Patents
Literature
35 results about "Critical point drying" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
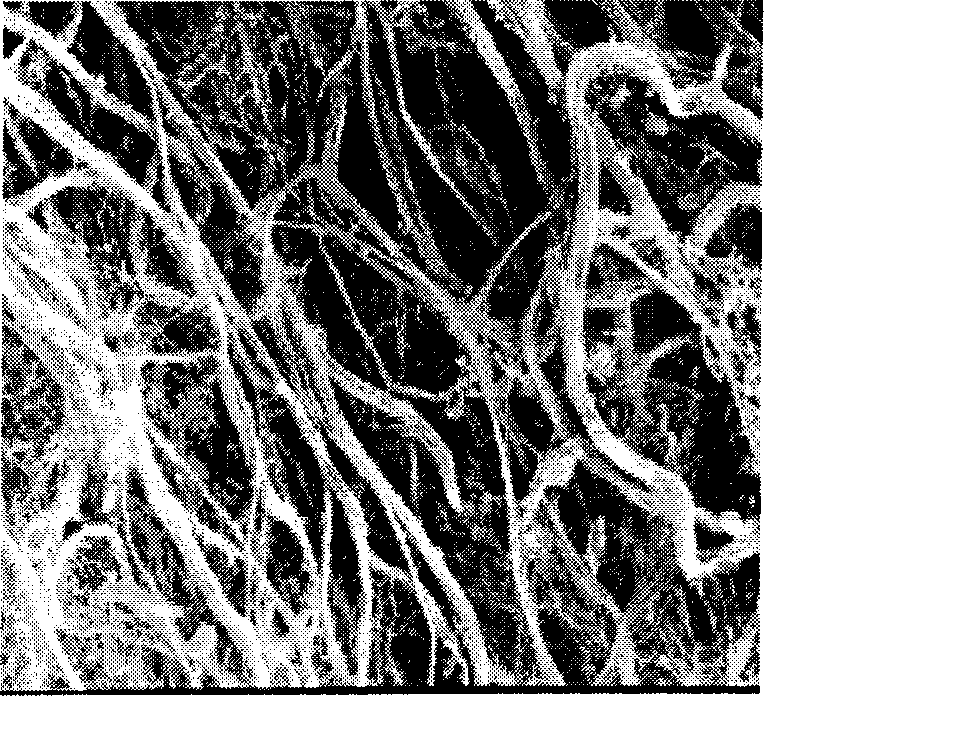
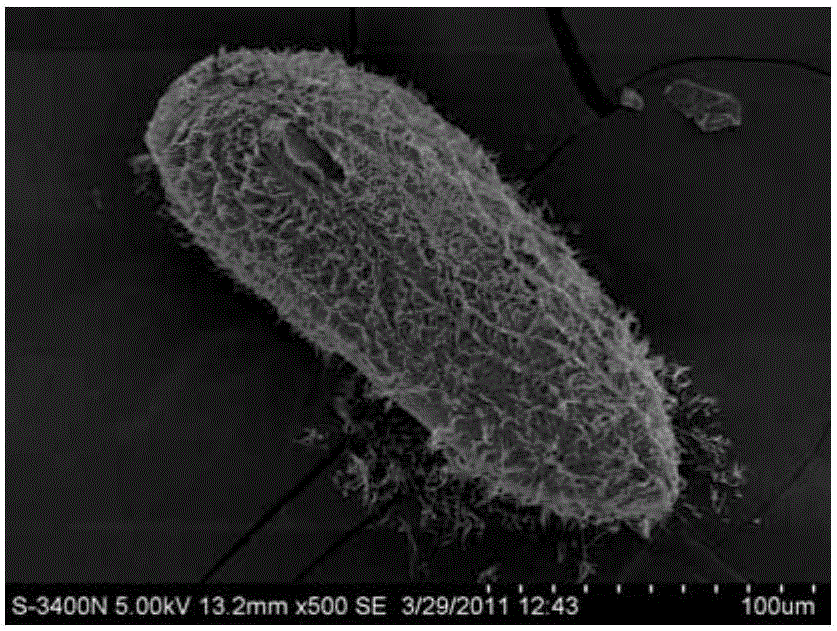
Critical point drying (sometimes called supercritical drying) is an established method of dehydrating biological tissue prior to examination in a scanning electron microscope (SEM).
Method of preparing bone material having enhanced osteoinductivity
ActiveUS20140205674A1Good osteoinductivityIncrease surface areaPeptide/protein ingredientsMammal material medical ingredientsFiberCritical point drying
Methods for increasing osteoinductivity and / or surface area of bone material are provided. The methods include providing bone material and dehydrating the bone material with a solvent at its critical point. A useful solvent for critical point dehydrating is carbon dioxide. Critical point dehydration resulting in increased osteoinductivity and / or surface area can be applied to many types of bone material including bone particles, bone chips, bone fibers, bone matrices, both demineralized and non-demineralized. An implantable composition having an enhanced osteoinductivity and / or osteoconductivity is also provided. The implantable composition contains demineralized bone matrix dried at critical point of carbon dioxide. Critical point dried fibers of a demineralized bone matrix have a BET value from about 40 m2 / gm to about 100 m2 / gm, a value that is 100 times higher than corresponding vacuum dried or lyophilized DBM fibers.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method for preparing lignocellulose aerogel by using ionic liquid
A method for preparing lignocellulose aerogel by using ionic liquid relates to a method for preparing lignocellulose aerogel, and aims to solve the problems of the prior art that during the preparation of aerogel by directly using woods, macroscopic gommures can not be shaped, and treatment of the raw material is complicated. The method is realized through the following steps: step I, timbers are smashed and then sieved to obtain wood flour, the wood flour and the ionic liquid are dried and mixed, and the mixture is heated to 80-130 degree C and stirred to obtain a mixed solution; step II, the mixed solution is refrigerated and thawed; step III, the step II is repeated for 1 to 9 times, and then displacement liquid I is added, so that lignocellulose gel is obtained; and step IV, the lignocellulose gel is treated by means of critical point drying or freeze drying, so that the lignocellulose aerogel can be obtained.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing amorphous cellulose aerogel with ionic liquid
InactiveCN102443188AEasy to shapeHigh mechanical strengthBulk chemical productionSupercritical dryingFreeze thawing
The invention relates to a method for preparing an amorphous cellulose aerogel, and concretely relates to an amorphous cellulose aerogel with an ionic liquid. The invention aims to solve technical problems of shapelessness and bad toughness in present inorganic aerogel preparation processes. The method comprises the following steps: 1, dissolving cellulose in the ionic liquid, freeze-thawing multiple times, and displacing the ionic liquid out with a displacement liquid to obtain an amorphous cellulose hydrogel; and 2, carrying out supercritical drying and critical point drying on the hydrogelto obtain the amorphous cellulose aerogel. A novel cellulose material amorphous cellulose aerogel is prepared in the invention. The ionic liquid can be recovered and recycled, so a green preparation technology is realized, and the prepared aerogel has the advantages of nontoxicity, good shape and very good mechanical strength. The prepared new product cellulose aerogel can be applied to heat insulation, sound insulation, inorganic nanoparticle loading, virus filtration, biological scaffolds and the like, and the preparation method provides a new approach for the high efficiency utilization oflow quality biomass resources.
