Patents
Literature
85results about How to "More balanced" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
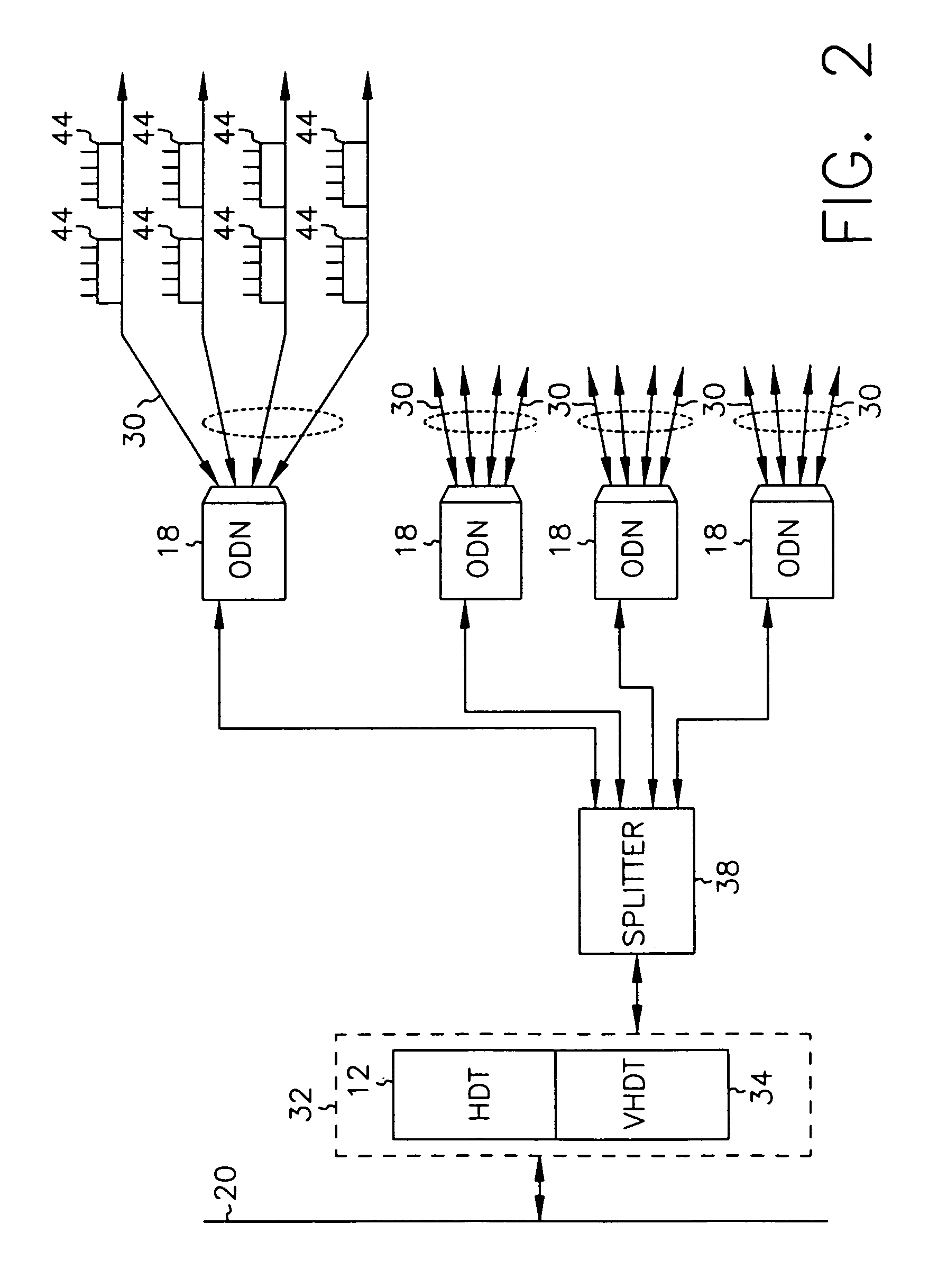
Dynamic bandwidth allocation
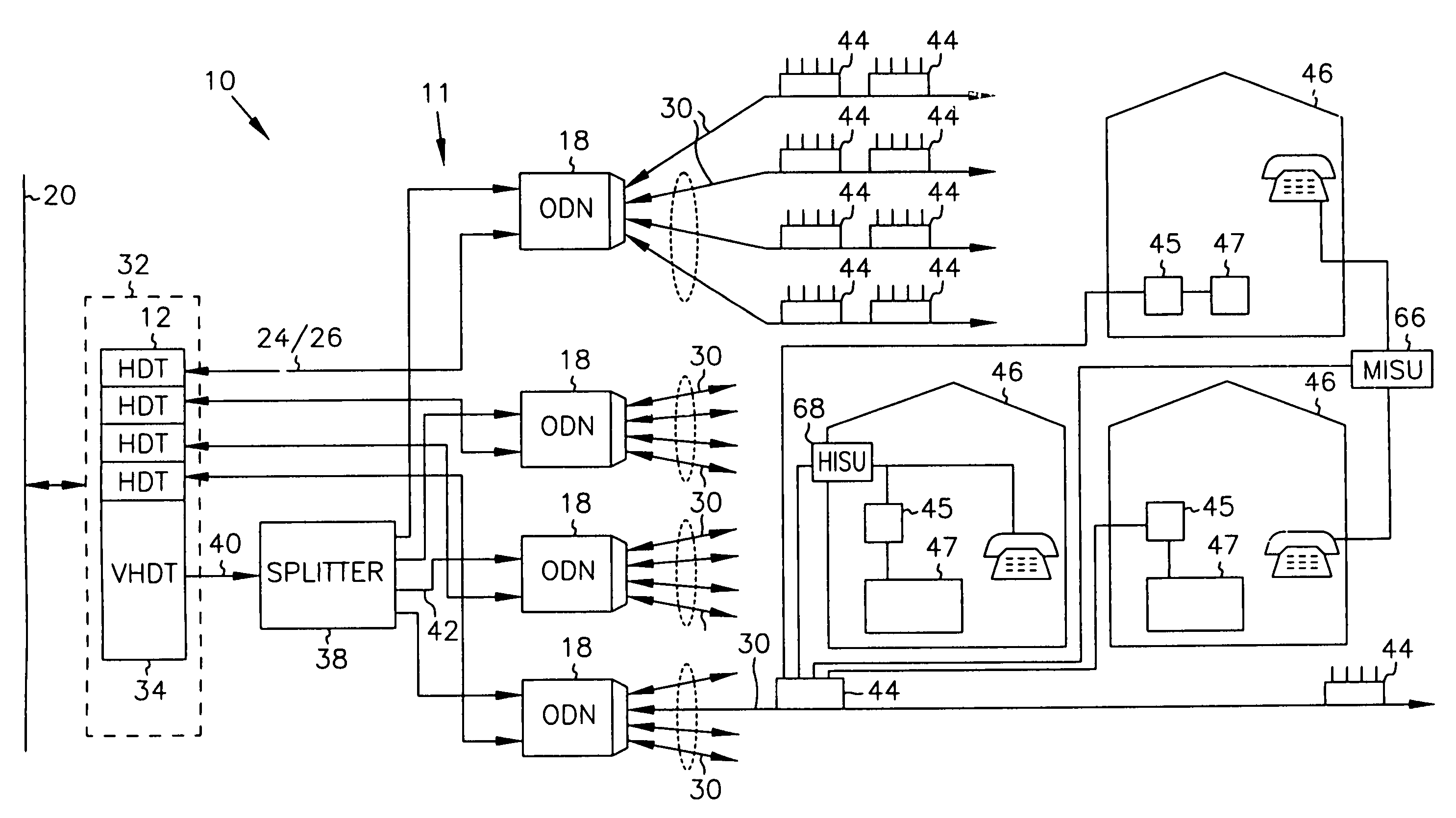
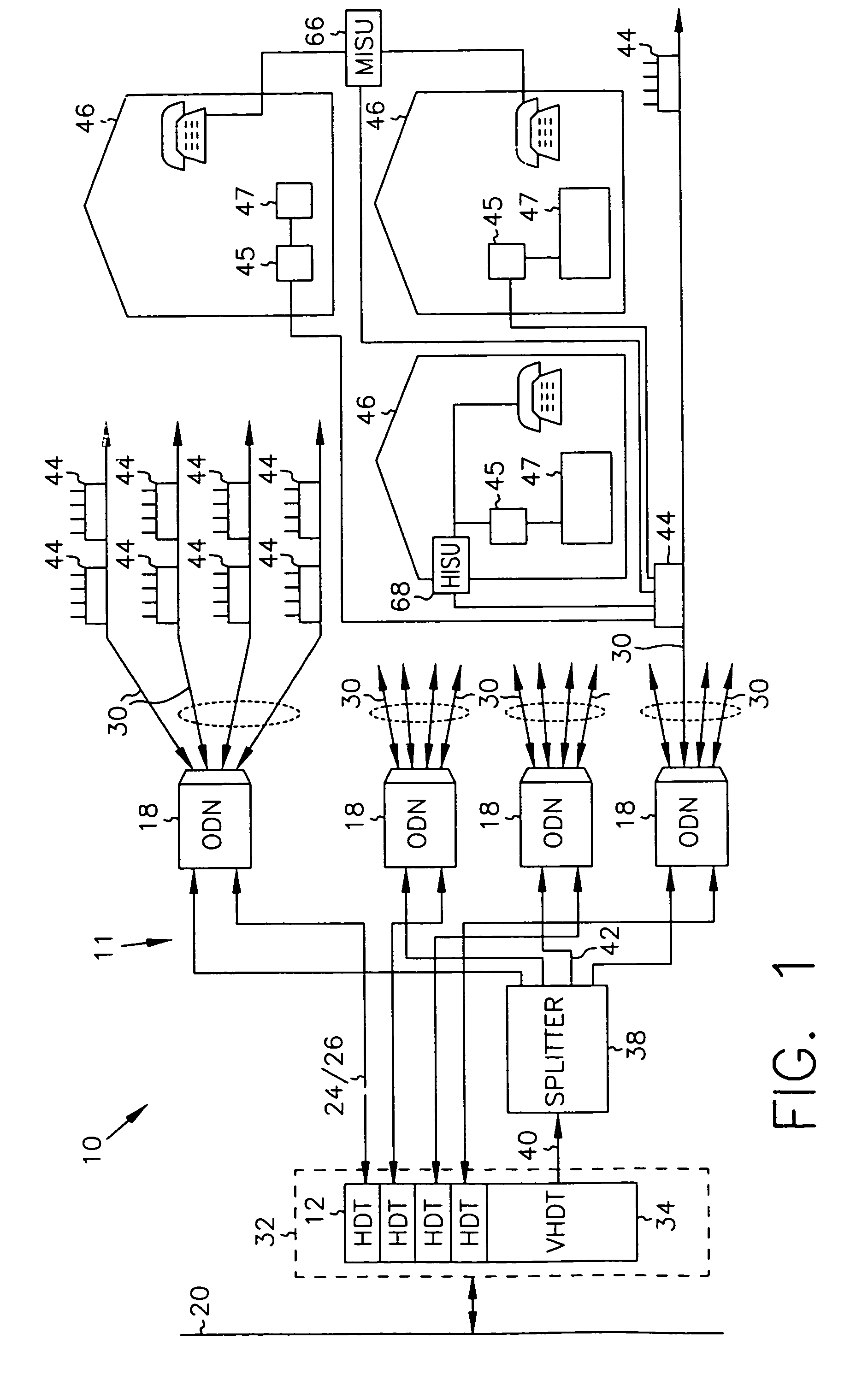
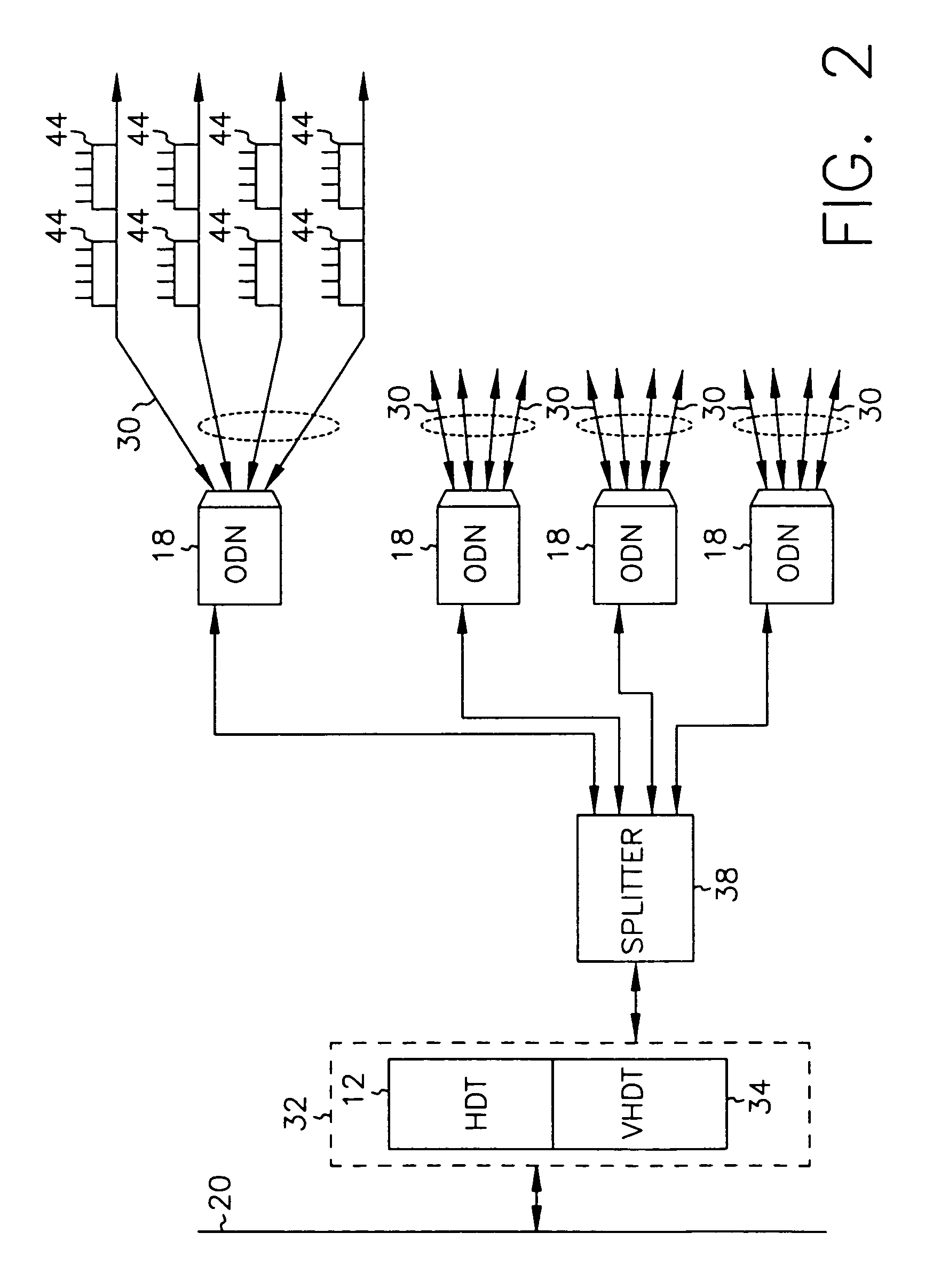
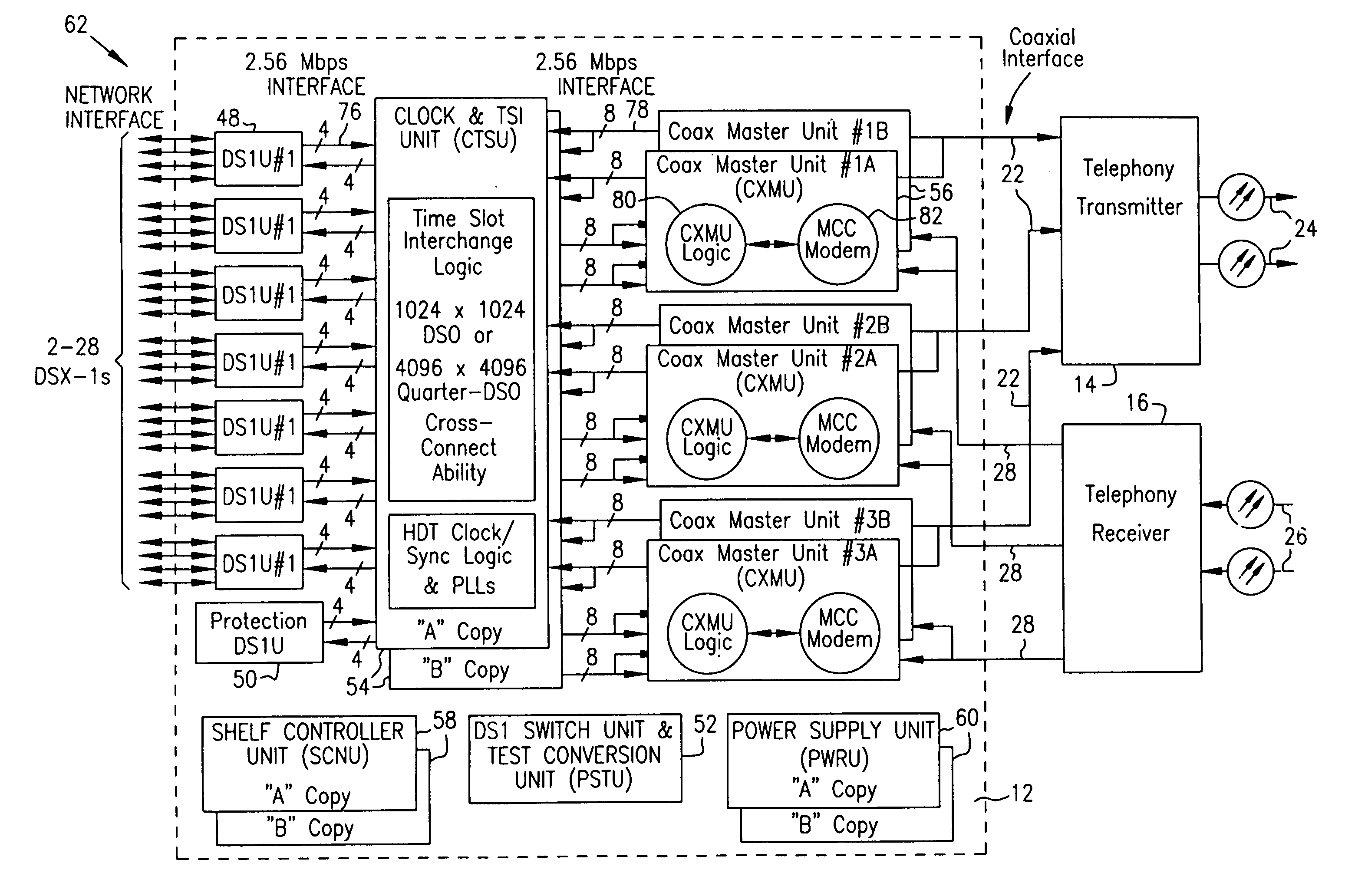
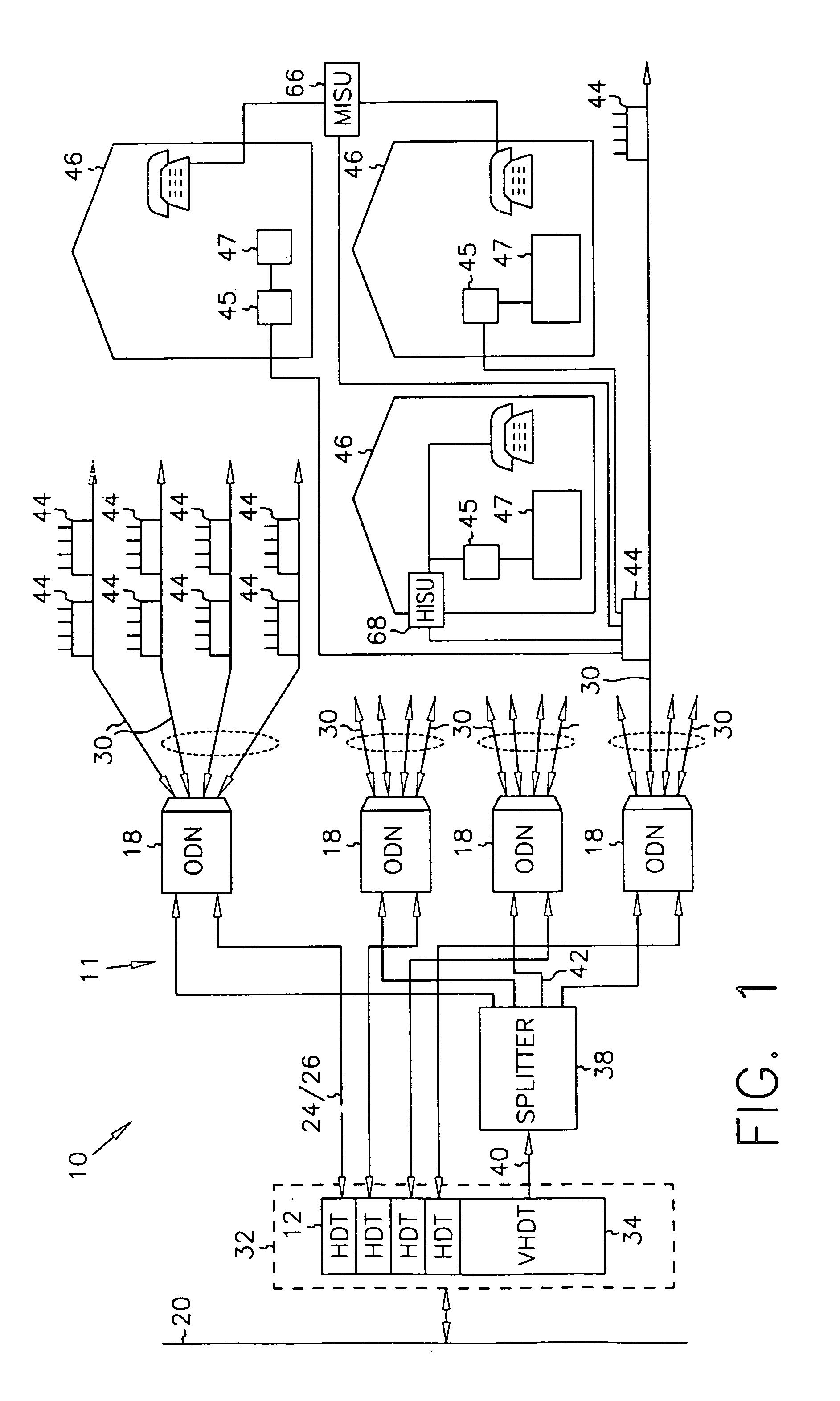
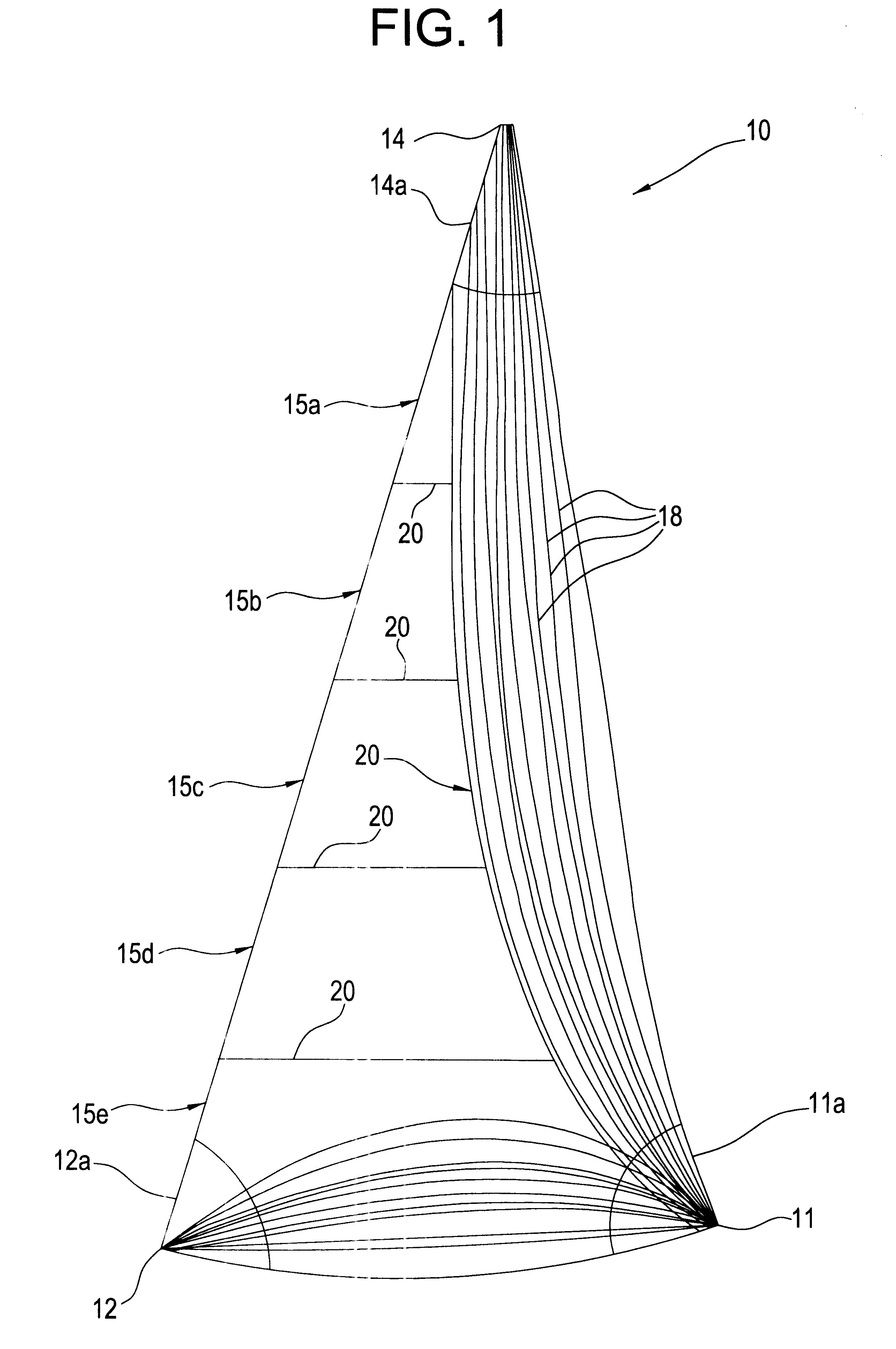
InactiveUS7069577B2Prevents untoward spectral effectMore balancedError preventionModulated-carrier systemsFiberModem device
The communication system includes a hybride fiber / coax distribution network. A head end provides for downstream transmission of telephony and control data in a first frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network and reception of upstream telephony and control data in a second frequency bandwidth over the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network. The head end includes head end multicarrier modem for modulating at least downstream telephony information on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth and demodulating at least upstream telephony information modulated on a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the second frequency bandwidth. The head end further includes a controller operatively connected to the head end multicarrier modem for controlling transmission of the downstream telephony information and downstream control data and for controlling receipt of the upstream control data and upstream telephony information. The system further includes service units, each service unit operatively connected to the hybrid fiber / coax distribution network for upstream transmission of telephony and control data in the second frequency bandwidth and for receipt of the downstream control data and telephony in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit includes a service unit multicarrier modem for modulating at least the upstream telephony information on at least one carrier orthogonal at the head end terminal to another carrier in the second frequency bandwidth and for demodulating at least downstream telephony information modulated on at least a band of a plurality of orthogonal carriers in the first frequency bandwidth. Each service unit also includes a controller operatively connected to the service unit multicarrier modem for controlling the modulation of and demodulation performed by the service unit multicarrier modem. A method of monitoring communication channels, a distributed loop method for adjusting transmission characteristics to allow for transmission of data in a multi-point to point communication system, a polyphase filter technique for providing ingress protection and a scanning method for identifying frequency bands to be used for transmission by service units are also included. Also provided is a method and apparatus for performing a Fast Fourier Transform (FFT). In one embodiment, a scalable FFT system is built using a novel dual-radix butterfly core.
