Immobilized nucleic acid probe for non-labeling detection
A technology for detection of nucleic acid probes and markers, which can be used in biological testing, material inspection products, microbial measurement/inspection, etc. In order to achieve the effect of overcoming multiple PCR fluorescently labeled target sequences, reducing the difficulty and cost of use, and reducing time
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
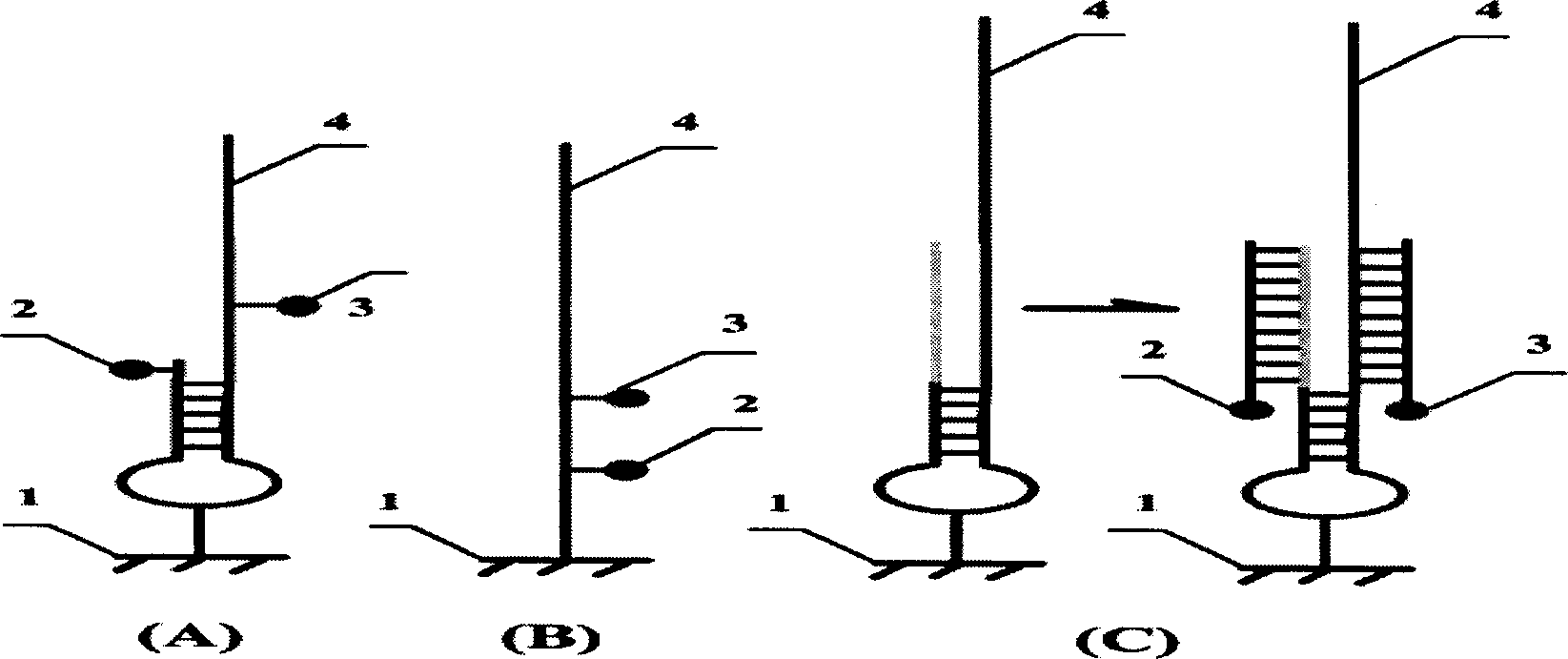
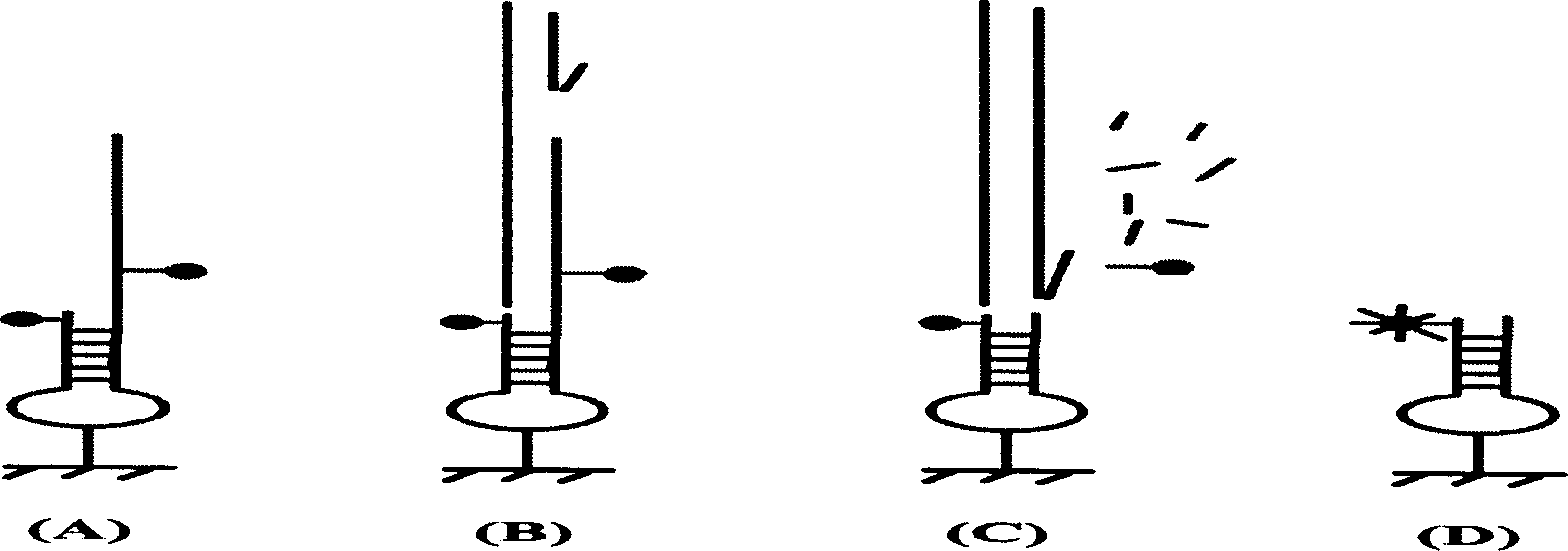
[0017] The solid-phase nucleic acid probe proposed by the present invention includes two protruding ends formed by hybrid double strands of a fluorescent chromophoric group and a fluorescent quenching group, and is fixed on a solid substrate through an arm molecule in the middle of the double strands. The target sequence is capable of forming a complete duplex when complementary to a specific sequence on one overhang of the probe. Under the action of E.coliexonucleaseI, the other single-strand overhang together with the quencher molecule is excised, and the fluorescent chromophore can emit a fluorescent signal under excitation. In the presence of non-specific target sequences, the target sequence cannot hybridize to the specific sequence on the probe. E.coli exonuclease I cannot recognize and excise the overhang of the other single strand, so that the double strand remains intact, the fluorescent signal is still quenched, and no fluorescent signal is released ( figure 2 ). ...
Embodiment 3