Owner:NORTHEAST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Moss scanning electron microscope observation material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104374626ASimple methodEasy to storePreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionCritical point dryingHistiocyte
The invention relates to a preparation method of moss scanning electron microscope observation material. The method includes: sorting, to be more specific, sorting moss materials from biological crusts, and stripping leaves after cleaning; fixing, to be more specific, fixing the leaves in glutaraldehyde solution, and washing with buffer solution; dehydrating step by step with alcohol with gradient concentration; replacing, to be more specific, placing the leaves in ethanol-isoamyl acetate mixture for replacing, and placing the leaves in isoamyl acetate solution for replacing; critical point drying; loading onto a table. The method has the advantages that the method is simple and practical, and good in effect, the glutaraldehyde solution serving as the fixing solution is good in fixing effect on polysaccharide, glycoprotein, microtubule and the like, tissue cells do not become brittle after fixing, the influence of leaf cell surface tension can be avoided by the critical point drying, and the microstructures of samples are well preserved; reference is provided for the preparation of ideal moss samples, and the technical blank of related fields in China is filled.
Owner:刘永英
Seawater fish ovum electron-microscope scanning sample preparing method
InactiveCN1865901AQuality assurancePrevent collapsePreparing sample for investigationScanning probe techniquesAlcoholPhosphate
The disclosed preparation method for ovum of sea fish as TEM sample comprises: fixing fresh fish ovum by glutaral solution diluted by phosphate buffer, cleaning, dewatering the ovum by 20-70% alcohol with concentration gradient increased by 10% and 75-100% alcohol with concentration gradient increased by 5% as two stages, then dewatering in pure acetone with CaCl2 as agent; then, drying at critic point, and spraying gold for the sample. This invention has ovum completion rate as 93.8-96.7% with low cost and convenient operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
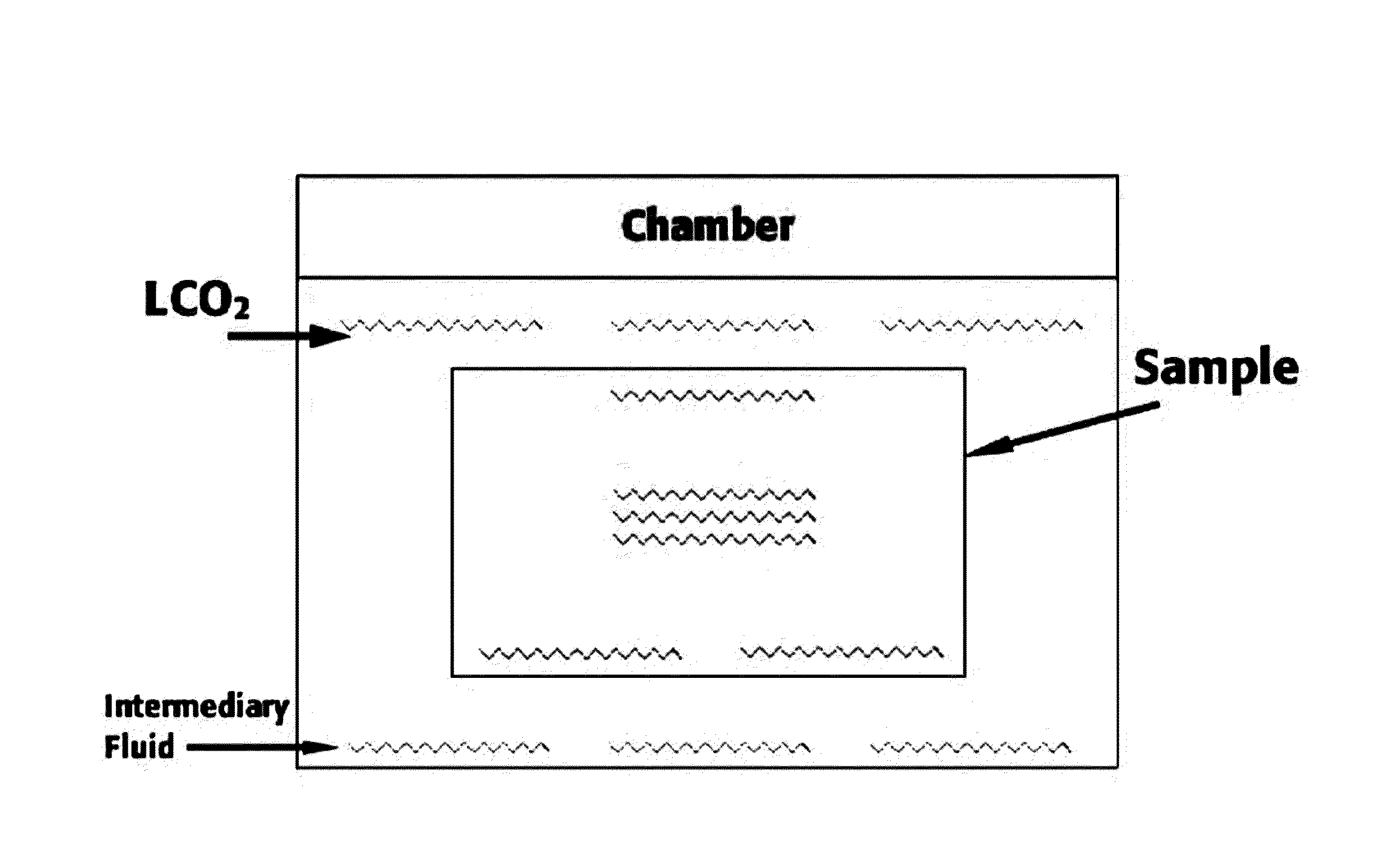
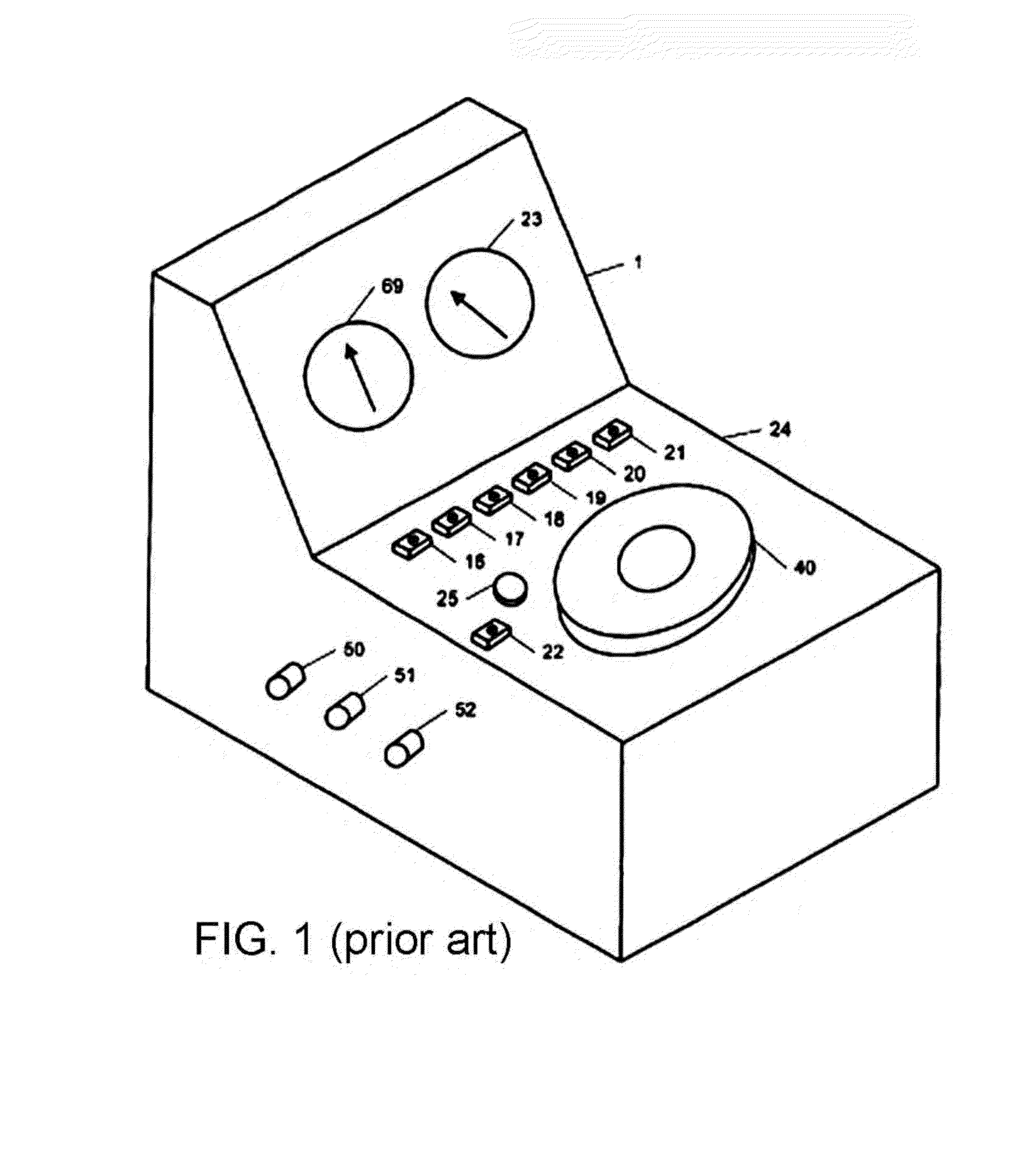
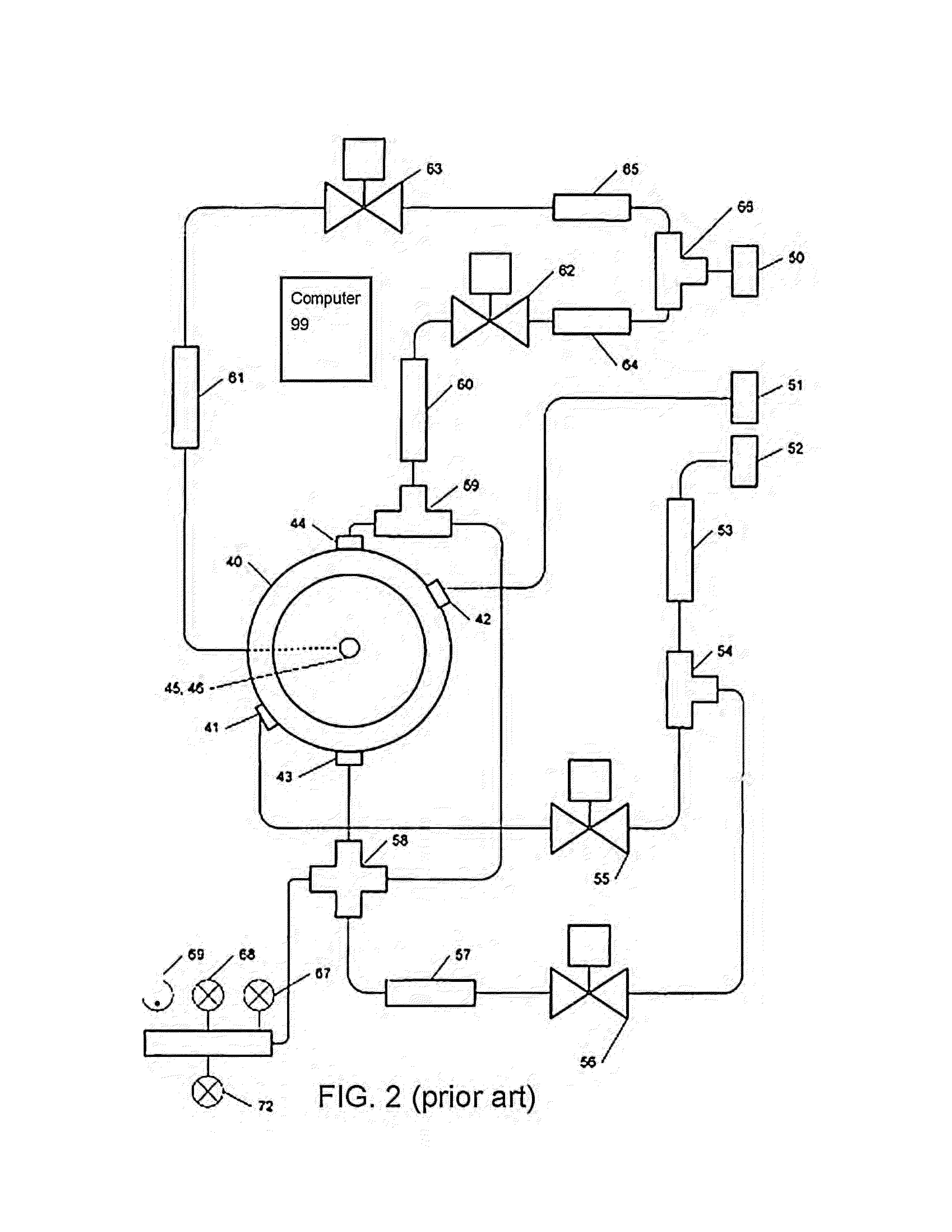
Supercritical point drying apparatus for semiconductor device manufacturing and bio-medical sample processing
InactiveUS6857200B1Chamber pressure to dropPreparing sample for investigationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMode controlCritical point drying
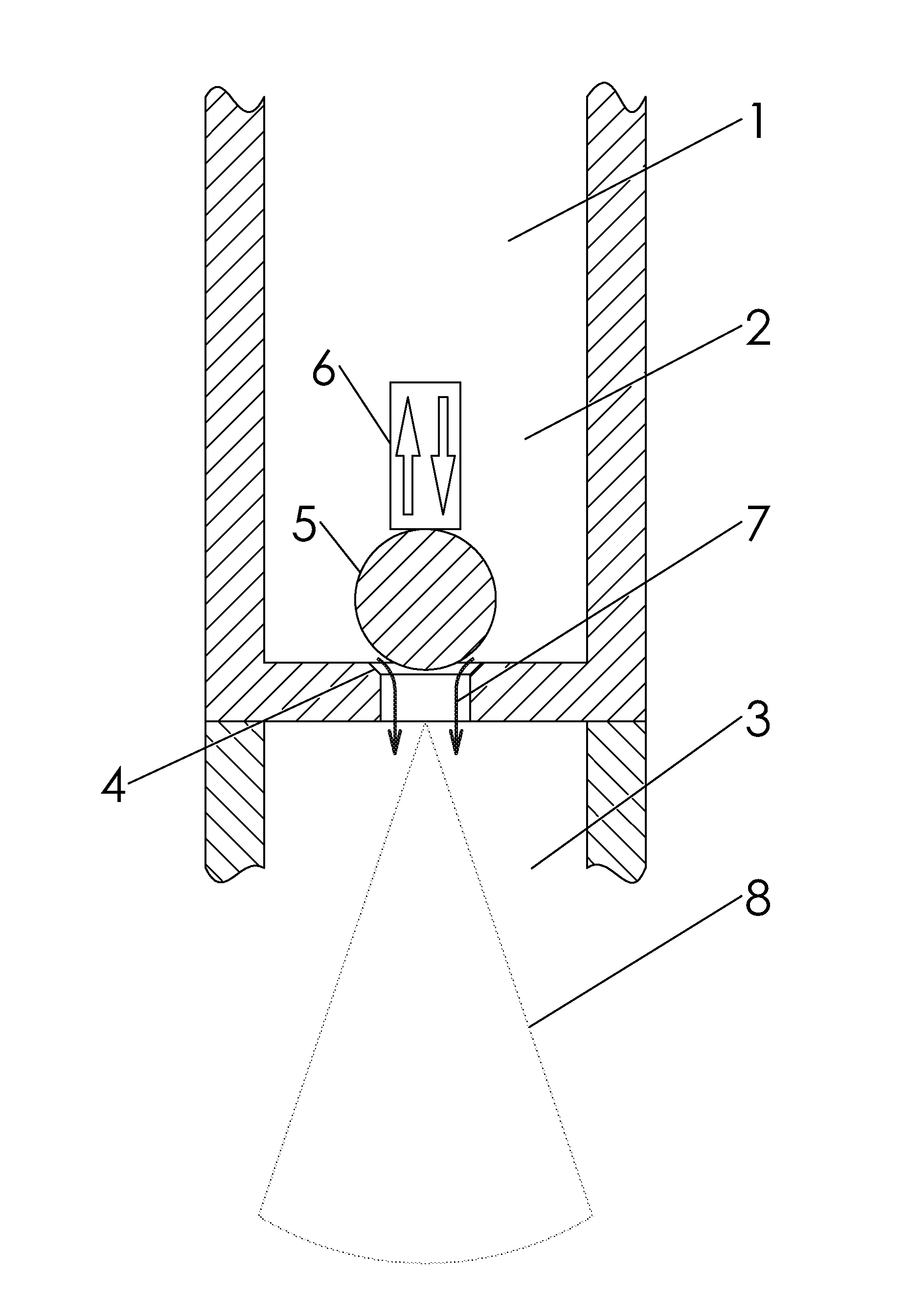
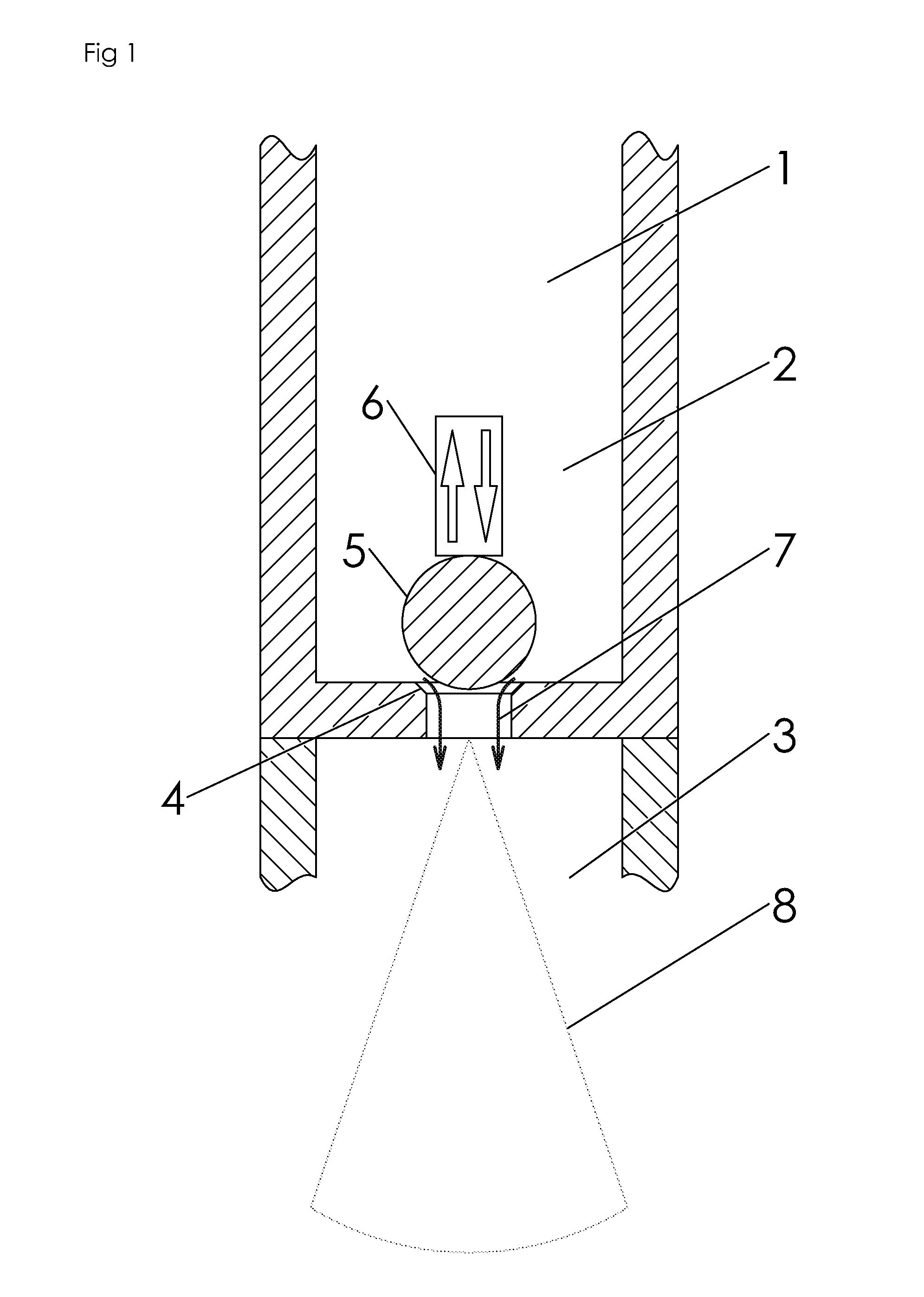
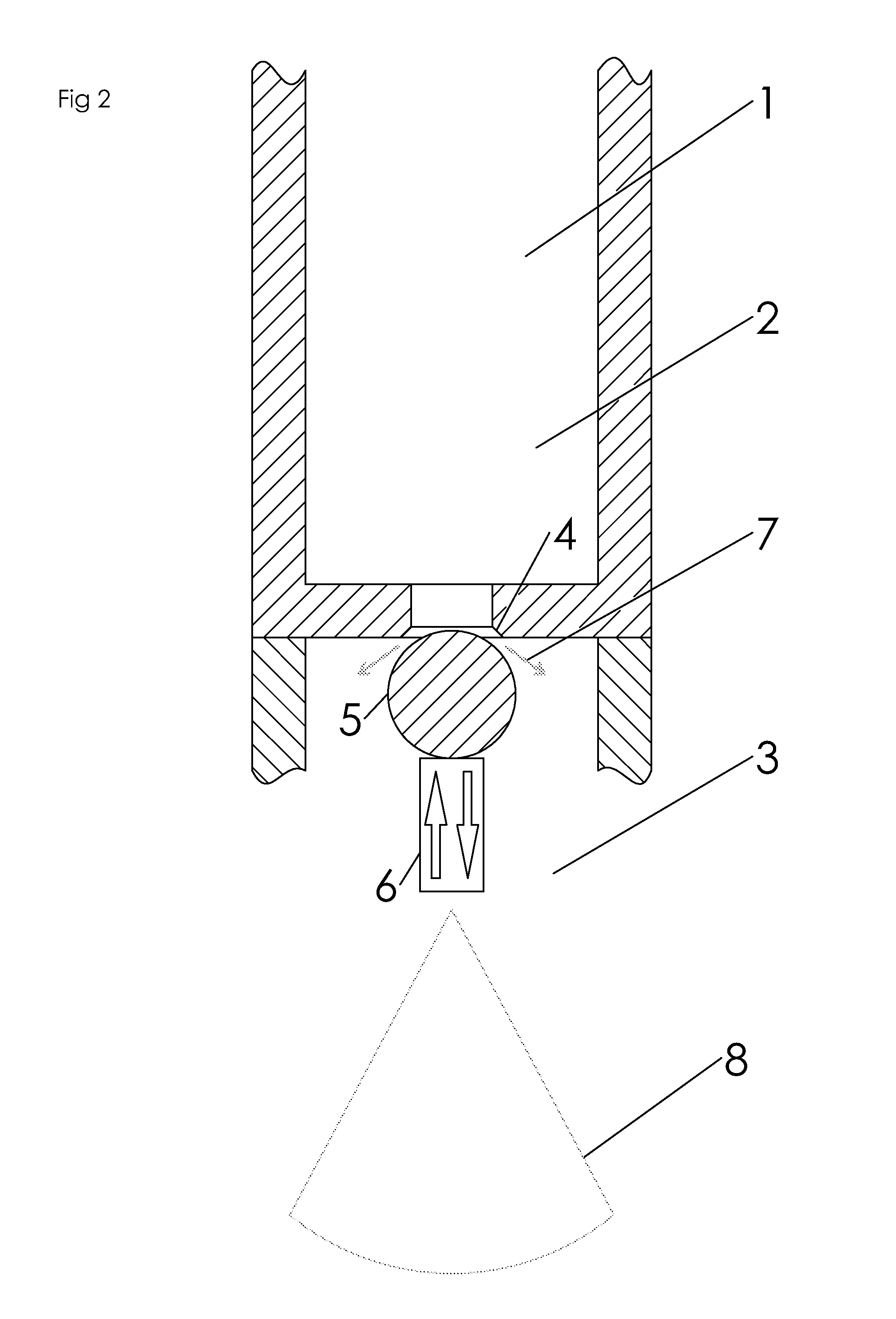
A critical point drying apparatus for sample preparation in electron microscopy and semiconductor wafer production includes a computer system to automate the operational modes in drying the specimen. These operational modes controlled by the computer system are: cooling, in which a drying chamber is cooled; starting, in which the specimen chamber is filled with a transitional fluid; purging, in which the transitional fluid purges an intermediary fluid from the drying chamber and the purged internediary fluid is collected by a collector condenser; heating, in which the drying chamber is heated to elevate the transitional fluid to its critical point temperature and pressure; and bleeding, in which the drying chamber is depressurized to atmospheric pressure at a very slow rate until the drying chamber is completely vented, which signals the end of the drying operation. The drying chamber incorporates concave surfaces for pressure dispersal and to facilitate purging the intermediary fluid completely. The drying chamber incorporates angled inlet ports and windows that are sealed with gaskets. The drying chamber also incorporates the usage of a wafer holder, spacer rings and inserts to allow for the secure suspension of wafers being processed. Passing the cooling fluid through a closed loop refrigeration system may also cool the drying chamber.