Owner:HTC CORP
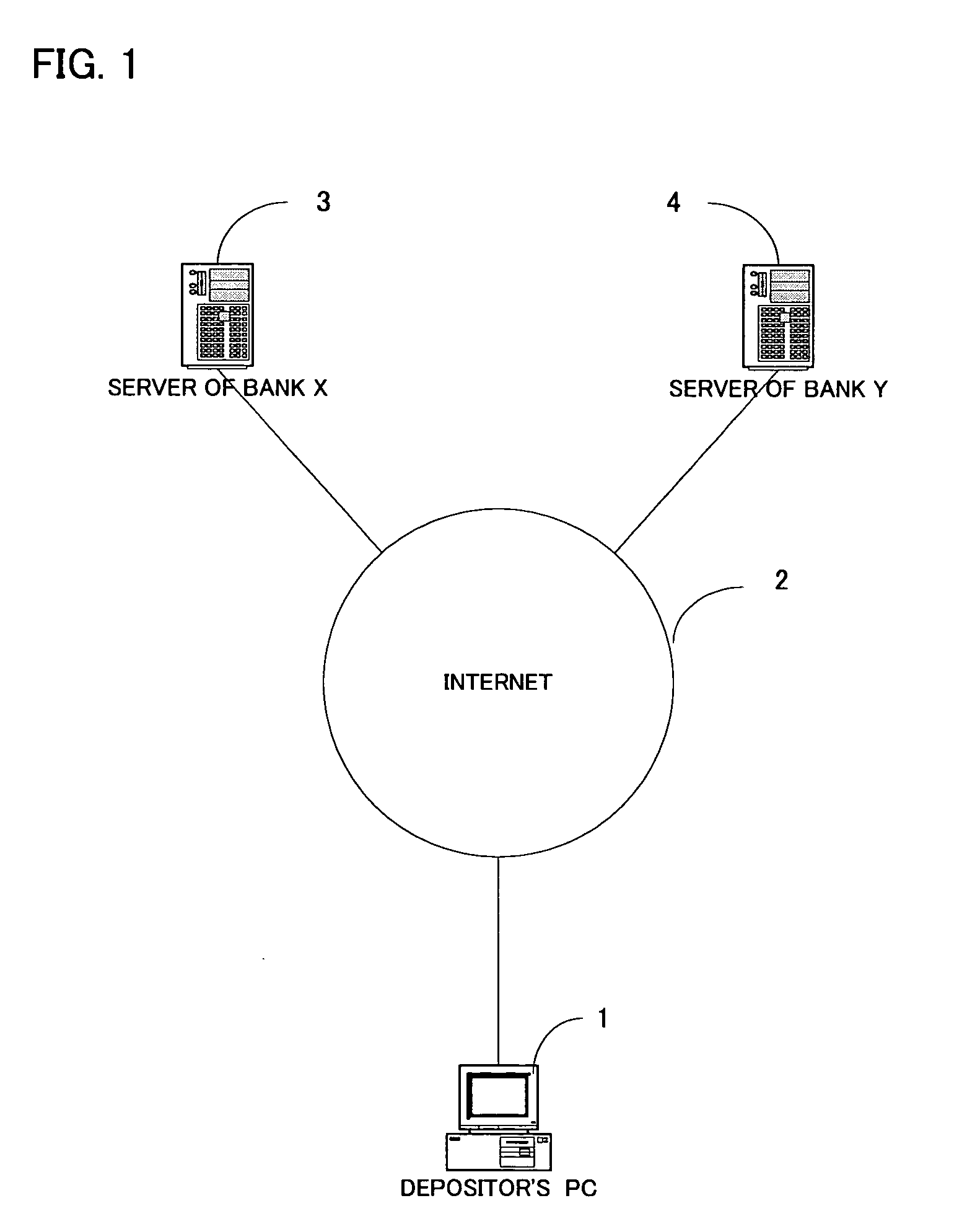
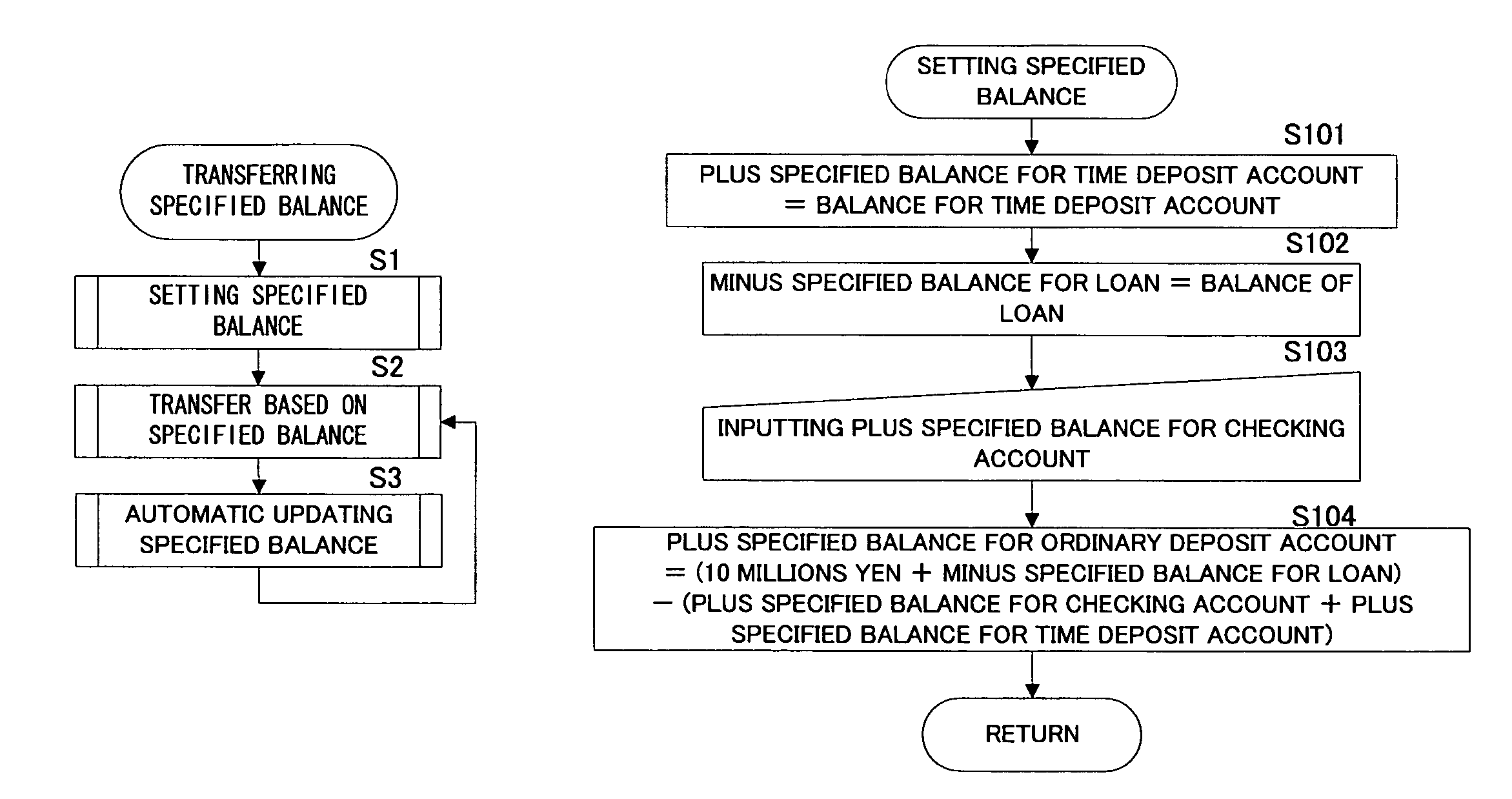
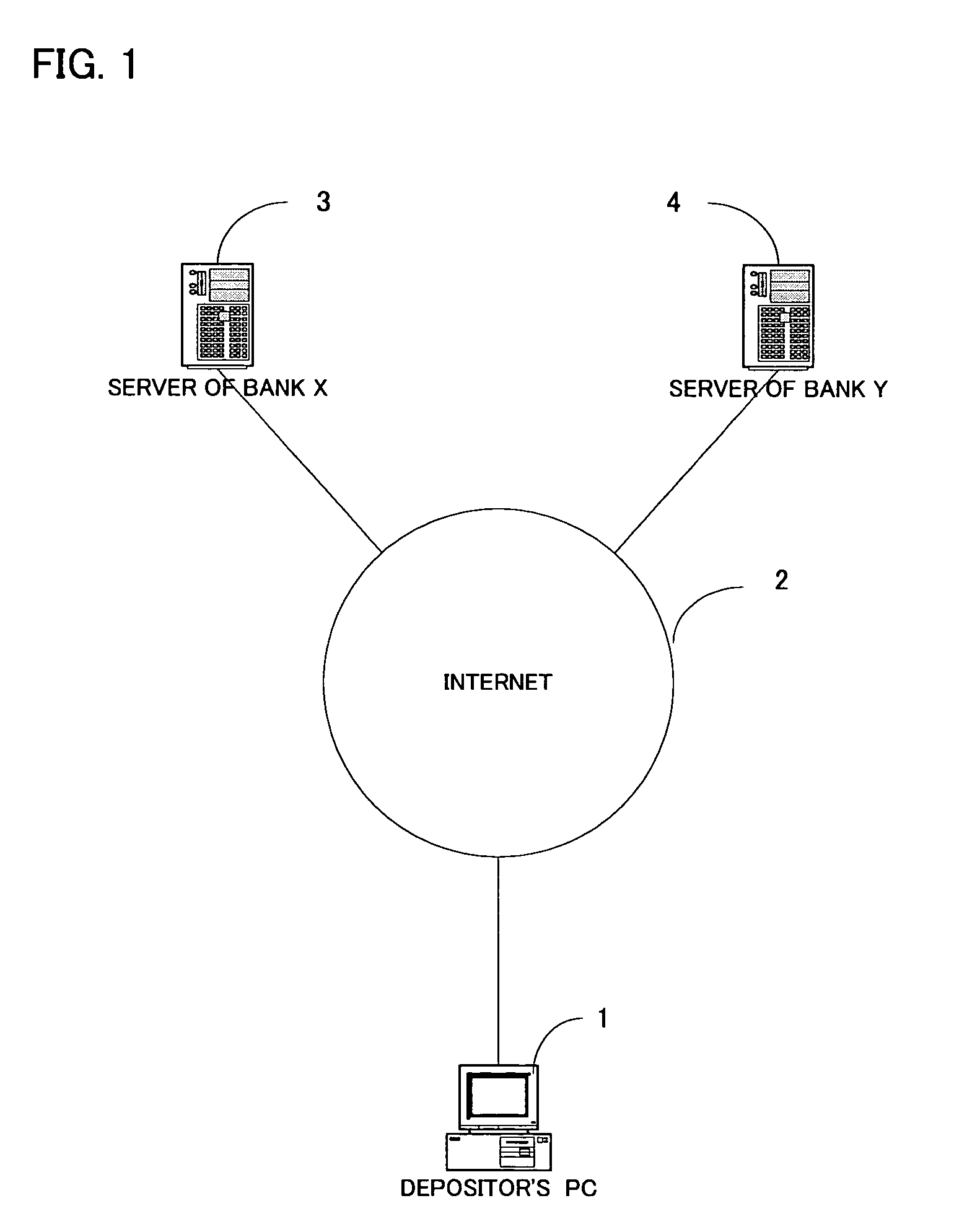
Bank account automatic adjustment system
InactiveUS20040177036A1More balancedMinimize as littleFinanceComputer security arrangementsDeposit accountBank account
The present system for automatically adjusting deposit balance is the effective measure for pay-off which calculates the excess amount by subtracting from the balance of the account established in one financial institution, the specified balance for the account and calculates the allowable amount by subtracting from the specified balance for the account established in other financial institution, the balance of the account and compares said excess amount with said allowable amount and sets the transfer amounts as the one lesser of either said excess amount or said allowable amount. Specifically the system for automatically adjusting deposit sets in addition the plus specified balance for checking and savings accounts and time deposit account respectively when said accounts include checking account and savings account and time deposit accounts. The system for automatically adjusting deposit further sets the minus specified balance for the debt amount. Preferably the system for automatically adjusting deposit is an apparatus which enables to maintain the necessary balance and calculates the deficit amount by subtracting from the balance for the account established in one financial institution, the necessary balance for the account and calculates the surplus amount by subtracting from the necessary balance for the account established in said other financial institution, the balance for the account and compares said deficit amount with the surplus amount and sets the amount that is lesser of said deficit or surplus amounts for the transfer amount.
Owner:NUTAHARA ATSUO +1
Bank account automatic adjustment system
InactiveUS7509287B2More balancedMinimize as littleFinanceComputer security arrangementsDeposit accountBank account
The present system for automatically adjusting deposit balance is the effective measure for pay-off which calculates the excess amount by subtracting from the balance of the account established in one financial institution, the specified balance for the account and calculates the allowable amount by subtracting from the specified balance for the account established in other financial institution, the balance of the account and compares said excess amount with said allowable amount