Tripod type constant velocity universal joint
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
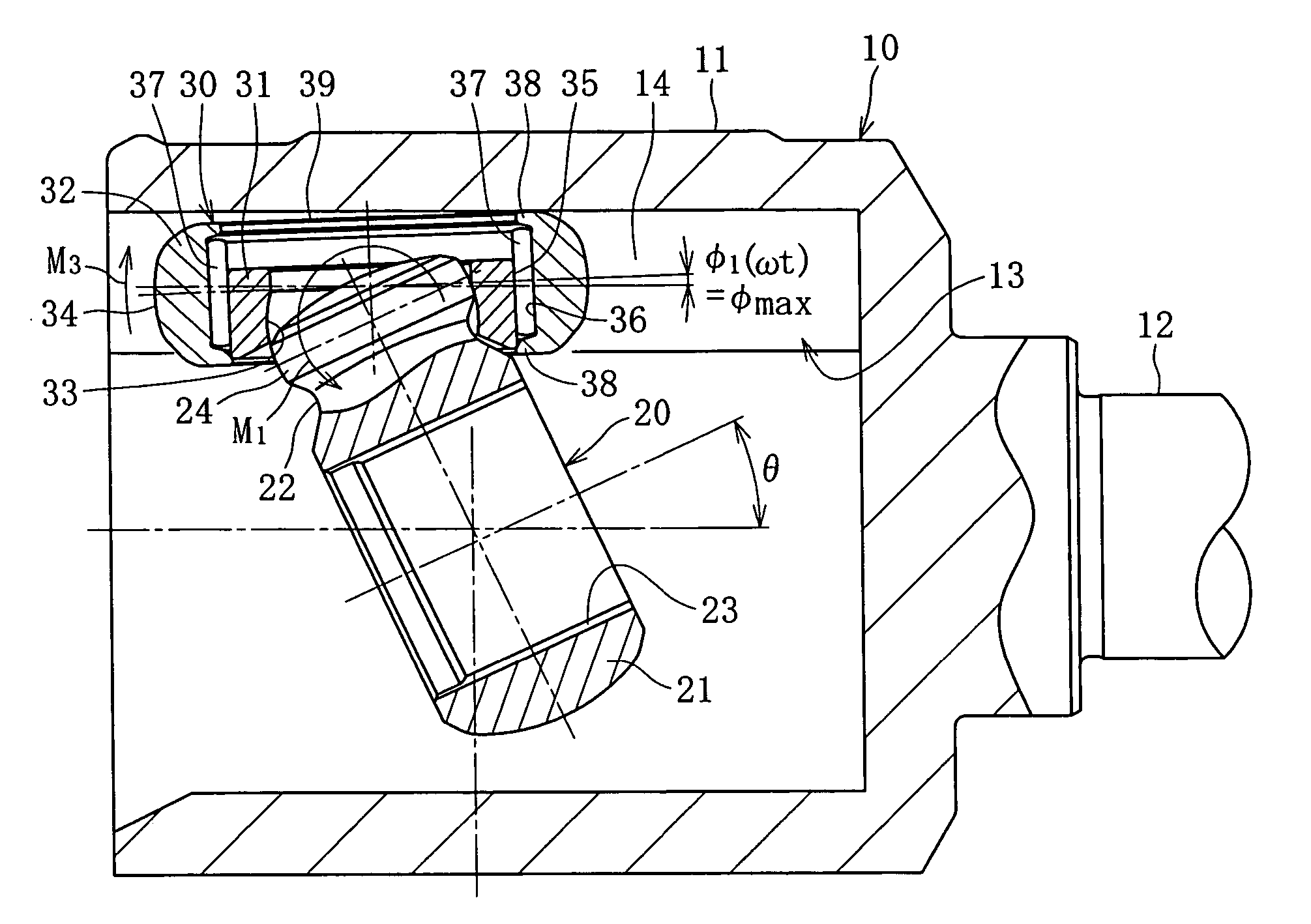
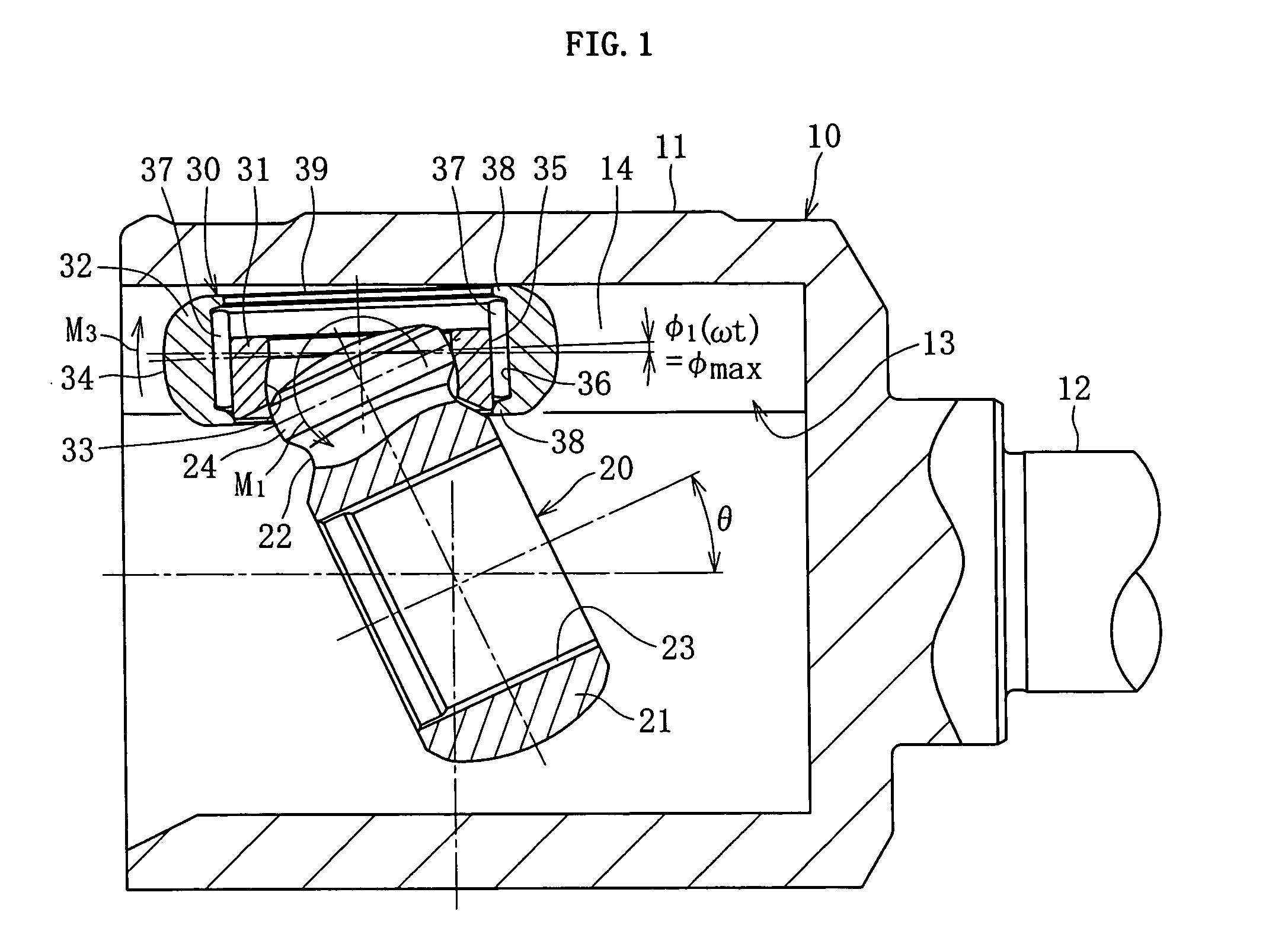
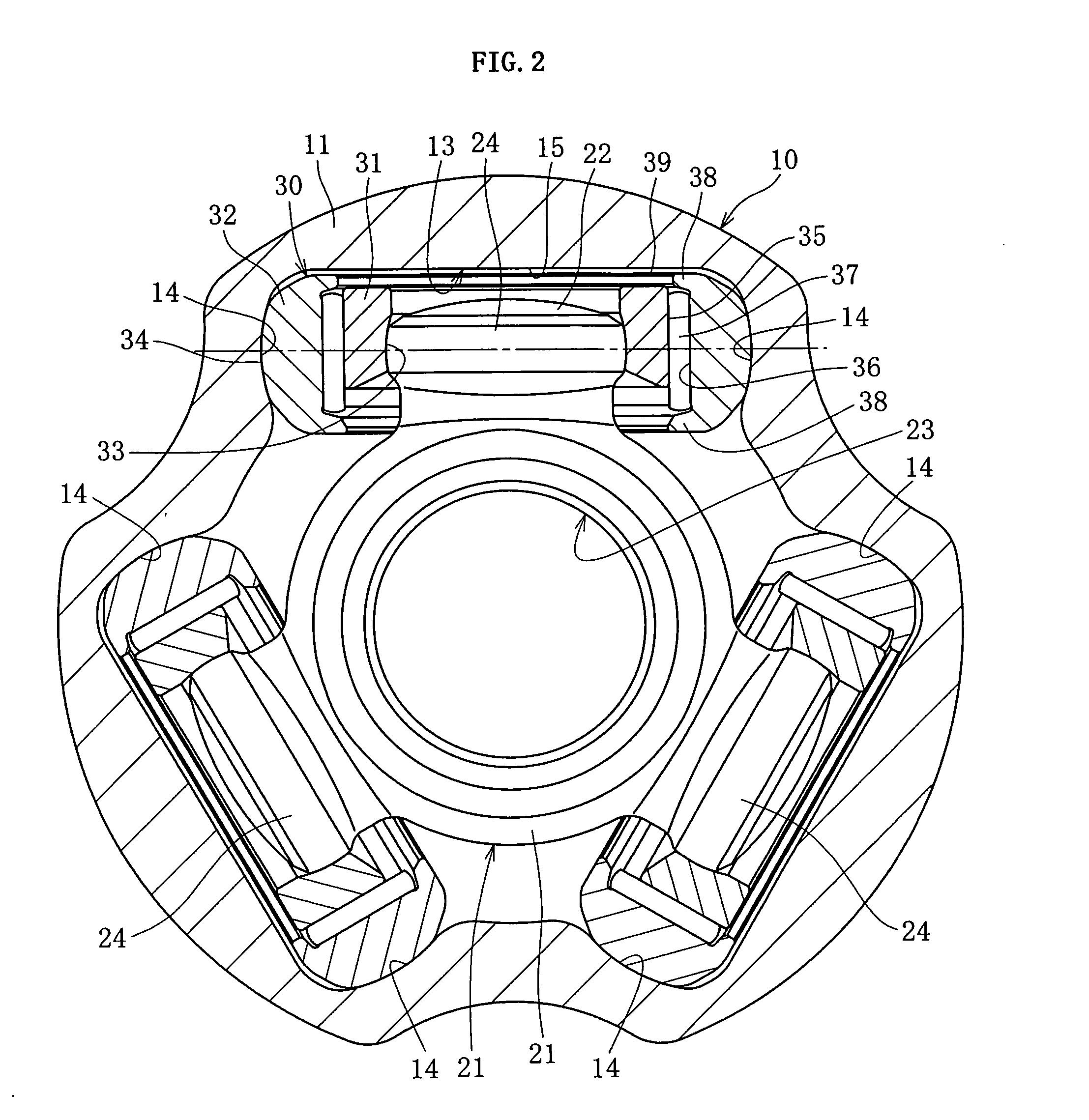
[0046] That is the basic structure of the tripod type constant velocity universal joint in which, as shown in FIG. 2, the track groove bottom portion 15 opposing a facet 39 of the outer roller 32 is formed in a flat surface communicating between outer end portions in a radial direction of the pair of roller guide sections 14, and the track groove bottom portion 15 is located close to the facet 39 of the outer roller, so that the facet 39 of the outer roller, which is inclined when a torque is applied, can contact the track groove bottom portion 15. When a torque is not applied, the track groove bottom portion 15 and the facet 39 of the outer roller define a predetermined clearance therebetween, as shown in FIG. 2.
[0047] The following passage covers an operation of the tripod type constant velocity universal joint according to the first embodiment. Referring to FIG. 1, when a torque is applied with the outer joint member 10 and the inner joint member 20 oriented with an operating an...