Owner:TOUSIMIS RES
Method for preparing scanning electron microscope samples from biological samples
InactiveCN102680289AAccurate distinctionPreparing sample for investigationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionNanoparticleProtein molecules
The invention provides a method for preparing scanning electron microscope samples from biological samples. The method comprises enabling a first antibody marked with first gold nanoparticles and a second antibody marked with second gold nanoparticles to contact with a biological sample after the biological sample is in resistance treatment; and then successively performing fixation, gradient dehydration and critical point drying. The shapes of the first gold nanoparticles are different from those of the second gold nanoparticles, and the first gold nanoparticles and the second gold nanoparticles are one or more from cylindrical gold nano bars, octahedral gold nanoparticles, spherical gold nanoparticles and arrow-shaped gold nanoparticles. The scanning electron microscope samples prepared by the method can accurately distinguish two types of different protein molecules in a low-vacuum mode.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Method for preparing graphene porous membrane
InactiveCN106395802AUniform sizeGood for research and understanding storageGrapheneOrganic solventMicrosphere
The invention provides a method for preparing a graphene porous membrane. The method includes the steps that oxidized graphite is added into water, oxidized graphite dispersion liquid is obtained and subjected to ultrasonic dispersion, and an oxidized graphene solution is obtained; a pore forming agent is added into the oxidized graphene solution and evenly dispersed into oxidized graphene, the mixture is subjected to suction filtration and / or dried, and a composite membrane of the oxidized graphene and the pore forming agent is obtained; the composite membrane of the oxidized graphene and the pore forming agent is reduced and washed, and a composite membrane of graphene and the pore forming agent is obtained; the pore forming agent is removed with an organic solvent, and under the moist condition, the product is further treated with the critical point drying method, and the graphene porous membrane is obtained; the pore forming agent is one or more of homopolymer microspheres and copolymer microspheres. The size of pores inside the graphene porous membrane prepared with the method ranges from 100 nm to 1,000 nm, the porosity can be regulated and controlled by regulating the concentration or the size of the pore forming agent, the yield of the graphene porous membrane is high, and an operating device is simple.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV OF TECH
Graphene materials and improved methods of making, drying, and applications
ActiveUS20190169033A1Large specific surface areaHigh capacitanceHybrid capacitor electrodesGrapheneCritical point dryingSupercapacitor
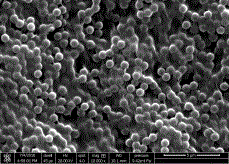
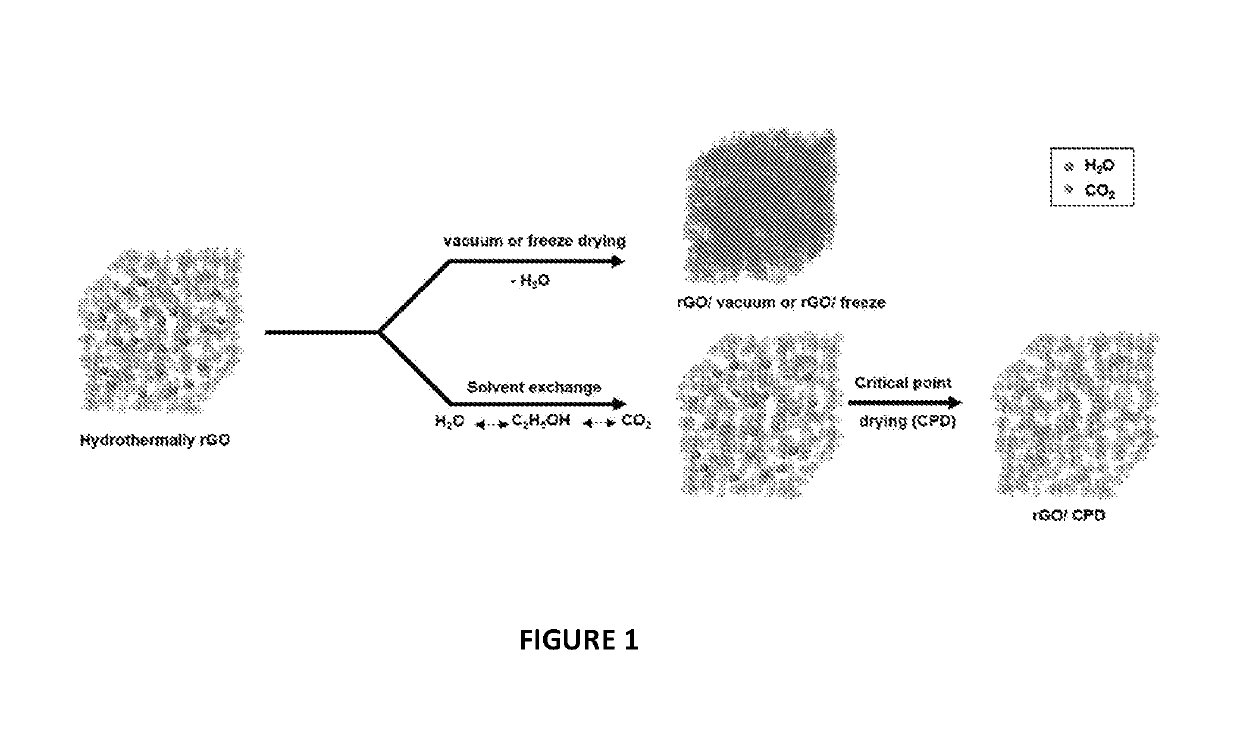
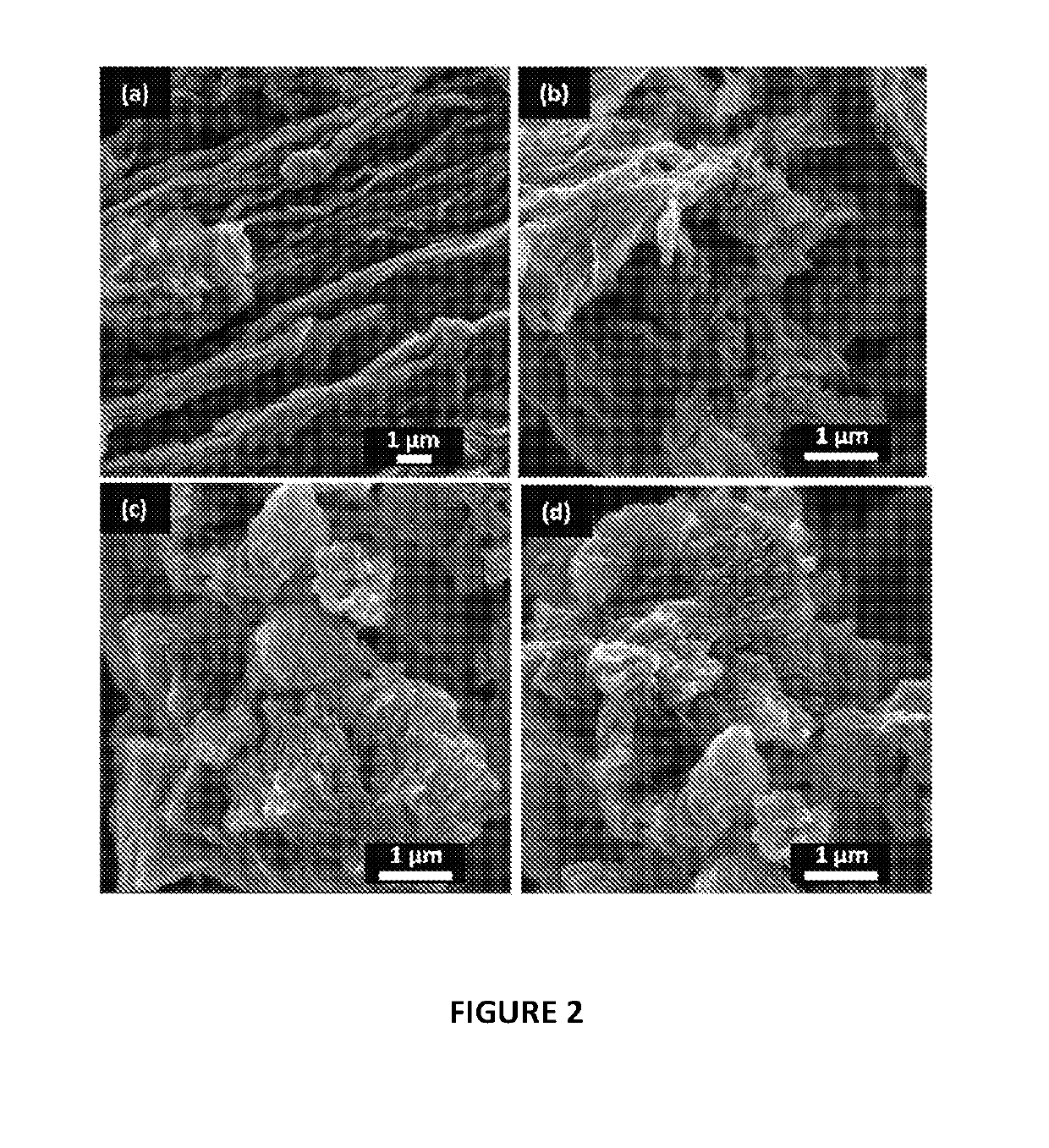
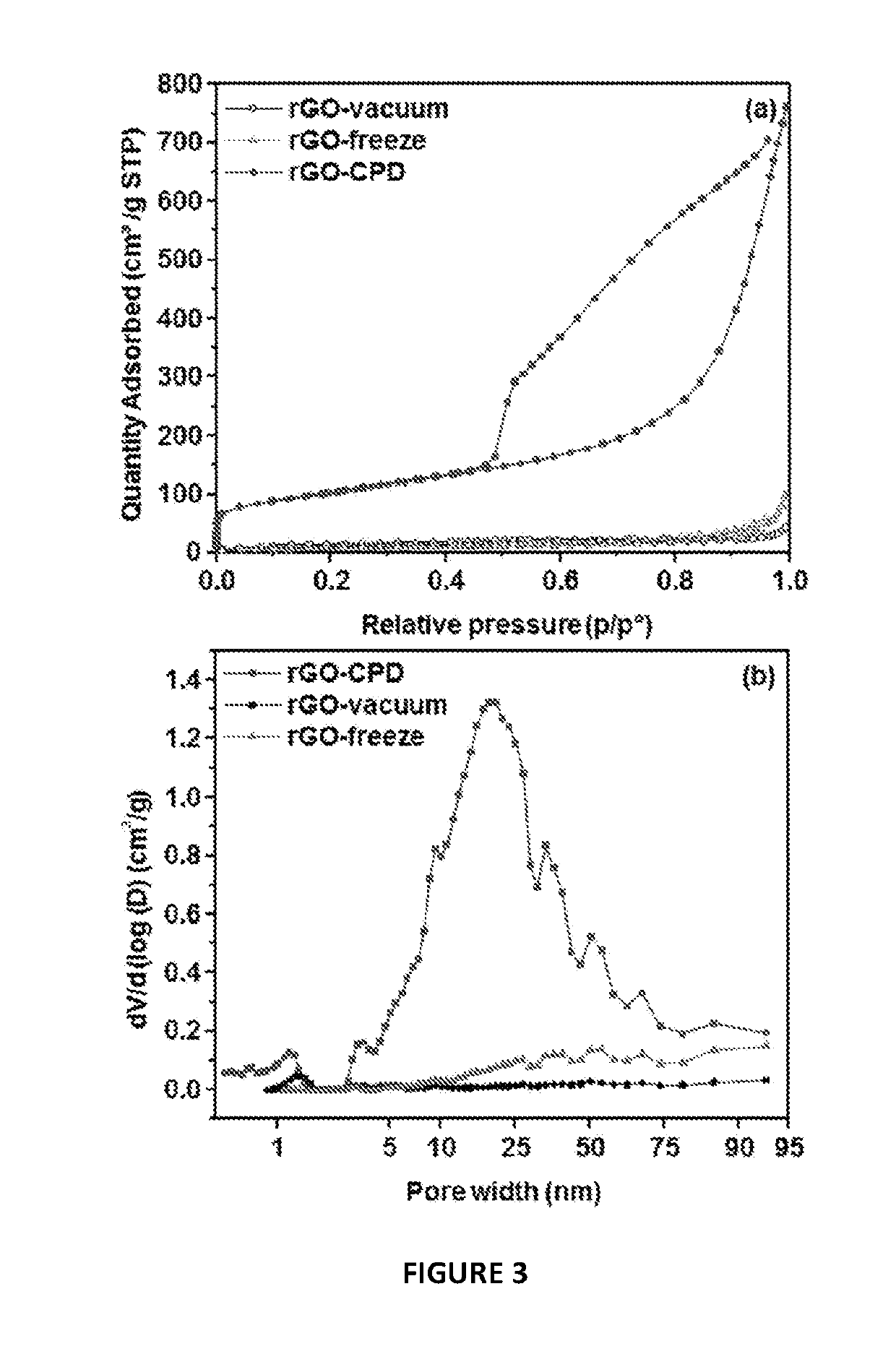
The impact of post-synthesis processing in, for example, graphene oxid or reduced graphene oxide materials for super-capacitor electrodes has been analyzed. A comparative study of vacuum, freeze and critical poin drying was carried out for graphene oxide or hydrothermally reduced graphene oxide demonstrating that the optimization of the specific surface area and preservation of the porous network is important to maximize its properties such as supercapacitance performance. As described below, using a supercritical fluid as the drying medium, unprecedented values of specific surface area (e.g., 364 m2g−1) and supercapacitance (e.g., 441 F g−1) for this class of materials were achieved.
