Methods for assaying inhibition of HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion
a glycoprotein and membrane fusion technology, applied in the field of methods for inhibiting the assaying of the hiv-1 envelope glycoprotein-mediated membrane fusion, can solve the problems of inability to perform fluorescence measurements, inability to perform assays easily, and inability to be performed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0045] The plasmid designated pMA243 was deposited pursuant to, and in satisfaction of, the requirements of the Budapest Treaty on the International Recognition of the Deposit of Microorganisms for the Purposes of Patent Procedure with the American Type Culture Collection (ATCC), 12301 Parklawn Drive, Rockville, Md. 20852 under ATCC Accession No. 75626. The plasmid pMA243 was deposited with the ATCC on Dec. 16, 1993.
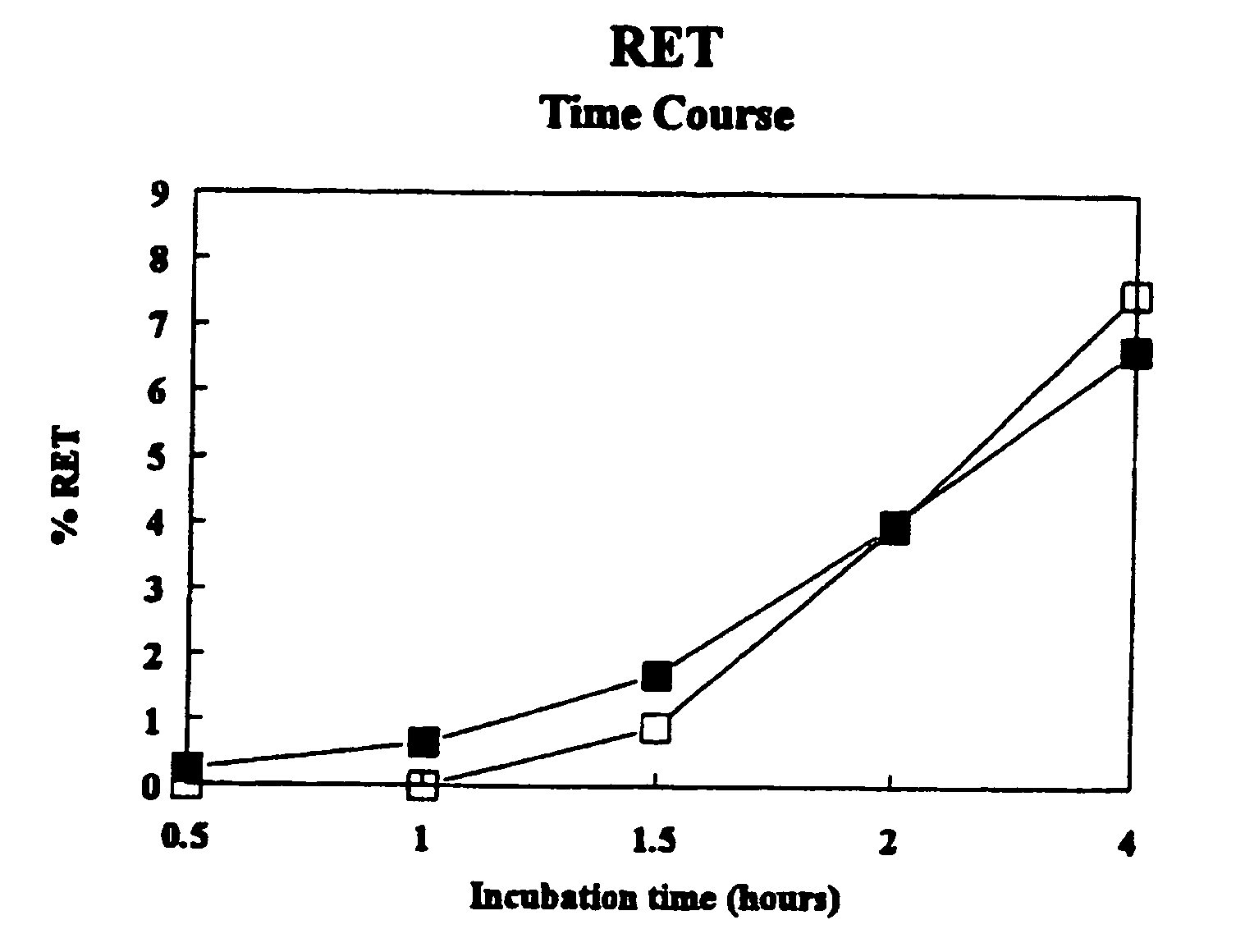
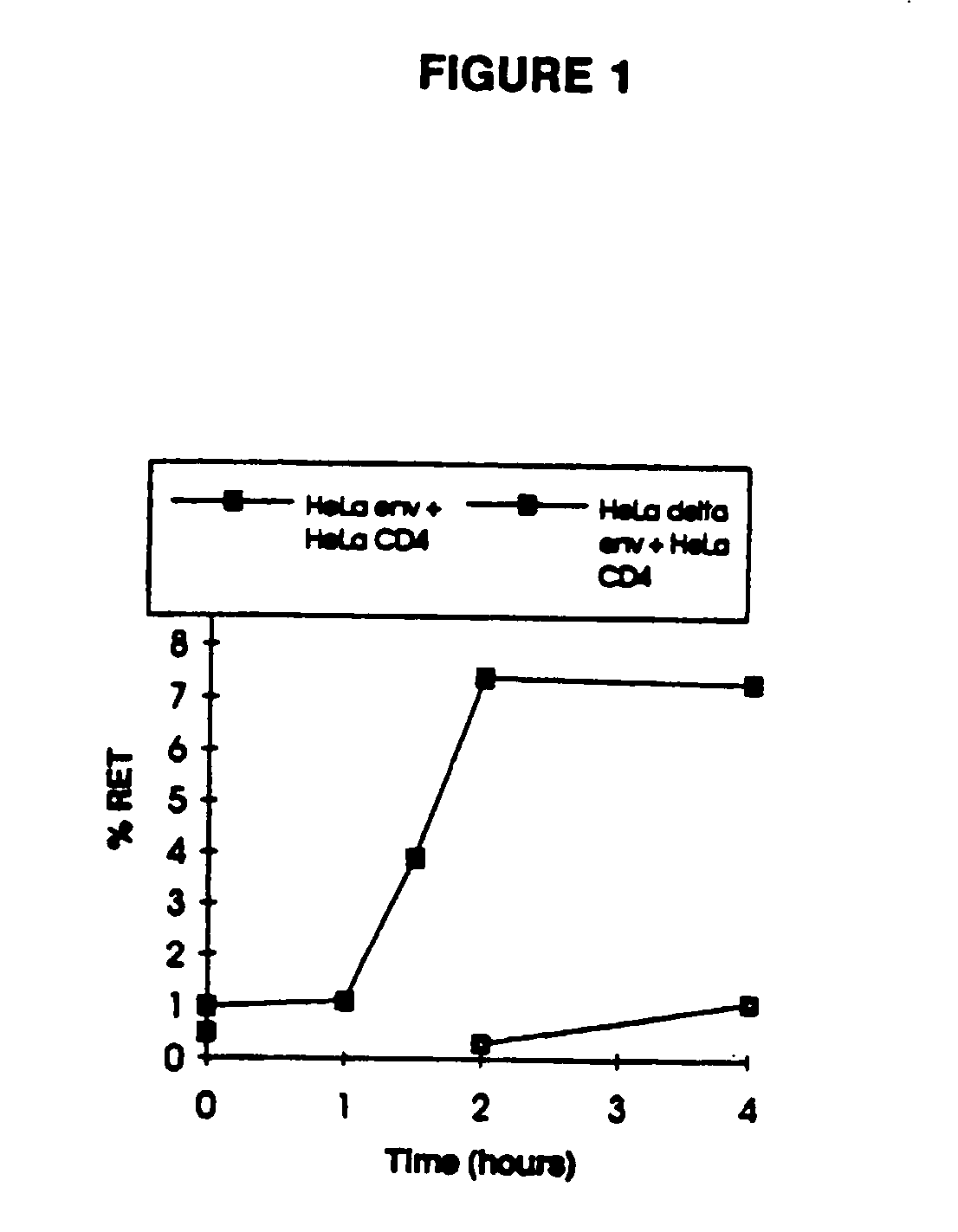
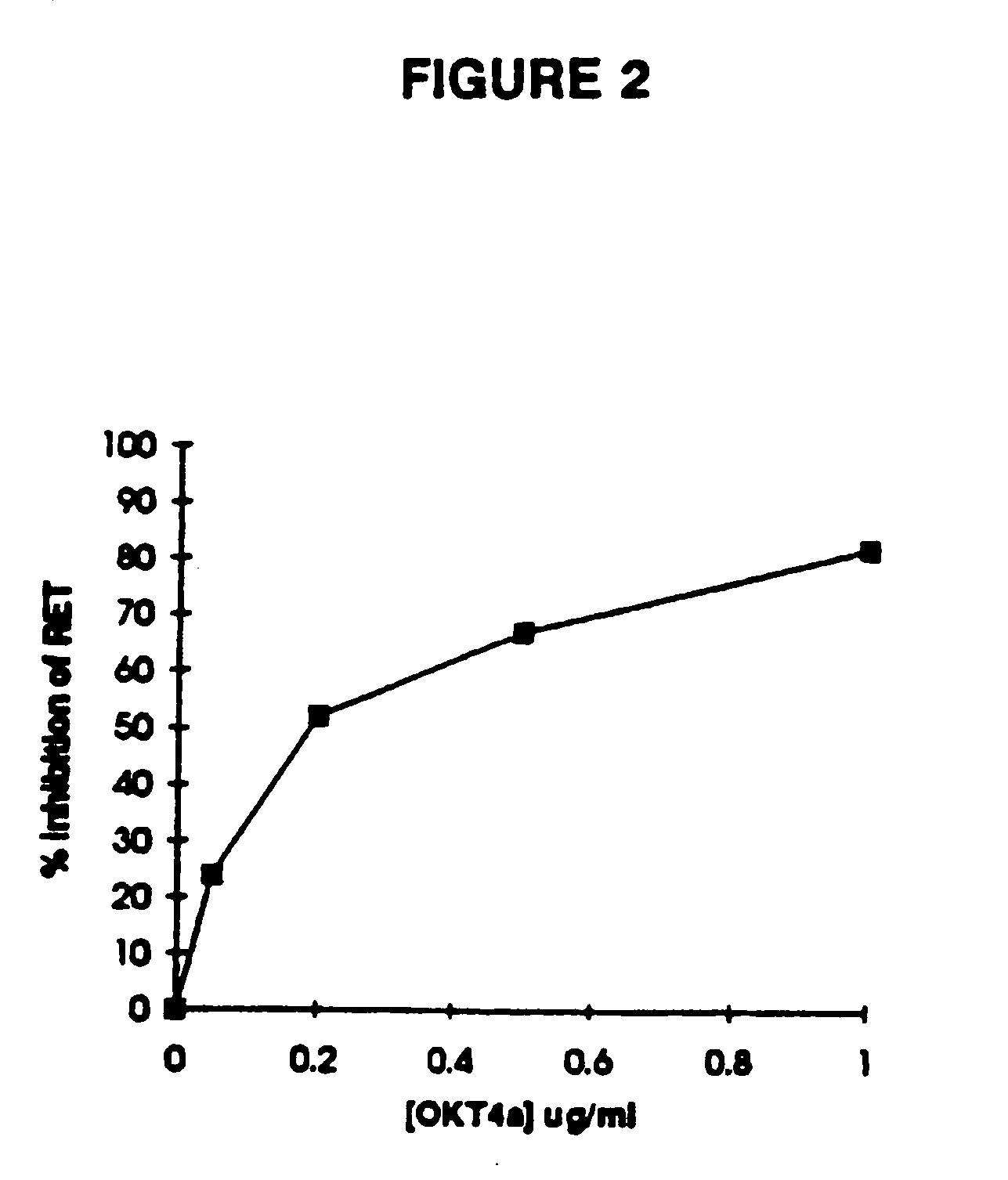
[0046] This invention provides a method for determining whether an agent is capable of inhibiting the fusion of a macrophage-tropic primary isolate of HIV-1 to a CD4+ cell which comprises: (a) contacting (i) an appropriate CD4+ cell, which is labeled with a first dye, with (ii) a cell expressing the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein of the macrophage-tropic primary isolate of HIV-1 on its surface, which is labeled with a second dye, in the presence of an excess of the agent under conditions permitting the fusion of the CD4+ cell to the cell expressing the HIV-1 envelope glyco...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| OD | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| OD | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| concentrations | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com