Anti-Cancer DNA Vaccine Employing Plasmids Encoding Signal Sequence, Mutant Oncoprotein Antigen, and Heat Shock Protein
a plasmid encoding and anti-cancer technology, applied in the field of molecular biology, immunology and medicine, can solve the problems of lack of potency of vaccines, limited administration, and none of these vaccines have been ideally designed for humans use, and achieve enhanced immunogenicity and promote the processing of antigens.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
Materials and Methods
[0200]Mice: Six- to eight-week-old female C57BL / 6 mice were purchased from the National Cancer Institute (Frederick, Md.) and kept in the oncology animal facility of the Johns Hopkins Hospital (Baltimore, Md.). All animal procedures were performed according to approved protocols and in accordance with the recommendations for the proper use and care of laboratory animals.
[0201]Plasmid DNA Construction: The E7 / 70 gene was cloned into pNGVL4a (National Gene Vector Laboratory) using the EcoRI and KpnI restriction sites. Using site-directed mutagenesis, two point mutations, which had previously been found to reduce Rb binding (Munger, K et al., EMBO J 1989, 8:4099-4105), were introduced into the E7 gene. The primers used to introduce these mutations were as follows:
[0202]mE7 Forward: 5′ ctgatctotacggttatgggcaattaaatgacagetc 3′ [SEQ ID NO: 14] and
[0203]mE7 Reverse: 5′ gagctgtcatttaattgcccataaccgtagagatca 3′ [SEQ ID NO: 15].
[0204]For construction of pNGVL4a-Sig / E7(deto...
example ii
pNGVL4a-Sig / E7(Detox) / FISP70 DNA Vector Administered by Gene Gun Generated Highest Number of E7-Specific CD8+ T Cells in Immunized Mice
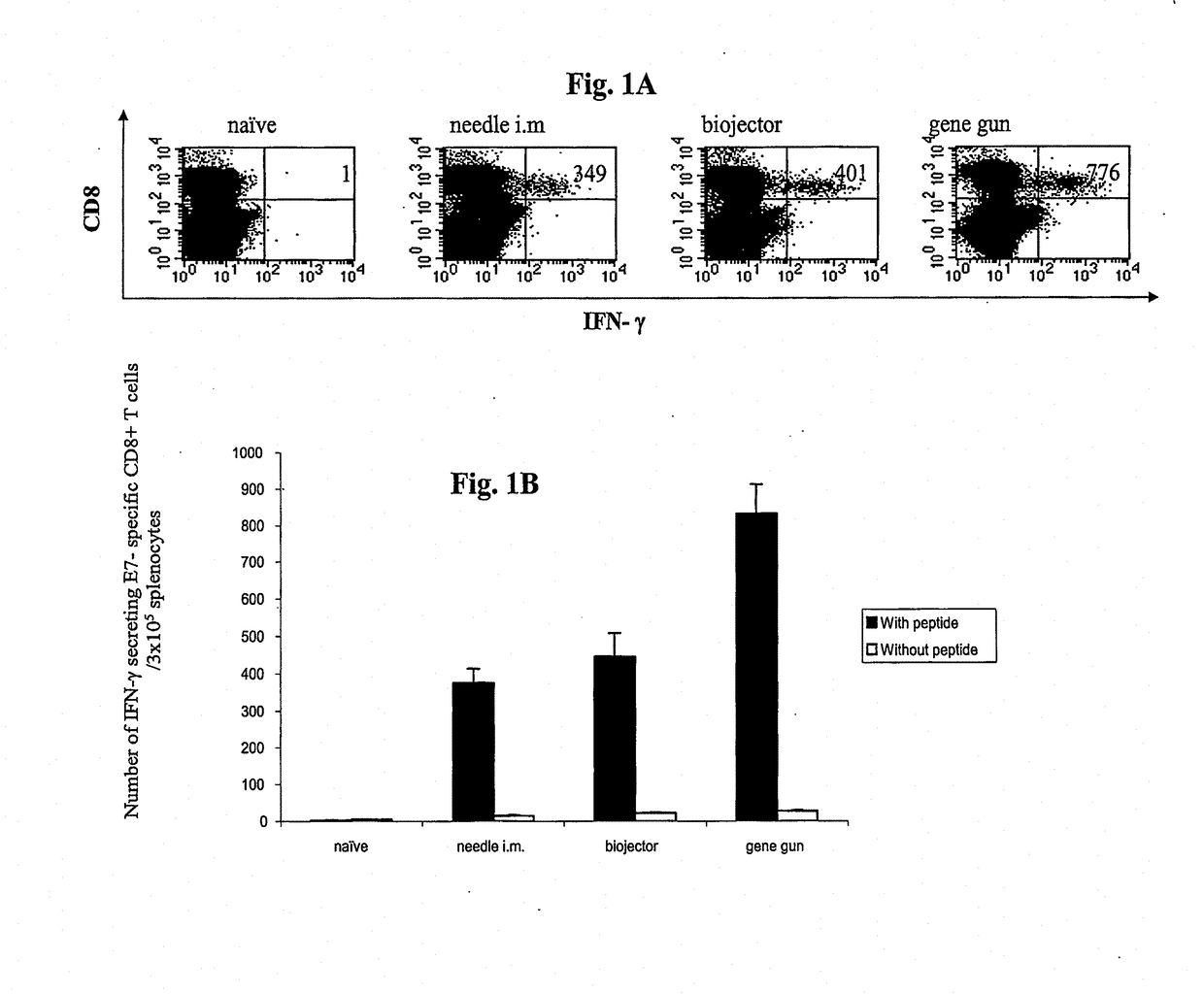
[0213]This study compared the ability of the pNGVL4a-Sig / E7(detox) / HSP70 DNA vaccine composition to generate E7-specific CD8+ T cell precursors by evaluation intracellular cytokines in splenocytes from mice vaccinated with the same DNA construct by three different modes of administration: needle i.m., biojector, and gene gun. Splenocytes from nave or immunized vaccinated groups of mice were incubated with or without the MHC class I (H-2 Db)-restricted E7 peptide (aa 49-57) (SEQ ID NO:2) to detect E7-specific CD8+ T cells.
