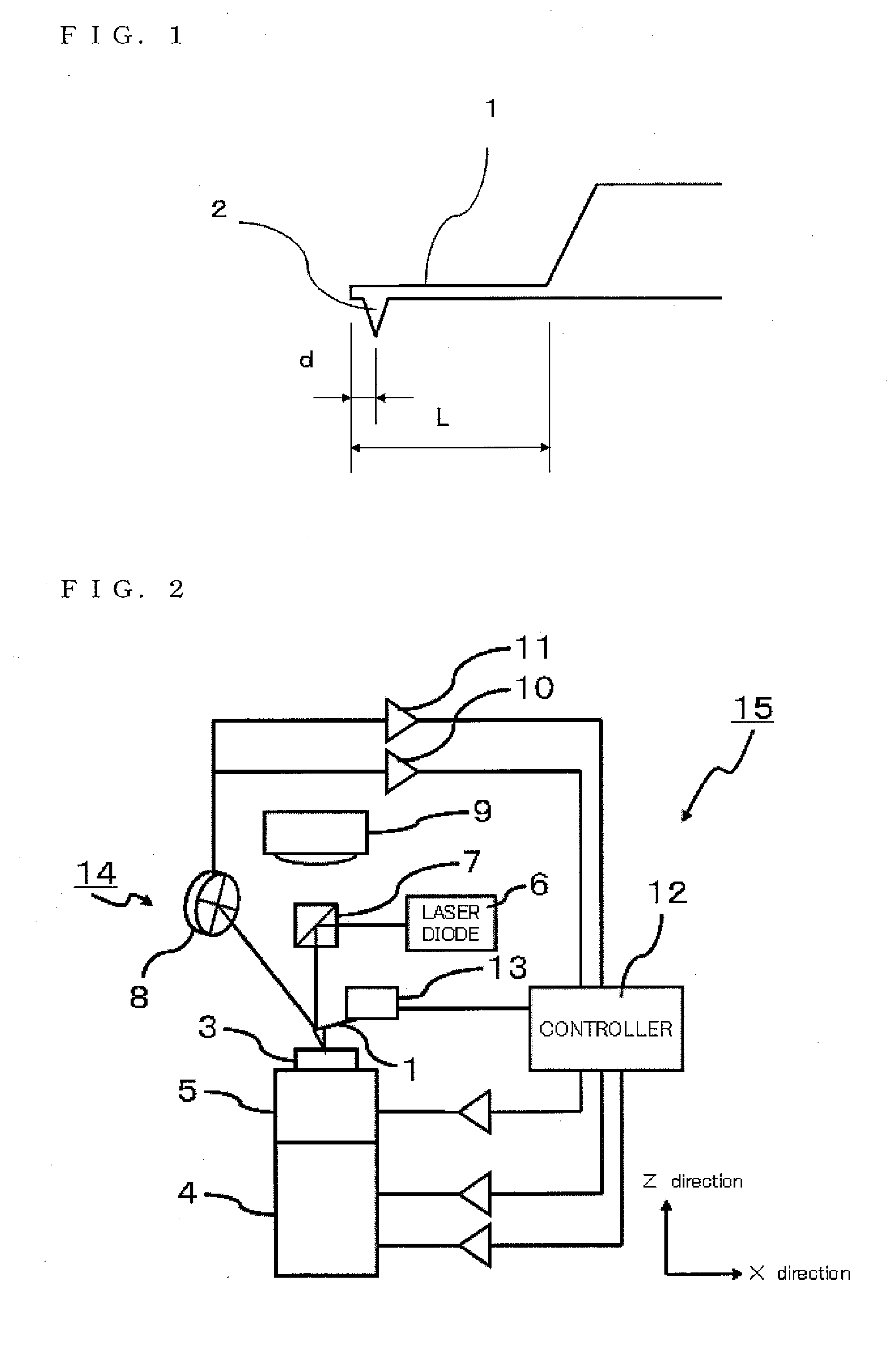
Friction force microscope
ActiveUS20120227139A1Accurate measurementAvoid less frictionNanotechnologyScanning probe microscopyEngineeringTorsional vibration
Provided is a friction force microscope that can measure a friction force by a cantilever in a quantitative manner. The friction force microscope includes a friction force calculating mechanism that calculates an effective probe height and a torsional spring constant of the cantilever from bending sensitivity determined from displacement information in a bending direction of the cantilever and torsional sensitivity determined from displacement information in a torsional direction of the cantilever, respectively, so as to use the calculated values for calculating the friction force.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH SCI CORP
Asymmetrical brake torque plate back leg
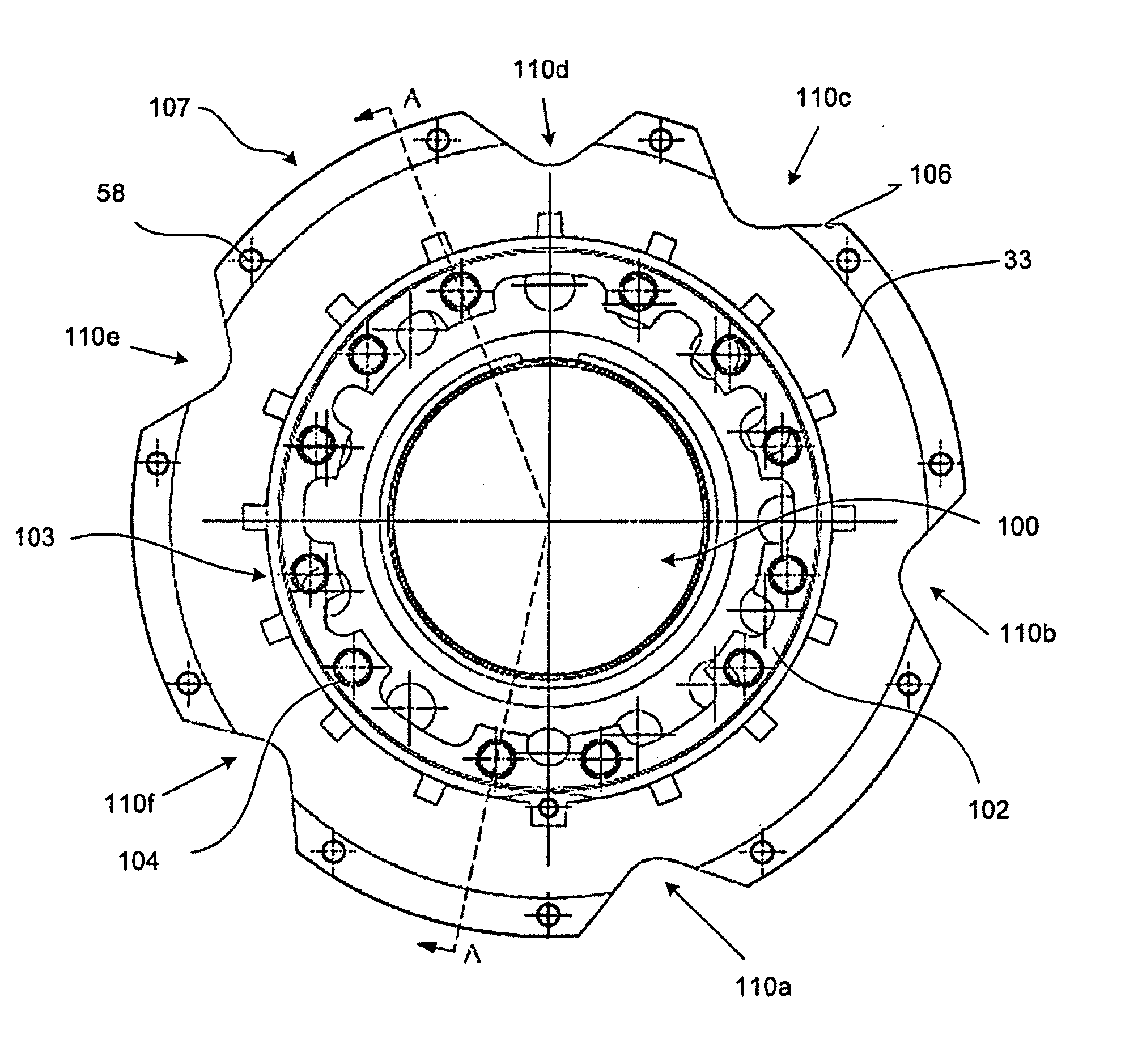
ActiveUS20100140027A1Reduce vibrationReduce symmetryFluid actuated brakesNoise/vibration controlBrake torqueActuator
