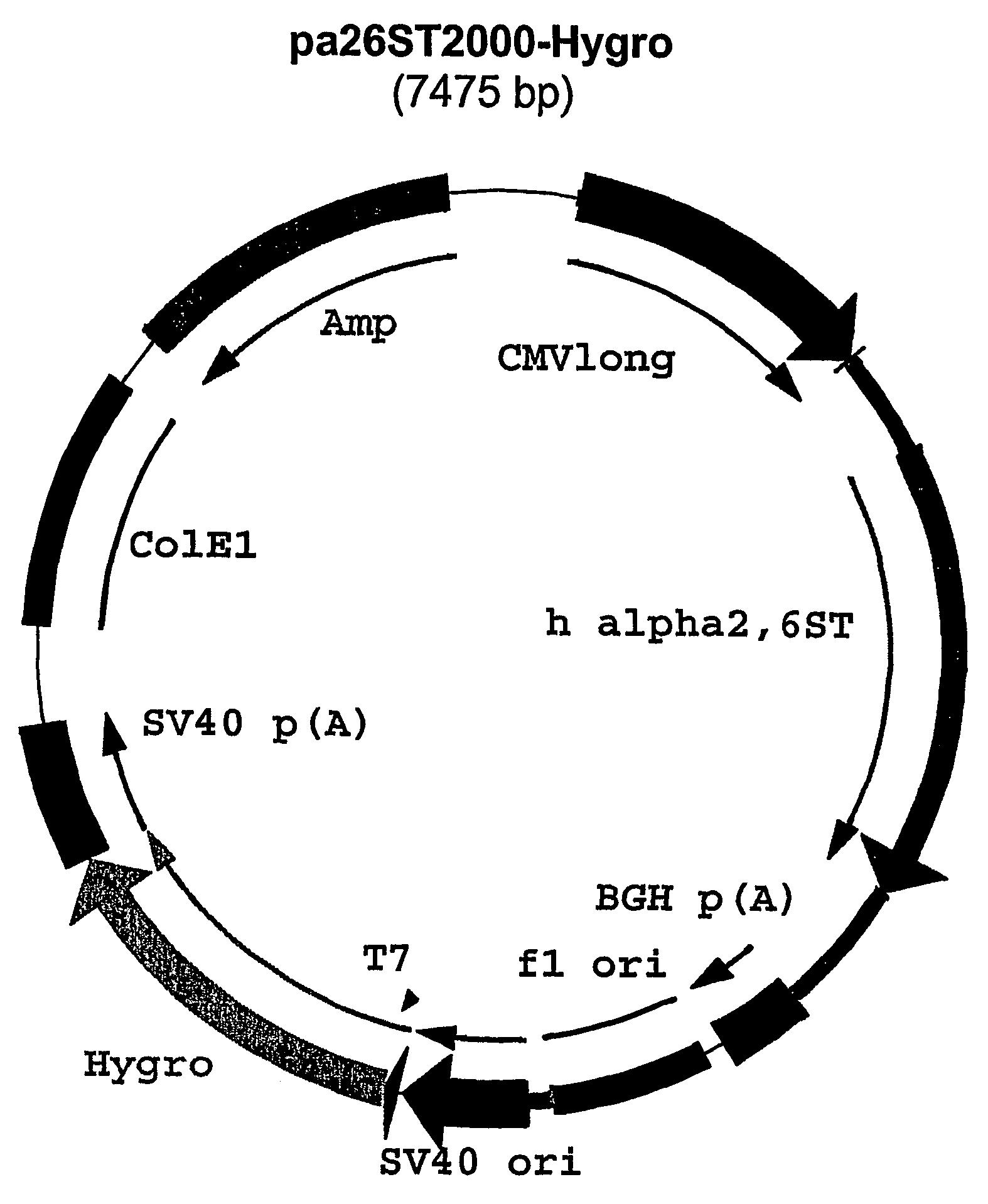
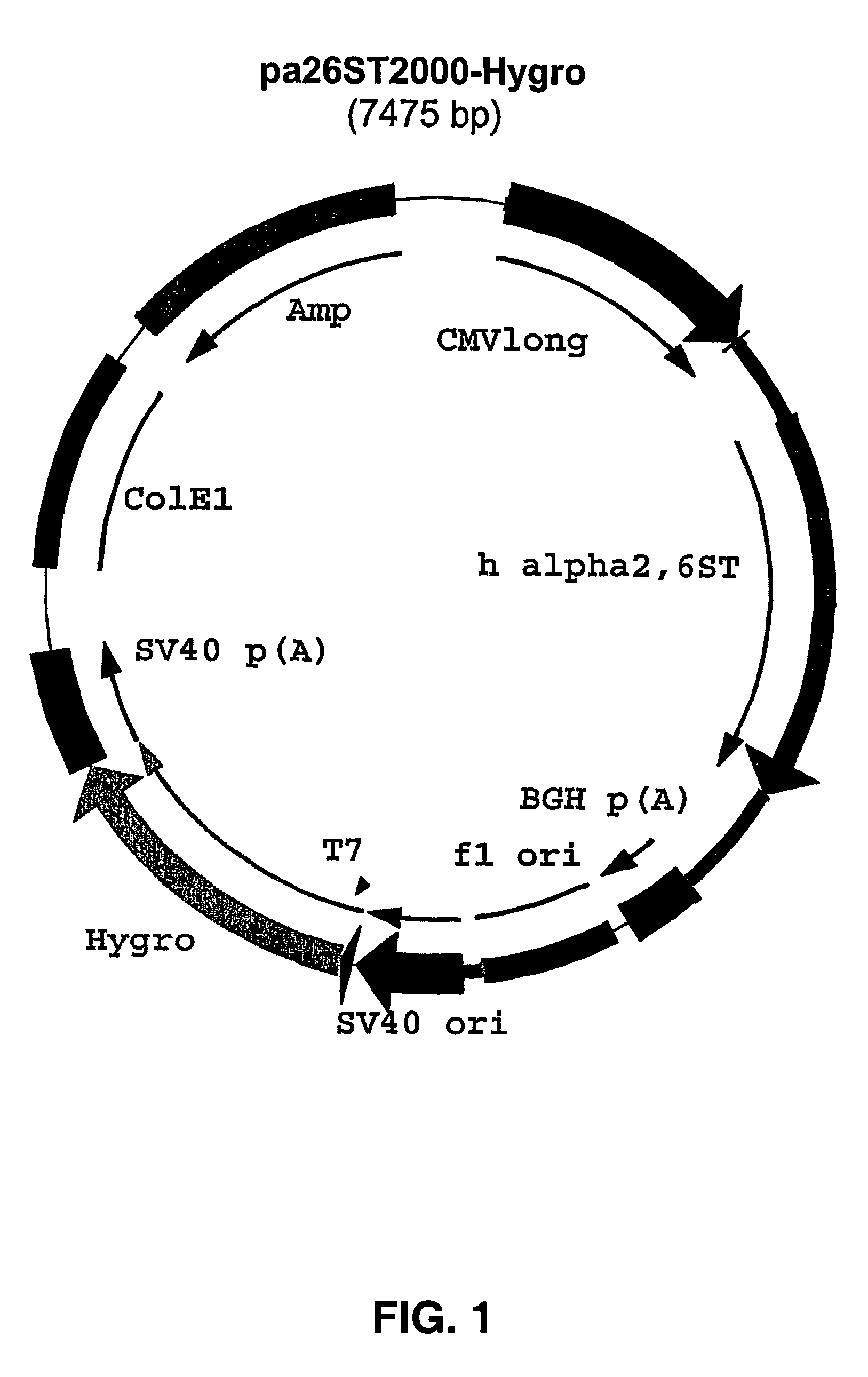
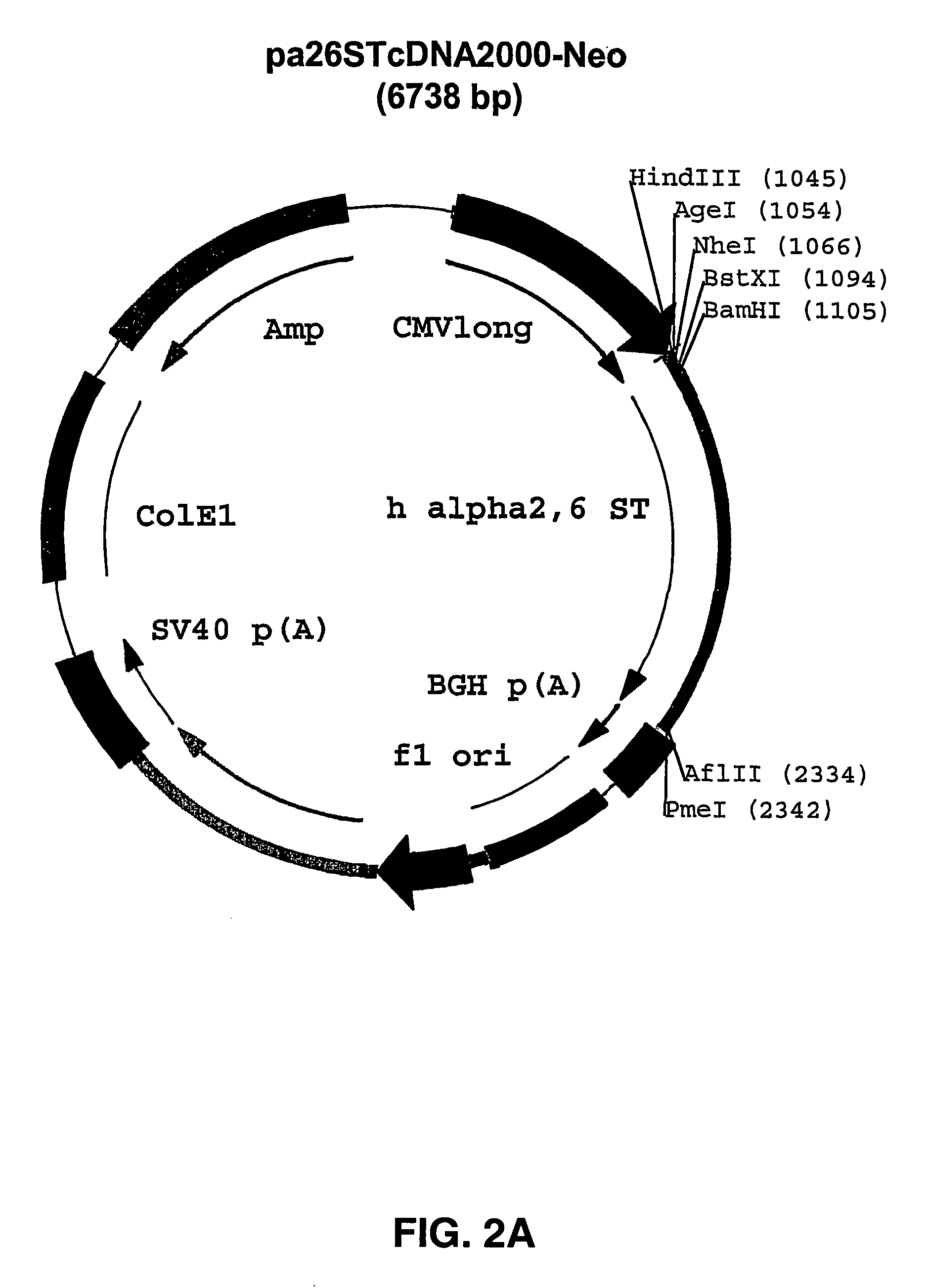
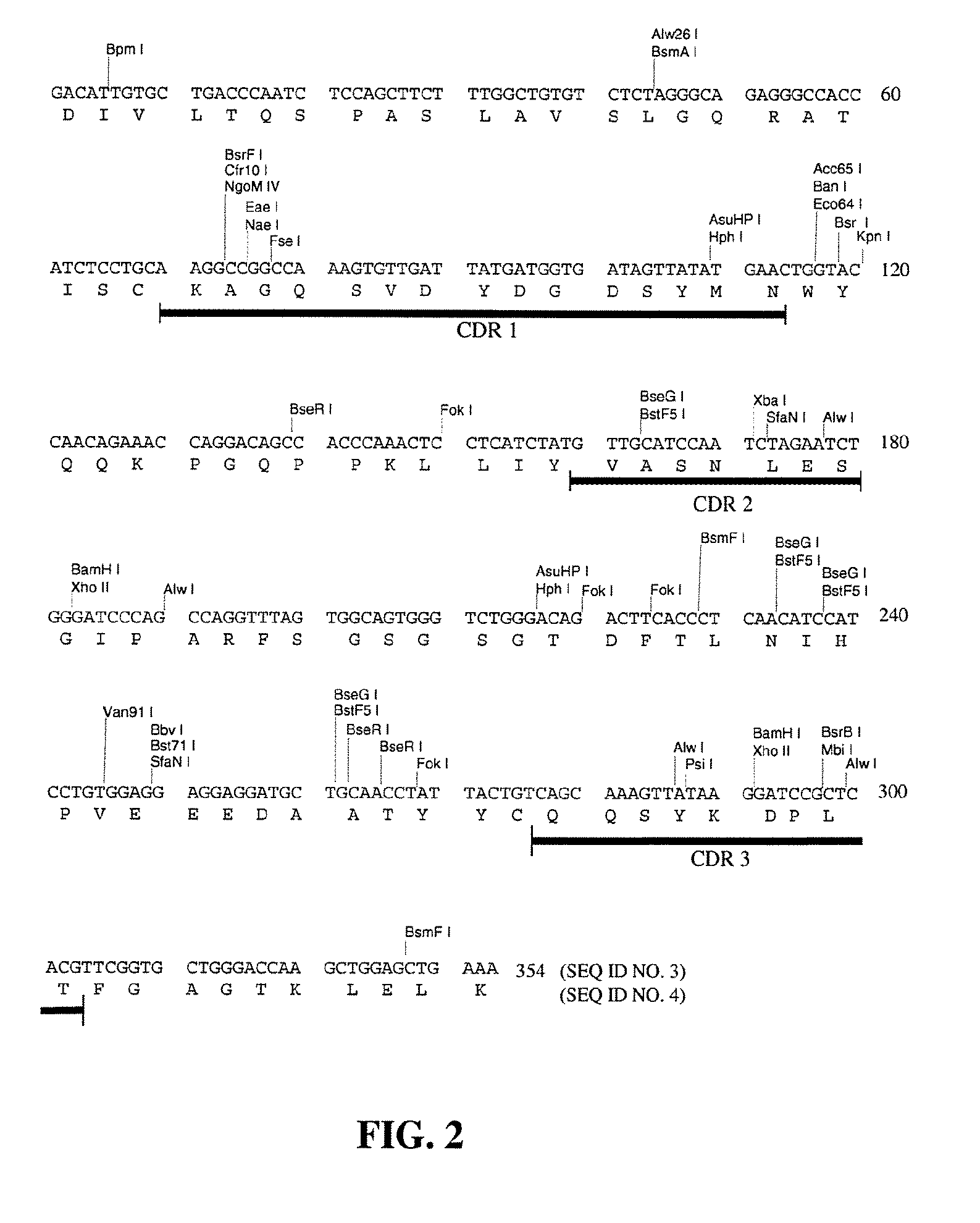
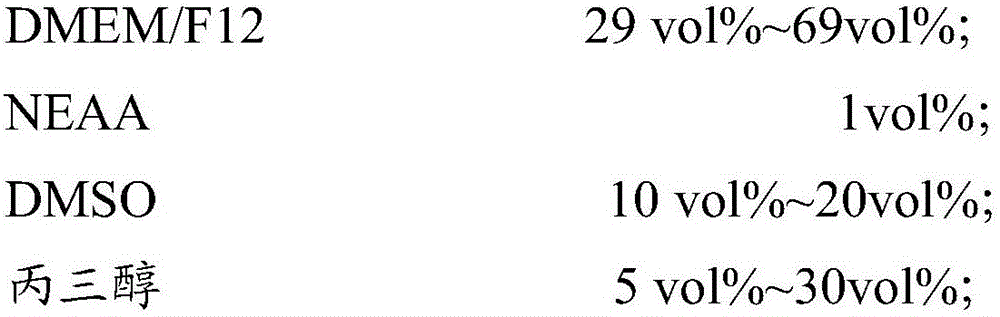Patents
Literature
69 results about "Viral isolate" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Primary isolate. Primary isolate is a pure microbial or viral sample that has been obtained from an infected individual, rather than grown in a laboratory. In chemistry and bacteriology, the verb isolate means to obtain a pure chemical, bacteriological or viral sample. The noun 'isolate' refers to the sample itself.
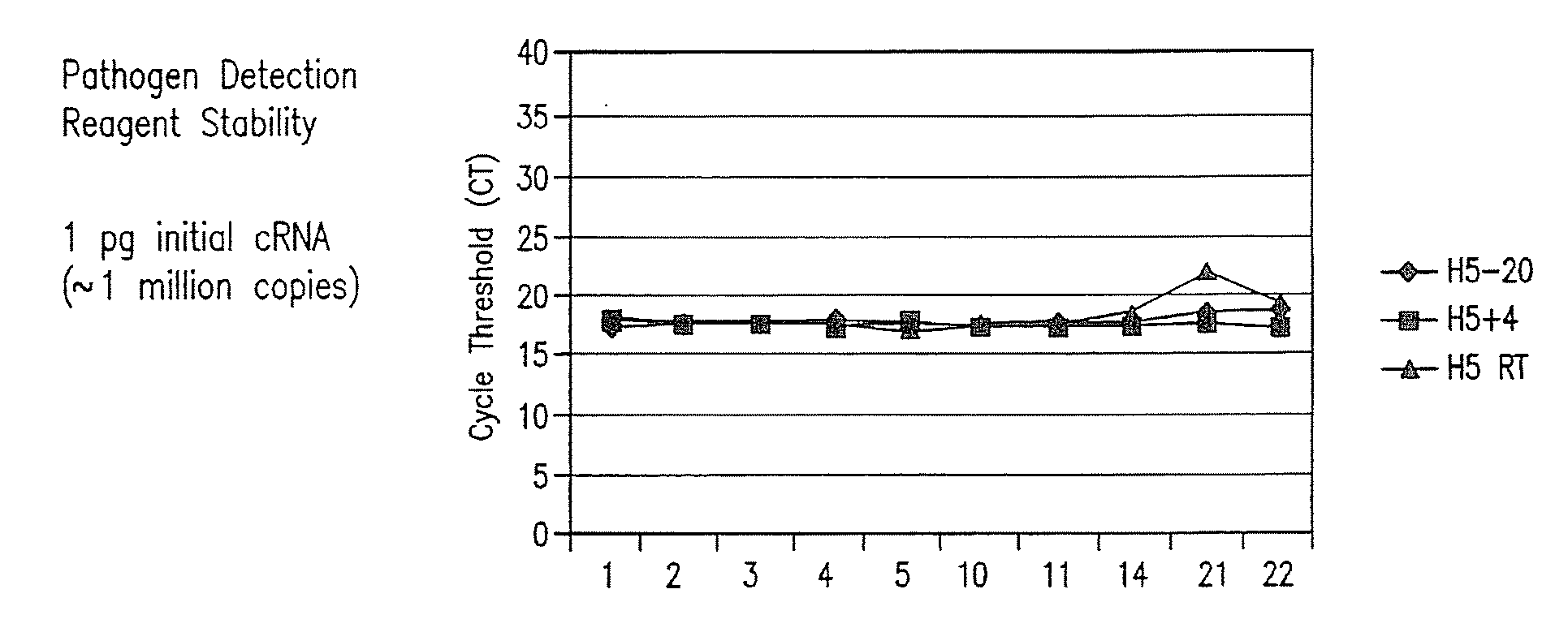
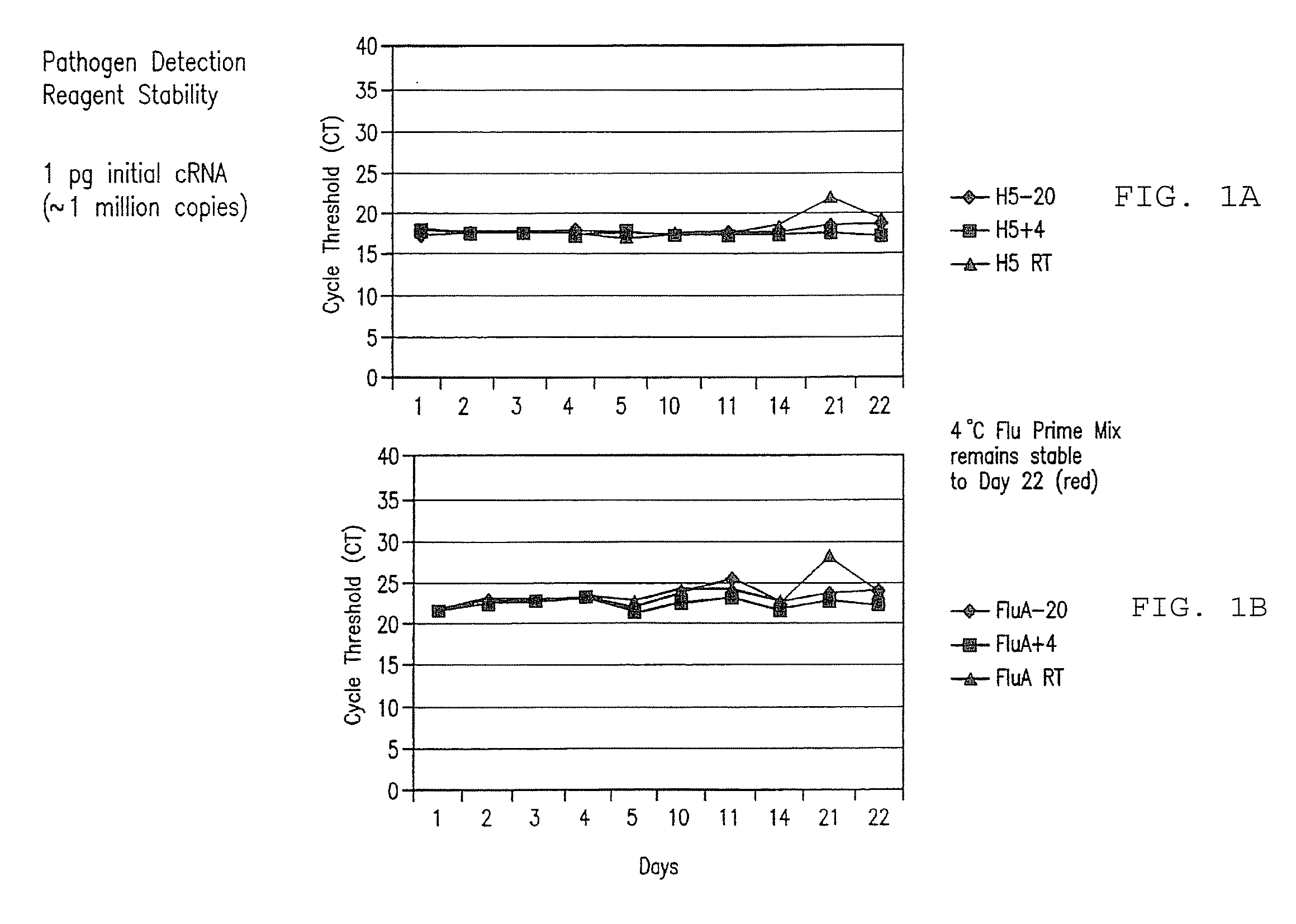
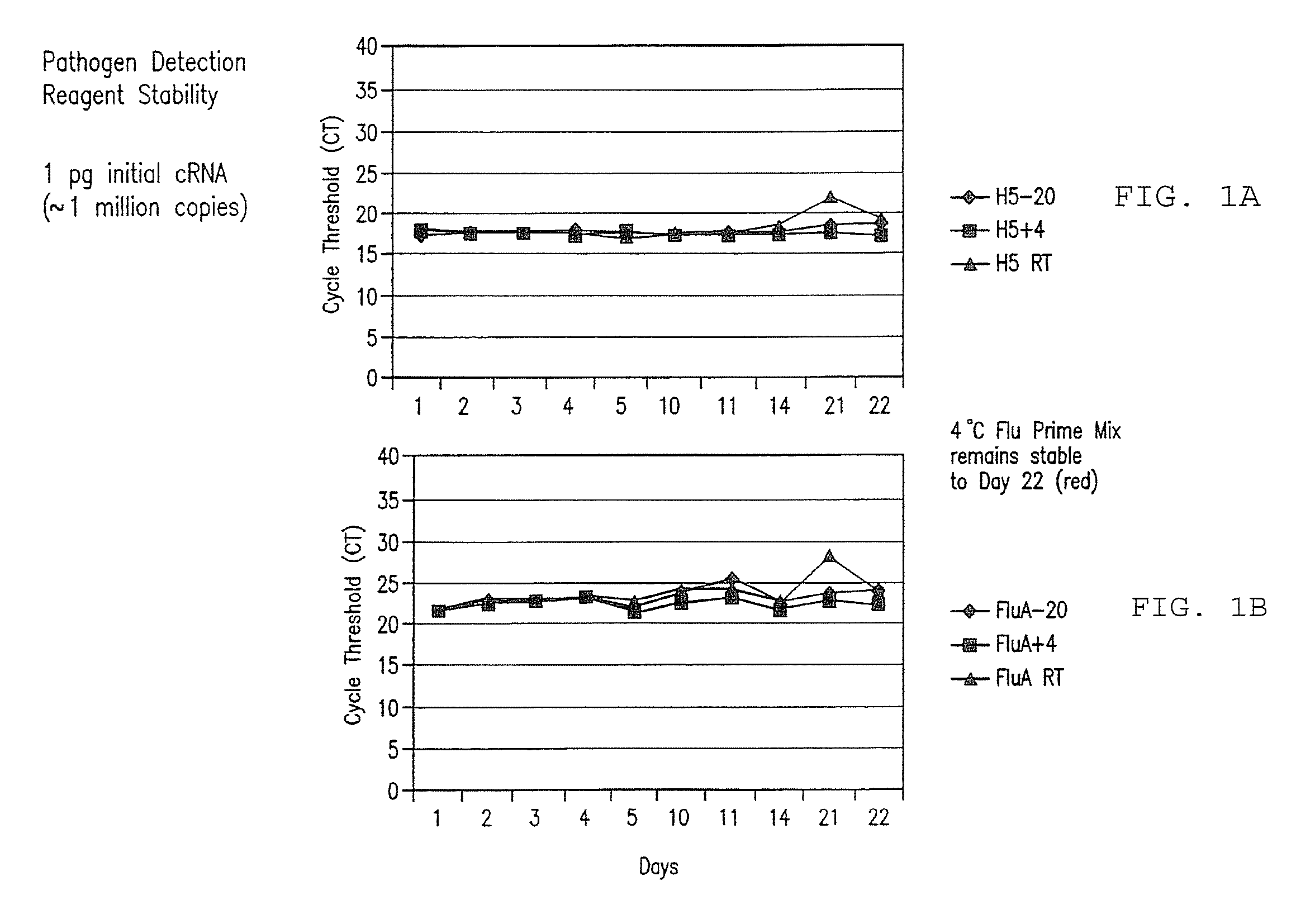
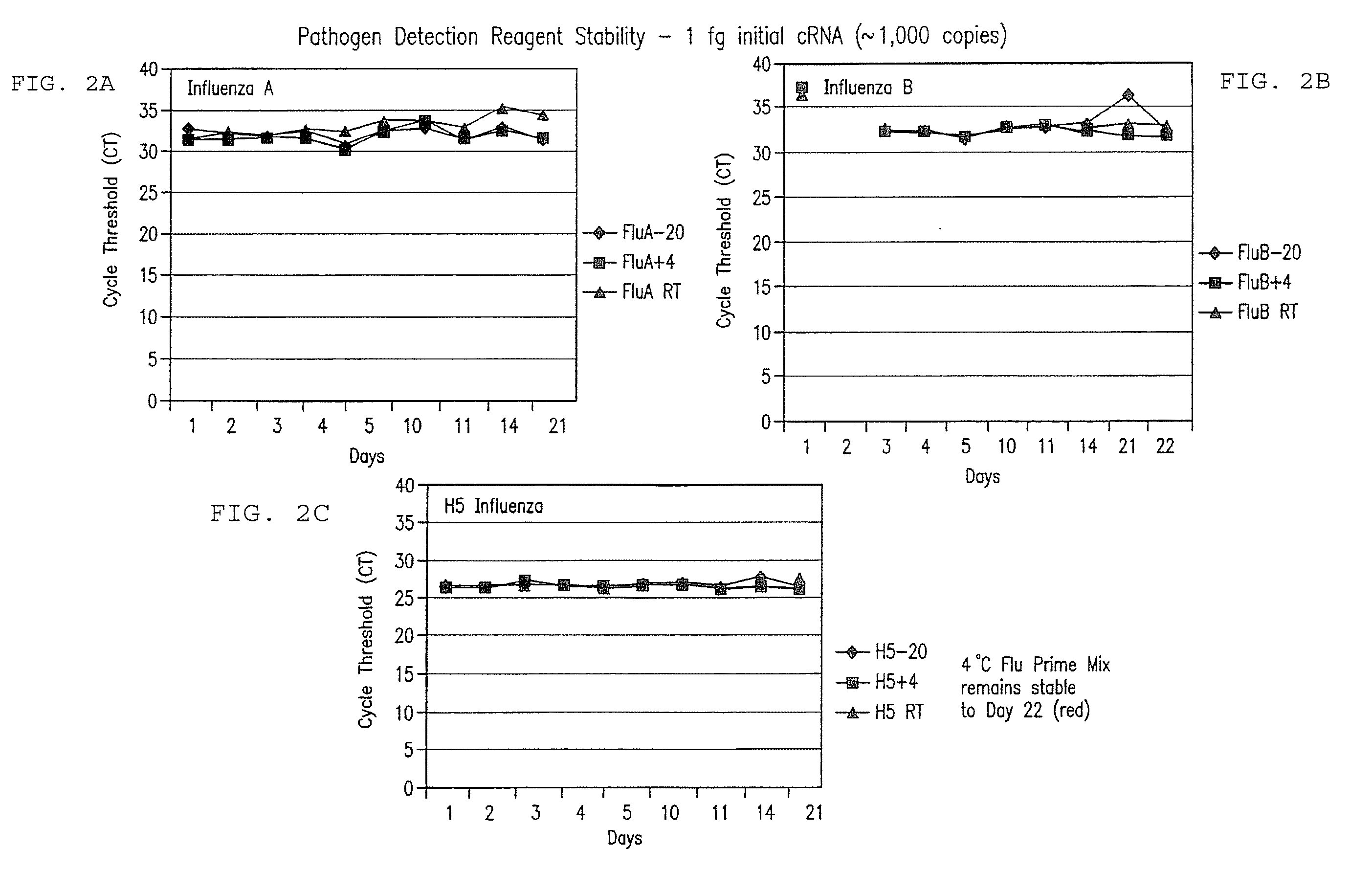
Compositions and method for rapid, real-time detection of influenza a virus (H1N1) swine 2009