and sets the transfer amounts as the one lesser of either said excess amount or said allowable amount. Specifically the system for automatically adjusting deposit sets in addition the plus specified balance for checking and savings accounts and time deposit account respectively when said accounts include checking account and savings account and time deposit accounts. The system for automatically adjusting deposit further sets the minus specified balance for the debt amount. Preferably the system for automatically adjusting deposit is an apparatus which enables to maintain the necessary balance and calculates the deficit amount by subtracting from the balance for the account established in one financial institution, the necessary balance for the account and calculates the surplus amount by subtracting from the necessary balance for the account established in said other financial institution, the balance for the account and compares said deficit amount with the surplus amount and sets the amount that is lesser of said deficit or surplus amounts for the transfer amount.
Owner:NUTAHARA ATSUO +1
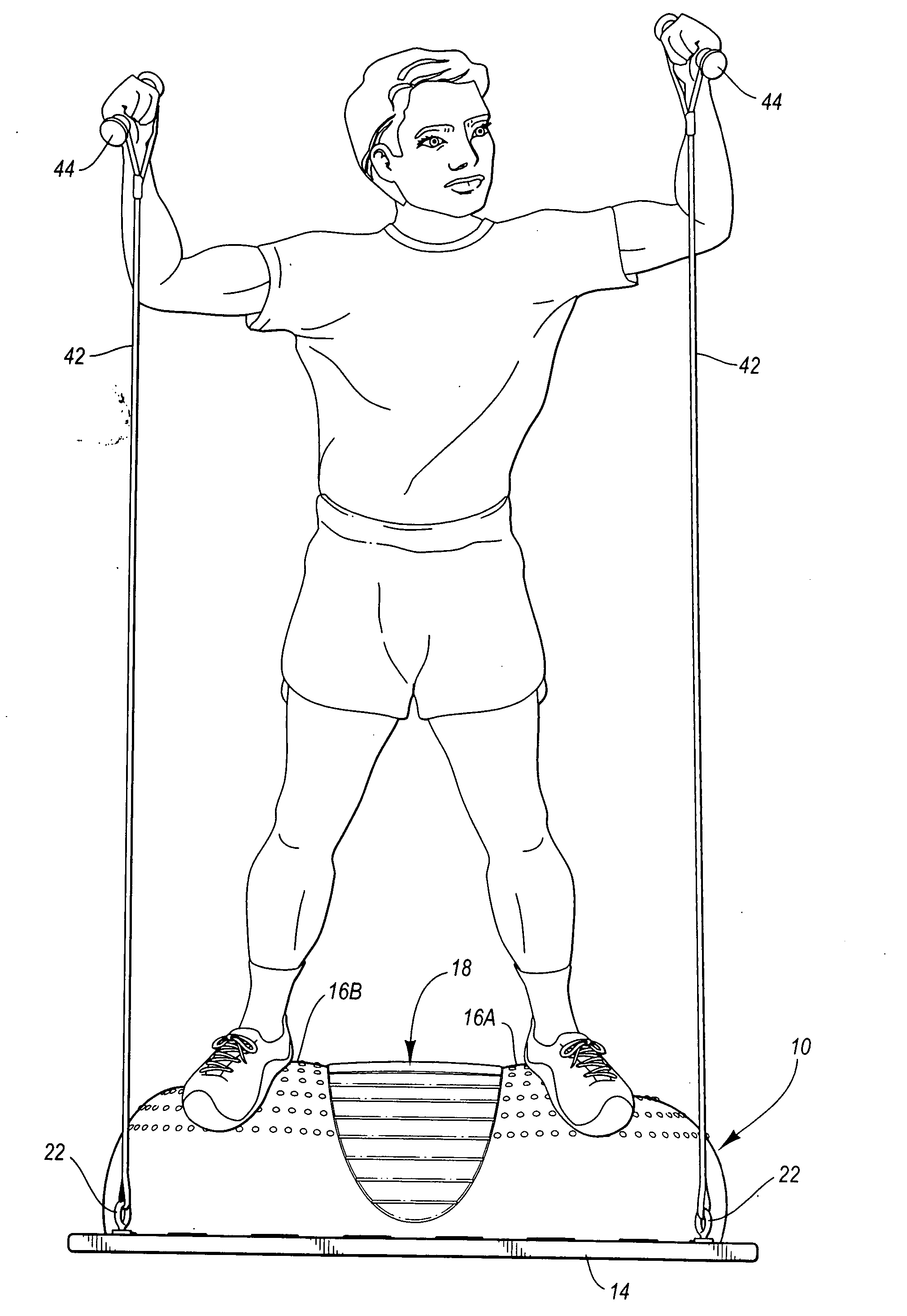
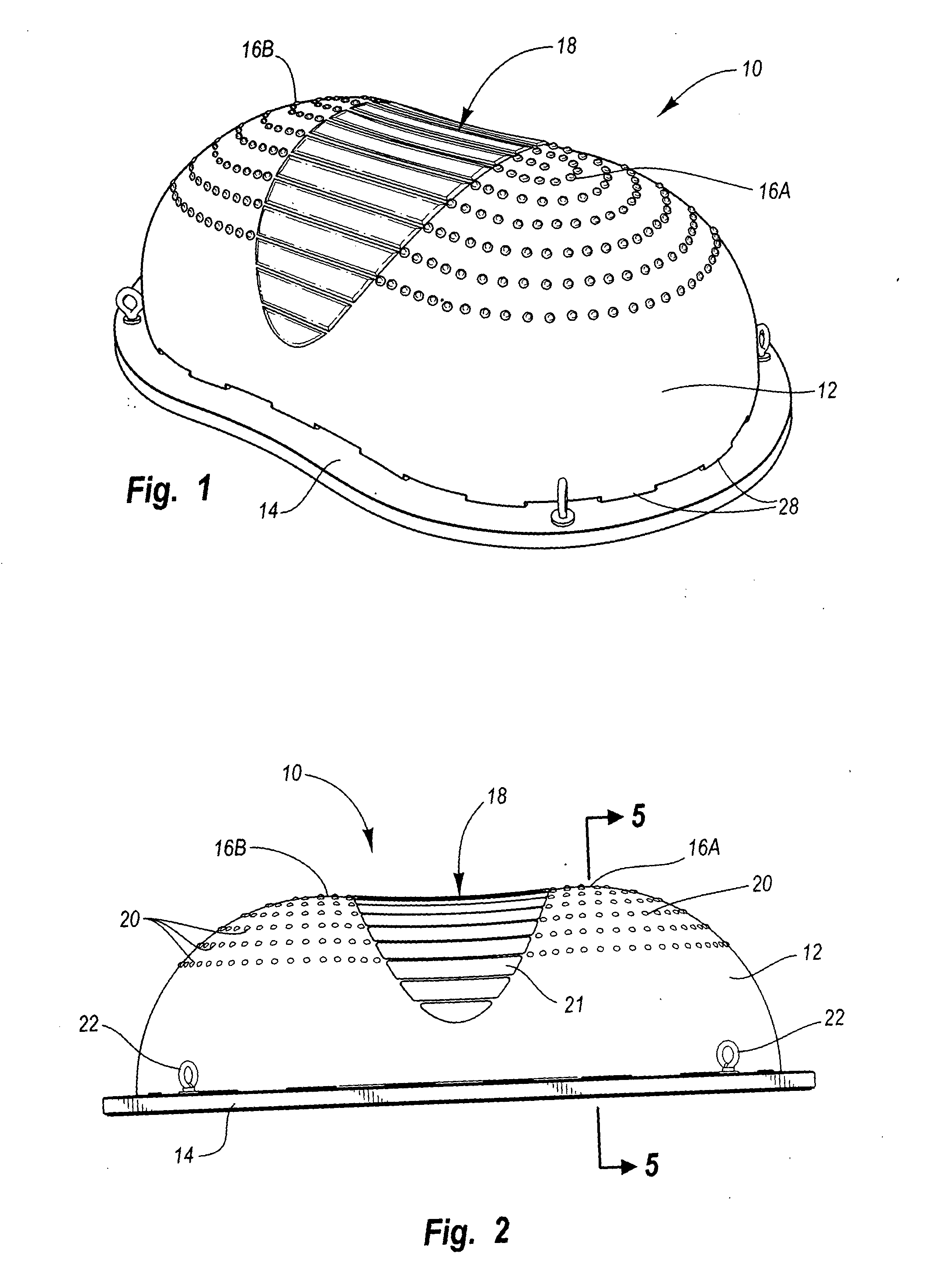
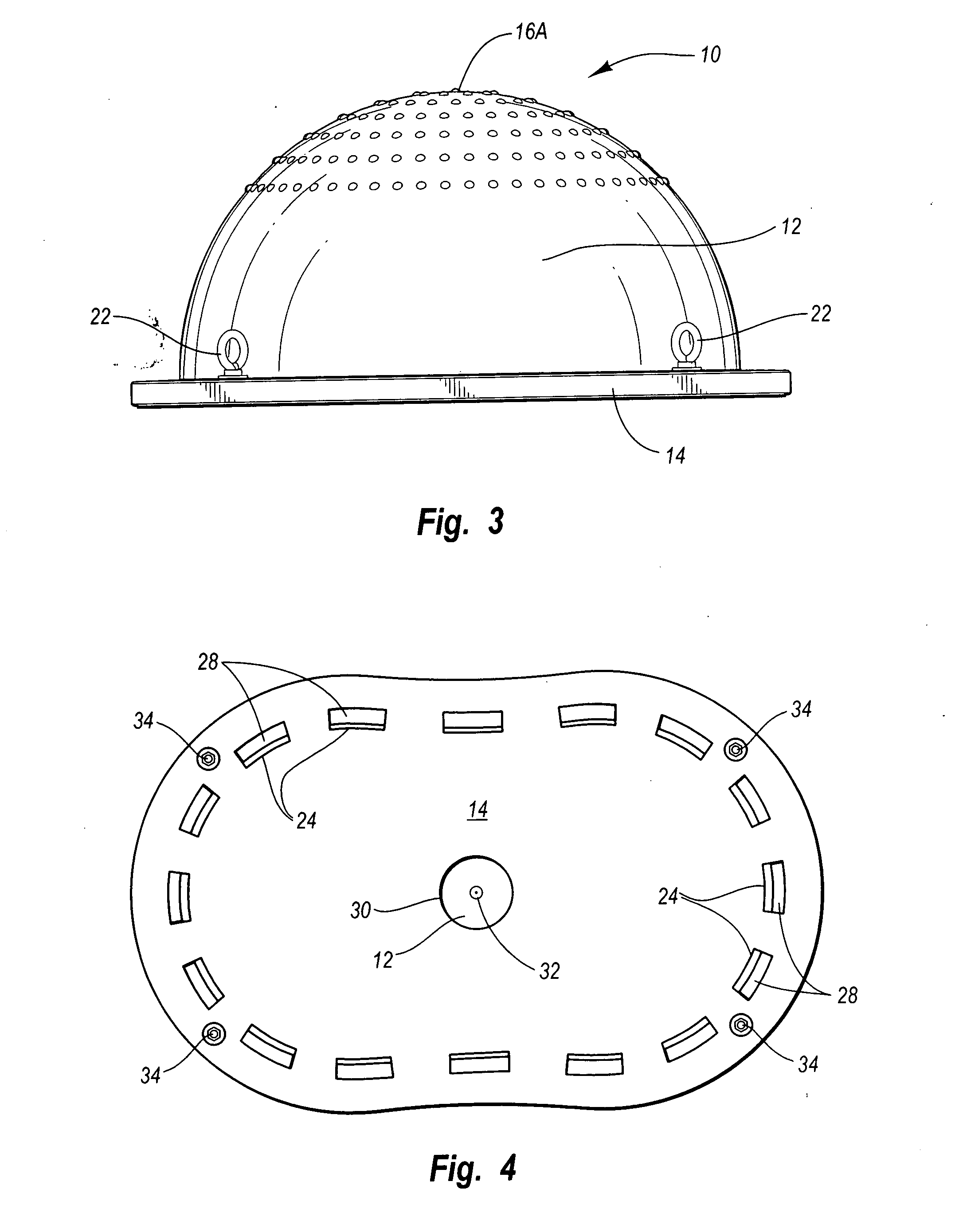
Exercise device with elongate flexible member
InactiveUS20050049123A1Ensure sufficient separationReduce instabilityStiltsMuscle exercising devicesEngineeringExercise balance
The present invention is directed to an exercise device that enhances a body workout by requiring a user to maintain balance while exercising. The exercise device has an elongate flexible member connected to a base. The flexible member has an upper surface and a lower surface. The upper surface has a pair of foot placement portions configured and arranged such that a user positioned thereon must exercise balance. The foot placement portions are separated along the longitudinal axis such that a user standing thereon assumes an athletic stance.
Owner:ICON IP
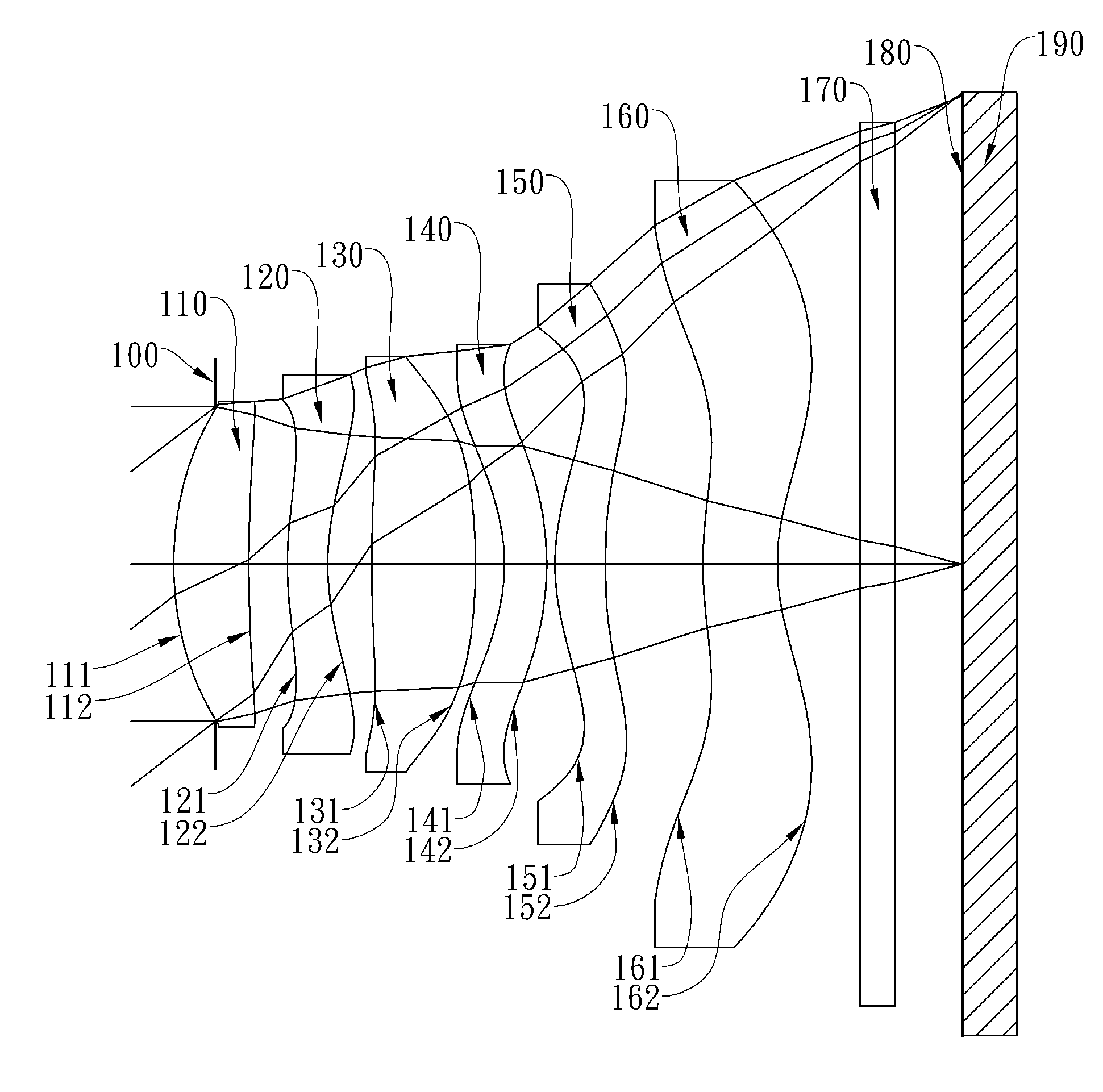
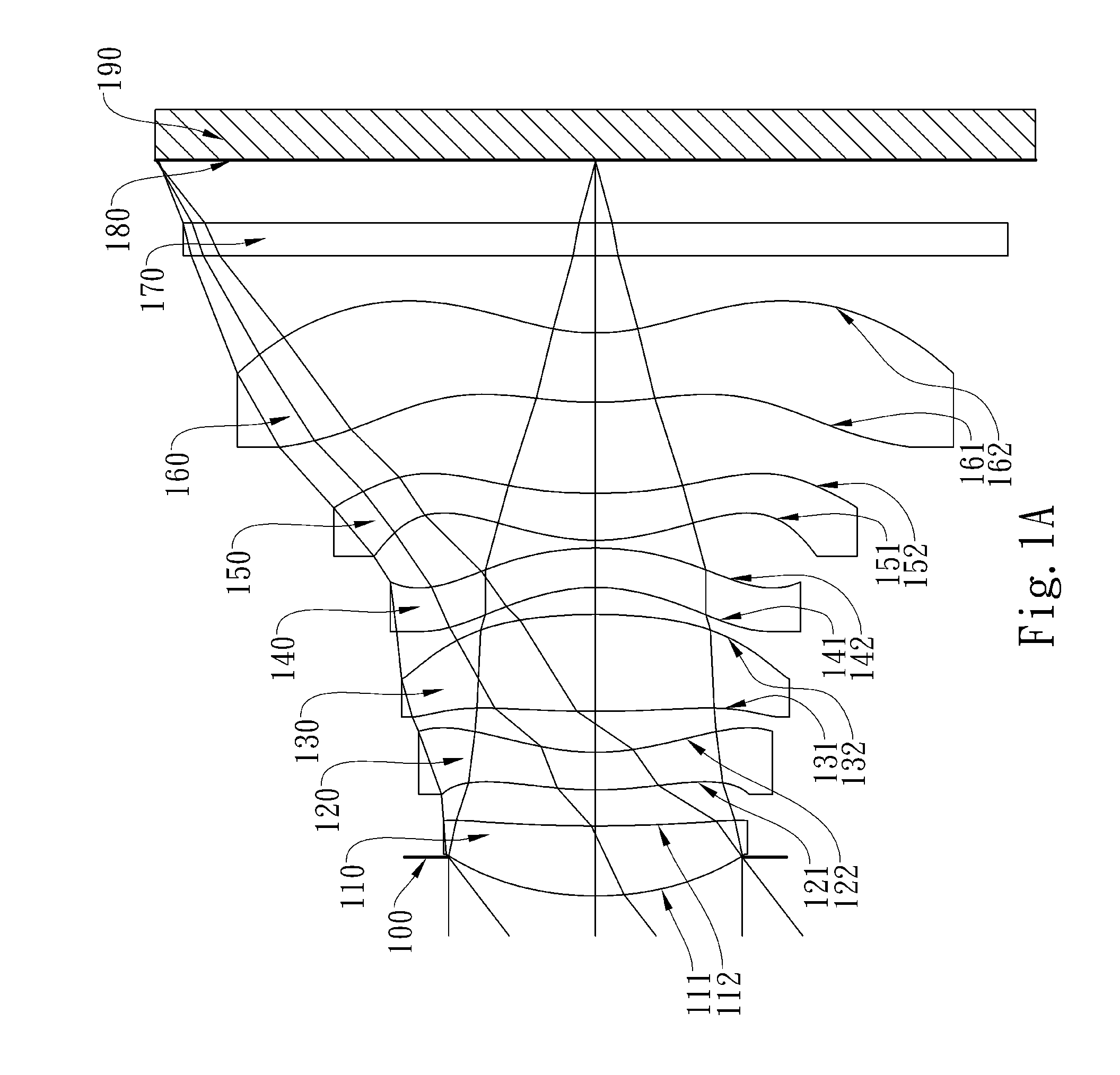
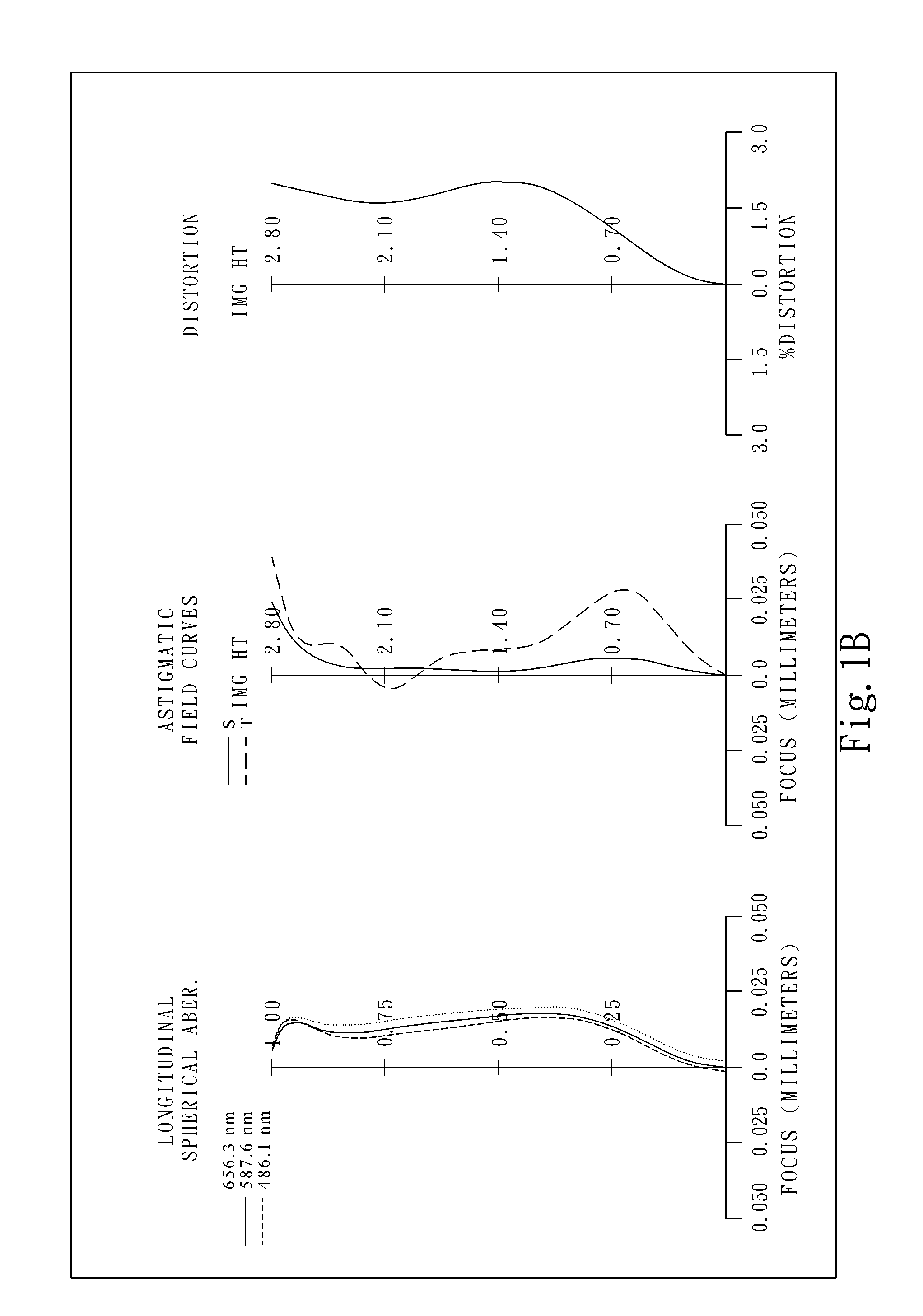
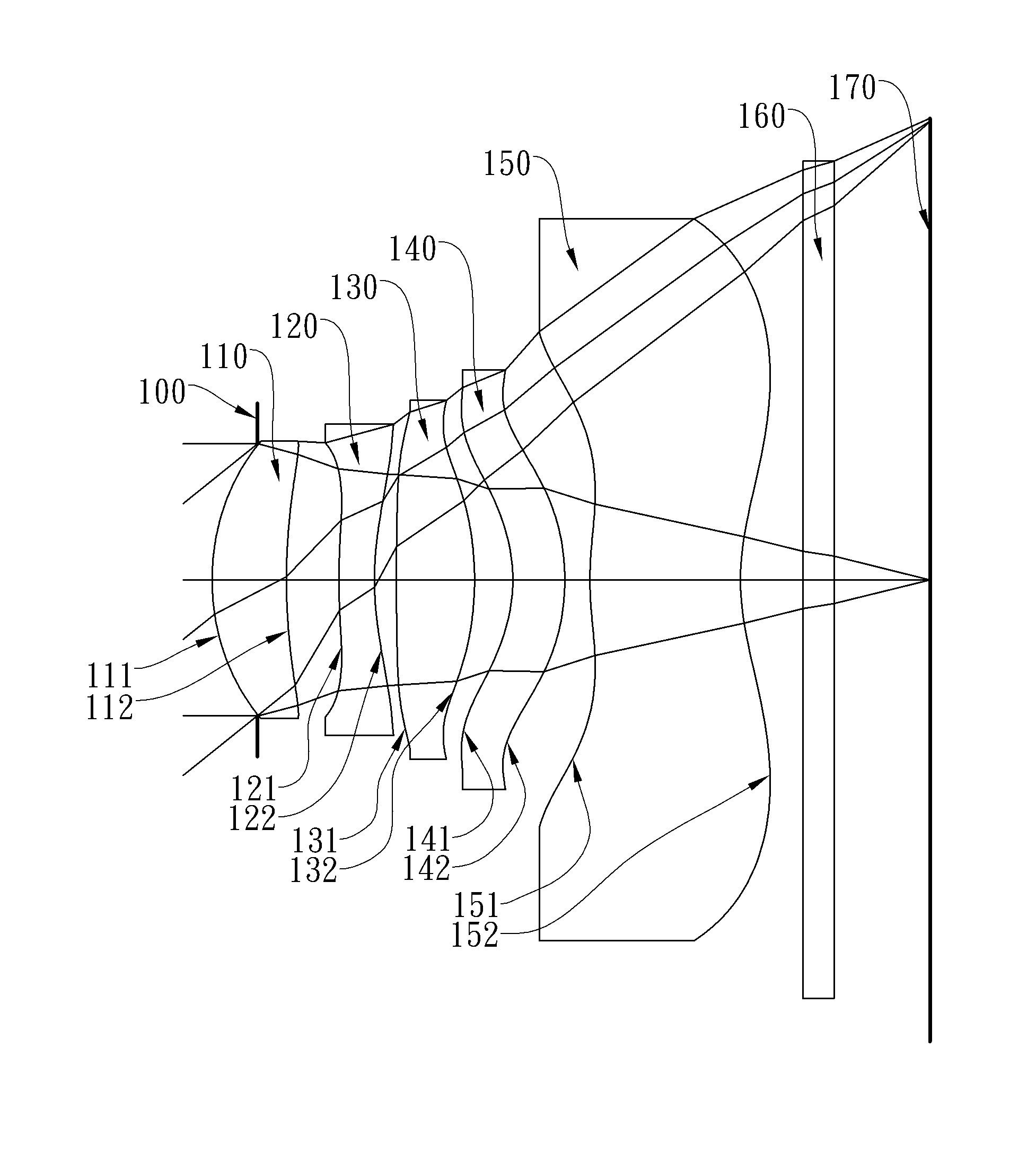
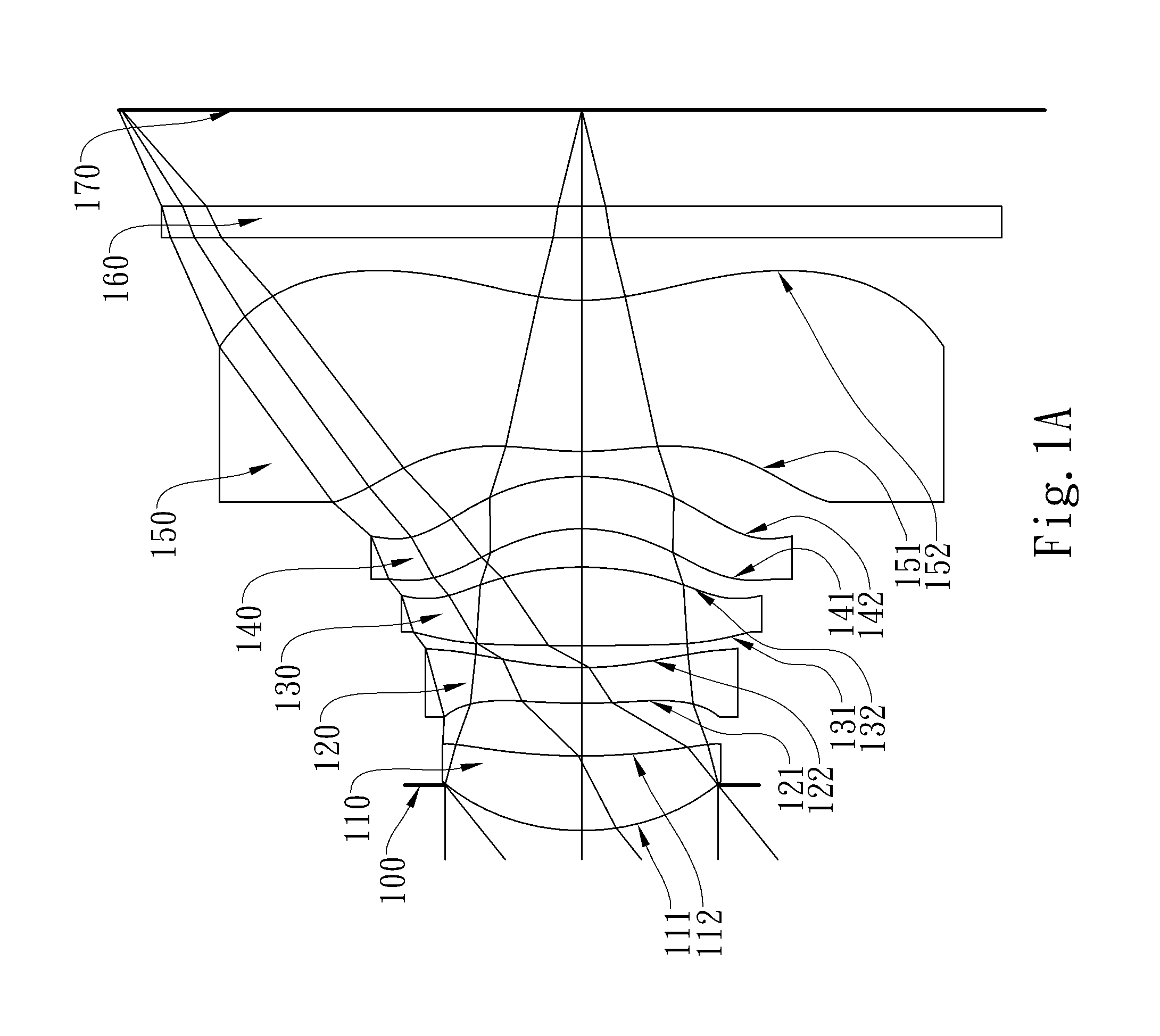
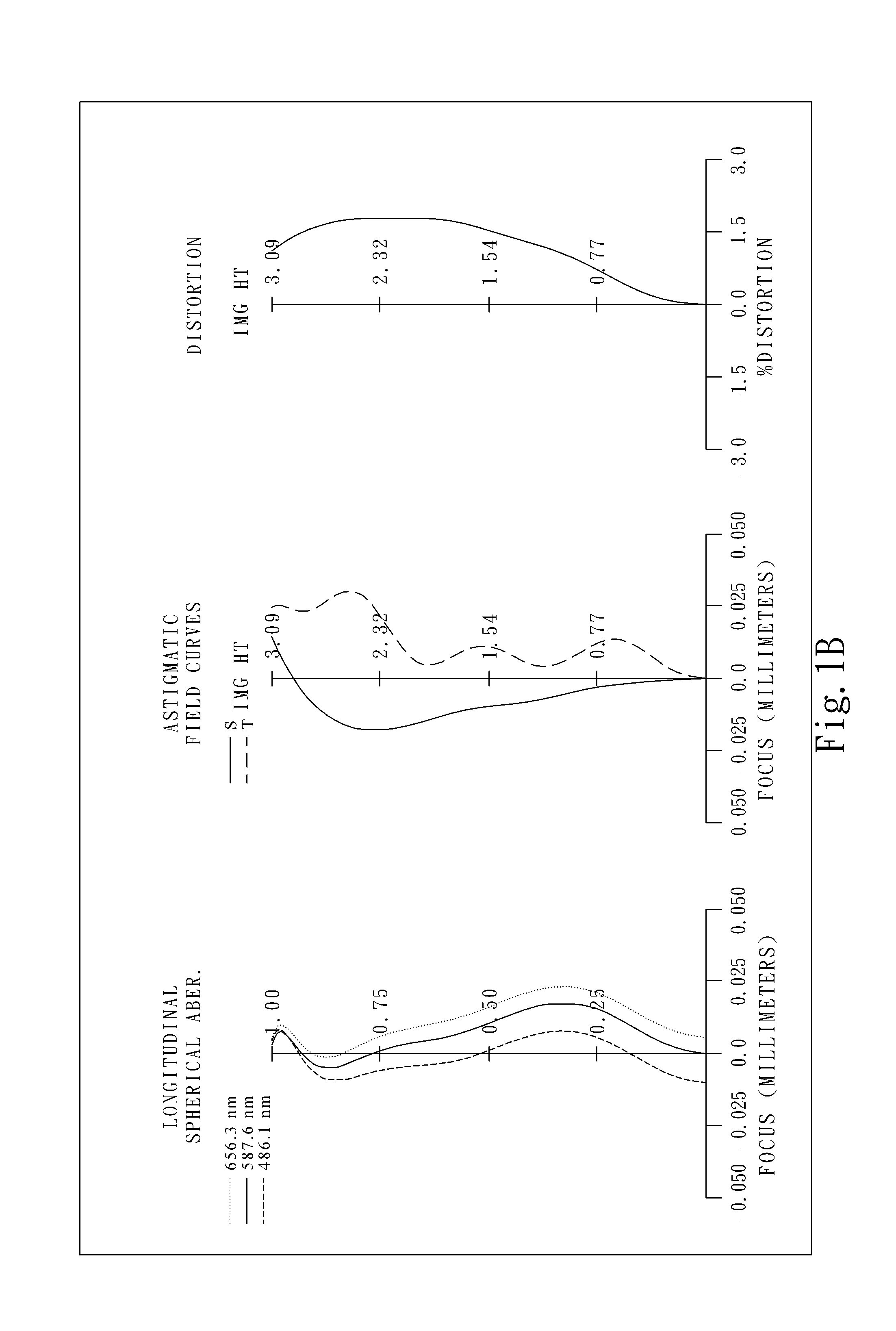
Optical image lens system
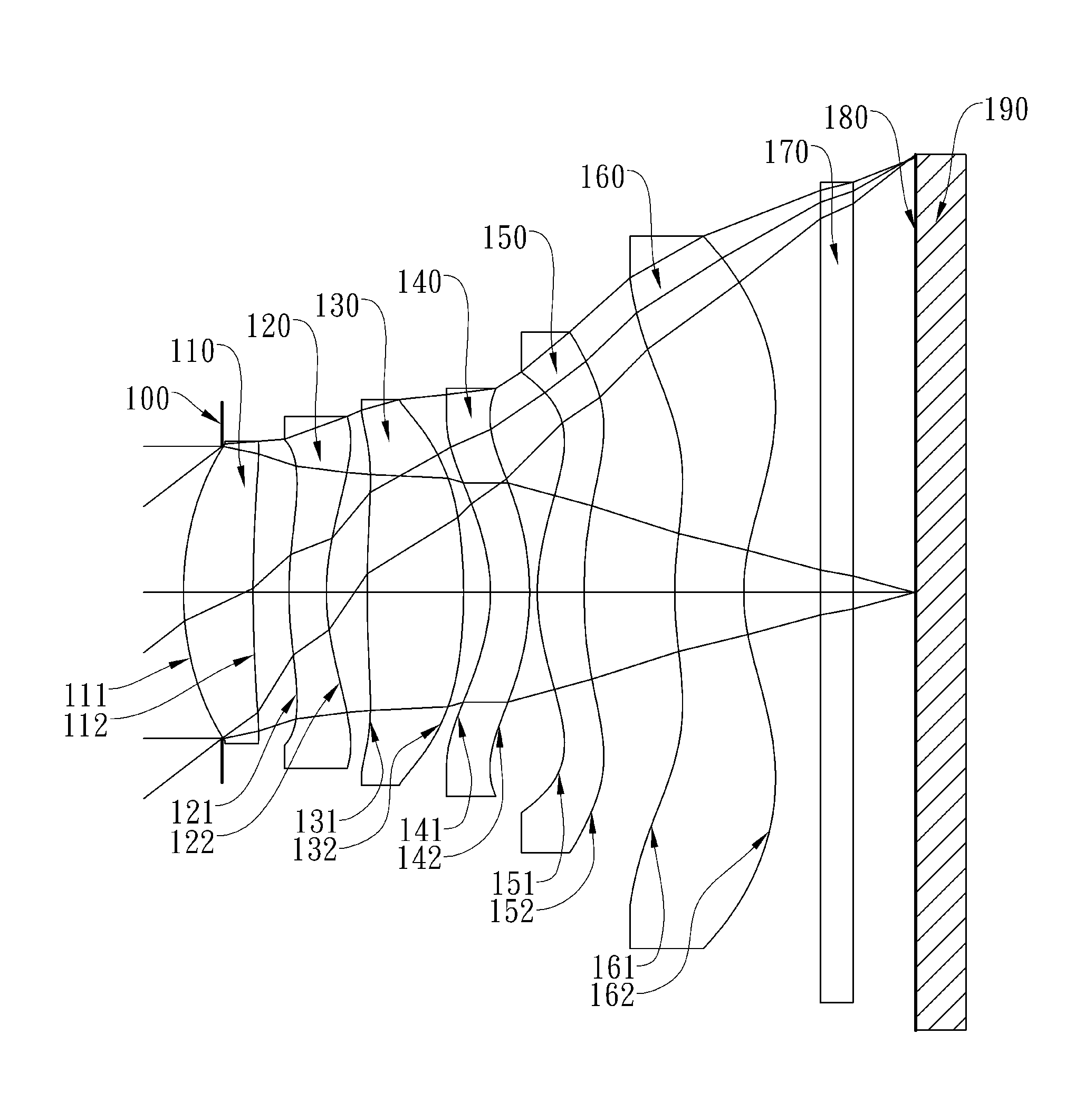
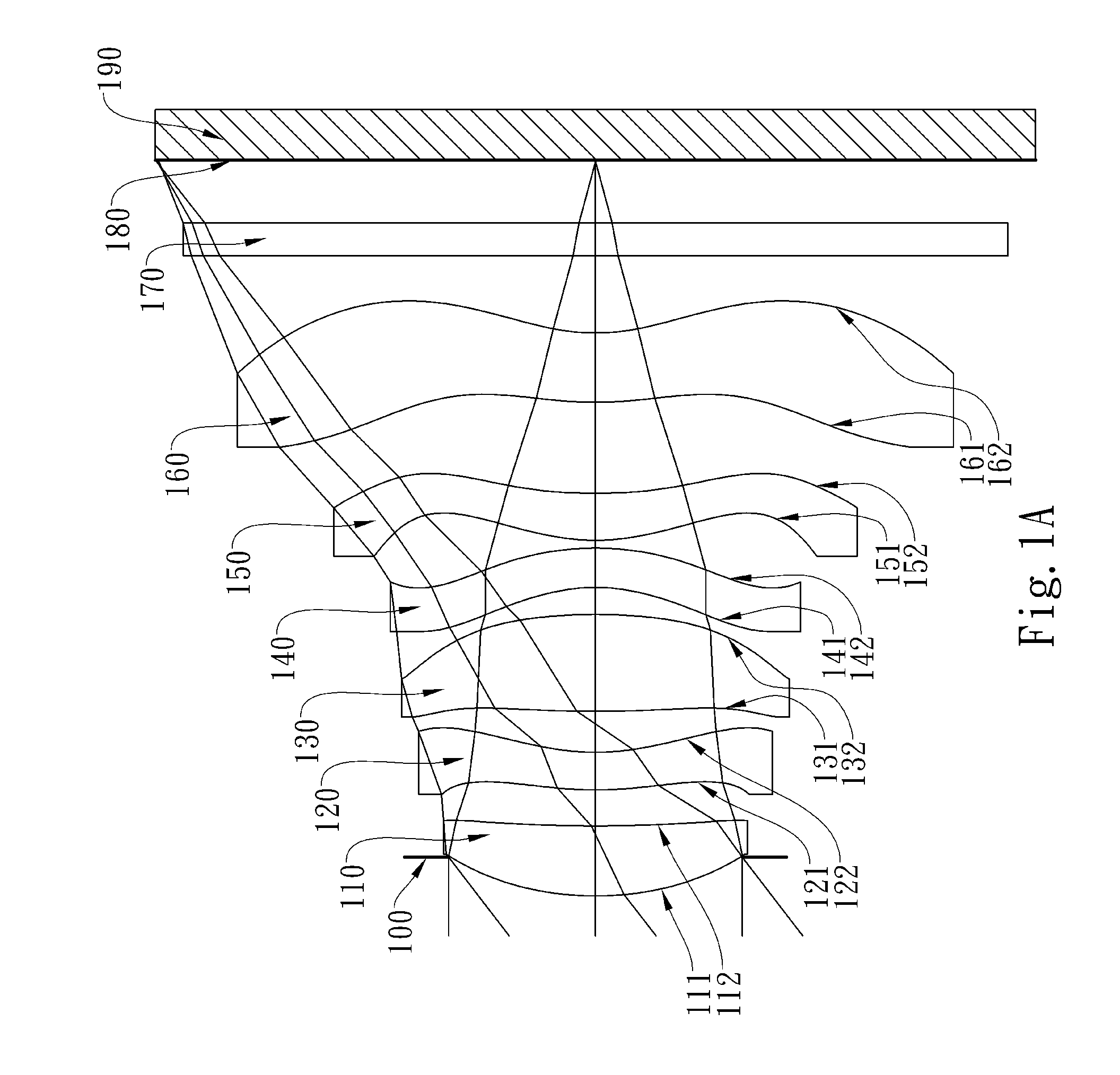
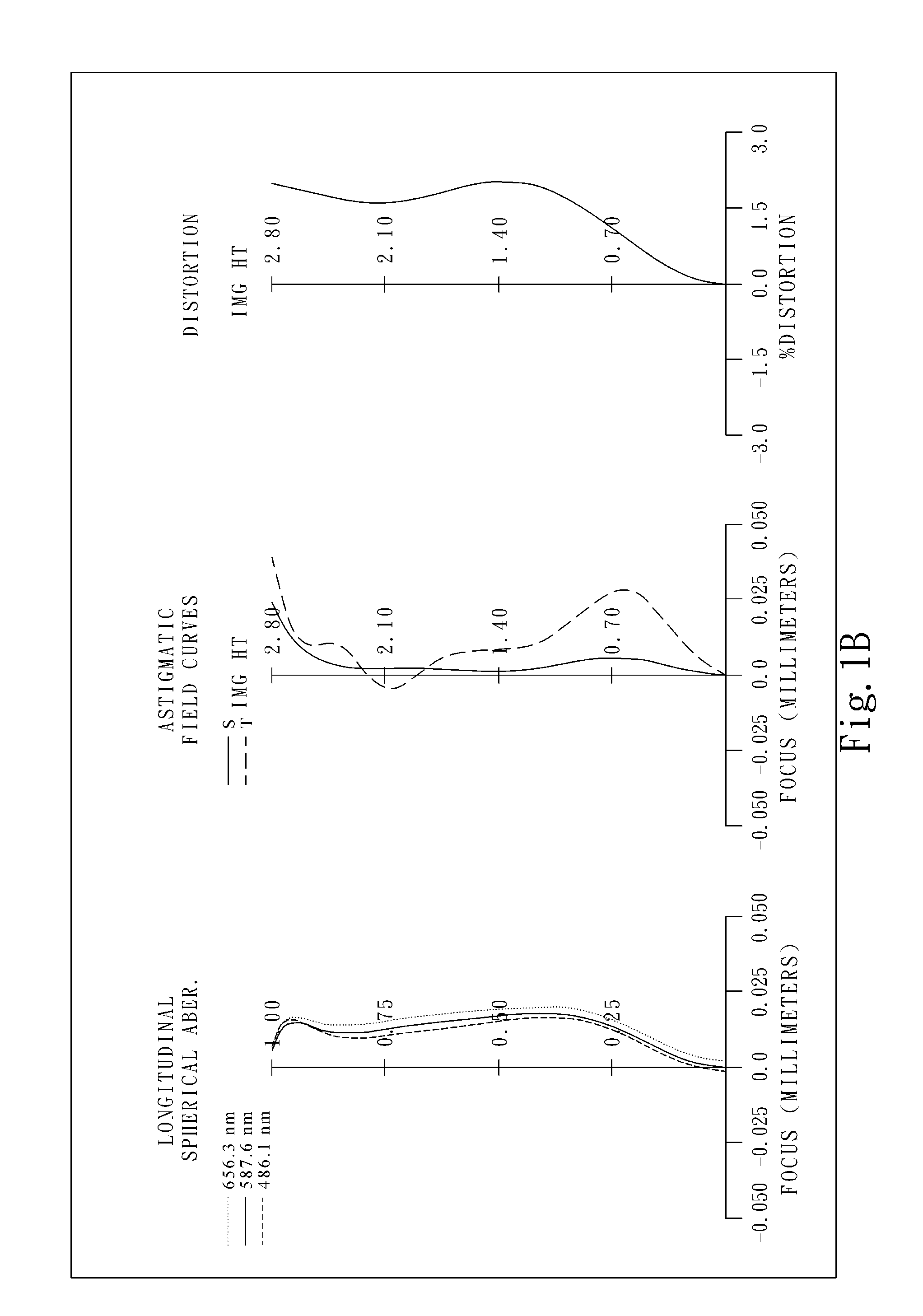