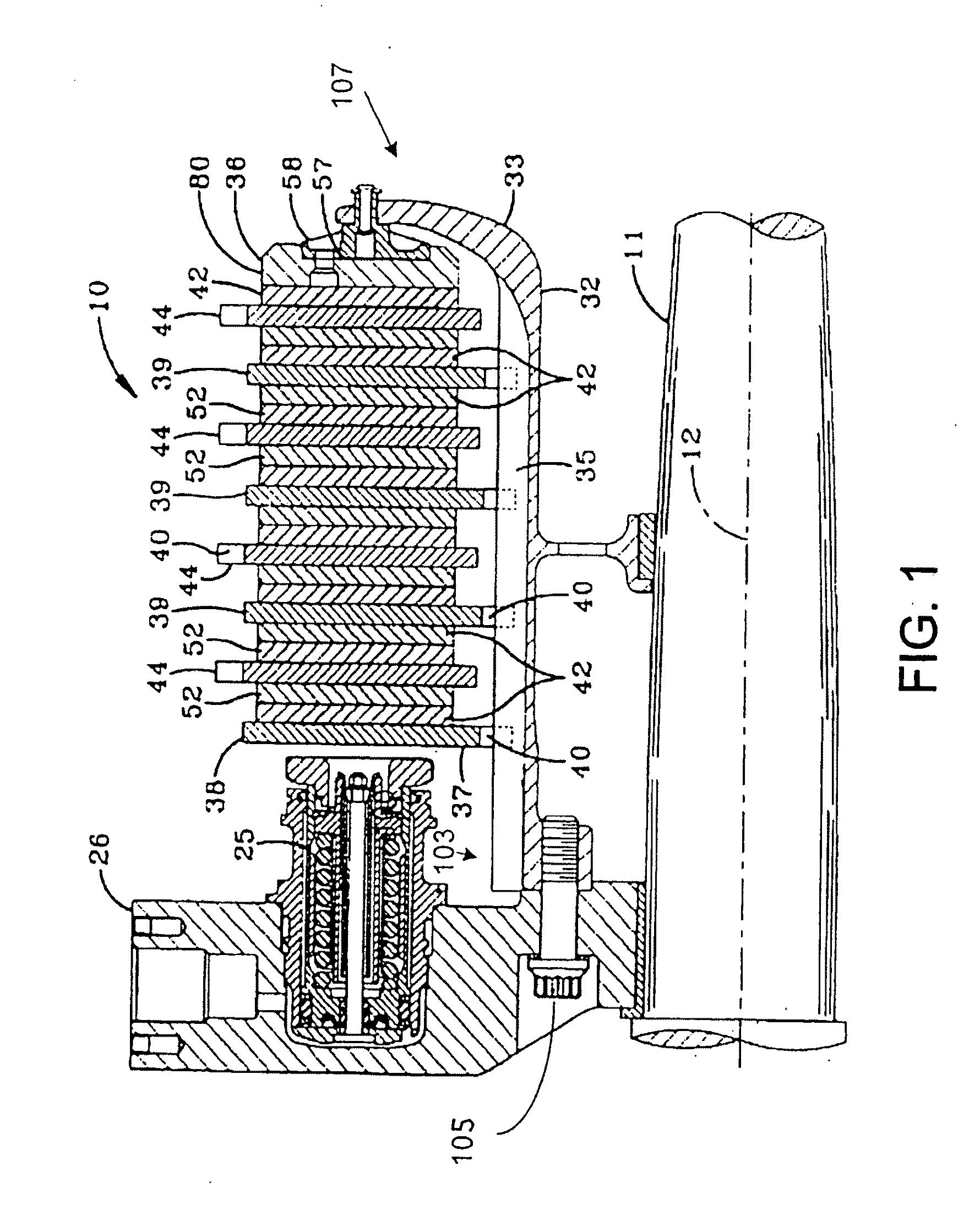
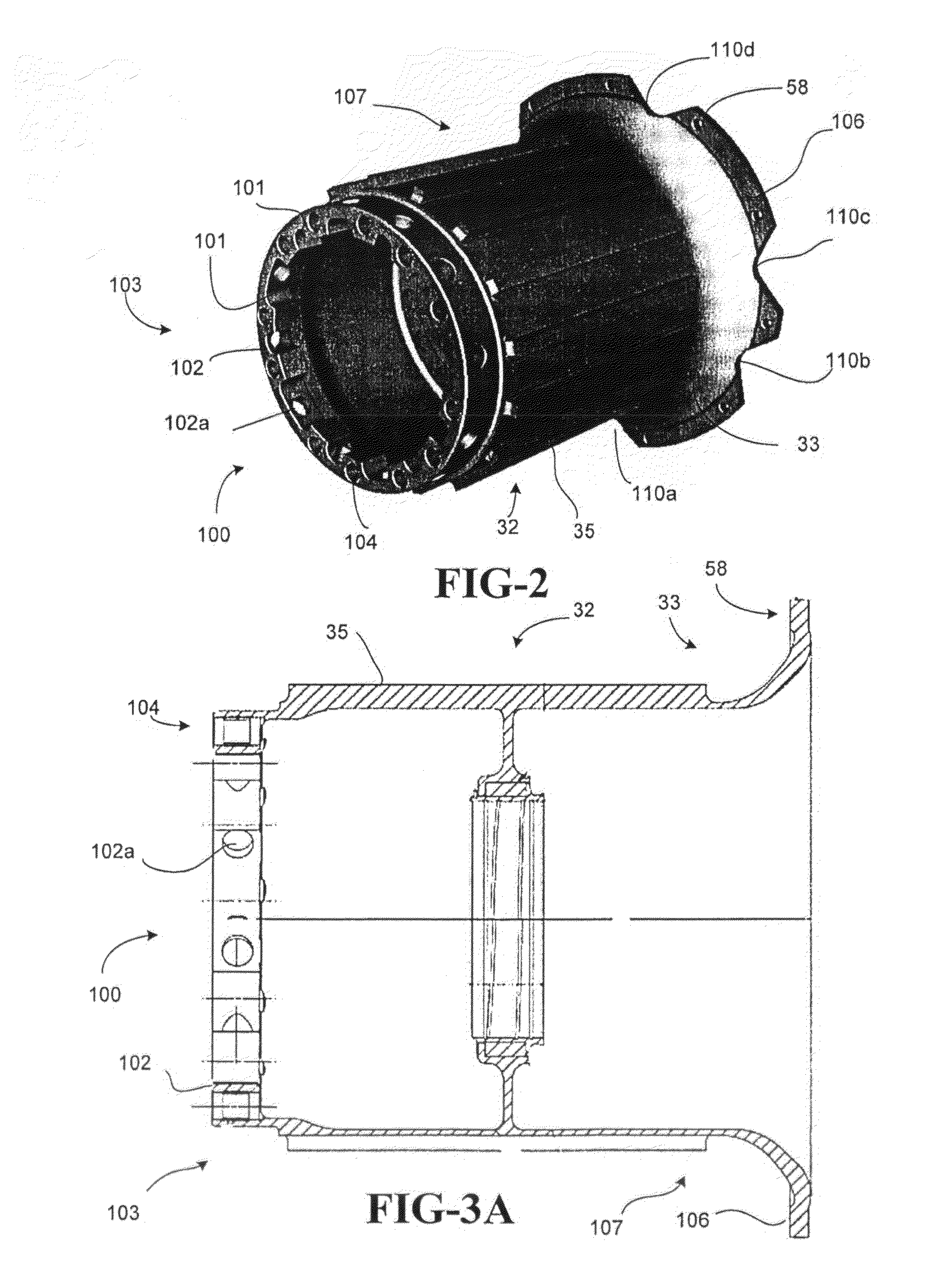
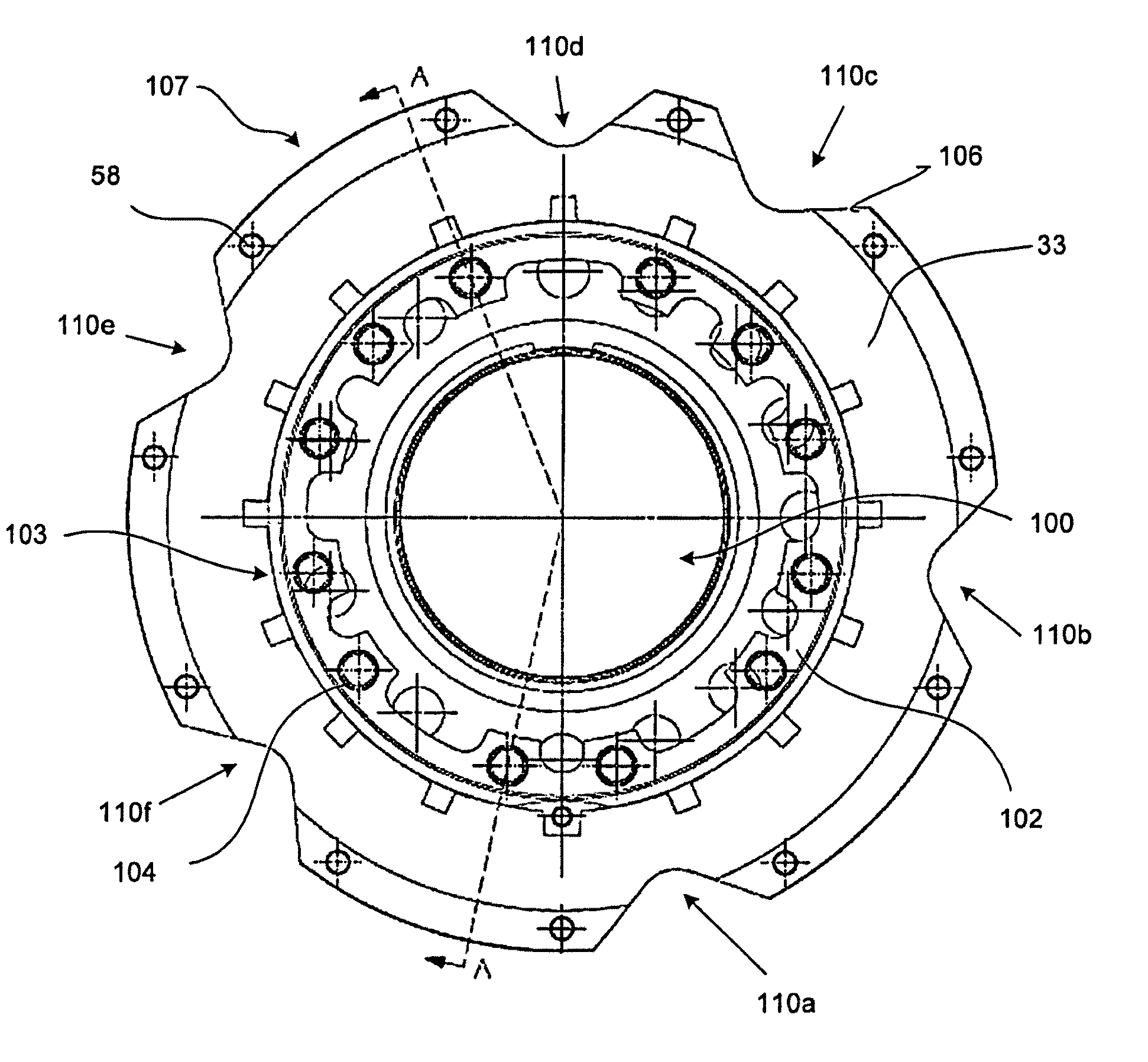
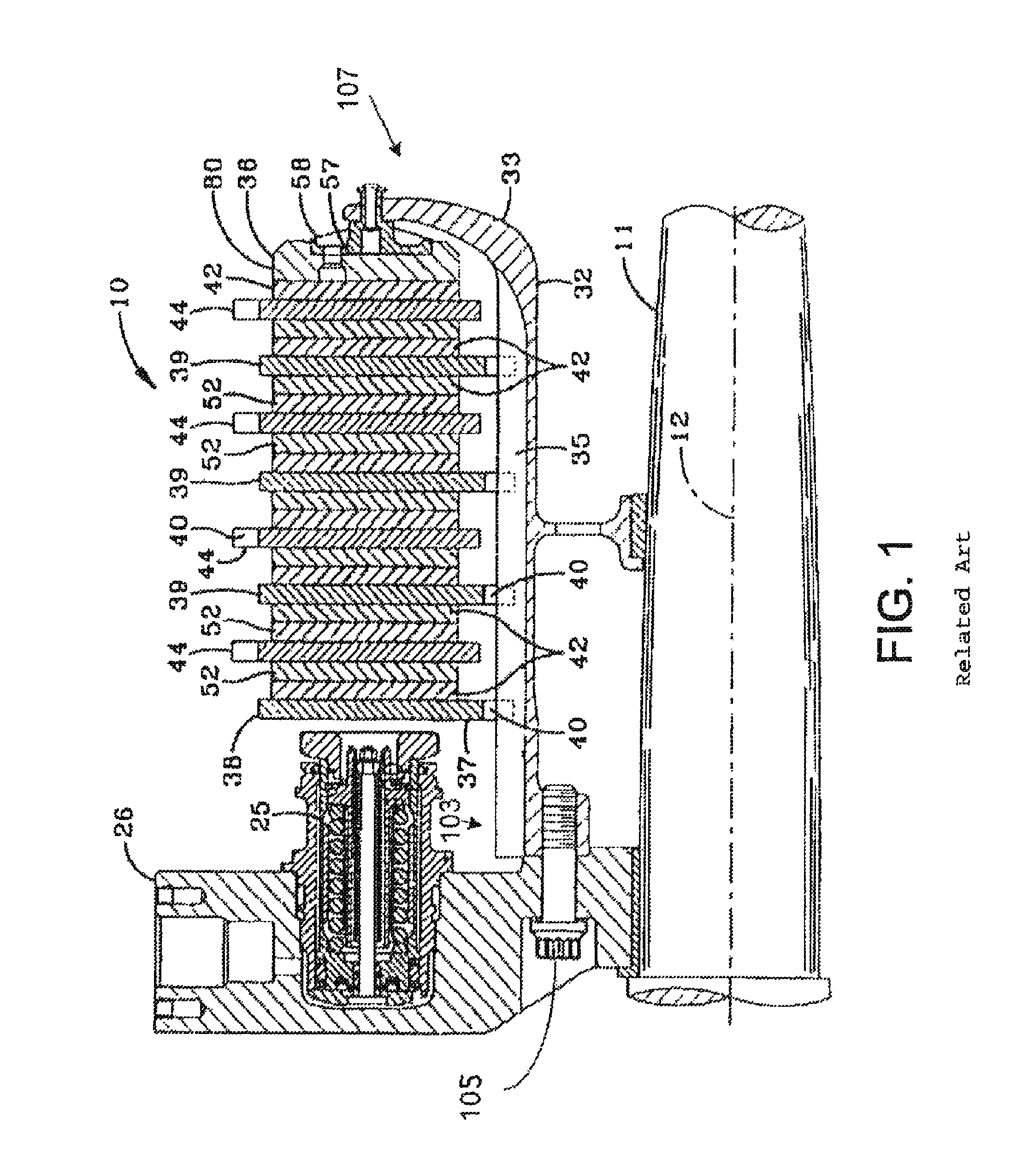
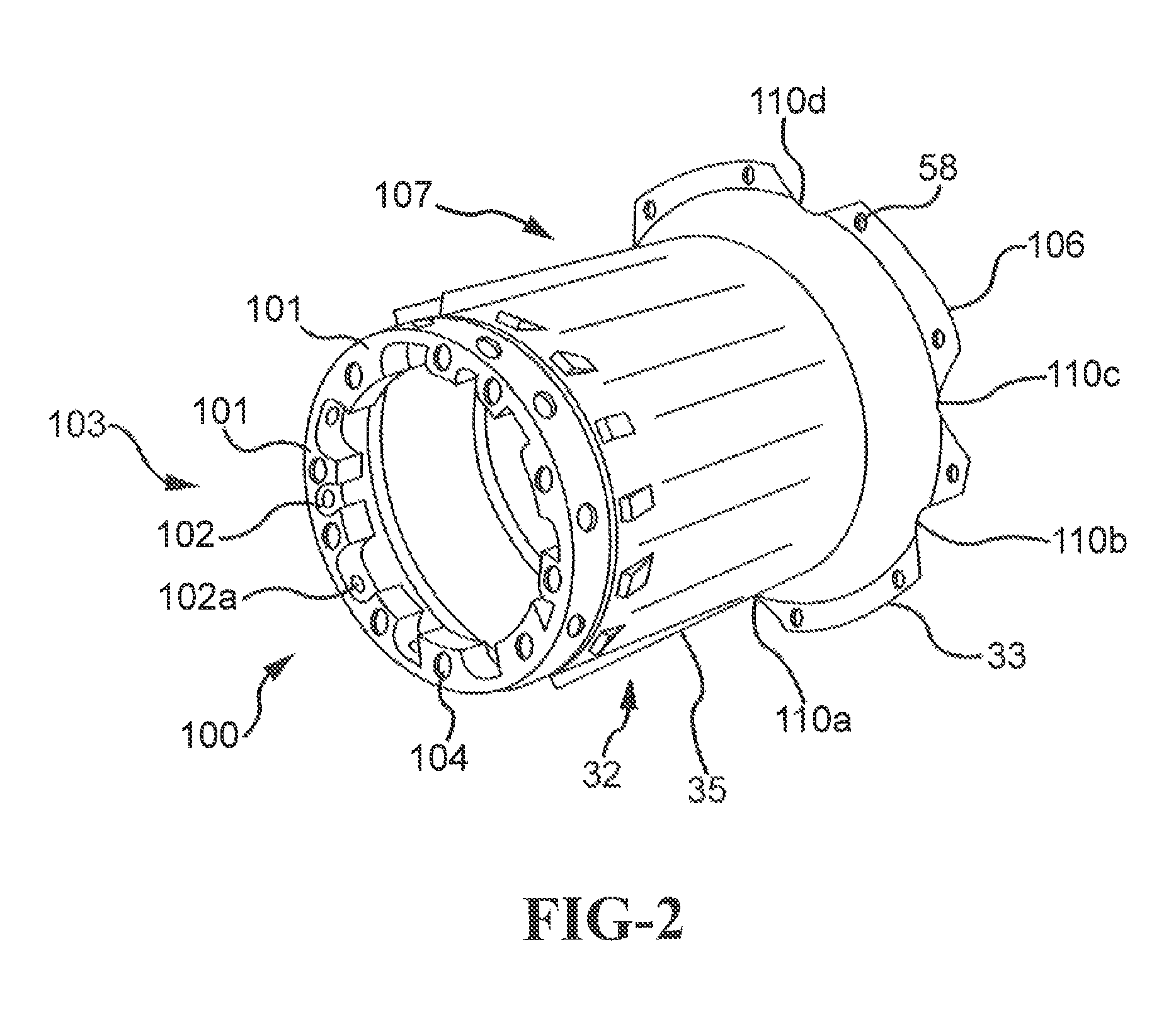
A brake comprising a brake disk stack including stators alternating with rotors that are rotatable relative to the stators about an axis of the disk stack, an annular torque plate at one axial end of the brake disk stack, and a circumferential arrangement of actuators at the other axial end of the brake disk stack for urging the brake disk stack against the torque plate thereby to effect a braking force on the rotors. A back leg (33) of the annular torque plate includes a plurality of apertures (110a-110f) arranged asymmetrically around the axis of the brake disk stack.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Asymmetrical brake torque plate back leg
ActiveUS8616344B2Reduce vibrationReduce symmetryFluid actuated brakesNoise/vibration controlBrake torqueActuator