ActiveUS20100009343A1Quick checkQuick identificationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic Acid ProbesField analysis
Disclosed are oligonucleotide amplification primers and detection probes specific for the amplification and detection of pathogenic organisms, including for example, specific Influenza A H1N1 viral isolates. Also disclosed is a biological organism identification kit including the disclosed nucleic acid probes and primers, as well as thermal cycling reagents that is both portable and durable, and may also be self-contained for remote, or in-field analysis and identification of particular influenza isolates from a variety of biological specimen types.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Methods for using resonance energy transfer-based assay of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion, and kits for practicing same
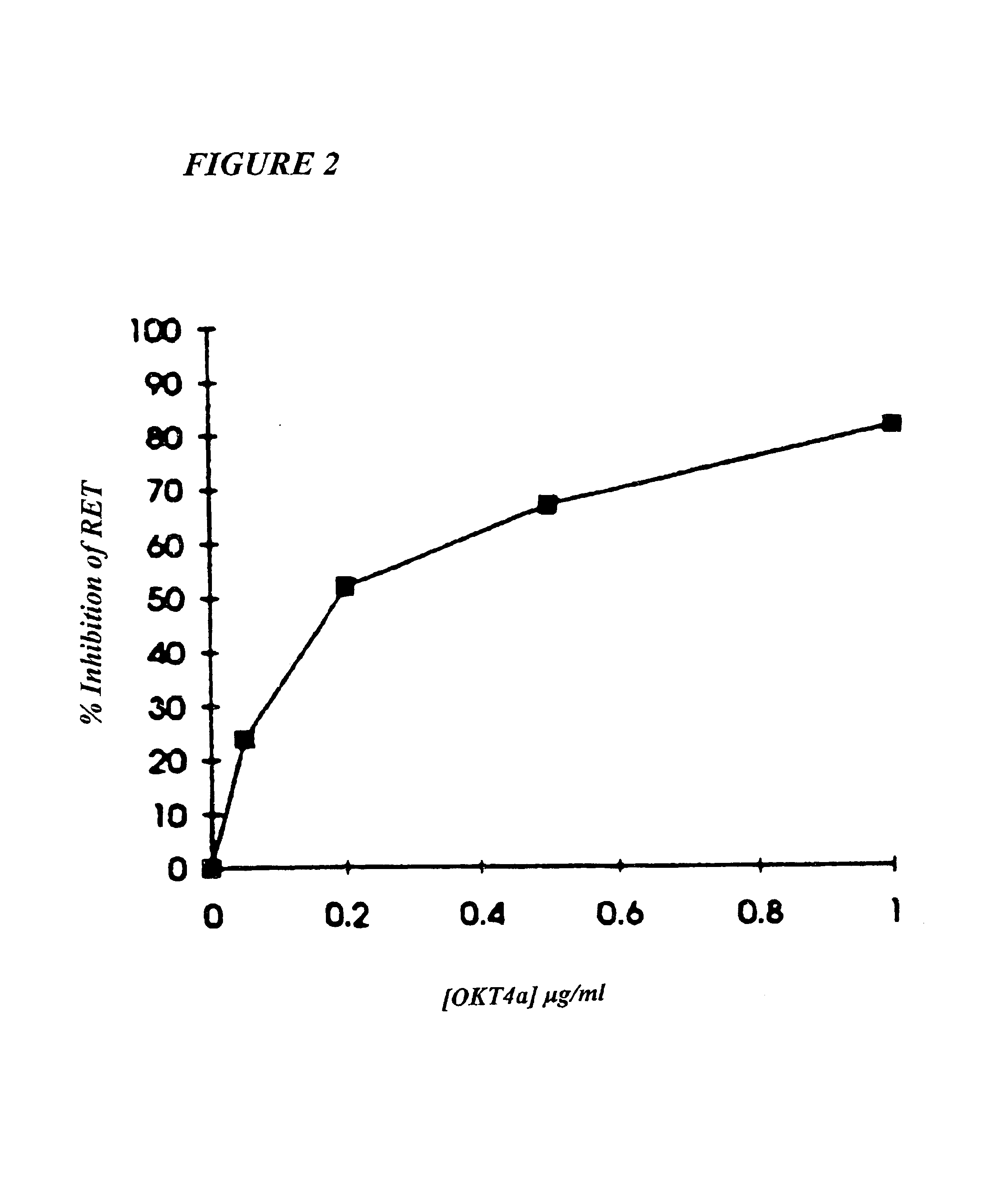
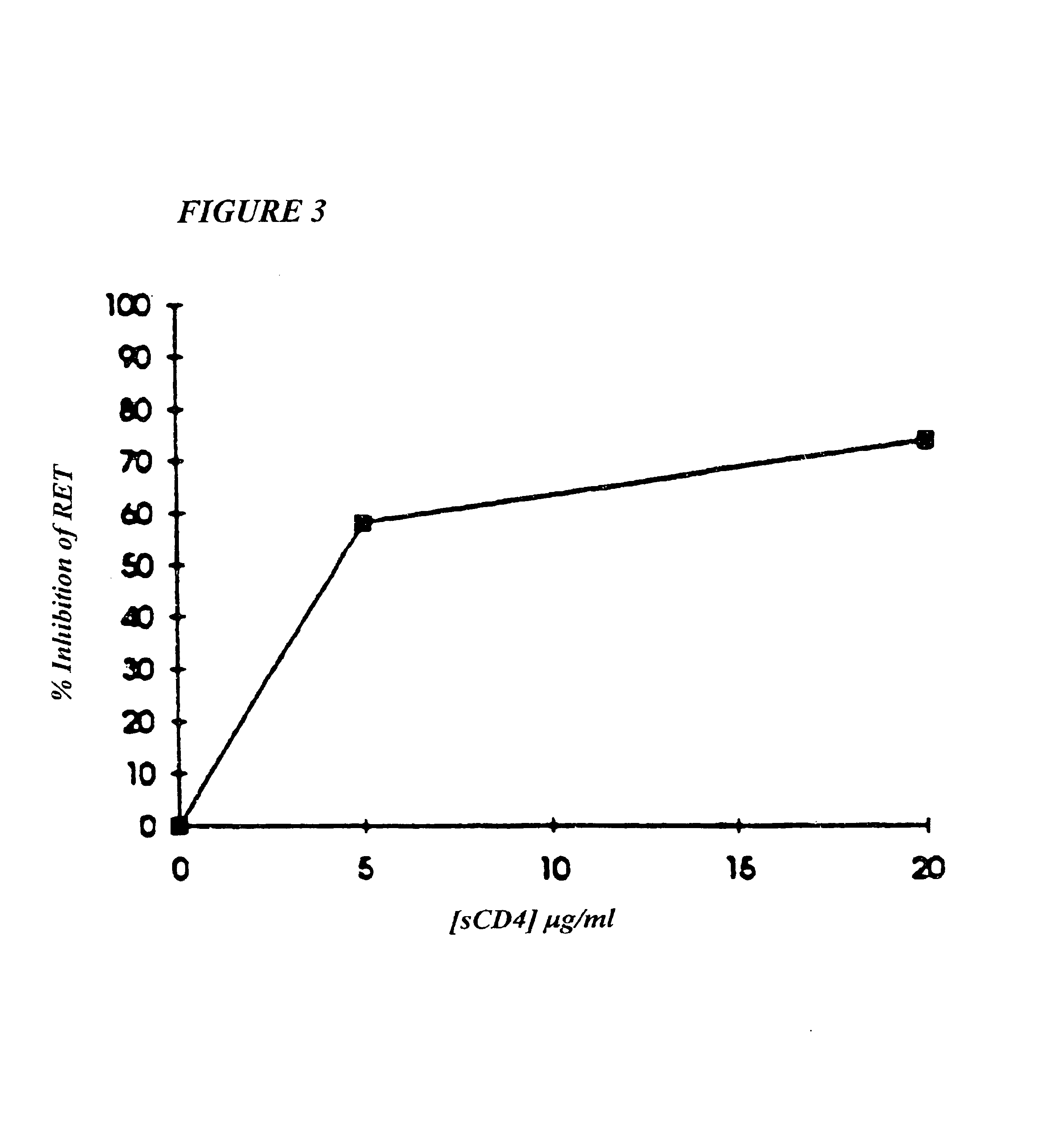
This invention provides: agents determined to be capable of specifically inhibiting the fusion of a macrophage-tropic primary isolate of HIV-1 to a CD4+ cell, but not a T cell-tropic isolate of HIV-1 to a CD4+ cell; and agents determined to be capable of specifically inhibiting the fusion of a T cell-tropic isolate of HIV-1 to a CD4+ cell, but not a macrophage-tropic primary isolate of HIV-1 to a CD4+ cell. This invention also provides: agents capable of specifically inhibiting the fusion of a macrophage tropic primary isolate of HIV-1 with a CD+ cell susceptible to infection by a macrophage-tropic primary isolate of HIV-1; and agents capable of specifically inhibiting the fusion of a T cell-tropic isolate of HIV-1 with a CD4+ cell susceptible to infection by a T cell-tropic isolate of HIV-1. The agents include but are not limited to antibodies. This invention further provides: methods of inhibiting fusion of a macrophage-tropic primary isolate of HIV-1 with a CD+ cell susceptible to infection by a macrophage-tropic primary isolate of HIV-1 which comprises contacting the CD4+ cell with an amount of an agent capable of specifically inhibiting such fusion so as to thereby inhibit such fusion; and methods of inhibiting fusion of a T cell-tropic isolate of HIV-1 with a CD4+ cell susceptible to infection by a T cell-tropic isolate of HIV-1 which comprises contacting the CD4+ cell with an amount of an agent capable of specifically inhibiting such fusion so as to thereby inhibit such fusion.