This invention provides an optical image lens system comprising: a positive first lens element having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element; a positive third lens element; a fourth lens element; a positive plastic fifth lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces is aspheric; and a negative plastic sixth lens element having a concave image-side surface, at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces is aspheric, wherein the shape of the image-side surface changes from concave at the paraxial region thereof to convex while away from the paraxial region thereof.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
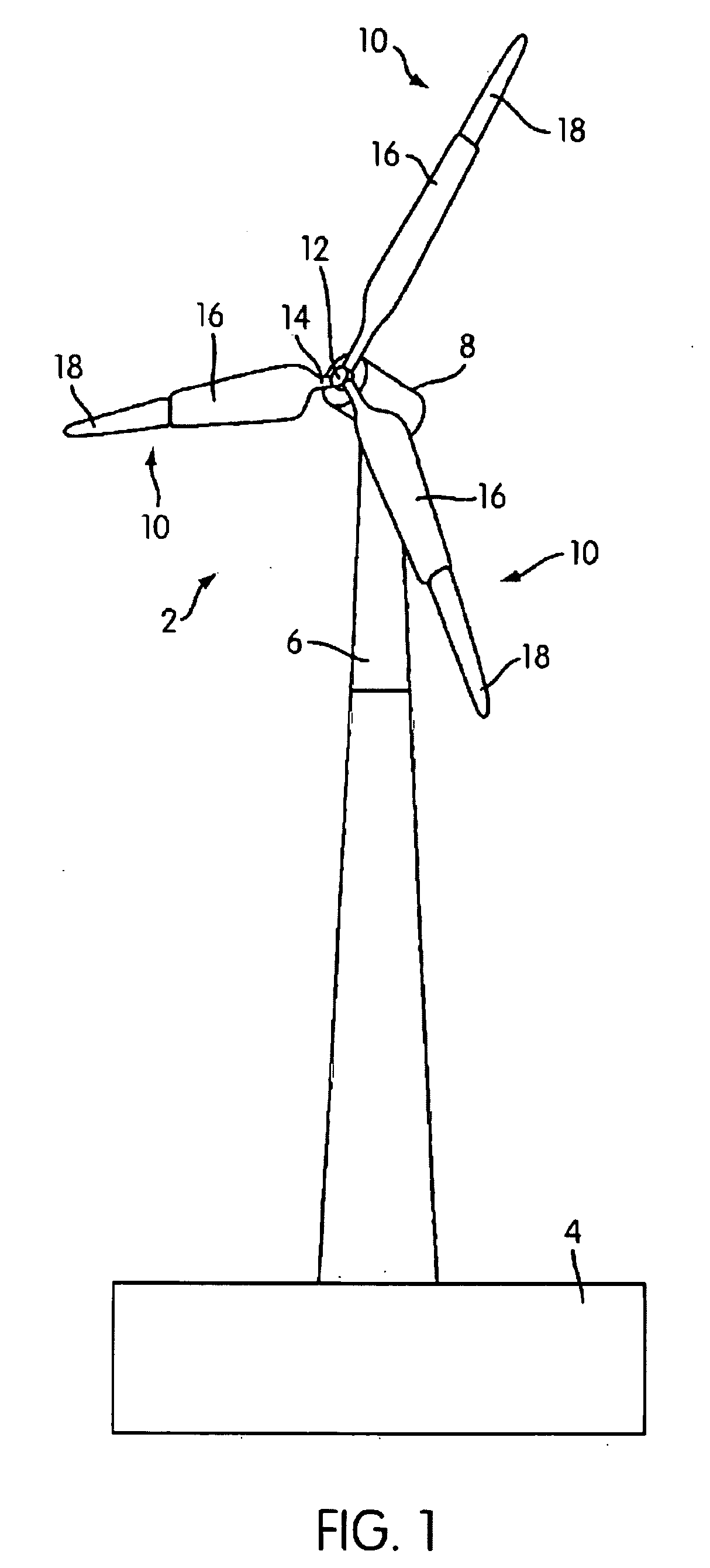
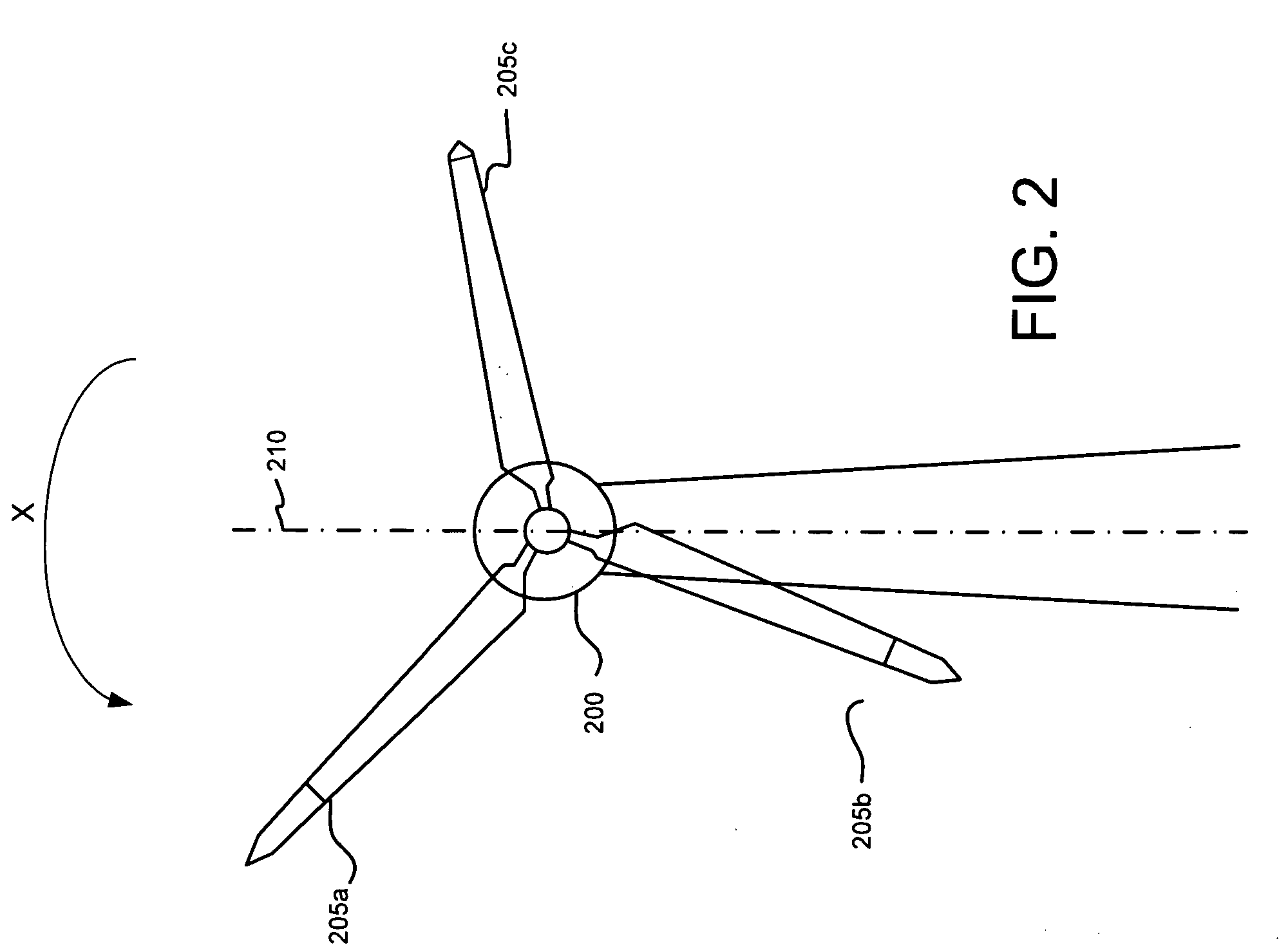
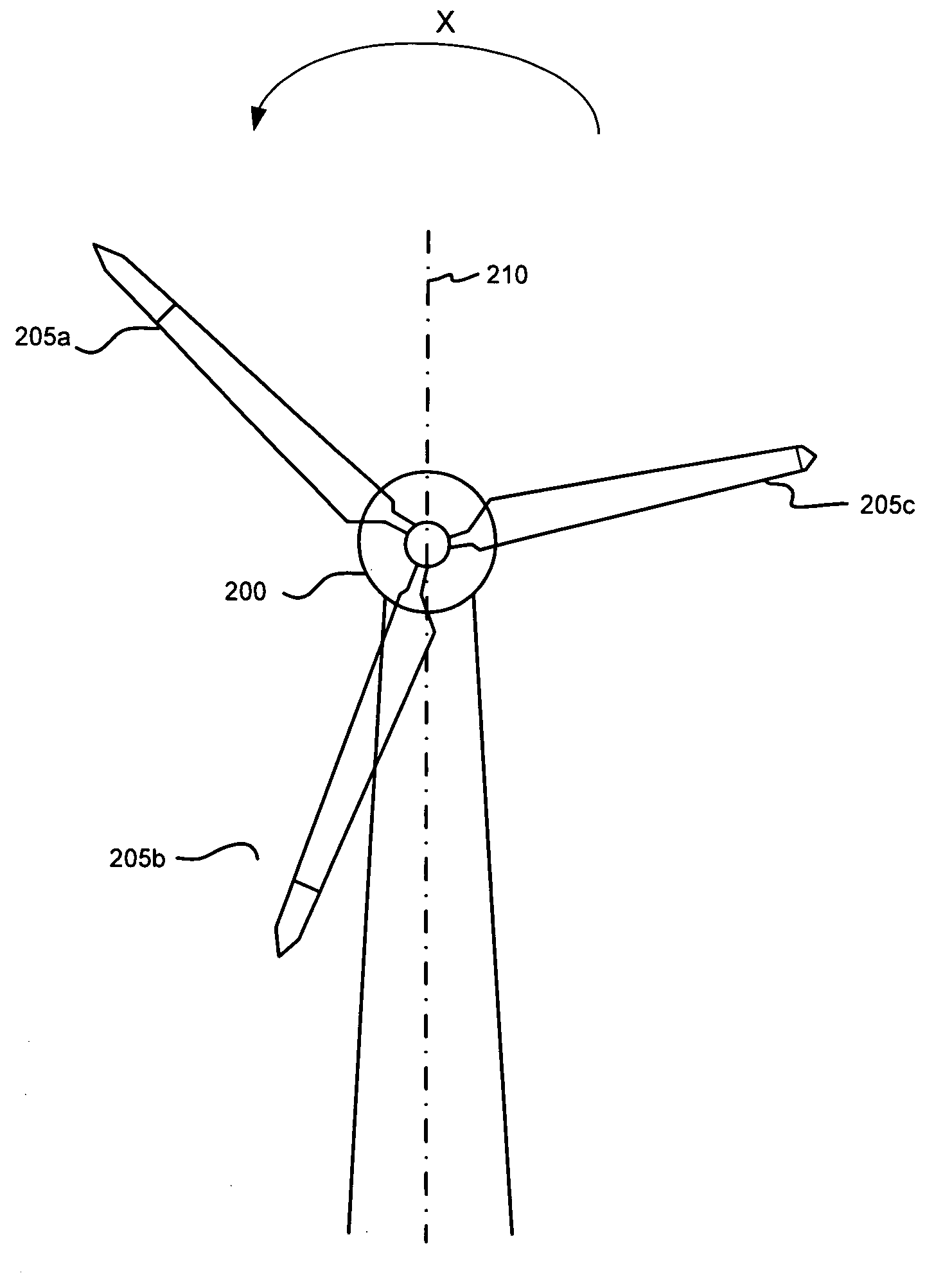
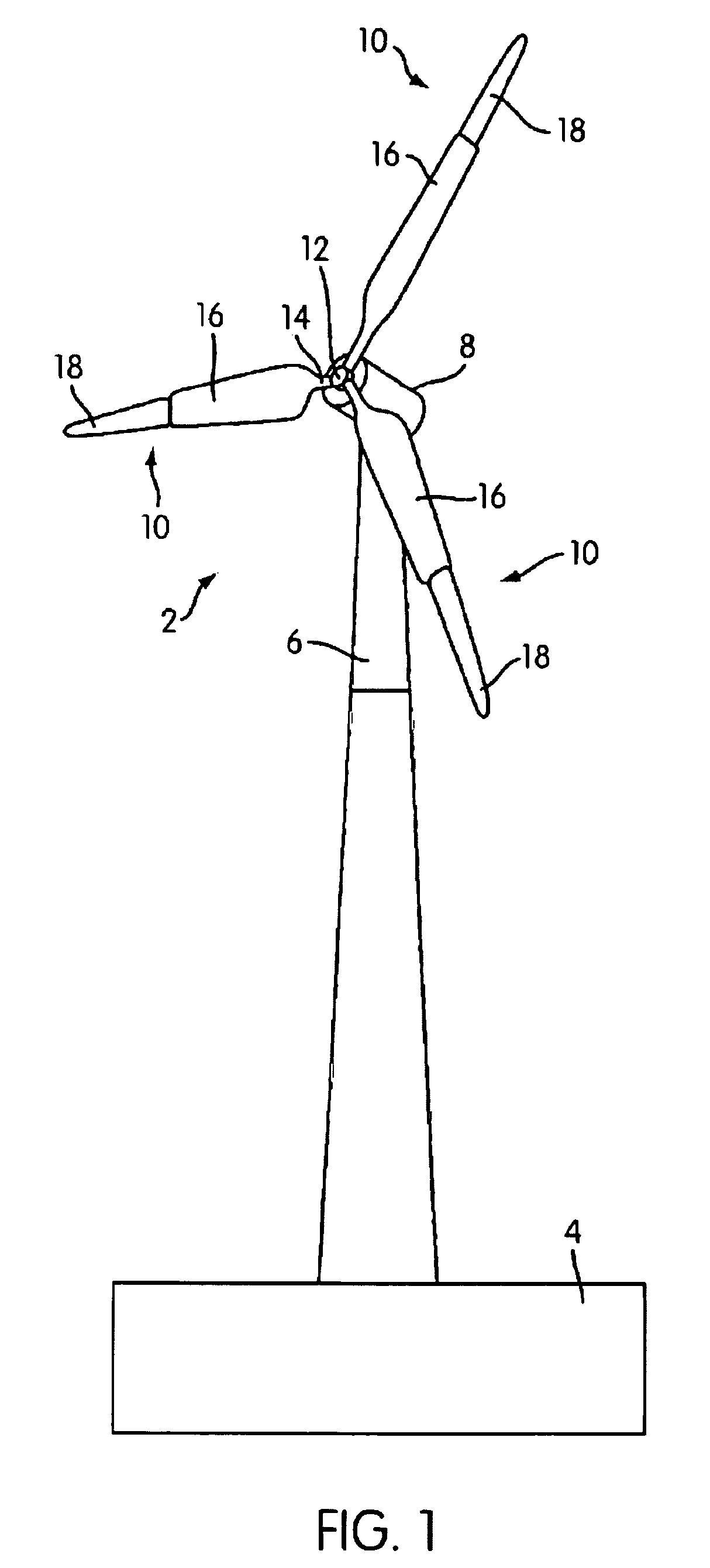
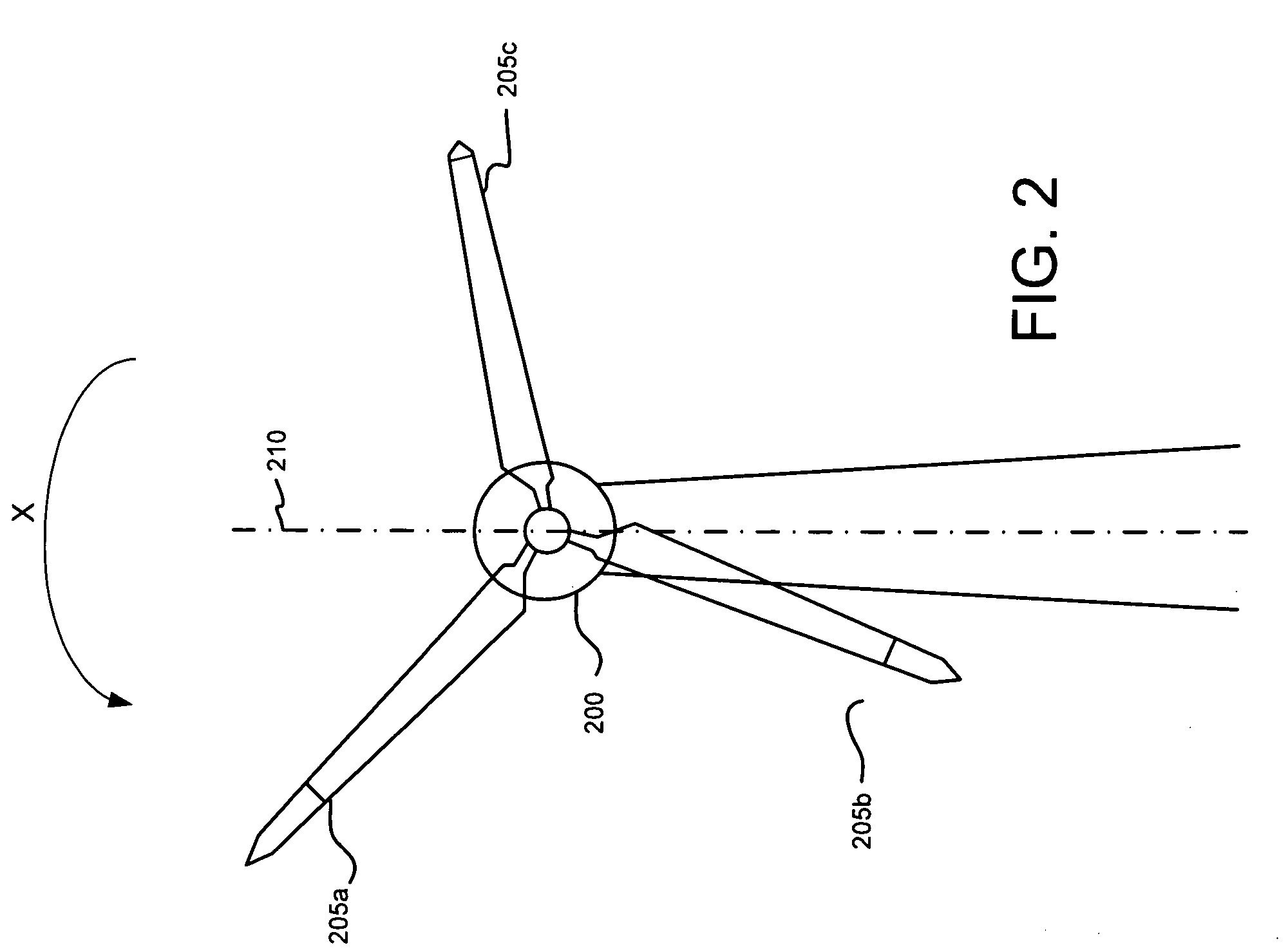
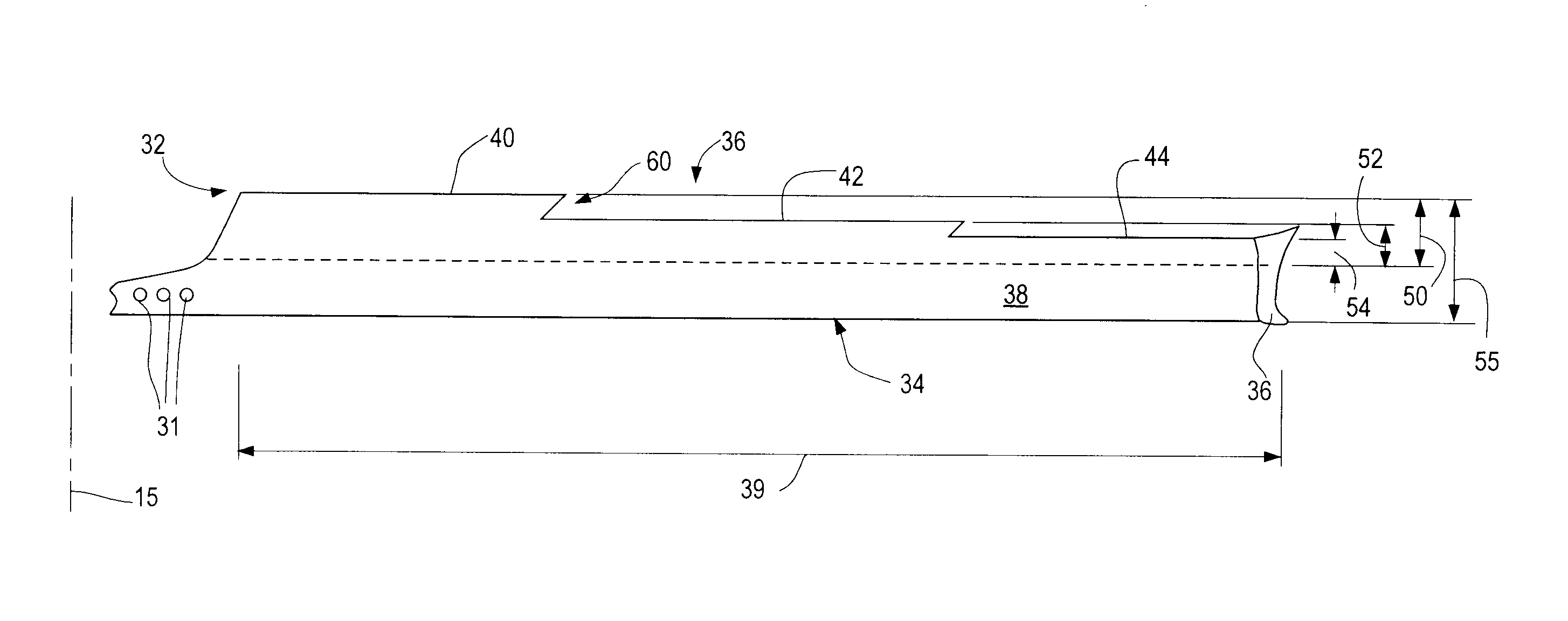
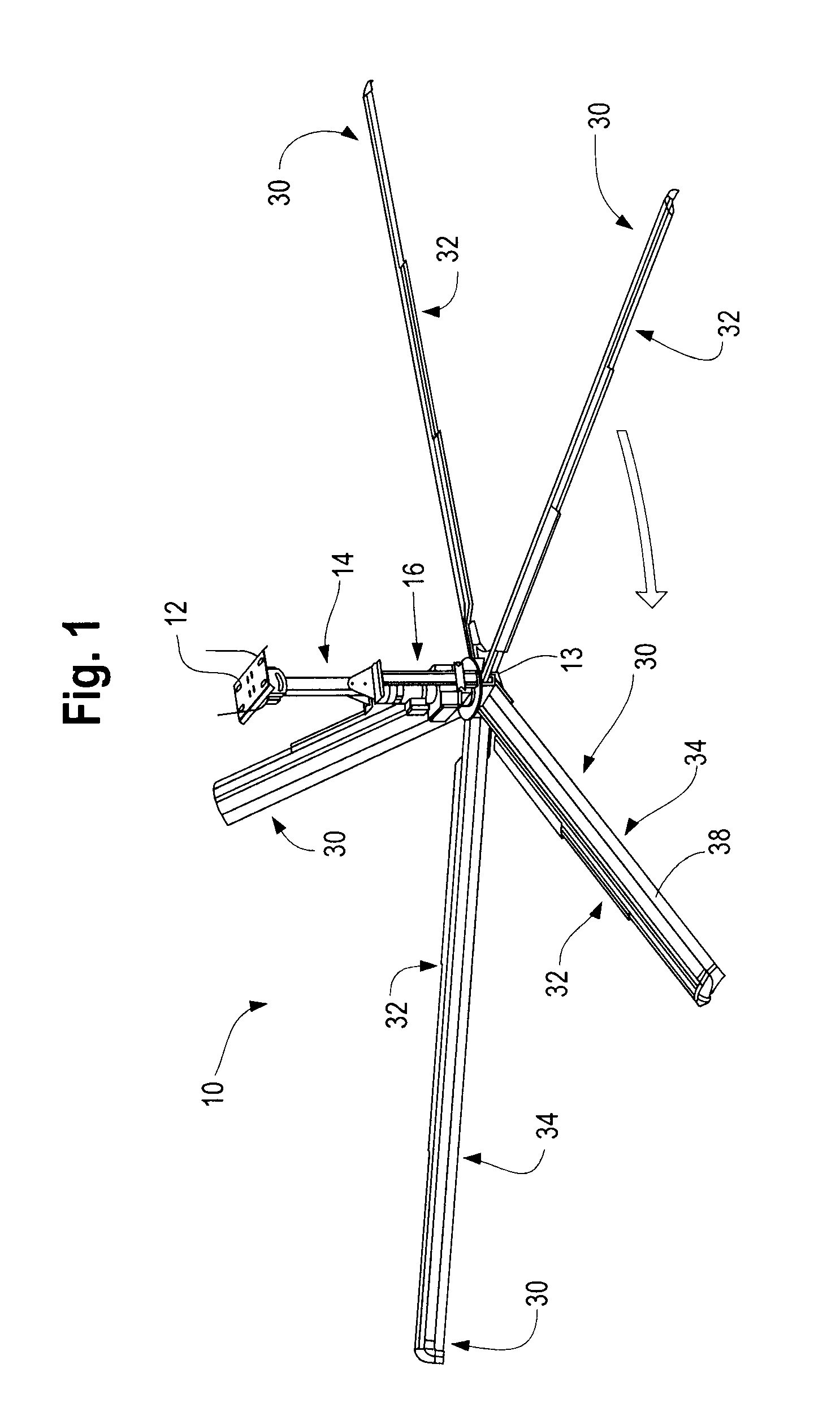
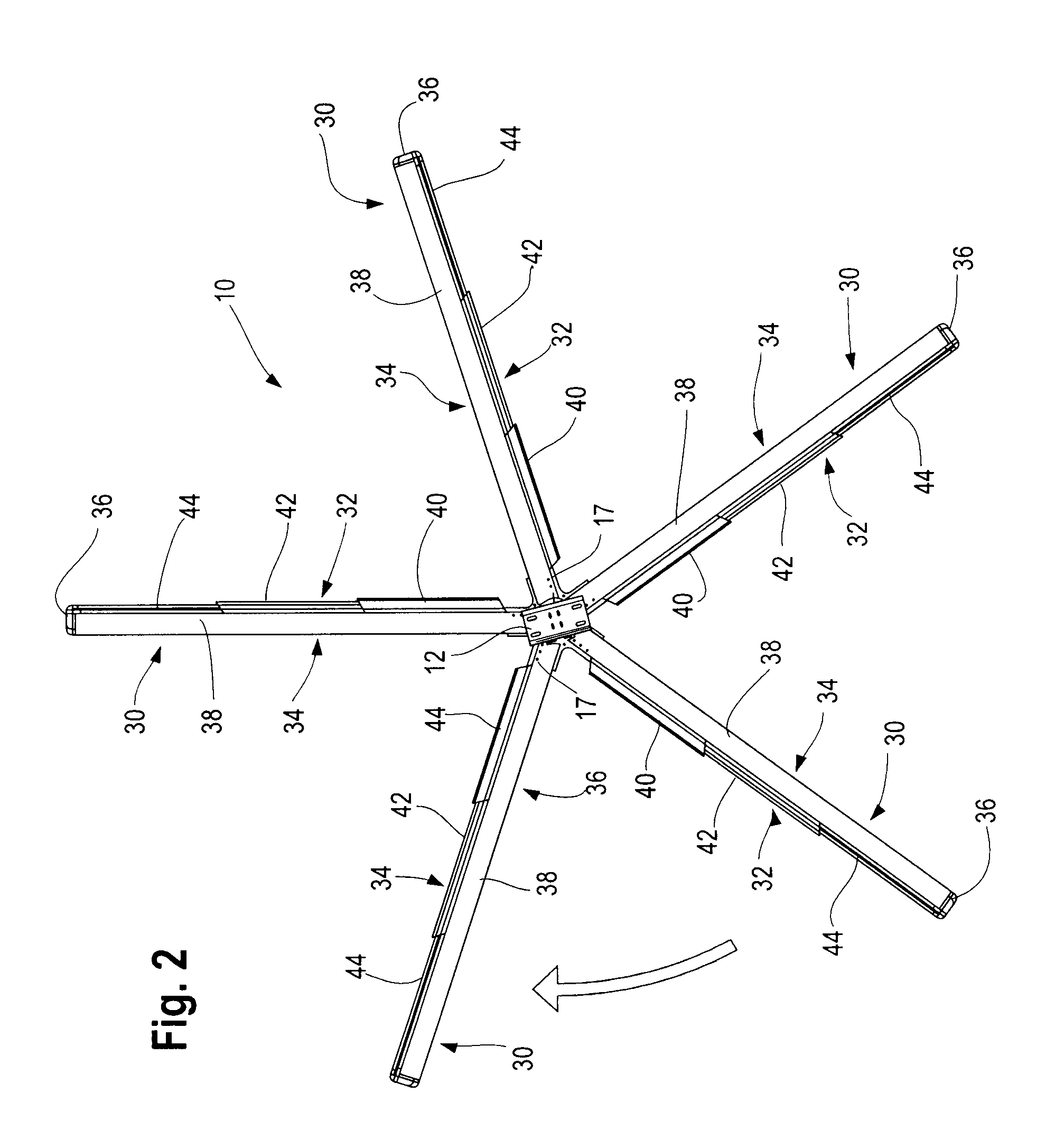
Control Modes for Extendable Rotor Blades
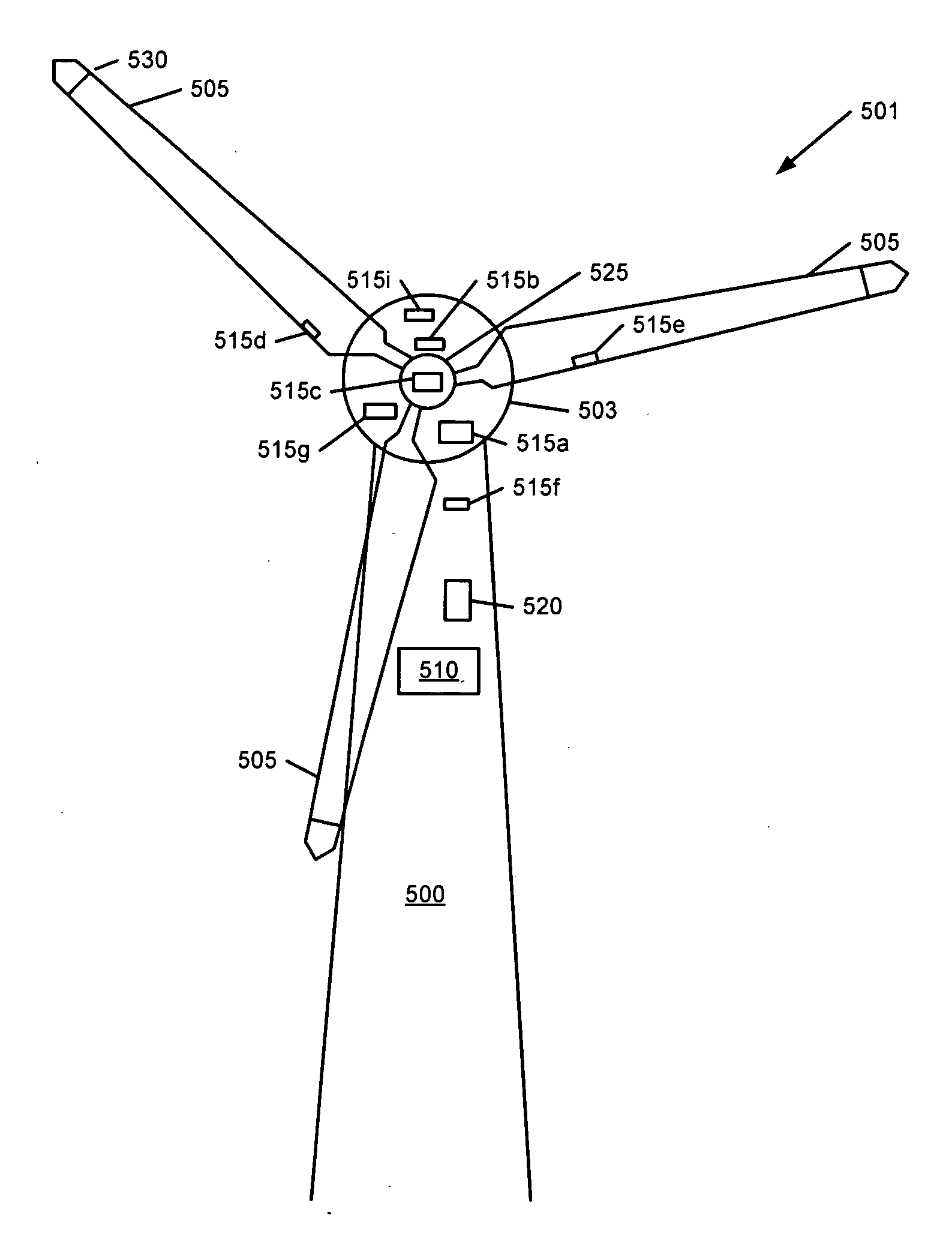
InactiveUS20100158687A1Maximize incomeReduce paymentPropellersRotary propellersAccelerometerEngineering
A wind turbine may be controlled in a variety of manners to optimize operating parameters. In one arrangement, for example, the length or the pitch of a wind turbine rotor blade may be adjusted to avoid harmonic resonance frequencies. In another example, the length of a rotor blade may be modified to reduce noise or to optimize profits or both. The controls may be based on data from various types of sensors including accelerometers, sound meters, strain gauges and the like. Actuation of extendable rotor blades can rotate wind turbine rotors without wind or generator pulsing affording multiple advantages. A battery test control may also be used to determine the operational readiness of a battery useful for a variety of purposes in a turbine.
Owner:FRONTIER WIND LLC
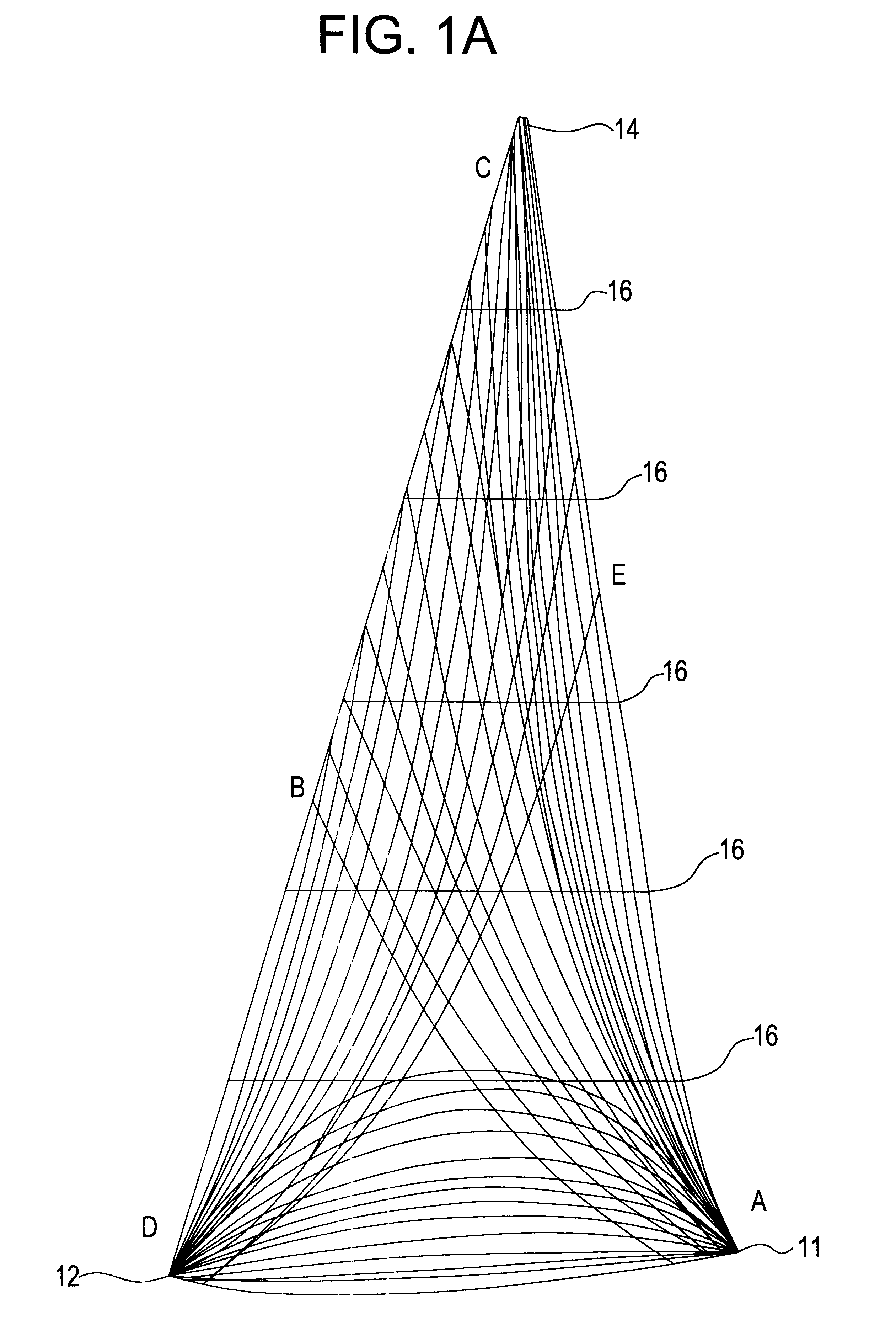
Dynamic allocation of transmission bandwidth in a communication system
InactiveUS7123592B2Prevents untoward spectral effectMore balancedError preventionModulated-carrier systemsCommunications systemModem device
A head end is provided. The head end includes at least one modern for communicating with service units over a transmission bandwidth, the transmission bandwidth being divided into a number of subbands, each subband including a plurality of payload channels and at least one control channel and a control circuit, communicatively coupled with the at least one modem, that assigns each service unit to a subband such that the service units are substantially evenly distributed over the subbands.