A brake comprising a brake disk stack including stators alternating with rotors that are rotatable relative to the stators about an axis of the disk stack, an annular torque plate at one axial end of the brake disk stack, and a circumferential arrangement of actuators at the other axial end of the brake disk stack for urging the brake disk stack against the torque plate thereby to effect a braking force on the rotors. A back leg (33) of the annular torque plate includes a plurality of apertures (110a-110f) arranged asymmetrically around the axis of the brake disk stack.
Owner:THE BF GOODRICH CO
Hemostasis pad and method
InactiveUS20050222615A1Easy to disassembleApply evenlySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsPuncture WoundMedicine
The present invention relates generally to medical devices for applying hemostatic composition to a puncture or wound site with indwelling tubular element, such as catheter, introducer or tube therein, particularly a hemostatic pad with an opening therethrough in order to allow egress of the indwelling tubular element through the hemostatic pad as the hemostatic pad provide hemostasis at the hemorrhaging site. The device may be applied to, or removed from, the wound site while the tubular element is in place. A method for effecting hemostasis at a puncture wound, includes applying pressure proximal to the puncture wound, and directing a cationic biopolymer of glucosamine application surface of a closure pad against the puncture wound with force sufficient to prevent fluid from exiting the puncture wound. Then the pressure proximal to the puncture wound is removed and the force on the closure pad is maintained for at least a first predetermined time period. The force on the closure pad is removed if hemostasis is verified. The puncture wound may then be dressed over the closure pad, and the dressing and the closure pad removed after a second predetermined time period.
