Supercritical drying of chromatography media
A critical point drying, supercritical fluid technology, applied in the field of supercritical drying of chromatographic media
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1- 1
[0151] Example 1 - General Materials and Methods
[0152] Chemicals
[0153] Liquefied carbon dioxide (medical grade 99.99%) was obtained from PraxAir Canada Inc., absolute alcohol reagent (<0.005% water) and calcium chloride were obtained from MilliporeSigma, and buffer solution 1OX PBS liquid concentrate (growing cells) was purchased from VWR.
[0154] protein
[0155] Affinity purified human IgG was obtained from Innovative Research Inc. (Novi, MI, USA).
[0156] Membrane material
[0157] Epoxy resin films are prepared by polymerizing acrylate and or acrylamide monomers and a crosslinking agent within a support web material in a UV-initiated reaction. By introducing suitable polymerizable functional groups into the gel polymerization solution, various functional membranes containing protein-binding groups (eg, ion exchange, hydrophobic interactions, and hydrophilic interactions) can be produced in a single polymerization step. Wet cleaned membranes can also be ...
Embodiment 2
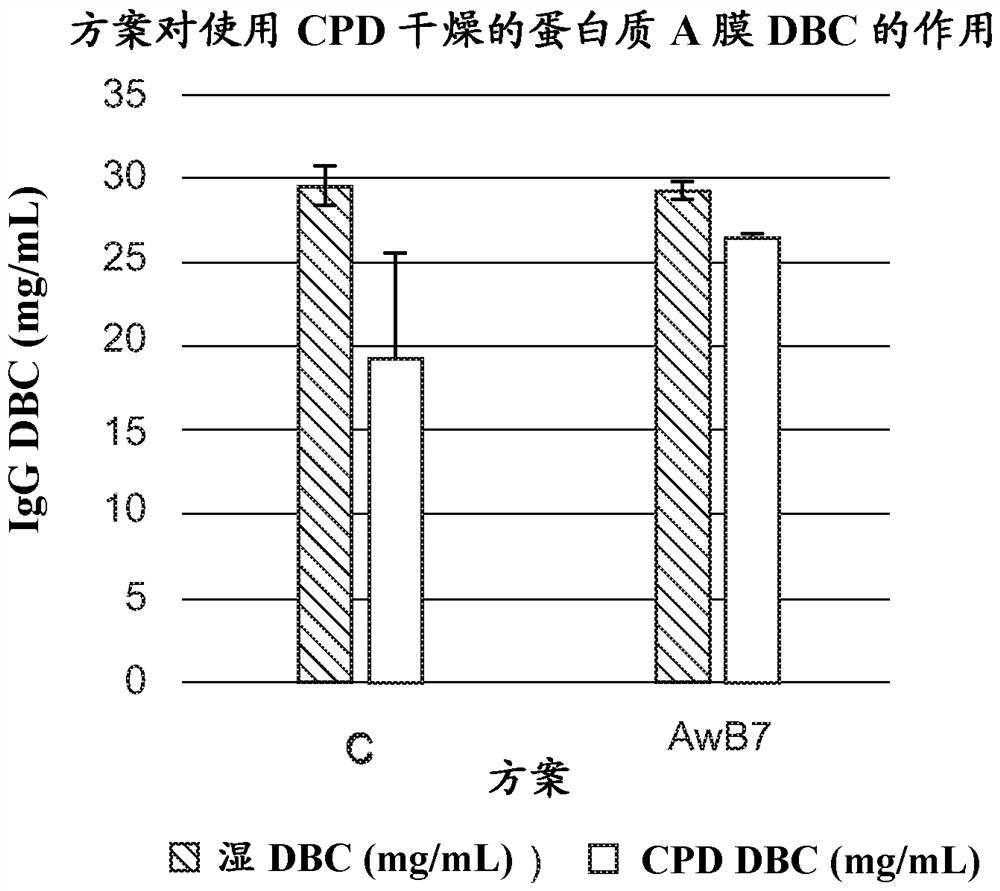
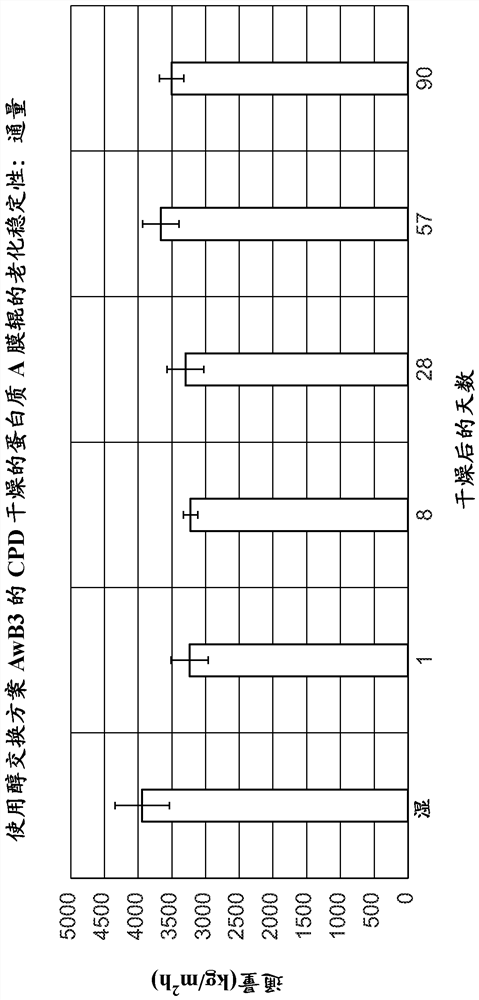
[0191] Example 2 - Comparison of critical point drying epoxy-containing films to other drying methods and their effect on performance during shelf life role
[0192] Different batches of epoxy resin membranes with similar permeability and their bioligand-derived forms with comparable protein binding capacity were dried using a two-step critical point drying method. In the first step, the membrane in roll form is subjected to a water / ethanol exchange process, in which the membrane roll is placed in an exchange solvent of a certain alcohol content for a specified time, the reagents are subsequently decanted, and fresh specified amount of the next step is added amount of alcohol solution, as outlined in Exchange Scheme B (Table 2). In the second step, the ethanol-wetted film roll was placed in a critical point drying instrument chamber (Leica CPD300) and subjected to a purging process for liquid CO 2 Instead of ethanol, the drying chamber conditions were subsequently shifted...