third embodiment
[0058] For the tripod type constant velocity universal joint a relation between an annularity A (=r1, / R1) represented by a ratio of the generatrix curvature radius with respect to the outer radius R1 of the outer roller 32 and various inclinations of the outer roller 32 inside the track groove 13 has been focused, so as to determine the clearance δ1 between the outer circumferential surface 34 of the outer roller and the non-load side roller guide section 14, as well as the clearance δ2 between the facet 39 of the outer roller and the track groove bottom portion 15. Specifically, when the annularity A is smaller, the outer roller 32 is inclined by a greater angle in a cross-section perpendicular to an axial line of the outer joint member 10, and the outer circumferential surface 34 of the outer roller and the non-load side roller guide section 14 more readily contact each other, while in a cross-section including an axial line of the outer joint member 10, a restoring couple M3 (Re...
fourth embodiment
[0065] In FIG. 12, the numeral 110 designates an outer joint member, which includes a one-end open cylindrical mouth portion 111 and a stem portion 112 to be connected to one of two shafts to be joined (not shown), so as to transmit a torque. On an inner circumferential surface of the mouth portion 111, three axially extending track grooves 113 are provided on positions equally dividing the circumference into three portions, as shown in FIG. 13. On both sides of the track grooves 113 in a circumferential direction, a pair of roller guide sections 114 is located so as to oppose each other. Each of the roller guide section 114 is a curved recess having a generally arc-shaped cross-section. The track groove bottom portion 115 is formed in a flat surface communicating between outer end portions in a radial direction of the pair of roller guide sections 114. The outer joint member 110 includes a first reduced-thickness portion 116 having a smaller diameter than a maximum rotation diamete...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com