Molecular vaccine linking intercellular spreading protein to an antigen
a technology of intercellular spreading protein and molecular vaccine, which is applied in the field of molecular biology, immunology and medicine, can solve the problems of achieve limited potency of naked dna vaccine, enhance vaccine potency, and enhance spreading and mhc class i presentation of antigens
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Materials and Methods for HSV-VP22 DNA Study
Plasmid DNA Construction
[0189]The pcDNA3 expression vector and pcDNA3-E7 have been described (Chen, C H et al., 1999, Gene Ther 6:1972-81; Ji, H. et al., 1999, Human Gene Therapy 10:2727-2740). pcDNA3 has been used successfully in DNA vaccine induced immune responses and antitumor effects (Chen, C H et al., 2000, Cancer Res 60:1035-42; co-pending, commonly assigned U.S. patent applications U.S. Ser. No. 09 / 421,608, filed 20 Oct. 1999, U.S. Ser. No. 0911,097, filed 9 Feb. 2000 and U.S. Ser. No. 09 / 693,450; filed 20 Oct. 2000, which are incorporated by reference). For the generation of pcDNA3-VP22, VP22 was subcloned from pVP22 / myc-His (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.) into the unique EcoRV and BamHI cloning sites of the pcDNA3.1(−) expression vector (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, Calif.) downstream of the CMV promoter. The generation of pcDNA3-E7 has been described previously (Chen et al., supra). For the generation of pcDNA3-VP22 / E7, VP22 was subclon...
example ii
Enhanced Intercellular Spreading of VP22 Fusion Proteins
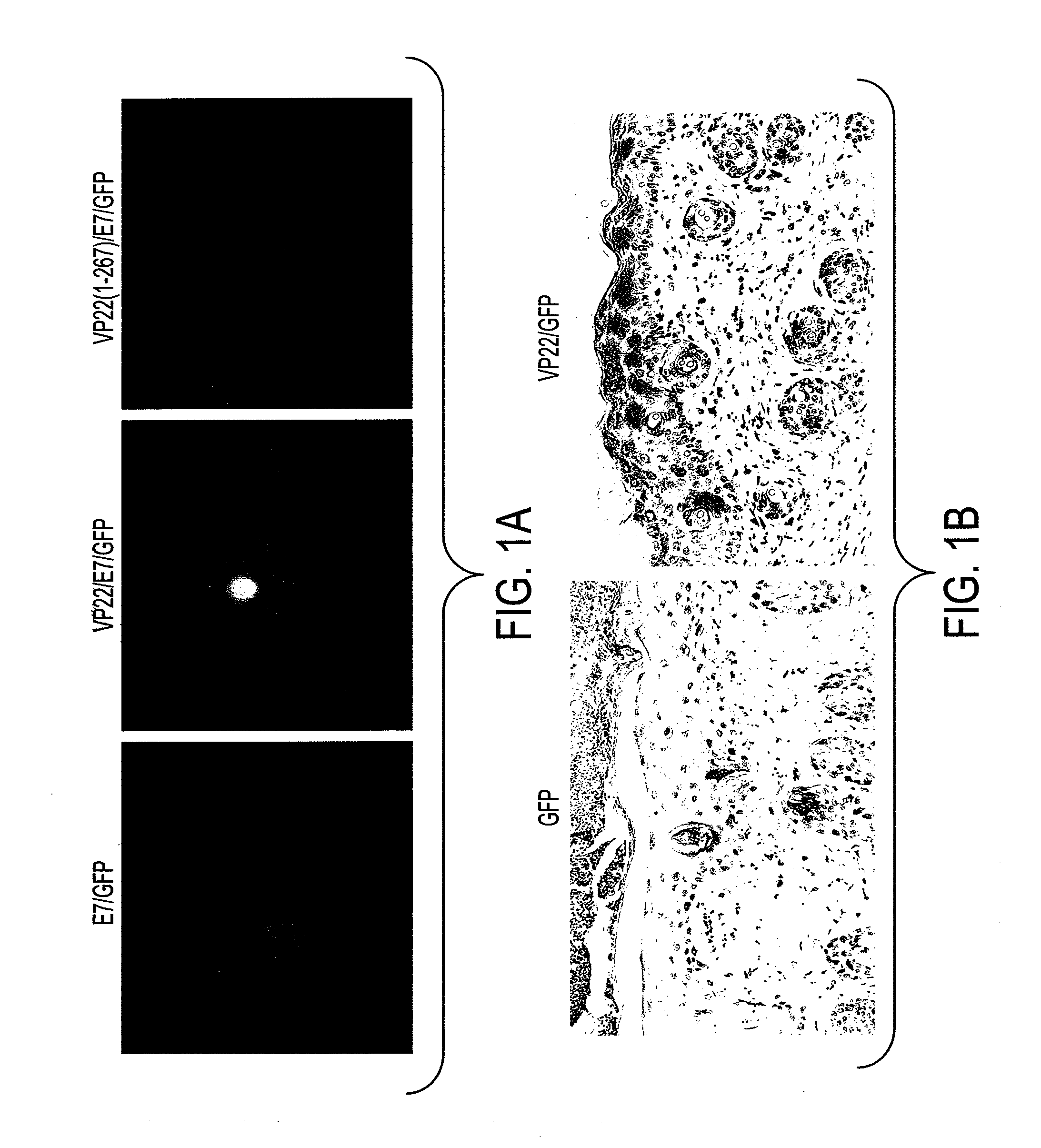
[0207]We initially generated several DNA constructs (E7, VP22, VP22 / E7, VP22(1-267) / E7, E7 / GFP, VP22 / GFP, VP22 / E7 / GFP, and VP22(1-267) / E7 / GFP) using a mammalian cell expression vector (pcDNA3). To demonstrate if VP22 / E7 protein generated enhanced intercellular spreading of E7 in 293 DbKb cells, we used green fluorescent protein (GFP) as a marker protein and examined green fluorescence. 293 DbKb cells were transfected with E7 / GFP, VP22(1-267) / E7 / GFP, or VP22 / E7 / GFP DNA. We performed fluorescent microscopic examination of 293 DbKb cells to investigate the topological distribution of GFP protein. We observed significant spread of GFP protein in cells transfected with VP22 / E7 / GFP DNA but not in cells transfected with E7 / GFP or VP22(1-267) / E7 / GFP DNA (FIG. 1A).