Owner:LEVINSON MELVIN
Control system for a start-up element of an automated or automatic transmission at limp home mode
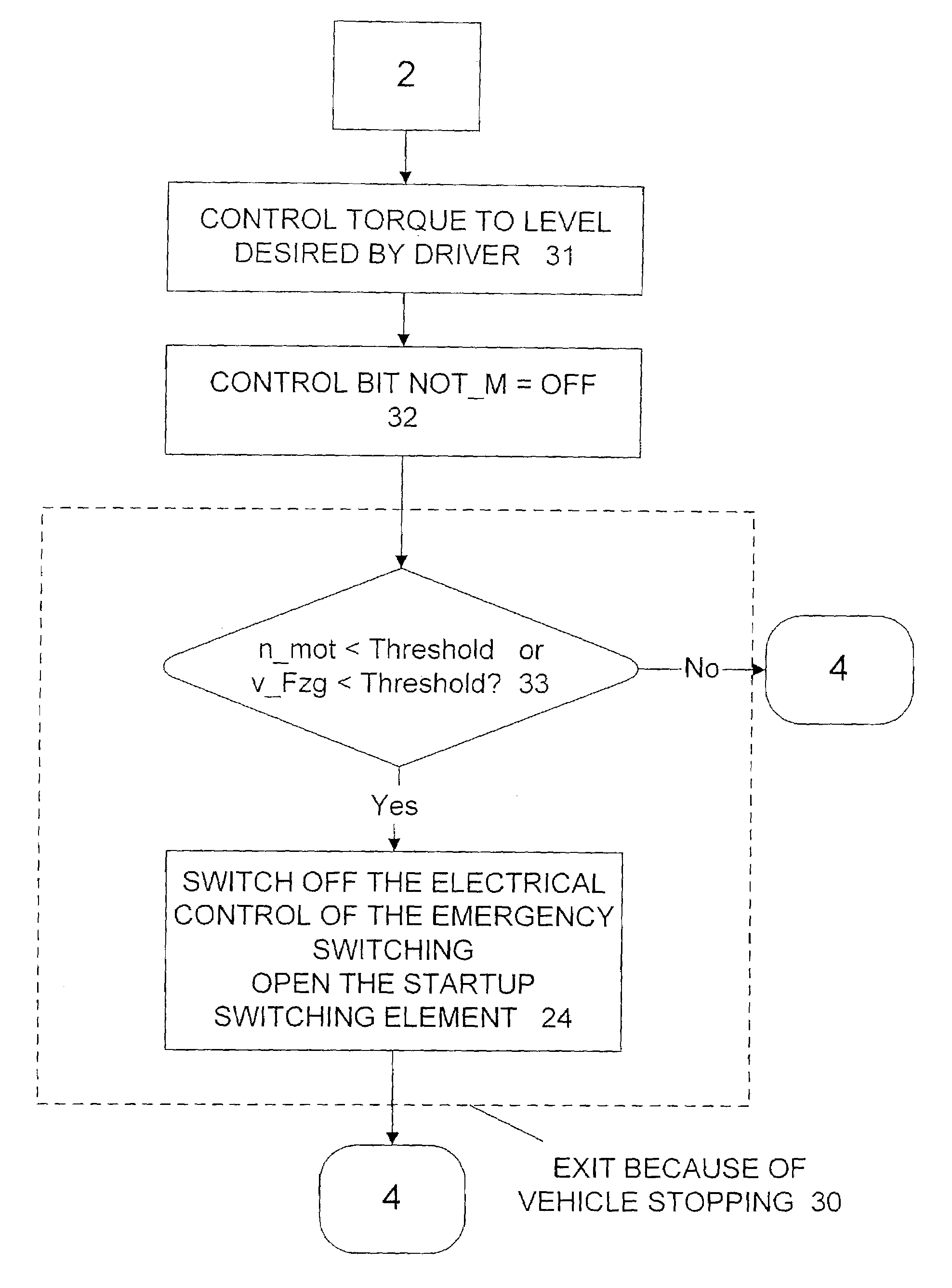
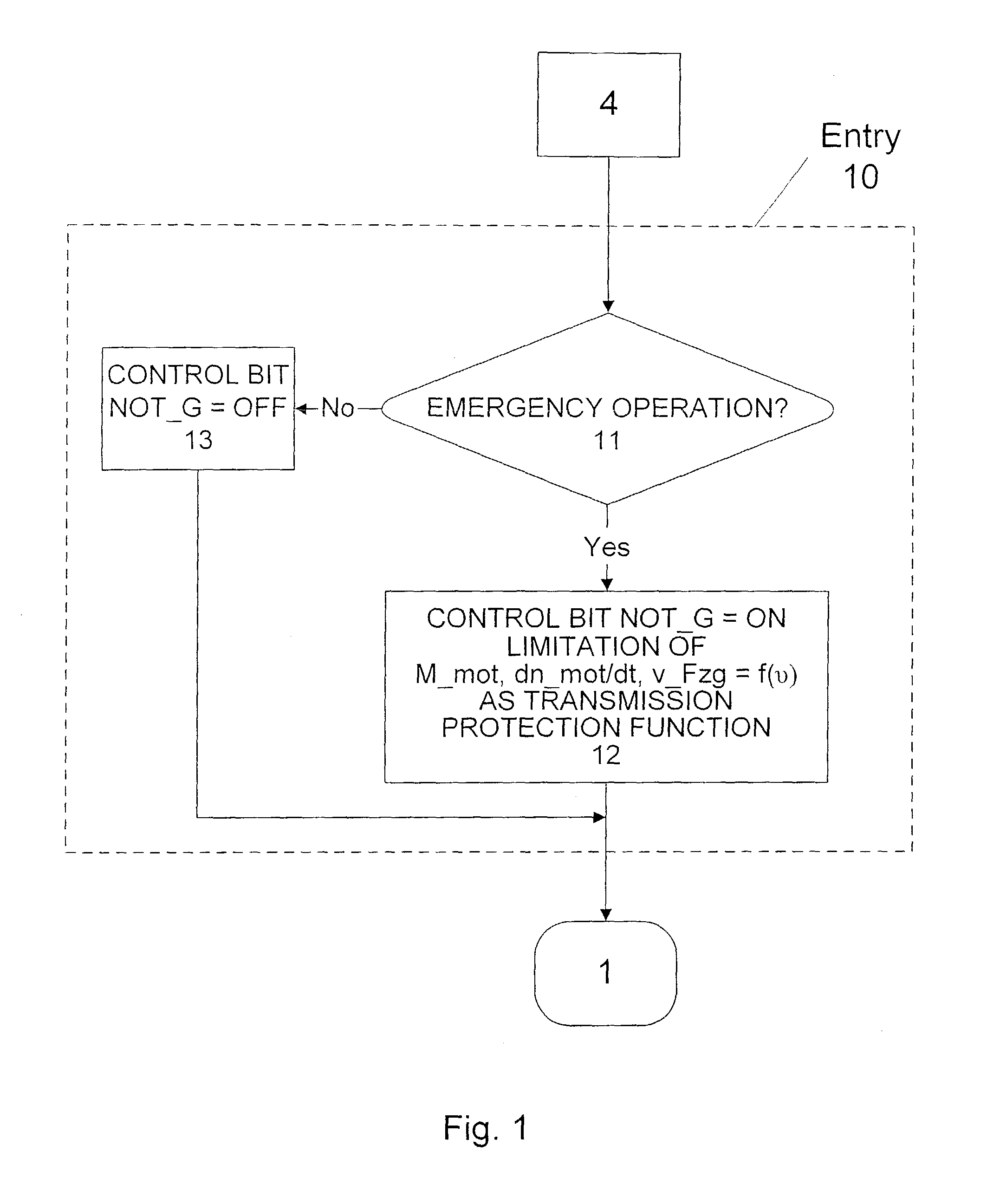
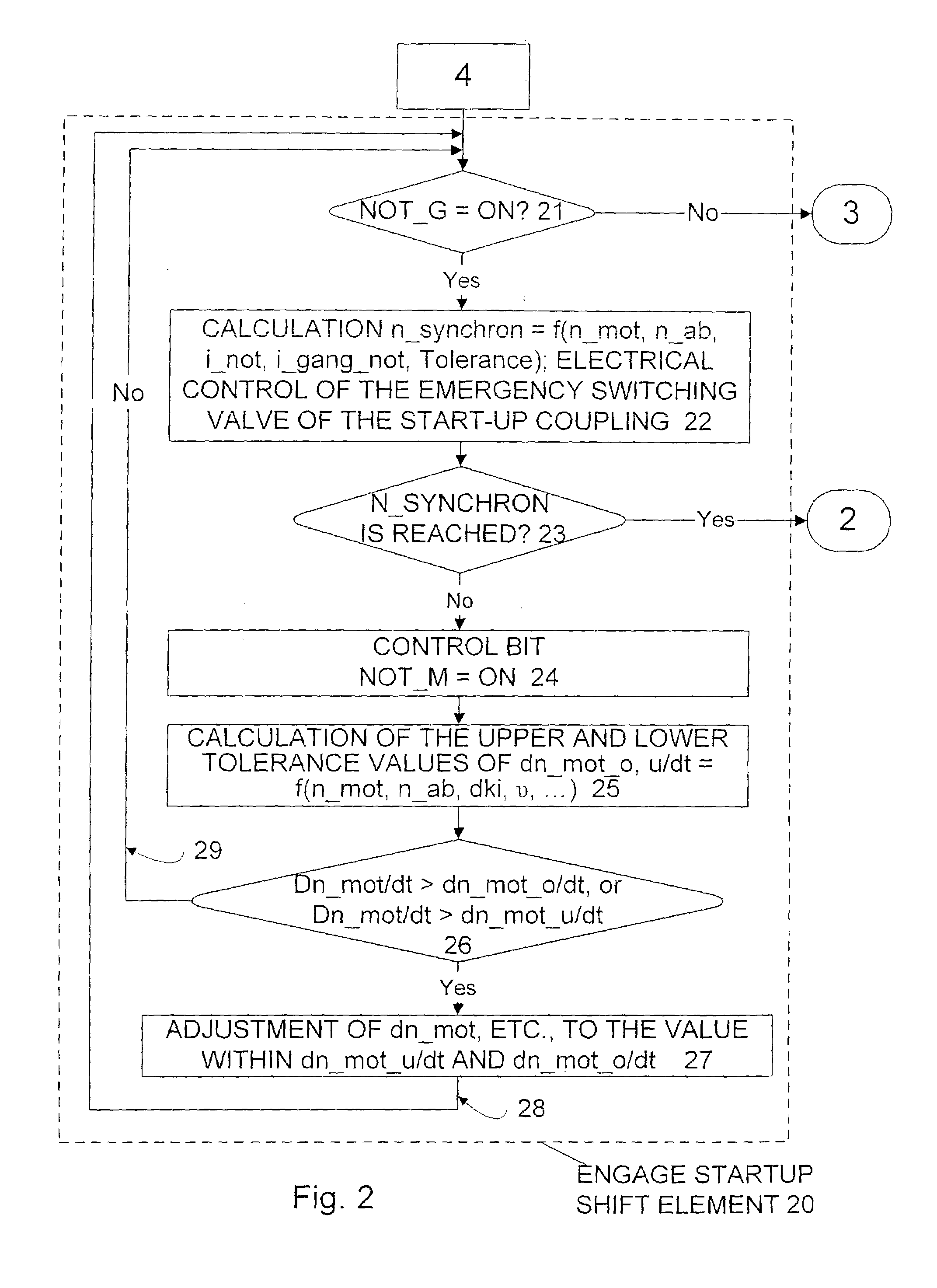
InactiveUS7044889B2Excessive friction wearExcessive friction wear of startupClutchesGearing controlElectricityElectronic transmission
A control system, method for control, and control software for operating a startup shift element of an automated motor vehicle transmission or automatic transmission capable of electro-hydraulic or electro-pneumatic actuation with an electronic transmission control device, whereby the startup shift element may be shifted hydraulically or pneumatically in emergency mode even if the electronic control device fails. The control system includes a transmission-independent control module, and a emergency-operation mode shift valve capable of electrical triggering, that controls the hydraulic or pneumatic actuation device of the startup shift element. If the transmission-independent control module fails during transmission emergency-mode operation, the startup shift element is capable of actuation by means of the electrical triggering of the emergency-operation mode shift valve via the transmission-independent control module. This may particularly control a motor-vehicle startup procedure.
Owner:ZF FRIEDRICHSHAFEN AG
Performance enhanced snowboard
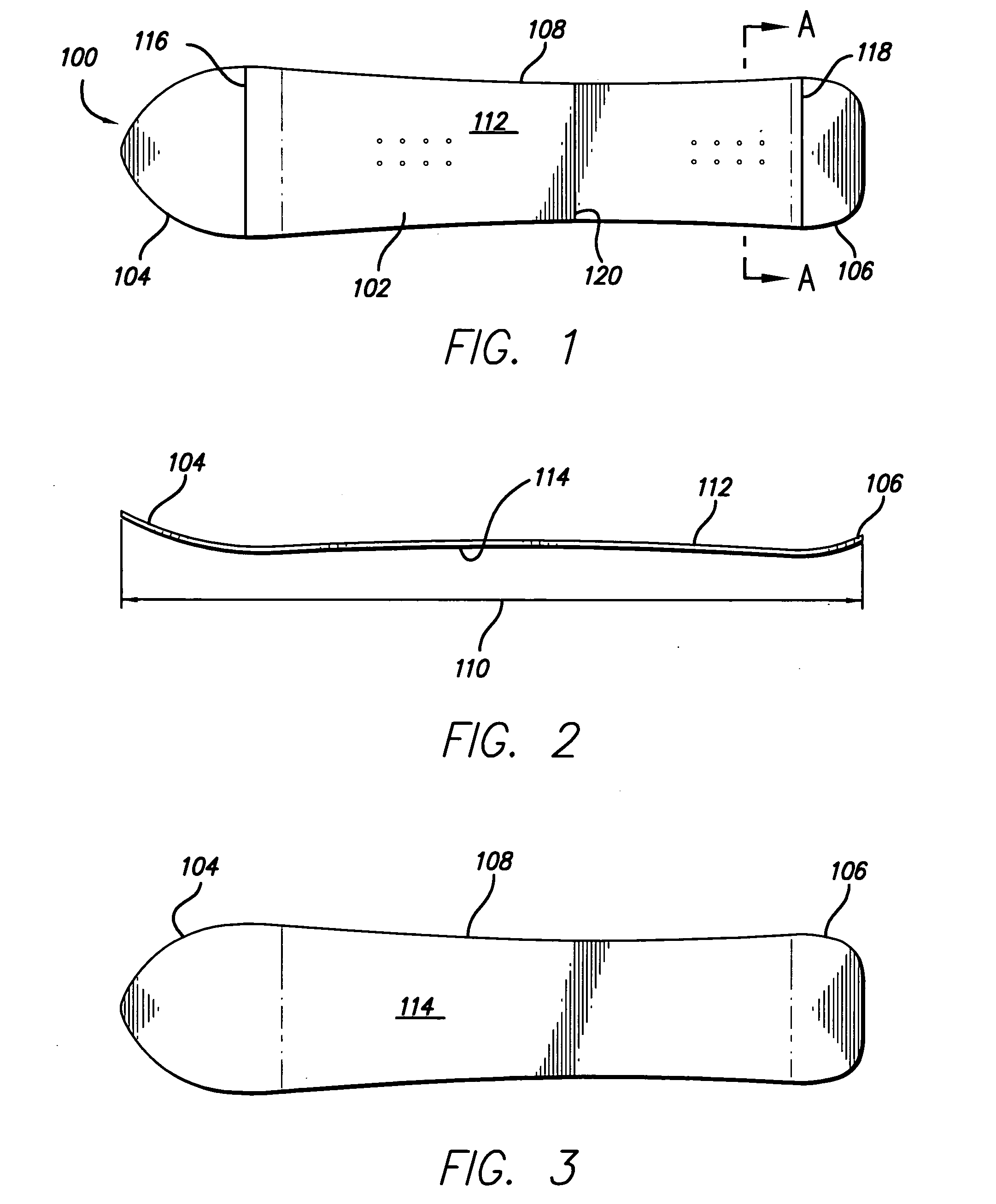