Owner:HTC CORP
Optical image lens system
ActiveUS8717685B2Suppressing the field curvatureReduce sensitivityStereoscopic photographyLensSurface changePhysics
This invention provides an optical image lens system comprising: a positive first lens element having a convex object-side surface; a second lens element; a positive third lens element; a fourth lens element; a positive plastic fifth lens element having a convex object-side surface and a concave image-side surface, at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces is aspheric; and a negative plastic sixth lens element having a concave image-side surface, at least one of the object-side and image-side surfaces is aspheric, wherein the shape of the image-side surface changes from concave at the paraxial region thereof to convex while away from the paraxial region thereof.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
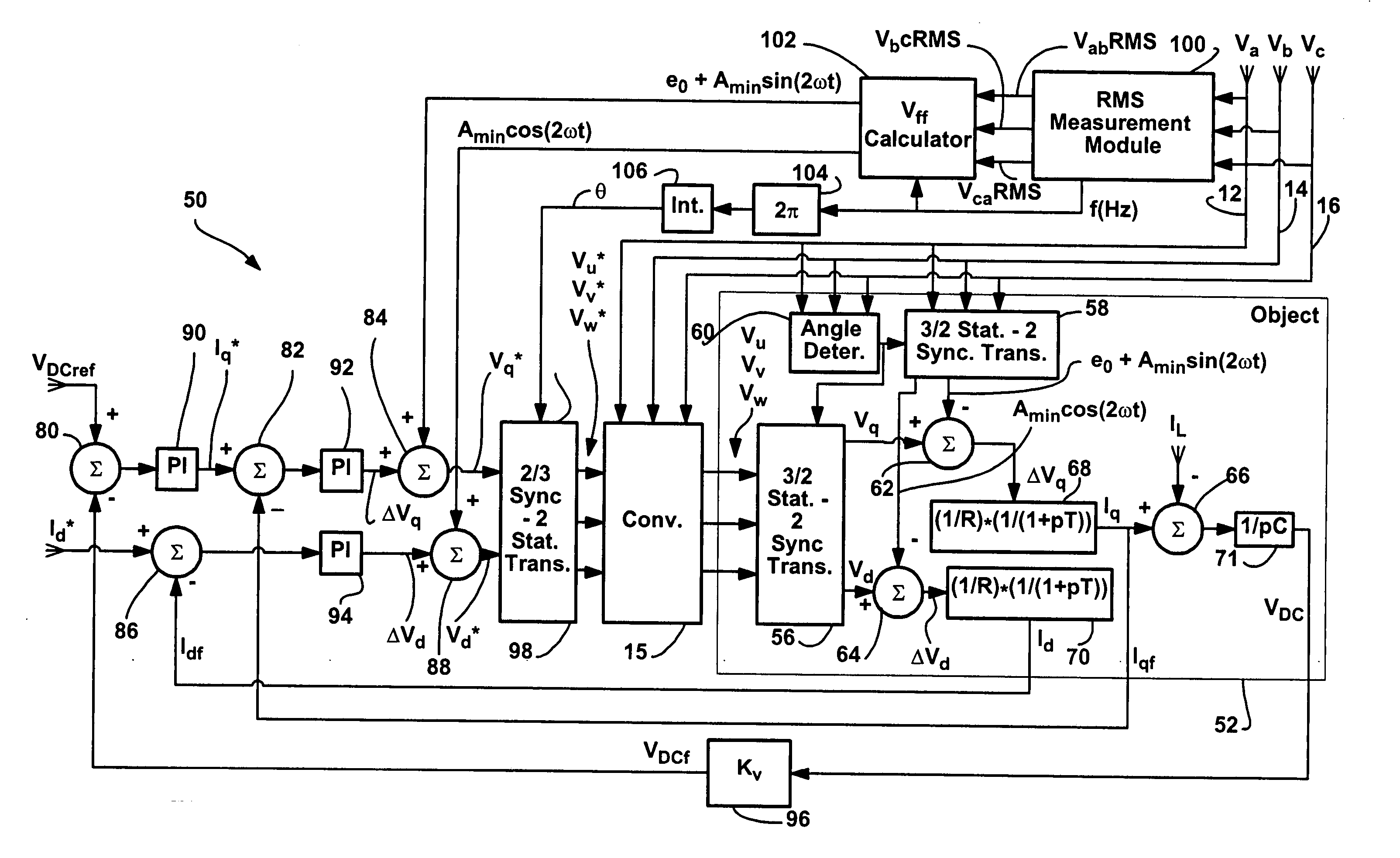
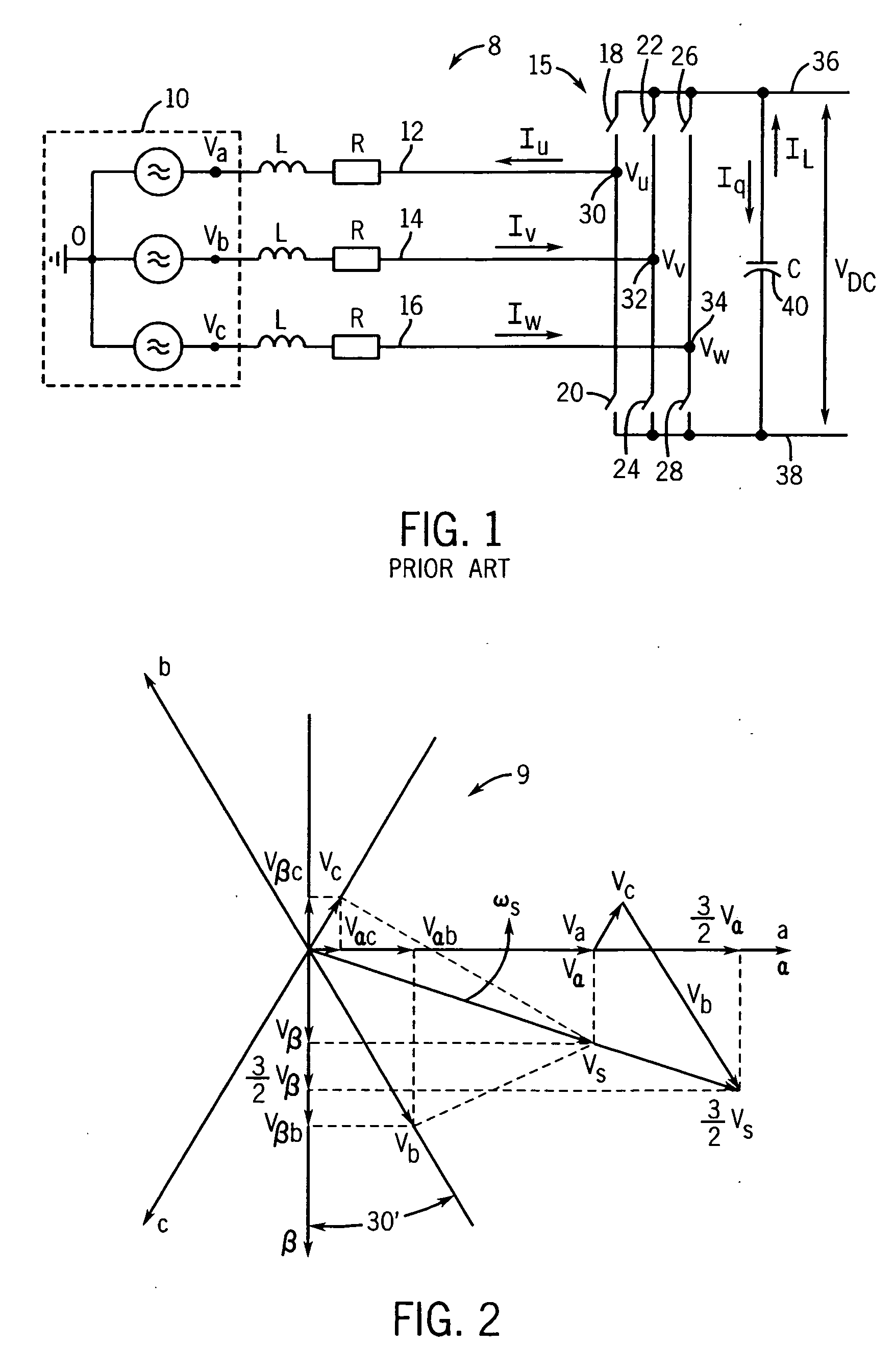
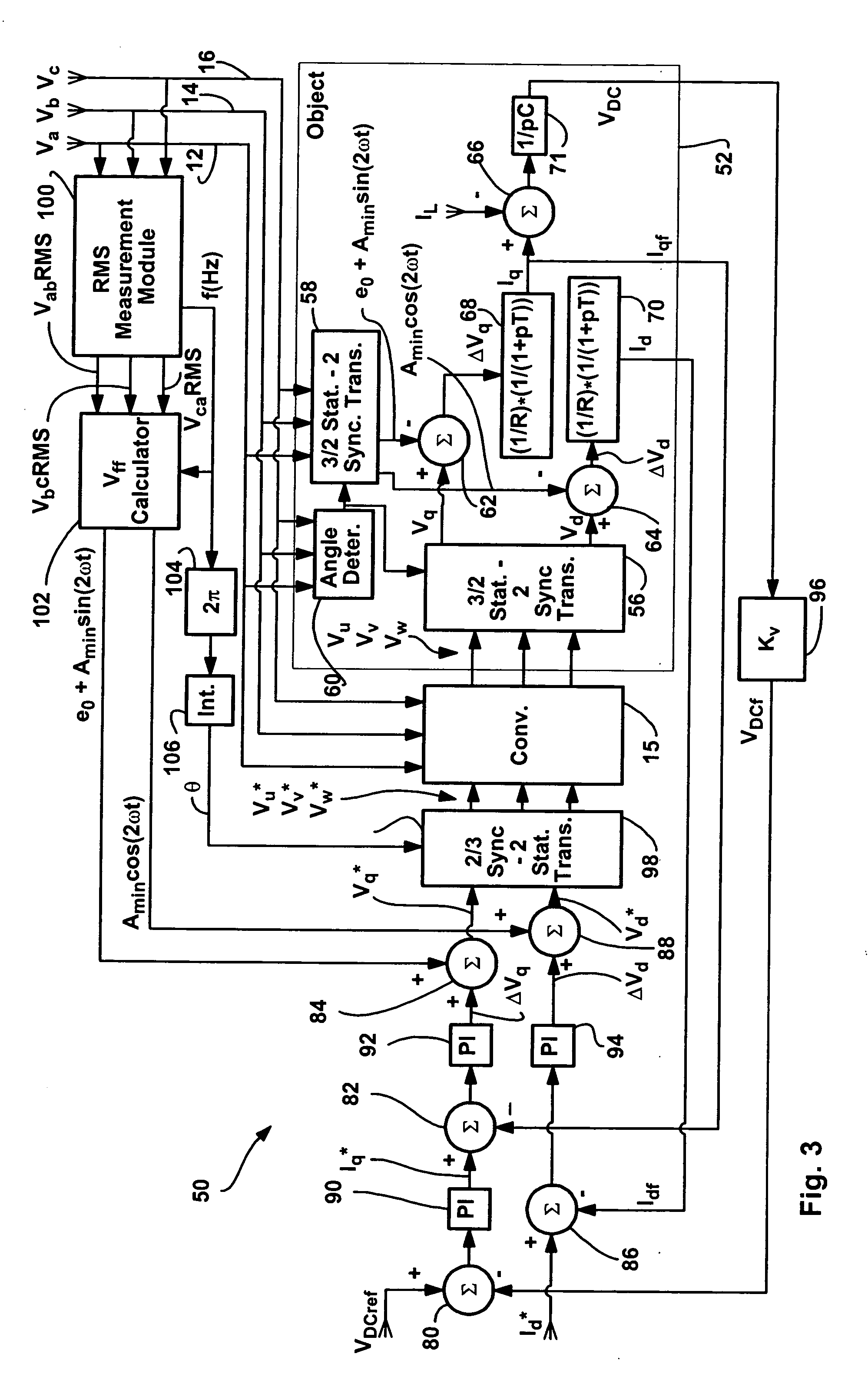
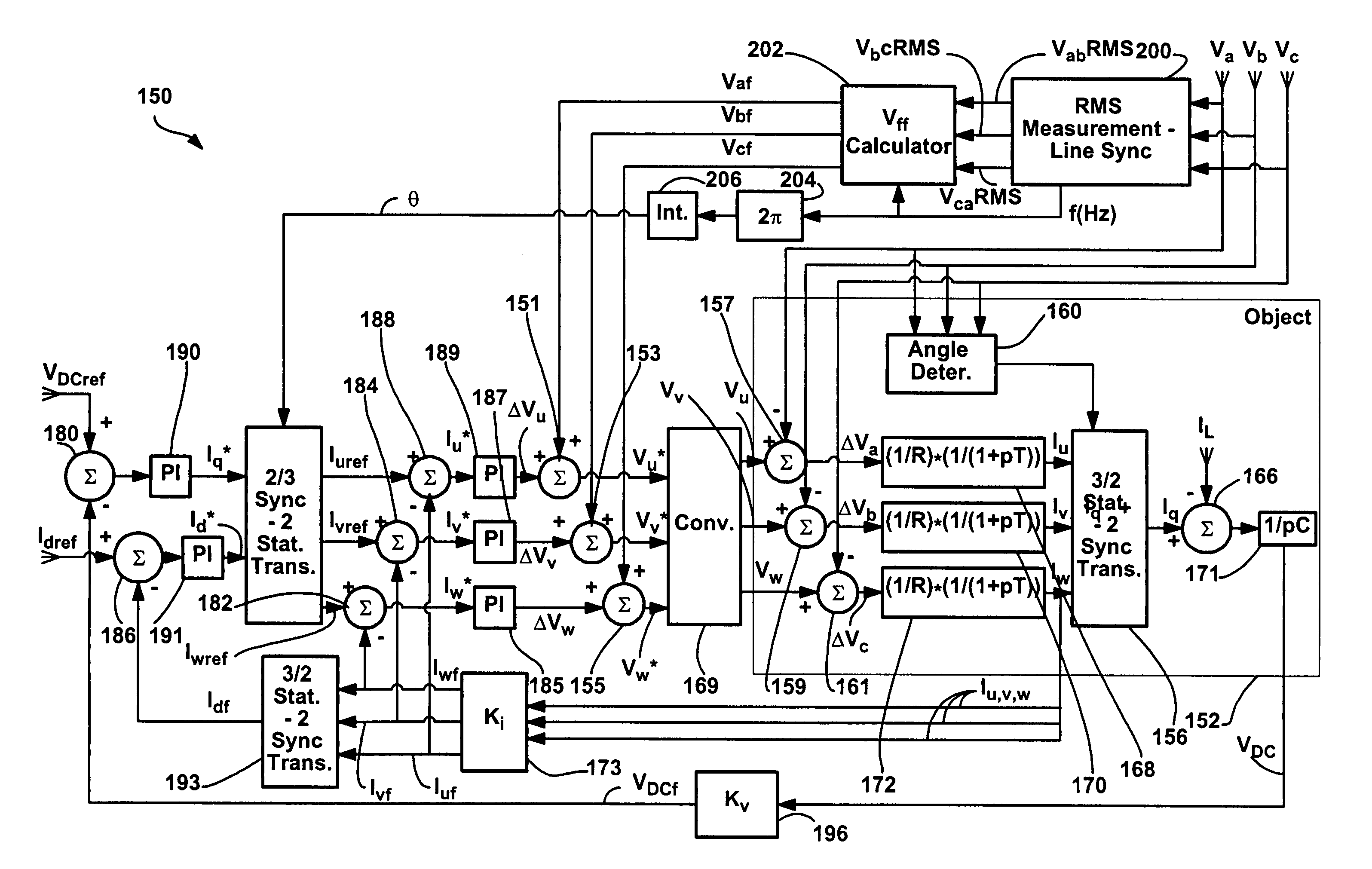
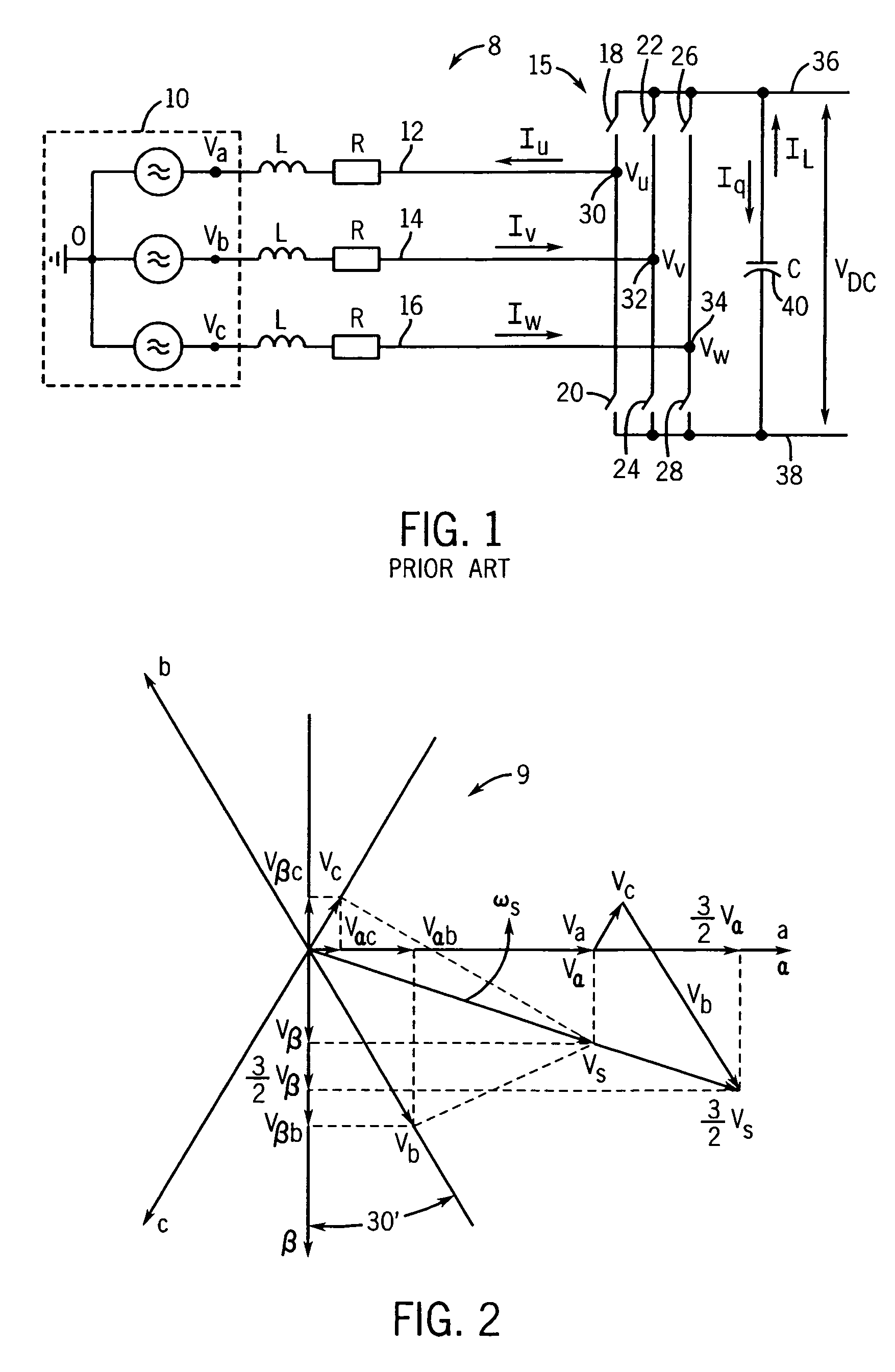
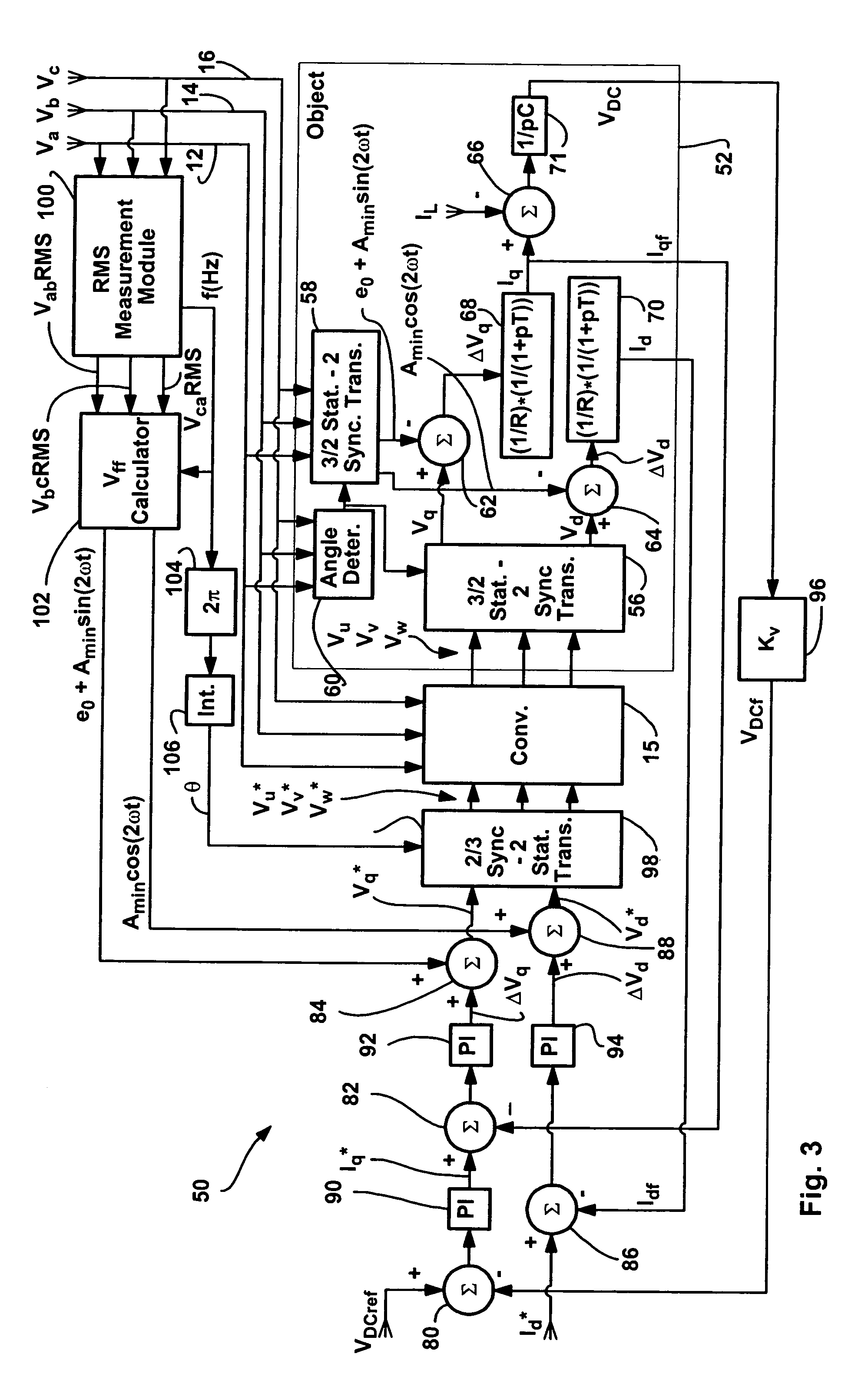
Method and apparatus for rejecting the second harmonic current in an active converter with an unbalanced AC line voltage source
ActiveUS20060034104A1Reducing second harmonicEliminate generationAc-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionTransverterHarmonic
A method and apparatus for altering converter control as a function of the degree of unbalance in supply line voltages to substantially eliminate second harmonics on the supply lines caused by active control of the converter including identifying supply line peak amplitude values and using the peak values to identify potential second harmonics and then altering command values as a function of the potential second harmonic components.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
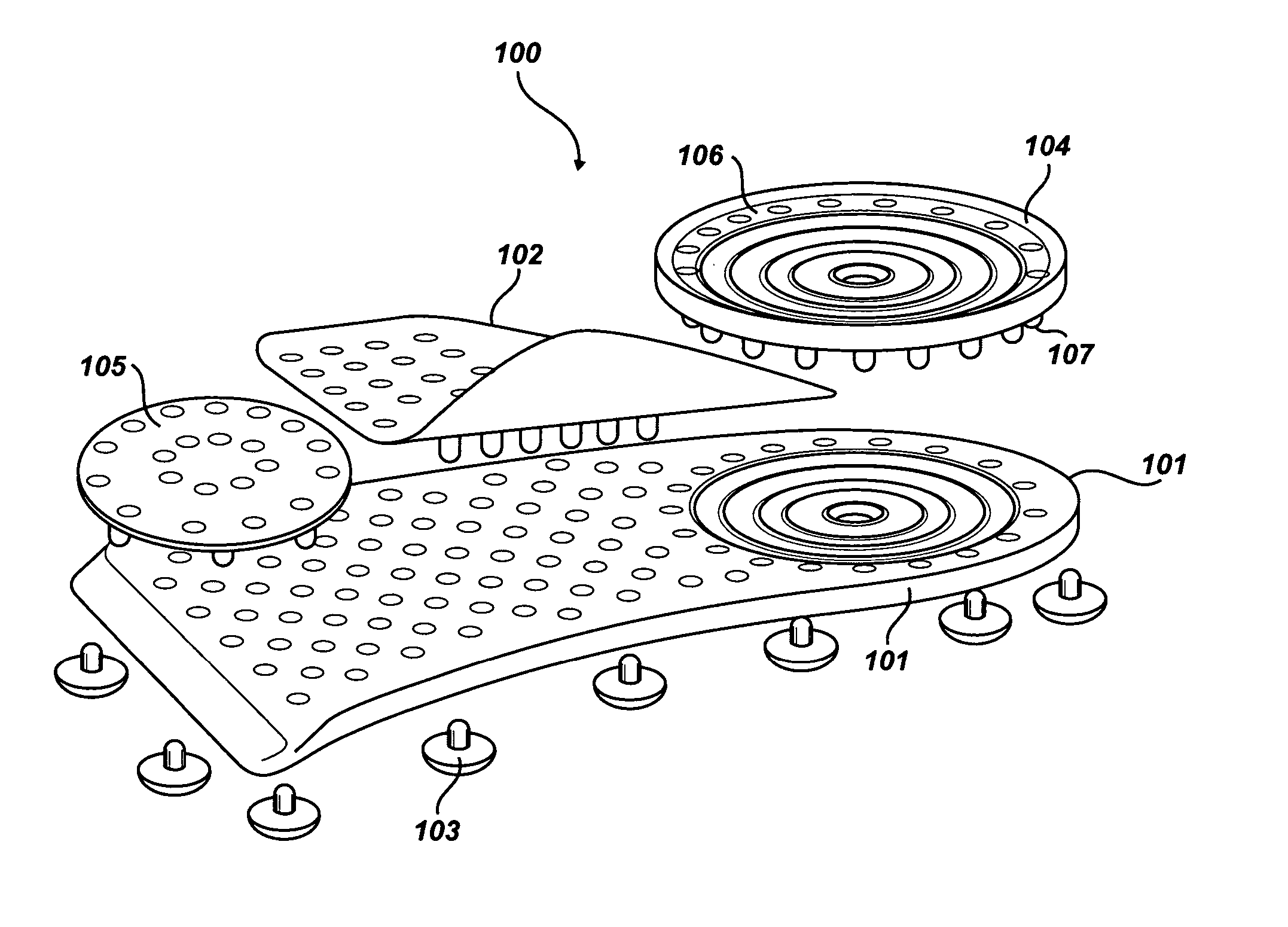
