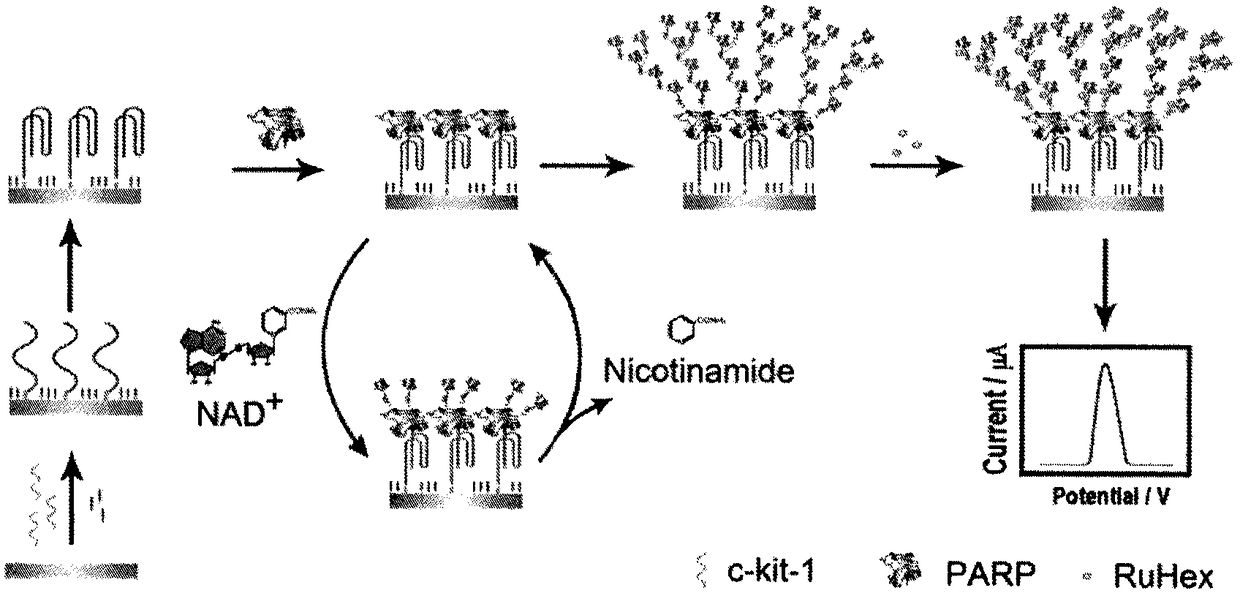
A detection method for polyadenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase
A polyadenosine diphosphate-ribose and detection method technology, applied in the field of analytical chemistry, can solve the problems of biomolecular denaturation, expensive instruments, expensive and other problems, achieve high sensitivity, avoid the labeling process, and the method is simple and fast
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
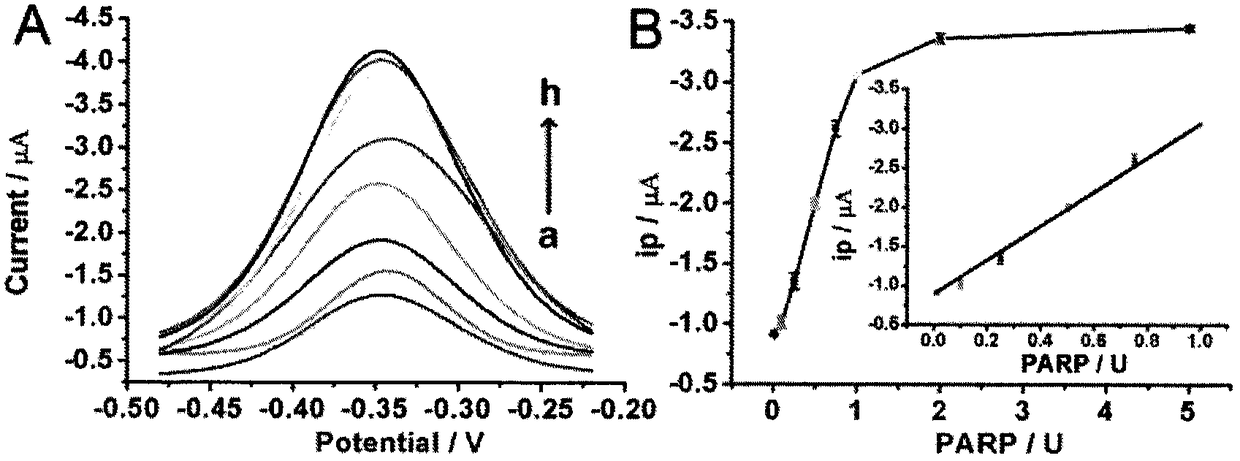
[0023] Example 1. Determination of electrochemical signal value-concentration standard curve of PARP standard solution
[0024] 100 μL of PARP standard solutions of different concentrations were respectively incubated with c-kit-1 modified gold electrode according to the above steps, catalyzed and measured electrochemical signals. Such as figure 2 The curve showing the relationship between the electrochemical signal value (ip) and the concentration of PARP, within the range of PARP0.01U-1U, there is a linear relationship between