Owner:KING ABDULLAH UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Electronically-controlled, high pressure flow control valve and method of use
ActiveUS9010329B2RespiratorsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesCritical point dryingEngineering
Owner:AEROPHASE
Method for membrane breaking production of protozoa single cell scanning electron microscopy sample
InactiveCN106093091APreserve in situ featuresObservations are rich and detailedMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionProtozoaPresent method
A method for membrane breaking production of a protozoa single cell scanning electron microscopy sample is provided to solve the problems of unstable result, frequently appearing organelle missing, cell internal structure damages, only observation of the structure cling to the lower surface of a surface membrane and unable observation of the structure in the mitochondria of protozoa single cell scanning electron microscopy samples produced through present methods. The method comprises the following steps: 1, material drawing and cleaning; 2, fixing and membrane breaking; 3, water washing; 4, dehydration; 5, CO2 critical point drying; 6, table bonding; 7, ; and 8, electron microscope observation. The method has the advantages of step simplification, simplicity in convenience, observation of the complete and meticulous cell internal structure, and realization of the 90% or above success rate, and can be used for membrane breaking production of the protozoa single cell scanning electron microscopy sample.
Owner:HARBIN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for observing collagenous fibre of fresh and alive trepang with electron microscope
InactiveCN101545876ASusceptible to corruptionHas metamorphismMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationFiberPhosphoric acid
The invention relates to a method for observing the collagenous fibre of fresh and alive trepang with an electron microscope, which is characterized by comprising the steps: firstly, the body wall muscles of the trepang are cut into pieces, the trepang pieces are cleanly washed by phosphoric acid buffer solution, the cleanly washed trepang pieces are fixed by glutaraldehyde phosphoric acid buffer solution for 0.5-5 hours under the temperature of -5-10 DEG C, and a trepang sample which is soaked in NaOH aqueous solution for 1-10 hours under the temperature of 10-50 DEG C is washed by normal saline solution until the PH value reaches 6.0-8.0; and secondly, the trepang sample is dyed by tannin, fixed by the glutaraldehyde phosphoric acid buffer solution under the temperature of 0-10 DEG C, sequentially dehydrated by alcohol with concentration ranging from low to high, dried at critical point, processed by gilded film and observed by a scanning electron microscope. Because trepang sample has the characteristics of easy putrescence, easy degenerescence of the marine product and isophagy per se, the two steps of collagenous fibre fixation and conductive dying are added to the preparation process of the electron microscope sample thereof, and the tissue constitution of the collagenous fibre of the fresh and alive trepang can be observed, thereby achieving the ideal effect.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method of supercritical point drying with stasis mode
InactiveUS20130174440A1High success rateDrying using combination processesDrying solid materials without heatLiquid stateCritical point drying
An improved method for supercritical point drying of a treated sample immersed in an intermediate drying fluid (e.g., ethanol or acetone), by purging the intermediary fluid with transitional fluid, and then entering a “stasis mode” allowing the sample to sit in its liquid state in the transitional fluid for a predetermined amount of time to extract any residual intermediary fluid into the transitional fluid. This ensures more thorough purging of the intermediary fluid from the sample and drying chamber, ultimately yielding a much higher success rate when drying thicker samples in the dryer.