Owner:CYTODYN
INDUCTION OF BROADLY REACTIVE NEUTRALIZING ANTIBODIES BY FOCUSING THE IMMUNE RESPONSE ON V3 EPITOPES OF THE HIV-1 gp120 ENVELOPE
InactiveUS20080279879A1Vigorous Ab responseViral antigen ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousNeutralizing antibody
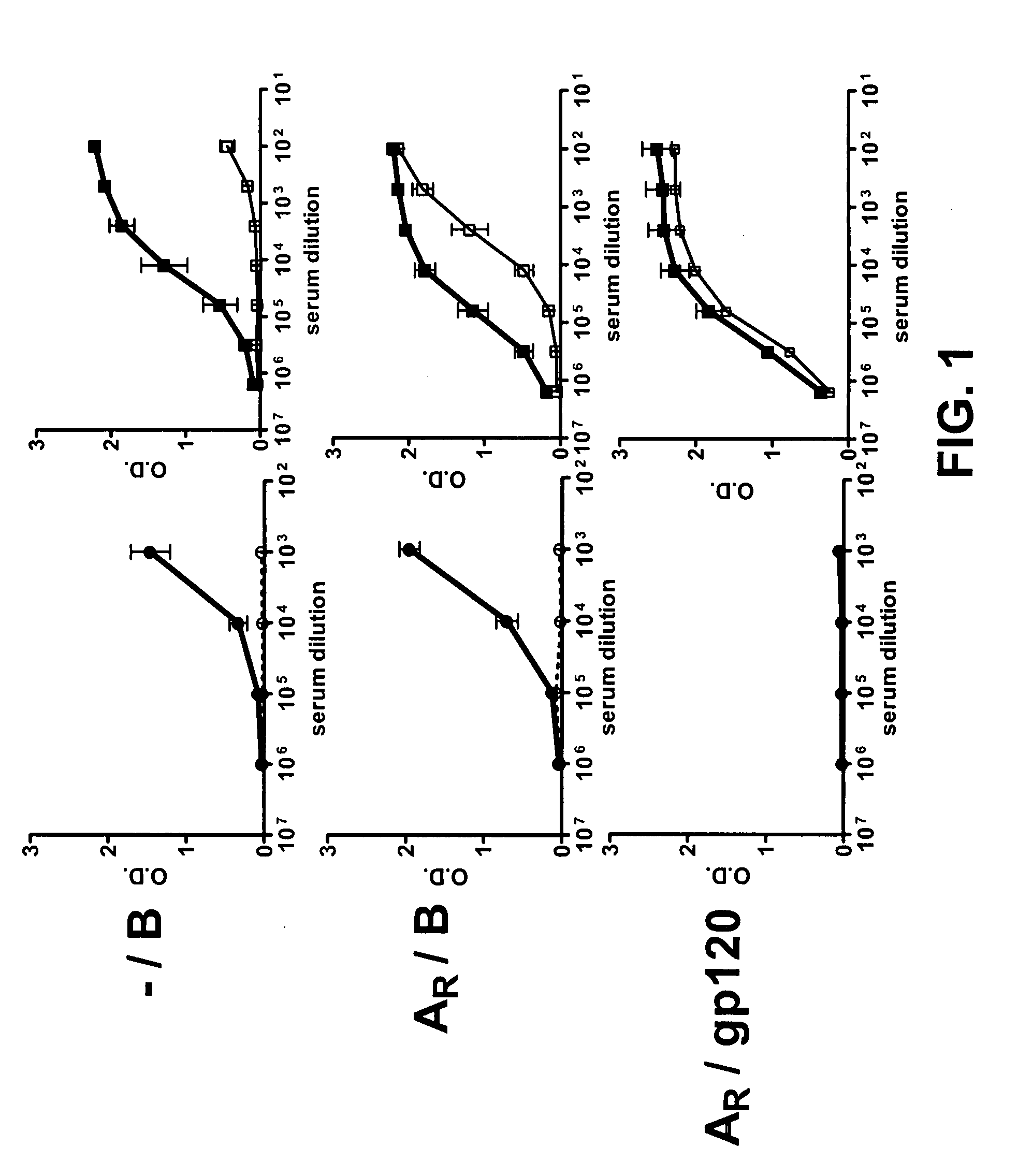
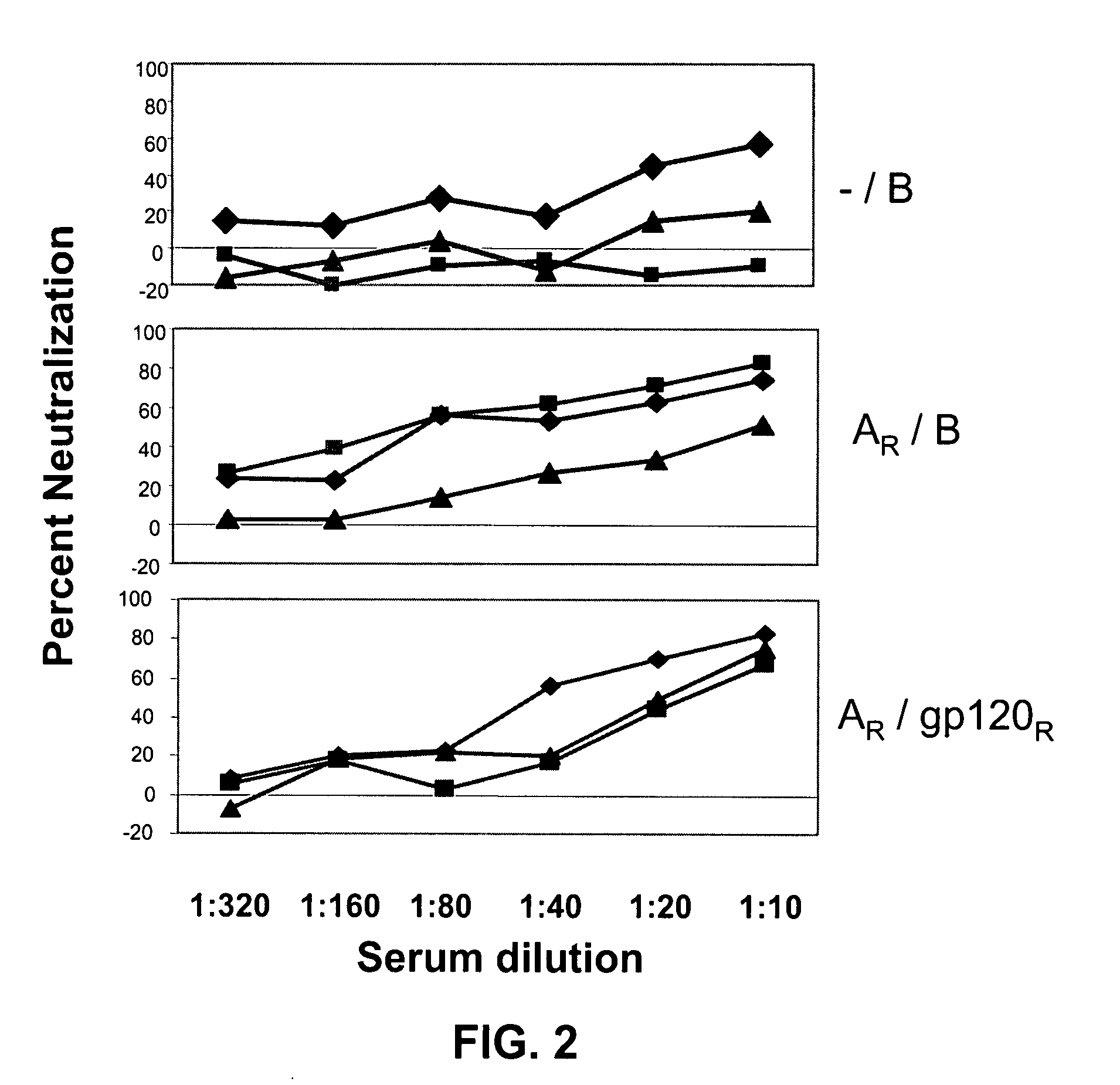
Compositions, kits and methods for boosting, or for priming and boosting, high titer broadly neutralizing cross-clade antibody responses focused on single HIV-1 neutralizing epitopes are disclosed. gp120 DNA plasmids comprising HIV env genes are used to prime the antibody response. Primed subjects are immunized with recombinant fusion proteins that comprise a “carrier” protein fusion partner, preferably a truncated form of the MuLV gp70 Env protein, and a desired HIV neutralizing epitopes. Preferred epitopes are epitopes of V3 from one or more HIV clades. Immune sera from such immunized subjects neutralized primary isolates from virus strains heterologous to those from which the immunogens were constructed. Neutralizing activity was primarily due to V3-specific antibodies and cross-clade neutralizing Abs were present. This approach results in more potent and broader neutralizing antibody levels, a result of “immunofocusing” the humoral immune response on neutralizing epitopes such as V3.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Porcine reproductive and respiratory syndrome isolates and methods of use
InactiveUS20060063151A1Improve immunityIncrease virulenceSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementVirulent characteristicsImmunogenicity
A method of predicting the virulence of a new or uncharacterized PRRS virus isolate is provided wherein the isolate is injected into swine and allowed to replicate for a period of from about 3-15 days. During this period, the rate of virus growth and / or the magnitude of viremia is determined, and this data is compared with a corresponding growth rate and / or viremia magnitude of a PRRS virus isolate of known virulence, as a measure of the virulence of the new or uncharacterized isolate. Additionally, a method of selecting an isolate for inclusion in an immunogenic composition based on the predicted virulence is also provided, together with compositions incorporating attenuated forms of viruses predicted to be virulent.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Compositions and method for rapid, real-time detection of influenza A virus (H1N1) swine 2009
ActiveUS8097419B2Rapid detection and identificationMinimize and eliminate contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsH1n1 virusNucleic Acid Probes
Disclosed are oligonucleotide amplification primers and detection probes specific for the amplification and detection of pathogenic organisms, including for example, specific Influenza A H1N1 viral isolates. Also disclosed is a biological organism identification kit including the disclosed nucleic acid probes and primers, as well as thermal cycling reagents that is both portable and durable, and may also be self-contained for remote, or in-field analysis and identification of particular influenza isolates from a variety of biological specimen types.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Consensus/ancestral immunogens
The present invention relates, in general, to an immunogen and, in particular, to an immunogen for inducing antibodies that neutralizes a wide spectrum of HIV primary isolates and / or to an immunogen that induces a T cell immune response. The invention also relates to a method of inducing anti-HIV antibodies, and / or to a method of inducing a T cell immune response, using such an immunogen. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding the present immunogens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA +2
Methods for genetic analysis of SARS virus
The invention provides arrays and probes for resequencing a SARS virus using an array of probes that are complementary to a SARS reference sequence and to each possible single nucleotide substitution of the reference sequence. Methods of identifying mutations in viral sequences and methods of characterizing viral isolates are also provided. The invention also provides high throughput methods to monitor epidemics and pandemics caused by pathogens such as viruses.
Owner:AFFYMETRIX INC
Nucleic acids encoding modified human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) group M consensus envelope glycoproteins
The present invention relates, in general, to an immunogen and, in particular, to an immunogen for inducing antibodies that neutralizes a wide spectrum of HIV primary isolates and / or to an immunogen that induces a T cell immune response. The invention also relates to a method of inducing anti-HIV antibodies, and / or to a method of inducing a T cell immune response, using such an immunogen. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding the present immunogens.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ALABAMA +2
Compositions and Methods for Rapid, Real-Time Detection of Influenza A Virus (H1N1) Swine 2009
ActiveUS20120115126A1Rapid detection and identificationMinimize and eliminate contaminationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsH1n1 virusNucleic Acid Probes
Disclosed are oligonucleotide amplification primers and detection probes specific for the amplification and detection of pathogenic organisms, including for example, specific Influenza A H1N1 viral isolates. Also disclosed is a biological organism identification kit including the disclosed nucleic acid probes and primers, as well as thermal cycling reagents that is both portable and durable, and may also be self-contained for remote, or in-field analysis and identification of particular influenza isolates from a variety of biological specimen types.
Owner:LONGHORN VACCINES & DIAGNOSTICS LLC
Methods for assaying inhibition of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
Method for Replicating Influenza Virus in Culture
InactiveUS20080187546A1Save critical timeShorten the timeSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntiviralsTissue cultureInfluenza C Virus
The invention is related to a method for selecting an influenza virus for growth on tissue culture cells to produce a tissue-culture adapted viral isolate. The invention also includes vaccines produced from the isolate.