[0214]Results are shown in FIGS. 1A and 1B / Mice vaccinated via gene gun exhibited significantly higher numbers (p+ CD8+ T cell precursors per fixed number of splenocyte (832.5) compared to mice vaccinated via biojector (445.5) and needle i.m. (375.5). These findings suggest that the gene gun approach was somewhat more potent in this ...
example iii
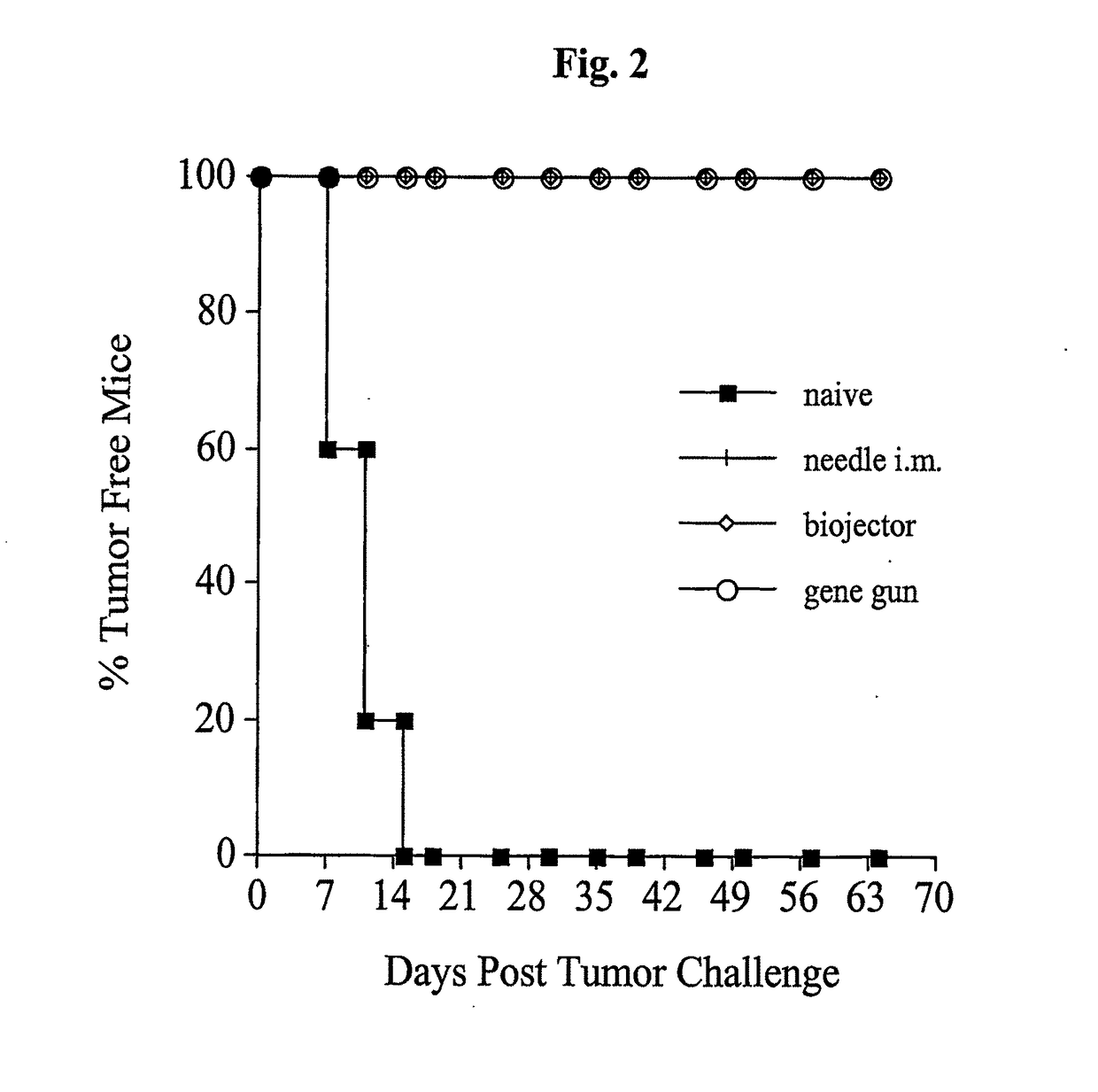
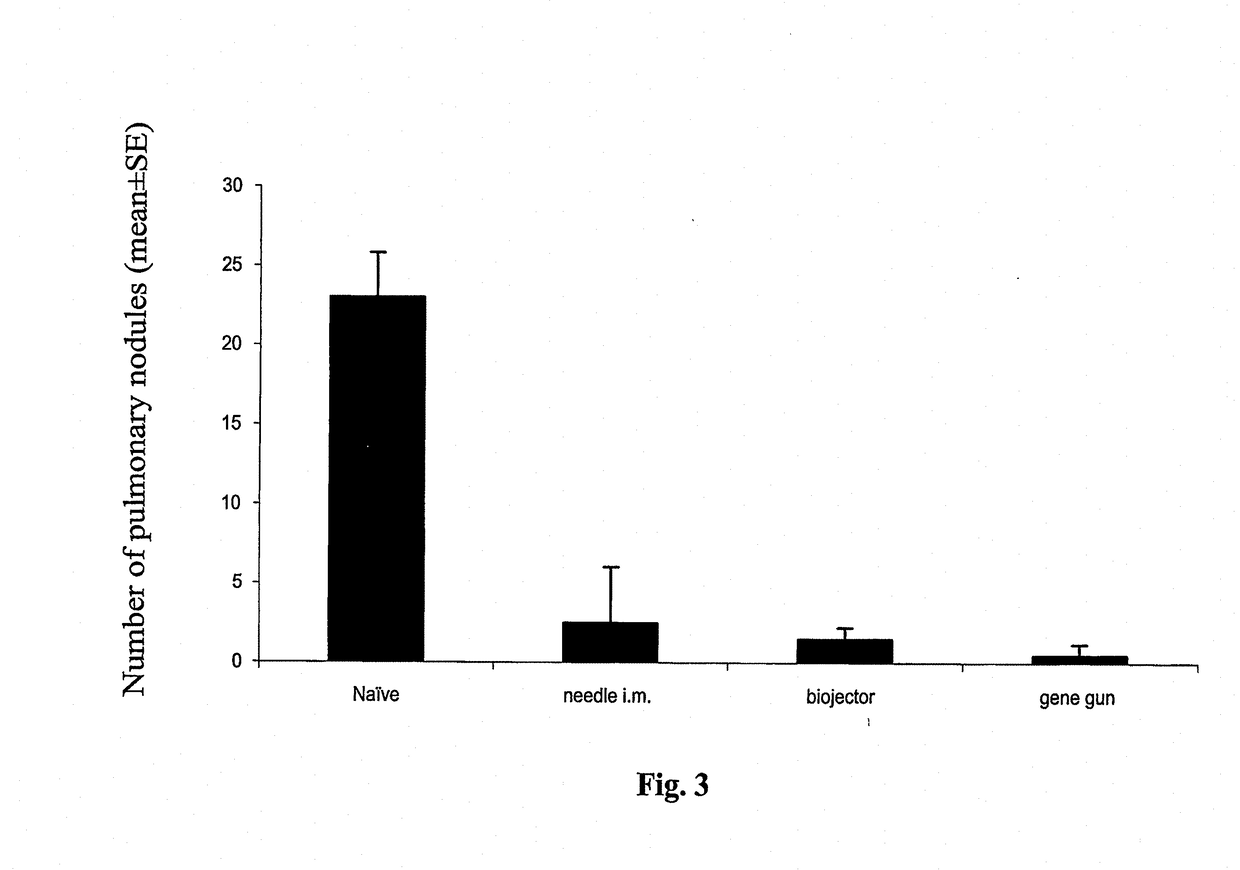
Vaccinated Mice Were Protected In Vivo Against E7-Expressing Tumors
[0215]The next study investigated protection against TC-1 tumor, expressing the same antigen, E7, as the pNGVL4a-Sig / E7(detox) / HSP70 vaccine, administered by the three routes. In vivo tumor protection experiment (vaccination before tumor challenge) used the well-characterized E7-expressing tumor model, TC-1. As shown in FIG. 2, mice receiving pNGVL4a-Sig / E7(detox) / HSP70 via gene gun, biojector, or needle i.m. remained 100% tumor free after TC-1 tumor challenge. Thus, this vaccine vector administered by different routes generated total protection against growth of later-administered tumor cells expressing the E7 antigen.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com