Methods for treating infectious diseases and tumors
A technology for infectious diseases and effects, applied in the field of treating infectious diseases and tumors, and can solve the problem of inability to respond to tumor antigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
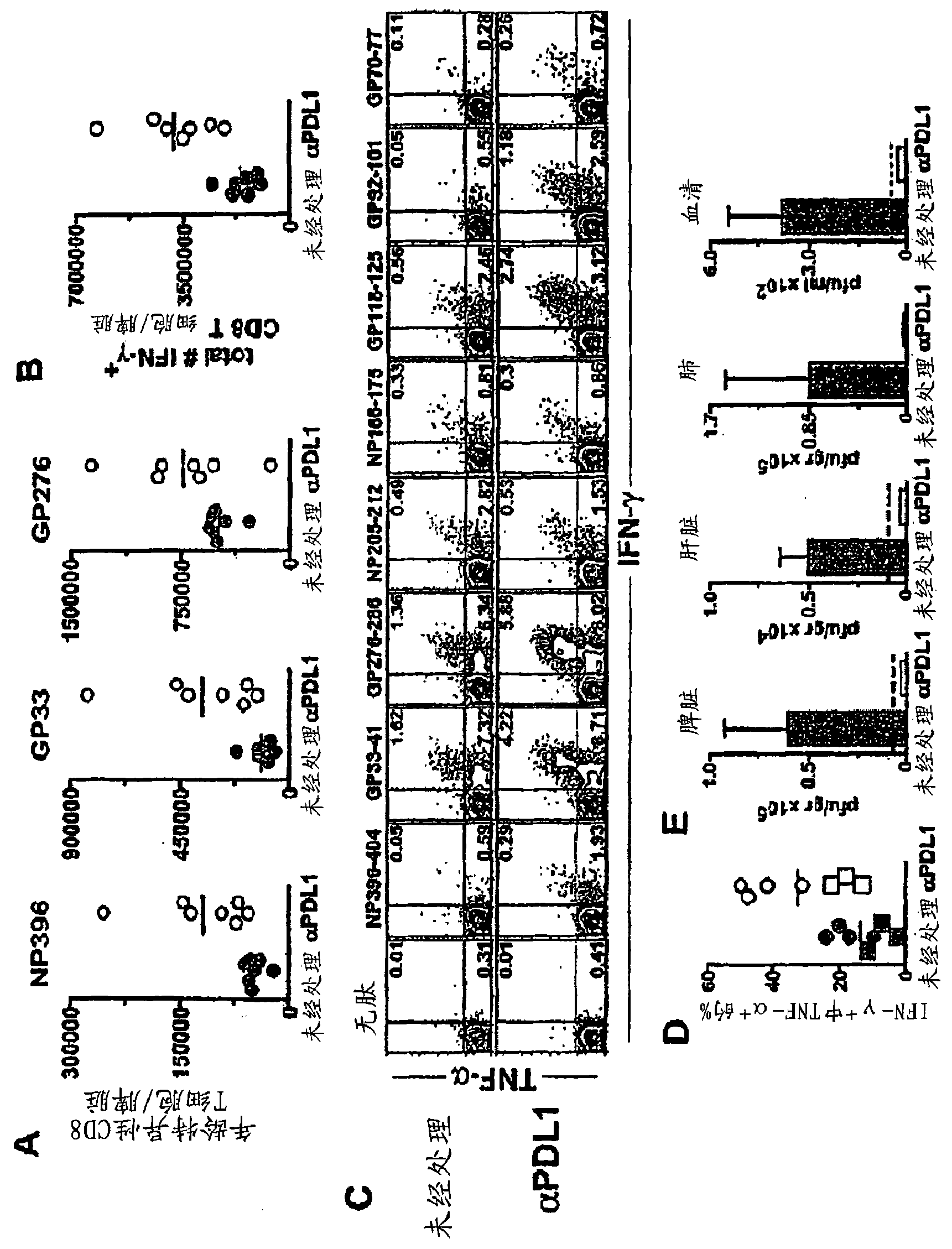
[0438] Example 1: Inhibition of PD-1 using anti-PD-L1 antibodies in chronically infected mice way
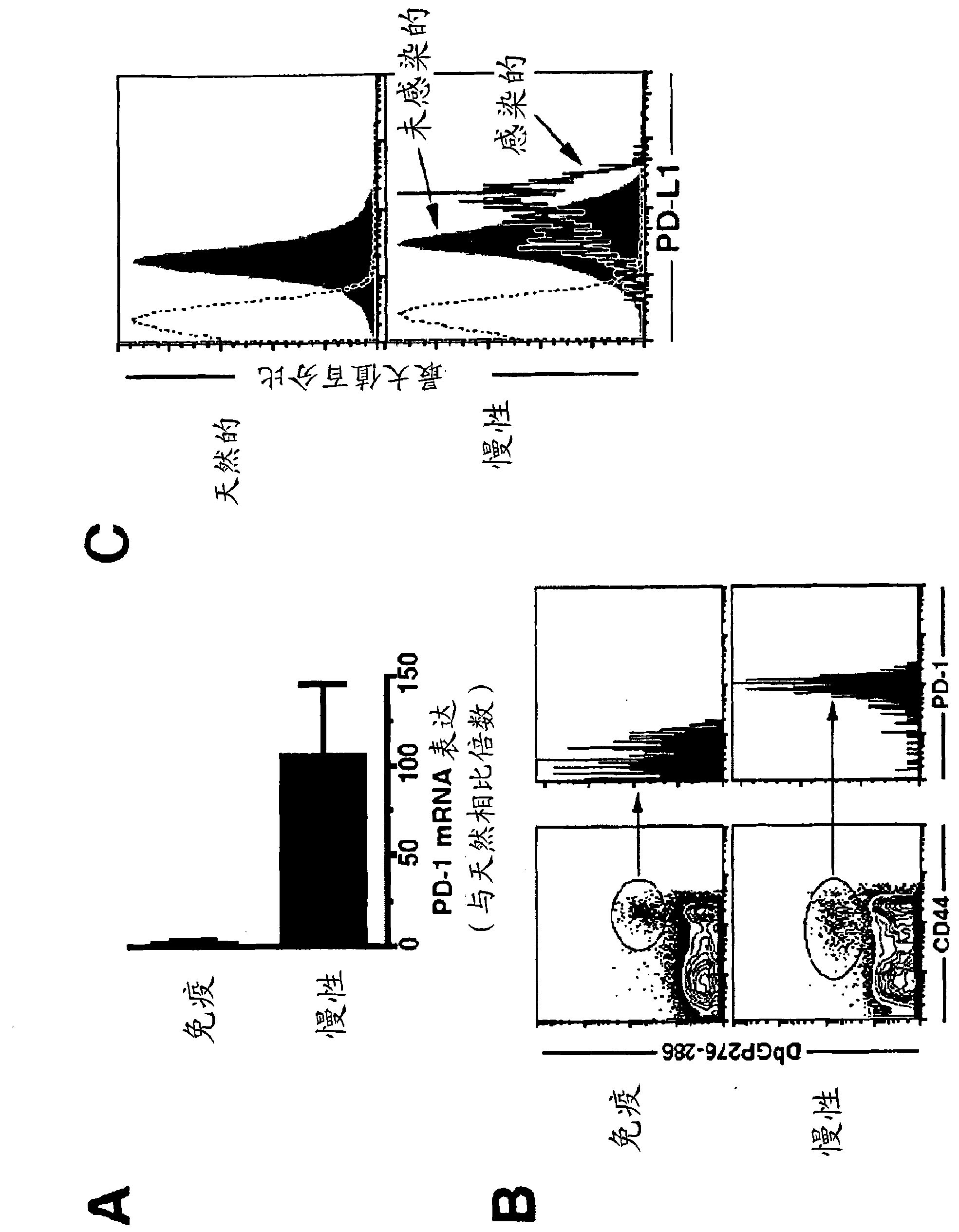
[0439] Mice infected with different lymphocytic choriomeningitis viruses (LCMV) were used to study the effect of chronic viral infection on CD8+ T cell function. The Armstrong strain of lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) causes an acute infection that is evident within 8 days, producing long-lived, highly functional, memory-storing CD8+ T cells . In contrast, the lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) Cl-13 strain produces a persistent infection in the host that results in viral sepsis lasting up to 3 months. The virus persists in some indeterminate tissue, and the function of antigen-specific CD8+ T cells is attenuated. DbNP396-404 CD8+ T cells disappeared from the body when DbGP33-41 and DbGP276-286 CD8+ T cells were present but these cells did not have the ability to proliferate or secrete antiviral cytokines such as interferon ( IFN)-γ and TNF-α.
[0440] C...