Owner:INTERVET INC
Modified HIV-1 clade C envelope glycoprotein immunogens comprising deletions in the gp120/gp41 cleavage site and gp41 fusion domain
The present invention relates, in general, to an immunogen and, in particular, to an immunogen for inducing antibodies that neutralize a wide spectrum of HIV primary isolates and / or to an immunogen that induces a T cell immune response. The invention also relates to a method of inducing anti-HIV antibodies, and / or to a method of inducing a T cell immune response, using such an immunogen. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding the present immunogens.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
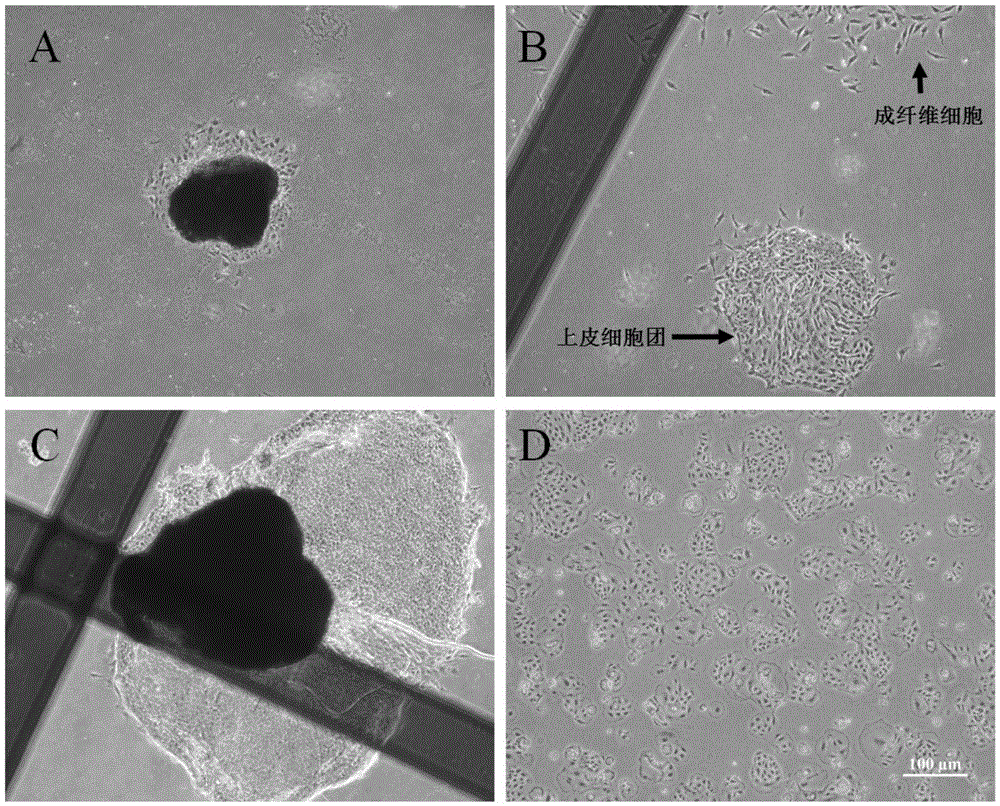
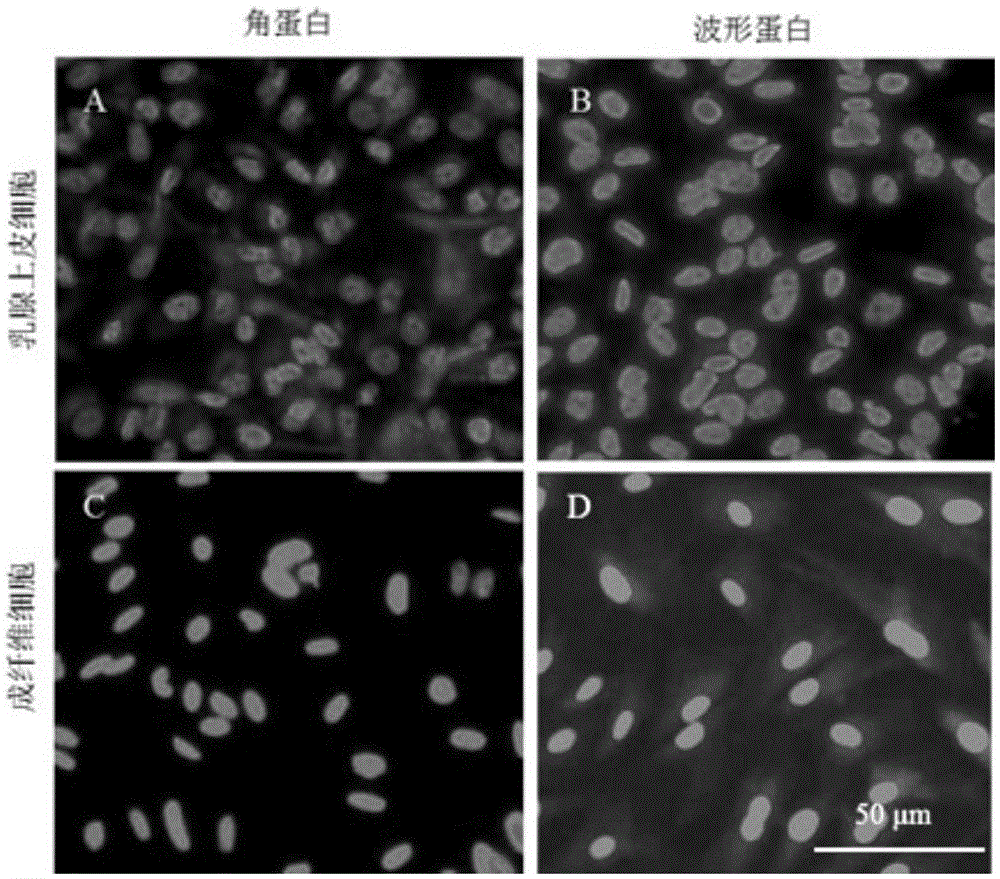
Primary isolated culture method for dairy cow mammary epithelial cells
InactiveCN105543164AReduced activityShorten the timeCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsHyaluronidaseMammary gland structure
The invention discloses a primary isolated culture method for dairy cow mammary epithelial cells. The primary isolated culture method comprises steps as follows: mammary tissue of a dairy cow in the lactation period is shorn into tissue blocks, the tissue blocks are digested with collagenase / hyaluronidase digestive juice, a culture dish is inoculated with the digested chylous tissue blocks for culture, cells get free from tissue on peripheries of the tissue blocks after 1-2 days and grow along the wall of the culture dish, fusiform fibroblast is removed with a mechanical scraping method every day during culture, and initial passage is performed when a large quantity of cobblestone-like mammary epithelial cells grow in clusters and in patches and are mutually fused after about 4-5 days. During initial passage, a little fibroblast which is probably mixed is eliminated with trysin with a differential digestive method, and the dairy cow mammary epithelial cells with high purity are obtained. The mammary epithelial cells can emigrate from chylous tissue in a short time; a little mixed fibroblast is removed mainly with a mechanical scraping method, and accordingly, the obtained mammary epithelial cells are seldom damaged and are high in purity.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Production of viruses, viral isolates and vaccines
InactiveUS20080050403A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseViral antigen ingredientsBiologyReceptor for activated C kinase 1
The present invention discloses methods for producing and / or propagating virus particles, such as influenza virus particles, that are present in a virus isolate obtained from an infected subject by contacting a host cell with a virus particle and culturing the cell under conditions conducive to propagation of the virus particle. The invention also provides a method for selective propagation of a set of virus particles, such as influenza virus particles present in an influenza isolate, which have an affinity for receptors comprising a specific glycosylation residue.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Isolated culture method of porcine fat stem cells
InactiveCN104673745AEasy to isolate and cultureStrong proliferative growth abilitySkeletal/connective tissue cellsAnimal sciencePhosphate
The invention discloses an isolated culture method of porcine fat stem cells, which comprises the following steps: extracting porcine subcutaneous fat tissues, washing the fat tissues with a double-antibody-containing PBS (phosphate buffer solution), adding a I-type collagenase digestive juice into the fat tissues for digestion to obtain porcine fat stem cells, and culturing in an EGF-containing serum-free culture medium. The porcine fat stem cell isolated culture method can reduce the influence of blood and other impurities in the fat tissue source on the enzymolysis fat and shorten the fat enzymolysis time of the I-type collagenase; the serum-free culture medium is utilized to culture the primary cells; and proper growth factors are added into the culture medium, so that the porcine fat stem cells can be better subjected to isolated culture and maintain high proliferation and growth capacity, thereby establishing a porcine fat stem primary isolated culture method conforming to the Standard Specification.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Recombinant HIV-1 gp120 immunogen with three different V3 loops from viruses of different clades
InactiveUS7847085B2Minimize potentialUtility in researchSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsDNA constructImmunogenicity
A novel immunogenic HIV-1 Env, particularly gp120, DNA construct is disclosed in which either the V1 / V2 loop and the V4 loop, or all three variable loops, including V3, are replaced with a V3 sequence each of which is from a different viral isolate. Preferably, each replacement V3 loop is a consensus sequence of V3 of a different clade. Such constructs are useful as immunogens as each presents three independent V3 epitopes, so that the immunized subject generates a more broadly reactive neutralizing antibody response than with conventional gp120 or V3 DNA or polypeptide immunogens. Also disclosed are methods of using the DNA construct to immunize a mammal, preferably a human, particularly in a priming regiment in which the DNA immunogen is followed by administration of a V3 fusion protein boosting immunogen.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
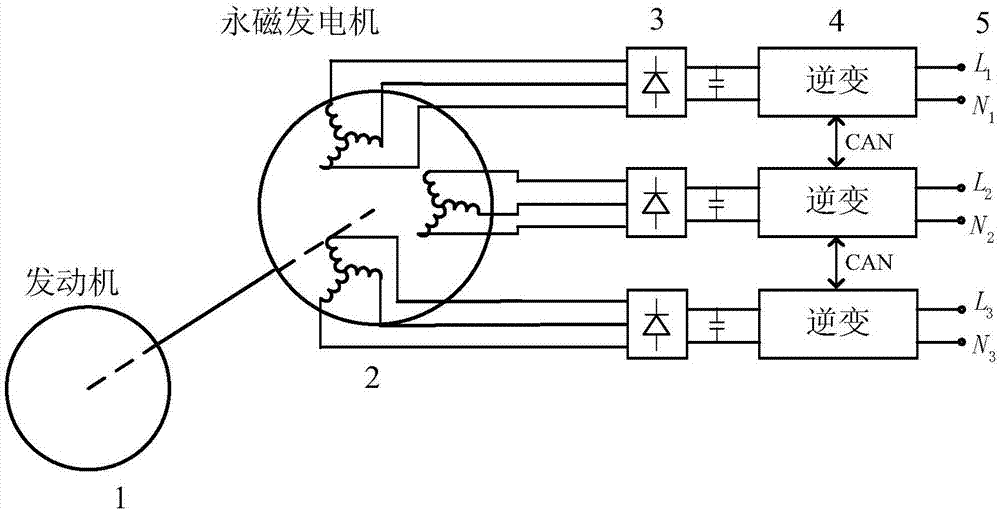
Single-phase/three-phase combined inverter power supply device for independent power generation situation
InactiveCN106972758AReduce pressure requirementsSimple structureAc-ac conversionEngineeringConductor Coil