Embodiment 3
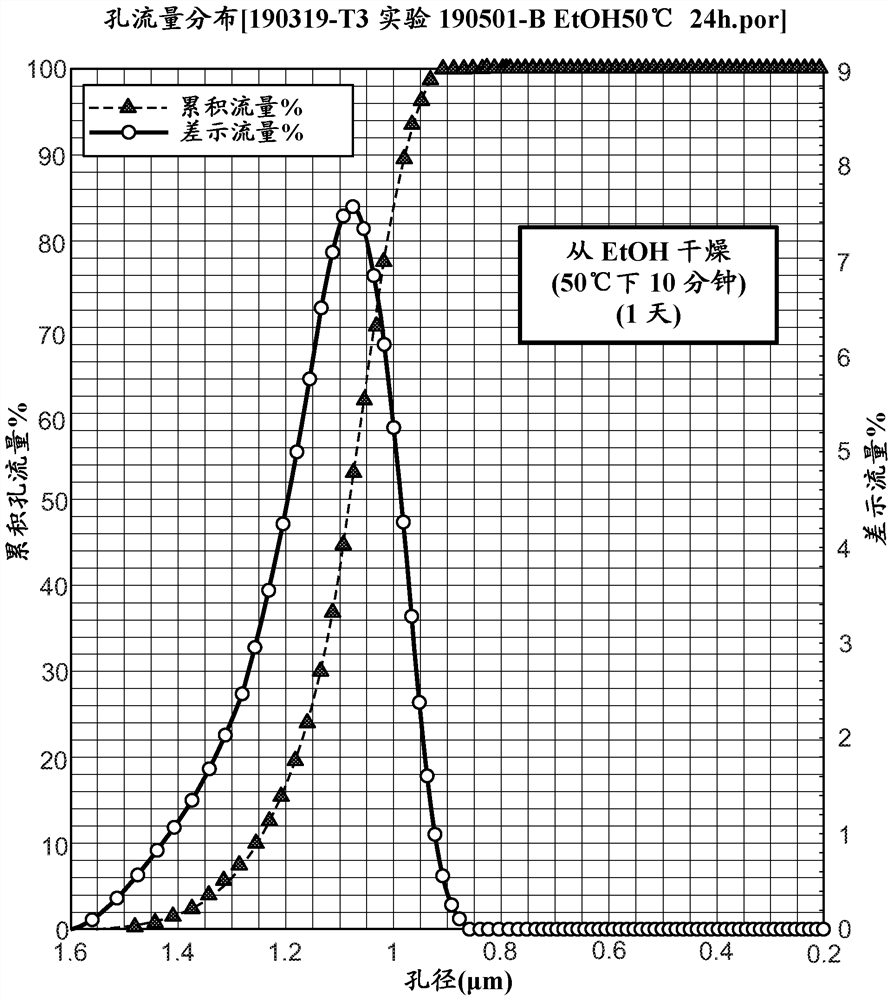
[0195] Example 3 - Critical point drying of epoxy-containing membranes using different exchange protocols
[0196] In order to obtain a successful drying method using supercritical fluids, water must be removed and replaced with ethanol. Several factors are expected to affect the water removal process: water content in the ethanol exchange solution, exchange time, number of exchange steps, sandwich screen material and final membrane to solution ratio.
[0197] Two different exchange schemes with graded ethanol content were examined. In Scheme A, the membrane is exchanged with an ethanol solution to replace the water in the membrane with alcohol by a five-step exchange scheme using a solution with progressively lower water content to finally achieve exchange with anhydrous ethanol reagent step. In Scheme B, the exchange process was carried out throughout the eight exchange steps to replace water in the membrane with ethanol. The two protocols A and B are summarized in Tabl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| critical point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com