ip and concentration, and the linear regression equation is y=-0.8912-2.17559x, R 2 =0.998, where y is the peak current ip (μA) of SWV, and x is the concentration of PARP (U).
Embodiment 23-A
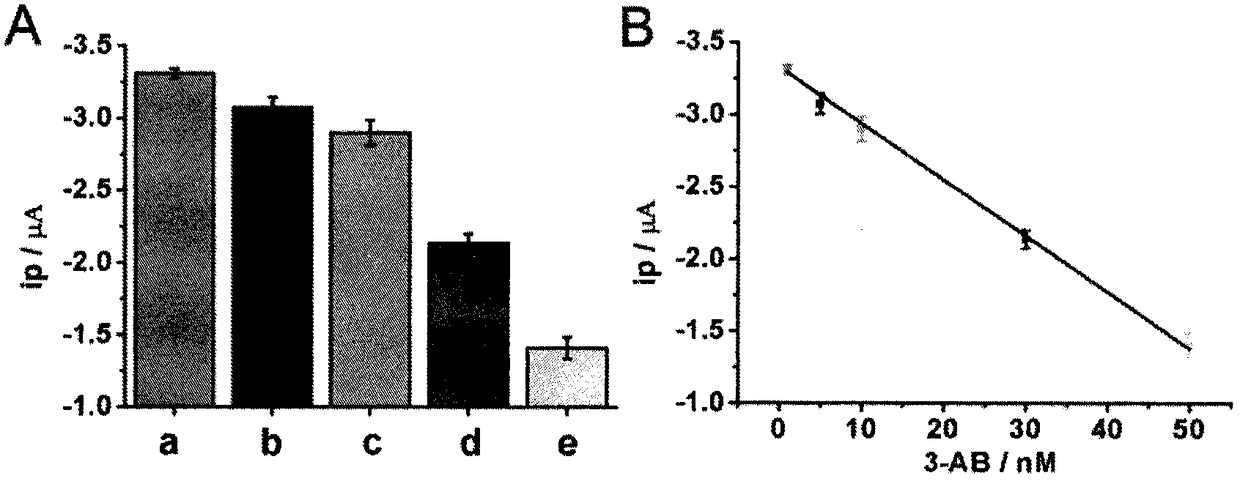
[0025] Example 2.3 Determination of electrochemical signal value-concentration standard curve of AB standard solution
[0026] Different concentrations of 3-AB were incubated with 100 μL of the reaction solution containing 1 U of PARP at 4°C for 12 hours. Incubate with c-kit-1 modified gold electrode, catalyze and measure the electrochemical signal according to the above steps. Such as image 3 The curve showing the relationship between the electrochemical signal value (ip) and the concentration of 3-AB, 3-AB is in the range of 1nM-50nM, and there is a linear relationship between ip and the concentration. The linear regression equation is y=-3.32915+0.03898x, R 2 =0.997, where y is the peak current ip (μA) of SWV, and x is the concentration of 3-AB (nM).
[0027]
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com