The invention relates to a single-phase / three-phase combined inverter power supply device for an independent power generation situation, which belongs to the field of independent power generation and power supply. The device comprises a permanent magnet generator with output of three sets of isolated three-phase windings, three rectifier modules and three single-phase inverters, wherein the permanent magnet generator outputs three ways of isolated AC; and three ways of isolated DC are obtained through the rectifier modules as input of the three single-phase inverters. Due to the independent winding structure of the generator, DC bus isolation of the system inverter is realized, no primary isolated DC / DC converter needs to be added, the structure is simplified, and the size and the weight is little. Through reasonably arranging the generator winding distribution, the output voltage harmonic can be reduced.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
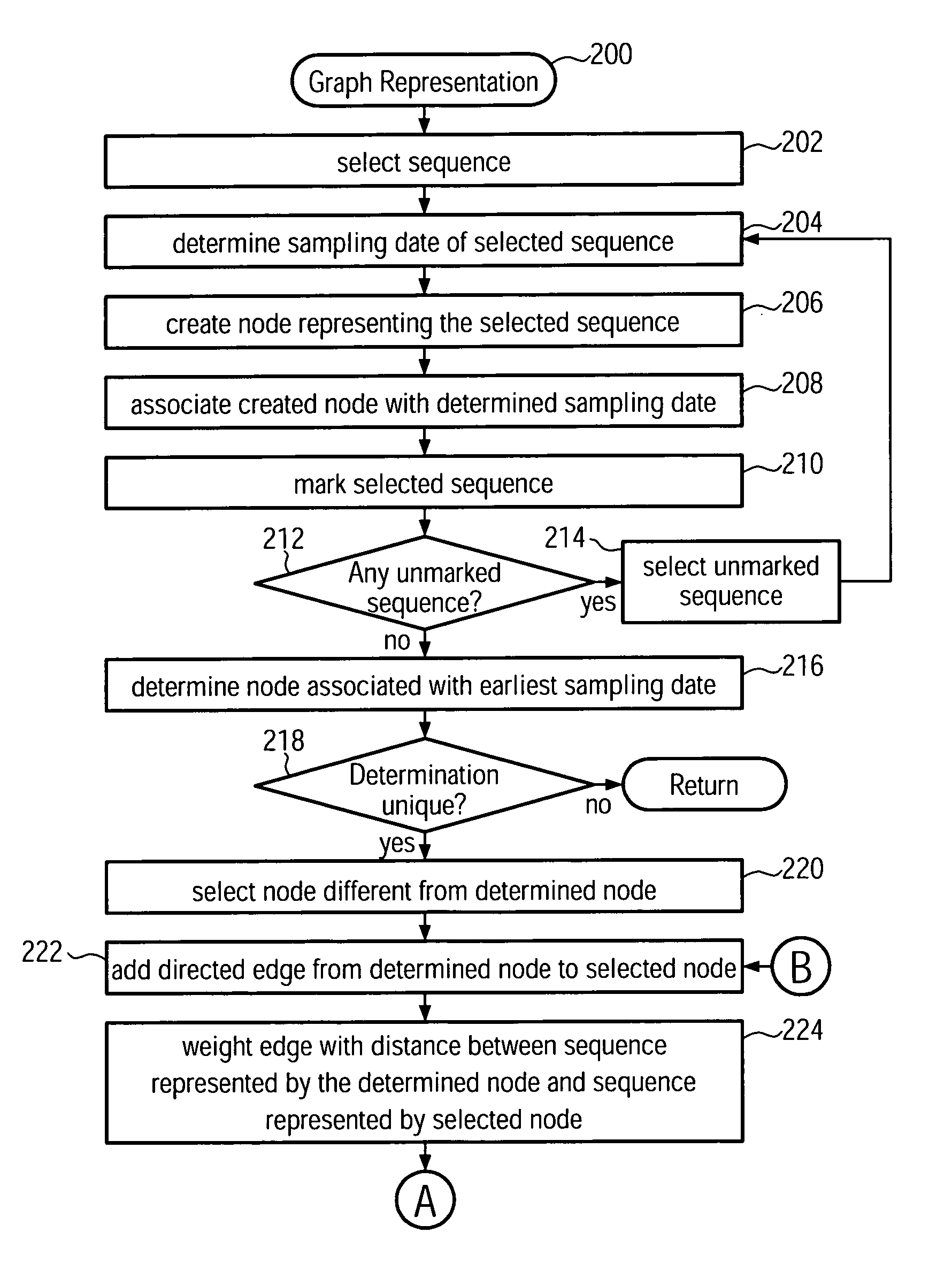
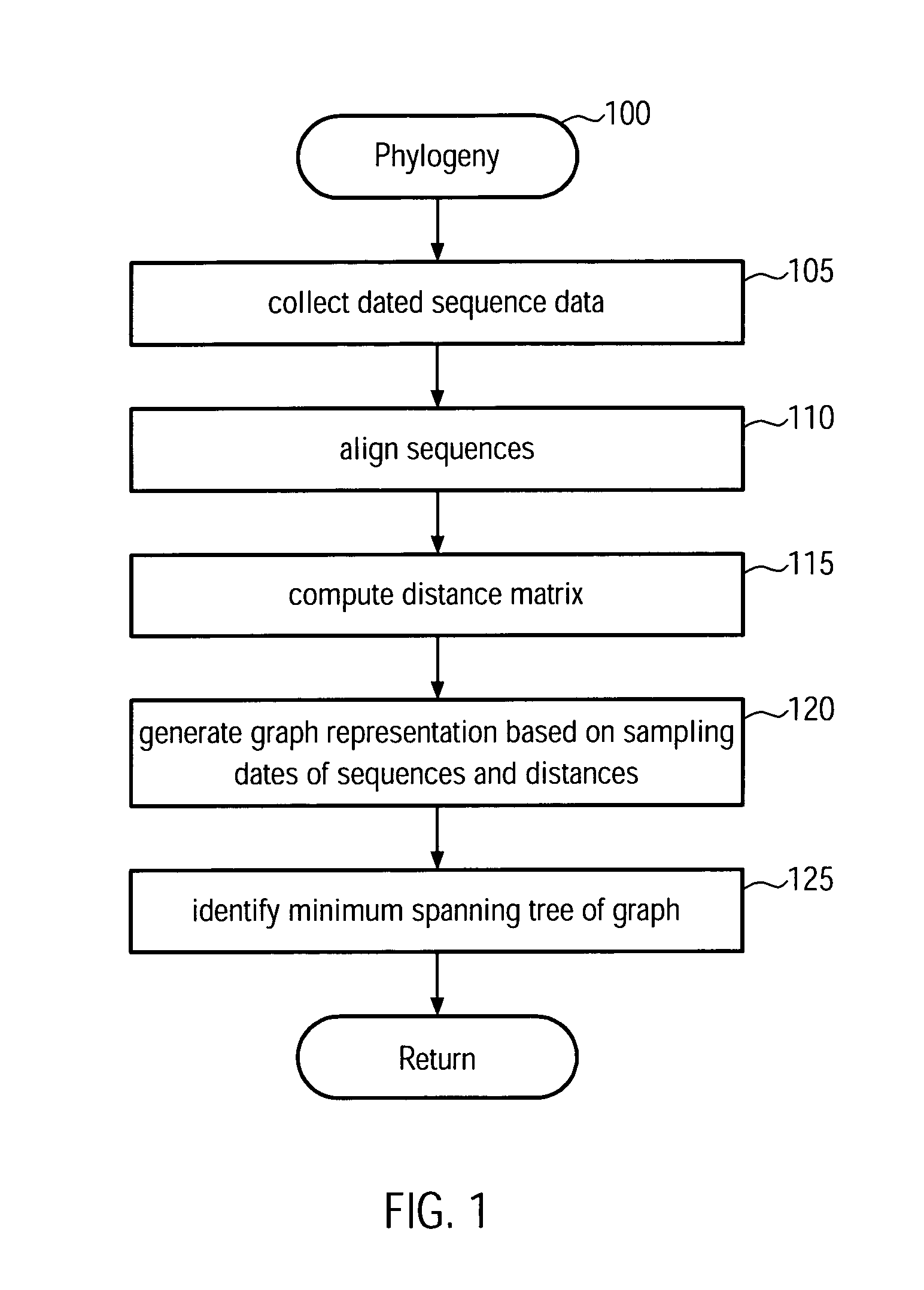
Method and system for building a phylogeny from genetic sequences and using the same for recommendation of vaccine strain candidates for the influenza virus
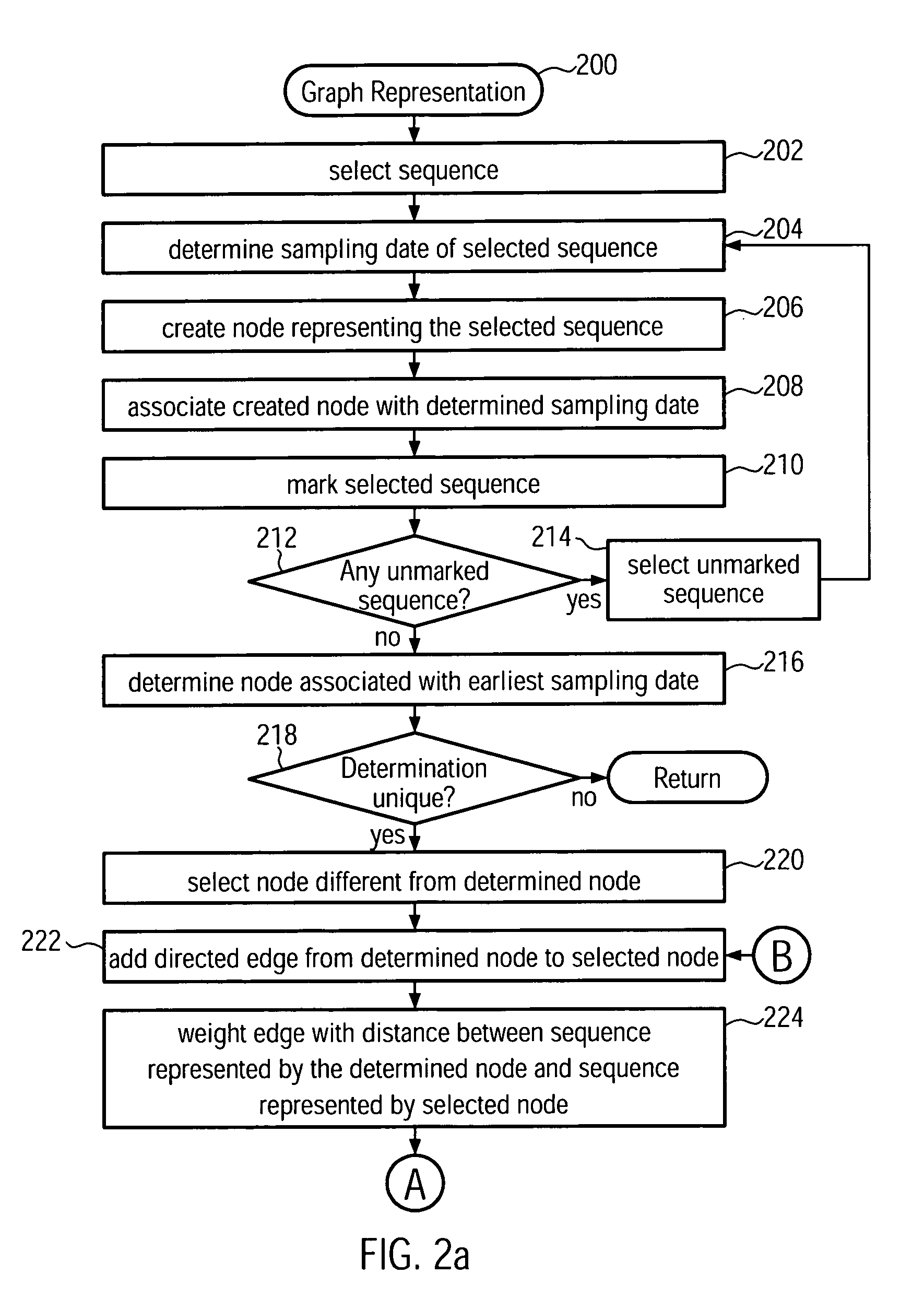
A computer-implemented method and a computer system for identifying a phylogenetic tree from a plurality of biological sequences is provided. Each biological sequence is associated with a sampling date. First, the plurality of biological sequences is aligned and a distance matrix is obtained. Then, a subset of these sequences without any duplicated sequences is selected and a directed graph representation of the subset of biological sequences is generated based the associated sampling dates. Then, a minimum spanning tree is computed from the weighted directed graph representation. Then, in an iterative procedure, the sequences of unsampled evolutionary intermediates are inferred from mutation patterns that reflect the difference in sequence between the nodes in the minimum spanning tree. The new sequences are added with associated time stamps to the sequence set. Then, sets of identical sequences are removed. Then, an optimum branching is recomputed. This step is repeated until no new intermediates are found. In the final step, the sequences that have been set aside in the initializing step are added to the plurality of sequences derived in the update step. From this plurality of sequences an optimum branching is computed and identified as the phylogenetic tree. Amino acid changes repeatedly occurring on the internal branches of the obtained tree can be used to identify sequences and associated viral isolates suitable as vaccine strains for the following influenza season.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Infectious bursal disease virus strain A11 and application thereof
ActiveCN105802920AStrong immune protectionResistance to virulent attacksViral antigen ingredientsMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBiological property
The invention discloses an infectious bursal disease virus strain A11 and application thereof, and belongs to the field of the microbial technology. Infectious bursal disease viruses are separated from infectious bursal disease vaccine immunity failure chicken flocks appearing in recent years, biological characteristic analysis is carried out on obtained virus isolate strains, and the infectious bursal disease virus strain A11 with good biological characteristics is screened out from the obtained virus isolate strains and is a currently-popular infectious bursal disease virus with super-strong virulence. The virulence of the virus is attenuated with a chicken embryo and cell continuous passage method to culture the low-virulence strain A11, the low-virulence strain A11 has super-strong reproductivity in cells, the virus yield in cells reaches up to 10<11> TCID50 / 0.1 ml, immune protection resisting infectious bursal disease viruses can be rapidly generated by immunizing chicks with the strain A11, immune protection can be achieved after 1 week, and the strain A11 has huge application value in developing new specific infectious bursal disease vaccines.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Consensus/ancestral immunogens
InactiveUS20090162384A1Viral antigen ingredientsSnake antigen ingredientsNucleic acid sequencingT cell immunity
The present invention relates, in general, to an immunogen and, in particular, to an immunogen for inducing antibodies that neutralize a wide spectrum of HIV primary isolates and / or to an immunogen that induces a T cell immune response. The invention also relates to a method of inducing anti-HIV antibodies, and / or to a method of inducing a T cell immune response, using such an immunogen. The invention further relates to nucleic acid sequences encoding the present immunogens.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Seneca valley virus SVV-ZM-201801 and application thereof
ActiveCN109554352APromote rapid proliferationHigh titerSsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsCytopathic effectCulture cell
The invention provides a Seneca valley virus SVV-ZM-201801 and an application thereof. Separation is performed from pig tissues, and sub-culture and plaque purification are performed, so that the Seneca valley virus is obtained. The separated strain can be stably proliferated on sub-culture cells, typical cytopathic effects are formed, and the virus titer is as high as 108.5-1010.5TCID50 / mL. The separated strain does not have obvious pathogenicity on piggies. The Seneca valley virus separated strain has good proliferating properties, and is good in immunogenicity. Vaccines prepared from the separated strain can induce the piggies to generate high-level neutralizing antibodies, and powerful technical support is provided for effective prevention and control of the Seneca valley virus.
