Vaccine for House Dust Mite Allergen Using Naked DNA
a technology of tcell epitopes and naked dna, which is applied in the direction of antibody medical ingredients, peptide sources, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of poor immunogens of peptides and substantial limitations of vaccinations using peptides
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Human Epitope Vaccination
[0016]Introduction
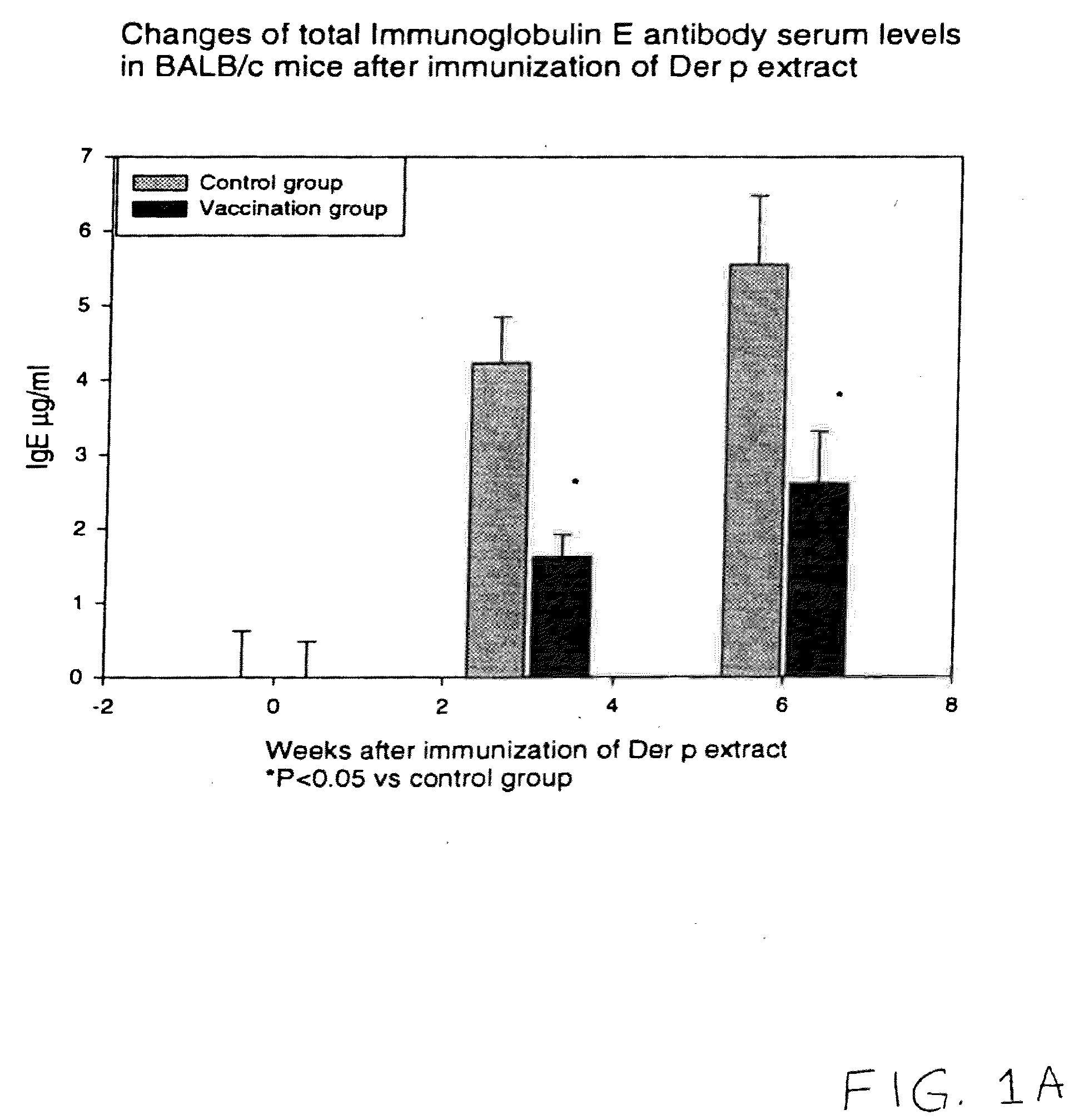
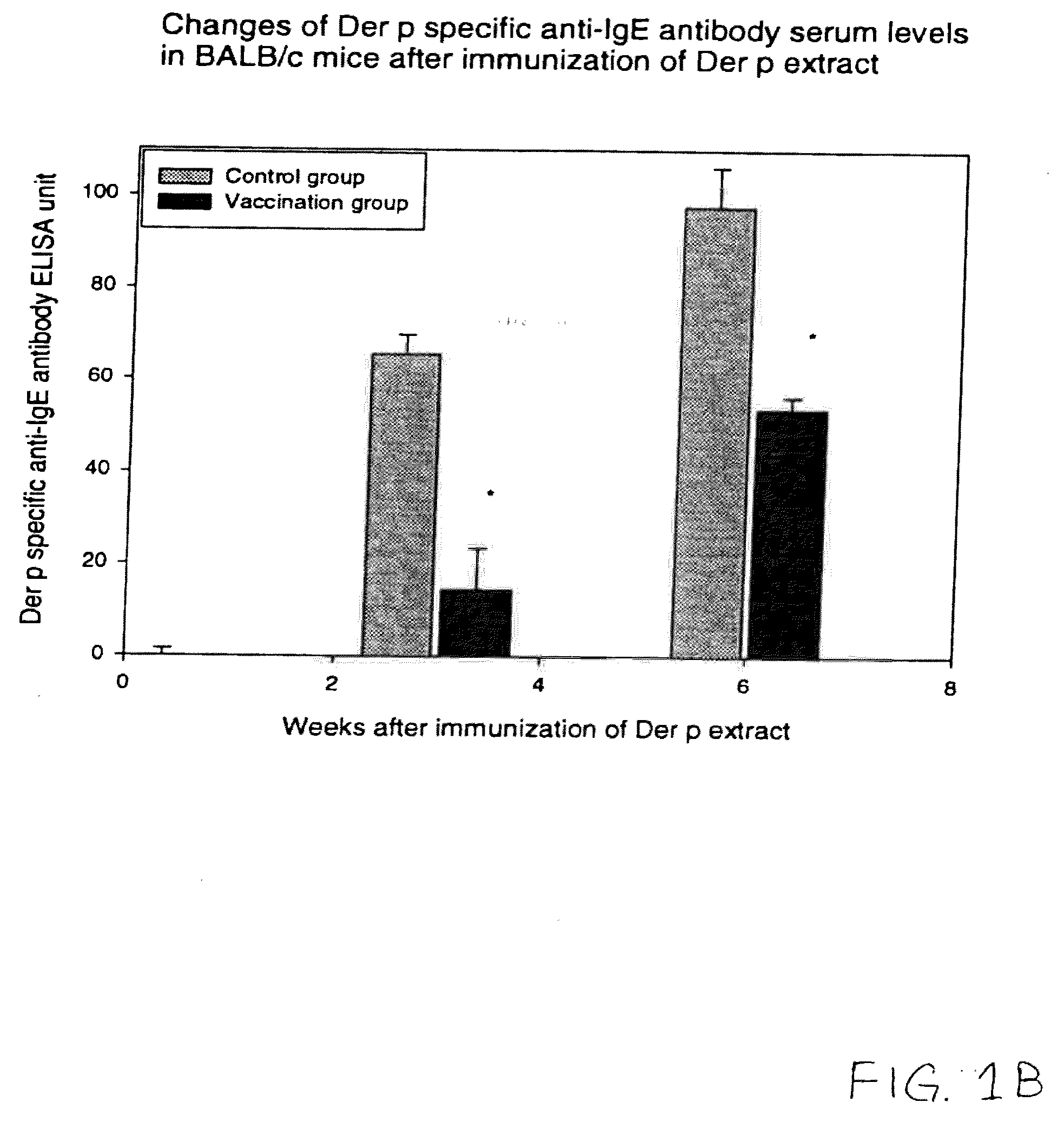
[0017]To determine whether the vaccination with naked plasmid DNA encoding only a T-cells epitope peptide is able to suppress the allergic reaction in vivo, the mixed naked DNA plasmids encoding the five classes of human T-cell epitopes on Der p 1 and Der p 2 were used for genetic vaccination of BALB / c mice. The control mice were injected with the pcDNA 3.1 blank vector. There was a reduction in the total and Der p-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) synthesis in the vaccinated mice compared with the control mice. In the Der p specific-IgG2a antibody response, the vaccinated mice showed more prominent responses than the control mice. Also analysis of the cytokines serum levels after immunization of Der p extract revealed that in the vaccinated mice there was an elevation in the level of interferon-γ, a Th1 cytokine associated with suppression of IgE production. The histologic studies showed that there was much less infiltration of inflammatory ...
example 2
The Effect of Vaccination with DNA Encoding Murine T-Cell Epitopes on Der p 1 and 2 Induced Immunoglobulin E Synthesis
[0054]We would like to examine the effect of vaccination with DNA encoding only the murine T-cell epitopes on the IgE production. Our results suggested that genetic vaccination indeed induced the Th1 cytokine immune responses which in turn reduced the IgE antibody production and allergic responses against Der p. Therefore it would be ideal to develop an alternative naked DNA vaccination method which could be even safer than injecting whole segments of the encoding region of Der p 1 or Der p2.