Owner:TOUSIMIS CHRIS
Sticking agent for making bacterial scanning electron microscope observation slice and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN106596608AEnriching Microscopic Observation and Production TechniquesRich technical approachesMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionEmulsionDistilled water
A sticking agent for making a bacterial scanning electron microscope observation slice and a preparation method thereof are disclosed; every 100 ml of the sticking agent comprises 3-5mL of egg white, 5-7mL of glutinous rice powder emulsion, and balance of distilled water; the preparation method is as follows: respectively taking 3-5mL of the egg white and 5-7mL of the glutinous rice powder emulsion to put into a beaker, using sterile water to fix the volume to 100mL, evenly mixing, using a disposable needle filter with the specification of 0.22 mu m for filtering to obtain filtrate as the sticking agent; a method for making the scanning electron microscope bacterial ultramicroscopic morphology observation slice from the sticking agent comprises the steps of collection of bacteria, fixation, sticking, dehydration, replacement, critical point drying, sticking on a sample platform and ion sputtering; the effective sticking agent aiming at bacterial scanning electron microscope observation experiments and the preparation method thereof and a slice preparation method are provided, and the effective sticking agent solves slice shedding and mixing phenomena in the bacterial scanning electron microscope observation experiments.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
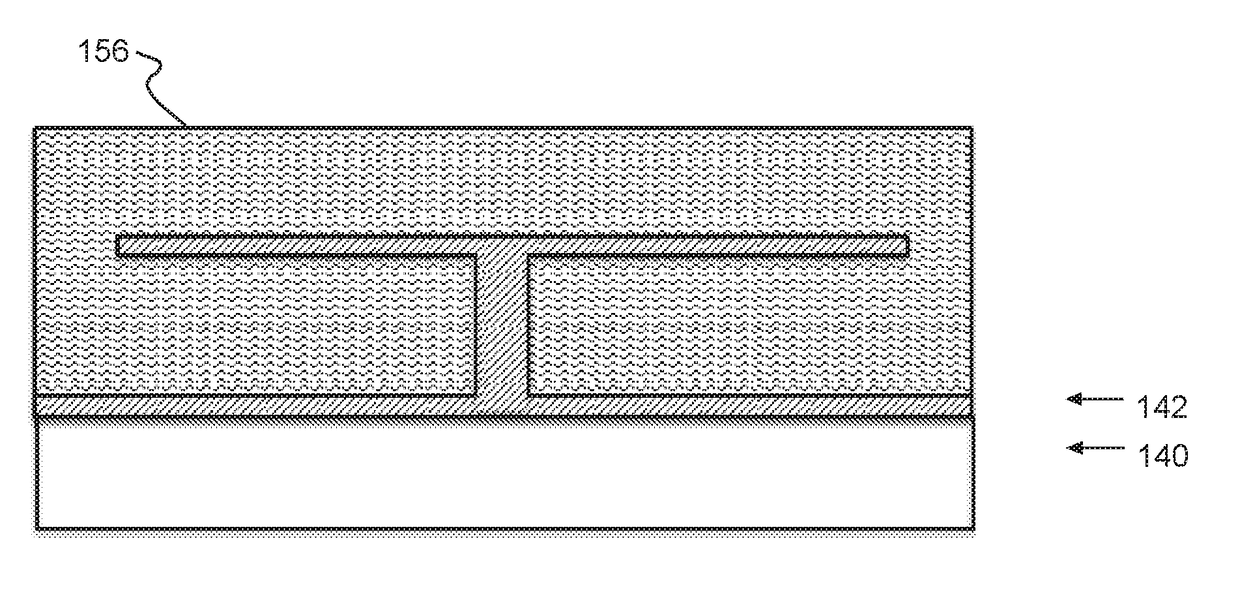
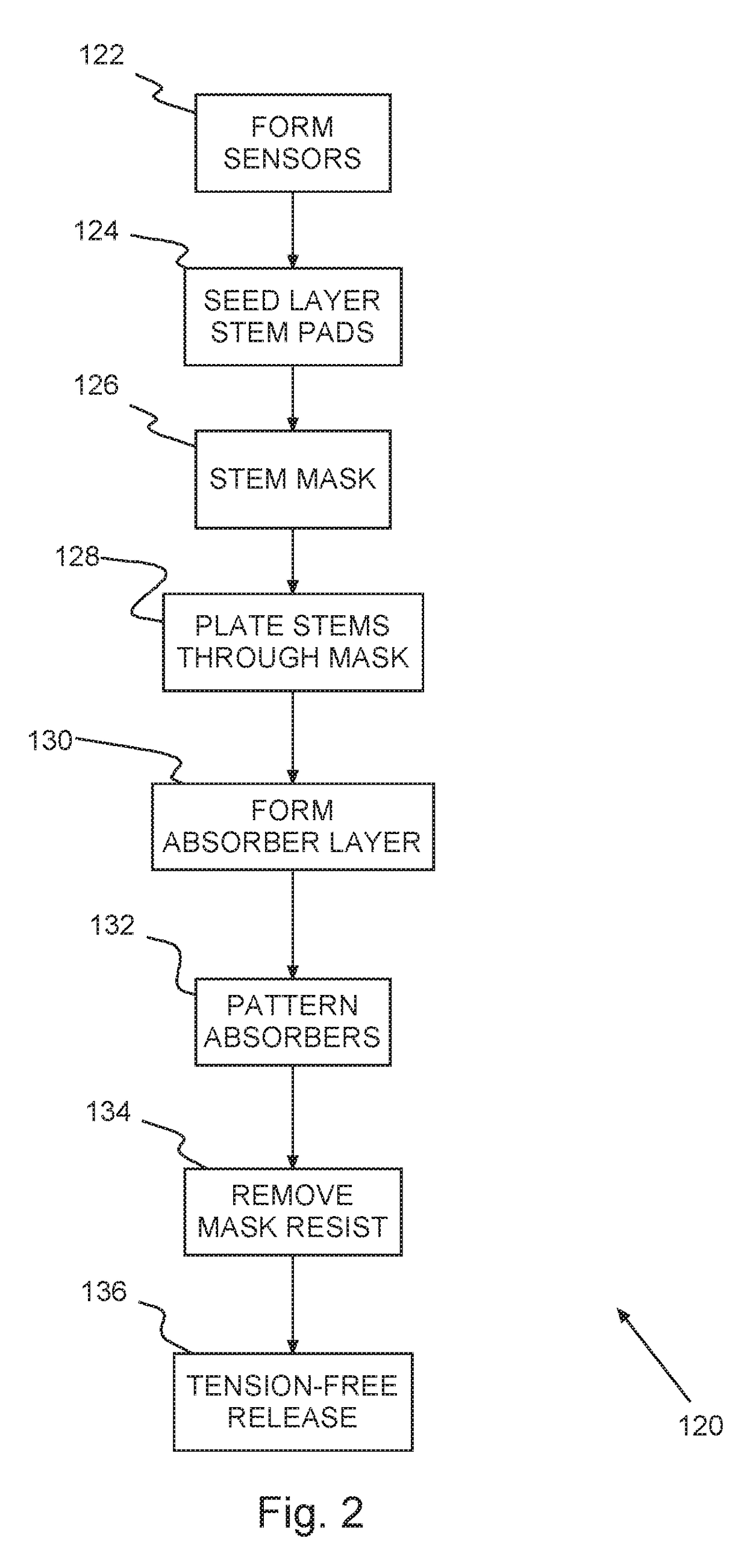
Method of fabricating x-ray absorbers for lowenergyx-ray spectroscopy
InactiveUS20180090662A1X-ray spectral distribution measurementMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayCritical point drying
A method of forming low-energy x-ray absorbers. Sensors may be formed on a semiconductor, e.g., silicon, wafer. A seed metal layer, e.g., gold, is deposited on the wafer and patterned into stem pads for electroplating. Stems, e.g., gold, are electroplated from the stem seed pads through a stem mask. An absorber layer, e.g., gold, is deposited on the wafer, preferably e-beam evaporated. After patterning the absorbers, absorber and stem mask material is removed, e.g., in a solvent bath and critical point drying.
Owner:NASA
Method of preparing bone material having enhanced osteoinductivity
ActiveUS9675645B2Increase the areaGood osteoinductivityPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsFiberCritical point drying
Methods for increasing osteoinductivity and / or surface area of bone material are provided. The methods include providing bone material and dehydrating the bone material with a solvent at its critical point. A useful solvent for critical point dehydrating is carbon dioxide. Critical point dehydration resulting in increased osteoinductivity and / or surface area can be applied to many types of bone material including bone particles, bone chips, bone fibers, bone matrices, both demineralized and non-demineralized. An implantable composition having an enhanced osteoinductivity and / or osteoconductivity is also provided. The implantable composition contains demineralized bone matrix dried at critical point of carbon dioxide. Critical point dried fibers of a demineralized bone matrix have a BET value from about 40 m2 / gm to about 100 m2 / gm, a value that is 100 times higher than corresponding vacuum dried or lyophilized DBM fibers.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
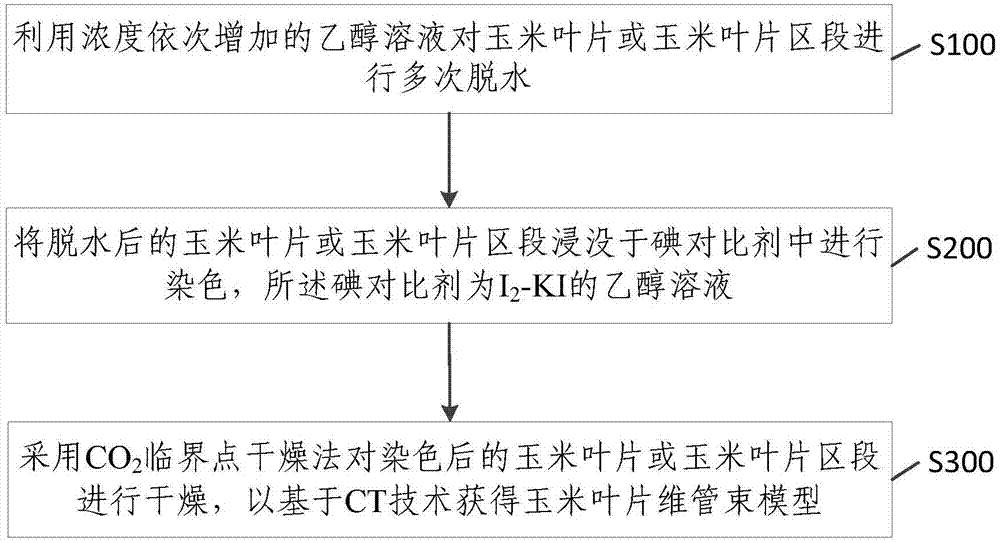
Modeling method for vascular bundle model of maize leaves
InactiveCN107884249ASolve the problem of dry deformationEasy to identifyPreparing sample for investigationInvestigating moving sheetsVascular bundleModel method
In one embodiment, the invention provides a modeling method for vascular bundle model of maize leaves, wherein the method includes steps of: 1) with ethanol solutions in increasing concentrations, performing multi-dehydration to a maize leaf or a maize leaf section; 2) soaking the dehydrated maize leaf or maize leaf section in an iodine contrast agent to dye the raw materials, wherein the iodine contrast agent is an I2-KI ethanol solution; 3) with CO2 critical point drying method, drying the dyed maize leaf or a maize leaf section, and based on CT technology, acquiring the vascular bundle model of maize leaves. According to the embodiment, the maize leaves are subjected to multi-dehydration with the ethanol solutions in increasing concentrations, so that complete dehydration is ensured; bymeans of dyeing with the iodine contrast agent, recognition degree on vascular bundles is increased; with the CO2 critical point drying method for drying the sample, a problem of drying deformation of the maize leaves is solved; and after drying, high-quality vascular bundle model of the maize leaves can be obtained through CT scanning.