Owner:CHINA ANIMAL HUSBANDRY IND
Designed deimmunized monoclonal antibodies for protection against HIV exposure and treatment of HIV infection
ActiveUS7501494B2Low costProphylaxis of HIV exposureAntiviralsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsDiseaseImmunodeficiency virus
This invention is directed to deimmunized antibodies that are useful as immunotherapeutic drugs against Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and CD4-mediated autoimmune disorders. More specifically, antibodies expressed by clones, Clone 7 containing the recombinant genes B4DIVHv1 / VK1CHO#7, Clone 16 containing the recombinant genes B4DIVHv1 / VK1#16, and clone 21 containing the recombinant genes B4DIVHv1 / VK1#21, are derived from mouse monoclonal B4 antibody (mAb B4). The antibodies were produced by removing particular murine determinants recognized as foreign by the human immune system. These recombinant antibodies were generated by the chimerization and deimmunization of the Fv region of mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) B4. For improved safety, the coding sequence may further be mutated to express an aglycosylated IgG1 antibody that is unable to bind complement. The deimmunized antibodies retain the specificity of the murine mAb B4 for a receptor complex involving CD4 on the surface of the host T cells, and retain the characteristic ability of mAb B4 to neutralize primary isolates of HIV.
Owner:UBI US HLDG LLC
Ethernet port lightning protection device and lightning protection circuit
ActiveCN101719665AImprove lightning protection effectImprove lightning protection levelEmergency protective arrangements for limiting excess voltage/currentEngineeringPrinted circuit board
The invention relates to an Ethernet port circuit and provides an external Ethernet port lightning protection circuit, an external lightning protection device and an internal Ethernet port lightning circuit which are used for improving the lightning surge preventing capability of the traditional Ethernet port. A primary isolated transformer is added on the basis of the traditional first-stage isolated transformer to form a double isolated protection; the Ethernet port lightning protection device is added on the external Ethernet port lightning protection circuit under the condition without making any change on the traditional network equipment, so that the lightning preventing capability of the network equipment is remarkably improved, an extra grounded wire is free from being arranged and the deployment is convenient. The internal Ethernet port lightning circuit adopts the compatible design, and an RJ45 with a transformer port is used to doubly improve the lightning preventing capability while not adding the area of a printed circuit board when the lightning preventing protection needs enhancing.
Owner:MAIPU COMM TECH CO LTD
Deimmunized monoclonal antibodies for protection against HIV exposure and treatment of HIV infection
InactiveUS20090060914A1Low costMass productionAnimal cellsSugar derivativesDiseaseImmunodeficiency virus
This invention is directed to deimmunized antibodies that are useful as immunotherapeutic drugs against Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) and CD4-mediated autoimmune disorders. More specifically, antibodies expressed by clones, Clone 7 containing the recombinant genes B4DIVHv1 / VK1CHO#7, Clone 16 containing the recombinant genes B4DIVHv1 / VK1#16, and clone 21 containing the recombinant genes B4DIVHv1 / VK1#21, are derived from mouse monoclonal B4 antibody (mAb B4). The antibodies were produced by removing particular murine determinants recognized as foreign by the human immune system. These recombinant antibodies were generated by the chimerization and deimmunization of the Fv region of mouse monoclonal antibody (mAb) B4. For improved safety, the coding sequence may further be mutated to express an aglycosylated IgG1 antibody that is unable to bind complement. The deimmunized antibodies retain the specificity of the murine mAb B4 for a receptor complex involving CD4 on the surface of the host T cells, and retain the characteristic ability of mAb B4 to neutralize primary isolates of HIV.
Owner:UBI US HLDG LLC
Freezing medium, application thereof and adipose tissue freezing method
InactiveCN106719602AImprove protectionHigh activityDead animal preservationCell activityEssential amino acid
The invention relates to the technical field of cells, in particular to a freezing medium, application thereof and an adipose tissue freezing method. The freezing medium comprises a basic culture solution, an NEAA (non-essential amino acid), DMSO, glycerol and 1,2-propanediol, and has a good protection effect on adipose tissue. Cells in adipose tissue which is thawed after being frozen by the freezing medium keep good activity. The success rate of obtaining adipose-derived stem cells by primary isolated culture is 100 percent.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Fibroblasts derived from multiple tissue sources of native dog through primary isolated culture and immortalization construction method of fibroblasts
PendingCN112574946AHigh activitySimple and fast operationCell dissociation methodsArtificial cell constructsDiseaseMuscle tissue
The invention provides fibroblasts derived from multiple tissue sources of a native dog through primary isolated culture and an immortalization construction method of the fibroblasts, and belongs to the technical field of cell culture. Heart tissue, lung tip muscle tissue or leg muscle tissue of the native dog are used as materials and subjected to enzymolysis and separation of pancreatin and / or collagenase II, and myocardial fibroblasts, lung fibroblasts and myofibroblasts with typical fibroblast morphological characteristics are obtained. The myocardial fibroblasts, the pulmonary fibroblastsand the myofibroblasts which are subjected to primary isolated culture are transfected by SV40T virus liquid, and then puromycin screening culture and passage are performed to obtain immortalized myocardial fibroblasts, pulmonary fibroblasts and myofibroblasts. Compared with primary culture cells, the immortalized constructed cells are higher in growth speed and remarkably improved in activity, and a material basis is provided for dogs in the aspects of scientific research, disease research and the like.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Primary isolated culture method for amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells
ActiveCN104830764AAvoid damageAvoid pollutionSkeletal/connective tissue cellsCulture fluidAmniotic fluid
The invention relates to the technical field of stem cell culture, in particular to a primary isolated culture method for amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells. The method includes that according to a differential attachment principle, endothelial cells are enabled to grow along a wall under proper conditions while the mesenchymal stem cells are not adhered to the wall yet. By accurate control of culture time, culture solution containing the amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells is transferred after wall adherence of the endothelial cells is finished, and the culture solution is subjected to subculturing to obtain the amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells. The method is simple in operation, less devices are required, manual scraping operations are avoided, and accordingly cell damages and contamination are avoided. According to detection results, viability of the amniotic fluid mesenchymal stem cells contained in the culture solution acquired at the step 1 is not lower than 89.28%; after three generations, flow cytometry detection results show that surface antibodies of the cells still accord with characteristics of the stem cells, and differentiating tendency is avoided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU SALIAI STEMCELL SCI & TECH CO LTD
Production of viruses viral isolates and vaccines
The present invention discloses methods for producing and / or propagating virus particles, such as influenza virus particles, that are present in a virus isolate obtained from an infected subject by contacting a host cell with a virus particle and culturing the cell under conditions conducive to propagation of the virus particle. The invention also provides a method for selective propagation of a set of virus particles, such as influenza virus particles present in an influenza isolate, which have an affinity for receptors comprising a specific glycosylation residue.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Method for primary isolated culture of porcine mammary epithelial cells (PMEC)
InactiveCN112048465AAvoid complex environmentsCell dissociation methodsEpidermal cells/skin cellsDiseaseCultured cell
The invention relates to a method for primary isolated culture of porcine mammary epithelial cells (PMEC). The method includes the following steps: (1) performing sampling; (2) performing pretreatment; (3) performing isolation; (4) performing culture; (5) performing subculturing; and (6) performing cell purification. The beneficial effects of the method are as follows: complex environment in vivocan be avoided by establishing a porcine mammary epithelial cell model in vitro; researches on the influences of specific conditions and treatment on the growing status of cells can be carried out without being affected by individual difference; and mammary epithelial cell cultures can be taken as models to research bio-mechanism and disease mechanism in mammary gland organs.
Owner:陈浩东 +1
Method for replicating influenza virus in culture
InactiveCN101610787ASave critical timeSsRNA viruses negative-senseRecovery/purificationTissue cultureInfluenza C Virus
The invention is related to a method for selecting an influenza virus for growth on tissue culture cells to produce a tissue-culture adapted viral isolate. The invention also includes vaccines produced from the isolate.
Owner:SCHERING PLOUGH ANIMAL HEALTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com