Embodiment 2
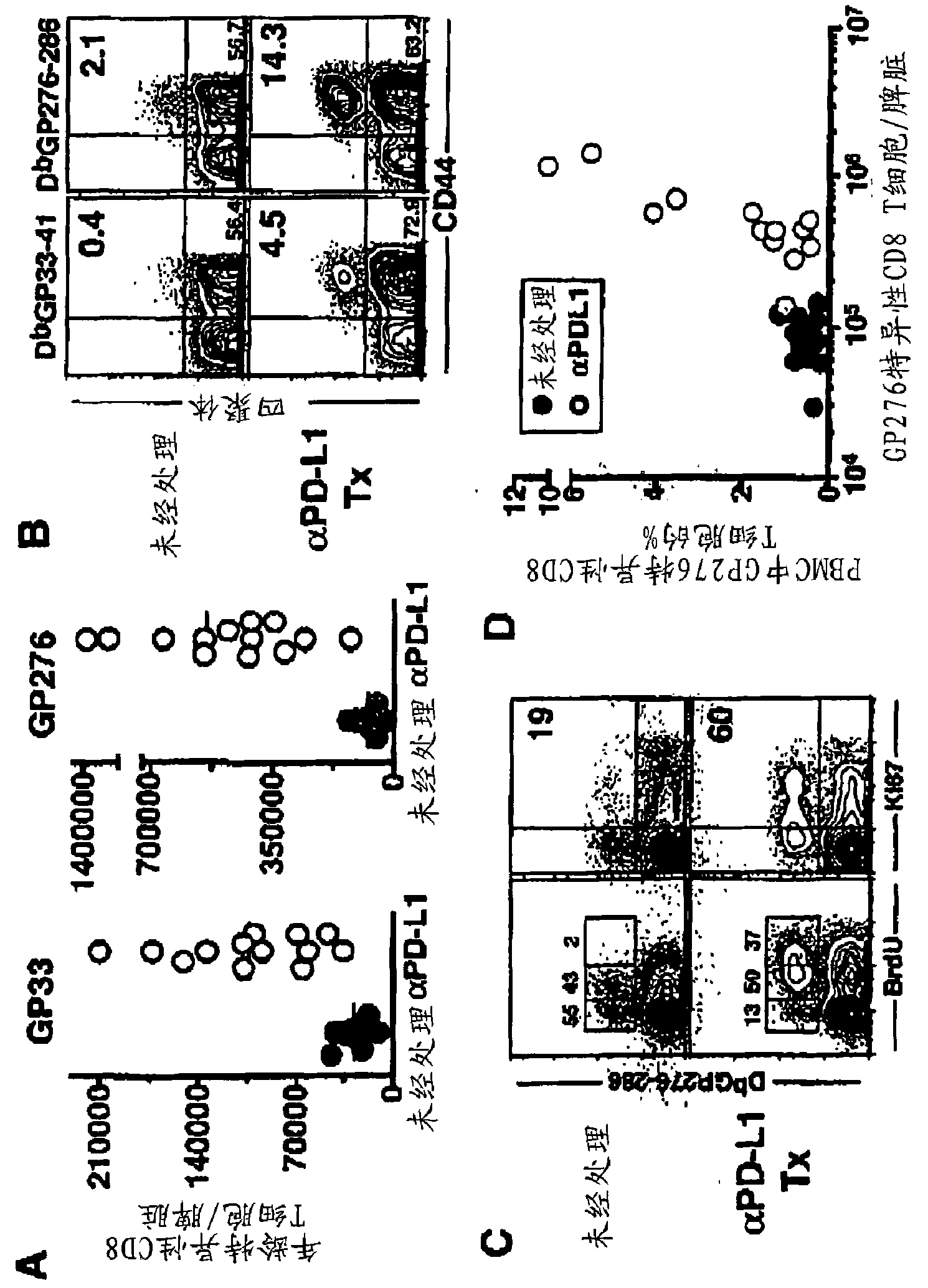
[0449] Example 2: Administration of antiviral vaccines and PD-1 antagonists
[0450] A method used to boost T cell responses during persistent infection is therapeutic vaccination. The rationale for this approach is that during chronic viral infection, endogenous antigens may not be present in an optimal or immunogenic manner, and antigens delivered in the form of vaccines can provide more effective stimulation of virus-specific T and B cells . Using the chronic lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) model, mice were administered a recombinant vaccinia virus capable of expressing lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus (LCMV) as a therapeutic vaccine (VVGP33) GP33 epitope, resulting in a moderately enhanced CD8+ T cell response in chronically infected mice. Four of nine infected mice treated with the therapeutic vaccine showed a positive response, while none of the control mice showed a significant increase in the immune response to GP33. When therapeutic vaccination was co...
Embodiment 3
[0451] Example 3: Use of PD-1 RNA interference in chronically infected mice (RNAi) inhibits the PD-1 pathway
[0452] Ribonucleic acid interference (RNAi) can stop gene expression in mammalian cells. Long double-stranded RNAs (dsRNAs) are introduced into cells and subsequently processed into smaller quiescent RNAs (siRNAs) that target specific mRNA molecules or small groups of mRNAs. This technique is especially effective at sites where the antibody is not functional. For example, RNAi can be performed at a position where unique splice variants are capable of producing soluble forms of PD-1 and CTLA-4.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com