Owner:BEIJING RES CENT FOR INFORMATION TECH & AGRI
Preparing method for biomass-cellulose nanometer fiber
InactiveCN106087505AHigh aspect ratioGood fiber distributionPulp properties modificationPulping with acid salts/anhydridesSupercritical dryingWater baths
The invention discloses a preparing method for a biomass-cellulose nanometer fiber. The preparing method includes the steps that a biomass fiber and a benzene-alcohol solution in the mass ratio of 1:(50-100) are weighed and put into a sodium chlorite solution, and the mixture and a KOH solution are mixed, sealed and mixed in a water bath kettle; the mixture is subjected to ultrasonic treatment and corona treatment; nanometer fiber suspension liquid is frozen, dried and subjected to supercritical drying or subjected to critical point drying. According to the preparing method, the biomass fiber is extracted through the benzene-alcohol solution, soluble substances in the biomass fiber are removed, then lignin is removed through sodium chlorite, hemicellulose is removed through the KOH solution, and the lignin and the hemicellulose are removed again; alkali-insoluble hemicellulose and alkali-insoluble lignin are treated and removed through hydrochloric acid, ultrasonic disruption treatment is finally carried out, then corona flow impacting is carried out, and the biomass-cellulose nanometer fiber with the high long diameter ratio and the high biomass cellulose is obtained. The nanometer fiber has better fiber distribution, the microstructure evenness performance is good, and the better mechanical performance is achieved.
Owner:ANHUI XINSHENGLI BIOLOGY TECH
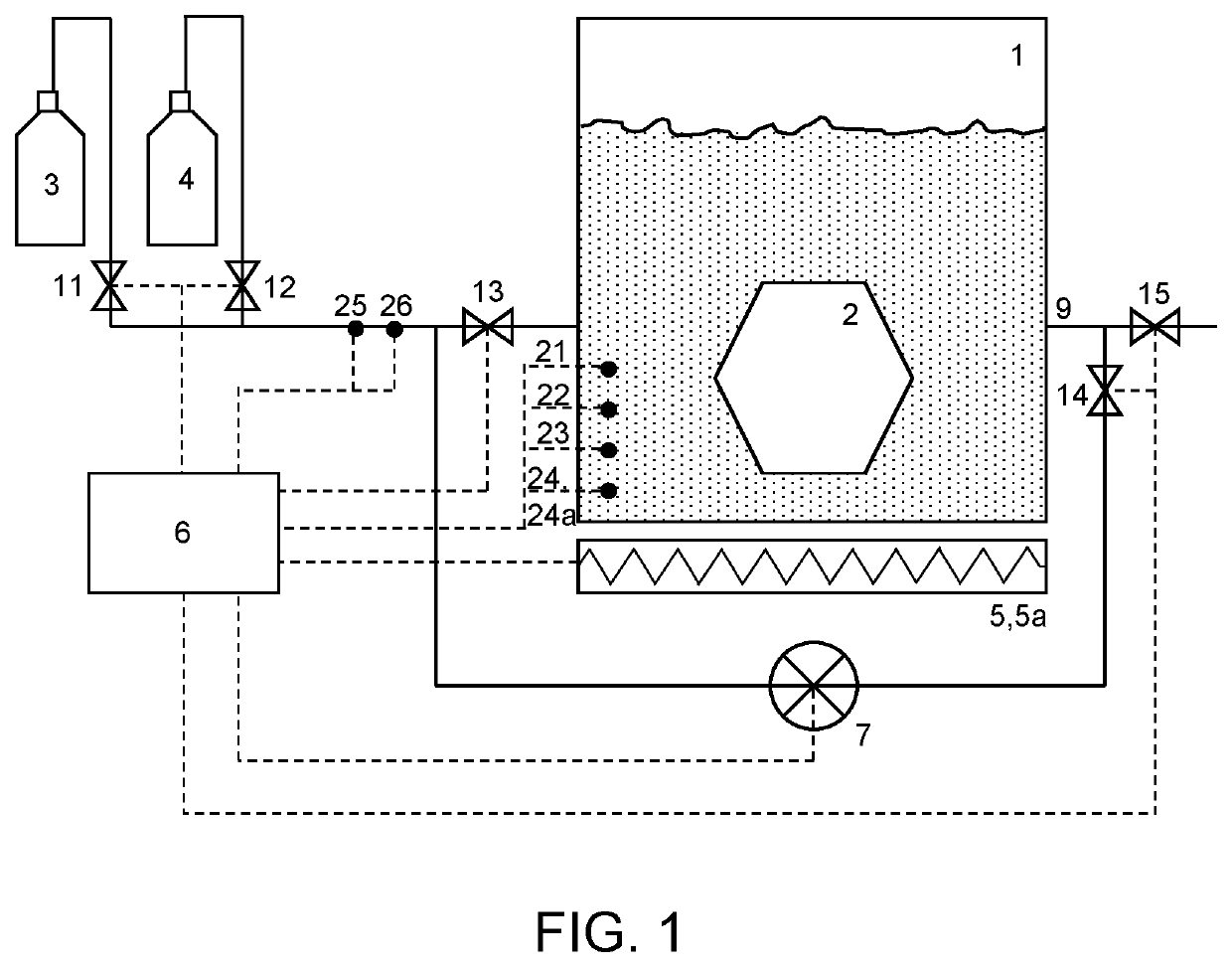
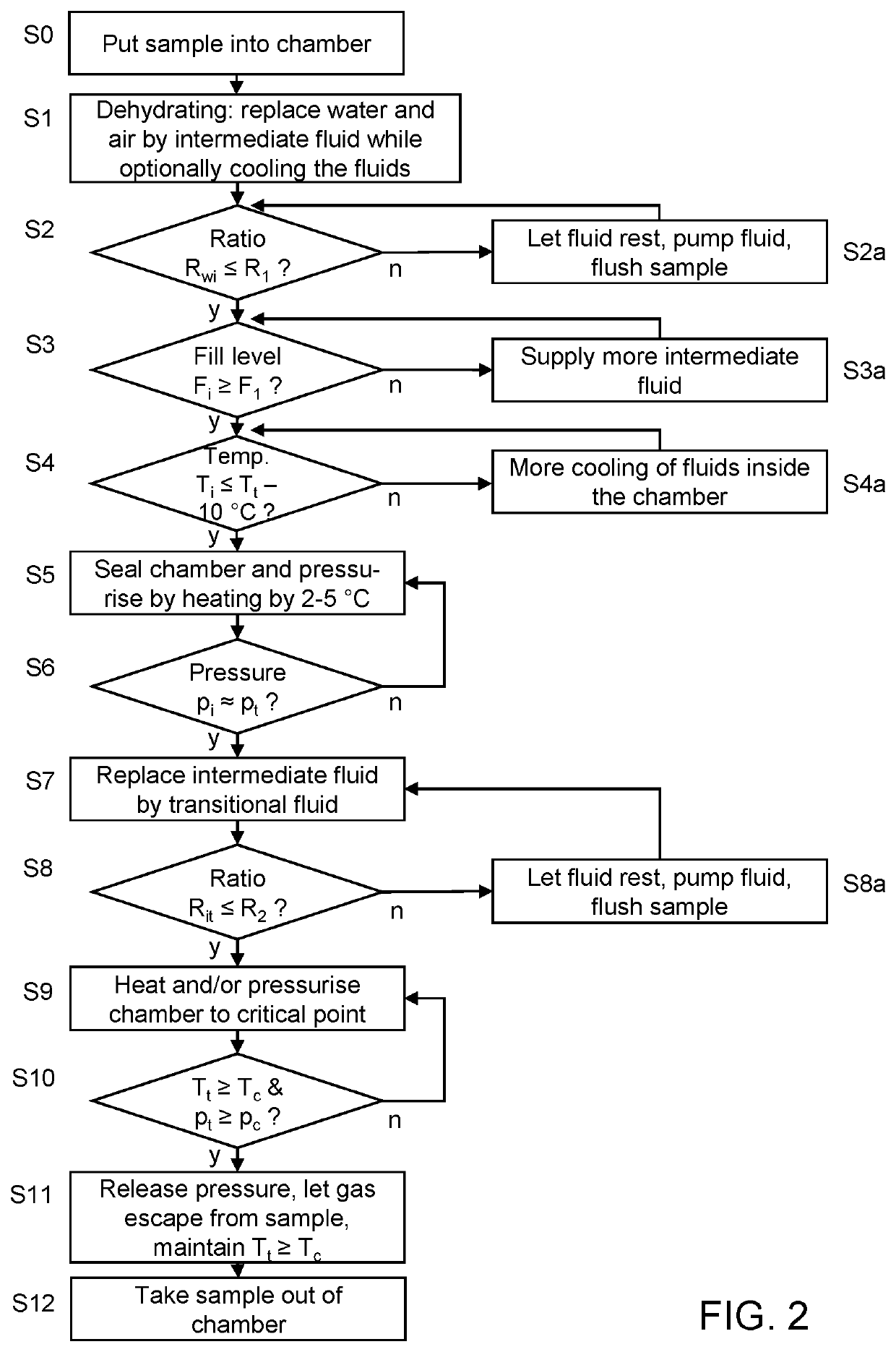
Method for dehydration and critical point drying
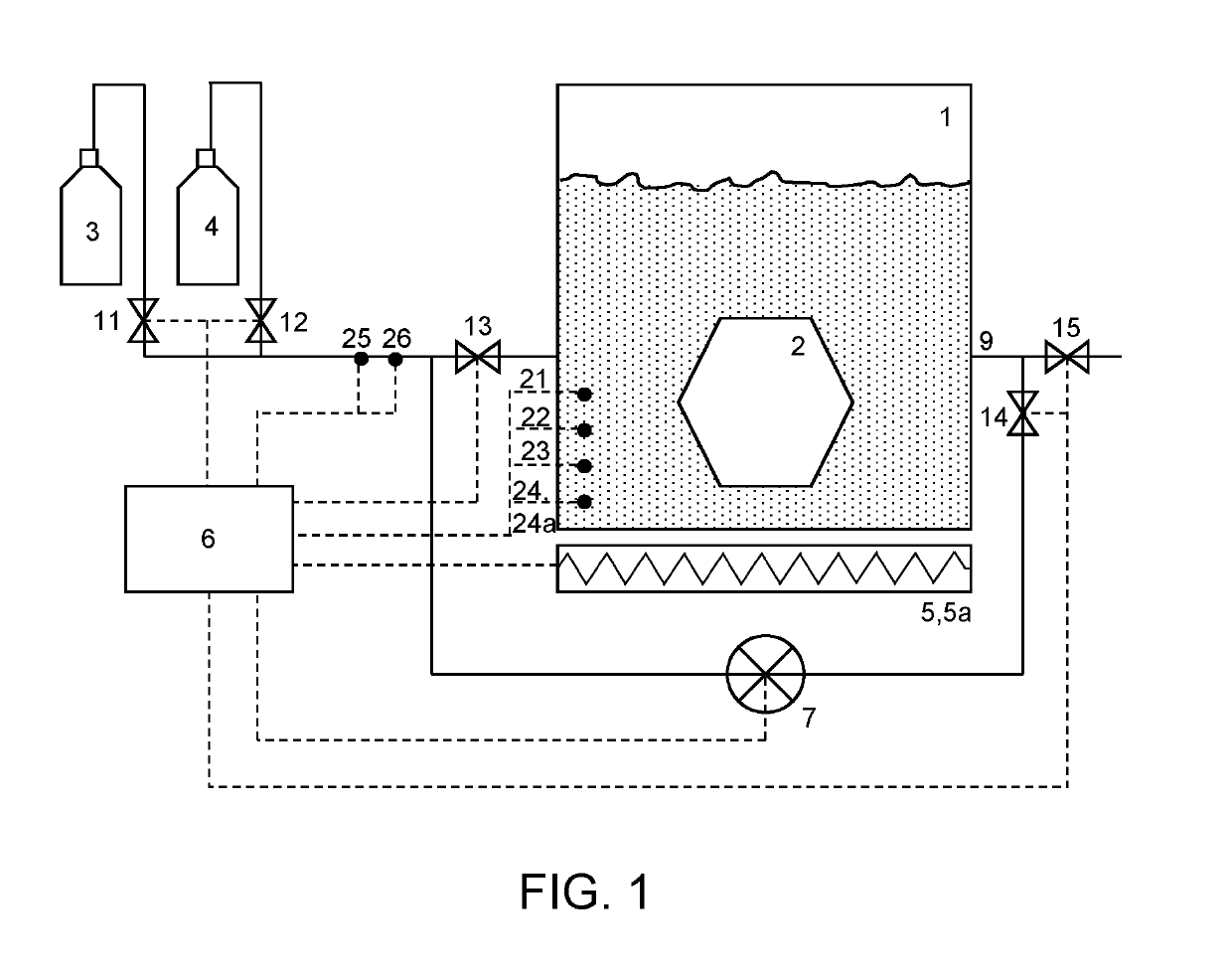
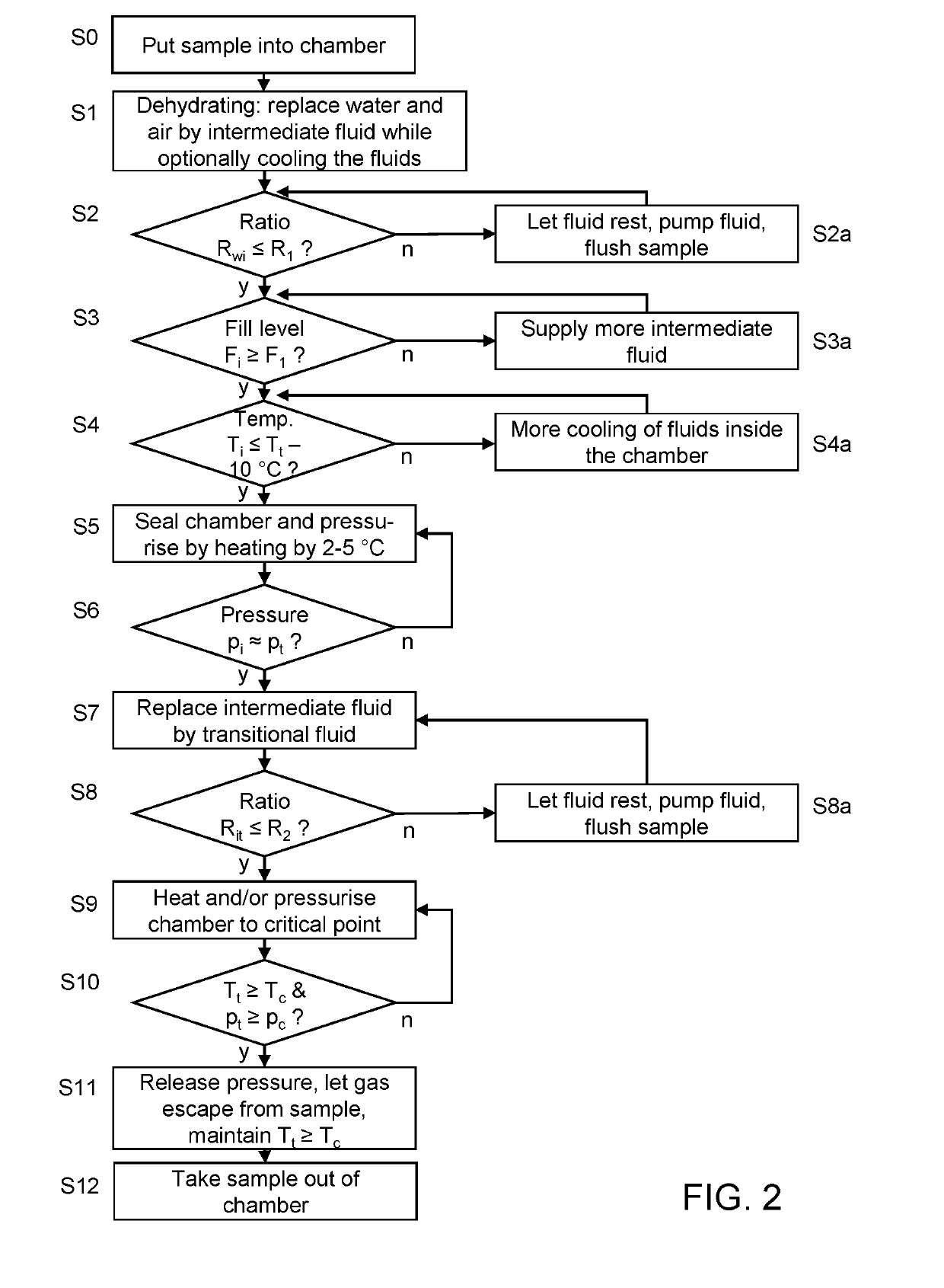
ActiveUS20190195556A1Well mixedReduce consumptionDrying solid materials with heatDrying solid materials without heatCritical point dryingSingle chamber
A method for dehydration and critical point drying of a sample in a single chamber is introduced, comprising the steps of (a) dehydrating the sample by replacing water by an intermediate fluid, (b) replacing the intermediate fluid by a transitional fluid, (c) pressurising the transitional fluid to or beyond its critical pressure and / or heating the transitional fluid (4 to or beyond its critical temperature, and (d) in response to gradually releasing the pressure, letting the transitional fluid gasify and escape from the sample. In step (a) and / or step (b), a ratio of the fluid to-be-replaced to the replacing fluid is measured and used to control a supply of the replacing fluid.The method reduces consumption of intermediate fluid and / or transitional fluid, making the process more efficient in terms of duration and user interaction while ensuring a high degree of dryness and the integrity of the sample.
Owner:SAFEMATIC GMBH
Method for dehydration and critical point drying
ActiveUS10767925B2Reduce consumptionDrying solid materials with heatDrying solid materials without heatCritical point dryingSingle chamber
A method for dehydration and critical point drying of a sample in a single chamber is introduced, comprising the steps of (a) dehydrating the sample by replacing water by an intermediate fluid, (b) replacing the intermediate fluid by a transitional fluid, (c) pressurising the transitional fluid to or beyond its critical pressure and / or heating the transitional fluid (4 to or beyond its critical temperature, and (d) in response to gradually releasing the pressure, letting the transitional fluid gasify and escape from the sample. In step (a) and / or step (b), a ratio of the fluid to-be-replaced to the replacing fluid is measured and used to control a supply of the replacing fluid.The method reduces consumption of intermediate fluid and / or transitional fluid, making the process more efficient in terms of duration and user interaction while ensuring a high degree of dryness and the integrity of the sample.
Owner:SAFEMATIC GMBH
Carbon nano particles and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108341406AAdvantages of preparation methodGood lookingNano-carbonCritical point dryingPrecipitation
The invention provides carbon nano particles and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of nanometer materials. The preparation method of the carbon nano particles comprises the following steps that (1) biomass tar is subjected to centrifugal separation, supernatant liquid is filtered with filter cloth to obtain a filtrate, and the filtrate is distilled to acquire a fraction; (2) the fraction obtained in the step (1) is continuously put into concentrated sulfuric acid under the condition of constant-temperature stirring reaction, constant-temperature stirring is performed after charging is finished, then heating is stopped, and cooling is performed to room temperature; (3) a reaction product obtained in the step (2) is repeatedly washed with water and an organic liquid until the reaction product is neutral, precipitation is performed, and a lower solid-liquid mixture is taken out after centrifugal separation is performed; and (4) the lower solid-liquid mixtureobtained in the step (3) is dried at a critical point to obtain the carbon nano particles. The preparation method of the carbon nano particles provided by the invention is simple in technology, good in the form of a product and available in raw material and has environment-friendly value.
Owner:海若斯(北京)环境科技有限公司
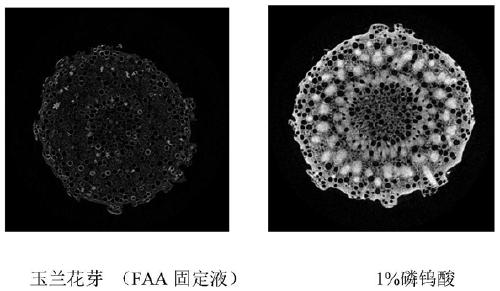
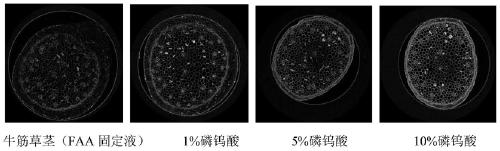
Method for enhancing contrast of microscopic CT plant sample
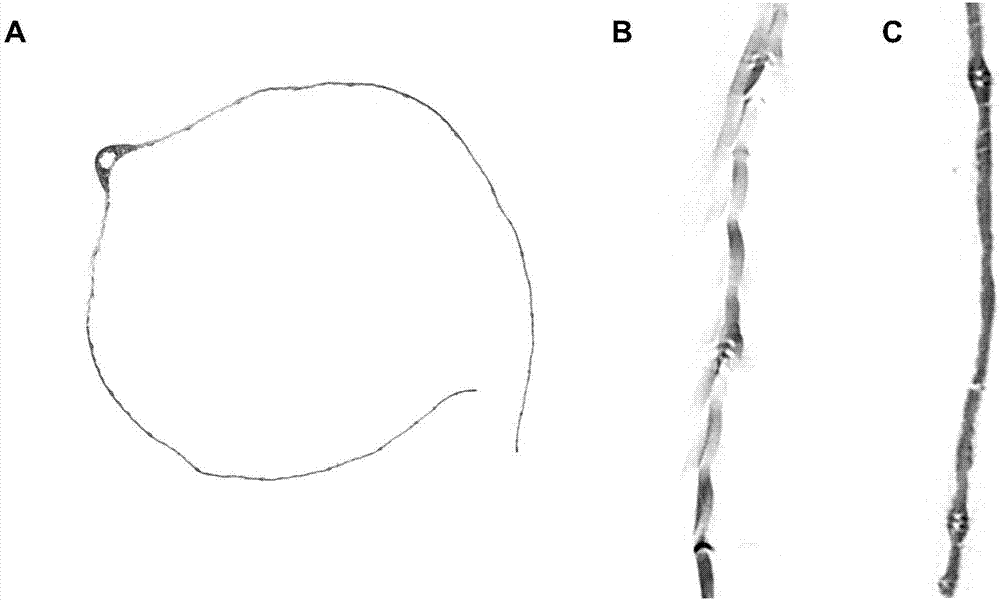
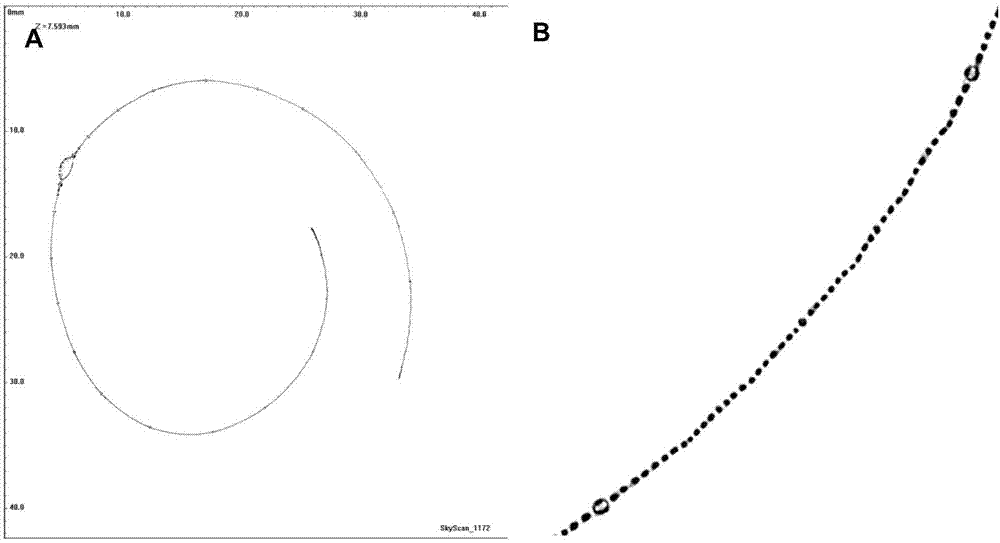