[0055]Materials and Methods
[0056]Mice
[0057]20 BALB / c mice at the age of 6-8 weeks were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, Me.) and bred at the University of Tennessee (Memphis, Tenn.). This study was performed in accordance with the PHS Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animal Welfare Act (7 U.S.C. et...
example 3
Suppressive Effect on the Allergen-Induced Immunoglobulin E Production by the Naked DNA
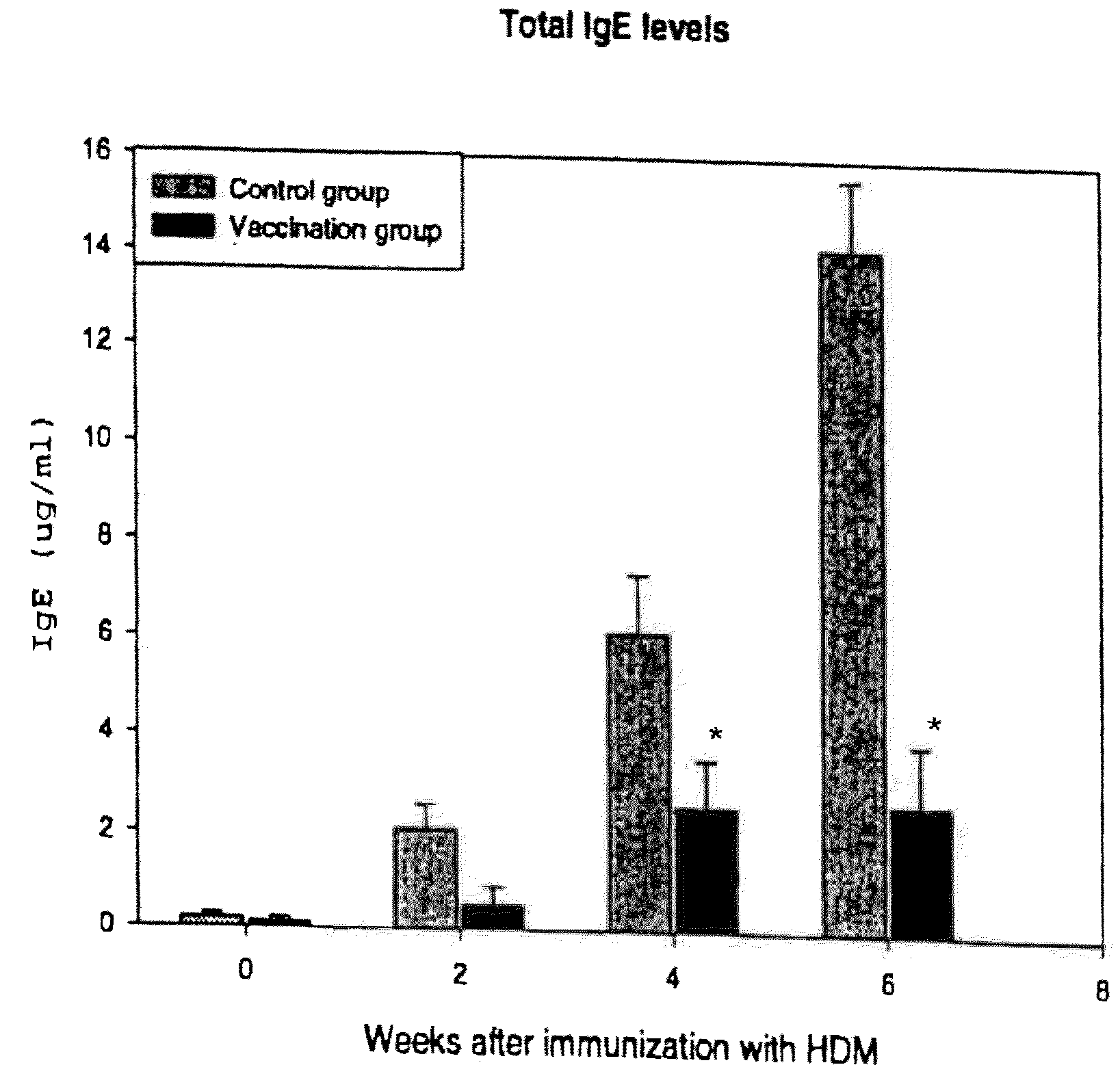
[0092]We have investigated immune responses resulting from gene immunization with plasmid DNA encoding major HDM allergen (Der p 1, 2, 3, Der f 1, 2, and 3) followed by challenges with whole HDM crude extract in mice to mimic a realistic clinical setting. We have demonstrated that gene vaccination indeed induced strong Th1 immune responses, which reduced the IgB antibody production and allergic responses against HDM.
[0093]Methods
[0094]Mice
[0095]20 BALB / c mice at the age of 6-8 weeks were purchased from Jackson Laboratory (Bar Harbor, Me.) and bred at the University of Tennessee (Memphis, Tenn.) This study was performed in accordance with the PHS Policy on Humane Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animal Welfare Act (7 U.S.C. et seq.); the animal use protocol was approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) of the University o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com