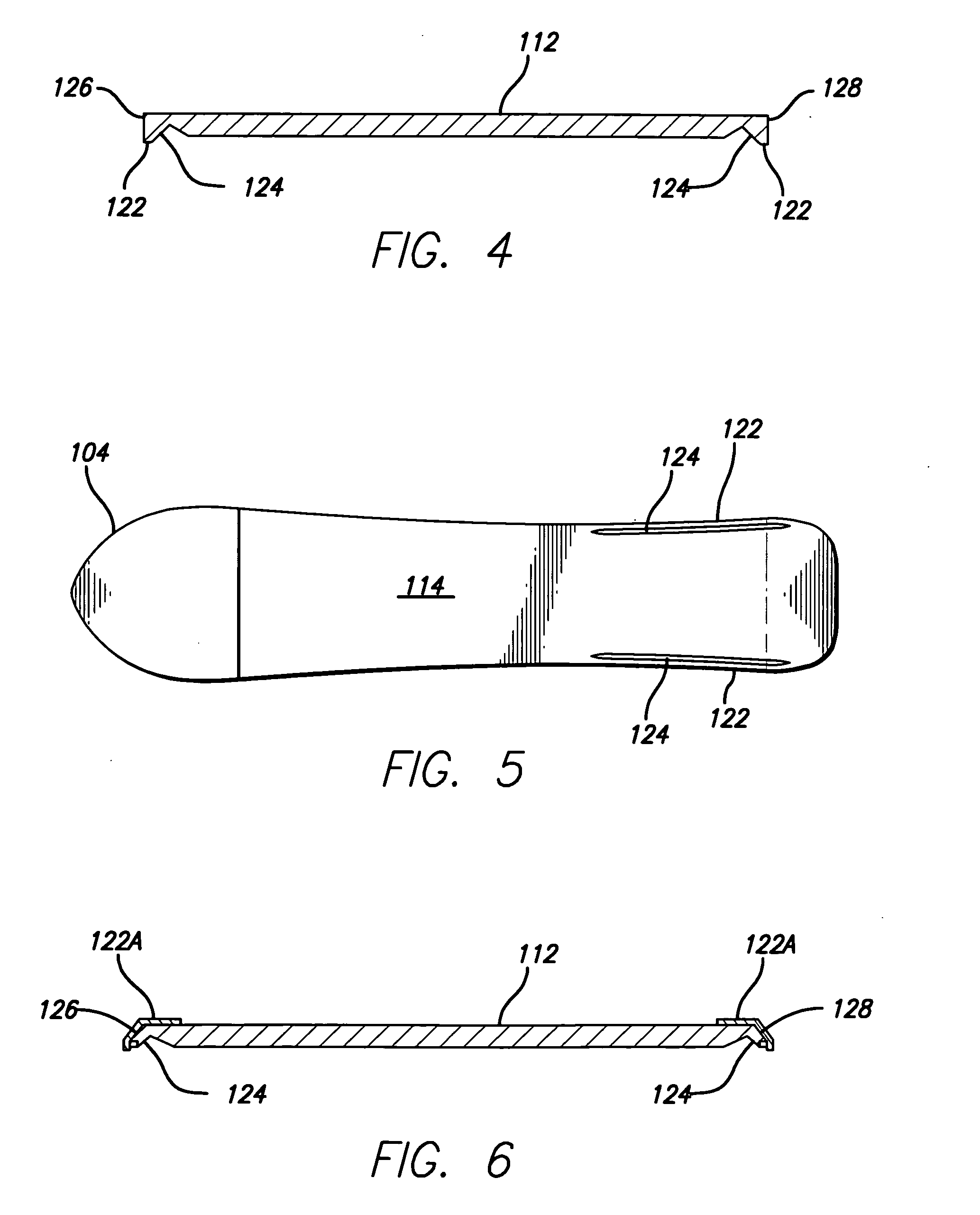
InactiveUS20100013191A1Effectively floatIncrease frictionSki bindingsSki-brakesNinetieth percentileEngineering
A performance enhanced snowboard having an extended, generally planar deck with a nose, a tail, and a central section. The deck also has an overall length, a top surface, and a bottom surface. The nose has a widest portion that defines a nose chord line having a nose chord length. The tail has a widest portion that defines a tail chord line having a tail chord length, and the central section has a narrowest portion that defines a central chord line having a central chord length. The nose chord length is greater than the central chord length, and the nose chord length is between about fifteen and thirty-five percent of the overall length of the deck. The tail chord length is between about one percent and ten percent greater than the central chord length, while the distance between the tail chord line and the central chord line is between about forty to ninety percent of the distance between the nose chord line and the central chord line. The structure permits the invented board to function like a surfboard or skateboard while also sliding like a conventional snowboard.
Owner:MCKEEVER NATHANIEL W
Transmission gear control apparatus for vehicle
Under an abnormal determination, when a transmission gear stage is switched, a torque limit value is changed from a value before switching of the transmission gear stage to a value after switching thereof in a period in which this transmission gear stage is switched.
