Methods, strains, and compositions useful for microbially enhanced oil recovery: Arcobacter clade 1
a technology of microorganisms and oil recovery, applied in the direction of bacteria based processes, sealing/packing, borehole/well accessories, etc., can solve the problems of poor sweep efficiency, poor sweep efficiency, and inability to recover oil in the less permeable zone, so as to achieve the effect of enhancing oil recovery
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Anaerobic Enrichment for Indigenous Microbes from Oil Reservoir Samples
[0155]To enrich for species that could reduce any of the electron acceptors nitrate, fumarate or the ferric ion (Fe (III), we inoculated 1 mL of either injection water or production water from Well #2, described in General Methods, into 9 mL of minimal salts media (Table 4) in 20 mL anaerobic serum vials, supplemented with lactate (2000 ppm) as the carbon source, sodium chloride to 4300 ppm and as electron acceptor either 1.6 g / L sodium nitrate, or 3.5 g / L sodium fumarate, or 13,000 ppm NaEDTAFe(III). A fourth enrichment having a rich medium, Marine broth (Difco™ B. D. Diagnostics Sparks Md.), which was supplemented with sodium chloride to 3900 ppm and lactate to 2000 ppt, was used to enrich for microbes that require more than a minimal medium for growth. The electron acceptor in the Marine broth sample was scavenged from the Fe (III), sulfate, nitrate and organic molecules in the formulation that could be used a...
example 2
Characterization of Isolated Strains with Respect to Arcobacter sp.
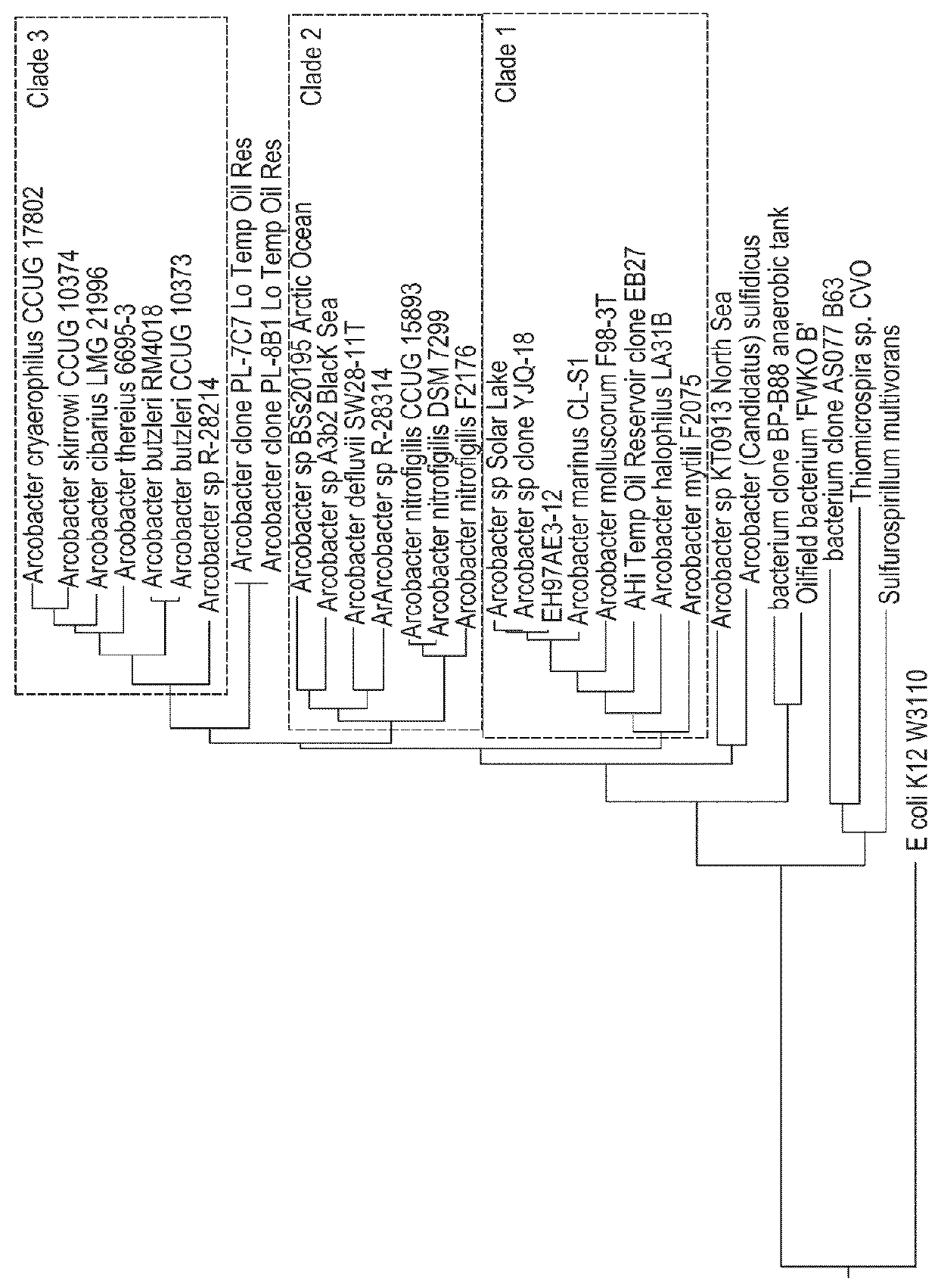
[0161]To determine the 16S rDNA sequence of the seven isolates named 97AE 3-12, 97AE3-1, 97AE 3-3, 97AE 3-7, 97AE 4-6, 97AE 4-5, and 97AE4-1 (Example 1), each of the seven isolates was picked as a pure single colony, DNA was isolated and the 16S rRNA gene was amplified by PCR using the procedures in General Methods. The amplified sequences were cloned into pCR-TOPO4 vector using the TOPO TA cloning system (Invitrogen), as recommended by the manufacturer, and then sequenced multiple times using primers 1492R, 8F, M13 Reverse, and M13 Forward of SEQ ID NOs:43-46, respectively, to obtain the near full sequence. Each strain 16S rDNA sequence (97AE 3-12: SEQ ID NO:1, 97AE3-1: SEQ ID NO:33, 97AE 3-3: SEQ ID NO:34, 97AE 3-7: SEQ ID NO:35, 97AE 4-6: SEQ ID NO:38, 97AE 4-5: SEQ ID NO:37, and 97AE4-1: SEQ ID NO:36) was queried against the NCBI (National Center for Biotechnology Information) database using the BLAST (Basic Loca...