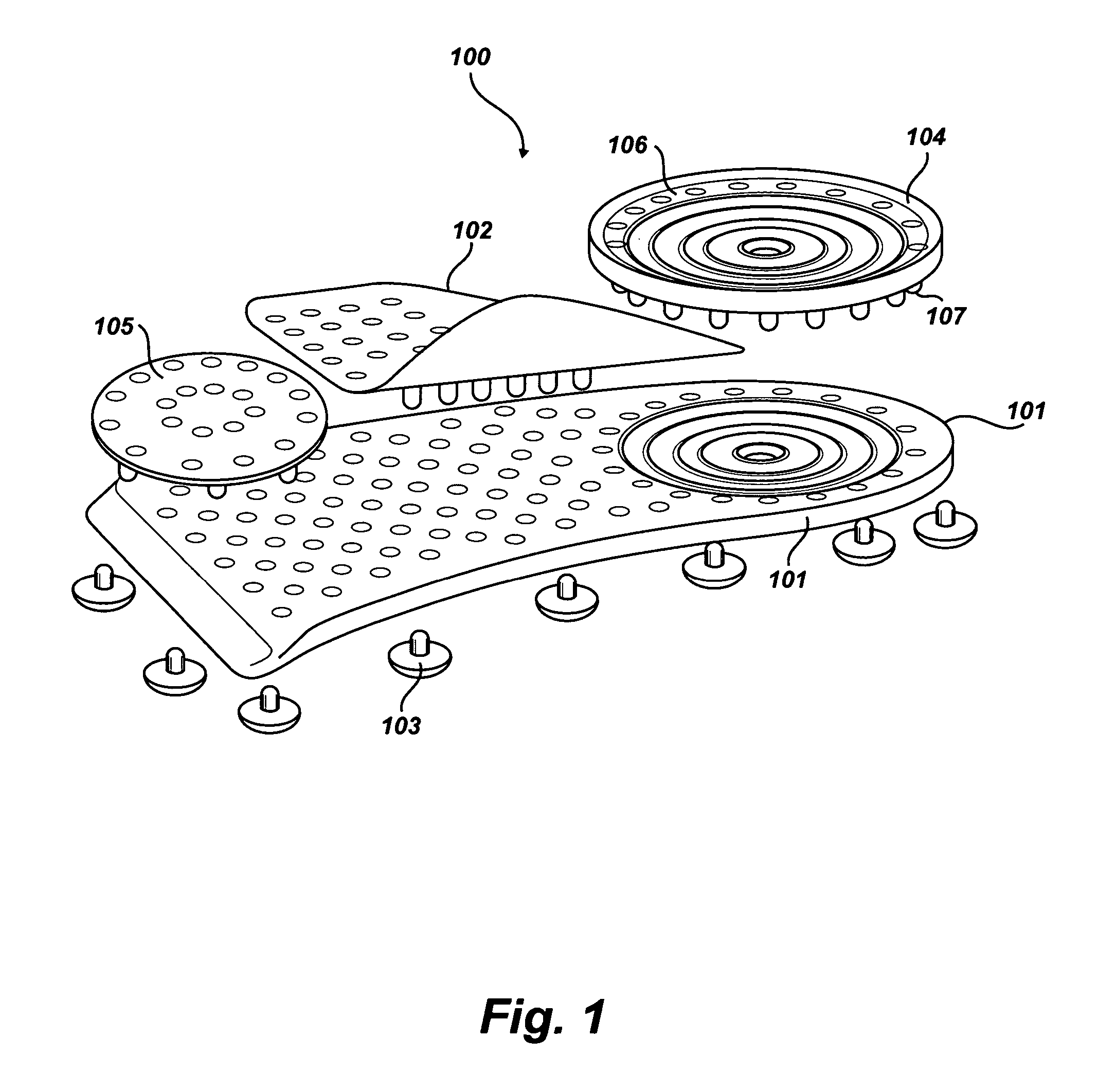
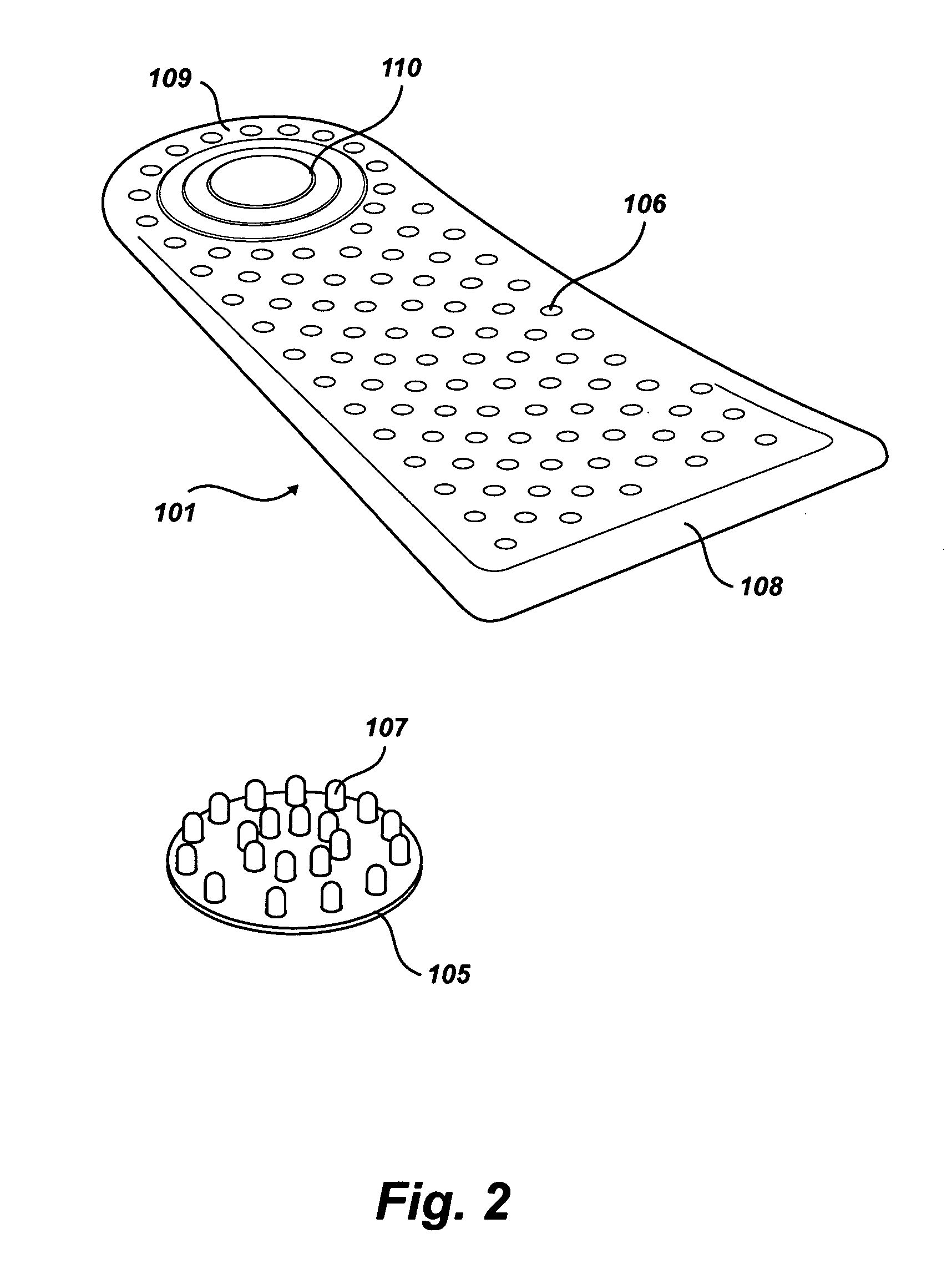
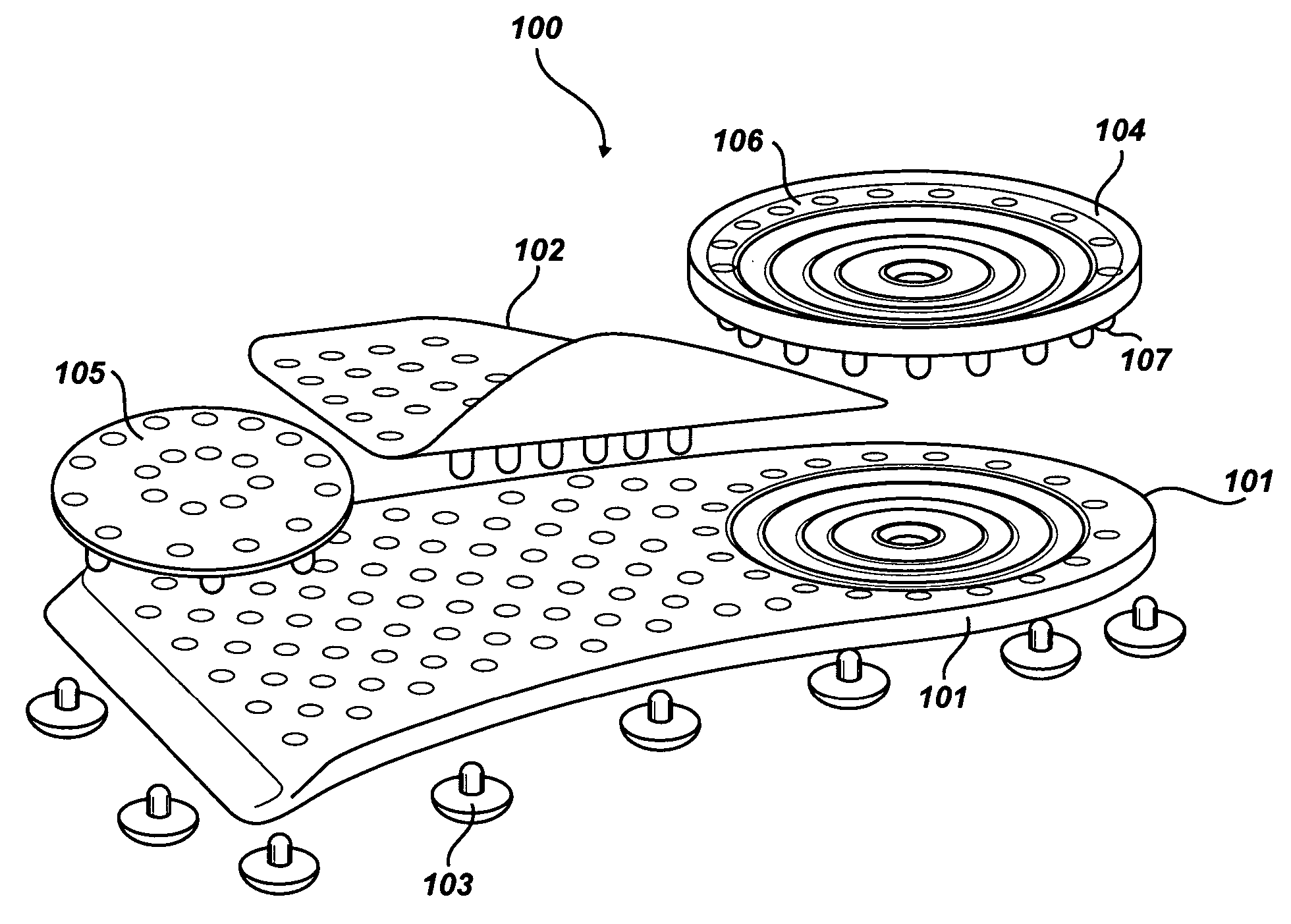
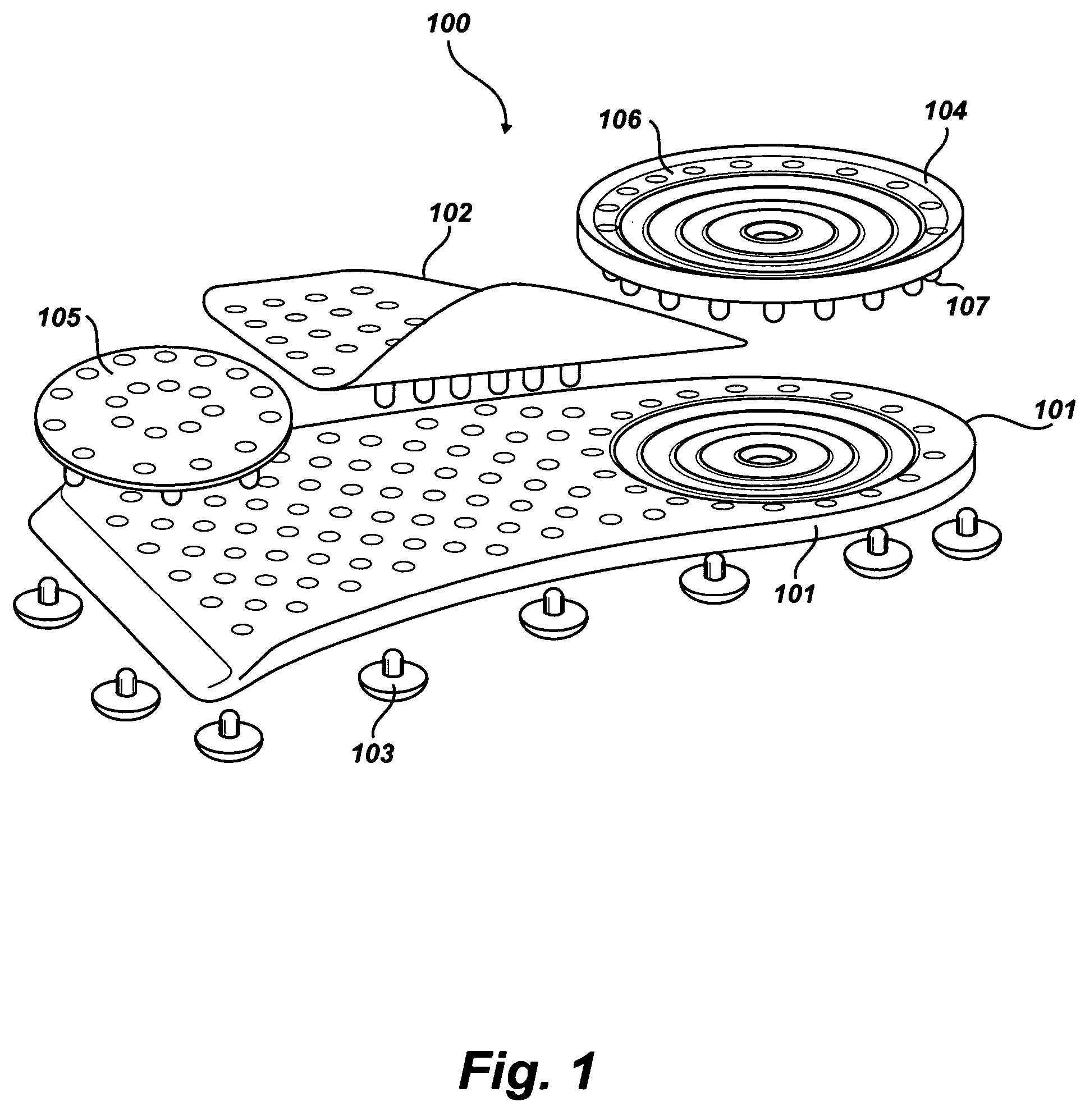
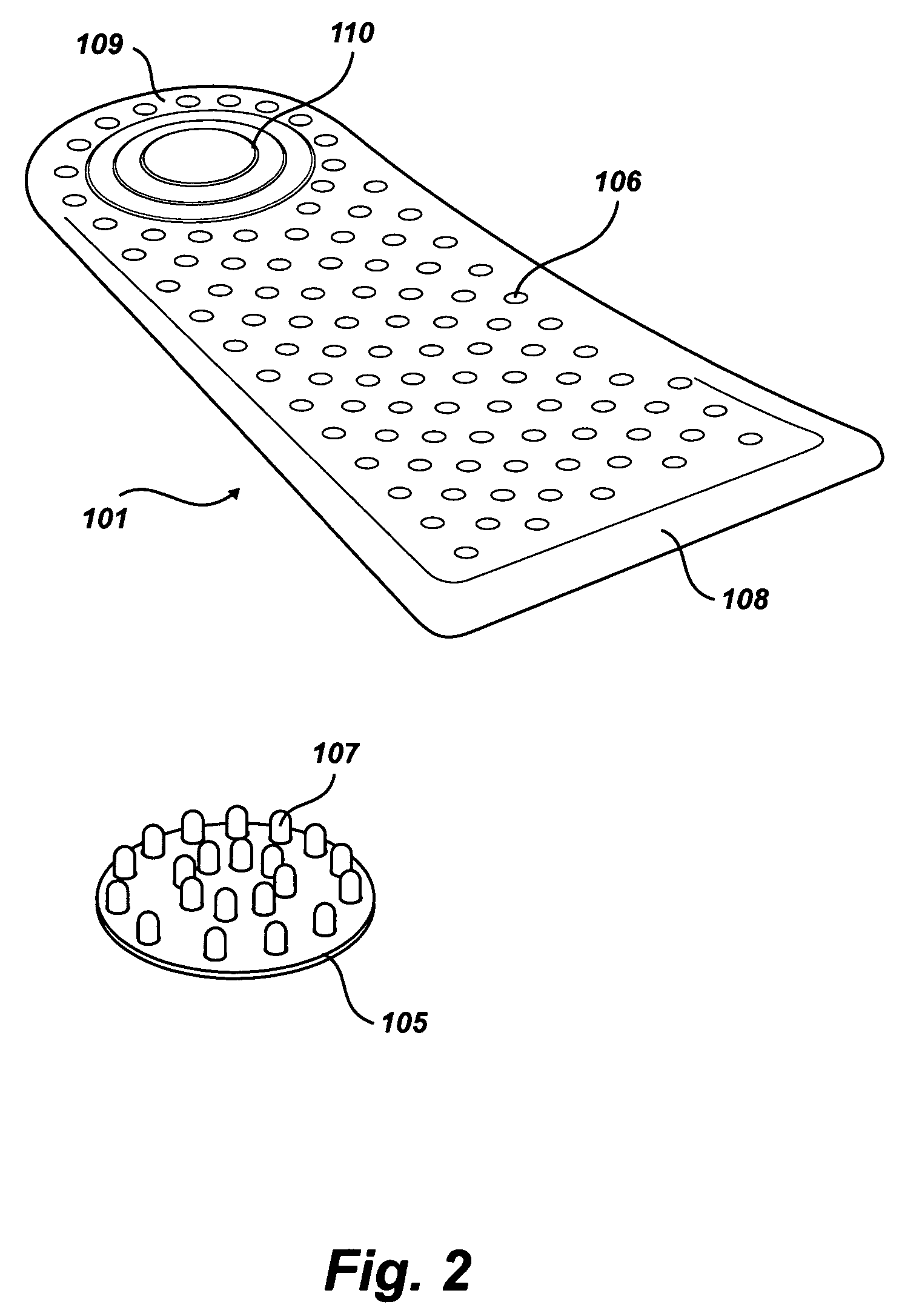
Soles with adjustable and interchangeable supports
A shoe insert system with adjustable and interchangeable supports comprising: a base sole, a longitudinal arch, a heel insert, and a transverse arch; the base sole being generally planar and having a perimeter which covers the underside of a foot from the heel region up to the bottom of a person's toes, a longitudinal arch, the longitudinal arch having a d-shape with perforated holes and a row of pins sized to mate with perforations of the base sole, a heel insert, the heel insert having alternating perforated holes and pins near the edge defining a general circumference of the heel insert, the pins are sized to mate with corresponding perforated holes on the base sole, the transverse arch having a hole side and a pin side, the transverse arch having a series of perforated holes on the hole side and at least one pin sized to mate with a corresponding perforated hole on the base sole on the hole side.
Owner:RAMIREZ MANUEL RAMIREZ MARTINEZ
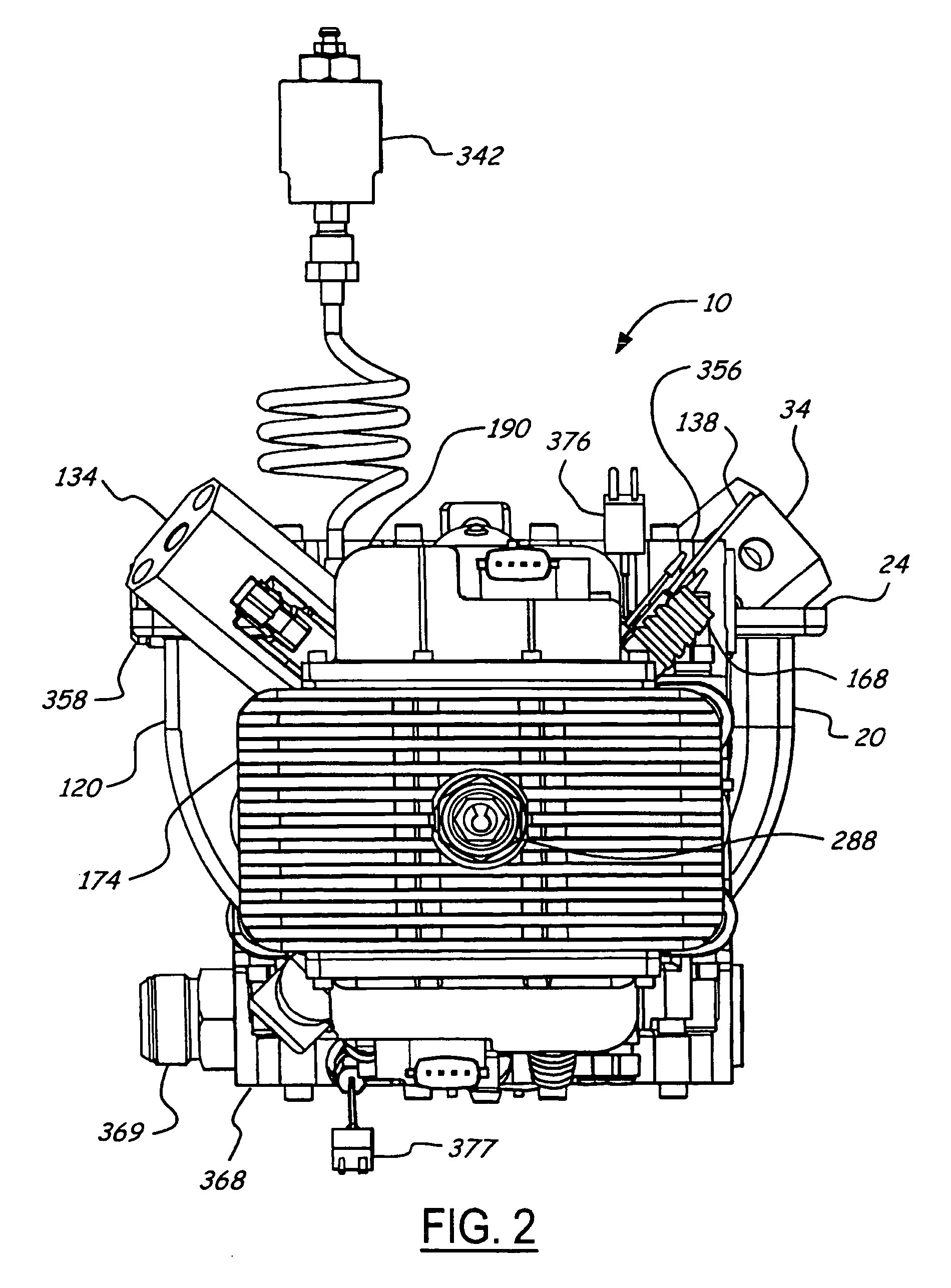
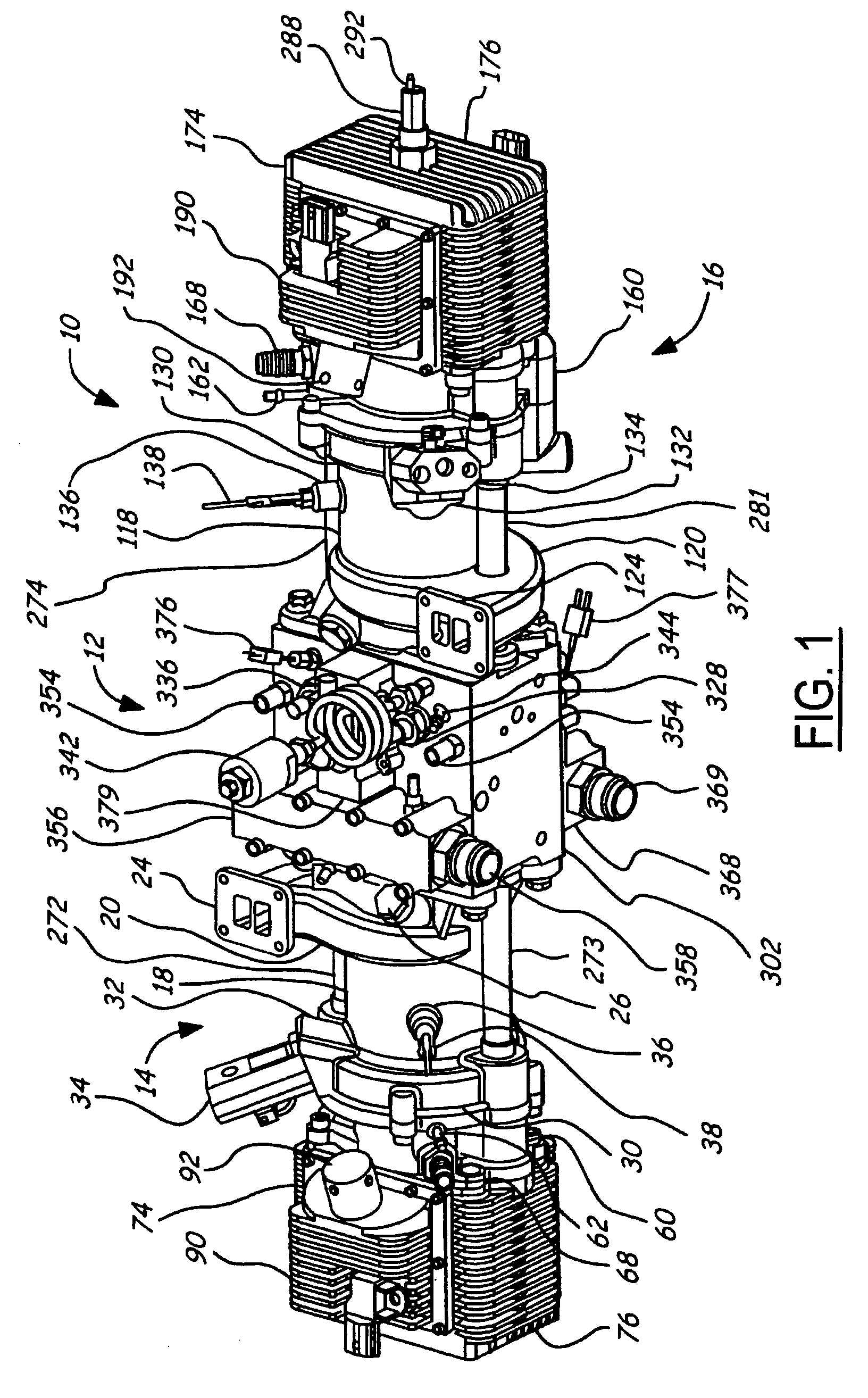
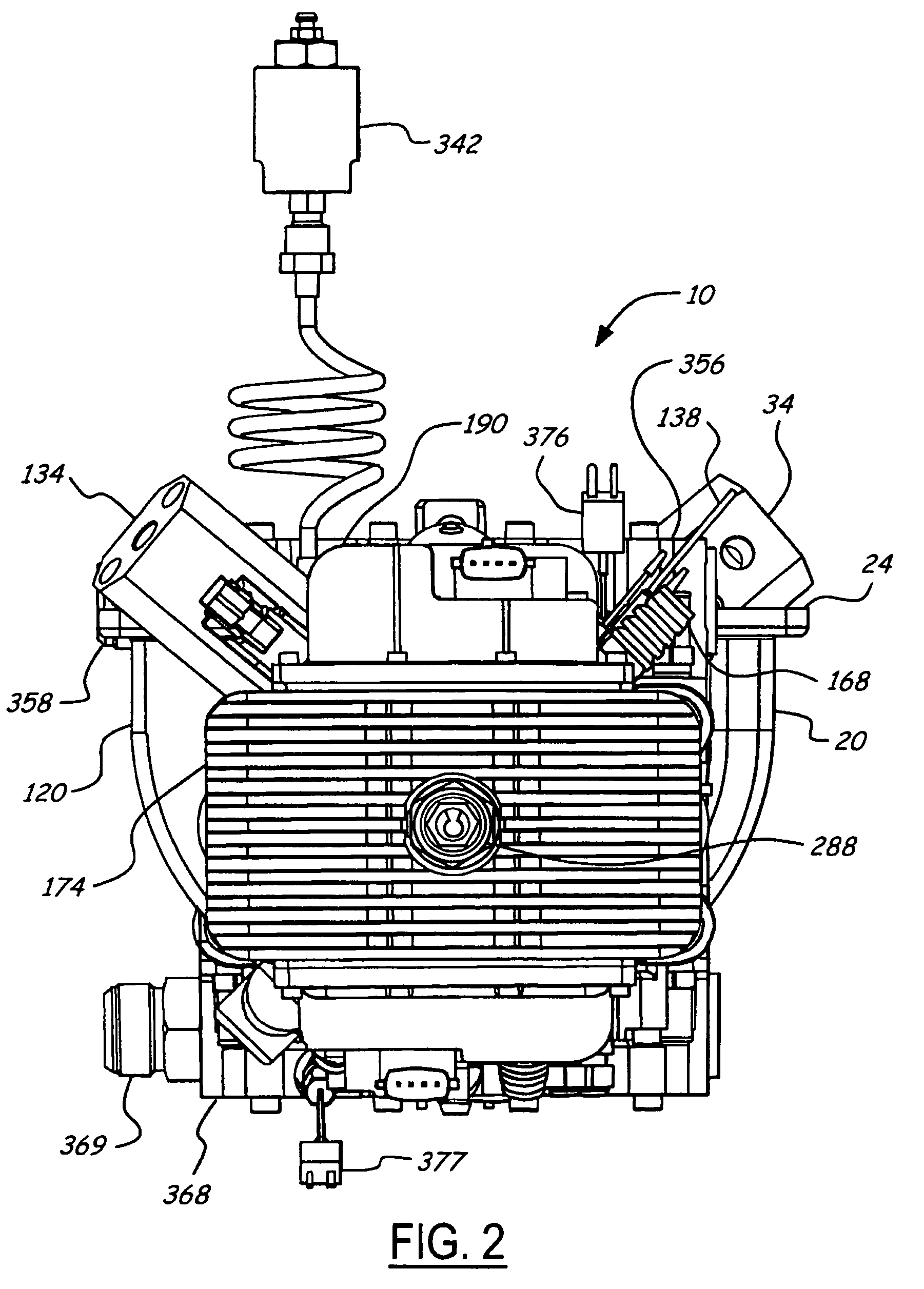
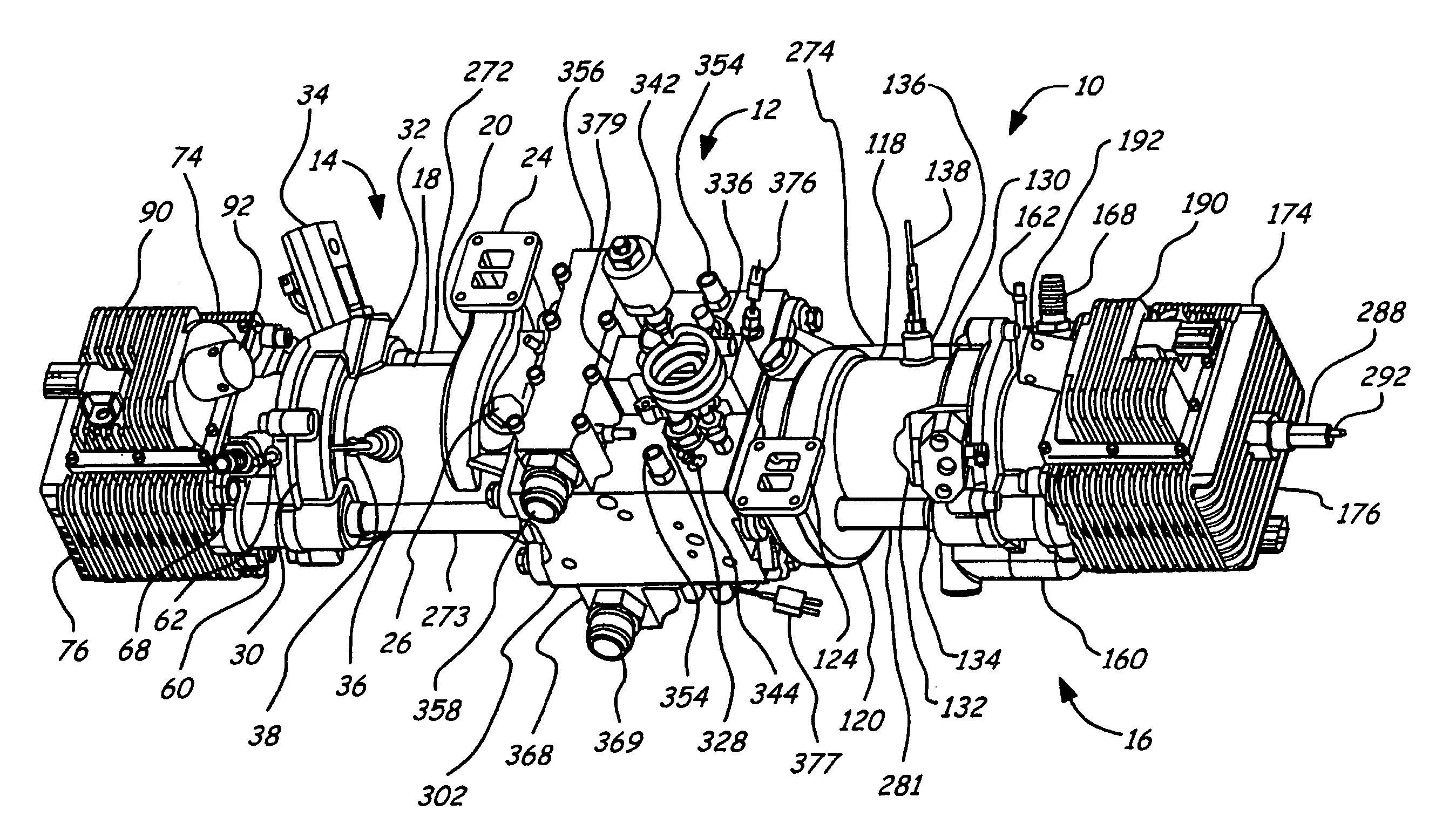
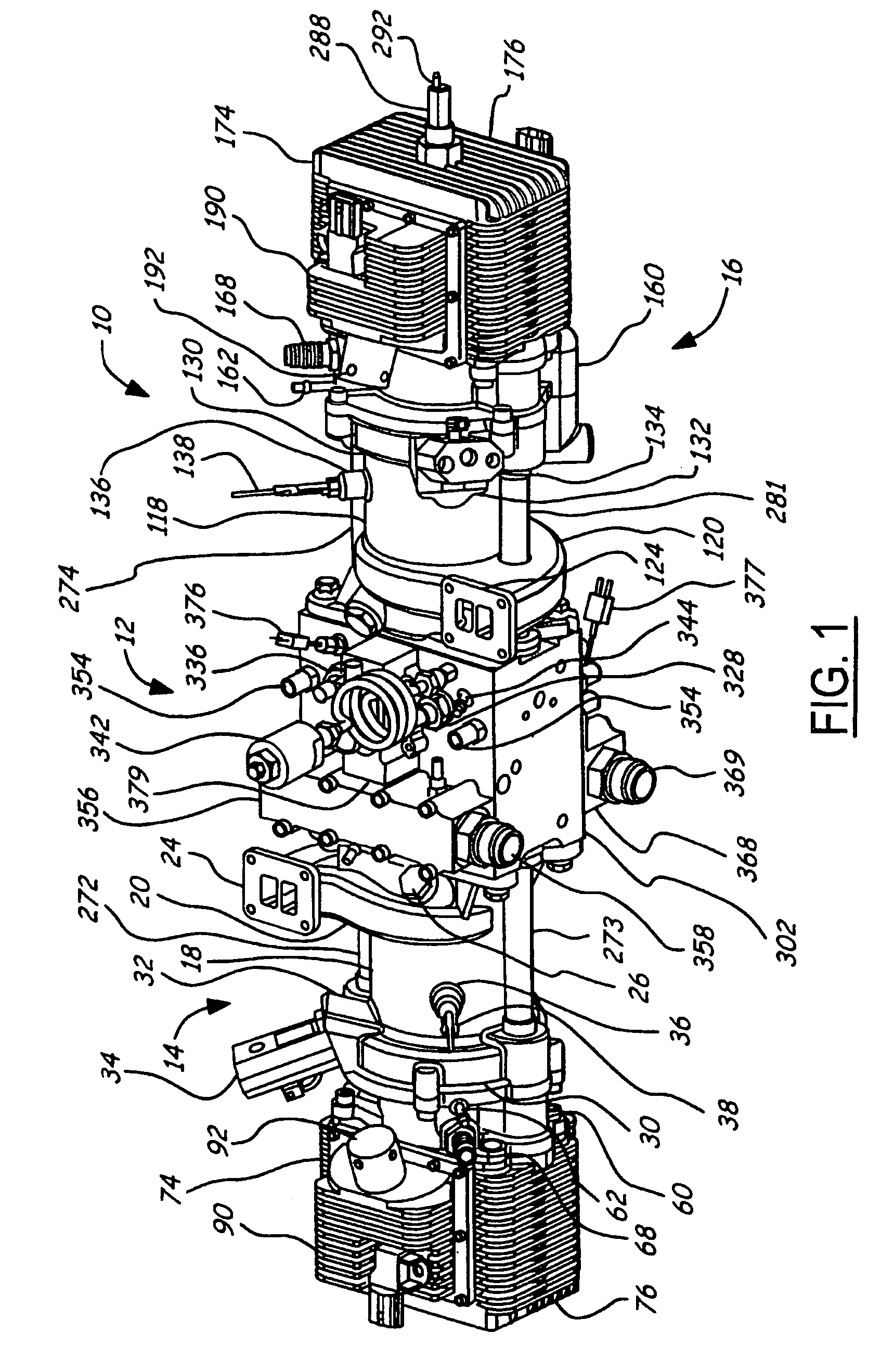
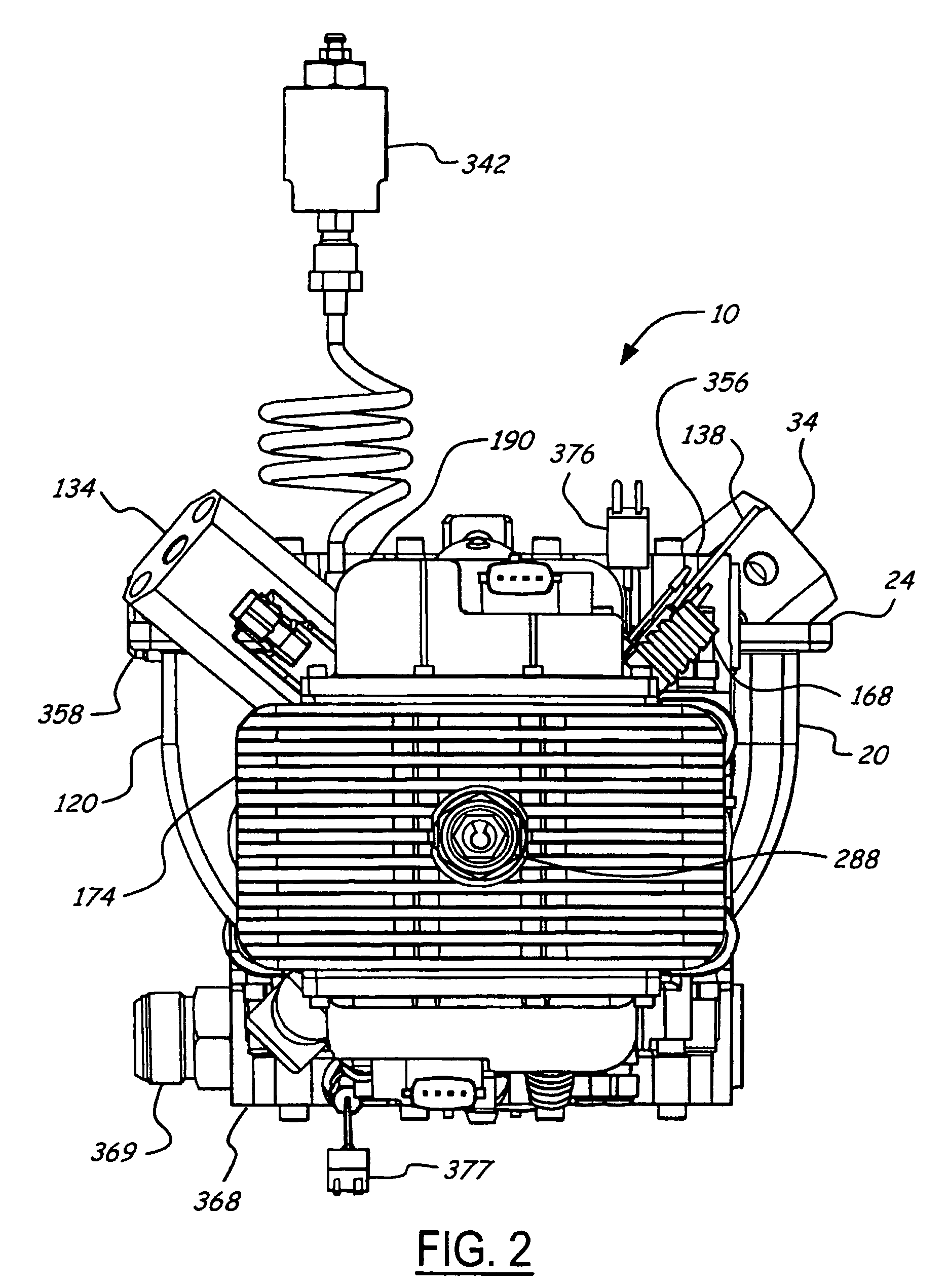
Position sensing for a free piston engine
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also connected between the pistons are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the inner piston assembly. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. Also engaging the outer piston assembly are a position sensor and a calibration position sensor that are employed to determine the position and velocity of the outer piston assembly. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine.