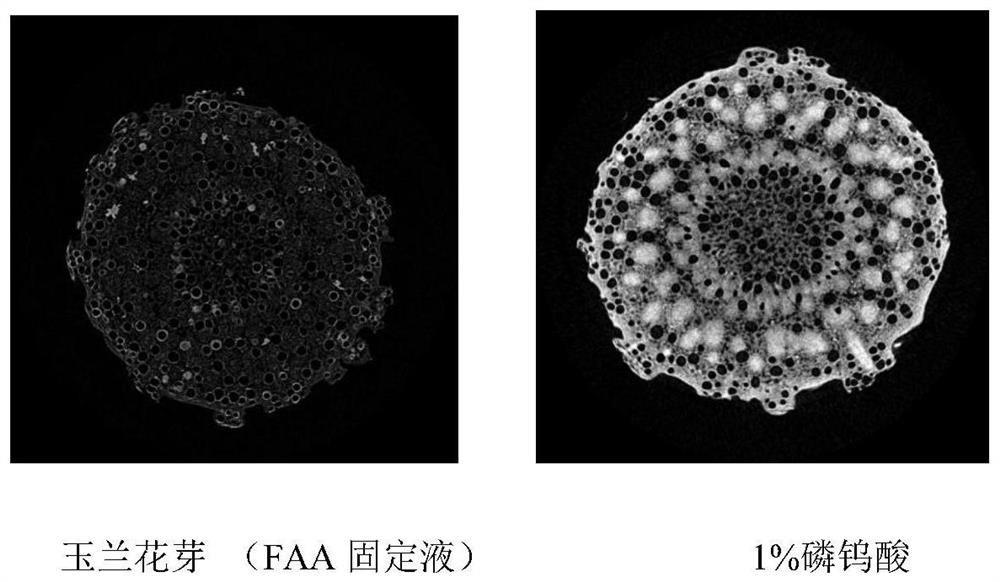
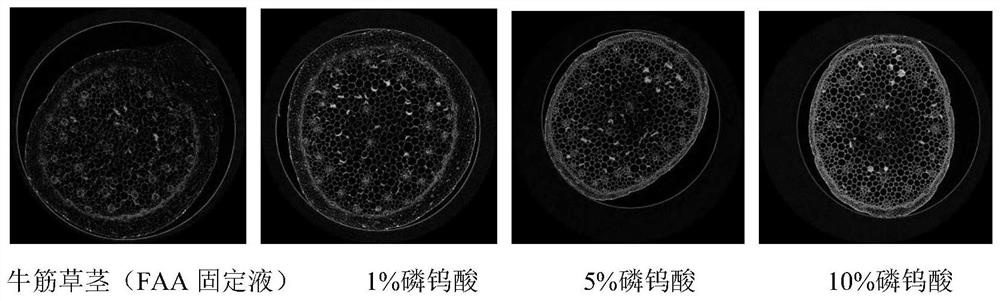
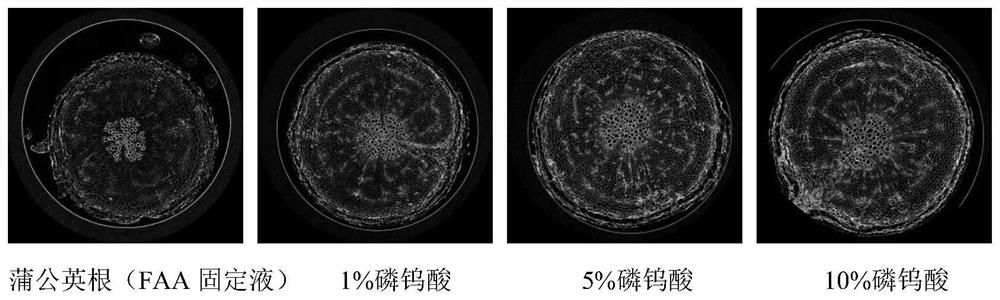
ActiveCN111398000AIncrease contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationStainingCritical point drying
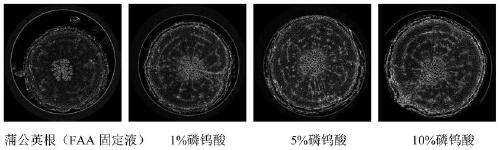
The invention discloses a method for enhancing contrast of a microscopic CT plant sample. The method comprises the following steps: 1) dissolving phosphotungstic acid in an FAA stationary liquid to obtain a phosphotungstic acid solution; 2) soaking a plant part to be detected in the phosphotungstic acid solution for fixing and dyeing treatment; and (3) sequentially carrying out dehydration and carbon dioxide critical point drying on the plant part fixed and dyed in the step (2) so as to enhance the contrast ratio of the microscopic CT of the plant sample. Microscopic CT scanning (Skyscan1172,Brook Company) is performed on the sample subjected to carbon dioxide critical point drying, the scanning voltage can be 41V-59V, the resolution can be 0.56-1.76 mu m, a cross section picture is obtained through NRecon software reconstruction after the sample is scanned, the contrast ratio of plant samples at different parts is greatly improved, and the contrast ratio of parts rich in cytoplasm and protein, such as magnolia flower buds, is more remarkably improved.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Holder for use in semiconductor device manufacturing and bio-medical sample processing
InactiveUS6883674B1Chamber pressure to dropPrevent escapePreparing sample for investigationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingHydrofluoric acidAlcohol
Multipurpose holders for electronic components utilized during a fabrication process must allow the components to be submerged into baths of hydrofluoric acid, rinsed in de-ionized water (D.I.), placed into baths of alcohol for dehydration, and ultimately dried prior to further processing. The holders provide both fluid flow around the wafers while in each bath of fluid and while being processed by the critical point dryer, and a containment system to keep the wafer submerged in fluid at all times during the transfer between baths and the drying equipment.
Owner:TOUSIMIS RES
Seawater fish ovum electron-microscope scanning sample preparing method
InactiveCN100427918CQuality assurancePrevent collapsePreparing sample for investigationSurface/boundary effectAlcoholPhosphate
The disclosed preparation method for ovum of sea fish as TEM sample comprises: fixing fresh fish ovum by glutaral solution diluted by phosphate buffer, cleaning, dewatering the ovum by 20-70% alcohol with concentration gradient increased by 10% and 75-100% alcohol with concentration gradient increased by 5% as two stages, then dewatering in pure acetone with CaCl2 as agent; then, drying at critic point, and spraying gold for the sample. This invention has ovum completion rate as 93.8-96.7% with low cost and convenient operation.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A scanning electron microscope sample processing method of termite head sensory appendage
ActiveCN107014843BShrinkage and deformation will notAvoid surface contaminationMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationAdhesiveCritical point drying
The invention discloses a scanning electron microscope sample processing method for head sensory appendages of white ants. The method comprises the steps of putting white ants into a specially-made wind washing device, carrying out wind washing, feeding the white ants into a specially-made auxiliary vacuumizing device, carrying out vacuumizing operation to sink the white ants, carrying out front fixing and dissection, sequentially carrying out front rinsing under the view of a stereoscope and in an ultrasonic cleaner, carrying out rear fixing, rear rinsing and step-by-step gradient dehydration, putting the white ants into a specially-made filter paper cylinder, sealing the filter paper cylinder, putting the filter paper cylinder into a critical point drying frame, carrying out critical point drying, bonding samples close to a platform under the stereoscope, further dissecting target tissues of partial samples, carrying out secondary sample bonding, connecting the samples which are not subjected to secondary sample bonding with sample bonding adhesive tapes in a non-target observation region by virtue of a conductive silver adhesive, and carrying out all-direction gold sputtering after the conductive silver adhesive is dried. According to the scanning electron microscope sample processing method, multi-aspect technical problems in the background art that the surfaces of the samples are polluted, the samples are difficult to sink in fixation liquid and shrink to deform, different tissue parts of the samples are mutually shaded, and the samples are charged and discharged when being observed in an electron microscope are effectively solved, the cost for solving the problems is low, and the method has relatively high application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Method for preparing scanning electron microscope samples from biological samples
InactiveCN102680289BAccurate distinctionPreparing sample for investigationNanoparticleProtein molecules
The invention provides a method for preparing scanning electron microscope samples from biological samples. The method comprises enabling a first antibody marked with first gold nanoparticles and a second antibody marked with second gold nanoparticles to contact with a biological sample after the biological sample is in resistance treatment; and then successively performing fixation, gradient dehydration and critical point drying. The shapes of the first gold nanoparticles are different from those of the second gold nanoparticles, and the first gold nanoparticles and the second gold nanoparticles are one or more from cylindrical gold nano bars, octahedral gold nanoparticles, spherical gold nanoparticles and arrow-shaped gold nanoparticles. The scanning electron microscope samples prepared by the method can accurately distinguish two types of different protein molecules in a low-vacuum mode.