example 3
Riboprinting to Determine Strain Differences
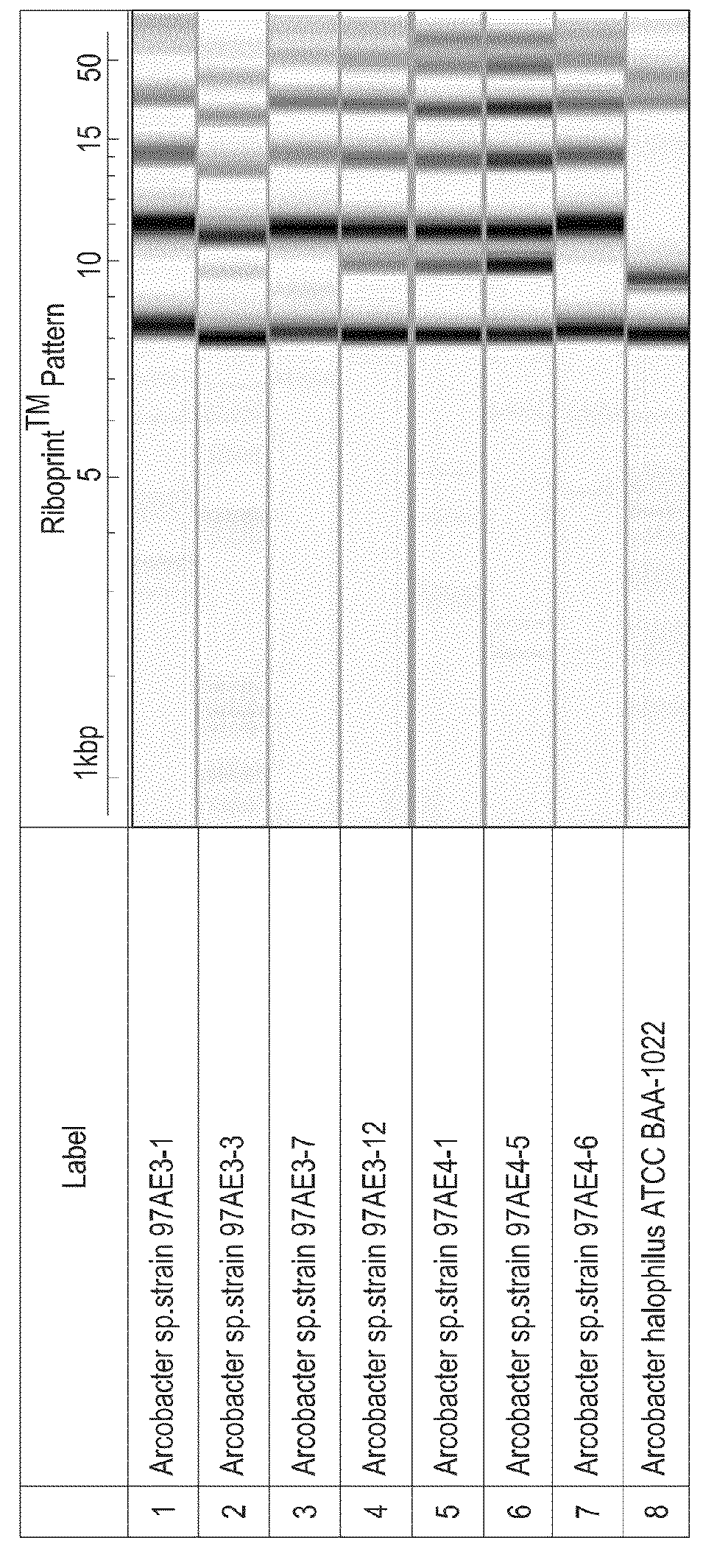
[0186]The Arcobacter sp. strains isolated in Example 1: 97AE3-12, 97AE3-1, 97AE 3-3, 97AE 3-7, 97AE 4-6, 97AE 4-5, and 97AE4-1 were subjected to automated Riboprinter® analysis, as described in General Methods, to determine whether these isolated strains were unique with respect to one another. As a reference strain, Arcobacter halophilus (ATCC strain BAA-1022), which has 16S rDNA with 96.4% sequence identity to strain 97AE3-12, was included in the analysis. While all of these strains have significant sequence identity to one another in the 16S rDNA, several unique rDNA RiboPrint™ patterns were obtained. As shown in FIG. 4, the patterns of EcoRI restriction fragments which hybridized to 16S and 23S rDNA probes were different for Arcobacter sp. representative strains 97AE3-12 (ATCC #PTA-11409), 97AE3-3 (ATCC #PTA-11410), and 97AE3-1. This analysis showed that the genomic sequences surrounding the 16S and 23 rRNA genes in these strains are d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| viscosity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| volume | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com