[0023] Another solid-phase nucleic acid probe proposed by the present invention includes a fluorescent chromophoric group and a fluorescent quenching group, a specific nucleic acid sequence region, a non-specific spacer region and an arm molecule region. The probes are connected with the solid support to form a microarray chip. Immobilize the probe with an appropriate method, wash with 0.1% SDS for 5 min, then block with sodium borohydride, and then use MilliQ H 2 O wash slides, N 2 blow dry. Store in the dark at 4°C for later use or use directly.
[0024] For the G / C mutation at position 92 of the uid gene in E.coli O157:H7, three corresponding probes were designed, including a negative control, and a specific restriction endonuclease site was included in the reporter molecule and the quencher molecule point. When the wild-type target sequence exists, the endonuclease cannot recognize it, and no enzyme cleavage reaction occurs; when the mutant target sequence exists, the ...
Embodiment 4
[0026] The solid-phase nucleic acid probe proposed by the present invention includes a fluorescent chromophoric group and a fluorescent quenching group, which can be fixed on microspheres or microbeads (microparticles or microbeads) to form a suspended microarray. Nucleic acid probes labeled with different fluorescent chromophores can be immobilized in combination on each microsphere or microbead, and the instant detection of multiple sites in a single reaction tube can be completed through specific excitation wavelength combination coding. Design specific probes for virulence factors in E.coliO157:H7 such as rfbE, flicH7, hlyA, etc. When these corresponding target sequences exist, under the action of 5' exonuclease activity, along with the corresponding nucleic acid chain As the displacement reaction proceeds, the quencher molecule is excised and the fluorescent signal is released. Analysis of the detected fluorescent signal can give information about the presence of the corr...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com