Owner:FORD MOTOR CO
Method and apparatus for rejecting the second harmonic current in an active converter with an unbalanced AC line voltage source
ActiveUS7355865B2More balancedConverter capacity)Ac-dc conversion without reversalEfficient power electronics conversionHarmonicEngineering
A method and apparatus for altering converter control as a function of the degree of unbalance in supply line voltages to substantially eliminate second harmonics on the supply lines caused by active control of the converter including identifying supply line peak amplitude values and using the peak values to identify potential second harmonics and then altering command values as a function of the potential second harmonic components.
Owner:ROCKWELL AUTOMATION TECH
Method for converting input image data into output image data, image conversion unit for converting input image data into output image data, image processing apparatus, display device
InactiveUS20110310116A1High reproduction qualityPleasant and natural appearanceTelevision system detailsImage enhancementDisplay deviceStretch ratio
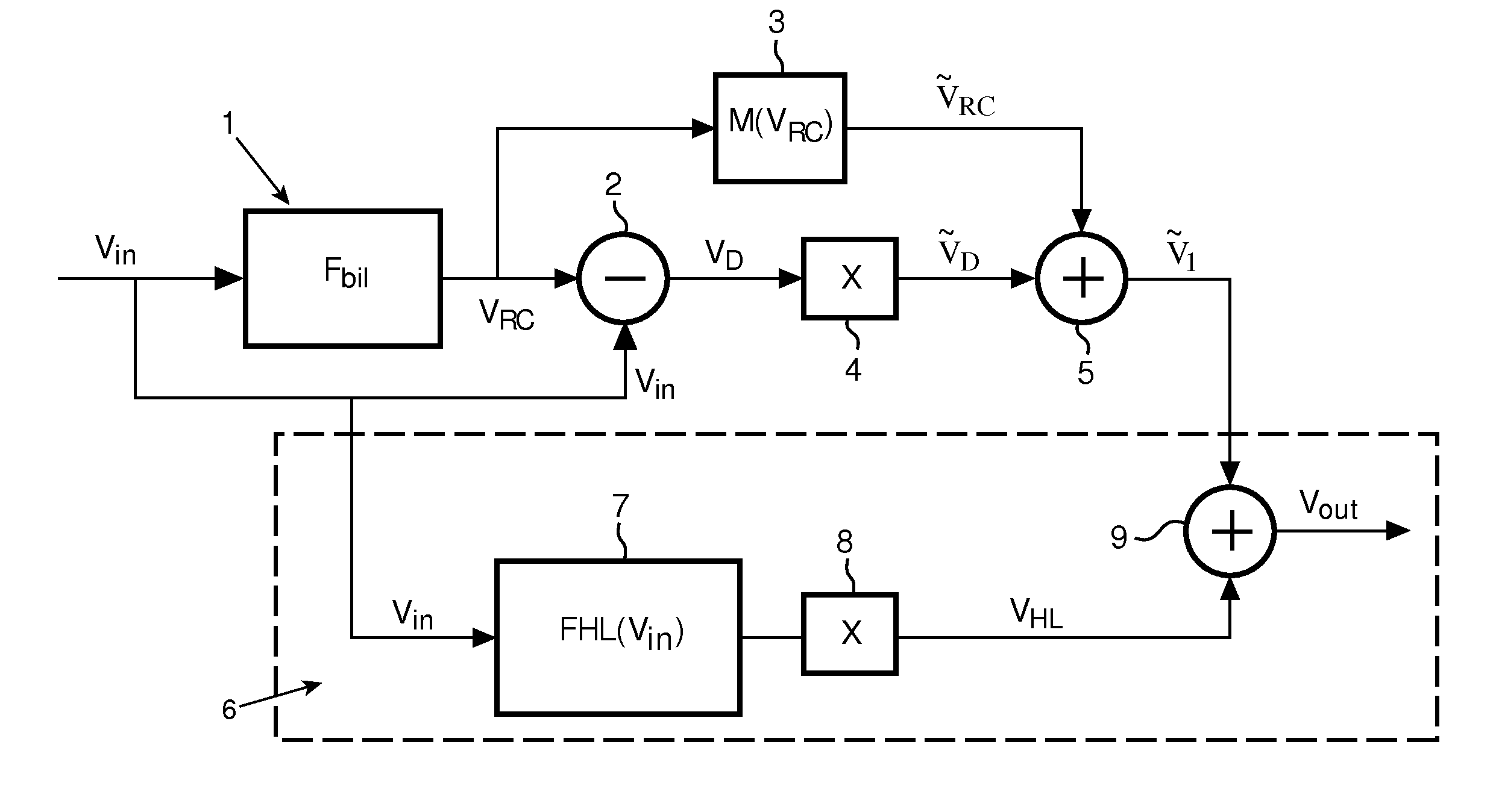
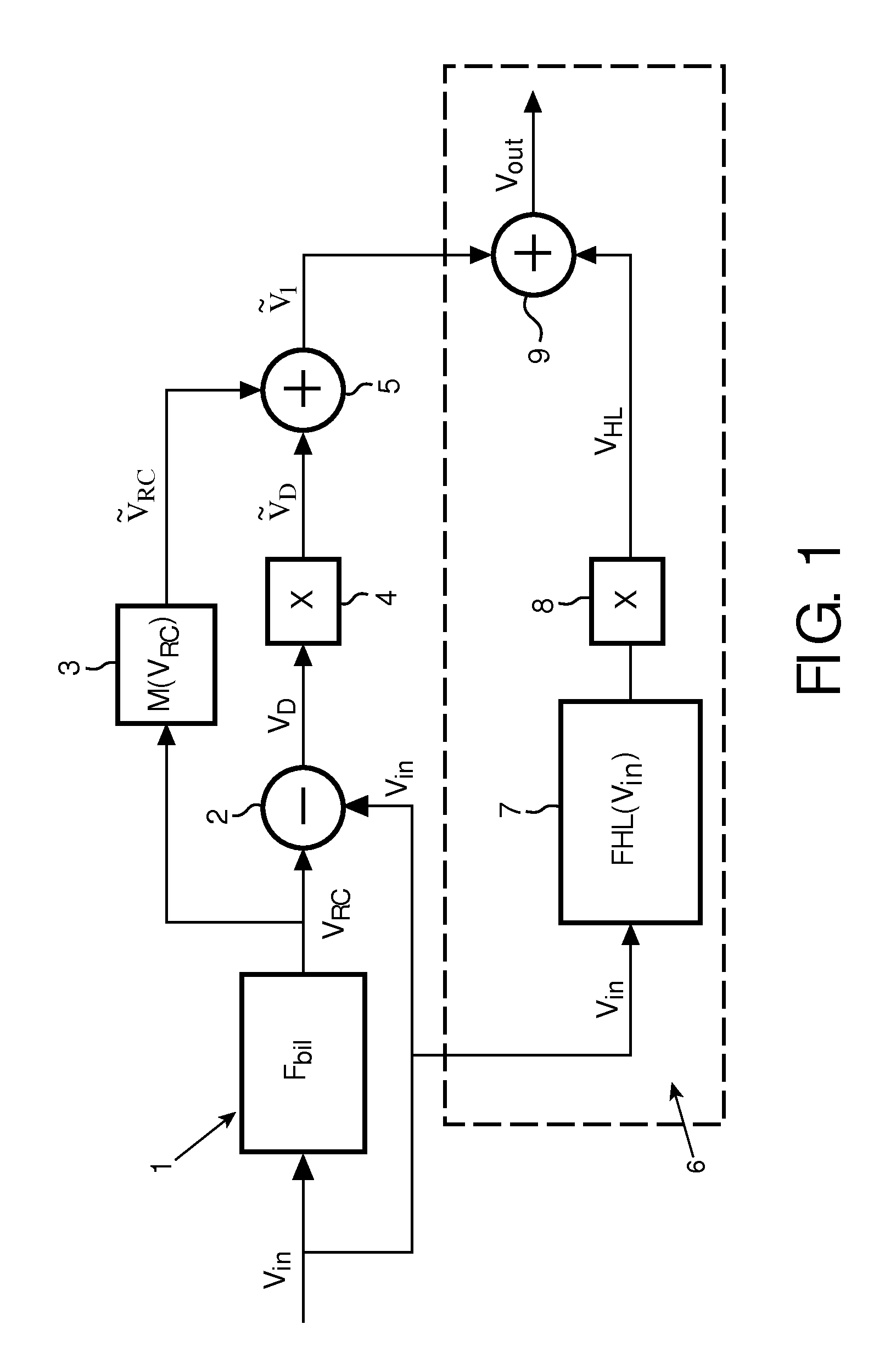
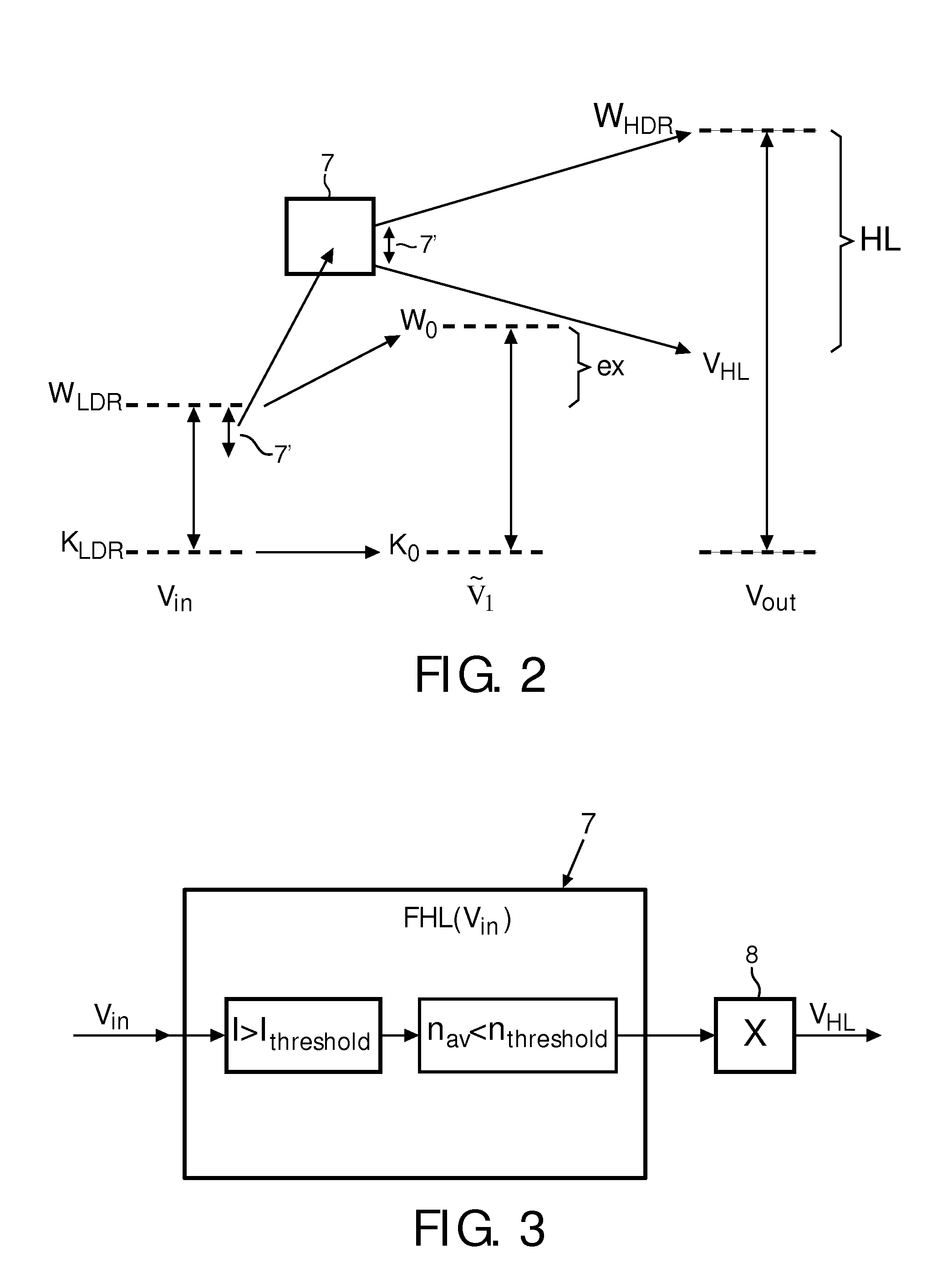
In a method, unit and display device the input image signal is split into a regional contrast signal (VRC) and a detail signal (VD), followed by stretching separately the dynamic ranges for both signals, wherein the dynamic range for the regional contrast signal is stretched with a higher stretch ratio than the dynamic range for the detail signal. Preferably the stretch ratio for the detail signal is near 1 or preferably 1. In preferred embodiment highlights are identified and for the highlights the dynamic range is stretched to an even higher degree than for the regional contrast signal.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Piston guides for a free piston engine
InactiveUS7032548B2More balancedEfficient chargingFree piston enginesFree-piston engineReciprocating motion
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. Piston guide posts are fixed and guide the outer pistons as they reciprocate within the engine cylinders.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
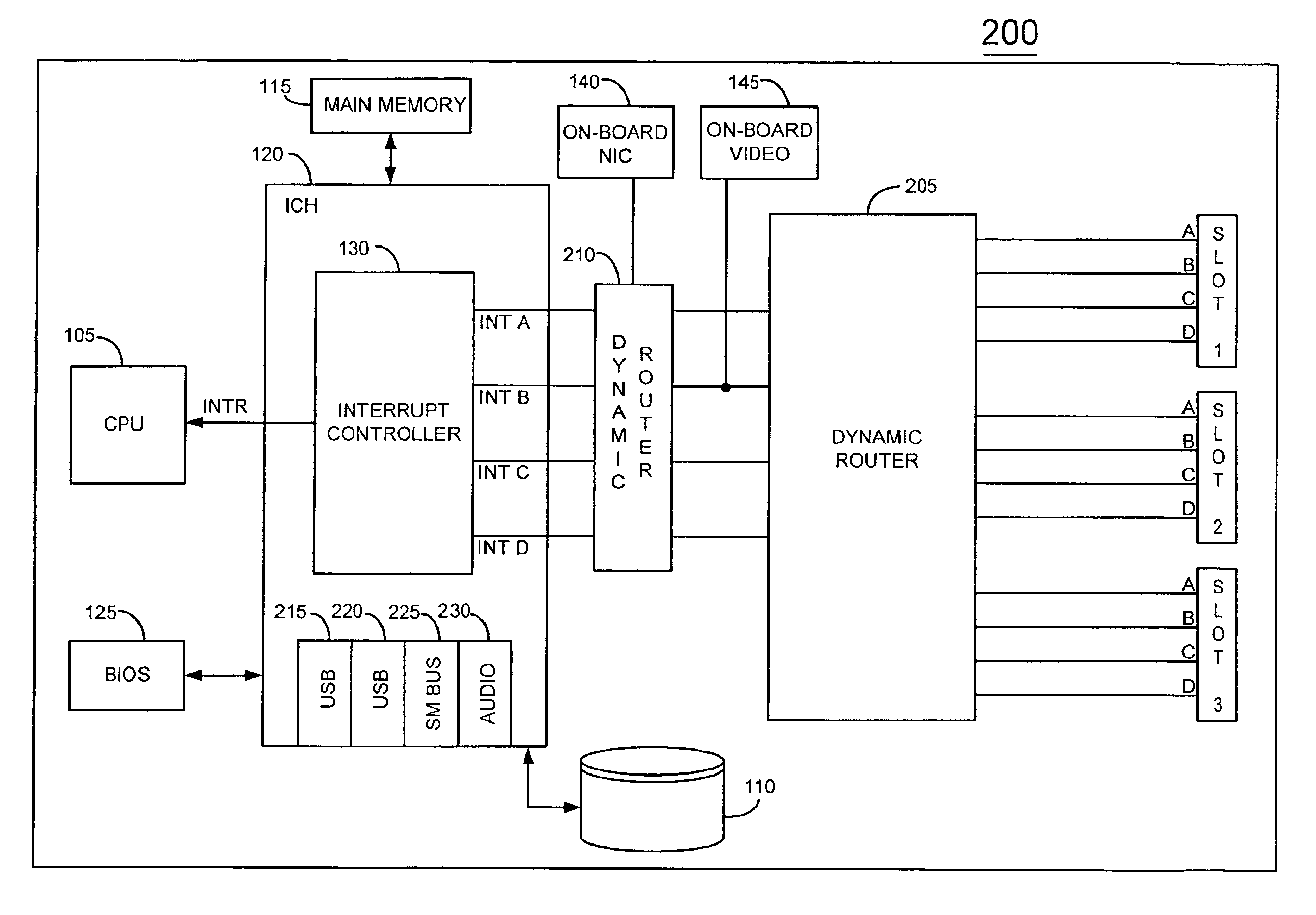
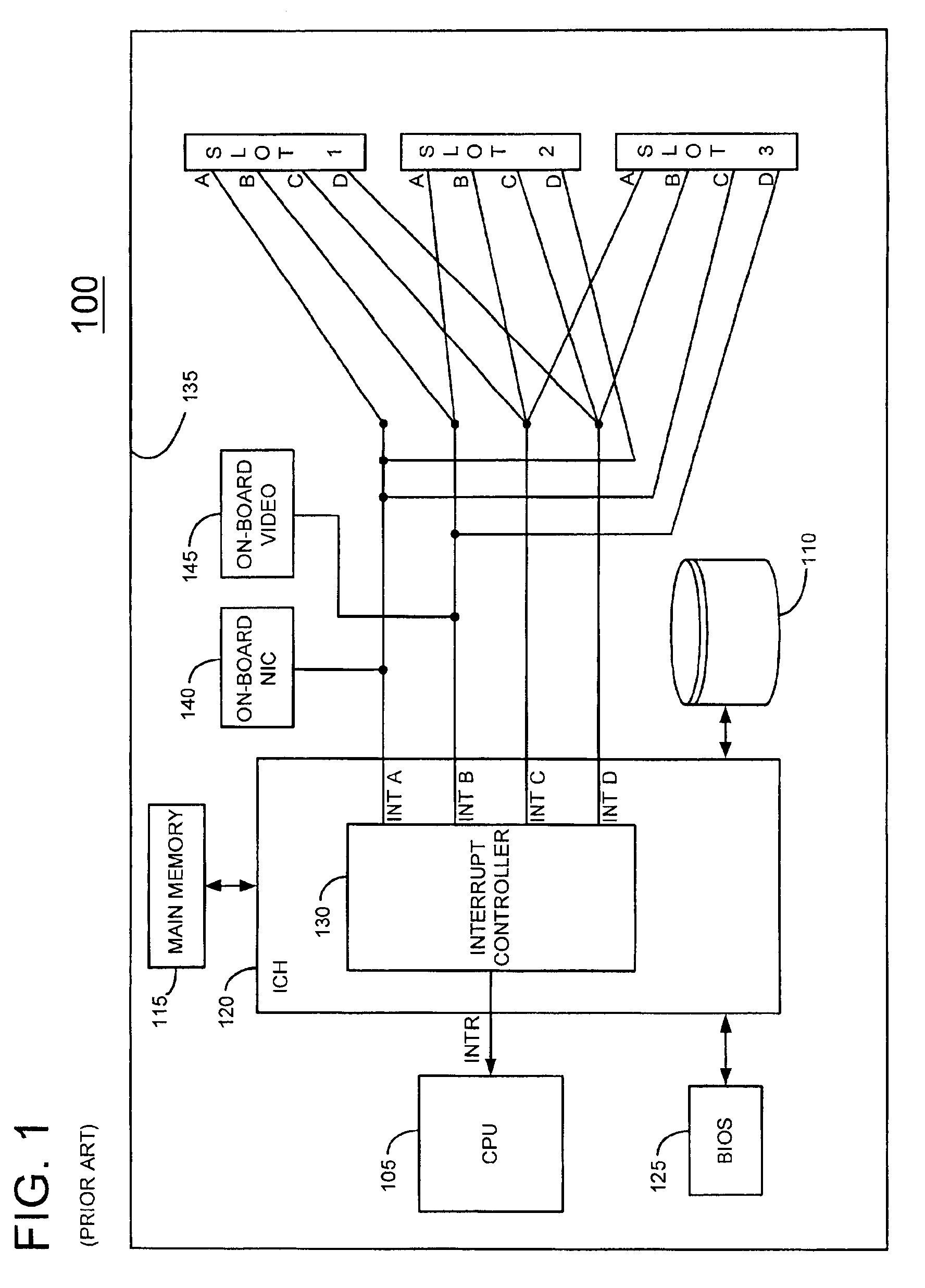
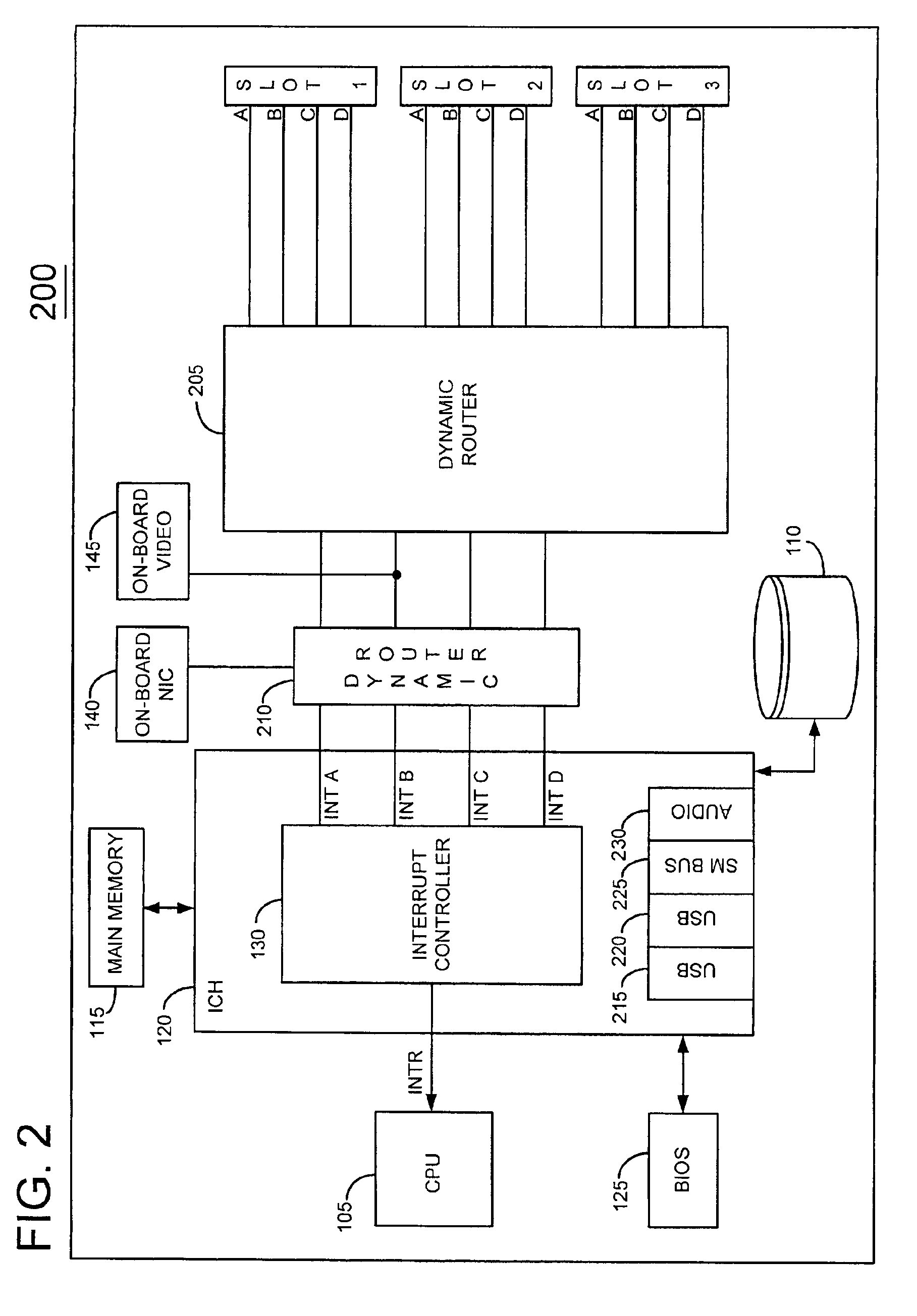
Information handling system with dynamic interrupt allocation apparatus and methodology
InactiveUS6877057B2More balancedUniform distribution of interruptElectric digital data processingHandling systemInformation handling system
An information handling system is provided which includes a dynamic interrupt router for balancing interrupt assignments among a plurality of devices requesting interrupt assignments. The system balances interrupt assignments among both fixed devices mounted on the processor board and interrupt assignments to devices situated in expansion slots. When the system is populated with a large number of devices relative to the number of available interrupts, improved interrupt sharing is desirably achieved by causing a device which generates a large number of interrupt requests to share a common interrupt with a device which generates a lower number of interrupts.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
Soles with adjustable and interchangeable supports
A shoe insert system with adjustable and interchangeable supports comprising: a base sole, a longitudinal arch, a heel insert, and a transverse arch; the base sole being generally planar and having a perimeter which covers the underside of a foot from the heel region up to the bottom of a person's toes, a longitudinal arch, the longitudinal arch having a d-shape with perforated holes and a row of pins sized to mate with perforations of the base sole, a heel insert, the heel insert having alternating perforated holes and pins near the edge defining a general circumference of the heel insert, the pins are sized to mate with corresponding perforated holes on the base sole, the transverse arch having a hole side and a pin side, the transverse arch having a series of perforated holes on the hole side and at least one pin sized to mate with a corresponding perforated hole on the base sole on the hole side.
Owner:RAMIREZ MANUEL RAMIREZ MARTINEZ
Hydraulic synchronizing coupler for a free piston engine
InactiveUS20060042575A1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeFree piston enginesFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. A hydraulic coupler in communication with the pumping chambers will synchronize the motion of the inner and outer piston assemblies to assure that the pistons in the opposed cylinders are operating in opposition to one another.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Sodium cooled pistons for a free piston engine
InactiveUS6904876B1Easy to changeConducive effective homogeneous chargeAir coolingPistonsFree-piston enginePump chamber
A free piston engine is configured with a pair of opposed engine cylinders located on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with a push rod connected between the inner pistons. The push rod extends through an inner pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each operatively located in a respective one of the engine cylinders, with at least one pull rod connected between the outer pistons. The pull rod extends through an outer pumping chamber in the fluid pumping assembly and forms a fluid plunger within this chamber. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output from the engine. Alternatively, the piston assemblies may drive a linear alternator. At least one of the pistons includes one or more generally axially extending bores partially filled with a sodium compound. As the piston reciprocates, the sodium moves back and forth in each cooling bore, thereby better distributing heat in the piston.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Walking Stick with S-Shaped Flexure Mechanism to Store and Release Energy
ActiveUS20140332045A1Improve abilitiesMinimize discomfortWalking sticksCrutchesStored energyAbsorbed energy
A walking stick that takes inspiration from nature to absorb energy in the downward first motion of a walking stride and then return the stored energy to aid in propelling the walker forward in the final forward motion of the walking stride all the while keeping the walker in an ergonomically correct position which minimizes discomfort and reduces wasted energy. The walking stick that is the subject of this patent application utilizes a dual flexure spring configured in an S-shape (hereafter referred to as an S-flexure spring) as an extension of the straight shaft of the stick. The shape and location of the S-flexure spring are such that the spring force helps propel the walker forward.