Owner:THE NAT CENT FOR NANOSCI & TECH NCNST OF CHINA
Young plant sample critical point drying method for scanning electron microscope
InactiveCN104977431APrevent natural dryingAccurate volumeScanning probe techniquesPlant tissueCritical point drying
The invention discloses a young plant sample critical point drying method for a scanning electron microscope. The critical point drying method comprises the following steps: 1) respectively covering the top and the bottom of a sample basket of a critical point dryer by filter paper, wherein each piece of filter paper is provided with a plurality of holes for facilitating exchange between isoamyl acetate and CO2, and placing a preprocessed plant sample into the sample basket; 2) placing the sample basket with the preprocessed plant sample on the bottom of the sample room of the critical point dryer, closing the sample room, performing inflation and exhaustion twice, and after final inflation, replacing the isoamyl acetate in the plant sample by CO2; and 3) adjusting the temperature of the sample room of the critical point dryer to 35-40 DEG C, discharging the CO2, taking the sample out, and the dried sample is obtained. The experiment of the young plant sample critical point drying method proves a fact that the young plant sample critical point can realize a purpose of drying the sample without deformation; and the drying effect is remarkable for a plant tissue which is tender and soft and easily deforms after shrinkage.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Scanning electron microscope sample processing method for head sensory appendages of white ants
ActiveCN107014843AShrinkage and deformation will notAvoid surface contaminationMaterial analysis by measuring secondary emissionAdhesiveCritical point drying
The invention discloses a scanning electron microscope sample processing method for head sensory appendages of white ants. The method comprises the steps of putting white ants into a specially-made wind washing device, carrying out wind washing, feeding the white ants into a specially-made auxiliary vacuumizing device, carrying out vacuumizing operation to sink the white ants, carrying out front fixing and dissection, sequentially carrying out front rinsing under the view of a stereoscope and in an ultrasonic cleaner, carrying out rear fixing, rear rinsing and step-by-step gradient dehydration, putting the white ants into a specially-made filter paper cylinder, sealing the filter paper cylinder, putting the filter paper cylinder into a critical point drying frame, carrying out critical point drying, bonding samples close to a platform under the stereoscope, further dissecting target tissues of partial samples, carrying out secondary sample bonding, connecting the samples which are not subjected to secondary sample bonding with sample bonding adhesive tapes in a non-target observation region by virtue of a conductive silver adhesive, and carrying out all-direction gold sputtering after the conductive silver adhesive is dried. According to the scanning electron microscope sample processing method, multi-aspect technical problems in the background art that the surfaces of the samples are polluted, the samples are difficult to sink in fixation liquid and shrink to deform, different tissue parts of the samples are mutually shaded, and the samples are charged and discharged when being observed in an electron microscope are effectively solved, the cost for solving the problems is low, and the method has relatively high application value.
Owner:ZHEJIANG FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Supercritical drying of chromatography media
PendingCN114787571ADrying solid materials with heatOther chemical processesChromatographic separationSupercritical drying
A method for critical point drying of a composite material is disclosed. After the composite material is exposed to the supercritical fluid, the composite material is dried as the supercritical fluid evaporates under reduced pressure. The composite material can be used as a chromatographic separation medium.
Owner:MERCK MILLIPORE LTD
A method for enhancing the contrast of micro-CT plant samples
ActiveCN111398000BIncrease contrastMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationPreparing sample for investigationStainingCritical point drying
The invention discloses a method for enhancing the contrast of micro-CT plant samples. The method comprises the following steps: 1) dissolving phosphotungstic acid in FAA fixative solution to obtain a phosphotungstic acid solution; 2) using the phosphotungstic acid solution to soak the plant parts to be tested for fixation and dyeing; 3) through the steps 2) The fixed and dyed plant parts are sequentially dehydrated and dried at the critical point of carbon dioxide, which can enhance the contrast of the micro-CT of the plant sample. Micro-CT scanning (Skyscan1172, Bruker Company) was performed on the sample dried at the critical point of carbon dioxide. The scanning voltage can be 41V-59V, and the resolution can be 0.56-1.76μm. , the contrast of plant samples in different parts has been greatly improved, and the contrast of the cytoplasm-rich and protein-rich parts such as magnolia flower buds has been improved more significantly.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com