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Variable friction hinge
InactiveUS20090144933A1Reduce frictionAvoid less frictionDetails for portable computersHingesEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A variable friction hinge is mounted between a cover and a base of an electronic device and has a pintle, a stationary leaf and a washer assembly. The pintle is connected to the cover. The stationary leaf is connected to the base and has an activating panel with an activating edge. The washer assembly has a movable washer, an abrasion washer and a biasing member. The movable washer selectively abuts the activating edge of the activating panel and has an elongated hole slidably mounted securely around the pintle. The movable and the abrasion washers have teeth corresponding to and selectively engaging each other, causing less friction when engaged and more friction when disengaged. When rotated the movable washer selectively disengages the teeth causing the hinge to have greater friction when being rotated one way than the other.
Owner:SHIN ZU SHING
Device and method for launching a projectile across a range
ActiveUS9757632B2Facilitates launching projectileEasy to controlThrow gamesSpace saving gamesGolf course turfDistal portion
A device and method for launching a projectile, such as a golf ball, across a range. The device enables a golf ball to be launched across a golf course with greater control than is possible with a traditional golf club. The ease of loading the projectile into the launching device and swinging the launching device forward adds greater distance to the projectile due to an increase in angular momentum and back spin on the projectile. The device includes a C-shaped head defined by a nest, a pair of lateral retention arms, and a base. A distal portion is longer than a proximal portion to create backspin on the projectile. The concavity and lateral arms hold the projectile in place. The distal and proximal portions terminate at concave points that grip dimples on the projectile. The base is fixedly attached to a shaft, which is used for swinging the head.
Owner:SYMTAR VENTURES
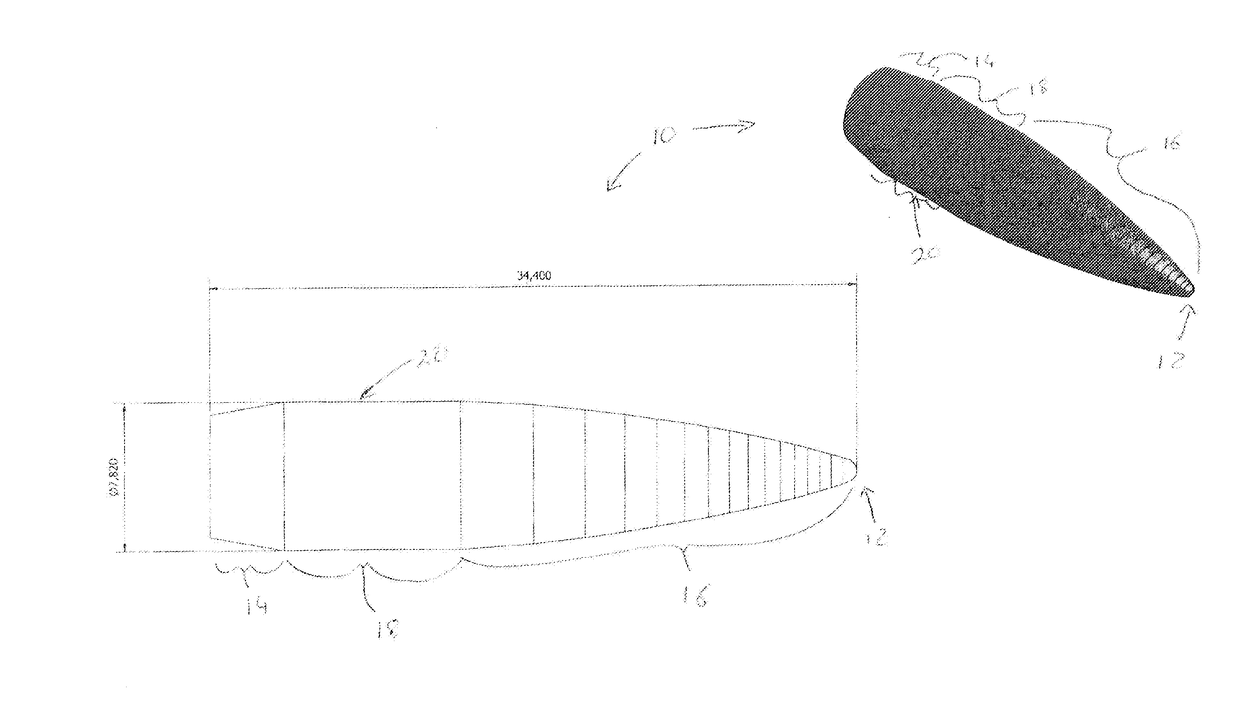
Long range bullet
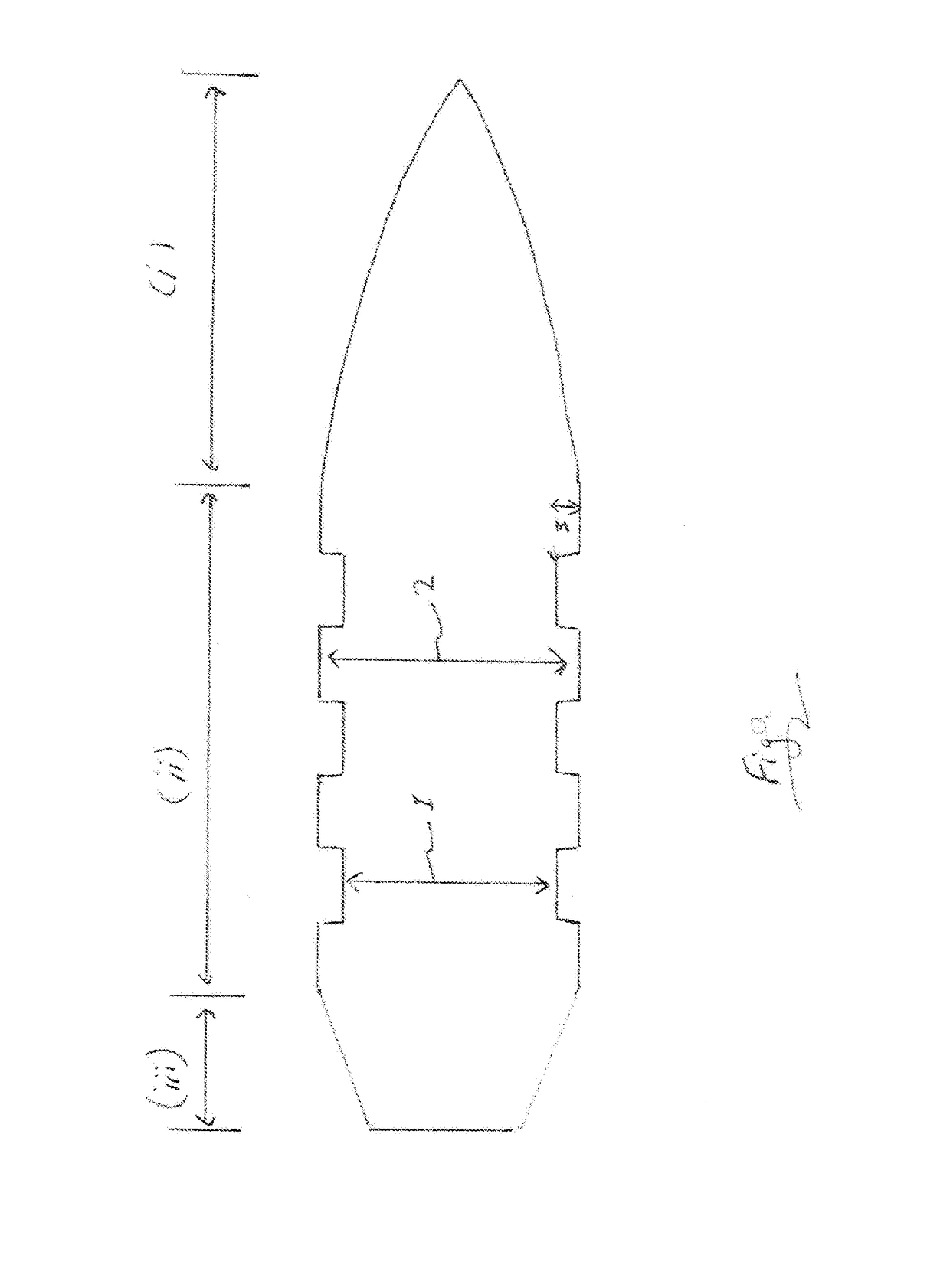
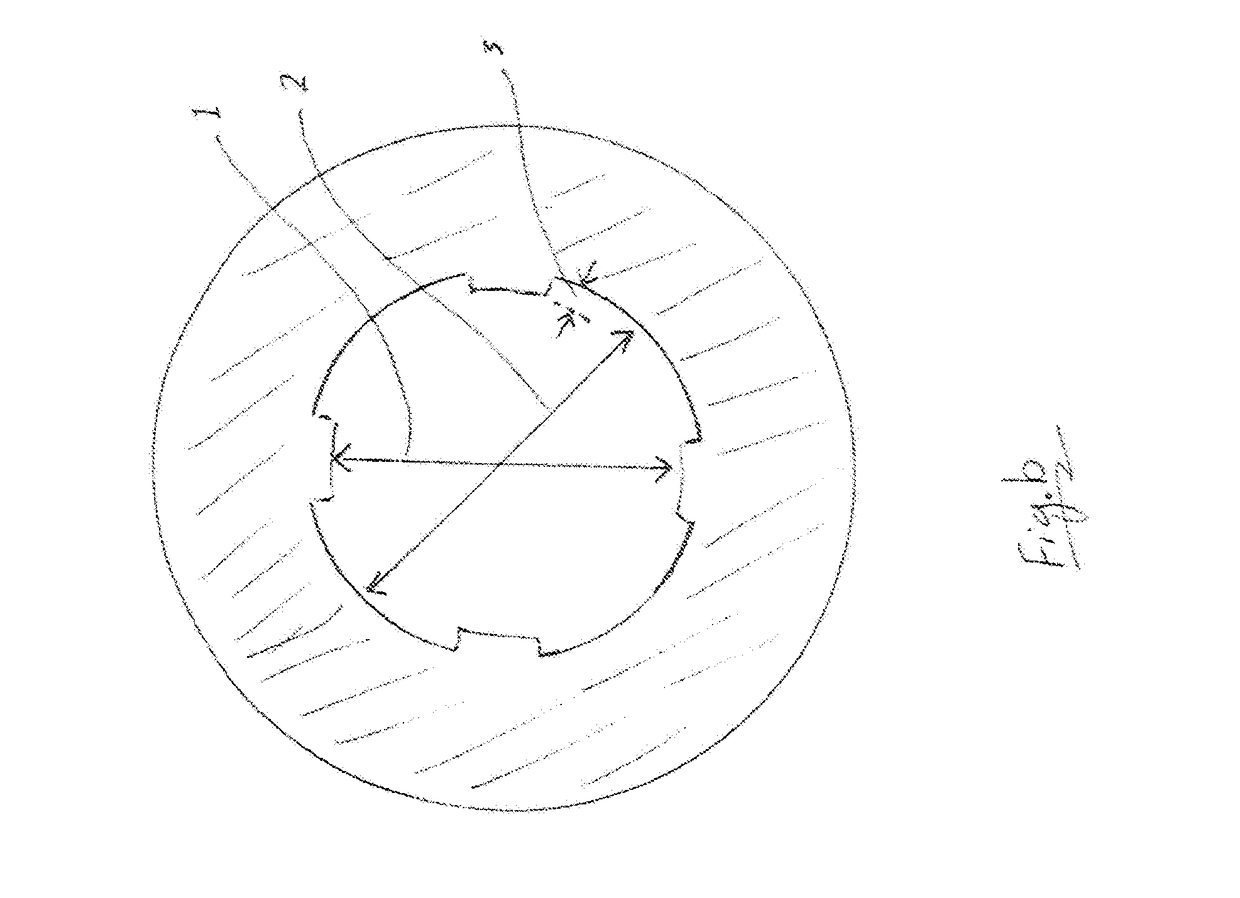
ActiveUS20170138709A1Reduce frictionLong processAmmunition projectilesProjectilesBearing surfaceEngineering
The invention provides a long range bullet. The bearing surface of the body of the bullet is provided with one or more annular narrows of which the combined length is at least one third of the length of the bearing surface of the bullet and which depth is between 0.005 mm up to half of the groove depth of a barrel in which the bullet is intended to shoot.
Owner:PEREGRINE BULLETS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com