[0208]We also administered VP22 / GFP or GFP intradermally into C57BL / 6 mice via gene gun. To demonstrate if the linkage of VP22 to protein led to enhanced intercellular spreadi...
example iii
Enhanced T Cell Activities Induced by VP22 Linked to Antigen
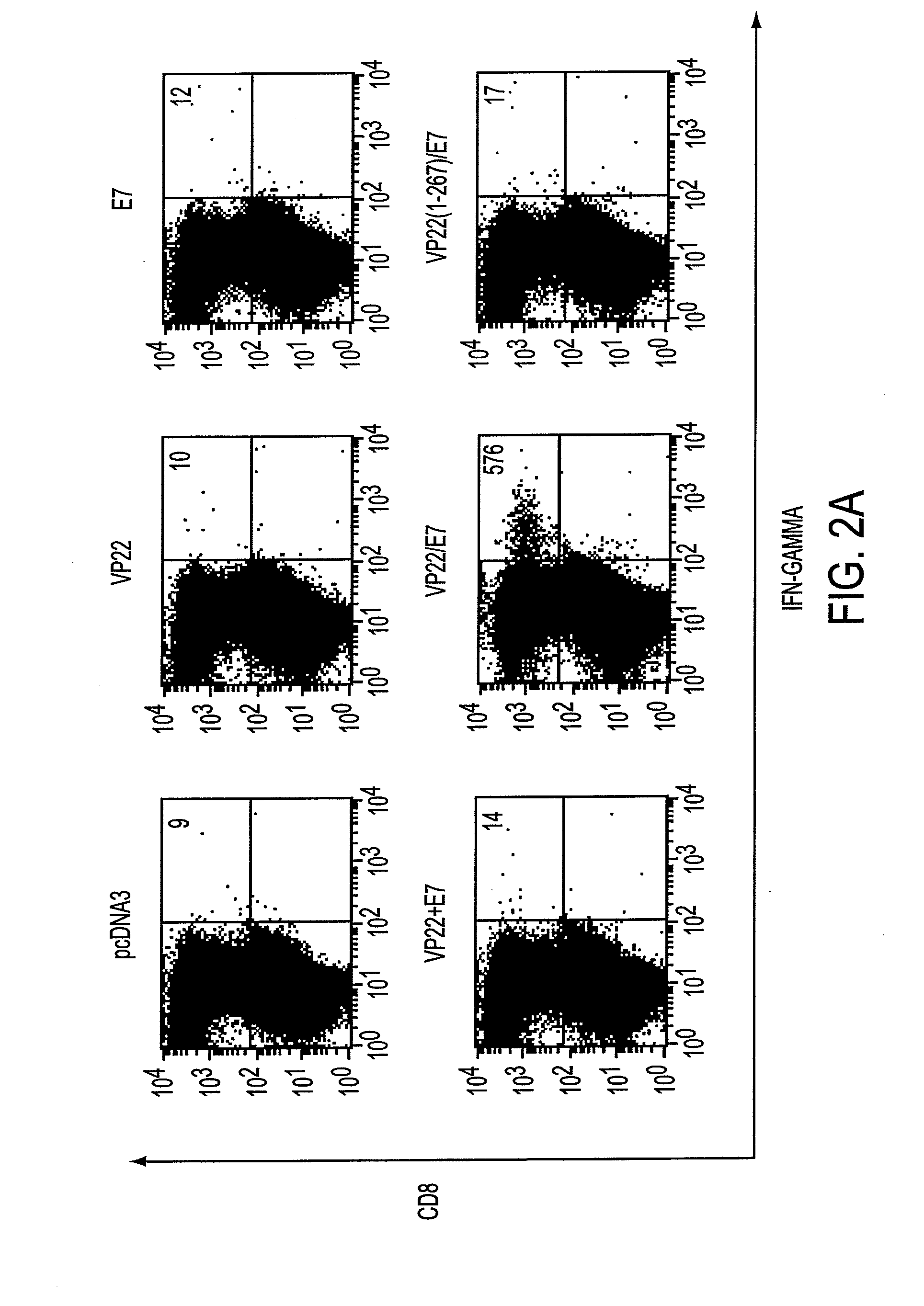
[0209]The observed increase in intercellular spreading of the marker protein within the epidermis raises the possibility of generating an increased number of antigen presenting cells (APCs) that present the linked protein since the epidermis is rich with Langerhans' cells, the professional APC precursors. To further investigate if such increased spreading can lead to enhanced antigen-specific T cell activities, we linked VP22 to a model antigen, HPV-16 E7, which is associated with a majority of cervical cancers. E7 is important in the induction and maintenance of cellular transformation and co-expressed in most HPV-containing cervical cancers and their precursor lesions and therefore represents an ideal target for vaccine development (21).
[0210]The importance of CD8+ cytotoxic T cells for the control of viral infections and neoplasms has been demonstrated in several pre-clinical models (9, 22). To determine whether vaccinat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| temperatures | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com