Owner:LAND FLYERS LLC
Hydraulic synchronizing coupler for a free piston engine
A free piston engine has a pair of opposed cylinders on opposite sides of a fluid pumping assembly. An inner piston assembly includes a pair of inner pistons, one each in a respective one of the cylinders, with a push rod connected therebetween. The push rod forms a fluid plunger. An outer piston assembly includes a pair of outer pistons, one each in a respective one of the cylinders, with a pull rod connected therebetween. The pull rod forms a fluid plunger. The movement of the inner and outer piston assemblies during engine operation will cause the fluid plungers to pump fluid from a low pressure container into a high pressure chamber as a means of storing the energy output. A hydraulic coupler synchronizes the inner and outer piston assemblies.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
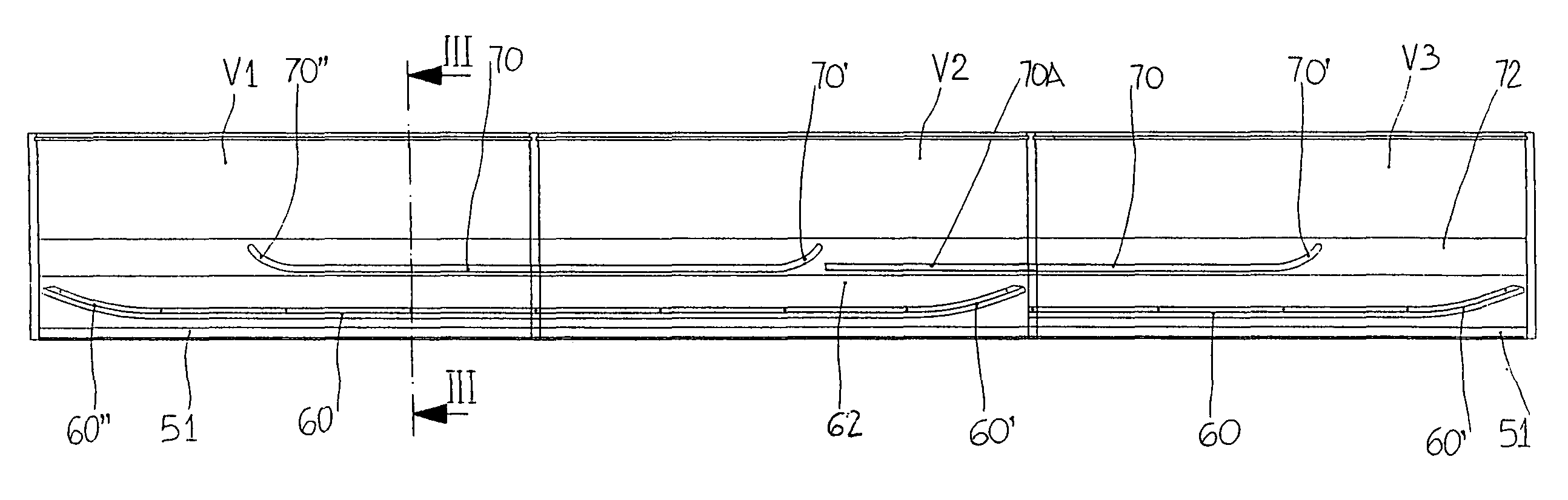
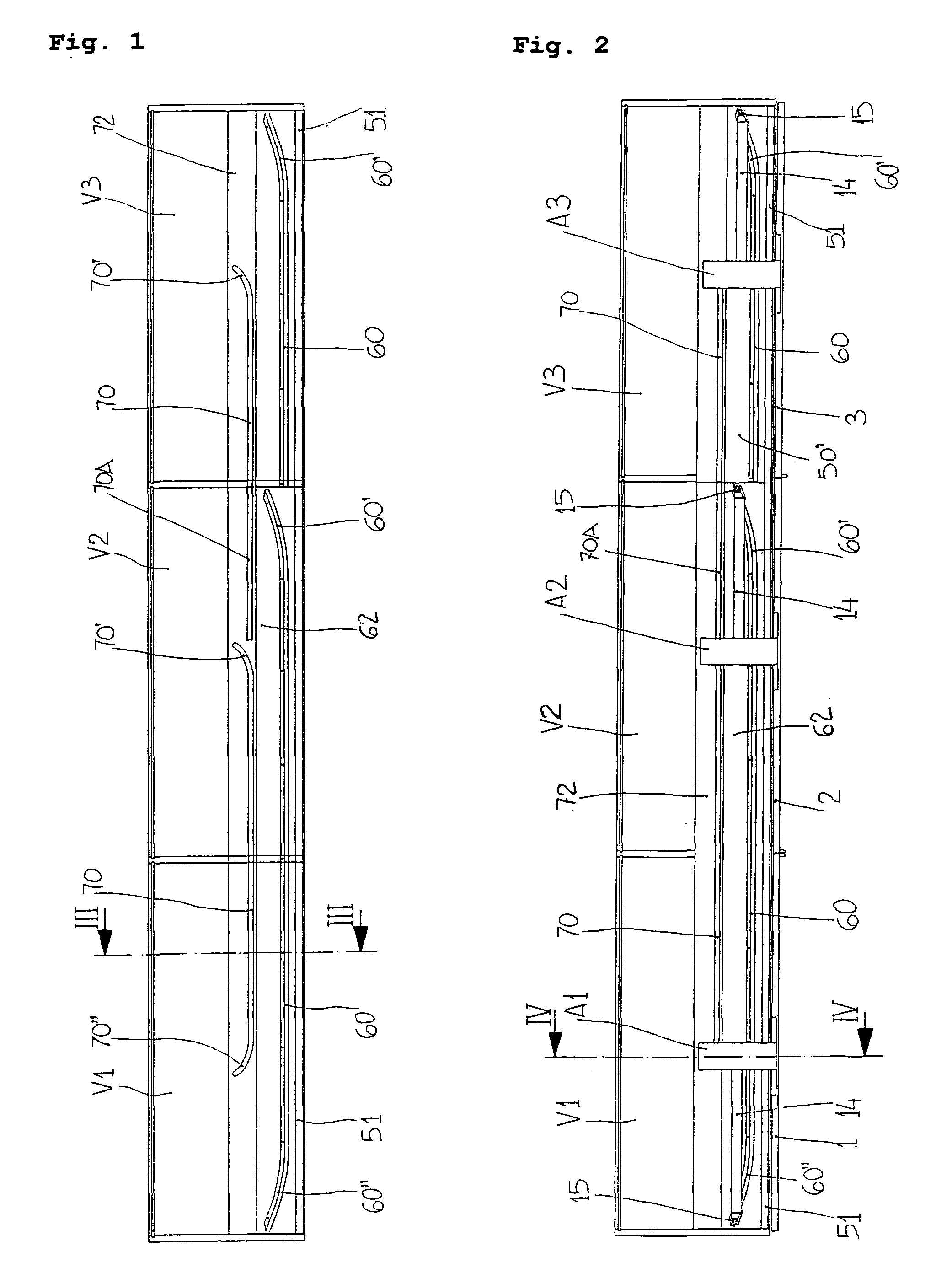
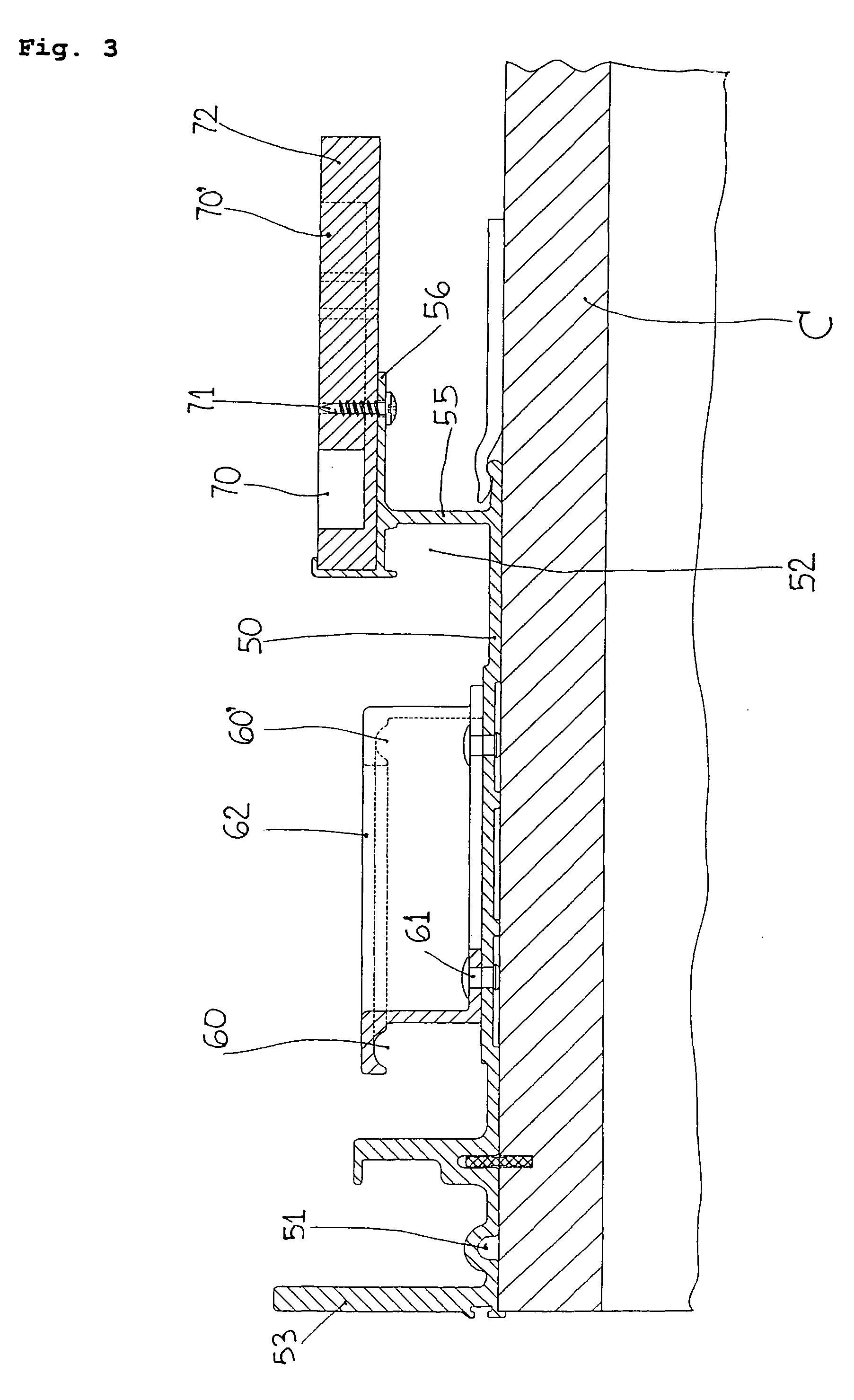
Mechanism for the aligned closure of sliding doors, in particular for units of furniture or compartments with two or more doors
The invention regards to a mechanism for the aligned closure of sliding doors (1-3), in particular for furniture or compartments (V1-V3) with two or more doors, with a sliding door (1, 2 or 3) for each compartment, and where each compartment opens by sliding and overlapping of one door with one of the adjacent doors and closes in alignment with the adjacent doors. The mechanism consists of a single bracket (10) for each door, one end of the bracket (10) being fixed on the door, and its opposite end being equipped with a first sensing bearing (13) to run along a cam guide (70), said bracket (10) being suitable for inclination and transversal movement with a carriage (30), which also allows it to slide along a rail (50) to be positioned on the upper surface of the compartments. The carriage (30) can be adjusted transversally and the bracket (10) can move axially in relation to the carriage (30). An arm (14), one end of which is firmly attached to the bracket (10), while the other end (14a) is equipped with at least a second sensing device having a bearing (15, 15′), can run along an other longitudinal cam guide (60) using the same bracket (10) for inclination and movement.
Owner:BORTOLUZZI SISTEMI SPA
Control modes for extendable rotor blades
InactiveUS8128361B2Reduce noiseVibration minimizationPropellersWind motor controlAccelerometerEngineering
A wind turbine may be controlled in a variety of manners to optimize operating parameters. In one arrangement, for example, the length or the pitch of a wind turbine rotor blade may be adjusted to avoid harmonic resonance frequencies. In another example, the length of a rotor blade may be modified to reduce noise or to optimize profits or both. The controls may be based on data from various types of sensors including accelerometers, sound meters, strain gauges and the like. Actuation of extendable rotor blades can rotate wind turbine rotors without wind or generator pulsing affording multiple advantages. A battery test control may also be used to determine the operational readiness of a battery useful for a variety of purposes in a turbine.
Owner:FRONTIER WIND LLC
Integral gas turbine compressor and rotary fuel injector
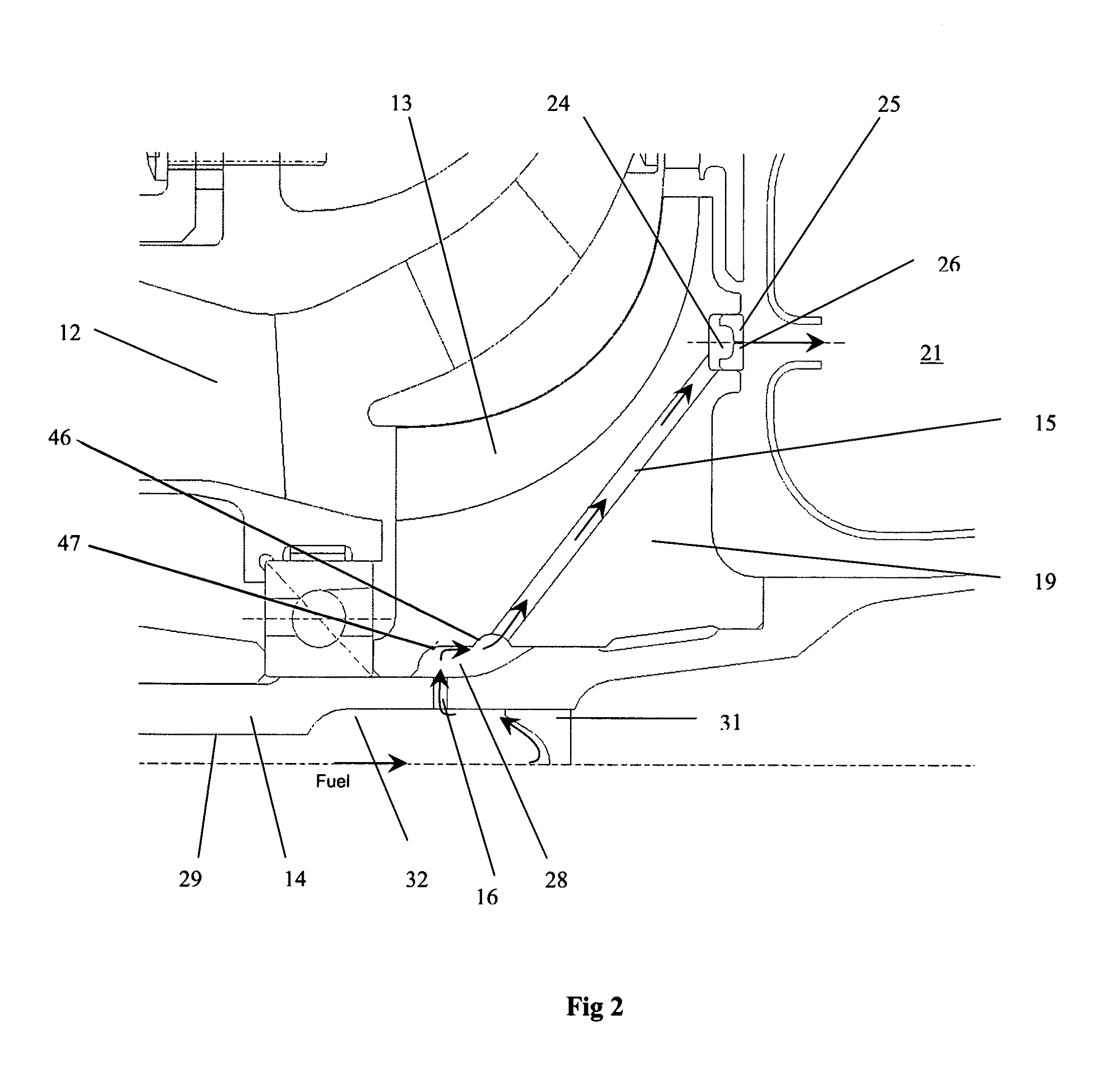
InactiveUS7896620B1Rapid and effective fuel atomizationPromote combustionPropellersEngine manufactureCombustion chamberCombustor
An integral impeller and fuel pump for a small gas turbine engine, the impeller being a centrifugal impeller to supply compressed air to the combustor, the rotor disk of the centrifugal compressor having at least one radial fuel passage connecting a central bore of the rotor disk to a fuel nozzle located on the rear face of the rotor disk. A low pressure fuel supplied by a small pump delivers the fuel to the central bore where the fuel is collected within helical grooves and channeled into the radial fuel passages where the fuel is pressurized to a relatively high pressure due to the high rotational speed of the centrifugal compressor. Highly compressed fuel is injected into the combustor through fuel nozzles in an axial direction as the rotor disk rotates. Helical grooves in the central bore each connected to a radial fuel passage move the fuel to an opposite side of the central bore to counteract rotor imbalance. In another embodiment, a primary annular groove collects fuel and, at a low speed, passes all of the fuel to a first radial fuel passage into a first fuel nozzle such that only some of the fuel nozzles inject fuel into the combustor. At a higher speed, some of the fuel collected in the primary annular groove is spilled over into a secondary annular groove that passes the spilled-over fuel into a second radial passage and second fuel nozzle such that all of the fuel nozzles inject fuel into the combustor.
Owner:FLORIDA TURBINE TECH
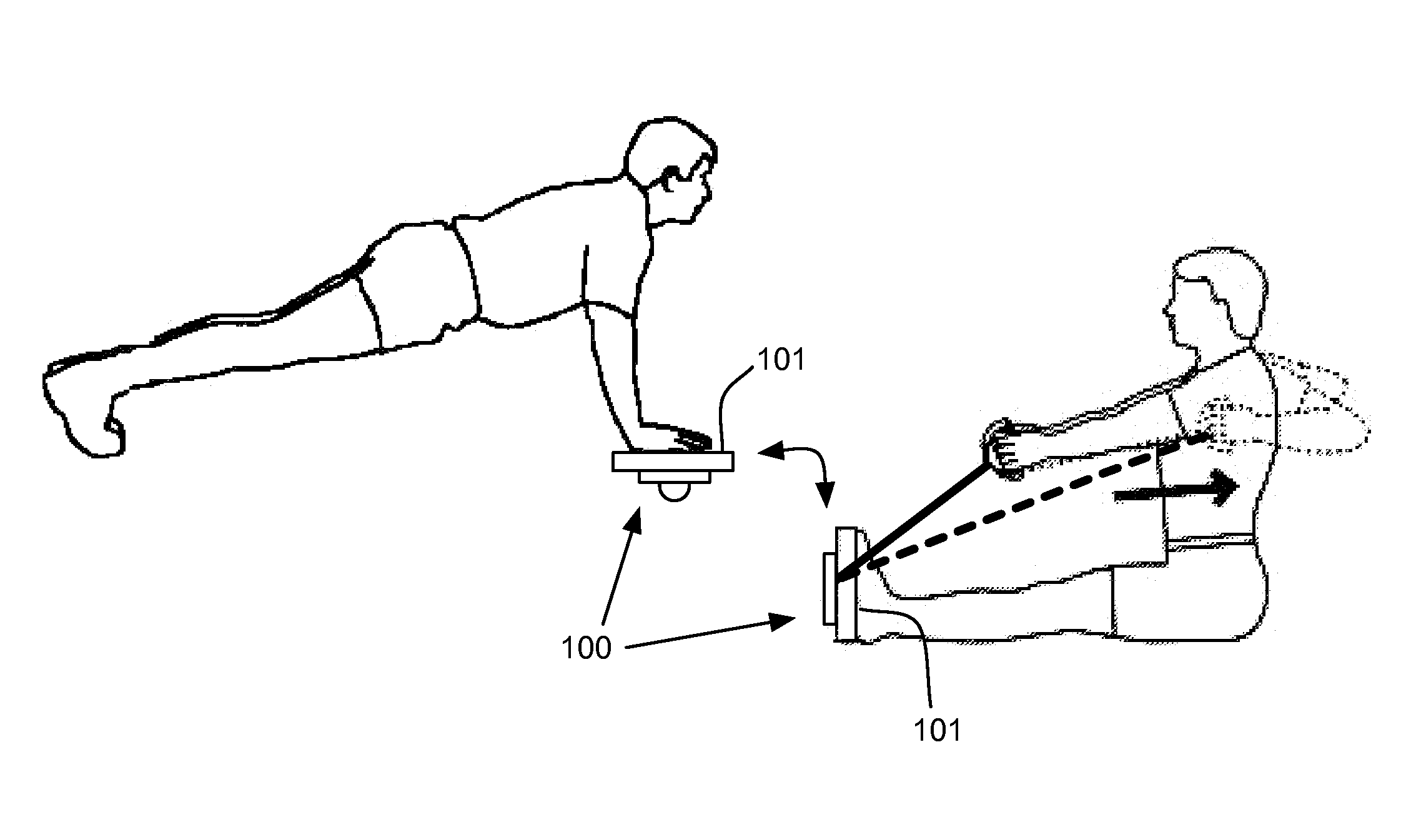
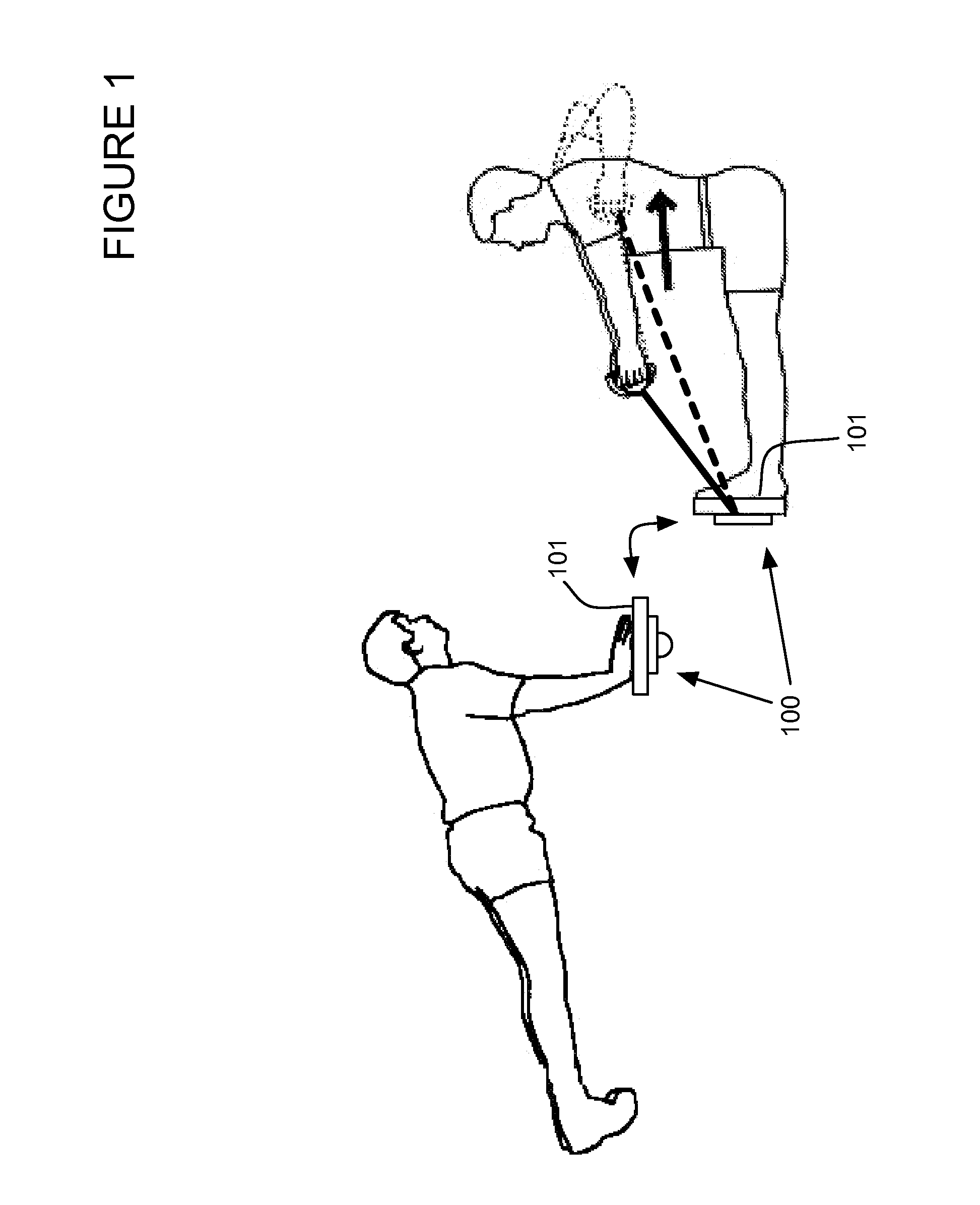
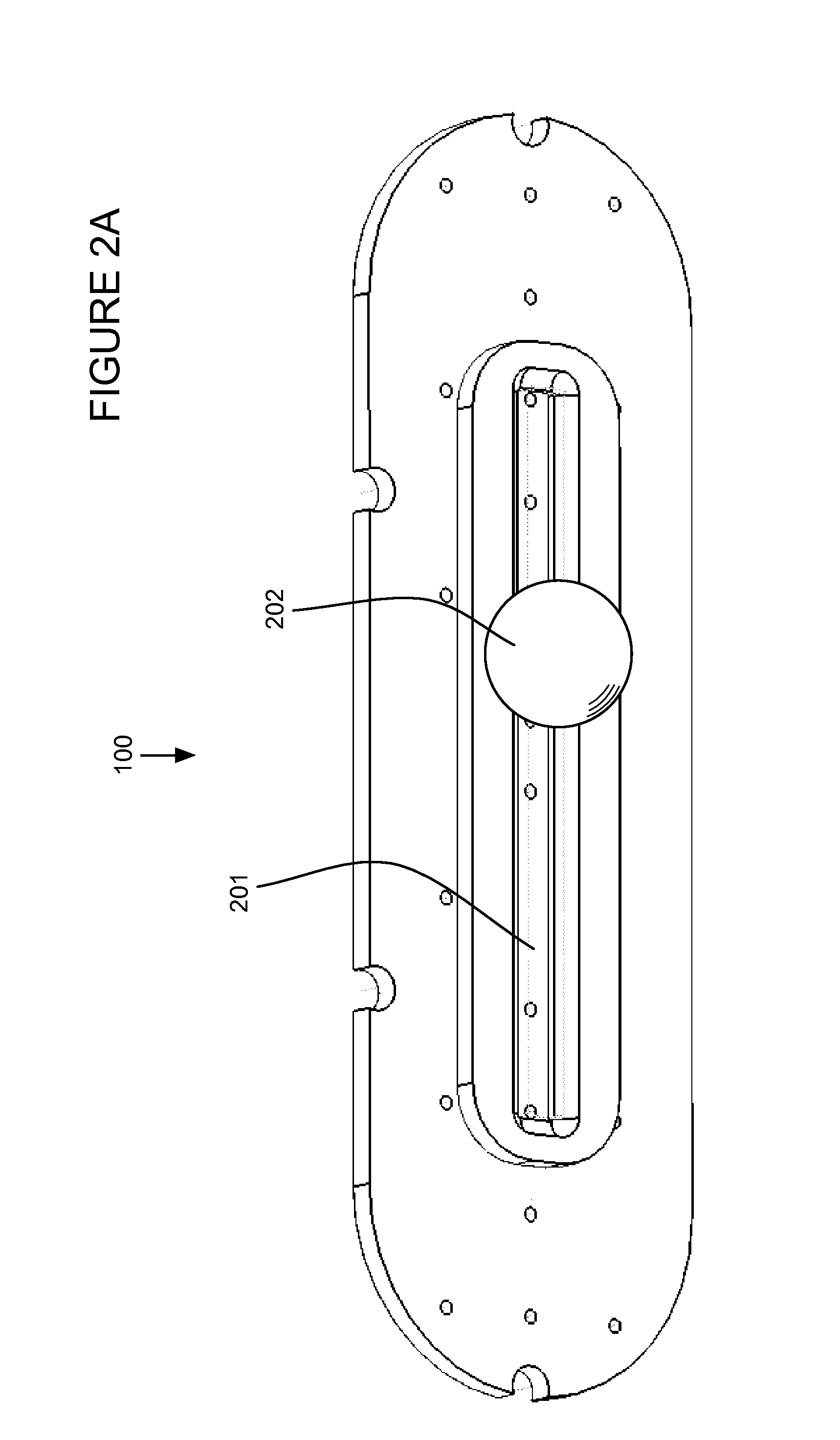
Exercise apparatus for balance and strength training
ActiveUS20130123077A1Easy to carryEasy to transportMovement coordination devicesMuscle exercising devicesPush and pullRange of motion
Exercise apparatus for balance and strength training that enables a user to perform push and pull oriented exercises with the user's hands or feet against the apparatus. Includes a pivot space, for example a slot or area or area with higher or lower areas, wherein the pivot space is configured to couple with a pivot element, for example a ball, cylinder, wheel or any other type of element that may move with respect to the pivot space and exercise interface. The movable pivot element enables force and hence torque required to balance to differ on each side of the apparatus. For example, a user with an injured shoulder may desire to utilize more force to balance during a push-up with the uninjured shoulder and less force and more range of motion to balance with the injured shoulder.
Owner:DUNEGAN TIM
Image capturing system
An image capturing system includes, in order from an object side to an image side, a first lens element, a second lens element, a third lens element, a fourth lens element and a fifth lens element. The first lens element with positive refractive power has a convex object-side surface at a paraxial region. The second lens element and the third lens element have refractive power. The fourth lens element with negative refractive power has a concave object-side surface at a paraxial region and a convex image-side surface at a paraxial region. The fifth lens element with refractive power has an image-side surface, wherein the image-side surface changes from concave at a paraxial region to convex at a peripheral region, and an object-side surface and the image-side surface of the fifth lens element are aspheric. The image capturing system has a total of five lens elements with refractive power.
Owner:LARGAN PRECISION
Exercise apparatus for balance and strength training
ActiveUS8888669B2Alter pointConvenient amountResilient force resistorsStiltsPush and pullRange of motion
Exercise apparatus for balance and strength training that enables a user to perform push and pull oriented exercises with the user's hands or feet against the apparatus. Includes a pivot space, for example a slot or area or area with higher or lower areas, wherein the pivot space is configured to couple with a pivot element, for example a ball, cylinder, wheel or any other type of element that may move with respect to the pivot space and exercise interface. The movable pivot element enables force and hence torque required to balance to differ on each side of the apparatus. For example, a user with an injured shoulder may desire to utilize more force to balance during a push-up with the uninjured shoulder and less force and more range of motion to balance with the injured shoulder.
Owner:DUNEGAN TIM
Piezoelectric device
InactiveUS20110133605A1More balancedAvoid vibrationImpedence networksPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesMechanical engineeringEngineering
A piezoelectric device includes: a piezoelectric vibrating reed; and a package, wherein the piezoelectric vibrating reed has a vibrating part and first and second supporting arms extending from a base end part, the package has a base, a lid, a cavity defined by the base and the lid, a convex part projecting from the base or the lid into the cavity, a length of the first supporting arm is shorter than a length of the second supporting arm, and the convex part is provided in a range ahead of a leading end of the first vibrating arm in an extension direction of the first supporting arm and at least partially overlapping with the second supporting arm in a length direction of the piezoelectric vibrating reed so as not to overlap with the piezoelectric vibrating reed in a plan view.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Direct application brush having flow regulator assembly
InactiveUS8336558B2Super light weightHighly reliable in operationCarpet cleanersBrush bodiesBristleEngineering
A brush assembly releases a fluid and / or liquid solution directly onto a surface, such as a coat of an animal during grooming, or onto inanimate surfaces such as vehicles. The brush assembly includes a molded brush having a plurality of apertures integrated therein for delivery of a fluid. At least one base plate with grooming implementations, such as bristles or a sponge, is interchangeably attached to the brush base. An ergonomical handle is provided having a palm conforming top and finger indentation sides constructed to form an internal cavity. The ergonomical handle is ambidextrous in nature for interchangeable left and right handedness. A center cylinder is located within said internal cavity of said ergonomical handle and includes a bladder which aligns with the mid portion of the brush base for fluid delivery controlled upstream by a flow regulator. An optional mixing chamber housing a water soluble compound containing active ingredients may be attached to the flow regulator to form a liquid solution. The fluid and / or liquid solution is delivered directly to the surface during grooming.
Owner:I DID IT
Stepped-louvre heating, ventilating and air conditioning unit used in high-velocity, low speed fan
ActiveUS20170030361A1More balance airflowLarge coverage areaPump componentsLighting and heating apparatusLeading edgeLow speed
A manifold including a stepped louvre to control airflow along a fan blade. A fan blade for use in a high-volume, low-speed fan, wherein the fan blade includes a body portion, a leading edge portion and a trailing portion. The leading edge portion of the fan blade includes a series of steps extending along the length of the leading edge. The fan distributes airflow from the manifold.
Owner:GO FAN YOURSELF LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com